-
磷是生物体必需的营养元素之一,同时也是限制大多数水生生态系统营养的关键因素[1]。水体中磷浓度过高将会引起富营养化[2],危及水生生态系统。因此,高效去除水中过量磷是一个亟待解决的问题[3]。
目前,已得到广泛应用的水中除磷方法有生物法(微生物除磷工艺)、化学沉淀法、离子交换法等,但生物法将产生大量剩余污泥[4],化学沉淀法中投加的药剂容易对水体造成二次污染[5],离子交换法易受共存离子的干扰[6]。相比而言,操作简单[7]、效果稳定[8]的吸附法逐渐受到关注。
性能优良的吸附剂是吸附法成功的关键。水中除磷常用的吸附剂主要有黏土矿物[9]、活性炭[10]、树脂[3]、生物质材料[8]等。其中,生物质材料价格低廉[8]、来源广泛,是其作为吸附剂的重要优势。但未经处理的生物质对磷的吸附效率有限,有研究通过在生物质表面负载金属的方式提高其吸附能力,如铝改性小麦秸秆[11],铁改性花生壳[12]等。因此,利用高价态金属改性生物质材料去除水中磷具有一定的应用潜力。近年来,镧和锆2种金属元素因化学性质稳定,且对磷有较强的选择性而成为水中除磷的研究热点[13-14],但是金属氧化物或氢氧化物粉末易随水流失,难于从水中分离[9],这就限制了他们在吸附磷方面的工程化应用。若将其负载到生物质材料上以制成颗粒状除磷吸附剂,不仅可以提高吸附剂的机械强度,还能降低其使用成本。目前,利用镧和锆改性生物质材料去除水中磷的有关研究还较少,镧和锆改性材料吸附特征的对比探究也鲜见报道。
油菜和菱角作为2种经济作物,我国每年产量巨大,在其生产加工过程中所产生的废弃物亟待处理。同时,油菜秆和菱角壳中含有丰富的纤维素和木质素,含有大量羟基和羧基结构,是2种潜在载体材料。选择油菜秸秆和菱角壳作为载体,负载以镧或锆2种金属,制成新型吸附剂,既有望解决水体中磷含量过高而导致的富营养化的问题,又可为其本身的资源化处置开辟新途径。此外,用于吸附过后的材料可作为含磷丰富的还田物质,无须进行后处理。
本研究采用共沉淀法制得镧改性油菜秆(La-BC)、锆改性油菜秆(Zr-BC)、镧改性菱角壳(La-TN)、锆改性菱角壳(Zr-TN)4种材料,分别探究了其投加量、溶液的pH、磷的初始浓度、吸附时间等影响因素对4种改性材料吸附水中磷的影响规律,并在实际养猪废水中进行验证,旨在今后的磷去除和农业废弃物的资源化利用上提供一定参考。
全文HTML
-
本研究采用油菜秆(BC)和菱角壳(TN) 2种原始材料,其中,油菜秆来源于四川农业大学崇州基地;菱角为市购。将油菜秸秆和菱角壳先用自来水洗净,去除表面污垢,再用去离子水润洗3次,置于60 ℃烘箱中干燥24 h,粉碎后过60目筛,装入自封袋中备用。
实验试剂包括氯化镧(LaCl3·7H2O)、氧氯化锆(ZrOCl2·8H2O)、氢氧化钠、磷酸二氢钾、钼酸铵、酒石酸锑氧钾、抗坏血酸等,均为分析纯,购自四川西陇科学有限公司。实验用水为去离子水。
实验所用模拟废水采用磷酸二氢钾配制。实验所用养猪废水采自四川省某养殖基地,其磷浓度约为28
mg⋅L−1 、pH=8.23。 -
分别称取40 g油菜秆和菱角壳于1 000 mL聚四氟乙烯瓶中,以固液比1:25向瓶中加入质量分数为5%的NaOH溶液,密封后放入恒温振荡培养箱,以200
r⋅min−1 ,在30 ℃振荡2 h。用蒸馏水将多余NaOH洗净直至材料呈中性,放入60 ℃烘箱中干燥24 h,取出冷却备用。分别准确称取15 g NaOH预处理后的2种材料于500 mL聚四氟乙烯瓶中,以固液比1∶25向瓶中加入质量分数为2%的LaCl3或ZrOCl2溶液;密封后放入恒温水浴搅拌锅,25 ℃恒温搅拌3 h;用20mol⋅L−1 的NaOH调至pH为10,继续搅拌12 h;静置后倒出上浑浊液,再用蒸馏水冲洗材料,直至向最后一次洗液中加入0.1mol⋅L−1 的AgNO3不产生白色悬浊物为止。将洗净后的材料放于60 ℃烘箱中干燥24 h,研磨粉碎后过60目筛备用。 -
2种原材料改性前后的表面形貌用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,ZEISS Sigma 300,英国)观察;X射线能谱分析采用布鲁克电制冷X射线能谱仪(EDS,Xflash6,德国)分析;特征官能团采用傅里叶红外光谱仪(FT-IR,Nicolet S10,Thermo Scientific,美国)测定。
-
称取一定质量的吸附剂于100 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL一定质量浓度的磷,以模拟废液,封口后放进温度为25 ℃、转速为150
r⋅min−1 的恒温振荡箱中振荡2 h,过滤分离,将滤液稀释一定倍数后,以钼锑抗分光光度法测定其中的磷含量。吸附量根据式(1)进行计算。式中:
C0 为初始废液浓度mg·L−1;Ce 为吸附后废液浓度,mg·L−1;V是废液体积,L;m为吸附剂用量,g。1)吸附剂投加量实验。向50 mL质量浓度为20 mg·L−1的磷溶液中分别投加0.025、0.05、0.1、0.15、0.2 g吸附剂,在25 ℃下,以150 r·min−1的转速振荡120 min,模拟磷废液的pH=5。
2)溶液初始pH影响实验。以适当浓度的NaOH和H2SO4将模拟废液pH分别调至3、4、5、6、7、8。向50 mL模拟废液中投加0.05 g吸附剂,在25 ℃下,以150 r·min−1振荡2 h,废液浓度为20
mg⋅L−1 。3)吸附动力学实验。向50 mL质量浓度为20
mg⋅L−1 的模拟废液中投加0.05 g吸附剂,在25 ℃下,以150 r·min−1分别振荡30、60、120、240、480、720 min,模拟磷废液pH=5。分别用准一级动力学方程(式(2))、准二级动力学方程(式(3))、叶诺维奇方程(式(4))拟合实验结果。式中:
qt 为t时刻4种吸附剂对磷的吸附量,mg⋅g−1 ;k1 为准一级吸附速率常数,g⋅(mg⋅min)−1 ;k2 为准二级吸附速率常数,g⋅(mg⋅min)−1 ;qe 为平衡时吸附量,mg⋅g−1 ;βs 为任意一次实验的解吸常数,g⋅mg−1 ;αs 为初始吸附速率,mg⋅(g⋅min)−1 。4)等温吸附实验。废液浓度为10、20、50、80、120 mg·L−1。向50 mL模拟废液中加入0.05 g吸附剂,在25 ℃下,以150 r·min−1振荡2 h,废液pH为5。分别用Langmuir(式(5))和Freundlich(式(6))模型拟合实验数据。
式中:
qe 为平衡时吸附量,mg⋅g−1 ;qm 为理论最大吸附量,mg⋅g−1 ;ka 为Langmuir模型常数,L⋅mg−1 ;ce 为吸附平衡时浓度,mg⋅L−1 ;kf 为Freundlich方程常数;n为常数,表示吸附强度大小。 -
将养猪废水调至pH=5,取50 mL废水向其中加入0.05 g吸附剂,在25 ℃下,以150 r·min−1振荡2 h,过滤分离,将滤液稀释一定倍数后,测定其中的磷含量。
-
使用SPSS 19.0统计软件对实验数据进行分析。对同一材料在不同pH、浓度、吸附时间、投加量条件下吸附量的差异及同一反应条件下不同材料间吸附量的差异采用单因素方差分析(One-Way ANVON),平均值差异采用L-S-D法检验,当P<0.05时,认为差异显著。对吸附剂投加量实验结果及溶液pH影响结果采用相关分析及回归分析,最后使用Origin 8.5作图。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 改性材料的制备
1.3. 材料的表征
1.4. 对模拟废水中磷的吸附去除
1.5. 养猪废水中磷的吸附去除
1.6. 数据处理
-
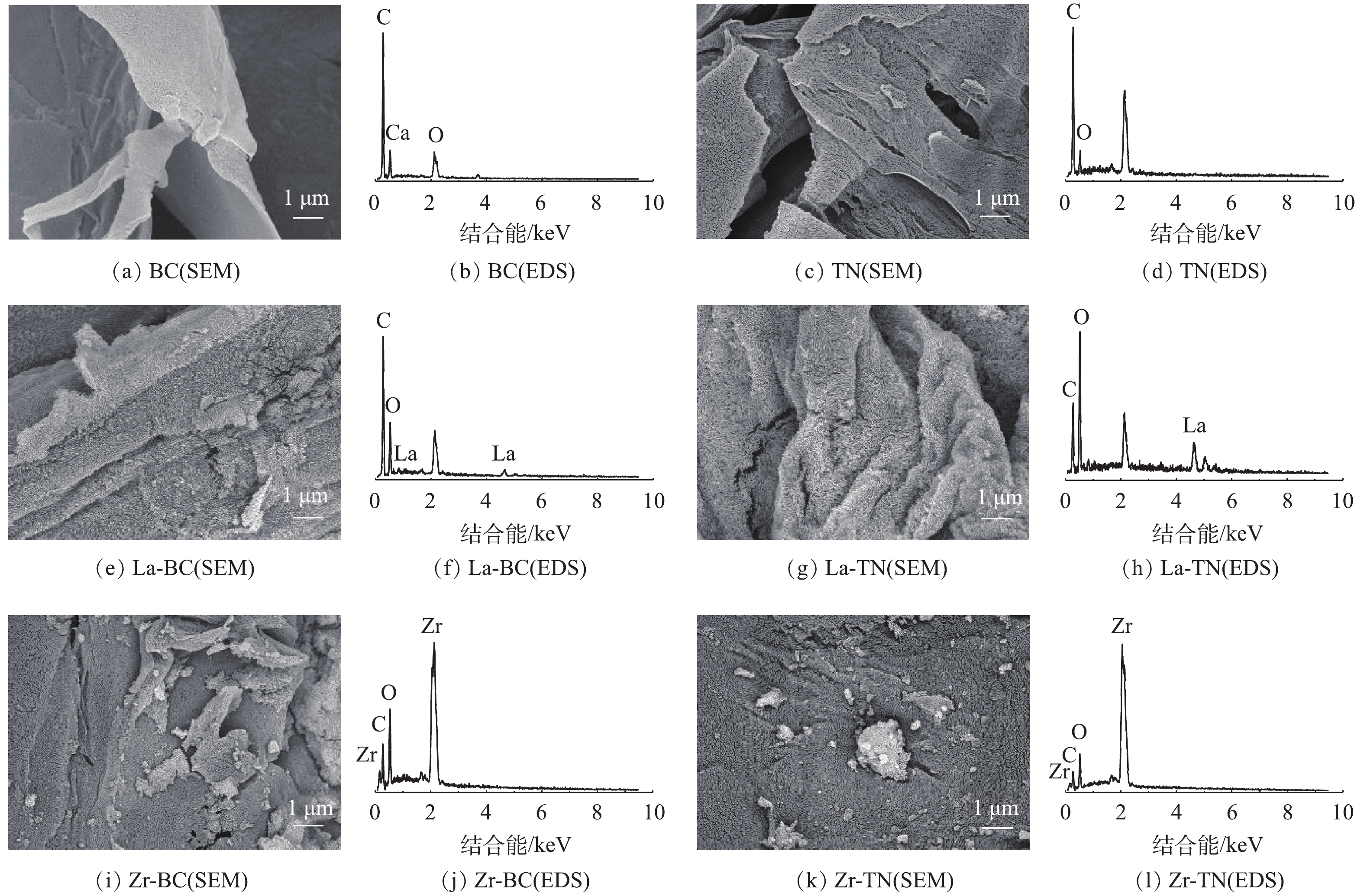
1)表面微观形态和X射线能谱分析。改性前油菜秆和菱角壳表面较为光滑平整(图1)。经镧改性后,2种材料表面被大量絮绒状金属化合物包裹并出现明显的褶皱和凸起;而锆改性材料上附着有团块状或颗粒状金属化合物,表面由光滑变为粗糙。这可能是因为NaOH在分解过程中破坏了材料结构,为金属离子提供了更多的附着点。因此,经镧和锆改性后材料的比表面积和吸附位点有所增加,这有利于吸附的进行。对比6种材料的表面能谱分析结果(表1)可看出,经改性后材料表面的碳含量减少,而氧含量有所增加,这可能是金属负载物呈氢氧化物或氧化物存在并覆盖材料表面所致。4种改性材料表面均出现了La或Zr的谱峰,这表明2种金属已成功负载到2种原材料的表面上。
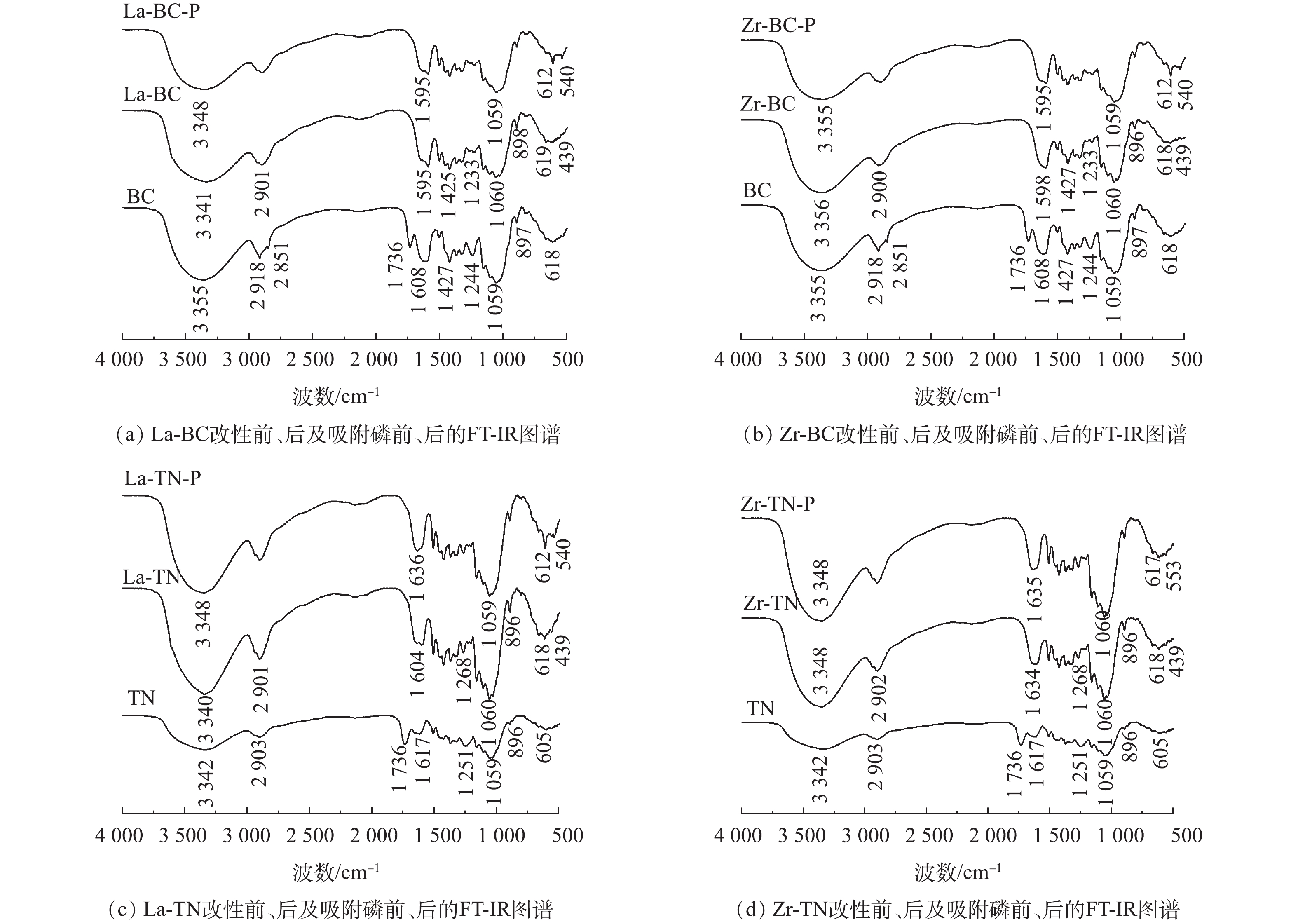
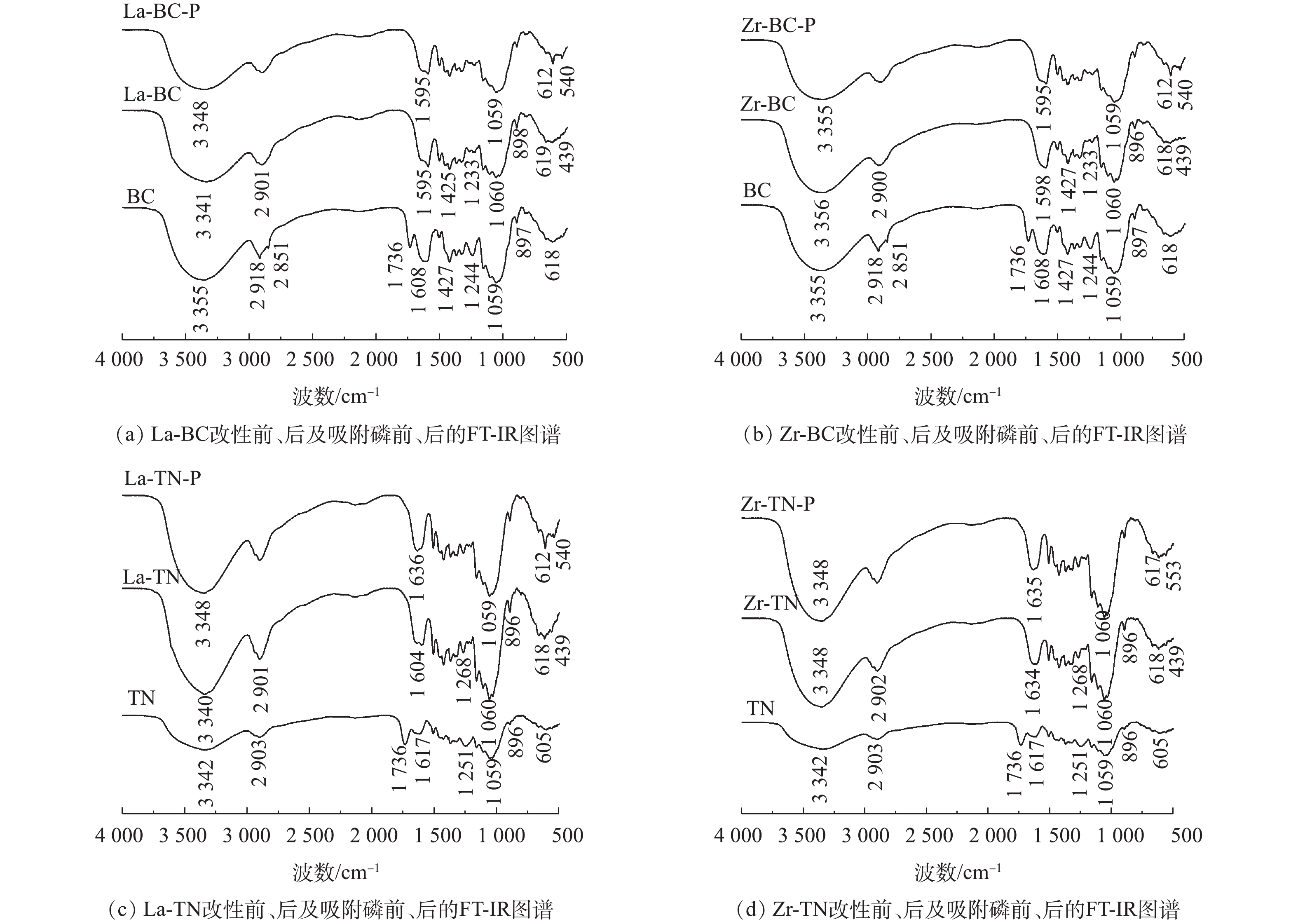
2)傅里叶变换红外光谱分析。改性前油菜秆和菱角壳的特征吸收峰大致相似(图2)。其中,3 342 cm−1和3 355 cm−1处吸收峰为二者表面羟基的伸缩振动所致[7];2 900 cm−1附近的吸收峰对应C—H的拉伸振动[6];1 736 cm−1处的特征吸收峰来自酯基的—C=O;1 251 cm−1和1 244 cm−1处的吸收峰归属于C—O;1 059 cm−1处为C—OH的伸缩振动吸收峰。
2种原材料经镧或锆改性后,1 736 cm−1和1 251 cm−1处的吸收峰减弱或几乎消失。这是NaOH水解原材料中的酯键所致。改性后的菱角壳在3 342 cm−1与1 059 cm−1处的吸收峰均增强,这表明酯键在水解后增加了羟基的数量。这2种原材料经镧和锆改性后均在439 cm−1附近出现了La—O[15]或Zr—O—Zr[16]的特征吸收峰,这表明镧和锆已负载到2种原料载体上。在吸附磷后,4种改性材料在3 341 cm−1附近的吸收峰均存在不同程度的降低,这可能是—OH与磷酸根发生配位交换所致[6]。同时,4种改性材料在540 cm−1附近均出现新的特征吸收峰,其可归属于O—P—O[17],这表明磷已被吸附在改性材料的表面。
-
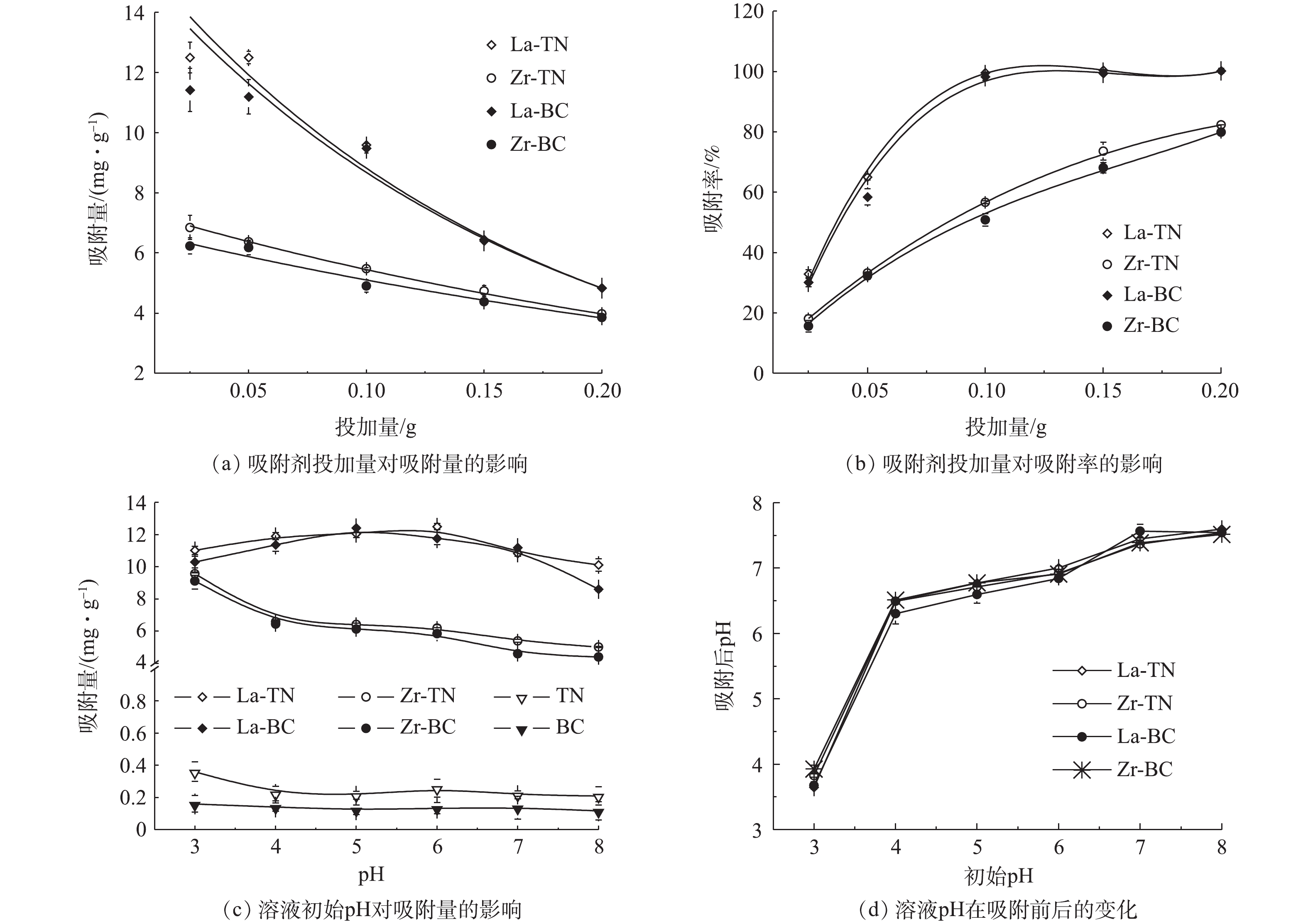
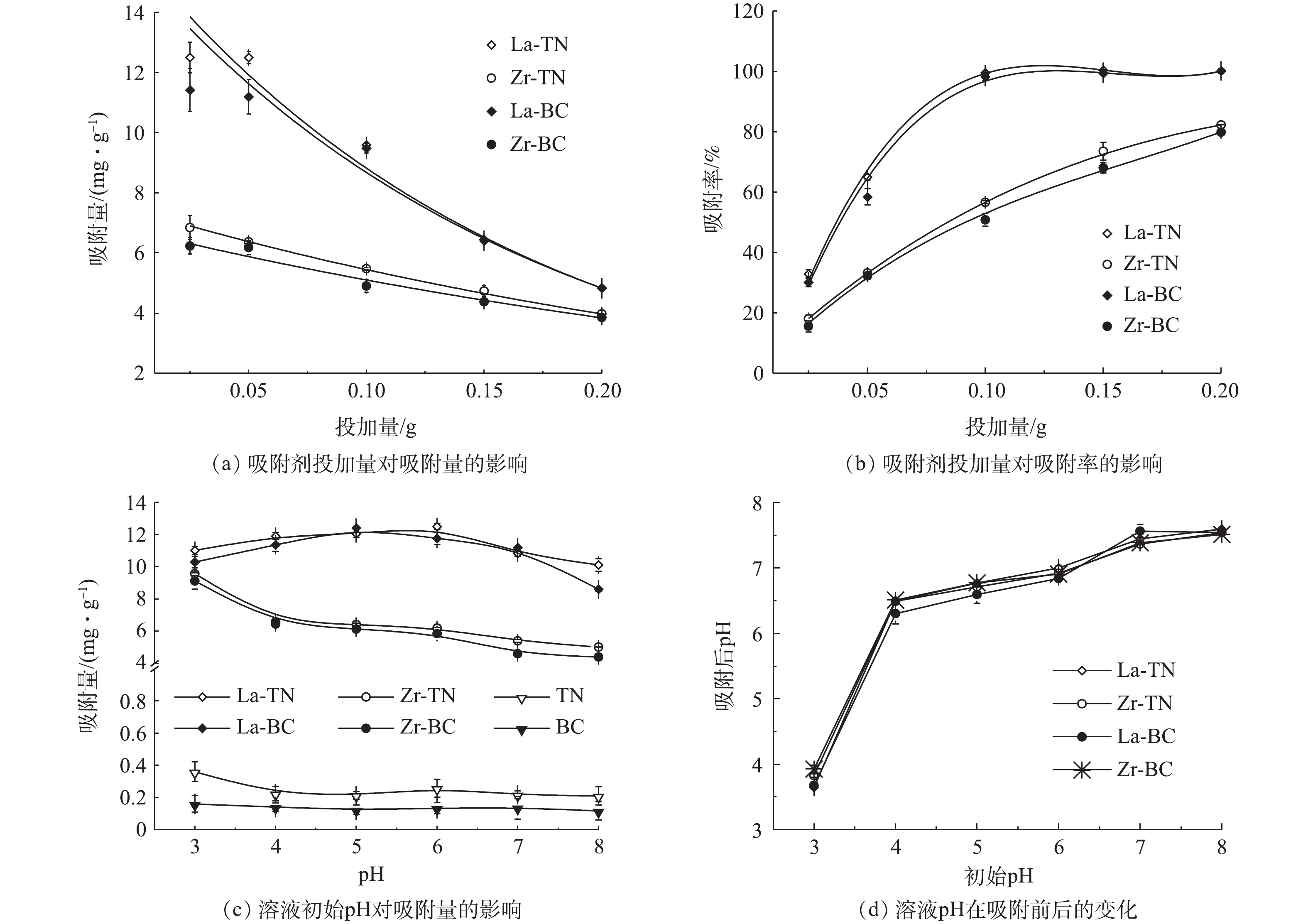
1)吸附剂投加量对磷吸附效果的影响。吸附剂投加量及溶液初始pH对吸附效率的影响效果如图3所示。4种改性材料对磷的吸附量随其投加量的增加均呈指数下降(图3(a)),而吸附率相应上升(图3(b))。该变化趋势与锆交联壳聚糖颗粒对磷的吸附相似[16]。这是由于溶液中磷含量一定,随着投加量的增加,吸附剂表面的活性位点逐渐趋于不饱和,因此,单位吸附量减少;但总吸附量有所增加,所以吸附率逐渐上升。其吸附量均在投加量为0.025 g处达到最大,La-TN和La-BC吸附量分别为12.49 mg
⋅g−1 和11.41 mg⋅g−1 ,显著大于Zr-TN(6.85 mg⋅g−1 )和Zr-BC(6.83 mg⋅g−1 )(P<0.05)。2)溶液pH对磷吸附量的影响。随溶液pH升高,改性前2种材料对磷的吸附量较低且无明显变化(图3(c))。镧改性的2种材料对磷的吸附量先增加后减少,原因在于初期pH升高使得溶液中H3PO4(pH<2.13)向利于吸附的
H2PO−4 (2.13<pH<7.20)转变[18],因此,通过配体交换作用使得吸附的磷有所增加;但当pH继续上升后,磷的主要存在形态变为HPO2−4 (7.20<pH<12.33),其相对H2PO−4 不易被吸附[9];同时,吸附剂表面去质子化作用有所增强[7]。因此,通过配位作用和静电作用吸附的磷均有所减少。此外,高浓度的OH−将会与磷酸根竞争吸附位点[2]。这3种作用带来的正负综合效应表现为磷的吸附量先增加后减少。该变化趋势与镧改性活性炭纤维受pH影响的变化趋势相似[2]。锆改性的2种材料对磷的吸附量随pH的增加而呈幂函数式减少,与先前报道中锆改性豆渣的变化趋势相似[8]。这可能是因为酸性环境下的锆改性材料质子化程度较高,静电吸附作用较明显。因此,吸附量随pH升高而持续下降。4种改性材料吸附后pH的变化趋势相似(图3(d)),当pH从3上升到7时,吸附后溶液pH较初始pH均有所上升,说明有OH−从吸附剂表面释放,这表明配位体交换是4种改性材料的吸附机理之一[19]。当初始pH为8时,吸附剂表面与金属离子配合的—OH可能存在脱H+现象[18]。因此,吸附后的pH较初始pH有所降低。综合溶液pH对实验结果的影响,4种材料的吸附机制主要为静电吸附和配位交换作用。
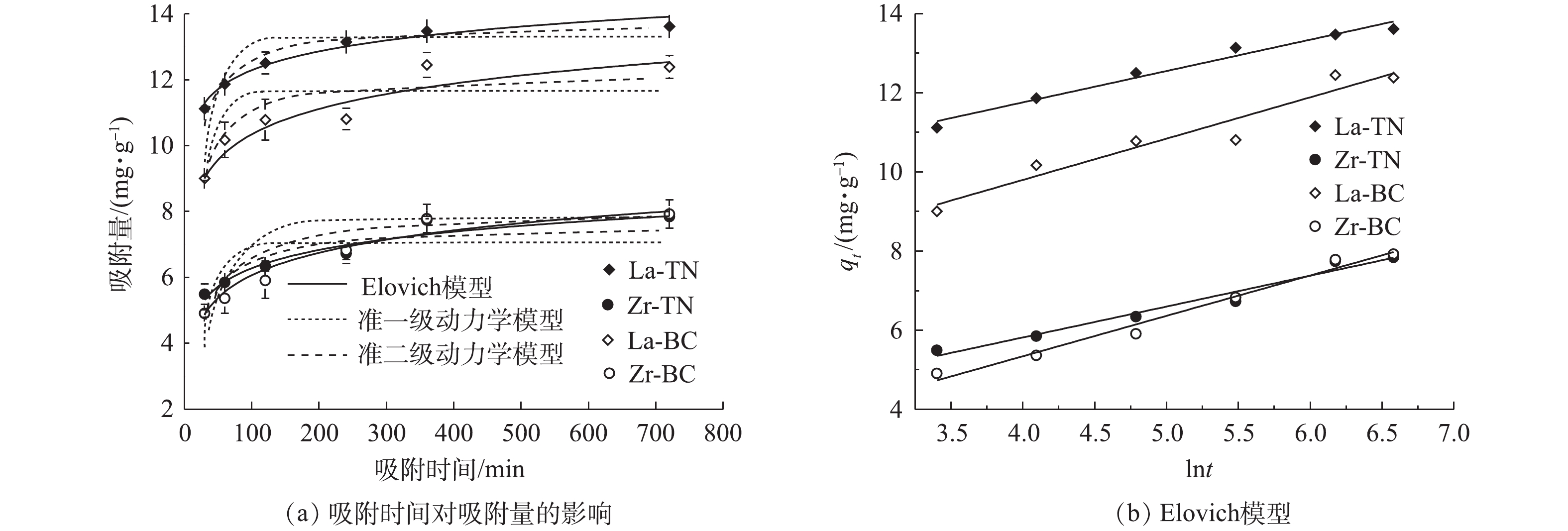
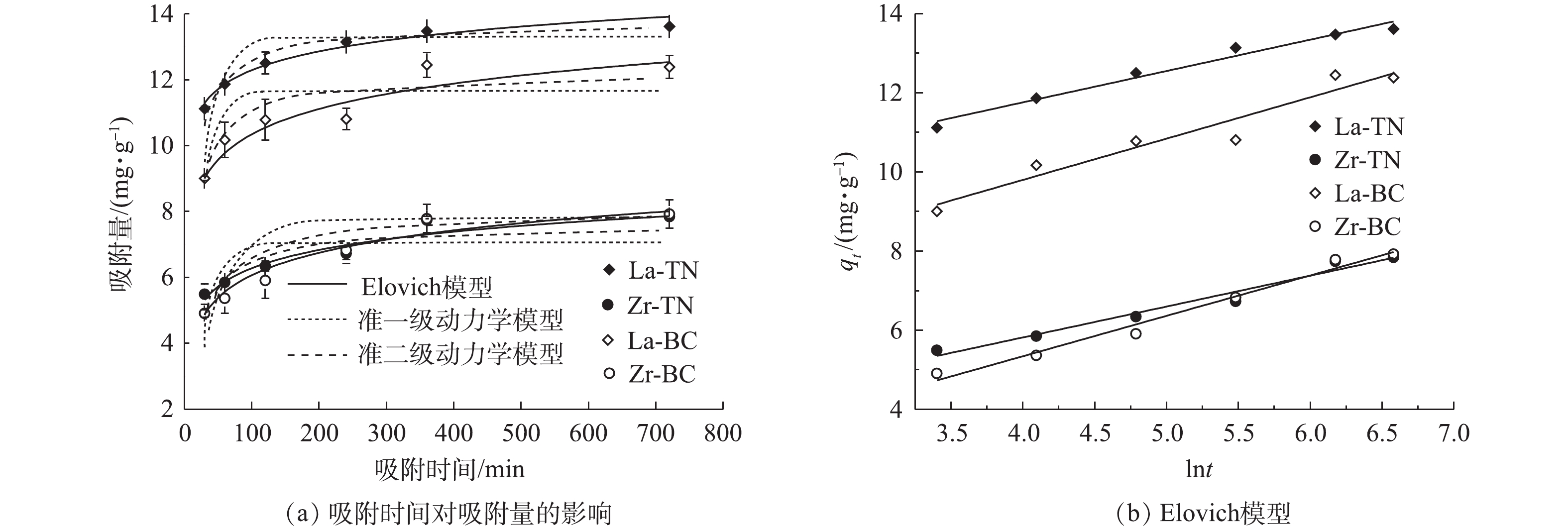
3)吸附动力学。吸附时间是影响吸附效率的重要因素之一。在本研究中,4种改性材料初期吸附速率较快(图4),但随吸附时间的增加,吸附速率逐渐减小。其原因可能有2方面:在吸附初期,吸附剂表面与溶液中磷浓度差较大,因此,吸附推动力较大;初期吸附剂表面活性位点较多,与磷的接触概率较高,因此,吸附速率较快。随吸附时间的延长,La-TN、Zr-TN、La-BC和Zr-BC可达到的最高吸附量分别为13.61、7.84、12.38和7.92
mg⋅g−1 。其中,La-TN显著高于其他3种材料(P<0.05)。为研究改性材料的总体吸附机制,分别采用准一级动力学模型、准二级动力学模型和叶诺维奇模型对4种材料对磷的吸附量随时间的变化曲线进行了拟合(图4)。与准一级动力学和准二级动力学模型相比,叶诺维奇模型的可决系数更高(R2>0.95)(表2),叶诺维奇模型能更好地描述4种改性材料对于磷的吸附过程。这表明4种材料对溶液中磷的吸附为非均相界面的化学过程,活性位点位于不均一的材料表面,且该吸附过程伴随反应活化能的改变[20]。这可能与油菜秆和菱角壳内含有纤维素、木质素、单宁酸及酚类化合物等多种物质有关[20]。4种材料的
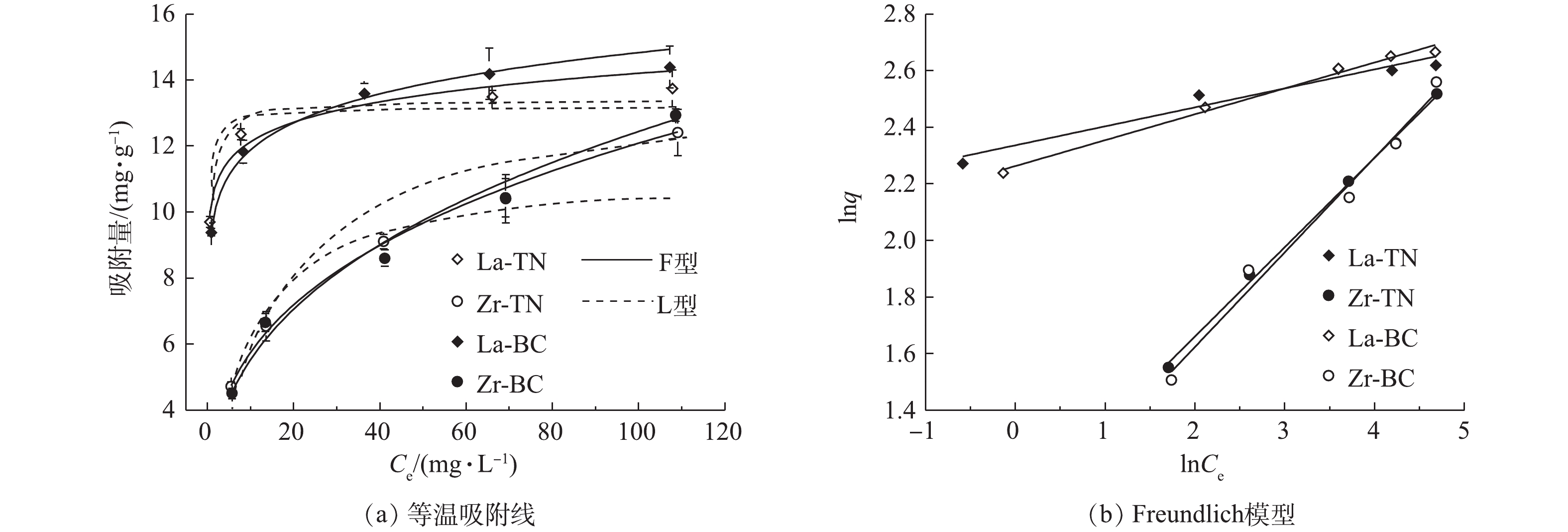
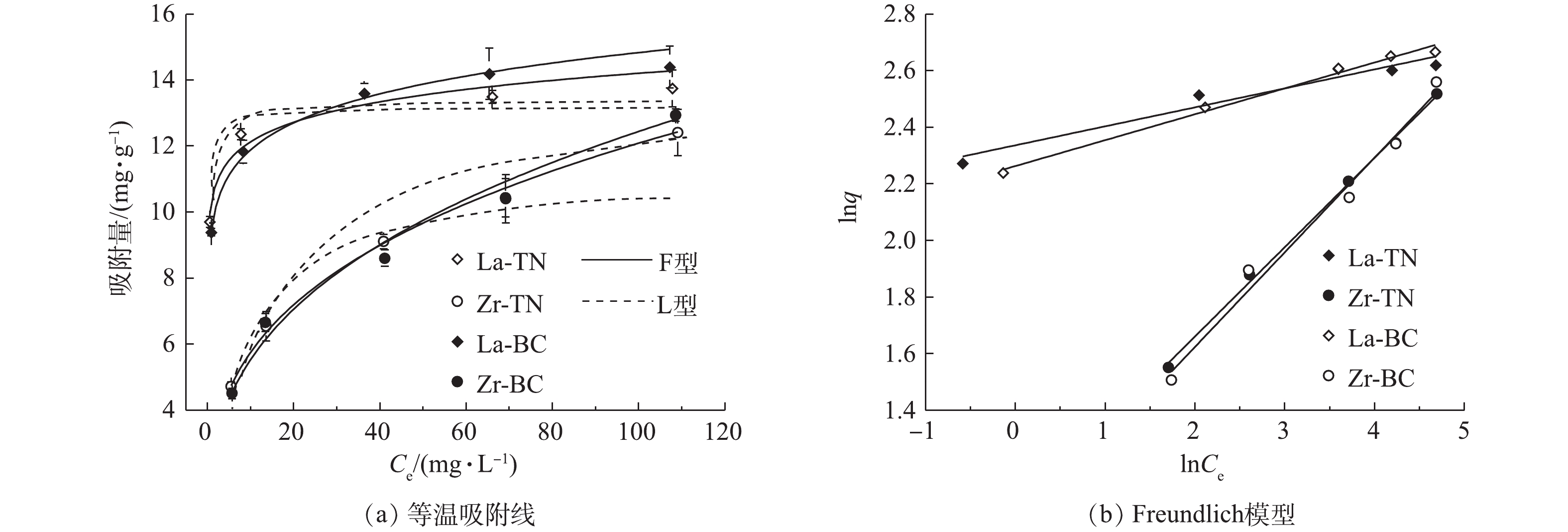
αs 值均大于βs 值,表明吸附反应为正向进行[21]。其中,La-TN和La-BC的初始吸附速率均大于Zr-TN和Zr-BC,这表明镧改性的2种材料相较于锆改性的2种材料对磷更具亲和力。4)等温吸附。吸附等温线的研究有助于了解吸附过程中固液界面反应和探究吸附剂的吸附能力[22]。在本研究中,随着磷浓度的增加,4种改性材料对磷的单位吸附量先增加后逐渐趋于稳定(图5)。在低浓度的磷溶液中,同一原材料经镧改性后对磷的吸附量显著高于经锆改性的材料(P<0.05),而随着磷浓度的逐渐增加,两者差距逐渐减小。这表明与低浓度的含磷废水比较,锆改性的2种材料在高浓度含磷废水的吸附应用中更具潜力。
采用Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型对4种材料的吸附等温线进行拟合,拟合后的部分参数如表3所示。由相关系数来看,Freundlich模型拟合优度较高,这表明4种改性材料对于磷的吸附属于非均质界面的多层吸附[7],这与用叶诺维奇模型拟合的吸附动力学所得结果相符。4种改性材料的n值均大于2,故其对磷的吸附均属于容易吸附[12]。由Langmuir模型可得La-TN和La-BC的最大吸附量分别为13.18
mg⋅g−1 和13.40mg⋅g−1 ,均高于镧改性凹凸棒土(12.08 mg⋅g−1 )[23];Zr-TN和Zr-BC最大吸附量分别为11.16mg⋅g−1 和13.76mg⋅g−1 ,均高于锆改性沸石(1.546 mg⋅g−1 )[9]。因此,4种改性材料均具有较好的吸附性能。 -
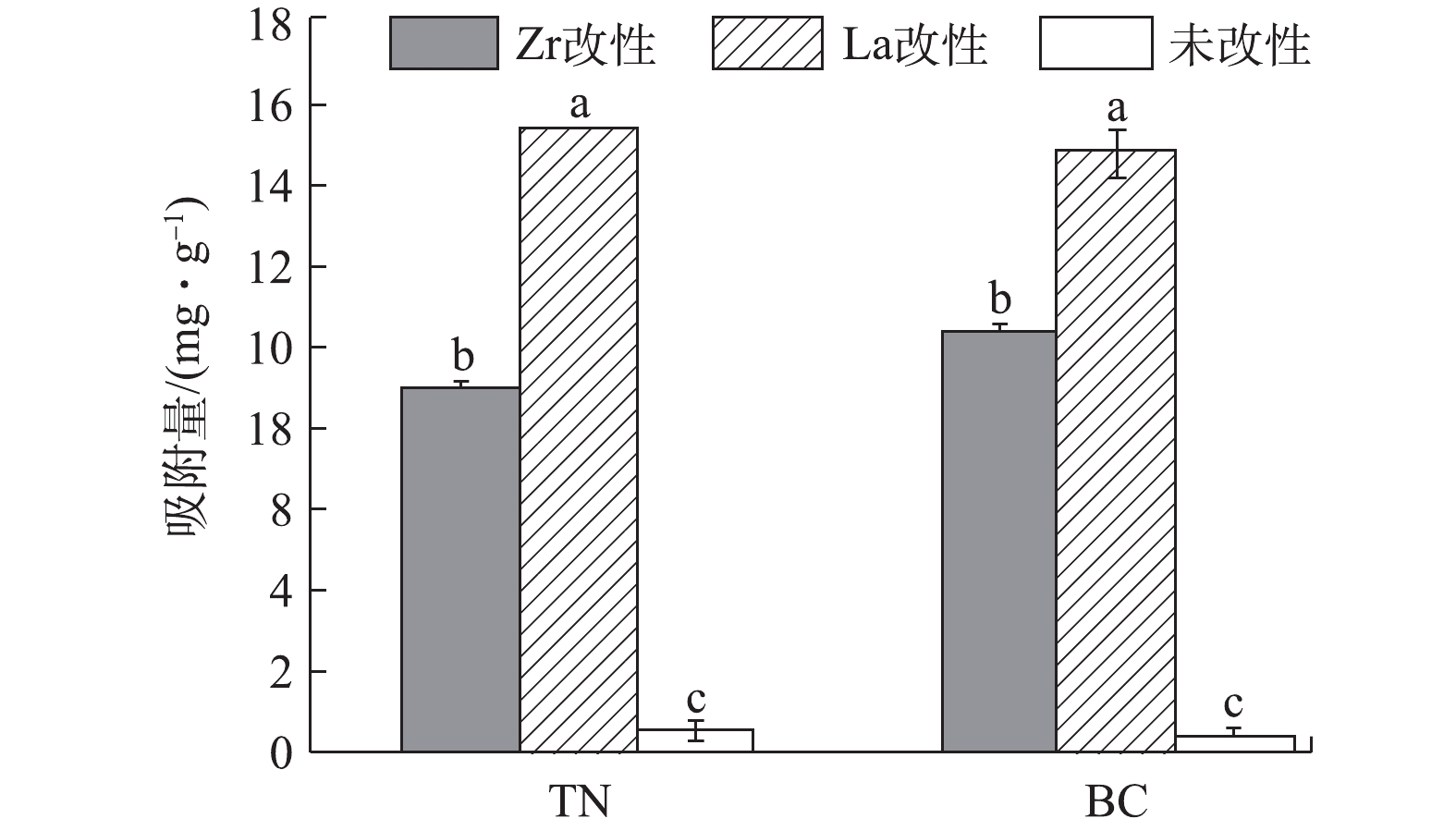
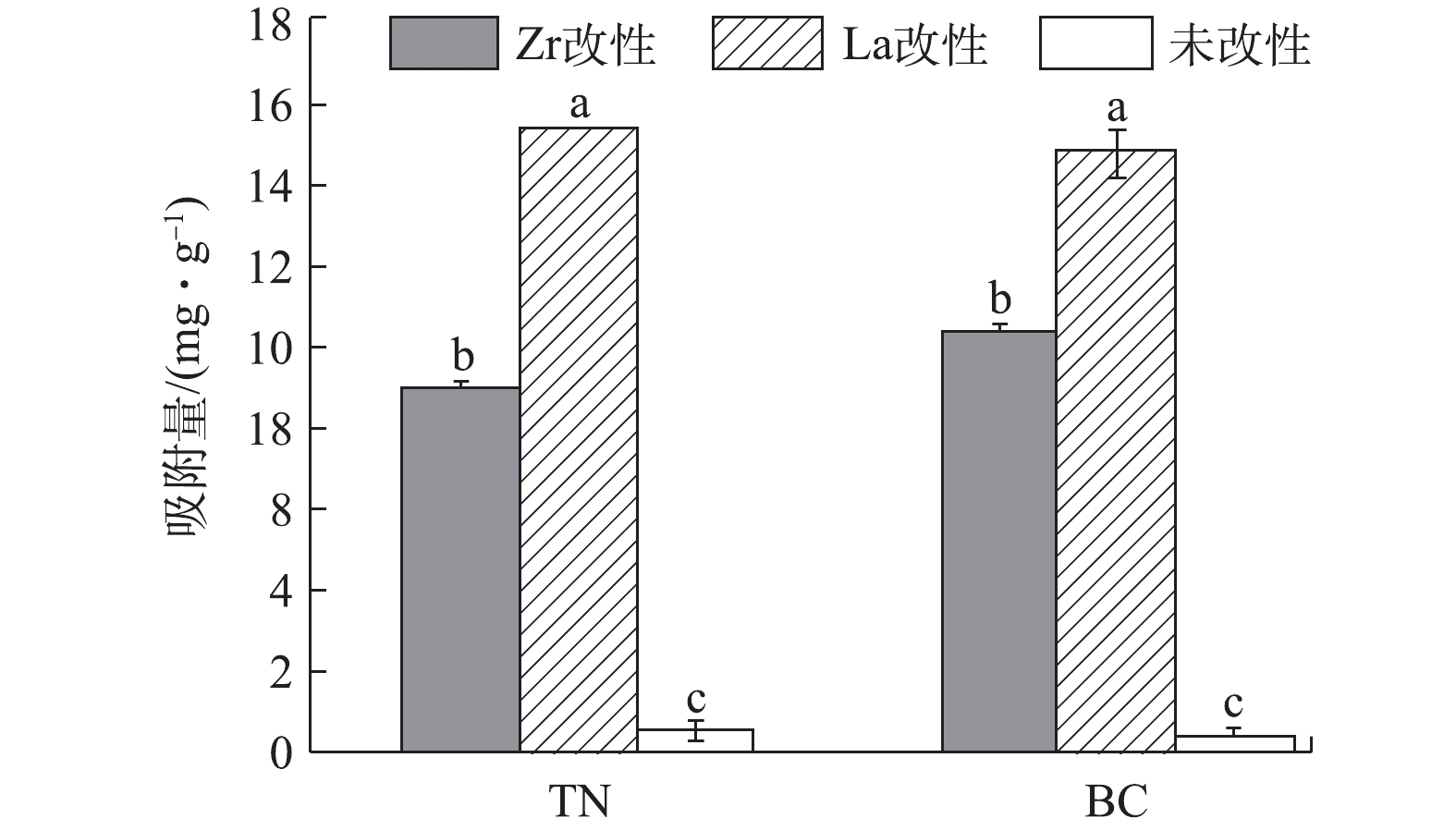
本研究采用养猪废水对菱角壳和油菜秆改性前后的磷吸附效果进行验证(图6)。未改性菱角壳和油菜秆对养猪废水中磷的吸附量分别为0.45
mg⋅g−1 和0.28mg⋅g−1 。而改性后La-TN、Zr-TN、La-BC和Zr-BC对养猪废水中磷的的实际吸附量分别为15.41、8.91、14.82和10.36mg⋅g−1 ,较改性前分别提升了34、20、53和37倍。因此,4种改性材料对养猪废水中的磷具有良好的吸附潜力。其中,镧改性材料显著高于锆改性材料(P<0.05),La-TN对磷的吸附量显著高于其他3种改性材料(P<0.05),Zr-TN显著低于其他3种改性材料(P<0.05)。
2.1. 样品表征
2.2. 改性材料在模拟废水中的吸附实验
2.3. 改性材料在养猪废水中的吸附效率
-
1) FT-IR和SEM-EDS的表征结果表明,镧和锆均已成功负载于油菜秆和菱角壳的表面上。
2)随4种改性材料投加量的增加,其对磷的吸附量呈指数下降。在投加量为0.1 g时,La-TN和La-BC对模拟废水中磷的去除率可达98%以上;在投加量为0.2 g时,Zr-TN和Zr-BC的吸附率分别可达82.29%和79.87%。随pH的增加,La-BC和La-TN对磷的吸附量呈先增大后减小的趋势,其分别在pH=5和pH=6处达到最大;锆改性油菜秆和菱角壳吸附量呈幂函数减小趋势,均在pH=3处有最大吸附量。
3)叶诺维奇模型(R2>0.95)能够更好地描述4种改性材料的吸附动力学。改性后材料表面活性位点不均一,吸附过程伴随活化能的改变,吸附机制为静电吸附和配位交换作用。相较于Langmuir模型,4种改性材料的吸附等温线采用Freundlich模型拟合度更优,这表明吸附过程为不规则的多分子层吸附。
4) La-TN、Zr-TN、La-BC和Zr-BC对养猪废水中磷的吸附量较改性前均有较大的提升,其分别为改性前的34、20、53和37倍。








 下载:
下载: