-
混凝/絮凝是去除水中悬浮物常用的水处理方法。19世纪末,人类就开始使用含铝混凝剂进行水质净化,但对于铝可能对人类健康和环境造成的不利影响却一直存在争议[1]。为避免残余铝潜在的生物毒性,铁混凝剂越来越多地被开发和应用,铁混凝剂对溶解有机碳(DOC)的去除率高于铝混凝剂,对人类健康的不利影响较小[2]。但使用铝、铁混凝剂在混凝-絮凝过程中会产生大量的污泥,增加后续污泥处理成本[3]。近年来,钛盐因其具有绿色、低毒、高效的特点,在水处理上的应用及研究发展迅速[4],利用钛盐制备混凝剂也成为水处理药剂的研究热点之一。据报道[5-6],钛盐混凝剂水解迅速,在处理低温低浊度水方面表现出比铁盐、铝盐混凝剂更好的混凝效果和对污染物的去除能力。但对于在混凝过程中的传统钛盐混凝剂,钛水解导致大量的H+释放,导致处理水样pH过低,从而需要增加碱的投加量。有研究[7-8]表明,传统钛混凝剂引起水样pH降低的问题可以通过聚钛混凝来解决。聚钛混凝剂通过预水解的方式,使钛离子在制备过程中将H+释放,进而使其在混凝过程中对水样pH的影响降到最低。此外,聚钛混凝剂在有机物去除和对pH的依赖性方面也比传统钛混凝剂更佳。
煤矸石是采煤和洗煤过程中排放的固体废物。在我国,煤矸石已成为一种排出量和储存量最大的工业废弃物[9],且煤矸石在放置过程中易被风化,能够产生大量有毒物质及有害气体,对人体、生态都造成极大的危害[10]。煤矸石既是固体废物,也是难得的矿物资源,其富含Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO和MgO等金属氧化物,以煤矸石为原料来制备含铝、铁等产品是煤矸石资源化利用的一个重要途径[11-12]。
国内外关于无机高分子混凝剂的研究较多,但如何降低混凝剂的成本、提高混凝效率并解决原料不足的问题依然是目前研究的热点。煤矸石作为一种含有益矿物的资源型矿物,以其为原料制备的混凝剂已有大量研究和应用,但以煤矸石为原料制备钛掺杂聚合氯化铝铁还鲜有报道。本研究在煤矸石制备聚合氯化铝铁的基础上进行钛掺杂的尝试,研究了制备条件对混凝性能的影响规律,确定了聚合氯化铝铁钛(PTAFC)的最佳制备条件,并将其应用到城镇污水处理厂中二沉池出水的深度处理研究,以期为有效减少煤矸石的堆存量、拓宽煤矸石利用渠道并实现聚钛混凝剂的低成本、高效率工业化生产及应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
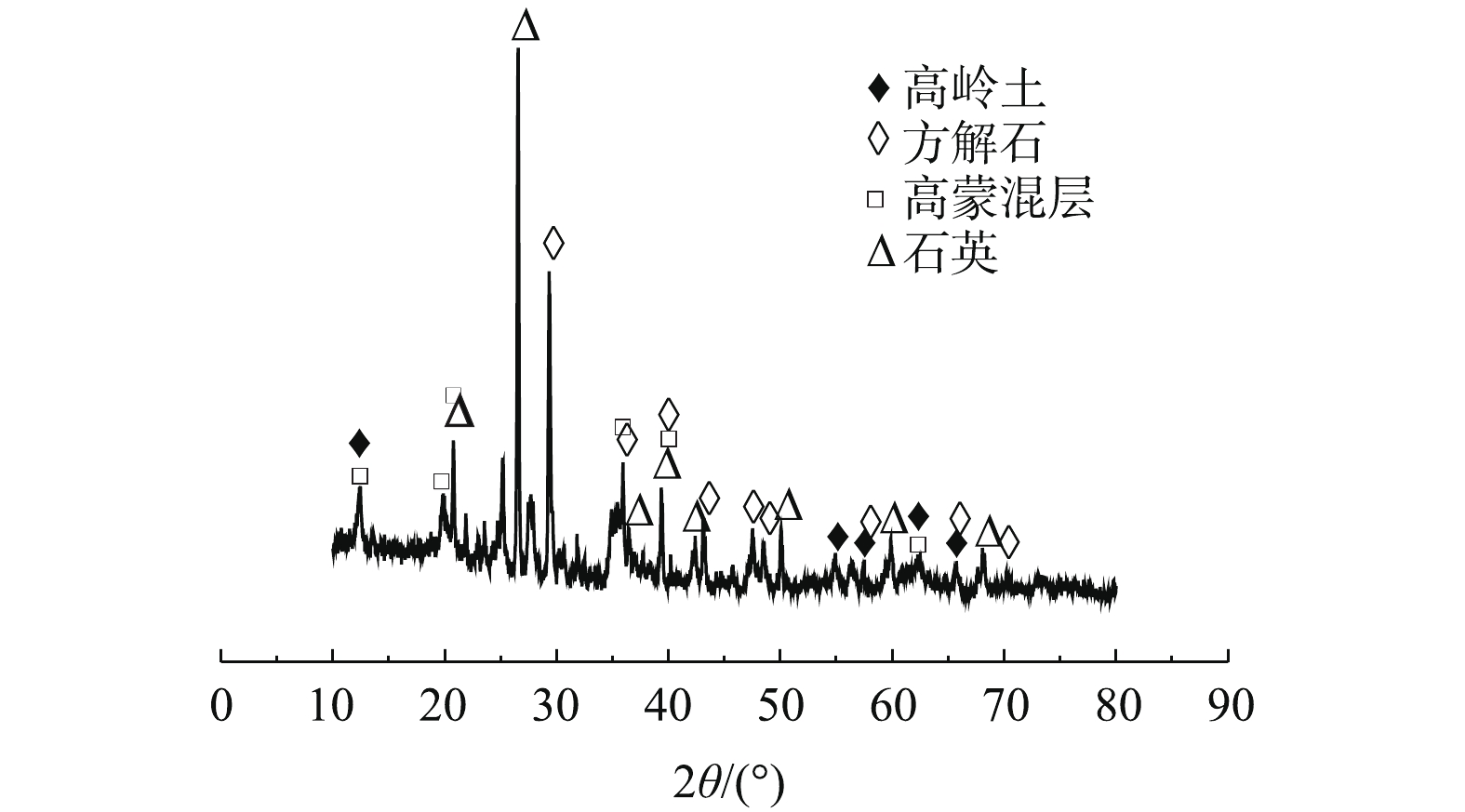
本实验煤矸石取自宜宾市鲁班山北矿矸石山,主要化学成分为SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO和TiO2,相对含量分别为43.97%、18.43%、14.75%、12.11%和4.45%,主要矿相为石英、高岭土、方解石和高蒙混层(图1)。
在进行煤矸石酸浸液的制备时,将160目的煤矸石粉末在马弗炉中于800 ℃焙烧2 h,自然冷却后,设置盐酸浓度为8 mol·L−1,按固液比为1∶7于100 ℃的恒温水浴锅搅拌反应3 h后取出,离心取上清液得到煤矸石酸浸液,其主要化学成分为Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO和TiO2,相对含量分别为1.27%、1.54%、0.046%和0.008%。主要实验试剂有盐酸、硫酸、氧化钙、高岭土、四氯化钛等,除高岭土外,试剂均为分析纯。
实验所用主要仪器设备有SHJ-A4恒温磁力搅拌水浴锅、101-3AB型电热鼓风干燥箱、FA224电子天平、UpHW-IV-90T优普系列超纯水器、XA-2固体样品粉碎机、TD-420台式低速离心机、JC-101W微波消解仪、WFZ UV-4802H型紫外可见分光光度计、SGZ-1A数显浊度仪、JJ-4六联数显电动搅拌器、smartlab 9kw X射线衍射仪、PANalytical Epsilon 3XLE能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪、Zetasizer3000HSa型Zeta电位分析仪和Mastersizer2000型激光粒度仪等。
-
影响无机高分子混凝剂混凝性能的制备条件很多,如聚合温度、聚合时间、搅拌方式、搅拌速度、pH、原料配比、混凝剂种类、熟化温度、熟化时间、碱化度等[13]。碱化度是影响以预水解方式制备出来的混凝剂混凝效果的一个重要因素,碱化度的大小影响混凝剂的聚合度。有研究[14]表明,混凝剂的碱化度有其最佳的范围,其他制备条件对碱化度的影响将直接影响到混凝剂的聚合度。其中,pH、原料配比、聚合时间、聚合温度对碱化度的影响较大,因此,本研究选pH、钛铁摩尔比、聚合时间、聚合温度为制备的影响因子,考察其对PTAFC混凝效果的影响规律。由于所用的煤矸石中钛含量不高,且钛的溶出条件较为苛刻,因此,需要补充钛源以考察钛铁摩尔比对混凝性能的影响。
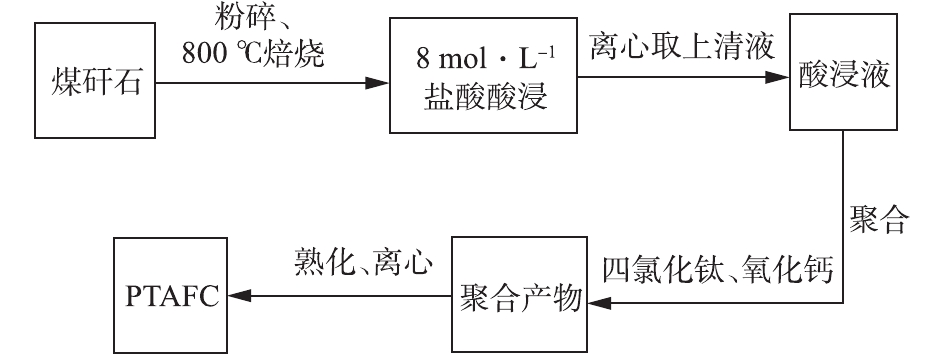
以煤矸石为原料制备聚合氯化铝铁钛的过程主要包括酸浸、钛掺杂、调节pH、聚合、熟化、浓缩干燥等。具体工艺流程如图2所示。
首先根据预先设定的钛铁摩尔比(0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9、1.1、1.3、1.5),用移液管吸取20 mL最佳条件制得的酸浸液,移入烧杯,置于低温磁力搅拌水浴锅冰水浴中,加入四氯化钛,加盖表面皿,搅拌至四氯化钛完全溶解;接着根据预先设定的初始pH (0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4),用氧化钙对钛掺杂后的酸浸液进行pH调节;将其置于适宜的聚合温度(30、40、50、60、70、80、90、100 ℃)下,持续搅拌一定时间(1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8 h)后取出,常温熟化24 h,即制备出聚合氯化铝铁钛PTAFC。
-
影响混凝剂混凝效果的因素除混凝剂本身的性质外,还有操作条件和环境因子,如投加量、pH、混凝时间、反应温度和搅拌速度等。为了考察环境因子和操作条件对混凝剂混凝效果的影响,本实验采用最佳制备工况下制备的PTAFC及市购PAFC,选择对混凝过程影响较大的投加量、pH、沉淀时间、反应温度和搅拌速度等因素,分别研究其对混凝效果的影响。
在进行自配水混凝实验时,采用去离子水、高岭土、邻苯二甲酸氢钾配制成COD为500 mg·L−1、UV254 为2.738、浊度为100 NTU的原水。在150 mL原水加入10、30、50、70、90、110、130、150 mg·L−1的混凝剂,使用0.1 mol·L−1氢氧化钠溶液和盐酸溶液调节pH至5、6、7、8、9、10,使用六联数显电动搅拌器在温度为10、20、30 ℃的条件下,快搅(300 r·min−1) 1 min,中搅(150 r·min−1)3 min,慢搅(0、40、50、70、90、110、130、150 r·min−1) 8 min,取出搅拌桨。静置沉降0.25、0.5、1、3、5、10、15、30 min后,使用虹吸法吸取上清液(液面下1~2 cm处),分析其浊度、COD和UV254。
取实际污水对PTAFC的性能进行验证,并与市购传统聚合氯化铝铁(PAFC)进行对比。所取水样为四川省德阳广汉某镇污水处理厂二沉池出水,水样显轻微黄色,无味,浊度为7.8 NTU、氨氮为12.51 mg·L−1、COD为98.75 mg·L−1、总磷为0.96 mg·L−1,分别在PAFC、PTAFC的最佳混凝条件下进行效果对比,具体混凝操作同自配水混凝实验。
-
本研究中主要的检测指标为浊度、UV254、COD、氨氮和总磷,检测方法参考文献中的方法[15]。浊度测定采用SGZ-1A数显浊度仪;采用WFZ UV-4802H型紫外可见分光光度计测定UV254,将混凝出水经过0.45 µm的滤膜过滤后,测定其在254 nm处的吸光度;采用重铬酸钾法测定COD;采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定氨氮;采用过硫酸钾消解-钼锑抗分光光度法测定总磷;采用smartlab 9 kW X射线衍射仪分析煤矸石物相;采用PANalytical Epsilon 3XLE能量色散射线荧光光谱仪分析煤矸石化学成分;采用Zetasizer3000HSa型Zeta电位分析仪测定原水及出水水样中的絮体Zeta电位;采用Mastersizer2000型激光粒度仪监测混凝动态过程。
酸浸液中各金属离子的检测方法参考《高岭土及其试验方法》(GB/T 14563~14565-1993)。Fe2O3、Al2O3和CaO的测定采用络合滴定法,采用分光光度法测定TiO2;采用氟盐遮蔽中和法[16]测定碱化度。
1.1. 原料、试剂及仪器
1.2. PTAFC的制备条件影响分析及制备方法
1.3. 混凝操作条件影响分析及实验方法
1.4. 检测分析方法
-
钛铁摩尔比对PTAFC的碱化度和污染物去除性能的影响如图3所示。可以看出,PTAFC对浊度、UV254、COD的去除率在开始时随着钛铁摩尔比的升高而升高,在钛铁摩尔比为0.3时,浊度去除率最高达98.67%,碱化度为71.36%,UV254去除率为23.05%,COD去除率为25.15%。之后随着Ti∶Fe(摩尔比)的升高,浊度去除率逐渐下降。因为随着PTAFC中Ti(Ⅳ)浓度的升高,反应体系中形成更多中高聚合度的钛配合物,从而使PTAFC 具有一定的链网状结构,提高了混凝过程中架桥与网捕作用。当继续增加钛铁摩尔比时,混凝效果降低,一方面,如果钛离子含量过高,其较强的水解性导致水体pH降低,不利于混凝[17];另一方面,随着钛铁摩尔比的增加,在反应体系中Ti(Ⅳ)含量逐渐增加,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)含量相对减少,Ti(Ⅳ)水解同Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)水解存在对OH−的竞争作用。由于钛元素价态高于铝、铁的价态,Ti(Ⅳ)对OH−竞争作用强于Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ),Ti(Ⅳ)水解形态倾向于中高聚合度的钛配合物,而Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)水解形态倾向于自由离子、单体和初聚物[18],抑制了水解聚合物之间的协同作用,故钛含量过高反而造成混凝效果降低。因此,确定最佳钛铁摩尔比为0.3。
-
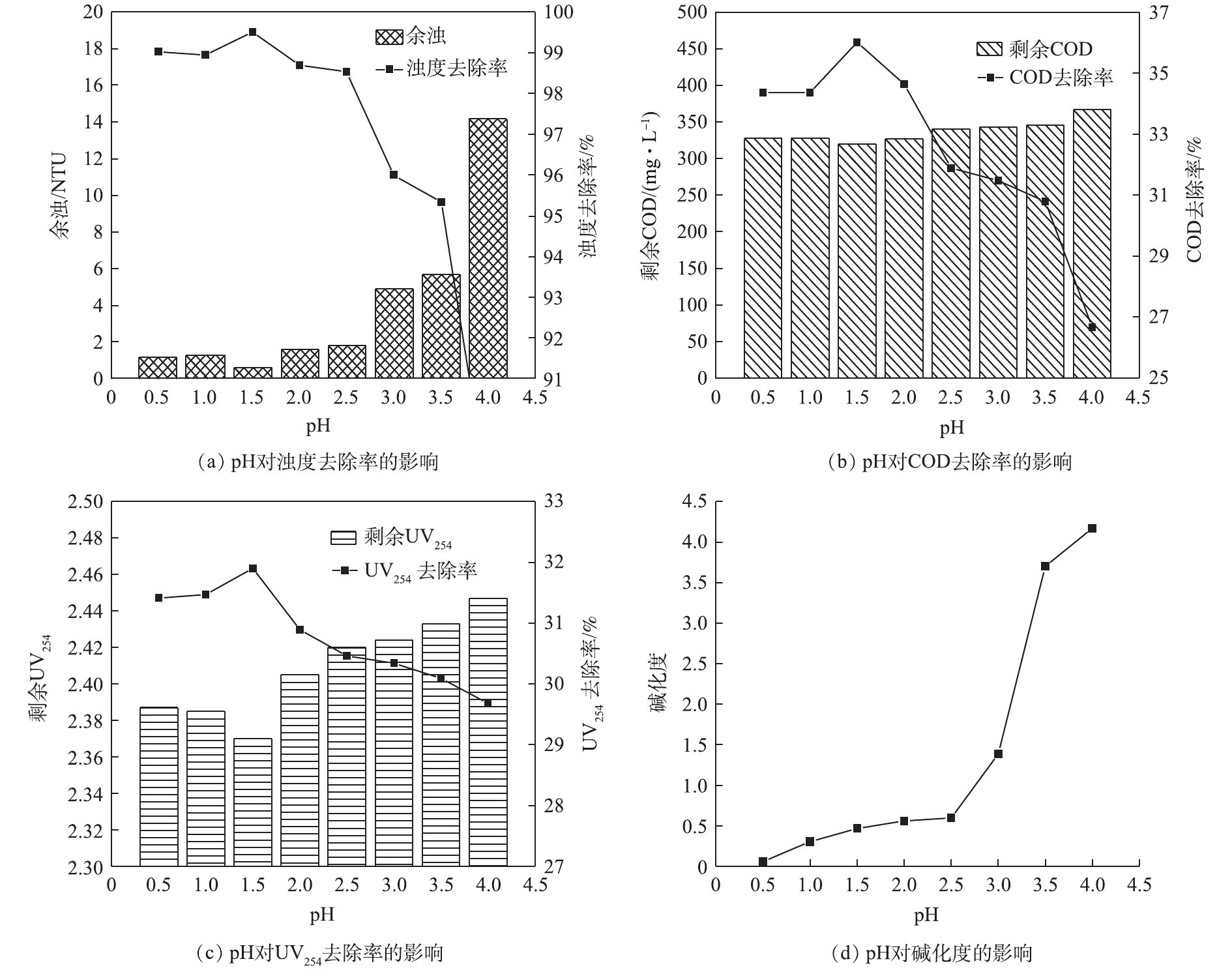
聚合pH对PTAFC的碱化度和污染物去除性能的影响如图4所示。由图4(a)~图4(c)可知,pH对浊度、UV254、COD的去除率皆先上升后下降。随着pH的升高,样品的碱化度也逐渐升高(图4(d))。在pH=1.5时,去除效果最佳,浊度、UV254和COD的去除率分别为99.51%、31.90%和36.02%。铝、铁化合物在体系中水解聚合主要有3种形态:Al-Fea(快速络合的自由离子、单体和初聚物)、Al-Feb(慢速络合的低聚和中等聚合物)、Al-Fec(高聚物和溶胶态)。随着碱化度的增加,Al-Fea含量逐渐减少而Al-Fec含量逐渐增加,Al-Fea单位正电荷高,电中和能力强,但架桥能力弱;Al-Feb具有良好的吸附、电中和与架桥能力;Al-Fec正电性较弱、粒度大、易于沉淀,且具有良好的吸附架桥和沉淀能力[18]。有研究[19]表明,Alb、Alc对浊度的去除效果优于Ala。随着碱化度的提高,Ti(Ⅳ)由单体状态逐渐向聚合态转化,但部分高聚合度钛羟基聚合物不稳定,容易分解[20]。所以在碱化度较低时,Ti(Ⅳ)化合物水解产物聚合度低,吸附架桥能力弱;随着碱化度的增加,Ti(Ⅳ)化合物水解可形成大量多核钛羟基聚合物,具有极强电中和、吸附架桥和网捕卷扫能力,对水体中污染物进行电中和、吸附架桥与网捕卷扫作用,从而使污染物脱稳形成沉淀,达到去除水体中污染物的目的[21]。Fe(OH)3开始沉淀和完全沉淀的pH分别为1.14和3.0,Al(OH)3开始沉淀和完全沉淀的pH分别为3.0和4.7[22]。当碱化度过大时,Ti(Ⅳ)水解化合物形成的高聚合度钛羟基聚合物稳定性降低而容易分解,铁和铝随着碱化度升高而形成的不能聚合的氢氧化物(Fe(OH)3、A1(OH)3)沉淀,使PTAFC混凝性能降低。因此,确定PTAFC制备的最佳pH为1.5。
-
聚合反应温度对PTAFC的碱化度和混凝性能的影响如图5所示。聚合反应为吸热反应,由化学平衡原理[15]可知,提高温度有利于聚合反应的进行。由图5(a)~图5(c)可知,随着反应温度的升高,PTAFC对浊度、UV254和COD去除率逐渐增加,当聚合温度为60 ℃时,碱化度为76.20%,浊度、UV254和COD的去除率达到最高,分别为98.71%、29.28%、33.68%。继续升高反应温度,浊度去除率开始逐渐降低。这是由于金属离子的水解反应为吸热反应,适当地升高反应温度,一方面可以加速水解过程,另一方面可促进反应体系朝着深层水解方向进行,从而使金属离子配合物中羟基增多,形成高聚合度羟基配合物,样品的碱化度增加(图5(d)),进而有利于污染物的去除。当温度高于60 ℃时,由于反应温度过高,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)形成的高聚合度羟基配合物的相对稳定性有所降低,分解速率加快,羟基配合物羟基数量减少,聚合度降低[21-24],从而使PTAFC的吸附架桥、网捕卷扫效果降低,不利于颗粒间凝聚。由此确定最佳聚合温度为60 ℃。
-
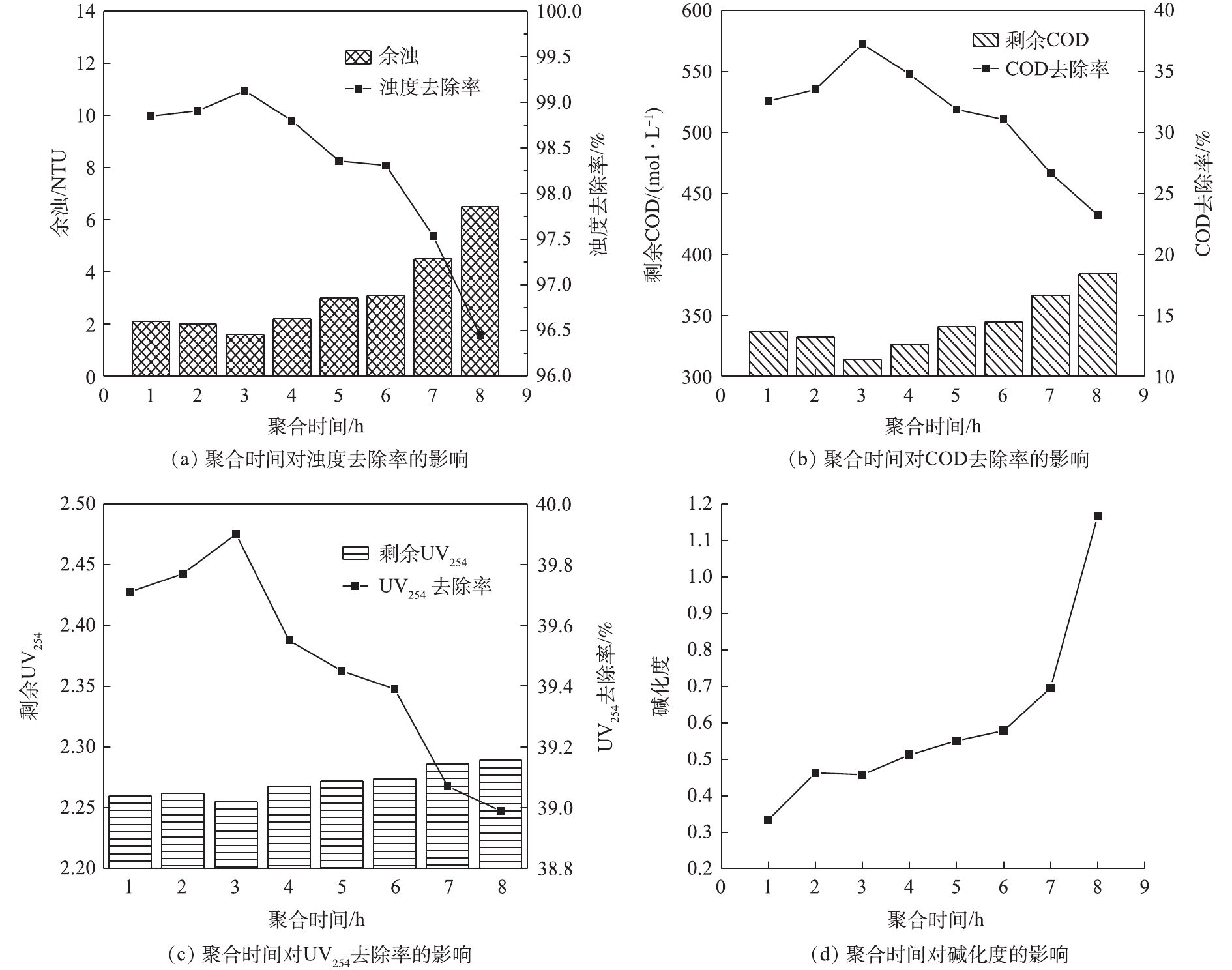
聚合时间对PTAFC的碱化度和污染物去除性能的影响如图6所示。在1~3 h内,随着反应时间的增长,PTAFC对浊度、COD和UV254的去除率均缓慢增大。当聚合时间为3 h时,浊度、COD和UV254的去除率最大,分别达到99.13%、37.25%和39.9%(图6(a)~图6(c))。随聚合时间进一步增加,浊度的去除率开始逐渐降低。这是因为聚合反应是吸热反应,在反应刚开始时,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)不能从外界吸收足够的热量水解,此时样品的聚合度不高,反应体系中以单体和低聚体为主,聚合链较短,架桥能力较弱;随着反应时间的增长,外界提供的热量促进聚合反应向聚合的方向进行[25],样品的碱化度增加,低聚物逐渐向中聚和高聚物转变,聚合链增长,吸附架桥能力强,浊度去除率上升。当时间继续增长时,高聚合度羟基配合物会因为搅拌时间过长而断链,从而影响混凝效果[26]。因此,确定最佳聚合反应时间为3 h。
综上所述,煤矸石制备PTAFC最佳工况为Ti∶Fe(摩尔比)=0.3、pH=1.5、聚合温度60 ℃、聚合时间3 h,在此条件下制备的PTAFC对浊度、COD和UV254的去除率分别达到99.13%,37.25%和39.9%。
-
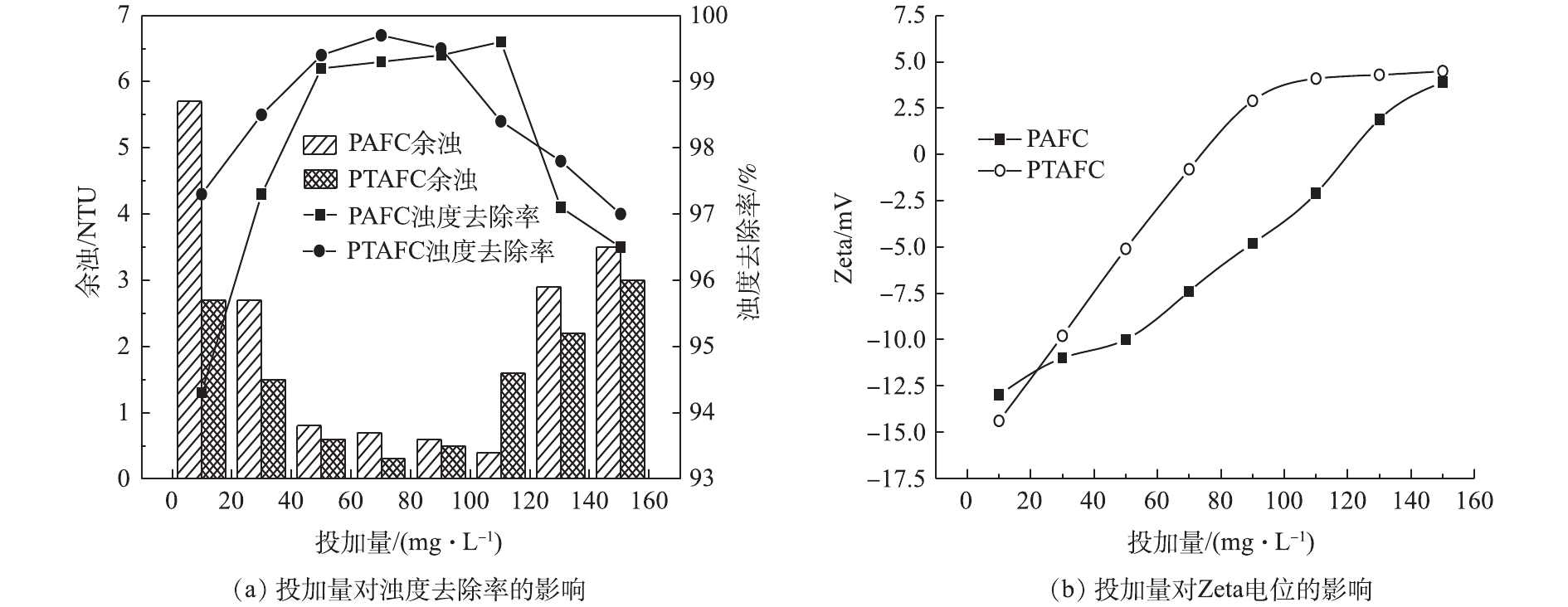
PTAFC和PAFC的投加量对浊度去除率及Zeta电位的影响如图7所示。随着投加量的增加,浊度去除率先提高后减少(图7(a))。PTAFC投加量为70 mg·L−1时,除浊效果最好,达到99.7%,余浊仅为0.3 NTU,PAFC投加量为110 mg·L−1时达到最佳去浊效果,余浊为1.4 NTU;随着投加量的继续增加,浊度去除率开始缓慢下降。对PTAFC而言,由于在水体中加入PTAFC,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)迅速水解生成了带正电的水解产物,在电性中和及吸附架桥作用下使得高岭土脱稳而凝聚。若混凝剂投加量过少,PTAFC中Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)水解产生的正电荷离子降低高岭土颗粒动电势有限,此外,金属离子水解生成的高分子聚合物不足,吸附架桥作用得不到很好的发挥,混凝效果不佳;当混凝剂投加过量时,一方面,原水中带负电的高岭土颗粒表面电性反转而带正电[27],另一方面,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)生成的高分子聚合物过多,将水中胶体微粒包裹,使胶体微粒之间无法凝聚,而使混凝效果变差[28];PAFC的投加量的影响机理与PTAFC相近。因此,确定PTAFC和PAFC的最佳投加量分别为70 mg·L−1和110 mg·L−1。
絮体Zeta电位与混凝剂投加量的关系见图7(b)。可以看出,PTAFC、PAFC的投加量分别在72、116 mg·L−1时达到零电位点,零电位点处的混凝剂投加量一定程度上表征了混凝剂的混凝脱稳能力[29]。由本研究结果可知,PTAFC的混凝脱稳能力强于PAFC。另外,絮体Zeta电位的变化能够有效表征混凝剂的混凝作用机理[30],在最佳混凝剂投加量条件下,PTAFC和PAFC所生成絮体的Zeta电位分别为-0.8 mV和-2.1 mV。这表明除了电中和作用外,吸附架桥和卷扫网捕在混凝过程中也发挥了重要作用。
-
水样初始pH对浊度去除率及Zeta电位的影响如图8所示。由图8(a)可知,剩余浊度随着pH的升高而逐渐降低,投加PAFC的实验水样在pH>7时逐渐稳定,而投加PTAFC的实验水样在pH>6时趋于稳定,且在pH为7~8时除浊效果最好,浊度去除率可达到99.8%。在逐渐升高pH的过程中,PTAFC对浊度的去除率并未出现显著降低的趋势。在pH<7时,PTAFC混凝后的剩余浊度明显低于PAFC,且拥有比PAFC更广的pH适用范围。在混凝剂加入水中后,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)会迅速水解,水解产物带有大量正电荷,水中带有负电荷的胶体粒子会在吸附电中和及压缩双电层的作用下脱稳[31]。当pH较低时,较低的OH−浓度可能会导致Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)的水解不完全,反应体系中金属离子主要以
Al(H2O)3+6 、Fe(H2O)3+6 等水合离子和其他电荷高而聚合度低的多核配离子形态存在,因而混凝效果较差;随着初始pH的升高,水解产物逐渐转化为电荷低而聚合度高的无机高分子物质,并进一步转化为电中性的聚合度极高的氢氧化物沉淀,聚合物基本形态结构单元增大,混凝效果变好。PTAFC在初始pH为6~10时对浊度都有优良的去除效果,pH为7时最佳。PAFC在初始pH为9时浊度的去除率最高。因此,确定PTAFC和PAFC的最佳pH分别为7和9。絮体Zeta电位随着水样pH的变化趋势如图8(b)所示。对于投加PTAFC的实验组,随着水样pH的增大,絮体Zeta电位逐渐由正值降低至负值;而对于投加PAFC的实验组,絮体Zeta电位由负值增大至正值,再逐渐降低至负值。絮体的Zeta电位随着初始水样pH的变化而变化,这与不同初始pH条件下混凝剂水解产物的不同有关。对于PAFC,在pH=5时,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)的水解受到抑制,其主要水解产物为带正电荷的单体Al-Fea[32]。这些水解产物能够中和污染颗粒上的负电荷,使颗粒物脱稳,但是在此条件下的正电荷不足以中和所有的负电荷,所以pH=5时,絮体的Zeta电位为负值,这也是在pH为5的条件下浊度去除率较低的原因。当水样pH由5增大至7时,形成了载有较多正电荷且具有较大比表面积的水解产物(Al-Feb、Al-Fec)。这些水解产物通过吸附、电中和及共沉作用可有效地去除水体中的有机物,从而达到较高的浊度去除率,所得絮体的Zeta电位升高到正值。相似地,对于投加PTAFC的组,当水样pH<7时,混凝剂载有正电荷的水解产物与载有负电荷的污染物通过电中和作用发生反应,絮体Zeta电位为正值,这是由多余的载有正电荷的混凝剂水解产物吸附在颗粒物表面导致的;在较高水样pH条件下,混凝剂迅速水解,主要水解产物载有较少的正电荷,甚至出现Ti(OH)4、Fe(OH)3和A1(OH)3沉淀。因此,污染物负电荷不能够被完全电中和,并且较高的pH可引入浓度极高的带负电的氢氧根离子,使得絮体Zeta电位为负值,这也是PTAFC呈现出在较高pH条件下,浊度去除率略有下降的原因。在2种混凝剂对应的最佳pH条件下,絮体Zeta电位值分别为1.1 mV和2 mV,这表明电中和作用是PTAFC和PAFC的主要作用机理,此外,吸附和卷扫网捕在混凝过程中也发挥了重要的作用。
-
水体剩余浊度与沉降时间的关系如图9所示。随着沉降时间的增加,剩余浊度急剧下降,在5 min后逐渐达到平稳。PTAFC所生成的絮体具有较高的沉降速度,这说明PTAFC混凝性能明显优于PAFC。在0~5 min,PTAFC的浊度去除率随着沉降时间的增长而显著升高,这是因为在较慢的搅拌速度下,絮体开始生长,Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)的形态从Al-Fe-Tia (快速络合的自由离子、单体和初聚物)向Al-Fe-Tib(慢速络合的低聚和、中等聚合物)和Al-Fe-Tic(高聚物和Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)的溶胶态)转变,形成的一些大的矾花快速沉淀,故开始时浊度降低较快;静置5 min后,浊度去除率趋于稳定,此时水体中Al(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)和Ti(Ⅳ)的形态主要为Al-Fe-Tib、Al-Fe-Tic而沉降下去,但也有一些不易沉降的小矾花悬浮在水中,因此,在沉淀5 min后,大的矾花已沉降完全,而小的矾花不易沉淀,从而使得上清液浊度降低较慢。沉淀10 min后,浊度去除率达到99%以上,且增加不明显,因此,确定10 min为最佳沉淀时间。
-
搅拌速度对浊度去除率的影响如图10所示。整个混凝过程分为混合和反应2个阶段:混合阶段通过较短时间的剧烈搅拌,使药剂在水体中均匀分散,形成较小的絮体;反应阶段通过缓慢地搅拌,从而使在混合阶段生成的细小絮体碰撞、凝聚而逐渐长大[33]。由图10可知,搅拌速度为0时混凝效果不佳,在40 r·min−1时混凝效果最好,浊度去除率可达到99%以上,之后继续增加搅拌速度,浊度去除率开始下降。这是因为搅拌速度增大,对絮体施加的剪切力增加,不利于絮体的稳定生长,继续增加剪切力会导致新生成的絮体破碎,从而影响混凝效果。因此,确定40 r·min−1为最佳搅拌速度。
为了进一步研究搅拌速度对絮体特性的影响,从絮体的抗破碎和破碎后再生能力入手,分析搅拌速度对絮体再生的影响。根据图10,选取40 r·min−1对絮体施加慢搅速度,慢搅结束后,对所产生的絮体施加200 r·min−1的剪切力,5 min之后,恢复到不同的慢搅速度(40、70、110、150 r·min−1),实现絮体的破碎后再生过程(图11)。由图11可知,与PAFC相比,PTAFC所产生的絮体具有较大的絮体粒径和较高的生长速度。在混凝慢搅阶段,PTAFC在2 min内即达到最大粒径,随着慢搅时间的增加,絮体粒径呈现逐渐下降的趋势;而对PAFC来说,需要5~8 min达到稳定粒径,且在生长阶段,絮体粒径较为稳定。絮体生长阶段的稳定粒径PTAFC>PAFC,絮体生长速度的大小PTAFC>PAFC。慢搅阶段结束后,2种混凝剂所产生的絮体被施加200 r·min−1的破碎剪切力,在剪切力作用下絮体粒径迅速下降,当恢复不同的慢搅速度时,絮体呈现一定程度的再生,对于不同的慢搅速度,2种混凝剂表现有一定的一致性,搅拌速度对絮体的再生粒径的影响结果为40 r·min−1>70 r·min−1>110 r·min−1>150 r·min−1,这说明在慢速搅拌的状态下有利于絮体的再生,这与图10的结果一致。由图11可知,在200 r·min−1的剪切力下,PTAFC所产生的絮体具有较高的强度因子,这说明PTAFC所产生的絮体具有较强的抗破碎能力。但是,PTAFC所产生絮体的恢复因子远小于PAFC,这表明PTAFC所产生的絮体在破碎后具有较弱的再生能力。
-
在考察反应温度对混凝效果的影响时,使用恒温水浴锅控制温度,分别在10、20、30 ℃进行混凝实验,反应温度对浊度去除率的影响如图12所示。PTAFC和PAFC的浊度去除率随着温度的升高而升高,这可能是因为在低温下颗粒间运动碰撞概率减少,不利于混凝过程的进行。温度影响了水体黏度,进而影响了混凝搅拌效率和混凝剂的水解速度和絮体性质,较低的水温对混凝动力学具有明显的反作用。也有研究[33-34]发现,水样温度对絮体强度造成了影响,铝盐在低温条件下所形成的絮体比在20 °C条件下形成的絮体强度差,更易在外界剪切力下破碎,在低温条件下,絮体的粒径通常较小。由图12可知,PAFC在低温下处理效果不佳,浊度去除率仅为76.9%,随着温度的增加,PAFC浊度去除率趋于稳定,达到98%。PTAFC在10 ℃时余浊为3.3 NTU,在温度为20 ℃和30 ℃时,余浊分别为0.4 NTU和0.8 NTU,浊度去除率均达到99%以上,PTAFC在低温下也可以达到较好的去除效果。PTAFC在低温下之所以有比较好的混凝效果可能是由于Ti(Ⅳ)化合物水解形成大量多核钛羟基聚合物,具有极强压缩双电层、电中和、吸附架桥与网捕卷扫能力而引起的。
综上所述,PTAF在混凝过程中最佳的反应条件为:投加量70 mg·L−1、pH=7、反应温度20 ℃、快速(300 r·min−1) 1 min、中速(150 r·min−1) 3 min、慢速(40 r·min−1) 8 min,最佳工况下,当进水浊度为100 NTU时,出水浊度低至0.4 NTU。
-
在考察PAFC和PTAFC对二沉池出水的处理效果对比时,实验水样为城镇污水处理厂二沉池出水,分别在PAFC、PTAFC最佳混凝条件下进行效果对比,结果如表1所示。PTAFC对浊度、COD、氨氮和总磷的去除效果均优于PAFC。COD反映了水中还原性物质的含量,包括有机物与其他还原性无机物质[35],这里的有机物也包含了带负电的有机物和中性以及带正电的有机物等,混凝剂去除有机物的过程以吸附电性中和为主导。PTAFC对COD去除率更高的原因在于钛具有生物亲和性[36],同时钛的电荷高,能使混凝剂电性中和和压缩双电层能力加强[37]。PAFC和PTAFC对水样中氨氮的去除效果不佳,这与其他混凝剂一样,对氨氮的去除率普遍较低[38]。氨氮在水处理中一般采用生物法和活性炭吸附法[39]等方法,主要原因是:混凝剂对大分子物质有较好的吸附作用,而氨氮是小分子物质且性质稳定,难以被氧化还原和沉淀,混凝剂的电性中和、吸附架桥作用均表现的比较弱[40-41]。PTAFC对二沉池出水总磷表现出较强的去除能力,出水优于《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002)Ⅲ类水标准0.2 mg·L−1。
2.1. 钛铁摩尔比对PTAFC混凝性能的影响
2.2. 聚合pH对PTAFC混凝性能的影响
2.3. 聚合反应温度对PTAFC混凝性能的影响
2.4. 聚合反应时间对PTAFC混凝性能的影响
2.5. 投加量对混凝效果的影响
2.6. 水样初始pH对混凝效果的影响
2.7. 沉降时间对混凝效果的影响
2.8. 搅拌速度对混凝效果的影响
2.9. 反应温度对混凝效果的影响
2.10. PAFC和PTAFC对二沉池出水的处理效果的对比
-
1)煤矸石酸浸液制备钛掺杂聚合氯化铝铁钛(PTAFC)的最佳条件为钛铁摩尔比0.3、pH=1.5、聚合温度60 ℃、聚合时间3 h、常温熟化24 h。
2) PTAFC对浊度有很好的去除效果,对自配水浊度去除率最高可达99.8%,同时对COD和UV254也有一定的去除率。PTAFC最佳混凝条件为投加量70 mg·L−1、慢速搅拌速度40 r·min−1、pH=7、反应温度20 ℃。PTAFC对初始pH的适用范围广,在pH= 6~10时均具有很好的去浊效果。PTAFC混凝形成的矾花大而密实,容易沉淀,沉淀5 min即可得到较好的去浊效果,10 min后趋于稳定;PTAFC在处理低温水时具有比PAFC更高的浊度去除率。
3) PAFC和PTAFC对城镇污水处理厂二沉池出水的污染物有一定去除的能力,PTAFC在去除浊度、氨氮、COD、总磷方面都比PAFC强,特别对浊度和总磷表现出极其优异的去除效果。PTAFC的成功制备为污水处理站提标改造或在现有基础上提质增效提供了新的材料和方法。
4)以煤矸石制备混凝剂对推动煤矸石和综合利用和混凝剂产业发展均具有较积极的意义,能有效降低煤矸石的污染,提高煤炭企业效益,降低水处理的成本,提高水处理效果,具有很大的推广价值。




 下载:
下载: