-
面对日益严重的水资源紧缺以及水体富营养化等问题,世界各国对直接排入河流及地下水的处理出水水质标准正在进一步提高。为满足不断提高的污水排放标准,污水处理厂提标改造势在必行。膜生物反应器由于其具有容积负荷高、抗冲击性强、出水水质好等优点,十分适用于出水要求较高或土地资源紧张的现有污水处理工艺的提标改造[1]。此前,有研究人员[2-4]分别尝试了将膜组件与氧化沟、序批式反应器等组合以提高相应工艺的处理效能和出水水质,其运行结果均表明出水水质有明显的提升,均实现了扩能提标的目标,且土地利用效率高,这说明膜组件应用于污水处理厂的提标扩容改造是较为可行的选择。在实际工程运用中,A2O工艺是污水处理厂应用最广泛的工艺,脱氮除磷中存在的基质竞争、泥龄不同的矛盾和反硝化碳源不足等缺点使其处理效率相对较低,其与膜组件的结合对于现有A2O工艺的提标改造受到广泛关注[5-9]。然而,无论是与何种工艺结合,膜组件应用的单元及由此引发的膜通量降低、使用寿命下降一直是限制膜组件广泛运用的主要瓶颈。
已有研究[10]表明,将膜组件运用于A2O工艺不同工段时,其膜污染特性可能存在显著差异。为此,本研究采用三维荧光光谱、红外光谱、分子排阻色谱和恒压膜过滤装置分析了A2O工艺不同阶段混合液的膜污染特性,揭示了不同阶段混合液中悬浮物和溶解性有机物对膜组件的污染机制,为膜组件运用于现有A2O工艺提标改造提供参考。
全文HTML
-
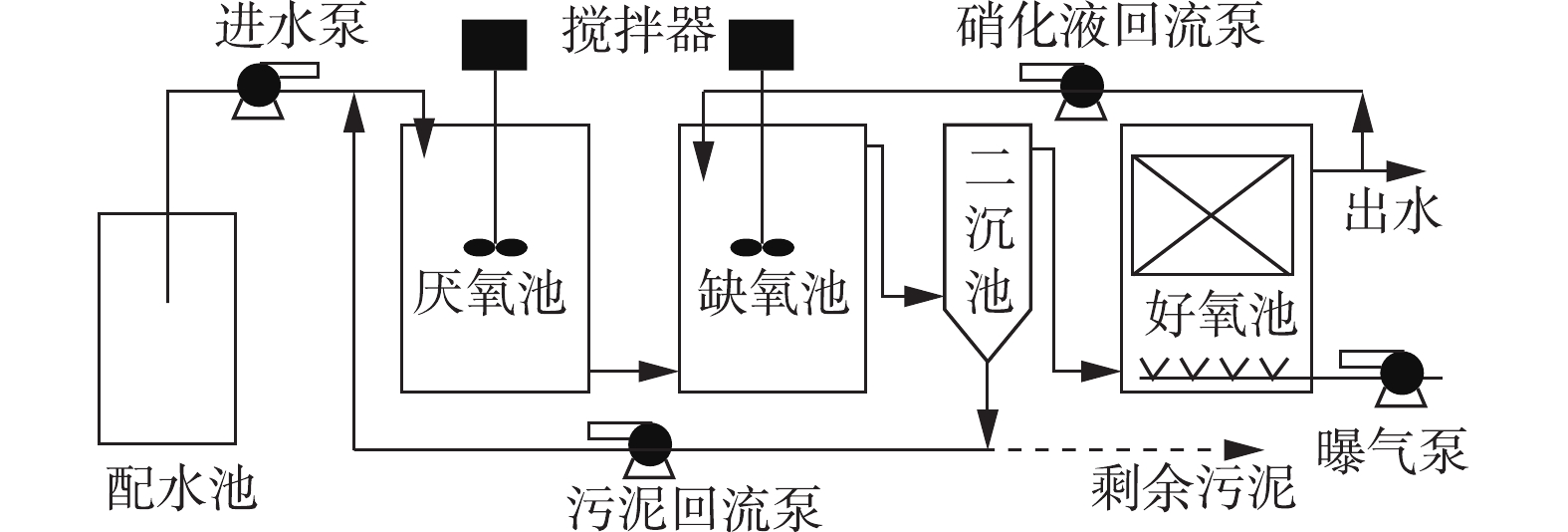
实验室A2O工艺小试装置流程如图1所示。原水依次经厌氧池、缺氧池处理后进入二沉池,经二沉池泥水分离后污泥回流至厌氧池,上清液溢流进入好氧池;好氧池设置有膜组件,利用硝化液回流泵将分离的硝化液回流至缺氧池。厌氧、缺氧和好氧单元的有效容积分别为3、6、12 L,厌氧和缺氧池设置有搅拌器,好氧池配置有曝气装置。
-
实验所用污泥取自上海闵行区江川水质净化厂,进水按照葡萄糖150 mg·L−1、蛋白胨30 mg·L−1、NH4Cl 80 mg·L−1、KH2PO4 5 mg·L−1配制,以模拟生活污水。定期采集配水和厌氧、缺氧、好氧单元混合液进行恒压膜过滤分析,用于水质检测的水样采样后立即用0.45 μm的有机水系膜过滤,并于4 ℃低温保存。
-
膜通量的大小可以作为衡量膜污染程度的重要指标之一。在恒定压力下,水样的膜通量越小,表明其膜过滤阻力越大,更容易造成膜污染。本实验利用隔膜真空泵,在恒定压力20 kPa下抽滤水样,依据水样在一定时间内透过滤膜的水量来评估各水样的膜污染潜力。滤膜为混合纤维素MCE膜,平均孔径为0.45 μm,有效膜直径为4 cm。膜通量的计算方法见式(1)。
式中:J为膜通量,L·(m2·h)−1;A为有效膜面积,m2;t为过滤时间,h;V为时间t时过滤的水样体积,L。
-
采用HITACHI F-7000FL型荧光光度计测定水样的三维荧光光谱,激发波长为200~550 nm,发射波长为200~550 nm,扫描速度为12 000 nm·min−1,激发与发射的步长和狭缝均为5 nm,光电倍增管的电压为400 V,响应时间为自动。以去离子水为空白样品,进行荧光扫描,减少拉曼散射的影响,再利用Matlab 2014a自动去除三维荧光光谱中的拉曼和瑞利散射,并通过插值算法补齐缺失的光谱。
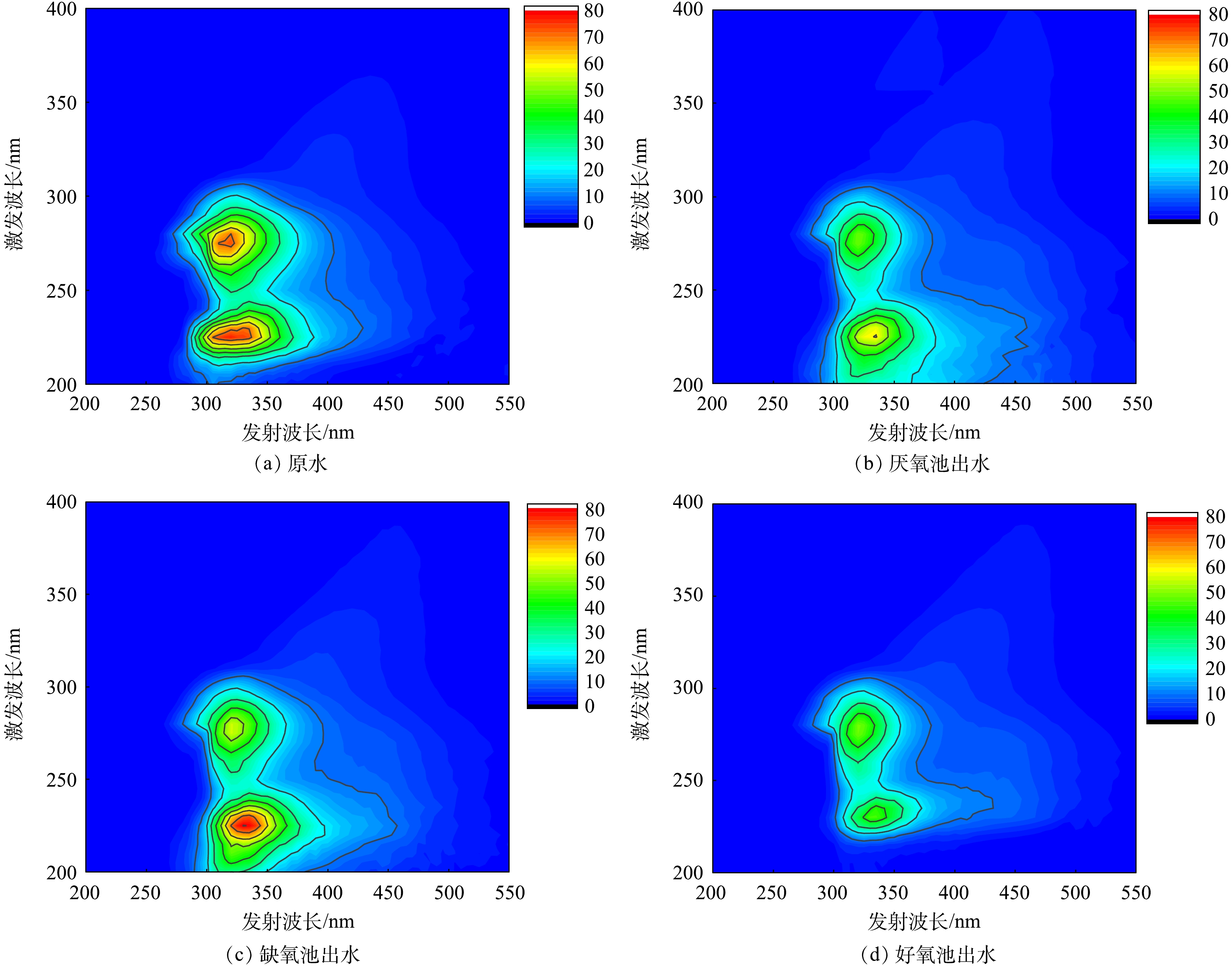
利用荧光区域积分法对所得的荧光光谱数据进行分析。荧光区域积分法根据溶解性有机物化学基团的荧光特性按不同的激发/发射波长主要划分为5个区域:区域Ⅰ(Ex/Em =(200~250) nm/(280~330) nm)表征酪氨酸类蛋白质;区域Ⅱ(Ex/Em =(200~250) nm/(330~380) nm)表征色氨酸类蛋白质;区域Ⅲ(Ex/Em =(200~250) nm/(380~550) nm)表征富里酸类物质;区域Ⅳ(Ex/Em =(250~400) nm/(280~380) nm)表征溶解性微生物代谢蛋白质;区域Ⅴ(Ex/Em =(250~400) nm/(380~550) nm)表征腐殖酸类物质。对各荧光区域的响应值进行体积积分计算,归一化处理后,分析各荧光区域的荧光强度变化[11]。
-
凝胶渗透色谱法(gel permeation chromatography, GPC)是依据分子筛效应,利用各物质分子大小和凝胶孔洞的差别而对其进行分离,广泛用于测定有机物相对分子质量和相对分子质量的分布。本实验采用Waters 1515-2414仪器,色谱柱为UltrahydrogelTM Linear柱(7.8 mm×300 mm),流动相为超纯水溶液,流速1 mL·min−1,采用示差折光检测器,柱温40 ℃,进样量20 μL。以保留时间为横坐标,以相对强度为纵坐标,绘制相对分子质量分布曲线。
-
傅里叶变换红外光谱一般用于分析化合物官能团信息,在本研究中,用其对水样中溶解性有机物进行定性分析。将水样经真空冷冻干燥机干燥后获得的固体样品与溴化钾以大约 1∶100 的比例混合,研磨均匀、压片制成透明薄片后进行测定,分辨率为4 cm−1,测定时采用的红外波段为400~4 000 cm−1。
1.1. 实验装置
1.2. 运行条件
1.3. 水样膜污染特性测定
1.4. 荧光光谱分析
1.5. 有机物的分子质量分布
1.6. 傅里叶红外光谱分析
-
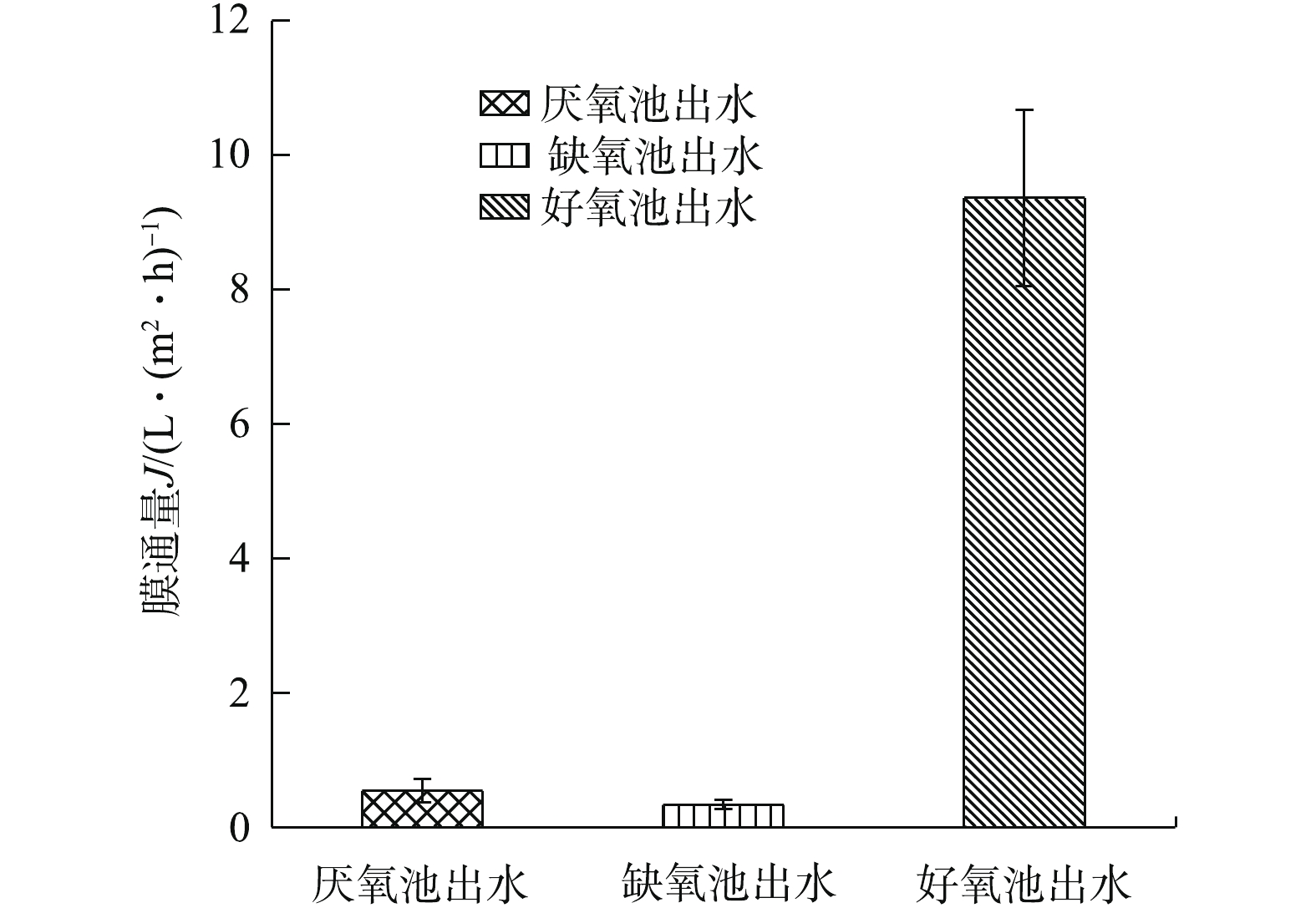
膜污染是指污水中的污泥絮体、胶体粒子、无机溶质或有机物等在膜表面或膜孔中沉积堵塞、吸附沉积,从而导致跨膜压力增加或渗透通量降低的现象[12]。当系统在恒定压力下运行时,膜污染表现为通量的降低。在实验中,依据A2O各阶段混合液恒压过滤下的膜通量大小,可分析其水样对膜污染的潜力。选取各阶段混合液的3次水样进行恒压过滤实验,结果见图2。可以看出,好氧阶段的混合液膜通量远大于厌氧和缺氧阶段的混合液,厌氧阶段混合液的膜通量略大于缺氧阶段混合液的膜通量。与厌氧和缺氧段相比,好氧段的混合液膜污染潜力较小,好氧段更适合与膜组件结合,且可作为最终出水的固液分离单元,可以大幅降低出水的SS。
-
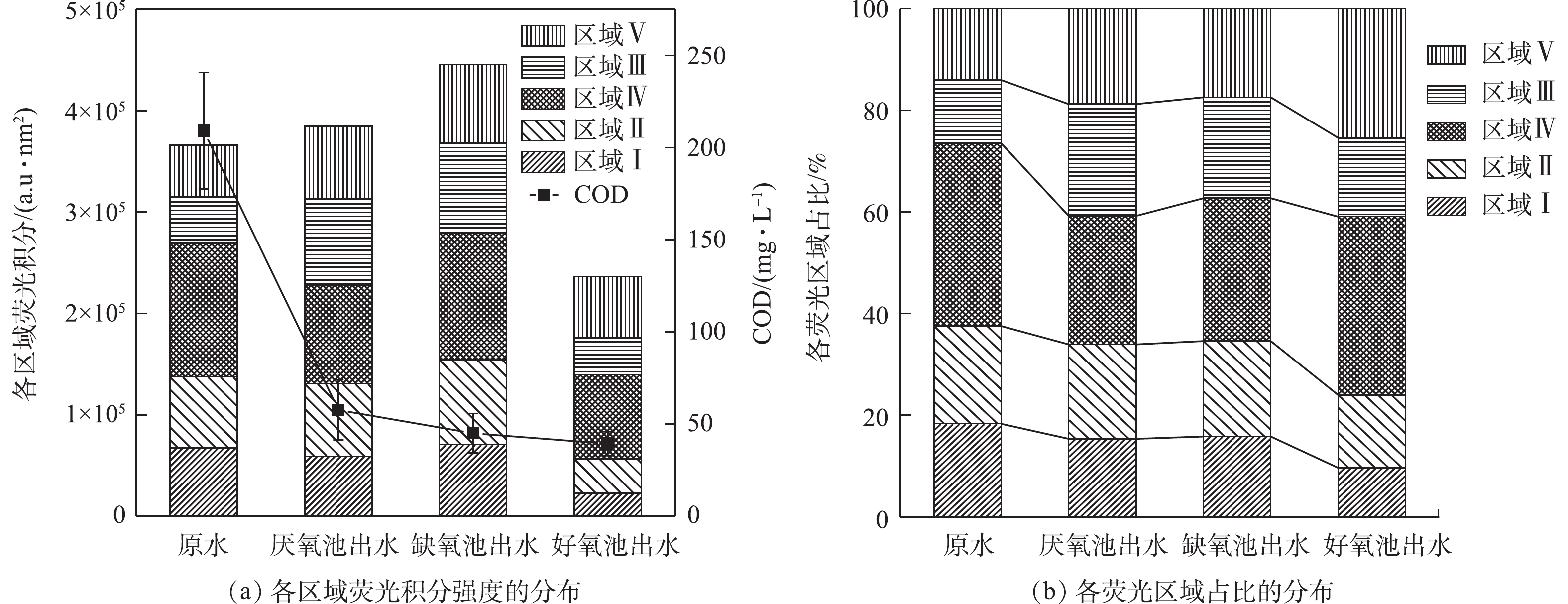
三维荧光光谱能够较好地揭示水体中溶解性有机物组分。如图3所示,A2O工艺沿程各段水样的三维荧光特征总体相似,主要有2个较为明显的荧光峰。其中,位于区域Ⅰ和区域Ⅱ荧光峰(Ex/Em =225 nm/335 nm)属于酪氨酸、色氨酸类蛋白质;位于区域Ⅳ的荧光峰(Ex/Em =230 nm/410 nm)代表微生物代谢蛋白质。这说明A2O工艺各段水样含有的荧光类有机物主要为蛋白质类物质。依据进水和A2O各阶段混合液的5个荧光区域强度及各区域的积分体积占比,进一步分析了各反应器出水的溶解性有机物质的变化(图4)。相对于原水,厌氧池出水的区域Ⅰ、Ⅳ的积分值和组分占比均有所减少,而区域Ⅲ、Ⅴ反而增加,区域Ⅱ的积分强度虽然增加,但其占比却下降。这意味着原水中大量易降解的酪氨酸、微生物代谢蛋白质被微生物分解利用,促进自身繁殖,并合成结构复杂的富里酸、腐殖酸物质。当进入缺氧段后,混合液各区域荧光强度均有所上升,类富里酸和腐殖质组成有所减少,而酪氨酸、溶解性微生物代谢蛋白质反而增加。区域Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅳ属于类蛋白质物质,区域Ⅲ、Ⅴ属于类腐殖质物质,而一般认为区域(Ⅰ+Ⅱ+Ⅳ)/(Ⅲ+Ⅴ)荧光强度的比值可表征有机物的可生物降解性[13],由此表明,缺氧池出水的可生物降解性大于厌氧池出水。然而,类蛋白质属于疏水性物质,分子质量大,容易被膜截留,其对膜污染的贡献大,是造成膜污染的主要物质[14]。胡以松[15]对A2O-MBR污水处理系统中膜污染行为的研究也发现,尽管蛋白质类物质可生物降解,但易在膜表面沉积黏附,对膜污染的贡献大于腐殖酸类物质,由此导致缺氧池出水比厌氧池出水的过滤性更差。
进入好氧段处理单元后,出水的总荧光强度和各区域荧光强度明显低于厌氧和缺氧池出水,表明好氧池出水的溶解性有机物含量相对较少,这与胡以松[15]对A2O-MBR污水处理系统分析溶解性有机物沿程变化时,好氧池有机物质各峰的荧光强度最小的结果一致。相比厌氧和缺氧池出水,好氧池出水类蛋白物质的占比明显减少,但微生物代谢蛋白质和腐殖质占比相对增加。这说明在好氧段微生物代谢旺盛,水溶性色氨酸、酪氨酸和富里酸等有机物被大量去除,而腐殖酸和微生物代谢蛋白质作为微生物代谢过程产生的主要物质,其组分占比明显增加。好氧段对各区域荧光物质均有很好的去除效果,剩余有机物主要是腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物,且总含量较少,从而使其膜污染潜力最小。
-
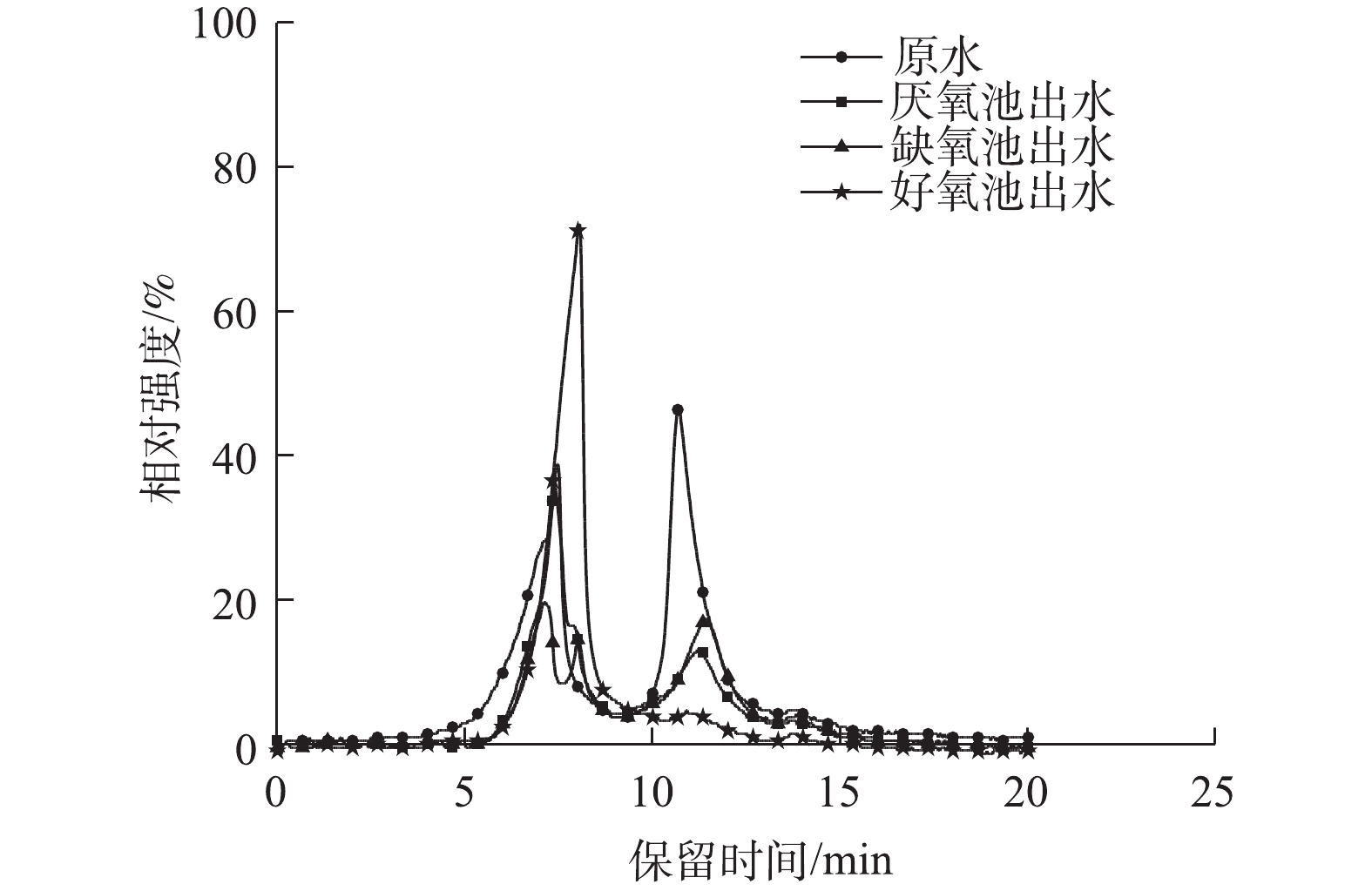
凝胶色谱图可用于分析有机溶剂可溶物的相对分子质量分布,常用于表征膜污染物的特征分子质量。在本研究中,A2O各阶段水样的溶解性有机物分子质量分布情况如图5所示。原水经厌氧段后,去除了大部分的小分子有机物质和小部分大分子物质,经缺氧处理后,大分子物质进一步减少,小分子物质组成增多,这与缺氧池提高了污水的可生物降解性结论相一致。好氧池混合液只有一个窄峰,其有机物主要集中在>23 000 Da的分子质量范围内,基本不含小分子物质。好氧池混合液的三维荧光光谱分析结果与此相一致,即残留的溶解性有机物为腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物类大分子有机物。一般认为,小分子质量有机物在膜孔中吸附造成膜孔堵塞或使膜孔变小[16],大分子有机物则倾向于在膜表面形成滤饼层[17],不同分子质量的有机物共同作用会加快膜污染的发生[18]。综上所述,好氧池混合液由于有机物含量少,且主要为是腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物的大分子物质,因此,其具有较小的膜污染潜力。
-
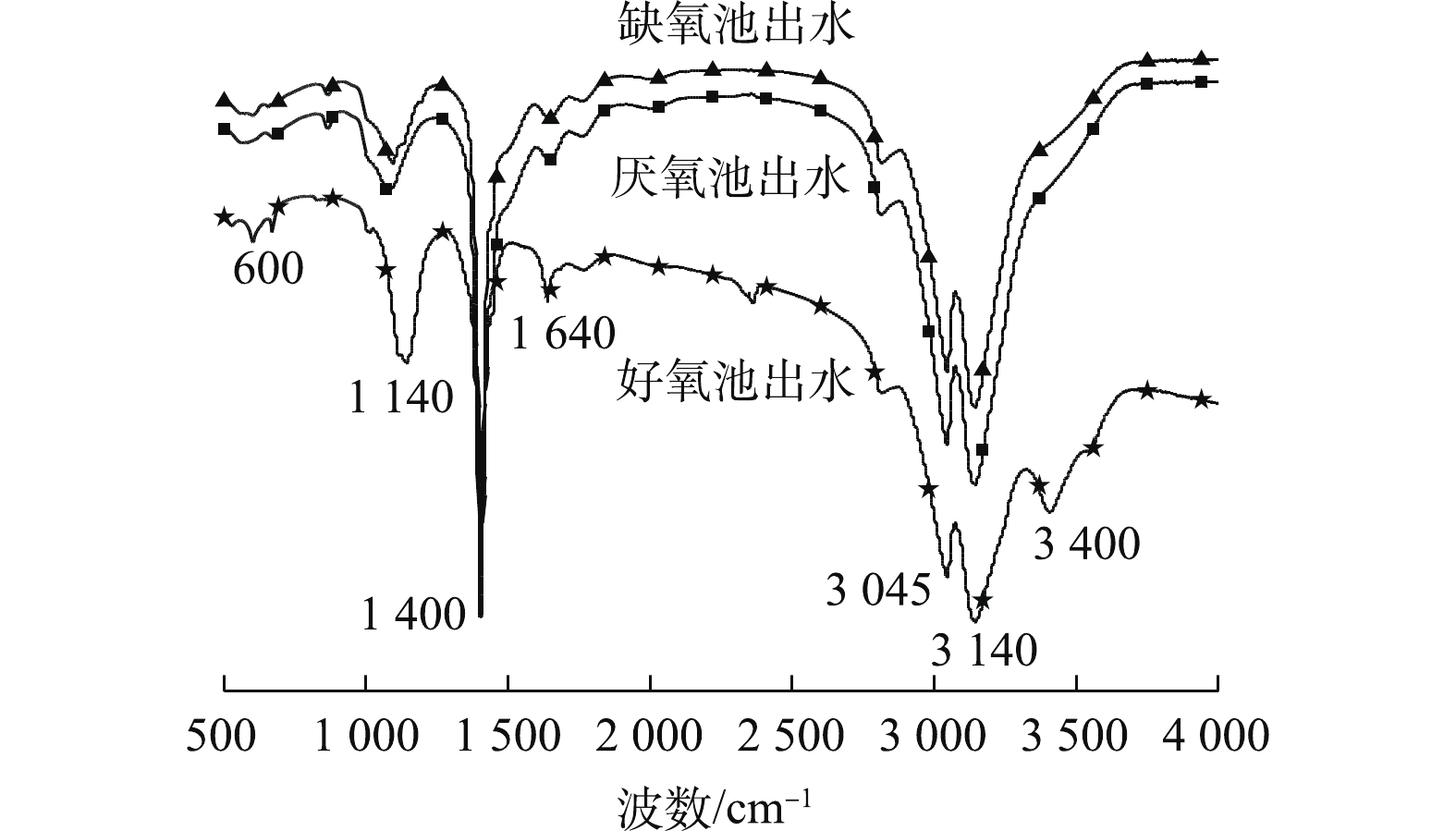
对比图6中厌氧、缺氧和好氧段上清液的红外光谱发现,红外光谱分析主要是利用化合物分子对红外光谱特征吸收定性检测其化学键的方法,一般可将红外吸收光谱分为400~1 350 cm−1的指纹区和1 350~4 000 cm−1的官能团区。对比厌氧、缺氧和好氧段上清液的红外光谱图发现,厌氧和缺氧段的红外光谱的峰形状和峰位置等基本相似,主要以1 400 cm−1的芳香族羧基峰、3 045 cm−1和3 140 cm−1的不饱和碳氢峰为主。在好氧段的红外光谱中,除了含有上述代表性官能团之外,在1 640 cm−1、1 140 cm−1处的峰明显增强,且在高频3 400 cm−1处存在独有的特征峰。3 400 cm−1处的特征峰可能是酚类、羟基和羧基的O—H伸缩振动峰[19],在1 640 cm−1区域的吸收峰可能是酰胺I带羰基C=O伸缩振动或氨基酸
NH+3 不对称变角和NH+2 变角振动[20],而1 140 cm−1处为糖类C—O—C键伸缩振动和O—H面内弯曲振动[21]。这表明好氧池出水的不饱和结构化合物组分增加,氧化聚合度增加,这与好氧池出水的荧光峰较厌、缺氧出水出现红移的现象一致。基于如上分析,通过对A2O工艺各阶段混合液的恒压膜通量测试,以及混合液中溶解性有机物的三维荧光光谱、分子排阻色谱和红外光谱分析表明,厌氧和缺氧段混合液中含有大量溶解性蛋白质类物质,且总体有机物含量较高,具有较强的膜污染潜力;而好氧段混合液中有机污染明显降低,且主要是大分子的腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物,膜污染潜力较小。因此,在A2O工艺与膜组件结合时,建议将膜组件用于好氧段泥水分离,从而有效提高出水水质并延长膜使用寿命。
2.1. 各反应器出水膜污染特性分析
2.2. 各反应器出水的三维荧光光谱分析
2.3. A2O各反应器出水的有机物分子质量分布
2.4. 红外光谱分析
-
1)恒压膜通量的测试结果表明,A2O工艺好氧段混合液的膜通量分别是厌氧段和缺氧段混合液的17倍和28倍,说明好氧段混合液发生膜污染的潜力最小。
2)三维荧光光谱分析结果表明,厌氧池和缺氧池中有机物的荧光积分强度分别为好氧池出水的1.63倍和1.88倍,且主要是酪氨酸、色氨酸类蛋白质物质;而凝胶色谱分析结果表明,好氧池出水中有机物主要是分子质量大于23 000 Da的腐殖酸类微生物代谢产物,而非氨基酸类蛋白质物质,故导致其膜污染潜力较小。
3)根据A2O工艺以及各阶段混合液的恒压膜通量和所含有机物的组成特性,建议在对A2O工艺进行提标改造时,将膜组件用于好氧段泥水分离,以缓解膜污染,降低污水处理成本。





 下载:
下载: