-
挥发性有机物(VOCs)是导致城市雾霾与光化学污染等大气复合污染的重要前体物,对人类健康和生态环境产生重大影响,已经引起了政府和公众的广泛关注[1-3]。因此,打好蓝天保卫战,VOCs治理是关键。在众多VOCs末端控制技术中,催化氧化技术因其具有高效性和彻底性等优势引起了学界的极大关注[4-5]。催化氧化技术的核心问题是开发出高效稳定且具有低温活性的新型催化剂[4-6]。一般而言,能够催化降解VOCs的催化剂有贵金属和过渡金属2大类,其中,贵金属催化剂具有催化活性高、稳定性差等特点,此外,贵金属催化剂因其价格昂贵和易中毒失活使其在工业应用中受到了极大的限制[5]。因此,研究开发低温高效的过渡金属氧化物催化剂成为了目前研究的热点[4-5, 7]。
近年来,Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂因具有良好的催化氧化性能受到了研究人员极大的关注[7-11]。Mn-Ce复合氧化物一方面具备CeO2优异的储氧/释氧能力[12-13],另一方面MnOx具有环保、廉价易得且存在多种价态等优点[14-17]。然而传统制备工艺合成的Mn-Ce催化剂存在颗粒易团聚和形貌不可控等问题,这在一定程度上限制了该类催化剂的改进和应用。本研究通过简单的水热合成法制备了一系列Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂,有望解决上述提及的问题。
目前研究结果表明,纳米材料在催化过程中具有形貌效应[15-17],将其应用于催化氧化VOCs方面也取得了大量的研究成果[6-7, 12]。纳米材料的催化性能与其形貌特性密切相关。LIAO等[7]通过水热法制备的具有纳米棒形貌的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂在反应温度225 ℃下即可实现甲苯的完全降解。YU等[11]采用溶胶凝胶法制备了一系列MnOx/TiO2和MnOx-CeO2/TiO2催化剂,考察了Ce添加量对催化降解性能的影响,结果表明MnOx-CeO2/TiO2(Ce/Ti=0.05)催化剂活性最高(T90=180 ℃),高度分散的无定型Mn及催化剂表面存在大量活性氧物种是其具有优异低温催化氧化甲苯性能的关键。郑宽等[18]通过共沉淀法制备不同Mn/Ce比的复合氧化物,发现Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂的甲苯催化降解性能高于单一MnOx和CeO2。大多数报道的催化剂均未通过对催化剂形貌进行控制从而调控催化剂的反应活性[5, 18]。因此,本研究以具有表面纳米针的氧化锰微球为基础,通过在水热前驱液中加入不同含量的Ce,原位合成出具有一定形貌的Mn-Ce复合氧化物,通过SEM、XRD、H2-TPR、O2-TPD、BET及拉曼光谱等手段对所合成的复合材料进行表征,并深入研究分析催化剂催化氧化甲苯的构效关系。
全文HTML
-
将2.700 g MnSO4·H2O和13.185 g (NH4)2S2O8溶解于60 mL去离子水中,待完全溶解后,定容至80 mL,转移到100 mL的聚四氟乙烯的反应釜中,80 ℃反应4 h后,自然冷却至室温。将所得沉淀物用去离子水洗涤至中性,最后在80 ℃条件下干燥后保存备用,所制备的样品记为MnO2。
其他过程与氧化锰微球的制备过程相同,不同之处是,在加入MnSO4·H2O和(NH4)2S2O8的过程中同时加入不同含量的Ce(SO4)2·4H2O(Ce的摩尔分数为5%、10%、20%和40%)。所制备样品分别记为Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox、Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox、Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox和Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox。
-
催化剂的甲苯催化氧化性能的测定在连续流动的固定床反应器中进行[15-16]。催化反应器为自制的内径为8 mm 的U型石英管,固体催化剂床层由0.13 g(40~60目)催化剂和0.52 g的石英砂组成。采用质量流量器控制气体流量,以甲苯为目标反应物,体积分数为550×10−6,空气总流量为200 mL·min−1,重时空速(GHSV)约为92 300 mL·(g·h)−1。由气质联用仪(7890B-GC,5977B-MSD,Agilent Technologies)对甲苯降解前后的尾气进行在线检测。甲苯利用MS(分析柱为TG-BOND Q:30 mm×0.32 mm×20 μm)进行检测。配备的FID与镍转化炉连接,用于CO和CO2的检测,其分析柱为5A分子筛(2 m×2 mm)、Porapak Q(1.83 m×1.2 mm)和Porapak Q(0.91 m×2 mm)。
-
SEM结果采用S-3400N电子显微镜(日立,日本)对催化材料的形貌进行观察。
XRD采用D8 ADVANCE X射线衍射仪(Bruker,德国)进行测定(Cu Kα射线,扫描角度为5°~90°)。
N2吸附-脱附采用日本BEL公司的BELSORP-miniⅡanalyzer全自动比表面积及微孔孔隙分析仪测定催化剂的比表面积和孔结构参数。测试时,取110 mg样品,在120 ℃下脱气4 h,脱气完毕后,以N2为吸附质,于−196 ℃下进行测定。采用BET方法计算样品的比表面积[15-16],而样品的孔容和孔径采用BJH法。
H2-TPR在FINESORB-3010(浙江泛泰仪器有限公司)全自动物理化学分析仪上进行。将100 mg催化剂置于U型管中,以高纯Ar为载气(30 mL·min−1),10 ℃·min−1升至120 ℃,维持30 min。然后降到50 ℃,将气路切换为10% H2/Ar。等基线稳定后,从50 ℃程序升温至600 ℃,升温的速率为10 ℃·min−1。在升温过程中,利用TCD检测器对耗氢量[15-16]进行检测。O2-TPD的测定也是在FINESORB-3010全自动物理化学分析仪上进行的。将100 mg催化剂置于U型管中,以高纯Ar (30 mL·min−1)为载气,10 ℃·min−1的升温速率升至120 ℃,加热30 min。降温至50 ℃,将气路切换为10% O2/Ar(30 mL·min−1),吸附60 min。然后再把气路切换为高纯Ar,基线稳定后,以10 ℃·min−1程序升温至700 ℃。升温过程中氧的脱附量利用TCD检测器[15-16]进行检测。
拉曼光谱分析(Raman)在法国HJY公司LabRAM Aramis拉曼光谱仪上进行,主要技术参数如下:532 nm激光波长,扫描范围为100~1 000 cm−1,样品每次扫描采集时间为60 s。
1.1. 催化剂的制备
1.2. 催化剂活性评价
1.3. 材料表征
-
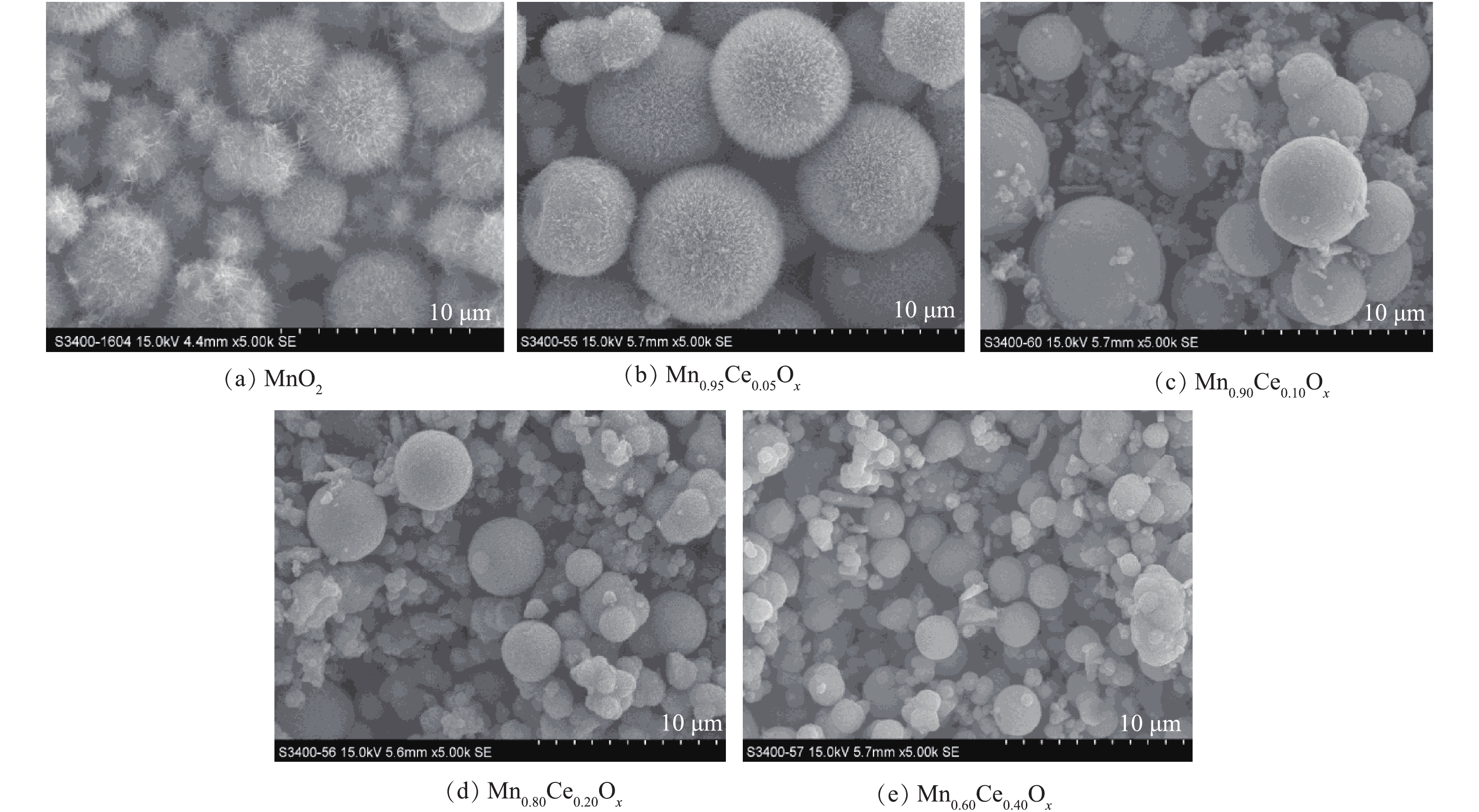
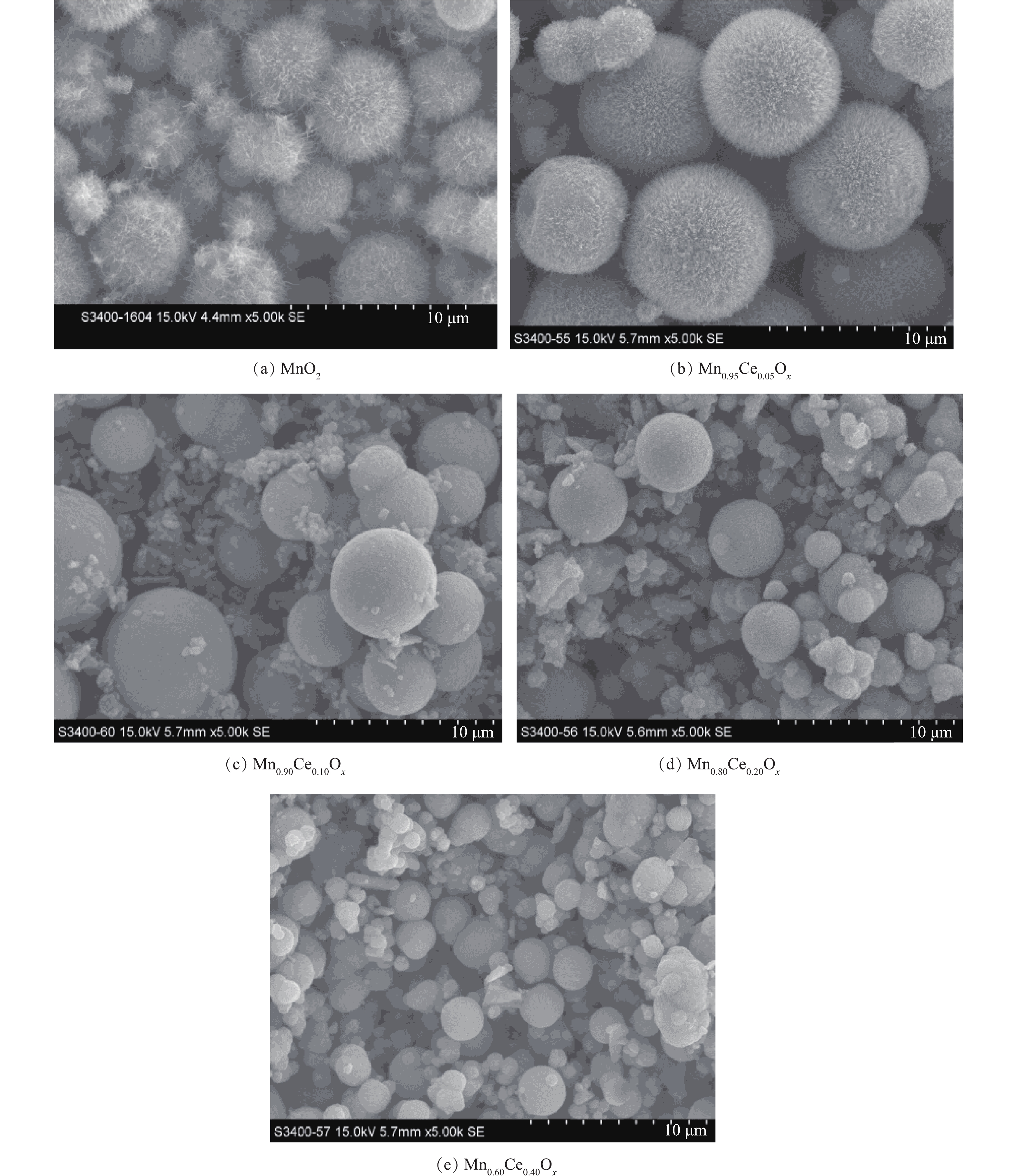
通过水热反应制备了一系列不同锰铈比例的氧化物催化剂,SEM结果如图1所示。在MnSO4·H2O为前驱体、(NH4)2S2O8为氧化剂条件下,合成的MnO2呈现出表面为纳米针的海胆状微球结构,其直径为4.0~5.0 μm。而在海胆状MnO2微球制备的基础上,掺入一定比例的铈制备Mn-Ce复合氧化物,SEM结果如图1(b)~图1(e)所示。当Ce掺杂量为5%时,形成的复合材料的形貌仍为海胆状微球结构,其微球颗粒粒径较纯的MnO2有所增加(7.0~8.5 μm)。但随着Ce掺杂量的增加,产物微球表面的针状结构逐渐消失,变为表面光滑的微球,其颗粒粒径呈现下降趋势。在含量为10%时,微球直径为4.0~5.0 μm,且在微球的周围出现了较多无固定形态的物质(图1(c))。当含量增加到20%时,粒径进一步降低,约为3.59 μm(图1(d))。在含量为40%时,微球的粒径进一步降低至2.2 μm左右(图1(e))。但随着Ce含量的增加,微球的周围也生成了越来越多的表面碎片。在水热反应过程中,通过对生成物产率的观察,发现随着Ce含量的增加,生成产物的量逐步减少,当不添加Mn时,利用Ce(SO4)2·4H2O与(NH4)2S2O8进行水热反应,在80 ℃反应4 h后,只有很少量淡黄色的物质生成,推测为CeO2,但产量极低,所以该方法不适合进行CeO2纳米材料的合成。
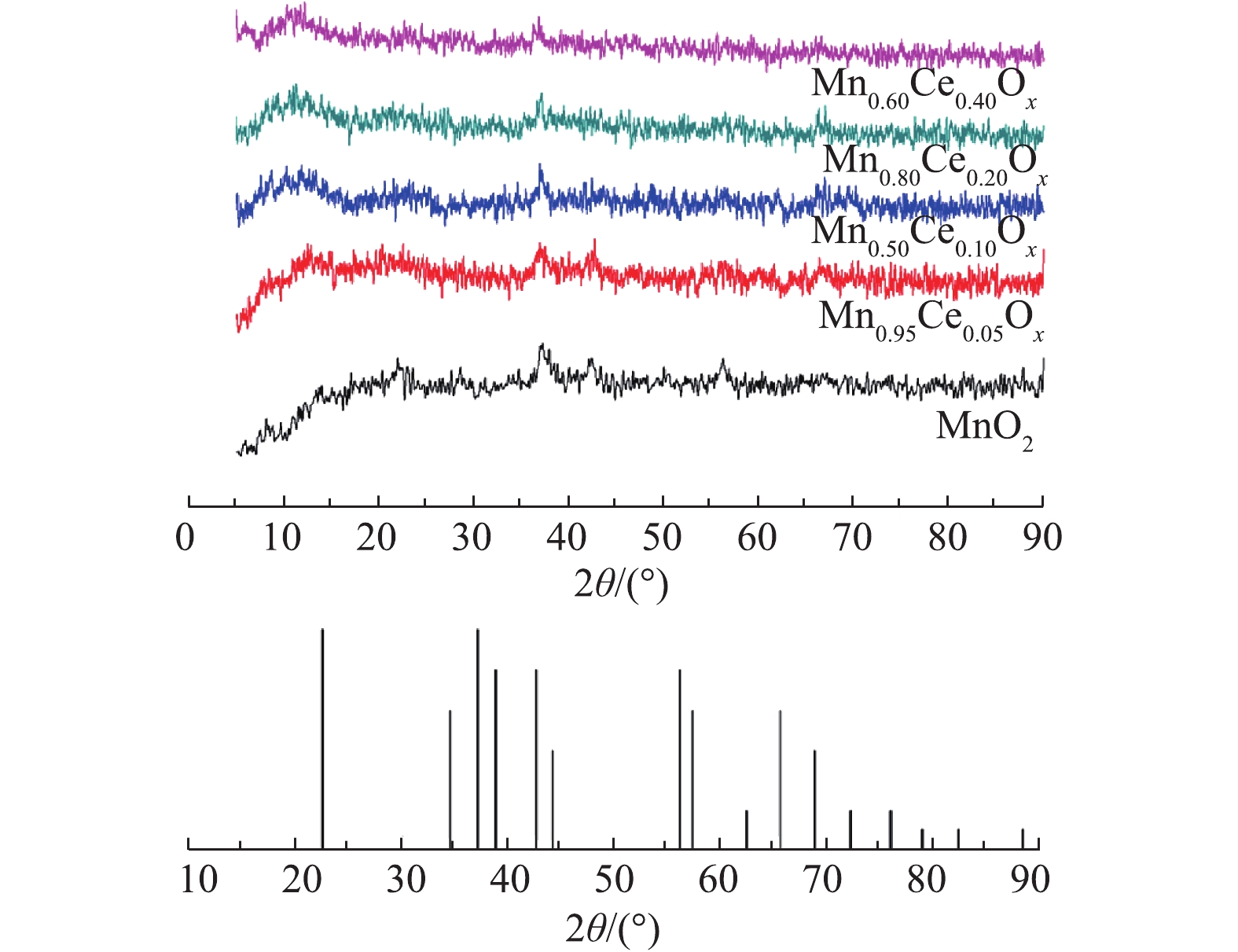
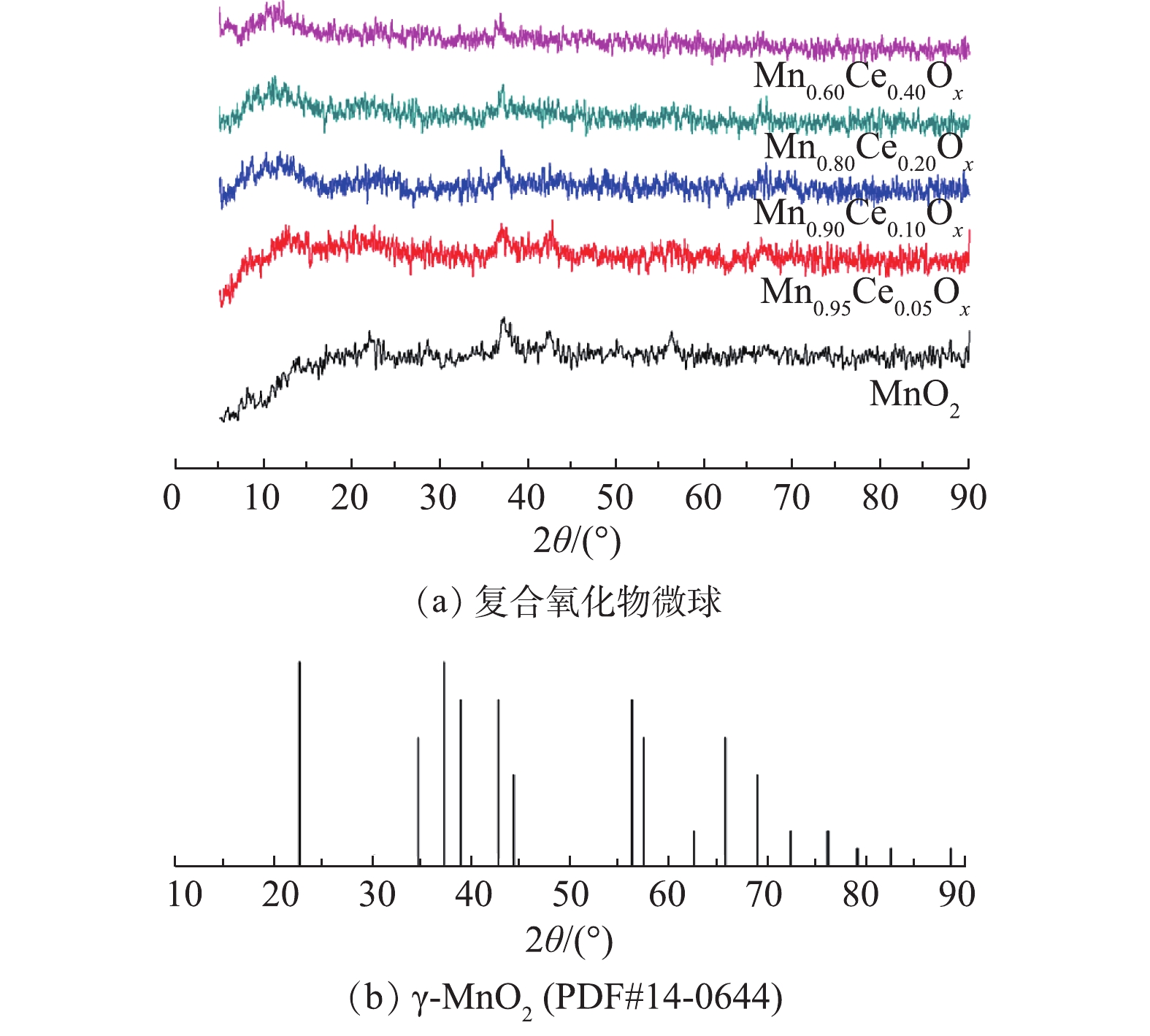
不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物的XRD谱图如图2所示。MnO2微球催化剂XRD谱图中在2θ=37.0°、42.0°,56.7°处出现的特征衍射峰归属于γ-MnO2(PDF#14-0644)[19]。但在所合成的含Ce微球催化剂XRD谱图中,除37.0°处的峰没有变化外,其他对应的γ-MnO2特征峰均存在消失的现象,且没有观察到明显的CeO2的峰。这是因为在Ce的含量很低时(小于50%),在复合氧化物中仍以MnOx为主,因而无法探测到CeO2的衍射峰,这与之前研究报道的MnOx-CeO2催化剂所得出的结论[7]相似。
结合SEM结果可知,在加入Ce以后,在微球的周围出现了大量的颗粒物,说明Ce的加入会对催化剂的形貌产生较大的影响。但从XRD的结果可看出,这些小的颗粒物可能是一些无定型的Mn-Ce复合氧化物。随着Ce含量的增加,2θ=42.0°、56.7°处的衍射峰的强度降低,说明MnO2的结晶度随着Ce含量的增加而下降。
-
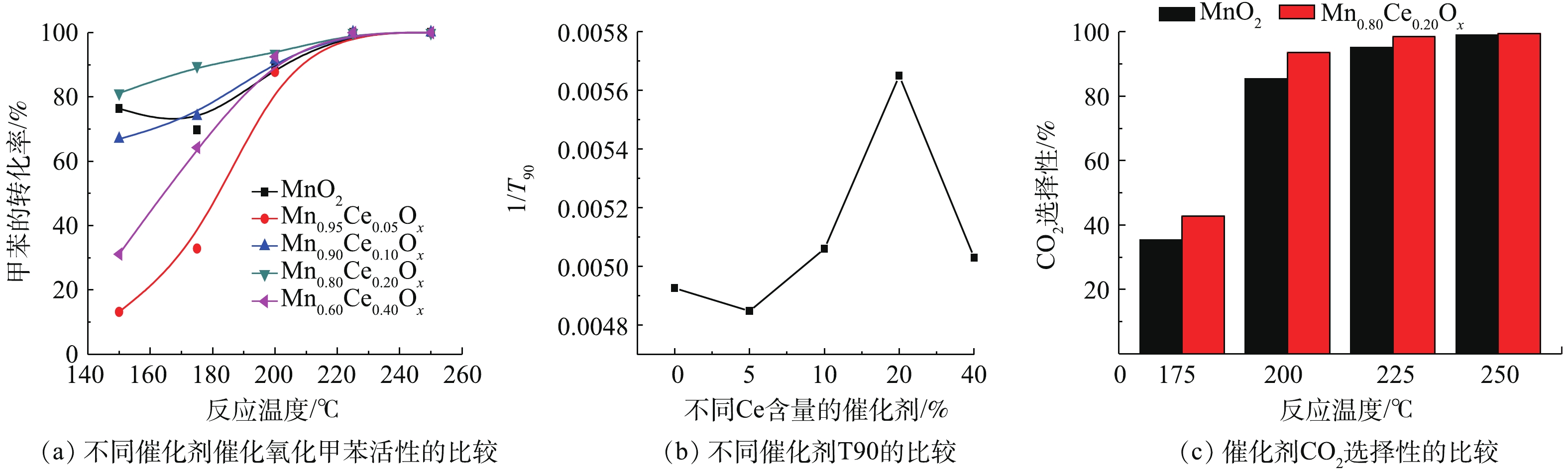
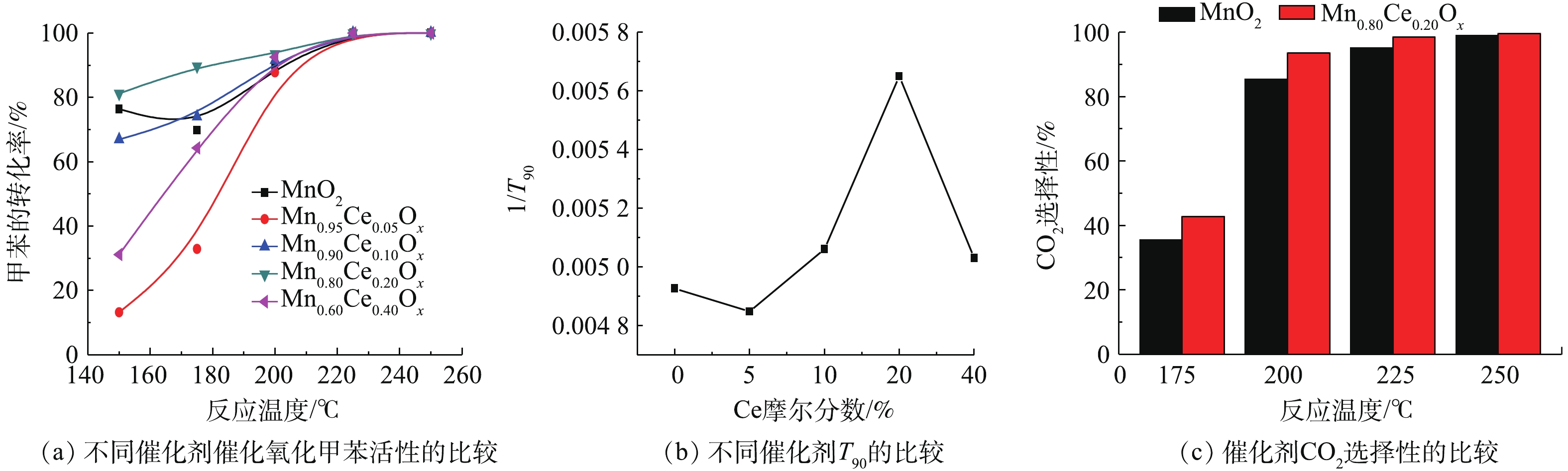
不同Mn-Ce比例的复合氧化物催化降解甲苯的性能如图3所示。由图3(a)可知,所制备的纯MnO2微球对甲苯的降解率随着反应温度上升呈现先降低后升高的趋势。在150 ℃时,降解率达到76.4%;但当温度升高至175 ℃时,却降低为65.3%。随着温度的进一步升高,降解率又开始增加,在200 ℃时,达到了89.8%,在225 ℃达到完全转化。这可能是由于MnO2催化剂在低温区对甲苯主要为吸附作用,当吸附未达到饱和时,表现为甲苯的出口浓度在下降,因而甲苯的转化率偏高;当这个吸附作用达到饱和时,甲苯的出口浓度达到最低,随着反应温度的升高,吸附在催化剂表面的反应物逐渐脱附,甲苯的出口浓度增大,其降解率下降;当达到一定温度时,催化剂对甲苯的催化反应作用占主导地位,这种作用反应迅速,对甲苯的降解程度大,表现为甲苯的出口浓度迅速下降,因而甲苯的转化率急剧升高[7, 20]。LIAO等[7]和廖银念等[20]的研究也出现了类似的实验现象。
当加入不同含量的Ce后,所形成的Mn-Ce复合氧化物对甲苯的降解率都随着温度的升高而升高,达到完全转化时的温度均为225 ℃,但含Ce的催化剂在催化降解甲苯时未出现甲苯脱附现象。在较低的反应温度区域(<200 ℃),不同的Ce含量的催化剂对甲苯的降解性能具有明显差异,随催化剂中Ce含量的增加呈现先降低后升高再降低的趋势,活性顺序为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox。已有研究[15-16, 20]用T90(甲苯转化90%所需的温度)来表示催化剂的活性,T90越低,表明催化剂的活性越高。为了更直观反映不同Mn-Ce比例的复合氧化物和催化活性的关系,本研究采用插值法估算了各催化剂降解甲苯转化率达90%时所需温度(T90),利用1/T90来表示催化剂的活性,结果如图3(b)所示。结果发现,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂T90值最低,表明该催化剂具有最佳的低温催化氧化甲苯活性。此外,纯MnO2和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂在催化氧化甲苯过程中对CO2的选择性存在一定的差异(图3(c)),Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂的CO2选择性略优于纯MnO2催化剂,且在反应温度200 ℃后,CO2生成率高于93.5%,由此说明,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂实现完全甲苯催化氧化时,甲苯几乎都转化为CO2。
-
不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂的比表面积、孔容、孔径的结果见表1。由表1可知:单一MnO2和Mn-Ce复合氧化催化剂的比表面积随着Ce的含量的增加,出现先减少后增加最后再减少的趋势;比表面积最大和最小的分别为Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox(162.29 m2·g−1)和Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox (68.07 m2·g−1);催化剂的孔容最大和最小的分别为Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox(0.33 cm3·g−1)和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox(0.15 cm3·g−1);而催化剂的最大和最小的平均孔径分别为Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox(17.57 nm)和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox(5.48 nm)。由于甲苯催化氧化性能最优的为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂,在所有合成的催化剂中,其具有最小的孔容和平均孔径,且具有适中的比表面积,这说明比表面积等物理性质并不是催化剂在低温催化氧化甲苯反应中起主导作用的影响因素。此外,由图3可知,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂的低温催化氧化活性略优于MnO2催化剂,但具有少量Ce的Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox催化剂的活性却明显低于比表面积接近的MnO2催化剂,这可能是由于比表面积等物理性质并不是催化剂在低温催化氧化甲苯反应中起主导作用的因素,催化剂的低温催化氧化甲苯关键因素是催化剂的氧化还原性能和反应过程中的活性氧物种[15]。
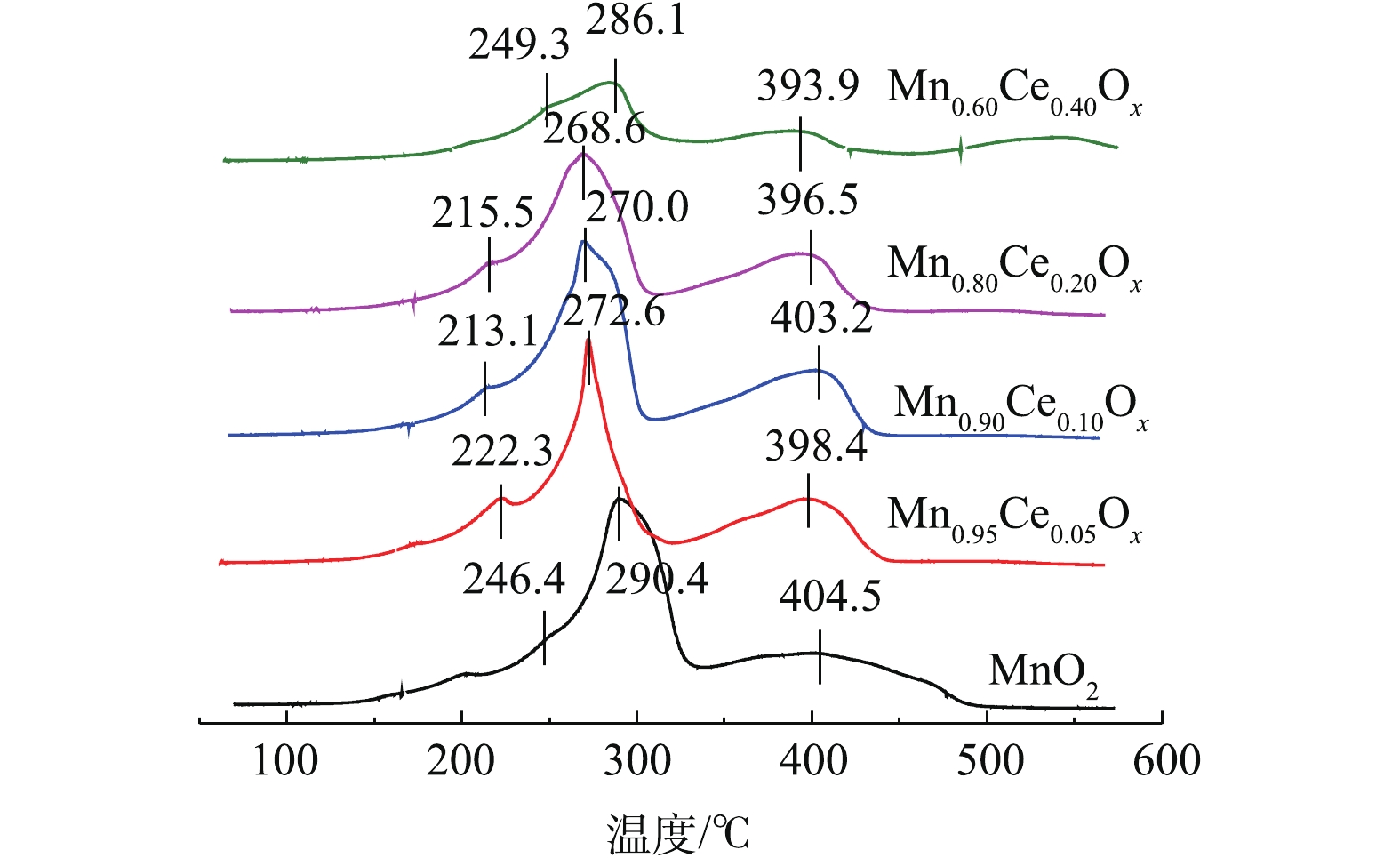
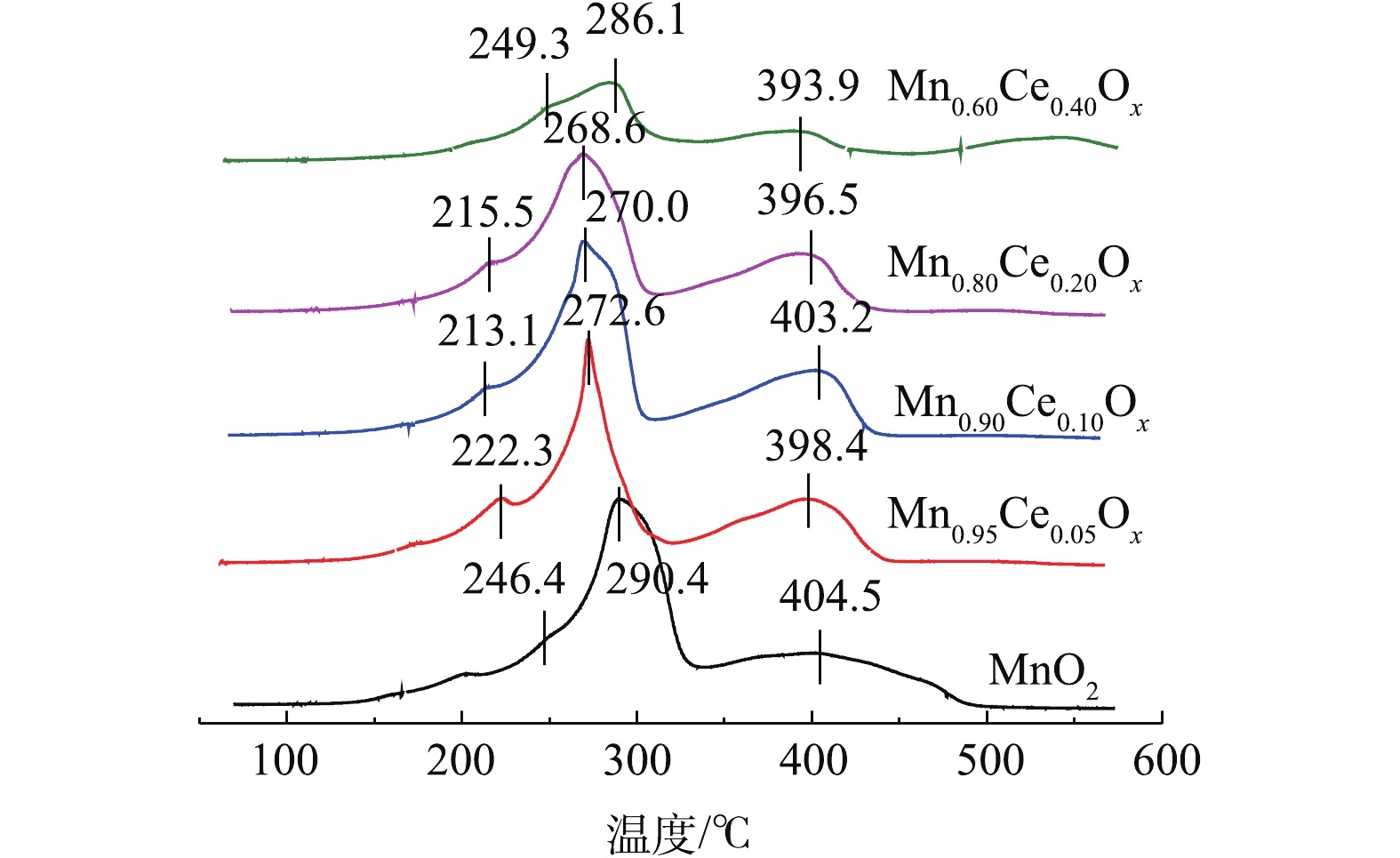
H2-TPR可以反映催化剂的氧化还原性能,其中氧物种伴随变价金属氧化还原循环与催化氧化反应密切相关[9, 15, 20]。不同比例的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂的H2-TPR结果如图4所示。可以看出,纯的MnO2在246.4 ℃和290.4 ℃出现了2个还原峰,分别归属为MnO2→Mn2O3及Mn2O3→Mn3O4的还原,大约在400 ℃的还原峰归属为Mn3O4→MnO的还原峰[21-22]。据报道[7, 18],CeO2向Ce2O3的还原出现在380~450 ℃,而高于650 ℃才可能出现体相氧化铈的还原。深入分析Mn-Ce氧化物催化剂的TPR谱图可知,由于催化剂中Ce含量少,没有出现新的还原峰,说明在催化剂中Ce的还原峰面积比较小,极有可能被Mn2O3→Mn3O4的还原峰所掩盖,但随着Ce含量的增加,MnOx的还原温度向低温偏移。一般而言,催化剂还原峰中心所对应的温度越低,说明催化剂的氧化性越强[23-25],因此,催化剂的氧化性能依次为Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox>MnO2>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox。结合各催化剂催化氧化甲苯活性的结果,可以看出,催化剂的氧化还原性能与其在低温区催化氧化甲苯的性能存在一定的相关性,也间接说明催化氧化还原能力是影响催化剂催化氧化甲苯性能的重要指标。
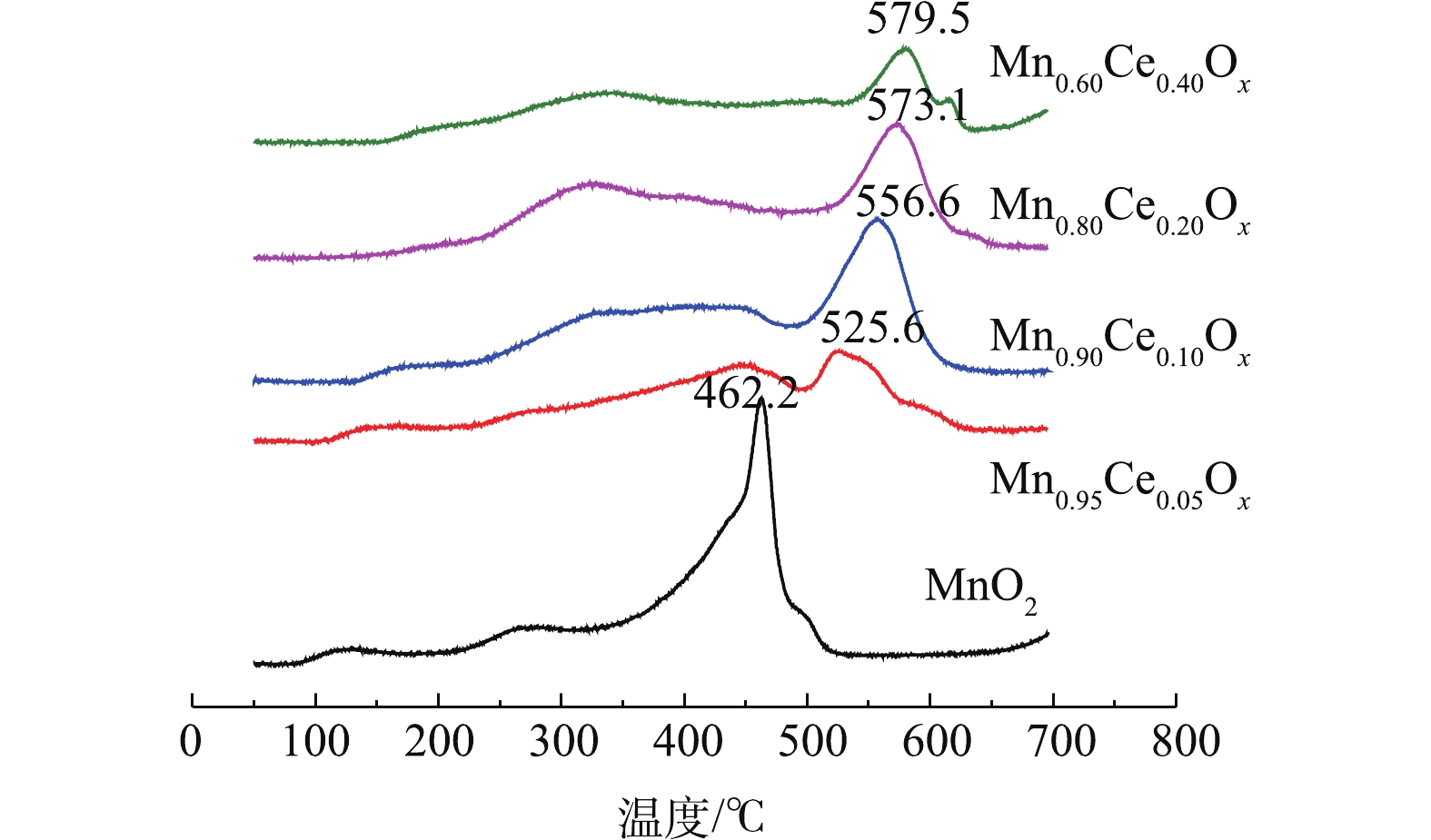
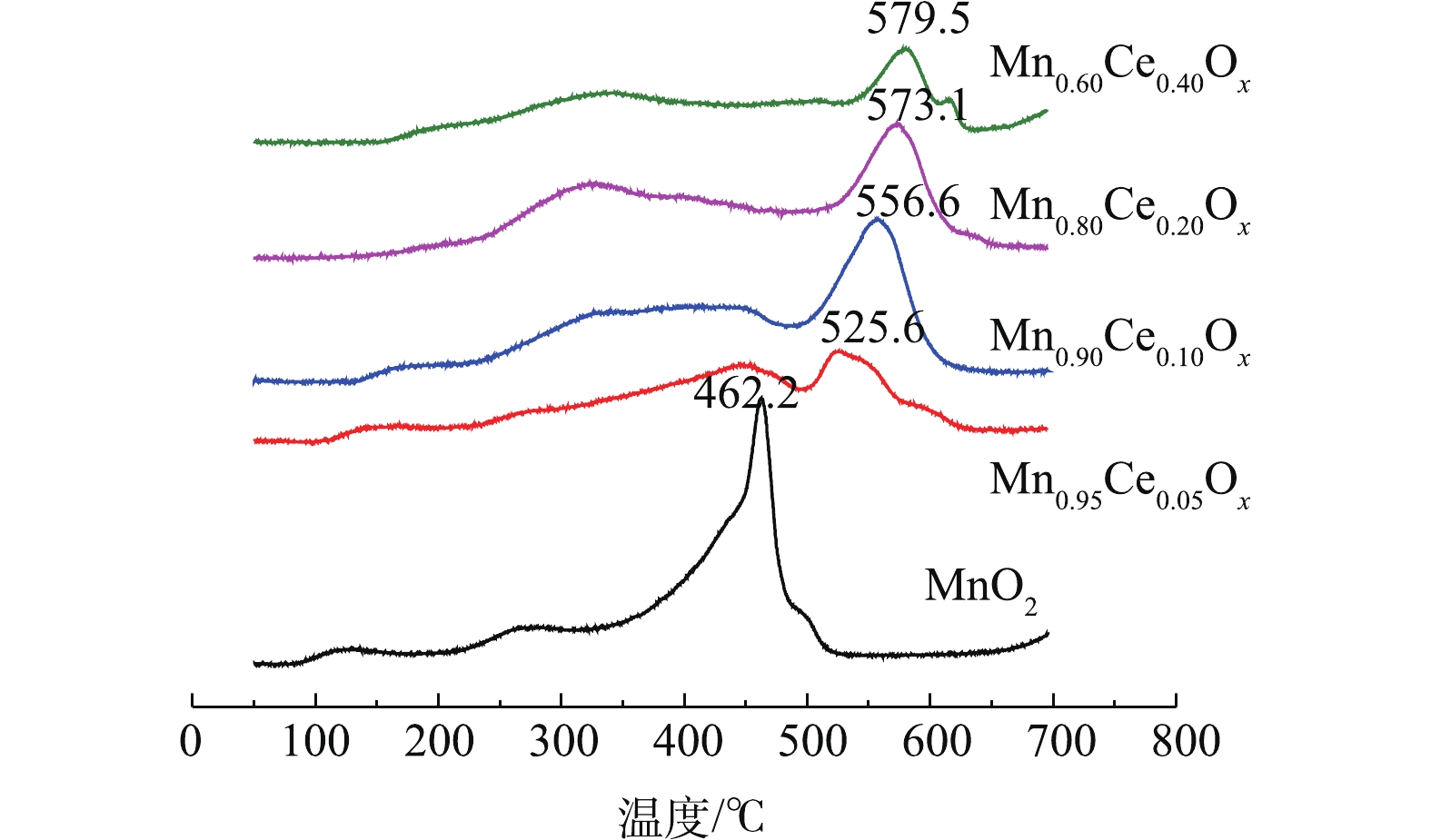
O2-TPD 可对催化剂表面的氧空位以及物种存在状况[6, 7, 15, 26]进行测定。不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物的O2-TPD的结果如图5所示。其中在80 ℃、300~400 ℃和大于500 ℃出现的氧脱附峰可分别归属于弱的分子吸附氧(
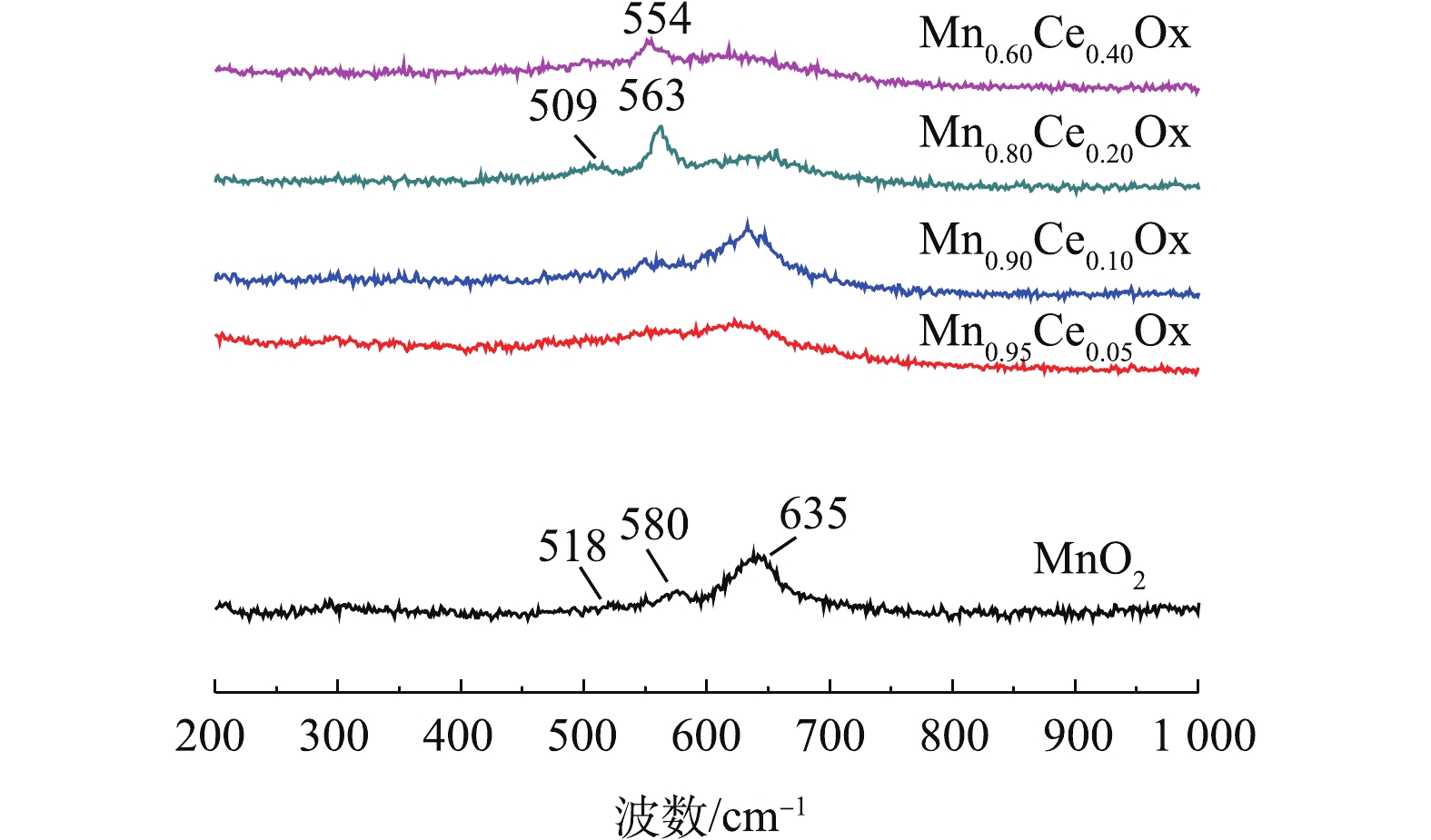
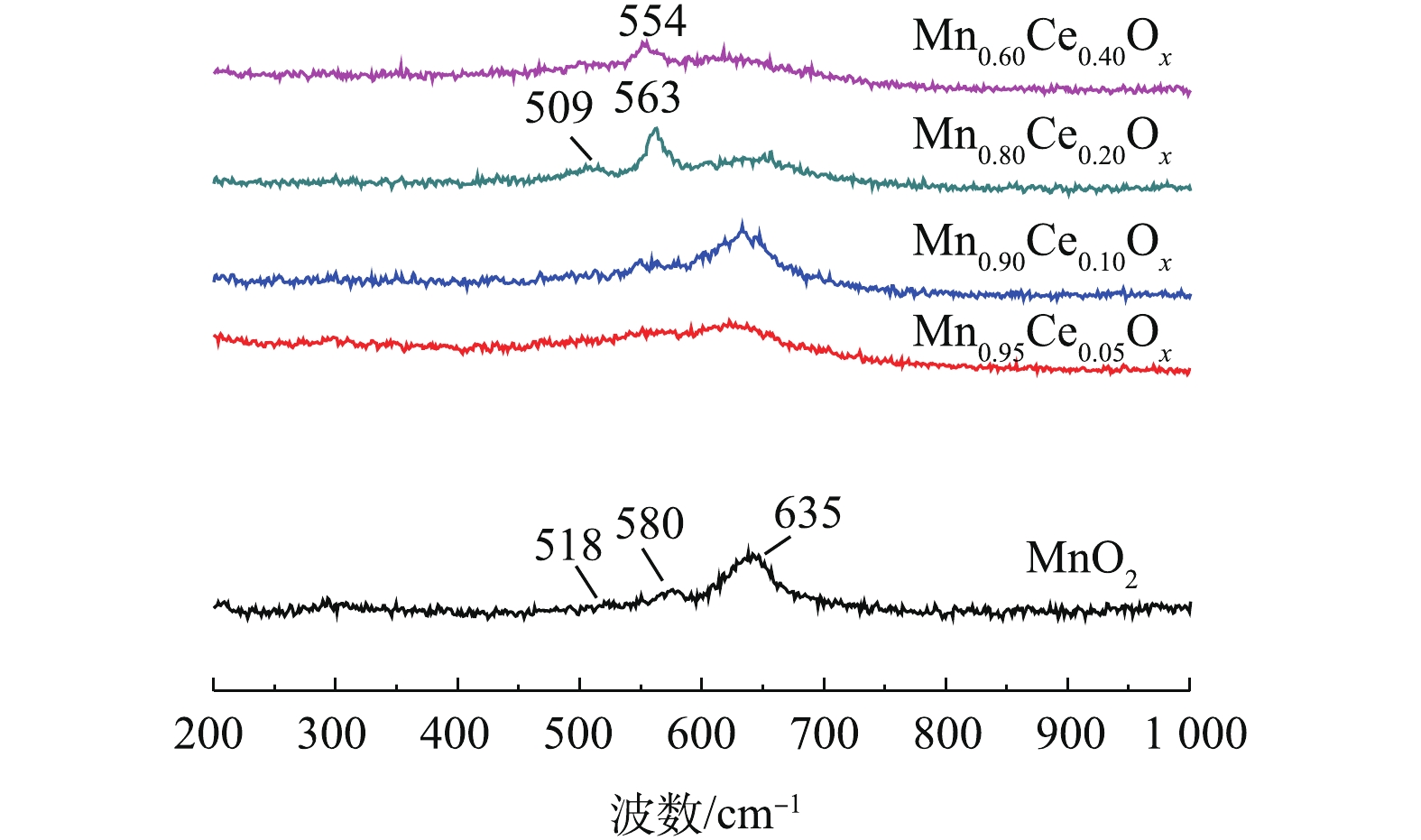
O−2 )、化学吸附氧(O−)和晶格氧O2−的脱附峰[6, 7, 15]。如图5所示,不同比例的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂在300~400 ℃的氧脱附峰峰面积大小依次为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>>Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox。这与催化氧化甲苯的活性评价结果一致,表明化学吸附氧的含量是低温催化氧化甲苯性能的重要因子。此外,含Ce微球催化剂的低温催化氧化甲苯的活性存在差异主要包括2个原因:1)催化剂还原峰中心所对应的温度越低,说明催化剂的氧化性越强,因此,催化剂的氧化性能依次为Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox>MnO2>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox,结合活性评价的结果,可以看出,催化剂的氧化还原性能与其在低温区间催化氧化甲苯的性能存在一定的相符性;2)催化剂的氧化还原性能接近(Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox),而低温区催化氧化甲苯的性能存在差异,这是由于不同比例的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂在300~400 ℃的氧脱附峰峰面积大小依次为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>>Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox。这与催化氧化甲苯的活性评价结果一致,表明化学吸附氧的含量是低温催化氧化甲苯性能的重要因子,这些化学吸附氧物种对于完成催化氧化循环起着关键作用。图6是不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物微球催化剂的拉曼光谱图。其中纯MnO2和Mn-CeOx催化剂中都出现了500~700 cm−1的特征峰,该峰被认为是MnO2中[MnO6]八面体的伸缩振动,且纯MnO2所对应的特征峰正好与γ-MnO2的特征峰完全吻合[27],这一表征结果也更好地验证了前面的XRD结论。值得注意的是,与纯MnO2所对应的特征峰相比,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂所对应的2个特征峰(509 cm−1和563 cm−1)及Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox催化剂所对应的1个特征峰(554 cm−1)都明显向低波数偏移,表明Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂中都可能存在Mn-Ce固溶体,这与文献报道的结论[28]相符。而具有较低Ce含量的Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox和Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox所对应的特征峰并没有出现明显偏移现象,这说明当Ce掺杂量较低时,Mn-Ce催化剂中未形成固溶体。正由于Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂中形成了固溶体,使催化剂具有更优异的储氧能力,这与O2-TPD分析得出的该催化剂具有最高含量的化学吸附氧的结果(图5)相符。因此,Mn-Ce催化剂中存在固溶体也是其具有优异催化氧化甲苯性能的关键原因之一。值得一提的是,Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox催化剂中虽然也存在固溶体,但Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂具有比Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox催化剂更强的氧化还原性能和更高的化学吸附氧的含量,故Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂呈现更优异的低温催化氧化甲苯性能。
2.1. Mn-Ce复合氧化物的可控制备
2.2. Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂催化氧化甲苯性能
2.3. 催化剂的表征
-
1) 采用简单的水热法成功合成出了Mn-Ce氧化物微球,且铈摩尔含量占5%、10%和20%的产物结晶都比较完整,而铈摩尔含量为20%时,其形貌为较光滑的微球,结晶较完整,颗粒尺寸较小。MnO2微球催化剂中存在γ-MnO2的特征峰,而随着Ce的加入,催化剂的结晶度有所下降。
2) Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂呈现最佳的催化氧化甲苯性能,较强的氧化还原性能和较高的化学吸附氧的含量是其具有优异的低温催化氧化甲苯性能的重要原因。
3) Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂中存在Mn-Ce固溶体,这也是其具有最佳催化氧化甲苯性能的关键原因之一。



 下载:
下载: