-
电除尘器是工业烟气的主流除尘设备,在燃煤电厂的应用占比约为70% [1-3],烧结机机头的烟尘治理设备几乎全部为电除尘器[4-6]。随着燃煤电厂烟气超低排放的实施,湿式电除尘技术在燃煤电厂得到广泛应用。电除尘器主要分为电控和本体2个部分,近年来,针对燃煤电厂及非电行业的超低排放改造技术频有报道。在本体技术方面,超低排放技术包括低低温电除尘技术、湿式电除尘技术、颗粒团聚技术等[7-11]。在电源技术方面,朱法华等[12]分析了电除尘器高频电源节能减排的机理,介绍了国内外高频电源的研究与应用情况,并基于实际工程案例,介绍了高频电源的节能、减排幅度;李纪等[13]针对我国冶金转炉冶炼周期内工艺波动大、粉尘浓度及比电阻大等情况,提出了三相电源改造思路,提高了除尘器的除尘效率,并优化了电控性能;汤铭等[14]提出了一种低成本高压脉冲静电除尘电源,分析了该高压脉冲电源的稳态工作原理以及电场发生闪络时工作的情况;丁鑫龙等[15]通过实验方法,研究了脉冲电源技术对高比电阻粉尘的脱除特性;张滨渭等[16]研究发现,三相电源适合高粉尘负荷,高频电源在匹配良好条件下可实现较好的提效作用,而脉冲电源更多的研究是针对性地脱除细颗粒物和高比电阻粉尘。
按输出特性分类,电源可分为电压源和电流源,上述研究多针对干式电除尘器配套的电压源,对于湿式电除尘器配套高压恒流源的供电特性及对电除尘提效及能耗的分析,国内鲜有文献报道。电除尘器供电电源的工作状态直接影响除尘器的运行稳定性及除尘性能,对于湿式电除尘器而言,因其工作在饱和湿烟气状态,且存在喷淋冲洗环节,电场的放电状态变化大、干扰因素多,电源工作的稳定性至关重要。尤其是导电玻璃钢管式湿式电除尘器,鉴于其阳极管内壁材料的特殊性,必须尽量减少火花放电,防止电极灼伤甚至起火,保证设备安全、稳定运行。近年来,因火花控制不当等原因,山西、河南、山东等地频有导电玻璃钢管式湿式电除尘器着火事故报道。本研究通过实验室研究及现场实测相结合的手段,定量分析了导电玻璃钢管式湿式电除尘器的高压恒流源供电特性及其对电除尘提效、能耗的影响,为后续湿式电除尘器的性能提升及节能优化提供参考。
全文HTML
-
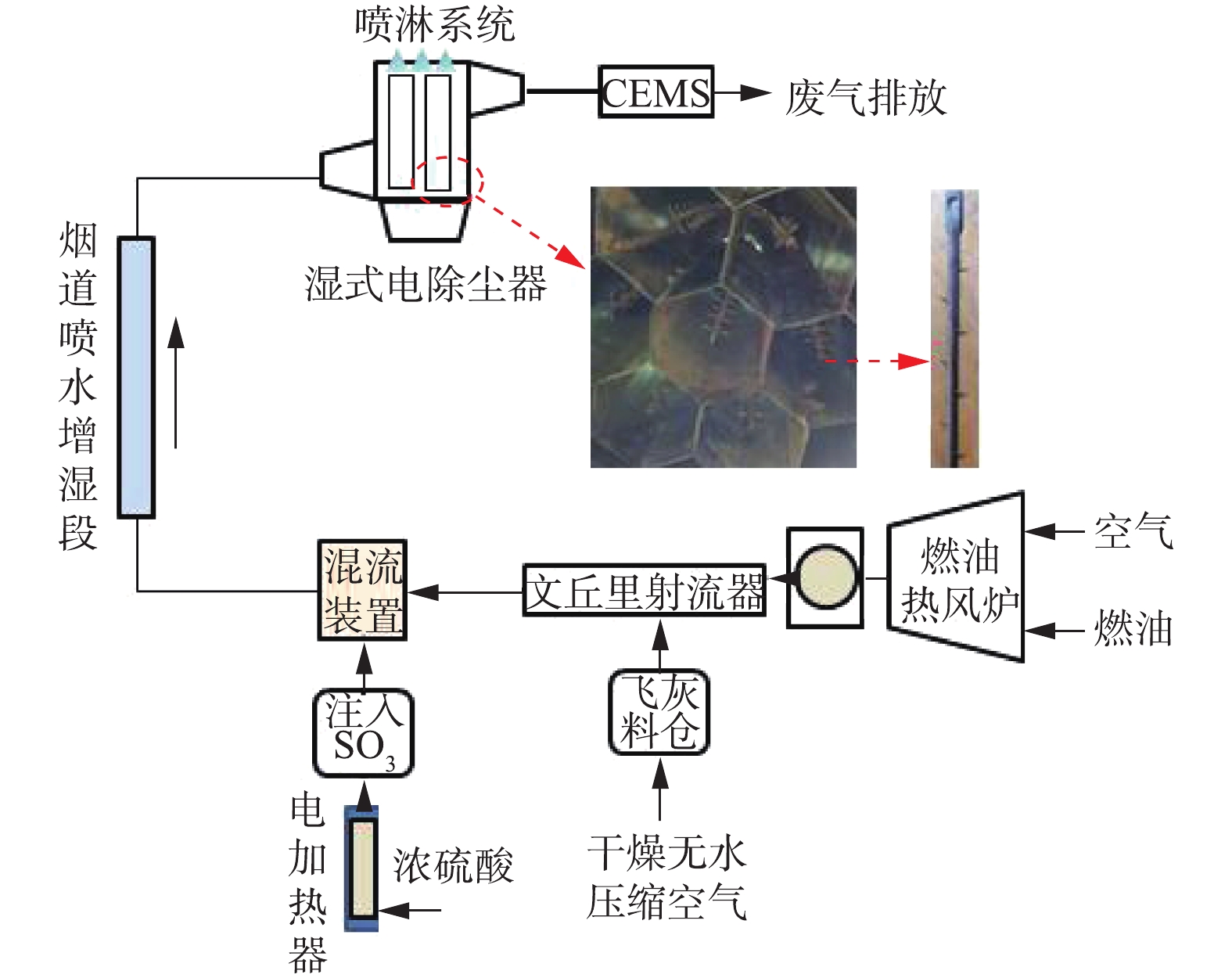
湿式电除尘器实验系统如图1所示,通过燃油热风炉产生高温烟气,设计烟气量为1×104 m3·h−1,炉膛出口烟气温度控制在70 ℃左右。通过飞灰料仓、文丘里射流器向实验系统内喷射燃煤飞灰。通过浓硫酸电加热方式产生气态SO3,以恒定流量均匀注入系统,并通过混流装置将其与烟气充分混合。通过向烟道内喷水增湿,使烟气达到湿饱和,并控制湿式电除尘器入口烟气温度在50 ℃左右。湿式电除尘器为导电玻璃钢管式湿式电除尘器,阳极板为正六边形(内切圆直径为φ300 mm),阳极管长度为4.7 m,湿式电除尘器的总集尘面积约为180 m2,阴极线为合金锯齿线,喷淋系统每次冲洗时间为5 min,冲洗水量约为0.2 t。湿式电除尘器的供电电源分别有72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒流源、恒压源和72 kV/200 mA高频高压恒流源,不同电源间可灵活切换。湿式电除尘器出口布置CEMS,用于监测出口烟气中的烟尘浓度,在实验期间,采用手工测试方法对CEMS进行数据校准。
-
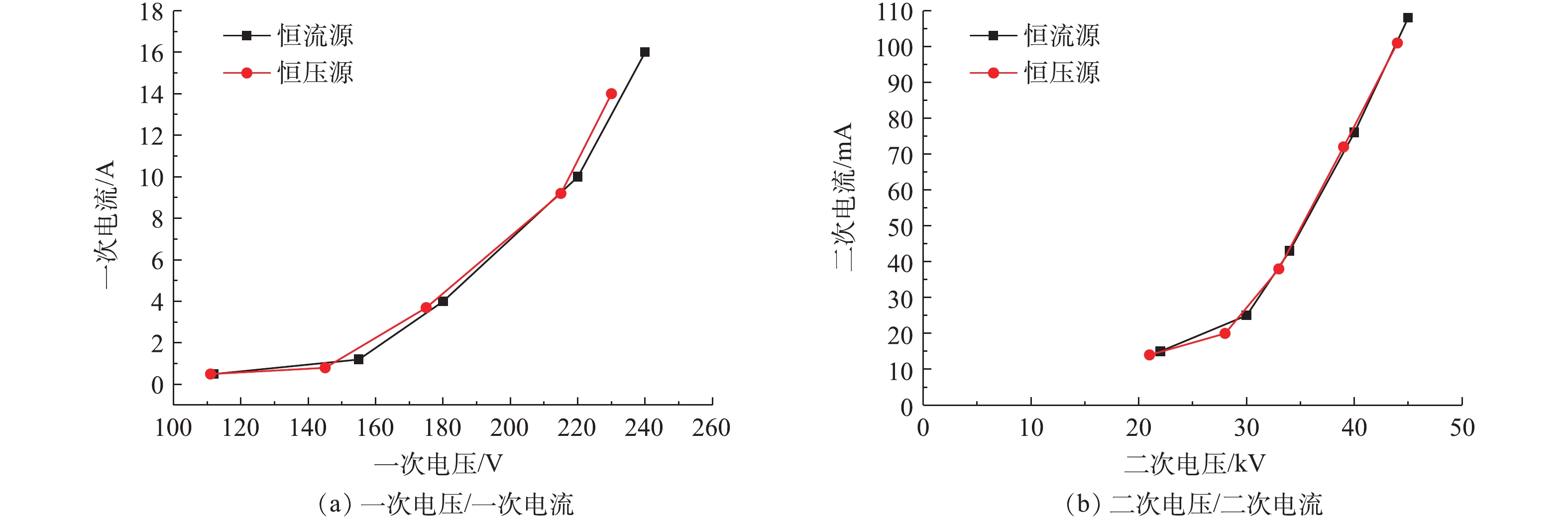
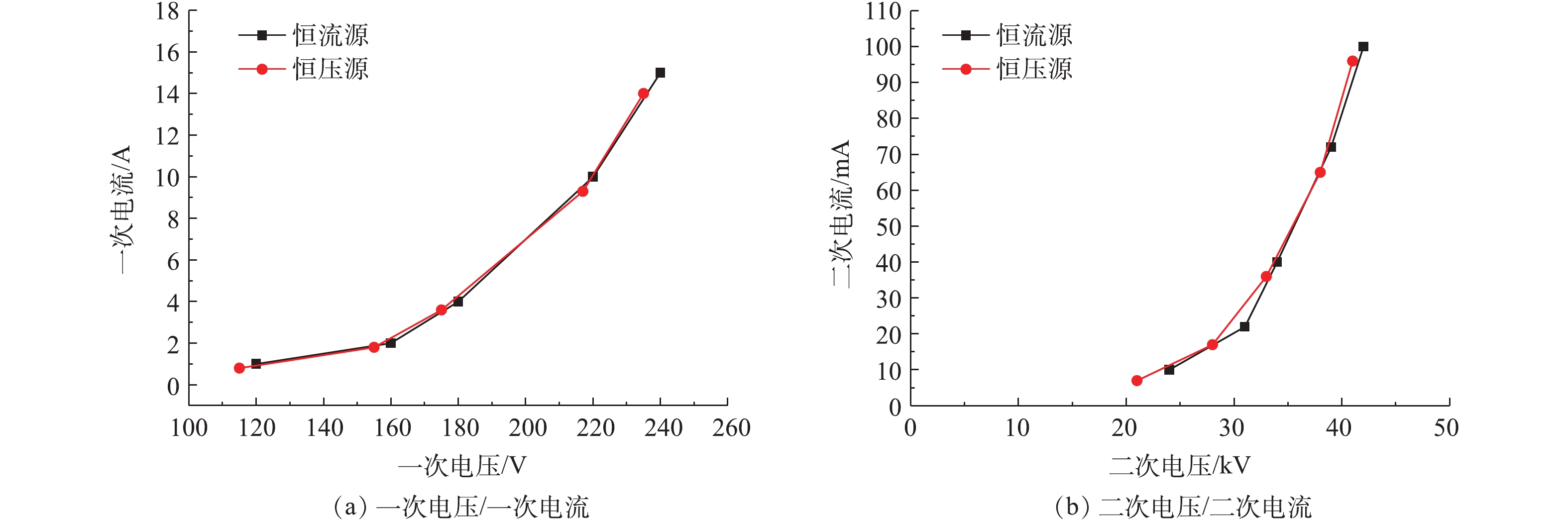
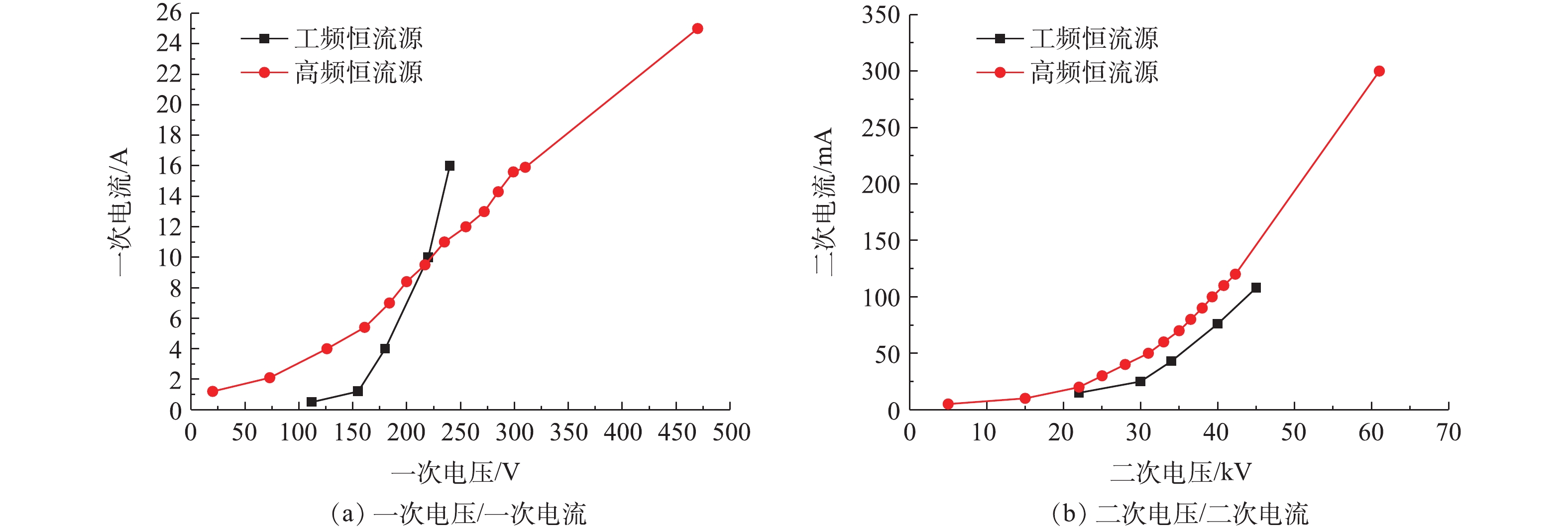
工频电源是目前电除尘器应用最为成熟和应用最多的电源[17-18]。工频恒压源输出电压恒定且可控,电流随负载变化;恒流源输出电流恒定且可控,电压随负载变化[19-21]。首先,参照行业标准《电除尘器设计、调试、运行、维护安全技术规范》(JB/T 6407-2017)的相关规定,分别在72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒流源和72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒压源供电情况下对湿式电除尘器进行空载升压实验,对应的一次电压/电流、二次电压/电流分别如图2(a)和图2(b)所示。在空载条件下,工频高压恒流源和工频高压恒压源的一次、二次电压/电流信号基本一致。
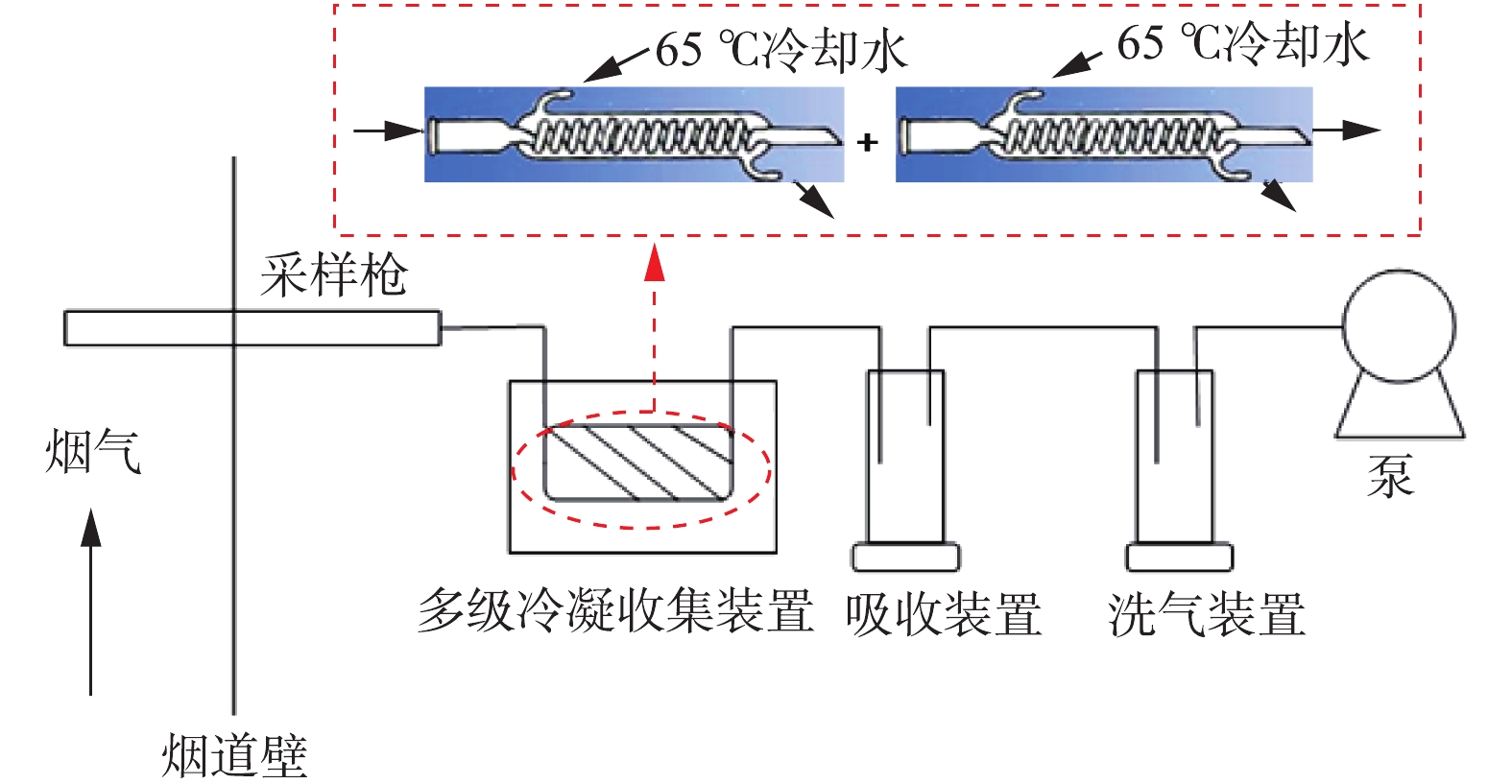
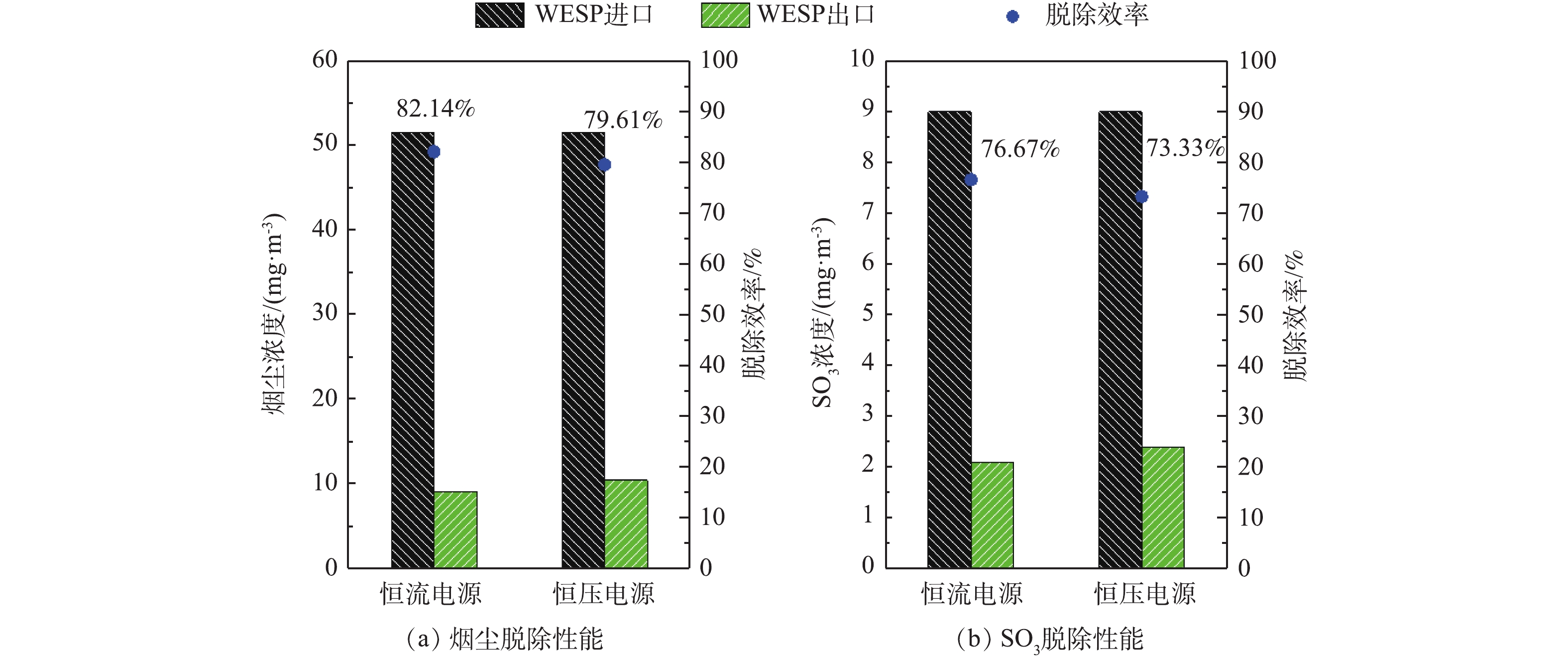
控制湿式电除尘器入口烟气温度为50 ℃,烟尘浓度为51.5 mg·m−3,SO3浓度为9 mg·m−3(大约为当前超低排放机组中湿法脱硫出口的SO3平均浓度[21])。烟尘浓度的测定采用ZR-D09A型一体化采样枪和ZR-3260型自动烟尘测试仪,测试方法符合行业标准《固定污染源废气低浓度颗粒物的测定重量法》(HJ 836-2017)的相关规定。SO3测定采用国家标准《燃煤烟气脱硫设备性能测试方法》(GB/T 21508-2008)所规定的控制冷凝法,采样系统如图3所示,水浴温度为65 ℃,多级冷凝装置为两级蛇形盘管,采样枪加热温度>280 ℃,抽气流量为20 L·min−1。采样后,用去离子水清洗蛇形盘管,之后用DR 6000型分光光度计测定溶液中的硫酸根,换算得到SO3浓度值。在上述带负载工况下,再次分别在72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒流源和72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒压源供电情况下对湿式电除尘器进行升压实验,对应的一次电压/电流、二次电压/电流分别如图4(a)和图4(b)所示。在负载条件下,工频高压恒流源和工频高压恒压源的一次、二次电压/电流信号一致性仍较好,且与空载升压时所示的运行电源参数相比差异不大。经测定,72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒流源和72 kV/100 mA工频高压恒压源供电情况下湿式电除尘器出口烟尘、SO3浓度及其脱除效率如图5所示,两者的污染物脱除性能也大致相当。
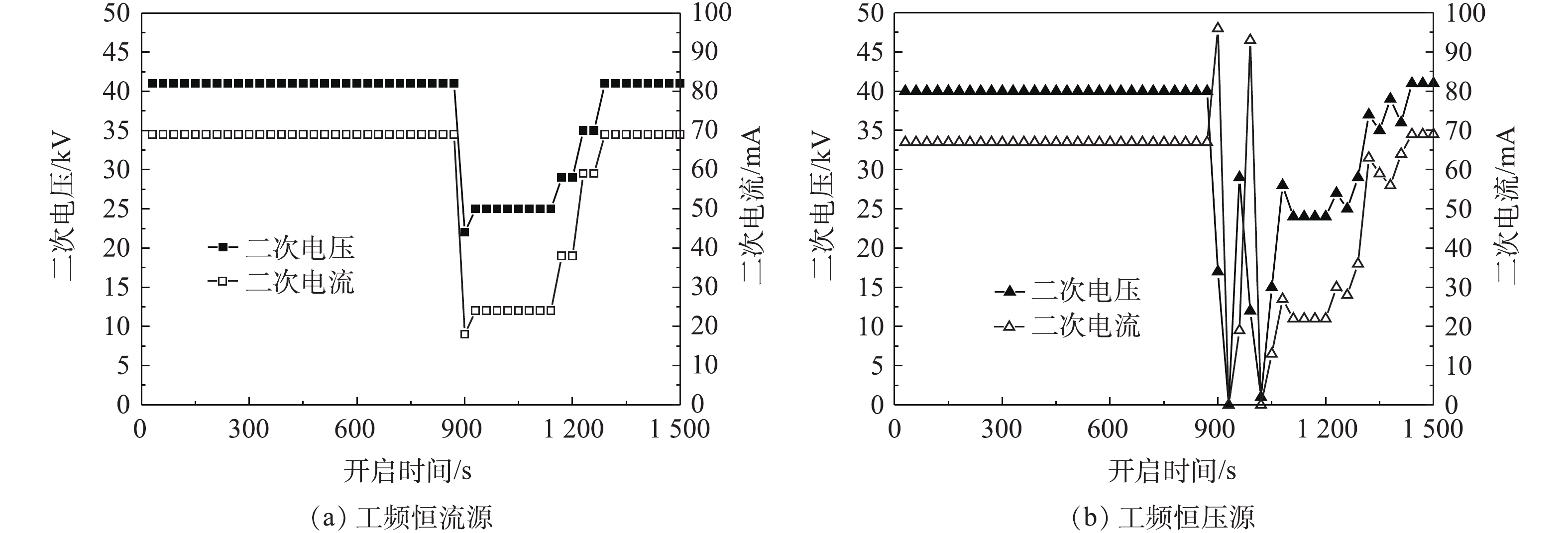
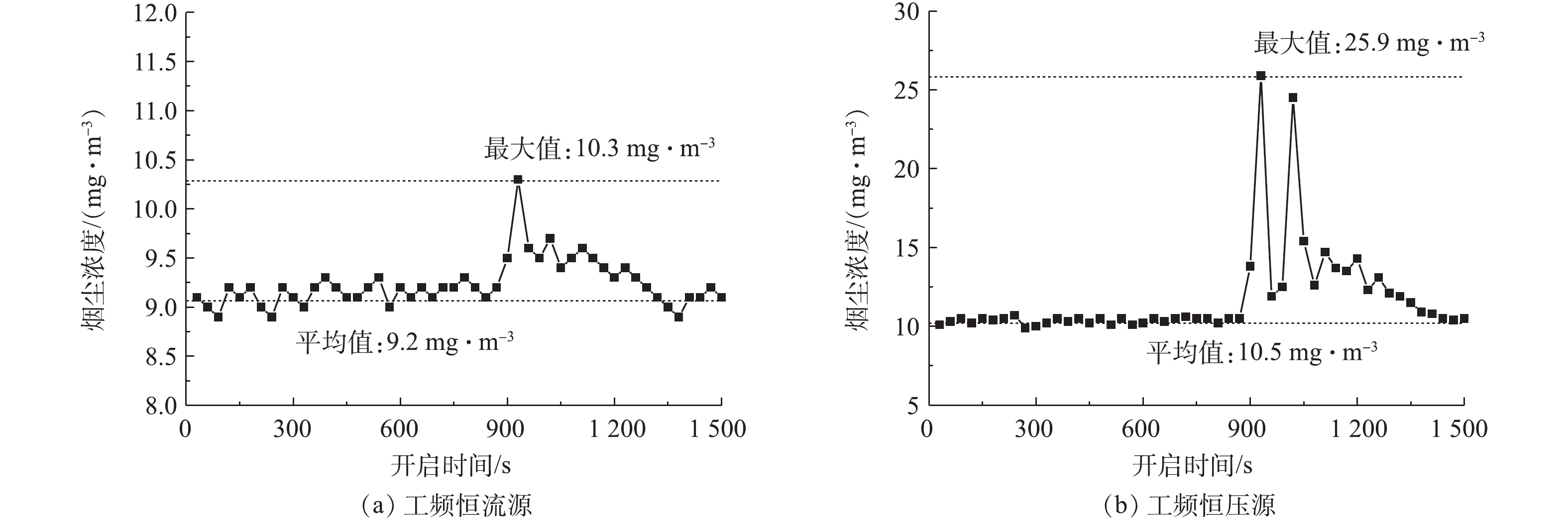
开启湿式电除尘器的喷淋系统,开启后约5 s后电场出现闪络,此时电源的二次电压、二次电流分别如图6(a)和图6(b)所示。对于工频恒流源来说,电源检测到火花放电后,自动下调电源运行参数,使得电流/电压稳定运行在相对较低的参数范围。虽然仍会有零星放电发生,但电源运行参数相对平稳,且喷淋系统关闭后,电源可自动回复到原设定参数运行。对于工频恒压源来说,在喷淋开启初期阶段,电场内频繁产生火花放电,电源运行参数不稳定,有一段明显的振荡区,且喷淋系统关闭后,其电源参数的回复过程也较恒流源慢一些。这是因为,恒流源输出特性受负载干扰产生的电流变量的约束,负载特性总能回到原来的平衡点,工作状态都是稳定的;恒压源输出存在不稳定的工作点,抗干扰能力差,喷淋系统开启后会使电除尘器进入负阻区,电流瞬间增大、电压下降,产生火花击穿,然后电源保护,停止供电,电压源既不能约束负载电压的减少又不能约束负载电流的增加,因而失去对负载的控制能力,造成电源运行参数振荡。
为研究不同电源供电特性对湿式电除尘器性能的影响,分别调取2种电源供电时湿式电除尘器出口CEMS测得烟尘浓度数据,显示喷淋系统开启前后湿式电除尘器出口烟尘浓度变化,结果如图7(a)和图7(b)所示。喷淋系统开启后,随着电源运行参数的降低,烟尘排放浓度均有不同程度的增加,其中,工频恒流源供电时,湿式电除尘器出口烟尘浓度最大值为10.3 mg·m−3,较喷淋前平均值(9.2 mg·m−3)增加了约12%;但恒压源存在一个电源参数振荡区,此时,出口烟尘浓度最大值达25.9 mg·m−3,较喷淋前平均值(10.5 mg·m−3)增加了约147%。因此,对于湿式电除尘器而言,应优先考虑采用抗干扰能力强的恒流源,尤其是导电玻璃钢管式湿式电除尘器,由于其阳极管内壁材料的特殊性,因此,必须尽量减少火花放电,防止电极灼伤甚至起火,保证设备安全、稳定运行。
-
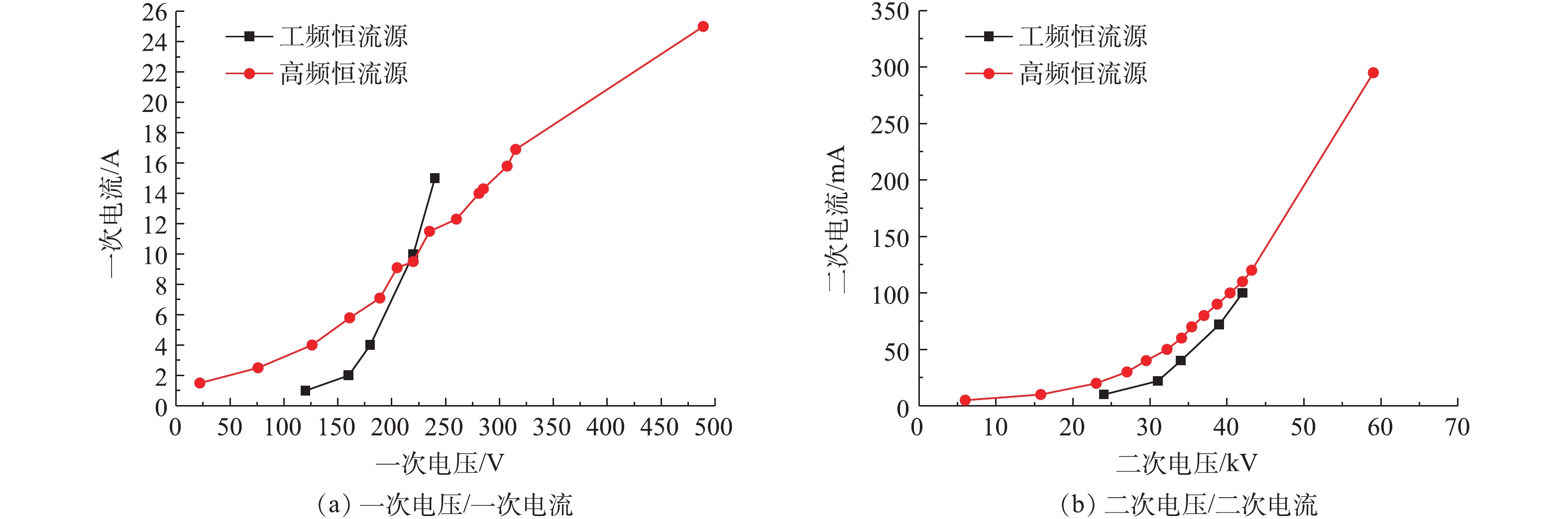
参照JB/T 6407-2017的相关规定,分别对72 kV/200 mA高频高压恒流源进行空载、负载升压实验,对应的一次电压/电流、二次电压/电流曲线及与工频恒流源对比分别如图8和图9所示。在负载条件下,高频电源的一次、二次电压/电流信号与空载升压时所示的运行电源参数相比差异不大。值得注意的是,空载实验前实际上也已通过湿烟气,只是空载时临时停掉了风机跟加灰装置,所以湿电场内的烟气仍基本处在湿饱和状态。推测是因湿电场内湿饱和烟气中水分子导电性能好,因此,运行电流较大,是否有烟气流动及飞灰加入,对升压实验的结果影响不大,这与某实际工程项目的通水升压实验/锅炉投运升压实验规律[18-19]一致。与工频恒流源相比,高频电源的功率因数更高,一般情况下,功率周数≥0.92,有效电能的转化率高,同样具有电除尘负载跟踪特性和火花抑制特性的自适应特点。因此,在相同的供电电压条件下,高频电源的运行电流更大,且在额定容量放开运行时,二次电压、二次电流可分别高达60 kV、300 mA,这更有利于湿式电除尘器的污染物脱除性能的提升。
为进一步分析高频与工频恒流源,对湿式电除尘器的提效特性,分别在相同供电电耗及高频恒流源最大电耗条件下,测定湿式电除尘器对烟尘及SO3的脱除性能。根据国家标准《电除尘器性能测试方法》(GB/T 13931-2017)的规定,采用三相有功电能表测定不同电源配置实验期间湿式电除尘器的电耗,分别记录电能表读数和测量时间,并参照式(1)计算湿式电除尘器电耗。
式中:
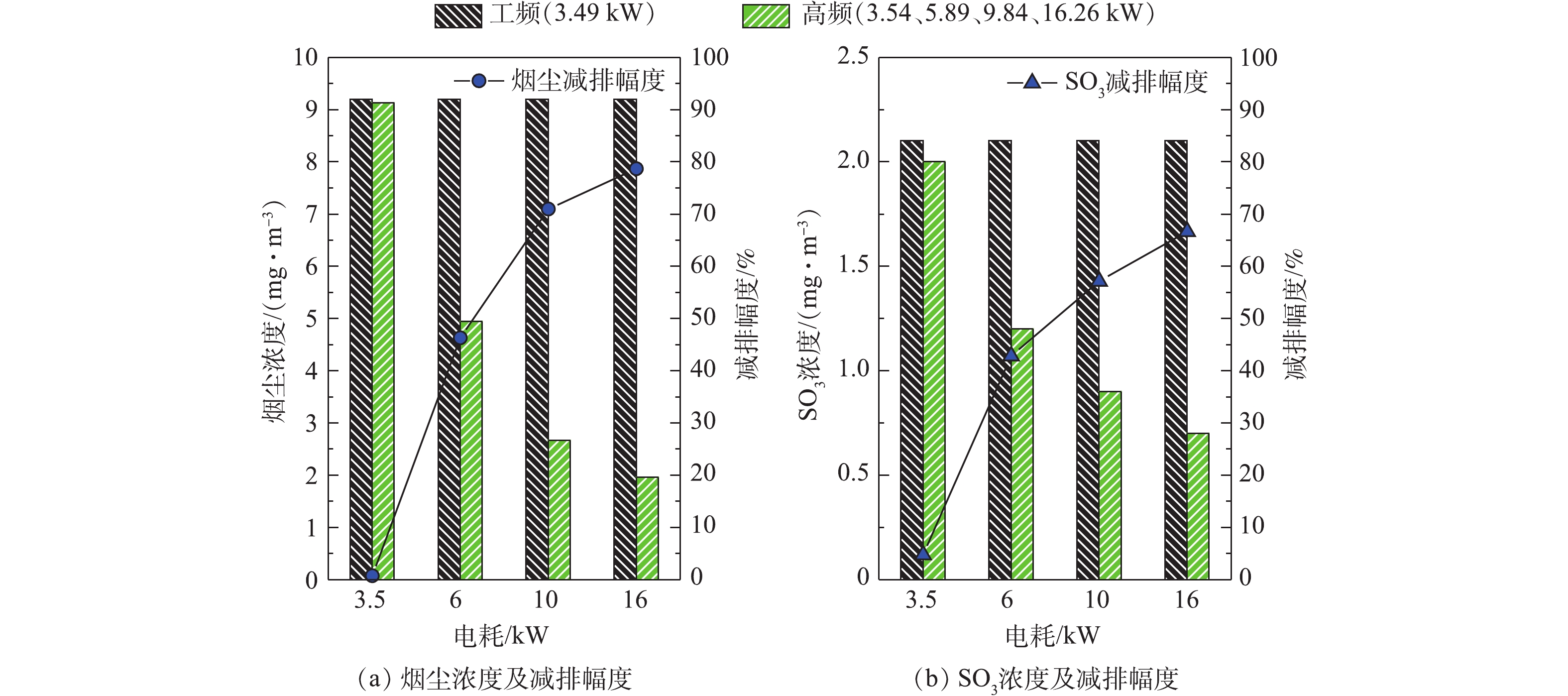
W 为湿式电除尘器电耗,kW;W2 为测量后电能表读数,kWh;W1 为测量前电能表读数,kWh;t 为测量时间,h。分别在工频恒流源电耗3.49 kW,高频恒流源电耗3.54、5.89、9.84和16.26 kW条件下,测定湿式电除尘器出口烟尘及SO3质量浓度,结果如图10所示。在供电电耗相当(工频3.49 kW、高频3.54 kW)的情况下,湿式电除尘器出口的烟尘、SO3浓度变化不大,可以认为两者具有相同的污染物脱除性能。分别将高频电源的电耗提高至5.89、9.84和16.26 kW,湿式电除尘器出口的烟尘、SO3浓度不断降低,与工频相比,烟尘的减排幅度分别为46.30%、70.98%、78.69%,SO3的减排幅度分别为42.86%、57.14%和66.67%。与烟尘的减排幅度相比,SO3减排幅度略小,这主要是因为此时SO3是以硫酸气溶胶颗粒的形式存在,粒径小(纳米级),驱进速度低,且荷电后的气溶胶颗粒还会在放电极周围产生空间电荷效应[20-23],影响电场放电。
另外,值得注意的是,随着供电电耗的增加,湿式电除尘器出口的烟尘、SO3浓度虽然不断降低,但减排幅度与电耗的增加并非呈线性关系,高频电源的供电电耗从3.54 kW增加至5.89 kW,仅增加了2.35 kW电耗,烟尘、SO3的减排幅度分别为46.30%、42.86%;但从9.84 kW增加至16.26 kW,电耗增加了6.42 kW,烟尘的减排幅度仅从70.98%增加至78.69%,增加了不足8个百分点,SO3的减排幅度仅从57.14%增加至66.67,增加了约9个百分点。因此,从节能角度来说,在满足5 mg·m−3超低排放要求的前提下,可适当减少湿式电除尘器的电能消耗,尤其是针对湿式电除尘器运行在2.5 mg·m−3甚至1 mg·m−3以下的工况,节能空间较大。该发现可为实际工程项目的节能优化运行提供有效的数据支撑。
1.1. 实验系统
1.2. 工频电源实验
1.3. 高频电源实验
-
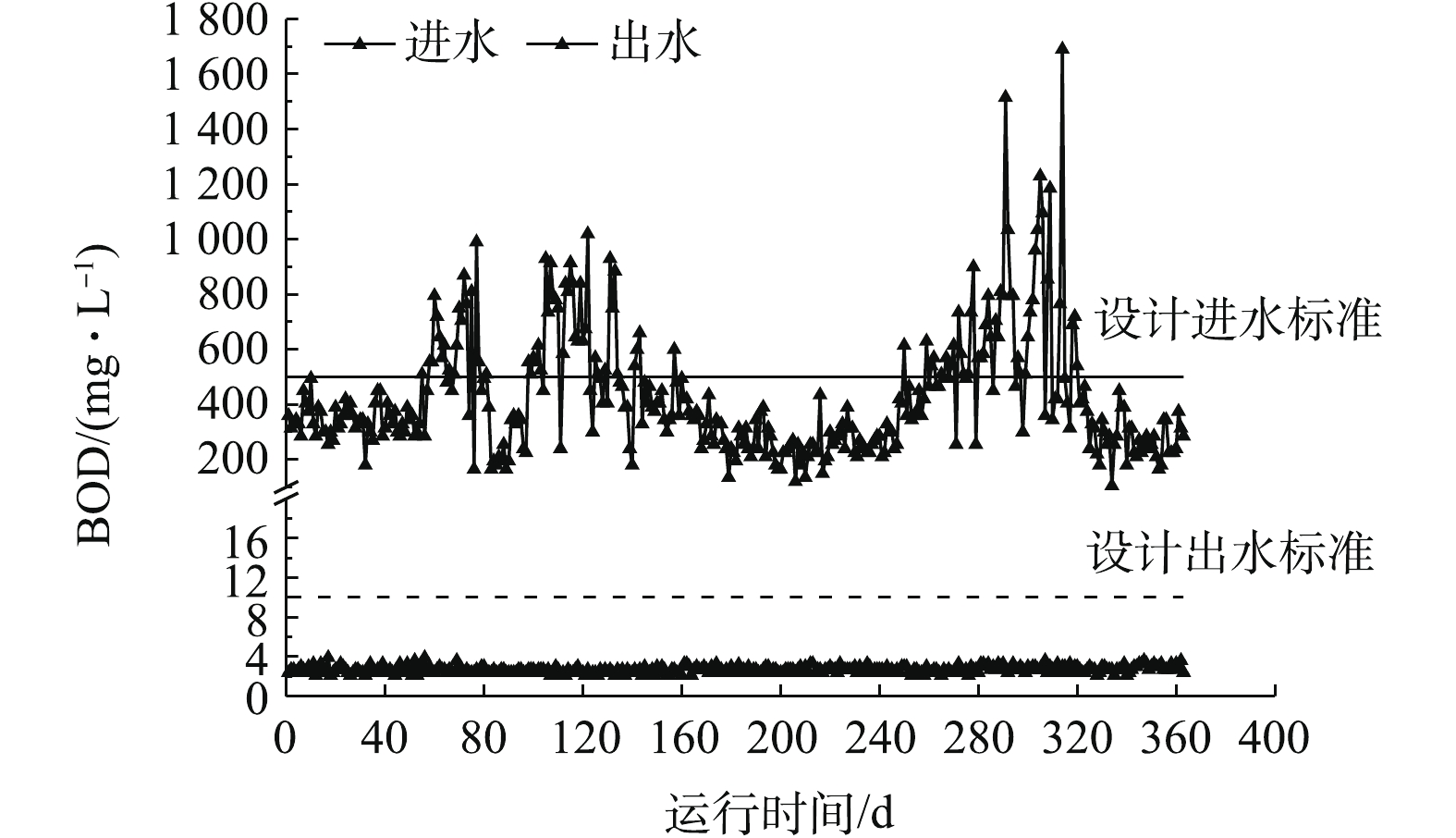
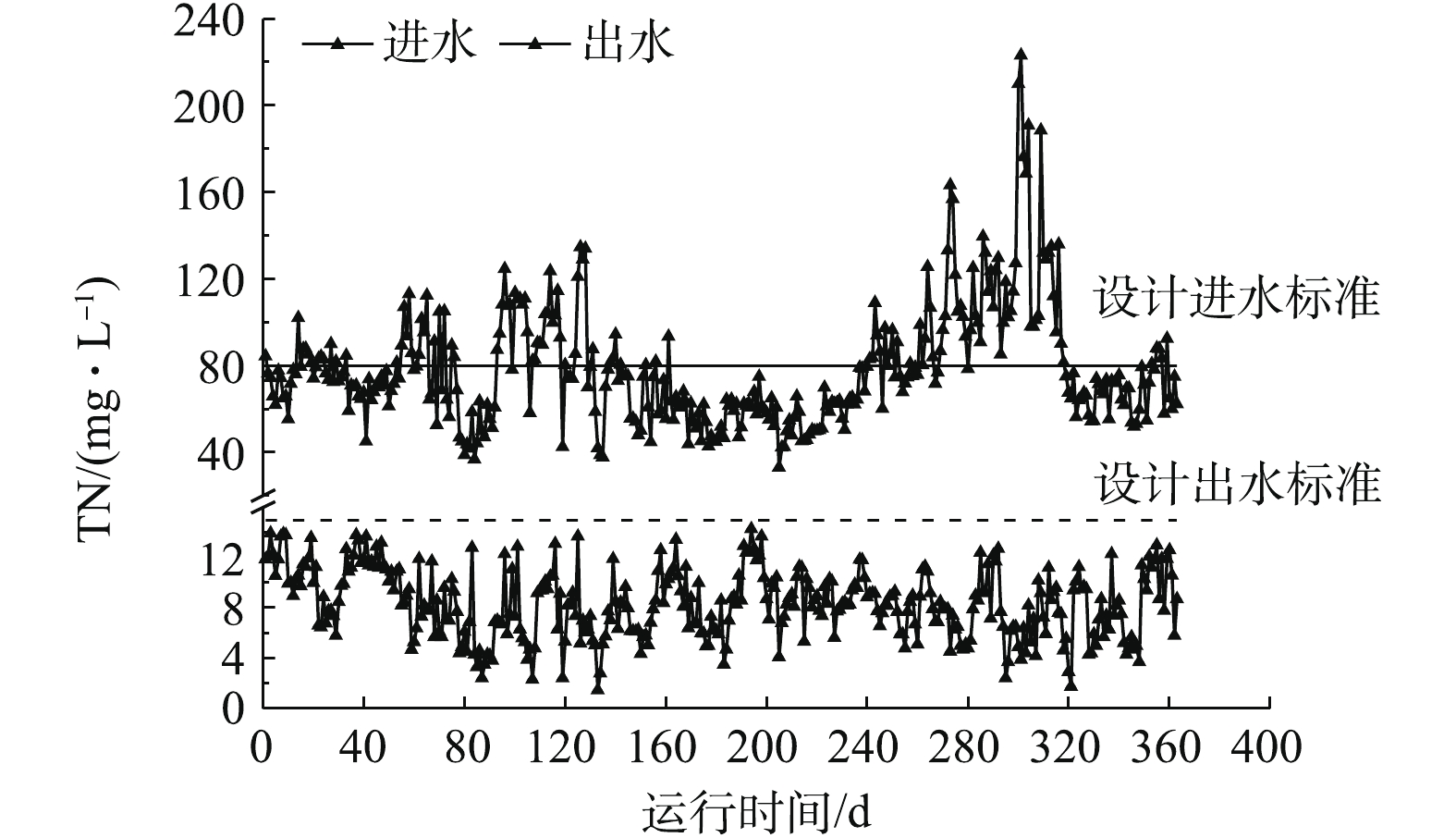
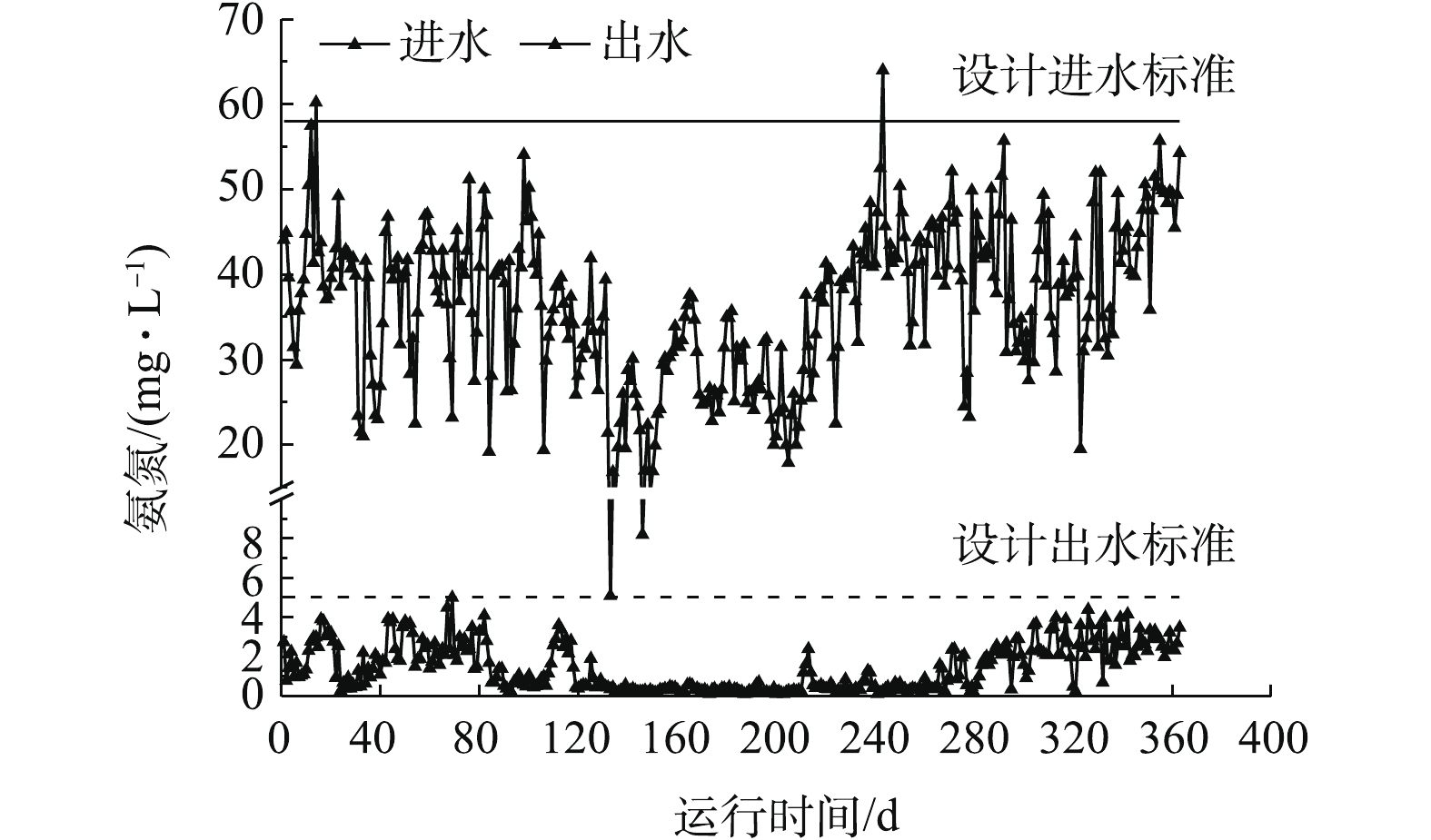
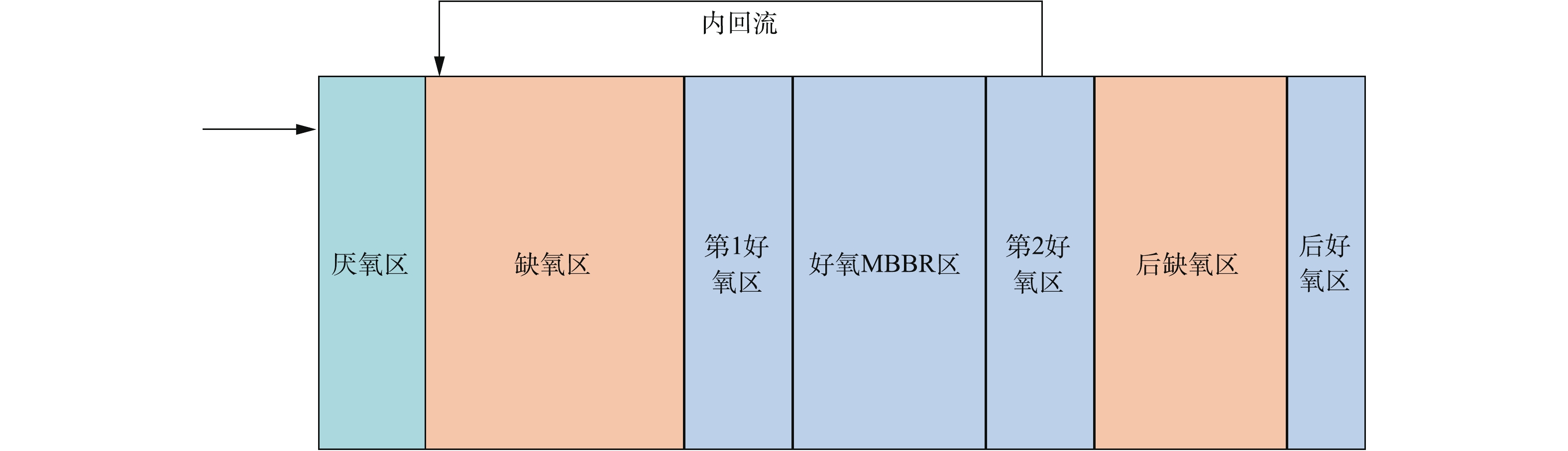
某660 MW机组锅炉为亚临界压力中间再热式直流炉,原配套双室四电场电除尘器出口烟尘浓度为35.7 mg·m−3,经石灰石-石膏湿法脱硫的协同除尘后仍无法满足超低排放要求,因此,在脱硫吸收塔出口烟气烟道上增设导电玻璃钢管式湿式电除尘器,分体(独立)布置,共布置4个电室,阳极采用正六边形导电玻璃钢,阴极线采用锯齿线型,喷淋系统采用间断冲洗方式,冲洗后的水进入吸收塔集水坑,作为脱硫部分用水。配套80 kV/1 600 mA高频高压恒流源。烟气量为2 127 660 m3·h−1,入口烟气温度为49~53 ℃,煤的水分、灰分、硫分含量分别为7.79%、16.59%、1.2%,低位发热量为21.4 kJ·g−1。
采用ZR-D09A型一体化采样枪、ZR-3260型自动烟尘测试仪、DEKATI PM2.5测定装置、DR 6000型分光光度计、ZR-D03A型高温采样枪等测试仪器分别测定湿式电除尘器进、出口的烟尘浓度、PM2.5浓度和SO3浓度等,并将三相有功电能表安装在湿式电除尘器除尘变出口母线处,用于读取并计算湿式电除尘器的电耗。
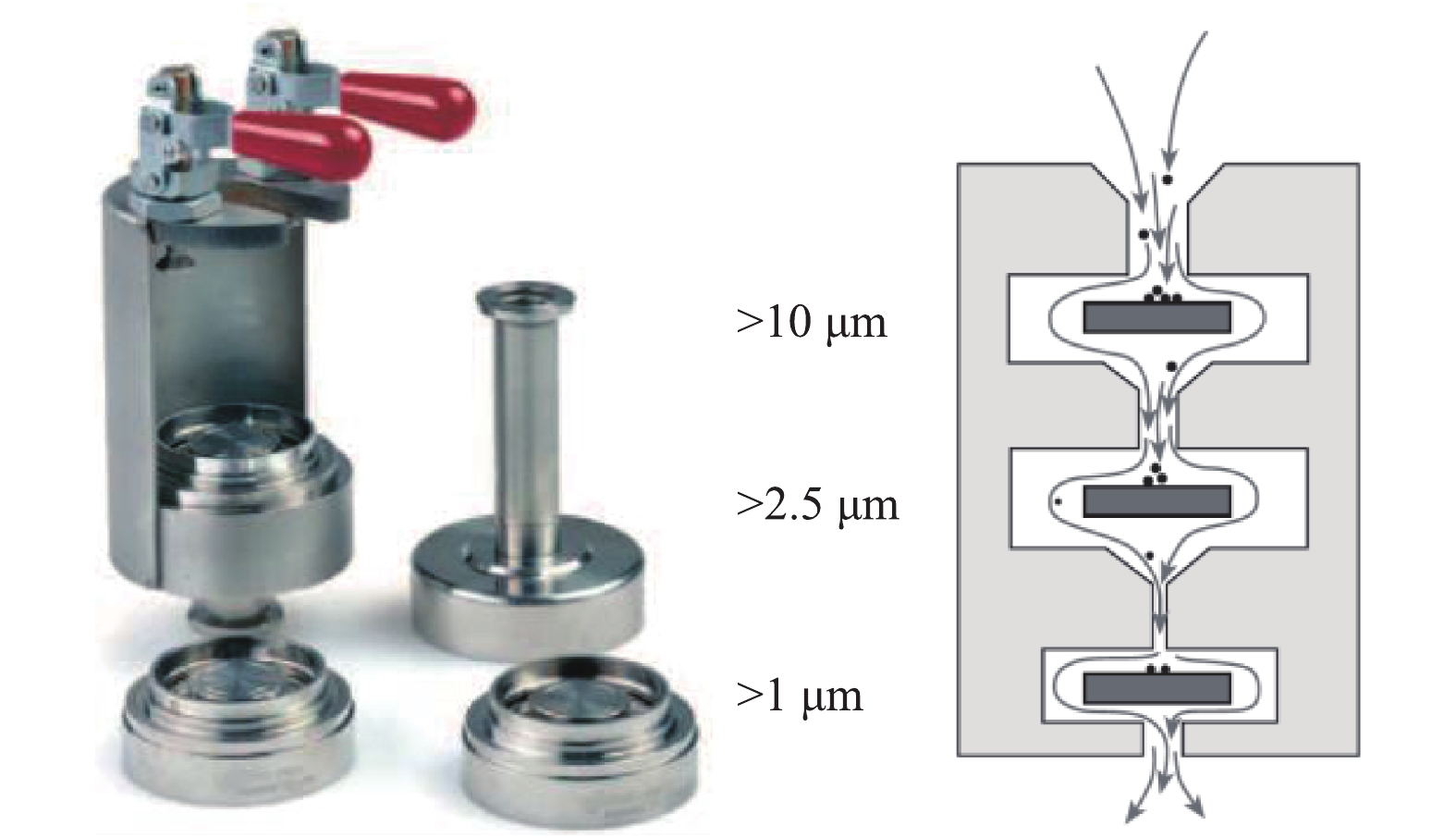
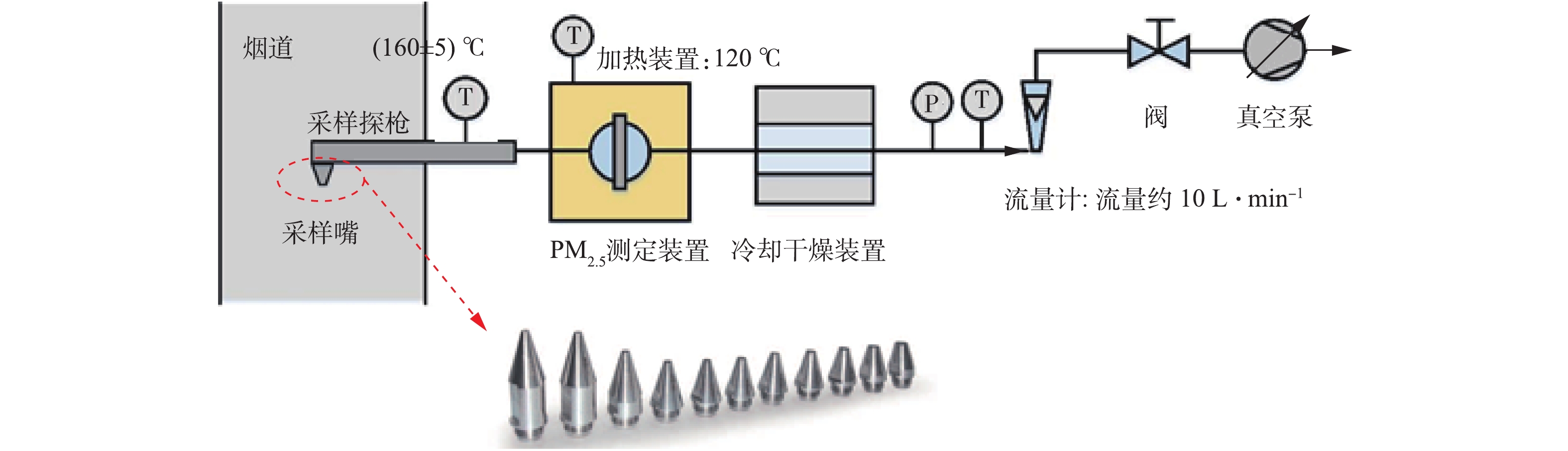
PM2.5测试采用DEKATI公司的PM2.5测试装置,测试方法参照行业标准《火电厂烟气中细颗粒物(PM2.5)测试技术规范重量法》(DL/T 1520-2016)中的规定,采样枪温度宜控制在(160 ±5)℃,PM2.5测定装置如图11所示。装置由三级撞击器组成,每级撞击器上布置滤膜,并涂上耐高温松脂,分别用于收集大于10、2.5、1 μm的颗粒,在最末级布置石英滤膜,石英滤膜对0.3 μm颗粒的拦截效率达99.9%,最末级撞击器和滤膜收集的颗粒累计为PM2.5,后二级撞击器和滤膜收集的颗粒累计为PM10。为防止液滴对颗粒分级及铝箔集尘的影响,对撞击器进行加热保温,温度为120 ℃。PM2.5的采样系统如图12所示。根据烟道流速、温度、压力等参数,选择合适的采样嘴及抽气流量,以保证各级撞击器收集的颗粒粒径在规定范围内。
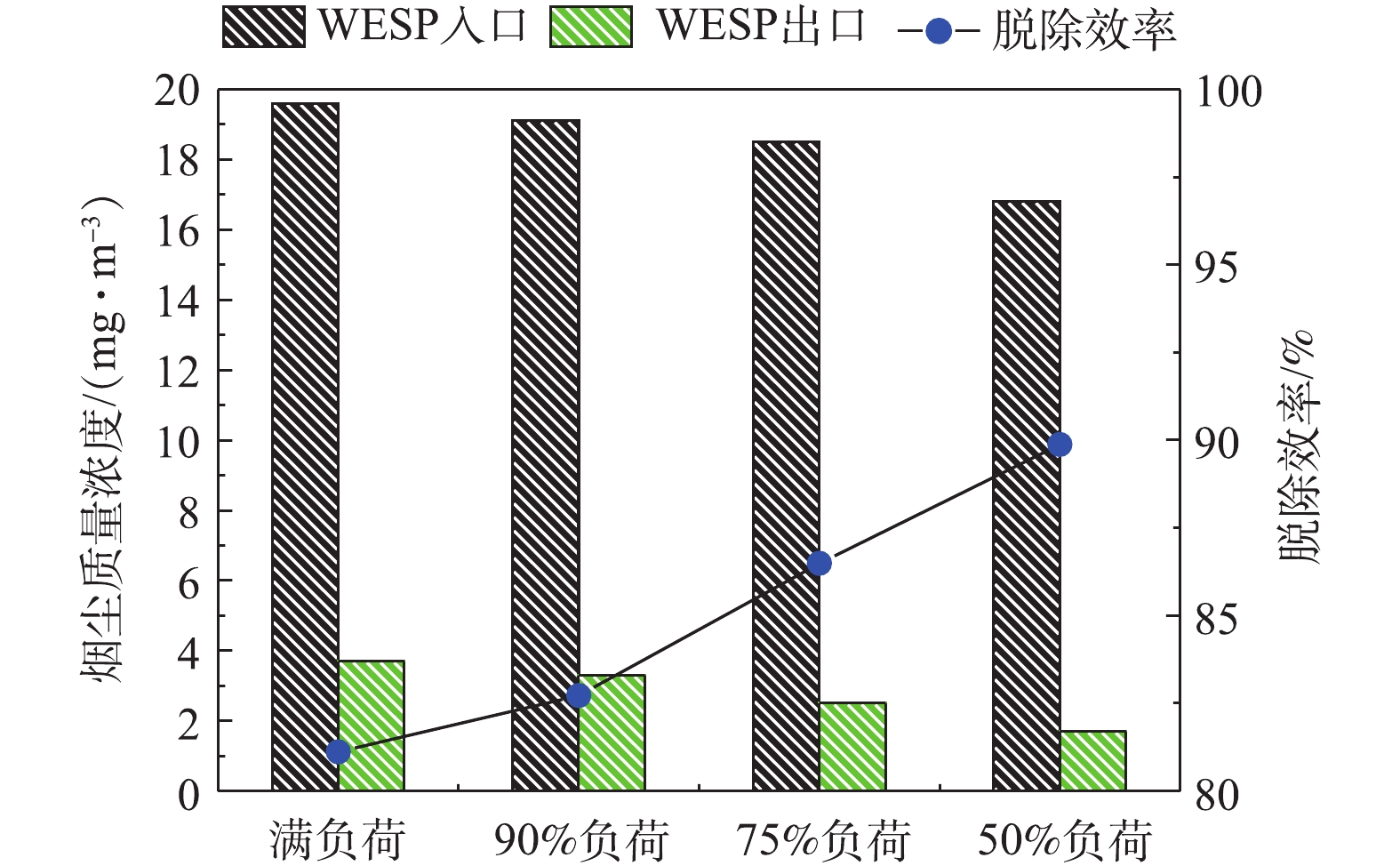
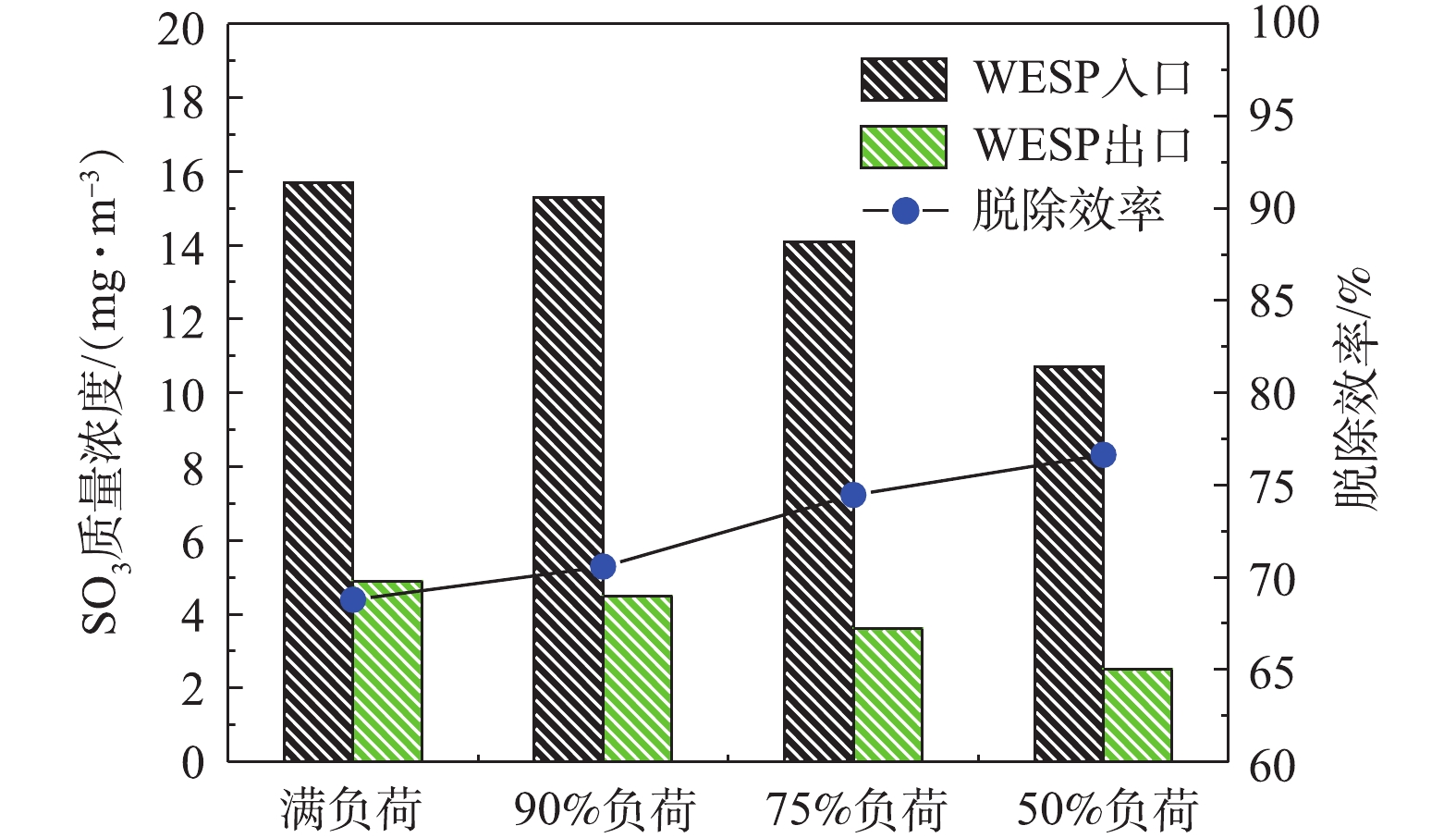
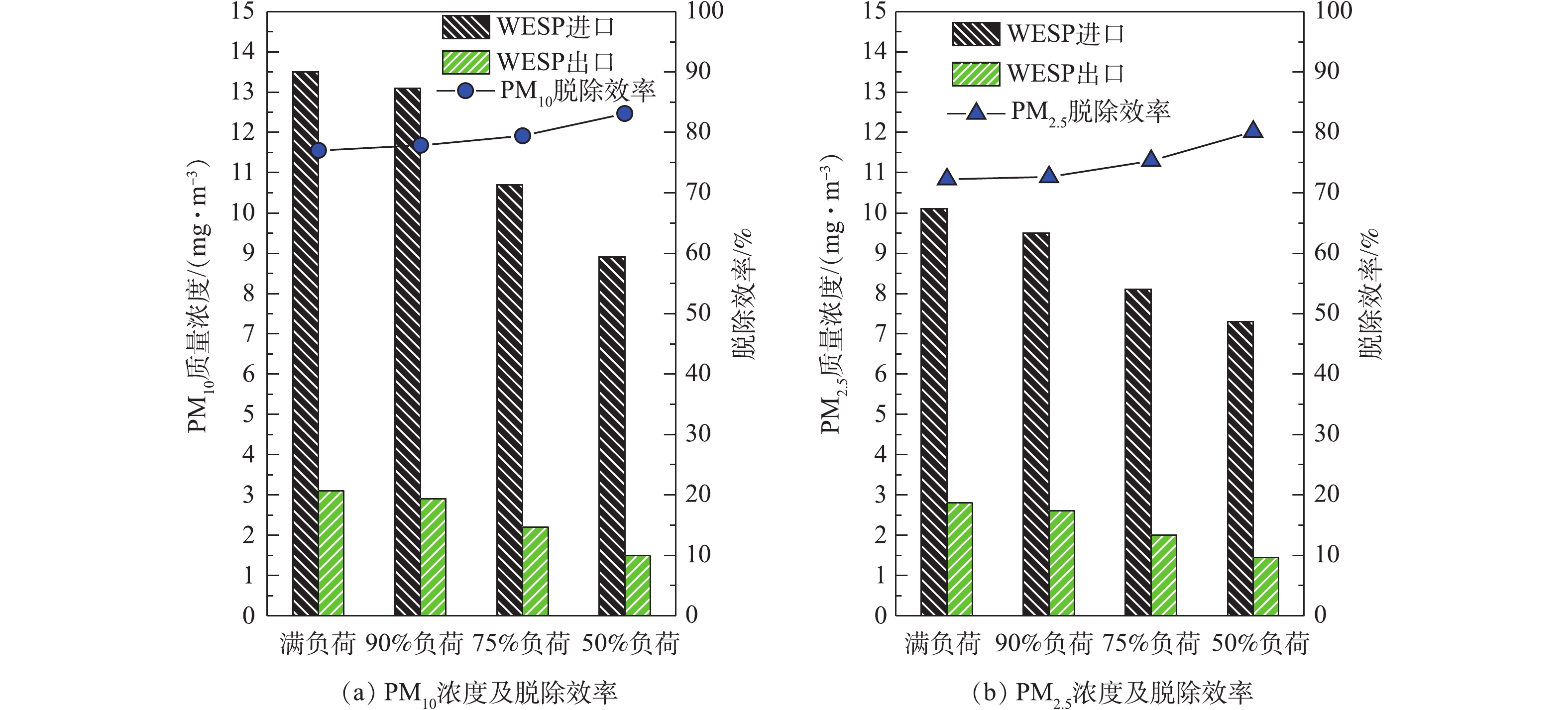
分别在满负荷、90%负荷、75%负荷、50%负荷条件下,测定湿式电除尘器对各污染物的脱除性能。烟尘测试结果如图13所示,随着机组负荷的降低,湿式电除尘器入口烟尘浓度有所降低,从19.6 mg·m-3降至16.8 mg·m−3,推测是因为负荷降低,烟气流速下降,前端电除尘器的除尘性能提升[24-25]所致。机组负荷降低,烟气流速下降,湿式电除尘器的除尘性能也得到提升,满负荷、90%负荷、75%负荷、50%负荷条件下湿式电除尘器的除尘效率分别为81.12%、82.72%、86.49%、89.88%。SO3测试结果如图14所示,随着负荷降低,湿式电除尘器入口的SO3浓度也有所下降,这主要是因为负荷降低后SCR脱硝的烟气温度降低,此处的SO2/SO3转化率减小[26-28]。同烟尘类似,烟气流速下降,湿式电除尘器对SO3气溶胶颗粒的脱除性能也得到提升,满负荷、90%负荷、75%负荷、50%负荷条件下湿式电除尘器对SO3的脱除效率分别为68.79%、70.59%、74.47%、76.64%,较烟尘的脱除效率要低一些。PM10/PM2.5测试结果如图15所示,随着负荷的降低,前端电除尘器对PM10/PM2.5的脱除性能提升,湿式电除尘器入口浓度均有所下降,同时,烟气流速下降,湿式电除尘器除尘也得到提升,满负荷、90%负荷、75%负荷、50%负荷条件下湿式电除尘器对PM10的脱除效率分别为77.04%、77.86%、79.44%、83.15%,对PM2.5的脱除效率分别为72.28%、72.63%、75.31%、80.14%。
为科学评价电除尘器的电耗水平,《高效能大气污染物控制装备评价技术要求第2部分:电除尘器》(GB/T 33017.2-2016)中给出了比电耗的概念,即处理单位工况烟气量所消耗的电量,计算方法如式(2)所示。
式中:
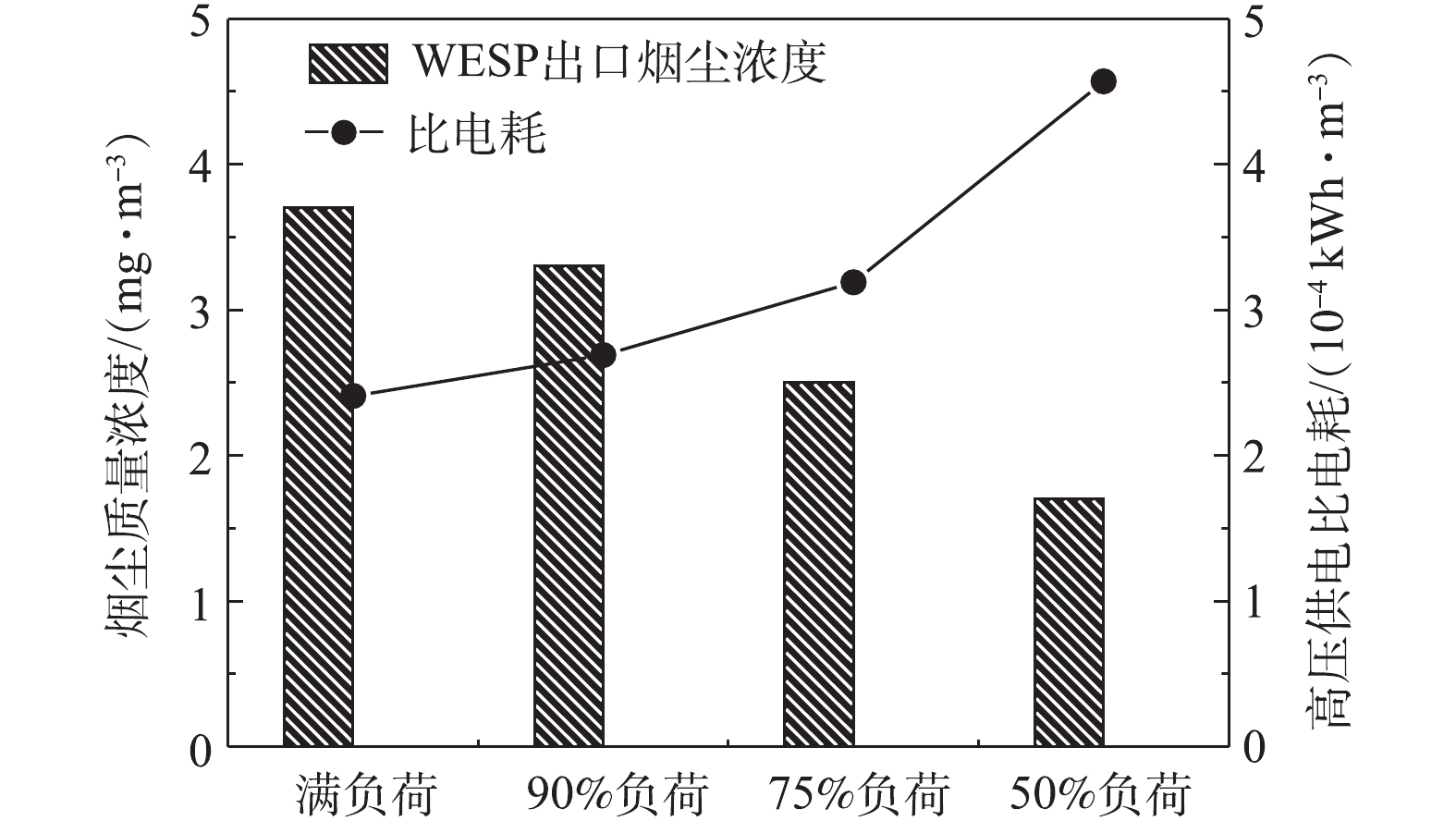
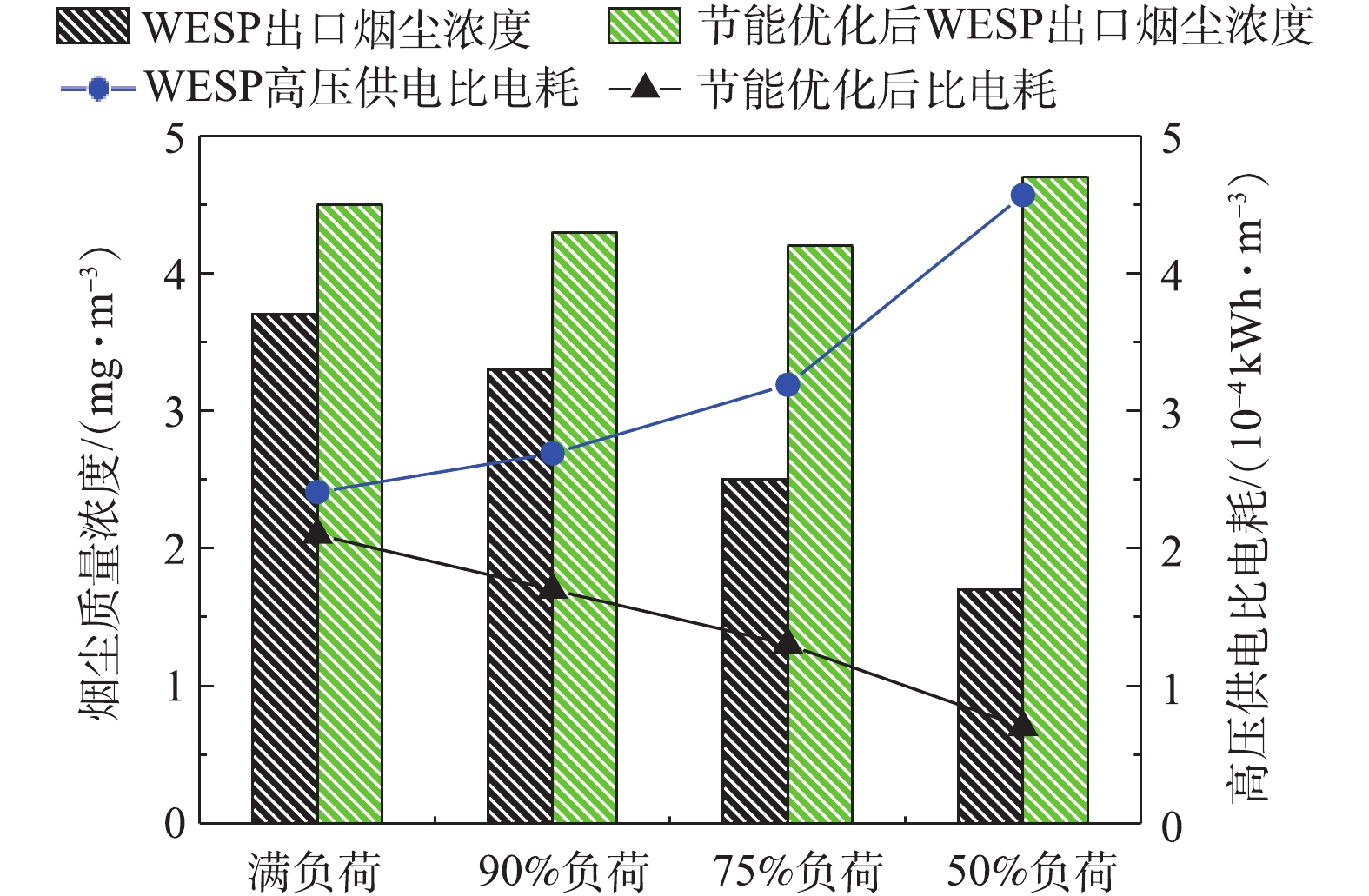
C 为湿式电除尘器比电耗,kWh·m−3;W 为湿式电除尘器的电耗,kW;Q 为进入湿式电除尘器入口的工况烟气量,m3·h−1。为对比不同负荷条件下湿式电除尘器的高压电耗,式(2)忽略了低压电耗、引风机阻力电耗等对比电耗的影响,湿式电除尘器的高压供电电耗采用三相有功电能表测定,经计算,不同负荷条件下,湿式电除尘器的高压供电比电耗如图16所示。随着负荷的降低,湿式电除尘器的高压供电比电耗大幅增加,从满负荷到50%负荷,比电耗从2.41×10−4 kWh·m−3升至4.57×10−4 kWh·m−3,有较大的节能空间。通过调整电源参数,控制湿式电除尘器出口烟尘浓度在4~5 mg·m−3,在满足5 mg·m-3超低排放要求的前提下,最大幅度地降低比电耗,实现节能最优化。节能优化后的比电耗结果如图17所示,湿式电除尘器的高压供电比电耗降幅显著,以50%负荷为例,节能优化后,比电耗从4.57×10−4 kWh·m−3降至0.7×10−4 kWh·m−3,节能优化后的比电耗下降达84.68%,即便是对于满负荷工况,烟尘浓度从3.7 mg·m−3增到4.5 mg·m−3,比电耗也下降了12.86%。该节能优化思路同样适用于其他工程项目及满负荷时烟尘排放远低于超低排放限值要求的工况。
-
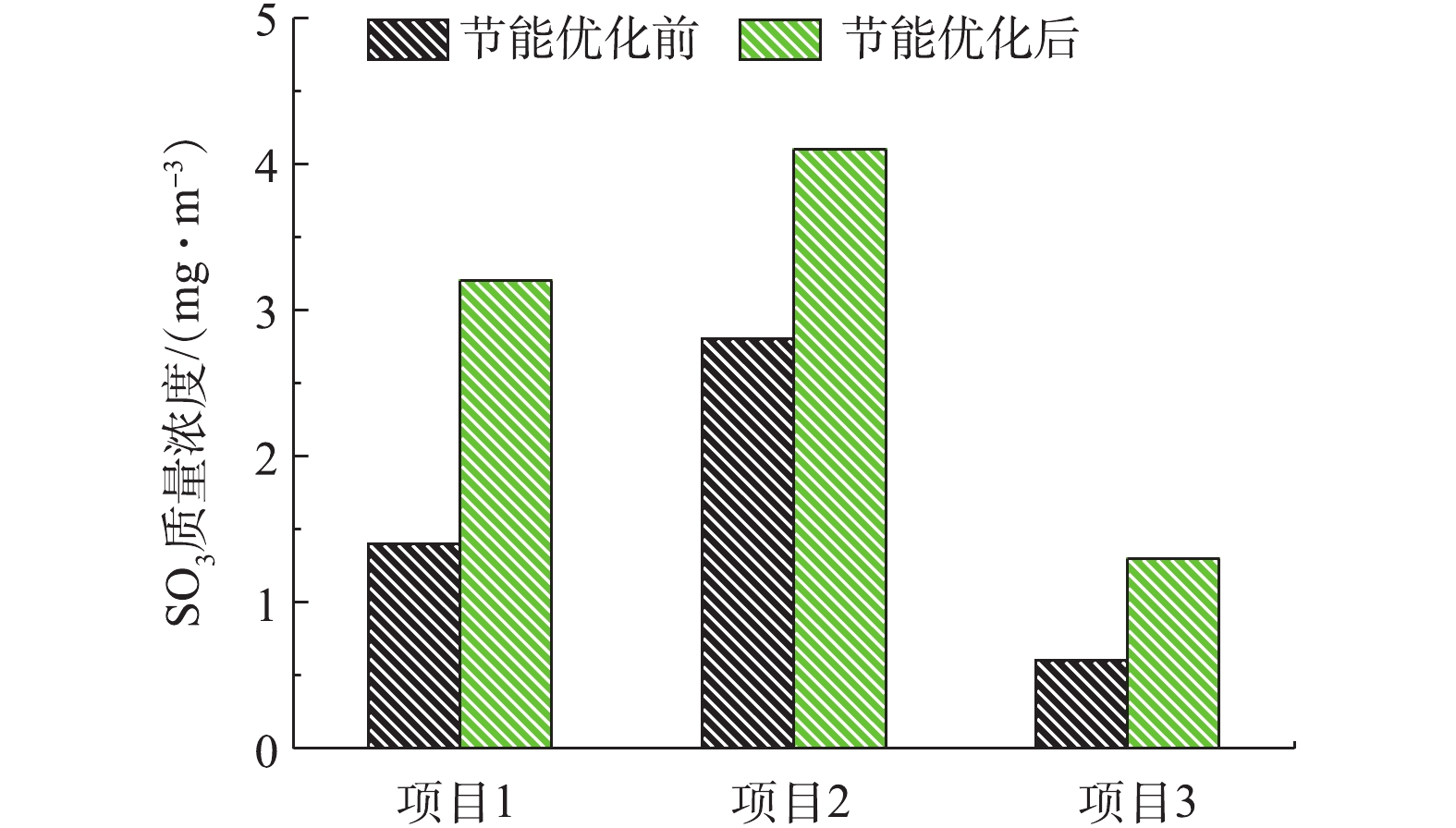
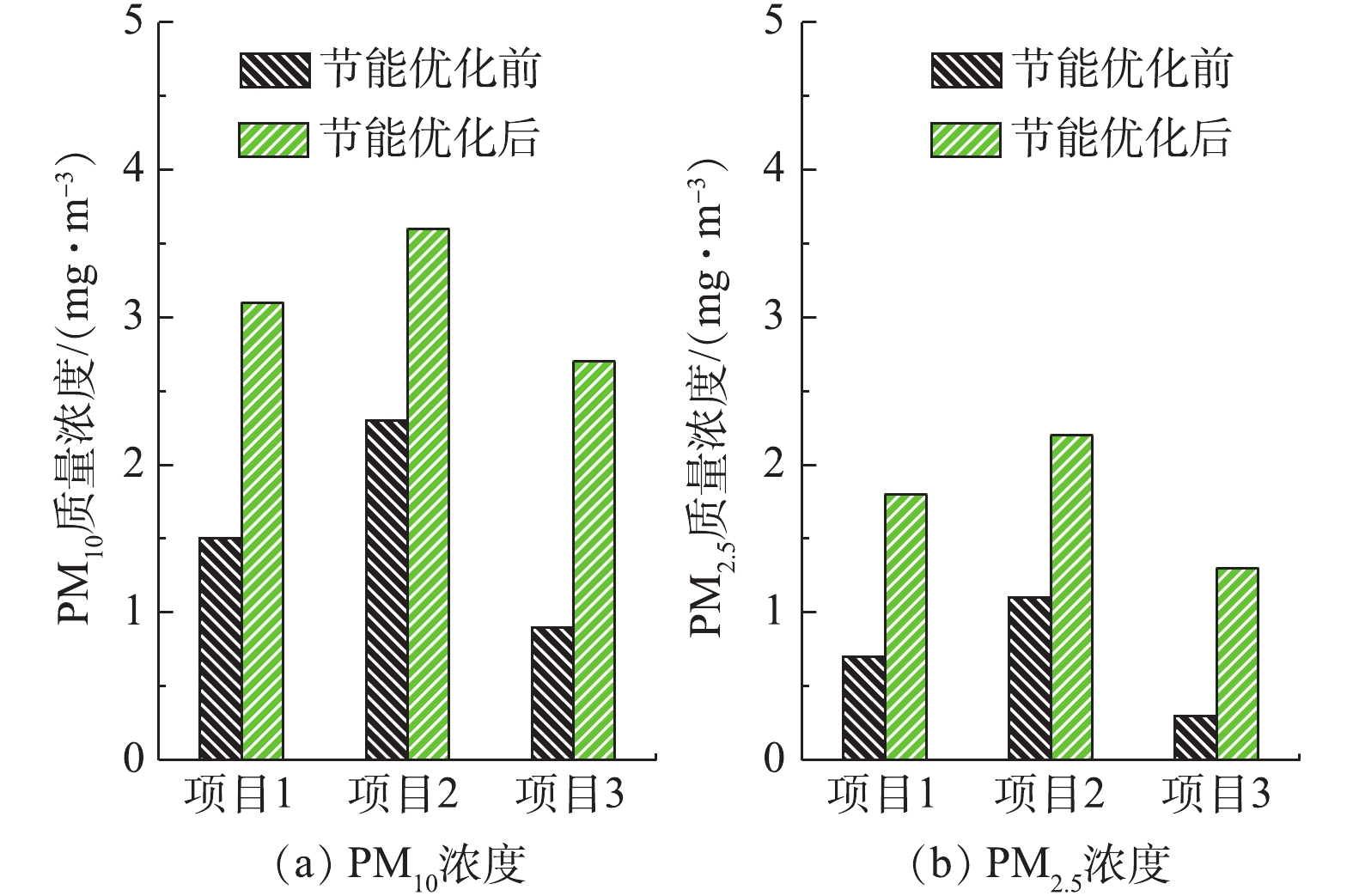
对其他3个导电玻璃钢湿式电除尘项目实施上述节能优化实验,相关数据如表1所示。在满负荷条件下,3个项目原烟尘排放浓度分别为1.9、2.7、1.2 mg·m−3,经节能优化,控制烟尘排放浓度在4.5 mg·m−3以内,此时比电耗下降幅度分别为32.65%、27.15%、41.64%。对应节能优化前后的SO3、PM10/PM2.5浓度测试结果分别如图18、图19所示。节能优化后,污染物排放浓度略有升高,但均在可承受范围内,如SO3浓度未超过5 mg·m−3,不会出现烟囱蓝烟拖尾的风险。值得注意的是,目前实际上有许多电厂的烟尘排放在2.5 mg·m−3甚至1 mg·m−3以下[29-37],此时的高压供电比电耗值较高,具有较大的节能优化空间,建议这类电厂在满足烟尘超低排放要求的前提下,适当降低电源运行参数,以达到节能的目的。
2.1. 典型工程案例实测及分析
2.2. 其他工程项目的节能优化实验
-
1)在正常工况下,工频高压恒流源和恒压源的空载/负载伏安特性曲线差别不大,两者的污染物脱除性能也大致相当。一旦喷淋系统开启,恒流源检测到火花放电后,自动下调电源运行参数,使电流/电压稳定运行在相对较低的参数范围,且运行相对平稳。恒压源则有一段明显的振荡区,抗干扰能力差。湿式电除尘器出口CEMS数据显示,喷淋系统开启后,工频恒流源供电的湿式电除尘器出口烟尘浓度最大值较喷淋前平均值增加了约12%;但恒压源因存在一个电源参数振荡区,出口烟尘浓度增加了约147%。因此,对于湿式电除尘器而言,应优先考虑抗干扰能力强的恒流源。
2)在供电电耗相当(工频3.49 kW、高频3.54 kW)的情况下,工频恒流源和高频恒流源供电的湿式电除尘器污染物脱除性能差异不大。但额定容量放开运行时,高频电源的运行电压/电流参数变大,其供电电耗分别提高至5.89、9.84、16.26 kW时,与工频相比,烟尘的减排幅度分别为46.30%、70.98%、78.69%,SO3的减排幅度分别为42.86%、57.14%、66.67%。
3)某660 MW机组典型工程的深度测试表明,随负荷的降低,湿式电除尘器的污染物脱除性能有所提升,在满负荷、90%负荷、75%负荷、50%负荷条件下,湿式电除尘器的除尘效率分别为81.12%、82.72%、86.49%、89.88%,SO3脱除效率分别为68.79%、70.59%、74.47%、76.64%,PM10脱除效率分别为77.04%、77.86%、79.44%、83.15%,PM2.5脱除效率分别为72.28%、72.63%、75.31%、80.14%。但随负荷的降低,湿式电除尘器高压供电比电耗大幅增加,从满负荷到50%负荷,比电耗从2.41×10-4 kWh·m-3升至4.57×10-4 kWh·m-3,有较大的节能空间。通过调整电源参数,控制湿式电除尘器出口烟尘浓度在4~5 mg·m-3,比电耗显著降低,满负荷的比电耗也下降了12.86%,50%负荷的比电耗下降达84.68%,实现了湿式电除尘器的节能优化运行。
4)根据本研究得到的节能优化思路,对其他3个工程项目实施运行优化,优化前烟尘排放浓度分别为1.9、2.7、1.2 mg·m−3,经节能优化,控制烟尘排放浓度在4.5 mg·m−3以内,比电耗下降幅度分别为32.65%、27.15%、41.64%。该思路同样适用于其他除尘项目及满负荷时烟尘排放远低于超低排放限值(5 mg·m−3)要求的工况,尤其是部分烟尘排放长期在2.5 mg·m−3甚至1 mg·m−3以下项目,建议这类电厂在满足烟尘超低排放要求的前提下,适当降低电源运行参数,以达到节能的目的。



 下载:
下载: