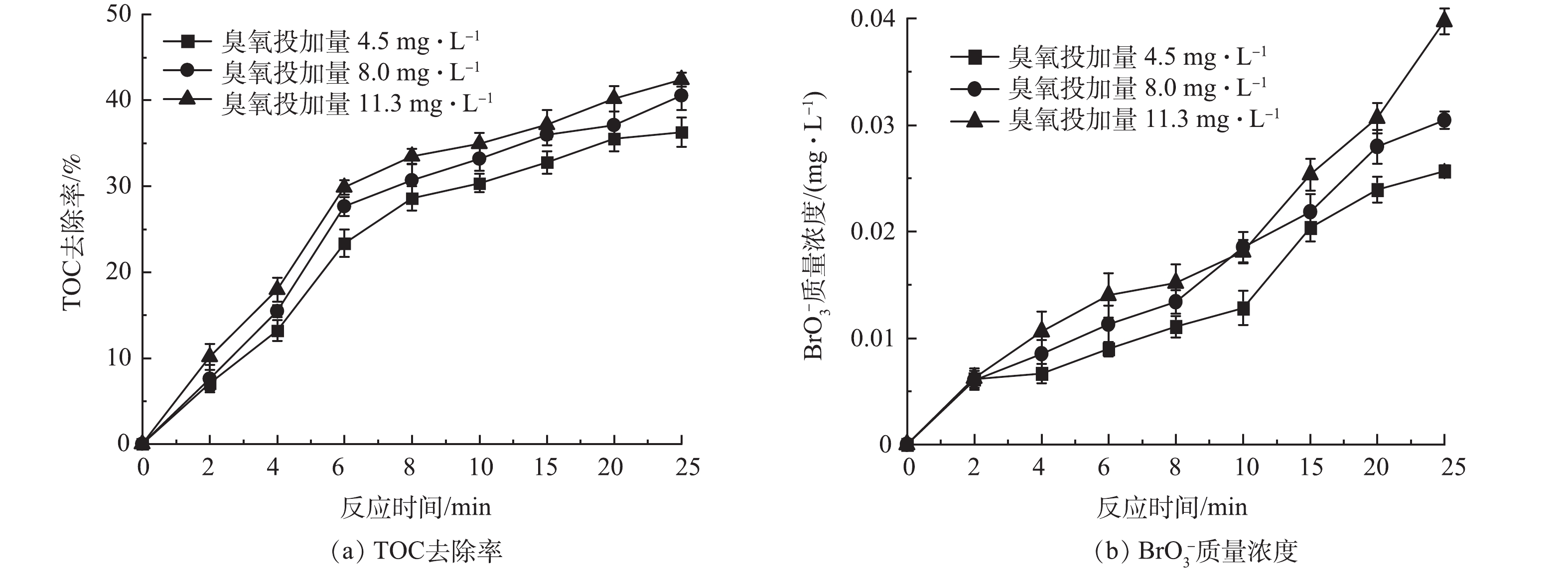
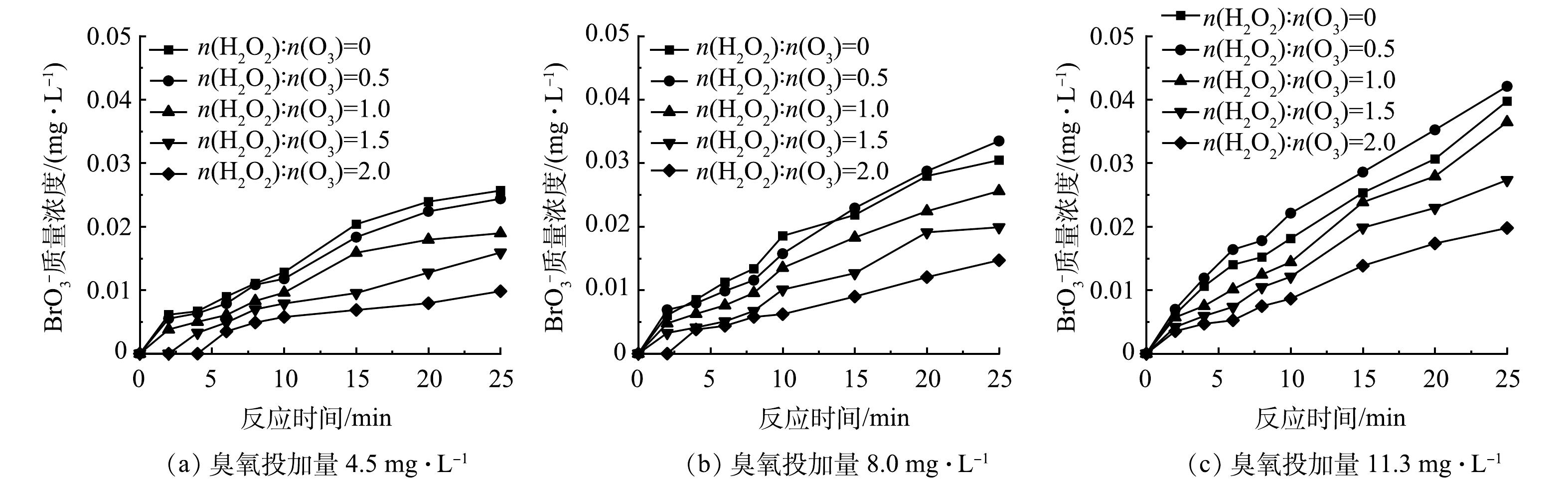
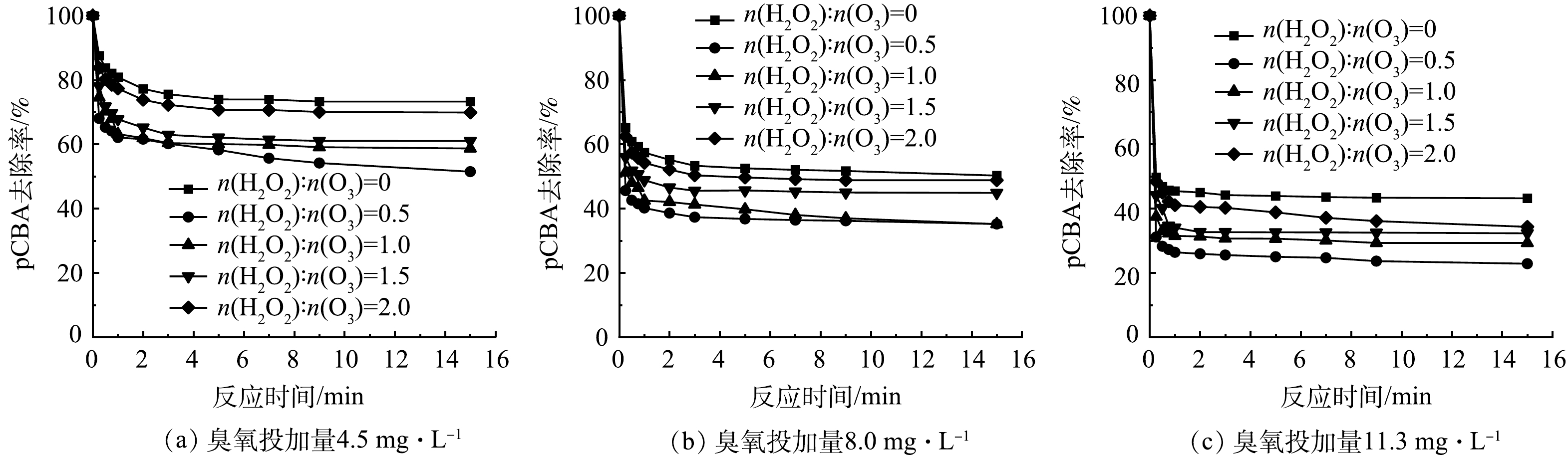
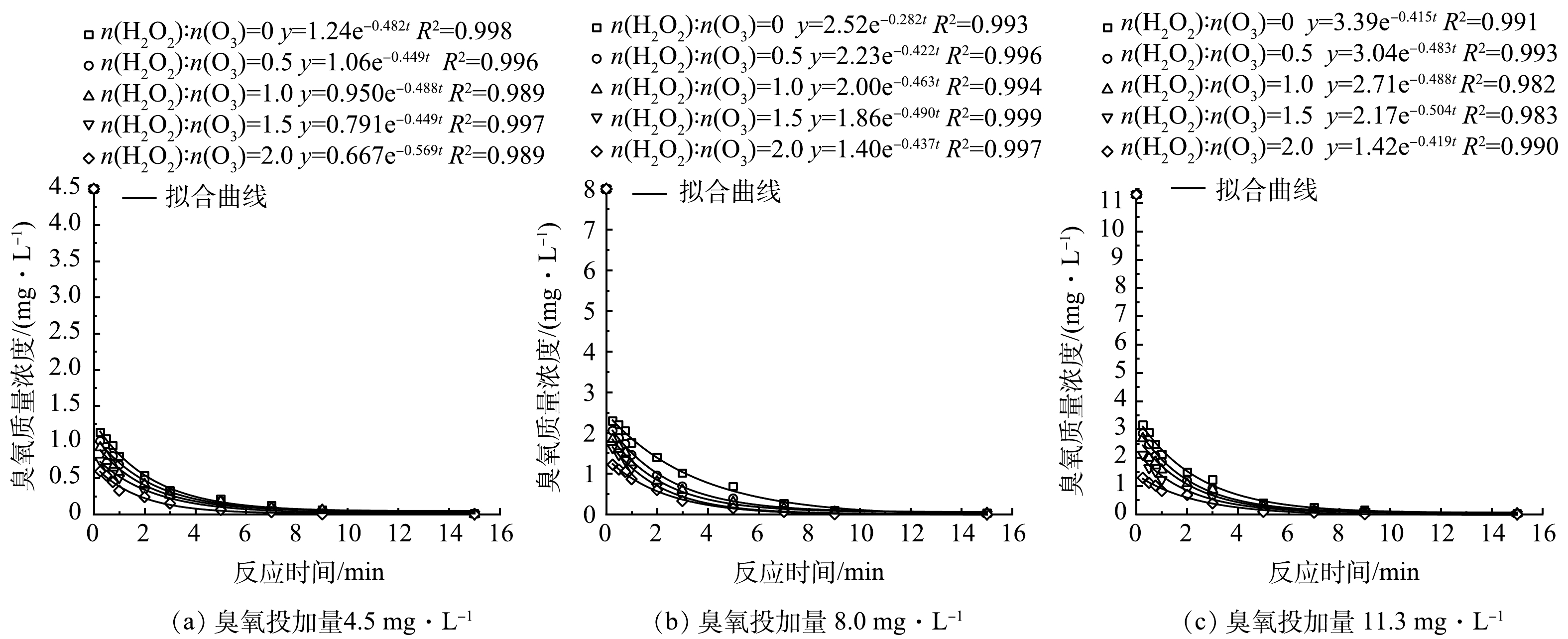
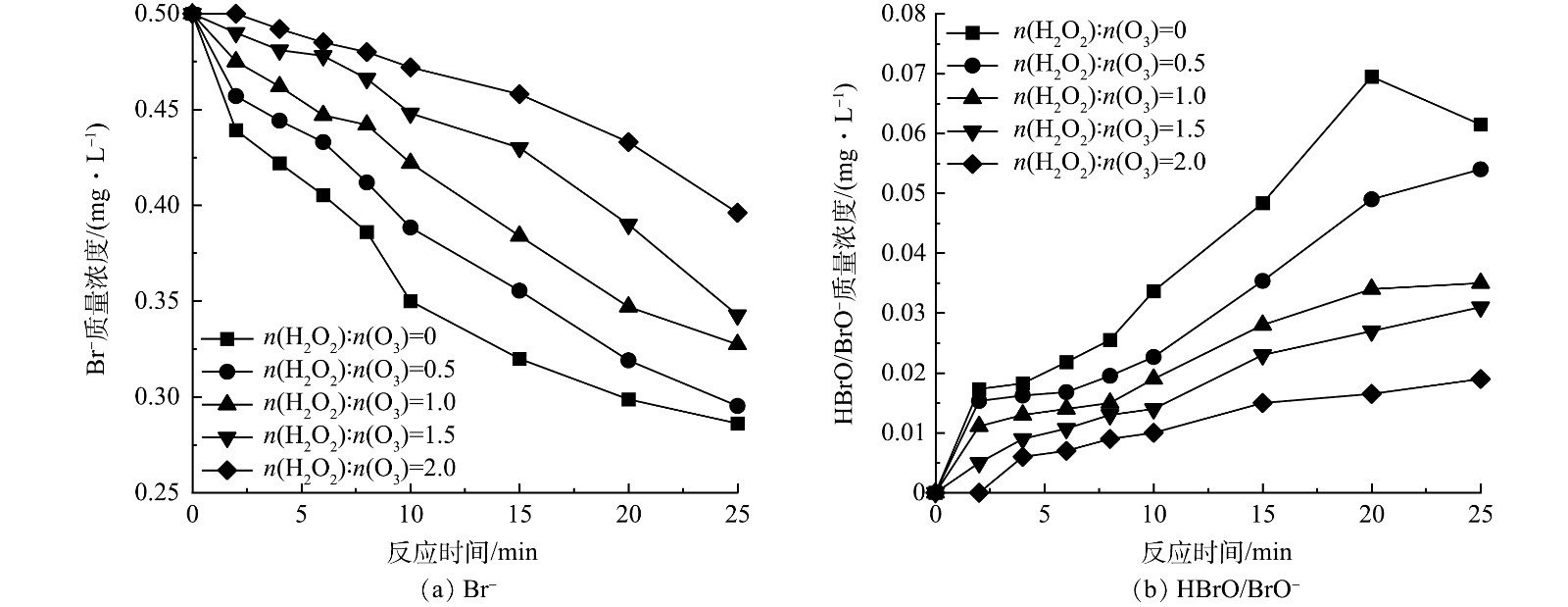
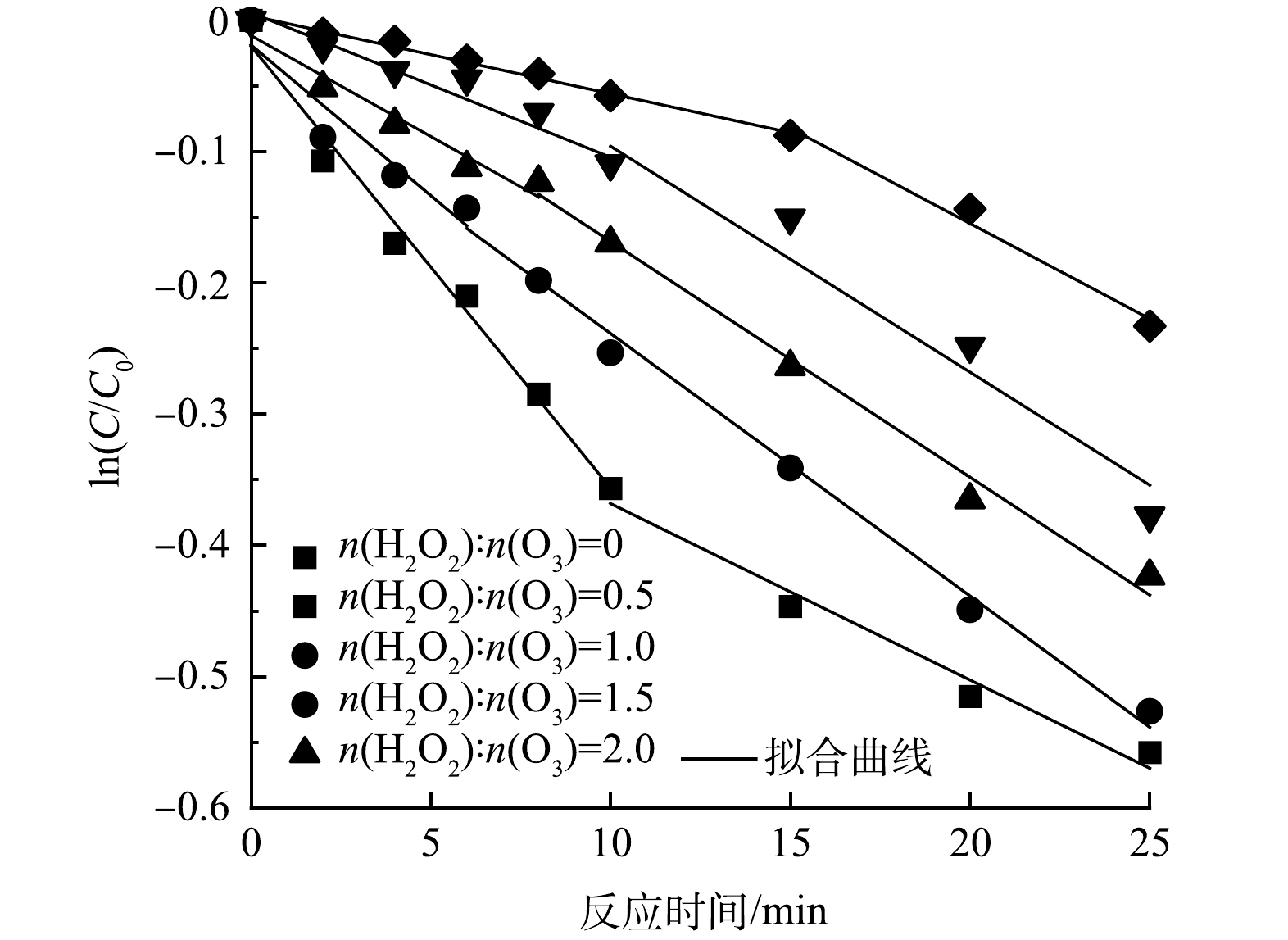
-
近年来,由于世界范围内的工业发展,人们越来越重视污染物排放[1-2]。静电除尘器(ESP)作为一种能够有效地从干或湿空气流中去除细微颗粒物的装置[3-4],被广泛应用于各种工业领域生产设施中的尾气处理[5-7],其总体除尘效率超过99%,并且具有效率高、阻力小、适用性强等优点。然而,由于细颗粒携带的电荷较低,传统的静电除尘器对亚微米颗粒的去除率相对较低,而且尺寸较小的颗粒更倾向于与烟气一起运动而被排放到空气中,这些细微颗粒物很可能被人体吸入肺部而引起各种呼吸道疾病,特别是对儿童和老年人造成巨大的健康危害[8-9]。因此,提高静电除尘器对细微颗粒物的捕集性能,使其满足更严格的排放标准,已成为目前亟待解决的问题。
国内外学者对影响静电除尘器除尘效率的因素开展了较深入的研究,而烟气流速作为影响其性能的主要参数一直被广泛关注[10-11]。东明等[12]分析了不同烟气流速下静电除尘器的捕集性能,得出了烟气流速越大,颗粒捕捉效果越差、除尘性能就越低的结论。周海军[13]探究了烟气流速对除尘效率的影响,并对引起烟气流速变化的原因及其最佳选取值进行了深入讨论。为了测试不同环境下烟气流速对ESP除尘性能的影响,沈之旸等[14]针对宽间距ESP内大流量高温烟气中的细微颗粒物进行了研究,揭示了温度和烟气流速等关键因素对细微颗粒物静电捕捉的影响规律。
将磁场引入到ESP中,因其具有良好的性能表现,从而受到了广泛的重视[15-20]。磁分离技术最早应用于工业中金属粒子的分离[21-22],之后将其引入到ESP[17, 20],发现其可以有效地提高除尘效率。孙英浩[23]分析了磁增强电晕放电的放电特性及其对细微颗粒物的荷电机理。米俊锋等[24]比较了磁增强预荷电器和传统预荷电器的荷电效率,揭示了磁增强电晕放电的放电机理。毕业武等[25]研究了磁增强负电晕放电特征,分析了这一过程的放电特性和磁场对极间不同区域的影响。ELABBAS[26]的研究表明,放电电极附近磁场的增强对放电电流的增加有显著影响。ZHANG等[27]发现磁场对静电除尘器的捕集性能的提高具有促进作用。
鉴于上述研究成果,为了更好地展现磁场对ESP颗粒物除尘效率的影响,本研究建立了磁场环境下静电除尘器的多场耦合模型,基于不同的烟气流速,探究ESP中同种颗粒的运动特性和捕集性能,以期揭示磁场的贡献及其规律,并为设计新型ESP提供参考。
全文HTML
-
烟气流动满足质量守恒方程(连续性方程)和动量守恒方程[28](Navier-Stokes方程),方程见式(1)和式(2)。
式中:
ρg 为烟气密度,kg⋅m−3 ;ui 和uj 为气体速度,m⋅s−1 ;p 为气体平均静压,Pa ;μeff 为有效扩散系数,μeff=μ+μt ;μ 为气体动力黏性系数,kg⋅(m⋅s)−1 ;μt 为湍流动力黏性系数,kg⋅(m⋅s)−1 ;Sj 为广义源项;i 和j 分别代表x 和y 方向。 -
对于线板式静电除尘器,在电晕稳定放电的情况下,可由Poisson方程和电流连续性方程[29]描述其计算过程,方程见式(3)和式(4)。
式中:
⇀E 为电场强度,N⋅C−1 ;U 为电势,V ;ε0 为真空介电常数,F⋅m−1 ;ρ 为空间电荷密度,C⋅m−2 ,⇀J 为电流密度矢量,可分为x 和y 方向的分量,A⋅m−2 。电流密度的计算方法可以简化为式(5)。
式中:
bion 为离子迁移率,m2⋅(V⋅s)−1 ;ρ 为空间电荷密度,C⋅m−2 。结合电场强度的表达式
⇀E=−∇U ,式(5)可表示为式(6)。考虑离子迁移率为常数(
∇bion=0 ),结合式(3)和式(4),可得电流连续性方程(式(7))。需要指出的是,本研究引入的线板式ESP中的磁场是稳恒的,在时间和空间上是不变的,不涉及方程组的求解。
-
细微颗粒物在外加磁场作用下,x-y坐标下的动量方程包含颗粒惯性力、洛伦兹力、电场力和拖曳力,由于细微颗粒物质量很小,重力被忽略,则具体颗粒动力场动量方程见式(8)。
式中:
mp 为颗粒质量,kg ;u 为运动速度,m⋅s−1 ;Fm 为洛伦兹力(Fm=QpvpB ,其中QP=Qdiff+Qsat ,Qdiff 为扩散荷电带电量,Qsat 为电场荷电带电量,vp 为颗粒作回转的运动速度,B为磁感应强度);Fe为电场力(Fe=QPE );FD为拖曳力(FD=mpFd ,FD指的是颗粒和黏性流体进行相对运动时,流体作用于颗粒上的阻碍物体相对运动的力,Fd=12ApρgCD(ug−up)|ug−up| ,Ap 为颗粒的迎流面积,ug 和up 分别为烟气平均流速¯ug 和尘粒平均速度¯up 的标量值,CD 是气流和颗粒间的阻力系数)。
1.1. 气体流场
1.2. 电磁场
1.3. 颗粒动力场
-
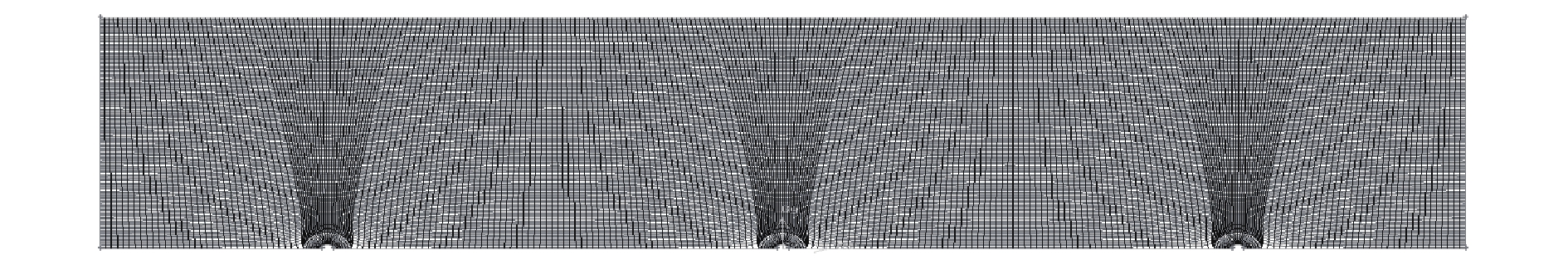
图1为二维线板式ESP的网格划分图。这里将计算区域分为3个电晕区和其他部分。由于电晕区附近的电势梯度较高,因此,需要对这一区域的网格进行细化,以确保计算的准确性。
不同网格数量下线板式ESP的除尘效率及其相对误差结果如图2所示。可以看出,随着网格数量的增加,除尘效率的相对误差呈下降的趋势。当网格数量为41 440个时,相对误差达到最小,仅为1.5%,可满足工程实际计算的要求,因此,选择此网格数进行计算。
-
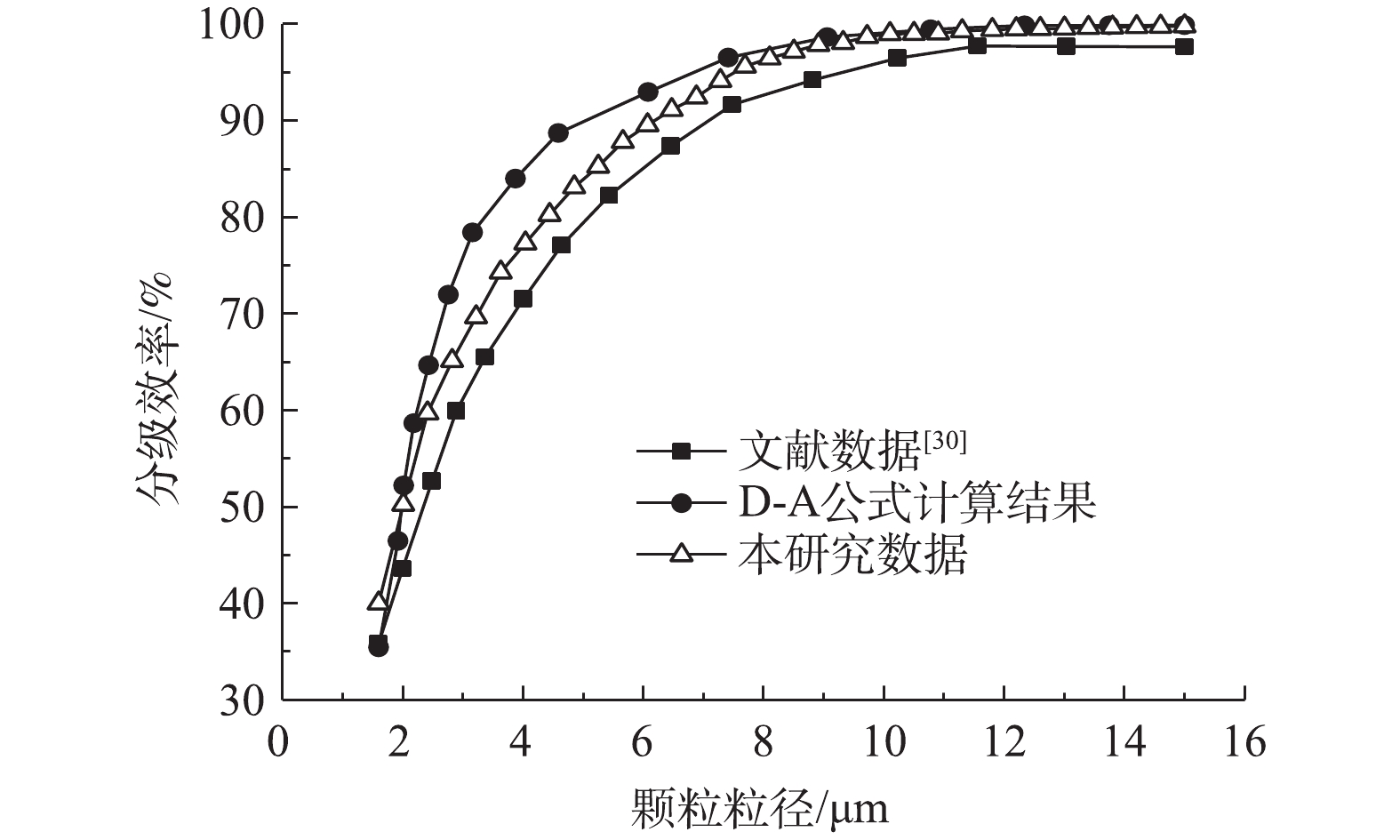
Deutsh-Anderson(D-A)公式是目前计算分级除尘效率普遍采用的公式,能准确地反映实际工况。为了使数值结果更加可靠,这里计算了与已有研究[30]相同结构和工况下的线板式ESP分级除尘效率,并与D-A公式的计算结果进行了对比,结果如图3所示。可以看出,相比D-A公式,本研究的数值模拟结果更加接近于文献实验数据,分级效率的计算精度更高,从而验证了本研究理论数值模型及计算方法的可靠性。
-
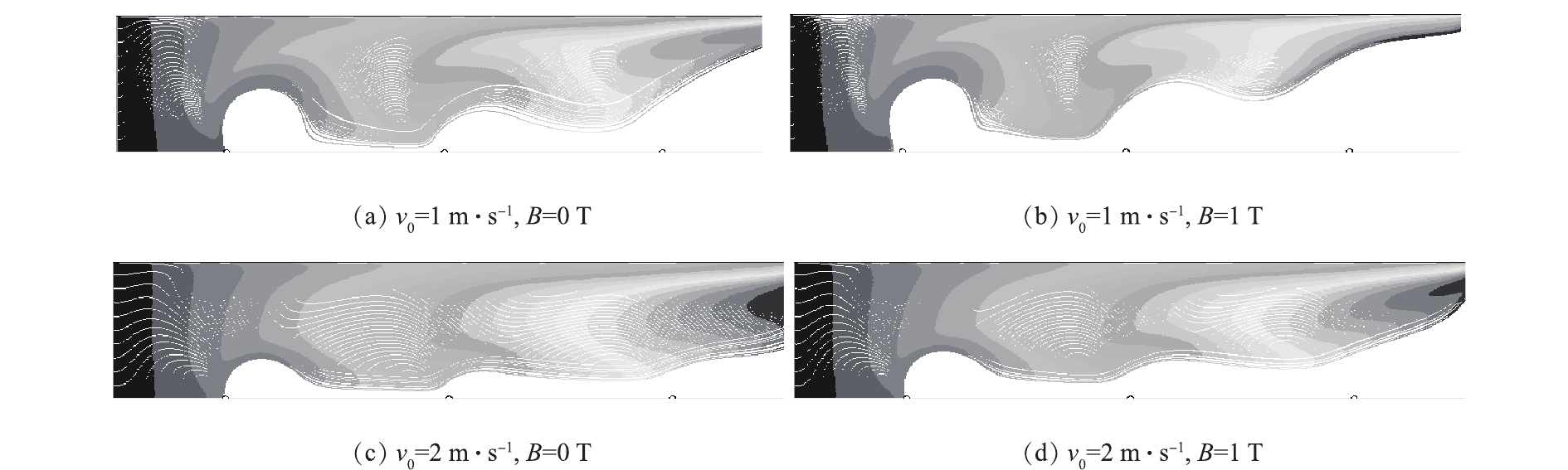
为了直观地考察磁场效应对颗粒轨迹的影响情况,本研究给出了工作电压为50 kV时2.5 μm粒径颗粒在线板式ESP的运动轨迹,如图4所示。可以发现:在同一烟气流速下,外加磁场作用时,颗粒的运动轨迹更偏向于收尘板,这是由于磁场产生的洛伦兹力使得颗粒在ESP中作螺旋运动,颗粒荷电更充分,促进了颗粒的捕集作用;在同一外加磁场环境中,随着烟气流速的变小,颗粒更易靠近收尘板,这是因为烟气流速越小,颗粒停留时间越长,扩散荷电作用更明显,有利于颗粒的捕获。
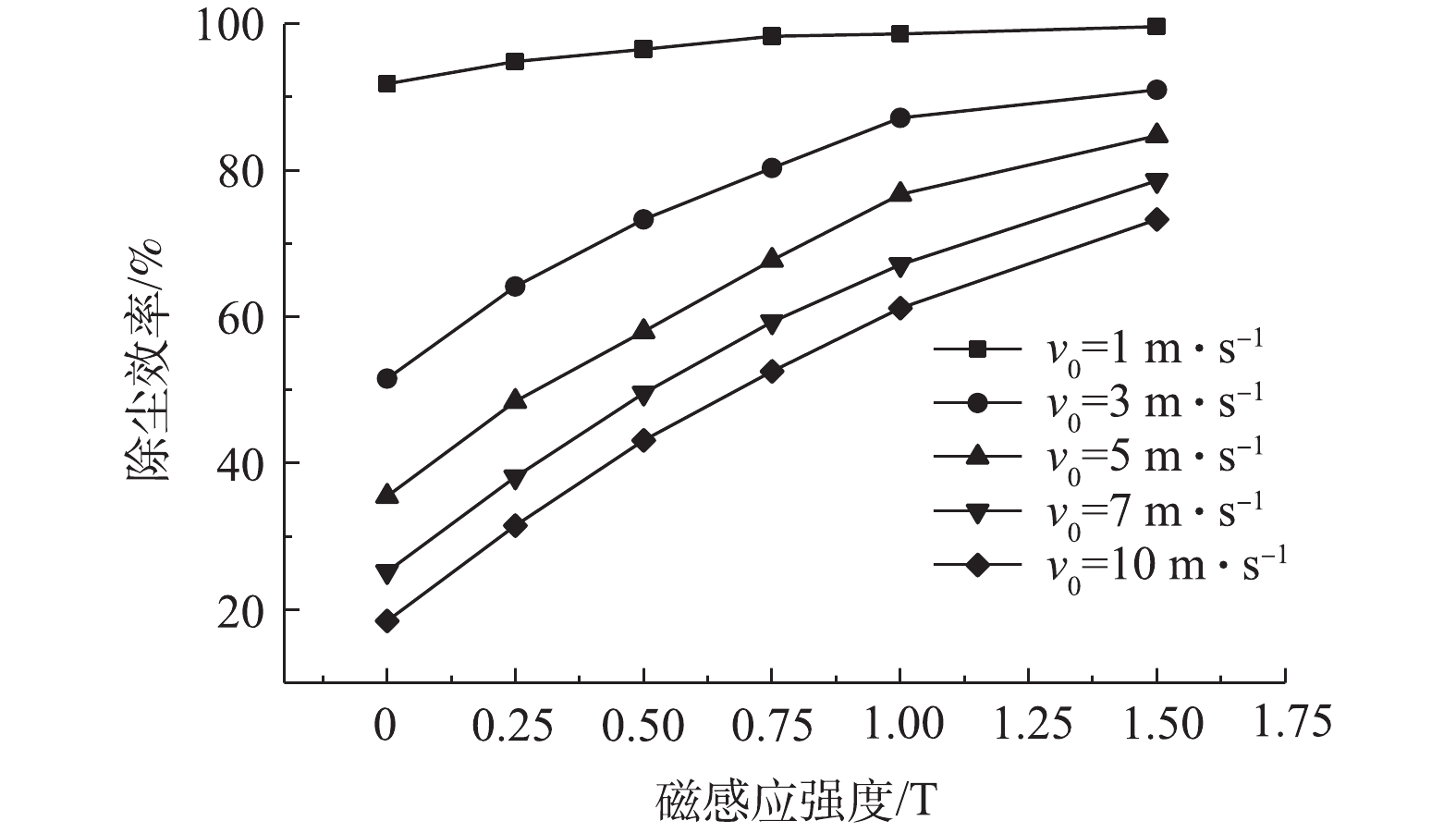
图5反映了不同烟气流速下磁感应强度对颗粒除尘效率的影响。可以发现:不论是否存在外加磁场,除尘效率均随着烟气流速的增大不断下降,且下降幅度逐步减小;在同一烟气流速下,相比无磁场环境,磁场效应能有效地提高除尘效率,并且随着磁感应强度的增大,除尘效率呈增大的趋势;随着烟气流速的增大,除尘效率随磁感应强度变化的上升曲线越陡峭,说明磁场作用在高烟气流速下对ESP除尘性能的提升幅度更大;相邻2条曲线的除尘效率差值逐渐减小,表明烟气流速削弱除尘效率的程度在低磁感应强度时更大,且在无外加磁场时最大。
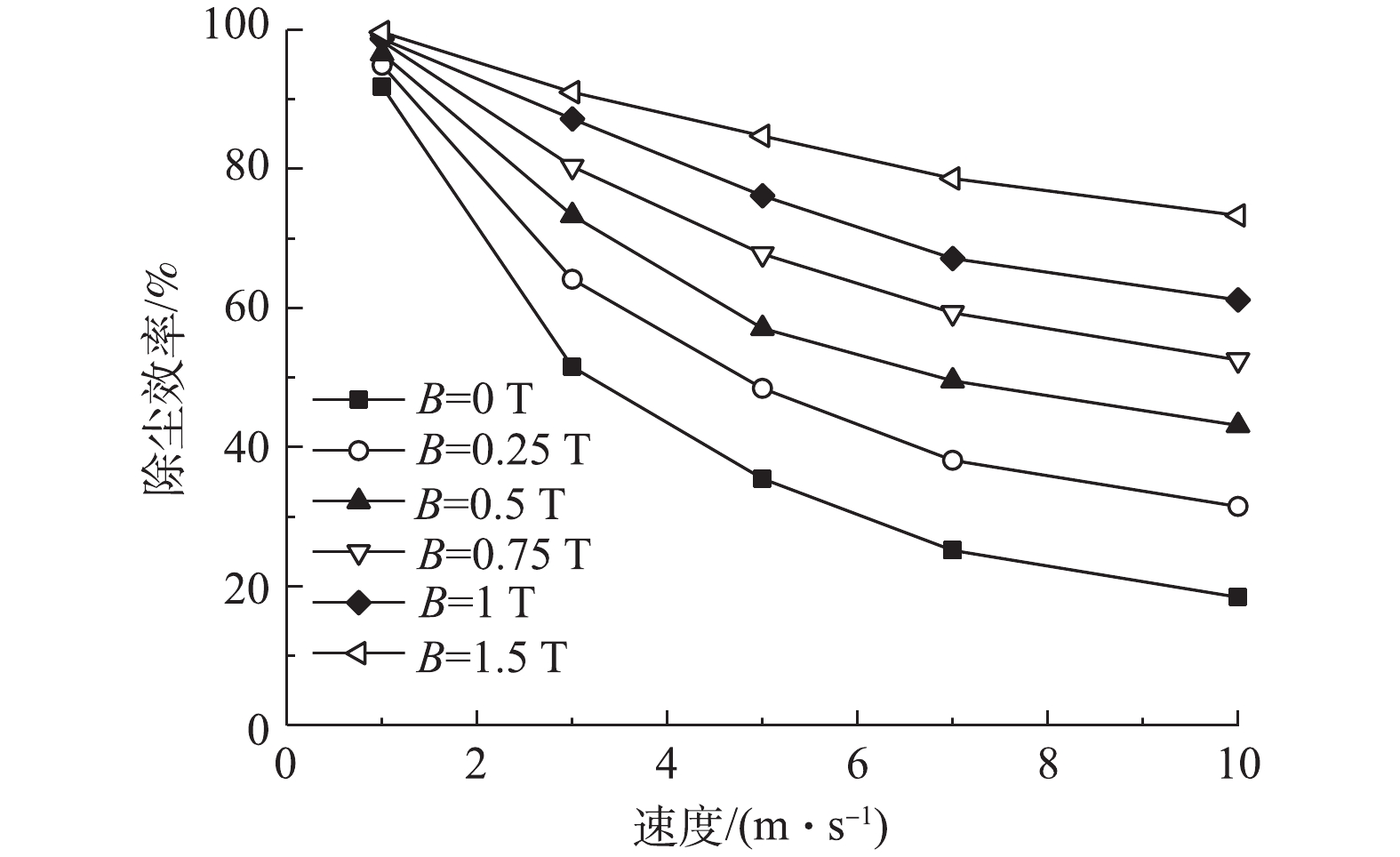
不同磁感应强度下除尘效率随速度的变化情况如图6所示。可以看出:随着烟气流速的增大,除尘效率均呈非线性下降的趋势,并逐渐趋于平缓,而相邻2条曲线的差值逐渐变大,也说明了低烟气流速下磁场对颗粒物除尘效率的贡献更小;磁感应强度越大,除尘效率随速度变化的下降曲线越缓慢,说明烟气流速降低除尘效率的幅度在高磁感应强度时更小;在同一烟气流速下,磁感应强度越大,颗粒的除尘效率越高,且随着磁感应强度等幅增大,除尘效率的增幅逐步减小,这表明磁场可有效地提高颗粒的捕集效果,但提高幅度随着磁感应强度的增大而降低。
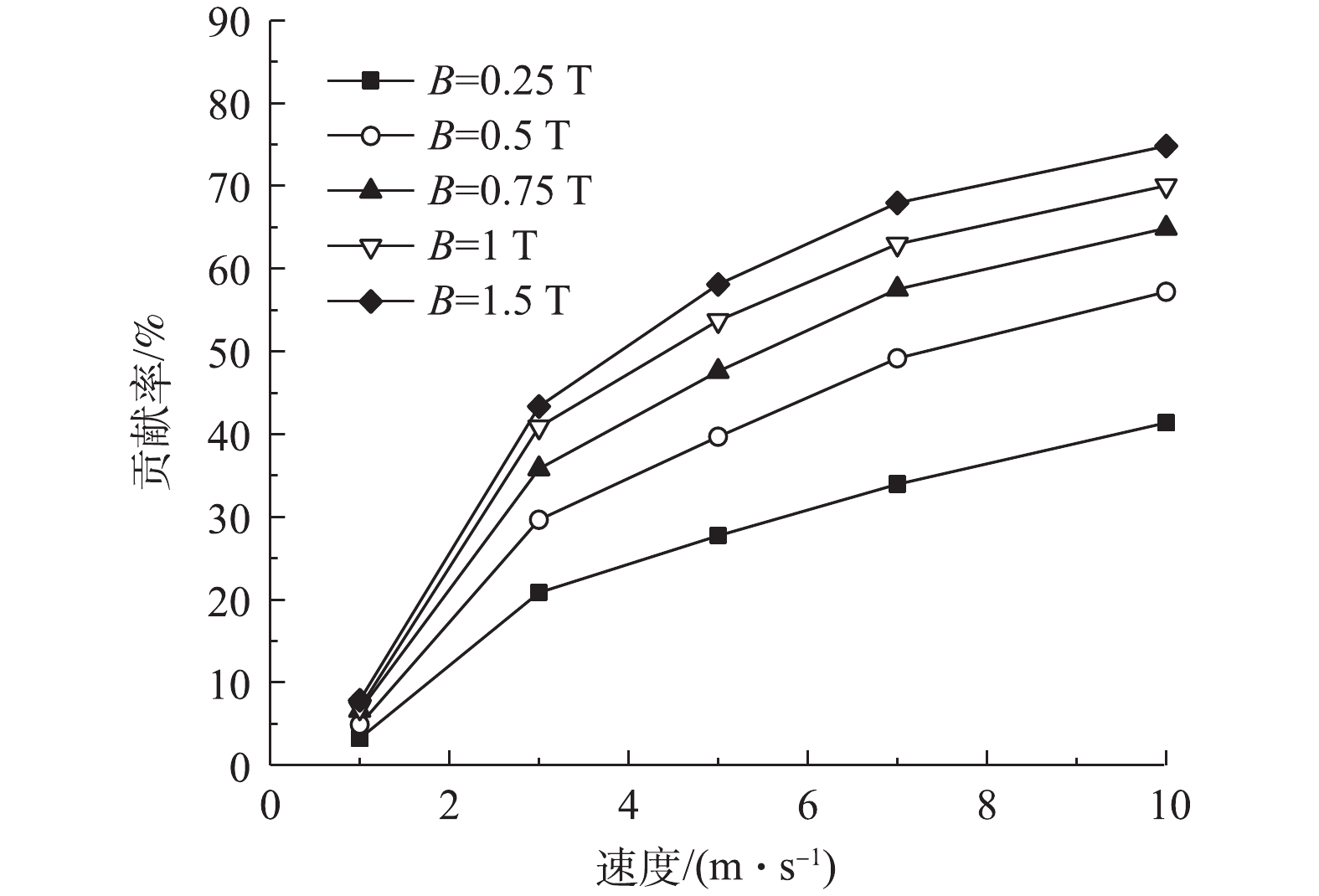
为了进一步分析磁场对颗粒捕集性能的影响,根据图6中的数据,给出了不同烟气流速下贡献率,结果如图7所示。可以看出:随着烟气流速的增大,磁场对颗粒捕集的贡献率均呈增大且逐渐变缓的趋势,相邻2条曲线的差值逐渐增大,同样说明了高烟气流速下外加磁场的贡献率更显著;在同一烟气流速下,磁感应强度的增大使得ESP中同种颗粒除尘效率的贡献率不断增大,而增幅逐步减小,这也表明磁场对颗粒捕集的促进效果随着磁感应强度的增大而不断减小。
2.1. 网格无关性验证
2.2. 可靠性验证
2.3. 不同烟气流速下的磁场效应
-
1)无论烟气流速为何值,磁场环境下ESP的除尘效率均更高,证明磁场的引入可有效提高线板式ESP的除尘性能。
2)随着烟气流速的增大,颗粒的除尘效率逐渐下降,而外加磁场对其贡献逐渐升高,说明高烟气流速时磁场效应更明显。
3)在磁感应强度不断增大时,烟气流速对除尘效率的削弱程度逐步降低,且同种颗粒的除尘效率逐渐增大,但增长幅度不断较小,表明磁场对除尘性能的贡献程度随着磁感应强度的减小而逐步增大。



 下载:
下载: