-
土壤作为地球生命赖以生存的重要资源与环境基础,是自然界物质和能量参与转化、迁移、积累等循环过程的重要场所。石油由多种复杂的烃类化合物组成,一旦进入土壤,将对人类健康和生态环境安全造成严重威胁[1]。根据环境保护部和国土资源部已公布的《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》,我国土壤总超标率高达16.1%[2],有机类污染物,特别是石油污染物已成为造成土壤安全问题的主要因素之一。因此,石油污染土壤的修复工作迫在眉睫。
采用热脱附技术,可对石油污染土壤进行高温加热处理,使石油污染土壤中的污染成分裂解为轻质组分后挥发,然后对其收集并进行达标处理。热脱附处理过程除受土壤本身属性影响外,处理温度、处理时间等工艺条件也将对热解效果带来一定的影响[3-4]。原地异位建堆热脱附技术[5-6]属于热脱附技术的一种,其技术原理是在微负压条件下,对建成堆体的污染土壤进行加热并维持在一定温度,促使污染物从土壤中脱附并进入气相,并通过抽提的方式将污染物抽出,再进行气处理,最终实现石油污染土壤的修复。该技术具有现场处置便利、无需长距离运输、二次污染少和对有机污染土壤修复效果好[7-10]等优点。采用该技术进行污染土壤修复的过程包含污染物在受热过程中从石油污染土壤中挥发并转移到尾气中和尾气中污染物的处理2个阶段[11]。
近年来,国内研究者已经开展了关于热处理技术的在苯系物[12]、PCBs[13]、PAHs[14]等土壤污染修复领域的应用探索,针对有机物污染场地修复技术的专利也日益增多[15]。原地异位建堆热脱附技术作为一项重要的非燃烧技术[16-19],在有机污染(包括石油污染)土壤修复领域具有较好的应用前景[20-23]。截至目前,国内外针对原地异位建堆热脱附技术在石油污染土壤修复领域的应用研究较少[20-24],因此,有必要开展该项技术在石油污染土壤修复领域的应用探究,为石油污染土壤的修复提供新思路。本研究采用杰瑞环保科技有限公司现有的原地异位建堆热脱附设备,对新疆某地区石油污染土壤进行热脱附处理实验,从修复过程、温度场模拟、温升曲线分析、设备投入、设备运行能耗及土壤修复效果评估等多个方面进行了综合分析,以期为原地异位建堆热脱附技术在石油污染土壤修复领域的工业化应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
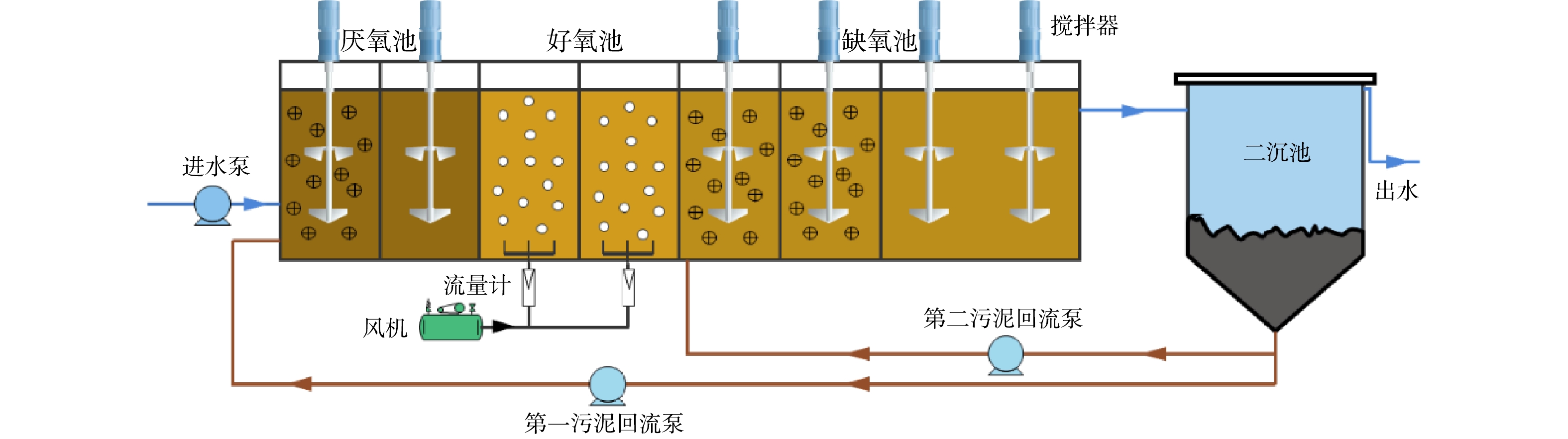
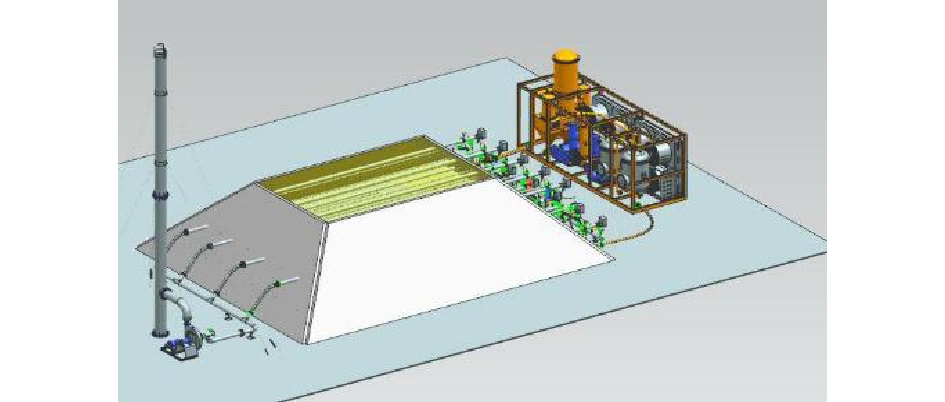
原地异位建堆热脱附技术的工艺原理如图1所示。该技术是通过将挖掘堆放的污染土壤加热至污染组分的沸点以上,使污染物从土壤中挥发、分离,这一过程包括了污染组分的挥发、裂解等物理化学变化[6,25]。当污染组分变为气态后,其流动性将大大增加,可通过风机抽提的方式进行收集。根据热源的不同,热脱附技术可分为燃气式和电加热式2种方式。新疆地区自然能源丰富,结合这一特点,本研究采用天然气作为热源。污染土壤将以四棱台式堆体的形式进行搭建,建堆过程中分层安装加热管和抽提管。污染土壤建堆示意图如图2所示。天然气在燃烧器内燃烧产生高温烟气,经加热管内管传输至加热管外管中,外管在辐射传热和烟气对流传热的双重作用下实现升温,并以热传导的方式加热污染土壤;当污染土壤被加热至一定温度后,附着在土壤颗粒上的污染物将由液相变为气相,并得以挥发,从而实现从污染土壤表面的剥离,然后经抽提管和风机抽出,并送入尾气处理系统从而实现石油组分的冷凝回收。
-
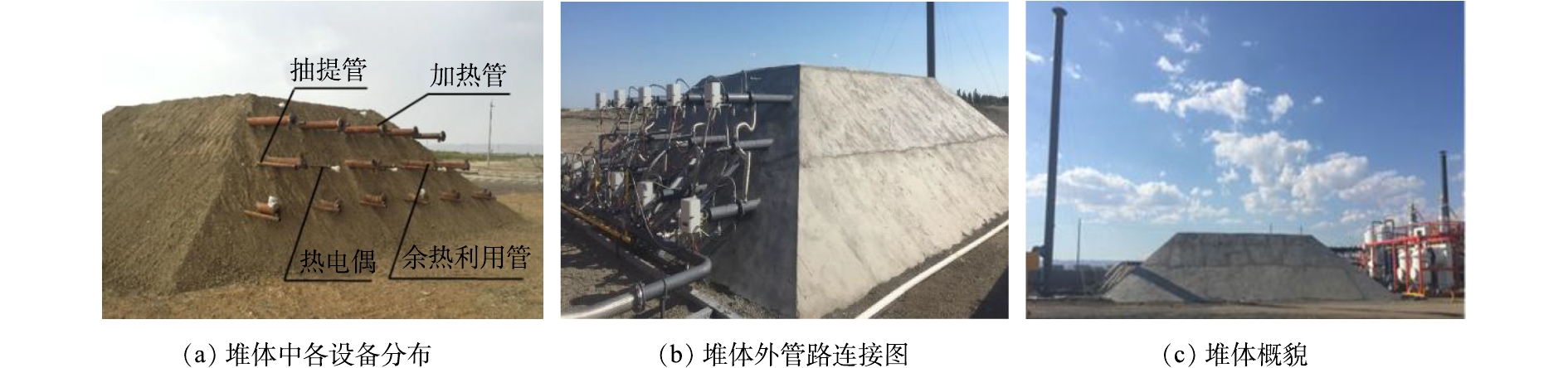
本研究挖掘的污染土壤总量约506 t,堆体搭建过程中配备加热管外管11根、内管11根、抽提管16根、余热利用管5根、热电偶8个、压力变送器3个、高压风机1台、燃烧器11台、耐火管11根、烟囱1个,如表1所示。天然气燃烧后产生的高温烟气(700~800 ℃)通入加热管中,通过间接换热的方式对土壤进行加热;加热管排出的烟气温度仍高达400 ℃,为实现该部分热量的利用,将在土壤中插入余热利用管,并将排出的高温烟气注入到余热利用管中,对污染土壤进行加热,从而实现余热利用。
气处理系统主要由气液分离器、列管换热器、罗茨风机、活性炭罐、板翅式换热器、齿轮泵等组成,见表2。
-
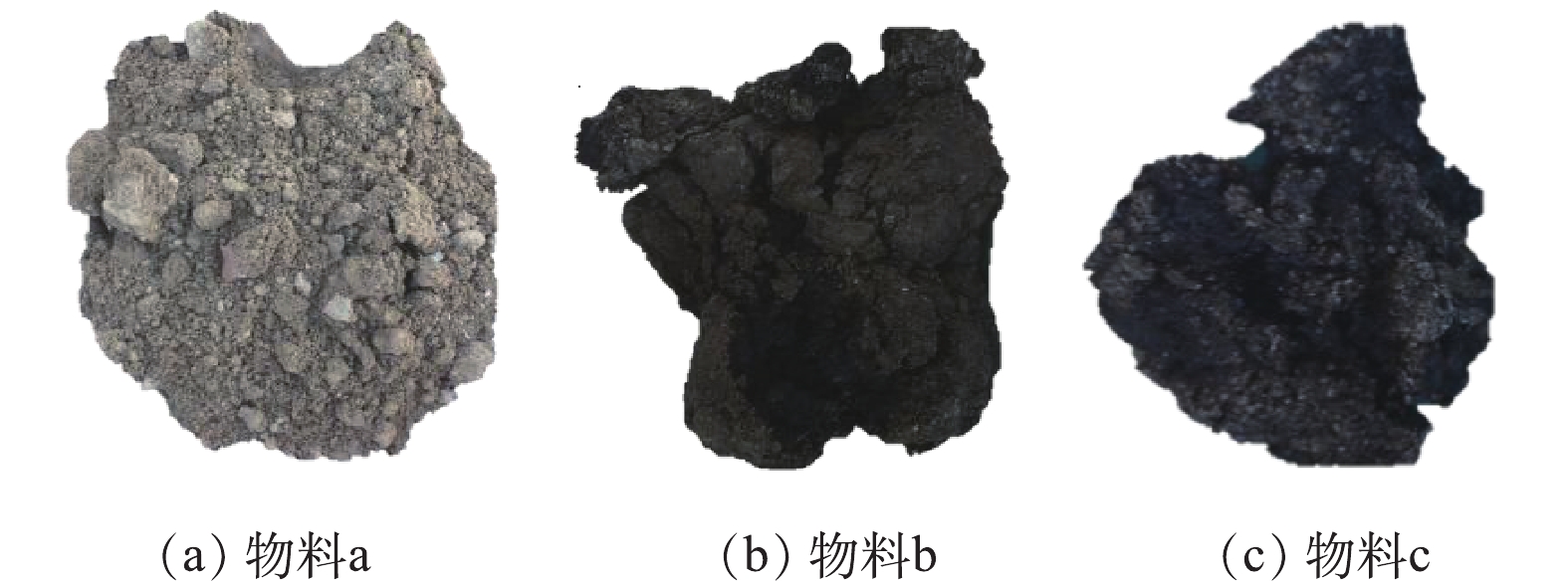
污染土壤自身的属性对于热脱附处理过程具有一定的影响。对污染物料区域(待修复的污染土壤)开挖后发现,污染状况较为复杂。对代表性污染物料进行分析后,将待处理物料分为3类,对应物料的表观性状如图3所示,对应物料的检测分析结果如表3所示。
-
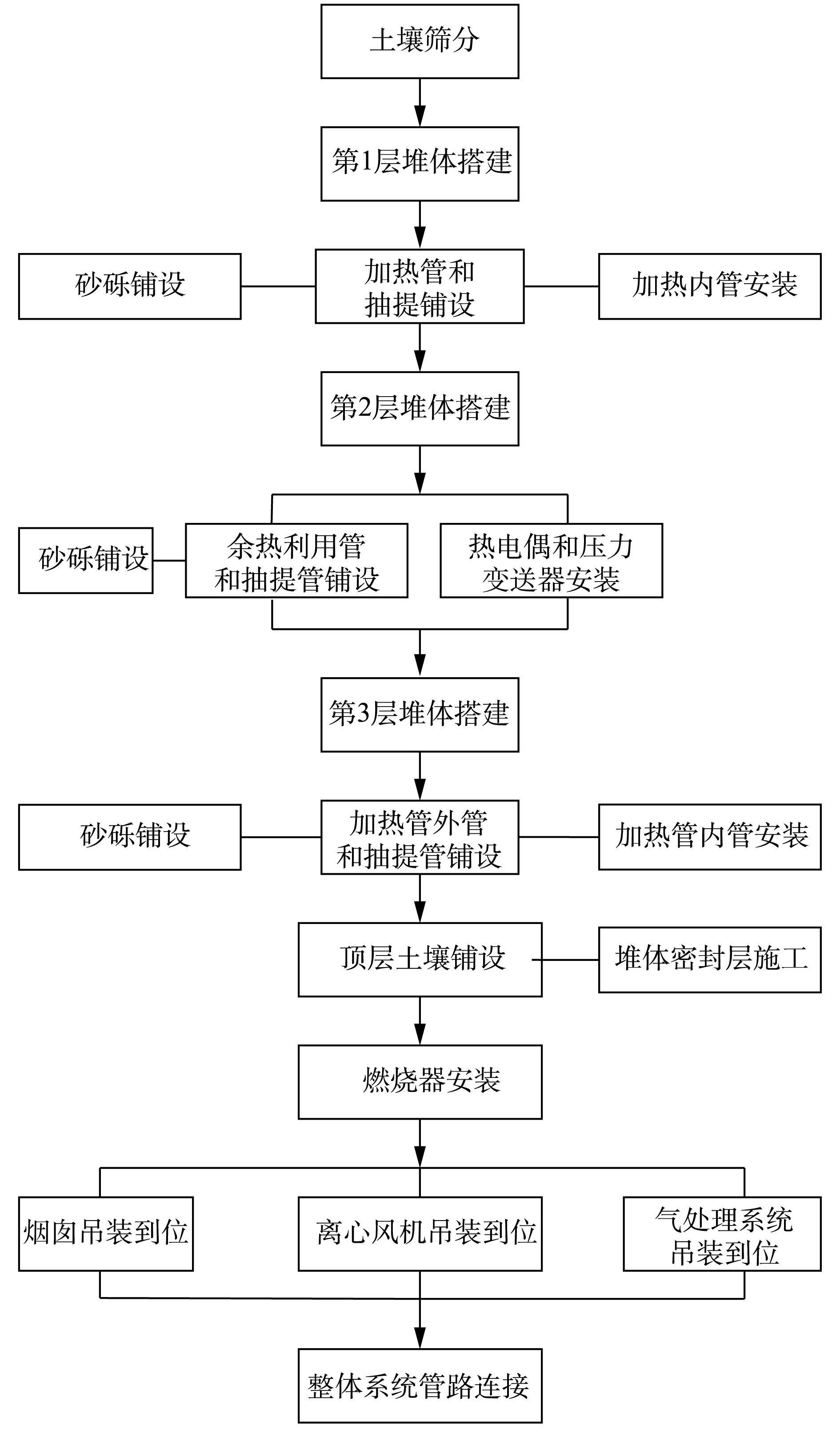
根据待处理物料的属性,共分4层进行修复堆体的搭建,物料a、b、c在堆体内的分布位置如表4所示。本研究石油污染土壤总量约506 t,总方量297.6 m3,堆体搭建尺寸如表4所示。待处理物料经筛分等预处理后作为堆体物料进行堆体的搭建。物料a按照设定尺寸平铺于底层,并分别按照1.5 m的间距铺设加热管(包括内管、外管)和抽提管(图4(a)),完成第1层堆体的搭建。在第2层堆体搭建的过程中,物料b铺设完成后,安装余热利用管(图4(a))和抽提管,并在本层安装热电偶(图4(a))和压力变送器,以实现堆体温度和负压的监测。物料c分布于第3层堆体中,并再次铺设加热管和抽提管。再将物料a铺于第4层,封顶。堆体搭建完成后,开始表面隔离层的施工,堆体四周只采用混凝土抹面固封(厚度6 cm),堆体顶部加盖岩棉板(厚度8 cm)进行隔热。同时,为了防止雨水的干扰,在岩棉板铺设完毕后,再覆盖混凝土层(厚度6 cm),如图5所示。
最终成形的四棱台形式的堆体如图4(b)所示,堆体搭建的详细工艺路线如图6所示。堆体外将安装燃烧器、烟囱、离心机和气处理系统,实现堆体系统管路的连接,形成待修复的石油污染土壤堆体,如图4(c)所示。
-
天然气在燃烧器内燃烧时产生的高温烟气进入加热管内管,经加热管外管排出后,再进入余热利用管进行热量的二次利用,最终由烟囱排出。在整个过程中,加热管外管以热传导的形式加热污染土壤,实现污染物的挥发和分离。在加热过程中,为保证燃烧器的正常运行,对加热管外管温度进行实时监测,既防止由于长时间持续加热而导致加热管因温度过高受损,又保证加热管外管温度不低于550 ℃,以满足污染土壤修复效果。在热脱附过程中,堆体内冷点[26]位置的污染土壤加热温度至少应达到300 ℃。在建堆过程中,在含油率最多的物料b所在的第2层设置土壤取样口,修复完成后,从取样口取样并送到具有相关资质的第三方检测机构进行检测,评估土壤修复效果。
-
热脱附处理后,石油烃类物质转移到气相中。为满足《大气污染物综合排放标准》(GB 16297-1996)的相关要求,须进行后续气处理。本研究气处理系统主要包含气液分离器、列管换热器、罗茨风机、活性炭罐、板翅式换热器、齿轮泵等。气处理工艺流程如下。
1)经抽提收集的污染气体首先进入一级气液分离器,实现气体与其携带的土壤颗粒和大液滴的分离。
2)分离后的气相进入列管式换热器,实现石油烃组分的冷凝回收。
3)冷凝处理后的气相进入二级气液分离器,实现冷凝后气体与其夹带的雾状液滴的分离,防止雾状液滴进入风机。
4)处理后的气相以风机为动力源,依次通过两级活性炭体系,利用活性炭的吸附作用对气体进行净化处理[27-28]。
5)气体处理达标后通过烟囱排放。
6)经两级气液分离和列管换热器冷凝后的油水混合物收集至吨桶中,定期交由当地污水处理厂进行处理。
1.1. 原地异位建堆热脱附技术的工艺原理
1.2. 堆体内设备和尾气处理系统设备
1.3. 修复过程
1.3.1. 污染物料性状分析
1.3.2. 堆体搭建
1.3.3. 热脱附处理
1.3.4. 气处理
-
根据污染土壤中含有的石油烃的性质,为达到修复效果,堆体内土壤的平均温度须达到300 ℃以上。修复前,为保证各管件、设备布局的合理性,保证污染土壤修复效果,特针对污染土壤的处理过程进行温度场模拟。
-
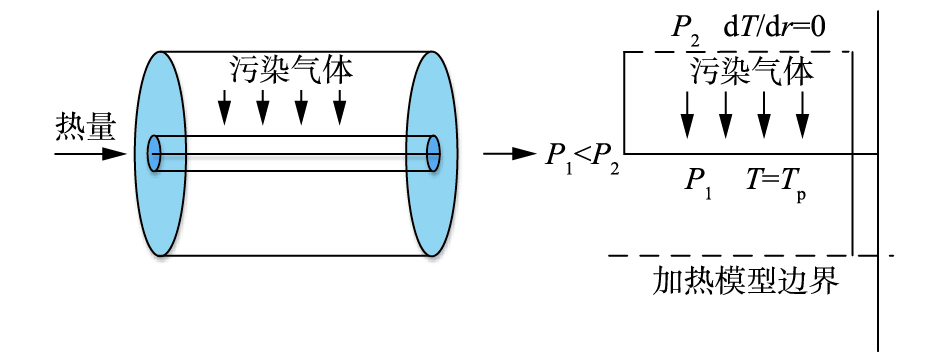
在数学模拟过程中,参考TSOKUR等[29]的研究,建立数学模型。为实现温度场模拟,假设每个燃烧器所形成的温度场为一圆柱体模型,如图7所示。
土壤热处理过程能量平衡方程如式(1)所示。
土壤热处理过程物料平衡方程如式(2)和式(3)所示。
式中:λ为土壤导热系数,W·(m·℃)−1;r为加热半径,m;T为加热温度,℃;t为加热时间,s;
Cp,m 为土壤比热容,J·(kg·K)−1;Cp,g 为气体比热容,J·(kg·K)−1;ε为土壤孔隙度;Sg为土壤中气体饱和度,即气体填充在土壤内部孔隙之间的体积分数;Ug为污染气体流速,m·s−1;K为渗透面积,m2;k为渗透系数,m·s−1;ρg为气体密度,kg·m−3;μg为气体黏度,kg·(m·s)−1;h为蒸发焓变,J·kg−1;m为单位体积内液相蒸发速度,kg·(m3·s)−1。关联式如式(4)~式(11)所示。
式中:A为单位体积土壤的传质面积,m2·m−3;Cg为传质过程中污染物气相浓度,kg·m−3;
Ceq,g 为传质平衡状态下污染物气相浓度,kg·m−3;Sl为土壤中液体饱和度,即液体填充在土壤内部孔隙之间的体积分数;Re为雷诺数;Sc为施密特准数;a,b,c为安托尼常数;de为当量直径,m。边界条件如式(12)~式(16)所示。
-
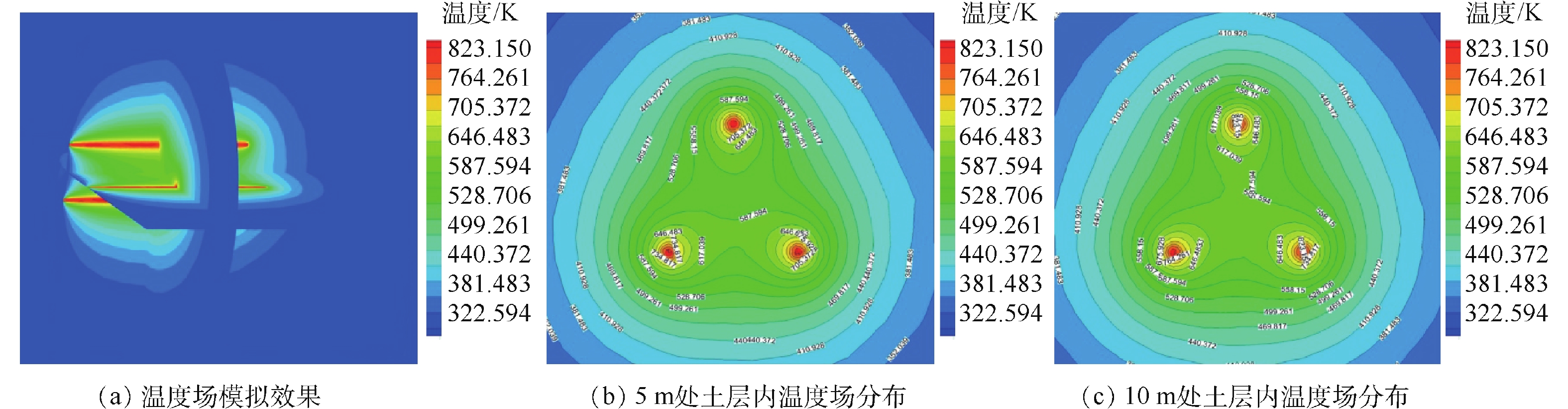
采用ANSYS 15.0软件对上述圆柱模型进行结构化网格划分,然后采用FLUENT软件中的有限控制体积法计算网格节点上的温度等数值解。在模拟过程中,以间距1.5 m对加热管进行布置,当加热管外管管壁温升至550 ℃时,考察任意3根加热管组成的三角区域内温度场的分布,以此分析修复过程中堆体内全部污染土壤的温度状况。
2.1. 数学模型
2.2. 温度场模拟
-
采用FLUENT软件进行温度场模拟的结果如图8所示。图8(a)为3根间距1.5 m的加热管温度场模拟效果。由图8可见,温度在加热管处高达550 ℃,并沿着加热管向四周递减。每根加热管长14 m,分别模拟此3根加热管在5 m和10 m位置组成的三角区域内的温度场分布。如图8(b)和图8(c)所示,土壤各点温度均超过300 ℃,冷点位置的温度高达314 ℃。由此可见,当设计加热管间距为1.5 m时,3根加热管所覆盖的区域内无温度场盲点,各点温度均能够满足最低要求,具备除去污染土壤中所含的石油烃类物质的条件。
-
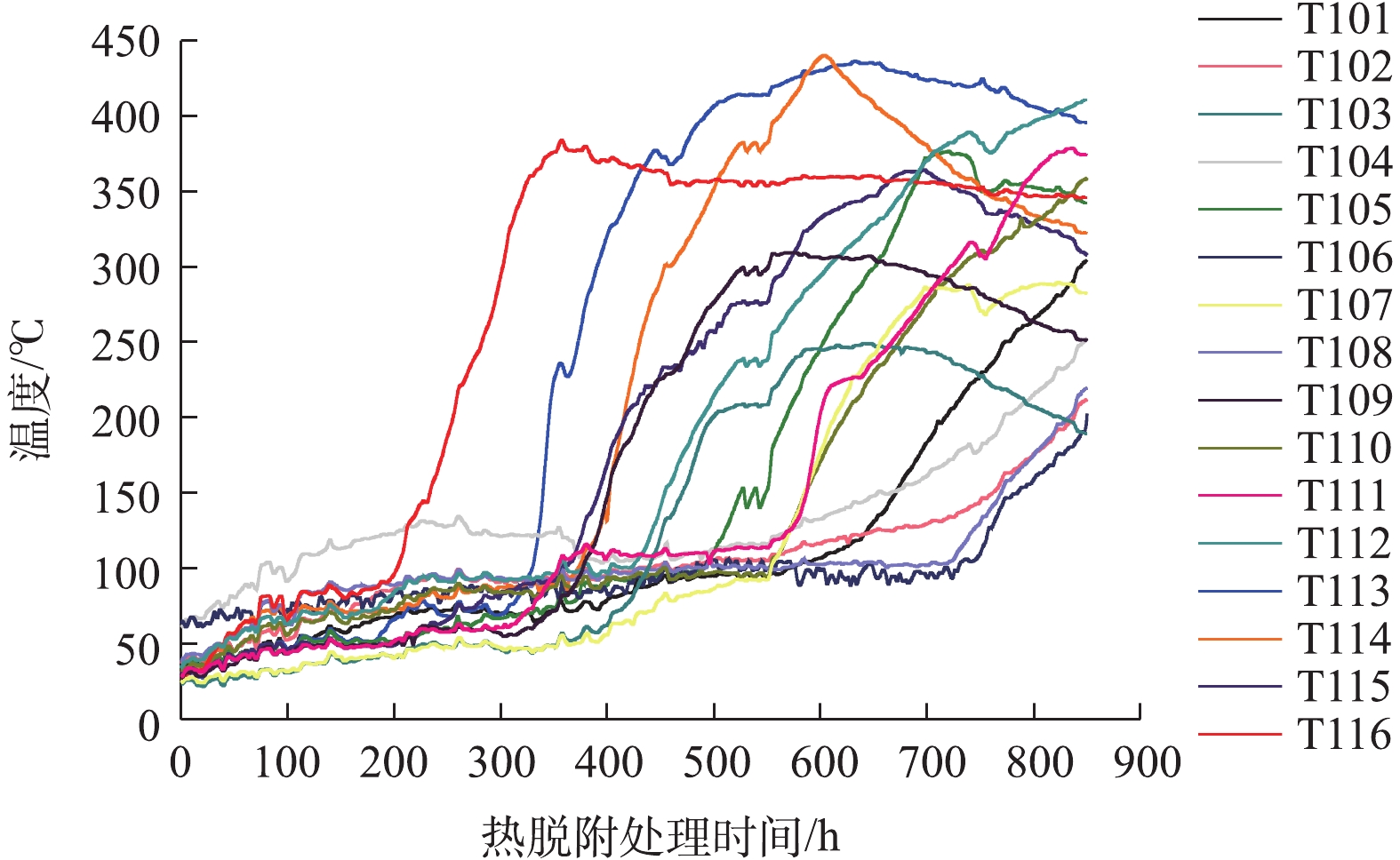
在污染土壤处理过程中,以K型热电偶的形式实现对污染土壤的温度监测。结合本研究中污染土壤的处理量,在堆体搭建过程中设置了8个热电偶,分别安装于第2层污染土壤(6个)和顶层污染土壤(2个)中,每根热电偶设2个测温点位,共16个测温点位,点位编号为T101~T116。由图9可见,温升曲线T101~T112为第2层污染土壤在热脱附处理过程中的温度变化情况;T113~T116为顶层污染土壤在热脱附处理过程中的温度变化情况。当温度低于100 ℃时,各测温点位的升温速率较慢,这是因为污染土壤中含有水,水的比热容高于干土壤的比热容,因此该阶段加热过程中土壤升温较慢。由图9可见,当测温点位的温度达到100 ℃后,温度会在一段时间内保持恒定。在此期间内,污染土壤中所含的水分将逐渐蒸发并经抽提管抽出。由于本阶段的热量主要转化为水的气化潜热,因此,此阶段内土壤温度趋于稳定。温升曲线T113~T116在该阶段的持续时间明显低于其他点位,这是因为顶层污染土壤的含水率低于1%,水体气化用时较短。由此可见,温度恒定阶段的时间随着待处理土壤含水率的升高而变长。水分被蒸发抽提后,堆体内土壤的升温速率大幅加快,石油烃各组分随之挥发,通过罗茨风机将污染物蒸汽抽提、收集,统一进行气处理。
-
含油率较高的污染土壤b位于第2层堆体内,其原始含油率为23.1%;经原地异位建堆热脱附处理后的样品送至SGS-CSTC检测中心进行检测,2个平行样品中总石油烃含量分别为496 mg·kg−1和602 mg·kg−1,处理后土壤中石油烃平均含量约549 mg·kg−1,能够满足《土壤环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 36600-2018)中的相关要求。
-
在处理过程中,堆体自2017年10月19日开始修复,至11月24日实验结束,共施工运行37 d,天然气总用量14 977 m3。利用原地异位热脱附技术处理该项目506 t石油污染土壤,天然气用量统计分析结果如下:天然气用量14 977 m3,污染土方量297.6 m3,污染土总重量506 t,1 t用气量29.6 m3,1 m3用气量50.3 m3。每处理1 m3石油污染土壤约消耗天然气50.3 m3。
3.1. 温度场模拟分析
3.2. 温升曲线分析
3.3. 土壤修复效果分析
3.4. 能耗分析
-
1)通过数学模型进行温度场模拟,在加热管外壁温度达到550 ℃、加热管和抽提管间距分别为1.5 m的条件下,堆体内所有污染土壤均能达到目标温度(300 ℃),满足去除污染土壤中所含石油烃类物质的条件。
2)采用原地异位建堆热脱附技术进行土壤修复处理时,待处理物料(污染土壤)的含水率对污染土壤升温速率有较大影响。含水率越低的物料,升温速率越快。
3)采用原地异位建堆热脱附技术能够实现石油污染土壤的修复,修复后土壤样品中总石油烃的含量能够达到《土壤环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 36600-2018)的修复要求。在应用过程中,原地异位建堆热脱附技术具有设备投入少、人员投入少、场地限制低的优势,处理后土壤能够满足国家和地区对相关指标的管控要求,具备开展大规模现场应用的条件。



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: