-
近年来,工业化的迅速发展造成了许多环境污染问题。染料废水作为一种典型的工业废水因其水量大、色度高、组成成分复杂而导致其处理难度非常高[1]。若未经处理而排放到自然水体,将会污染水源,威胁生态环境,并且其生物毒性通过食物链而最终在人体积累,严重危害人体健康[2]。目前,染料废水的去除方法主要有物理法、化学法及生物法[3-4]。物理法是目前研究染料废水处理最为广泛的一种处理方法,其中吸附法作为一种绿色高效的去除技术被广泛地应用于染料废水的去除。吸附剂的选择对于使用吸附法去除染料废水至关重要。目前,常用的吸附材料有活性炭、焦炭、沸石、壳聚糖以及天然黏土矿物等[5]。但是这些吸附剂的吸附容量不高,或者选择吸附性差。因此,开发一种高效和大吸附量的吸附剂用于染料废水的去除非常必要。
金属有机骨架是通过共价键或者离子共价键自组装金属中心离子和有机配体形成的具有周期性网络结构的配位聚合物[6]。因其高的比表面积和可调的孔径[7]、丰富的结构和组成成分、配位不饱和位点能够结合特定官能团[8]等特点而被广泛应用于储能、气液相分离、催化、光学和磁学等领域[9-11]。沸石咪唑基骨架(ZIFs)作为MOFs材料的一种,具有优异的化学稳定性和吸附性能。张琪颖[12]研究了ZIF-8对硝基苯酚(PNP)的吸附效果,研究表明,ZIF-8在反应最佳条件下能够高效选择性地吸附PNP。同时,磁性纳米复合材料作为吸附剂应用于水处理中也受到广泛关注。孙杨等[13]利用自制Fe3O4磁性材料与MOF-5合成磁性Fe3O4@MOF-5复合材料,被证明Fe3O4@MOF-5复合材料对于刚果红是良好的吸附剂。基于上述研究,本研究采用聚苯乙烯磺酸钠(PSS)处理Fe3O4表面诱导生长ZIF-8壳层,在常温搅拌下,成功合成磁性核壳金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8,通过SEM、TEM、XRD、FT-IR及VSM对其进行形貌分析,考察了刚果红初始浓度及接触时间、Fe3O4@ZIF-8用量、pH等因素对Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附偶氮染料刚果红废水的影响;确定了其吸附动力学和吸附等温线;探讨了Fe3O4@ZIF-8的选择吸附性能以及循环再生性能,研究可为复合金属有机骨架材料在染料吸附去除方面的应用提供参考。
-
仪器:电子天平(AL104,梅特勒-多利多仪器上海有限公司);超纯水机(Ther-mo Scientific Barnstead EasypureⅡ);精密增力电动搅拌器(金坛市新航仪器厂);真空干燥箱(DZF-6020型,上海浦东荣丰科学仪器有限公司);恒温干燥箱(101-1型,上海东星建材实验设备有限公司);pH计(PHB-4型,上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司);双功能水浴恒温振荡器(SHA-B,金坛市科析仪器有限公司);扫描电镜(Quanta FEG型,美国FEI公司);分光光度计(PhotoLab-7600型,赛莱默中国分析仪器有限公司)。
材料与试剂:六水合硝酸锌(Zn(NO3)2·6H2O)(分析纯,国药化学试剂有限公司);2-甲基咪唑(C4H6N2)(分析纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司);聚苯乙烯磺酸钠(PSS)(30%,阿拉丁试剂有限公司);甲醇(CH3OH)(分析纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司);Fe3O4纳米颗粒(99%,成都麦卡希有限公司);氢氧化钠(NaOH)(分析纯,重庆川东化工有限公司);盐酸(HCl)(分析纯,重庆川东化工有限公司);氯化钠(优级纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司);刚果红(分析纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司);去离子水,实验室自制。
-
Fe3O4@ZIF-8的合成参照文献中的方法[14]。将1.5 g的聚苯乙烯磺酸钠(PSS)溶解在150 mL去离子水中并超声处理30 min,配制成PSS溶液,将0.25 g的Fe3O4纳米颗粒加入到PSS溶液中并在室温下超声30 min,然后,通过外部磁体将Fe3O4纳米粒子与溶液分离并用水洗涤3次;处理后的Fe3O4纳米微粒投加到ZIF-8的合成液中(1.19 g硝酸锌,2.63 g二甲基咪唑和80 mL甲醇),在50 ℃水浴条件下,机械搅拌8 h,然后通过磁铁把合成的Fe3O4@ZIF-8磁性核壳颗粒与反应体系分离。用甲醇溶液洗涤磁性粒子3次,并在真空干燥箱中60 ℃烘干12 h,最后获取Fe3O4@ZIF-8。
-
采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Quanta FEG,FEI公司,美国)和透射电子显微镜(TEM,Tecnai F30,FEI公司,美国)对磁性金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8的微观形貌进行分析。采用X射线衍射(XRD,X/Pert PRO MPD,帕纳科分析仪器有限公司,荷兰)对Fe3O4@ZIF-8的晶体结构进行表征。Fe3O4@ZIF-8表面官能团信息采用傅里叶变换红外分光光度计(FT-IR,Nicolet iS50,Nicolet公司,美国)测定。Fe3O4@ZIF-8的磁学性能采用振动样品磁强计(7400型,Lake shore公司,美国)进行测试。
-
本实验选择阴离子偶氮染料刚果红为模拟染料废水,研究磁性金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8材料对其去除效果,在一系列规格为50 mL的锥形瓶内,倒进20 mL刚果红染料溶液,准确投加一定质量的Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂,把锥形瓶放入振荡器中,25 ℃下恒温振荡,吸附一段时间后,用磁铁将吸附剂Fe3O4@ZIF-8从溶液中分离出来,取上层溶液用分光光度计测定光度值,然后分别计算Fe3O4@ZIF-8的吸附容量和刚果红去除率。
去除率和单位吸附量的计算方法见式(1)和式(2)。
式中:
η 为去除率;C0为刚果红的初始浓度,mg·L−1;C为刚果红浓度,mg·L−1;q为吸附剂的吸附量,mg·g−1;V为溶液体积,L;m为Fe3O4@ZIF-8质量,g。1)吸附动力学实验。取不同初始浓度的20 mL刚果红溶液,并投加Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂10 mg。在25 ℃下进行恒温振荡,分别吸附5、10、20、30、60、90、120、180和240 min后,离心混合溶液并测定上清液的吸光度。吸附数据由一级动力学方程[15]和二级动力学方程[16]来进行拟合。一级动力学方程见式(3),二级动力学方程见式(4)。
式中:qe为吸附剂的平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;q为吸附剂在t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,min;K1为一级动力学速率常数,min−1;K2为二级动力学速率常数,g·(mg·min)−1。
2)吸附等温线测定。配置20 mL初始浓度为50~300 mg·L−1的刚果红溶液,加入10 mg的Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂。将混合溶液的pH调节至6,并在25、30、35 ℃下进行振荡,直至吸附达到平衡。吸附数据由Langmuir吸附等温方程[17](见式(5))和Freundlich吸附等温方程[18](见式(6))进行拟合。
式中:qe为吸附剂的平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;q为Fe3O4@ZIF-8的最大吸附量,mg·g−1;b为吸附能有关常数;Kf为Freundlich系数;n为Freundlich常数。
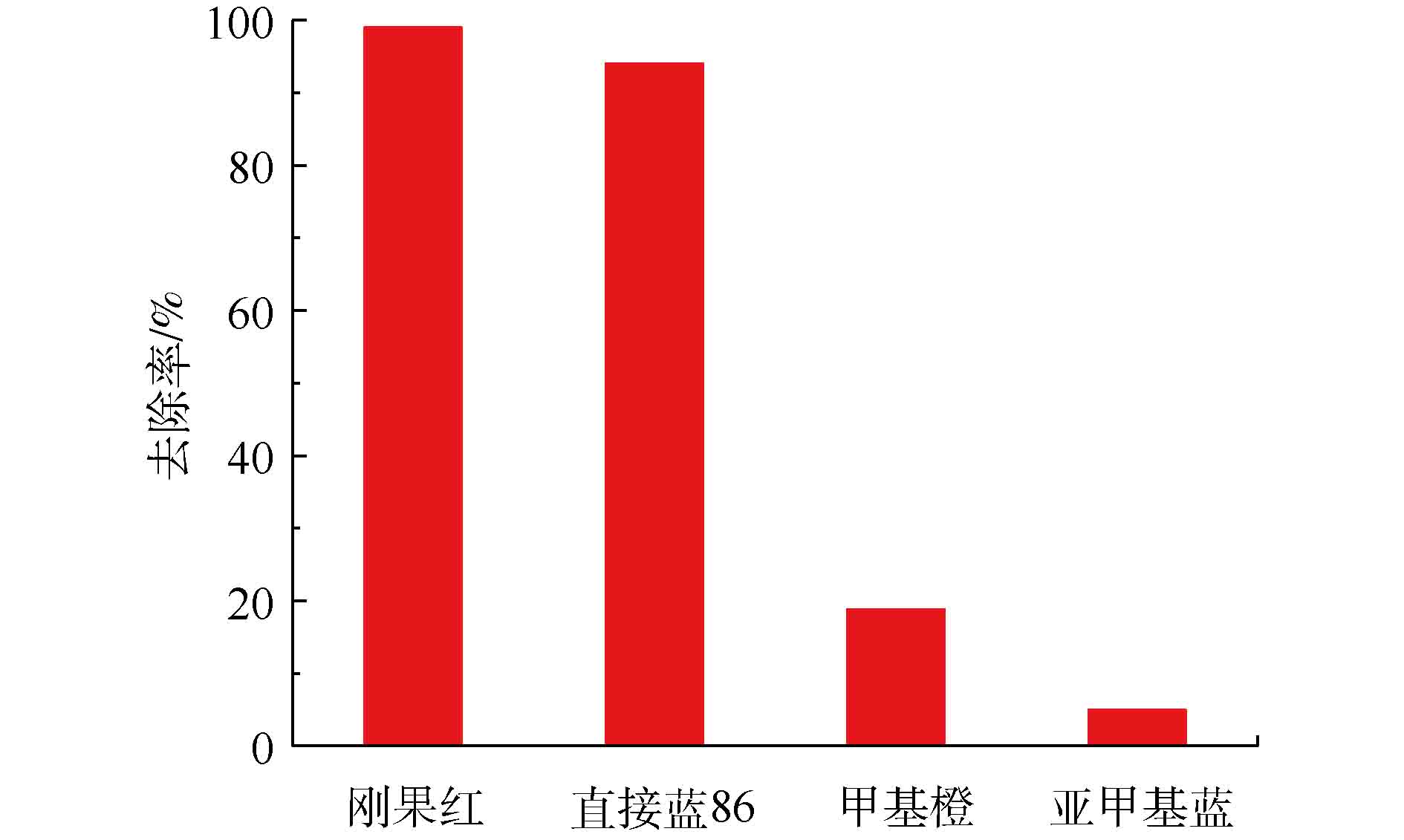
3)选择吸附实验。在实验中,使用Fe3O4@ZIF-8作为吸附剂以吸附刚果红、直接蓝86、甲基橙、亚甲基蓝染料,以此来考察Fe3O4@ZIF-8的选择吸附性能。取30 mg·L−1的不同染料20 mL,加入10 mg的Fe3O4@ZIF-8,在恒定温度下吸附12 h,测定吸附后的浓度。
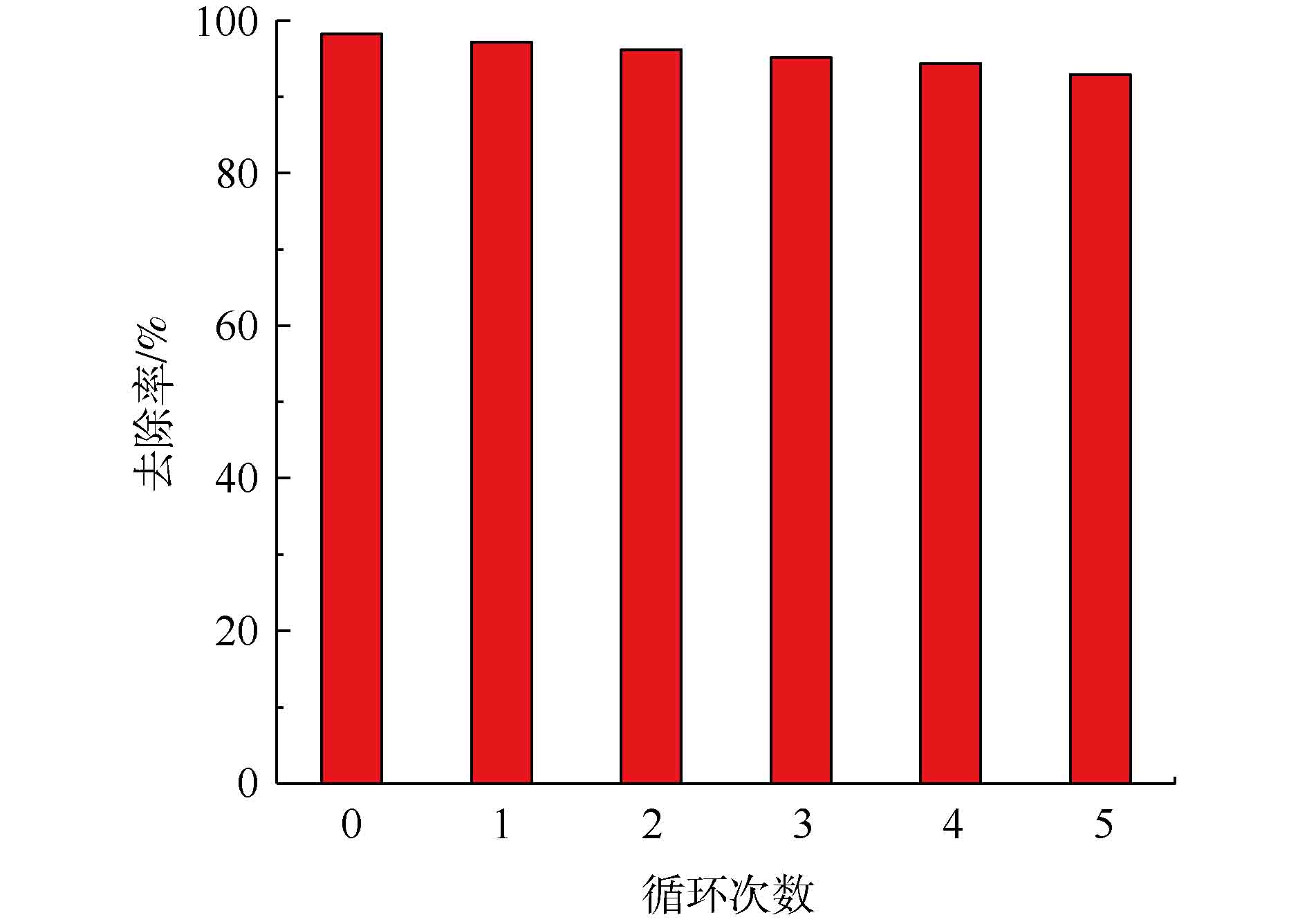
4)循环性能实验。Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附50 mg·L−1的刚果红溶液后,使用蒸馏水反复冲洗吸附剂,随后采用0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液进行解吸,然后烘干用于下一个周期中。重复5次,考察Fe3O4@ZIF-8的吸附解吸能力。
-
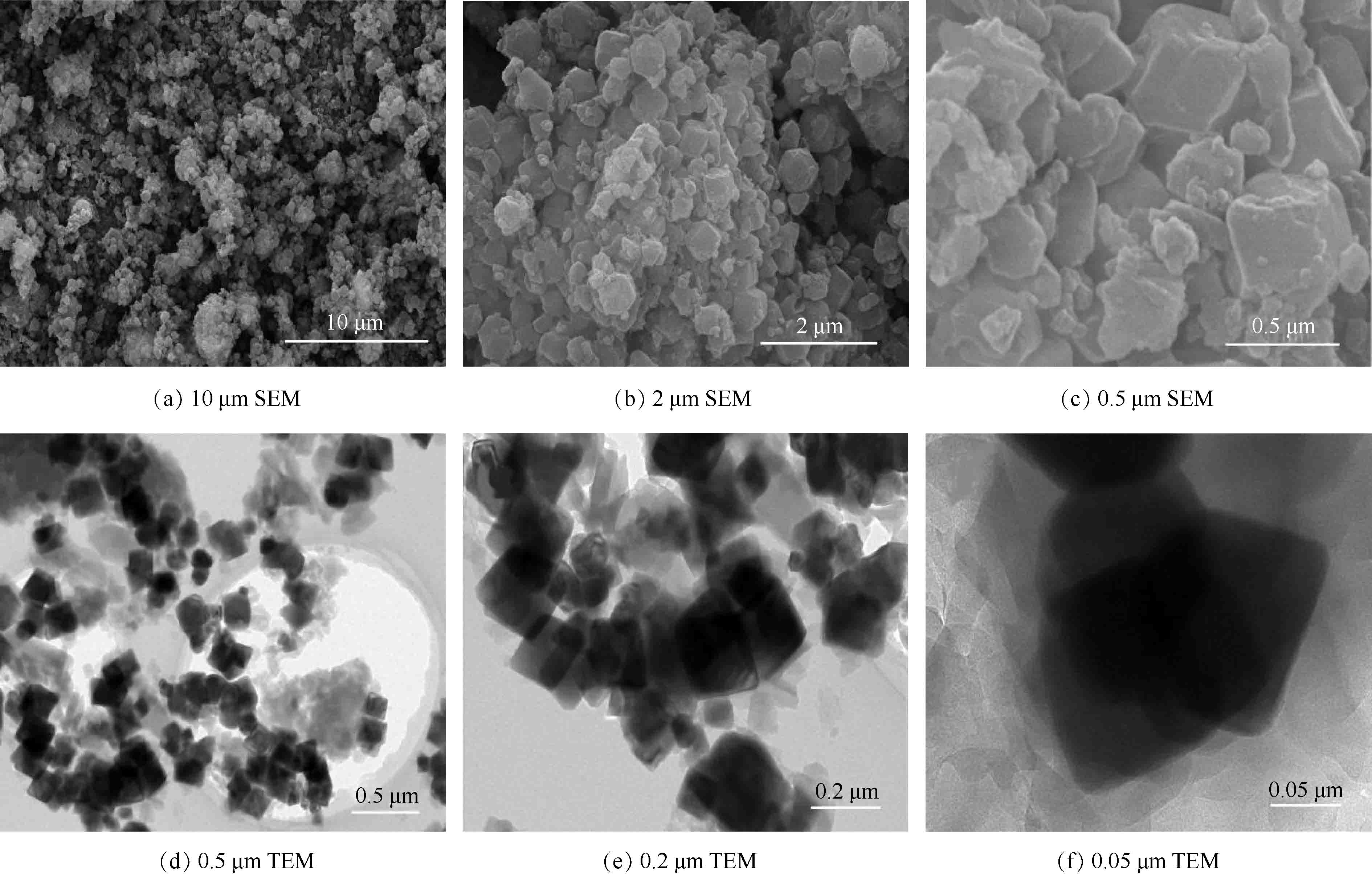
1) SEM和TEM分析。图1(a)~(c)是在不同放大倍数下的SEM图,可以看出,Fe3O4@ZIF-8纳米粒子呈现不规则的立方体结构,并且表面分布了很多ZIF-8晶体。图1(d)~(f)为Fe3O4@ZIF-8在不同放大倍数下的TEM图,可以看出,该复合材料呈现明显的核壳形态,ZIF-8已成功地生长在Fe3O4纳米颗粒表面。这种磁性复合材料的平均粒径在200 nm左右。SEM和TEM表征很好地证明了合成的材料即为核壳结构的Fe3O4@ZIF-8。
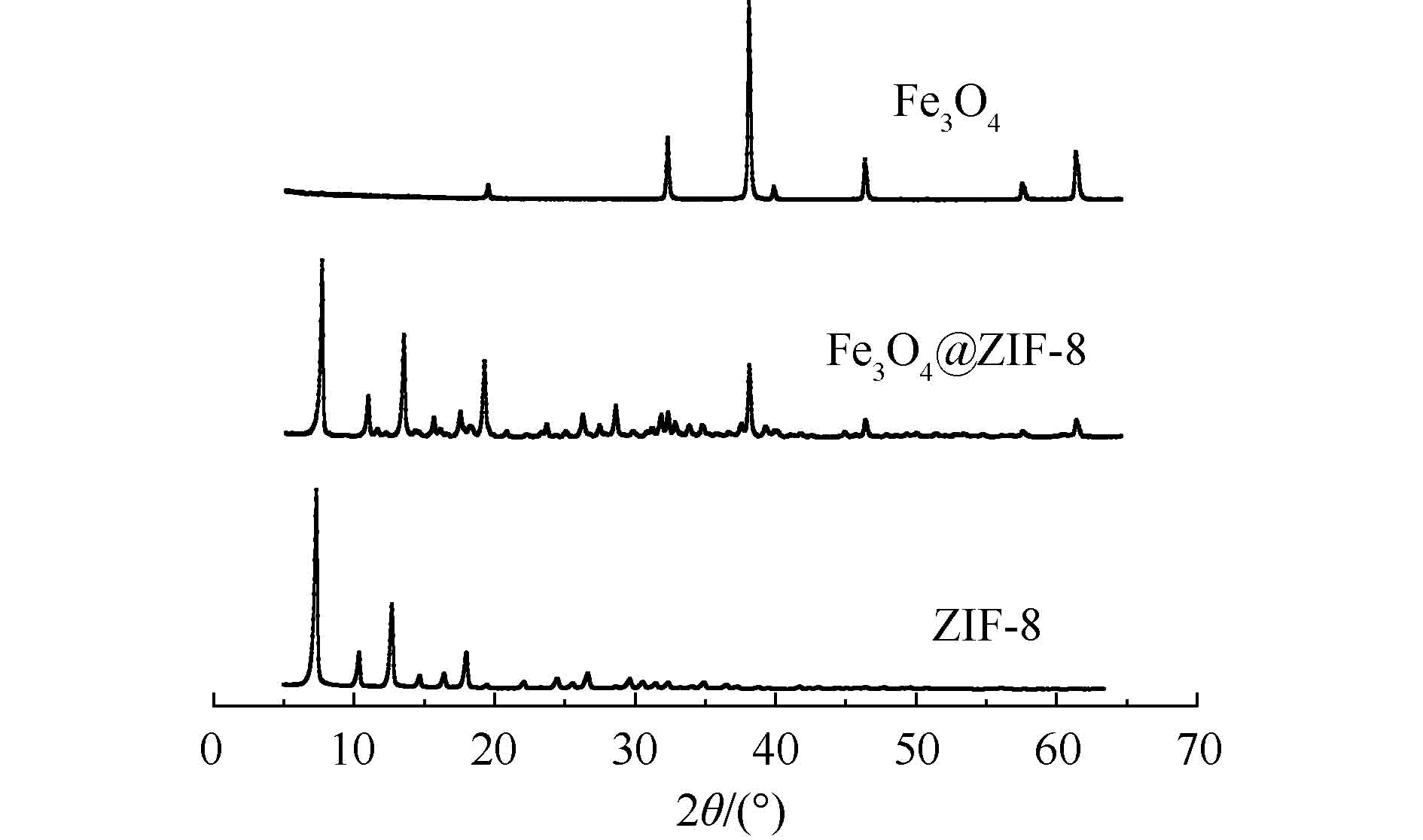
2) XRD分析。由图2可知,Fe3O4@ZIF-8材料在2θ为30.16°、35.52°、43.18°、53.52°、57.06°处均出现了特征峰,与实验中Fe3O4的表征图谱比较,特征峰的位置相同,分别对应的是Fe3O4的(220)、(311)、(400)、(422)和(511)衍射晶面。同时,在(011)、(002)、(112)、(022)、(013)、(222)处均出现了与实验表征的ZIF-8 图谱对应一致的衍射峰。所以,可断定Fe3O4@ZIF-8已成功合成,且Fe3O4@ZIF-8中Fe3O4的晶型结构没有遭到破坏。这说明Fe3O4@ZIF-8不仅具备ZIF-8的高效吸附性能,同时还具有Fe3O4的磁性分离性能。
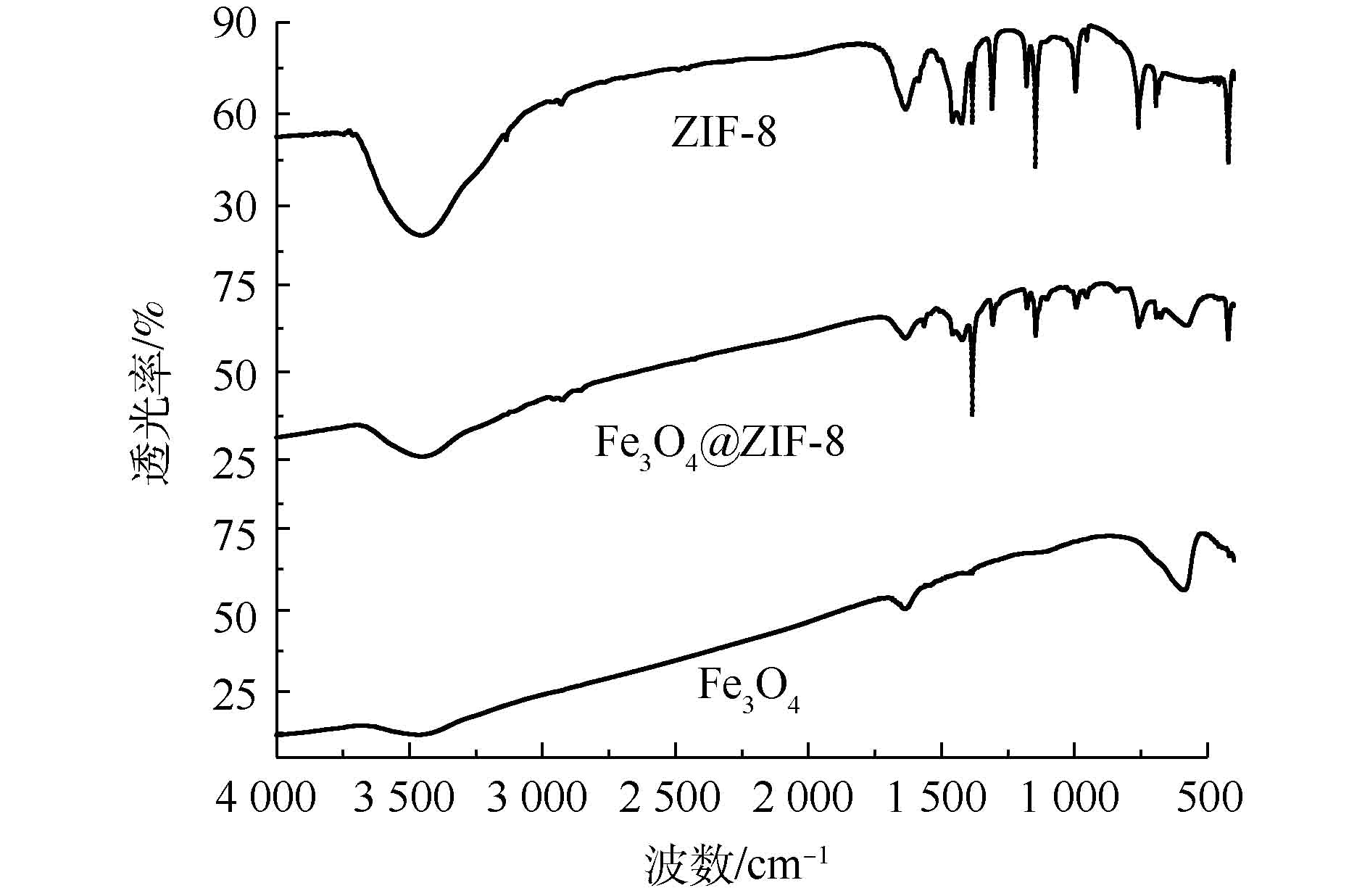
3) FT-IR分析。从图3中的Fe3O4@ZIF-8红外图谱可知,在3 454 cm−1处出现了对应于水分子中的O—H键的特征吸收峰。3 135 cm−1和2 926 cm−1分别归属于ZIF-8结构中咪唑分子芳香族与脂肪族的C—H键的特征峰。咪唑环中C=N键的伸缩振动峰出现在1 565 cm−1处,C—N键的振动吸收峰出现在1 146和993 cm−1处。在420 cm−1处出现了Zn—N官能团振动峰,最重要的是在580 cm−1处出现了属于Fe3O4的Fe—O振动吸收峰[19]。综合上述分析,可以进一步确定成功合成的核壳结构物质就是Fe3O4@ZIF-8。
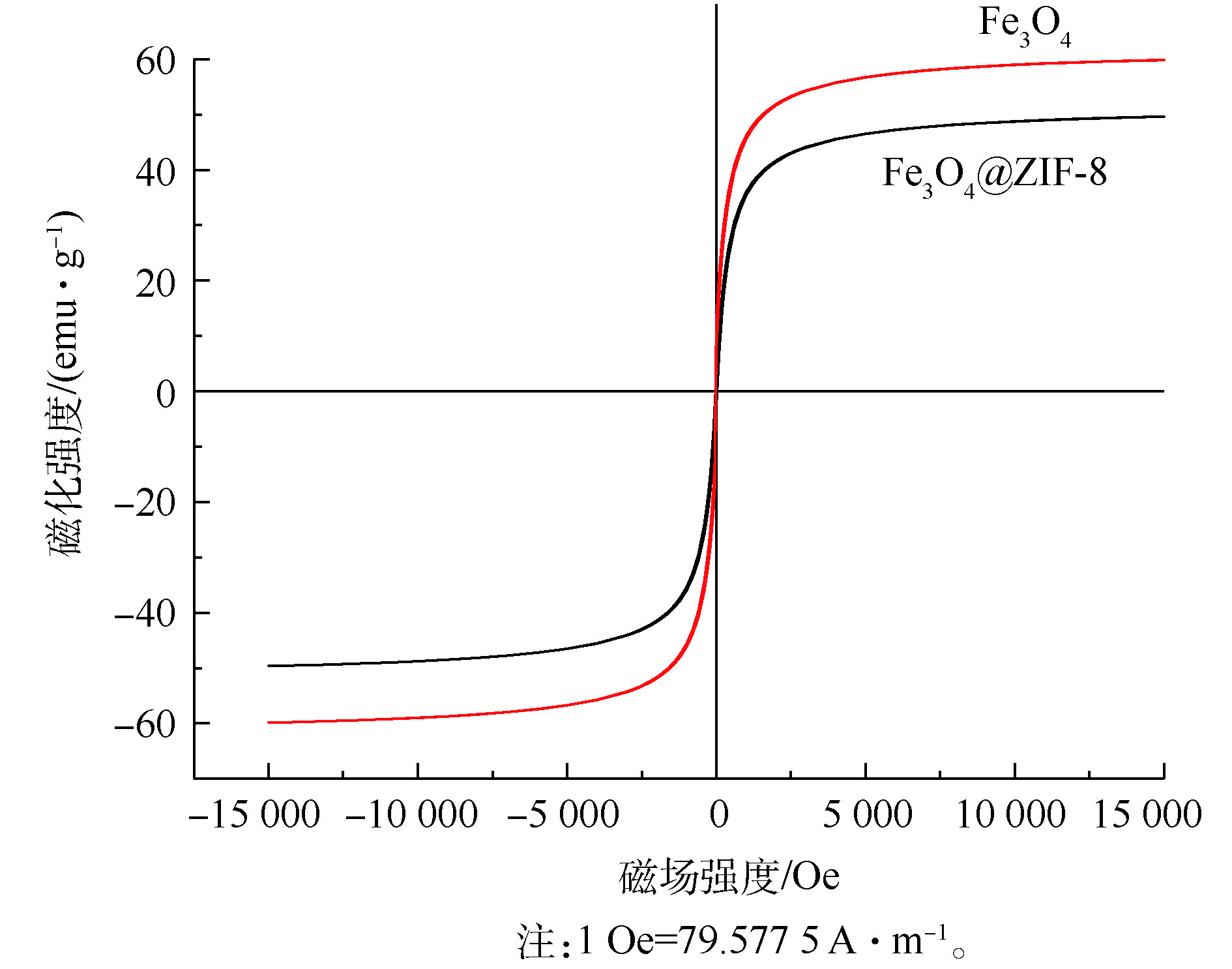
4) VSM分析。如图4所示,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的磁滞回线为过原点的S型曲线,表明Fe3O4@ZIF-8材料是典型的超顺磁性。Fe3O4@ZIF-8的饱和磁化强度为49.68 emu·g−1,由于ZIF-8在壳层的覆盖,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的磁饱和度相对于Fe3O4有所降低,但是Fe3O4@ZIF-8仍然具有优异的磁学性能。
-
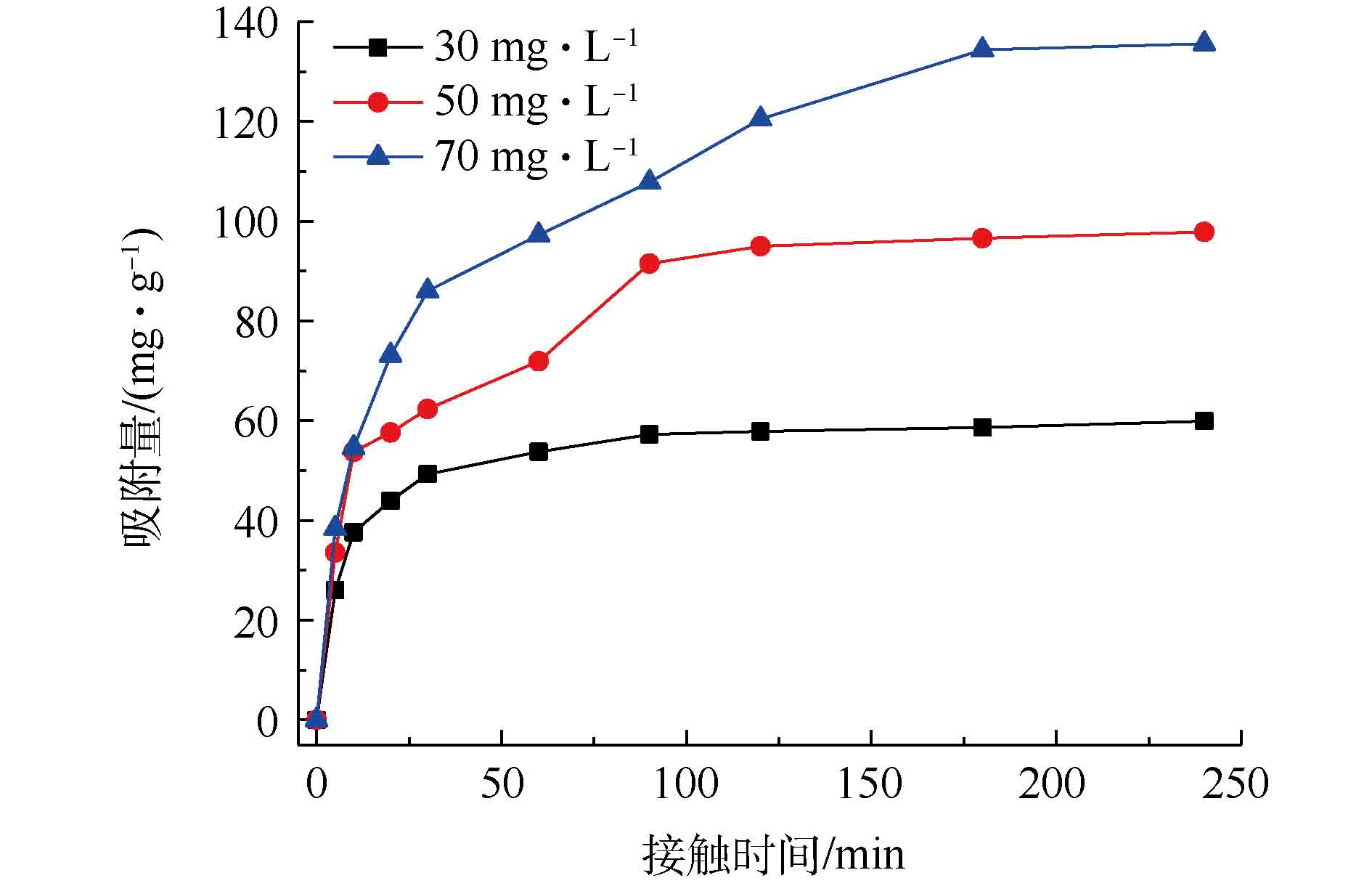
从图5可以看出,在同一浓度下,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的单位吸附容量随着反应时间的增加而增加,在反应的前10 min左右,单位吸附容量已达平衡吸附量的50%。这表明反应最初是快速吸附阶段。当反应时间为180 min时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的单位吸附量逐渐达到平衡。并且在不同的刚果红初始浓度下,随着初始浓度的升高,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的单位吸附量也逐渐升高。当初始浓度由30 mg·L−1升高到70 mg·L−1时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的单位吸附量由60 mg·g−1升高到136 mg·g−1。
-
图6为Fe3O4@ZIF-8投加量对吸附效果的影响,当Fe3O4@ZIF-8投加量为5 mg时,吸附除去率达到68.7%,从5 mg变化到10 mg时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红染料的去除率升高到95.2%。当Fe3O4@ZIF-8投加量大于10 mg,其去除率约为98%,刚果红的吸附去除率升高幅度不大,并且随着Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂投加量的不断增长,其单位吸附容量是一直减少的,这是因为当染料初始浓度和体积恒定时,单位质量的吸附剂吸附染料的量随着吸附剂投加量的增多而减少。并且过多的吸附剂量将导致吸附剂位点的聚集和重叠,增加了扩散的难度。同时,从经济角度来看,过多的吸附剂投加会造成成本的增加。因此,选择Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂的用量为500 mg·L−1。
-
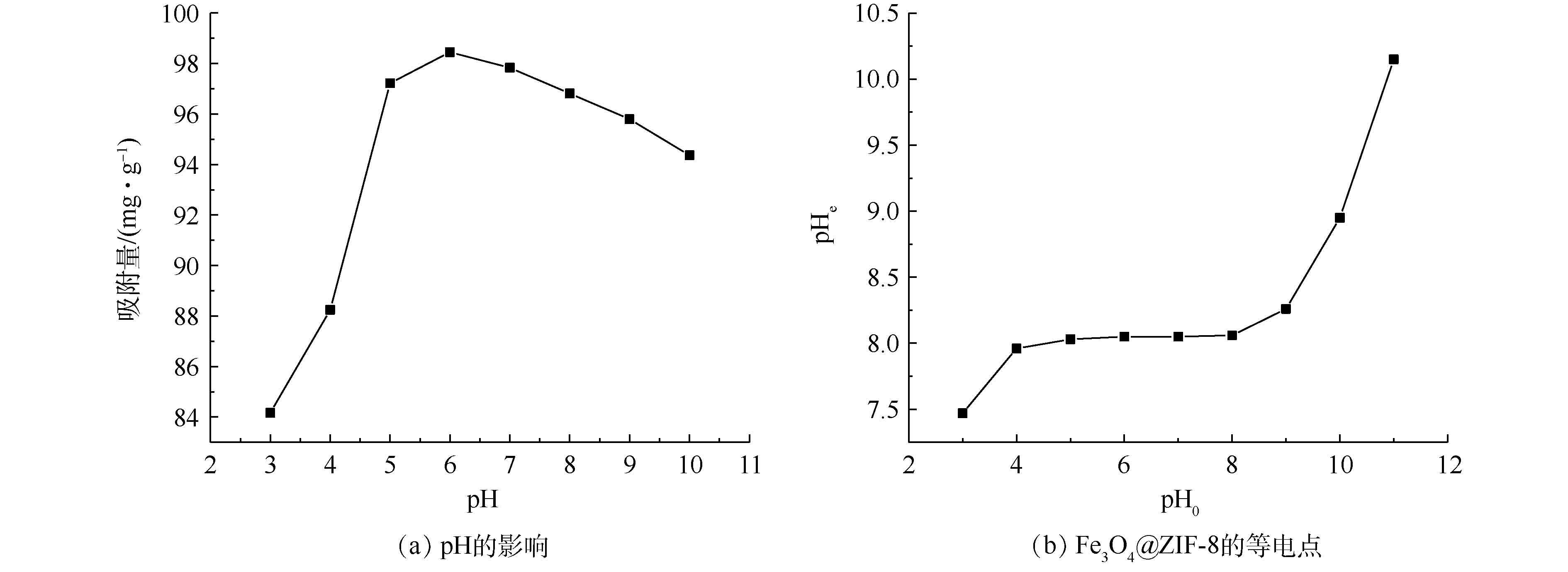
移取20 mL的 50 mg·L−1的刚果红溶液,通过0.05 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液和0.05 mol·L−1的HCl溶液调节pH从3变化到10,Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂的投加量为10 mg,在 25 ℃条件下以180 r·min−1的速度恒温振荡6 h,利用磁铁将吸附剂与溶液分离,然后通过分光光度计测定溶液的分光度,考察初始的pH对Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附效果的影响,实验结果如图7所示。如图7(a)所示,当pH<6.0时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的单位吸附容量随着pH的升高而升高,而且升高幅度很大;在pH=6.0时,单位吸附量达到最大值,这是由于Fe3O4@ZIF-8表面带的正电荷数量增加,与刚果红分子产生静电引力导致吸附量升高;当pH>6.0时,单位吸附量随着pH的升高而减小。这可由图7(b)来解释。实验测得Fe3O4@ZIF-8的等电点为8.37。当pH<8.37时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8表面是带有正电荷的,而刚果红分子带有负电荷,Fe3O4@ZIF-8因为强烈的静电引力而吸附刚果红染料,随后pH的升高,溶液中的OH−逐渐增多并且和阴离子刚果红染料竞争Fe3O4@ZIF-8的吸附位点,从而导致吸附量下降。当pH>8.37时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8表面由原来的正电荷转为负电荷,它与带负电的刚果红分子相互排斥导致其单位吸附容量减少有关。因此,在低pH时,静电引力使刚果红吸附量增加,随着pH的升高,刚果红与Fe3O4@ZIF-8之间产生静电斥力,吸附量逐渐降低。
-
由图8可知,吸附数据的拟合结果是二级动力学模型明显优于一级动力学模型,其线性相关性更高。具体的拟合数据如表1所示,一级动力学模型和二级动力学模型拟合的效果都很好,其中二级动力学模型拟合的可决系数R2均大于0.99,并且在不同初始浓度的刚果红溶液下,通过二级动力学模型计算的Fe3O4@ZIF-8单位吸附容量与通过实验获得的实际单位吸附容量相接近。这与之前报道的ZIF-8吸附刚果红染料的研究[20]一致。因此,偶氮染料刚果红在Fe3O4@ZIF-8上的吸附过程满足二级动力学模型。这表明Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附刚果红的过程属于化学吸附过程。
-
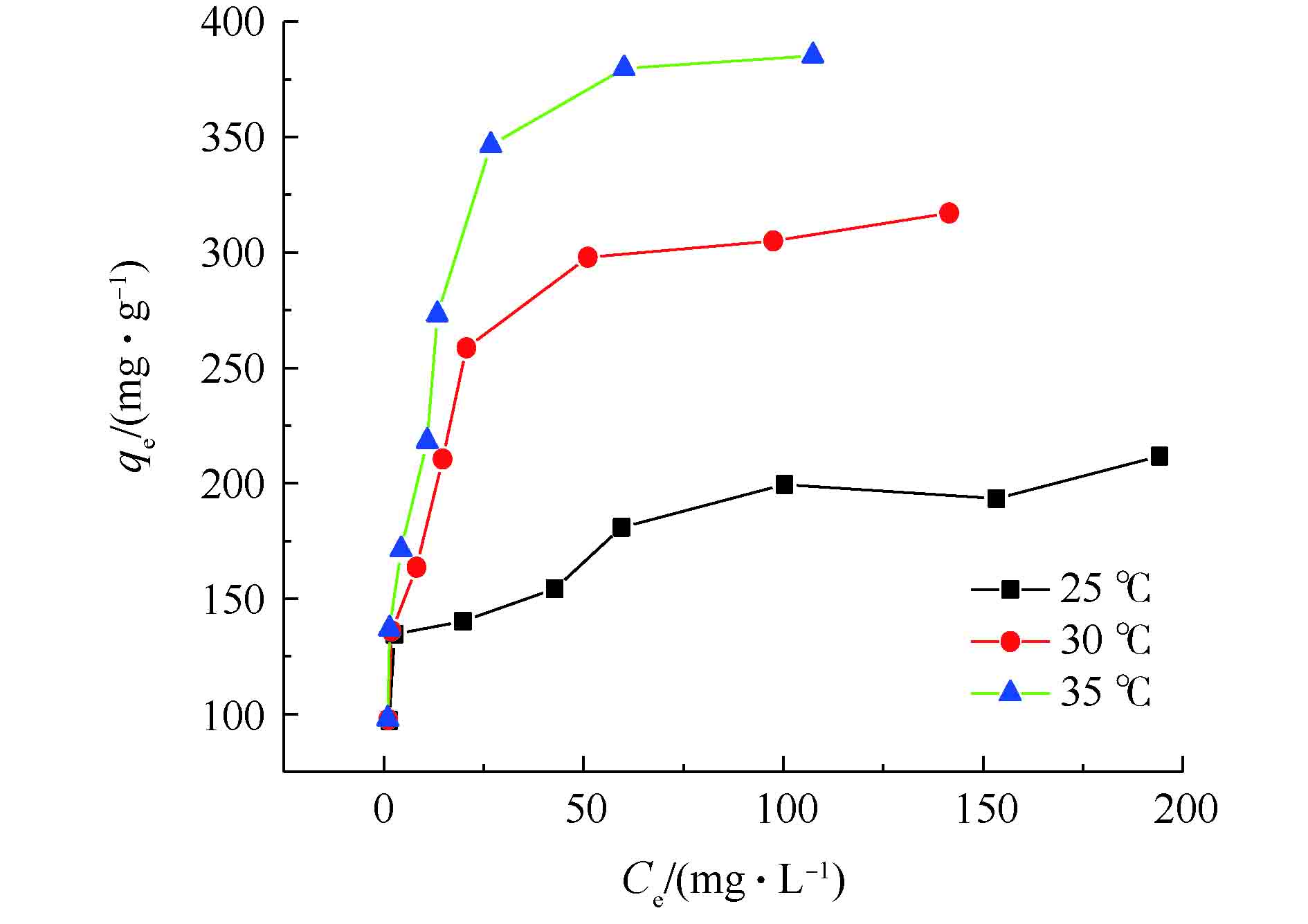
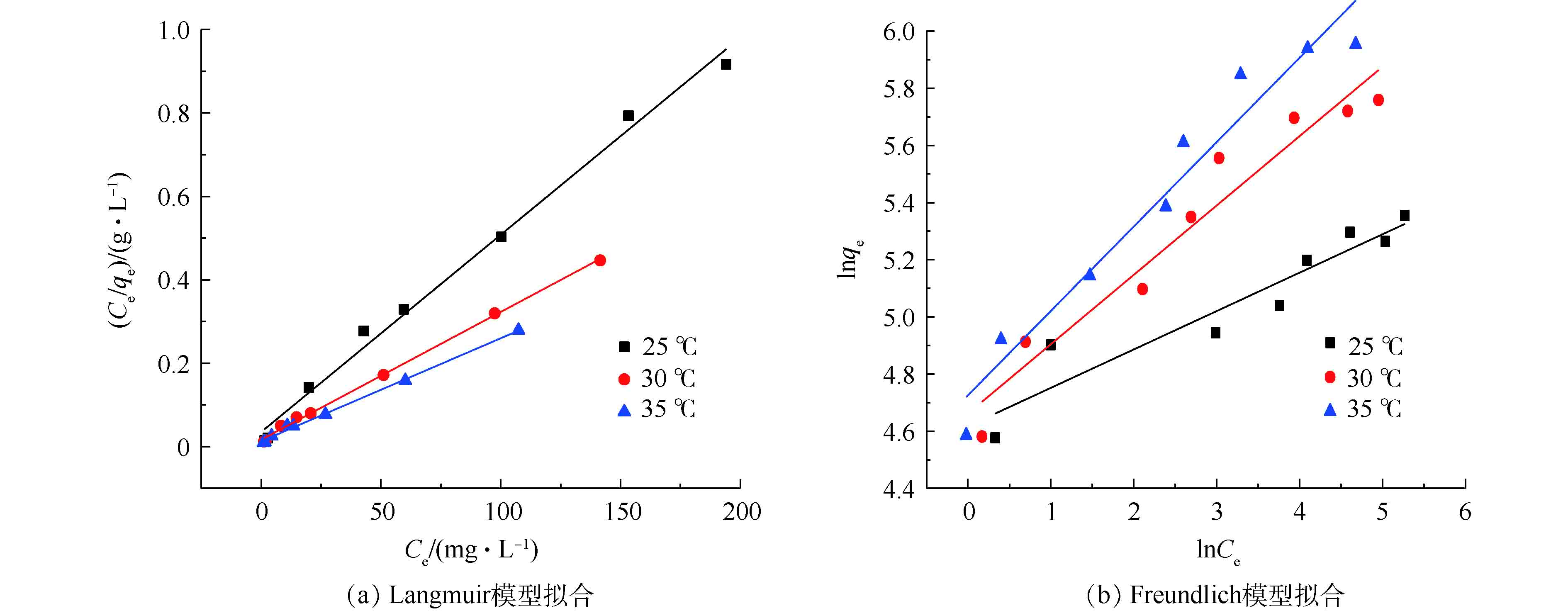
由图9可知,当反应温度升高时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8对偶氮染料刚果红的单位吸附容量不断增加。温度由25 ℃升到35 ℃时,平衡吸附量由211 mg·g−1升高到385 mg·g−1,说明吸附反应为吸热反应。并且随着刚果红初始浓度C0的增加,吸附达到饱和时的平衡浓度Ce增加,平衡吸附量的变化趋势是先快速增加后逐渐变缓。利用Langmuir吸附等温方程和Freundlich吸附等温方程分别线性拟合吸附等温线中的数据,得到等温方程的模拟结果(如图10所示)。吸附等温方程相关参数见表2。由图10可知,Langmuir等温吸附模型具有更高的线性相关性。由表2可知,Langmuir模型计算得到的可决系数更高(R2>0.99),故Fe3O4@ZIF-8的吸附等温线符合Langmuir模型。这表明Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红染料的吸附行为是单层吸附。同时,RL值均在0~1之间,表明吸附容易进行。因此,Langmuir吸附等温线模型适用于Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红的去除。通过Langmuir吸附等温模型计算得到的Fe3O4@ZIF-8最大单位吸附容量为405 mg·g−1。
-
本实验考察了Fe3O4@ZIF-8对染料的选择吸附性能,结果如图11所示。Fe3O4@ZIF-8对于染料的去除率为刚果红>直接蓝86 >甲基橙>亚甲基蓝。这说明Fe3O4@ZIF-8对染料分子的结合能力有差别,并且可能和染料分子的结构和组成有关系。亚甲基蓝是表面带有正电荷的阳离子类型的偶氮染料,在实验条件下,表面带有正电荷的Fe3O4@ZIF-8和亚甲基蓝染料发生静电互斥,造成亚甲基蓝的吸附容量非常低。而其他3种染料都是表面带负电荷的阴离子型偶氮染料,Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红的去除率接近100%,对直接蓝86的去除率也非常高,甲基橙的去除率就非常低。这可能是因为刚果红和直接蓝86染料分子带有2个—SO3基团,而甲基橙带有1个—SO3基团,造成Fe3O4@ZIF-8对染料分子的静电引力的强弱存在差别[21]。同时,直接蓝86染料的分子质量和分子体积大于刚果红染料,造成直接蓝86的去除率低于刚果红染料。因此,Fe3O4@ZIF-8适用于去除阴离子类型的偶氮染料刚果红。
-
在实验中,对吸附剂Fe3O4@ZIF-8的重复利用效果进行了实验验证。由图12可知,当循环次数增加时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红染料的去除率是不断下降的,但是下降的幅度非常小。经过5次循环后,去除率从最开始的98%下降到93%,只下降了5%。显然,Fe3O4@ZIF-8具备非常优异的循环吸附特性,该材料可以重复用于阴离子偶氮染料刚果红废水的去除。
-
1)采用常温机械搅拌法成功将Fe3O4纳米颗粒和金属有机骨架ZIF-8复合,制备出磁性核壳金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8。
2) 将Fe3O4@ZIF-8作为新型吸附材料,系统考察了其对刚果红染料的吸附效果。当刚果红初始浓度为70 mg·L−1时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红的去除率达到98%。实验表明,Fe3O4@ZIF-8的吸附量随着刚果红初始浓度的增加而增加,同时pH对吸附效果有很大的影响,低pH时,Fe3O4@ZIF-8和刚果红之间产生静电吸引;随着pH的不断升高,刚果红与Fe3O4@ZIF-8之间产生静电斥力,吸附量逐渐降低。
3) Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附刚果红的动力学符合二级动力学模型,等温线符合Langmuir模型,Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红的吸附是物理吸附与化学吸附并存,静电引力是其主要的吸附机理。
4) Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附材料展示出优异的循环吸附性能以及对刚果红染料的高效选择性。因此,磁性核壳金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8作为新型吸附材料在去除刚果红染料方面有着巨大的潜力。
磁性金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8的制备及对偶氮染料刚果红的高效吸附
Preparation of magnetic metal organic framework Fe3O4@ZIF-8 and its high efficient adsorption towards azo dye congo red
-
摘要: 采用常温搅拌法,在聚苯乙烯磺酸钠(PSS)处理过的Fe3O4表面诱导生长ZIF-8壳层,成功合成了磁性核壳金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8,并对其吸附去除偶氮染料刚果红的性能进行了探究,考察了刚果红初始浓度和接触时间、Fe3O4@ZIF-8投加量以及pH对刚果红去除的影响。SEM、TEM、XRD、FT-IR及VSM表征结果证明,ZIF-8纳米颗粒已成功负载于Fe3O4表面,形成了典型的核壳结构,并且具有优异的磁学性能。吸附实验结果表明,反应最佳pH为6,吸附剂投加量为500 mg·L−1;当反应时间达到180 min 时,吸附达到平衡。吸附反应的吸附动力学和吸附等温线分析表明,刚果红染料在Fe3O4@ZIF-8上的吸附动力学符合二级动力学方程,吸附等温线符合Langmuir模型。Fe3O4@ZIF-8吸附剂对刚果红具有高效的选择吸附性能并且在循环吸附中展现出良好的循环吸附性能。因此,磁性核壳金属有机骨架Fe3O4@ZIF-8作为吸附剂在去除刚果红染料方面有着广阔的应用前景。
-
关键词:
- 磁性金属有机骨架 /
- Fe3O4@ZIF-8 /
- 刚果红 /
- 吸附动力学
Abstract: The magnetic core-shell metal organic framework Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was successfully synthesized by treating the surface of Fe3O4 with sodium polystyrene sulfonate (PSS) and inducing ZIF-8 shell growth on it under continuous stirring at room temperature. The performance of adsorption and removal of azo dye congo red by Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was investigated. The effects of initial concentration and contact time, Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dosage and pH on congo red removal were investigated. The characterization of SEM, TEM, XRD, FT-IR and VSM showed that ZIF-8 nanoparticles have been successfully loaded on the surface of Fe3O4 to form a typical core-shell structure with excellent magnetic properties. The experimental results showed that the optimum pH was 6, the dosage of adsorbent was 500 mg·L−1, and the adsorption equilibrium was achieved at the reaction time of 180 min. The adsorption kinetics of congo red on Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was in accordance with the second-order kinetic equation, and the adsorption isotherm followed Langmuir model. Fe3O4@ZIF-8 adsorbent had high selective adsorption performance for congo red and presented good reusability in cyclic adsorption. Therefore, magnetic core-shell metal-organic framework Fe3O4@ZIF-8 had broad application prospects in the removal of congo red dyes as adsorbent.-
Key words:
- magnetic metal organic framework /
- Fe3O4@ZIF-8 /
- congo red /
- adsorption kinetics
-
随着工农业生产力水平的提高,国民经济发展步入迅猛增长时期,同时也带来了水体富营养化问题[1]。氨氮的超标是我国水体污染治理首要难题,其原因在于生活污水工业废水排放不达标[2]。“十三五”生态环境保护规划中指出,我国要进一步推广再生水的循环和利用,而污水厂二级生化出水中氨氮含量过高影响了再生水的利用。为使污水厂二级生化出水作为再生水重复利用,需要对其进行深度脱氮处理。
目前,污水厂常用的深度脱氮方法主要有生物法、人工湿地法和离子交换法等[3-5]。由于二级生化出水COD较低,采用生物法进行深度脱氮,需要外加碳源,成本较高[6]。人工湿地法水量处理有限,在规划完善的城镇区域内难以临时建设人工湿地用于二级生化出水的深度处理[7]。离子交换法通过应用对氨氮有较强选择性吸附作用的材料对水中氨氮进行处理。该方法具有性能稳定、可再生性强、原料来源广泛、成本低廉、不受场地的制约等优势,可以进行大规模推广使用[8]。常见的吸附材料有活性炭、蒙脱石、硅胶、氧化铝和沸石等[9]。
沸石凭借着价格低廉、吸附量大、可再生等优点成为广泛应用的脱氮材料[10]。天然沸石是一种以硅氧四面体为骨架的含水铝硅酸盐晶体化合物,其骨架中部分硅被铝替换,导致电荷失衡才有了电荷补偿而吸附的可交换性金属阳离子,使沸石具有离子交换性[11]。沸石去除氨氮的能力与其离子交换性和吸附性有关。天然沸石含有杂质较多,吸附效果不够理想。国内外众多研究人员致力于提升沸石对氨氮的吸附量[6-8]。粉末状沸石比表面积大,吸附效果好,但由于粉体颗粒细小,遇水容易泥化导致难以分离。亟需开发一种颗粒更大、适用于工程填料、且价格低廉的沸石。本研究选用20~40目天然斜发沸石进行改性,通过批次实验探究了其对氨氮的吸附效果和特征,分析了吸附热力学动力学规律,可为这种改性沸石的实际工程应用提供基础数据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 原料与试剂
实验中所选的吸附材料为河南信阳生产的天然斜发沸石,沸石为颗粒状,颜色为砖红色。经超纯水清洗后破碎、烘干、过筛,取20~40目粒径沸石进行实验。
实验主要试剂:酒石酸钾钠、纳氏试剂、NaOH、HCl、NH4Cl、NaCl均为分析纯。实验选用模拟废水以1 000 mg·L-1的氨氮储备液稀释而成,实际废水选自成都安靖镇污水处理站出水。
1.2 实验仪器
UV2600型紫外可见分光光度计(上海精密科学仪器有限公司)、HNY-100D型恒温振荡培养箱(天津市欧诺仪器仪表有限公司)、PHS-3C型数显pH计(上海仪电分极仪器有限公司)、L420型台式低速自动平衡离心机(湘仪离心机仪器有限公司)、YFX12程控马弗炉(上海意丰电炉有限公司)、Frontier型红外光谱仪(PerkinElmer)、EVO18型扫描电子显微镜(ZEISS)、QUANTAX 400型X射线能谱仪(Bruker)、NOVA4200E型比表面积测定仪(美国康塔仪器公司)、Empyrean型X射线衍射仪(荷兰帕纳科公司)。
1.3 实验方法
1)沸石改性实验。预实验考察了酸碱盐及高温改性对沸石吸附效果的影响,研究表明酸碱改性不能提高氨氮的去除率,氯化钠和高温改性可提高沸石对氨氮的去除效果。本研究通过实验确定了最佳氯化钠浓度和焙烧温度。NaCl浓度对吸附效果影响:将10 g预处理后的沸石放入250 mL锥形瓶中,并加入不同浓度的NaCl溶液100 mL,恒温振荡24 h,再经超纯水多次漂洗,最后300 ℃高温焙烧4 h。焙烧温度对吸附效果影响:各取10 g经NaCl(0.8 mol·L-1)溶液改性后沸石在100~800 ℃焙烧4 h。
选取多个250 mL锥形瓶,各加入以上不同条件下改性沸石1.0 g,并加入100 mL氨氮浓度为8 mg·L-1的模拟废水,振荡120 min后测定剩余氨氮浓度。
2)吸附效果影响因素。研究pH对吸附效果的影响,将pH设置在2~11,氨氮浓度为8 mg·L-1;研究投加量对吸附效果的影响,称取不同质量改性前后沸石于250 mL锥形瓶中,氨氮浓度为8 mg·L-1;研究温度对吸附效果的影响,将改性前后的沸石分别放入不同氨氮浓度的模拟废水中,在15、25、35 ℃的不同温度条件下反应;选取实际污水厂出水,测定改性沸石吸附前后的氨氮浓度。
3)吸附动力学和等温曲线实验。吸附动力学:天然及改性沸石各1 g于250 mL锥形瓶中,放入初始浓度为8 mg·L-1的模拟氨氮废水100 mL,分别振荡不同的时间,计算其吸附量。吸附等温曲线:天然及改性沸石各1 g于250 mL锥形瓶中,分别加入100 mL不同浓度的模拟氨氮废水,放入恒温振荡培养箱于25 ℃振荡120 min,计算沸石吸附量。
氨氮吸附量及去除率计算方法
吸附量、去除率依次按式(1)和式(2)计算。
q=(C0−C)Vm (1) η=C0−CC0×100% (2) 式中:q为沸石对溶液中氨氮的吸附量,mg·g-1;
η 为去除率,%;C0为初始Na+浓度,mg·L-1;C为平衡液中Na+浓度,mg·L-1;V为溶液体积,L;m为沸石质量,g。1.4 测定方法
氨氮测定方法选用《纳氏试剂分光光度法》(HJ535-2002)[12]。阳离子测定交换量选用pH计指示电位滴定法。其中测定扫描电镜(SEM)、X射线能谱(EDS)、比表面积(BET)、阳离子交换量(CEC)使用的沸石为20~40目的天然及改性沸石,测定X射线衍射(XRD)和傅里叶光谱(FTIR)选用的是的是经磨碎,过300目筛的沸石。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 沸石改性过程及对氨氮的吸附效果
图1为NaCl浓度对改性沸石去除氨氮的影响结果。由图1可知,随着NaCl浓度升高,氨氮的去除率也随之升高。这与林海等[13]的研究结果相似。产生该现象的原因是溶液中Na+与沸石中原有的半径较大的阳离子(Ca2+和Mg2+等)发生了置换。原有的阳离子半径较大,置换后导致沸石的孔径增大,进而增强沸石去除氨氮的能力[8]。由于Na+与
NH+4 的离子半径相近,改性沸石更易与离子交换NH+4 离子交换:Z−Na++NH+4←→Na++Z−NH+4 (3) 图2为温度对改性沸石去除氨氮的影响结果。由图2可知,在温度比较低的情况下,温度升高可导致去除率升高,在300 ℃时,去除效果最佳,但温度超过300 ℃后,氨氮的去除率明显下降。其原因是:高温焙烧可以清理内部孔道,去除杂质,增强氨氮去除率[14],而过高的温度的焙烧会使沸石产生过热效应,使沸石内部结合水去除,导致内部孔道受热膨胀,破坏原有的孔道结构,增大了孔径,使之大于
NH+4 的直径,此时沸石吸附氨氮的能力开始减弱。综上所述,本研究确定氯化钠联合高温改性沸石的最佳条件为氯化钠浓度为0.8 mol·L-1、焙烧温度为300 ℃。
2.2 氨氮吸附性能的影响因素
1)pH对吸附效果的影响。图3为pH对氨氮吸附量和去除率的影响结果。由于酸性条件下H+浓度较高,H+半径小于
NH+4 离子的半径,抢占了沸石上与NH+4 的结合位点。在pH为4~10时稳定,然后随着pH的进一步升高迅速下降。碱性环境中对氨吸附效果下降的原因是,碱性环境中以NH+4 形式存在的游离态氨氮会与OH-生成溶解态的NH3,不利于NH+4 与沸石内的阳离子发生离子交换反应,所以氨氮去除率达到峰值后随着pH升高开始下降;实际污水处理过程中pH通常为6~8,改性沸石的吸附特性满足一般废水的要求。2)沸石投加量对吸附效果的影响。图4为沸石投加量对吸附量和去除率的影响结果。由图4可知,氨氮去除率随沸石投加量增大呈先升高后缓慢下降的趋势,这与ZHENG等[15]研究结果相一致,由于吸附点位叠加导致吸附面积减少。而氨氮的去除在达到最大值后逐渐降低,这是由于在投加量较低时,颗粒与颗粒之间的间距较大,每个颗粒之间都会有较多的
NH+4 聚集,有利于改性沸石与NH+4 进行离子交换,因此,改性沸石的投加量增加会提供更多的吸附位点来吸附氨氮,去除率也随之增加。本研究的沸石最佳投加量为10 g·L-1,此时氨氮的去除率为70.82%,远远高于天然沸石对氨氮的去除率(45.8%)。3)温度对吸附效果的影响。图5为不同温度下氨氮浓度对天然及改性沸石吸附量影响。当氨氮浓度小于50 mg·L-1时,氨氮的吸附量受到温度的影响较小。浓度大于50 mg·L-1时,温度对两类沸石吸附量影响较大,这与巩师俞[16]的研究结论类似。反应温度为15 ℃时的吸附效果与25 ℃和35 ℃的吸附效果相比较差,说明温度升高有利于提高沸石对水中氨氮的去除率。
2.4 改性沸石处理废水的实际应用
实际水样来自于四川省成都市污水处理厂二级生化出水,锦江和镜湖,河水和湖水分别经过絮凝沉淀处理的到氨氮的初始浓度,从表1中可以看出,实际污水厂出水浓度较低,为4.82 mg·L-1,满足《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)中规定氨氮一级A标准,二级生化出水经改性沸石分子筛的最佳条件静态吸附处理后浓度降低至0.91 mg·L-1,满足《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002)中规定IV类排放标准。满足国内大部分地区中水回用的标准,且改性沸石对低浓度的氨氮废水处理效果更好。经处理的河水、湖水样品中氨氮的水质由IV类提高到II类标准,但湖泊与河流对氨氮去除率相对略低,可能是由于河水和湖水中污染成分较复杂,矿物质含量较多,抢占了沸石分子筛中与
NH+4 的结合的孔道或空穴,降低了沸石对氨氮的吸附能力。综上可以看出改性沸石应用二级生化污水和湖泊河流水样中都有较好的效果。表 1 实际应用案例中氨氮浓度的变化Table 1. Changes of ammonia nitrogen in practical application cases水样种类 pH 初始氨氮浓度/(mg·L-1) 出水氨氮浓度/(mg·L-1) 去除率/% 污水厂二级生化出水 7.36 4.82 0.91 81.1 锦江 6.52 1.26 0.36 71.4 镜湖 7.84 1.92 0.48 75.0 2.5 改性沸石的形貌及结构表征
1)沸石形貌表征。为了进一步探讨NaCl高温改性对沸石表面形貌和元素组成的影响,分别对天然及改性沸石进行了扫描电镜(SEM)和X射线能谱(EDS)分析,结果见图6。由图6可知,沸石改性后有较大变化,天然沸石表面疏松,孔道较少,改性后的沸石表面更加粗糙,孔道增多,这说明了NaCl高温改性可以去除沸石内的水分、碳酸盐和有机物等杂质,拓宽了沸石内部孔道,增加了氨氮的内扩散速率,使沸石去除氨氮的能力大大提高。
从能谱图中可以看出,天然沸石中含有铁元素,所以其颜色呈砖红色,改性后铁元素被交换,导致沸石表面颜色变暗,且沸石改性前后元素的含量发生了一定的变化。无论沸石改性前后主要构成物质是Al2O3、SiO2碱金属离子,改性后沸石的Na+含量增多。由于改性后的沸石中Na+交换了原沸石中Fe3+、Mg2+等大半径的阳离子,沸石中的内扩散速率增大,导致沸石的去除氨氮的能力增强。高温焙烧可以去除沸石内部的水分子、碳酸盐、少量的有机物。
2)比表面积和阳离子交换量测定。表2为改性前后沸石的比表面积的变化以及阳离子交换量的变化。从表2可知,改性后的沸石拥有更大的比表面积、孔容和孔径,这与扫描电镜所显示的特征一致。天然沸石改性前后阳离子交换量提升约20%,这主要来源于NaCl改性作用,Na+交换了半径较大的金属阳离子,拓宽了沸石内部孔径,增加了沸石的阳离子交换量[17]。
表 2 改性前后沸石的比表面积和阳离子交换量Table 2. BET and CEC of zeolite before and after modification沸石种类 比表面积/(m2·g-1) 孔容/(cm3·g-1) 孔径/nm 阳离子交换量/(mmol·g-1) 天然沸石 22.47 0.041 13.16 2.76 改性沸石 31.62 0.063 18.67 3.31 3)XRD表征。图7为天然沸石及改性沸石的X射线衍射图。参照XRD数据库可知,该沸石由72%的天然斜发沸石组成,少部分是丝光沸石和其他黏土矿物,石英和长石占比小于1.00%。由图7可知,改性前后沸石的特征峰数量和位置没有变化,说明沸石的晶体结构不会发生改变,这与刘思远等[18]的研究结论一致。但是改性后的沸石主衍射峰的强度都要低于天然沸石,说明改性后结晶度略微下降。这是由于沸石经过高温焙烧后,发生一定程度的失水,使其结晶度降低。过高温度的焙烧会破坏沸石的内部晶体结构,降低沸石对氨氮的吸附能力。改性过程使其内部结晶化降低,晶格缺陷度增加,表面活性增加,增强了其对氨氮的去除能力。
4)FT-IR表征。有研究[19]表明,材料表面的结构可以通过沸石骨架振动光谱和羟基吸收峰来表征,且这些官能团对材料的性能影响较大。图8为300 ℃氯化钠改性沸石、天然沸石、吸附NH4Cl后的改性沸石、吸附污水厂出水后的改性沸石的红外光谱。由图8可以看出,天然沸石和300 ℃氯化钠改性沸石在结构上并没有较大差异,光谱图的趋势基本一致,3 600~3 700 cm-1处的宽吸收峰是由于羟基的收缩振动引起的[20]。天然沸石在2 924 cm-1处出现较小的吸收峰,是由于天然沸石孔道内含有少量受热易挥发的有机物,在此处产生了C—H伸缩振动,这与杨淑佳[21]的研究结论一致。而吸附NH4Cl和污水厂出水后的沸石在此处的伸缩振动峰从1 648 cm-1处偏移至1 635 cm-1,这说明吸附的氨氮使该处的吸收峰发生偏移,原因是吸附后结晶水或吸附水的含量增多;在1 050 cm-1附近的Si—O—Si不对称伸缩振动峰在吸附氨氮后和表面的—NH2弯曲三原子基团不对称收缩峰重叠形成较突出的吸收峰,这与刘国栋等[22]的研究结果一致。在430~800 cm-1处的较宽峰是由于沸石四面体骨架T—O(T为Si或Al)对称伸缩振动和T—O弯曲振动产生的吸收峰,吸附后的沸石在这区间峰强度变化较为明显,说明沸石吸附氨氮后脱铝效果明显,硅铝比升高。吸附污水厂出水后的沸石在617 cm-1处T—O对称伸缩振动峰消失是由于污水厂实际出水中含有SO42-,两者之间相互叠加消除了其吸收峰[23]。
2.6 吸附动力学分析
为探究吸附动力学机理,分别采用拟一级和拟二级反应动力学模型对结果进行拟合,实验结果如图9所示,动力学参数见表3。结果表明拟二级动力学拟合性和拟一级相比更好,这说明沸石去除水中氨氮的过程更符合拟二级动力学过程。因为沸石在水中吸附氨氮过程呈现“快速吸附、缓慢平衡”的现象[24]。吸附刚开始时,溶液中氨氮浓度较大,推动力强,所以吸附速率较快。随着反应的进行,溶液中的氨氮浓度减少,传质推动力逐渐降低,吸附速率变慢,达到了缓慢平衡的过程。
表 3 动力学拟合模型参数Table 3. Kinetic parameters沸石种类 拟一级动力学参数 拟二级动力学参数 qe1/(mg·g-1) k1 R2 qe2/(mg·g-1) k2 R2 天然沸石 0.352 0.056 0.950 0.352 0.187 0.985 改性沸石 0.559 0.036 0.986 0.560 0.063 0.992 2.7 吸附热力学分析
图10为Langmuir和Freundhlich方程对实验数据进行拟合的结果,拟合参数见表4,改性沸石在不同温度下都较好的满足Langmuir等温曲线。说明氨氮在沸石表面吸附更倾向于单分子层吸附,表现出沸石对氨氮吸附为化学吸附,即离子交换性。此时沸石对氨氮的理论最大吸附量为5.98 mg·g-1。
表 4 等温吸附曲线常数Table 4. Constants of adsorption isotherms改性温度/℃ Langmuir Freundhlich qm/(mg·g-1) KL/(L·mg-1) R2 KF 1/n R2 15 4.22 0.03 0.987 3 0.81 0.23 0.851 5 25 5.47 0.05 0.998 4 1.24 0.25 0.839 1 35 5.98 0.05 0.977 9 1.27 0.27 0.847 4 如表5所示,在不同沸石对氨氮吸附过程均都满足Langmuir模型。在单一污染条件下改性沸石对氨氮的最大吸附量为5.98 mg·g-1,远远高于许育新等[25]测得的天然缙云斜发沸石的对氨氮的最大吸附量(4.05 mg·g-1),说明高温联合氯化钠改性能大幅度提高沸石对氨氮的吸附能力。而本研究的高温联合氯化钠改性沸石吸附量较大,与铝锰负载改性方法相比,具有成本低廉、制备方便、不产生二次污染的优点。
表 5 不同沸石对水中氨氮的吸附效果Table 5. Adsorption of ammonia nitrogen from wastewater by various zeolites2.8 吸附热力学分析
表6为对天然及改性沸石的热力学方程拟合结果。由表6可见,不同温度下的ΔG均小于0 kJ·mol-1,且温度越高,ΔG越小,说明该反应为自发吸热过程,高温更利于该过程。吸收焓变ΔH大于0 kJ·mol-1,说明沸石吸附氨氮的过程是吸热过程,此结论与吸附等温线结论相吻合。吸附熵变ΔS大于0 kJ·mol-1,说明吸附前后体系无序性变大。因此,沸石吸附水中氨氮为自发、吸热、熵增过程。该结论与张亚峰等[27]的研究结果一致。
表 6 热力学参数Table 6. Thermodynamic parameters沸石种类 C0/(mg·L-1) △H/(kJ·mol-1) △S/(J·mol-1) △G/(kJ·mol-1) 15 ℃ 25 ℃ 35 ℃ 天然沸石 90 8.83 57.39 -7.91 -8.70 -9.05 改性沸石 90 18.9 97.60 -9.48 -10.84 -11.41 3. 结论
1)氯化钠联合高温改性能够显著提升沸石对氨氮的吸附性能。本研究得到的最佳改性条件为:氯化钠浓度为0.8 mol·L-1,焙烧温度为300 ℃,此时改性沸石的饱和吸附量可达5.94 mg·L-1。此外,改性沸石对实际水样中氨氮的去除效果较好。
2)通过SEM、EDS、XRD、FT-IR等分析结果表明,沸石表面呈现出大量的孔道,比表面积较大,故可以为氨氮的吸附提供结合位点。NaCl改性沸石过程中Na+交换了天然沸石中Fe3+、Mg2+等大半径的阳离子,增强了沸石对氨氮的去除能力。
3)拟二级动力学模型和Langmuir模型对氨氮的吸附过程具有更好的拟合度,在35 ℃时,由Langmuir模型拟合得到氨氮最大吸附量为5.98 mg·L-1。
4)吸附热力学计算结果表明,沸石对氨氮的吸附过程是自发的吸热过程,沸石对氨氮的吸附能力随着温度的升高而增强。
-
表 1 Fe3O4@ZIF-8对刚果红染料的动力学拟合参数
Table 1. Parameters of kinetic models for CR onto Fe3O4@ZIF-8
初始浓度/(mg·L−1) qe, exp/(mg·g−1) 一级动力学模型 二级动力学模型 qe, cal/(mg·g−1) K1 R2 qe, cal/(mg·g−1) K2 R2 30 60 26 0.021 0.947 61 0.002 25 0.999 50 98 71 0.024 0.978 104 0.000 63 0.995 70 136 124 0.023 0.963 145 0.000 32 0.993 注:qe,exp和qe,cal为平衡吸附量实验值和拟合值。 表 2 Langmuir和Freundlich常数及可决系数
Table 2. Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption constants and correlation coefficients
温度/℃ Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 qmax /(mg·g−1) b/(L·mg−1) RL R2 Kf /(L·g−1) n R2 25 211 0.135 0.024 0.992 101.21 7.44 0.881 30 327 0.184 0.018 0.998 105.81 4.12 0.934 35 405 0.192 0.017 0.996 112.78 3.39 0.944 -
[1] 龚正君, 周文波, 陈钰. 花生壳活性炭对水中荧光素钠的吸附及动力学[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(1): 221-225. [2] 叶琳. 改性豆渣对污水中染料物质的吸附研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2014. [3] GREENWALD M J, REDDING A M, CANNON F S. A rapid kinetic dye test to predict the adsorption of 2-methylisoborneol onto granular activated carbons and to identify the influence of pore volume distributions[J]. Water Research, 2015, 68: 784-792. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.022 [4] LIU F, GUO Z, LING H, et al. Effect of pore structure on the adsorption of aqueous dyes to ordered mesoporous carbons[J]. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 227: 104-111. [5] YANG R, LI H J, HUANG M, et al. A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment[J]. Water Research, 2016, 95: 59-89. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.02.068 [6] CHAMPNESS N R, SCHRODER M. Extended networks formed by coordination polymers in the solid state[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 1998, 3(4): 419-424. [7] LU W G, WEI Z W, GU Z Y, et al. Tuning the structure and function of metal-organic frameworks via linker design[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(16): 5561-5593. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00003J [8] EVANS J D, SUMBY C J, DOONAN C J. Post-synthetic metalation of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(16): 5933-5951. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00076E [9] LEE J Y, FARHA O K, ROBERTS J, et al. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1450-1459. doi: 10.1039/b807080f [10] KRENO L E, KIRSTY L, FARHA O K, et al. Metal-organic framework materials as chemical sensors[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2011, 112(2): 1105-1125. [11] LI J R, JULIAN S, ZHOU H C. Metal-organic frameworks for separations[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(2): 869-932. doi: 10.1021/cr200190s [12] 张琪颖. 基于金属有机骨架材料的高效吸附剂研发[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2016. [13] 孙杨, 陆广明, 唐祝兴. 磁性纳米材料Fe3O4@MOF-5的制备及其对刚果红吸附性能的研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2017, 46(11): 12-14. [14] 张通. ZIF-8包覆的核-壳结构材料的合成及其应用[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015. [15] ZHOU L C, MENG X G, FU J W, et al. Highly efficient adsorption of chlorophenols onto chemically modified chitosan[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 292(1): 735-741. [16] MOGHADDAM H K, PAKIZEH M. Experimental study on mercury ions removal from aqueous solution by MnO2 /CNTs nanocomposite adsorbent[J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 21: 221-229. [17] LORENC-GRABOWSKA E, RUTKOWSKI P. High basicity adsorbents from solid residue of cellulose and synthetic polymer co-pyrolysis for phenol removal: Kinetics and mechanism[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 316(1): 435-442. [18] YANG G, CHEN H L, QIN H D, et al. Amination of activated carbon for enhancing phenol adsorption: Effect of nitrogen-containing functional groups[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 293(3): 299-305. [19] LI B J, CAO H Q, SHAO J, et al. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals@graphene composites for energy storage devices[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(13): 5069-5075. doi: 10.1039/c0jm03717f [20] 顾兵. 沸石咪唑酯骨架结构材料(ZIF-8)对染料废水中刚果红的吸附效果和特征分析研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. [21] 张湛杭, 张景丽, 刘建明. 金属有机骨架ZIF-67对刚果红的吸附性研究[J]. 天津城建大学学报, 2017, 23(4): 267-272. 期刊类型引用(14)
1. 白文广,徐金兰. 生物改性沸石层抑制沉积物氮污染释放实验研究. 水处理技术. 2025(03): 37-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 卢亚丽,殷智威,王海舟,吴代赦. 分子筛对养猪废水中氨氮的吸附及再生研究. 水处理技术. 2025(03): 91-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张航,崔建国,李红艳. 改性沸石/活性炭复合材料的制备及深度处理含氮废水的研究. 应用化工. 2025(02): 282-286 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈元天,曾贵禄,李德晓,张龙斌,高剑雄,吕树光. 改性沸石/聚合氯化铝造粒复合材料对水中氨氮和磷的吸附性能研究. 水处理技术. 2024(04): 32-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨光,李佩钢,王若凡,刘雨欣,田开栋,谢微,唐悦. 黄河兰州段河岸带沉积物氨氮吸附特征及影响因素. 绿色科技. 2024(18): 170-179 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈媛媛,王宁,李玉成,李舜尧,李珊珊. 电化学法处理蚀刻液中高氨氮废水研究. 云南大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 171-179 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 罗志伟,刘健峰,王昌梅,赵兴玲,吴凯,尹芳,梁承月,张无敌. 基于氨氮低吸附的折流式沉降滤过装置去除沼液中悬浮物研究. 农业现代化研究. 2022(02): 360-368 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王迪迪,尹志轩,乔春蕾,何德明,刘长青. 河道底泥/粉煤灰复合吸附剂的制备条件优化及吸附过程影响因素研究. 水处理技术. 2022(07): 83-87+97 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 唐玉朝,陈徐庆,薛莉娉,伍昌年,王坤,王品之,黄显怀,傅前君,刘俊,宋永莲. 两段SBR串联工艺处理低C/N城市污水的效率研究. 环境科学与技术. 2022(05): 15-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘俊. 不同改性吸附剂去除废水中氨氮的研究进展. 节能. 2022(07): 93-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 武旭源,郑晓英,郝瑞霞,王鸿博,孙彤,李嘉雯,李鹏. 天然沸石结构对合成分子筛吸附脱氮性能影响. 中国环境科学. 2021(07): 3193-3200 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 喻岚,徐冰峰,庹婧艺,王雪颖,郭露遥,赵顺宇. 改性沸石处理氨氮废水的研究进展. 工业安全与环保. 2021(09): 88-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 魏超,陈涛,江桥,王姝,邱伟建,成小英. 黑臭河道中聚乙烯醇/海藻酸钠固定微米沸石粉去除氨氮. 环境科学. 2021(12): 5884-5895 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 曹蕾,张龙,张效华,白永刚,蒋永伟,王瑶瑶,王皓. 新型复合材料处理氮磷废水的性能研究. 环境科学学报. 2020(11): 3950-3957 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(30)
-







 下载:
下载: