-
随着经济发展和城市化进程的加快,我国城镇生活污水排放量急剧增加。截至2017年底,全国城镇生活污水排放总量为600×108 t,并以6%的速度逐年递增[1]。剩余污泥是污水处理的副产物,产量大且对环境造成二次污染。国家 “十三五”规划明确提出,到2020年底,地级及以上城市污泥无害化处置率达到90%以上[2],这对污泥处理处置将是巨大挑战。剩余污泥中含有大量水分(含水率约为99.7%~99.1%),脱水是污泥减量化、无害化、资源化最关键的一步[3]。目前,城镇污水处理厂污泥脱水工艺主要为简单的机械脱水与化学絮凝工艺,很难满足目前的脱水要求。经大量研究发现,污泥絮体结构和水分存在形式复杂,其中含有部分较难去除的结合水[4],这成为污泥脱水的瓶颈问题。
近10多年来,经过大量的实践证明,破坏污泥絮体结构使其胞内物质和部分结合水释放,可有效缓解污泥脱水困难的问题[5]。高级氧化技术由于其二次污染小、反应快、易操作等特点逐渐成为污泥调理脱水性能的研究热点。过硫酸盐氧化法属于高级氧化技术的一种方法,已在剩余污泥脱水处理方面取得诸多应用,有研究[6-8]表明,过硫酸盐调理剩余污泥可改善污泥脱水性能。宋秀兰等[9]发现Fe2+活化过硫酸盐可提高污泥的脱水效果。ZHEN等[10]指出硫酸根自由基的强氧化性可对污泥絮体中EPS和微生物细胞产生显著的破坏作用。徐文迪等[11]研究了Fe2+与
S2O2−8 投加比对污泥脱水效果的影响,发现Fe2+和S2O2−8 的最佳投加摩尔比为1:1。这些研究均表明Fe2+活化过硫酸盐调理可提高污泥的脱水效果。然而,由于污泥的特性及脱水过程的复杂性,过硫酸盐改善污泥脱水性能及其相关机理的认识仍不全面。基于此,本研究采用亚铁离子(Fe2+)活化过硫酸钾,分析了过硫酸钾、硫酸亚铁、反应时间和pH对污泥脱水效果的影响,并探究了不同过硫酸钾投加量条件下污泥中胞外聚合物(EPS,主要包括蛋白质和多糖)和调理污泥上清液中SCOD的分布状况;探讨了过硫酸钾调理污泥的机理,为污泥的强化脱水及资源化处理提供技术参考。
-
剩余污泥取自西安市第三污水处理厂浓缩池,该水厂的处理规模为5×104 m3·d−1,采用改良型底曝氧化沟与滤布滤池组合工艺。剩余污泥基本特征:含水率 97.3%,pH 8.01~8.07,总固体含量 26.2 g·L−1,COD 4 738.7 mg·L−1,总氮 8.8 mg·L−1,总磷 18.7 mg·L−1。
-
六轴联合搅拌器(JJ-4,常州智博瑞仪器制造有限公司);紫外-可见分光光度计(DR5000,美国哈希公司);电子天平(CP213,奥豪斯仪器有限公司);污泥比阻测定装置(TG-250,上海同广科教仪器有限公司)。
过硫酸钾(K2S2O8)、七水合硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、蒽酮(C14H10O)、浓硫酸(H2SO4)、重铬酸钾(K2Cr2O7)均为分析纯。
-
采用布氏漏斗法[12]测定污泥比阻;采用重量法[13]测定污泥含水率;采用碱性过硫酸钾高压消解紫外分光光度法测定总氮[14];采用过硫酸钾消解钼酸铵分光光度法测定总磷[15];采用修正的Folin-Lowry法[16]和蒽酮-硫酸法[17]测定污泥调理前后EPS中蛋白质和多糖的浓度变化;采用重铬酸钾法[18]测定SCOD浓度变化。
EPS是微生物在一定条件下分泌于体外的一些高分子聚合物[19],按分布形式可分为溶解型EPS(SL-EPS)、松散型EPS(LB-EPS)和紧密型EPS(TB-EPS)[20]。EPS的提取采用热提取法[21]。
利用SPSS 24.0软件进行Pearson相关性分析,研究过硫酸钾不同投加量时与调理污泥上清液中SCOD含量的相关关系。P<0.001表示数据间极显著相关,P<0.01表示数据间显著相关,P<0.05表示数据间相关。
-
取100 mL实验原泥于烧杯中,投加药剂后,置于六联搅拌器上进行污泥脱水实验研究。本研究中实验参数的选择参照徐鑫[22]和宋秀兰等[9]的研究,具体实验参数如表1所示。
-
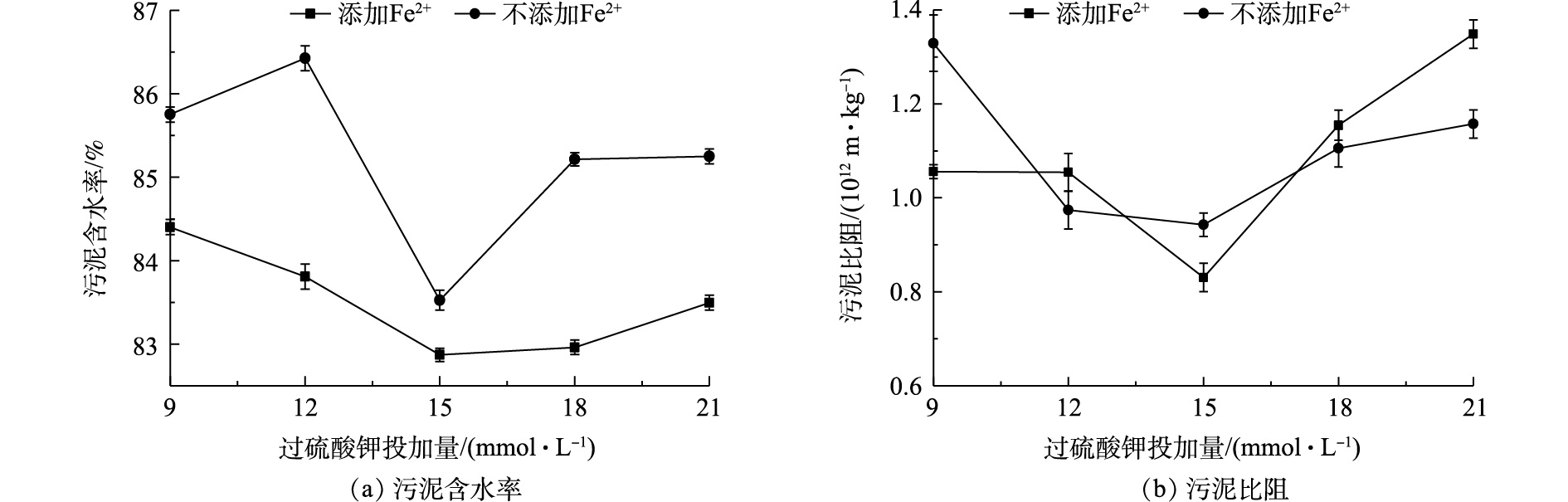
过硫酸钾投加量和Fe2+对污泥含水率和污泥比阻的影响结果如图1所示。由图1可以看出,随着过硫酸钾投加量的增加,污泥比阻和污泥含水率均表现为先降低后升高的趋势;Fe2+的投加提高了过硫酸钾调理剩余污泥脱水效果;与未投加亚铁离子和过硫酸钾的污泥含水率(97.30%)和污泥比阻(4.51×1012 m·kg−1)相比,过硫酸钾显著降低了污泥含水率和污泥比阻,从而改善了污泥的脱水效果。
在投加Fe2+离子时,过硫酸钾投加量从9 mmol·L−1增加到15 mmol·L−1,污泥含水率由84.36%降低到82.87%,污泥比阻由1.06×1012 m·kg−1降低到0.83 ×1012 m·kg−1;而过硫酸钾投加量从15 mmol·L−1增加到21 mmol·L−1,污泥含水率和污泥比阻均呈上升的趋势。这说明过硫酸钾投加量为15 mmol·L−1时,污泥脱水效果最佳。未投加Fe2+离子的污泥含水率和污泥比阻变化趋势与投加Fe2+基本一致,且相同条件下污泥含水率和污泥比阻值显著高于投加Fe2+的结果。这说明Fe2+离子投加对污泥脱水起到促进作用。在投加Fe2+离子时,对不同过硫酸钾投加量下污泥含水率在置信区间为95%条件下进行显著性分析,得P=0.012<0.05,表明了不同条件下含水率间有显著性差异。常温下,如式(1)所示,Fe2+能够活化
S2O2−8 产生SO−4⋅ ,SO−4⋅ 破坏污泥絮体结构,促进污泥脱水[23];然而当pH为3~5时,如式(2)所示,过量的Fe2+会与SO−4⋅ 发生自我消除反应,消耗SO−4⋅ 生成SO2−4 [24]。降低了活化基团SO−4 ·的含量,从而降低污泥脱水效果。 -
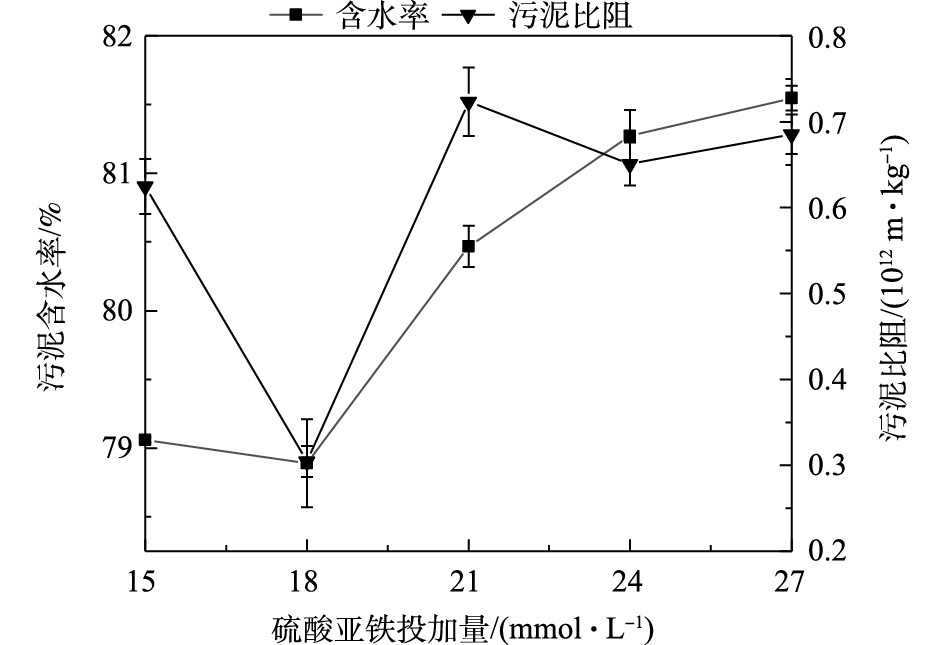
不同硫酸亚铁投加量条件下污泥含水率和污泥比阻的分布结果见图2。由图2可见,硫酸亚铁投加量对污泥含水率及比阻有较大的影响。随着硫酸亚铁投加量的增加,污泥含水率和污泥比阻呈现先降低后增加的趋势,在投加量为18 mmol·L−1时污泥含水率和污泥比阻最低,污泥脱水效果最佳。硫酸亚铁投加量由15 mmol·L−1增加到18 mmol·L−1时,含水率和污泥比阻值分别由79.06%和0.62×1012 m·kg−1降低至78.89%和0.30×1012 m·kg−1;当硫酸亚铁由18 mmol·L−1增加至27 mmol·L−1时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻逐渐增加,污泥脱水效果变差。Fe2+与
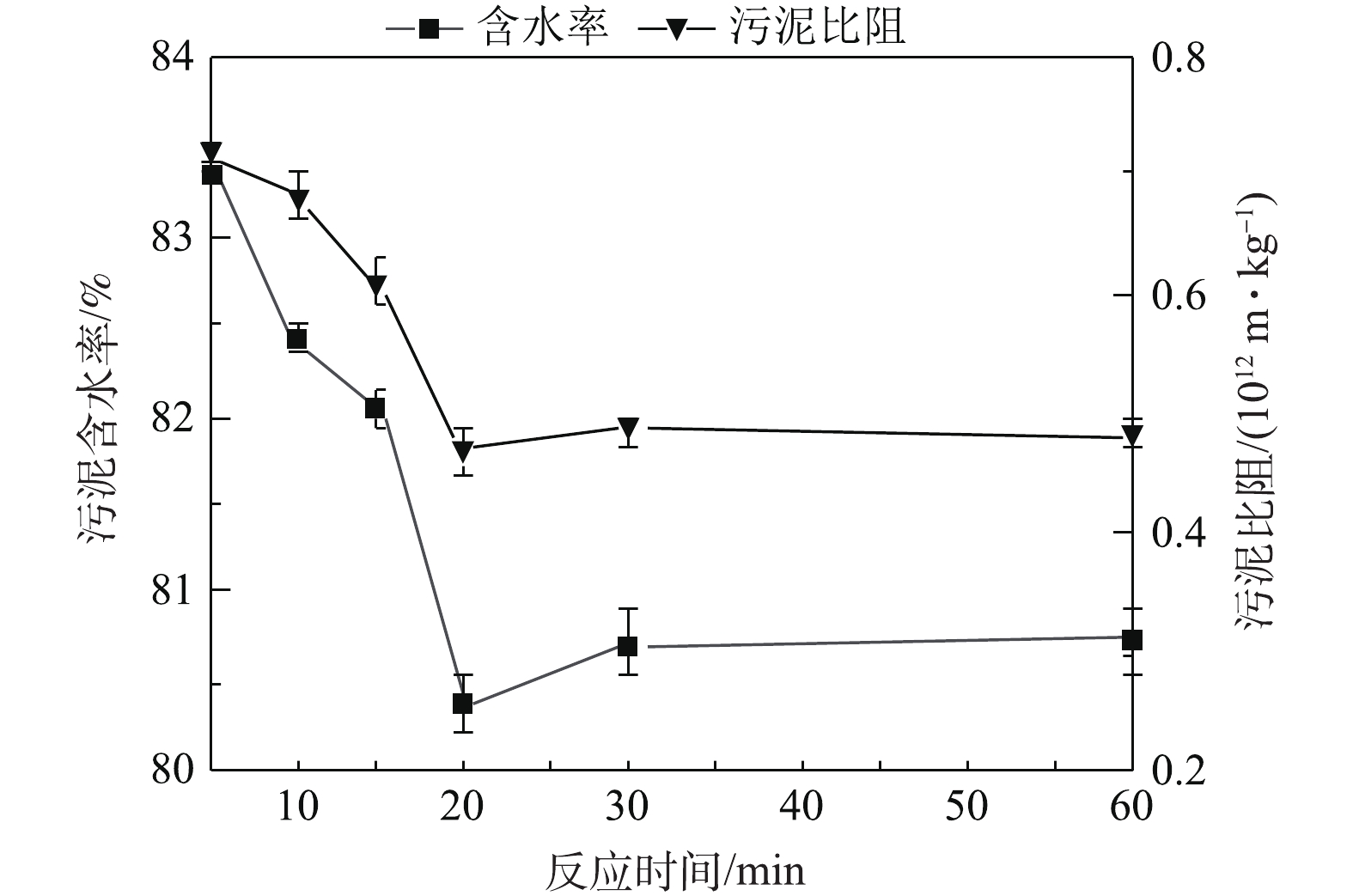
S2O2−8 的投加比影响了硫酸根自由基的活化效果,进而影响其对污泥絮体的氧化性能。在合适的Fe2+投加量条件下,可使S2O2−8 活化达到最佳效果,从而提高污泥脱水效果。当S2O2−8 浓度为18 mmol·L−1,Fe2+投加量为15 mmol·L−1 (即Fe2+与S2O2−8 投加比例为1.2∶1)时,含水率和污泥比阻降低,可达到较佳的脱水效果,该结果与宋秀兰等[9]的研究结果相似。也有研究[11, 22]表明,两者的最佳投加比例为1∶1时,硫酸根自由基含量较高,对污泥絮体破坏程度较大,其脱水效果较好。过量Fe2+与硫酸根自由基发生反应被氧化为Fe3+,消耗一部分硫酸根自由基,进而影响硫酸根自由基对污泥絮体的氧化,絮体结构破坏程度降低,污泥比阻和含水率增大。此外,根据已有研究[25-26]可知,通过化学调理,将污泥含水率降至80.00%左右后,通过板框压滤机进行深度脱水,可将污泥含水率降至53.80%,通过超高压压滤技术可将污泥含水率降低至36.85%。因此,本研究结果在实际工程中具有一定的应用潜力。不同反应时间条件下污泥含水率和污泥比阻分布结果见图3。由图3可见,随着时间的增加,污泥含水率与污泥比阻呈现先降低后基本保持恒定的趋势,当反应时间≤20 min时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻随时间的增加逐渐降低;在反应时间为20 min时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻最低,分别为80.37%和0.47×1012 m·kg−1,污泥脱水效果最佳;当反应时间>20 min时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻基本保持恒定。这主要由于
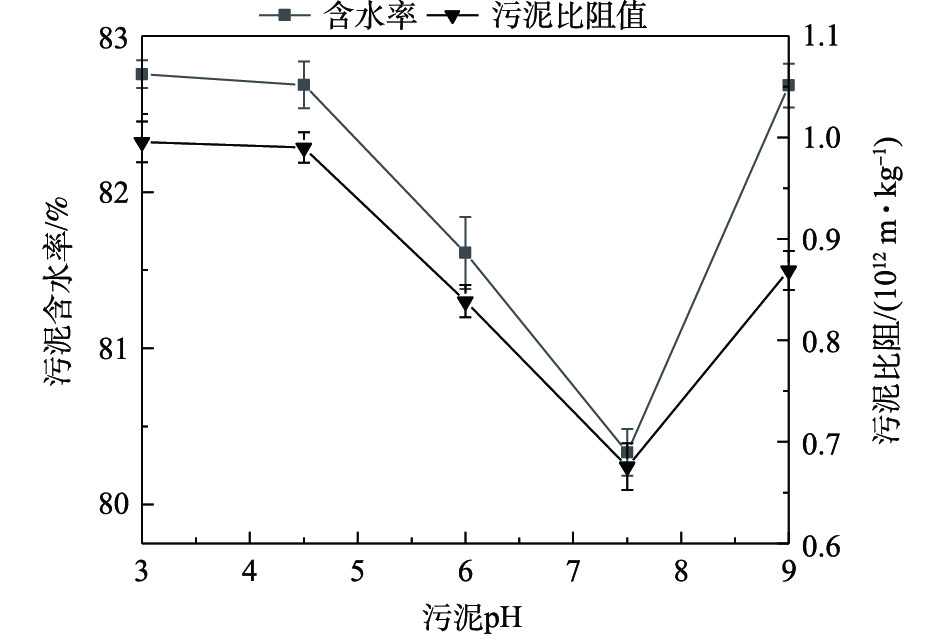
SO−4 ·具有较高的氧化性,污泥在反应前20 min内迅速被氧化破解,但随反应时间的增加,污泥胞内有机物中较为容易氧化的物质逐渐减少,使得在20 min后,污泥脱水效果基本保持恒定[22]。不同pH条件下污泥含水率和污泥比阻的分布情况如图4所示。由图4可见,pH对污泥含水率和污泥比阻影响较大,中性条件下污泥含水率和污泥比阻较低,污泥脱水效果较佳,该结果与相关研究结果[21]一致。当pH为3~7.5时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻呈现下降趋势;在pH为7.5时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻值均达到最低,分别为80.33%和0.68×1012 m·kg−1;当pH大于7.5时,污泥含水率和污泥比阻呈现上升趋势。过硫酸钾在不同pH条件下产生自由基的浓度不同,主要机理[27]参考式(3)~式(7),在酸性条件下,催化反应会加速自由基的形成,而自由基浓度较高时,会发生自我消除反应,导致与污泥作用的自由基浓度较小,对污泥絮体的改善不足。该过程参考式(2)~式(5),随着pH的增大,自由基生成速度降低,自由基浓度未达到自我消除的浓度范围,生成的自由基均用于调理污泥,破坏污泥絮体结构;当pH增大到碱性条件时,由于Fe2+会与OH−生成氢氧化物沉淀[28],导致激发硫酸根自由基的能力降低,对污泥絮体的破坏能力较小,反应见式(6)。因此,Fe2+活化过硫酸钾的最佳反应pH为7.5。
-
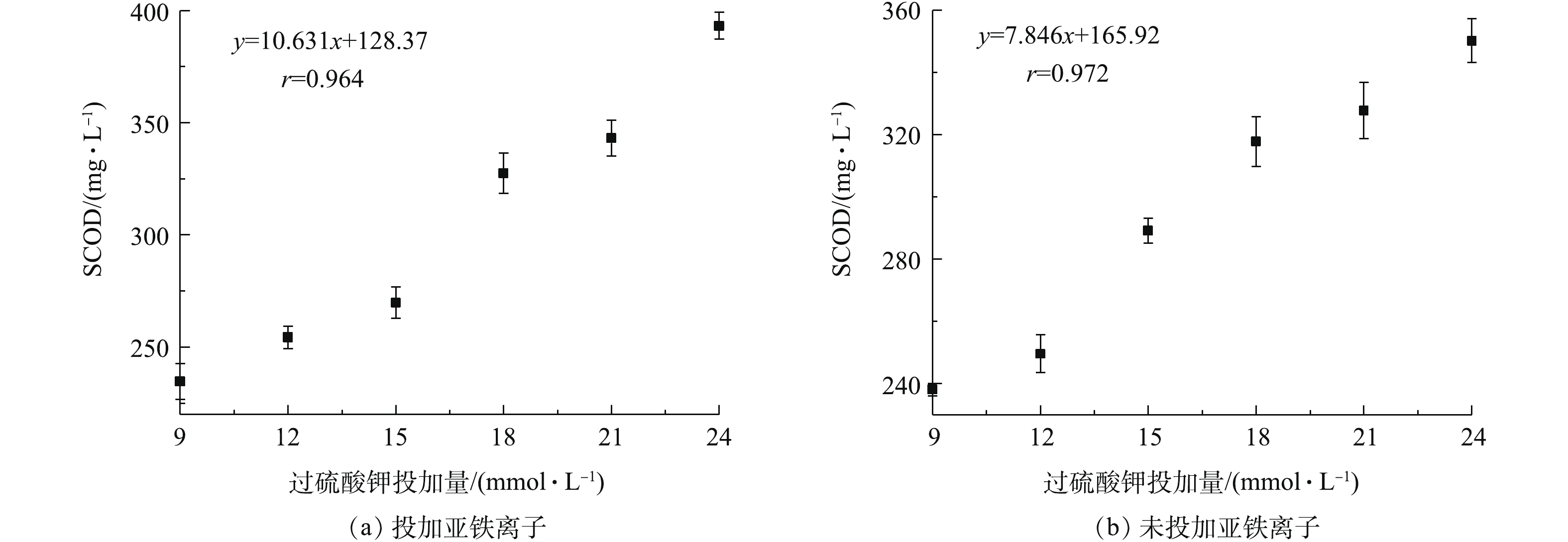
过硫酸钾、硫酸亚铁、反应时间和pH对污泥脱水效果的影响表明:过硫酸钾调理污泥的关键机制是严格控制Fe2+离子与过硫酸钾的摩尔比,确保硫酸根自由基的高生成率,以达到提高污泥脱水效果的目的。为进一步研究硫酸根自由基的生成率与污泥絮体结构组分变化的关系,研究了过硫酸钾投加量对SCOD和污泥EPS组分的影响,结果如图5和图6所示。过硫酸钾投加量对SCOD含量的影响结果如图5所示。由图5可见,随着过硫酸钾投加量的增加,SCOD含量逐渐增加。图5(a)为投加Fe2+离子时SCOD的变化情况。SCOD含量与过硫酸钾投加量呈显著正相关关系(r=0.964,P=0.01),在过硫酸钾为最大投加量时,SCOD含量可达到峰值。图5(b)是未投加Fe2+离子时SCOD的变化情况。与投加Fe2+离子相比,未投加Fe2+离子时SCOD含量变化趋势基本相同,其与过硫酸钾投加量呈显著正相关关系(r=0.972,P=0.01)。其原因为,污泥脱水过程中过硫酸钾氧化促使污泥细胞及絮体稳定性破坏,导致絮体间的有机物和细胞内的有机物释放到上清液,SCOD的含量增加。SCOD值可用于表征污泥絮体的破坏程度和溶出效应[29],SCOD含量增加,表明污泥絮体破解,胞内物质溶出,有利于结合水的释放,从而降低污泥含水率。
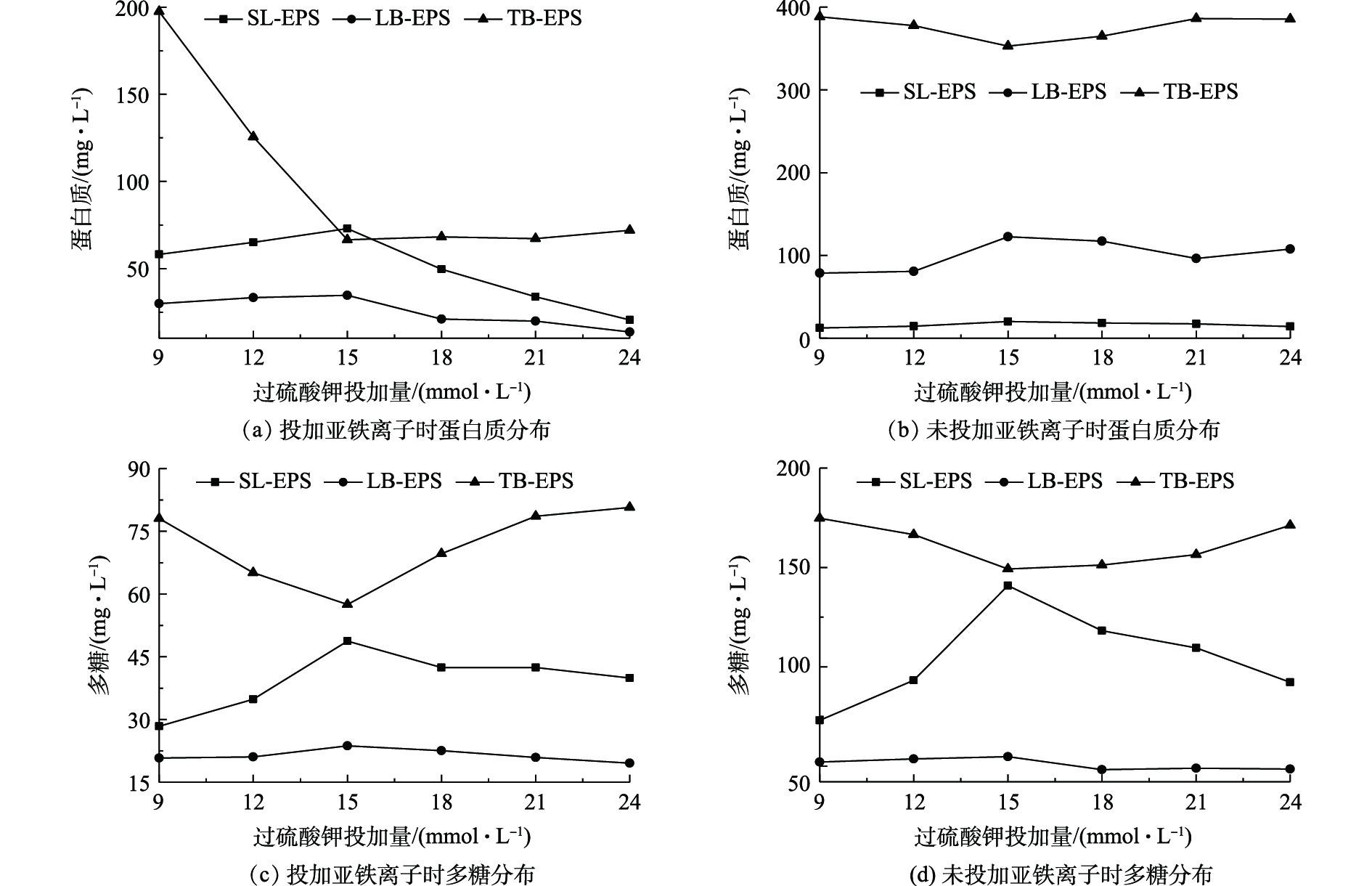
过硫酸钾投加量对EPS不同组分分布的影响结果如图6所示。由图6可见,过硫酸钾投加量对EPS不同组分含量分布有较大影响。图6(a)和图6(c)分别是投加Fe2+时,蛋白质和多糖含量的变化情况。随着过硫酸钾投加量的增加,SL-EPS和LB-EPS中蛋白质和多糖浓度均呈先升高后降低的变化趋势,在15 mmol·L−1时达到最大值;而TB-EPS中蛋白质和多糖浓度呈现相反趋势,在15 mmol·L−1时达到最小值。图6(b)和图6(d)分别是未投加Fe2+时蛋白质和多糖含量的变化情况。与投加Fe2+离子相比,未投加Fe2+离子时,EPS不同组分含量变化趋势大致相同。由于过硫酸根离子未被活化,氧化性较低,不同类型EPS不同组分的含量均偏高。有研究[30]表明,SL-EPS和LB-EPS中蛋白质和多糖含量与污泥脱水性能呈正相关关系;相反,TB-EPS中蛋白质和多糖含量的增加对污泥脱水起抑制作用。TB-EPS中含有较少的结合水,但其对污泥絮体、微生物细胞以及结合水具有较大的黏附和附着作用,导致污泥脱水困难[31]。硫酸根自由基能够氧化TB-EPS,从而分解污泥基质;同时使得附着的微生物细胞被氧化,促使污泥絮体中的自由水释放,达到污泥脱水的目的。该结果与MO等[32]研究一致。
-
1) Fe2+活化过硫酸钾调理剩余污泥可显著改善污泥脱水性能。K2S2O8和Fe2+离子投加量、反应时间与pH均对过硫酸钾改善污泥脱水性能具有显著影响。
2)污泥脱水性能最佳反应条件为pH=7.5,过硫酸钾和Fe2+投加量分别为15 mmol·L−1和18 mmol·L−1时,在最佳反应条件下含水率为78.89%、污泥比阻值为3.04×1011 m·kg−1。
3)过硫酸钾投加量与污泥上清液中SCOD呈现显著正相关关系,且影响污泥不同类型EPS含量的分布,其中TB-EPS的减少使得污泥絮体解体,释放部分胞内水,从而改善污泥的脱水性能。
Fe(II)活化过硫酸盐改善污泥脱水性能
Improvement of sludge dewatering performance by Fe(II)-activated persulfate
-
摘要: 针对污水处理厂剩余污泥脱水困难的问题,采用Fe2+活化过硫酸钾高级氧化法提高剩余污泥脱水性能,使用污泥含水率和污泥比阻对调理前后污泥脱水效果进行分析;研究了过硫酸钾投加量、Fe2+投加量、pH和反应时间对污泥调理效果的影响;探究了过硫酸盐调理污泥过程中溶解性有机物质和胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substance,EPS)的变化特性。结果表明:过硫酸钾调理的最佳反应条件为pH=7.5,反应时间为20 min,过硫酸钾和Fe2+的最佳投加量分别为15 mmol·L−1和18 mmol·L−1,在此条件下,污泥含水率和污泥比阻值分别可达78.89%和0.3×1012 m·kg−1;污泥含水率和比阻的变化可能与污泥调理后絮体结构形态变化有关;调理污泥后,上清液中溶解性有机物质含量与过硫酸钾投加量呈显著正相关关系,而EPS不同组分中蛋白质和多糖含量在Fe2+投加后均减少,表明Fe2+的投加可以破坏污泥絮体,分解胞内物质;利用Fe2+激活过硫酸钾所生成的硫酸根自由基可极大改善污泥的脱水性能。Abstract: Aimed at the difficult dewatering of excess sludge in sewage treatment plants, the dewatering performance of excess sludge was improved by the advanced oxidation method of Fe2+-activated potassium persulfate in this study, and the sludge dewatering effect before/after conditioning were characterized by sludge moisture content and sludge specific resistance to filtration (SRF). The effects of potassium persulfate dosage, Fe2+ dosage, pH and reaction time on sludge conditioning performance were studied. The changes of dissolved organic matter and extracellular polymers during the persulfate conditioning process were investigated. The experimental results showed that the optimal reaction conditions for potassium persulfate conditioning were following: pH=7.5, the reaction time of 20 min, potassium persulfate dosage of 15 mmol· L−1 and Fe2+ dosage of 18 mmol· L−1. Under this condition, the sludge moisture content and sludge specific resistance to filtration could reach 78.89% and 0.3×1012 m·kg−1, respectively. The changes in sludge water content and specific resistance may be related to the change of flocs structure and morphology after sludge conditioning. For the conditioned sludge, there was a significant positive correlation between the content of soluble organic matter in the supernatant and the amount of potassium persulfate, the content of protein and polysaccharide in EPS decreased after Fe2+ addition, indicating that the intracellular substance and part of the bound water in the sludge flocs were released. The sulfate radicals produced by Fe2+-activated potassium persulfate can greatly improve the sludge dewaterbility.
-
随着水域富营养化现象频发,藻类爆发性生长繁殖,其产生的嗅味物质等次级代谢产物污染了水源水,造成了经济与环境损失,影响着饮用水的供水安全,引发了社会各界的关注[1]。在水体污染物中,嗅味物质是国内外饮用水处理中较为容易见到也是十分难解决的问题之一[2]。饮用水中出现嗅味将引起群众大范围恐慌,嗅味目前已被列为水厂出厂水和管网水的必检项目之一。
水中的嗅味问题在各个地方有不同的成因,所形成的臭味种类也不同,但土臭素(GSM)和2-甲基异莰醇(2-MIB)是引起水质问题的众多恶臭物质中最突出的,饮用水中二者的含量均不能超过10 ng·L−1。常规水处理工艺,如混凝、沉淀、过滤、消毒等,无法有效减少水中的GSM和2-MIB,不能达到《生活饮用水卫生标准》要求[3]。常用控制嗅味物质的方法包括活性炭吸附、生物降解、高级氧化、臭氧氧化等。其中高级氧化技术(AOPs)被普遍认为是一种高效降解GSM和2-MIB的方法,其中紫外联用高级氧化(UV-AOPs)技术是近年来研究的热点[4]。UV-AOPs技术实质是通过利用某些活性物质较强的氧化能力,如氯自由基、羟基自由基,氧化降解污染物,将其分解成水、二氧化碳等无机小分子[5]。该技术具有氧化电位高、选择性低、碱干扰小、对大多数有机污染物降解迅速、操作过程简单、反应条件温和等优点。
本文通过对比不同UV-AOPs工艺降解嗅味物质的效能,考察了光照强度、氧化剂投加量、目标物初始浓度、反应时间、pH、腐殖酸浓度及水体所含无机阴离子(SO42-、Cl−、HCO3−)等对降解效果的影响,并对比了在实际水体中UV-AOPs工艺对嗅味物质的去除效果,以期为UV-AOPs工艺去除嗅味物质在实际运用中提供理论参考与技术支持。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 试剂与材料
土臭素(GSM)、2-甲基异莰醇(2-MIB)购自日本Wako,纯度大于98%,30%双氧水(H2O2)、硫代硫酸钠(Na2S2O3)、次氯酸钠(NaClO)、氯化钠(NaCl)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)、无水硫酸钠(Na2SO4)、磷酸二氢钠(NaH2PO4),腐殖酸(HA)购自美国Aldrich-sigma公司。
1.2 实验流程
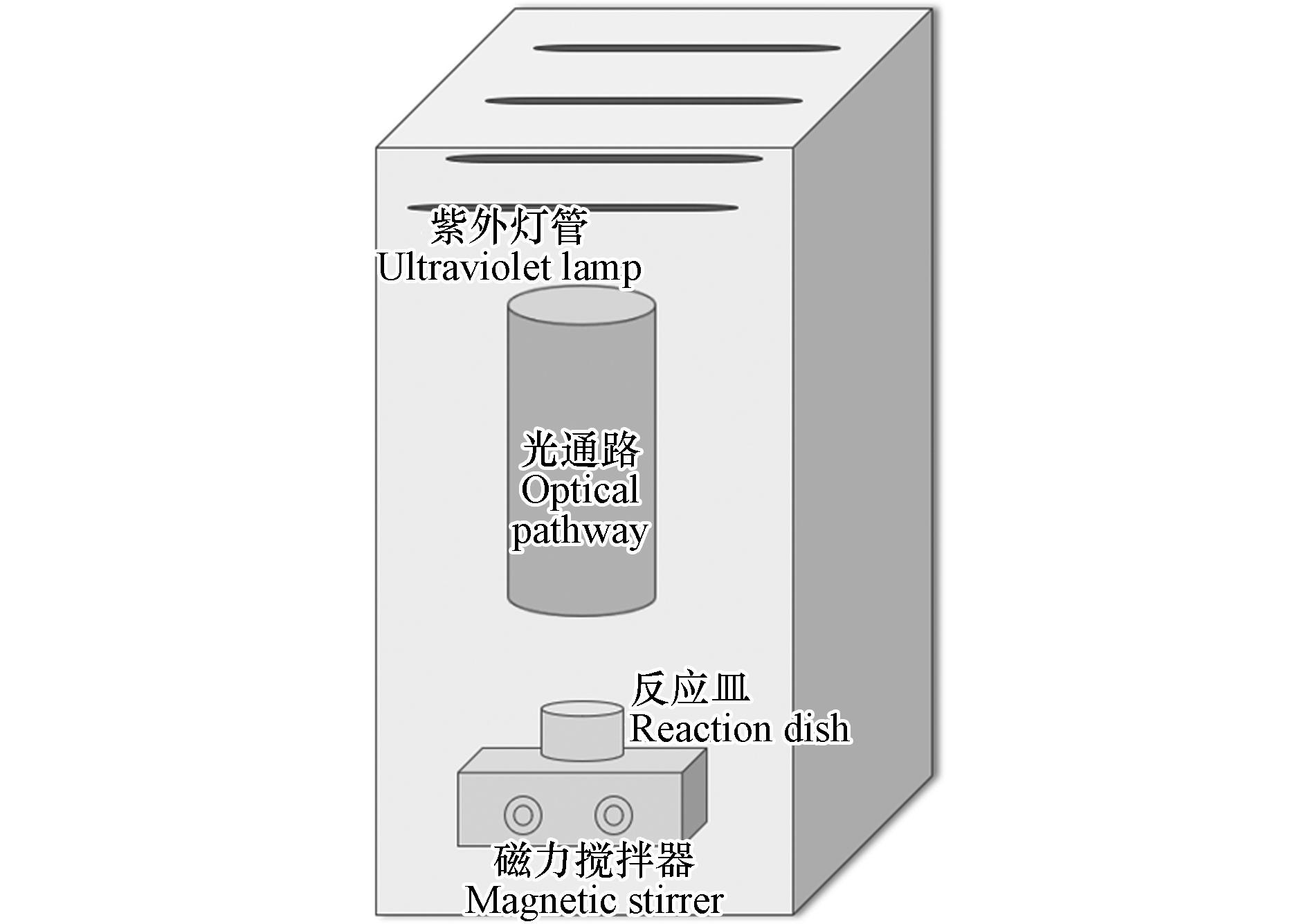
实验主要依托平行光束仪进行,黑色不透光箱体装置中设有4根紫外灯管,每根灯管的发射波长为254 nm,功率为10 W,其中1、2、3、4根灯管的光强分别为8.9×10−5、2.0×10−4、2.1×10−4、2.2×10−4 W·cm−2,实验装置见图1。
实验操作流程如下:
(1)打开UV灯管预热稳定30 min,用光强测定仪监测反应皿上液面的光照强度,核对并计算达到所需紫外剂量的光照时间;
(2)配制所需浓度的目标污染物缓冲液置于反应皿中,将反应皿置于光通路的正下方;
(3)把所需浓度的氧化剂(如H2O2、NaClO水溶液)加入反应皿中,开启磁力搅拌器混合1 min,打开遮光板开始计时,到达设计反应时间后关闭遮光板以停止反应,滴入硫代硫酸钠终止反应,取40 mL水样测定GSM和2-MIB浓度。其中,H2O2储备液浓度为1000 mg·L−1,HOCl储备液浓度为620 mg·L−1。
1.3 检测方法
本实验中的光照强度采用光强测定仪进行测定,H2O2浓度检测使用便携式过氧化氢测定仪,pH值检测使用FE28型pH计,氯浓度采用滴定法[6]。
硫酸盐、氯化物的检测采用离子色谱法。准备电导率小于0.5 μS·cm−1的二次去离子水,并经0.45 μm微孔滤膜进行过滤。碳酸氢钠、碳酸钠淋洗贮备液浓度分别为0.17 mol·L−1、0.18 mol·L−1;碳酸氢钠、碳酸钠淋洗使用液浓度分别为0.0017 mol·L−1、0.0018 mol·L−1。硫酸根离子和氯离子标准贮备液浓度均为1000.0 mg·L−1。进样量约为1.0—2.0 mL·min−1。
GSM和2-MIB的测定参照国标《GB/T32470-2016》。使用顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱法,通过固相微萃取纤维吸附待测样中的GSM和2-MIB,顶空富集样品后通过气相色谱-质谱联用仪分离测定。气相色谱仪进样口压力56.5 kPa,进样口温度:250 ℃;程序升温:起始温度60 ℃保持2.5 min,以8 ℃·min−1速率升至250 ℃,保持5 min;质谱仪离子源:电子电离源(EI),离子源温度:230 ℃,接口温度:280 ℃,离子化能量:70 eV,扫描模式:选择离子检测(SIM)。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 工艺参数对不同UV-AOPs工艺降解GSM和2-MIB降解效率的影响
2.1.1 光照强度对目标污染物降解效率的影响
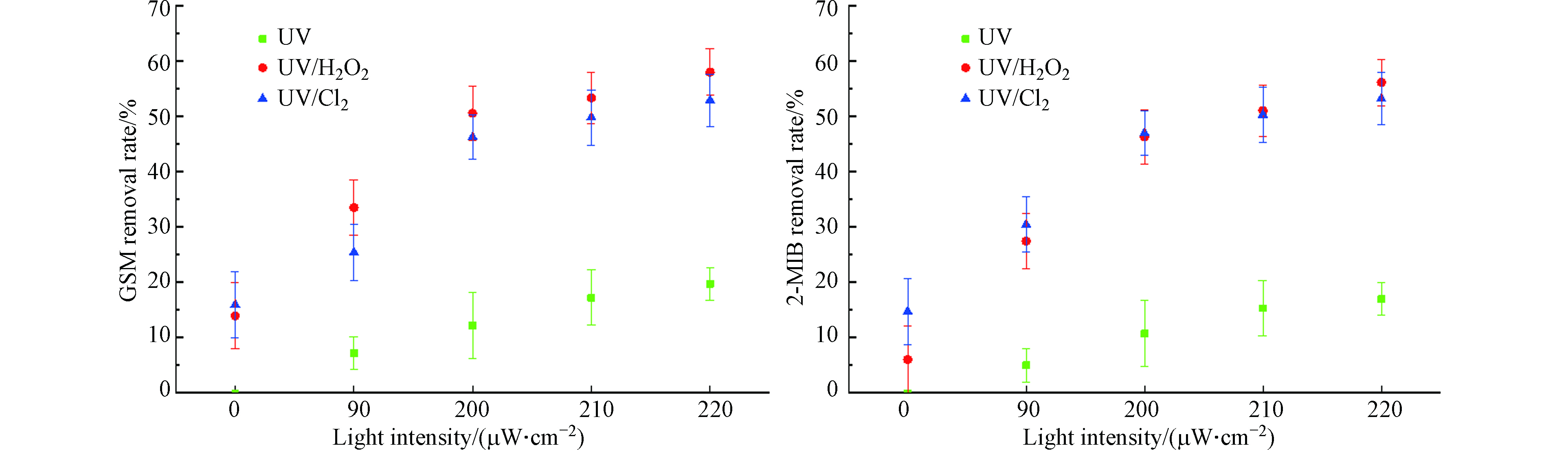
使用目标污染物浓度为100 ng·L−1的GSM和2-MIB混标溶液,降解时间40 min,加入8 mg·L−1的H2O2与NaClO,分别打开0、1、2、3、4根灯管,光照强度分别为0、90、200、210、220 μW·cm−2,分析2-MIB和GSM的降解情况。去除效果如图2所示。
当光照强度从90 μW·cm−2提高至220 μW·cm−2时,UV、UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺对GSM的去除率分别从7.2%、33.5%、25.4%升至19.7%、58.0%、53.0%;对2-MIB的去除率分别从5.0%、27.5%、30.5%升至17.0%、56.2%、53.3%。随着光照强度的提高,各工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率不断升高。当光照强度为0 μW·cm−2,即单独投加H2O2时,对GSM的去除率为14%,2-MIB的去除率为6.1%;单独投加NaClO时,GSM的去除率为16%,2-MIB的去除率为14.8%。单独投加H2O2或ClO−对GSM和2-MIB的去除效果一般。在相同的光照强度下,UV/H2O2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除效果要优于UV/Cl2工艺[7]。随着光照强度的增加,反应体系内光子量在逐渐增多,自由基数量增多,对嗅味物质的反应速率增大,对污染物的去除量增大。在实际工程中,可通过增加紫外灯管数或增大功率来提高光照强度,加强GSM和2-MIB的去除效果。
2.1.2 氧化剂浓度对目标污染物降解效率的影响
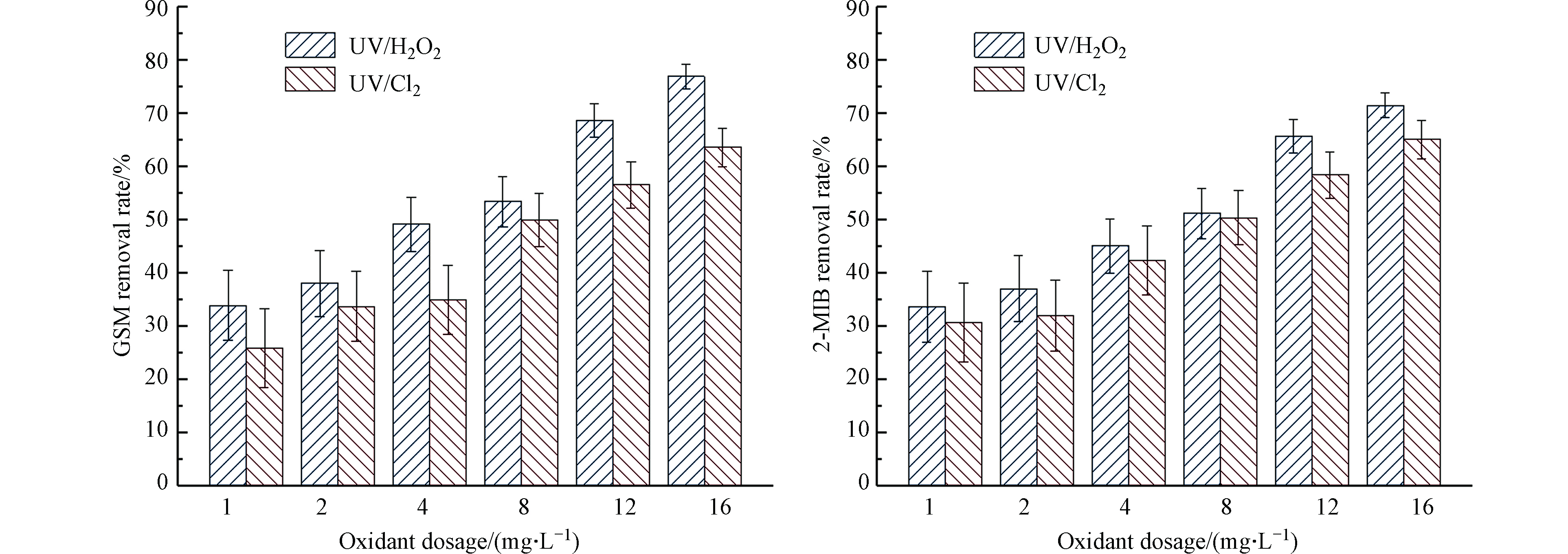
固定紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,向反应皿中加入GSM和2-MIB浓度均为100 ng·L−1的混标溶液,反应时间为40 min,分别加入1、2、4、8、12、16 mg·L−1的H2O2与NaClO,分析GSM和2-MIB的降解情况。其降解效果如图3所示。
当H2O2浓度从1 mg·L−1增加至16 mg·L−1时,对GSM的去除率从33.8%升至76.9%,对2-MIB的去除率从33.6%升至71.4%;当氯的浓度从1 mg·L−1增加至16 mg·L−1时,对GSM的去除率从25.9%升至63.5%,对2-MIB的去除率从30.6%升至65%。增大氧化剂的量,GSM和2-MIB的去除率随之升高。在氧化剂投加量相同的条件下,UV/H2O2对GSM和2-MIB的去除率要高于UV/Cl2对二者的去除率。在水体为中性或弱碱性的实验条件下,UV/Cl2工艺中自由氯的主要形态是OCl−,其会影响自由基的生成,使体系中的自由基浓度降低[8],选用的紫外波长距离OCl−的最大吸收波长较远,影响其自由基的形成。同时OCl−与·OH的反应速率比HOCl高出5个数量级,进而导致体系氧化能力下降[9-10],故去除率略低。在降解相同浓度的GSM和2-MIB时,UV/H2O2工艺去除GSM的效果略优于2-MIB;UV/Cl2工艺去除2-MIB的效果略优于GSM。
当氧化剂的用量小于某个限值时,氧化剂的用量越多,生成的自由基越多。H2O2的投加量过多会对羟基自由基起捕获作用,而H2O2比羟基自由基的氧化性小,因此使GSM和2-MIB的降解速率常数降低[11]。在本实验中随氧化剂投加量的增加,GSM和2-MIB的去除率升高,未出现该情况。实际工程中,氧化剂的最佳投加量应根据实际工程去除效果进行试验得出。
2.1.3 反应时间对目标污染物降解效率的影响
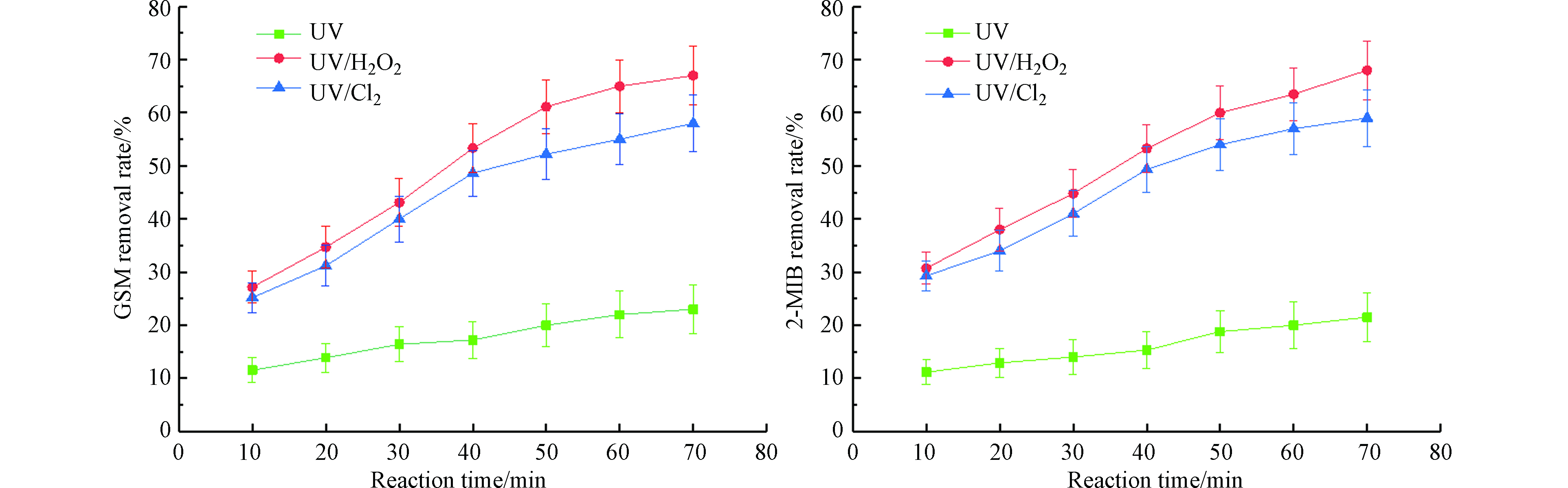
固定紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,投加8 mg·L−1的H2O2与NaClO,目标污染物为100 ng·L−1的GSM和2-MIB混标溶液,降解时间为10、20、30、40、50、60、70 min,比较GSM和2-MIB的去除效果。其降解效果如图4所示。
当反应时间从10 min升至70 min时,3种工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除效果都在提升,UV工艺对GSM的去除率从11.5%升至23%,对2-MIB的去除率从11.1%升至21.5%;UV/H2O2工艺对GSM的去除率从27.2%升至67.0%,对2-MIB的去除率从23.7%升至65.0%;UV/Cl2工艺对GSM的去除率从28.2%升至58.0%,对2-MIB的去除率从29.3%升至60.0%。随着反应时间的增加,各工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率不断提升;UV/H2O2工艺去除效果的增加幅度高于UV工艺及UV/Cl2工艺,随着反应时间的增加,3种不同的UV-AOPs工艺对GSM和2-MIB去除效果增加的幅度均减弱。反应时间为10 min时,UV/Cl2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除效果优于UV/H2O2工艺,但随着反应时间的增加,UV/H2O2工艺对二者的去除效果逐渐优于UV/Cl2工艺。
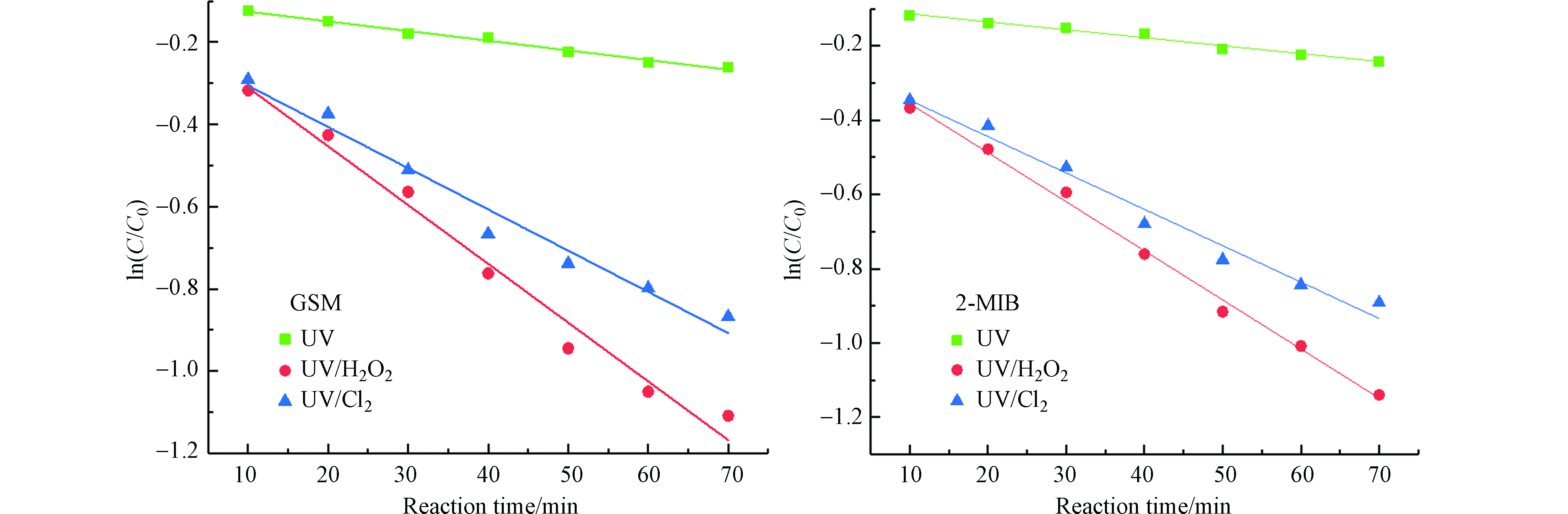
由图5和表1可知,在该实验条件下,各反应的降解曲线呈一级反应动力学的形式,UV/H2O2工艺降解GSM和2-MIB的反应速率常数略大于UV/Cl2工艺。这是由于在水体为中性或弱碱性的实验条件下,UV/Cl2工艺所受的影响较大,此时OCl−占据优势地位,其对·OH有一定的清除作用,使体系中的自由基大量淬灭,影响反应速率。
表 1 不同UV-AOPs降解GSM和2-MIB的拟一级反应动力学参数Table 1. Quasi-first-order reaction kinetic parameters for degradation of GSM and 2-MIB by different UV-AOPs嗅味物质Odorants 工艺Method 一级反应动力学方程First order kinetic equation K/min-1 R2 GSM UV ln(C/C0)=−0.0024t−0.1021 0.0024 0.989 UV/H2O2 ln(C/C0)=−0.0143t−0.1671 0.0143 0.9822 UV/Cl2 ln(C/C0)=−0.0100t−0.2054 0.0100 0.9741 2-MIB UV ln(C/C0)=−0.0021t−0.0925 0.0021 0.9788 UV/H2O2 ln(C/C0)=−0.0132t−0.2235 0.0132 0.9956 UV/Cl2 ln(C/C0)=−0.0098t−0.2488 0.0098 0.9783 2.1.4 目标污染物浓度对目标污染物降解效率的影响
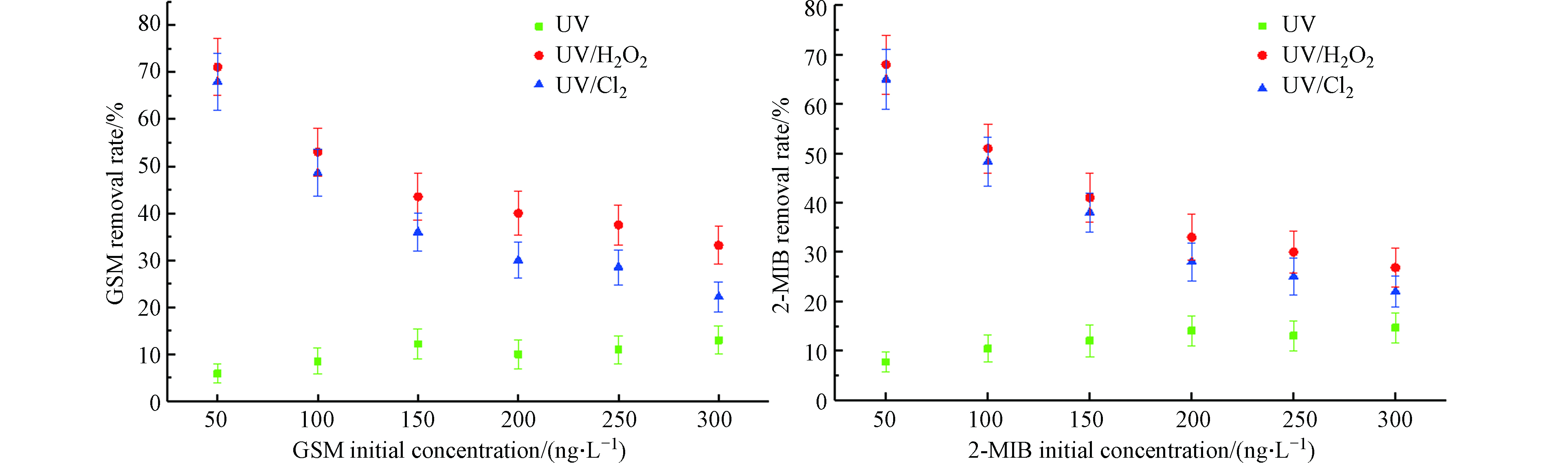
固定紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,投加8 mg·L−1的H2O2与NaClO,降解时间为40 min,投加不同初始浓度50、100、150、200、250、300 ng·L−1的GSM和2-MIB混标溶液,比较GSM和2-MIB的去除效果。其降解效果如图6所示。
当目标污染物初始浓度从50 ng·L−1升至300 ng·L−1时,UV工艺对GSM的去除率从5.9%升至13.0%,2-MIB的去除率从7.7%升至14.6%;UV/H2O2工艺对GSM的去除率从71.1%降低至33.2%,2-MIB的去除率从68.0%降低至26.8%;UV/Cl2工艺对GSM的去除率从68.0%降低至22.2%,2-MIB的去除率从65.0%降低至22.0%。增加目标污染物初始浓度,UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺对嗅味物质的去除率也随之降低,但UV工艺对嗅味物质的去除率反而略微提高,推测随着GSM和2-MIB浓度的增加,UV的利用率也得到提高[12]。不断增加目标污染物初始浓度时,UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺对嗅味物质去除效果减少的幅度随之变小,污染物去除总量是不断提高的。
2.2 水体背景成分对不同UV-AOPs工艺降解GSM和2-MIB降解效率的影响
2.2.1 pH对目标污染物降解效率的影响
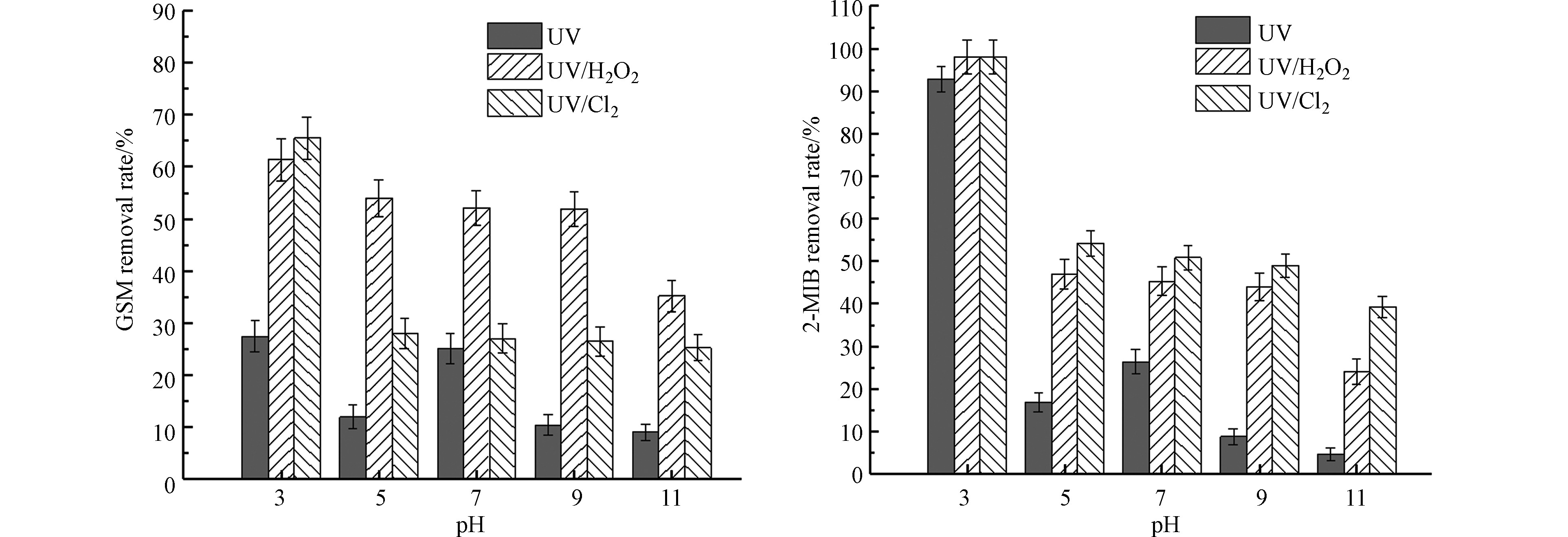
固定紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,氧化剂H2O2与NaClO的浓度为8 mg·L−1,降解时间为40 min,初始浓度为100 ng·L−1的GSM和2-MIB混标溶液,控制溶液pH分别为3、5、7、9、11,对比GSM和2-MIB的去除效果。其降解效果如图7所示。
随着pH的升高,UV/Cl2工艺对GSM去除效果的衰减远大于UV/H2O2工艺。不同酸碱条件下,3种UV-AOPs工艺对GSM和2-MIB的降解效率不同。当pH为3时,UV、UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺对2-MIB的去除率分别为92.8%、98.0%、98.0%。当水体环境为酸性时,即使不加氧化剂,UV工艺对2-MIB的去除效果也较好。当pH从酸性升至中性,UV工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率先降低再升高,pH从中性升高至碱性时,UV工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率降低。随着pH的升高,UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率不断降低。当pH值从3升至11时,二者对GSM的去除率分别为35.2%、25.2%,分别降低了26.2%、40.4%;对2-MIB的去除率分别为24.1%、39.2%,分别降低了73.9%、58.8%。
不同pH条件下自由基的不同存在形式对结果产生了一定的影响[13]。当pH升高时,HOCl的比例减少,OCl−的比例增加;pH为5时,游离氯主要以HOCl的形式存在,而在pH大于7的条件下,游离氯主要以OCl−的形式存在。游离氯作为自由基的淬灭剂,在pH升高的条件下,对自由基的淬灭作用增强,体系中自由基含量降低,使2-MIB和GSM的去除率降低[14]。一般来说,UV/H2O2高级氧化工艺在酸性条件下具有更强的氧化性[15]。过氧化氢是弱酸,在酸性及中性环境下较稳定,碱性环境中H2O2会发生一定程度的解离,影响参与反应的H2O2的浓度,降低自由基的生成量,影响反应效率。
2.2.2 无机阴离子对目标污染物降解效率的影响
天然水体中含有成分复杂、含量各异的无机阴离子(如SO42-、Cl−、HCO3−),部分无机阴离子可能会影响高级氧化工艺对嗅味物质的去除效果。固定紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,氧化剂H2O2与NaClO的浓度为8 mg·L−1,降解时间40 min,初始浓度为100 ng·L−1的GSM和2-MIB混标溶液,投加0.5 mmol·L−1的硫酸钠、氯化钠与碳酸氢钠,对比GSM与2-MIB的去除效果。其降解效果如图8所示。
添加SO42-后,UV工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率基本没有变化;而UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率升高。在紫外光的辐照下,硫酸根离子与羟基自由基发生反应,生成硫酸根自由基,导致对嗅味物质的去除效果增加[16]。用含氯化钠、高氯酸钠、硝酸钠、硫酸钠的废水实施芬顿实验,发现氯离子、硝酸根离子和高氯酸盐离子不影响芬顿试剂的氧化效果,而在硫酸盐离子的存在下,芬顿试剂的氧化效率得到了提高[17]。
添加Cl−后,UV和UV/H2O2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率减小,UV/Cl2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率略微增加。氯基自由基的反应速率常数为10−3—10−1 L·mol−1·s−1,羟基自由基的反应速率常数为107—1010 L·mol−1·s−1[18],但Cl−与·OH或Cl·反应后生成一系列氯基自由基(Cl·、Cl2·、ClOH·等),故去除效果得到部分提高。
在3种离子中,投加HCO3−离子后对嗅味物质去除效果的影响最为显著。HCO3−是一种有效的·OH淬灭剂,它会使·OH的浓度降低,其存在是AOPs实际应用中的最不利条件之一[19]。同时,HCO3−和·OH反应产生的碳酸根将与H2O2反应,进一步降低UV-AOPs的氧化效率。
在实际应用中,溶液中的主要阴离子HCO3−和Cl−等对·OH有淬灭作用,它们的大量存在会致使UV/H2O2工艺的氧化剂投加量增大或反应时间延长。
2.2.3 腐殖酸对目标污染物降解效率的影响
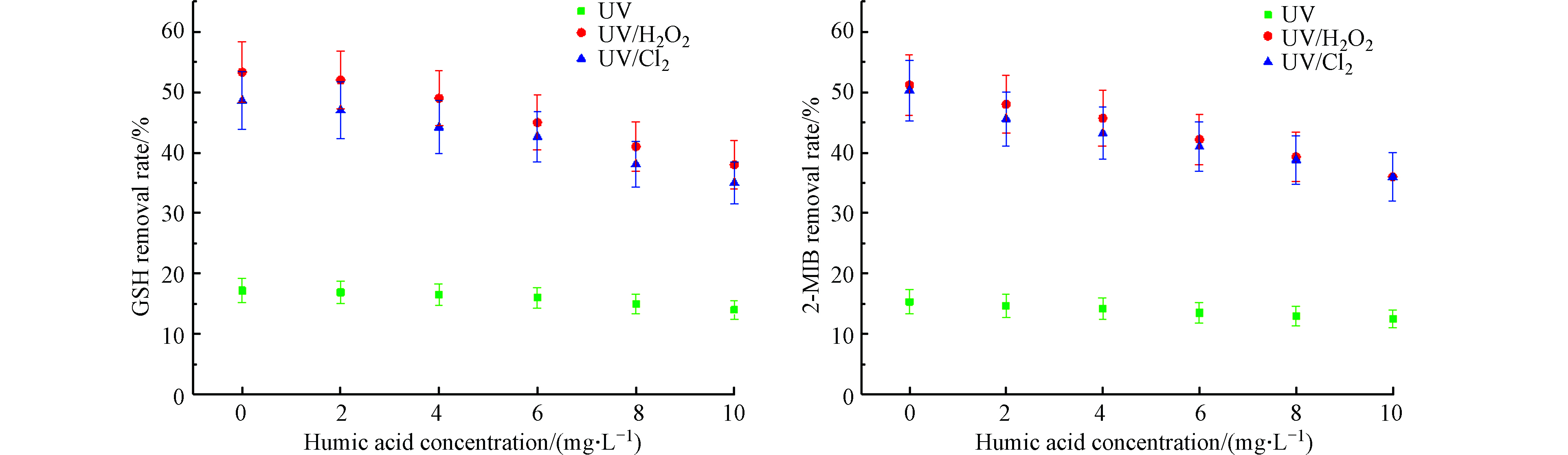
腐殖酸(HA)广泛存在于天然水体中,其对AOPs工艺去除水体中嗅味物质的效能存在一定的影响。固定紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,H2O2与NaClO的浓度为8 mg·L−1,降解时间40 min,初始浓度100 ng·L−1的GSM和2-MIB混标溶液,分别投加0、2、4、6、8、10 mg·L−1的腐殖酸,比较对GSM和2-MIB的去除效果。其降解效果如图9所示。
结构复杂的腐殖酸,对UV-AOPs工艺去除致嗅物质的效果存在一定影响。当HA投加量从0 mg·L−1升到10 mg·L−1时,UV、UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺对GSM的去除率分别为14%、38%、35%,降低了3.2%、15.3%、13.6%;对2-MIB的去除率分别为12.5%、36%、36%,降低了2.8%、15.2%、14.3%。在投加HA的条件下,不同UV-AOPs工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率均受到抑制,且抑制程度随HA的增多而增大。其中,HA对UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺降解嗅味物质的抑制作用较为显著。HA可以吸收紫外线并形成能级跃迁至激发状态,产生较多活性物质,如·OH等自由基,增大了体系中氧化剂的含量,促进氧化降解[20];HA存在一定的不饱和化学键,可吸收部分紫外光,因而降低了被激发氧化剂的光子数,使产生自由基的效率降低,进而抑制了GSM和2-MIB等的去除[21];腐殖酸可作为活性自由基受体对自由基进行消耗,且会升高溶液色度,减小紫外光的穿透性,降低其利用率,抑制高级氧化作用[22]。
2.3 UV/H2O2工艺氧化降解GSM、2-MIB的可能途径
通过顶空固相微萃取(HS-SPME)对处理后出水形成的中间产物进行富集来探究UV/H2O2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的实际降解途径及中间产物。GSM和2-MIB的初始浓度为1 μg·L−1,H2O2的投加量约为13.0 mg·L−1。取样并加入0.1 mol·L−1的Na2S2O3溶液,快速停止反应。通过全扫描GC-MS鉴定GSM和2-MIB的氧化降解中间产物,质谱结果与NIST 11.0数据库进行匹配。
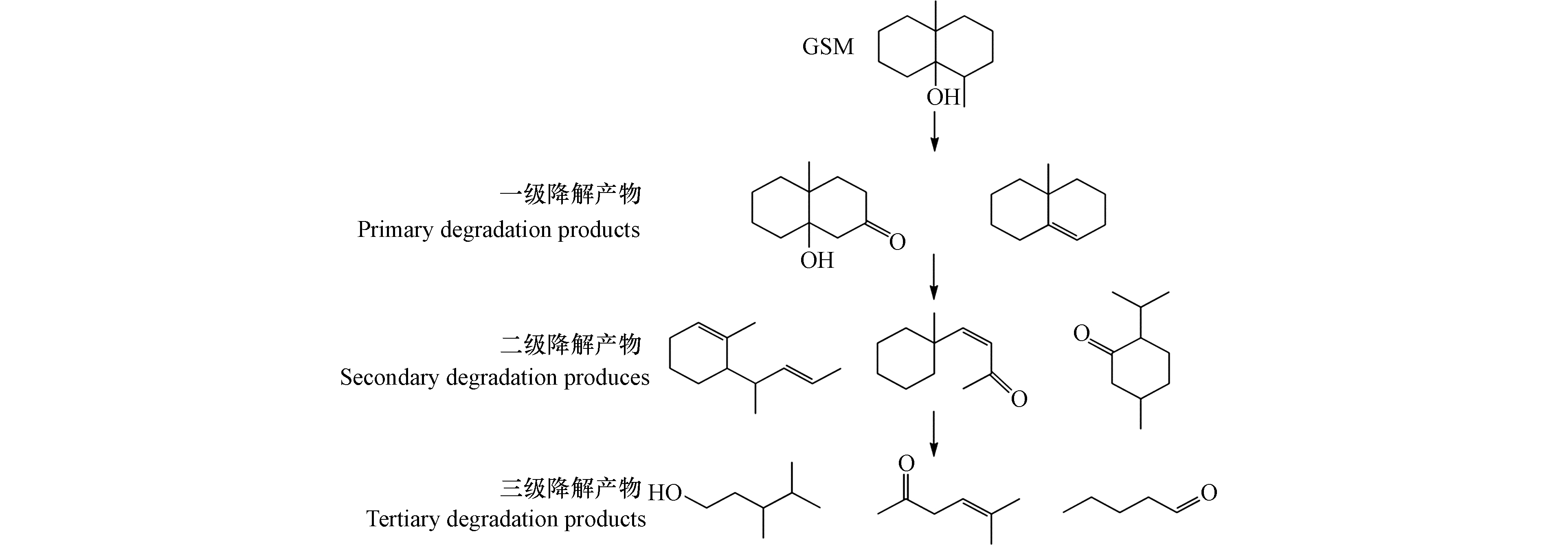
对比色谱图和质谱图分析结果,GSM可能的降解途径如图10所示,GSM中间产物仍存在原来的环状结构。光催化降解GSM中间产物的途径与此较为相似[23]。·OH在GSM侧链上发生氧化脱氢与去甲基反应,将自由电子移至GSM上对其化学结构进行破坏,产生的一级降解产物存在环内不稳定双键。·OH与一级降解产物的加成反应和电子转移使C—C键断裂,改变双环结构,形成单环结构的二级氧化降解产物。·OH继续加成反应,C—C或C=C键断裂,导致环结构断裂,生成三级氧化降解产物,如小分子醛、酮等。醛、酮等小分子产物最终被·OH矿化成水和二氧化碳。
对比色谱图和质谱图分析结果,2-MIB可能的降解途径如图11所示,·OH先氧化2-MIB侧链,通过脱水脱甲基反应改变2-MIB的结构,生成含酮基及环内双键的一级降解产物。·OH继续氧化该产物,进行加成反应并将自由电子转移至桥环内部,致使桥环结构断开,形成二级单环醛酮类分子。·OH通过环内加成反应转移电子,打破环结构的化学键,生成三级醛、酮和酸等小分子产物。·OH继续降解链状小分子产物,矿化成CO2和H2O。这与双氧水/臭氧氧化降解2-MIB生成中间产物的降解途径较为相似[24].
采用GC-MS法对GSM和2-MIB降解的中间产物进行全扫描鉴别,结果与GSM和2-MIB的前线轨道分析结果一致。
2.4 不同UV-AOPs工艺对实际水体的处理效能
为了探究不同UV-AOPs工艺对实际水体水质指标的去除效果,并验证以上实验结果。选取3个实际水厂的原水及滤后水进行实验,紫外灯光照强度为210 μW·cm−2,氧化剂H2O2与NaClO的浓度为8 mg·L−1,降解时间为50 min,水体的水质指标以及处理后的水质指标如表2所示。
表 2 不同UV-AOPs工艺对实际水体的处理效能Table 2. Treatment efficiency of different UV-AOPs processes for real water名称Name GSM/(ng·L−1) 2-MIB/(ng·L−1) 浊度/NTUTurbidity UV254 耗氧量/(mg·L−1)Oxygen consumption 可溶性有机碳/(g·kg−1)DOC 比紫外吸光度SUVA 北控水厂 水厂原水 20.99 115.23 4.50 0.048 2.58 2.93 1.655 原水经UV/H2O2处理后 2.51 28.24 4.11 0.039 2.05 2.87 1.367 原水经UV/Cl2处理后 5.25 42.02 4.18 0.041 2.21 2.90 1.407 水厂滤后水 7.54 85.66 0.22 0.027 1.6 2.76 0.987 滤后水经UV/H2O2处理后 1.20 17.40 0.20 0.021 1.25 2.56 0.810 滤后水经UV/Cl2处理后 3.73 34.67 0.21 0.022 1.33 2.62 0.846 众兴水厂 水厂原水 15.89 81.67 2.58 0.069 3.84 4.25 1.634 原水经UV/H2O2处理后 2.41 20.14 2.30 0.056 3.27 4.09 1.359 原水经UV/Cl2处理后 6.74 31.82 2.34 0.058 3.52 4.13 1.408 水厂滤后水 10.40 50.62 0.46 0.049 2.14 3.10 1.576 滤后水经UV/H2O2处理后 1.92 8.54 0.40 0.038 1.7 2.91 1.311 滤后水经UV/Cl2处理后 4.23 15.90 0.41 0.040 1.79 2.98 1.341 白浪河水厂 水厂原水 28.42 106.5 4.30 0.048 2.4 3.62 1.336 原水经UV/H2O2处理后 2.46 68.19 3.86 0.039 1.89 3.49 1.110 白浪河水厂 原水经UV/Cl2处理后 4.31 84.10 3.92 0.041 1.99 3.50 1.176 水厂滤后水 14.81 44.06 2.32 0.020 1.42 2.23 0.901 滤后水经UV/H2O2处理后 1.22 12.52 2.01 0.015 1.14 2.16 0.700 滤后水经UV/Cl2处理后 6.84 19.62 2.08 0.016 1.26 2.18 0.742 经高级氧化工艺处理后GSM、2-MIB、浊度、UV254、耗氧量、DOC、SUVA等水质指标均得到进一步去除,水质得到明显改善,UV/H2O2工艺对实际水体的处理效果优于UV/Cl2工艺对实际水体的处理效果。当GSM的浓度为20—30 ng·L−1时,UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺的处理效果均能满足饮用水标准规定;当2-MIB浓度较高时,UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺对2-MIB的降解效能差强人意,需要增加紫外光剂量或氧化剂投加量以改善去除效果。由于实际水体的复杂性,UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺对嗅味物质的部分去除效果未达到实验室效果,因此高级氧化技术在实际运用中,应根据实际水体水质情况选择适宜的工况条件。UV/H2O2和UV/Cl2工艺对浊度及有机物浓度的降低均有一定的效果,且UV/H2O2技术的去除效果更稳定。污染物的降解会消耗电能,而电耗与净化水的成本相关,根据国际理论与应用化学联合会(IUPAC)提出的高级氧化技术处理水中低浓度污染物的电能效率评价指标公式计算[25],在该实验条件下,UV、UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺降解GSM的平均电耗为1440、241.68、345.6 kW·h·m−3,降解2-MIB的平均电耗为1645.71、261.82、352.65 kW·h·m−3。相较而言,UV/H2O2技术降解嗅味物质及去除部分污染物的效果更优。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)UV、UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺对GSM和2-MIB均有一定的去除效果,其中UV/H2O2工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除效果较优。在氧化剂投加量增加、光照强度增大、反应时间增长及目标污染物初始浓度降低的条件下,三种工艺对GSM和2-MIB的去除率也会相应升高。
(2)3种工艺去除GSM和2-MIB的效果受水体中pH值、无机阴离子、腐殖酸等条件的影响。pH越高,去除GSM和2-MIB的效果越差。SO42-可以促进UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺去除嗅味物质,HCO3−的存在会抑制二者对嗅味物质的去除,Cl−会促进UV/Cl2工艺去除嗅味物质,抑制UV/H2O2工艺去除嗅味物质。腐殖酸浓度过高对UV/H2O2、UV/Cl2工艺去除GSM和2-MIB的抑制作用更为显著。
(3)根据不同UV-AOPs工艺对实际水体水质指标的实验结果,其对GSM、2-MIB、浊度、UV254、耗氧量、DOC、SUVA等水质指标均有一定的去除效果,同时电能消耗较低,相比其他两种工艺,UV/H2O2工艺对实际水体的处理效果较优。
-
表 1 实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters
实验编号 过硫酸钾/(mmol·L−1) Fe2+/(mmol·L−1) pH 快搅反应时间/min 慢搅反应时间/min 1# 9~21 0 8 10 0 2# 9~21 18 8 10 20 3# 15 15~27 8 10 20 4# 15 18 3~9 10 20 5# 15 18 8 10 5~60 注:所有实验在20 ℃条件下进行;加入K2S2O8后快速搅拌;加入Fe2+后慢速搅拌。 -
[1] 杨航, 俞雅乖. 中国水环境治理的成本-收益测度及影响因素分析[J]. 科技与管理, 2018, 20(5): 57-65. [2] 新华社. 年底前直辖市省会城市建成区要基本消除黑臭水体[J]. 北方建筑, 2017, 2(2): 76. [3] 唐建国, 吴炜, 周振, 等. 污泥脱水性能测定对污泥调理与脱水的重要性分析[J]. 给水排水, 2017, 53(12): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2017.12.002 [4] 汤连生, 张龙舰, 罗珍贵. 污泥中水分布形式划分及脱水性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(2): 309-314. [5] 吴岸峰. 超声破解技术在污水污泥处理中的应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2008. [6] ZHOU X, WANG Q, JIANG G, et al. A novel conditioning process for enhancing dewaterability of waste activated sludge by combination of zero-valent iron and persulfate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 185: 416-420. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.088 [7] LEE K M, KIM M S, LEE C. Oxidative treatment of waste activated sludge by different activated persulfate systems for enhancing sludge dewaterability[J]. Sustainable Environment Research, 2016, 26(4): 177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.serj.2015.10.005 [8] ZHEN G Y, LU X Q, LI Y Y, et al. Innovative combination of electrolysis and Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation for improving the dewaterability of waste activated sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 136(3): 654-663. [9] 宋秀兰, 石杰, 吴丽雅. 过硫酸盐氧化法对污泥脱水性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(11): 5585-5590. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20151172 [10] ZHEN G Y, LU X Q, LI Y Y, et al. Novel insights into enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge by Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 119(9): 7-14. [11] 徐文迪, 常沙, 明铁山, 等. 基于硫酸根自由基( SO−4⋅ )的污泥预处理技术[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1528-1535.[12] 俞庭康, 刘涛, 沈洪. 污泥比阻实验中几个问题的探讨[J]. 实验室研究与探讨, 2009, 28(1): 68-70. [13] 中华人民共和国建设部. 城市污水处理厂污泥检测方法: CJ/T 221-2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005. [14] 陈杰, 吴亦红. 碱性过硫酸钾消解测定城市污泥中总氮[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2005(1): 35-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2005.01.013 [15] 孙伟香, 李淑栋, 李慧. 城镇污泥中总磷测定条件的优化选择: 过硫酸钾消解后钼酸铵分光光度法[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2018, 37(2): 94-97. [16] 刘翔, 黄映恩, 刘燕, 等. 活性污泥和生物膜的胞外聚合物提取方法比较[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2011, 50(5): 556-562. [17] 夏晨娇. 剩余活性污泥脱水的高级处理方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2009. [18] 张小玲, 赵艳红, 李正群, 等. 曝气及搅拌强化超声预处理污泥试验研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18(2): 755-760. [19] 袁冬琴, 王毅力. 活性污泥胞外聚合物(EPS)的分层组分及其理化性质的变化特征研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(10): 3522-3528. [20] MAHMOUD A, OLIVIER J, VAXELAIRE J, et al. Electro-dewatering of wastewater sludge: Influence of the operating conditions and their interactions effects[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(9): 2795-2810. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.02.029 [21] 任杰辉, 程文, 万甜, 等. 缓冲液盐度对热提取活性污泥胞外聚合物的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(8): 3054-3060. [22] 徐鑫. 过硫酸盐与烷基糖苷用于污泥调理及脱水机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2013. [23] HUANG C, PAN J R, FU C G, et al. Effects of surfactant addition on dewatering of alum sludges[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2002, 128(12): 1121-1127. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2002)128:12(1121) [24] 戴永康. 短期中温厌氧消化预处理联合芬顿氧化与氧化钙对污泥深度脱水性能影响的研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2017. [25] 梁嘉林. 芬顿氧化联合氧化钙对五种市政污泥深度脱水性能影响的研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2016. [26] LIU H, YANG J K, ZHU N R, et al. A comprehensive insight into the combined effects of Fenton’s reagent and skeleton builders on sludge deep dewatering performance[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 258-259: 144-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.04.036 [27] WANG C W, LIANG C. Oxidative degradation of TMAH solution with UV persulfate activation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 254: 472-478. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.116 [28] RASTOGI A, Al-ABED S R, DIONYSIOS D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2008, 85(3): 171-179. [29] 李丹熠, 桑稳姣, 张倩, 等. 2 450 MHz电磁波污泥脱水过程中的温度效应[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(11): 4147-4152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.11.020 [30] 邢奕, 王志强, 洪晨, 等. 不同pH值下胞外聚合物对污泥脱水性能及束缚水含量的影响[J]. 工程科学学报, 2015, 37(10): 1387-1395. [31] KEKE X, WAN Y S, YUN C, et al. Effects of thermal-Fe (II) activated oxone treatment on sludge dewaterability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 322: 463-471. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.055 [32] MO R S, HUANG S S, DAI W C, et al. A rapid Fenton treatment technique for sewage sludge dewatering[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 269: 391-398. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.001 -






 下载:
下载: