-
近年来,集中收集-卫生填埋已成为我国城市生活垃圾的主要处理处置方式[1]。然而,垃圾填埋会产生大量高氨氮、低C/N的垃圾渗滤液,由于其高浓度的氨氮和复杂的有机物组成将对水体环境和人体健康带来严重影响和危害,因此,对于这类废水的处理已成为研究焦点和难点[2]。
目前,短程硝化反硝化耦合厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonia oxidation, ANAMMOX)工艺已成功应用于多种低碳氮比(C/N)的高氨氮废水处理,如垃圾渗滤液、养殖废水及味精加工废水脱氮[3-6]。与常规硝化-反硝化工艺相比,短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺可节省60%的需氧量,且ANAMMOX工艺无须外加碳源,是一种高效低耗、运行成本低廉的废水生物脱氮技术[7-8]。但是,理论上,ANAMMOX细菌将1 mol
NH+4 -N和1.32 molNO−2 -N转化为N2的同时,会生成0.26 mol硝态氮,约占反应总氮的10%(如式(1)所示),造成出水中硝态氮浓度较高,总氮超标[9]。因此,使用短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液,无法达到我国2008年新修订并实施的《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》[10]中规定的垃圾渗滤液处理厂出水排放标准(NH4+-N≤25 mg·L−1、TN≤40 mg·L−1)。垃圾填埋场填埋气中含有大量硫化氢气体,垃圾渗滤液中硫化物含量也会随着垃圾填埋时间的增加而增加[11]。以深圳某垃圾填埋场为例,填埋场产气量为35 000 m3·h−1,其中,硫化氢气体浓度为150~300 mg·L−1。近年来,以硫化物(H2S/HS−/S2−)作为电子供体的硫自养反硝化(sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification, SAD)脱氮技术受到广泛关注,SAD生物脱氮过程无需外加碳源,可以有效去除水中
NO−x -N污染物,同时硫化物被转化为氧化态硫酸盐,且对下游水厂或水环境不会造成不良影响[12-13]。SAD技术已逐步开始应用于低负荷的水体环境修复[14]、生活污水深度处理[15]、水产养殖废水处理[16]和海水冲厕水处理[17]等。目前,对硫自养反硝化的研究比较深入,已具备一定的理论基础[18-20]。因此,利用SAD技术应用于垃圾渗滤液处理,既能解决异养反硝化脱氮中有机碳源(电子供体)不足的问题,又能实现对垃圾填埋气中硫化氢气体无害化处理并回收电子,避免空气污染的同时又节省了填埋气脱硫成本。本研究在实现短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液稳定运行的基础上,进一步耦合SAD反应器,构建了两级自养脱氮深度处理工艺,并探究了其工艺效能。 -
本研究实验装置和反应器照片见图1,反应器均由有机玻璃制成。短程硝化反硝化反应器(SBR)内径18 cm、有效高度33 cm、有效容积3 L。ANAMMOX反应器为向上流厌氧污泥床反应器(UASB),内径6 cm、有效高度40 cm、有效容积1 L。SAD反应器为向上流厌氧污泥床反应器(UASB),内径6 cm、有效高度80 cm、有效容积2 L。
-
本研究所用垃圾渗滤液取自深圳市某垃圾填埋场,水质见表1。在SAD反应器启动阶段,进水为人工模拟废水,主要试剂为九水合硫化钠(Na2S·9H2O)、硝酸钾(KNO3)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)、氯化镁(MgCl2),均为分析纯。在SAD反应器运行阶段,进水为ANAMMOX反应器处理垃圾渗滤液的出水。
-
短程硝化反硝化反应器接种污泥取自深圳市某垃圾渗滤液处理厂AO工艺曝气池;ANAMMOX反应器污泥为本实验室培养驯化好的污泥;SAD反应器接种污泥取自广州市某生活污水处理厂二次沉淀池。SAD反应器启动阶段,逐步提高反应器进水中硝态氮的负荷,启动过程中运行条件见表2。SAD反应器成功启动后串联至短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺(见图1),实现对垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮。3个反应均在室温下运行,短程硝化反硝化反应器以进水-搅拌-沉淀-出水-静置的方式运行,处理垃圾渗滤液的负荷为2 L·d−1;ANAMMOX与SAD反应器均以连续流进水方式运行(外回流比均为3),水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time, HRT)分别为3 h和6 h,垃圾渗滤液(调节后)处理负荷均为8 L·d−1。
-
各项指标测定方法均按照已有的方法[21]。采集进出水水样经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,分别采用纳氏试剂法、N-(1-萘基)乙二胺分光光度法和紫外分光光度法测定样品中的
NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N和NO−3 -N;水中SO2−4 、SO2−3 、S2O2−3 离子浓度采用离子色谱仪(IC-AS23阴离子检测器,DIONEX ICS-900)检测;溶解性硫化物H2S/HS−/S2−采用亚甲基兰分光光度法检测;COD采用哈希DRB200快速消解仪测定;碱度采用五点滴定法;实验过程中,定期取反应器中均匀混合的污泥,测定MLSS、MLVSS;pH、温度采用便携式pH计(FG2-FK,METTLER TOLEDO)进行测定。 -
本研究中使用了已经稳定运行的短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX反应器,并对其进行了参数优化[22];短程硝化反硝化反应器中参与硝化反应的菌属Nitrosomonas(AOB)得到富集,Nitrospira(NOB)的丰度下降至<0.01%,保证了反应器中高效的亚硝化率[22-23]。如图2(a)所示,通过控制曝气时间(22.7 h)和DO浓度(≤0.5 mg·L−1)实现垃圾渗滤液短程硝化,同时消耗垃圾渗滤液中可生物降解的有机碳,为后续厌氧氨氧化脱氮提供了保障。在进水垃圾渗滤液TN为2 560 mg·L−1时,50%~60%的
NH+4 -N被转化为NO−2 -N,短程硝化反硝化反应器出水NH+4 -N为1 013.6 mg·L−1,NO−2 -N为1 206.3 mg·L−1,NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N的平均浓度比例为1∶1.21,说明短程硝化反硝化反应器中AOB为优势菌属 [22-23]。短程硝化反硝化反应器出水NO−3 -N基本维持稳定,平均浓度为247.8 mg·L−1,反硝化脱氮92.2 mg·L−1。短程硝化反硝化反应器出水符合厌氧氨氧化反应对NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N比例的要求[24]。本研究通过人工配水培养驯化的ANAMMOX颗粒污泥呈橙红色,平均粒径为762 μm(如图1所示)。由图2(b)可知,厌氧氨氧化反应器进水中NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N平均浓度分别为259.2 mg·L−1和275.1 mg·L−1,进水总氮为500~600 mg·L−1;通过厌氧氨氧化反应,NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N的去除率为91.6%和94.9%,ANAMMOX反应器出水NH+4 -N和NO−2 -N平均浓度分别21.9 mg·L−1和14.0 mg·L−1。短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX系统TN的平均去除率为93.1%,出水TN=176.3 mg·L−1。但是,由于厌氧氨氧化反应本身会将约10%的进水TN生成NO−3 -N,使得ANAMMOX出水TN>170 mg·L−1。其中,NO−x -N=154.5 mg·L−1,造成短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液出水未能达到国家规定的排放标准(GB 16889-2008)(TN≤40 mg·L−1)。因此,本研究采用硫化物作为电子供体,通过SAD脱氮技术,对短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺出水进行深度脱氮。 -
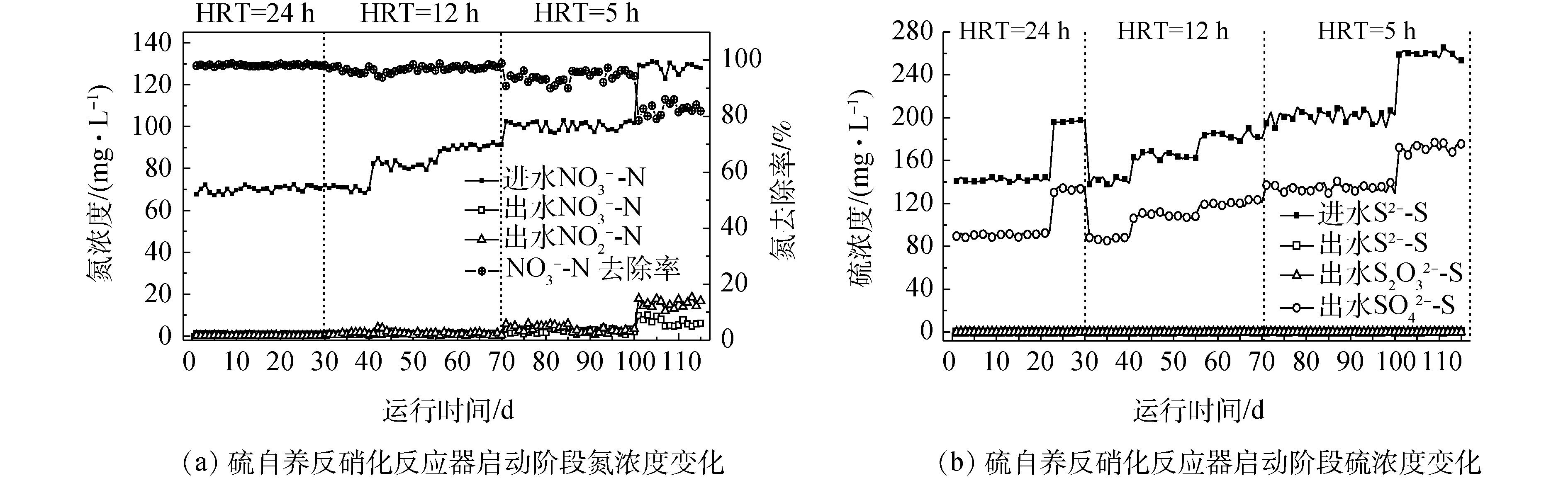
本研究采用人工配水启动SAD反应器,通过逐步提高SAD反应器进水中
NO−3 -N的负荷,使反应器内微生物能适应高负荷的含氮废水。为了探究SAD反应器的脱氮能力,启动期间,将进水pH控制在7.6~7.8之间,实验启动过程根据HRT的不同分为为3个阶段(表2)。阶段I(0~30 d)是污泥筛选的重要阶段,如图3所示,通过提高进水硫化物浓度,氮去除率达99%。该阶段使反应器中异养菌减少,硫自养菌进一步富集。在阶段II(31~70 d)中,将HRT缩短至12 h,当SAD反应器氮去除率稳定在90%以上时,将进水NO−3 -N浓度由70 mg·L−1逐步提升至90 mg·L−1,避免了高浓度NO−3 -N对反应器的冲击,反应器进水氮负荷由0.14 kg·(m3·d)−1提升至0.18 kg·(m3·d)−1。在第71天,将进水NO−3 -N浓度提升到100 mg·L−1,并且HRT由12 h缩短至5 h,氮负荷提升至0.43 kg·(m3·d)−1,出水中NO−3 -N和NO−2 -N平均浓度分别保持在1.5 mg·L−1和4.2 mg·L−1,TN去除率保持在94%左右。在100~115 d内,进水NO−3 -N浓度由100 mg·L−1提升至130 mg·L−1, 反硝化率略有降低。研究中发现,SAD反应器经过115 d的启动和运行,当HRT为5 h、进水NO−3 -N浓度为100 mg·L−1、S/N质量比率为2时,氮去除率为94%;同时,SAD反应器中出水中的硫代硫酸盐和硫化物浓度均在0.1 mg·L−1以下,出水硫酸盐浓度会随着不同阶段进水硫化物浓度的改变而变化,其中约64.2%的硫化物转化为硫酸盐(部分生成硫单质),硫化物去除率为100%。 -
将短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX与SAD反应器进行耦合,形成短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX-SAD两级自养深度脱氮反应系统(图1),其脱氮效果如图4所示。SAD反应器通过调节池调节ANAMMOX出水pH为7.6~7.8,利用ANAMMOX反应器出水提供的
NO−3 -N与NO−2 -N作为电子受体、投加的硫化物作为电子供体进行硫自养反硝化反应。根据启动期间SAD反应器的氮去除负荷,设置HRT为6 h,设置S/N质量比率为2。由图4(a)、图4(d)、图4(g)可知,通过控制短程硝化反硝化反应器的曝气时间和DO浓度,使进水中50%~60%的NH+4 -N被转化为NO−2 -N,NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N的浓度比例为(1∶1)~(1∶1.4)。由图4(c)、图4(f)、图4(i)可知,在进水NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N、NO−3 -N平均浓度分别为4.2、3.6、88.5 mg·L−1时,SAD反应器出水NO−3 -N平均浓度为9.7 mg·L−1,NO−3 -N平均去除率为89.3%,出水NO−2 -N平均浓度为0.6 mg·L−1。短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX耦合SAD反应器在连续64 d处理垃圾渗滤液的过程中,SAD反应器稳定运行,出水水质稳定。由图4(b)、图4(e)、图4(h)可知,ANAMMOX反应器运行过程中,进水NO−3 -N平均浓度为97.8 mg·L−1,出水NO−3 -N增加为140.5 mg·L−1。ANAMMOX进出水NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N浓度会有些许波动,主要是由于短程硝化反硝化反应器溶解氧浓度波动导致,溶解氧会促进亚硝化细菌(NOB)的生长,导致厌氧氨氧化反应底物的不足(NO−2 -N不足),从而影响脱氮效率[25]。本研究采用了短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化(ANAMMOX)-硫自养反硝化(SAD)工艺,通过两级自养反硝化实现了垃圾渗滤液深度脱氮。将启动成功的SAD反应器与短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX反应器串联,通过基于硫化物的自养反硝化去除了ANAMMOX产生的
NO−x -N,提高了整体工艺的总氮去除率,出水水质达到《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》氮排放标准(TN≤40 mg·L−1)。在目前处理垃圾渗滤液脱氮的同类研究中,普遍难以实现垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮[26-27],而本研究在无需投加高成本碳源的情况下,实现了垃圾渗滤液的高效、深度脱氮处理。 -
1)短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液脱氮效果较好,总氮去除负荷可达1.19 kg·(m3·d)−1,总氮去除率可达93.1%。但工艺出水中
NO−3 -N浓度为140.5 mg·L−1(TN=176.3 mg·L−1),无法达到(GB 16889-2008)中规定的垃圾渗滤液处理厂出水排放标准。2)SAD反应器成功启动,反应器进水氮负荷为0.43 kg·(m3·d)−1,氮去除率为94%,硫化物去除率为100%,实现了反应器中硫自养反硝化菌的富集。
3)短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX-SAD工艺出水TN均值<12 mg·L−1、TN去除率达到99.5%、总氮去除负荷达到0.85 kg·(m3·d)−1,实现了处理垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮。同时,垃圾填埋场中的硫化氢气体以回收与再循环的方式为本工艺提供硫源,这为硫化氢气体的去除提供了新思路。
两级自养反硝化实现垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮
Deep denitrification of landfill leachate by two-stage autotrophic denitrification process
-
摘要: 针对目前生物工艺难以解决垃圾渗滤液深度脱氮的问题,探究了短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化-硫自养反硝化(两级自养)工艺处理高氨氮、低C/N比垃圾渗滤液的脱氮效果。结果表明, 当进水垃圾渗滤液中氨氮平均浓度为2 560 mg·L−1,COD值为4 000~5 000 mg·L−1时,经过短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化处理后,总氮去除负荷可达1.19 kg·(m3·d)−1、总氮去除率可达93.1%(出水TN=176.3 mg·L−1)、COD去除率可达52.2%。但是,厌氧氨氧化反应器出水中
NO−x -N浓度为154.5 mg·L−1,仍未达到我国生活垃圾填埋场垃圾渗滤液处理排放标准(TN≤40 mg·L−1)。在厌氧氨氧化反应器之后串联硫自养反硝化,整体工艺最终出水NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N、NO−3 -N平均浓度分别为1.9、0.6、9.7 mg·L−1,TN≤15 mg·L−1,进水总氮去除率为99.5%。在短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化-硫自养反硝化两级自养深度脱氮反应系统中实现了垃圾渗滤液深度脱氮。Abstract: In view of the difficulty of deep denitrification in the treatment of landfill leachate by biological process at present, a new process coupling partial nitrification-denitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation (ANAMMOX) and sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification (SAD) was applied to treat the landfill leachate with high ammonia nitrogen and low C/N ratio. The results showed that at the ammonia concentrations of 2 560 mg·L−1 and COD of 4 000~5 000 mg·L−1 in the influent landfill leachate, the total nitrogen removal load, nitrogen removal efficiency and COD removal efficiency were 1.19 kg·(m3·d)−1, 93.1% (the total nitrogen concentration in effluent was 176.3 mg·L−1), and 52.2% after partial nitrification-denitrification-ANAMMOX treatment, respectively. However,NO−x -N concentration in the effluent of the ANAMMOX reactor was 154.5 mg·L−1, which could not meet the effluent quality standard of TN≤40 mg·L−1 in domestic solid waste landfill. When the SAD was coupled with partial nitrification-denitrification-ANAMMOX process in a series connection mode, the average concentrations ofNH+4 -N,NO−2 -N,NO−3 -N in the effluent of the whole process were 1.9, 0.6 and 9.7 mg·L−1, respectively, the total nitrogen concentration was below 15 mg·L−1, the nitrogen removal efficiency reached 99.5%. Deep denitrification of landfill leachate was achieved by two-stage autotrophic deep denitrification process of partial nitrification-denitrification-ANAMMOX-SAD. -
近年来,集中收集-卫生填埋已成为我国城市生活垃圾的主要处理处置方式[1]。然而,垃圾填埋会产生大量高氨氮、低C/N的垃圾渗滤液,由于其高浓度的氨氮和复杂的有机物组成将对水体环境和人体健康带来严重影响和危害,因此,对于这类废水的处理已成为研究焦点和难点[2]。
目前,短程硝化反硝化耦合厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonia oxidation, ANAMMOX)工艺已成功应用于多种低碳氮比(C/N)的高氨氮废水处理,如垃圾渗滤液、养殖废水及味精加工废水脱氮[3-6]。与常规硝化-反硝化工艺相比,短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺可节省60%的需氧量,且ANAMMOX工艺无须外加碳源,是一种高效低耗、运行成本低廉的废水生物脱氮技术[7-8]。但是,理论上,ANAMMOX细菌将1 mol
NH+4 -N和1.32 molNO−2 -N转化为N2的同时,会生成0.26 mol硝态氮,约占反应总氮的10%(如式(1)所示),造成出水中硝态氮浓度较高,总氮超标[9]。因此,使用短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液,无法达到我国2008年新修订并实施的《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》[10]中规定的垃圾渗滤液处理厂出水排放标准(NH4+-N≤25 mg·L−1、TN≤40 mg·L−1)。NH+4+1.32NO−2+0.066HCO−3→1.02N2+0.26NO−3+0.66CH2O0.5N1.5+2.03H2O (1) 垃圾填埋场填埋气中含有大量硫化氢气体,垃圾渗滤液中硫化物含量也会随着垃圾填埋时间的增加而增加[11]。以深圳某垃圾填埋场为例,填埋场产气量为35 000 m3·h−1,其中,硫化氢气体浓度为150~300 mg·L−1。近年来,以硫化物(H2S/HS−/S2−)作为电子供体的硫自养反硝化(sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification, SAD)脱氮技术受到广泛关注,SAD生物脱氮过程无需外加碳源,可以有效去除水中
NO−x -N污染物,同时硫化物被转化为氧化态硫酸盐,且对下游水厂或水环境不会造成不良影响[12-13]。SAD技术已逐步开始应用于低负荷的水体环境修复[14]、生活污水深度处理[15]、水产养殖废水处理[16]和海水冲厕水处理[17]等。目前,对硫自养反硝化的研究比较深入,已具备一定的理论基础[18-20]。因此,利用SAD技术应用于垃圾渗滤液处理,既能解决异养反硝化脱氮中有机碳源(电子供体)不足的问题,又能实现对垃圾填埋气中硫化氢气体无害化处理并回收电子,避免空气污染的同时又节省了填埋气脱硫成本。本研究在实现短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液稳定运行的基础上,进一步耦合SAD反应器,构建了两级自养脱氮深度处理工艺,并探究了其工艺效能。1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
本研究实验装置和反应器照片见图1,反应器均由有机玻璃制成。短程硝化反硝化反应器(SBR)内径18 cm、有效高度33 cm、有效容积3 L。ANAMMOX反应器为向上流厌氧污泥床反应器(UASB),内径6 cm、有效高度40 cm、有效容积1 L。SAD反应器为向上流厌氧污泥床反应器(UASB),内径6 cm、有效高度80 cm、有效容积2 L。
1.2 进水水质
本研究所用垃圾渗滤液取自深圳市某垃圾填埋场,水质见表1。在SAD反应器启动阶段,进水为人工模拟废水,主要试剂为九水合硫化钠(Na2S·9H2O)、硝酸钾(KNO3)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)、氯化镁(MgCl2),均为分析纯。在SAD反应器运行阶段,进水为ANAMMOX反应器处理垃圾渗滤液的出水。
表 1 垃圾渗滤液水质Table 1. Characteristic of landfill leachatepH COD/(mg·L−1)  -N/(mg·L−1)
-N/(mg·L−1) -N/(mg·L−1)
-N/(mg·L−1) -N/(mg·L−1)
-N/(mg·L−1)碱度/(mg·L−1) 8.3~8.8 4 000~5 000 2 300~2 700 <5 <50 10 000~13 000 1.3 反应器运行
短程硝化反硝化反应器接种污泥取自深圳市某垃圾渗滤液处理厂AO工艺曝气池;ANAMMOX反应器污泥为本实验室培养驯化好的污泥;SAD反应器接种污泥取自广州市某生活污水处理厂二次沉淀池。SAD反应器启动阶段,逐步提高反应器进水中硝态氮的负荷,启动过程中运行条件见表2。SAD反应器成功启动后串联至短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺(见图1),实现对垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮。3个反应均在室温下运行,短程硝化反硝化反应器以进水-搅拌-沉淀-出水-静置的方式运行,处理垃圾渗滤液的负荷为2 L·d−1;ANAMMOX与SAD反应器均以连续流进水方式运行(外回流比均为3),水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time, HRT)分别为3 h和6 h,垃圾渗滤液(调节后)处理负荷均为8 L·d−1。
表 2 SAD反应器启动过程中运行条件Table 2. Operation conditions during start-up of SAD reactor阶段 运行时间/d HRT/h 进水流量/(L·d−1) 氮负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) 硫负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) I 0~30 24 2 0.07 0.14 II 31~70 12 4 0.14~0.18 0.28~0.36 III 71~115 5 9.6 0.43~0.56 0.86~1.12 1.4 分析项目与方法
各项指标测定方法均按照已有的方法[21]。采集进出水水样经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后,分别采用纳氏试剂法、N-(1-萘基)乙二胺分光光度法和紫外分光光度法测定样品中的
NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N和NO−3 -N;水中SO2−4 、SO2−3 、S2O2−3 离子浓度采用离子色谱仪(IC-AS23阴离子检测器,DIONEX ICS-900)检测;溶解性硫化物H2S/HS−/S2−采用亚甲基兰分光光度法检测;COD采用哈希DRB200快速消解仪测定;碱度采用五点滴定法;实验过程中,定期取反应器中均匀混合的污泥,测定MLSS、MLVSS;pH、温度采用便携式pH计(FG2-FK,METTLER TOLEDO)进行测定。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺构建及其对垃圾渗滤液处理效果
本研究中使用了已经稳定运行的短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX反应器,并对其进行了参数优化[22];短程硝化反硝化反应器中参与硝化反应的菌属Nitrosomonas(AOB)得到富集,Nitrospira(NOB)的丰度下降至<0.01%,保证了反应器中高效的亚硝化率[22-23]。如图2(a)所示,通过控制曝气时间(22.7 h)和DO浓度(≤0.5 mg·L−1)实现垃圾渗滤液短程硝化,同时消耗垃圾渗滤液中可生物降解的有机碳,为后续厌氧氨氧化脱氮提供了保障。在进水垃圾渗滤液TN为2 560 mg·L−1时,50%~60%的
NH+4 -N被转化为NO−2 -N,短程硝化反硝化反应器出水NH+4 -N为1 013.6 mg·L−1,NO−2 -N为1 206.3 mg·L−1,NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N的平均浓度比例为1∶1.21,说明短程硝化反硝化反应器中AOB为优势菌属 [22-23]。短程硝化反硝化反应器出水NO−3 -N基本维持稳定,平均浓度为247.8 mg·L−1,反硝化脱氮92.2 mg·L−1。短程硝化反硝化反应器出水符合厌氧氨氧化反应对NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N比例的要求[24]。本研究通过人工配水培养驯化的ANAMMOX颗粒污泥呈橙红色,平均粒径为762 μm(如图1所示)。由图2(b)可知,厌氧氨氧化反应器进水中NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N平均浓度分别为259.2 mg·L−1和275.1 mg·L−1,进水总氮为500~600 mg·L−1;通过厌氧氨氧化反应,NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N的去除率为91.6%和94.9%,ANAMMOX反应器出水NH+4 -N和NO−2 -N平均浓度分别21.9 mg·L−1和14.0 mg·L−1。短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX系统TN的平均去除率为93.1%,出水TN=176.3 mg·L−1。但是,由于厌氧氨氧化反应本身会将约10%的进水TN生成NO−3 -N,使得ANAMMOX出水TN>170 mg·L−1。其中,NO−x -N=154.5 mg·L−1,造成短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液出水未能达到国家规定的排放标准(GB 16889-2008)(TN≤40 mg·L−1)。因此,本研究采用硫化物作为电子供体,通过SAD脱氮技术,对短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺出水进行深度脱氮。2.2 硫自养反硝化反应器启动与脱氮效果
本研究采用人工配水启动SAD反应器,通过逐步提高SAD反应器进水中
NO−3 -N的负荷,使反应器内微生物能适应高负荷的含氮废水。为了探究SAD反应器的脱氮能力,启动期间,将进水pH控制在7.6~7.8之间,实验启动过程根据HRT的不同分为为3个阶段(表2)。阶段I(0~30 d)是污泥筛选的重要阶段,如图3所示,通过提高进水硫化物浓度,氮去除率达99%。该阶段使反应器中异养菌减少,硫自养菌进一步富集。在阶段II(31~70 d)中,将HRT缩短至12 h,当SAD反应器氮去除率稳定在90%以上时,将进水NO−3 -N浓度由70 mg·L−1逐步提升至90 mg·L−1,避免了高浓度NO−3 -N对反应器的冲击,反应器进水氮负荷由0.14 kg·(m3·d)−1提升至0.18 kg·(m3·d)−1。在第71天,将进水NO−3 -N浓度提升到100 mg·L−1,并且HRT由12 h缩短至5 h,氮负荷提升至0.43 kg·(m3·d)−1,出水中NO−3 -N和NO−2 -N平均浓度分别保持在1.5 mg·L−1和4.2 mg·L−1,TN去除率保持在94%左右。在100~115 d内,进水NO−3 -N浓度由100 mg·L−1提升至130 mg·L−1, 反硝化率略有降低。研究中发现,SAD反应器经过115 d的启动和运行,当HRT为5 h、进水NO−3 -N浓度为100 mg·L−1、S/N质量比率为2时,氮去除率为94%;同时,SAD反应器中出水中的硫代硫酸盐和硫化物浓度均在0.1 mg·L−1以下,出水硫酸盐浓度会随着不同阶段进水硫化物浓度的改变而变化,其中约64.2%的硫化物转化为硫酸盐(部分生成硫单质),硫化物去除率为100%。2.3 短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX-SAD耦合工艺实现垃圾渗滤液深度脱氮
将短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX与SAD反应器进行耦合,形成短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX-SAD两级自养深度脱氮反应系统(图1),其脱氮效果如图4所示。SAD反应器通过调节池调节ANAMMOX出水pH为7.6~7.8,利用ANAMMOX反应器出水提供的
NO−3 -N与NO−2 -N作为电子受体、投加的硫化物作为电子供体进行硫自养反硝化反应。根据启动期间SAD反应器的氮去除负荷,设置HRT为6 h,设置S/N质量比率为2。由图4(a)、图4(d)、图4(g)可知,通过控制短程硝化反硝化反应器的曝气时间和DO浓度,使进水中50%~60%的NH+4 -N被转化为NO−2 -N,NH+4 -N与NO−2 -N的浓度比例为(1∶1)~(1∶1.4)。由图4(c)、图4(f)、图4(i)可知,在进水NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N、NO−3 -N平均浓度分别为4.2、3.6、88.5 mg·L−1时,SAD反应器出水NO−3 -N平均浓度为9.7 mg·L−1,NO−3 -N平均去除率为89.3%,出水NO−2 -N平均浓度为0.6 mg·L−1。短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX耦合SAD反应器在连续64 d处理垃圾渗滤液的过程中,SAD反应器稳定运行,出水水质稳定。由图4(b)、图4(e)、图4(h)可知,ANAMMOX反应器运行过程中,进水NO−3 -N平均浓度为97.8 mg·L−1,出水NO−3 -N增加为140.5 mg·L−1。ANAMMOX进出水NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N浓度会有些许波动,主要是由于短程硝化反硝化反应器溶解氧浓度波动导致,溶解氧会促进亚硝化细菌(NOB)的生长,导致厌氧氨氧化反应底物的不足(NO−2 -N不足),从而影响脱氮效率[25]。本研究采用了短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化(ANAMMOX)-硫自养反硝化(SAD)工艺,通过两级自养反硝化实现了垃圾渗滤液深度脱氮。将启动成功的SAD反应器与短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX反应器串联,通过基于硫化物的自养反硝化去除了ANAMMOX产生的
NO−x -N,提高了整体工艺的总氮去除率,出水水质达到《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》氮排放标准(TN≤40 mg·L−1)。在目前处理垃圾渗滤液脱氮的同类研究中,普遍难以实现垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮[26-27],而本研究在无需投加高成本碳源的情况下,实现了垃圾渗滤液的高效、深度脱氮处理。3. 结论
1)短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX工艺处理垃圾渗滤液脱氮效果较好,总氮去除负荷可达1.19 kg·(m3·d)−1,总氮去除率可达93.1%。但工艺出水中
NO−3 -N浓度为140.5 mg·L−1(TN=176.3 mg·L−1),无法达到(GB 16889-2008)中规定的垃圾渗滤液处理厂出水排放标准。2)SAD反应器成功启动,反应器进水氮负荷为0.43 kg·(m3·d)−1,氮去除率为94%,硫化物去除率为100%,实现了反应器中硫自养反硝化菌的富集。
3)短程硝化反硝化-ANAMMOX-SAD工艺出水TN均值<12 mg·L−1、TN去除率达到99.5%、总氮去除负荷达到0.85 kg·(m3·d)−1,实现了处理垃圾渗滤液的深度脱氮。同时,垃圾填埋场中的硫化氢气体以回收与再循环的方式为本工艺提供硫源,这为硫化氢气体的去除提供了新思路。
-
表 1 垃圾渗滤液水质
Table 1. Characteristic of landfill leachate
pH COD/(mg·L−1) NH+4 -N/(mg·L−1)NO−2 -N/(mg·L−1)NO−3 -N/(mg·L−1)碱度/(mg·L−1) 8.3~8.8 4 000~5 000 2 300~2 700 <5 <50 10 000~13 000 表 2 SAD反应器启动过程中运行条件
Table 2. Operation conditions during start-up of SAD reactor
阶段 运行时间/d HRT/h 进水流量/(L·d−1) 氮负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) 硫负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) I 0~30 24 2 0.07 0.14 II 31~70 12 4 0.14~0.18 0.28~0.36 III 71~115 5 9.6 0.43~0.56 0.86~1.12 -
[1] 袁文祥, 陈善平, 邰俊, 等. 我国垃圾填埋场现状、问题及发展对策[J]. 环境卫生工程, 2016, 24(5): 8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8206.2016.05.002 [2] 吴迪, 王凯, 刘宇, 等. 低C/N比老龄化垃圾渗滤液处理工程的提标改造[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(3): 843-847. [3] ZHANG F Z, PENG Y Z, WANG S Y, et al. Efficient step-feed partial nitrification, simultaneous ANAMMOX and denitrification (SPNAD) equipped with real-time control parameters treating raw mature landfill leachate[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 364: 163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.066 [4] ZHOU Q, LIN Y, LI X, et al. Effect of zinc ions on nutrient removal and growth of lemna aequinoctialis from anaerobically digested swine wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249: 457-463. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.044 [5] 王凡, 陆明羽, 殷记强, 等. 反硝化-短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺处理晚期垃圾渗滤液的脱氮除碳性能[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3782-3788. [6] XIANG L, YAN Y, FAN W, et al. Highly efficient of nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate using a combined DN-PN-Anammox process with a dual recycling system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 265: 357-364. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.023 [7] SRI S S, JOSEPH K. Nitrogen management in landfill leachate: Application of SHARON, ANAMMOX and combined SHARON-ANAMMOX process[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(12): 2385-2400. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.06.006 [8] LACKNER S, GILBERT E M, VLAEMINCK S E, et al. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences: An application survey[J]. Water Research, 2014, 55: 292-303. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.02.032 [9] SHALINI S, JOSEPH K. Start-up of the SHARON and ANAMMOX process in landfill bioreactors using aerobic and anaerobic ammonium oxidizing biomass[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 149: 474-485. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.104 [10] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准: GB 16889-2008[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2008. [11] HU L, DU Y, LONG Y Y. Relationship between H2S emissions and the migration of sulfur-containing compounds in landfill sites[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2017, 106: 17-23. [12] SAHINKAYA E, YURTSEVER A, AKTAS O, et al. Sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification of drinking water using a membrane bioreactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 268: 180-186. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.045 [13] 黄奕亮, 张立秋, 李淑更, 等. 短程硝化厌氧氨氧化联合处理实际垃圾渗滤液[J]. 工业水处理, 2018, 38(3): 37-41. [14] LU H, WANG J, LI S, et al. Steady-state model-based evaluation of sulfate reduction, autotrophic denitrification and nitrification integrated (SANI) process[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(14): 3613-3621. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.05.013 [15] 任争鸣, 刘雪洁, 苏晓磊, 等. 硫自养反硝化深度脱氮中试研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(19): 31-35. [16] CHRISTIANSON L, LEPINE C, TSUKUDA S, et al. Nitrate removal effectiveness of fluidized sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification biofilters for recirculating aquaculture systems[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2015, 68(4): 10-18. [17] WANG J, LU H, CHEN G H, et al. A novel sulfate reduction, autotrophic denitrification, nitrification integrated (SANI) process for saline wastewater treatment[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(9): 2363-2372. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.02.037 [18] YANG W, ZHAO Q, LU H, et al. Sulfide-driven autotrophic denitrification significantly reduces N2O emissions[J]. Water Research, 2016, 90: 176-184. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.032 [19] LU H, HUANG H, YANG W, et al. Elucidating the stimulatory and inhibitory effects of dissolved sulfide on sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) driven autotrophic denitrification[J]. Water Research, 2018, 133: 165-172. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.022 [20] YANG W, LU H, KHANAL S K, et al. Granulation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria for autotrophic denitrification[J]. Water Research, 2016, 104: 507-519. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.08.049 [21] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [22] 梁俊宇, 周鸿, 赵晴, 等. 垃圾渗滤液部分亚硝化的启动运行及菌群分析[J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(3): 99-103. [23] 梁俊宇. 短程硝化反硝化-厌氧氨氧化联合工艺处理垃圾渗滤液[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2018. [24] YAMAMOTO T, TAKAKI K, KOYAMA T, et al. Long-term stability of partial nitritation of swine wastewater digester liquor and its subsequent treatment by ANAMMOX[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(14): 6419-6425. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.052 [25] WANG H L, KIM M, LI K, et al. Effective partial nitrification of ammonia in a fluidized bed bioreactor[J]. Environmental Technology, 2019, 40(1): 94-101. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2017.1380710 [26] MIAO L, WANG K, WANG S Y, et al. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using real-time controlled three-stage sequence batch reactor (SBR) system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 159: 258-265. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.058 [27] PHAN T N, VAN TRUONG T T, HA N B, et al. High rate nitrogen removal by ANAMMOX internal circulation reactor (IC) for old landfill leachate treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 234: 281-288. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.117 期刊类型引用(6)
1. 王馥容,张雨,冯诗语,王宇航,郑伊宁,张家豪,王连顺,卢亚楠,王丽,谷晶,丛玉婷,杨国军,王华. 新型生物脱氮技术及其相关酶系的研究进展. 海洋科学. 2024(06): 106-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘冬冬,王健. 自养脱氮技术处理老龄填埋场渗滤液的中试研究. 给水排水. 2024(S1): 186-190+195 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋韶华,刘永军,杨璐,刘磐,张爱宁. 厌氧氨氧化技术在废水处理中的研究与应用进展. 水处理技术. 2022(10): 6-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘宝峰,郭宇平. 硫自养反硝化技术用于市政污水深度处理. 中国给水排水. 2022(22): 91-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 尼马泽郎,穆永杰,薛晓飞,张丽丽,苏本生,曹之淇. 一段式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合缓释碳源滤柱深度去除总氮. 环境工程学报. 2021(07): 2468-2479 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王刚,高会杰,孙丹凤,陈明翔,徐晓晨. 厌氧氨氧化技术在废水脱氮领域的应用进展. 化工环保. 2020(02): 111-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)
-















 下载:
下载: