-
沼气、天然气、页岩气等能源中都含有一定量的H2S,已成为影响这些能源安全应用的重要因素之一[1-3],这些能源在综合利用前须对H2S气体进行脱除。脱除H2S的方法主要包括化学法和生物法[4-6]。生物法脱硫在工程中的应用非常广泛,它具有运行条件温和、去除H2S比例高、耗费能量少,并且几乎无废液生成等优点[7-9]。根据脱硫细菌适宜环境的差异,生物脱硫法可分为酸法生物脱硫和碱法生物脱硫[10]。氧化硫硫杆菌和氧化亚铁硫杆菌是酸法生物脱硫中常用的2类细菌[11-12],其氧化产物主要是
SO2−4 ,生物反应器中的溶液呈酸性,pH通常为2~6。碱法生物脱硫通常采用排硫硫杆菌作为脱硫细菌进行生物脱硫[13-14],氧化产物主要是单质S,生物反应器中溶液呈碱性。碱法生物脱硫工程由吸收塔和生物反应器2部分构成。在吸收塔中,H2S气体和碱性溶液进行逆相接触后被吸收在碱液中,这个过程对H2S的吸收效率高、停留时间短。在生物反应器中,溶液中的硫化物先与O2反应生成单质S,同时伴随着OH−的产生。但是在脱硫反应中,部分单质S也会与O2反应产生SO2−4 和H+,为保证较高脱硫效率,必须补充碱中和这些H+,中和反应产生的盐会增加系统的盐度,为了维持脱硫细菌的活性,通过定期补充部分清水以控制吸收液的盐度。此外,产生的单质S可被进一步回收利用,碱法生物脱硫反应如式(1)~式(3)所示。荷兰帕克公司自1993年开发沼气碱法生物脱硫工艺,并且在多个行业得到应用,但是对于在生物脱硫过程中如何增加单质S的生成比例,并无相关报道。SAN-ALERO等[15]开发了一套全好氧生物脱硫装置,H2S去除率超过80%,这套装置利用吸收塔和鼓泡塔生物反应器进行耦合。SONG等[16]开发了上流式内循环缺氧反应器,H2S去除率最高可达95.2%。陆慧锋等[17]对一体式沼气安全脱硫反应器的使用进行优化,沼气脱硫率达到93.8%。在刘卫国[18]的碱法生物脱硫技术的中试项目中,沼气中H2S的含量为3~4 g·m−3,硫化物去除率为95%。但因为生物脱硫过程中单质硫的生成率难以控制,除了帕克公司,生物脱硫技术在实际生物脱硫工程中运用较少。
影响碱法生物脱硫氧化产物中单质硫的生成比例的因素很多,对于如何在工程上利用综合性的参数控制生物脱硫运行过程,同时实现较高脱硫效率和单质S的生成率目标的研究不多。本研究在批量反应器中探索硫化物浓度、盐度、氧化还原电位(ORP)、溶解氧(DO)、温度等运行参数对碱法生物脱硫效果的影响,优化碱法生物脱硫技术的控制参数,为实际碱法生物脱硫工程提供参考。
全文HTML
-
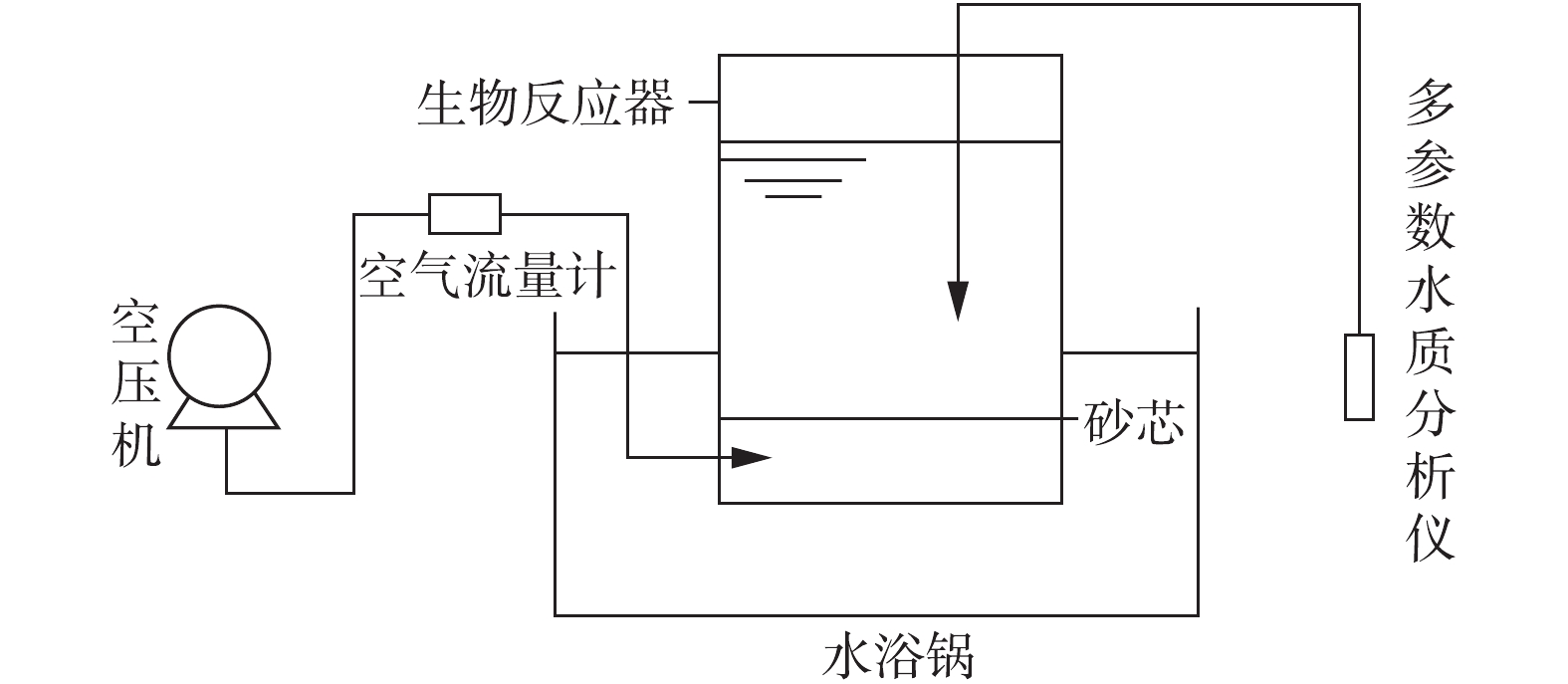
实验装置包括1个批量生物反应器、水浴锅、曝气系统、多参数水质分析仪,如图1所示。批量生物反应器(半径为6 cm,高为16 cm)体积为1 100 mL,主要材质为玻璃,为使空气均匀地分布在反应器中,在反应器底部装有砂芯(孔径50~70 μm),空气从反应器底部通入。为控制溶液的温度,将反应器置于水浴锅内。曝气系统由空压机和空气流量计组成,反应器中溶液的氧气浓度可通过空气流量计调节。多参数水质分析仪(德国WTW公司Multi 3420)可以快速检测溶液的盐度、ORP、pH、DO以及温度参数。
-
生物反应器中的脱硫污泥取自某沼气生物脱硫工程,污泥的浓度为19 950 mg·L−1。硫化物模拟废水使用工业级的硫化钠(Na2S)配制,反应开始时,迅速加入硫化物模拟废水和1∶1盐酸(HCl),调节溶液中硫化物的浓度为500 mg·L−1,起始pH调节为7.0。向反应器中添加以固定比例调配的尿素((NH2)2CO)、硫酸镁(MgSO4)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)营养液,提供脱硫细菌需要的微量元素。在脱硫过程中,添加的Na2S会造成溶液盐度的上升,可通过使用少量自来水置换反应器内的上清液调节溶液的盐度。此外,当脱硫反应中盐度和温度环境发生变化时,须驯化脱硫细菌10 d和4 d,这样可使脱硫细菌充分适应变化后的脱硫环境。硫化物的浓度采用碘量法[19]测定。
实验探究了脱硫效率受盐度条件变化的影响,生物脱硫效率受DO浓度变化和温度变化的影响,同时研究了实验中ORP和pH随时间的变化过程。
在盐度对脱硫效率的影响实验中,探索了脱硫细菌对硫化物无预吸附和脱硫细菌对硫化物有预吸附2种环境条件下,硫化物浓度变化受盐度条件的影响。控制溶液温度为30 ℃,溶解氧约为1 mg·L−1,控制盐度分别为1.5%、2.5%、3.5%、4.5%和5.5%。脱硫细菌对硫化物无预吸附环境[10]的研究是在上一次生物脱硫反应基本结束时开始的,即硫化物的浓度下降至10 mg·L−1后,加入硫化物模拟废水迅速开始实验,研究溶液中硫化物的浓度随反应时间的变化,在实验开始时,硫化物的起始浓度为500 mg·L−1。脱硫细菌对硫化物有预吸附环境[10]的研究是在上一次迅速去除过程基本完成时开始的,可通过2次添加硫化物废水实现,当反应器内硫化物浓度降低到320 mg·L−1左右时,再次快速添加模拟废水,调节溶液中硫化物浓度为500 mg·L−1,然后开始实验。
在DO浓度对生物脱硫效率的影响实验中,控制溶液温度为30 ℃,盐度为3.5%,DO浓度分别为1、2和3 mg·L−1。
在温度对生物脱硫效率的影响实验中,调节溶液DO浓度为1 mg·L−1,盐度为3.5%,溶液温度为15、20、25、30和35 ℃。化学氧化对脱硫效率的影响实验是指在不加污泥的条件下,在自来水中加入硫化物模拟废水,研究溶液中硫化物的浓度随运行时间的变化。
1.1. 实验装置
1.2. 实验方法
-
盐度是生物脱硫效率重要的影响因素之一[20-21],如果脱硫细菌在较高盐度环境中仍有较高活性,就能够减少碱法生物脱硫中自来水更换溶液的次数,进而减少脱硫过程中碱液的添加量,降低运行成本。
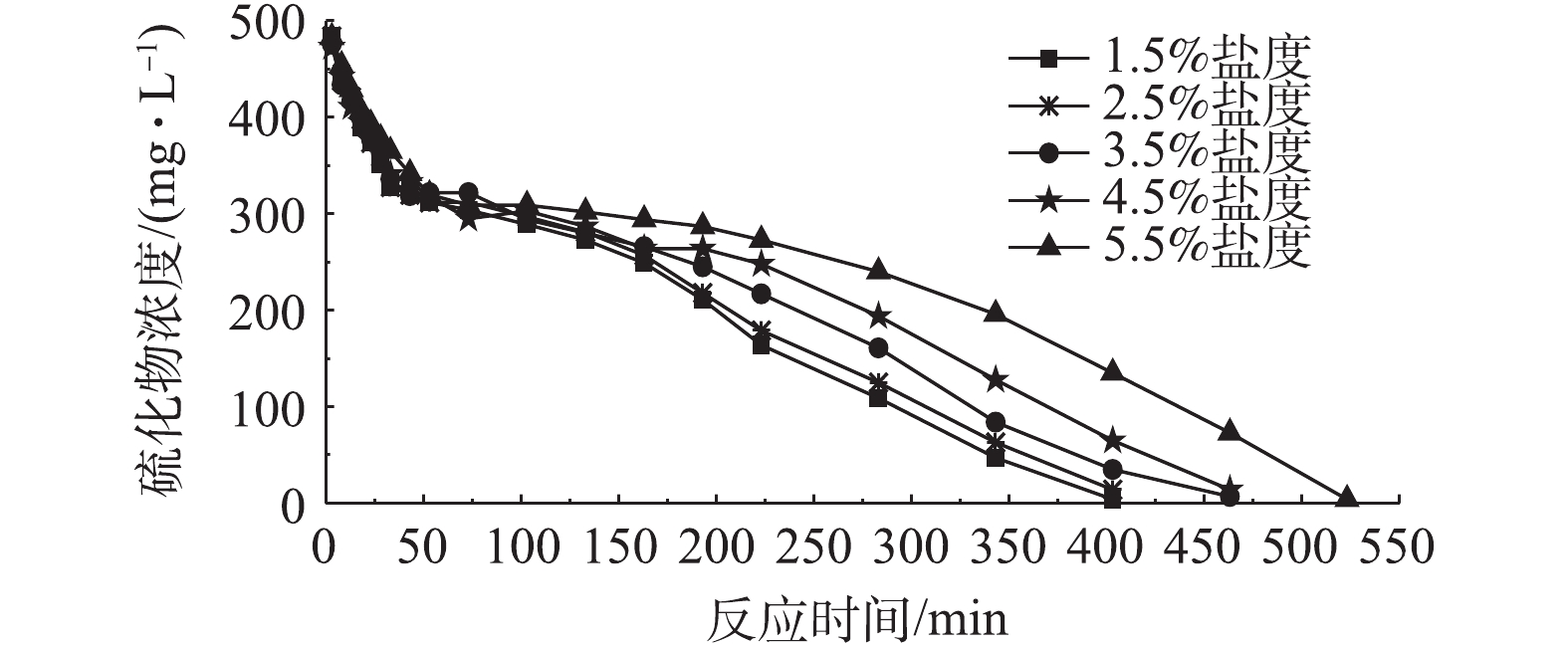
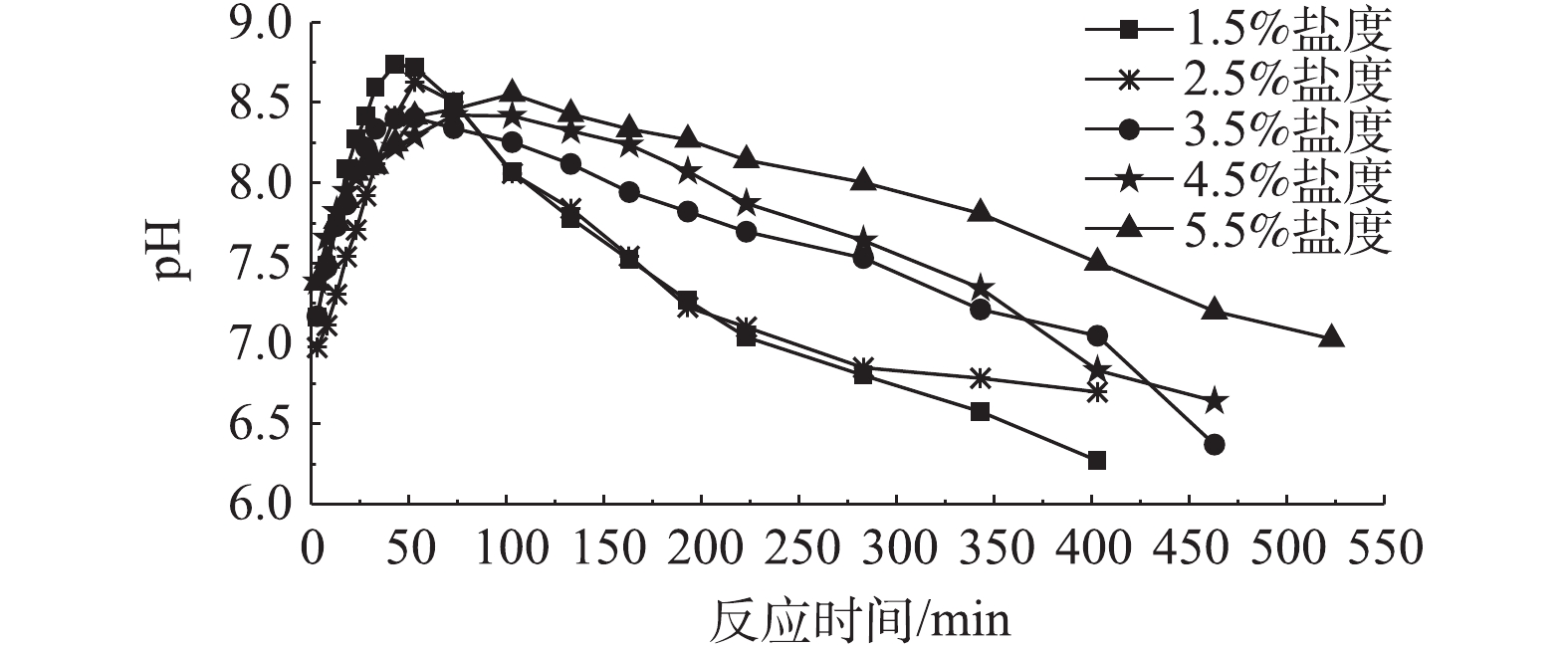
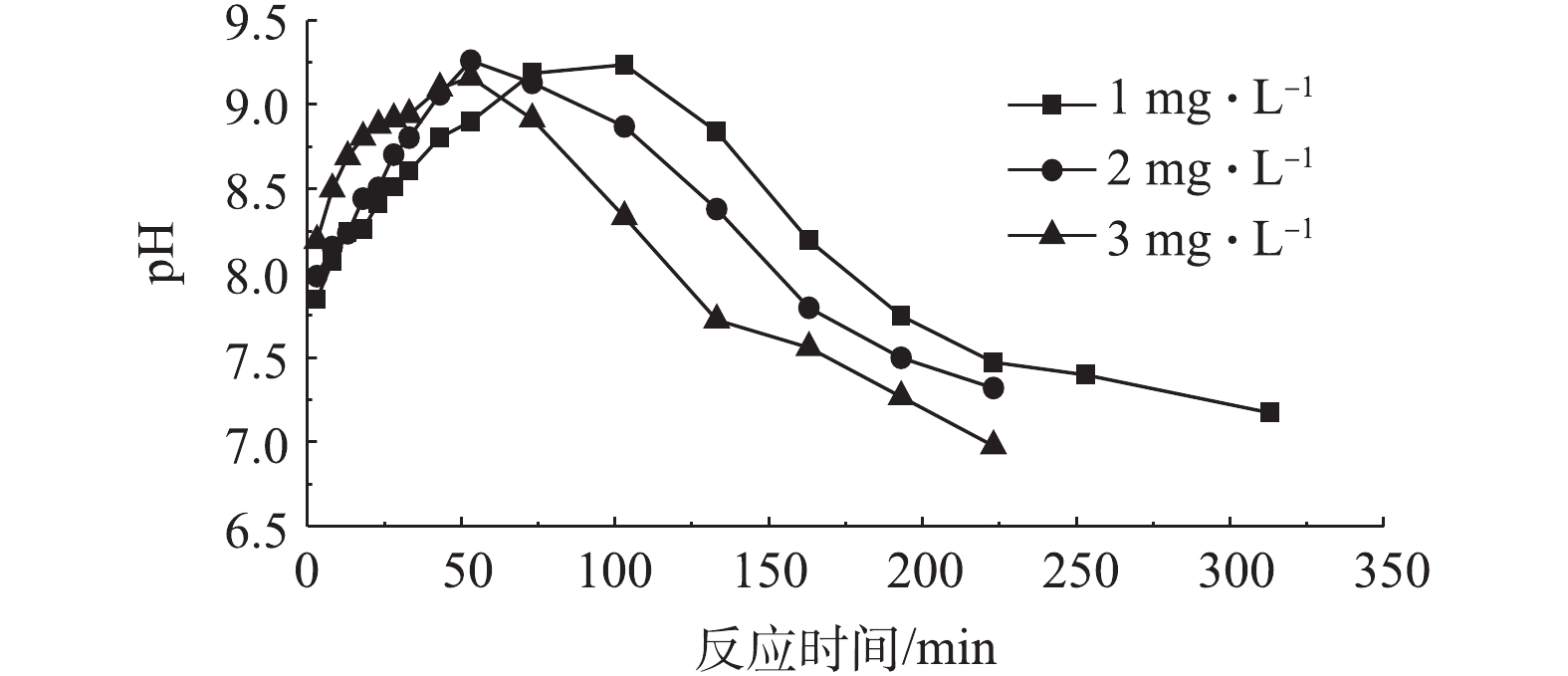
脱硫细菌在硫化物无预吸附环境下,反应器内硫化物浓度受溶液盐度变化的影响如图2所示。溶液pH受盐度变化的影响如图3所示。硫化物的去除率随着盐度的上升而逐渐减小。当盐度为1.5%~3.5%时,在约343 min的时间内,硫化物浓度从500 mg·L−1降低至10 mg·L−1,脱硫效率高,但当盐度上升为4.5%和5.5%时,硫化物的去除率明显变低。同时,脱硫的过程可分为以下3个过程。
第1个过程为溶液中硫化物迅速下降过程。在大约53 min的运行时间内,反应器中的硫化物被迅速去除。当溶液盐度不大于3.5%时,溶液中硫化物浓度降低为280~300 mg·L−1。当溶液的盐度继续上升时,在同样的运行时间内,硫化物浓度仅下降至320 mg·L−1,硫化物去除率明显降低。在此过程中,反应器内pH由7.0快速上升至8.5左右,表明在这个运行过程中,硫化物的主要氧化产物为单质S。
第2个过程为溶液中硫化物去除停滞过程。在80 min的反应时间内,硫化物浓度基本维持在320~280 mg·L−1,溶液硫化物并无明显减少的现象。当盐度小于3.5%时,硫化物浓度变化基本处于停滞状态,约为280 mg·L−1,随着溶液盐度逐渐增加,这个停滞的过程逐渐消失。当盐度被提高至5.5%时,溶液中硫化物的去除率明显降低。在这个过程中,溶液的pH不再上升反而开始缓慢下降,表明在这段时间内,硫化物的主要产物变为
SO2−4 。第3个过程为溶液中硫化物低速下降过程。在210~360 min的运行过程中,反应器中硫化物的浓度都降低至10 mg·L−1,溶液pH下降至7.0以下,且下降速度随着盐度的降低而变快,这说明溶液盐度越小时,氧化产物中单质S的比例越小。
在迅速下降过程中,硫化物浓度快速下降可能是因为溶液中硫化物被脱硫细菌快速吸附。当脱硫细菌在硫化物浓度为500 mg·L−1环境中时,会将水溶液中的硫化物快速吸附到细菌体内,使得硫化物浓度迅速减小,在这个过程中,脱硫细菌体内的部分硫化物与酶作用,被氧化为单质S和
SO2−4 。在停滞过程中,溶液中硫化物浓度的变化很小,甚至处于停滞状态,原因可能是经过迅速下降过程中脱硫细菌对溶液中硫化物的快速吸附后,细菌体内体外的硫化物浓度处于平衡状态,几乎不再吸附溶液中的硫化物,所以溶液中硫化物浓度变化处于停滞状态,在这个过程中,脱硫细菌主要氧化体内的硫化物。在低速下降过程中,溶液中硫化物被脱硫细菌吸附和氧化的现象同时存在,硫化物浓度继续降低,但由于溶液中大多数的硫化物已经被脱硫细菌吸附氧化,硫化物浓度降低的速度变慢。为了进一步探索生物脱硫过程中硫化物浓度对脱硫效率的影响,在脱硫细菌对硫化物有预吸附环境下继续进行研究。脱硫细菌在硫化物有预吸附环境下,反应器内硫化物浓度受溶液盐度条件变化的影响如图4所示,溶液pH受盐度变化的影响如图5所示,在生物脱硫反应的前53 min内,脱硫效率仍然较高,但与无预吸附环境相比,硫化物去除率有所减少。当盐度低于3.5%时,硫化物有预吸附环境与无硫化物预吸附环境相比,迅速下降过程结束时,溶液中硫化物浓度由280 mg·L−1变为320 mg·L−1,说明在这个过程中,溶液中硫化物在有预吸附环境下依旧存在迅速下降的过程,但脱硫细菌对硫化物的吸附量变少。在停滞过程中,硫化物浓度的降低过程在改变盐度条件的情况下均产生停滞,表明此过程脱硫细菌几乎不再吸附溶液中的硫化物,主要氧化吸附在细菌体内的硫化物。改变盐度条件时,迅速下降过程中pH均快速升高。当盐度降低为1.5%时,溶液pH增高为8.7。与脱硫细菌对硫化物无预吸附环境条件相比,有预吸附环境下溶液pH的峰值会增高,这表明当硫化物浓度较高时,氧化产物中单质S的比例会增加。综上所述,如果能够使得生物脱硫的过程一直被控制在迅速下降过程中,就能够在硫化物被快速吸附氧化的同时,增加氧化产物中单质S的比例。控制溶液盐度条件在3.5%以内,可实现较优的脱硫效果。
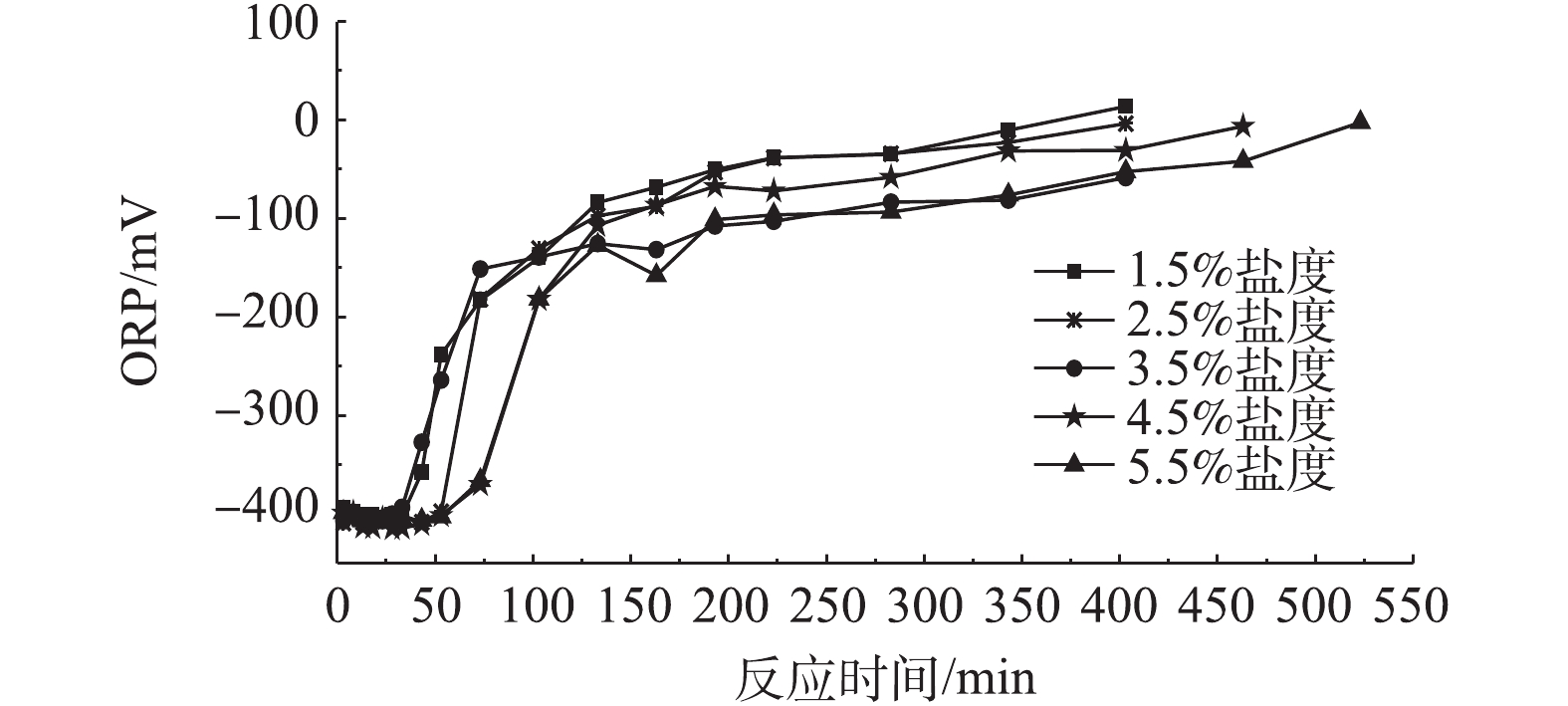
此外,随着反应时间的推移,生物反应器内溶液ORP值的变化如图6所示。在硫化物浓度迅速降低过程中,虽然溶液盐度不断上升,但ORP并未发生明显变化,可以稳定维持在−400 mV附近;在停滞过程中,溶液的ORP发生快速上升的现象,由−400 mV非常迅速地升高到−150 mV附近;在低速下降过程中,ORP的变化非常缓慢,由−150 mV缓慢增高到0 mV附近。在实际生物脱硫工程中,如果可以将溶液的ORP值维持在−400 mV附近,就能够将控制生物脱硫反应持续在迅速下降过程中,从而达到较好的脱硫效果。
-
为了增加单质S的生成量,减少产物中
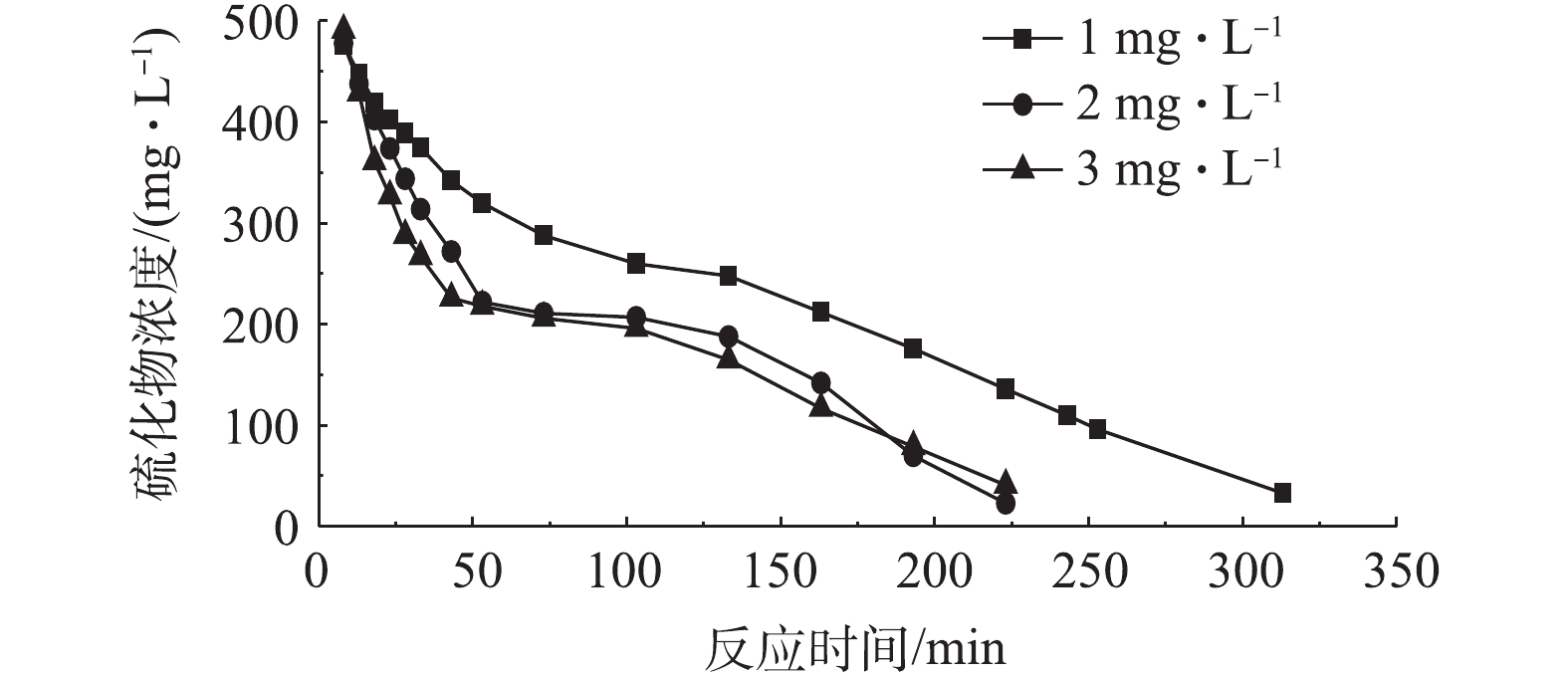
SO2−4 ,可通过调节反应器内溶液的氧气含量,控制硫化物的氧化产物[22-23]。反应器中硫化物浓度受DO浓度变化的影响如图7所示。在生物脱硫反应开始的53 min内,即迅速下降过程中,如果控制溶液中DO浓度为1 mg·L−1,溶液中硫化物的浓度以较快的速度从500 mg·L−1降低为320 mg·L−1;控制DO浓度为2 mg·L−1和3 mg·L−1,溶液中硫化物浓度分别变为222 mg·L−1和218 mg·L−1,此时,硫化物的去除率明显高于DO为1 mg·L−1的去除率。溶液pH受DO浓度的影响如图8所示,在停滞和低速下降过程中,控制溶液DO浓度为3 mg·L−1,与浓度为2 mg·L−1条件下相比,溶液的pH下降速度增快,表明溶液DO浓度较高时,会有更多SO2−4 生成。综上所述,若要达到较优的脱硫效果,可通过控制曝气量,使DO浓度保持在2 mg·L−1左右。 -
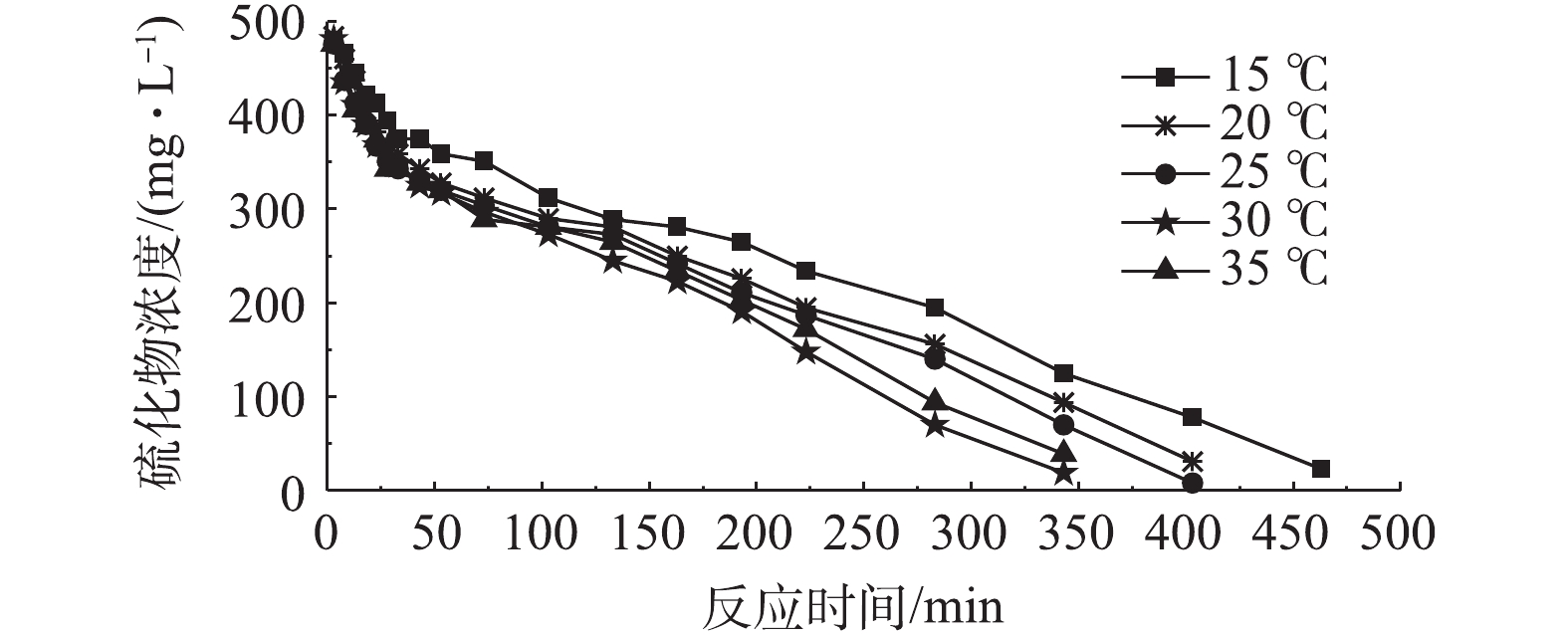
适宜的温度能够促进微生物体内生物酶的高效表达,所以温度是保证生物脱硫体系高效运行的重要条件之一[24]。改变温度环境时,溶液中硫化物浓度的变化情况如图9所示,在迅速下降过程结束后,当温度条件为30 ℃时,硫化物浓度降为317 mg·L−1。反应器内硫化物去除率随温度条件从15 ℃升高至30 ℃而逐渐升高,当溶液温度为15 ℃时,硫化物浓度仅降低至359 mg·L−1。硫化物去除率在温度达到35 ℃时不再升高,这可能是由于较高的温度环境会抑制脱硫细菌体内的酶的高效表达,对脱硫效果产生影响。值得注意的是,除去高温对酶活性的抑制,在实际生物脱硫工程中,为了维持反应器内较高的温度条件,须增加加热器的运行时间,选择温度条件为30 ℃,可在实现较优的脱硫效果的同时降低运行成本。
-
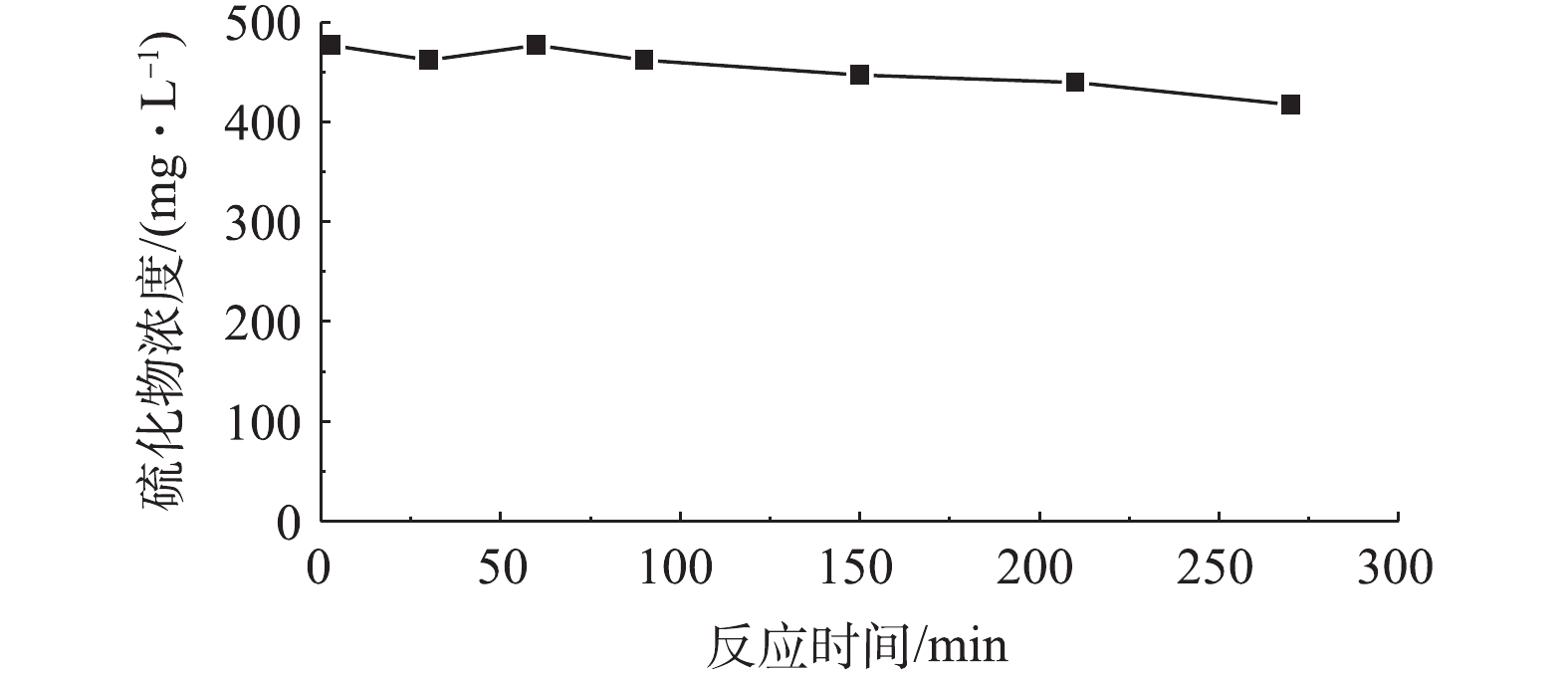
如果反应体系中没有脱硫污泥仅发生化学氧化现象,硫化物浓度随时间的变化情况如图10所示。实验过程中溶解氧浓度大约为8.85 mg·L−1。在无脱硫污泥环境中,经过约4.5 h的充分曝气后,反应器中硫化物的浓度变为417 mg·L−1,仅降低了60 mg·L−1,这说明空气氧化较污泥中脱硫细菌对硫化物浓度变化的影响是微不足道的。在生物脱硫的硫化物浓度迅速下降过程中,硫化物的浓度由500 mg·L−1下降为320 mg·L−1仅需53 min,脱硫细菌对硫化物去除作用是空气氧化作用的16倍。所以,在批量反应器中进行碱法生物脱硫运行参数的优化研究里,空气氧化的因素可忽略不计。
2.1. 脱硫效率受盐度变化的影响
2.2. 脱硫效率受DO的影响
2.3. 脱硫效率受温度的影响
2.4. 脱硫效率受空气氧化的影响
-
1)脱硫细菌对硫化物的去除可分为迅速下降、停滞和低速下降过程。迅速下降过程约53 min,溶液中硫化物浓度由500 mg·L−1迅速降低至320 mg·L−1,脱硫细菌快速吸附硫化物,并将体内的部分硫化物氧化为单质S,此时,反应器中ORP值稳定地停留在−400 mV附近。在约80 min停滞过程中,硫化物浓度持续停留在320~280 mg·L−1内,脱硫细菌主要氧化细菌体内的硫化物,几乎不再吸附溶液中的硫化物。在低速下降过程中,硫化物浓度能够匀速地降至10 mg·L−1,硫化物的吸附和氧化同时低速发生。
2)与脱硫细菌对硫化物无预吸附环境相比,有预吸附环境条件下,脱硫效率会降低,但脱硫效率在迅速下降的过程中依旧最高,同时会产生更多的单质S。
3)在反应器内溶液盐度不高于3.5%,温度、DO浓度条件为30 ℃和2 mg·L−1时,控制反应体系中ORP值一直保持在−400 mV附近,即将生物脱硫反应持续控制在迅速下降过程中,就能够实现较优的脱硫效果。



 下载:
下载: