-

图 1 紫外/氯体系中PRM和NB的降解
Figure 1. Degradation of PRM and NB in the UV/chlorine process
-
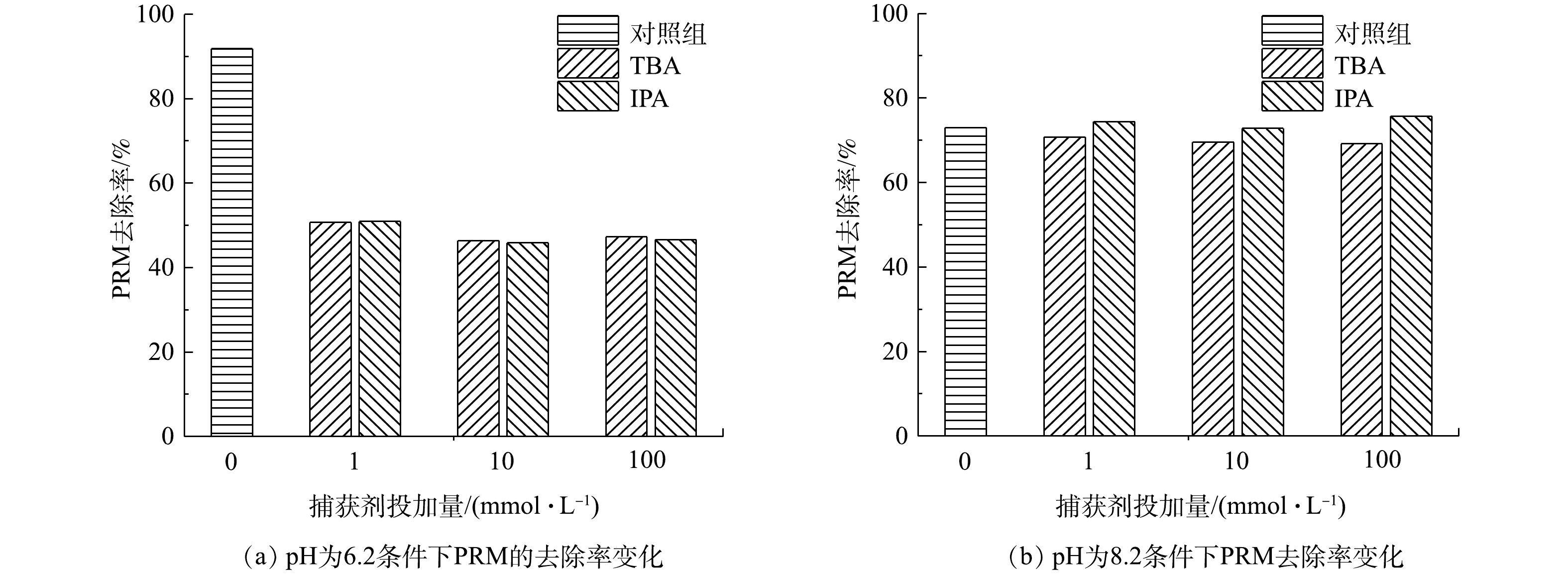
图 2 TBA和IPA在pH=6.2和pH=8.2条件下对紫外/氯体系降解PRM的影响
Figure 2. Effect of TBA and IPA on the degradation of PRM at pH 6.2 and 8.2
-
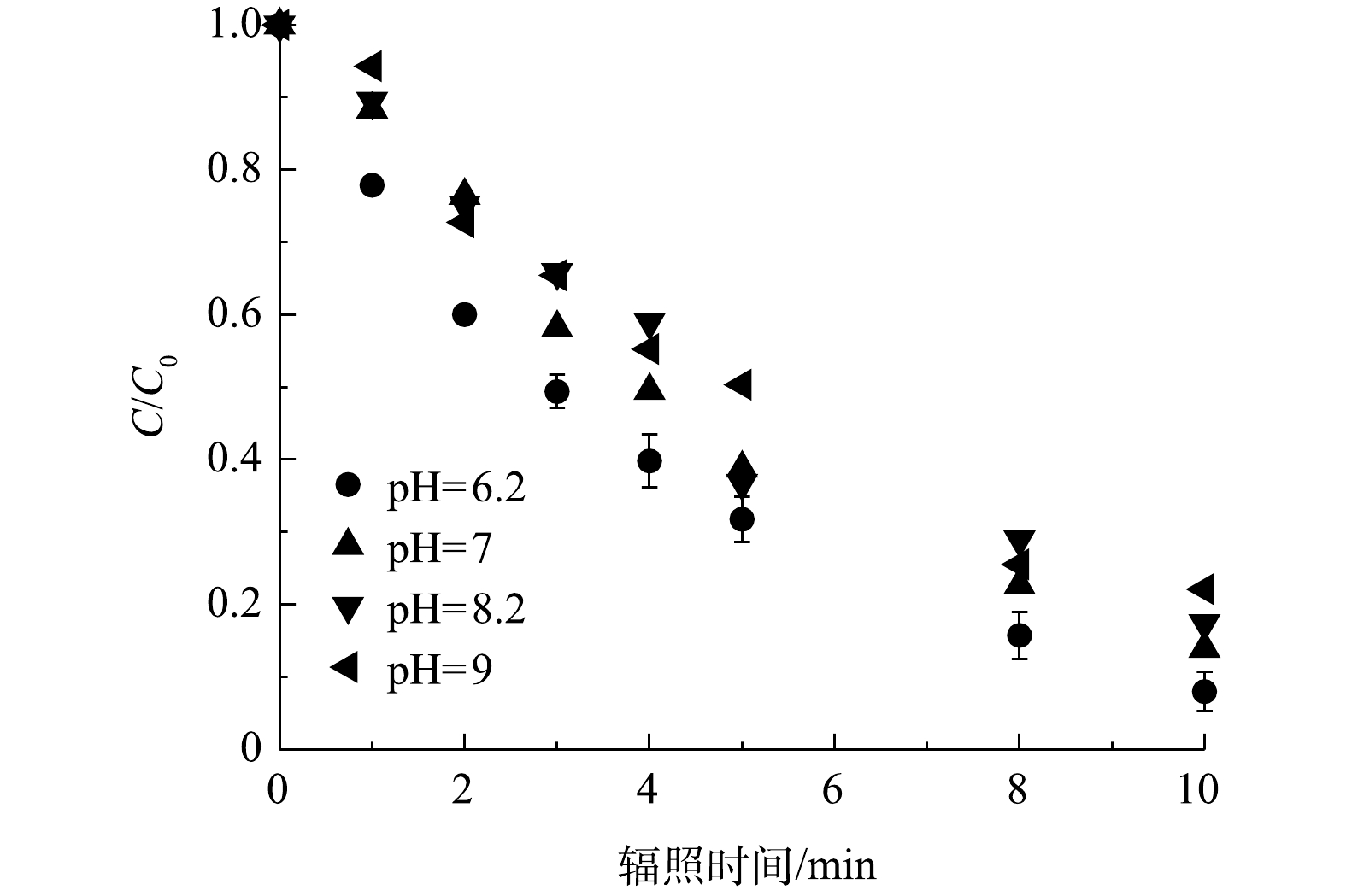
图 3 不同pH对PRM降解的影响
Figure 3. Effect of pH on the degradation of PRM
-
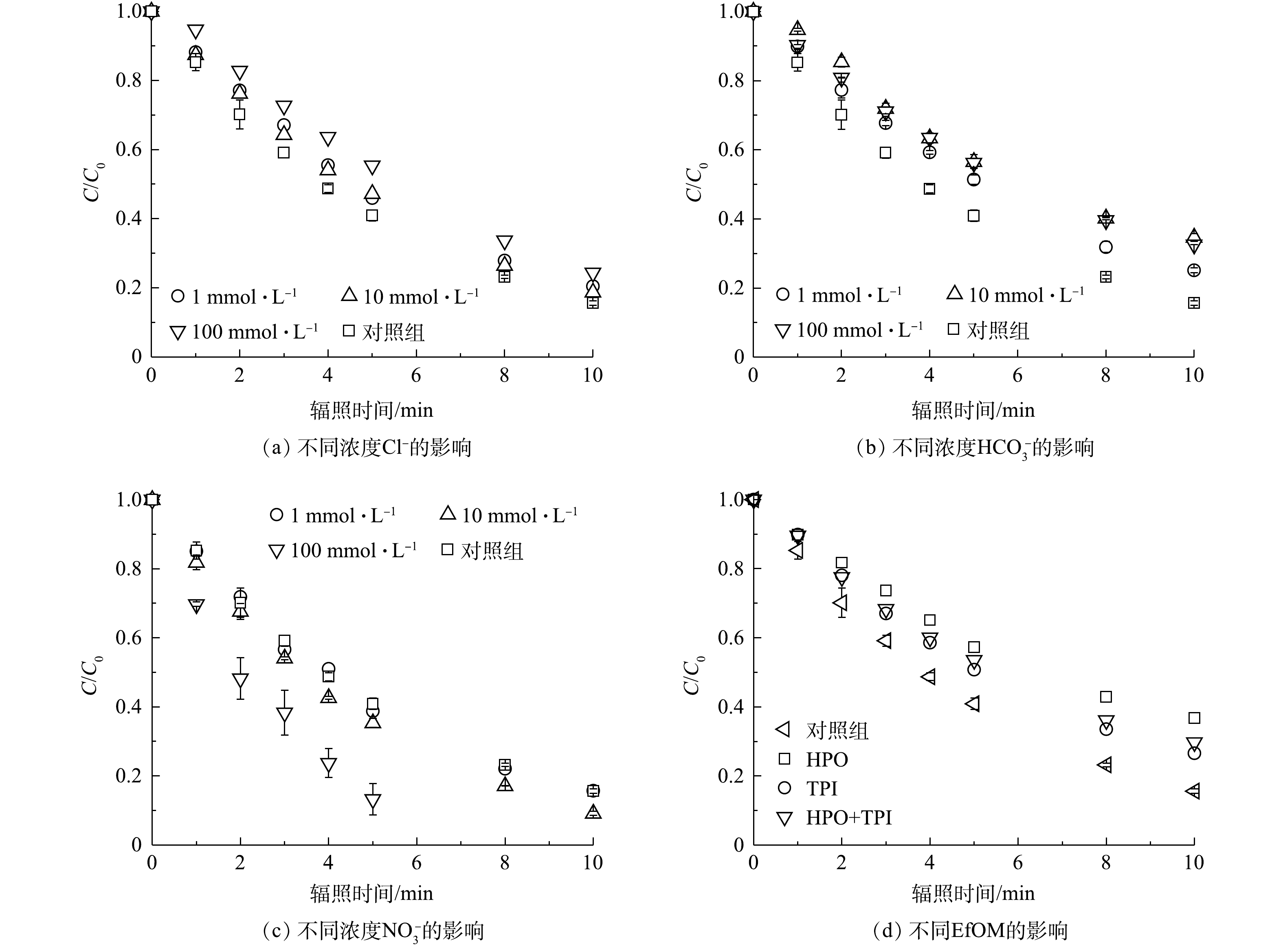
图 4 Cl−、HCO3−、NO3−和 EfOM对PRM降解的影响
Figure 4. Effect of Cl−, HCO3−, NO3− and EfOM on the degradation of PRM.
-
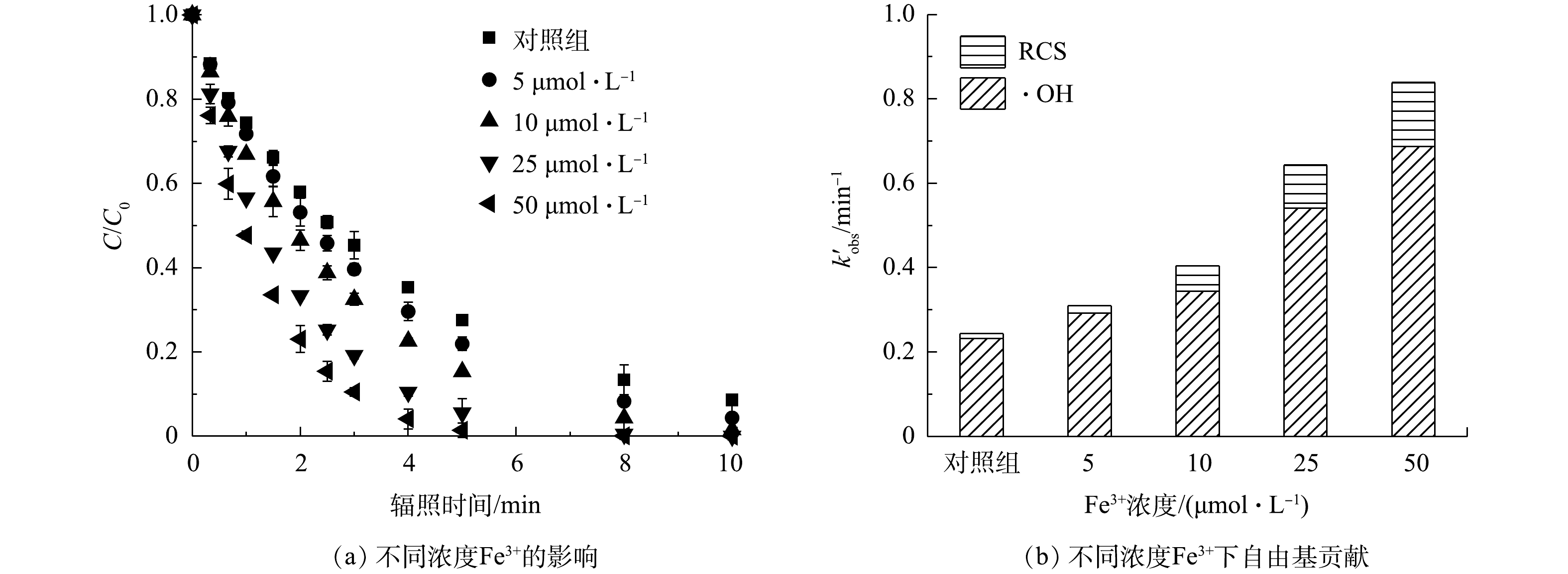
图 5 不同浓度Fe3+对紫外/氯体系降解PRM的影响及自由基贡献
Figure 5. Effect of different concentrations of Fe3+ on PRM degradation by the UV/chlorine and the corresponding contribution of radicals
-
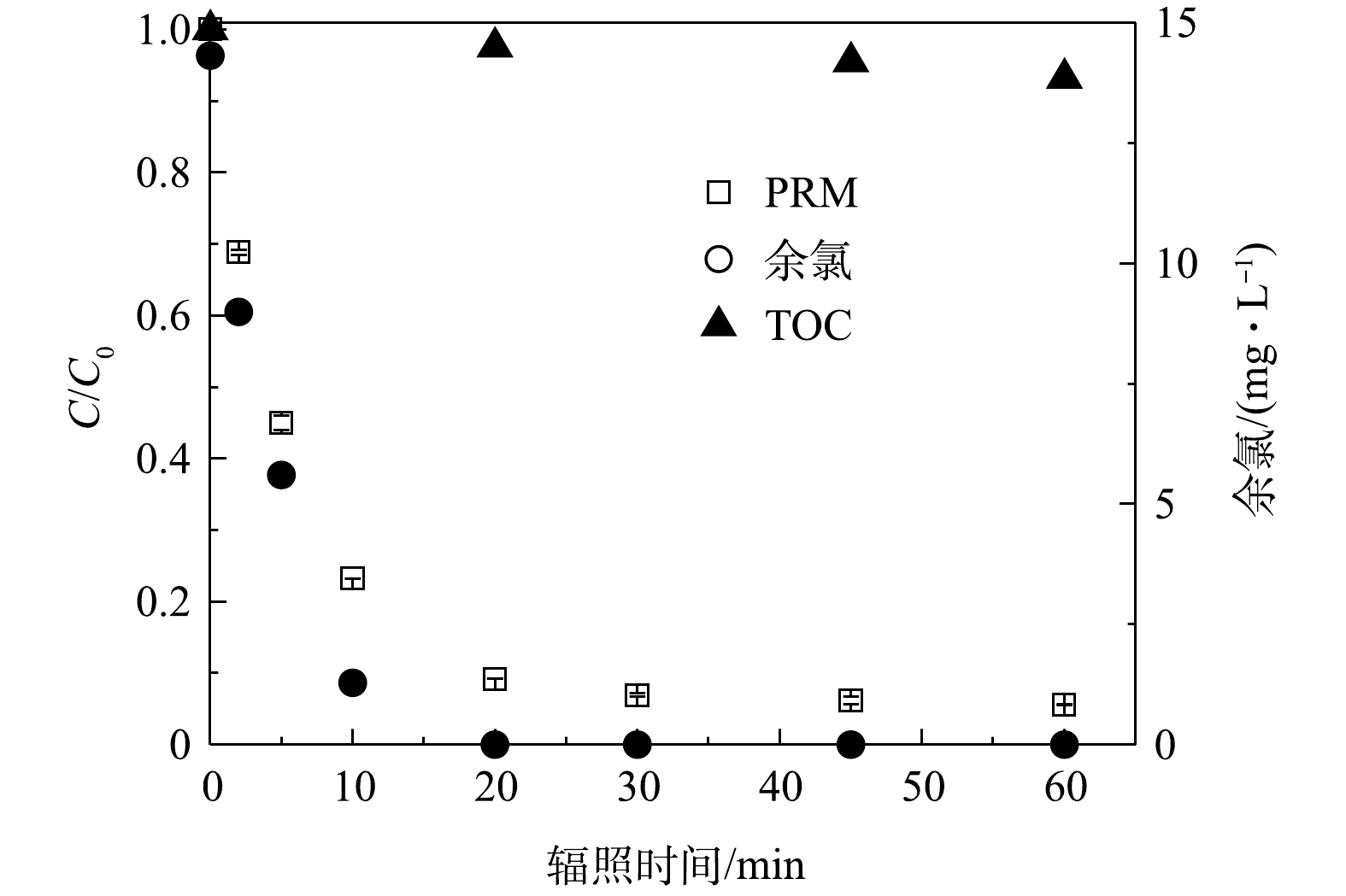
图 6 PRM在紫外/氯体系中的降解、矿化和FC的消耗
Figure 6. PRM degradation, variation of TOC, and consumption of free chlorine in the UV/chlorine process
-
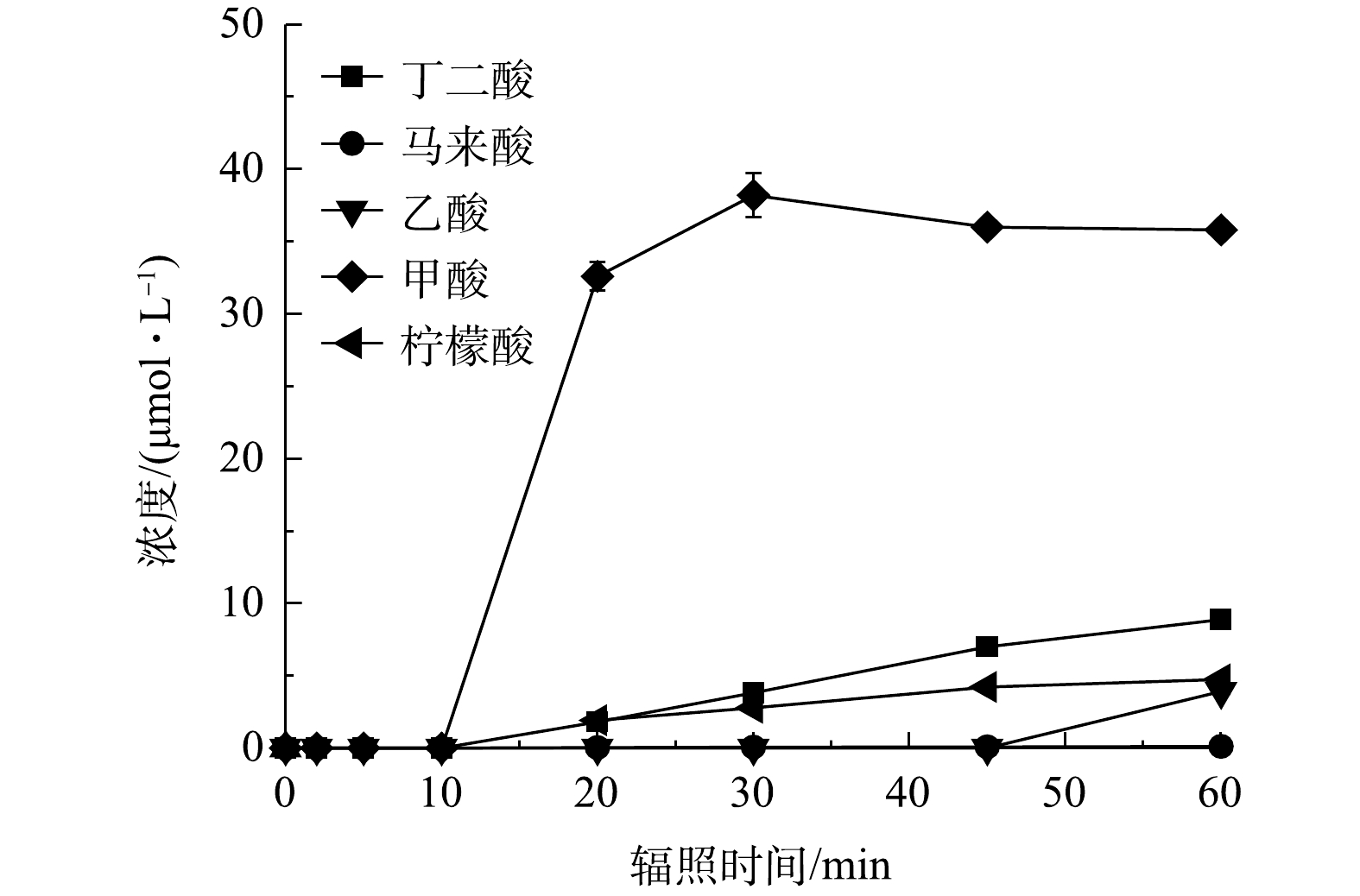
图 7 PRM在紫外/氯体系降解过程中小分子有机酸的浓度变化
Figure 7. Variation in the concentrations of low molecular weight organic acids during PRM degradation in the UV/chlorine process
-
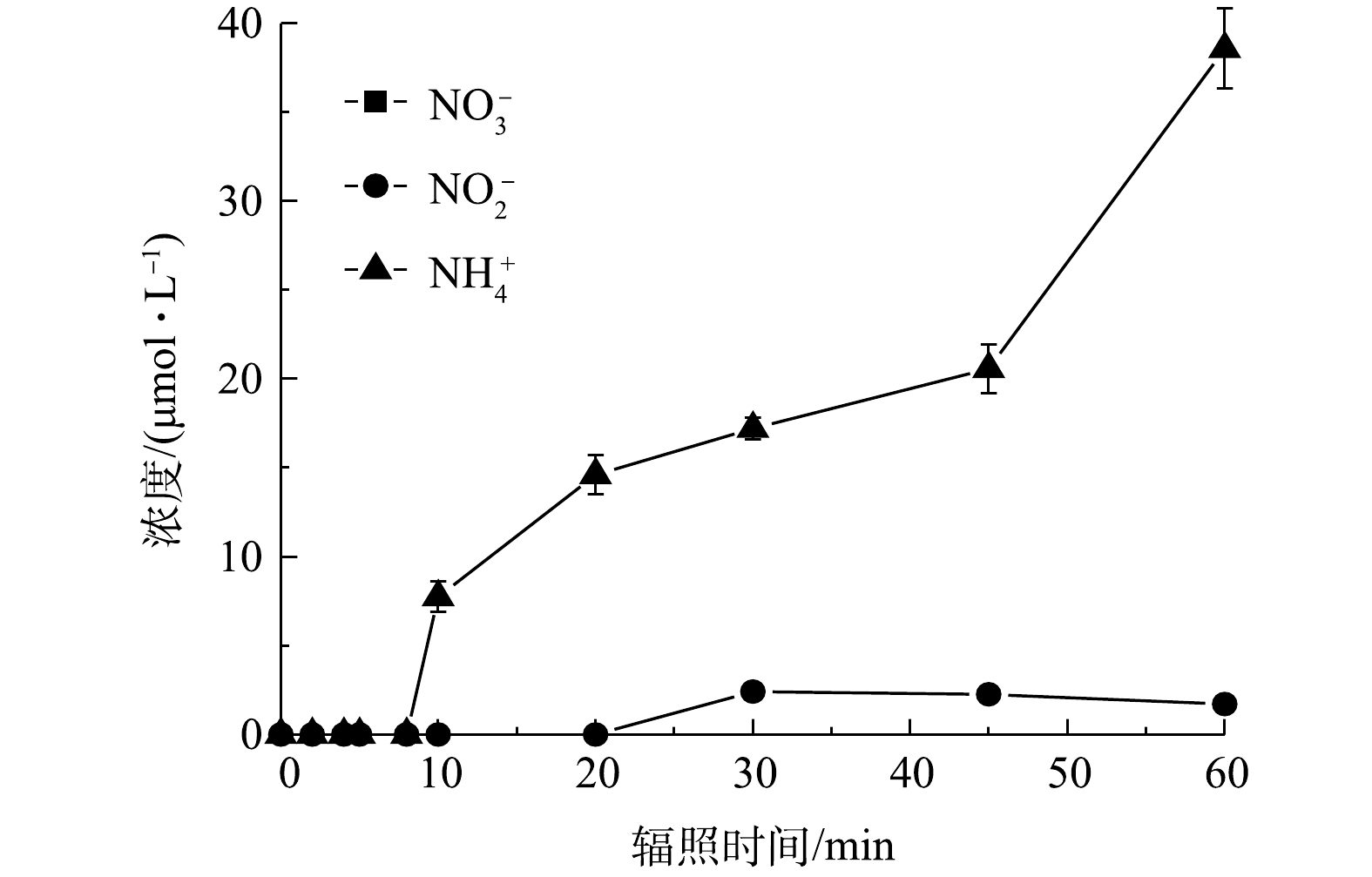
图 8 PRM在紫外/氯体系降解过程中
${{\bf{NO}}_3^{-} }$ ${{\bf{NO}}_2^{-} }$ ${{\bf{NH}}_4^{+} }$ Figure 8. Variation of the concentrations of
${{\rm{NO}}_3^{-} }$ ${{\rm{NO}}_2^{-} }$ ${{\rm{NH}}_4^{+} }$ -
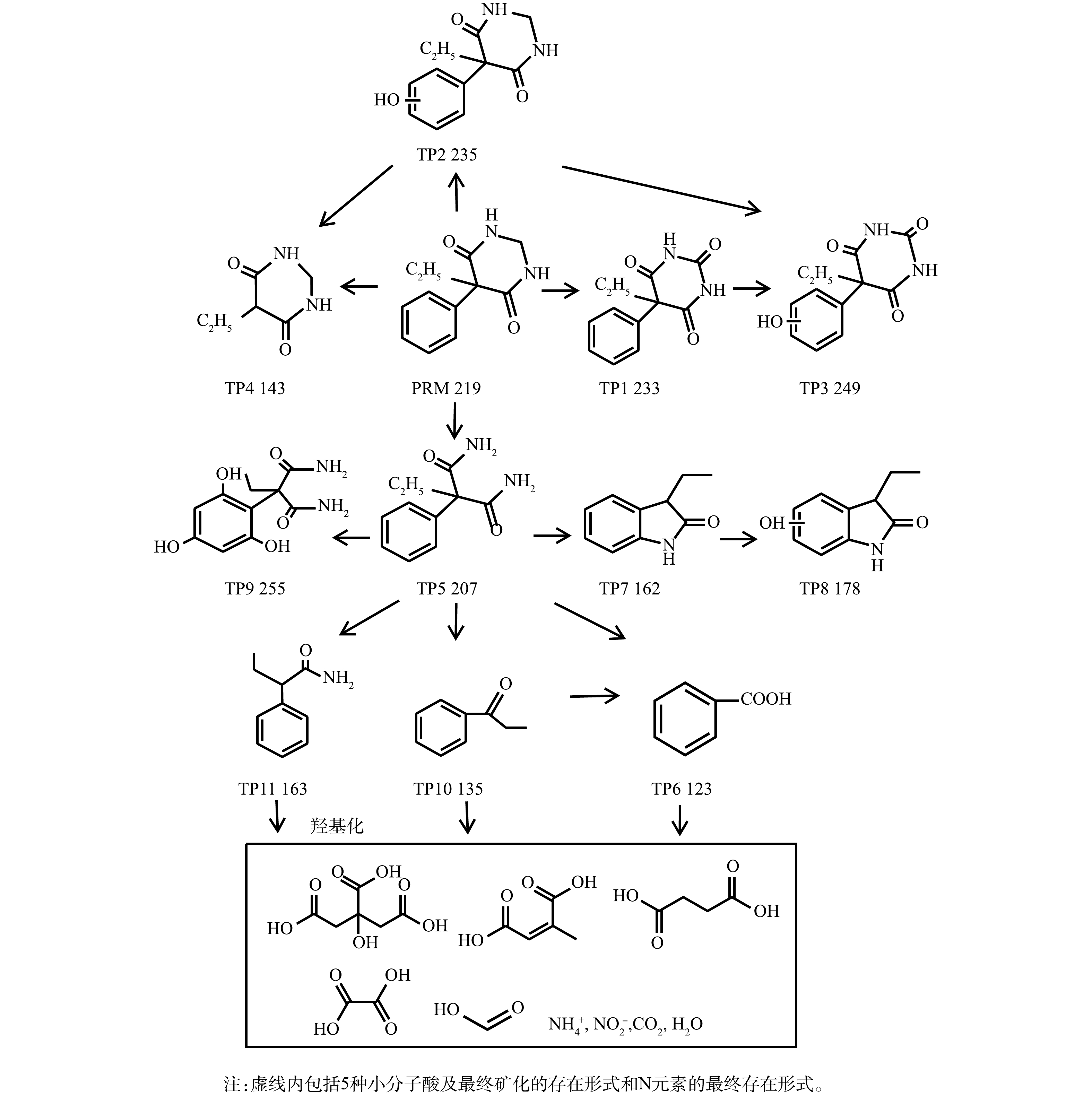
图 9 紫外/氯高级氧化体系降解PRM路径图
Figure 9. Proposed pathways of PRM degradation by the UV/chlorine process
Figure
9 ,Table
0 个