-
近年来,我国越来越重视臭氧(O3)污染,在多区域范围内O3已取代颗粒物成为首要污染物[1 − 3]. 苏皖鲁豫交界地区位于汾渭平原和长三角之间,已成为继京津冀等区域之后,新的联防联控重点控制区域[4 − 6]. 该地区位于共有22个城市,基础排放量大,空气质量改善进程总体相对滞后,臭氧浓度高且上升趋势明显,光化学污染过程呈现出与周边地区的同步性[7]. 目前针对该区域研究较少,相关监测持续时间较短,无法表征长时间的光化学污染特征变化. 亟需对苏皖鲁豫区域加以重点关注,补齐大气污染防治短板,对于该区域的O3污染治理能力提高和大气光化学污染防治策略制定具有重要的意义.
过氧乙酰硝酸酯(CH3C(O)OONO2,PAN)是光化学烟雾的关键产物[8 − 10]. PAN属于非自然过程排放的污染物,仅通过人类活动排放的前体污染物的光化学反应生成,是光化学污染的重要指示剂[11 − 12]. 大气中挥发性有机物(VOCs)在氧化过程中,可生成PA自由基(Peroxyacetyl Radical),而后PA可与NO2结合生成PAN[13 − 14]. PAN在对流层上部稳定,但在大气对流层下部具有明显的热不稳定性,与O3相比不易远距离输送,能更好地反映本地区域的光化学污染情况[15 − 17]. 在国内,包括城市、郊区、农村和偏远地区,都有PAN的时空变化及其形成机制的相关研究. Yuan等[18]研究表明,在珠三角农村地区,PAN的增加主要受气相化学控制,其次是垂直运输,而其损失主要受水平运输和干沉积的调节. Liu等[19]研究表明,高环境浓度的细颗粒物和气态亚硝酸可以显著促进PAN的形成. Xia等[20]基于稳态模型研究表明,在东南沿海地区生物质燃烧源是PA自由基的重要来源.
淮北市位于苏皖鲁豫交界地区中心位置,地处苏豫皖三省交界,经济发展迅速,近年来光化学污染频发. 本研究于2021年秋季(10月)和2022年夏季(6月)利用PAN在线监测,在淮北市开展PAN污染特征分析与来源研究,对于探究苏皖鲁豫交界地区大气光化学污染及变化规律,加强局地区域光化学污染的理解和防控,将具有积极意义.
-
本研究于2021年10月和2022年的6月,在淮北市进行PAN浓度在线监测. 用10月份的监测数据代表秋季,6月份的代表夏季,分别获得了21 d和16 d的PAN有效浓度数据. 采样地点位于淮北市(116.73°E,33.89°N)某开发区空旷地,采样高度4.5 m左右,空间位置如图1所示.
监测点周边无高大建筑遮挡,采样和数据审核符合《环境空气质量自动监测技术规范》和《国家大气光化学监测网自动监测数据审核技术指南(2021版)(试行)》中的相关要求.
本研究使用PAN大气在线监测系统(PANs-1000,聚光科技,2020.11),该分析仪包含气相色谱仪(GC-ECD)、校准仪和零气发生器. 可支持5 min分辨率的大气环境PAN浓度自动连续监测,以采样泵为动力,控制三通电磁阀选择通过空气样品或校准样品. 在采样模式下,样品通过聚四氟乙烯微孔滤膜过滤后进入系统,通过六通阀进入定量环;采样结束后,通过六通阀切换,开始进样. 在进样模式下,定量环与载气气路连接,样品随载气进入色谱柱后进行分离. 分离后的组分被带入到ECD检测器中,得到PAN检测结果. 标定时,校准仪和零气发生器配合在紫外光照下光解生成PAN标气;再与稀释气混合稀释到所需标定浓度进行分析. 为保证数据准确性,在观测期间每周绘制一条标准曲线,每条标准曲线采用6个浓度梯度(0—10)×10−9,标准曲线R2均大于0.98,重复性≤3%,最低检出限0.5×10−9.
-
本研究将利用潜在源贡献函数(potential source contribution function,PSCF)评估该监测点PAN污染最可能的来源区域. 研究首先基于美国国家环境预测中心全球资料同化系统数据GDAS(ftp://arlftp.arlhq.noaa.gov/pub/archives),使用HYSPLIT模型在监测点(500m AGL)处模拟气团的后向轨迹. 考虑到PAN热解大气寿命较短,本研究进行1 h后向轨迹计算. 结合后向轨迹与PAN的监测值,利用TrajStat软件对PSCF值进行计算. PSCF值表示特定网格中污染轨迹数(污染物浓度超过设定阈值)占通过该网格轨迹总数的概率,在0—1范围内,其数值越高,表示该网格区域对受体点污染物浓度的潜在源贡献值越大. 研究区域空间网格分辨率为1°×1°,污染标准值设置为观测期间PAN小时浓度的第50百分位数,引入了权重函数以降低不确定性[21].
-
基于国家气象科学数据中心(http://data.cma.cn),采集了58113气象站点(116.45°E,33.56°N)的温度(T)和相对湿度(RH)气象数据. 观测站点光解速率常数的监测采用大气光解速率分析仪(PFS-100,Focused Photonics Inc,2020.9),利用石英接收头收集来自各个方向的太阳辐射,可获得210—790 nm的光谱,并能计算J(O1D)的光解速率. 基于安徽省生态环境厅空气质量实时数据发布平台(https://sthjt.ah.gov.cn/site/tpl/5371),采集距PAN监测点最近(7.7 km)的烈山区政府国控站点(116.80°E,33.90°N)的地面NO2、NO、O3浓度数据. 气象数据和大气污染物浓度数据覆盖PAN的观测期间,时间分辨率为1 h.
-
2021年10月,PAN的体积分数平均值为(0.42±0.24)×10−9,远低于2022年6月夏季的浓度均值为(1.87±0.86)×10−9,主要原因是PAN作为一种典型的光化学反应二次污染物,夏季的高温强辐射都会造成PAN的形成和累积. 观测期间PAN体积分数范围在2021年10月和2022年6月分别为(0.08—1.44)×10−9和(0.61—5.72)×10−9. 淮北市PAN体积分数水平均值和最大值与国内其他重点区域城市文献观测结果对比如表1所示. 本监测点10月份的PAN均值浓度低于苏皖鲁豫交界地区的青岛市. 在其它3个重点区域中与深圳市相近,但仍高于国内外各背景站[22],说明秋季淮北市大气光化学污染问题依然存在. 夏季时段内苏皖鲁豫区域的PAN最大值浓度明显高于表中所列其它三大重点区域城市. 这表明了目前苏皖鲁豫区域内夏季的光化学污染仍处在较严重范围内,应加强对该区域内光化学污染的研究.
-
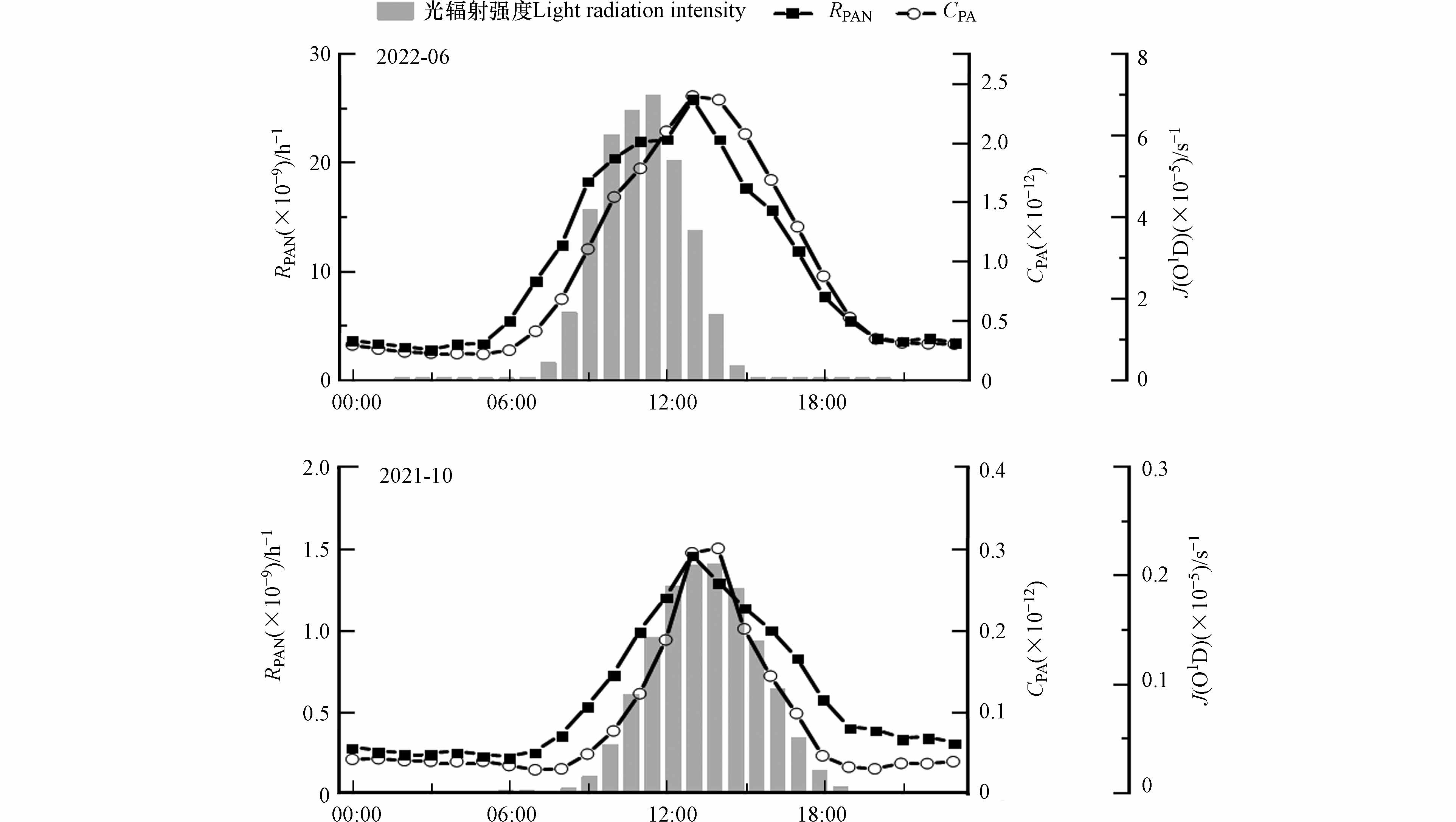
大气污染物的日变化特征可以反映源排放和大气化学反应的综合影响[14]. 观测期间PAN、O3、NO2和气象因子的日变化趋势如图2所示. 两个季节PAN日变化浓度均呈单峰型特征,在2021年秋季峰值(0.56×10−9)出现在12:00—13:00;在2022年夏季提前两小时(10:00—12:00)达到峰值,而其峰值浓度是秋季的4.88倍. PAN体积分数在上午随着太阳辐射加强而不断升高,正午达峰,夏季PAN出现较早且较高的峰值是由于较高的太阳辐射强度和温度,这促进了PAN的产生和热分解[27]. 受强烈的光化学反应条件、周边地区的区域输送和大气背景水平增加的影响,淮北市夏季的PAN浓度水平高于秋季,这和其它地区的研究一致[13,28].
淮北市PAN日变化特征与合肥市[25]和厦门市[14]相一致,而北京市[23]和青岛市[13]均为双峰型,在18时至20时出现第二个相对低的峰值. 这种情况的主要原因可能是与观测地点和时段有关,本研究监测点位于郊区,呈双峰型变化的城市监测点多数位于市区内,城市晚高峰期间前体物的排放会促使光化学反应活性升高,促进PAN浓度的二次抬升. 除此之外,相对南方城市,北方城市夏秋季夜间温度较低,不利于PAN热解,仍有较高残留.
NO2是PAN的主要前体物之一,日变化趋势呈双峰分布,秋季两个峰值出现在08:00和19:00,夏季则出现在03:00和22:00,白天的趋势符合光化学生成特征. NO两个季节最高值均出现在08:00—09:00,与早高峰汽车尾气排放有关. 氮氧化物夏季整体平均浓度低于秋季,与气象条件和输送等因素有很大关系[29]. O3日变化趋势与温度的相一致,呈单峰型,峰值出现在午后,夏季O3平均浓度高于秋季. 有研究表明,高温低湿环境条件下,更容易产生光化学污染[5 − 6].
-
PA自由基(Peroxyacetyl Radical)在光化学反应中起着非常重要的作用,目前直接测量PA自由基仍然非常困难[30 − 31]. 除化学过程外,动力和沉积过程也会影响PA的变化. 在短时间内和稳定的大气条件下,可以忽略物理过程的贡献,用d[PAN]/dt表示PAN的瞬时变化率来体现化学过程影响[32]. 假设PAN的生成过程(1)和热分解过程(2)相对平衡,PA自由基可通过与NO反应去除(3),则PA自由基浓度可使用公式(4)进行估算. PAN生成速率(RPAN)可直接反映光化学污染前体物的贡献,同时规避了PAN的热解,因此本研究拟采用Zhang等[32]的方法,使用公式(5)来进行小时分辨率的生成速率计算,用RPAN表征光化学污染生成特征,单位为10−9·h-1.
式中,k1(9.5×10-12 cm³·(molecule·s)-1、k2(2.52×1016exp-13573/T s-1)分别是反应式(1)和(2)的速率常数,T表示温度(单位:℃)[13]. 本研究中,用臭氧光解速率常数J(O1D)来近似反映近地面的光辐射强度变化趋势[26].
计算结果如图3所示,夏季CPA自由基浓度均值为(0.91±0.90)×10-12,范围为(0.02—5.02)×10-12;而秋季CPA自由基浓度均值为(0.08±0.19)×10-12,范围为(0.001—1.75)×10-12.
CPA自由基昼高夜低的日变化规律与其主要基于日间光化学反应生成相一致. RPAN变化规律与CPA自由基一致,夏季RPAN均值为(7.43±6.44)×10−9·h-1,峰值出现在13:00,与CPA自由基峰值时间一致. 秋季RPAN均值为(0.56±0.95)×10−9·h-1. 值得注意的是,秋季RPAN与夏季略有不同,除了在13:00的第一个峰值外,在20:00出现第二个较小的峰,结合图2可知与这一时段氮氧化物的排放增加有关. 夏季CPA自由基和RPAN显著高于秋季,与夏季强烈的光辐射有关. 可以看出,夏季光辐射强度达到最大值后CPA自由基和RPAN仍在升高,说明淮北市夏季光化学反应更加强烈.
-
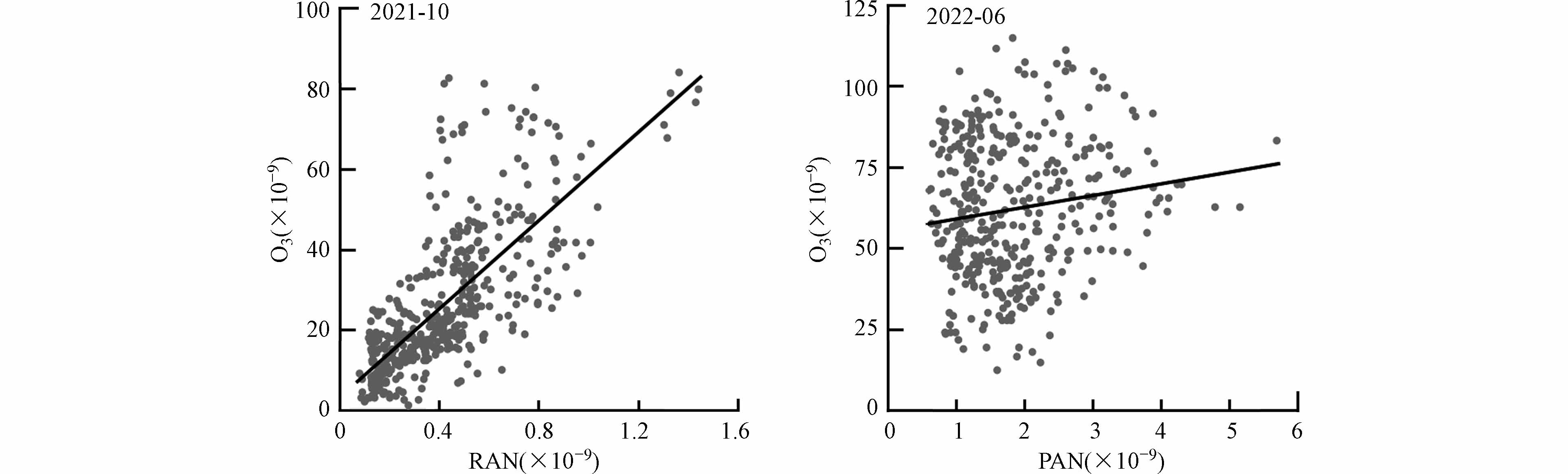
由于挥发性有机物和氮氧化物的光化学反应都产生PAN与O3,因此可通过分析PAN和O3相关性,作为判断空气质量的指标[19]. 图4给出了两个观测月份PAN与O3小时均值散点图和线性拟合. 秋季时PAN与O3呈现较好的正相关(r=0.72),表明它们很可能来自相同的光化学过程,或者来自共同的传输区域. 整个秋季观测期间PAN与O3的斜率为0.01,低于京津廊城市[22,24]和其他区域背景点[18,23],这意味着PAN相对于O3的生产效率相对较低,可能是由于挥发性有机物和氮氧化物等前体物水平下降,或者受其他地区清洁空气输送的影响. 而夏季时PAN与O3的相关性不明显,夏季温度更高,而PAN具有热不稳定性,高温时段可通过热分解反应生成PA自由基和NO2[19]. 同时这也表明夏季观测期间光化学污染物可能存在不同的来源,PAN高温条件下主要来自于本地生成,O3的来源还有区域传输,也与各自不同的去除途径有关. 这也表示秋季时苏皖鲁豫区域应控制本地光化学污染物生成,而夏季时本地生成和区域传输都应该加以重视.
-
化学反应式(1)、式(2)和式(3)表明PAN与NO2之间存在相互关系. 本研究中PAN与NO2的相关性如图5所示.
十月份二者皮尔逊积矩相关系数为0.028,六月份相关系数为0.194;两个月份的观测结果均显示相关性较差. 由反应式(1)可以看出NO2是PAN生成的重要前体物,但高浓度的NO2会和VOCs形成竞争,从而制约PA自由基的生成,这会抑制PAN的生成产生. 本研究获取的PAN与NO2的相关性与其他城市地区[23,26]的研究较为一致,但有研究[22]显示偏远地区背景站的观测中PAN与NO2的呈现很强的相关性,这可能与城市地区NO2的浓度水平较高有关.
-
众多研究[12,26]指出NO/NO2的值是影响PAN热分解速率的重要因素,从反应式(1)、式(2)和式(3)也可推导出. 本研究中PAN与NO/NO2的相关性如图6所示,两个月份80%以上的PAN散点落在NO/NO2比值0.4下方. 这和PAN的热解去除途径有关,反应式(3)中NO可通过消耗PA自由基降低PAN的生成速率,当比值较低时,更多的PA自由基参与到与NO2的反应,最终生成PAN[33]. 因此大多数高浓度的PAN通常出现在NO/NO2比值较低的时候,进一步证实了NO对PAN去除的重要作用. 本研究中两者相关性不显著,与长三角区域城市地区[26]研究结果较为一致.
-
为判断PAN的空间来源解析,研究区域输送对监测点光化学污染的影响,采用HYSPLIT模型开展监测点处500 m气团的后向轨迹聚类分析,同时利用TrajStat软件绘制PAN空间来源解析结果,结果如图7所示. 分析结果表明,2021年10月,该监测点主要受东北、北部和南部三个方向气团的影响,占比分别为34.48%、25.82%和18.06%;而2022年6月主要受东南、西南和南部气团的影响,占比分别为41.43%、17.93%和17.33%.
2021年10月PSCF高值区域主要出现在监测点南部,即所有通过该区域的气团后向轨迹的PAN浓度超过设定阈值的概率为40%—60%,证明该区域对监测点PAN浓度的潜在源贡献较高. 这可能主要源于西南方向的安庆市石化行业发达,VOCs排放量较高;淮南市的电力产业发达,氮氧化物排放量较高,都为PAN生成提供了丰富的前体物.
2022年6月PSCF高值区主要出现在北部,PSCF值达到0.7—0.9,显示了山东省西南部是PAN的潜在源贡献地区;而在17.93%的西南部气团输送情况下,该监测点西部方向亦未发现PSCF高值区,表明该气团污染较轻;41.43%东南方向的气团,表明在工业化程度较高的城市群(马鞍山、芜湖、南京)之间存在长距离运输. 有研究表明,PAN可作为NOx和自由基的临时贮存器,输送到偏远地区,重新分配NOx,并在大尺度区域范围内干预O3的生成[34 − 35].
-
(1)淮北市PAN的体积分数范围在2021年10月和2022年6月分别为(0.08—1.44)×10−9和(0.61—5.72)×10−9. 两个季节PAN日变化浓度均呈单峰型特征,东北方向的高值区显示出淮北市中心城区城市羽流的影响. 区别于O3的长距离迁移特征,秋季和夏季PAN污染主要来自当地产生和积累,但相邻城市的短程迁移可能在一定程度上导致PAN浓度较高.
(2)夏季PA自由基和PAN生成速率显著高于秋季,与夏季强烈的光辐射有关. 结合PAN和O3的观测值及其比值,发现淮北市不仅在夏季遇到光化学污染,而且秋季也存在光化学污染,体现了苏皖鲁豫区域较强的大气氧化环境.
(3)该观测处PAN浓度的潜在源,2021年10月高值区主要出现在监测点南部,可能是因为西南方向相近城市较高的前体物排放. 2022年6月高值区主要出现在北部和东南部,显示了泰安市是该监测点PAN的潜在源贡献地区;东南方向的气团,在工业化程度较高的城市群(马鞍山、芜湖、南京)之间存在长距离运输. 这证明苏皖鲁豫交界地区当前光化学污染是一个区域性问题,需要从区域尺度联防联控.
苏皖鲁豫典型城市过氧乙酰硝酸酯(PAN)污染特征分析
Analysis of photochemical pollution potential characteristics based on PAN observation in the border area of Jiangsu, Anhui, Shandong and Henan
-
摘要: 为探究苏皖鲁豫区域光化学污染特征,于2021年10月和2022年6月在淮北市开展光化学污染产物过氧乙酰硝酸酯(peroxyacetyl nitrate,PAN)的在线监测,分析了PAN浓度特征、空间来源、产生速率和变化趋势. 观测结果表明,观测处2021年10月PAN的浓度范围为(0.08—1.44)×10−9,2022年6月的浓度范围为(0.61—5.72)×10−9;PAN的峰值大部分出现在NO/NO2比值较低的时段. 结合气团后向轨迹,2021年10月观测处PAN的潜在源贡献函数(PSCF)高值区范围出现在南部方向,可能是因为西南方向相近城市较高的前体物排放;2022年6月高值区主要出现在北部和东南部,显示山东省西南部是潜在源贡献地区,东南方向的气团在工业化程度较高的城市群之间存在长距离运输.
-
关键词:
- 过氧乙酰硝酸酯(PAN) /
- 光化学污染特征 /
- 苏皖鲁豫 /
- 在线监测.
Abstract: In order to explore the potential of photochemical pollution in the regions of Jiangsu, Anhui, Shandong and Henan, the online monitoring of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN), a product of photochemical pollution, was carried out in Huaibei City in October 2021 and June 2022, and the concentration characteristics, spatial sources, production rate and change trend of PAN were analyzed. The observation results show that the concentration range of PAN at the observation site is (0.08—1.44)×10−9 in October 2021 and (0.61—5.72)×10−9 in June 2022. Most of the peak of PAN appeared in the period of low NO/NO2 ratio. In combination with the backward trajectory of the air mass, the high value range of the potential source contribution function (PSCF) of PAN at the observation site in October 2021 appears in the south, which may be due to the higher precursor emissions in the cities near the southwest. In June 2022, the high value areas mainly appeared in the north and southeast, indicating that the southwest of Shandong Province is a potential source contribution area, and the air mass in the southeast has long distance transportation between the urban agglomerations with a high degree of industrialization. -
随着环保意识的增强,天然气作为一种清洁能源被广泛使用,但天然气中含有的大量H2S,不仅会对设备和管线造成腐蚀,而且也是造成酸雨的污染源之一,严重危害环境和人类健康[1-2]。因此,脱除天然气中的H2S,对保护设备、管线和环境等具有重大意义。
目前,工业中应用较多的天然气脱硫工艺主要有湿法、干法和膜法脱硫。湿法脱硫技术主要有乙醇胺(MEA)法[3]、低温甲醇法[4]、DDS脱硫技术[5]和LO-CAT硫磺回收技术[6];干法脱硫技术主要有活性炭法、分子筛法和氧化铁法[7];膜法脱硫技术主要有膜基吸收法和膜蒸馏法[8]。尽管这些技术已经在工程中得到了较为广泛的应用,却不能忽视其在实际应用中存在的问题:湿法脱硫技术存在工艺复杂、投资费用高、能耗大和产生大量的脱硫废水等缺点[9];干法脱硫技术存在脱硫条件要求严格、不适用于高浓度H2S脱除和再生困难等缺点[10];膜法脱硫技术存在制膜工艺较为复杂、膜的使用寿命短和处理后浓缩液难处理等缺点[11-12]。因此,亟需研发一种工艺简单、成本低、安全高效的脱硫技术,探究内循环微电解技术应用于天然气中H2S处理的可行性及其对天然气中H2S的处理效果,旨在为内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理提供指导,同时为天然气中H2S处理提供一种简单高效的技术方法。
内循环微电解技术将铁作为阳极,将活性炭作为阴极,当混合浸入废水时,形成大量的微小原电池,其主要通过微电池、氧化还原、絮凝、吸附沉淀和微电场附集等作用去除废水中的污染物[13-14]。内循环微电解具有成本低、工艺简单、使用范围广、使用寿命长、处理效果好及操作维护简单等优点[15],在印染[16]、焦化[17-18]、石油[19]、制药[20]、造纸[21]等工业废水的处理中得到了广泛的应用,对COD和色度的去除具有很好的效果,但内循环微电解技术应用于天然气脱硫的研究却鲜有报道。
本研究采用内循环微电解技术处理天然气中的H2S,考察了反应时间、通气速率、铁炭比和pH等4个因素对H2S去除效果的影响,筛选出3个影响H2S去除效果的主控因子,采用Box-Behnken响应曲面法,对处理H2S的反应条件进行了优化,以得到内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理的最佳工艺条件。最终可以得出内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理是可行的,研究结果为内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理提供参考,同时,为天然气中H2S的处理提供了一种简单高效的技术方法。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 主要试剂与仪器
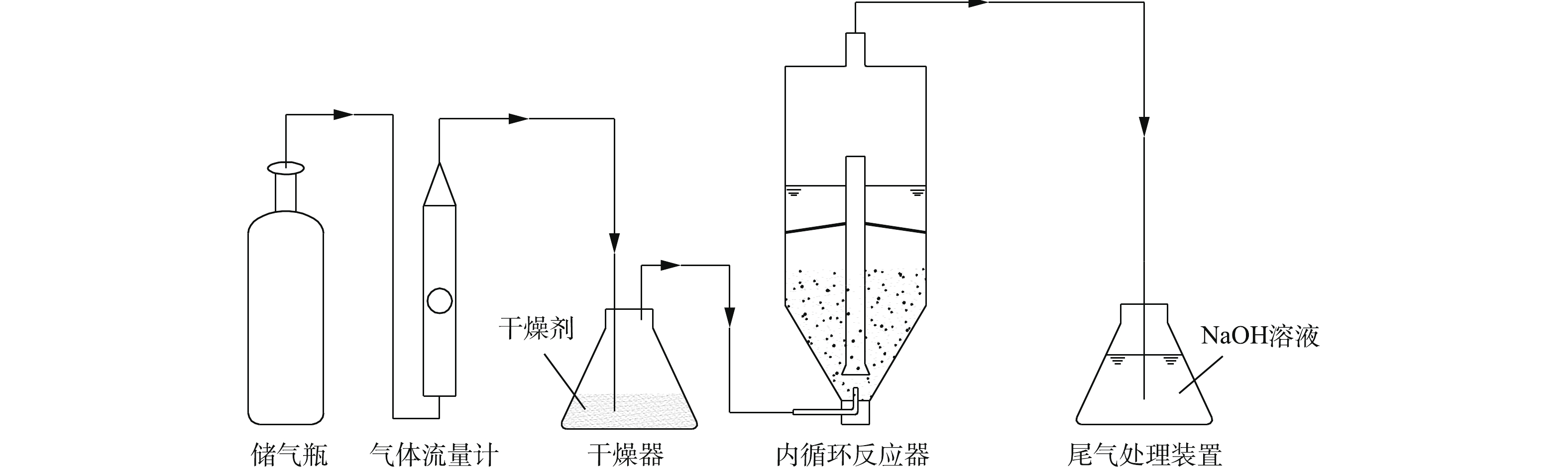
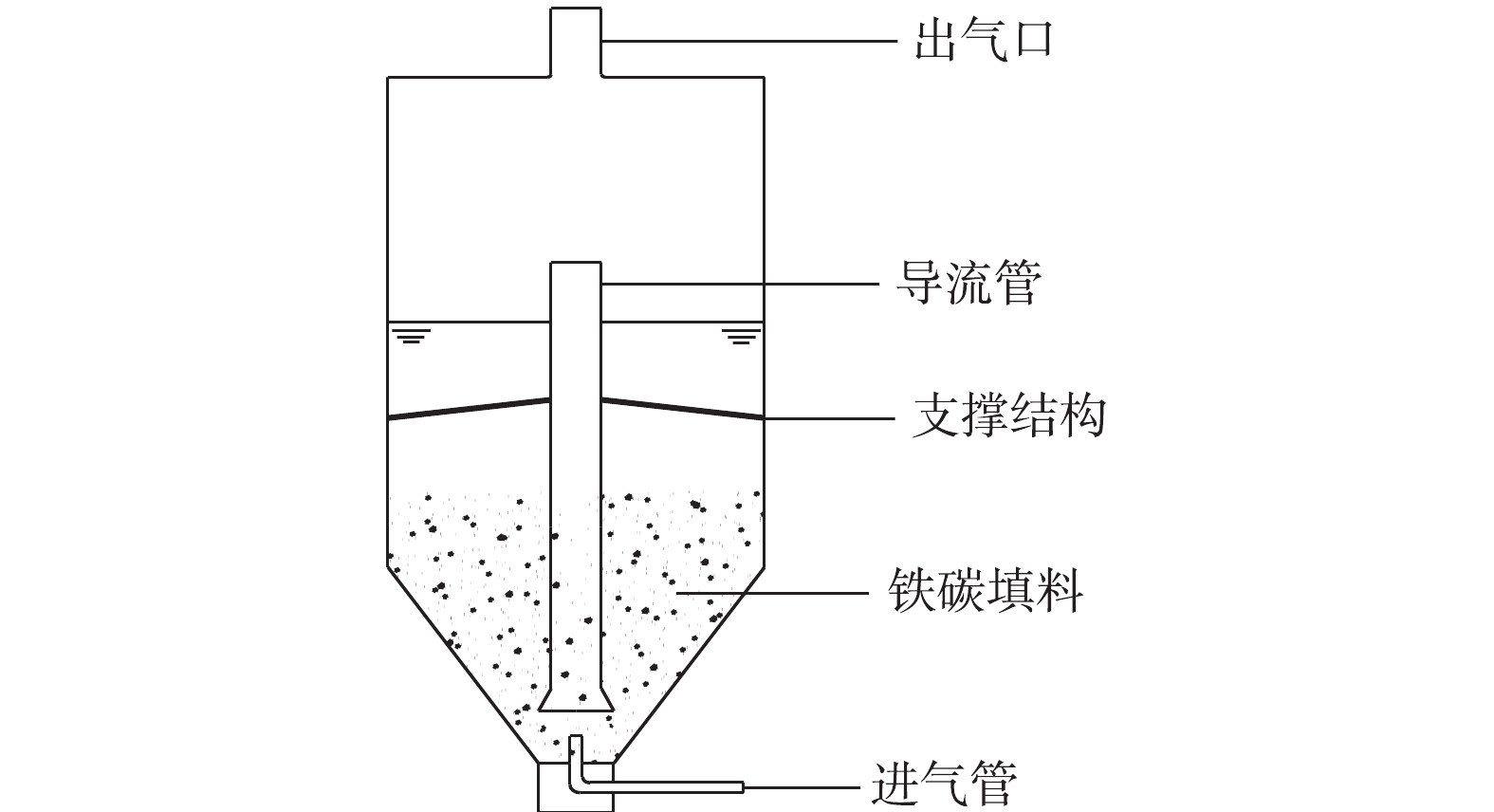
实验中使用的NaOH、Na2S、盐酸和丙酮等试剂,均为分析纯;实验室用水为去离子水。使用的主要仪器有Multi3420型pH计、TD5002C分析天平、YQY-12氧气减压阀、CHYS-241硫化物测量仪、A14 H2S气瓶、LZB型空气流量计和内循环式反应器,反应器为自制,结构如图1所示。
1.2 实验方法
实验装置如图2所示。在进行铁屑预处理时,首先用去离子水反复清洗3~5遍,以去除表面的灰尘,然后将铁屑置于丙酮溶液中浸泡30 min,去除表面的油污及其他杂质,再用5%的盐酸浸泡30 min,去除铁屑表面的氧化膜,使铁屑活化,最后用去离子水清洗至中性[22]。
在进行活性炭预处理时,首先,用去离子水反复清洗3~5遍,以去除表面的灰尘和杂质,然后将活性炭浸泡在高浓度的Na2S溶液中3 d以上,以消除实验过程中活性炭吸附作用的影响[23]。
将预处理后的铁屑和活性炭按照一定的质量比(总质量为300 g)混合后,置于内循环式反应器中,并在反应器中加入适量的水,气瓶中含有H2S的天然气(为了防止甲烷引起爆炸,本研究采用N2和H2S的混合气体进行模拟),用空气流量计控制流量,经过干燥器(防止水蒸气进入气体流量计和储气瓶而发生腐蚀泄露)干燥后,通入反应器中进行反应,尾部通过NaOH溶液吸收尾气中的H2S,以测定处理后H2S的剩余含量,计算H2S的去除率。
1.3 分析方法
使用Multi3420型pH计进行pH的测定;处理后,H2S的剩余含量使用CHYS-241硫化物测量仪进行测定,此方法具有简便快捷的优点,准确度和精密度均可达到检测要求[24]。
内循环微电解技术脱除天然气中H2S见反应式(1)和式(2),同时会有Fe(OH)3的生成(见式(3)),可以通过混凝沉淀作用加快FeS的沉淀。
Fe−2e−→Fe2+ (1) Fe2++S2−→FeS↓ (2) 4Fe2++8OH−+O2+2H2O→4Fe(OH)3(胶体) (3) 1.4 实验设计
1)单因素实验设计。通过控制变量,分别研究不同反应时间、通气速率、铁炭比和pH对H2S去除率的影响,筛选出影响H2S去除效果的3个主要因素。
2)响应曲面优化实验设计。在单因素实验的基础上,采用Design Expert软件中Box-Behnken法进行设计,以H2S去除率为响应值,确定3因素3水平的响应曲面分析实验,对实验结果进行ANOVA分析及二次回归拟合,确定模型的可行性。最终获得各因素间的交互作用对响应值的影响和最优反应条件。采用二阶模型[22]计算H2S去除率,计算方法如式(4)所示。
Y=∝0+k∑i=1∝iXi+k∑i=1∝iiX2i+k∑1<i<j<k∝ijXiXj (4) 式中:Y为H2S去除率的预测值;
∝0 为偏移项;∝i 为线性偏移系数;∝ii 为二阶偏移系数;∝ij为交互作用系数。3)验证实验设计。在模型预测的最佳反应条件下进行实验,测定H2S剩余含量,计算去除率,验证模型的可靠性。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 单因素实验
1)反应时间对处理效果的影响。在实验中,天然气中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1、铁炭比为1∶1和pH为7的条件下,研究了反应时间对H2S去除率的影响,实验结果如图3所示。由图3可见,随着反应时间的增加,H2S剩余含量逐渐减少,H2S去除率逐渐增大。反应30 min前,H2S剩余含量迅速减少,H2S去除率迅速增大,这是由于反应初期水中不断产生Fe2+,从而加速FeS的生成,同时氧化还原、絮凝沉淀等作用也起到很好的脱硫促进作用[25],进而可以迅速去除H2S;在30 min时,H2S剩余含量为377.5 mg·m−3,其去除率达到52.81%;而在反应30 min后,H2S剩余含量随着时间的延长缓慢减少,H2S去除率随着时间的延长缓慢升高,这主要是因为随着反应的进行,Fe被大量消耗,形成的原电池数量减少,从而使反应速率下降;在反应进行到120 min时,H2S剩余含量仅剩63.5 mg·m−3,去除率高达92.06%。由于在反应时间为30 min时,剩余H2S的浓度接近《天然气》(GB 17820-2012)中三类标准,综合因素优化和经济因素考虑,后续实验中的反应时间设为30 min。
2) 通气速率对处理效果的影响。控制天然气中H2S初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、反应时间为30 min、铁炭比为1∶1和pH为7的条件下,研究通气速率对H2S去除率的影响,实验结果如图4所示。由图4可知,随着通气速率的增大,H2S剩余含量先减少后增加,H2S去除率先升高后降低,当通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1时,H2S剩余含量达到最低值,为387.5 mg·m−3,其去除率为51.56%;当通气速率小于0.4 m3·h−1时,H2S去除率随着通气速率的增大而升高,这是因为在一定条件下,传质系数会随着通气速率的增大而增大[26],天然气中的H2S与铁炭的接触更加充分,从而使处理效果越来越好。当通气速率大于0.4 m3·h−1时,H2S去除率随着通气速率的增大而降低,分析其原因主要有以下2点:通气速率增大,气体对铁炭的作用力也相应增大,使得铁炭分离,形成的原电池数量大量减少而影响处理效果;随着通气速率增大,溶液中的气泡数量会随之增加,大量的气泡聚集导致气泡的体积增大,比表面积减少,使传质系数减少而影响处理效果。因此,最终确定反应的最佳通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1。
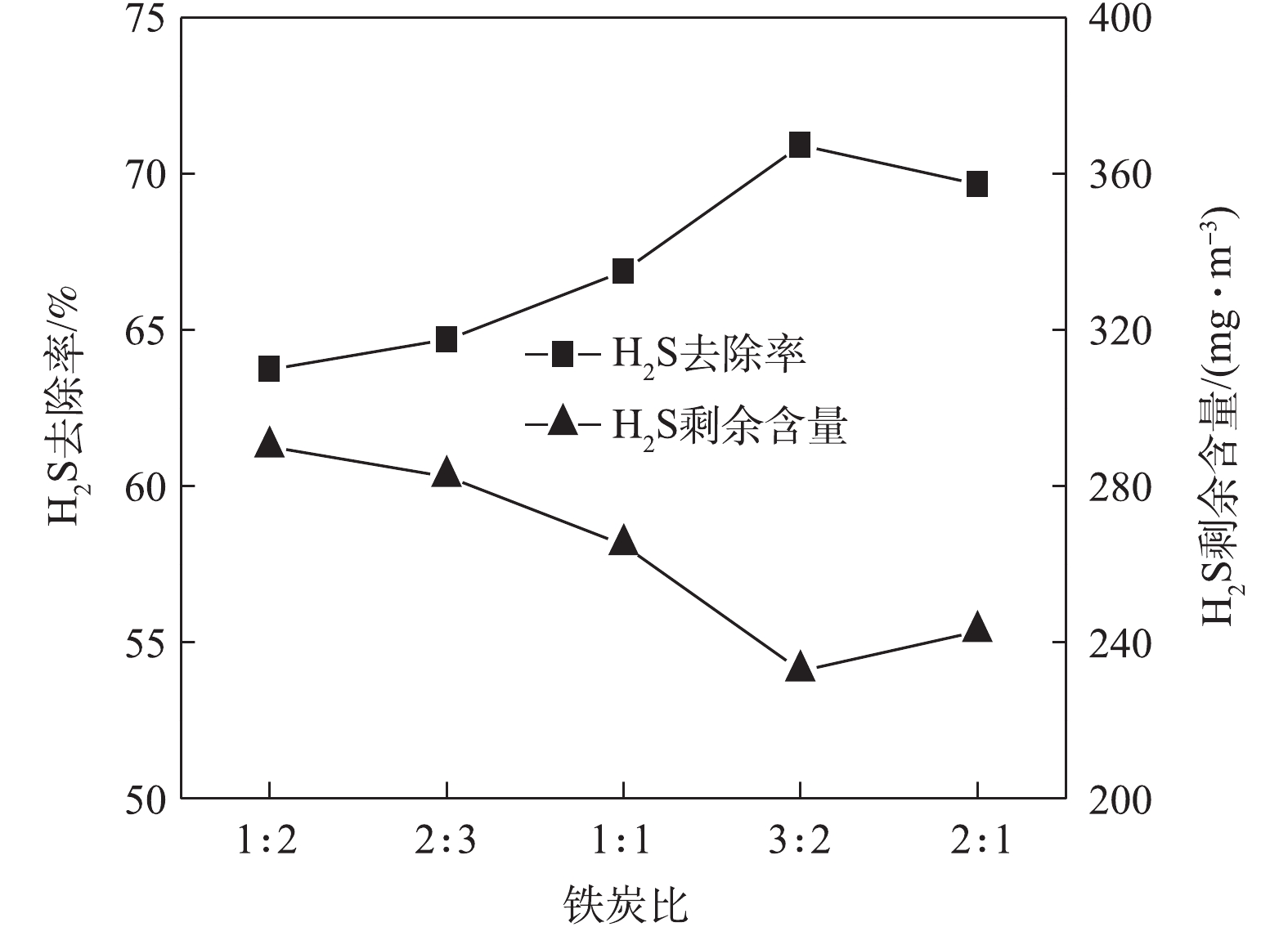
3) 铁炭比对处理效果的影响。控制天然气中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、反应时间为30 min、通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1和pH=7的条件下,研究了铁炭比(总质量不变)对H2S去除率的影响,实验结果如图5所示。由图5可见,随着铁炭比的增加,H2S剩余含量先减少后增加,H2S去除率先增大后降低,当铁炭比为3∶2时去除效果最好,H2S剩余含量达到最低值,为232.75 mg·m−3,H2S去除率达到70.91%。当铁炭比小于3∶2时,随着铁炭比的增加,反应体系中Fe的含量增加,使反应器中原电池的数量增加,有效地提高了H2S的去除效果,使得H2S去除率呈现逐渐升高的趋势;当铁炭比大于3∶2时,造成Fe大量剩余,当反应开始后,短时间内会形成过多的铁泥沉积在活性炭表面,使形成原电池数量减少,从而阻碍反应的进行[21],故导致H2S去除率呈现逐渐降低的趋势。因此,最终确定反应的最佳铁炭比为3∶2。
4) pH对处理效果的影响。控制天然气中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、反应时间为30 min、通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1和铁炭比为3∶2的条件下,研究pH对H2S去除率的影响,结果如图6所示。由图6可知,随着pH的增加,H2S剩余含量逐渐减少,H2S去除率逐渐升高;当pH为6时,H2S剩余含量为14.5 mg·m−3,去除率高达98.19%;而当pH为12时,H2S剩余含量为377.5 mg·m−3,去除率仅为52.81%,可见pH对H2S的去除效果有着重要的影响。这是因为当pH较低时,反应体系酸性越强,微电池的电位差越大,原电池的电动势越大,微电解反应较快,处理效果较好;随着pH的增加,微电池的电位差降低,反应变慢,导致处理效果下降[27]。
2.2 响应曲面优化
1) Box-Behnken设计。从以上单因素实验结果可知,反应时间对H2S的去除效果有一定的影响,但当反应一段时间后,对H2S的去除效果的影响很小。因此,最终选择铁炭比、通气速率和pH 3个因素进行响应曲面分析,采用Design Expert软件中的Box-Behnken法进行设计,以铁炭比、通气速率和pH作为自变量,以H2S去除率作为因变量,进行3因素3水平的响应曲面分析,确定各个因素对H2S处理效果的影响。实验设计因素与水平如表1所示,响应曲面实验运行结果如表2所示。实验中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3。
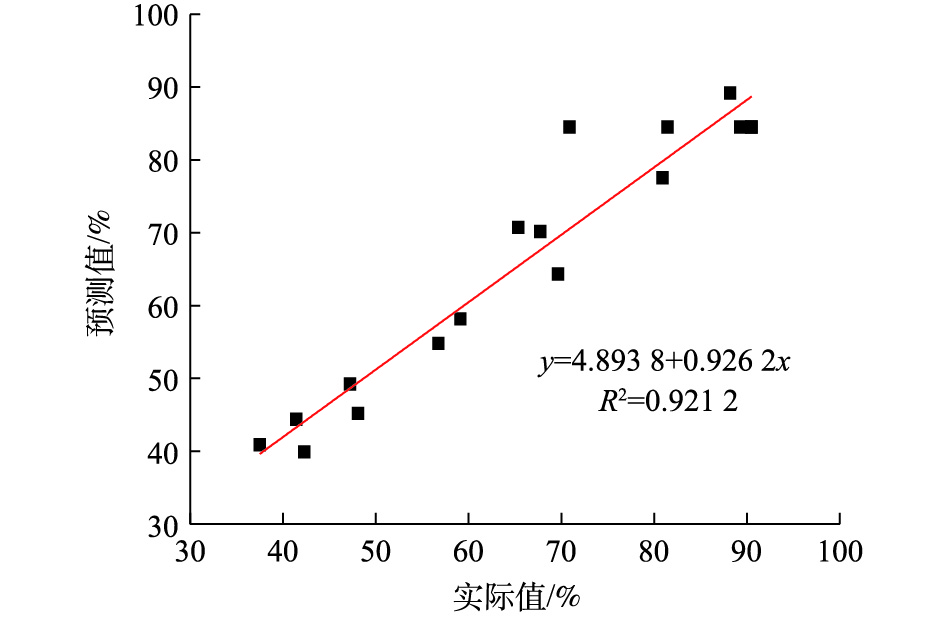
表 1 实验设计因素与水平Table 1. Influence factors and level design of experiment因素 编码 编码水平 −1 0 1 铁炭比 A 1∶2 3∶2 2∶1 通气速率/(m3·h−1) B 0.2 0.4 0.8 pH C 6 7 10 表 2 响应曲面实验运行结果Table 2. Response surface experimental program and results序号 A B C H2S去除率/% 1 0 0 0 70.91 2 0 1 −1 48.09 3 0 0 0 90.5 4 0 0 0 81.46 5 0 1 1 37.5 6 0 −1 1 41.45 7 −1 0 −1 65.37 8 1 0 1 69.66 9 0 0 0 89.29 10 0 −1 −1 80.91 11 1 −1 0 67.74 12 1 1 0 47.25 13 −1 0 1 59.13 14 1 0 −1 88.19 15 0 0 0 90.5 16 −1 1 0 42.31 17 −1 −1 0 56.75 2) ANOVA分析及二次回归拟合。根据Design Expert软件设计的实验模型进行ANOVA分析和模型的显著性分析,结果如表3所示。分析结果显示,在H2S去除率的模型中P=0.003 3,P<0.05,说明回归模型显著;失拟项不显著(P=0.676 9>0.05),这说明模型的预测值和实际值的误差较小,能够较好地反映响应值变化;在95%置信区间内,模型与实际值拟合较好。因此,可以将此模型用于内循环微电解处理天然气中H2S效果的预测。由图7可知,模型的实际值与预测值差别较小,R2为0.921 2,这说明模型可以较好地反映各个因素对H2S去除效果的影响。通过统计学分析,估计出二次回归方程中的回归系数(表3),由实验结果拟合得到天然气中H2S去除率的二次响应曲面方程(如式(5)所示)。
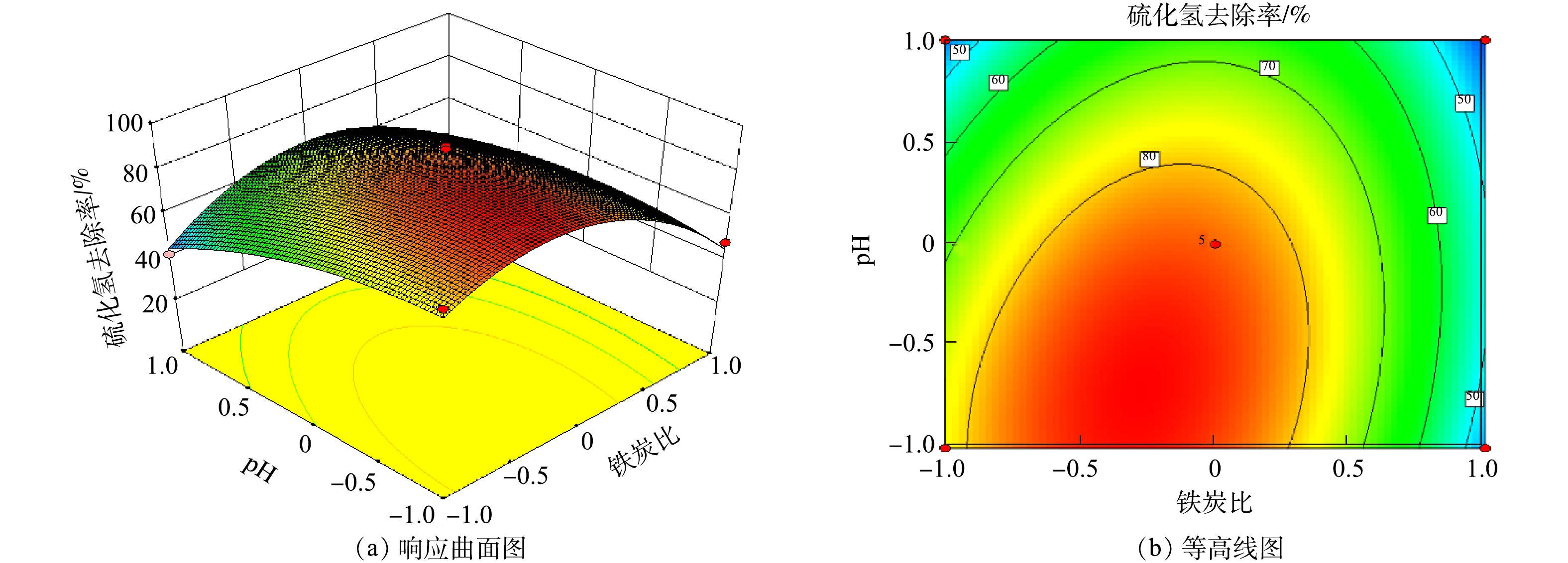
表 3 回归系数和模型的显著性分析Table 3. Regression coefficients and significant analysis因素 回归系数 标准误差 平方和 F P 显著性 截距(模型) 84.53 3.41 5 110.24 9.76 0.003 3 显著 A(铁炭比) 6.16 2.7 303.56 5.22 0.056 2 显著 B(通气速率) −8.96 2.7 642.61 11.05 0.012 7 显著 C(pH) −9.35 2.7 699.75 12.03 0.010 4 显著 AB −1.51 3.81 9.15 0.16 0.703 4 不显著 AC −3.07 3.81 37.76 0.65 0.446 9 不显著 BC 7.22 3.81 208.37 3.58 0.100 3 不显著 A2 −6.21 3.72 162.36 2.79 0.138 7 不显著 B2 −24.81 3.72 2 591.68 44.56 0.000 3 显著 C2 −7.73 3.72 251.9 4.33 0.076 0 显著 失拟项 118.24 0.55 0.676 9 不显著 Y=84.53+6.16A−8.96B−9.35C−1.51AB−3.07AC+7.22BC−6.21A2−24.81B2−7.73C2 (5) 3)交互作用的响应曲面分析。通过软件对实验数据进行回归分析,得到回归方程的响应曲面和等高线图,如图8~图10所示。在pH=7的情况下,考察了铁炭比和通气速率对H2S去除率的交互作用影响(见图8)。由图8可知,无论是铁炭比和通气速率如何改变,H2S去除率均随着通气速率和铁炭比的增加而呈现先增大后减小的趋势,因此,铁炭比和通气速率2个因素间的交互作用不明显。
在通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1的情况下,考察了铁炭比和pH对H2S去除率的交互作用影响(见图9)。由图9可知,无论铁炭比如何改变,H2S去除率总是随着pH的增大而减小;无论pH如何变化,H2S去除率总是随着铁炭比的增大而呈现先增大后减小的趋势。因此,铁炭比和pH 2个因素间没有明显的交互作用。
在铁炭比为3∶2的情况下,考察了通气速率和pH对H2S去除率的交互作用影响(见图10)。由图10可知,无论通气速率如何改变,H2S去除率都随着pH的增大而减小;无论pH如何变化,H2S去除率总是随着通气速率的增大而呈现先增大后减小的趋势。因此,通气速率和pH 2个因素间没有明显的交互作用。
综合响应曲面图和ANOVA分析中各因素的F值(C(12.03)>B(11.05)>A(5.22))可知,影响天然气中H2S去除效果的因素依次为pH>通气速率>铁炭比。通过Design Expert软件优化获得的最佳反应条件:铁炭比为3∶2,通气速率为0.33 m3·h−1,pH为6.1。在最优的条件下,模型预测H2S去除率为92.66%,模型预测值的95%置信区间为80.17%~100%。
2.3 验证实验
在上述最佳反应条件下进行实验,结果表明H2S去除率为84.6%,其落在模型预测值的95%置信区间(80.16%~100%)内。我国大部分气田的天然气中H2S含量小于800 mg·m−3,在最佳反应条件下,即使H2S的去除率取置信区间的下限80.16%,处理后H2S剩余含量小于158.72 mg·m−3,仍然可以达到《天然气》(GB 17820-2012)[28]中三类标准。通过验证实验证明,Design Expert响应曲面法具有较好的预测效果,可以利用响应曲面法对内循环微电解处理天然气中H2S的去除率进行预测。
3. 结论
1)采用内循环微电解对天然气中的H2S进行处理,单因素实验结果表明,采用内循环微电解技术处理天然气中H2S具有可行性。
2)通过Design Expert软件中Numercal优化功能,得到H2S去除效果最优时的反应条件:通气速率为0.33 m3·h−1、铁炭比为3∶2、pH为6.1。在此条件下,H2S的平均去除率为84.6%,处理后H2S剩余含量可从800 mg·m−3降至158.72 mg·m−3,可以达到《天然气》(GB 17820-2012)中三类标准。因此,内循环微电解技术可以有效地去除天然气中的H2S。
-
表 1 国内不同地区PAN浓度均值和最大值对比
Table 1. PAN concentrations in this study and comparison with the other sites in the urban regions
区域Region 城市City 观测时间Observation time 平均值/(×10−9)Average 最大值/(×10−9)Maximum 参考文献 京津冀 北京 2021年7月 0.89 — [23] 北京 2010年1—3月 0.70 3.51 [22] 京津冀 天津 2018年9月 0.93 — [8] 北京 2016年11月—2017年1月 1.1 7.1 [24] 苏皖鲁豫交界地区 淮北 2021年10月 0.42 1.44 本研究 淮北 2022年6月 1.87 5.72 本研究 青岛 2018年10—11月 0.75 5.83 [13] 2019年7—8月 0.81 7.82 [13] 长三角 上海 2017 0.7 7.0 [9] 合肥 2016年8月 1.10 4.65 [25] 浙江 2019年6—10月 0.66 4.35 [26] 珠三角 深圳 2018年9—10月 0.56 3.90 [20] 厦门 2020年3—11月 0.92 — [14] -
[1] 柴发合. 我国大气污染治理历程回顾与展望[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2020, 45(3): 5-15. doi: 10.19758/j.cnki.issn1673-288x.202003005 CHAI F H. Review and prospect on the atmospheric pollution control in China[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2020, 45(3): 5-15 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19758/j.cnki.issn1673-288x.202003005
[2] 姜华, 高健, 李红, 等. 我国大气污染协同防控理论框架初探[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(3): 601-610. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.01.11 JIANG H, GAO J, LI H, et al. Preliminary research on theoretical framework of cooperative control of air pollution in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(3): 601-610 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.01.11
[3] 张涵, 姜华, 高健, 等. PM2.5与臭氧污染形成机制及协同防控思路[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(3): 611-620. ZHANG H, JIANG H, GAO J, et al. Formation mechanism and management strategy of cooperative control of PM2.5 and O3[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(3): 611-620 (in Chinese).
[4] 花丛, 江琪, 迟茜元, 等. 我国中东部地区2015—2020年夏半年PM2.5和臭氧复合污染气象特征分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(3): 650-658. HUA C, JIANG Q, CHI X Y, et al. Meteorological characteristics of PM2.5-O3 air combined pollution in central and Eastern China in the summer half years of 2015-2020[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(3): 650-658 (in Chinese).
[5] 栗泽苑, 杨雷峰, 华道柱, 等. 2013—2018年中国近地面臭氧浓度空间分布特征及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(9): 2094-2104. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.06.16 LI Z Y, YANG L F, HUA D Z, et al. Spatial pattern of surface ozone and its relationship with meteorological variables in China during 2013-2018[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(9): 2094-2104 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.06.16
[6] 黄小刚, 赵景波, 曹军骥, 等. 中国城市O3浓度时空变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(3): 1120-1131. HUANG X G, ZHAO J B, CAO J J, et al. Spatial-temporal variation of ozone concentration and its driving factors in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(3): 1120-1131 (in Chinese).
[7] 汪旭颖, 严刚, 雷宇, 等. 苏皖鲁豫交界地区大气污染形势和问题分析[J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48(17): 45-48. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2020.17.008 WANG X Y, YAN G, LEI Y, et al. The status and problems of air pollution of the border area of Jiangsu, Anhui, Shandong and Henan[J]. Environmental Protection, 2020, 48(17): 45-48 (in Chinese). doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2020.17.008
[8] QIU Y L, LIN W L, LI K, et al. Vertical characteristics of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) from a 250-m tower in Northern China during September 2018[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2019, 213: 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.05.066 [9] ZHANG G, JING S G, XU W Y, et al. Simultaneous observation of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate and ozone in the megacity of Shanghai, China: Regional transport and thermal decomposition[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 274: 116570. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116570 [10] SUN M, ZHOU Y, WANG Y F, et al. Seasonal discrepancies in peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and its correlation with ozone and PM2.5: Effects of regional transport from circumjacent industrial cities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 785: 147303. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147303 [11] ZHANG G, MU Y J, LIU J F, et al. Seasonal and diurnal variations of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate, peroxypropionyl nitrate, and carbon tetrachloride in Beijing[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(1): 65-74. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60382-4 [12] ZHANG G, MU Y J, ZHOU L X, et al. Summertime distributions of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and peroxypropionyl nitrate (PPN) in Beijing: Understanding the sources and major sink of PAN[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 103: 289-296. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.035 [13] LIU Y H, SHEN H Q, MU J S, et al. Formation of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and its impact on ozone production in the coastal atmosphere of Qingdao, North China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 778: 146265. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146265 [14] LIU T T, CHEN G J, CHEN J S, et al. Seasonal characteristics of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) in a coastal city of Southeast China: Explanatory factors and photochemical effects[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 22(7): 4339-4353. doi: 10.5194/acp-22-4339-2022 [15] XU X B, ZHANG H L, LIN W L, et al. First simultaneous measurements of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and ozone at Nam Co in the central Tibetan Plateau: Impacts from the PBL evolution and transport processes[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(7): 5199-5217. doi: 10.5194/acp-18-5199-2018 [16] GAO T Y, HAN L, WANG B, et al. Peroxyacetyl nitrate observed in Beijing in August from 2005 to 2009[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(10): 2007-2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2014.08.002 [17] ZHANG J, XU Z, YANG G, et al. Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and peroxypropionyl nitrate (PPN) in urban and suburban atmospheres of Beijing, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 11(11): 8173-8206. [18] YUAN J, LING Z H, WANG Z, et al. PAN–precursor relationship and process analysis of PAN variations in the Pearl River Delta region[J]. Atmosphere, 2018, 9(10): 372. doi: 10.3390/atmos9100372 [19] LIU L, WANG X F, CHEN J M, et al. Understanding unusually high levels of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) in winter in Urban Jinan, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 71: 249-260. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.015 [20] XIA S Y, ZHU B, WANG S X, et al. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) in a coastal region in Southern China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2021, 260: 118553. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118553 [21] TUAZON E C, CARTER W P L, ATKINSON R. Thermal decomposition of peroxyacetyl nitrate and reactions of acetyl peroxy radicals with nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide over the temperature range 283-313 K[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1991, 95(6): 2434-2437. doi: 10.1021/j100159a059 [22] 廖敏萍, 龚道程, 王少霞, 等. 国庆期间南岭背景大气中PAN的浓度特征与来源[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(6): 2493-2503. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20210331.011 LIAO M P, GONG D C, WANG S X, et al. Concentration characteristics and sources of PAN at Nanling background station during the National Day holidays[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(6): 2493-2503 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20210331.011
[23] 王兴锋, 魏巍, 李睿, 等. 京津廊城市气团光化学污染潜势分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(5): 1985-1993. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.05.001 WANG X F, WEI W, LI R, et al. Analysis of photochemical pollution potential of air masses from various cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Langfang border[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(5): 1985-1993 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.05.001
[24] XU W Y, ZHANG G, WANG Y, et al. Aerosol promotes peroxyacetyl nitrate formation during winter in the North China plain[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(6): 3568-3581. [25] 张劲松, 魏桢, 陈志强, 等. 合肥市大气过氧乙酰硝酸酯污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(增刊1): 77-81. ZHANG J S, WEI Z, CHEN Z Q, et al. Research on characteristics of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate pollution in Hefei[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(Sup 1): 77-81 (in Chinese).
[26] 孙鑫, 唐倩, 邹巧莉, 等. 金华地区夏秋大气中过氧乙酰硝酸酯的污染特征[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 12(6): 721-728. SUN X, TANG Q, ZOU Q L, et al. Characteristics of atmospheric PAN pollution in Jinhua during summer and autumn[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 12(6): 721-728 (in Chinese).
[27] XUE L K, WANG T, LOUIE P K K, et al. Increasing external effects negate local efforts to control ozone air pollution: A case study of Hong Kong and implications for other Chinese Cities[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(18): 10769-10775. [28] QIU Y L, MA Z Q, LI K, et al. Markedly enhanced levels of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) during COVID-19 in Beijing[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(19): e2020GL089623. [29] 黄红铭, 黄增, 韦江慧, 等. 广西大气中过氧乙酰硝酸酯污染特征研究[J]. 化学工程师, 2020, 34(2): 36-39. doi: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20200236 HUANG H M, HUANG Z, WEI J H, et al. Research on characteristics of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate pollution in Guangxi[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2020, 34(2): 36-39 (in Chinese). doi: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20200236
[30] HU Y J, FU H B, BERNSTEIN E R. Generation and detection of the peroxyacetyl radical in the pyrolysis of peroxyacetyl nitrate in a supersonic expansion[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2006, 110(8): 2629-2633. doi: 10.1021/jp058196i [31] 陈瑾一, 彭月祥, 张成龙, 等. 过氧乙酰硝酸酯分析仪的光化学合成标定方法研究及应用[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(6): 1862-1870. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020012003 CHEN J Y, PENG Y X, ZHANG C L, et al. Study and application in calibration method of photochemical synthesis for peroxyacetyl nitrate analyzer[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(6): 1862-1870 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020012003
[32] ZHANG H L, XU X B, LIN W L, et al. Wintertime peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) in the megacity Beijing: Role of photochemical and meteorological processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(1): 83-96. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60384-8 [33] GONG D C, LIAO M P, WU G C, et al. Characteristics of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) in the high-elevation background atmosphere of South-Central China: Implications for regional photochemical pollution[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2021: 118424. [34] FISCHER E V, JAFFE D A, REIDMILLER D R, et al. Meteorological controls on observed peroxyacetyl nitrate at Mount Bachelor during the spring of 2008[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115(D3): D03302. [35] FISCHER E V, JACOB D J, YANTOSCA R M, et al. Atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN): A global budget and source attribution[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 14(5): 2679-2698. doi: 10.5194/acp-14-2679-2014 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴渴,王学中,张丹丹,朱华龙,闫永馨,李凡修,毋振海,郑振威,高祺凯. 2017~2022年亳州市PM_(2.5)与O_3复合污染演变特征及典型污染过程. 环境科学. 2024(10): 5715-5728 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载: