-
我国在碳达峰碳中和气候承诺及深入打好污染防治攻坚战的双重战略目标下,正以减污降碳协同增效为总抓手,推进清洁生产和能源资源节约高效利用,促进经济社会发展全面绿色转型。工业园区作为工业产业集约集聚的重要载体,具有资源和能源消耗量大、污染物和温室气体排放集中等特点,是开展减污降碳协同增效的重要领域之一。《中国开发区审核公告目录(2018年版)》和中国开发区网最新统计数据显示,截至2023年5月,全国省级和国家级开发区已达到2809家,具有较强的规模效应和示范引领优势。随着水、气、土等污染防治行动计划的深入实施,以及生态示范工业园区、循环化改造示范园区的推广,工业园区在污染物减排和绿色低碳发展方面积累了丰富的经验做法。在此基础上,《减污降碳协同增效实施方案》(环综合〔2022〕42号)进一步鼓励各类产业园区积极协同推进减污降碳,在空间布局优化、新能源推广使用、水资源节约集约高效循环利用、废物综合利用、绿色基础设施等方面提质增效。
减污降碳协同路径方面,除持续科技创新和产业优化升级等技术型路径外,“基于自然的解决方案”(nature-based solutions, NbS)越来越受到学术界、商业界和决策者的关注[1]。NbS通过挖掘和释放自然生态系统的多重服务功能,从而协同应对气候变化、生物多样性丧失、环境污染、水资源和粮食危机等各类挑战。相较于技术型路径,NbS具有成本优势,且为人类福祉和自然带来多重益处。作为NbS的倡导者和先行者,欧盟于2015年发布《基于自然的解决方案和自然化城市》(Nature-Based Solutions and Re-Naturing Cities)报告[2],并推动NbS写入世界自然保护大会(WCC)、联合国环境大会(UNEA)、联合国气候变化框架公约(UNFCCC)、生物多样性公约(CBD)等国际公约和进程的决定和决议[3],促使NbS成为协同应对多重挑战的主流工具。
尽管国际上NbS已成为解决工业园区生态环境问题的主流手段之一,但在我国工业园区尚未得到普及。“双碳”目标下,NbS路径的经济可行性、可持续性和减污降碳成效等尚缺乏有效评估,NbS在区域和全国范围内的示范和应用尚有待规范。对此,本研究回顾了NbS在国内外工业园区中的应用情况,并通过典型案例分析,为我国工业园区基于自然的协同减污降碳提出建议。
-
根据WCC和UNEA等多边进程对NbS的定义,其核心是保护、恢复和可持续管理自然或经改造的生态系统,提升生态系统服务功能,从而为人类和生物多样性带来惠益。具体路径方面,NbS以生态系统方式(Ecosystem approaches, EA)为基础,融合了其他与生态系统、土地和水资源管理相关的做法[4-6],如保护区、生态恢复、森林景观恢复、生态工程、生态农业、生态系统管理、基于生态系统的减灾、基于生态系统的气候变化减缓与适应、绿色基础设施、基于自然的气候解决方案、可持续土地管理、水资源综合管理、海绵城市等。在污染防治方面,污染物迁移路径管理与水循环和水资源管理密切相关,如通过建立绿色空间、渗漏性人行道、绿色屋顶等做法来管理水资源可用量和调节水循环过程,减少污水产生量;通过水源地保护、湿地净化等做法来调节水质,降低污染物浓度;通过河湖联通、河流再自然化、湿地保护修复、植被恢复等做法来降低水灾风险,提高污染物消纳能力。在固碳减排方面,森林、草地、湿地、农田等各类型生态系统的保护、恢复和可持续管理均有助于增加生态系统碳汇和减少温室气体排放[7]。在节能减排方面,太阳能、风能、潮汐能、生物质等可再生能源正逐步替代传统化石能源。尽管可再生能源是否属于NbS范畴尚存在争议,但这并不影响实践中将可再生能源与生态系统保护恢复等NbS路径相结合,以更好发挥减污降碳协同效应。
-
在国外的工业园区中,植被修复、生态恢复、生物降解[8]、绿色屋顶等NbS路径得到了很好的应用,并取得积极效果。例如,美国埃默里维尔的工业园区[9],历史上曾是煤炭和酸性煤废渣的主要生产地,环境污染较为严重。为减少污染物排放和改善生态环境质量,工业园区采用多种NbS路径。一是基于生态原则设计,将湿地、森林和土地利用策略纳入园区设计,以保护野生动植物、空气和水。二是植被修复,即利用植被修复、土地综合管理和沉淀池等方式,减少化学和有害物质的排放,同时过滤空气和改善水质。三是生物降解,发挥微生物、植物等生物体对有害物质的分解、转化和去除作用。
英国格拉斯哥市工业园区[9]在生态环境治理中融合了多种NbS路径,实现了环境质量改善与生态恢复,并为城市可持续发展和人类健康作出贡献。(1)生态修复与景观设计,通过植树造林、建设绿色广场和公园等增加绿化面积,满足居民休闲需求;(2)水质提升,通过升级城市排水体系,将过滤技术和生物处理技术应用于污水处理,降低污染物的不利影响;(3)绿色屋顶,通过增加绿色屋顶面积,利用雨水和植被等自然元素来抵御城市热岛效应,同时增加了鸟类和蝴蝶等野生动植物的栖息地。
-
针对减污降碳,我国工业园区发展过程中更注重技术创新和管理层面的协同效应。文献[10-12]也强调要加强污染防治的基础研究和技术研发,推广应用先进的减排技术和设备;加强对园区企业的环境管理和监管,完善园区环保监测体系;注重园区的能源节约和资源循环利用,尤其是在园区内部实施废弃物资源化和能源互联互通;强化制度建设和政策支持,推动产业结构调整和技术升级,提高园区的环保和能源效益。在此基础上,形成了绿色化生产模式、生态产业园区模式、环保合作模式等几种典型减污降碳模式。
-
绿色化生产模式通过升级改造工业园区内企业生产方式[13],实现资源高效利用和减污降碳目标。该模式包括3个方面:(1)优化生产工艺,采用先进的技术设备和清洁能源,减少排放量;(2)推广节能降耗措施,如智能化控制、制定用能指导计划等,从根本上减少了碳排放;(3)加强废弃物资源化利用,利用废弃物作为再生资源,减少污染物排放。该模式对资金和技术依赖性强,侧重于对污染物排放的源头预防和全生命周期管控。
-
生态产业园区是一种新型的工业园区模式[14],采用融合生态与工业的方式,实现了生态、经济和社会的良性互动关系,能够最大限度减少温室气体和污染物排放。同时,生态产业园区推广了循环经济模式,对生产过程可再生资源的二次开发和利用,进一步降低了碳排放。
-
工业园区内企业通过建立环保合作机制,实现资源利用和管理经验共享,达到减污降碳目标。其重要特点是基础设施共享,在园区物理边界内或周边通常建设有能源供应、污染治理基础设施,而此类设施普遍服役周期长,环境影响具有锁定效应[15]。此外,环保合作还可促进企业之间的交流合作,更好地实现工业园区绿色生产。
然而,相比于国外工业园区发展过程中对NbS路径的青睐,我国工业园区设计和建设过程中对NbS普遍认识不足,相关研究和实践探索还较为欠缺,尚不能充分发挥自然生态系统的污染物消减和碳汇功能。
-
温岭市东部产业集聚区是浙江省级经济开发区温岭经济开发区的核心区块,重点发展泵与电机、汽车摩托车及配件、机床装备等传统优势产业和新能源、新材料等战略新兴产业,2021年工业总产值822.8亿元,税收收入58.5亿元。截至2021年底,浙江省温岭经济开发区共拥有规模以上工业企业714家,国家级高新技术企业171家,上市企业7家。从建设之初起,就坚持全域生态化、海绵化,充分利用当地自然资源禀赋,在缓解水资源短缺、解决城市内涝、削减径流污染、提升园区清洁用能等方面均成效显著。
-
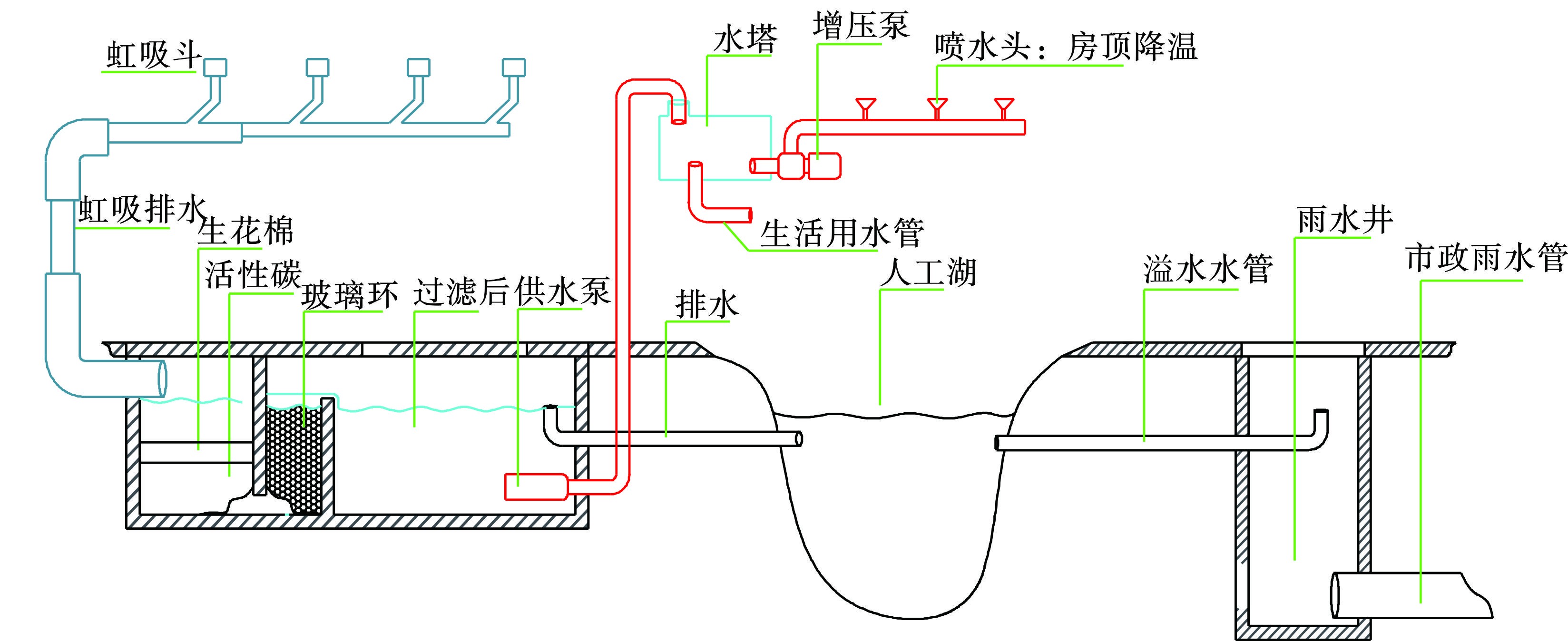
(1) 海绵型厂区。以浙江A食品机械有限公司为例,见图1。一是屋顶雨水通过企业厂房屋顶的虹吸系统汇集于一处,经过滤净化后储存于主厂房北侧的500 m3贮水池,蓄满后经管道流至厂前区的人工湖中;地面雨水经绿化带至集水井沉淀、自流、三次沉淀过滤后再汇集到人工湖,实现蓄水功能。二是暴雨时,人工湖满载后会自动溢流至市政雨水管道中,实现排水功能。三是可从人工湖抽水,经过滤后用于企业绿化、冲厕等,或从贮水池抽水至屋顶用于厂房物理降温,实现用水功能。该系统雨水收集有效容积3 900 m3,年可利用雨水近1万t。
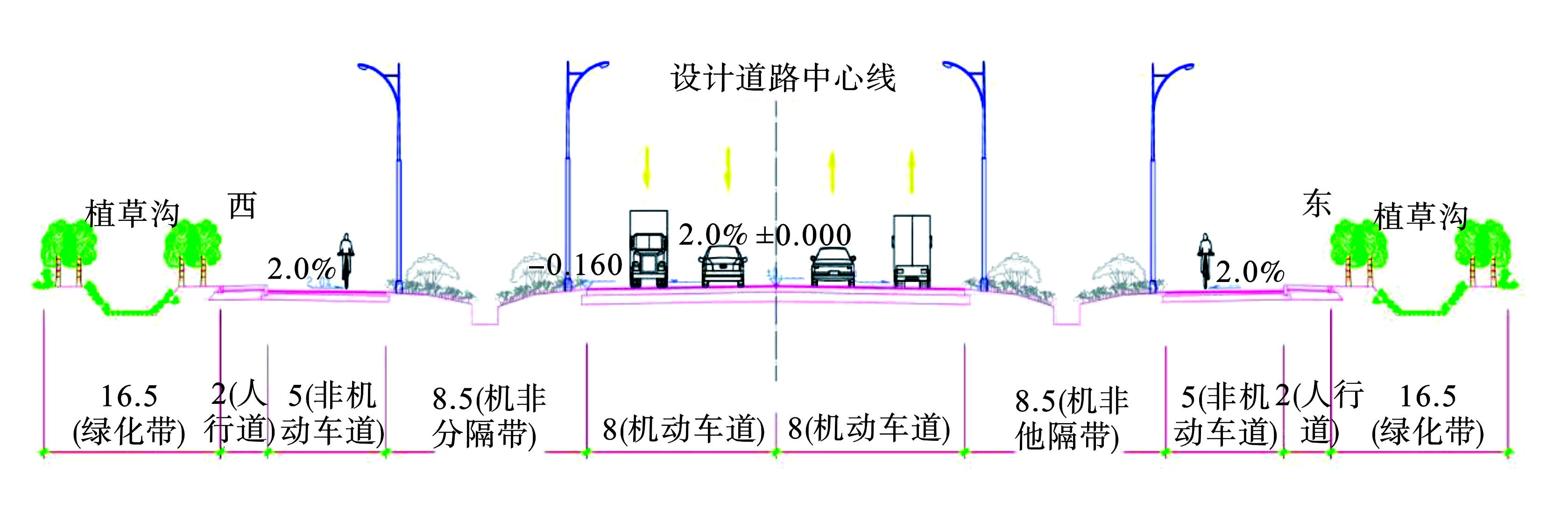
(2) 海绵型道路。以金塘北路为例,该路段位于浙江省温岭市东部产业集聚区北片区,是一条南北向城市主干道。北起28街,南至箬兴大道,全长约4.32 km,红线控制宽度47 m,红线外各有16.5 m绿化带,道路两侧主要为工业用地。在8.5 m机非分隔带内设置生物滞留设施,主要收集路面雨水,见图2。机非分隔带路牙采用平路牙,机动车道及非机动车道上地表径流分散进入生物滞留设施。生物滞留设施与道路坡度基本一致,平均深度约为30 cm,生物滞留设施底部设有下渗渠,通过下渗净化后进入底部盲管,最终接入绿化带内植草沟或市政排水管道。生物滞留设施中每隔一段设有溢流装置,溢流雨水同样接入绿化带内植草沟或市政管网。
(3) 海绵型污水处理厂尾水处理工程。污水处理厂尾水处理工程总规模4.06万 t/d,尾水经污水处理厂内提升泵提升至配水井后排至尾水生态处理系统。每级人工湿地设置多组平行湿地处理单元,在正常情况下,尾水经过先后“三级人工湿地+生态塘”组合工艺处理达到四类水标准后,出水排至园区河道。
(4) 龙门湖生态湿地。园区设计注重水系联通、园内小循环与园外大循环联通。秉承“人类宜居地和鸟类栖息地—两地共生”,以及“生态低碳、应急水源地、城市景观和休闲旅游—四位一体”的理念,结合东部新区整体城市设计,围绕都市田园、湿地湖泊和风情小镇三大功能板块,打造温台地区典型滨海湿地。
-
(1) 海上风电。园区引入浙江温岭东海塘风力发电有限公司,从2018年开始在东部产业集聚区沿海位置架设风力发电装置并运行,截至2021年底,总装机容量达到40 MW,全年发电量为6 637.18万 kW·h,可减少二氧化碳排放3.45万 t,削减大气污染物二氧化硫排放约3.89 t、氮氧化物约35.65 t、颗粒物约3.03 t。
(2) 分布式光伏发电。园区鼓励企业按照“自发自用、余量上网”的方式,建设屋顶分布式光伏发电系统,可再生能源使用比例逐年提升。截至目前,园区内部已有30%的企业,80万km2园区厂房屋顶安装光伏,总装机容量为60.2 MW,年均发电量为5 626.5万 kW·h,可减少二氧化碳排放2.92万 t,削减大气污染物二氧化硫排放约3.29 t、氮氧化物约30.25 t、颗粒物约2.57 t。
(3) 智慧能源管理系统。为加快构建“清洁低碳、安全高效”能源体系,打造绿色低碳园区,与浙江新奥能源发展有限公司签署低碳园区战略合作协议,引入低碳能效数智化解决方案,帮助企业实现能源管控、治理优化、资源协同及高效运维,并在此基础上实现全流程碳排放量化、碳资产智慧管理、碳咨询、碳核查和碳交易,进而实现区域或企业能源双控、低碳化、数智化的管理目标。
-
对降雨事件的监测与分析表明,温岭市东部产业集聚区径流污染调蓄效果明显,发生溢流时外排径流水中相关污染物浓度均低于《地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002)》Ⅳ类水标准,水环境改善成效显著。2021年园区供水量为1 112.18万 m3,单位建设用地综合用水量仅为43.7万 m3/(km2·a),远低于同类用地综合用水量水平,厂区等水资源利用体系对于优质水资源的减量使用效果明显,全区130家企业年雨水资源化利用近100万 t,节约水费600万元,可减少碳排放量194 t。2021年园区可再生能源发电量达1.22亿 kW·h,可减少二氧化碳排放6.37万 t,削减大气污染物二氧化硫排放约7.18 t、氮氧化物约65.9 t、颗粒物约5.6 t。
-
园区坚持人与自然和谐共生理念,工业发展的同时兼顾生态环境保护。通过建设的污水处理厂尾水处理湿地,使废水中的COD等污染物通过人工湿地生态系统进行降解固碳,达到水质净化、减少洪涝灾害,保护北部河湖水环境,改善水文循环,增加景观效果,改善城市环境的目的。龙门湖生态湿地公园于2019年5月份入选浙江省大花园建设行动计划五大工程中的生态环境质量提升工程和绿色产业发展工程。2021年温岭市东部产业集聚区工业增加值达36.34亿元,同比增速达到24.6%,实现了绿色高质量发展,且园区空气环境质量全年优良率为100%。
-
以问题和目标为导向,全域推进海绵城市建设,构建包含“海绵城市”“海绵建筑”“绿色湿地”3大标准子体系的“海绵城市”标准体系。《温岭市东部新区工业企业设计、建设和管理准则》将厂区海绵标准化流程,在与新入区企业签订出让用地合同时,将雨水生态化利用系统建设纳入合同条款,同时给予企业1.2352元/m2的海绵厂区建设补助。
-
目前,废水、废气处理设施应用广泛,然而仍有部分园区对生态环保认识不足、环保基础设施不到位,存在排放不达标、处理效率低等问题,严重影响了我国工业园区全面深入打好污染防治攻坚战和绿色低碳转型进度。为深入贯彻落实党中央、国务院关于碳达峰碳中和的决策部署和生态环境部等部门《减污降碳协同增效实施方案》,协同推进工业园区减污降碳工作,针对我国工业园现状,通过对浙江省温岭市东部产业集聚区NbS促进减污降碳协同增效的案例分析,本研究提出以下3点建议。
-
工业园区应根据自身主导产业和污染物、碳排放情况,积极探索适宜的NbS路径,衔接减污降碳管理要求。政府应加大对工业园区NbS项目的财政政策支持,引导金融机构和社会资本投资NbS,鼓励园区优化空间布局,大力推广使用新能源,优化能源系统和梯级利用、水资源集约节约高效循环利用、废物综合利用,提升基础设施绿色低碳水平。
-
统筹考虑生物多样性、气候变化和污染治理,研究制订工业园区NbS可行技术指南、NbS减污降碳成效评估指南等,推动污染物与温室气体排放协同控制,并从路径的经济可行性、可持续性、生态系统功能、减污降碳成效等方面进行成效评价。
-
结合当前正在开展的减污降碳协同治理工作,选择一批绿色发展基础好、NbS路径成熟且改善园区综合环境绩效较显著、经济实力有保障的园区,开展示范试点。同时,政府统筹谋划,争取给予专项预算资金支持,帮助企业完成高端化、数字化、绿色化升级。探索不同层级的协同,逐步从宏观布局产生的减污降碳并联效果向系统集成化前后端贯通产生的减污降碳串联效果转化,最终形成基于自然、协调有力的工业园区高质量发展新格局。
基于自然的解决方案促进工业园区减污降碳协同增效
——以温岭市东部产业集聚区为例Nature-based solutions to promote synergies in the reduction of pollution and carbon emissions in industrial parks
-
摘要: 工业园区是产业集聚、资源节约集约的重要载体,是开展减污降碳协同增效的重要领域之一。我国工业园区发展过程中较为注重技术创新对减污降碳的贡献,但对基于自然的解决方案(Nature-based Solutions, NbS)普遍认识不足,尚不能充分发挥自然生态系统的净化环境和固碳功能。文章选取浙江省温岭市东部产业集聚区为案例,评估了NbS在水环境治理、温室气体减排、生态保护、经济效益等方面取得的成效,进而对我国工业园区协同推进减污降碳提出:加强工业园区NbS路径设计和建设的政策引导和支持,开展工业园区NbS标准制定和成效评价工作和开展工业园区NbS试点建设3方面建议。Abstract: Industrial parks are important carriers for industrial agglomeration and resource conservation, playing a crucial role in promoting synergies in the reduction of pollution and carbon emissions. In the development of industrial parks in China, more attentions are paid to the technological innovation in the reduction of pollution and carbon emissions, the understanding of nature-based solutions (Nature-based Solutions, NbS) is insufficient and natural ecosystems have not been fully employed in environmental purification and carbon sequestration. Zhejiang Wenling Eastern Industrial Agglomeration Area was selected as a case to evaluate the effects of NbS in water environment management, greenhouse gas emission reduction, ecological conservation and economic benefits. Based on the results, three recommendations were proposed to synergy the reduction of pollution and carbon emissions in industrial parks: strengthening policy guidance and support for NbS pathway design and construction, establishing NbS standards and carrying out the effect evaluation in industrial parks, and conducting NbS pilot projects in industrial parks.
-
目前,国内外开发页岩气主要采用水力压裂的方法。水力压裂法主要是将压裂液(即水和化学试剂组成的混合液)和固体颗粒支撑剂在高压条件下泵入地层深处的岩石,压裂页岩层,形成缝隙,使页岩气更流畅地从岩石裂缝中释放[1]。压裂完成后,压裂液与页岩中的水混合作为返排液返回地面。非常规页岩气快速发展产生了许多环境问题,压裂过程中耗水量大和压裂液中添加的化学物质可能导致地下水和地表水污染[2]。页岩气压裂返排液具有成分复杂[3]、较高的化学需氧量(COD)[4]、处理难度大[5-6]的特点,因而是目前最具有挑战性的工业污水之一[2, 7]。因此,有必要找到具有成本效益的处理方案,以实现这种快速增长的非常规能源的可持续发展。
“深井回注技术”是前几年页岩气压裂返排液较普遍的处理方式,由于基础设施限制并且只有在地下深层地层具有足够的孔隙度能接收压裂返排液的地方才能使用深井回注技术,因此,许多井场由于地理位置的限制无法进行深井回注[8-9]。同时,深井回注有诱导地震发生的潜在风险[10],故其可行性越来越低。目前,为了减轻水资源的压力并节约成本,业界更趋向于将返排液重复用于压裂或处理达标后直接外排[11-12]。
混凝沉降是油气行业普遍采用的污水处理工艺,适用于大体积压裂返排液处理[13],可用于页岩气压裂返排液的预处理阶段[14-15]。混凝-吸附联用的实质属于强化混凝技术范畴[16],主要是利用吸附剂大的比表面积、微孔结构和表面反应性来吸附难以被混凝去除的溶解性有机物质[17],同时密度大的吸附剂可作为絮体的凝结核,可加快絮体沉降速度而且能减少混凝产生的污泥量[18],将两者优势互补,可提高废水有机污染物的去除率[19-20]。
本研究对四川省长宁地区页岩气压裂返排液进行预处理,旨在研究混凝-吸附联用作为页岩气压裂返排液中有机污染物去除的预处理工艺的可行性,为后续研究提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料、药剂和仪器
实验以四川省宜宾市长宁县某页岩气井场压裂返排液为研究对象,所取水样呈黄褐色,浑浊,黏度较低,有异味,含有悬浮物和杂质。对压裂返排液的基本性能进行测试,测试方法参见文献中的方法[21],测试结果如下:溶液pH为7~8,水温50~60 ℃,浊度22.8 NTU,化学需氧量(COD)为580 mg·L−1,氯离子浓度24 389 mg·L−1,总悬浮物浓度74.13 mg·L−1,溶液Zeta电位为−17.35 mV。
表 1 主要有机污染物种类分析Table 1. Analysis of main organic pollutants处理方法 GC-MS检出物质/种 GC-MS检出主要有机污染物 实验原水 43 2,3,6-三甲基辛烷;正己烷;甲基环己烷;间二甲基环己烷;2-甲基辛烷;异丙基环己烷;3-二甲基壬烷;2-环己基丁烷;3-甲基癸烷;正十一烷;2,3-二甲基癸烷;3-甲基十一烷;1,1-二甲氧基壬烷;2,10-二甲基十一烷;2,6-二甲基十一烷;2,5-二甲基十一烷;2-甲基十二烷;7-亚甲基十三烷;4-甲基十四烷;十五烷;十六烷;2,6,10-三甲基十五烷;十七烷;10-甲基十九烷;2-甲基二十烷;二十烷;1-戊基-2-丙基环戊烷;二乙基环戊烷;反式十氢化萘;硝基氯仿;2-溴壬烷;1,11-二溴十一烷;1-碘十一烷;2-己基-1-癸醇;环庚烷甲醇;2-丁基-1-辛醇;1-癸醇;2-己基-1-辛醇;癸基十四醇;2-甲基癸醇;3,7,11-三甲基-1-十二烷醇;邻苯二甲酸二丁酯;戊基环戊环烯酮 仅投加硅藻土J 36 2,3,6-三甲基辛烷;正己烷;甲基环己烷;间二甲基环己烷;2-甲基辛烷;异丙基环己烷;3-二甲基壬烷;2-环己基丁烷;3-甲基癸烷;正十一烷;2,3-二甲基癸烷;3-甲基十一烷;1,1-二甲氧基壬烷;2,10-二甲基十一烷;2,6-二甲基十一烷;2,5-二甲基十一烷;2-甲基十二烷;7-亚甲基十三烷;4-甲基十四烷;十五烷;十六烷;2,6,10-三甲基十五烷;十七烷;2-甲基二十烷;二十烷;反式十氢化萘;2-己基-1-癸醇;环庚烷甲醇;2-丁基-1-辛醇;1-癸醇;2-己基-1-辛醇;癸基十四醇;2-甲基癸醇;3,7,11-三甲基-1-十二烷醇;邻苯二甲酸二丁酯;戊基环戊环烯酮 先投加硅藻土J再投加PAC 21 2,3,6-三甲基辛烷;甲基环己烷;间二甲基环己烷;2-甲基辛烷;异丙基环己烷;3-二甲基壬烷;2-环己基丁烷;3-甲基癸烷;3-甲基十一烷;2,10-二甲基十一烷;2,6-二甲基十一烷;2,5-二甲基十一烷;2-甲基十二烷;7-亚甲基十三烷;4-甲基十四烷;2,6,10-三甲基十五烷;2-甲基二十烷;反式十氢化萘;2-甲基癸醇;3,7,11-三甲基-1-十二烷醇;戊基环戊环烯酮 药剂:硅藻土J购于吉林省嘉鹏硅藻土研发有限责任公司;聚合氯化铝(PAC)购于巩义市新一代净水材料厂;COD测定试剂购于哈希公司。
仪器:MY3000-6F六联搅拌仪(武汉市梅宇仪器有限公司);DRB200数字消解器(哈希公司);ET76020浊度测定仪(罗威邦公司);PALS 190 Plus Zeta电位分析仪(美国布鲁克海文公司);7890A-5925C气质联用仪(美国安捷伦科技有限公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1) 混凝-吸附联用实验。实验在室温下(25 ℃)进行,取页岩气压裂返排液样品500 mL,使用六联搅拌仪进行搅拌。投加PAC后,以300 r·min−1快搅1 min,再以50 r·min−1慢搅5 min;投加吸附剂后,100 r·min−1慢搅30 min,最后静置沉降30 min。先投加PAC或同时加入PAC和硅藻土J时,300 r·min−1快搅1 min后,100 r·min−1慢搅30 min,最后静置沉降30 min。除了联用顺序实验,所有实验均在PAC之前投加硅藻土J。在沉降结束后,使用移液管在水面下3 cm处取上清液以测定溶液浊度,将处理后样品用0.45 μm醋酸纤维滤膜过滤,测定溶液COD。
2) 处理后挥发性有机污染物分析。固相微萃取对水样进行前处理之后进样,通过7890A-5925C气质联用仪对处理前后水中有机污染物进行表征。气相色谱条件:柱箱温度40 ℃,进样温度250 ℃。载气:氦气,不分流进样。升温程序:40 ℃保持3 min,以5 ℃·min−1的速率升温至150 ℃保持2 min, 以10 ℃·min−1的速率升温至300 ℃保持5 min;总流量为7 mL·min−1,平衡时间为0.5 min。质谱条件:电子轰击(EI)离子源;离子源温度200 ℃,接口温度220 ℃,溶剂延迟时间0.1 min,扫描速度1 000 u·s−1,质荷比m/z为33.00~500.00。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 混凝-吸附联用可行性研究
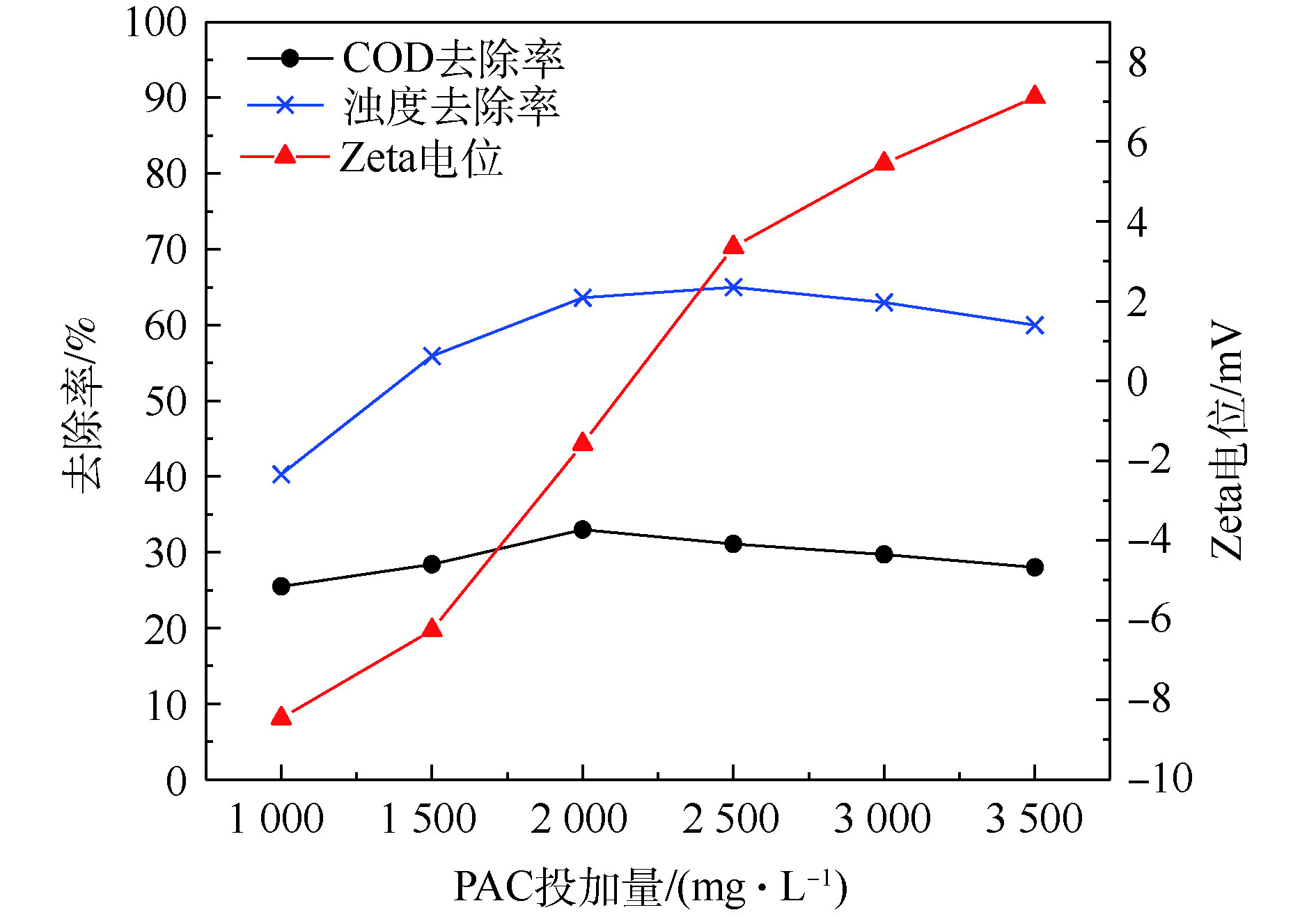
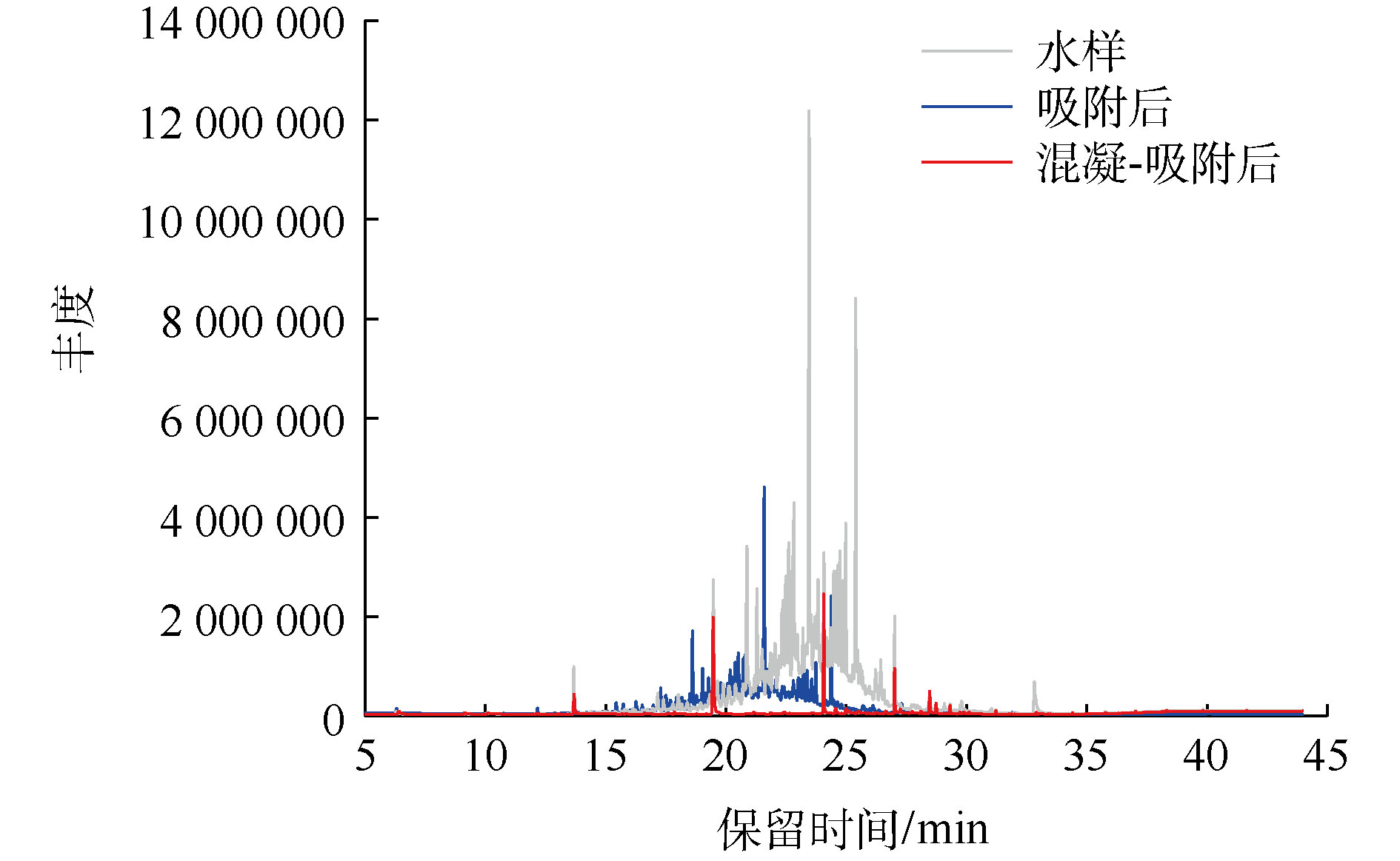
由图1可知,随着PAC投加量的增加,COD和浊度去除率先升高后呈下降趋势,ξ电位最初保持为负值逐渐接近0并最终变为正值。当PAC投加量增加到2 000 mg·L−1时,ξ电位接近等电点,COD和浊度去除率达到最大,分别为33.0%和63.6%;当投加量>2 000 mg·L−1时,COD和浊度去除率下降但变化不大,ξ电位值继续增大,由负值变为正值。
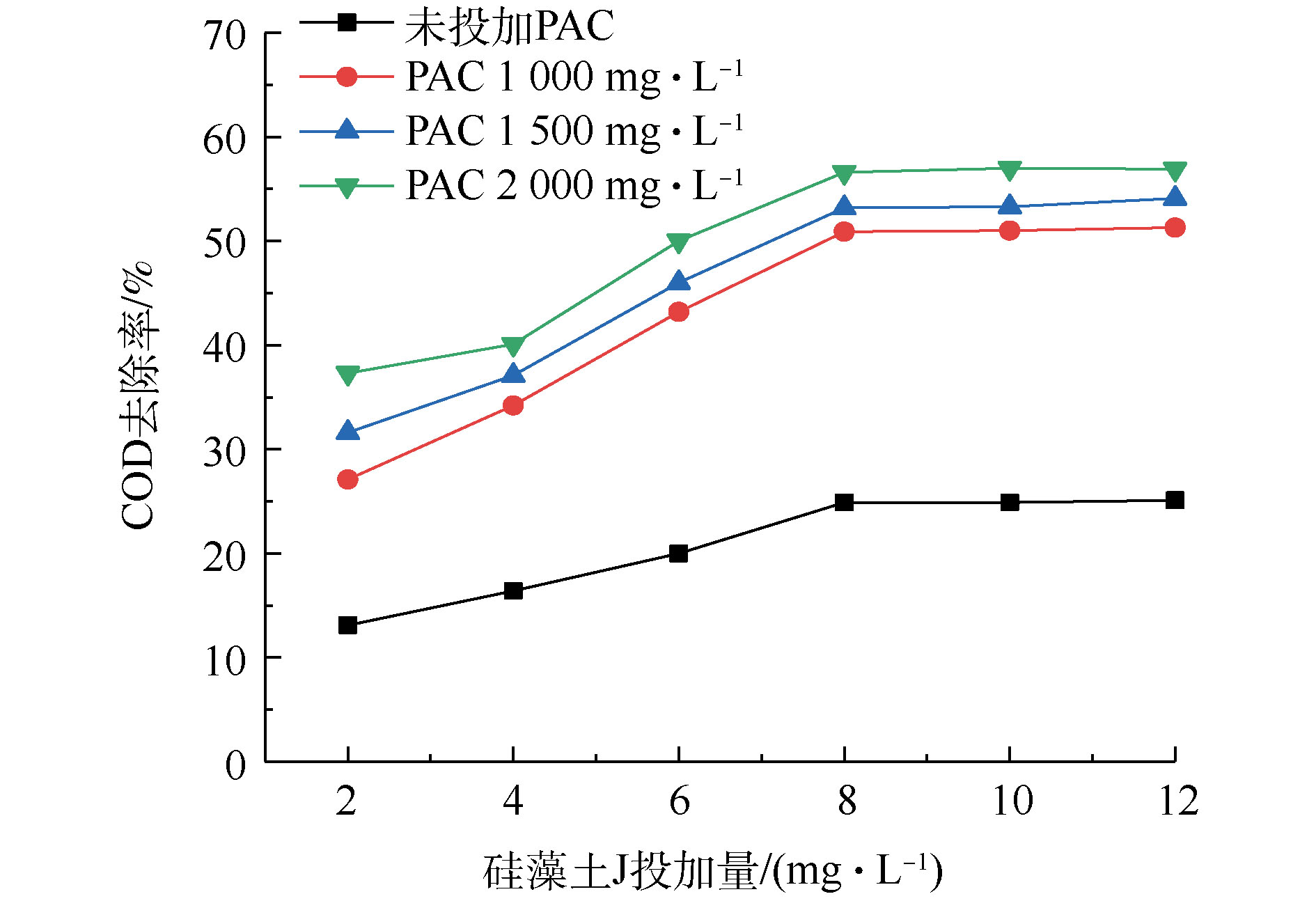
水样ξ电位为−17.35 mV,投加PAC后,ξ电位迅速上升。随着PAC投加量的逐渐增加,其水解产生带正电荷的水和羟基离子逐渐增多,阳离子进入胶体压缩扩散层,ξ电位逐渐趋近于0并靠近等电点,胶体脱稳开始集聚,形成絮体并沉降[22],混凝效果达到最佳。当PAC用量继续增加,污染物处理效果变化不大且呈下降趋势,这可能归因于混凝剂的过量添加造成多羟基金属络合离子电荷剩余,ξ电位变成正值并逐渐增大,它们之间的排斥力使体系重新稳定,凝聚效果下降。因此,可选择PAC投加量2 000 mg·L−1进行后续混凝-吸附联用实验。结果表明,仅投加硅藻土J进行吸附时,COD去除率随着投加量的升高而升高,达到8 mg·L−1时,COD去除率最大为24.9%,再增加投加量,去除率几乎不再变化。
与单独投加硅藻土J相比,PAC的投加有利于COD去除效果的提升(图2)。随着2种处理剂投加量的增加,COD去除率逐渐升高。在PAC投加量为2 000 mg·L−1和硅藻土J剂量为8 mg·L−1时,COD去除率可以达到57%,比只投加PAC或硅藻土J时去除率分别提升了24%和27%。可以看出,投加硅藻土J可以达到强化混凝的目的,混凝-吸附联用是一种有效可行的处理方法。
2.2 混凝-吸附联用顺序的确定
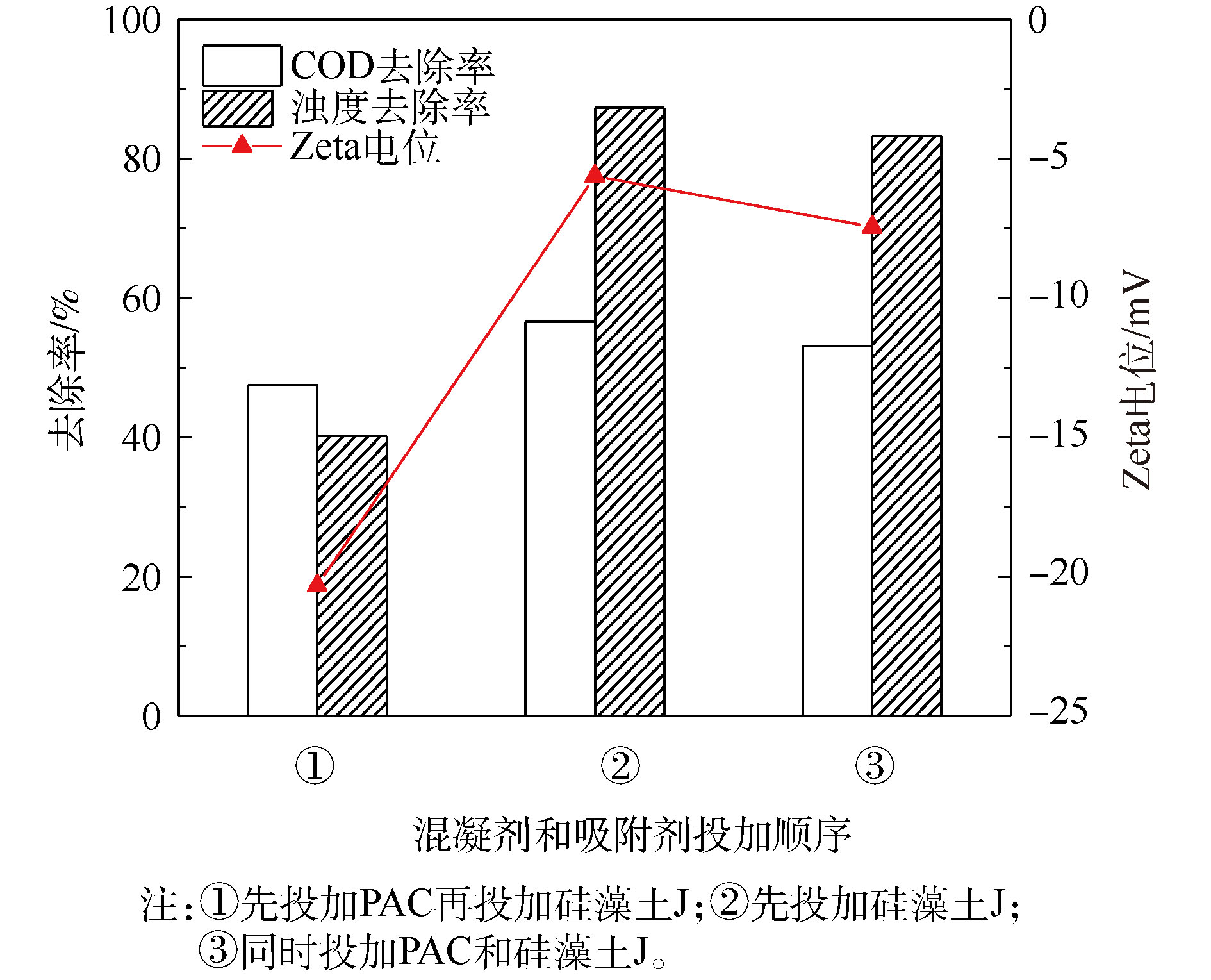
从图3可以看出,混凝剂和吸附剂的投加顺序对污染物的去除效果影响很大。先投加硅藻土J或2种处理剂同时投加的处理效果较先投加PAC效果好,先投加吸附剂时处理效果最佳,达到了溶液的最大污染物去除率,COD的去除率达到57%,浊度降低87%。先投加硅藻土J或2种处理剂同时投加时,ξ电位分别为−5.62 mV和−7.45 mV,更接近等电点,絮体形成迅速且致密;而在PAC之后加入硅藻土,ξ电位为−20.33 mV,远离等电点,絮体松散,残留浊度高。
已有研究表明:硅藻土表面在pH 2~12时带负电荷[23],先向水样中投加硅藻土J,能将小分子有机物和呈电中性的有机物吸附[24];继而投加混凝剂,混凝对胶体态物质和大分子有机物有良好的去除[25-26];此外,硅藻土可以嵌入絮体中作为絮体凝结核,改善絮状物的结构并增加絮体密度,使沉降速度加快。先投加PAC后再加入硅藻土J时,大多数硅藻土颗粒可能仅吸附在絮体的表面,使絮体ξ电位降低,水中胶体物质重新稳定,其余的硅藻土颗粒分散在溶液中会导致样本浊度升高,故采用先投加硅藻土J进行混凝-吸附联用实验。
2.3 混凝-吸附时间的确定
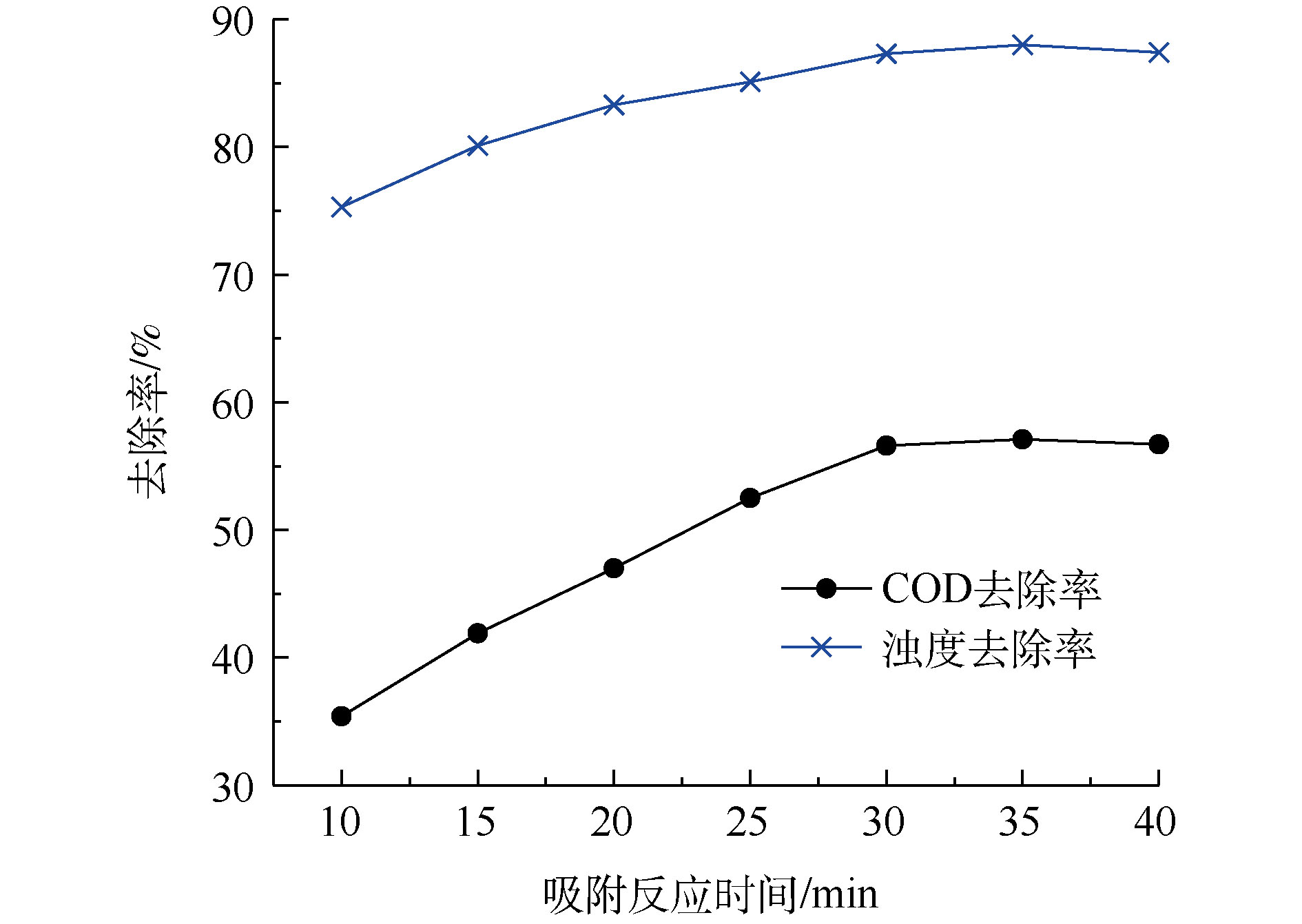
吸附剂对吸附质的吸附过程需要一定的反应时间才能取得较好的效果。因此,采用先投加硅藻土J后投加PAC的方式,考察其中吸附段反应时间对污染物去除效果的影响,如图4所示。由图4可知,30 min前,随着吸附时间的延长,污染物去除效果变好;30 min后,吸附过程逐渐达到平衡,去除效果不再随时间的变化而有明显改变。当吸附时间为30 min时,COD和浊度去除率分别达到57%和87%。
刚投加吸附剂时,水相中的污染物浓度与吸附剂表面浓度差较大,吸附剂表面的孔道和基团化学活性较高,污染物会迅速转移到吸附剂表面的吸附位点上[27];随着时间的推移,水相中竞争能力较强的污染物在吸附剂上已逐渐达到饱和,吸附速度变缓。为了使混凝和吸附时间具有更好的匹配性,并考虑综合处理成本,确定先投加硅藻土J吸附30 min后再投加PAC。
2.4 处理前后挥发性有机物分析
页岩气压裂返排液中含有压裂时用于钻井的残留化学添加剂,含量不高但是成分复杂[5]。图5显示了页岩气压裂返排液处理前后的总离子丰度,原水水样中检测到43种有机污染物。表1列出了检出的6类主要有机污染物。
在原水中检测到的有机污染物中包括烷烃类28种、芳香烃类1种、卤代烃类4种、醇类8种、酯类1种和酮类1种。投加硅藻土J后,有机污染物减少7种,卤代烃类得到良好的去除;进一步投加PAC后,有机物种类较原水水样减少了22种,可以将C20以下的饱和直链烷烃和邻苯二甲酸二丁酯完全去除,醇类物质可部分消除。
综合上述分析,混凝-吸附联用能够有效去除多种有机物,可为后续浓缩分离除盐段出水和不凝气COD达标提供保障。因此,混凝-吸附联用可以作为一种有效的页岩气压裂返排液预处理方法。
3. 结论
1)混凝剂PAC和硅藻土J联用具有去除页岩气压裂返排液中COD和浊度的能力。与仅投加PAC相比,硅藻土J的添加能有效加强吸附架桥作用,产生高密度、高强度的可沉降絮体。在PAC投加量为2 000 mg·L−1和硅藻土J剂量为8 mg·L−1时,有更好的污染物去除率和沉降效果。
2)联用顺序和硅藻土J作用时间可影响污染物的处理效果。在PAC之前或同时添加硅藻土可以大幅提高COD和浊度的去除率,吸附剂硅藻土J在PAC前30 min投加时处理效果最佳,COD的去除率达到57%,浊度降低87%。
3)混凝-吸附联用能去除多种有机污染物,有效降低页岩气压裂返排液有机负荷。硅藻土J-PAC联用,可处理去除页岩气压裂返排液种污染物22种,去除了大部分烷烃类、醇类、卤代烃和邻苯二甲酸二丁酯。
4) PAC和硅藻土J作为混凝剂和吸附剂进行混凝-吸附联用处理液页岩气压裂返排液,比传统的混凝/吸附处理工艺更有效、可行,能更好地降低有机负荷,并可为降低后续处理难度和成本提供参考。
-
[1] SEDDON N. Harnessing the potential of nature-based solutions for mitigating and adapting to climate change[J]. Science, 2022, 376: 1410 − 1416. doi: 10.1126/science.abn9668 [2] BAUDUCEAU N, BERRY P, CECCHI C, et al. Towards an EU research and innovation policy agenda for nature-based solutions & re-naturing cities: final report of the horizon 2020 expert group on ‘Nature-Based Solutions and Re-Naturing Cities’[R]. European Commission, Brussels, 2015. [3] 王金洲, 徐靖. “基于自然的解决方案”应对生物多样性丧失和气候变化: 进展、挑战和建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22496. [4] MASCOLI J R, PASSONI C M, SANTOS F M, et al. Assessment of surfactant removal capacity and microbial community diversity in a greywater-treating constructed wetland[J]. Resources, 2023, 12(3): 38. doi: 10.3390/resources12030038 [5] VASSALLE L, FERRER I, PASSOS F, et al. Nature-based solutions for wastewater treatment and bioenergy recovery: a comparative life cycle assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 880: 163291. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163291 [6] KALANTARI Z, FERREIRA C S S, PAN H Z, et al. Nature-based solutions to global environmental challenges[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 880: 163227. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163227 [7] GRISCOM B W, ADAMS J, ELLIS P W, et al. Natural climate solutions[C]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. USA, 2017, 114: 11645‒11650. [8] 王骞, 张崇军, 周丹丹. 基于微生物共代谢的工业废水混合处理研究现状与展望[J/OL]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文): 1-16[2023-06-12]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1218.TU.20221103.1259.002.html. [9] 生态环境部对外合作与交流中心. 欧美工业园区生态环境治理管理制度措施分析及对我国的启示[R]. 北京, 2020. [10] 费伟良, 李奕杰, 杨铭, 等. 碳达峰和碳中和目标下工业园区减污降碳路径探析[J]. 环境保护, 2021, 49(8): 61 − 63. [11] 周铭, 丁飞. 减污降碳协同增效背景下的产业园区环境管理对策探析[J]. 低碳世界, 2022, 12(8): 46 − 48. [12] 张潇天, 王维, 刘强. 园区高质量发展, 亟需减污降碳协同增效[J]. 环境经济, 2022(14): 38 − 41. [13] 吕一铮, 田金平, 陈吕军. 推进中国工业园区绿色发展实现产业生态化的实践与启示[J]. 中国环境管理, 2020, 12(3): 85 − 89. [14] 陈梅, 张龙江, 苏良湖. 国家生态工业示范园区建设进展及成效分析[J]. 环境保护, 2021, 49(20): 59 − 61. [15] 清华大学环境学院. 基于2℃温控目标的中国工业园区低碳发展战略研究[R]. 北京, 2020. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: