-
近年来,电力行业已率先完成电站锅炉超低排放改造工作,氮氧化物 (NOx) 固定源排放控制任务的重心转移到焦化、钢铁等行业[1]。当前,烟气净化领域中应用较多的脱硝技术有选择性催化还原法 (selective catalytic reduction,SCR) 和选择性非催化还原法 (selective non-catalytic reduction,SNCR) 等。然而,由于投资运行成本高、系统复杂和氨易泄漏会造成二次污染等问题,这部分行业的超净排放任务实现难度较大[2-4]。湿法氧化脱硝技术具有操作管理简便、烟气条件适应性强和可实现多污染物同时脱除等优点,有望实现超净排放,故成为众多学者研究的热点[5]。当前研究较多的是采用向液相中投加氧化剂的形式氧化脱除烟气中的NOx,其效果虽好,但氧化剂为一次性消耗品,产生的废液需要处理。
采用电解NaCl溶液产生强氧化性的有效氯组分可用于烟气脱硝,并通过现场制备的方式可有效解决众多湿法脱硝氧化剂 (H2O2、KMnO4和NaClO2等) 储存运输过程的安全隐患及氧化成分分解消耗问题,同时脱硝液可循环电解使用,从而可有效减少氧化剂的投加成本[6]。
基于以上思路,本研究采用无隔膜法电解NaCl制备有效氯溶液,考察NaCl质量浓度、电解时间对有效氯组分生成的影响,并在自制的小型湿法鼓泡喷淋反应器中以NaCl电解液作为氧化吸收液进行模拟烟气脱硝实验,对电解氧化吸收液脱硝机理进行分析,同时考察氧化吸收体系因素 (有效氯初始质量浓度、反应体系初始pH和温度) 对烟气脱硝效果的影响,以期为低温湿法氧化脱硝技术工业化应用提供参考。
-
实验采用NaCl、HCl、NaOH、C2H4O2、KI、NaS2O3·5H2O、Na2HPO4、KH2PO4等药品均为分析纯。本实验装置示意图如图1所示。装置可分为模拟烟气系统、有效氯溶液发生系统、氧化吸收系统及烟气分析系统。
在气体缓冲罐中,通入N2 (纯度为99.99%) 将NO (10%NO,N2为平衡气) 稀释至所需浓度,形成模拟烟气。本实验中,模拟烟气中的NO初始质量浓度设置为1 340 mg·m−3,烟气流量为2 L·min−1。有效氯溶液在电解发生器中产生,电解发生器槽电压电流可直接由直流恒压横流电源 (DQYY5-80,南通鼎麒电器有限公司) 进行调节。电解发生器阳极选用表面涂覆有钌铱等贵金属氧化物的纯钛板,阴级选用不锈钢板,电极板尺寸为80 mm×60mm×2 mm,并以3 mm的板间距并联均匀分布在发生装置内。氧化吸收过程是在实验室规模的底部带有砂芯布气器的鼓泡反应器 (
d =45 mm,h =500 mm,V =500 mL) 中进行。取300 mL NaCl电解液作为循环氧化吸收液,用蠕动泵 (WT600-2J,保定兰格恒流泵有限公司) 进行输送,在氧化吸收系统内采用单级喷淋循环,液体循环流量为200 ml·min−1。模拟烟气经鼓泡反应器底部布气器均匀分布并与氧化吸收液接触反应,且在上生过程与反应器顶部经喷嘴雾化的吸收液逆流接触,强化相间传质以提高烟气脱硝率。实验采用烟气分析仪 (Testo 350,德国德图公司) 分析进出口烟气中各组分的质量浓度,每次稳定采样时间为5 s。多余烟气通入5% HNO3和10% H2O2的混合液吸收瓶中,以吸收未被完全吸收的污染物。每次实验的循环保持15 min,所有实验重复3次。反应体系温度由恒温水浴锅 (HH-24,金坛市鑫鑫实验仪器有限公司) 控制;pH用pH计 (PHSJ-3F,上海雷磁科学仪器厂) 测定;有效氯质量浓度采用碘量法 (GB·T 5750.11-2006) [7]测定;电解液中各种氯氧化物的含量采用“五布碘量法”间接测定[8-9]。
-
电流效率 (current efficiency,
CE ) 计算定义式[10]见式 (1) 。式中:z为析氯反应转移的电荷数,z = 2;F为法拉第常数,F = 96 486 C·mol−1;
CFAC 为电解溶液中有效氯 (free available chlorine,FAC) 质量浓度,以 Cl2计,mg·L−1 ;V 为电解溶液体积 ,取2.20 L;I' 为电解电流,A;t 为电解时间,min;MCl2 为Cl2分子量,MCl2 =71 g·mol−1 。NO转化率、NOx去除率的计算公式见式 (2) 。
式中:
η 为气体污染物NO转化率、NOx去除率;C1 为气体污染物进口质量浓度,mg·m−3;C2 为气体污染物出口质量浓度,mg·m−3。 -
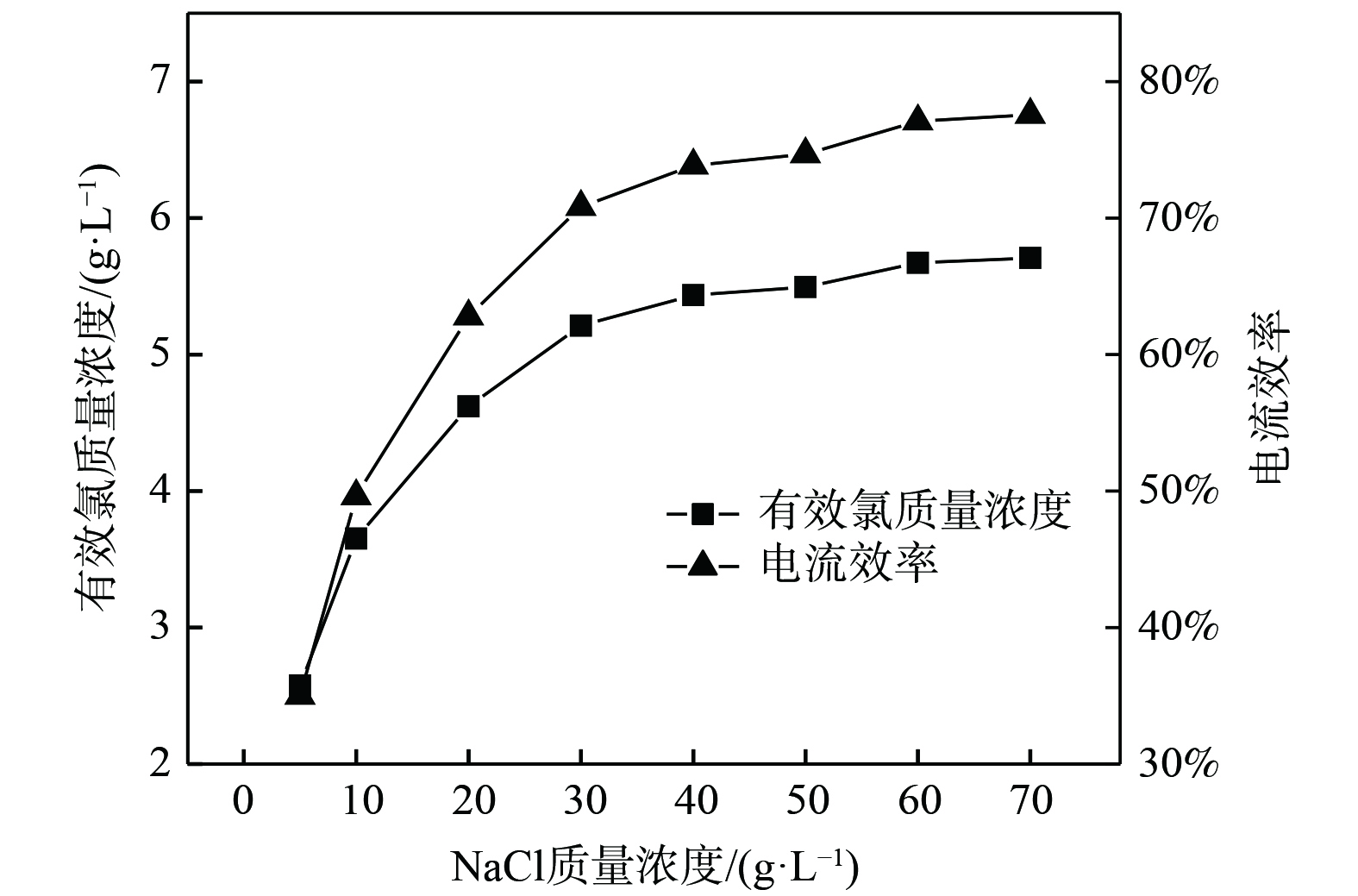
在电流密度为250 mA·cm−2、电解时间为5 min的条件下,研究了NaCl质量浓度对电解NaCl溶液制备有效氯质量浓度的影响,结果如图2所示。当电解时间一定时,电解液中有效氯质量浓度和电流效率随NaCl质量浓度增加而逐渐增加,而增幅不断减小。当NaCl质量浓度小于30 g·L−1时,电解液中Cl−质量浓度较低,有效氯生成速率主要受Cl−扩散速率的制约。同时,随着NaCl质量浓度增加,离子浓度也会增加,会使更多的离子参与电流传导,电导率随之增加,从而提高了电解过程的电流效率。当NaCl质量浓度大于30 g·L−1时,NaCl质量浓度继续增加对有效氯生成和电流效率影响较小。此时,电化学过程与电荷转移过程占主导作用。随着NaCl质量浓度继续增大,离子间距会缩小,离子间相互作用增强,离子运动阻力的增大会降低有效氯的生成速率[7]。综上所述,考虑到NaCl质量浓度超过30 g·L−1时,有效氯质量浓度增加量较少且会增大电解原料成本,将NaCl质量浓度定为30 g·L−1较合适。
-
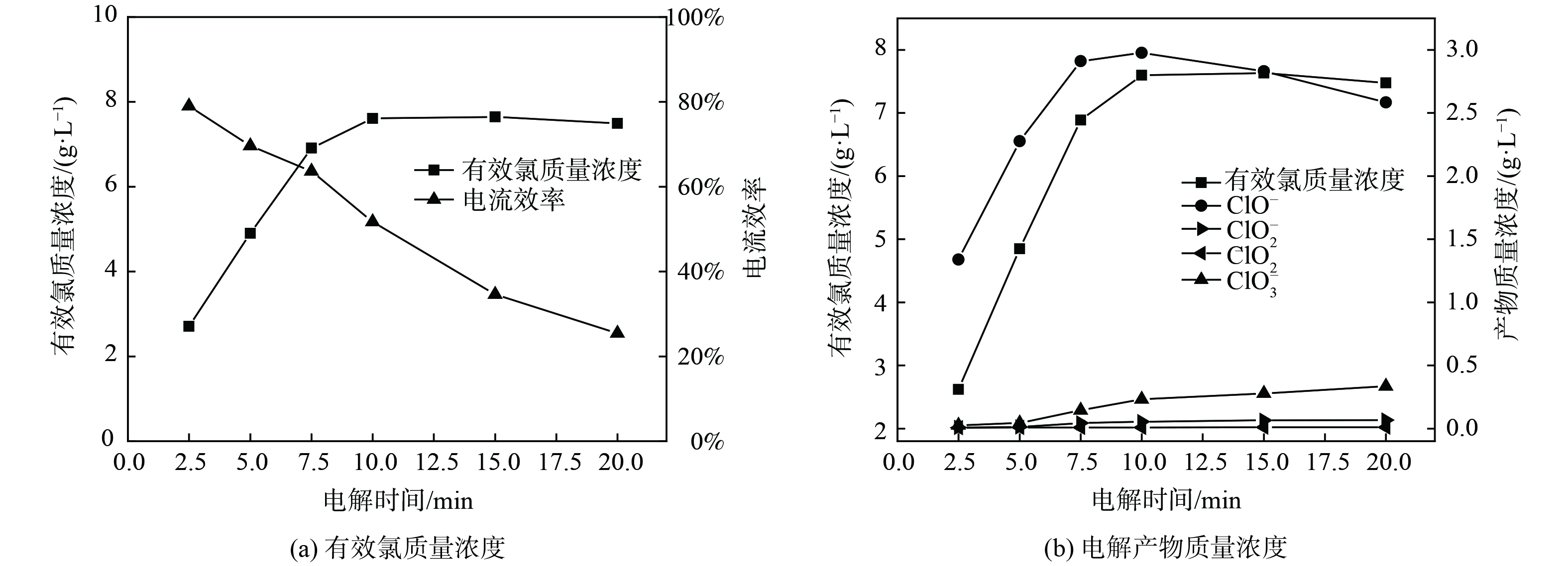
在NaCl质量浓度为30 g·L−1、电流密度为250 mA·cm−2的条件下,研究了有效氯的生成随电解时间变化的关系,结果如图3所示。图3 (a) 表明,随着电解时间延长,有效氯质量浓度逐渐增加而最终保持相对稳定,电流效率随电解时间的延长几乎呈线性下降。这是由于单位时间内参与阳极反应的Cl−因电解反应的发生不断消耗使得浓度降低;同时,在非恒温电解实验过程中,电流热效应会持续发生,温度升高会降低Cl2在电解液中的溶解度并促使有效氯组分扩散至阴级发生副反应,从而造成有效氯的分解[11]。图3 (b) 表明,当电解时间小于10 min时,ClO−质量浓度和副产物ClO3−质量浓度逐渐增高;当电解时间大于10 min后,ClO−质量浓度开始缓慢下降,而副产物ClO3−质量浓度持续增长。这是由于随着电解反应的发生,ClO−积累到一定浓度会加剧副反应的发生,ClO−进一步在阳极放电,产生ClO3−。电解过程ClO2−和ClO2的质量浓度始终不高,是由于电解反应主要以生成ClO−为主,生成ClO2−和ClO2的副反应不易发生。综上所述,为获得理想的电流效率 (效率大于60%) 和较高的有效氯质量浓度,电解时间可定为7.5 min。
-
烟气中95%以上的NOx是NO,而NO的溶解度极低[12]。湿法氧化脱硝技术是将烟气中的NO氧化为溶解度高、利于吸收的NO2,再进行下一步吸收反应。已知NO2/NO电对的标准电位为1.049 eV,故所采用的氧化剂电对的电势应大于该值[13]。表1为NaCl电解液中氧化成分、反应式及标准电位。NaCl电解液中氧化成分的电势高于1.049 eV的物质有Cl2、HClO、ClO2和NaClO3。
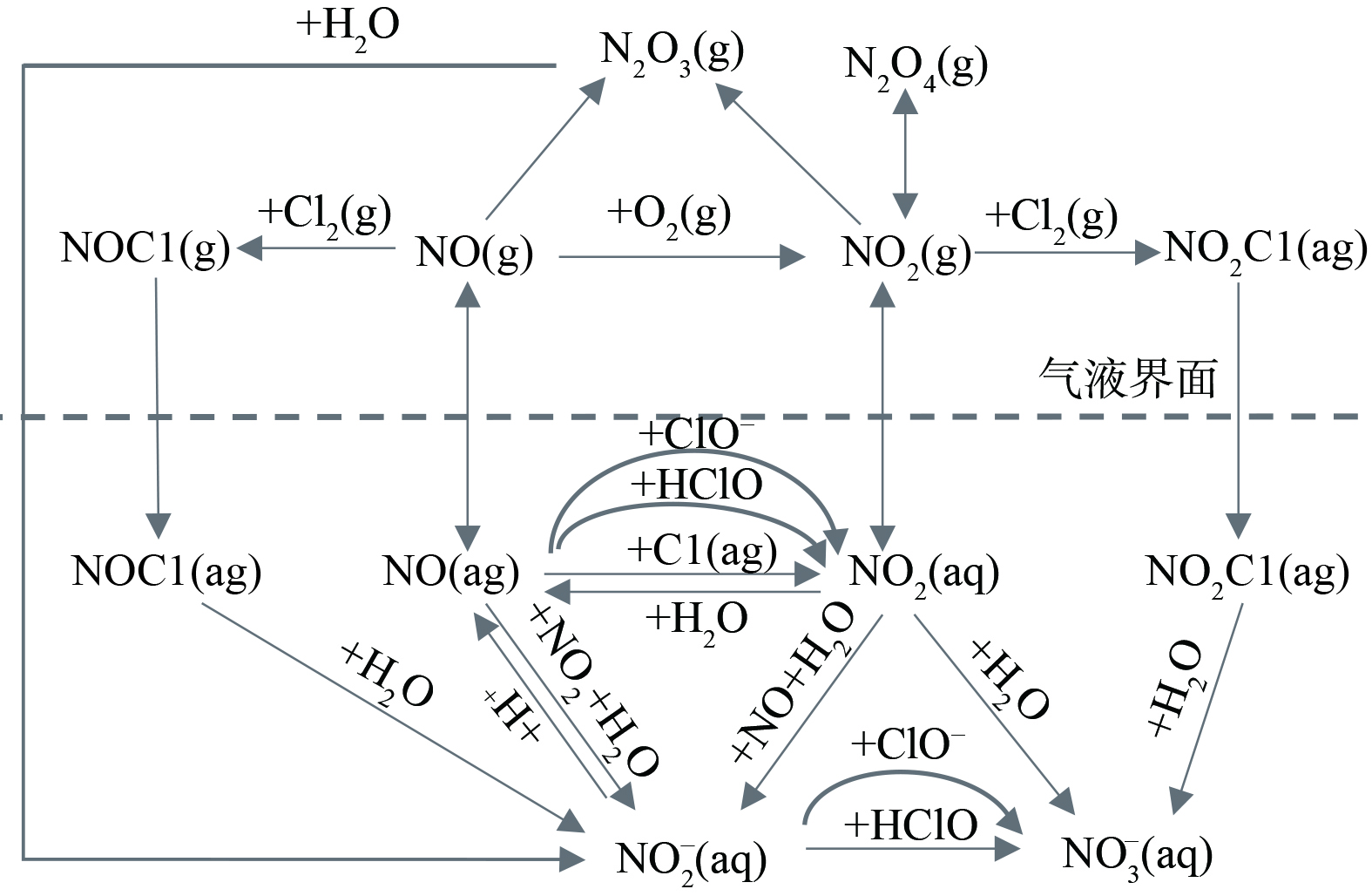
由2.2可知,电解反应主产物是ClO−,可推测有效氯溶液与烟气中的NOx发生氧化吸收的反应过程 (图4) [14-15]。NO的氧化吸收过程是从气相到液相的传质过程。由双膜理论可知,NO先由气膜进入液膜,在此过程中部分逸出Cl2可与NO反应结合,而在液膜中NO、NO2与有效氯组分反应,逐步被氧化为NO2−和NO3−,部分未被氧化的NO和NO2将以气态形式重新释放。
-
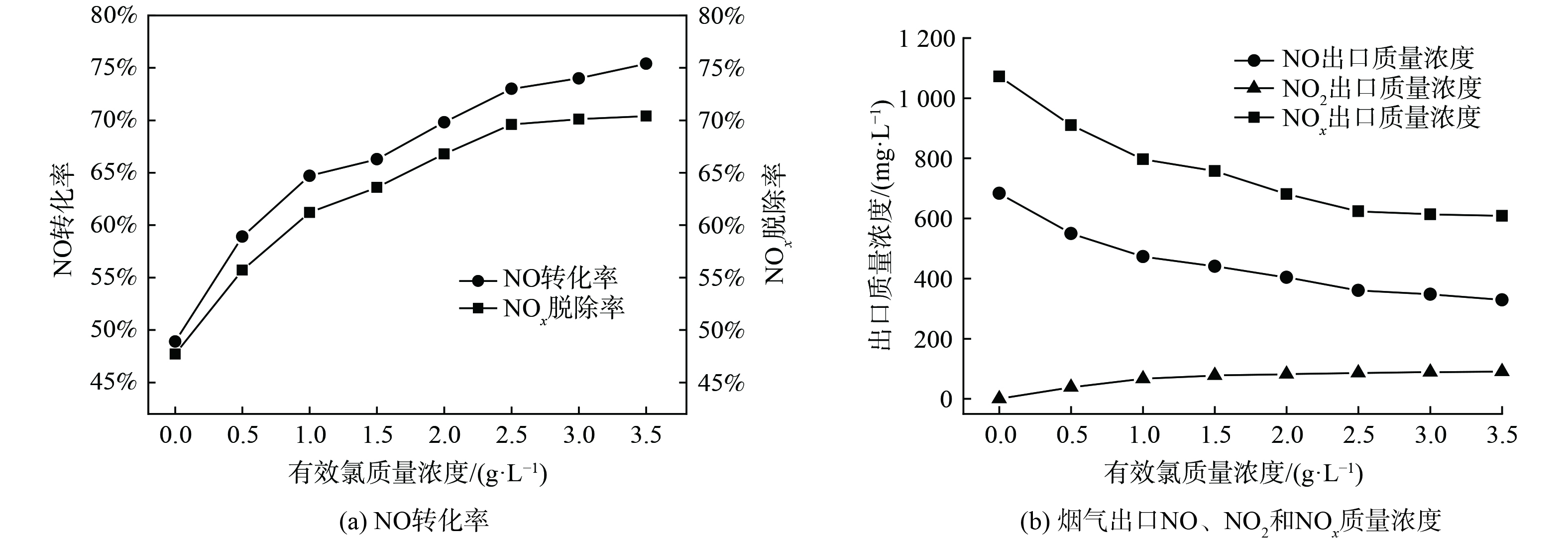
在反应体系温度为20 ℃、pH为9的实验条件下,研究了有效氯初始质量浓度对NOx脱除效果的影响,结果如图5所示。图5 (a) 是不同有效氯质量浓度对NOx脱除效果影响曲线图;图5 (b) 是不同有效氯质量浓度条件下的烟气出口NOx各组分质量浓度曲线图。随着有效氯初始质量浓度的增加,NO的转化率和NOx的去除率都逐渐增加后趋于平缓,烟气出口NOx各组分的质量浓度变化值减小。这是由于NO在液相中的溶解度较低,根据“双膜理论”,NO的氧化与吸收属于液膜控制,即由液相传质阻力控制。当溶液有效氯质量浓度从0增至2.5 g·L−1时,有效氯组分与NO间的传质增强,提高了NO的氧化率。当有效氯质量浓度达到2.5 g·L−1时,电解液氧化能力已满足氧化需求,继续提高质量浓度对NO氧化效果的提升较小[16]。综合考虑NO的转化率、NOx的去除率以及有效氯溶液的经济性,后续实验中有效氯质量浓度定为2.5 g·L−1。
-
在有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1、反应体系温度为20 ℃的条件下,研究了pH对NOx脱除效果的影响,结果如图6所示。图6 (a) 是有效氯溶液中的主要成分随pH的变化图。因吸收液中有效组分随pH的不同发生改变,使其对应的氧化脱硝能力也发生改变,不同组分的氧化还原电位大小顺序为E(HClO/Cl−) > E(Cl2(aq)/Cl−) > E(ClO−/Cl−)[17-18]。因此,本实验探讨了NOx氧化脱除效果与反应体系pH的关系,结果如图6 (b) 所示。当pH < 4时,溶液的氧化还原电位较高,脱硝反应主要是HClO和Cl2的氧化吸收过程,有较高NO的转化率,但该酸性条件不利于氧化产物NO2的溶解吸收[19]。当4<pH<6时,吸收液中Cl2/HClO摩尔比降低,脱硝反应主要是HClO的氧化吸收过程,此时NO的转化率逐渐下降,氧化产物NO2的溶解度随pH的增加显著提高,总NOx去除率在pH为5时出现峰值。当pH > 7时,氧化吸收液中HClO/ClO−摩尔比逐渐降低,吸收液的氧化还原电位持续降低,NO转化率下降使得NOx的去除率随之下降。因此,综合NO的转化率和NOx的脱除率,并考虑酸性条件下设备腐蚀损耗,吸收液pH为5时脱硝效果最佳。
-
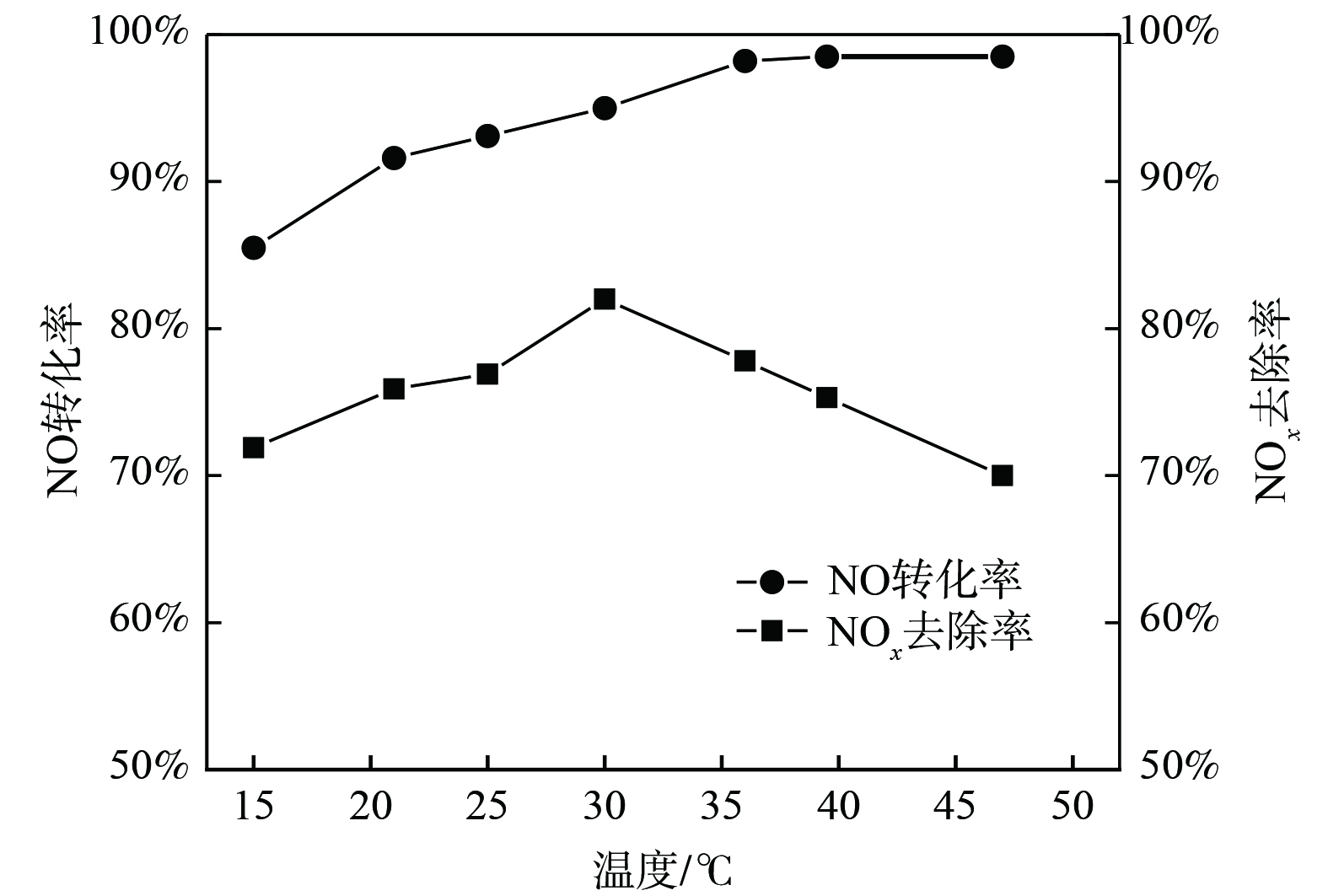
在有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1、反应体系pH为5的条件下,研究了吸收体系温度对NOx脱除效果的影响,结果如图7所示。随着吸收体系温度升高,NO转化率逐渐增加至稳定,而NOx去除率先增大后减少,并在30 ℃时取得峰值78.9%。NaCl电解氧化吸收液去除NO是气液传质反应,温度升高有助于增强液相组分的扩散传质并加快化学反应速率,从而促进NO的氧化[20-21];但温度升高增大了气液传质阻力,使得NO和氧化产物NO2溶解度降低。为获得较高NOx去除率,反应体系的温度控制在30 ℃为最佳。
-
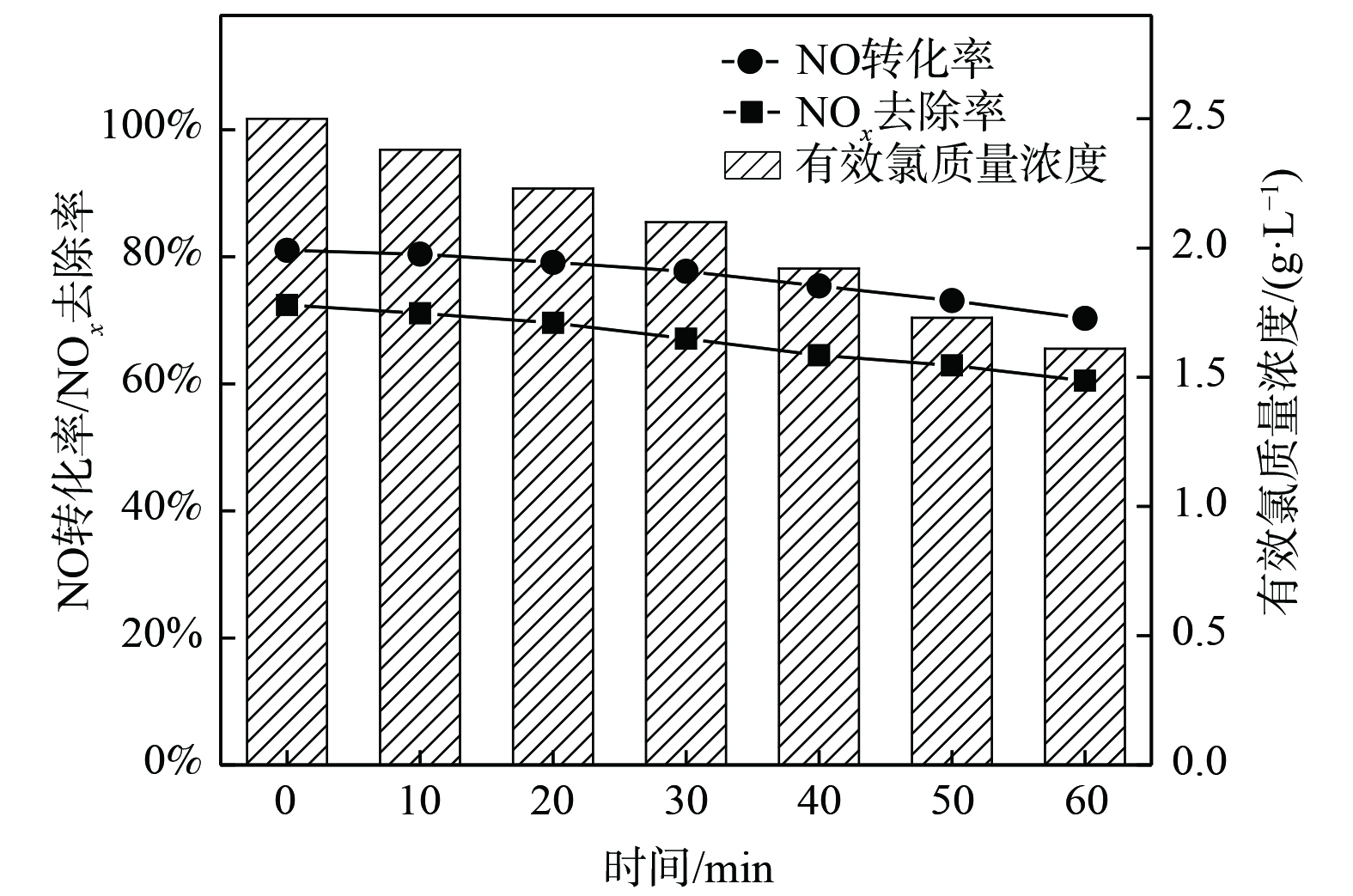
根据上述探讨的氧化吸收体系因素对烟气脱硝效果产生影响的所得结果,确定了最佳的反应条件:烟气流量为2 L·min−1,NO初始质量浓度为1 340 mg·m−3,吸收液有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1,反应体系pH为5,温度为30 ℃时,NO的转化率为91.1%,NOx去除率为78.9%。在最佳的反应条件下进行平行实验,结果如图8所示。在初始吸收液有效氯质量浓度一定的条件下,NO转化率、NOx去除率随时间的延长缓慢下降,在较长时间内保持较高的脱硝效果,NO的转化率从91.0%下降到80.3%,NOx的去除率从79%下降到60.5%。发生上述现象的原因有:一方面,随着氧化吸收液中有效成分与烟气中NO反应而被消耗,NO的氧化速率受到影响,同时溶液硝酸盐的累计也会影响NOx的吸收速率;另一方面,烟气中存在一定比例的酸性气体NO2,经吸收后会造成反应体系pH缓慢下降,有利于NO的氧化,但不利于氧化产物NO2的吸收,使得总NOx去除率降低加快。
-
1) 采用无隔膜法电解NaCl制备有效氯溶液,随着NaCl质量浓度和电解时间的增加,有效氯质量浓度逐渐增加,其增量逐渐减少,电解反应的主产物是ClO−,副产物主要是ClO3−。
2) 较高的有效氯NaCl质量浓度有利于NO氧化并促使NOx去除率升高;较低的pH有利于NO氧化,但不利于NOx去除,在弱酸条件下NOx去除效果最好;较高的温度有利于NO氧化,但不利于NOx去除。
3) 在最佳反应条件 (烟气流量为2 L·min−1,NO初始质量浓度为1 340 mg·m−3,吸收液有效氯初始NaCl质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1,反应体系pH为5,温度为30 ℃) 下,NO的转化率可达91.1%,NOx去除率可达78.9%,且能在较长时间内保持较高的烟气脱硝效果。
4) 基于研究结果,后期还应探讨更多的因素 (更加复杂的实际工业烟气、系统内氯气溢出逃逸、反应装置的氧化腐蚀等) 对NaCl电解氧化脱硝系统的影响,以期为其工业化应用提供更加全面的参考。
NaCl电解氧化吸收液脱除烟气中的NOx
NOx removal from flue gas by NaCl electrolytic oxidation absorption solution
-
摘要: 研究了NaCl质量浓度、电解时间对电解生成有效氯组分的影响,并以NaCl电解液作为氧化吸收液在自制的小型鼓泡喷淋吸收塔中进行模拟烟气脱硝实验,进一步研究了有效氯质量浓度、反应体系pH和温度对脱硝效果的影响,同时分析了脱硝机理。结果表明:有效氯质量浓度随着NaCl质量浓度和电解时间的增加逐渐增加,电解反应的主产物是ClO−。NOx去除率随着有效氯质量浓度增加而升高;氧化体系酸度和温度增高有利于NO氧化,但不利于NOx吸收去除。当烟气流量为2 L·min−1,NO初始质量浓度为1 340 mg·m−3,吸收液有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1,反应体系pH为5,温度为30 ℃时,NO的转化率可达91.1%,NOx去除率可达78.9%,且能在该条件下长时间保持较高的烟气脱硝效果。本研究结果可为低温湿法氧化脱硝技术的工业化应用提供参考。Abstract: An experiment simulating flue gas denitrification was conducted in a small bubble spray absorption tower using NaCl electrolyte as the oxidation and absorption solution. The effect of NaCl mass concentration and electrolysis time on the effective chlorine fraction generated by electrolysis was also investigated. The effects of effective chlorine mass concentration, pH and temperature of the reaction system on the denitrification effect were further studied, the denitrification mechanism was also analyzed. The results showed that the effective chlorine mass concentration increased gradually with the increase of NaCl mass concentration and electrolysis time, and the main product of the electrolysis reaction was ClO-. The removal rate of NOx increased with the increase of available chlorine mass concentration. The increase of acidity and temperature of the oxidation system was beneficial to NO oxidation, but not to NOx absorption and removal. At a flue gas flow rate of 2 L·min-1, an initial NO mass concentration of 1 340 mg·m-3, an initial absorption solution effective chlorine mass concentration of 2.5 g·L-1, a reaction system pH of 5 and a temperature of 30℃, the conversion rate of NO could reach 91.1% and the removal rate of NOx could reach 78.9%, and the high flue gas denitrification effect could be maintained for a long time under these conditions.
-
Key words:
- electrolytic oxidation /
- effective chlorine /
- flue gas denitrification /
- NOx emission
-
近年来,电力行业已率先完成电站锅炉超低排放改造工作,氮氧化物 (NOx) 固定源排放控制任务的重心转移到焦化、钢铁等行业[1]。当前,烟气净化领域中应用较多的脱硝技术有选择性催化还原法 (selective catalytic reduction,SCR) 和选择性非催化还原法 (selective non-catalytic reduction,SNCR) 等。然而,由于投资运行成本高、系统复杂和氨易泄漏会造成二次污染等问题,这部分行业的超净排放任务实现难度较大[2-4]。湿法氧化脱硝技术具有操作管理简便、烟气条件适应性强和可实现多污染物同时脱除等优点,有望实现超净排放,故成为众多学者研究的热点[5]。当前研究较多的是采用向液相中投加氧化剂的形式氧化脱除烟气中的NOx,其效果虽好,但氧化剂为一次性消耗品,产生的废液需要处理。
采用电解NaCl溶液产生强氧化性的有效氯组分可用于烟气脱硝,并通过现场制备的方式可有效解决众多湿法脱硝氧化剂 (H2O2、KMnO4和NaClO2等) 储存运输过程的安全隐患及氧化成分分解消耗问题,同时脱硝液可循环电解使用,从而可有效减少氧化剂的投加成本[6]。
基于以上思路,本研究采用无隔膜法电解NaCl制备有效氯溶液,考察NaCl质量浓度、电解时间对有效氯组分生成的影响,并在自制的小型湿法鼓泡喷淋反应器中以NaCl电解液作为氧化吸收液进行模拟烟气脱硝实验,对电解氧化吸收液脱硝机理进行分析,同时考察氧化吸收体系因素 (有效氯初始质量浓度、反应体系初始pH和温度) 对烟气脱硝效果的影响,以期为低温湿法氧化脱硝技术工业化应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与装置
实验采用NaCl、HCl、NaOH、C2H4O2、KI、NaS2O3·5H2O、Na2HPO4、KH2PO4等药品均为分析纯。本实验装置示意图如图1所示。装置可分为模拟烟气系统、有效氯溶液发生系统、氧化吸收系统及烟气分析系统。
在气体缓冲罐中,通入N2 (纯度为99.99%) 将NO (10%NO,N2为平衡气) 稀释至所需浓度,形成模拟烟气。本实验中,模拟烟气中的NO初始质量浓度设置为1 340 mg·m−3,烟气流量为2 L·min−1。有效氯溶液在电解发生器中产生,电解发生器槽电压电流可直接由直流恒压横流电源 (DQYY5-80,南通鼎麒电器有限公司) 进行调节。电解发生器阳极选用表面涂覆有钌铱等贵金属氧化物的纯钛板,阴级选用不锈钢板,电极板尺寸为80 mm×60mm×2 mm,并以3 mm的板间距并联均匀分布在发生装置内。氧化吸收过程是在实验室规模的底部带有砂芯布气器的鼓泡反应器 (
d h V 实验采用烟气分析仪 (Testo 350,德国德图公司) 分析进出口烟气中各组分的质量浓度,每次稳定采样时间为5 s。多余烟气通入5% HNO3和10% H2O2的混合液吸收瓶中,以吸收未被完全吸收的污染物。每次实验的循环保持15 min,所有实验重复3次。反应体系温度由恒温水浴锅 (HH-24,金坛市鑫鑫实验仪器有限公司) 控制;pH用pH计 (PHSJ-3F,上海雷磁科学仪器厂) 测定;有效氯质量浓度采用碘量法 (GB·T 5750.11-2006) [7]测定;电解液中各种氯氧化物的含量采用“五布碘量法”间接测定[8-9]。
1.2 数据处理
电流效率 (current efficiency,
CE CE=zFVCFAC6.00×104I′tMCl2×100% (1) 式中:z为析氯反应转移的电荷数,z = 2;F为法拉第常数,F = 96 486 C·mol−1;
CFAC V I' t MCl2 MCl2 NO转化率、NOx去除率的计算公式见式 (2) 。
η=C1−C2C1×100% (2) 式中:
η C1 C2 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 NaCl质量浓度对有效氯组分生成的影响
在电流密度为250 mA·cm−2、电解时间为5 min的条件下,研究了NaCl质量浓度对电解NaCl溶液制备有效氯质量浓度的影响,结果如图2所示。当电解时间一定时,电解液中有效氯质量浓度和电流效率随NaCl质量浓度增加而逐渐增加,而增幅不断减小。当NaCl质量浓度小于30 g·L−1时,电解液中Cl−质量浓度较低,有效氯生成速率主要受Cl−扩散速率的制约。同时,随着NaCl质量浓度增加,离子浓度也会增加,会使更多的离子参与电流传导,电导率随之增加,从而提高了电解过程的电流效率。当NaCl质量浓度大于30 g·L−1时,NaCl质量浓度继续增加对有效氯生成和电流效率影响较小。此时,电化学过程与电荷转移过程占主导作用。随着NaCl质量浓度继续增大,离子间距会缩小,离子间相互作用增强,离子运动阻力的增大会降低有效氯的生成速率[7]。综上所述,考虑到NaCl质量浓度超过30 g·L−1时,有效氯质量浓度增加量较少且会增大电解原料成本,将NaCl质量浓度定为30 g·L−1较合适。
2.2 电解时间对有效氯组分生成的影响
在NaCl质量浓度为30 g·L−1、电流密度为250 mA·cm−2的条件下,研究了有效氯的生成随电解时间变化的关系,结果如图3所示。图3 (a) 表明,随着电解时间延长,有效氯质量浓度逐渐增加而最终保持相对稳定,电流效率随电解时间的延长几乎呈线性下降。这是由于单位时间内参与阳极反应的Cl−因电解反应的发生不断消耗使得浓度降低;同时,在非恒温电解实验过程中,电流热效应会持续发生,温度升高会降低Cl2在电解液中的溶解度并促使有效氯组分扩散至阴级发生副反应,从而造成有效氯的分解[11]。图3 (b) 表明,当电解时间小于10 min时,ClO−质量浓度和副产物ClO3−质量浓度逐渐增高;当电解时间大于10 min后,ClO−质量浓度开始缓慢下降,而副产物ClO3−质量浓度持续增长。这是由于随着电解反应的发生,ClO−积累到一定浓度会加剧副反应的发生,ClO−进一步在阳极放电,产生ClO3−。电解过程ClO2−和ClO2的质量浓度始终不高,是由于电解反应主要以生成ClO−为主,生成ClO2−和ClO2的副反应不易发生。综上所述,为获得理想的电流效率 (效率大于60%) 和较高的有效氯质量浓度,电解时间可定为7.5 min。
2.3 NaCl电解氧化吸收液脱硝原理分析
烟气中95%以上的NOx是NO,而NO的溶解度极低[12]。湿法氧化脱硝技术是将烟气中的NO氧化为溶解度高、利于吸收的NO2,再进行下一步吸收反应。已知NO2/NO电对的标准电位为1.049 eV,故所采用的氧化剂电对的电势应大于该值[13]。表1为NaCl电解液中氧化成分、反应式及标准电位。NaCl电解液中氧化成分的电势高于1.049 eV的物质有Cl2、HClO、ClO2和NaClO3。
表 1 NaCl电解液中氧化成分、反应式以及标准电位Table 1. Oxidation components, reaction equations and standard potentials in NaCl electrolyte氧化成分 反应式 标准电位/eV Cl2 Cl2(aq)+2e = 2Cl− 1.358 HClO HClO+H++2e = Cl−+H2O 1.482 NaClO ClO−+H2O+2e= Cl−+2OH− 0.890 NaClO2 ClO2−+2H2O+4e = Cl−+4OH− 0.760 ClO2 ClO2+4H++5e = Cl−+2H2O 1.511 NaClO3 ClO3−+6H++6e = Cl−+3H2O 1.451 由2.2可知,电解反应主产物是ClO−,可推测有效氯溶液与烟气中的NOx发生氧化吸收的反应过程 (图4) [14-15]。NO的氧化吸收过程是从气相到液相的传质过程。由双膜理论可知,NO先由气膜进入液膜,在此过程中部分逸出Cl2可与NO反应结合,而在液膜中NO、NO2与有效氯组分反应,逐步被氧化为NO2−和NO3−,部分未被氧化的NO和NO2将以气态形式重新释放。
2.4 有效氯初始质量浓度对NOx脱除效果的影响
在反应体系温度为20 ℃、pH为9的实验条件下,研究了有效氯初始质量浓度对NOx脱除效果的影响,结果如图5所示。图5 (a) 是不同有效氯质量浓度对NOx脱除效果影响曲线图;图5 (b) 是不同有效氯质量浓度条件下的烟气出口NOx各组分质量浓度曲线图。随着有效氯初始质量浓度的增加,NO的转化率和NOx的去除率都逐渐增加后趋于平缓,烟气出口NOx各组分的质量浓度变化值减小。这是由于NO在液相中的溶解度较低,根据“双膜理论”,NO的氧化与吸收属于液膜控制,即由液相传质阻力控制。当溶液有效氯质量浓度从0增至2.5 g·L−1时,有效氯组分与NO间的传质增强,提高了NO的氧化率。当有效氯质量浓度达到2.5 g·L−1时,电解液氧化能力已满足氧化需求,继续提高质量浓度对NO氧化效果的提升较小[16]。综合考虑NO的转化率、NOx的去除率以及有效氯溶液的经济性,后续实验中有效氯质量浓度定为2.5 g·L−1。
2.5 氧化吸收液pH值对NOx脱除效果的影响
在有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1、反应体系温度为20 ℃的条件下,研究了pH对NOx脱除效果的影响,结果如图6所示。图6 (a) 是有效氯溶液中的主要成分随pH的变化图。因吸收液中有效组分随pH的不同发生改变,使其对应的氧化脱硝能力也发生改变,不同组分的氧化还原电位大小顺序为E(HClO/Cl−) > E(Cl2(aq)/Cl−) > E(ClO−/Cl−)[17-18]。因此,本实验探讨了NOx氧化脱除效果与反应体系pH的关系,结果如图6 (b) 所示。当pH < 4时,溶液的氧化还原电位较高,脱硝反应主要是HClO和Cl2的氧化吸收过程,有较高NO的转化率,但该酸性条件不利于氧化产物NO2的溶解吸收[19]。当4<pH<6时,吸收液中Cl2/HClO摩尔比降低,脱硝反应主要是HClO的氧化吸收过程,此时NO的转化率逐渐下降,氧化产物NO2的溶解度随pH的增加显著提高,总NOx去除率在pH为5时出现峰值。当pH > 7时,氧化吸收液中HClO/ClO−摩尔比逐渐降低,吸收液的氧化还原电位持续降低,NO转化率下降使得NOx的去除率随之下降。因此,综合NO的转化率和NOx的脱除率,并考虑酸性条件下设备腐蚀损耗,吸收液pH为5时脱硝效果最佳。
2.6 氧化吸收液温度对NOx脱除效果的影响
在有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1、反应体系pH为5的条件下,研究了吸收体系温度对NOx脱除效果的影响,结果如图7所示。随着吸收体系温度升高,NO转化率逐渐增加至稳定,而NOx去除率先增大后减少,并在30 ℃时取得峰值78.9%。NaCl电解氧化吸收液去除NO是气液传质反应,温度升高有助于增强液相组分的扩散传质并加快化学反应速率,从而促进NO的氧化[20-21];但温度升高增大了气液传质阻力,使得NO和氧化产物NO2溶解度降低。为获得较高NOx去除率,反应体系的温度控制在30 ℃为最佳。
2.7 最优条件下的平行实验
根据上述探讨的氧化吸收体系因素对烟气脱硝效果产生影响的所得结果,确定了最佳的反应条件:烟气流量为2 L·min−1,NO初始质量浓度为1 340 mg·m−3,吸收液有效氯初始质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1,反应体系pH为5,温度为30 ℃时,NO的转化率为91.1%,NOx去除率为78.9%。在最佳的反应条件下进行平行实验,结果如图8所示。在初始吸收液有效氯质量浓度一定的条件下,NO转化率、NOx去除率随时间的延长缓慢下降,在较长时间内保持较高的脱硝效果,NO的转化率从91.0%下降到80.3%,NOx的去除率从79%下降到60.5%。发生上述现象的原因有:一方面,随着氧化吸收液中有效成分与烟气中NO反应而被消耗,NO的氧化速率受到影响,同时溶液硝酸盐的累计也会影响NOx的吸收速率;另一方面,烟气中存在一定比例的酸性气体NO2,经吸收后会造成反应体系pH缓慢下降,有利于NO的氧化,但不利于氧化产物NO2的吸收,使得总NOx去除率降低加快。
3. 结论
1) 采用无隔膜法电解NaCl制备有效氯溶液,随着NaCl质量浓度和电解时间的增加,有效氯质量浓度逐渐增加,其增量逐渐减少,电解反应的主产物是ClO−,副产物主要是ClO3−。
2) 较高的有效氯NaCl质量浓度有利于NO氧化并促使NOx去除率升高;较低的pH有利于NO氧化,但不利于NOx去除,在弱酸条件下NOx去除效果最好;较高的温度有利于NO氧化,但不利于NOx去除。
3) 在最佳反应条件 (烟气流量为2 L·min−1,NO初始质量浓度为1 340 mg·m−3,吸收液有效氯初始NaCl质量浓度为2.5 g·L−1,反应体系pH为5,温度为30 ℃) 下,NO的转化率可达91.1%,NOx去除率可达78.9%,且能在较长时间内保持较高的烟气脱硝效果。
4) 基于研究结果,后期还应探讨更多的因素 (更加复杂的实际工业烟气、系统内氯气溢出逃逸、反应装置的氧化腐蚀等) 对NaCl电解氧化脱硝系统的影响,以期为其工业化应用提供更加全面的参考。
-
表 1 NaCl电解液中氧化成分、反应式以及标准电位
Table 1. Oxidation components, reaction equations and standard potentials in NaCl electrolyte
氧化成分 反应式 标准电位/eV Cl2 Cl2(aq)+2e = 2Cl− 1.358 HClO HClO+H++2e = Cl−+H2O 1.482 NaClO ClO−+H2O+2e= Cl−+2OH− 0.890 NaClO2 ClO2−+2H2O+4e = Cl−+4OH− 0.760 ClO2 ClO2+4H++5e = Cl−+2H2O 1.511 NaClO3 ClO3−+6H++6e = Cl−+3H2O 1.451 -
[1] 脱硫脱硝行业2015年发展综述[J]. 中国环保产业, 2017 (1): 6-21. [2] PATWARDHAN J A, JOSHI J B. Unified model for NOx absorption in aqueous alkaline and dilute acidic solutions[J]. AICHE Journal, 2003, 49(11): 2728-2748. doi: 10.1002/aic.690491106 [3] LIANG Z, MA X, LIN H, et al. The energy consumption and environmental impacts of SCR technology in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(4): 1120-1129. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.10.010 [4] ZHANG Z, LI J, TIAN J, et al. The effects of Mn-based catalysts on the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature: A review[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 230: 107213. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107213 [5] LI D, XIAO Z, AFTAB T B, et al. Flue gas denitration by wet oxidation absorption methods: current status and development[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2018, 35(11): 1151-1164. doi: 10.1089/ees.2017.0516 [6] GUO R T, HAO J K, PAN W G, et al. Liquid phase oxidation and absorption of NO from flue gas: A review[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2015, 50(2): 310-321. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2014.956761 [7] 国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 含氯消毒剂卫生要求[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018-09-17. [8] 张莲英, 朱琳, 董毅. 影响五步碘量法测定二氧化氯含量的因素探讨[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2005, 15(4): 504-505. [9] 张现兰, 王长德. 五步碘量法测定二氧化氯含量的影响因素研究[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2014, 31(11): 1164-1166. [10] ABDEL-AAL H K, SULTAN S M, HUSSEIN I A. Parametric study for saline water electrolysis: Part II—Chlorine evolution, selectivity and determination[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1993, 18(7): 545-551. doi: 10.1016/0360-3199(93)90172-7 [11] SZPYRKOWICZ L, CHERBANSKI R, KELSALL G H. Hydrodynamic effects on the performance of an electrochemical reactor for destruction of disperse dyes[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005, 44(7): 2058-2068. [12] ADEWUYI Y G, OWUSU S O. Aqueous absorption and oxidation of nitric oxide with oxone for the treatment of tail gases: process feasibility, stoichiometry, reaction pathways, and absorption rate[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 42(17): 4084-4100. [13] 张浩, 党小庆, 于瑞, 等. NaClO3电解液对工业废气中NOx的去除[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(1): 236-244. [14] HAN Z, YANG S, PAN X, et al. New experimental results of NO removal from simulated flue gas by wet scrubbing using NaClO solution[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(3): 3047-3054. [15] GUO R T, GAO X, PAN W G, et al. Absorption of NO into NaClO3·NaOH solutions in a stirred tank reactor[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(11): 3431-3435. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.03.020 [16] 何雷晶, 武斌, 陈葵, 等. Fe3+强化NaClO2溶液脱硝过程研究[J]. 化工环保, 2019, 39(6): 653-659. [17] POURMOHAMMADBAGHER A, JAMSHIDI E, ALE-EBRAHIM H, et al. Simultaneous removal of gaseous pollutants with a novel swirl wet scrubber[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing:Process Intensification, 2011, 50(8): 773-779. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2011.06.001 [18] 周相武, 汪晓军, 刘姣, 等. 次氯酸钠溶液的氧化性研究[J]. 氯碱工业, 2006(8): 28-30. [19] WANG J, ZHONG W. Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification of sintering flue gas via composite absorbent[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 24(8): 1104-1111. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2016.04.005 [20] ADEWUYI Y G, KHAN M A, SAKYI N Y. Kinetics and Modeling of the removal of nitric oxide by aqueous sodium persulfate simultaneously activated by temperature and Fe2+[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(2): 828-839. [21] KHAN N E, ADEWUYI Y G. Absorption and oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) by aqueous solutions of sodium persulfate in a bubble column reactor[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(18): 8749-8760. -





 下载:
下载: