-
多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)是一种广泛使用的溴代阻燃剂. 据统计,截至2020年,全球PBDEs的总产量已达约200万吨[1].PBDEs的大量生产和使用,使其不可避免地被释放至天然环境中[2-4]. 水体是PBDEs污染的主要环境介质之一,全球多数地区的水体,甚至南北极海洋,均有PBDEs检出[5-6]. 作为全球主要的PBDEs生产国 [1],我国也面临着严峻的水体PBDEs污染形势. 目前,我国华东、华北、华南地区的多数湖泊、河流、海洋均受到了不同程度的PBDEs污染,检出浓度为0.007—43.000 ng·L-1[2]. 水中的PBDEs不但可进入水生生物体内,产生神经发育毒性和内分泌干扰效应,还具备较高的生物放大系数(0.06)和生物蓄积潜力,可通过鱼、贝类等水生食物进入人体,增加神经发育障碍、生殖功能受损和遗传变异的风险[7-9]. 因此,PBDEs的监管对保障水环境安全具有重要意义. 发展水体PBDEs的高灵敏检测方法十分必要.
PBDEs在水体中的赋存浓度通常为痕量或超痕量水平,因此在对其进行检测时需要对样品进行富集等前处理. 固相微萃取(SPME)是一种新型、绿色的样品前处理技术[10]. 与液-液萃取、固相萃取等传统方法相比,SPME技术无需大量有机溶剂,灵敏度更高,且集采样、富集、浓缩、解吸于一体,极大地简化了前处理过程[11],已在多种有机污染物的分析检测中显示了优异的应用性能[12].SPME的技术关键是其涂层. 现有的商用涂层多以石英纤维为基底、机械性能较差,涂层材料热稳定性较低,对PBDEs这类高沸点污染物的分析性能不佳. 因此,亟需开发新型、稳定、可高效富集PBDEs的SPME涂层[13].
共价有机骨架(COF)是一类由C、N、O、H、B等有机元素共价整合而成,具有周期性骨架和有序纳米孔结构的结晶多孔聚合物[14]. 自2005年首次被报道以来,COF已在气体存储、催化、传感、吸附等领域广泛应用[15]. 这类材料比表面积大、孔径范围宽、官能团丰富、热稳定性和化学稳定性好,是理想的SPME涂层材料[12].
本研究采用水热法合成了酮胺型COF材料(TpBD),用硅酮胶黏附法在刻蚀的钢丝表面制得SPME涂层,并对其进行了结构表征. 研究了TpBD涂层对PBDEs的萃取性能,探讨了萃取温度、萃取时间、搅拌速度、解吸温度、解吸时间等条件对萃取过程影响. 优化了萃取条件,建立了基于TpBD涂层的PBDEs分析方法,并在实际水体样品中验证了检测方法的适用性.
-
2,4,4′-三溴联苯醚(BDE-28,97.9%)、2,2′,4,4′-四溴联苯醚(BDE-47,100.0%)、2,2′,4,4′,5-五溴联苯醚(BDE-99,99.1%)、2,2′,4,4′,6-五溴联苯醚(BDE-100,100.0%)、2,2’,3,4,4’,5’-六溴联苯醚(BDE-138,97.9%)、2,2’,4,4’,5,5’-六溴联苯醚(BDE-153,98.6%)均购自美国AccuStandard公司,其理化性质如表1所示[16]. 6种PBDEs的混合标准溶液配制于异丙醇(99.8%,美国Tedia)中,于4 ℃避光保存. 联苯胺(98.0%)和1,3,5-三甲苯(98.0%)购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司. 三醛基间苯三酚(97.0%)和1,4-二氧六环(99.5%)购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司. 乙酸(99.5%)购自南京化学试剂有限公司. 中性硅酮胶购自陶氏有机硅有限公司. 甲苯(99.5%)购自上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司.
-
本研究选用不锈钢丝作为自制SPME纤维的涂层基底. 不锈钢丝的预处理过程如下:将直径为0.15 mm、长度为10 cm的不锈钢丝依次浸泡在氢氟酸、甲醇、纯水中超声20 min、晾干,以提高基底表面粗糙度.
-
TpBD的制备方法参考文献[17]. 分别称取63.0 mg三醛基间苯三酚和82.8 mg联苯胺,溶于均三甲苯/1,4-二氧六环的混合溶液(1:1,V:V),边搅拌边滴加1.50 mL乙酸溶液(9.00 mol·L−1). 超声5 min后,将上述混合液转移至高压釜的聚四氟乙烯内衬中,于120 ℃水热反应72 h.反应完成后,过滤、收集暗红色固体,并以丙酮为溶剂对材料进行12 h索氏提取,除去材料孔道中残留的反应物. 最后,将材料于60 ℃真空干燥12 h,即得TpBD粉末.
-
将预处理后的不锈钢丝插入甲苯稀释的硅酮胶溶液、迅速抽出钢丝,重复数次,在钢丝表面形成均匀硅酮胶层. 用滤纸吸去硅酮胶层表面多余溶液后,将钢丝置于TpBD粉末中旋转,再于120 ℃烘箱中干燥20 min,获得涂覆均匀的TpBD涂层. 最后,将涂层长度截至1 cm.
-
采用D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪(XRD,德国Bruker)测定涂层材料的XRD图谱. 利用QUANTA FEG 250场发射环境扫描电子显微镜(SEM,美国FEI)观察涂层的微观形貌. 采用ASAP 2020型比表面积和孔径测定仪(美国Micromeritics)测定涂层材料的孔径分布和孔体积. 通过Pyris1 DSC热分析仪(TGA,美国Perkinelmer)对材料进行热重分析. 利用Nicolet 6700型傅立叶红外光谱仪(FTIR,美国Thermo)测定材料的FTIR光谱.
-
在40.00 mL具有聚四氟乙烯垫片的玻璃样品瓶(美国Supelco)中加入30.00 mL的PBDEs溶液,将SPME涂层插入溶液中进行萃取. 萃取温度和搅拌速度由加热磁力搅拌器(美国Scilogex)控制. 萃取完成后,将涂层置于气相色谱(GC,6890N,美国Agilent)进样口进行热解吸,并利用电子捕获检测器(ECD)测定PBDEs浓度. GC-ECD具体检测条件如下:分离色谱柱为TG-5MS毛细管柱(30 m×0.32 mm×0.25 μm,美国Thermo);载气为1.60 mL·min−1高纯氮(≥99.999%,南京天泽气体有限公司);柱温初始温度为80 ℃,保持1 min,再以20 ℃·min−1升至280 ℃,保持5 min,最后以2 ℃·min−1升至300 ℃,保持2 min;检测器温度为310 ℃[18].
-
图1为TpBD涂层材料的表征结果. 在XRD图谱中(图1a),2θ=3.42°(100)处的强尖峰体现了TpBD的高结晶度;2θ=26.35°(001)处的宽峰来源于TpBD中芳香结构的π-π堆积[19-20]. FTIR图谱(图1b)中也出现了TpBD的特征峰,包括芳香C=C在1573 cm−1和1450 cm−1处的振动峰,以及C—N在1284 cm−1处的振动峰,说明形成了β-酮胺连接的骨架结构[21]. 氮气吸附-脱附等温线测定结果(图1c)显示,所合成材料的BET比表面积达695.56 m2·g−1,孔体积为0.50 cm3·g−1,主要孔径分布在0.54—2.34 nm 之间,与文献报道的TpBD孔结构一致[17]. 以上结果证实TpBD的正确合成.TGA图谱表明(图1d),TpBD材料在30—360 ℃范围内无明显失重(低于10%),说明TpBD具有良好的热稳定性,适用于PBDEs等高沸点污染物的分析.
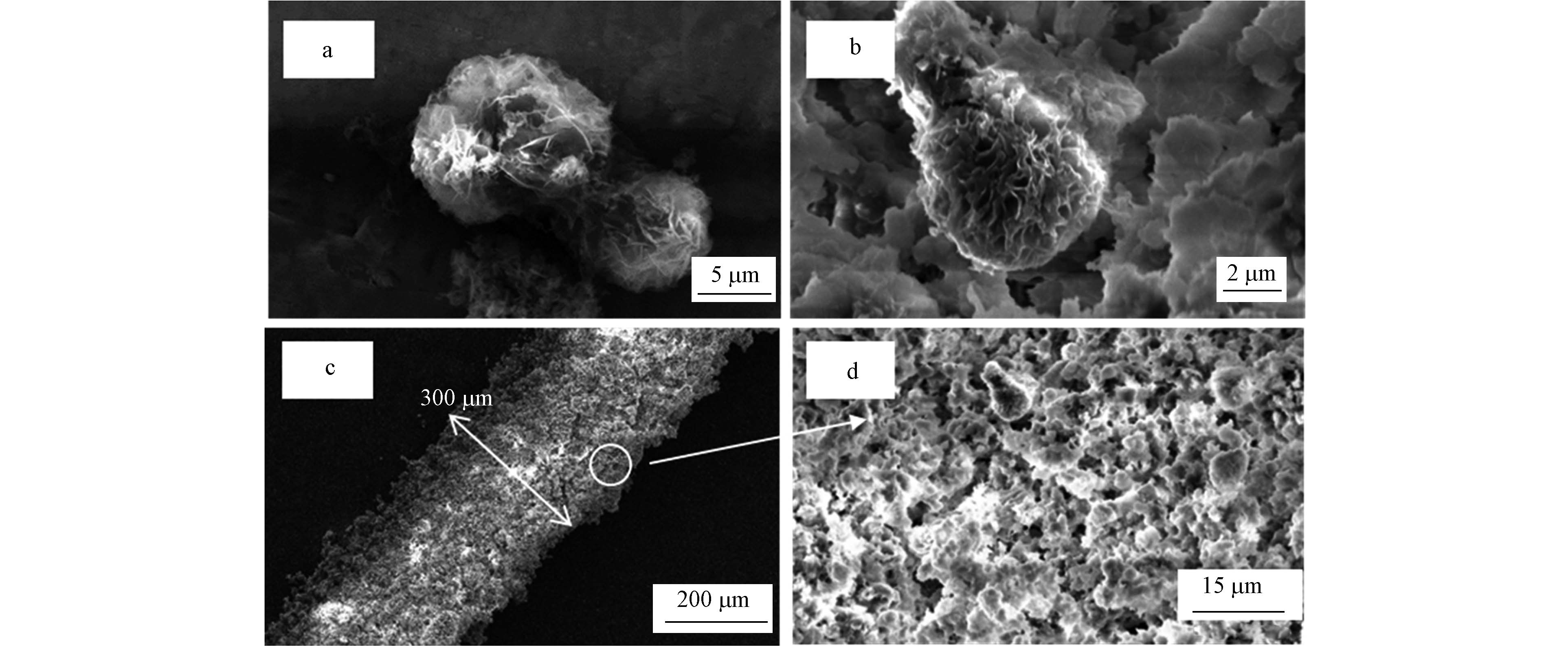
图2为TpBD粉末及涂层的SEM图.TpBD呈球状颗粒(图2a和b),直径在10 μm以内,与文献报道的形貌一致[17].图2c和d显示,在TpBD涂层中,TpBD粉末均匀分布于不锈钢丝基底表面,涂层厚度约为50 μm.
-
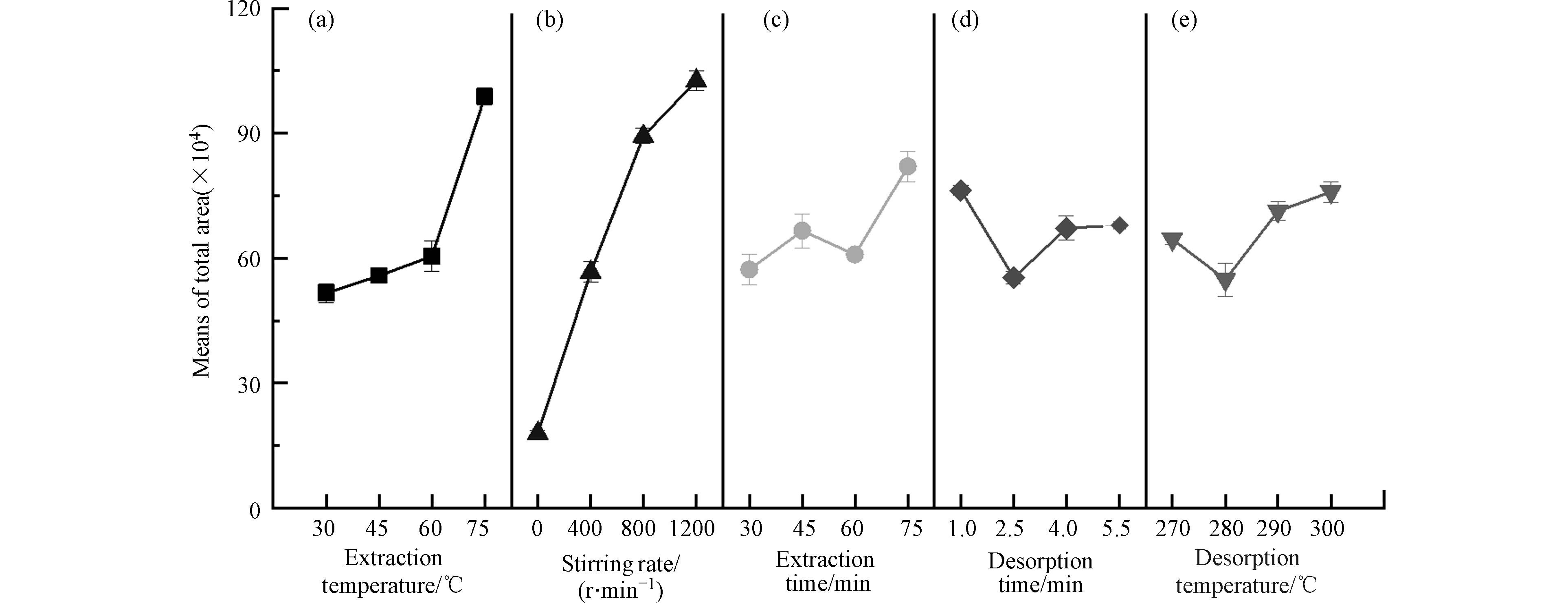
利用正交实验(L16(45)),对TpBD涂层萃取PBDEs的条件进行优化[22]. 其中PBDEs加标浓度为50.00 ng·L−1,所考察萃取条件因素包括萃取温度(30、45、60、75 ℃)、萃取时间(30、45、60、75 min)、搅拌速度(0、400、800、1200 r·min−1)、解吸温度(270、280、290、300 ℃)和解吸时间(1.0、2.5、4.0、5.5 min),以每个因素每个水平下萃取PBDEs的峰面积总和作为正交实验结果的响应值(图3)[23].
表2为正交实验的极差分析和方差分析结果. 可以看出,萃取温度和搅拌速度对TpBD涂层的萃取效率具有显著影响(P<0.05). 萃取温度的升高可以提高PBDEs的扩散速率,进而提高萃取效率. 如图3a所示,当萃取温度由30 ℃升至75 ℃时,TpBD涂层的萃取效率持续提高(图3a),故取75 ℃为最优萃取温度.图3b为搅拌速度对萃取效率的影响. 随着搅拌速度的提高,PBDEs的扩散加快[24],涂层的萃取效率也提高,因此选择1200 r·min−1为最优搅拌速度.图3c—e为其它因素对萃取过程的影响. 综合考虑萃取效率和分析速度,取最优萃取时间为45 min,解吸时间为1.0 min,解吸温度为290 ℃.
-
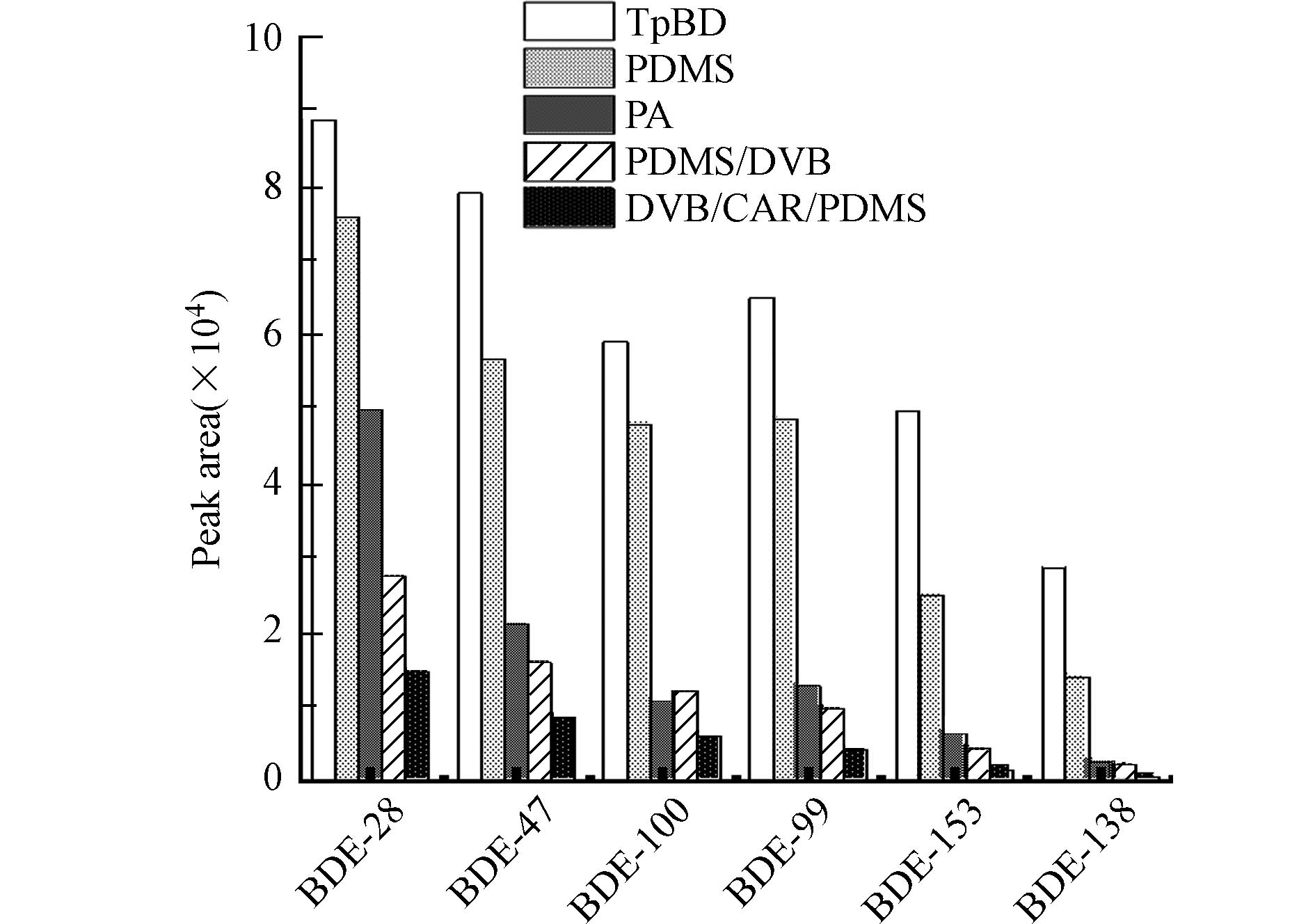
首先考察了TpBD涂层对PBDEs的萃取效率. 如图4所示,TpBD涂层可高效萃取水中的PBDEs,其对所测试6种PBDEs的富集倍数高达1970—3820(表3). 在相同萃取条件下,TpBD涂层的萃取效率是商用100 μm PDMS(聚二甲基硅氧烷)涂层的1.2—2.0倍,85 μm PA(聚丙烯酸酯)涂层的1.8—10.7倍,65 μm PDMS/DVB(聚二甲基硅氧烷/二乙烯基苯)涂层的3.2—11.9倍,50/30 μm DVB/CAR/PDMS(二乙烯基苯/羧基/聚二甲基硅氧烷)涂层的6.0—39.5倍.TpBD涂层的高萃取效率一方面源于其较高的比表面积和较强的表面疏水性,可通过疏水作用吸附PBDEs[25]. 与此相一致,实验发现除BDE-28之外,其余5种PBDEs在TpBD涂层上的富集倍数(表3)随其疏水性(表1)的增强而增大. 另一方面,TpBD富含芳香结构(见XRD和FTIR表征结果),因此能与PBDEs的苯环发生π-π相互作用,进而增强对PBDEs的富集. Li等[21]和Gao等[26]的研究也指出,π-π相互作用是TpBD吸附双酚A、四溴双酚A等芳香性污染物的重要机制. 此外,TpBD具有发达的孔道结构,其中孔径在1.00—1.36 nm之间的孔含量尤为丰富(图1c). 这些孔道的尺寸与PBDEs分子的大小(1.00 nm左右,表1)接近,因而可通过孔填充效应引起的吸附势能叠加,进一步促进TpBD涂层对PBDEs的富集[27-28].
除萃取效率外,稳定性也是SPME涂层的重要性能参数.TpBD在360 ℃时的热失重仅为10%(图1d),表明其具有优秀的热稳定性. 为进一步探究TpBD涂层的化学稳定性,将其依次浸入0.10 mol·L−1盐酸溶液(pH 1)、0.01 mol·L−1氢氧化钠溶液(pH 12)、极性溶剂甲醇和非极性溶剂正己烷中,分别浸渍12 h[29],对比浸渍处理前后涂层对PBDEs的萃取效果. 如图5所示,各项浸渍处理对TpBD涂层的萃取性能均没有显著影响,处理前后涂层萃取效率的相对标准偏差(RSD)为1.0%—14.6%.
图5表明,TpBD涂层在较宽的pH范围内(1—12)具有良好的稳定性,且对极性和非极性有机溶剂均具有较高的耐受性. 此外,重复使用实验显示,TpBD涂层在使用100次之后萃取效率没有明显降低,说明其具有较长的使用寿命.
-
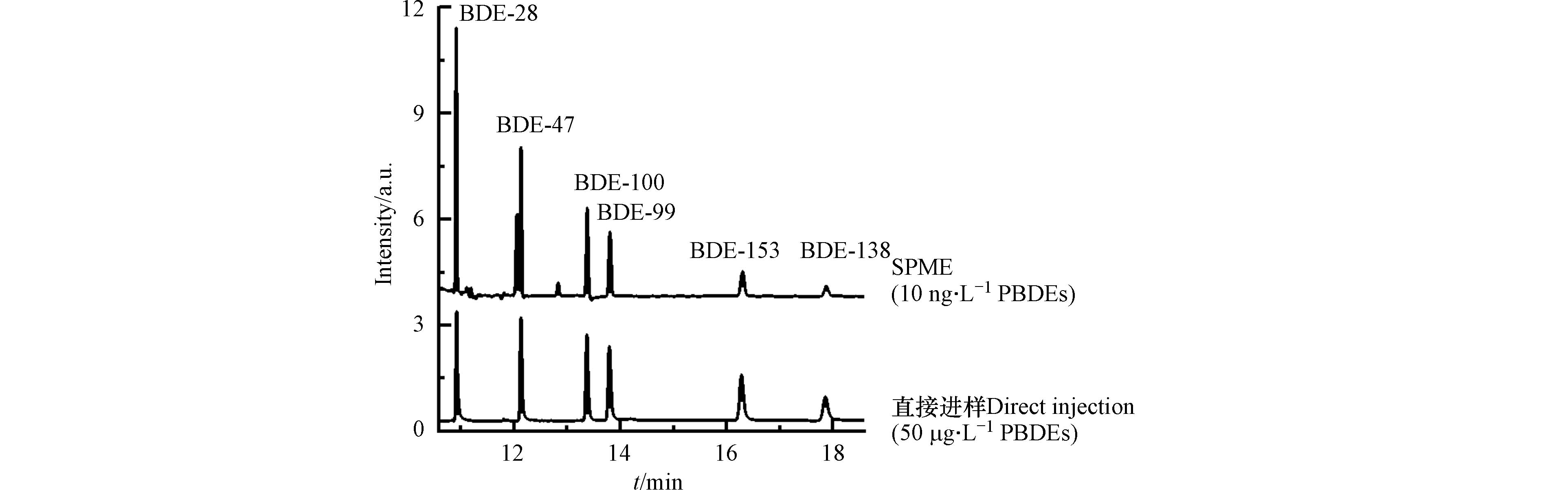
利用TpBD涂层,在优化的萃取条件下建立了所测试6种PBDEs的分析方法. 该方法测定PBDEs标准样品的色谱图如图6所示,方法的线性范围、检出限、精密度、重现性等分析参数列于表3. 结果表明,BDE-28、BDE-47、BDE-100、BDE-99和BDE-153在1.00—50.00 ng·L−1,BDE-138在2.00—50.00 ng·L−1范围内具有良好的线性(R2 > 0.992). 方法对PBDEs的检出限为0.16—0.45 ng·L−1,优于文献报道的其它自制SPME涂层,如石墨烯溶胶-凝胶涂层(0.2—5.3 ng·L−1)[30]、蚀刻的不锈钢丝(0.2—0.6 ng·L−1)[22]和基于四氧化三铁纳米粒子涂层的竹炭纤维(0.25—0.62 ng·L−1)[31]. 此外,该方法还具有良好的重复性,同批次涂层日内多次萃取的RSD为8.2%—14.7%(n=5),日间多次萃取的RSD为8.7%—13.5%(n=3);3批次涂层萃取的RSD为7.2%—13.1%.
为了验证所建立方法的实际应用性,采用该方法分析了某废旧电器拆解污染场地地下水中的PBDEs浓度. 如表4所示,在实际污染水样中检测出了4种PBDEs(BDE-100、BDE-99、BDE-153和BDE-138),浓度范围为0.25—4.26 ng·L−1;其它2种PBDEs的浓度低于本方法检出限. 我们进一步开展了实际水样的加标回收实验(水样3#,加标浓度5.00 ng·L−1),测得回收率为81.1%—106.5%,RSD低于12.5%(n=3). 这些结果表明,基于TpBD涂层的SPME/GC-ECD方法可用于检测实际环境水样中的PBDEs.
-
本研究通过水热法合成TpBD型COF,以不锈钢丝为基底,利用物理黏附法制得基于TpBD材料的SPME涂层,并将其应用于萃取和检测水体中的PBDEs. 研究结果显示,TpBD涂层具有优越的PBDEs萃取性能,其萃取效率是商用涂层的1.2—39.5倍. 这是因为TpBD具有较高的比表面积和表面疏水性,还可与PBDEs产生π-π作用和孔填充作用,能高效富集水体中的PBDEs. 此外,TpBD涂层还具有良好的热稳定性和化学稳定性,使用寿命较长. 基于该涂层的PBDEs检测方法线性范围较宽、检出限低、精密度和重现性好,在实际环境水样的分析中具有良好的应用潜能.
基于酮胺型共价有机骨架固相微萃取的水体多溴联苯醚检测
β-Ketoenamine-linked covalent organic framework coated solid-phase microextraction fiber for the determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water
-
摘要: 采用水热法合成了酮胺型共价有机骨架材料(TpBD),硅酮胶黏附法制得固相微萃取纤维涂层,探究了该涂层对水中多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)的萃取性能. 利用正交实验优化了TpBD涂层的萃取条件,结合气相色谱技术建立了基于该涂层的水体PBDEs定量分析方法. 研究结果显示,TpBD涂层不但具有良好的热稳定性和化学稳定性,还可高效富集水中的PBDEs,在相同萃取条件下,TpBD涂层对PBDEs的萃取效率是商用涂层的1.2—39.5倍. 基于TpBD涂层的PBDEs检测方法线性范围较宽(2.00—50.00 ng·L−1)、灵敏度高(检出限为0.16—0.45 ng·L−1)、精密度和重现性好(同批次涂层测定结果的日内相对标准偏差(RSD) <14.7%,日间RSD <13.5%;3批次涂层测定结果的RSD <13.1%),在实际环境水样的分析中表现出良好的适用性(加标回收率为81.1%—106.5%).Abstract: In this study, a β-ketoenamine-linked covalent organic framework (TpBD) coating was applied for the solid-phase microextraction (SPME) of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in water. The TpBD was prepared by the hydrothermal method and was coated on a stainless steel wire by physical adhesion using silicone glue. The PBDE analysis method was established by coupling the TpBD coated fiber with gas chromatography. The extraction conditions were optimized using the orthogonal experiment. The TpBD coating not only had good thermal and chemical stabilities, but also afforded high extraction efficiency for PBDEs (1.2—39.5 times higher than commercial coatings). The method based on TpBD coated fiber for PBDE determination exhibited relatively wide linear ranges (2.00—50.00 ng·L−1), high sensitivity (detection limits of 0.16—0.45 ng·L−1), high precision (intra-day relative standard deviations (RSD) < 14.7% and inter-day RSD < 13.5%), good reproducibility (RSD < 13.1%), and good recoveries (81.1%—106.5%) in real water samples.
-
《2017中国环境状况公报》显示,以地下水含水系统为单元,以浅层地下水和中深层地下水为对象,监测结果中主要超标物质为“三氮”(亚硝酸盐氮、氨氮和硝酸盐氮),且污染情况较重[1]。氮素作为生物生长的必需元素,是造成缓流水体富营养化的原因之一[2-3]。未经处理或处理不达标的含氮废水排放到水体中,会带来一系列的危害:湖泊、水库等缓流水体的富营养化,河流发黑发臭,水生生物大量死亡;硝态氮在人体肠道中可以被还原成亚硝态氮,对生物体有致癌、致变和致畸的作用[4],严重威胁人体健康。
从废水中除去氮有多种方法,目前利用生物进行脱氮的技术被公认为是最经济有效的脱氮方法[5],但温度会影响污水脱氮的效果。微生物正常生长的最佳水温为20~35 ℃,当≤15 ℃时(即属于低温),反硝化细菌的增殖代谢速率将降低,致使反硝化速率也降低[6]。在我国,由于一些生产工艺流程条件、区域性气候或是季节性等原因,无法避免在低温下排放污水[7]。如东北地区,冰冻期长达6个月,这样会使得污水生物脱氮过程在较长低温时段内效率变差,影响污水的处理达标。
目前,为了保证我国秋冬季污水中氮的排放达标,寒冷地区低温污水的处理一般采用改良传统工艺[8]、投加药剂[9]、降低污泥负荷、培养硝化细菌[10]或者将构筑物建于室内等措施。还有许多国内外学者对具有醌型结构的氧化还原介体的催化作用进行研究[9, 11-13]。氧化还原介体,也可称为电子穿梭体,具有可逆地被氧化和还原的功能,能够使反应速率成倍增加来加速反应的进行[9]。ARANDA-TAMAURA等[11]研究了二磺酸基蒽醌(AQDS)和1, 2-萘醌-4-磺酸(NQS)同步去除S和N的情况,并得出了NQS对N和S去除效果明显的结论。在低温10 ℃条件下,投加介体NQS时的脱氮效率与不投加介体的空白组对比,提高了1.5倍。赵丽君等[12]研究证明,投加蒽醌-2-磺酸钠(AQS)介体的反硝化过程能够促进亚硝酸盐转化为N2O。李海波等[13]在35 ℃条件下,投加蒽醌-2, 6-二磺酸钠(AQDS)、蒽醌-2-磺酸钠(AQS)、蒽醌-1-磺酸结构(α-AQS)和蒽醌-1, 5-二磺酸钠(1, 5-AQDS) 4种介体,当浓度均为240 μmol·L−1时,可提高硝态氮降解效率1.14~1.63倍。虽然氧化还原介体强化生物脱氮的研究较多,但对于氧化还原介体调控低温反硝化过程的相关研究还比较少。
课题组前期研究表明,在低温条件下投加氧化还原介体,有利于生物的反硝化脱氮[14],且最佳碳源为丙酸钠,但脱氮效果最好时投加丙酸钠的最佳剂量还尚未明确[15]。本研究投加课题组前期筛选出的浓度为100 μmol·L−1的氧化还原介体1, 2-萘醌-4-磺酸钠(NQS)[16],考察低温条件下碳源浓度(碳氮比)不同时对污水生物反硝化脱氮过程的影响,并利用生物化学手段(分析氧化还原电位的改变及微生物的测定)初步探讨低温引入介体强化污水生物反硝化脱氮过程的影响机制,以期提高实际污水处理的脱氮效率,为寒冷地区冬季低温条件下氮的生物去除提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
采用规格相同的序批式反应器。反应器内径为170 mm,高为360 mm,容积为7.6 L。内部装有数显电动搅拌器,反应时进行搅拌使污泥处于悬浮状态。实验装置如图1所示。
1.2 运行条件及实验用水
接种污泥为天津市某污水处理厂活性污泥,进行培养驯化,使其运行稳定。初始污泥的特性指标均按照实验室标准方法进行测定,pH为7~8,VSS/SS为0.4~0.5,MLSS为3 500~3 600 mg·L−1,SVI为80~90 mL·g−1。
对活性污泥进行驯化,通过污泥的颜色、形状、气味和测试指标来判断污泥驯化的成效。驯化15 d后,污泥臭味变淡,体积变大,硝酸盐氮、总氮、SCOD的去除率达到15%。驯化25 d后,基本没有臭味,开始成絮状,硝酸盐氮、总氮、SCOD的去除率提高到40%。驯化45 d后,污泥没有臭味,颜色变成土黄色,成颗粒状,硝酸盐氮、总氮、SCOD的去除率提高到70%。驯化60 d后,污泥中带点腥味,颜色变成棕色,污泥成颗粒状,硝酸盐氮、总氮的去除率达到95%,亚硝酸盐氮的生成率达到95%,SCOD的去除率也达到85%以上。通过观察,硝酸盐的去除率可连续1周大于95%,且SCOD的去除率可连续1周大于85%。这说明污泥有了很好的反硝化效果,反硝化细菌已经成为优势菌群,标志着污泥驯化成功。
将驯化好的活性污泥置于连续搅拌反应器(CSTR)中,并做空白对照实验。反应器由冷却水循环器(上海施都凯仪器设备有限公司生产,型号为IL-008-02)控制水温为10 ℃。反应器用黑色保温材料进行包裹,以保障实验运行的恒温条件。反应器的工作周期包括排水(15 min)、闲置(60 min)、进水(15 min)、反应(420 min)和沉淀(270 min)5个工序。在实验过程中,采用分开配水的方式,进水用计量泵调节控制,反应时间用计时器来控制。采用多次均匀投加的方式,每周期向非空白对照反应器投加1, 2-萘醌-4-磺酸(NQS)介体(浓度为100 μmol·L−1)。进水为人工配制的硝酸盐废水,浓度为70~90 mg·L−1,硝酸钾作为氮源,丙酸钠作为碳源。硝酸盐废水的成分及质量分数见表1。
表 1 实验用污泥基本参数Table 1. Basic parameters of experimental sewage sludgepH VSS/SS MLSS/(mg·L−1) SVI/(mL·g−1) 7~8 0.4~0.5 3 500~3 600 80~90 在其他指标不变的条件下,改变碳源浓度(碳氮比)并与空白反应作对照进行实验。其中碳源浓度已换算成COD。碳源浓度250 mg·L−1和400 mg·L−1分别代表我国典型的生活污水水质中COD的最低浓度和中等浓度。定时从反应器的出水口进行取样,测硝酸盐氮、亚硝酸盐氮、总氮和SCOD等指标,直至反应周期结束。分别选取6个碳源浓度梯度(碳氮比),各反应器中碳源浓度(碳氮比)具体情况见表2。
表 2 实验用水成分Table 2. Compositions of experimental wastewater名称 质量分数/% 名称 质量分数/% C3H5O2Na 16.230 3 ZnSO4 0.015 7 KNO3 44.785 9 MnSO4 0.036 2 KH2PO4 16.230 3 Na2MoO4·2H2O 0.008 0 MgSO4 12.172 7 CuSO4·5H2O 0.009 1 CaCl2·5H2O 10.143 9 CoCl2·6H2O 0.008 8 FeSO4 0.304 3 EDTA 0.054 8 1.3 分析方法
表 3 碳源浓度(碳氮比)Table 3. Carbon source concentration (carbon-nitrogen ratio)NQS介体投加量/(μmol·L−1) 碳源浓度/(mg·L−1) 碳氮比(C/N) 0 250 2.9 100 150 1.8 100 250 2.9 100 325 3.8 0 475 5.6 100 400 4.7 100 475 5.6 100 550 6.5 1.4 DNA提取和PCR扩增
实验中DNA提取采用土壤DNA试剂盒(Omega Bio-tek,Norcross,GA,U.S.)。在试样中加入干污泥和SLX Mlus缓冲溶液,放置于旋涡混合器裂解样品。之后加入缓冲液和HTR试剂,将其离心、培养,进行多次重复,使DNA完全洗脱。采用细菌16S rRNA通用引物515F(GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGG)和907R(CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTTPCR)对提取的DNA样品进行PCR扩增。采用TransGen AP221-02: TransStart Fastpfu DNA Polymerase,20 μL反应体系。用2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测PCR产物,本研究的生物群落DNA片段长度集中在500 bp左右。
1.5 MiSeq测序数据统计分析及多样性分析
通过Miseq测序得到双端序列数据,经处理后的优化数据统计及长度分布表明,DNA片段长度均在395~396 bp之间。通过对序列进行归类操作,可得到样本测序结果中的菌种、菌属等信息。依据相似度水平,对归类操作后的全部序列进行OTU划分。通常,相似水平在97%的OUT须进行生物信息统计分析。采用单样品多样性分析(Alpha多样性)方法,获取微生物群落丰度和多样性的相关信息。采用对序列进行随机抽样的方法,以抽到的序列数与它们所能代表OTU的数目构建稀疏曲线,曲线斜率较小,表明测序数据量合理,继续测序,只会产生较少量新的OUT。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 生物反硝化的脱氮效率
在碳氮比(C/N)不同的条件下,各反应器的脱氮效率见表4。由表4可知,当C/N为2.9时,投加介体的反应器与空白对照相比提高了1.5倍,总氮的去除率提高了近2.4倍;当C/N为5.6时,投加介体的反应器与空白对照相比,硝酸盐氮的去除率提高了1.2倍,而总氮的去除率变化不是很明显。由此可知,在相同C/N条件下,投加介体可以改善低温污水生物反硝化脱氮的效果,并且在低C/N条件下,介体的强化作用更明显。当C/N为4.7时,硝酸盐氮的去除率均可以达到63%以上,且随着C/N的大幅变化,去除率的变化不是很明显。亚硝酸盐氮的量先增加后减少,说明在生物反硝化脱氮过程中出现亚硝酸盐氮的积累,然后亚硝酸盐氮不断地转化为N2或N2O。在C/N为1.8和2.9的反应将近结束时,亚硝酸盐氮的量最后呈上升趋势,这对脱氮效果是不利的,说明C/N较低时不利于亚硝酸盐氮的转化。随着反应时间的进行,反应系统中总氮的浓度也逐渐降低。投加相同的介体,当C/N为4.7时,总氮的去除率达到最大。由表4可知,当C/N为1.8~3.8时,总氮的去除率与C/N的大小呈正相关;当C/N为4.7~6.5时,总氮的去除率与C/N的大小无相关性,且介体是否存在也对总氮的去除没有较大意义。
表 4 常规分析项目及检测方法Table 4. Routine analysis items and testing methods编号 分析项目 分析方法 所用仪器与设备 1 MLSS 重量法 烘箱和电子天平 2 MLVSS 重量法 烘箱、马弗炉和电子天平 3 NO3−-N 紫外分光光度法 T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计 4 NO2−-N N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺光度法 T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计 5 TN 过硫酸钾氧化 紫外分光光度法 T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计 6 ORP 铂电极测定 WTW, Multi-340i, 在线监测 7 SCOD 重铬酸钾法 — 综上所述,生物反硝化脱氮系统中C/N为4.7~5.6时,NQS介体强化低温污水生物反硝化脱氮效果最好。
2.2 生物反硝化脱氮速率
随着反应的进行,脱氮速率的变化如图2所示。图2显示了在低温10 ℃条件下,不同C/N对介体强化生物反硝化脱氮速率的影响。当C/N为2.9时,投加介体的反应器与空白对照相比,NOx-N脱氮速率从2.7 mg·(g·h)−1(以VSS计)提高到17.1 mg·(g·h)−1,提高了将近6.3倍;当C/N为5.6时,投加介体的反应器与空白对照相比,脱氮速率从11.0 mg·(g·h)−1提高到33.4 mg·(g·h)−1,提高了3.0倍。可见,在C/N相同的情况下,投加介体可以显著提高脱氮速率,且C/N越低,提高效果越明显,这与脱氮效率得出的结果一致。
图2表明,与不投加介体的空白对照相比,反应刚开始投加介体的反应器的脱氮速率最高,分别达到了3.6、17.1、27.1、30.1、33.4和51.6 mg·(g·h)−1。当C/N为5.6和6.5时,分别是C/N为4.7脱氮速率的1.1倍和1.7倍。可见,在介体浓度相同的情况下,C/N的大小显著影响脱氮速率,且脱氮速率随着C/N的升高而增大。相关研究表明,由于微生物的自身生长也需要碳源,实际C/N在4.0以上时才可能实现高效脱氮[18]。结合硝酸盐氮的浓度,当C/N为4.7时,可达到较好的脱氮效果。
2.3 生物反硝化SCOD的去除
在不同C/N的条件下,反应器中SCOD的去除率随时间的变化见表5。反应器开始进水的SCOD都稳定在投加值,随着反应的进行,SCOD的去除率在逐渐升高,说明实验期间反硝化脱氮系统运行稳定,对有机质的降解能力良好并且污泥有很好的活性。可以看出,当C/N相同时,投加介体可以提高SCOD去除率的1.1倍和1.2倍。当C/N不同时,投加介体的反应器反应结束时,SCOD最大去除率分别达到了78.4%、87.5%、87.2%、93.0%、87.2%和94.9%。
表 5 不同C/N各反应器脱氮效率Table 5. Nitrogen removal efficiencies under different carbon-nitrogen ratiosC/N NQS介体投加量/(μmol·L−1) 硝酸盐氮最大去除率/% 亚硝酸盐氮最大积累率/% 总氮最大去除率/% 2.9 0 22.2 19.7 13.0 1.8 100 11.7 10.9 17.4 2.9 100 33.7 24.0 30.8 3.8 100 54.0 23.8 53.6 5.6 0 53.2 10.0 64.4 4.7 100 64.3 10.7 64.7 5.6 100 63.0 19.4 64.4 6.5 100 65.5 13.3 64.2 投加氧化还原介体后,C/N的不同可以使系统中的活性污泥受到不同程度的影响,但效果不明显。从表5中可以看出,当C/N较高时,SCOD的去除率均较高,且无一定相关性。
2.4 探讨投加介体污水生物反硝化脱氮反应的机理
2.4.1 1) C/N不同的条件下介体强化低温污水生物反硝化ORP的变化。
1) C/N不同的条件下介体强化低温污水生物反硝化ORP的变化。在投加介体后,改变C/N的大小,反应器中氧化还原电位ORP的变化情况见表7。当C/N为4.7时,投加介体的反应系统相对空白而言,生物反硝化过程中氧化还原电位降低43 mV。廉静等[19]研究表明,当C/N为6时,投加介体可使生物反硝化过程中的ORP降低45 mV左右,同时可显著加快亚硝酸盐的生物降解过程。通过表6可以看出,随着反应时间的延长,氧化还原电位逐渐降低;当反应将近结束时,氧化还原电位出现小幅度升高的现象。反应结束时,反应器中的ORP最低值分别达到了−132、−136、−155、−201、−195、−214、−238和-259 mV,随着C/N的增大,ORP值上升幅度更小。
表 7 不同C/N对ORP的影响Table 7. Effect of different carbon-nitrogen ratio on ORP反应时间/min ORP/mV C/N=2.9(空白) C/N=1.8 C/N=2.9 C/N=3.8 C/N=5.6(空白) C/N=4.7 C/N=5.6 C/N=6.5 0.5 40 5 −28 −53 −57 −67 −84 −117 5 −31 −54 −81 −96 −65 −72 −109 −149 10 −65 −70 −99 −123 −80 −81 −120 −157 30 −78 −89 −121 −142 −104 −102 −135 −169 120 −132 −136 −155 −164 −133 −144 −165 −234 360 −75 −101 −155 −172 −195 −214 −233 −259 660 −75 −100 −146 −201 −190 −206 −238 −250 表 6 不同C/N各反应器SCOD去除率的变化Table 6. Change of SCOD removal rate under different carbon-nitrogen ratio反应时间/min 去除率/% C/N=2.9(空白) C/N=1.8 C/N=2.9 C/N=3.8 C/N=5.6(空白) C/N=4.7 C/N=5.6 C/N=6.5 0.5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 11.8 13.7 22.7 30.8 35.6 43.4 44.0 39.2 10 22.5 31.4 37.5 41.9 54.8 64.6 64.2 59.5 30 42.7 45.1 75.0 81.2 60.3 69.9 66.5 78.5 120 66.3 73.5 82.4 84.6 69.4 77.9 72.0 81.0 360 68.5 72.5 86.4 85.5 73.5 81.4 77.1 87.3 660 89.9 78.4 87.5 87.2 75.8 92.9 87.2 94.9 2.4.2 2) 介体强化低温污水生物反硝化微生物群落分析。
2) 介体强化低温污水生物反硝化微生物群落分析。取3个活性污泥样品并分别编号。L0代表初始污泥样品,取自未经驯化的天津市某污水厂的剩余污泥;L1、L2为取自低温10 ℃、经一段时间驯化的活性污泥,其中L1为未投加介体,L2为投加NQS介体。在不同分类水平上,通过统计学分析方法,可以检测出样本群落结构。本研究以门和属的水平进行分类,结果见图3。由图3可知,样品的优势菌门包括Proteobacteria(变形菌门)、Bacteroidetes(拟杆菌门)、Chlorobi(绿杆菌门)、Chloroflexi(绿弯菌门)、Planctomycetes(浮霉菌门)、Acidobacteria(酸杆菌门)、Candidate divisionc WS3。与初始污泥相比,培养后出现2个新的优势菌门,分别是Bacteria unclasscfied(未分类细菌门)和Fusobacteria(梭杆菌门)。样品中微生物群落组成情况见表7。
表 8 样品中微生物群落组成Table 8. Composition of microbial community in samples %微生物名称 原污泥L0 低温未加介体L1 低温加介体L2 黄单胞菌目(Xanthomonadales norank) 3 9 10 厌氧绳菌科(Anaerolineaceae uncultured) 2 9 11 丛毛单胞菌科(Comamonadaceae unclassified) 3 8 6 红环菌科(Rhodocyclaceae uncultured) 1 7 6 腐螺旋菌科(Saprospiraceae uncultured) 4 1 3 索氏菌属(Thauera) 1 3 4 屈挠杆菌属(Flexibacter) 5 6 5 副球菌属(Paracoccus) 1 0 0 假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas) 0 1 1 硫杆菌属(Thiobacillus) 1 0 0 其他(Others) 79 56 54 在自然界中,最普遍的反硝化细菌包括Pseudomonaceae(假单胞菌属)、Alcaligenes(产碱杆菌属)、Nitro bacteraceae(硝化细菌科)、Rhodospirillaceae(红螺菌科)、Bacillaceae(芽孢杆菌科)、Spirillaceae(螺菌科)等。
在低温条件下通过测序分析群落组成情况发现,接种污泥中没有优势菌属;未投加介体的污泥中优势菌属为黄单胞菌目、厌氧绳菌科和丛毛单胞菌科;投加介体的活性污泥优势菌属为厌氧绳菌科和黄单胞菌目。在经过驯化的活性污泥中,红环菌科和索氏菌属增长速率明显。红环菌科在低温下增长5~7倍,索氏菌属在低温下也可增长3~5倍。红环菌科和索氏菌属相似,都具有很好的反硝化功能,这说明经过驯化的活性污泥具有良好的脱氮优势。在低温条件下,投加氧化还原介体有利于索氏菌属的生长。
3. 结论
1)在低温(10 ℃)条件下,投加介体NQS,当C/N为1.8~3.8时,介体强化脱氮效率随C/N的升高而升高;当C/N为4.7~6.5时,介体强化脱氮效率随C/N的升高而降低。
2)当C/N为1.8~6.5时,介体强化脱氮速率随着C/N的升高而升高;但在低C/N条件时,介体的强化作用更明显。综合考虑脱氮效果并结合经济因素分析,当C/N为4.7左右时,脱氮效果最佳。
3)介体的投加改变了氧化还原电位的大小,在投加介体的反应系统中,氧化还原电位始终低于空白反应,这有利于反硝化脱氮反应的进行。随着脱氮效率的增加,体系ORP不断下降,推测介体可能通过加速ORP的降低来加快脱氮过程。
4)经过培养驯化的活性污泥具有良好的脱氮优势。在低温条件下,投加氧化还原介体有利于索氏菌属的生长。
-
表 1 PBDEs的理化性质
Table 1. Physico-chemical properties of PBDEs.
同类物Congeners 分子式Molecular formula lg KOW a 蒸气压/(Pa, 25 ℃)Vapor pressure 水溶解度/(mg·L−1, 25 ℃)Aqueous solubility 分子直径/nm bMolecular diameter BDE-28 C12H7Br3O 5.94 2.19×10−3 0.070 0.989 BDE-47 C12H6Br4O 6.55 2.50×10−4 0.002 0.998 BDE-100 C12H5Br5O 6.86 2.86×10−5 0.040 1.078 BDE-99 C12H5Br5O 7.13 6.82×10−5 0.009 0.995 BDE-153 C12H4Br6O 7.62 5.80×10−6 0.001 1.078 BDE-138 C12H4Br6O 7.91 1.58×10−6 0.001 0.995 注:a正辛醇-水分配系数;b由GaussView 5.0计算. a n-octanol-water partition coefficient; b calculated by GaussView 5.0. 表 2 正交实验的极差分析和方差分析结果
Table 2. Results of range analysis and analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the orthogonal experiments.
条件Conditions 方差分析 Analysis of variance (ANOVA) 极距(×105)Polar distance 方差和(×1011)Sum of variance 组间自由度Degree of freedom between groups 组内自由度Degree of freedom within the group F P 萃取温度/℃ 4.722 5.656 3 44 4.011 0.013* 萃取时间/min 2.479 6.812 3 44 0.842 0.478 搅拌速度/(r·min−1) 8.462 2.541 3 44 26.911 0.000* 解吸温度/℃ 2.110 6.928 3 44 0.582 0.630 解吸时间/min 2.096 6.960 3 44 0.513 0.676 注:* P<0.05. 表 3 基于TpBD涂层的SPME-GC/ECD方法对PBDEs的分析性能
Table 3. Analytical performance of the SPME-GC/ECD method based on TpBD coated fiber
同类物Congeners 线性范围/(ng·L−1)Linear range 相关系数Regressioncoefficient 检出限(S/N=3)/(ng·L−1) LOD 定量限(S/N=10)/(ng·L−1) LOQ 日内萃取重复性(n=5)/% Intra-day repeatability 日间萃取重复性(n=3)/% Inter-day repeatability 制备重复性(n=3)/% Fiber-to-fiber reproducibility 富集倍数Enhancement factor BDE-28 1.00—50.00 0.999 0.16 0.52 14.7 8.7 8.0 2990 BDE-47 1.00—50.00 0.998 0.20 0.66 14.1 11.3 7.6 2750 BDE-100 1.00—50.00 0.992 0.30 1.00 13.4 12.0 7.2 1970 BDE-99 1.00—50.00 0.996 0.24 0.80 8.2 9.1 9.7 2560 BDE-153 1.00—50.00 0.995 0.40 1.34 10.3 12.9 6.3 2790 BDE-138 2.00—50.00 0.994 0.45 1.50 13.9 13.5 13.1 3820 表 4 基于TpBD涂层的SPME-GC/ECD方法对实际水样中PBDEs的分析结果
Table 4. Analytical results for the determination of PBDEs in real water samples
同类物Congeners 1#水样 2#水样 3#水样 4#水样 5#水样 6#水样 加标回收率(n=3)/%Recoveries BDE-28 NDa ND ND ND ND ND 97.6 ± 8.1 BDE-47 ND ND ND ND ND ND 90.8 ± 9.8 BDE-100 0.93 0.32 ND ND ND ND 106.5 ± 11.8 BDE-99 2.45 0.71 0.38 0.25 ND 0.31 96.3 ± 10.6 BDE-153 2.20 0.64 ND ND ND ND 83.7 ± 12.2 BDE-138 4.26 1.05 0.54 ND ND ND 81.1 ± 12.5 注:a 未检出. a not detected. -
[1] ABBASI G, LI L, BREIVIK K. Global historical stocks and emissions of PBDEs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(11): 6330-6340. [2] JIANG Y F, YUAN L M, LIN Q H, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and human external and internal exposure in China: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 696: 133902. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133902 [3] WU Z N, HAN W, YANG X, et al. The occurrence of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) contamination in soil, water/sediment, and air [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(23): 23219-23241. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05768-w [4] XU J, QIAN W Y, LI J Y, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in soil and dust from plastic production and surrounding areas in eastern of China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2019, 41(5): 2315-2327. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00247-0 [5] AZNAR-ALEMANY Ò, SALA B, PLÖN S, et al. Halogenated and organophosphorus flame retardants in cetaceans from the southwestern Indian Ocean [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 226: 791-799. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.165 [6] SUN H Z, LI Y M, HAO Y F, et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their hydroxylated and methoxylated analogues in polar marine food webs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(23): 15086-15096. [7] PALIYA S, MANDPE A, BOMBAYWALA S, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment: A wake-up call for concerted action in India [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(33): 44693-44715. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15204-7 [8] DORMAN D C, CHIU W, HALES B F, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) neurotoxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal evidence [J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, 2018, 21(4): 269-289. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2018.1514829 [9] POSTON R G, SAHA R N. Epigenetic effects of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on human health [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(15): 2703. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16152703 [10] ARTHUR C L, PAWLISZYN J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1990, 62(19): 2145-2148. doi: 10.1021/ac00218a019 [11] 宋荣娜, 杨晓芳, 吕明晗, 等. HS-SPME-GC/MS同时测定污废水中多种VOCs异味物质 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1047-1056. SONG R N, YANG X F, LYU M H, et al. Simultaneous determination of various odorous VOC substances in sewage wastewater by HS-SPME-GC/MS [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1047-1056(in Chinese).
[12] PENG S, HUANG X Y, HUANG Y Y, et al. Novel solid-phase microextraction fiber coatings: A review [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2022, 45(1): 282-304. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202100634 [13] ŚMIEŁOWSKA M, ZABIEGAŁA B. Current trends in analytical strategies for determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in samples with different matrix compositions - Part 1. : Screening of new developments in sample preparation [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 132: 115255. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.09.019 [14] CÔTÉ A P, BENIN A I, OCKWIG N W, et al. Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks [J]. Science, 2005, 310(5751): 1166-1170. doi: 10.1126/science.1120411 [15] DIERCKS C S, YAGHI O M. The atom, the molecule, and the covalent organic framework [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): eaal1585. doi: 10.1126/science.aal1585 [16] U. S. EPA. An Exposure Assessment of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE) (Final Report) [EB/OL]. [2010-05-24]. [17] GAO W, TIAN Y, LIU H, et al. Ultrasensitive determination of tetrabromobisphenol A by covalent organic framework based solid phase microextraction coupled with constant flow desorption ionization mass spectrometry [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(1): 772-775. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04884 [18] JIA F, GAN J. Comparing black carbon types in sequestering polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 184: 131-137. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.009 [19] KARAK S, KANDAMBETH S, BISWAL B P, et al. Constructing ultraporous covalent organic frameworks in seconds via an organic terracotta process [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(5): 1856-1862. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08815 [20] LIU J M, HAO J L, YUAN X Y, et al. Spherical covalent organic frameworks as advanced adsorbents for preconcentration and separation of phenolic endocrine disruptors, followed by high performance liquid chromatography [J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(47): 26880-26887. doi: 10.1039/C8RA04321C [21] LI Y, YANG C X, YAN X P. Controllable preparation of core-shell magnetic covalent-organic framework nanospheres for efficient adsorption and removal of bisphenols in aqueous solution [J]. Chemical Communications , 2017, 53(16): 2511-2514. doi: 10.1039/C6CC10188G [22] CHEN X F, CHENG C G, WANG X, et al. Sensitive determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in environmental water samples with etched stainless steel wire based on solid-phase microextraction prior to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Analytical Methods, 2012, 4(9): 2908-2913. doi: 10.1039/c2ay25483b [23] WANG Y H, LI Y Q, FENG J F, et al. Polyaniline-based fiber for headspace solid-phase microextraction of substituted benzenes determination in aqueous samples [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2008, 619(2): 202-208. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.003 [24] 蒋慧, 李健生, 胡兴茹, 等. 基于有序介孔碳涂层的固相微萃取法测定水中多环芳烃 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(6): 1288-1294. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016090902 JIANG H, LI J S, HU X R, et al. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water using solidphase microextraction with ordered mesoporous carbon coating [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(6): 1288-1294(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016090902
[25] CHEN W, DUAN L, ZHU D Q. Adsorption of polar and nonpolar organic chemicals to carbon nanotubes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(24): 8295-8300. [26] GAO W, LI G L, LIU H, et al. Covalent organic frameworks with tunable pore sizes enhanced solid-phase microextraction direct ionization mass spectrometry for ultrasensitive and rapid analysis of tetrabromobisphenol A derivatives [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 764: 144388. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144388 [27] JI L L, LIU F L, XU Z Y, et al. Adsorption of pharmaceutical antibiotics on template-synthesized ordered micro- and mesoporous carbons [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(8): 3116-3122. [28] FU H Y, ZHU D Q. In situ hydrothermal grown silicalite-1 coating for solid-phase microextraction [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(5): 2366-2372. doi: 10.1021/ac203119k [29] WEI F X, HE Y H, QU X L, et al. In situ fabricated porous carbon coating derived from metal-organic frameworks for highly selective solid-phase microextraction [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1078: 70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.061 [30] ZHANG H, LEE H K. Plunger-in-needle solid-phase microextraction with graphene-based Sol-gel coating as sorbent for determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(28): 4509-4516. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.05.016 [31] 校瑞, 徐林芳, 张晓娜, 等. 环境样品中多溴联苯醚分析方法的研究进展 [J]. 化学研究, 2015, 26(4): 343-350. doi: 10.14002/j.hxya.2015.04.002 XIAO R, XU L F, ZHANG X N, et al. Advances of analytical methods for the determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in environmental samples [J]. Chemical Research, 2015, 26(4): 343-350(in Chinese). doi: 10.14002/j.hxya.2015.04.002
-





 下载:
下载: