-
重金属由于其毒性大、难降解、生物累积性并可对人类和海洋生物产生危害而广受关注[1]. 重金属不仅改变海洋生物的遗传物质,破坏海洋生物物种多样性和海洋生态平衡而且可通过食物链进入人体造成严重损害[2-3]. 与重金属对人类与海洋的危害相对的是日益严峻的海洋污染,研究表明我国东部海域均存在着不同程度的重金属污染. 如泉州湾和莱州湾重金属Hg和Cd超标,局部海域Hg和Cd污染[4-6]. 渤海湾存在着Cd中度污染风险,近海工业活动和陆源污染排放是污染的主要来源[7]. 胶州湾重金属Pb和Cr显著富集[8],三沙湾重金属Cu轻微超标[9],兴化湾存在Cd污染[10]. 鉴于严峻的海洋重金属污染状况,掌握近海重金属污染来源及其污染空间分布规律对海洋生态环境治理修复显得尤为重要.
目前重金属污染来源研究以定性的源识别和定量的源解析为主. 定性的源识别方法主要是主成分分析法和聚类分析等多元统计方法[11]. 主成分分析是通过把重金属元素降维并选取最主要的特征值划分为各主成分,操作简便但是会掩盖各种元素隐含的信息[12-13]. 聚类分析是根据事物之间的相似性来进行分类,相似程度越高的事物将会被划分为一类,但是不能处理大量数据且存在数据与实际情况相悖的情况[14]. 随着重金属污染研究的深入,主成分分析法和聚类分析的源识别方法因存在未能明确污染来源的贡献率,大型数据处理受到限制等缺陷而不适应发展的需要. 正定矩阵因子分析模型(PMF)是一种可在非负约束的条件下考虑数据的不确定性,对未知污染源进行定量分析的受体模型[11, 15-17]. 基于上述优点,近年来正定矩阵因子分析模型被广泛应用到环境污染的解析[18-21].
定海-黄岐湾地处闽北经济发展圈的重要北翼,同时也是海岸两峡沟通贸易的必经之地. 区域内水产养殖业发展突出,不仅是我国重要的海带鲍鱼生产基地还是福建省水产品第一大供应地[22]. 密集的人类活动必然会对定海-黄岐湾沿海地区生态环境造成影响,复杂的海域环境更是给海洋生态环境保护带来严重的挑战. 基于上述情况,掌握定海-黄岐湾重金属污染状况并采取相应治理措施对海洋环境保护是至关重要的,然而定海-黄岐湾重金属污染研究还处于起步阶段,现有研究主要集中在定海-黄岐湾的污染生态风险评估[23],缺乏对重金属污染来源定量解析. 因而本文利用地统计方法和内梅罗指数法来厘清定海-黄岐湾重金属(V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb)的污染特征及含量空间分布规律,并结合正定矩阵因子分析法对定海-黄岐湾沉积物重金属的来源进行定量解析,从而促进海洋生态环境治理修复工作的开展.
-
定海-黄岐湾位于北纬26°17′—26°22′,东经119°47′—119°57′,隶属福州市连江县,黄岐半岛将定海湾和黄岐湾隔开,以南为定海湾以北为黄岐湾. 区内为亚热带季风气候,气候温暖湿润雨量充沛,土壤以贫瘠酸性的华南红壤为主,主要发展丁香鱼、海带、鲍鱼和海参等水产养殖及船舶运输产业.
-
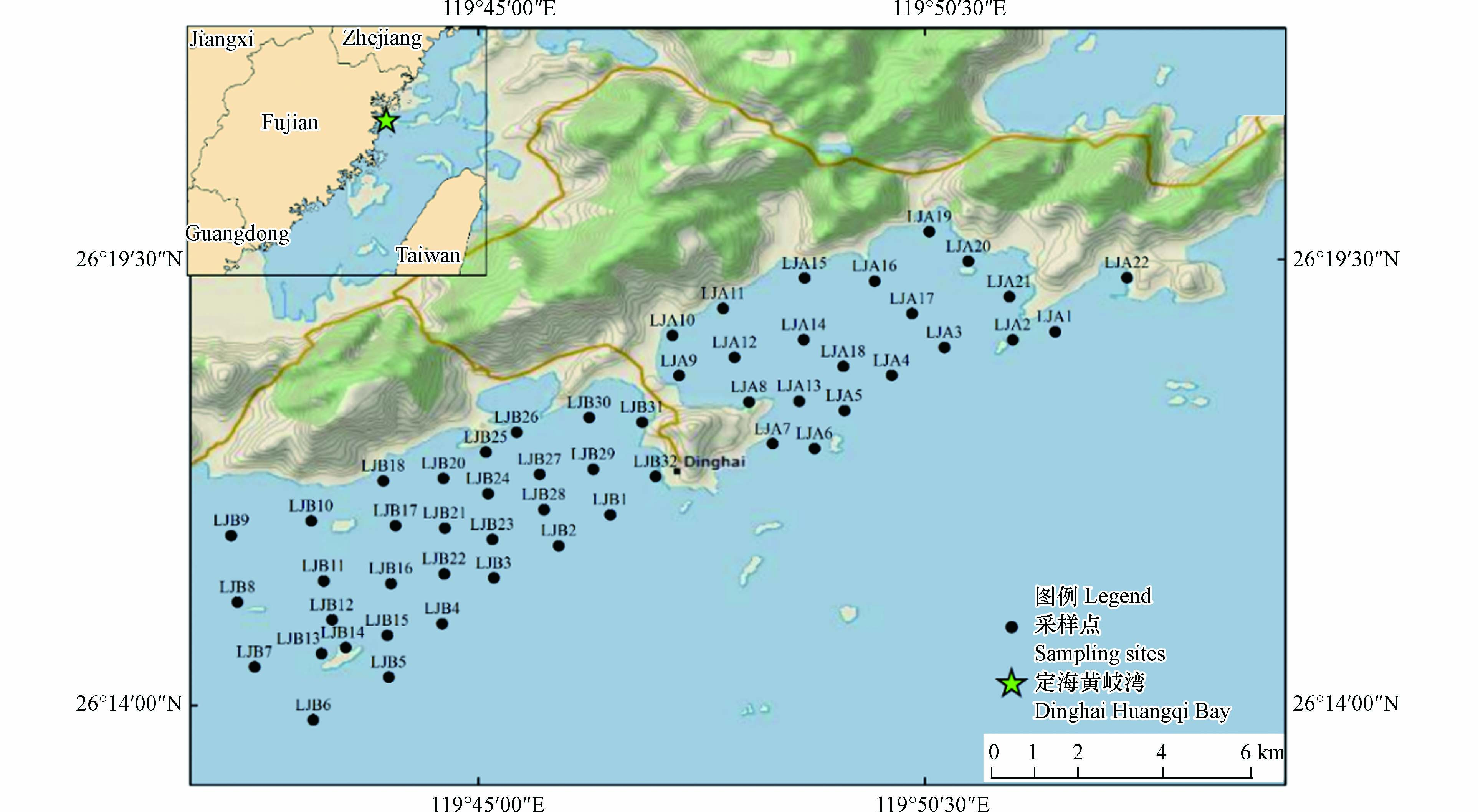
在定海-黄岐湾以约1—4 km2的网格面积尽量均匀设置采样点,在人类活动频繁的区域增加采样点的密度,共采取53个样品(见图1,LJA和LJB为连江定海-黄岐湾采样点,其中LJA为黄岐湾的采样点,LJB为定海湾的采样点). 采用抓斗式底泥采样器采集表层底泥,样品采集后使用聚丙烯样品袋,充分混合后装袋带回实验室进行处理,样品在实验室进行自然风干后,去除牡蛎贝壳等杂质后进行实验处理.
-
称取0.04 g风干样品于PTFE内胆中,加入1.5 mL HF、0.5 mLHNO3,将内胆密封,置于防腐高效溶样罐套内,于烘箱中150 ℃加热15 h. 冷却后取出内胆开盖,加入0.25 mL HClO4于150 ℃电热板上蒸至近干. 利用移液枪将2 mL超纯水和1 mLHNO3加入到罐子中密封,将内胆置于防腐高效溶样罐内,于150 ℃烘箱中回溶15 h. 冷却后取出内胆,将溶液转移到40 mL PTE瓶中,用高纯水稀释至大约40 mL摇匀待测. 采用美国 Thermo Fisher公司的X-SerieⅡ型电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS )进行重金属元素测定,样品平行测试 RSD<5%,同时测定国家标准土壤参比物质(GSS-1、GSS-3),实验过程中采用平行样进行质量监控,误差范围控制在 10%以内. 以上实验均在福建师范大学湿润亚热带山地生态教育部重点实验室完成. V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的方法检出限分别为0.26、2.05、0.09、3.57、0.96、45.49、0.08、0.67 mg·kg−1.
-
运用内梅罗指数对采集到的样品进行重金属污染研究,进而探究定海-黄岐湾生态状况. 采用SPSS21软件和Excel 2019来进行数据统计分析,重金属空间分布图由Arcgis10.7完成.
内梅罗指数法是一种兼顾极值或突出最大值的计权型多因子环境质量指数,多用于环境污染检测[24]. 其公式如下:
其中,Ci为底泥i的重金属实测值、Si为土壤背景值、 Pi在式1中为单项污染指数,在式2中为重金属i的单项污染指数平均值、 PiMax是重金属i的最大单项污染指数、P综合为重金属i的内梅罗综合污染指数. 内梅罗综合污染指数的等级划分见表1.
-
正定矩阵因子分析法(PMF)是由芬兰科学家Paatero和Tapper在因子分析法(FA)的基础上发展的可对未知污染源进行源解析的受体模型[18]. PMF模型最初应用于大气污染的源解析中,近年来被国内学者广泛应用于土壤以及沉积物[11, 18-21]. 鄱阳湖、杏林湾近郊流域以及黄河流域的沉积物源解析中表明正定矩阵因子分析法与传统源解析方法具有一致的结果且更能解析出各污染源的贡献率[21, 25-26]. 大量研究表明正定矩阵因子分析法适用于我国土壤及沉积物的重金属污染来源解析中,因而本文采取美国环保署发布的PMF5.0对定海-黄岐湾的重金属进行来源分析,PMF模型是将样品数据分解为污染源的贡献率矩阵以及污染源成分谱矩阵并运用最小二乘法迭代进行运算. 贡献率矩阵与成分谱矩阵经过不断优化可得到目标函数Q的最优化从而达到最优效果[18, 24].
在PMF中,样品浓度矩阵用X表示,污染源贡献因子矩阵用G表示,污染源因子含量矩阵用F表示,残差矩阵用e表示.
a 为定海 - 黄岐湾采集的沉积物样本数量;c为样品测试重金属类别;b为污染源数量,计算公式如下[19-20]. 式中,uij即第i个样品中第j个元素浓度的不确定性,δ为标准偏差,
C 为重金属元素实测含量,MDL为方法检出限[27],不确定性计算公式如下. -
在对定海-黄岐湾重金属进行描述性统计时发现(表2),定海-黄岐湾中V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb元素的重金属平均含量分别为86.55、61.50、13.50、30.42、30.60、116.58、0.11、39.94 mg kg−1,8种重金属元素平均含量均超出福建省近岸浅海沉积物背景值[23]. V和Pb的平均含量为背景值的1.34倍和1.30倍,Cu、Cd的平均含量分别为背景值的2.15倍和1.76倍.
变异系数是能够反映总体样本中各采样点平均变异程度,CV<15%表示弱变化,15%≤CV≤36%表示中等变化;CV>36%表示高变化[20]. 若变异大于50%,表明环境中重金属含量空间分布不均匀,局部存在点源污染[30]. 定海-黄岐湾中V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb元素的变异系数分别为34%、42%、33%、42%、91%、43%、79%和35%[23]. 其中V、Co和Pb为中等变异,Ni、Cr、Zn的变异系数相似,分别为42%、42%和43%,均已超过36%为高度变异. 同时Cu和Cd的变异系数更是高达91%和79%. 上述表明定海-黄岐湾中Cu和Cd的含量空间分布不均匀,受外界的影响大,存在着明显的点源污染.
由定海-黄岐湾表层沉积物重金属含量空间分布可知(图2),V、Cr、Co、Ni元素含量的低值区均出现在东北部和西部,重金属含量高值区出现在中部,且内部差异变化较小. Cu整体含量较低,只在黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22)和海湾内定海村码头(LJB31、LJB32)出现明显高值区. Cd的分布与其他元素存在比较明显的差异,其高值区主要出现在湾内中部偏南的大面积空阔海域,及定海村码头(LJB32)和黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22)处. Pb低值区出现在西部和湾内中部偏东大部分海域,海湾内中部偏西较高,而东北部高塘港(LJA22)和中部沿海定海村码头(LJB32)表现为明显高值. Zn含量的低值区分布在西北部以及北部的零散区域,高值区分布在中部沿岸的定海村码头(LJB32),筱埕村码头(LJB31)及东北部沿岸的高塘港(LJA21)、黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22)附近,及个别有渔船停泊(LJA8)和片状鱼排养殖区附近(LJA6)的样点,说明Zn可能与航运养殖等人为活动的排污有关.
-
通过内梅罗指数法对沉积物重金属进行污染评价结果如下所示(表3). 对定海-黄岐湾沉积物进行内梅罗指数评价可知(表3). 重金属V最小单项污染指数为0.23,最大单项污染指数为1.53,出现在海湾中部海域(LJA14). 重金属Cr最小单项污染指数为0.08,最大单项污染指数为2.58,出现在黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22). 重金属Co最小单项污染指数为0.30,最大单项污染指数为2.52出现在海湾中部海域(LJA13). 重金属Ni的最大污染指数为3.36出现在海湾中部海域(LJA14),最小单项污染指数为0.20. 重金属Cu元素的最大单项污染指数为9.68并出现在黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22),最小污染指数为0.11. 重金属元素Zn单项污染指数最大值为4.89并出现在黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22),最小值为0.49. 重金属元素Cd单项污染指数最大值13.27出现在黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22),最小值为0.18. 重金属元素Pb单项污染指数最大值为3.24出现在黄岐镇码头避风港(LJA22),最小值为0.1. 综上所述定海-黄岐湾重金属污染形势严峻,其中重金属元素Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的最大单项污染指数均出现在黄岐镇避风港码头内,说明黄岐镇避风码头可能存在重金属混合污染,Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb可能存在点源污染.
由定海-黄岐湾沉积物重金属内梅罗污染指数可知,元素V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的平均单项污染指数分别为1.11、1.49、1.82、2.25、1.42、1.41、2.13、1.14,平均单项污染指数从高到低依次为Ni>Cd>Co>Cr>Cu>Zn>Pb>V. 单项污染指数能反映某一个站点的污染状况,其数值大于1即表明存在污染. 在定海-黄岐湾共采集的54个样品中,重金属V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的单项污染指数大于1的,分别占72%、80%、83%、85%、74%、83.3%、90%、78%. 元素V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的综合污染指数分别为1.34、2.11、2.20、2.86、6.92、3.60、4.90、2.25,其中8种元素的综合污染指数均大于1,表明定海-黄岐湾存在着不同程度的重金属污染. 而其中Cu的综合污染指数更是高达6.92,而最小的V也明显大于1. 结合表3可知定海-黄岐湾中重金属V为轻度污染;Cr、Co、Ni、Pb均为中度污染;而Cu、Zn、Cd为重污染. 综上所述内梅罗指数分析表明定海-黄岐湾重金属污染严重. 8种重金属元素污染状况从高到低分别为Cd>Cu>Zn>Ni>Pb>Co>Cr>V,其中Cd、Cu和Zn为定海-黄岐湾的最主要污染源.
-
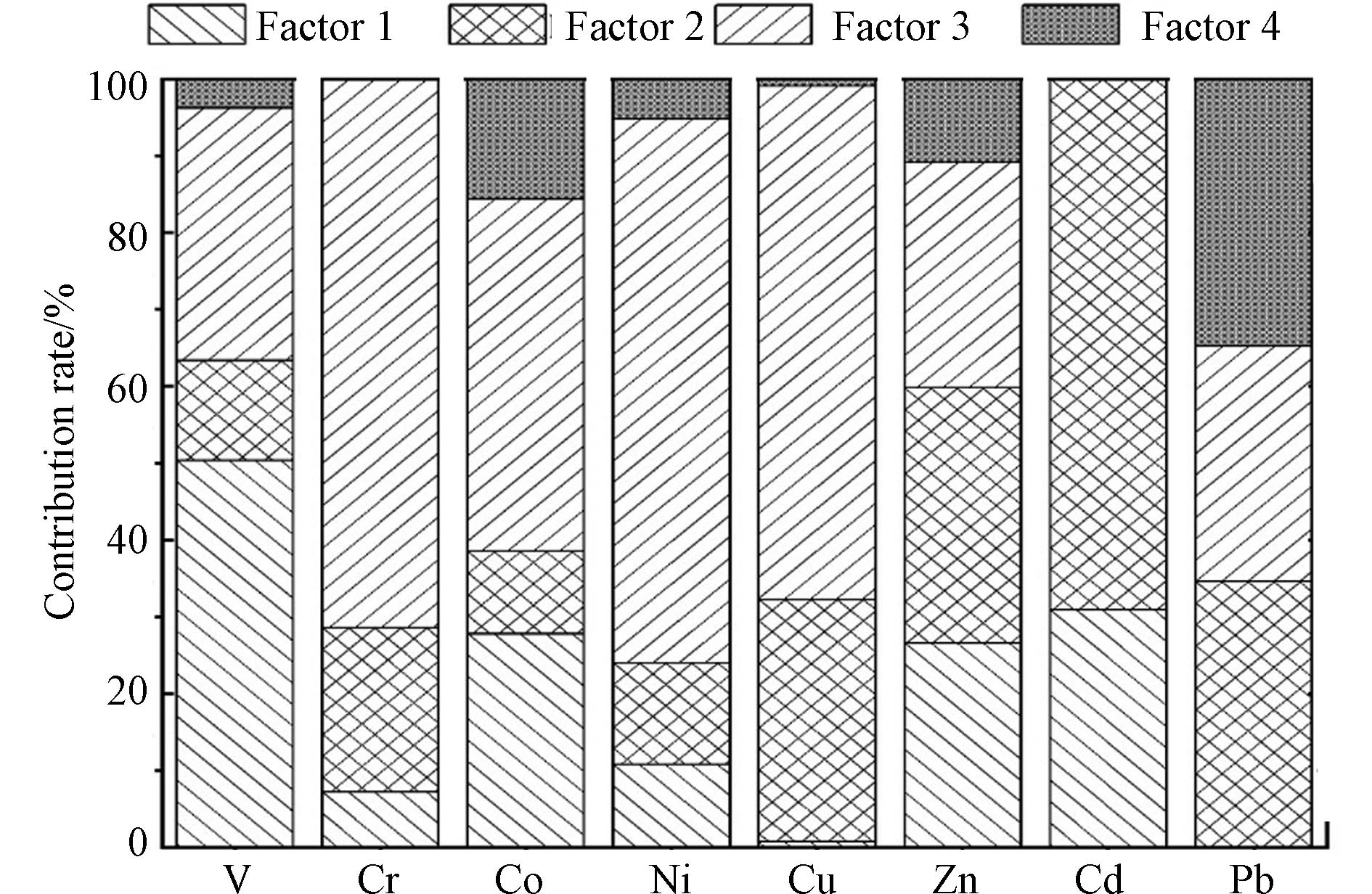
本文采取美国环保署发布的PMF5.0对定海-黄岐湾的重金属进行来源分析. 由于正定矩阵因子分析模型是对未知污染源进行源解析,为避免误差需要对因子数进行多次测试选择合适的因子数,实现Q值最小化才可达到最优结果. 本文选择了1—7个因子数进行调试,采用Robust模式,经过多次运算操作最终选择4个因子. 元素V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的相关系数r2均大于0.8,表明PMF拟合结果好,最终运算结果见图3.
由表4可以发现, V对因子1的贡献率为50.4%,为因子1的主导元素. 有研究显示沉积物中的V主要来自于成土母质或岩石风化侵蚀而成的自然源[26, 31]. 结合定海-黄岐湾中V较低的内梅罗指数和变异系数,表明V受人为因素影响较少,可能来自于区域岩石如石英、高岭土和长石风化侵蚀的自然来源. 因而因子1代表区域岩石风化的自然源.
Zn和Cd对4个因子均有相应的贡献率,但是对因子2的贡献率明显高于其余因子(33.1%, 69.1%),故Zn和Cd为因子2的主导元素. Zn和Cd为高度分异,表明Zn和Cd的空间分布不均匀,可能来自人为源. 在Zn和Cd空间分布图中(图2)发现两者均在东北部高塘港(LJA22)和中部沿岸的定海村码头(LJB32),筱埕村码头(LJB31)表现出异常高值,说明Zn和Cd元素存在着明显的点源污染,Zn和Cd的内梅罗指数分别为3.6和4.9也印证这一点. 定海村码头、筱埕村码头和高塘港避风港是人类活动密集区,人类生产生活活动频繁. 在高塘避风港中观察到多条排污管道,人们生活污水主要是通过排泄管道排入海洋中[4]. 这致使富含Zn和Cd等重金属元素的生活污水通过排污管道直接进入海洋中,导致局部地区Zn和Cd异常. 与此同时在海水的顶托下,Zn和Cd元素容易在浅海区域沉降积累造成区域Zn和Cd污染. 由此可知Zn和Cd元素可能来自于生活污水,经过排泄管道以及河流汇入海洋中. 总而言之,因子2代表生活排污源.
因子3中,Cr、Co、Ni、Cu为主导元素,其贡献率分别为71.4%、45.8%、70.7%和66.7%. 由Cr、Co、Ni、Cu的空间分布图可知,Cr、Co、Ni元素在个别区域和样点处没有出现明显高值分布的相对均匀,主要分布在研究区的中南部,结合Cr、Co、Ni的中等到高变异系数,表明Cr、Co、Ni污染面积较广;Cu在东北部高塘港(LJA22)和海湾内黄岐镇避风港码头(LJB31、LJB32)表现出异常高值,且变异系数为高度变异表明Cu受外在点源干扰影响. Ni、Co、Cr主要被用来制造不锈钢和其他抗蚀合金,是冶炼工业标识元素[32]. 现代渔船主要采用不锈钢等结构并在船体涂上耐蚀的金属涂层. 在海湾中部的定海村、筱埕村码头和黄岐镇码头避风港内船只往来频繁,往来的船只与当地渔民的渔船就近停泊在码头,繁忙的交通活动致使该区域容易发生船只碰撞摩擦,从而导致船体表面金属材料及涂层的剥落,其中便包括防污涂料识别元素的Cu和Cr. 因而重金属Ni、Co、Cr和Cu来自于船只表面金属涂层剥落.
因子4中,重金属Pb的贡献率最高(34.8%)为主导元素. 有研究表明Pb主要来源于工矿业活动及交通排放[11, 25]. Pb在黄岐湾东北部高塘港(LJA22)和海湾内黄岐镇避风港码头(LJB32)表现为明显高值,为中等变异程度,表明Pb空间分布不均匀. 结合黄岐镇高塘港的瀚海船业码头为交通部所属的“国际船舶航行临时停靠点”,大型船只在此停泊交通活动频繁. 船只在停泊运行过程中会泄露富含Pb的油料,并不断富集累积[33],表明Pb主要来自于船只海上交通泄露的油料. 由上所述可知,因子4主要为交通排放源.
进一步根据每种重金属的因子指纹计算每种来源的总体贡献百分比可以发现,定海-黄岐湾自然源、生活排污源、工业污染源和交通排放源的相对贡献率分别为19.3%、28.3%、43.4%和8.9%,其中贡献率最高的为工业污染源表明定海-黄岐湾重金属污染主要受工业污染影响.
-
(1)闽东定海-黄岐湾表层沉积物中重金属V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb元素的平均含量均超出福建省近岸浅海沉积物背景值,表明定海-黄岐湾潜在重金属污染.
(2)重金属V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb的含量空间分布均表现出差异性,但是八种重金属的高值区均出现在中部人类活动密集区且呈现出明显的一致性,表明重金属空间分布受人类活动影响较大.
(3)根据内梅罗指数法可知V为轻度污染;Cr、Co、Ni、Pb均为中度污染;而Cu、Zn、Cd为重污染. 正定矩阵因子分析模型获取了4个来源,8种重金属元素污染受多种因素影响而定海-黄岐湾中V主要来自区域岩石风化侵蚀的自然源;重金属Zn和Cd元素主要来自于生活排污源;Ni、Cr、Co和Cu主要来自于工业污染源;重金属Pb主要来自于交通排放源. 4种污染源的相对贡献率最高的为工业污染源表明人类工农业活动对定海-黄岐湾重金属污染具有突出影响,后续环境污染修复中对此应有所侧重.
致谢:感谢范逸飞在文章撰写过程中提供的帮助.
闽东定海-黄岐湾表层沉积物重金属污染特征及来源解析
Characteristics and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of Huangqi Bay, Dinghai, eastern Fujian
-
摘要: 定量解析沉积物重金属来源并绘制空间分布图可为海洋生态环境治理修复提供科学依据. 本文以定海-黄岐湾为研究区,分析其表层沉积物的重金属含量,通过内梅罗指数和地统计法探究其重金属空间分布规律,并基于正定矩阵因子分析模型(PMF)定量描述其重金属元素的污染来源. 研究结果表明定海-黄岐湾表层沉积物的V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb均值分别为86.55、61.50、13.50、30.42、30.60、116.58、0.11、39.94 mg·kg−1均超出福建省近岸浅海沉积物的背景值1倍以上;地统计和内梅罗指数表明V、Cr、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb含量的空间分布和污染特征具有差异性. 其中,V为轻度污染,Cr、Co、Ni、Pb均为中度污染而Cu、Zn、Cd为重污染,但是其高值区和污染严重区域均出现在人类活动密集区,呈现受人类活动影响的共性特征;PMF分析则阐释沉积物中的V来自于区域岩石风化的自然源,Zn和Cd元素来自于生活污水的排放,Ni、Cr、Co和Cu来自于船只表面金属涂层剥落,Pb来自于船只海上交通泄露的油料. 自然源、生活排污源、工业污染源以及交通污染源对定海-黄岐湾沉积物重金属的污染贡献率分别为19.3%、28.3%、43.4%、8.9%,贡献率最高的为船只金属涂层脱落的工业污染源.
-
关键词:
- 重金属 /
- 来源分析 /
- 正定矩阵因子分析模型 /
- 闽东
Abstract: Quantitative analysis of heavy metal sources in sediments and the creation of spatial distribution maps can provide a scientific basis for the treatment and restoration of the marine ecological environment. This paper examines the heavy metal content of surface sediments in Dinghai-Huangqi Bay, investigates the spatial distribution of heavy metals using the Nemero index and geostatistics, and quantitatively describes heavy metal pollution sources using a positive definite matrix factor analysis model (PMF). The results show that the average values of V, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in Dinghai-Huangqi Bay surface sediments are 86.55, 61.50, 13.50, 30.42, 30.60, 116.58, 0.11, 39.94 mg·kg−1, respectively, which are higher than the background values of coastal shallow sea sediments in Fujian Province. The Geostatistics and Nemero index show that the spatial distribution and pollution characteristics of V, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb contents are different. Of them, V is slightly polluted, Cr, Co, Ni, Pb are moderately polluted, while Cu, Zn, Cd are heavily polluted. However, both high-value areas and heavily polluted areas appear in human activity-intensive areas, demonstrating the common characteristics affected by human activities. PMF analysis showed that V in the sediment comes from the natural source of regional rock weathering, Zn and Cd elements come from domestic sewage discharge, Ni, Cr, Co, and Cu elements come from the peeling of metal coating on the surface of the ship, and Pb elements come from the oil leaked from the marine traffic. The natural sources, domestic sewage, industrial, and traffic pollution contributed 19.3%, 28.3%, 43.4%, and 8.9%, respectively, to heavy metals in Dinghai-Huangqi Bay sediments. The ship metal coating flaking off was the industrial pollution source with the highest contribution rate. -
长江流域是中国第一大流域,覆盖19个省级行政单位,以21%的国土面积承载了全国的40%的人口和经济总量[1-2]。长江流域的中下游人口密度、经济发展程度在改革开放以来均位居我国前列,随之而来的环境压力也不容忽视。随着经济高速发展,排放到长江的污染物总量和强度都在逐年上升,排放到长江的污水量同样占到全国污水总量的40%[1]。长江及其支流监控断面主要水质因子为高锰酸盐指数 (CODMn) 、氨氮 (NH3-N) 等耗氧物质[3]。根据《中国生态环境统计年报》,2008年长江流域接纳的COD和NH3-N负荷分别占到全国的40.2%和40.9%;到2020年,COD和NH3-N负荷仍然分别占据全国的37.3%和42.8%,长江流域的污染排放强度长期以来达到全国平均水平的1.5~2倍[1]。高强度污染物排放,造成长江流域水体耗氧物质的浓度升高[4],溶解氧 (dissolved oxygen, DO) 下降。
DO是地表水监控的基本指标,对于维持水生生态系统正常功能具有重要意义[5]。空气中的氧气溶解和水生植物的光合作用是补充水中DO的主要途径。大气溶氧主要受到气压、温度、水体盐度的影响,此外流量增加也有利于DO恢复[6]。人口密度高、工业发达区域排放的大量有机物质和氮磷含量高的污水进入受纳水体后,一方面会带来营养物质不断积累,引起浮游植物和藻类吸收NH3-N大量生长繁殖[7],造成水体底部造成缺氧,水体富营养化愈演愈烈[8];另一方面,NH3-N和有机物等耗氧物质进入水体后,NH3-N的硝化过程,有机物的降解过程会消耗大量溶解氧[9]。低DO状态的水体中,水质的变化还会引起沉积物中NH3-N的释放[10]。此外,DO低于3 mg∙L−1的缺氧水体会对水体中鱼类的呼吸作用产生影响,抑制鱼类的基因表达,从而导致鱼类和甲壳动物的死亡[11-12],进而破坏生态系统的稳定性和生物多样性。
伴随着长江流域中下游人口和用水量的激增,给水处理系统造成巨大压力,也意味着流域内大量污水排入长江[13]。随污水排放的耗氧污染物导致的水环境危机在流域经济快速发展的过程中已有显现,DO较低、CODMn和NH3-N负荷高为水体恶化的标志[14-15],CODMn和NH3-N与地表水的水质密切相关[16]。为探求长江流域多年的水质变化及其主要原因,本研究利用长江流域2008至2018年间重点监测断面的DO、CODMn和NH3-N质量浓度数据,分析了长江流域重点河段监控断面的DO以及耗氧污染物CODMn和NH3-N的时空变化特征,结合对沿岸污水排放数据的统计和相关性分析,探讨水质变化的关键驱动因素,总结长江流域过去的水污染防治成果,为制定未来的污染物控制目标制定提供参考。
1. 研究区域及数据分析
1.1 研究区概况
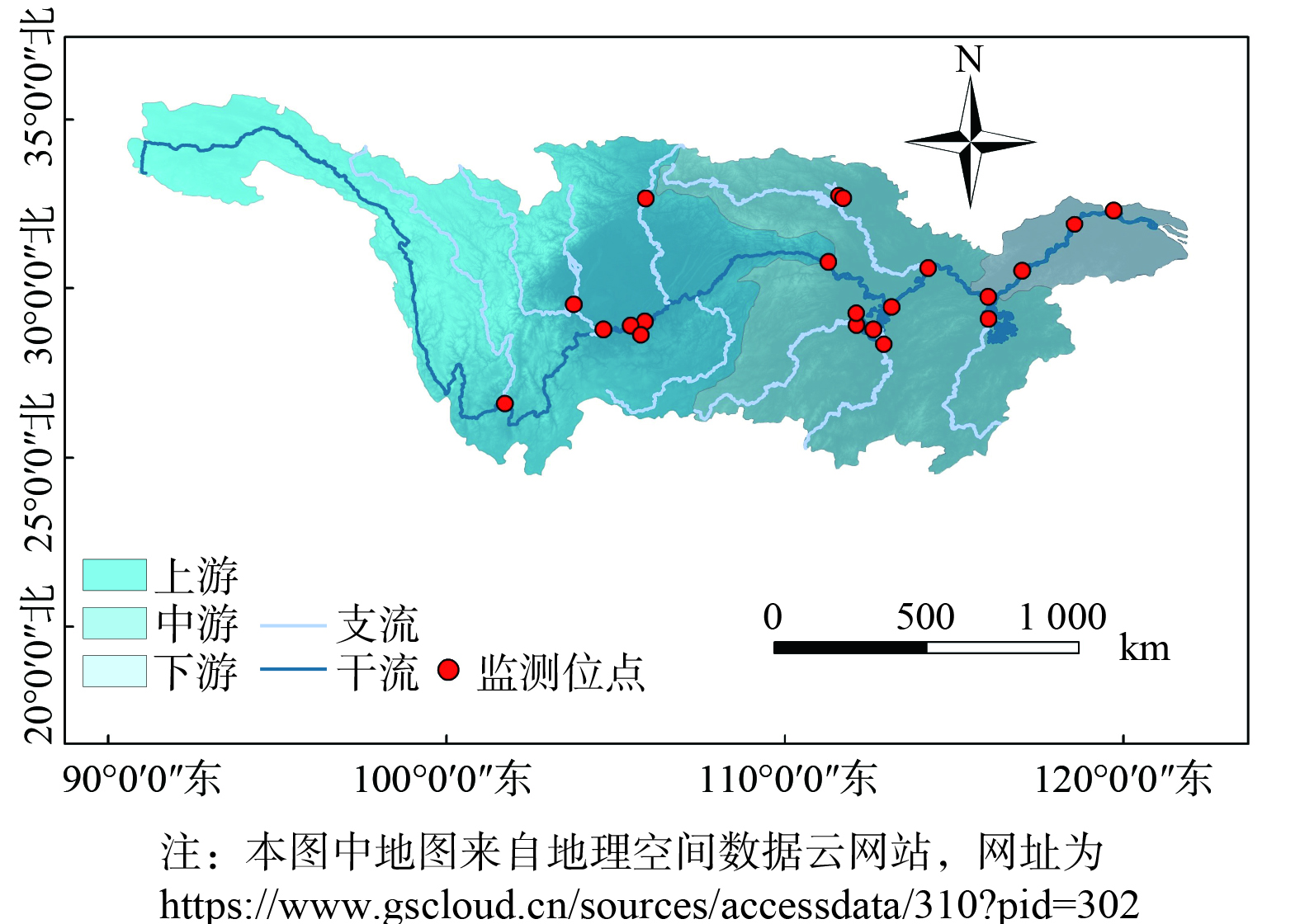
长江流域的范围位于东经90°~122°,北纬24°~36°,是中国覆盖面积最广的大河流域,干流横贯的省级行政单位数量达到11个,整个流域覆盖19个省、直辖市和自治区 (图1) ,为世界第三大流域[17]。长江西起青藏高原唐古拉山脉,东至上海市汇入东海,全长6 300 km,拥有复杂的支流和湖泊系统。长江的主要支流有雅砻江、岷江、沱江、嘉陵江、汉江、湘江、资江、沅江、澧水、赣江等;主要的湖泊包括我国五大淡水湖泊中的4个 (鄱阳湖、洞庭湖、太湖和巢湖) 。此外,长江流域还建有三峡水库这一世界最大河道型水库。长江流域可分为上游、中游和下游三部分,分别以湖北宜昌和江西九江为分界。长江流域支撑的长江经济带人口密集、工业集中、城市化水平高[18],污染物排放量超过全国的40%[19]。
1.2 数据来源
长江流域2008—2018年水质数据来自于《中国生态环境状况公报 (2008-2018年) 》 (https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/) 和《全国主要流域重点断面水质自动监测周报 (2008-2018年) 》 (https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/) ,以下简称《水质监测周报》。其中,《中国生态环境状况公报》涉及的国考断面逐年增加,从2008年的103个增加到2018年的510个断面;《水质监测周报》报告的长江流域重点监控断面如图1所示,共21个站点。2008—2018年,各监控断面每周的DO、CODMn和NH3-N数据来自于《水质监测周报》,其中赤水鲢鱼溪、益阳万家嘴、常德坡头和沙河口站点的监测数据起始自2012年。2008—2018年,长江干流沿岸行政单位的城市环境基础设施建设投资与污水排放数据来自《中国环境统计年鉴 (2009-2019) 年》 (https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/sthjtjnb/) 。研究区域图的底图来自地理空间数据云 (https://www.gscloud.cn/) ,流域边界数据来自http://120.26.232.88:6080/arcgis/rest/services/ROOT/QGSX/MapServer。相关统计计算使用Excel 2021软件进行,相关性分析采用SPSS 26软件进行,绘图分析使用Origin 2021软件进行。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 长江流域多年水质变化态势分析
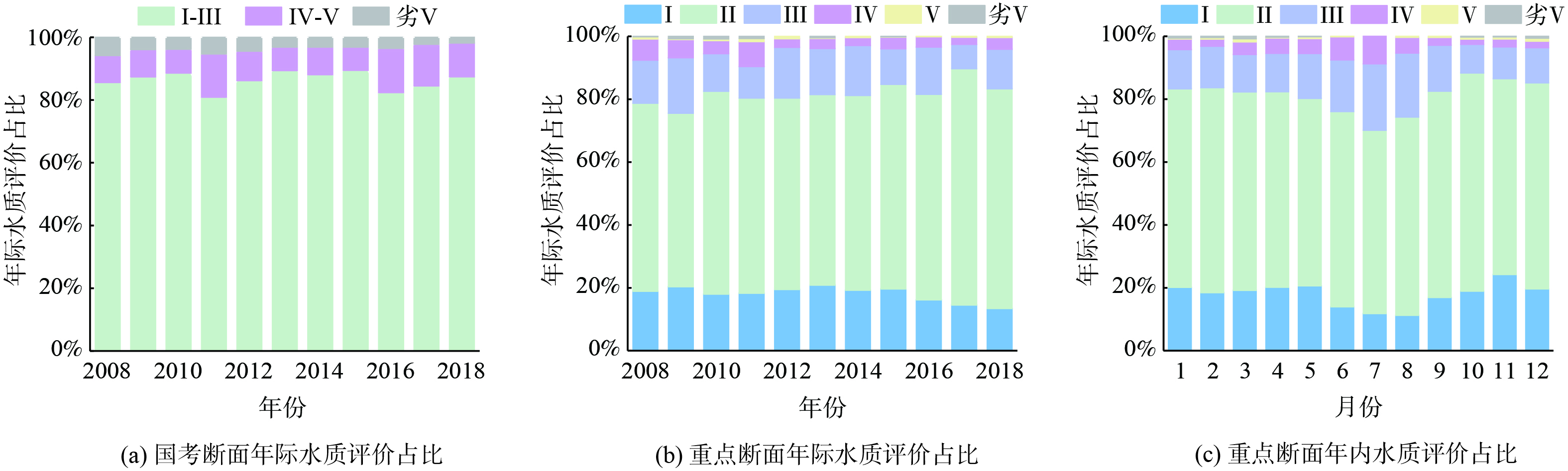
2008—2018年,长江流域水质逐渐转好,以Ⅱ类水质为主。如图2 (a) 所示,对《中国生态环境状况公报》的数据进行统计计算后发现,2008—2018年间长江流域的国考断面中,Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水质所占比例增加1.9%,Ⅳ、Ⅴ类水质所占比例增加2.2%,劣Ⅴ类水质减少4.0%。2018年统计的510个国考断面中Ⅰ~Ⅲ水质达到87.5%,劣Ⅴ类水质占比已经减少到1.8%,水质呈现良好状态。在十大流域中,长江流域的Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水质占比位列第4,Ⅳ、Ⅴ类水质占比位列第7,劣Ⅴ类水质占比位列第7,水质总体位于十大流域前列,仅次于西北诸河流域和西南诸河流域的水质。水质呈现周期性阶梯形波动,波动的变化时间点与监测站点数量的变化时间点基本一致。由此可推测纳入监测的站点,水质逐年转好,这可能与后续的污染控制措施有关。
长江流域的重点断面在2008—2018年间水质良好,超标现象发生频率较低,水质有所提升。如图2 (b) 所示,各监控断面各周的水质构成主要为Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水,多年平均占比为94.7%,水质的变化主要是Ⅰ~Ⅲ类的相互转化。其中,Ⅰ类水质平均占比为17.2%,Ⅱ类水质平均占比为61.6%,Ⅲ类水质平均占比为15.8%。出现Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水质的周数从2008年占比92.5%增加到2018年的95.9%,增加了3.4%。其中,Ⅰ类水从18.9%降低到13.4%,Ⅱ类水从59.9%增加到69.9%,Ⅲ类水从13.7%降低到12.6%。Ⅳ、Ⅴ类超标水质出现的周数占比较低,多年平均占比为5.1%。Ⅳ、Ⅴ类水质出现的周数占比从7.4%降低到4.1%,减少了3.3%。其中,Ⅳ类水从6.7%降低到3.7%,Ⅴ类水从0.07%降低到0.03%,劣Ⅴ类水消失。
对2008—2018年重点监控断面每周水质的年内变化进行统计分析,结果见图2 (c) 。流域主要断面水质有较为明显的年内变化,夏季的水质劣于其它季节。7月的Ⅳ类水占比最高,约占8.74%,10月份Ⅳ类水占比最低,约占1.66%。7月的Ⅰ类水占比低于平均值约6.1%,Ⅱ类水比平均低5.0%,Ⅲ类水比平均高7.2%,Ⅳ类水比平均高4.6%。水质变化主要体现在夏季的Ⅰ类水占比减少,Ⅲ、Ⅳ类水占比增加。夏季Ⅳ类水占比较高的原因主要是DO较低,低DO的贡献断面主要为乐山岷江大桥、宜宾凉姜沟、长沙新港、南昌滁槎、九江蛤蟆石,其中出现频率最高的断面为南昌滁槎。
2.2 长江流域关键水质因子时空特征分析
2.2.1 DO、CODMn和NH3-N随时间变化特征
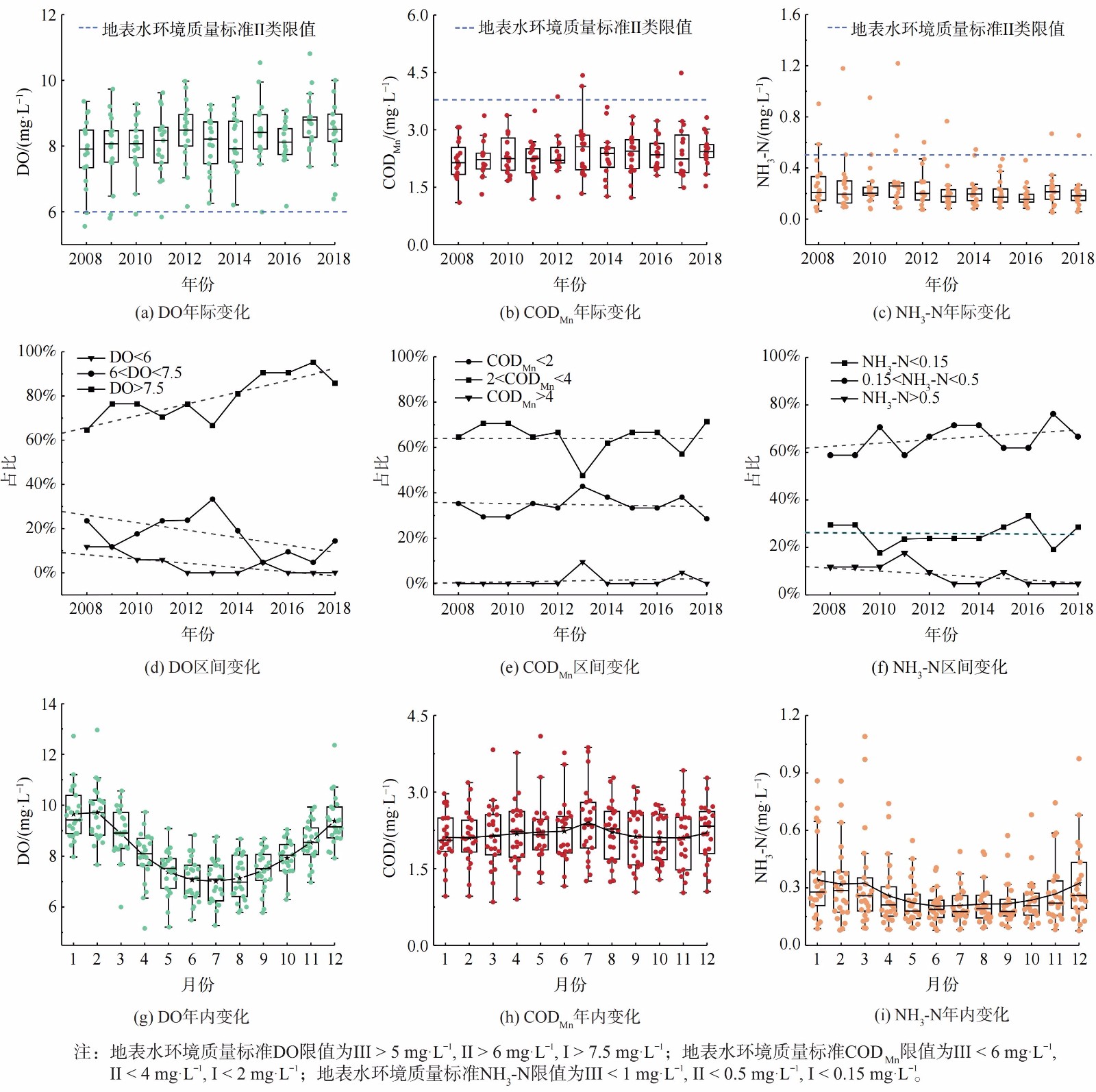
2008—2018年间,长江流域各重点监控断面的年DO平均值上升,高DO的断面数量增加。如图3 (a) 所示,2008年各监控断面的DO为5~11 mg∙L−1,平均值为7.81 mg∙L−1;2018年DO为6~10 mg∙L−1,平均值为8.39 mg∙L−1。长江流域的DO分布区间集中,平均值升高0.58 mg∙L−1。如图3 (d) 所示,年DO平均值大于地表水Ⅰ类标准 (7.5 mg∙L−1) 的断面占比逐年升高,到2018年已超过80%;2018年,年DO平均值高于7.5 mg∙L−1的断面比例比2008年高27%,而年DO平均值低于地表水Ⅱ类标准 (6 mg∙L−1) 的监控断面减少了21%。
各重点监控断面的CODMn有所波动,总体处于稳定状态。如图3 (b) ,长江流域各断面的CODMn为1.5~4.5 mg∙L−1,2008年的平均CODMn为2.15 mg∙L−1,2018年平均CODMn为2.32 mg∙L−1。如图3 (e) ,各断面年平均CODMn的变化趋势处于平稳状态,年平均CODMn基本处于Ⅱ类水限值内,均未超过地表水Ⅲ类限值。
各重点监控断面的NH3-N呈现下降趋势,且NH3-N波动范围缩小,高NH3-N的断面逐渐消失。如图3 (c) 所示,单个断面的最高NH3-N年平均值从2011年的1.22 mg∙L−1,降至2018年的0.67 mg∙L−1;每年的平均值从最高的0.27 mg∙L−1 (2011年) 降至0.23 mg∙L−1 (2018年) 。如图3 (f) 所示,年平均NH3-N处于Ⅱ类水质 (0.15~0.5 mg∙L−1) 区间内的断面数量增加,2018年比2008年增加7.8%;超过Ⅱ类水限值 (0.5 mg∙L−1) 的断面数量总体减少,2018年比2008年减少7.0%。这表明长江流域耗氧物质NH3-N水平在有效控制手段下处于稳定。有研究者通过M-K检验和R/S分析对长江流域地表水监测数据进行分析,预测2020年后的十余年间,NH3-N将持续降低[20]。此外,多年来NH3-N浓度超出Ⅱ类水标准 (0.5 mg∙L−1) 的监控断面位于四川岷江大桥和南昌滁槎。这些断面位于人口密集[21]和工业排放密集[22]的地区,NH3-N较高的原因可能与人类活动相关。
对各重点监控断面水质因子浓度的年内变化进行统计分析,发现水质因子的浓度表现出一定的季节变化趋势,其中DO和NH3-N的季节变化特征较为明显。如图3 (g) 所示,夏季的平均DO较低,在一年中表现为先降低后升高,7月的平均DO最低,为7.02 mg∙L−1,比各月平均DO低14.2%。夏季DO较低的原因可能是气温升高不利于水体复氧[23],DO低也是造成各断面夏季的水质低于其他季节的直接原因。如图3 (h) ,CODMn在一年间的变化幅度较小,各月平均值为2.10~2.41 mg∙L−1。如图3 (i) ,各断面的NH3-N分布表现为夏季最低,在一年中先降低后增加。6月的平均NH3-N最低,为0.20 mg∙L−1,比各月平均NH3-N低20.9%,且在夏季各断面NH3-N的离群点较少。这可能是由于夏季水温比其他季节高,微生物活性较强,硝化反应的速率较高[24-25],对水体自净有促进作用。
2.2.2 DO、CODMn和NH3-N随空间变化特征
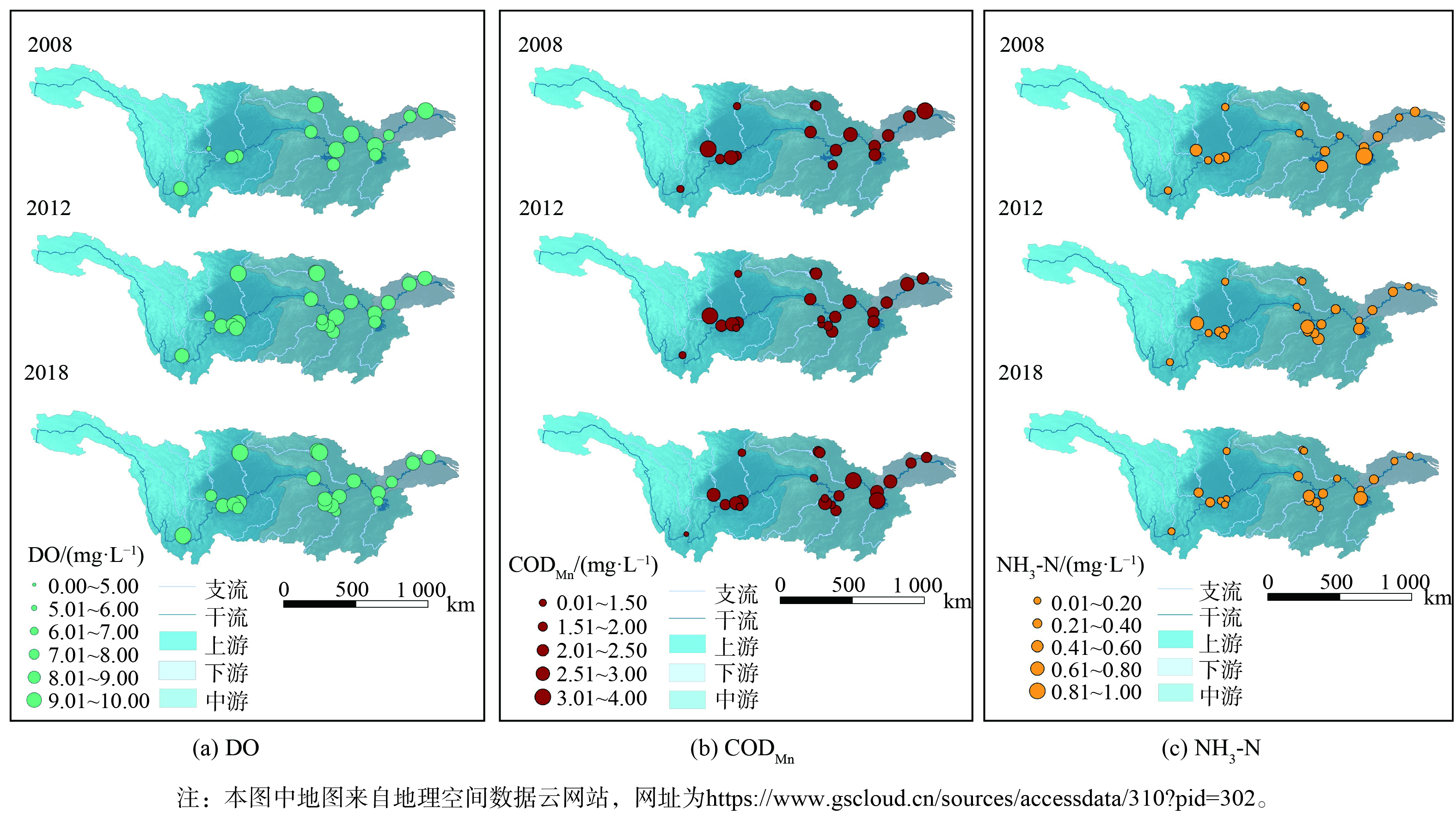
2008—2018年间长江流域主要监控断面的DO升高,且上游变化幅度最大。对比各重点监控断面2008年与2018年 (其中赤水鲇鱼溪、益阳万家嘴、常德坡头和沙河口断面监测数据的统计起始年为2012年) 的DO (图4) 。长江流域上游、中游、下游的平均DO分别升高了0.88 mg∙L−1,0.47 mg∙L−1和0.57 mg∙L−1。其中,上游DO升高最明显,平均增长率为12%,中游DO波动最剧烈。上游DO升高最为显著的断面为彭山岷江大桥 (1.87 mg∙L−1) ,增长比例为34%;中游DO升高最为显著的断面为常德沙河口断面 (1.61 mg∙L−1) ,增长比例为24%;下游DO升高最显著的断面为南京林山断面 (1.49 mg∙L−1) ,增长比例为22%。2018年,上游平均DO为8.59 mg∙L−1,中游平均DO为8.31 mg∙L−1,下游平均DO为8.15 mg∙L−1。
各断面的整体CODMn水平有所上升,变化最显著的区域是长江流域中游。上游、中游和下游的平均CODMn分别变化了0.19 mg∙L−1、0.60 mg∙L−1、-0.01 mg∙L−1。其中,上游重庆朱沱断面CODMn增加最多 (0.83 mg∙L−1) ,增加48%,南津关断面下降最多 (0.80 mg∙L−1) ,下降34%;中游CODMn升高最多的是常德坡头断面 (1.58 mg∙L−1) ,增加161%;下游三江营断面下降0.75 mg∙L−1,下降25%。长江流域的CODMn长期处于较低状态,2018年上游的平均CODMn为2.12 mg∙L−1,中游的平均CODMn为2.44 mg∙L−1,下游的平均CODMn为2.45 mg∙L−1。虽然长时间跨度以来有所波动,但处于地表水环境质量标准的Ⅲ类限值以内,表现出水质的稳定性和安全性。
各断面的NH3-N都有所降低,且长江中游最为显著。2018年上游、中游和下游的年平均NH3-N分别比2008年变化了-0.02 mg∙L−1、-0.09 mg∙L−1和-0.05 mg∙L−1。其中,上游降低最多的断面为乐山岷江大桥 (0.19 mg∙L−1) ,降低了42%;中游降低最多的断面为长沙新港 (0.45 mg∙L−1) ,降低了77%;下游下降最多的断面为扬州三江营 (0.16 mg∙L−1) ,下降了47%。2018年上游的平均NH3-N为0.18 mg∙L−1,中游的平均NH3-N为0.29 mg∙L−1,下游的平均NH3-N为0.18 mg∙L−1。NH3-N的下降代表长江流域的水质在趋于稳定过程中逐渐转好,这可能与重点断面区域的污染物质排放限制措施有关[20]。
2.3 长江流域水质关键影响因素分析
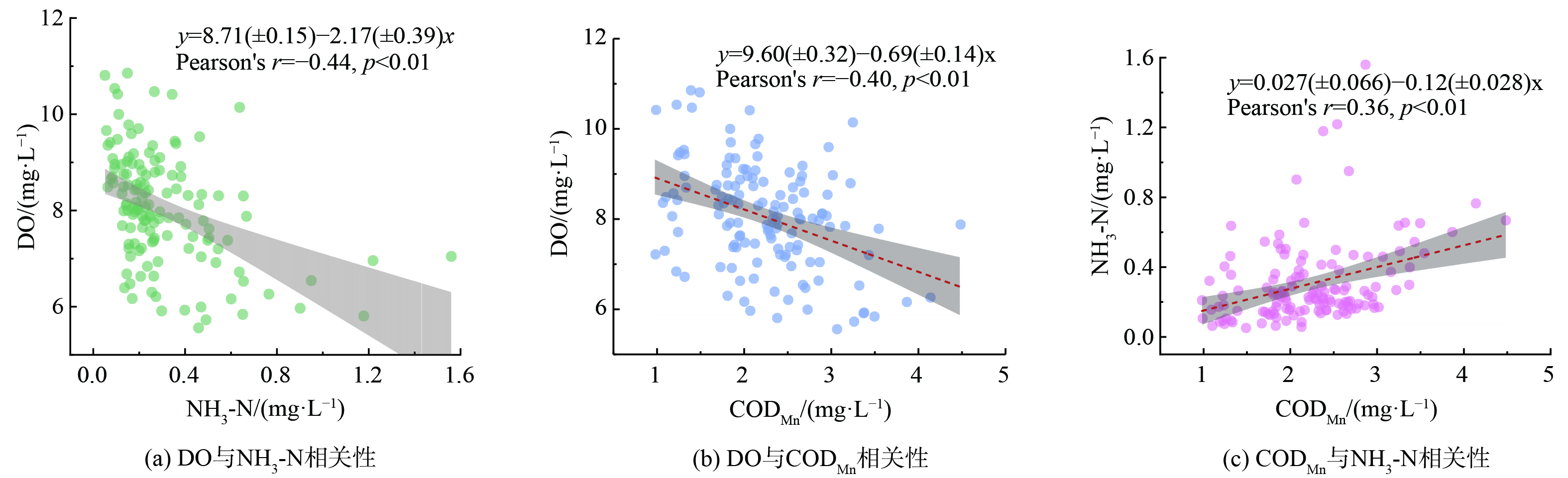
年DO平均值高于7.5 mg∙L−1的断面被认为是富氧河段,其水中溶解氧接近饱和状态[26],受CODMn和NH3-N变化影响小,将其剔除之后对DO与CODMn、NH3-N进行皮尔逊相关性分析(结果见图5)。DO与CODMn和NH3-N的数据均符合正态分布,双变量相关性p值均小于0.01,变量间有显著相关性。DO与NH3-N的浓度相关性系数均为负,DO与CODMn相关系数为-0.40,DO与NH3-N的相关系数为-0.44,CODMn和NH3-N的相关系数为0.36。CODMn与NH3-N呈现出线性相关关系,这可能是由于部分CODMn和NH3-N同为生活污水的点源排放[16]。DO与CODMn、NH3-N呈现出的相关系数均为负,这表明CODMn和NH3-N为长江流域的耗氧污染物。
长江流域各断面2018年的CODMn超出Ⅱ类水限值的周数为占比为4.08%,比最高的2013年下降了3.65%,超出Ⅲ类水限值的周数除2013年占比达到1.56%外,其余年份占比均小于1.00%。2018年NH3-N超出Ⅱ类水限值的周数最高占比为2010年,达到16.04%,2018年下降到占比为6.72%,减少了9.31%。超出Ⅲ类水限值的周数最高为2010年,占比达到6.19%,到2018年下降到1.05%,减少了5.14%。故CODMn常年处于较低水平,但NH3-N随时间变化较为明显。在研究时间段内,2013年以前出现高NH3-N的监控断面同时表现出相对较低DO,如乐山岷江大桥和南昌滁槎。到2018年,上述断面的年DO平均值有所升高,年平均NH3-N有所降低,也说明了DO与NH3-N相关系数为负,这是由于NH3-N的降低可能伴随耗氧量的降低[14]。但各重点断面2016—2018年仍出现高NH3-N (>0.5 mg∙L−1) ,这表明NH3-N对水质的恶化仍具有较大贡献[27],目前长江流域的主要耗氧污染物为NH3-N。
对比其他流域的耗氧污染,长江流域耗氧污染物浓度处于较低水平。海河流域2007—2011年间超标站点耗氧污染物浓度均值超出Ⅴ类标准1倍以上[15]。其中,NH3-N超标的站点比例达到18%,而长江流域耗氧污染物浓度均未超出V类水标准。但与海河流域相似,长江流域主要的耗氧污染物也已转变为NH3-N,且高浓度区域均为人口密集,经济活动高度发达区域[15]。
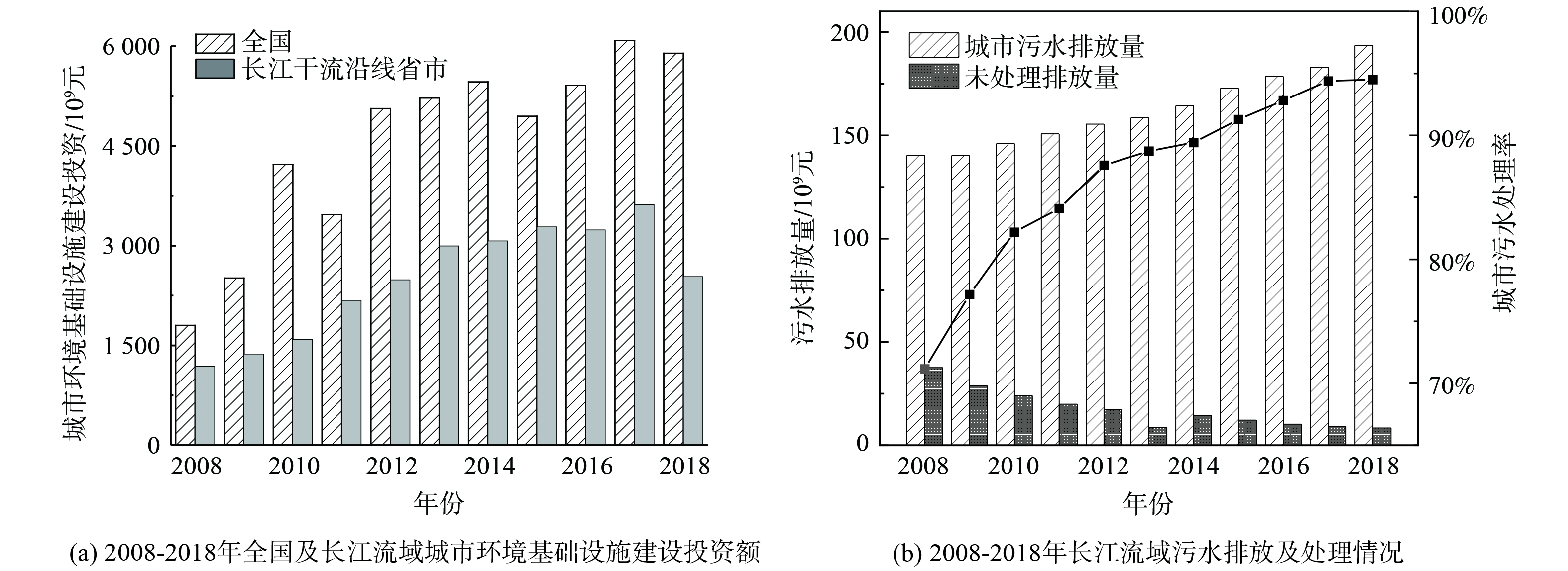
区域内的人类活动和经济发展水平将直接通过影响污染物排放[28]对水质产生影响,流域内污染负荷的贡献主要来自于人类活动,例如氮磷肥施肥、耕地灌溉[20]、工业排放、水电开发[29]、畜禽养殖[30]等。以目标污染物为核心的污染负荷削减对水质可起到稳定作用[31]。近年来,长江流域内CODMn和NH3-N超标断面的出现频率的减少与沿岸的污染治理投资和措施有关。如图6 (a) ,2008—2018年,全国环境污染治理投资总体上处于持续增加的状态,2018年全国环境污染治理投资比2008年增加约1倍,达到8 987.6亿元。其中城市环境基础设施建设投资是主要投资,2018年已经达到5 893.2亿元,比2008年增加4 092.2亿元;工业污染治理投资增加28.5%,到2018年已经达到697.5亿元。在全国环境污染治理投资逐年升高的背景下,2008—2018年长江干流沿线省市的城市环境基础设施建设投资呈现升高趋势,平均占全国的56%。城市环境基础设施建设投资中,对排水和绿化的投资占主要地位,长江流域内的污水排放量因此呈现减少的趋势。长江流域污水排放及处理情况如图6 (b) 所示,在2008—2018年间,长江干流沿线省市的城市污水排放总量和平均城市污水处理率逐年升高,2018年的污水排放总量比2008年增加37.9%;平均污水处理率增加23.3%,到2018年已经达到95.7%。污水处理率的明显升高意味着未处理污水量减少,2018年的未处理污水量比2008年减少了77.8%,海河流域耗氧污染物浓度得到控制也与污水处理率提高有直接联系[15]。由此可见,持续的污染治理投资和污水减排对长江流域水质好转有重要作用,流域耗氧污染得到有效控制,且耗氧污染物以NH3-N为主。相关研究结果对未来长江流域的水环境管理与相关控制对策制定具有重要参考意义。
3. 结论
1) 长江流域各重点断面水质良好,2008—2018年间稳步上升,水质由Ⅳ和Ⅴ类向Ⅱ和Ⅲ类转变,Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水质占比之和增加了3.4%,劣Ⅴ类水质趋于消失。水质表现出季节性,夏季水质劣于其他季节,表现在Ⅰ、Ⅱ类水占比减少,Ⅲ、Ⅳ类水占比增加,水质变差的原因是DO较低。
2) 2008—2018年,长江流域各重点监控断面整体的DO升高0.58 mg∙L−1,浓度区间集中;CODMn多年来稳定处于Ⅲ类水限值内;各重点监控断面NH3-N浓度下降0.04 mg∙L−1,年平均NH3-N极端值从1.22 mg∙L−1下降到0.67 mg∙L−1。DO变化最大的区域为上游,CODMn和NH3-N变化最大的为中游。
3) 相关性分析表明,DO恢复与NH3-N得到控制密切相关,DO和NH3-N的变化主要体现在高NH3-N下降导致低DO恢复的断面。在环境污染治理投资取得污水减排成效后,长江流域CODMn和NH3-N指标逐步好转,也成为流域重点断面水中溶解氧恢复的主要驱动力。
-
表 1 内梅罗指数法污染评价等级
Table 1. Pollution assessment level of Nemerow index
内梅罗综合污染指数Néméro Composite Pollution Index 污染等级Pollution levels 评价结果Evaluation results P综合≤0.7 1 清洁安全 0.7<P综合≤1.0 2 尚清洁(警戒线) 1.0<P综合≤2.0 3 轻度污染 2.0<P综合≤3.0 4 中度污染 P综合>3.0 5 重污染 表 2 定海-黄岐湾样点重金属描述性特征(mg·kg−1)
Table 2. Heavy metal content at sample sites in Huangqi Bay, Dinghai (mg·kg−1)
表 3 定海-黄岐湾沉积物重金属内梅罗污染指数
Table 3. Heavy metal Nemero pollution index for sediments in Huangqi Bay, Dinghai
V Cr Co Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb 平均单项污染指数 1.11 1.49 1.82 2.25 1.42 1.41 2.13 1.14 最小单项污染指数 0.23 0.08 0.30 0.20 0.11 0.49 0.18 0.10 最大单项污染指数 1.53 2.58 2.52 3.36 9.68 4.89 13.27 3.24 综合污染指数 1.33 2.11 2.20 2.86 6.92 3.60 9.50 2.43 污染等级 轻度污染 中度污染 中度污染 中度污染 重污染 重污染 重污染 中度污染 表 4 重金属元素源贡献率(%)
Table 4. Heavy metal elemental source contribution
元素Elements 因子1Factor 1 因子2Factor 2 因子3Factor 3 因子4Factor 4 V 50.4 13.0 32.9 3.8 Cr 7.2 21.4 71.4 — Co 27.8 10.7 45.8 15.7 Ni 10.8 13.2 70.7 5.3 Cu 0.7 31.6 66.7 1.0 Zn 26.6 33.1 29.3 10.9 Cd 30.9 69.1 — — Pb — 34.6 30.6 34.8 相对贡献率 19.3 28.3 43.4 8.9 -
[1] 公金文, 陈发荣, 郑立, 等. 红海湾表层海水重金属含量与污染评价 [J]. 海洋科学进展, 2021, 39(4): 570-580. GONG J W, CHEN F R, ZHENG L, et al. The concentrations and pollution assessment of heavy metal in surface seawater in Honghai Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2021, 39(4): 570-580(in Chinese).
[2] 贾广宁. 重金属污染的危害与防治 [J]. 有色矿冶, 2004, 20(1): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2004.01.013 JIA G N. Harm and defence of heavy metals [J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2004, 20(1): 39-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2004.01.013
[3] 田金, 李超, 宛立, 等. 海洋重金属污染的研究进展 [J]. 水产科学, 2009, 28(7): 413-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2009.07.013 TIAN J, LI C, WAN L, et al. The advances of heavy metal pollution in marine environment [J]. Fisheries Science, 2009, 28(7): 413-418(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2009.07.013
[4] 曹胜伟, 刘春雷, 李亚松, 等. 福建泉州湾近岸海域沉积物重金属来源分析与生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(5): 1841-1896 CAO S W, LIU C L, LI Y S, et al. Source analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the coastal waters of Quanzhou Bay, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(5): 1841-1896(in Chinese)
[5] 段云莹, 裴绍峰, 廖名稳, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征、污染评价与来源分析 [J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(6): 67-81. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020112601 DUAN Y Y, PEI S F, LIAO M W, et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay and their sources and pollution assessment [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(6): 67-81(in Chinese). doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020112601
[6] 胡宁静, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 莱州湾表层沉积物中重金属分布特征和环境影响 [J]. 海洋科学进展, 2011, 29(1): 63-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.01.008 HU N J, SHI X F, LIU J H, et al. Distributions and impacts of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2011, 29(1): 63-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.01.008
[7] 周笑白, 梅鹏蔚, 彭露露, 等. 渤海湾表层沉积物重金属含量及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(3): 452-456. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.03.012 ZHOU X B, MEI P Y, PENG L L, et al. Contents and potential ecological risk assessment of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bohai Bay [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(3): 452-456(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.03.012
[8] 魏璟弢, 张焕玲, 李铁, 等. 胶州湾及青岛近海表层沉积物重金属赋存形态研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 42(S1): 157-164. WEI J T, ZHANG H L, LI T, et al. Study of the geochemical forms of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay and Qingdao inshore areas[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2012, 42(Sup 1): 157-164(in Chinese).
[9] 郑钦华. 三沙湾海水增养殖区沉积物重金属变化特征及污染状况评价 [J]. 宁德师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2019, 31(4): 432-440. doi: 10.15911/j.cnki.35-1311/n.2019.04.020 ZHENG Q H. Changing characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in sediment in mariculture area of Sansha Bay [J]. Journal of Ningde Normal University (Natural Science), 2019, 31(4): 432-440(in Chinese). doi: 10.15911/j.cnki.35-1311/n.2019.04.020
[10] 王恩康, 丰爱平, 张志卫, 等. 兴化湾海域水体和表层沉积物中重金属分布及其源解析 [J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(4): 696-708. WANG E K, FENG A P, ZHANG Z W, et al. Heavy metal distribution and its source analysis in seawater and sediments of Xinghua Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(4): 696-708(in Chinese).
[11] 陈斌, 尹晓娜, 姜广甲, 等. 珠江口外陆架海域表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险评价及来源分析 [J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(3): 520-528. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.03.017 CHEN B, YIN X N, JIANG G J, et al. Assessment of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of continental shelf and their sources off the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 520-528(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2021.03.017
[12] 施亚盛, 李光耀, 吴爱静, 等. 东苕溪沉积物重金属生态风险评价和源解析 [J]. 生态科学, 2021, 40(6): 67-74. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2021.06.008 SHI Y S, LI G Y, WU A J, et al. Ecological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of East Tiaoxi River [J]. Ecological Science, 2021, 40(6): 67-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2021.06.008
[13] 尚婷婷, 张亚群, 周静, 等. 多元统计分析在农田土壤重金属污染源解析中的应用 [J]. 环境生态学, 2022, 4(4): 93-97. SHANG T T, ZHANG Y Q, ZHOU J, et al. Application of multivariate statistical analysis in the analysis of heavy metal pollution sources in farmland soil [J]. Environmental Ecology, 2022, 4(4): 93-97(in Chinese).
[14] 陈雪, 刘鸿雁, 吴攀, 等. 基于GIS和PMF的铜仁植烟土壤重金属污染特征与来源解析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(4): 794-801. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-0779 CHEN X, LIU H Y, WU P, et al. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in tobacco-planting soils in Tongren County based on GIS and PMF methods [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(4): 794-801(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-0779
[15] 阿地拉·艾来提, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 怕提古力, 等. 基于BM和PMF模型的库尔勒市地表灰尘重金属来源解析 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2021, 33(5): 31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2021.05.007 HAYRAT Adila, EZIZ Mamattursun, Patigu, et al. Source analysis of heavy metals in surface dust in Korla based on barycenter model and PMF model [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2021, 33(5): 31-35(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2021.05.007
[16] 任万辉, 李云丹, 苏枞枞, 等. 沈阳市大气PM2.5中重金属污染特征、来源解析及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1029-1037. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020093002 REN W H, LI Y D, SU C C, et al. Pollution characteristics, source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 in Shenyang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1029-1037(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020093002
[17] 吕建树. 烟台海岸带土壤重金属定量源解析及空间预测 [J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(3): 713-725. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202103015 LYU J S. Source apportionment and spatial prediction of heavy metals in soils of Yantai coastal zone [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(3): 713-725(in Chinese). doi: 10.11821/dlxb202103015
[18] 魏迎辉, 李国琛, 王颜红, 等. PMF模型的影响因素考察: 以某铅锌矿周边农田土壤重金属源解析为例 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(11): 2549-2559. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0492 WEI Y H, LI G C, WANG Y H, et al. Investigating factors influencing the PMF model: A case study of source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils near a lead-zinc ore [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(11): 2549-2559(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0492
[19] 比拉力·依明, 阿不都艾尼·阿不里, 师庆东, 等. 基于PMF模型的准东煤矿周围土壤重金属污染及来源解析 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(9): 185-192. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.09.022 Bilal Imin, Abdugheni Abliz, SHI Q D, et al. Pollution and source identification of heavy metals in surrounding soils of Eastern Junggar Coalfield based on PMF model [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(9): 185-192(in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.09.022
[20] 王星蒙. 基于PMF模型的葫芦岛锌厂周边农田土壤重金属源解析 [J]. 农业与技术, 2021, 41(13): 137-139. doi: 10.19754/j.nyyjs.20210715038 WANG X M. Analysis of heavy metal sources in farmland soil around Huludao zinc plant based on PMF model [J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2021, 41(13): 137-139(in Chinese). doi: 10.19754/j.nyyjs.20210715038
[21] 庞阔, 李敏, 刘璐, 等. 基于蒙特卡洛模拟与PMF模型的黄河流域沉积物重金属污染评价及源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(8): 4008-4017. PANG K, LI M, LIU L, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Yellow River Basin based on Monte Carlo simulation and PMF model [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(8): 4008-4017(in Chinese).
[22] 蔡继晗, 李凯, 郑向勇, 等. 水产养殖重金属污染现状及治理技术研究进展 [J]. 水产科学, 2010, 29(12): 749-752. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2010.12.015 CAI J H, LI K, ZHENG X Y, et al. Advancement in researches and treatment technology of heavy metals in aquaculture [J]. Fisheries Science, 2010, 29(12): 749-752(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2010.12.015
[23] 卢欣. 闽东近海水产养殖区表层沉积物重金属元素分布特征及来源解析[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2020. LU X. Distribution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from offshore aquaculture areas of eastern Fujian[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2020(in Chinese).
[24] 张金婷, 孙华. 内梅罗指数法和模糊综合评价法在土壤重金属污染评价应用中的差异分析 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2016, 28(4): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2016.04.007 ZHANG J T, SUN H. Differences of nemerow index method and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in evaluation heavy metal pollution in soil [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2016, 28(4): 27-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2016.04.007
[25] 沈宸宇, 闫钰, 于瑞莲, 等. APCS-MLR结合PMF模型解析厦门杏林湾近郊流域沉积物金属来源 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2476-2488. SHEN C Y, YAN Y, YU R L, et al. APCS-MLR combined with PMF model to analyze the source of metals in sediment of xinglin bay suburban watershed, Xiamen [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2476-2488(in Chinese).
[26] 匡荟芬, 胡春华, 吴根林, 等. 结合主成分分析法(PCA)和正定矩阵因子分解法(PMF)的鄱阳湖丰水期表层沉积物重金属源解析 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(4): 964-976. doi: 10.18307/2020.0406 KUANG H F, HU C H, WU G L, et al. Combination of PCA and PMF to apportion the sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Poyang during the wet season [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(4): 964-976(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0406
[27] 雷国建, 陈志良, 刘千钧, 等. 广州郊区土壤重金属污染程度及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(S1): 49-53. LEI G J, CHEN Z L, LIU Q J, et al. The assessments of polluted degree and potential ecological hazards of heavy metals in suburban soil of Guangzhou City[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(Sup 1): 49-53(in Chinese).
[28] 张开毕. 福建省近岸浅海沉积物地球化学环境质量 [J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(2): 45-52. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2008.02.009 ZHANG K B. Geochemistry environment quality of littoral and neritic sediments in Fujian Province [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(2): 45-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2008.02.009
[29] 赵一阳, 鄢明才. 中国浅海沉积物化学元素丰度 [J]. 中国科学 (B辑 化学 生命科学 地学), 1993, 23(10): 1084-1090. ZHAO Y Y, YAN M C. Abundance of chemical elements in shallow sea sediments in China [J]. Science in China, SerB, 1993, 23(10): 1084-1090(in Chinese).
[30] 林绍霞, 柳小兰, 张转铃, 等. 贵州草海表层沉积物重金属污染特征与源解析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(2): 390-399. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1078 LIN S X, LIU X L, ZHANG Z L, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and source apportionment in overlying deposits of Caohai Lake, Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(2): 390-399(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1078
[31] 李丽蓉, 王玉杰, 秦玉春. 三亚市生活污水中的重金属分布特性研究 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2013(12): 162. doi: 10.16317/j.cnki.12-1377/x.2013.12.099 LI L R, WANG Y J, QIN Y C. Study on distribution characteristics of heavy metals in domestic sewage in Sanya City [J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2013(12): 162(in Chinese). doi: 10.16317/j.cnki.12-1377/x.2013.12.099
[32] 钱力. 永康市城市表层土壤重金属污染现状及来源分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2015: 45-46. QIAN L. Situation analysis and source identification of heavy metals pollution in the urban topsoil of Yongkang City[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University, 2015: 45-46. (in Chinese)
[33] 黄磊, 孙桂华, 袁晓婕. 福建近岸海域表层沉积物重金属、PCBs潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2017, 36(2): 167-172,185. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2017.02.002 HUANG L, SUN G H, YUAN X J. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and PCBs in surface sediments at Fujian coastal sea area [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(2): 167-172,185(in Chinese). doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2017.02.002
-




 下载:
下载: