-
过量的氮释放到水生系统中会导致酸化和富营养化问题,污水水中的氮素去除是水资源保护重要内容. 硝化作用(NH
+4 →NO−2 /NO−3 )是工程系统中除铵应用最广泛的一种方法,然而,硝化作用需要氧气持续输入来支撑,曝气供氧占了污水处理厂的大量能源消耗. 多年来,反硝化一直被认为是生物圈和大气的唯一联系,直至厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonium oxidation, Anammox)的发现. 厌氧氨氧化也是自然环境中生物脱氮的一条途径[1−2],见式(1),但其仍需要一定的曝气来形成所需的NO2-,且厌氧氨氧化菌(AnAOB)倍增时间长(约11 d)和对环境敏感制约了其工程应用[3]. 铁可以促进AnAOB新陈代谢所必需的细胞色素c和Fe-S蛋白的合成[4],且不溶性氧化铁是环境中普遍存在的电子受体[5−6],因此发展了厌氧氨氧化与Fe(Ⅲ)还原耦合的反应,即铁氨氧化(Fe(Ⅲ) reduction coupled to anaerobic ammonium oxidation, Feammox) [7−8],其在热带旱地土壤[9]、富营养化湖泊[10]、人工湿地[11]和水稻土[12]中都有存在. 铁氨氧化在废水处理过程中,反应在缺氧和自养过程进行,这可以显著减少曝气、外部碳源投加量和污泥处理相关的费用[13],是一种绿色节能的新型生物脱氮反应.目前关于铁氨氧化的综述已有报道[14−17],因其最初发现于湿地土壤等环境中[7],其大多侧重于铁氨氧化的生态意义及影响因素的总结. 本综述侧重于近年来对铁氨氧化在污水脱氮领域中应用的研究梳理,介绍了其机理、优势菌种的种类和生长特性及电子穿梭体的影响,总结了铁氨氧化在污水环境中的脱氮效果及其与厌氧氨氧化、硝酸盐依赖型亚铁氧化和生物电化学系统的耦合技术,并指出目前铁氧化的应用问题及该技术未来的研究方向和重点可能是菌分离纯化、工艺参数控制,以期为其在污水处理领域的工程规模应用提供思路.
-
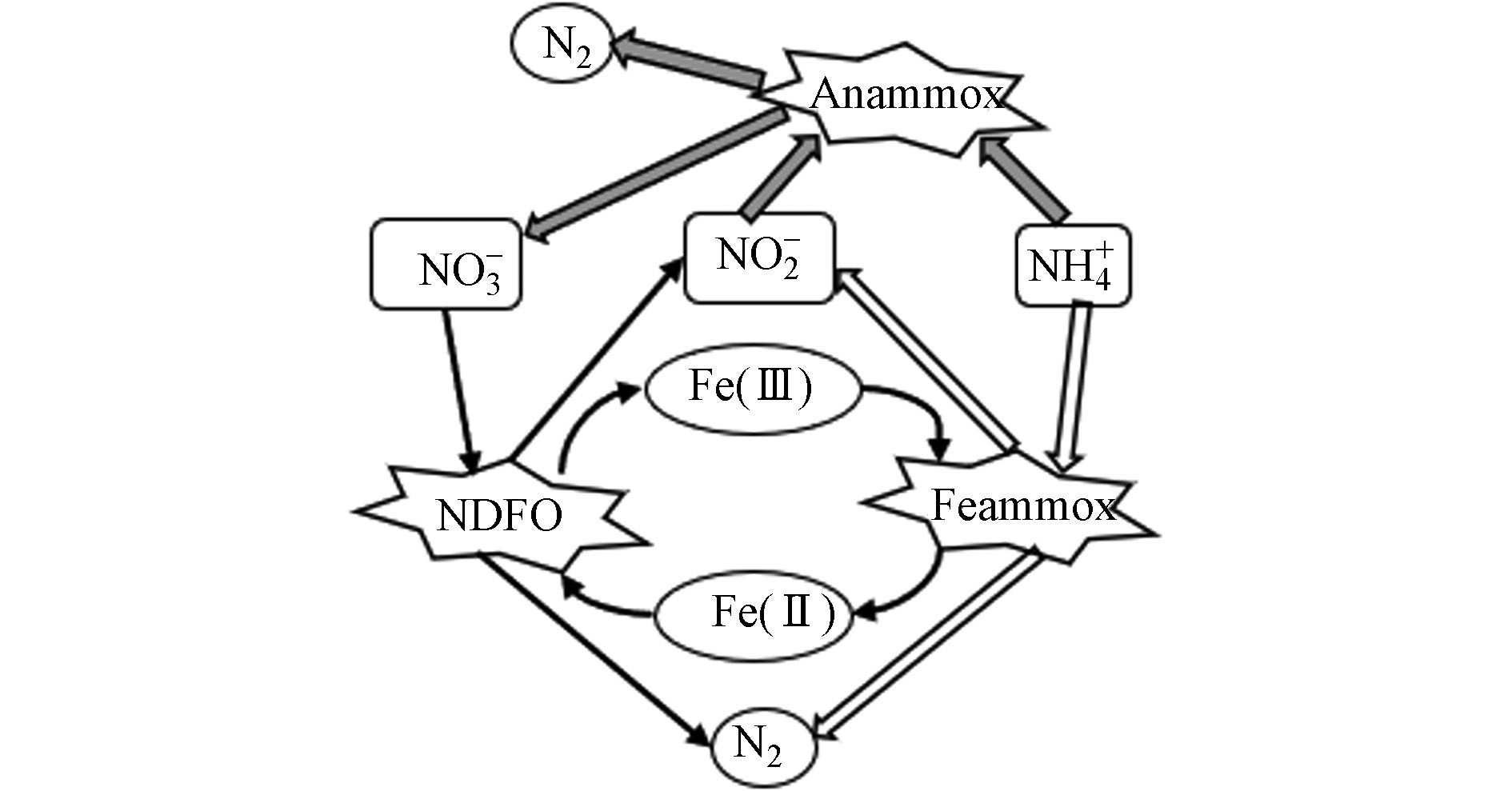
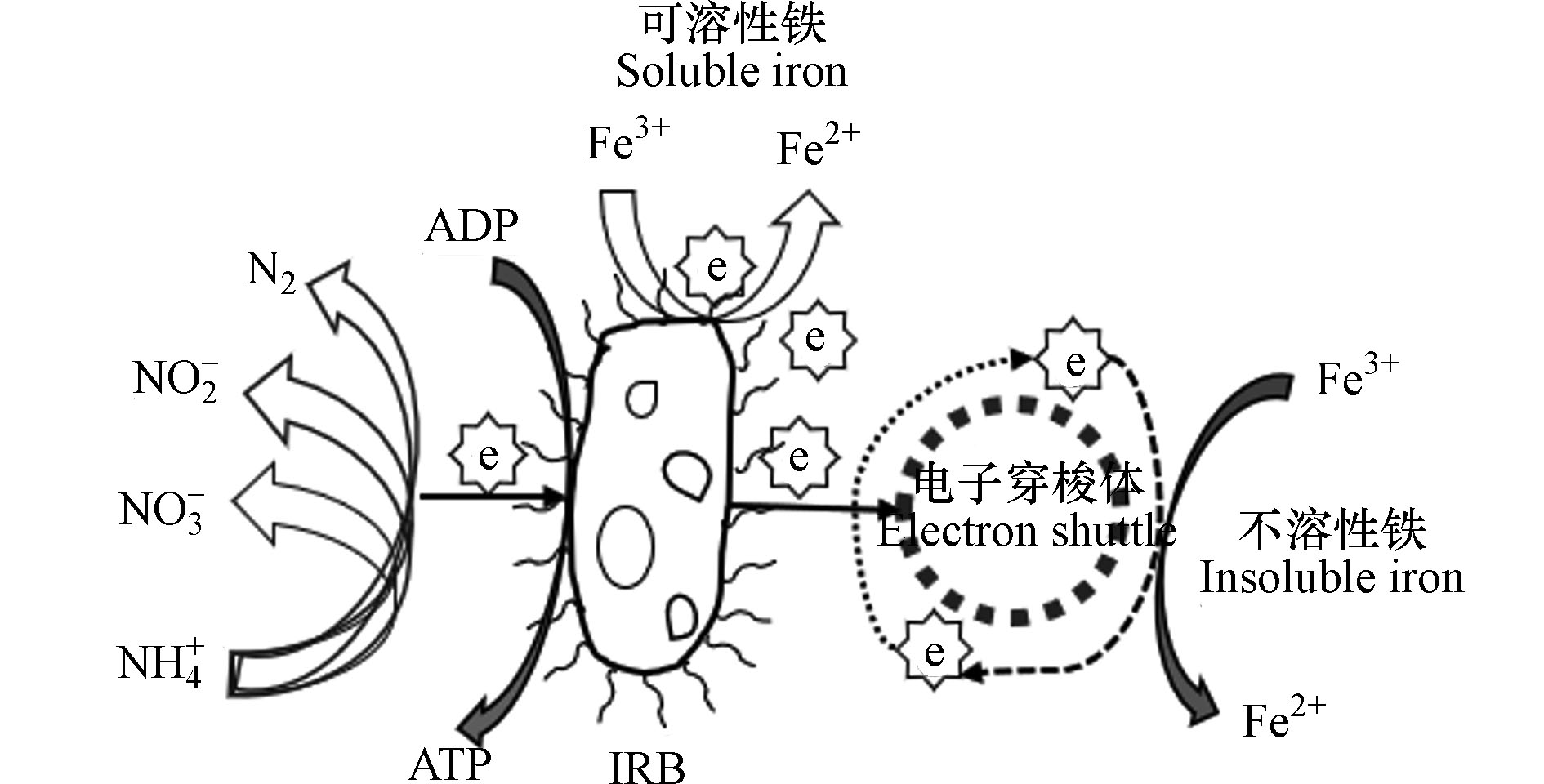
铁氨氧化是一种铁介导的自养生物脱氮过程,即在厌氧环境中,铁还原菌(Iron-reducing bacteria,IRB)以Fe(Ⅲ)作为电子受体,将NH
+4 氧化为N2、NO−2 和NO−3 的过程[14],见反应式(2)—(4)和图1. 从热力学角度,Feammox更易将NH4+氧化为N2. 有研究表明[18],Feammox反应直接产生的N2占其整个反应产物的67.0%—93.2%.铁氨氧化菌通过氧化电子供体NH4+同时耦联Fe(Ⅲ)还原,从这一过程中获取能量,合成细胞物质的一类微生物,其本质上是一类能驱动氨氧化的铁还原菌[9]. 铁还原菌包括Shewanella futrefaciens、Geobacter metallireducens、Geothrix fermentans、Desulfobulbus propionieus与Rhodoferax ferriredueens等,目前已完成了Geobacter和Shewanella两种菌的全基因组测序[19]. 与AnAOB相比,铁还原菌具有更高的生存能力、金属耐受性且广泛存在于自然界中[20],其还原铁的作用原理包括以下3种[21]:(1) 铁还原菌直接与还原铁氧化物接触;(2)铁矿物(溶解性较低)借助铁还原菌分泌的胞外螯合物,提高其溶解,从而促进铁的还原过程;(3)借助电子穿梭体:利用铁还原菌自身细胞分泌的电子穿梭体或是周围环境中的电子穿梭体,通过胞外电子转移过程进行铁还原. 1987年,Lovley等[22]首次分离出Geobacter metallireducens GS-15,该菌是一种具有铁还原功能的纯菌,能将乙酸乙酯氧化成二氧化碳,同时将无定形Fe(Ⅲ)氧化物还原成磁铁矿(Fe3O4). 2015年,Huang等[23]通过分离纯化出一株具铁氨氧化功能的酸微菌——Acidimicrobiaceae sp.A6菌(A6菌),并且在连续流膜反应器运行180 d后发现, 以A6菌为代表的酸微菌成为该反应器的优势菌. Yao等[24]利用qPCR技术发现酸微菌科(Acidimicrobiaceae)、地杆菌属(Geobacteraceae spp.)和希瓦氏菌属(Shewanella spp.)的丰度较高,并提出是这3种菌驱动湖泊底泥中的铁氨氧化反应. 3种与铁氨氧化相关性较强的菌属的特征见表1.
虽然铁还原菌广泛存在于厌氧消化反应器[28]、生态环境[29]、湿地[30]、水稻土[31−32]中,但目前被分离纯化出的还比较少,可能是由于污水中的复杂污染物质抑制了IRB的活性,相对污水而言,IRB更适于在自然界中的环境(如土壤)中生存[33].
-
电子穿梭体是一类可通过自身氧化还原介导电子转移的化学物质的统称. 由于固态的铁氧化物不能直接被铁还原菌利用,因此需要借助可溶性的外部电子穿梭体作为电子载体完成Fe(Ⅲ) 的还原(见图1),电子穿梭体可加速微生物向细胞外部进行的电子传递,是铁还原菌厌氧呼吸驱动的铁还原过程的重要参与者. 电子穿梭体对Feammox过程的促进作用主要在两个方面:一是加速铁循环,即加速铁氧化物的还原溶解;二是反作用于微生物,改变菌群的代谢繁殖,加速微生物生长.
腐殖质、硫单质、生物炭是自然界中常见的电子穿梭体[34],腐殖质含有外源电子梭子,可以通过缩小铁氨氧化细菌与不溶性氧化铁之间的距离来促进铁氨氧化的反应[35]. Guan等[36]在红树林沉积物添加石墨烯和腐殖质中醌类化合物(9,10-蒽醌-2-磺酸,AQDS),发现铁氨氧化的产率均有提高,分别提高了31%、56%和0.21 mg·kg−1d−1N、0.25 mg·kg−1d−1N. Yang等[37]取用自大连市某污泥处理厂的污泥(含铁和大量的铵)作为接种污泥,对照组(无添加)、只添加Fe2O3组、AQDS和Fe2O3都添加组的脱氮率分别为46.0%、64.3%和82.6%. AQDS促进了NH
+4 和Fe2O3之间的电子转移,提高了脱氮效率,且AQDS在不同底泥环境中均能加快氮损失. 此外,Zhou等[38]发现添加AQDS和生物炭能显著刺激铁还原菌生长. IRB是一种厌氧自养菌,其比增殖速率和产率都比较低,IRB氧化NH4+的速率并不高,因此完成脱氮过程较慢,而电子穿梭体的加入能促进这一过程,从而提高铁氨氧化污水处理效率. -
铁氨氧化作为一种新型的生物脱氮技术受到学者广泛关注,见表2. 从已有的研究可以看出:(1)在研究Feammox脱氮能力时采用不同接种污泥和合成废水(50—100 mg·L−1NH
+4 ),氨氮的转化率最高能达到80%,但并未全部转化气态氮,因此总氮去除率并不高. 此外,李海晖等[39]进行了铁氨氧化实际污水的研究,提出铁氨氧化可以用于实际生活污水处理,为铁氨氧化的实际应用提供了依据. (2)Fe(Ⅲ)的投加范围差异较大,但根据反应式(2)—(4) Fe(Ⅲ)/NH+4 的摩尔比在3—8之间,大多研究也符合此范围,低于此范围会影响氨氮转换率,过高则容易引起污泥矿化问题. (3)已有不同的类型的Fe(Ⅲ)(如海绵铁、FeCl3、两系水铁矿、Fe2O3、黄铁矿等)应用于Feammox,这可以从中比选出更为经济的铁源,为工程应用节约成本. (4)温度基本都在室温范围,pH由于接种污泥的不同而有所不同,一般在6.5—7.5之间,可能这也是铁氨氧化菌较适宜的生存范围. 有研究表明[40],在中性环境(pH=7)中,Feammox的总氮去除量最大;而氨氮的转化率最高则出现在pH为6.5时. (5)值得注意的是:固定化技术也是用于铁氨氧化菌富集的一种可行方法.铁氨氧化技术目前还未被大规模应用于实际污水处理中,仍有以下问题亟待解决:(1)目前已分离得到的纯种Feammox菌还较少,也缺乏特定的微生物作用机理的研究,目前发现的具有铁氨氧化功能的 A6菌的增殖速度比硝化细菌和反硝化细菌慢,其第一代倍增时间较长(约为6—8d),会增加其培养成本[47]. 因而Feammox机理及其功能菌有必要继续探索,包括污水环境中的Feammox菌的分离纯化及富集方法. (2)Feammox虽然可以提高脱氮率但是其贡献率相对较低(依然以反硝化为主)[12],如何提高Feammox的氮损失贡献率以及控制其产物转变为预期产物都需进一步研究. (3)Feammox需要投加大量Fe(Ⅲ),会增加污水处理的成本且在中性pH环境中有污泥矿化的风险,如何避免及寻找一种廉价的铁源也是接下来需要考虑的问题.
-
铁氨氧化从厌氧氨氧化中发展而来,许多学者认为是二者耦合促进脱氮. Park等[48]在接种厌氧污泥进行铁氨氧化驯化中发现过量NH
+4 -N的被去除,推测是Feammox与Anammox的共同作用. Li等[42]在接种成熟Anammox颗粒污泥的反应器中添加Fe(Ⅲ),首次证明了厌氨氧化体系中存在多个Feammox反应,并且N2可由Feammox将NH+4 氧化为NO−2 ,随后NO−2 与NH+4 进行Anammox产生,但其主要途径是Feammox直接产气. 这证实了Feammox和Anammox反应耦合的可行性以及二者耦合能促进水中氮素向气态氮转化,见图2. 吴悦溪等[43]通过定量分析得出在ASBR反应器中存在多反应协同作用(Feammox、Anammox和NDFO等)并构成其Feammox体系,且Feammox与Anammox除铵贡献率分别为57.7%、42.3%,但对于NDFO的贡献率尚不明确,还有待进一步考究. -
硝酸盐依赖型亚铁氧化(NOx--dependent Fe(Ⅱ) oxidation,NDFO)指NDFO菌能在厌氧环境中利用Fe(Ⅱ)提供电子将NO
−3 或NO−2 还原为气态氮的过程,见反应式(5)和(6) [49−50]. NDFO菌具有营养多样性,既可氧化亚铁获得能量营自养生长,亦可同化有机物营异养生长,取决于硝酸盐的还原产物:当硝酸盐还原产物为NH+4 和NO时,NDFO菌多营异养和混养生长;而当硝酸盐还原产物为NO−2 和N2时,则NDFO菌多营自养和混养生长[51−53]. Straub等[54]在1996年首次分离出3株NDFO菌,该菌能在厌氧环境中进行铁氧化过程以获得固定CO2和合成细胞所需有机物的能量,见式(7).在NDFO过程中,NO
−2 可通过NO−3 的部分反硝化生成,为Fe(Ⅱ)氧化成Fe(Ⅲ)提供连续的电子受体[55],从而促进脱氮. 然而,NDFO和Feammox微生物需要中性pH的环境才能保持高的脱氮活性[42, 56],但在中性pH水环境中,Fe2+/Fe3+会生成铁化合物沉淀(Fe(OH)2和Fe(OH)3的溶度积分别为4.87×10−17、2.64×10−39). 因此,在连续添加Fe3+(或Fe2+)以实现NH+4 -N(或NO−3 -N)转化的过程中,会出现污泥矿化问题,导致单个NDFO(或Feammox)反应器难以长期稳定运行[57],这一问题也会限制相关微生物富集和废水处理技术的应用和推广.NDFO与Feammox工艺的耦合为上述问题提供了解决思路,NDFO过程产生的Fe(Ⅲ)可成为Feammox中NH
+4 氧化过程的电子受体, Feammox过程产生的Fe(Ⅱ)作为NDFO中NO−3 还原过程的电子供体,则可实现铁离子的循环利用有效地降低各反应过程对铁离子的需求量,避免污泥矿化. 有研究表明[58],在厌氧条件下Fe(Ⅱ)能代替有机碳作为电子供体被Feammox产生的NO−2 和NO−3 氧化为Fe(III). 这意味着Fe(III)很有可能在参与Feammox反应后(Fe(Ⅲ)→Fe(Ⅱ))通过NDFO再生(Fe(Ⅱ)→Fe(Ⅲ)),而后进行下一轮Feammox以实现连续除铵和铁元素的循环利用,即Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)循环以催化剂的形式驱动NH+4 -N和NO−3 -N的同时转化,其总氮去除率可达90.1%[55]. Li等[59]接种成熟的Feammox污泥,以含有Fe(Ⅲ)、NH+4 、NO−3 等物质的合成废水为进水,考察了Feammox与NDFO偶联的可行性,结果表明,在NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N和Fe(Ⅲ)同时存在时,Fe(III)氧化NH+4 -N产生的Fe(Ⅱ)浓度(相较仅Feammox产生的Fe(Ⅱ)浓度)显著降低,推测Feammox反应产生的Fe(Ⅱ)与NO−3 -N发生了另一次NDFO反应,将Fe(Ⅱ)转化为Fe(III),导致Fe(Ⅱ)浓度的减少,并证实了NH+4 和NO−3 同步去除的可行性. 因此,Feammox与NDFO的耦合无论是从节约铁资源、解决污泥矿化问题,还是从提高脱氮效率方面都具有良好前景.Feammox反应往往伴随着Anammox、NDFO,三者共同作用促进脱氮,氮素转化途径见图2,但其耦合工艺及其氮素转化的调控措施还需进一步研究. Feammox、反硝化和厌氧氨氧化是目前仅有的三种能够在缺氧土壤环境中将无机氮转化为N2的途径,因此,分析它们在污水处理系统中对氮损失、NH
+4 、NO−2 的贡献具有重要意义. -
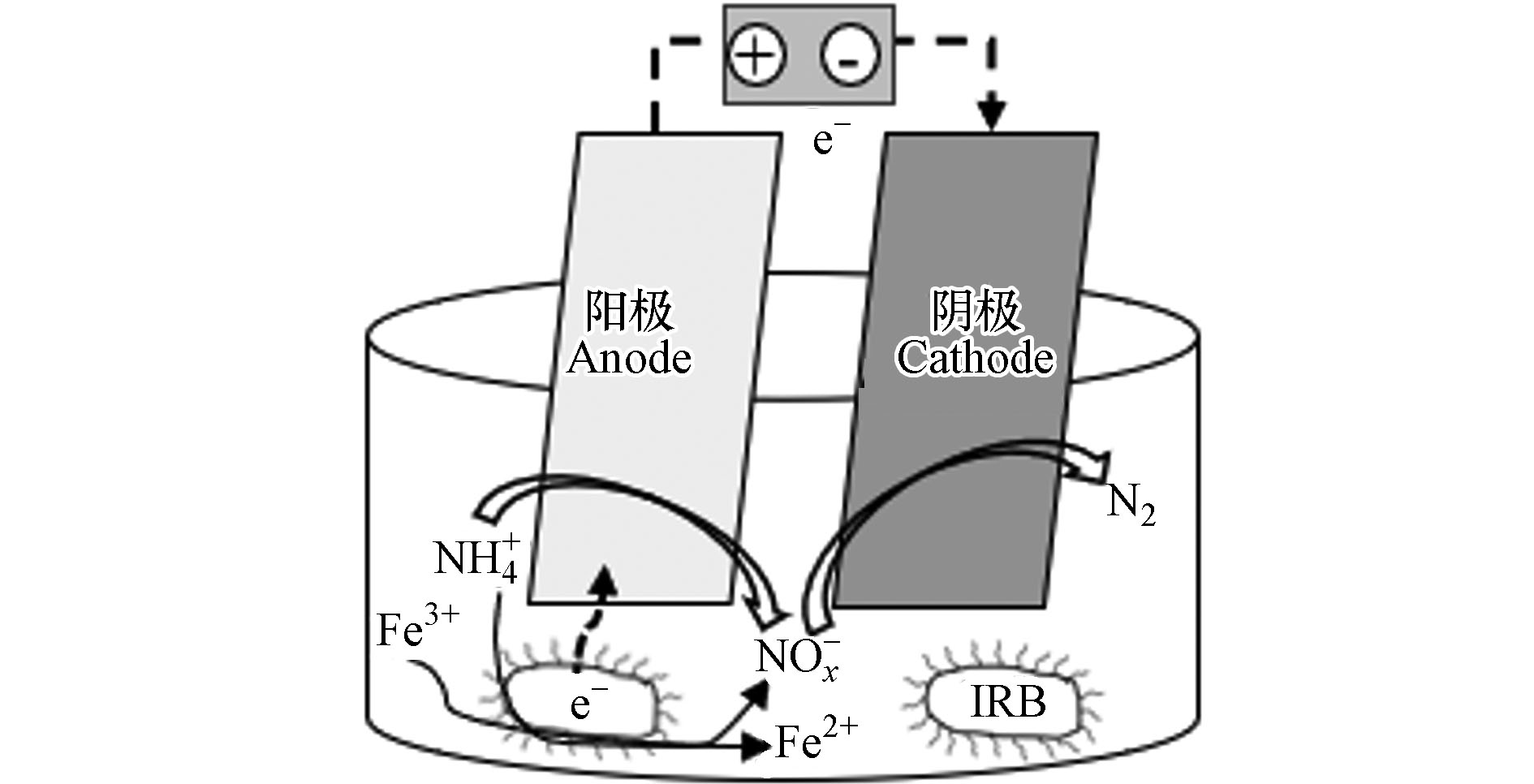
生物脱氮因其工艺成本低、处理效果稳定等优势目前被广泛应用,但在实际运行中反应启动时间长且占地面积大,后期设备维护成本较高. 而化学处理工艺能耗较大,将生物和化学处理工艺二者联合,则可改善生物法及解决电化学法能耗较高等问题. 生物电化学系统(Bioelectrochemical Systems,BESs)共具电化学法与生物法的优势,是二者的一种结合工艺, 且Feammox与BESs的耦合工艺的能耗和运营成本是传统废水处理的1/800[60].
BESs可作为废水脱氮的一种替代技术[61−62],其反应器的基本结构见图3,阴极室中的NO
−3 -N、NO−2 -N等电子受体可接受从阳极产生的电子,从而产生气态氮等还原产物. 电活性细菌(如属于IBR的Geobacter和Shewanella等)可氧化有机物或氢气,并将电子转移到BESs系统中的固体电极上,即经过微生物与电极的转化实现脱氮[63]. Zhu[60]在探究厌氧条件下BESs-Feammox工艺脱氮的可行性时,设置了对照组、BESs组(放置了一对石墨烯刷,加电压)、Fe(Ⅲ)组(投加Fe2O3)和Fe(Ⅲ)-BESs组(Feammox与BESs的耦合),结果表明Fe(Ⅲ)-BESs组脱氮效果最优,总氮去除负荷(TNRR)达(77.74±6.91)g·m−3·d−1N;其余脱氮效果依次为:Fe(Ⅲ)组,TNRR为(60.54±4.93) g·m−3·d−1N、 BES组(32.62±3.45)g·m−3·d−1N)、对照组(TNRR仅为(3.49±0.23)g·m−3·d−1N). 这意味着BESs与Feammox的联用强化了反应器中氮素的去除,其原因可能是在Feammox-BESs中,铁的加入可以促进IRB的富集改善了电化学性能,而Feammox又可推动阳极氨氧化,即Feammox-BESs和微生物的协同作用提高了氨氮的去除效果,在富铵的水体环境中该耦合工艺能实现高效且低成本脱氮. -
铁氨氧化是一种以铁介导的新型绿色环保的自养生物脱氮技术,具有无需曝气成本低、污泥产量小、无需外加有机碳源等优势,适用于低碳氮比废水的处理. 与厌氧氨氧化相比,Feammox具有更广阔的pH应用范围,且IRB也比厌氧氨氧化菌具有更强的生存能力,如A6菌更适合在酸性较强的环境中(厌氧氨氧化细菌则不适应)生长,可以用来处理酸性废水,且广泛存在于自然环境中. 虽然Feammox还没有应用于污水处理厂,但它是一种很有前景的方法:Feammox有可能取代传统的硝化方法,因为传统的硝化方法需要曝气而Feammox无需曝气;同时,Feammox工艺可以在缺氧环境下实现NH4+的氧化,生成NO
−2 和NO−3 可用于后续运行,如可以考虑将Feammox与其他成熟的脱氮技术(比如短程反硝化[64])相结合. 此外,将铁氨氧化与Anammox、NDFO和BESs工艺等氮素转化工艺结合是非常有前景的:如此既可以不同的氮素转化途径的共存使产物得到更充分的利用,还可以避免一些单个工艺产生的问题(如铁含量过量投加导致污泥矿化等),打破单个工艺应用的局限性以及节约成本.未来可以关注以下几个方面:(1)从蛋白质组学及宏基因角度探索Feammox的反应机理,以及对特定微生物作用机理的研究以分离和纯化更多的功能微生物. (2)与氮素转化途经相关的Feammox、Anammox、NDFO、反硝化和BESs等过程之间的相互作用关系及其共存模式的经济效益. (3)选择合适廉价的铁源以及如何实现对组合工艺的运行条件(温度、pH、铁源、Fe3+/NH
+4 浓度等)的控制管理以进一步推动Feammox在实际工程规模应用.
铁氨氧化污水脱氮的应用研究进展
Research advances on the application of nitrogen removal from wastewater via Feammox
-
摘要: 铁氨氧化(Feammox)是一种以廉价、易得的铁作为微生物电子供体的新型自养生物脱氮技术,即Fe(Ⅲ)还原与厌氧氨氧化的结合工艺,拥有成本低廉、无需有机碳源、污泥产量小、无温室气体产生等优势,是污水处理的一种潜在脱氮途径. 本文对铁氨氧化反应的机理、功能菌种的种类和特性及电子穿梭体对其的影响进行了介绍,总结了铁氨氧化在污水环境中的脱氮效果及其与厌氧氨氧化、硝酸盐依赖型亚铁氧化和生物电化学系统的耦合技术,并指出目前铁氨氧化的应用问题及该技术未来的研究方向和重点可能是菌分离纯化、工艺参数控制.Abstract: Feammox is a new autotrophic biological nitrogen removal technology with cheap and easily iron as microbial electron donor, that is, the coupling process of Fe(Ⅲ) reduction and anaerobic ammoxidation, which has the advantages of low cost, no need organic carbon source, low sludge yield and no greenhouse gas production, it is a potential nitrogen removal way for wastewater treatment. In this paper, the mechanism of Feammox, the species and characteristics of functional strains and the effect of electron shuttle on it are introduced. The nitrogen removal effect of Feammox in the sewage and its coupling technology with anammox, nitrate dependent ferrous oxidation and bioelectrochemical systems are summarized. It is pointed out that the current application of Feammox and the future research direction and focus of this technology may be bacteria separation and purification and process parameter control.
-
Key words:
- electron shuttle /
- bioelectrochemical system /
- coupling mechanism /
- application
-
表 1 铁氨氧化反应相关性较强的三种菌属的特征
Table 1. Characteristics of three genera of bacteria with strong relevance to Feammox reaction
铁氨氧化菌Feammox bacteria 特征Characteristics 文献References Geobacteraceae 在厌氧环境中可利用碳源(如乙酸盐、氢等)或电子供体维持自身生长代谢. 首先乙酸等小分子有机酸产生乙酰辅酶A,随后三羧酸循环将其完全氧化成CO2,该过程产生的电子转移至醒池用于进行物质还原. [19, 25] Shewanella 可以利用多种有机酸及氢为碳源或是电子供体以维持自身细胞代谢,是一种兼性厌氧菌. [26] Acidimicrobiaceae sp.A6菌 为革兰氏阳性菌,是一种酸性微生物类菌株(属Acidimicrobiaceae科),其类型为ATCC, PTA -122488(A6). 细胞外形呈杆状,长(1.5±3) µm,宽0.5 µm,是唯一一种利用Fe(Ⅲ)作为电子受体将NH4+氧化为N2的细菌. [23,27] 表 2 基于铁氨氧化的实际污水脱氮研究结果
Table 2. Research results of nitrogen removal based on Feammox in real sewage
环境Environments 有效体积/LEffective volume 接种污泥Inoculation sludge 基质Substrates 温度/℃Temperature pH 脱氮效果Nitrogen removal effects 文献References 厌氧消化反应器 0.7 厌氧消化污泥 5 mmol NH +4 35 6.7—7.8 AR:80%、TNR:71.8% [8] 生物膜反应器 3 实验室纯化培养的铁氨氧化菌液 75 mg·L−1 NH +4 25±3 4.5—5 AR:41.49% [41] 厌氧反应器 0.5 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥 100 mg·L−1NH +4 32±2 6.5 AR:80%,TNR:71.8% [42] ASBR 4 活性污泥 50 mg·L−1 NH +4 32±1 7.4—7.6 AR:53.8% [43] 磁性壳聚糖水凝胶珠的固定化 — — 60 mg·L−1NH +4 25 4.5 AR:53.8% [44] 人工湿地 — — 10 mmol两系水铁矿 20—25 — AR:53.6 [11] 生物膜反应器 6 厌氧消化颗粒污泥 20 mg·L−1NH +4 28±1 — AR:25.0%±7.3% [45] UASB 0.25 厌氧污泥 Fe2O3(粉末)、Fe3O4、Fe(OH)3(胶体)、柠檬酸铁(粉末)和黄铁矿,含铁量各2 mmol·L−1 6.8—7.2 AR:53% [46] 注:AR: ammonium removal rate氨氮去除率, TNR: Total nitrogen removal rate总氮去除率. -
[1] ZHU G, WANG S, ZHOU L, et al. Ubiquitous anaerobic ammonium oxidation in inland waters of China: An overlooked nitrous oxide mitigation process [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 17306. doi: 10.1038/srep17306 [2] 张鸿郭, 陈迪云, 阎佳, 等. 低氨氮垃圾渗滤液中有机污染物厌氧氨氧化处理 [J]. 环境化学, 2009, 28(4): 553-557. ZHANG H G, CHEN D Y, YAN J, et al. Removal effect of organic pollutants in landfill leachate of low ammonium nitrogen by anammox [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2009, 28(4): 553-557(in Chinese).
[3] MIAO Y Y, PENG Y Z, ZHANG L, et al. Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: Effect of influent C/N ratios [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 664-672. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.072 [4] FEROUSI C, LINDHOUD S, BAYMANN F, et al. Iron assimilation and utilization in anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria [J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 37: 129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.03.009 [5] 马艺鸣, 蒋杭城, 刘秀红, 等. 金属元素对厌氧氨氧化生化过程和工艺运行的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(9): 2041-2054. MA Y M, JIANG H C, LIU X H, et al. The effects of metallic elements on anaerobic ammonium Oxidation biochemical process and operation [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(9): 2041-2054(in Chinese).
[6] 段浩楠, 吕宏虹, 王夫美, 等. 生物炭/铁复合材料的制备及其在环境修复中的应用研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(3): 774-790. DUAN H N, LYU H H, WANG F M, et al. Preparation of biochar/iron composite and its application in environmental remediation [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(3): 774-790(in Chinese).
[7] CLÉMENT J C, SHRESTHA J, EHRENFELD J G, et al. Ammonium oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron under anaerobic conditions in wetland soils [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(12): 2323-2328. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.03.027 [8] SAWAYAMA S. Possibility of anoxic ferric ammonium oxidation [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2006, 101(1): 70-72. doi: 10.1263/jbb.101.70 [9] YANG W H, WEBER K A, SILVER W L. Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(8): 538-541. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1530 [10] YAO Z B, YANG L, SONG N, et al. Effect of organic matter derived from algae and macrophyte on anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to ferric iron reduction in the sediment of a shallow freshwater lake [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(21): 25899-25907. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06793-5 [11] SHUAI W T, JAFFÉ P R. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction in constructed wetland mesocosms [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 648: 984-992. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.189 [12] DING B J, ZHANG H, LUO W Q, et al. Nitrogen loss through denitrification, anammox and Feammox in a paddy soil [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 773: 145601. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145601 [13] 杜睿, 彭永臻. 城市污水生物脱氮技术变革: 厌氧氨氧化的研究与实践新进展 [J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2021: 51. DU R, PENG Y Z. Technical revolution of biological nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater: Recent advances in Anammox research and application [J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2021: 51(in Chinese).
[14] ZHU J X, LI T, LIAO C M, et al. A promising destiny for Feammox: From biogeochemical ammonium oxidation to wastewater treatment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 790: 148038. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148038 [15] TAN X, XIE G J, NIE W B, et al. Fe(Ⅲ)-mediated anaerobic ammonium oxidation: A novel microbial nitrogen cycle pathway and potential applications [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021: 1-33. [16] 吴莉娜, 闫志斌, 李进, 等. 铁氨氧化在环境系统中的研究进展及其应用性探究 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(35): 14377-14384. WU L N, YAN Z B, LI J, et al. Research progress and application of ferric ammonia oxidation in environmental system [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(35): 14377-14384(in Chinese).
[17] 钟小娟, 王亚军, 唐家桓, 等. 铁氨氧化: 新型的厌氧氨氧化过程及其生态意义 [J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 47(1): 1-7. ZHONG X J, WANG Y J, TANG J H, et al. Feammox: a novel anammox process and ecological significance [J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 47(1): 1-7(in Chinese).
[18] LI X F, HOU L J, LIU M, et al. Evidence of nitrogen loss from anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with ferric iron reduction in an intertidal wetland [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(19): 11560-11568. [19] 崔志成, 付亮, 赵琦, 等. 铁还原菌在水资源再生与能源转化领域的研究进展 [J]. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(8): 2219-2235. CUI Z C, FU L, ZHAO Q, et al. Iron-reducing bacteria in water regeneration and energy conversion [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2021, 61(8): 2219-2235(in Chinese).
[20] MEJIA J, RODEN E E, GINDER-VOGEL M. Influence of oxygen and nitrate on Fe (hydr)oxide mineral transformation and soil microbial communities during redox cycling [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(7): 3580-3588. [21] HERNANDEZ M E, NEWMAN D K. Extracellular electron transfer [J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences:CMLS, 2001, 58(11): 1562-1571. doi: 10.1007/PL00000796 [22] LOVLEY D R, PHILLIPS E J. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: Organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1988, 54(6): 1472-1480. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1472-1480.1988 [23] HUANG S, JAFFÉ P R. Characterization of incubation experiments and development of an enrichment culture capable of ammonium oxidation under iron-reducing conditions [J]. Biogeosciences, 2015, 12(3): 769-779. doi: 10.5194/bg-12-769-2015 [24] YAO Z B, WANG F, WANG C L, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to ferric iron reduction in the sediment of a eutrophic lake [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(15): 15084-15094. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04907-7 [25] LI D B, LI J, LIU D F, et al. Potential regulates metabolism and extracellular respiration of electroactive Geobacter biofilm [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(5): 961-971. doi: 10.1002/bit.26928 [26] NEALSON K H, SCOTT J. Ecophysiology of the genus Shewanella[M]//The Prokaryotes. New York: Springer New York, 2006: 1133-1151. [27] 张莉红, 李杰, 王亚娥, 等. Feammox: 一种新型自养生物脱氮技术 [J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(01): 391-399. ZHANG L H, LI J, WANG Y E, et al. Feammox: a novel autotrophic nitrogen removal technology [J]. Environmental Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(01): 391-399(in Chinese).
[28] YANG Y F, XIAO C C, YU Q, et al. Using Fe(II)/Fe(III) as catalyst to drive a novel anammox process with no need of anammox bacteria [J]. Water Research, 2021, 189: 116626. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116626 [29] DING B J, CHEN Z H, LI Z K, et al. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Iron reduction from ecosystem habitats in the Taihu Estuary region [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 600-606. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.231 [30] HU X J, WAN X D, TAN W, et al. More is better?Constructed wetlands filled with different amount of Fe oxides showed opposite phosphorus removal performance [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 329: 129749. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129749 [31] DING L J, AN X L, LI S, et al. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction from paddy soils in a chronosequence [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(18): 10641-10647. [32] YI B, WANG H H, ZHANG Q C, et al. Alteration of gaseous nitrogen losses via anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with ferric reduction from paddy soils in Southern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 652: 1139-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.195 [33] 吴彦成, 顾鑫, 朱继涛, 等. 铁氨氧化污水生物脱氮技术的研究进展 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(18): 38-44. WU Y C, GU X, ZHU J T, et al. Research advances of biological nitrogen removal from wastewater via Fe(Ⅲ) reduction coupled to anaerobic ammonium oxidation(feammox)process [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2020, 36(18): 38-44(in Chinese).
[34] 陈甜甜, 王先宝, 张雨笛, 等. 氧化还原介体强化生物反硝化脱氮研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(10): 3199-3206. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020060903 CHEN T T, WANG X B, ZHANG Y D, et al. Enhanced biological denitrification by redox mediators: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(10): 3199-3206(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020060903
[35] QIN Y B, DING B J, LI Z K, et al. Variation of Feammox following ammonium fertilizer migration in a wheat-rice rotation area, Taihu Lake, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.055 [36] GUAN Q S, ZHANG Y L, TAO Y R, et al. Graphene functions as a conductive bridge to promote anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with iron reduction in mangrove sediment slurries [J]. Geoderma, 2019, 352: 181-184. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.05.044 [37] YANG Y F, PENG H, NIU J F, et al. Promoting nitrogen removal during Fe(III) reduction coupled to anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Feammox) by adding anthraquinone-2, 6-disulfonate (AQDS) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 247: 973-979. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.008 [38] ZHOU G W, YANG X R, LI H, et al. Electron shuttles enhance anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron(III) reduction [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(17): 9298-9307. [39] 李海晖, 陈琛, 吴胤, 等. 厌氧铁氨氧化在三类污水中对氨去除的探索 [J]. 净水技术, 2017, 36(9): 14-22. LI H H, CHEN C, WU Y, et al. Ammonium oxidation under iron-reducing conditions in three different wastewater treatment [J]. Water Purification Technology, 2017, 36(9): 14-22(in Chinese).
[40] 陈方敏, 金润, 袁砚, 等. 温度和pH值对铁盐型氨氧化过程氮素转化的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 4289-4293. CHEN F M, JIN R, YUAN Y, et al. Effect of temperature and pH on nitrogen conversion in feammox process [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4289-4293(in Chinese).
[41] 吴胤, 陈琛, 毛小云, 等. 基于Feammox的生物膜反应器性能研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(9): 3353-3362. WU Y, CHEN C, MAO X Y, et al. Study on performance of the feammox biofilm-reactor [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(9): 3353-3362(in Chinese).
[42] LI X, HUANG Y, LIU H W, et al. Simultaneous Fe(III) reduction and ammonia oxidation process in Anammox sludge [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 64: 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.01.002 [43] 吴悦溪, 曾薇, 刘宏, 等. Feammox系统内氮素转化途径的研究 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2265-2272,1935. WU Y X, ZENG W, LIU H, et al. Exploration of nitrogen transformation pathway in Feammox [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2265-2272,1935(in Chinese).
[44] 刘志文. 厌氧铁氨氧化菌的固定化及其处理氨氮废水的研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2018. LIU Z W. Study on the treatment of ammonium in wastewater by immobilized feammox bacteria[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[45] YAO Z B, WANG C H, SONG N, et al. Oxidation of ammonium in aerobic wastewater by anoxic ferric iron-dependent ammonium oxidation (Feammox) in a biofilm reactor [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2020, 173: 197-206. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2020.24822 [46] ZHU T T, LAI W X, ZHANG Y B, et al. Feammox process driven anaerobic ammonium removal of wastewater treatment under supplementing Fe(III) compounds [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 804: 149965. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149965 [47] WAN L Y, LIU H, WANG X Z. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Fe(III) reduction: Discovery, mechanism and application prospects in wastewater treatment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021: 151687. [48] PARK W, NAM Y K, LEE M J, et al. Anaerobic ammonia-oxidation coupled with Fe3+ reduction by an anaerobic culture from a piggery wastewater acclimated to NH4 ^+/Fe3+ medium [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2009, 14(5): 680-685. doi: 10.1007/s12257-009-0026-y [49] ZHANG M, ZHENG P, WANG R, et al. Nitrate-dependent anaerobic ferrous oxidation (NAFO) by denitrifying bacteria: A perspective autotrophic nitrogen pollution control technology [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 117: 604-609. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.029 [50] 张萌, 郑平, 季军远. 厌氧铁氧化菌研究进展 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(8): 2377-2382. ZHANG M, ZHENG P, JI J Y. Research advances on anaerobic ferrous-oxidizing microorganisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(8): 2377-2382(in Chinese).
[51] 范梦雨. 硝酸盐还原亚铁氧化细菌的筛选及反硝化效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020. FAN M Y. Isolation and denitrification efficacy of A new nitrate-dependent Fe(Ⅱ) oxidation bacterium[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[52] JAMIESON J, PROMMER H, KAKSONEN A H, et al. Identifying and quantifying the intermediate processes during nitrate-dependent iron(II) oxidation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(10): 5771-5781. [53] JOKAI K, NAKAMURA T, OKABE S, et al. Simultaneous removal of nitrate and heavy metals in a continuous flow nitrate-dependent ferrous iron oxidation (NDFO) bioreactor [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 262: 127838. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127838 [54] STRAUB K L, BENZ M, SCHINK B, et al. Anaerobic, nitrate-dependent microbial oxidation of ferrous iron [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(4): 1458-1460. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.4.1458-1460.1996 [55] YANG Y F, XIAO C C, LU J H, et al. Fe(III)/Fe(II) forwarding a new anammox-like process to remove high-concentration ammonium using nitrate as terminal electron acceptor [J]. Water Research, 2020, 172: 115528. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115528 [56] LI X, YUAN Y, HUANG Y. Enhancing the nitrogen removal efficiency of a new autotrophic biological nitrogen-removal process based on the iron cycle: Feasibility, progress, and existing problems [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 317: 128499. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128499 [57] 姚海楠, 张立秋, 李淑更, 等. 厌氧铁氨氧化处理模拟垃圾渗滤液的影响因素研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(9): 2953-2963. YAO H N, ZHANG L Q, LI S G, et al. Study on the factors affecting simulated landfill leachate treatment by anaerobic ferric ammonia oxidation [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(9): 2953-2963(in Chinese).
[58] CARLSON H K, CLARK I C, BLAZEWICZ S J, et al. Fe(II) oxidation is an innate capability of nitrate-reducing bacteria that involves abiotic and biotic reactions [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2013, 195(14): 3260-3268. doi: 10.1128/JB.00058-13 [59] LI X, YUAN Y, HUANG Y, et al. A novel method of simultaneous NH4+ and NO3− removal using Fe cycling as a catalyst: Feammox coupled with NAFO [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 631/632: 153-157. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.018 [60] ZHU T T, ZHANG Y B, LIU Y W, et al. Electrostimulation enhanced ammonium removal during Fe(III) reduction coupled with anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Feammox) process [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 751: 141703. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141703 [61] WATANABE T, HASHIMOTO S, KURODA M. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a single reactor using bio-electrochemical process [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 46(4/5): 163-169. [62] SHI L, DONG H, REGUERA G, et al. Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(10): 651-662. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.93 [63] 杨慧敏, 何绪文, 何咏. 电化学氧化法处理微污染水中的氮 [J]. 环境化学, 2010, 29(3): 491-495. YANG H M, HE X W, HE Y. Removal of nitrogen in the micro-polluted water by electrochemicall oxidation process [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2010, 29(3): 491-495(in Chinese).
[64] 王建辉, 游庆国, 申渝, 等. 短程反硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合脱氮工艺影响因素与调控研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1216-1231. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020091302 WANG J H, YOU Q G, SHEN Y, et al. Research advances on influence factors and regulation of Partial denitrification and Anammox coupling denitrification process [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1216-1231(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020091302
-




 下载:
下载: