-
相较于传统硝化-反硝化生物脱氮工艺,厌氧氨氧化技术因其高效低耗的显著优势而受到研究者的广泛关注[1]。在实际应用中,厌氧氨氧化技术常常与亚硝化技术耦合,共同实现污水中氮素的去除,称为部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺(partial nitrification-anammox,PNA),也叫自养脱氮工艺。根据亚硝化与厌氧氨氧化2个反应是否在同一个反应器中发生,能将PNA工艺分为一段式和两段式。从经济性和操作方便来看,一段式PNA工艺更具优势,但工艺稳定运行的控制也更为困难。目前,PNA工艺已经成功应用于高氨氮污水处理(侧流污泥消化液、垃圾渗滤液等)[2-3],但是对于低氨氮浓度的主流城市污水,可以普及的工程化应用尚为空白。特别对于曝气量、溶解氧等环境条件的变化,会导致工艺性能失稳、脱氮效能下降,严重影响了该工艺的工程化推广,有效的恢复策略亟待研究。
在一段式PNA工艺中,曝气操作是控制工艺性能稳定性的关键因素[4],曝气速率能直接影响体系内溶解氧浓度的大小。亚硝化过程需要好氧条件,而厌氧氨氧化需要较为严格的厌氧环境,这给一段式PNA工艺高效脱氮性能的发挥带来了困难。曝气量较低,不利于亚硝化反应,同时也难以为厌氧氨氧化过程提供充足的反应基质;而曝气量过高,抑制了厌氧氨氧化反应活性,也会导致亚硝酸盐氧化菌的大量增殖,使得性能恶化、体系崩溃[5]。尽管通过曝气操作维持PNA工艺稳定性的相关研究已有报道[6],但是很少关注失稳后工艺性能恢复的调控策略,特别是仅通过曝气调控原位恢复工艺脱氮性能。
本研究采用气升式内循环反应器构建一段式PNA工艺系统,通过曝气调控考察反应器脱氮性能的变化,解析自养脱氮污泥变化特征及反应活性,探究过量曝气失稳后PNA工艺性能恢复的可行性及调控策略,解析恢复过程中功能微生物丰度变化,以期为厌氧氨氧化工艺在主流条件下应用提供理论指导和技术支持。
-
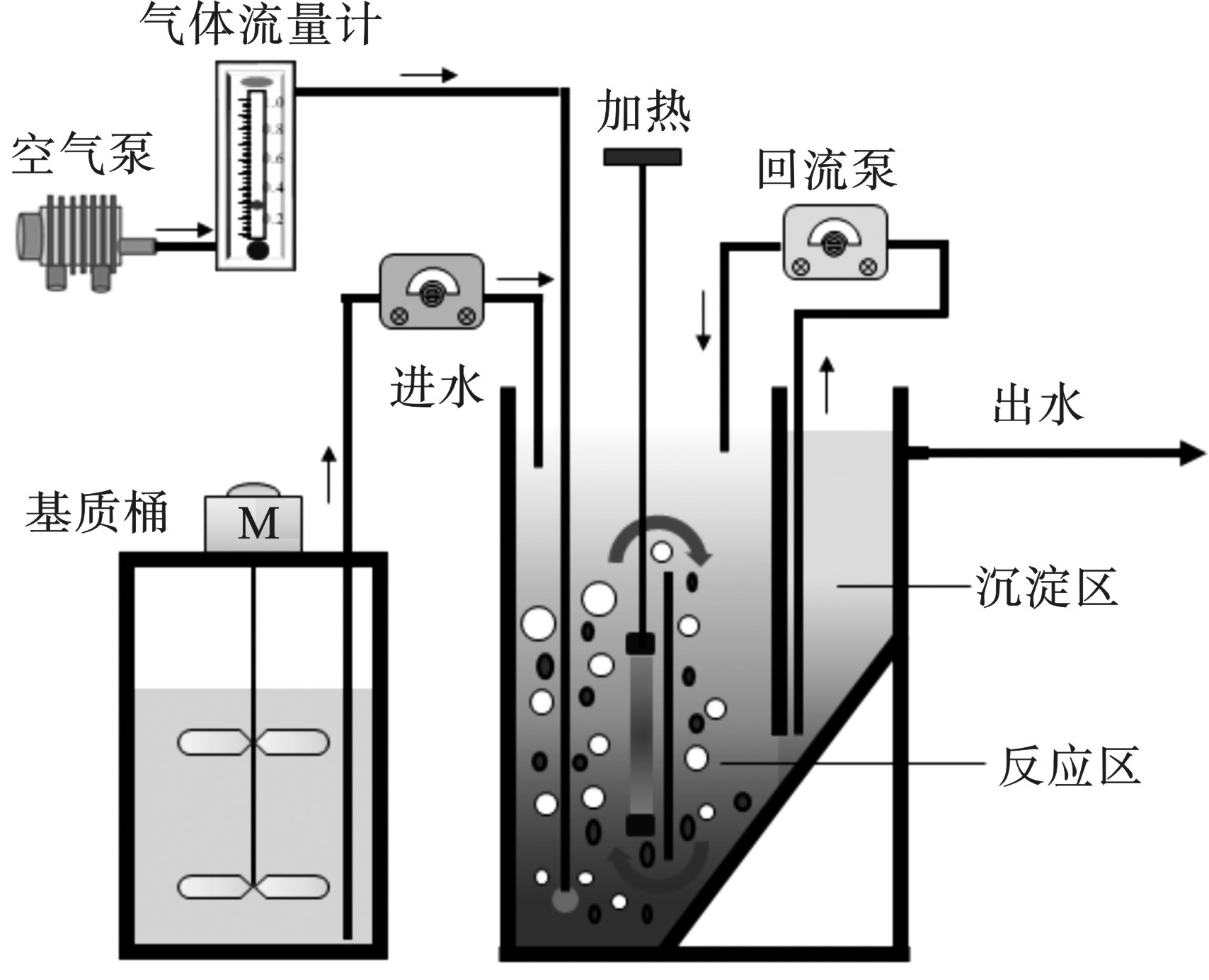
一段式PNA工艺系统,见图1。
主反应器由有机玻璃制成,总有效体积为2 L,其中反应区容积为1.6 L,沉淀区容积为0.4 L。空气泵为系统提供曝气,通过气体流量计调控曝气速率,曝气位点设置于反应区底部。利用进水泵将基质桶中的模拟废水输送至反应区,回流泵用于回流沉淀区底部的污泥。整个系统的混合液随着气泡的提升而在反应区形成循环。系统温度维持在25 ℃,进水pH值维持在7.8~8.2。
-
接种污泥取自实验室已稳定运行的一段式PNA反应器混合絮体污泥,VSS为0.67 g/L,TS为1.35 g/L,总氮去除率达到0.47 kg N/m3·d。
实验用水为人工配置的低氨氮废水[4],以NH4HCO3为唯一氮源,以KH2PO4为磷源,不含有机碳源。具体废水组成如下:NH4HCO3 50 mg/L,KH2PO4 41 mg/L,CaCl2 36 mg/L,MgCl2 40 mg/L, ZnSO4 0.215 mg/L,NiCl2 0.095 mg/L,NaSeO4 0.21 mg/L,MnCl2 0.495 mg/L,H3BO3 0.007 mg/L,Na2·EDTA 8.304 mg/L, CuSO4 0.125 mg/L,CoCl2 0.12 mg/L,NaMo4 0.11 mg/L,FeSO4 5 mg/L。
-
实验共连续运行160 d,整个过程可以分为4个阶段:阶段Ⅰ(启动及稳定阶段,1~25 d),阶段Ⅱ(失稳阶段,26~40 d),阶段Ⅲ(恢复阶段,41~134 d),阶段Ⅳ(再稳定阶段,135~160 d)。其中,失稳阶段人为地增大曝气速率,造成工艺脱氮性能恶化。各阶段的操作条件,见表1。分别在第20、40和155 d,采集污泥样品并测定污泥浓度,提取细胞外聚合物测定蛋白质含量。同时开展批次实验测定污泥的氨氧化活性(不含厌氧氨氧化)、亚硝酸盐氧化活性、厌氧氨氧化活性和反硝化活性,并送样检测微生物群落结构及多样性。
-
采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定氨氮浓度;采用离子色谱法测定亚硝氮、硝氮浓度;利用pH计原位测定反应区的pH;溶解氧浓度由便携式溶解氧仪原位测定;称量法测定污泥的VSS和TS;采用热碱水解结合高速离心和涡旋振荡的方法提取胞外聚合物中的蛋白质 [5],蛋白质浓度的测定采用考马斯亮蓝法;污泥活性的测定参考CHEN et al[4]的研究;氮反应速率的计算参考先前的研究报道[5];定期采集污泥样品并送检,在上海美吉生物公司云平台分析高通量测序结果。
-
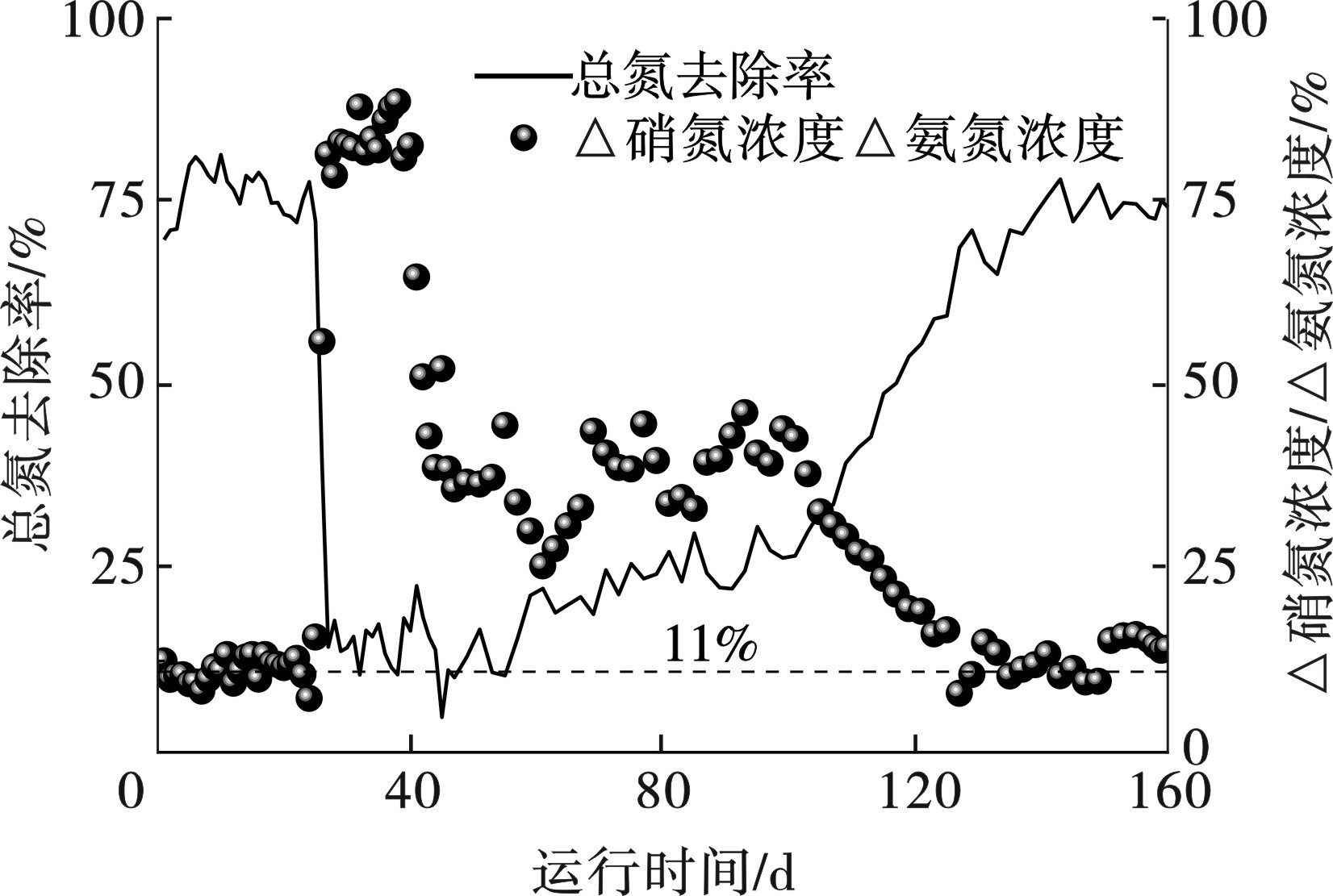
整个实验过程中,各阶段进出水氮浓度,见图2。
由于实验用泥直接取自运行稳定的PNA反应器,所以阶段Ⅰ中工艺的脱氮性能在初始就维持较高水平。在进水总氮浓度为(50±1.81) mg/L、曝气速率为0.20 L/min的条件下,出水氨氮、亚硝氮和硝氮浓度分别为5.69、0.24和4.79 mg/L。在阶段Ⅱ中,为了探究工艺性能恢复的可行性,人为的增大曝气速率、造成高溶解氧状态,破坏工艺稳定的运行性能。当曝气速率由0.20 升至1.00 L/min,出水氨氮和亚硝氮浓度迅速减至0.85和0.02 mg/L,硝氮浓度急剧增至40.94 mg/L。结果表明,过量的曝气造成的高溶解氧环境使得体系内氨氮和亚硝氮氧化完全,同时破坏了厌氧氨氧化所需的厌氧条件,导致出水中硝氮积累、体系失稳性能恶化。
增大曝气后总氮去除率由78.4%降至14.8%,这也表明工艺的脱氮性能失稳恶化。出水中硝氮浓度的生成量与氨氮浓度变化之比是衡量自养脱氮反应是否占主导的一个重要指标,△硝氮浓度/△氨氮浓度的比值越接近11%,表明反应体系中厌氧氨氧化脱氮过程为主要脱氮途径[7]。而在过量曝气条件下,△硝氮浓度/△氨氮浓度的比值也由11.3%增加至84.0%,说明亚硝化过程失稳、厌氧氨氧化反应完全被破坏,亚硝酸盐被氧化成硝酸盐,出水中硝氮积累,见图3。
在阶段Ⅲ中,通过调控曝气速率,探讨主流条件下工艺性能恢复的可行性。曝气速率由1.00降低至0.10 L/min,而后逐级增加至0.30 L/min,脱氮性能也逐渐实现了恢复。阶段Ⅳ的再稳定过程中,出水中氨氮、亚硝氮和硝氮浓度分别达到4.99、1.58和6.90 mg/L,总氮去除率也恢复至74.8%。结果表明,通过适宜的曝气调控,可以实现主流条件下失稳后PNA工艺的性能恢复。
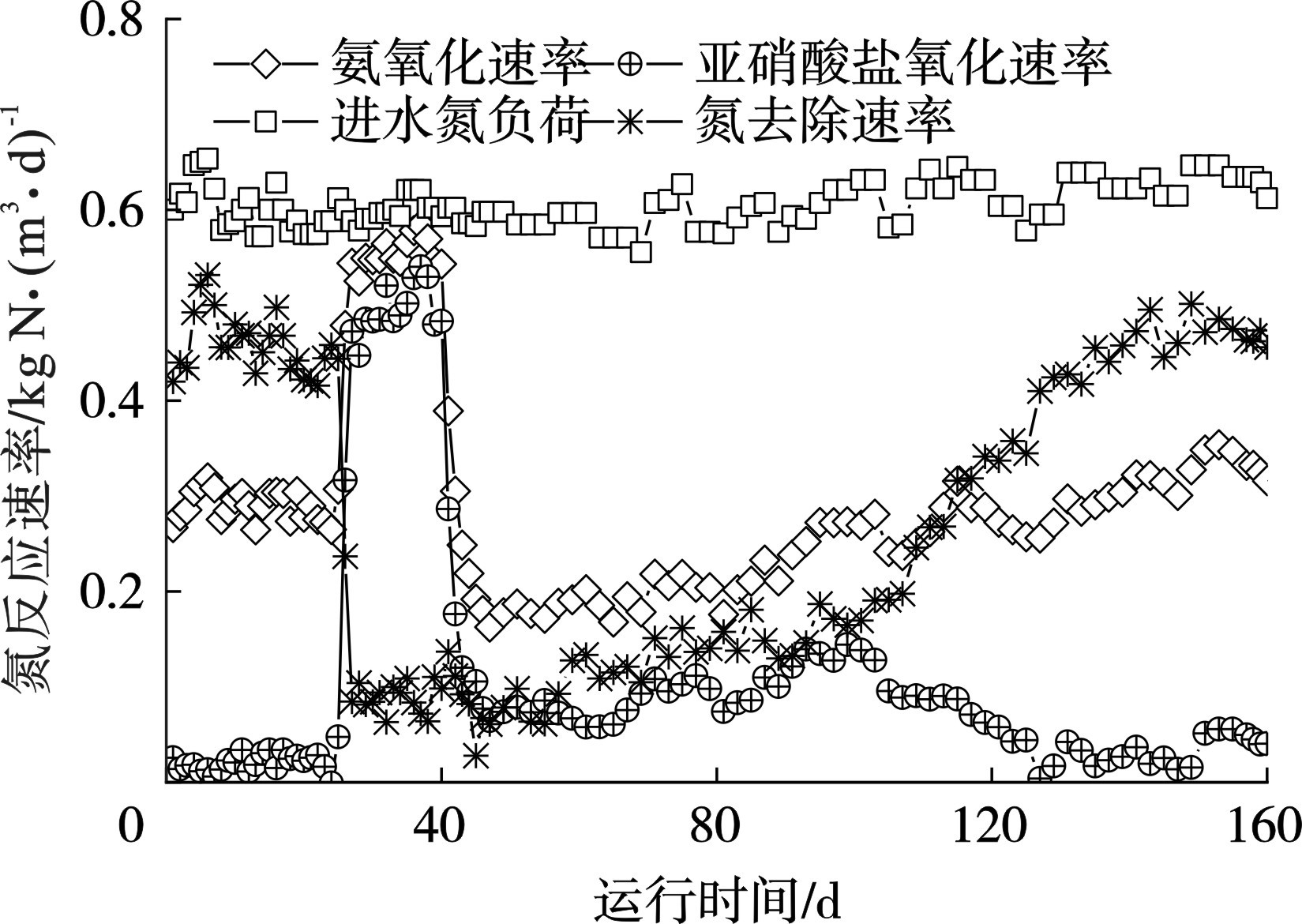
进一步计算分析反应体系中的氮反应速率(图4),进水氮负荷一直维持在0.60 kg N/m3·d,氮去除速率初始阶段稳定在0.42 kg N/m3·d。随着过量曝气的实施,氨氧化速率由0.28 增至0.56 kg N/m3·d,亚硝酸盐氧化速率由0.02增加至0.51 kg N/m3·d。这表明,过量曝气同步增强了氨氧化反应和亚硝酸盐氧化反应,使得亚硝化过程失稳。因此,氮去除速率也减少至0.07 kg N/m3·d。恢复阶段通过曝气速率的调控,氨氧化速率随着曝气量的增大而逐步提升,亚硝酸盐氧化速率被抑制,氮去除速率逐步恢复至0.46 kg N/m3·d。在性能恢复的过程中,曝气速率是重要的调控要素,曝气量较低无法促进氨氧化过程,也间接的抑制了后续的厌氧氨氧化反应。所以,曝气调控要结合出水中氨氮浓度综合考虑。实验结果表明,利用氨氧化反应和亚硝酸盐氧化反应的需氧差异,调控适宜的曝气能够强化氨氧化反应、控制亚硝酸盐氧化反应,有效地提升氮去除性能。
-
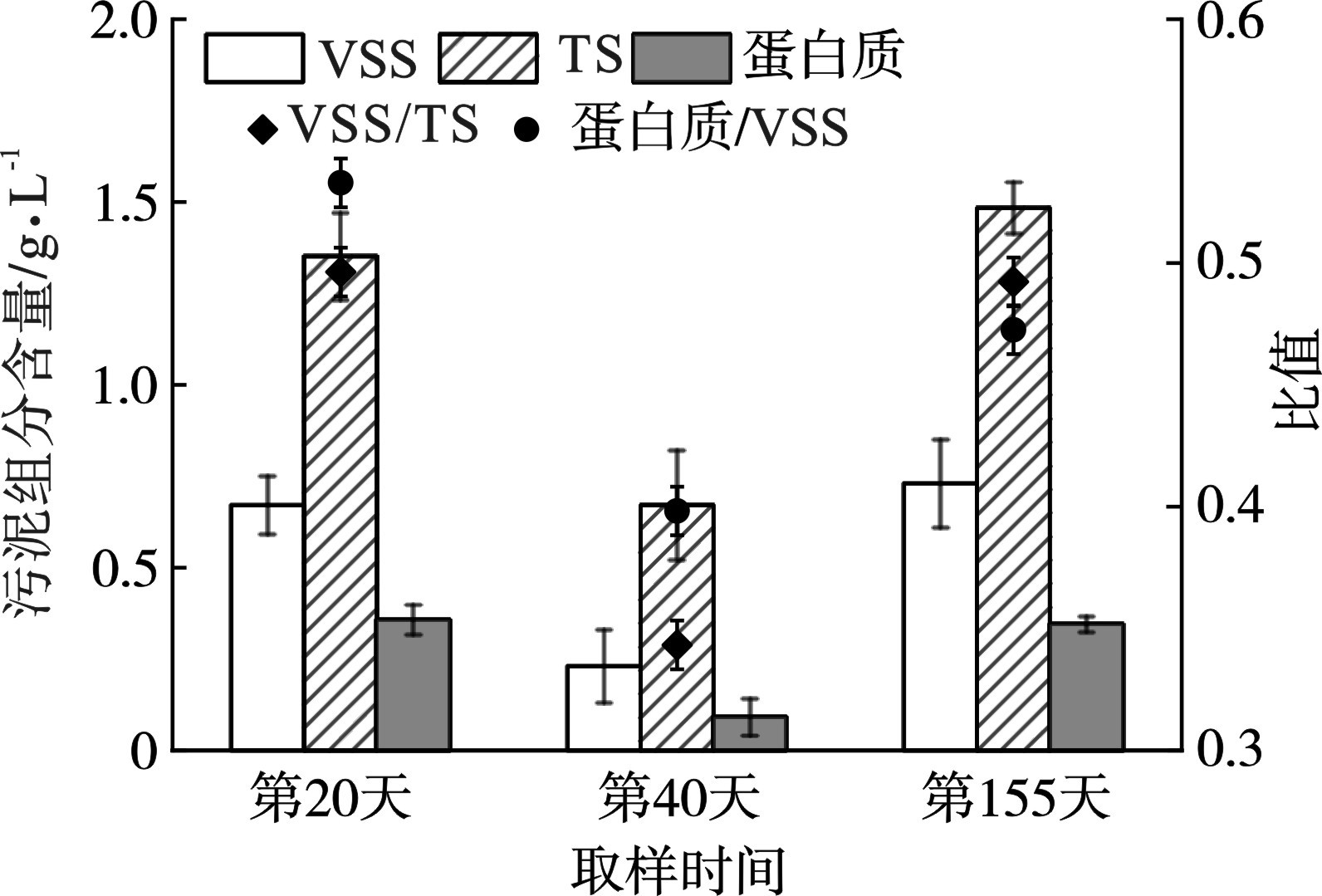
厌氧氨氧化菌具有较长的倍增周期[8],所以PNA工艺常常因为生物量流失而造成功能菌丰度不足,从而使得脱氮性能下降。实验各阶段污泥的组成及含量,见图5。
在过量曝气作用下,VSS由稳定阶段的0.67降至0.23 g/L,VSS/TS也由0.49减至0.34。这表明,过量曝气加速了生物量流失,降低了污泥浓度,也是性能下降的主要原因。此外,蛋白质含量和占比也明显下降。胞外聚合物中较高的蛋白质含量有利于颗粒化的形成,从而提高生物量的持留能力[9],所以蛋白质含量的降低也与污泥浓度变化相一致。随着恢复阶段的曝气调控,VSS和TS恢复至0.73和1.48 g/L,蛋白质含量也增至0.35 g/L。结果表明,有效的曝气调控可以强化生物量的持留,提高污泥浓度,这对于工艺脱氮性能的恢复有积极作用。
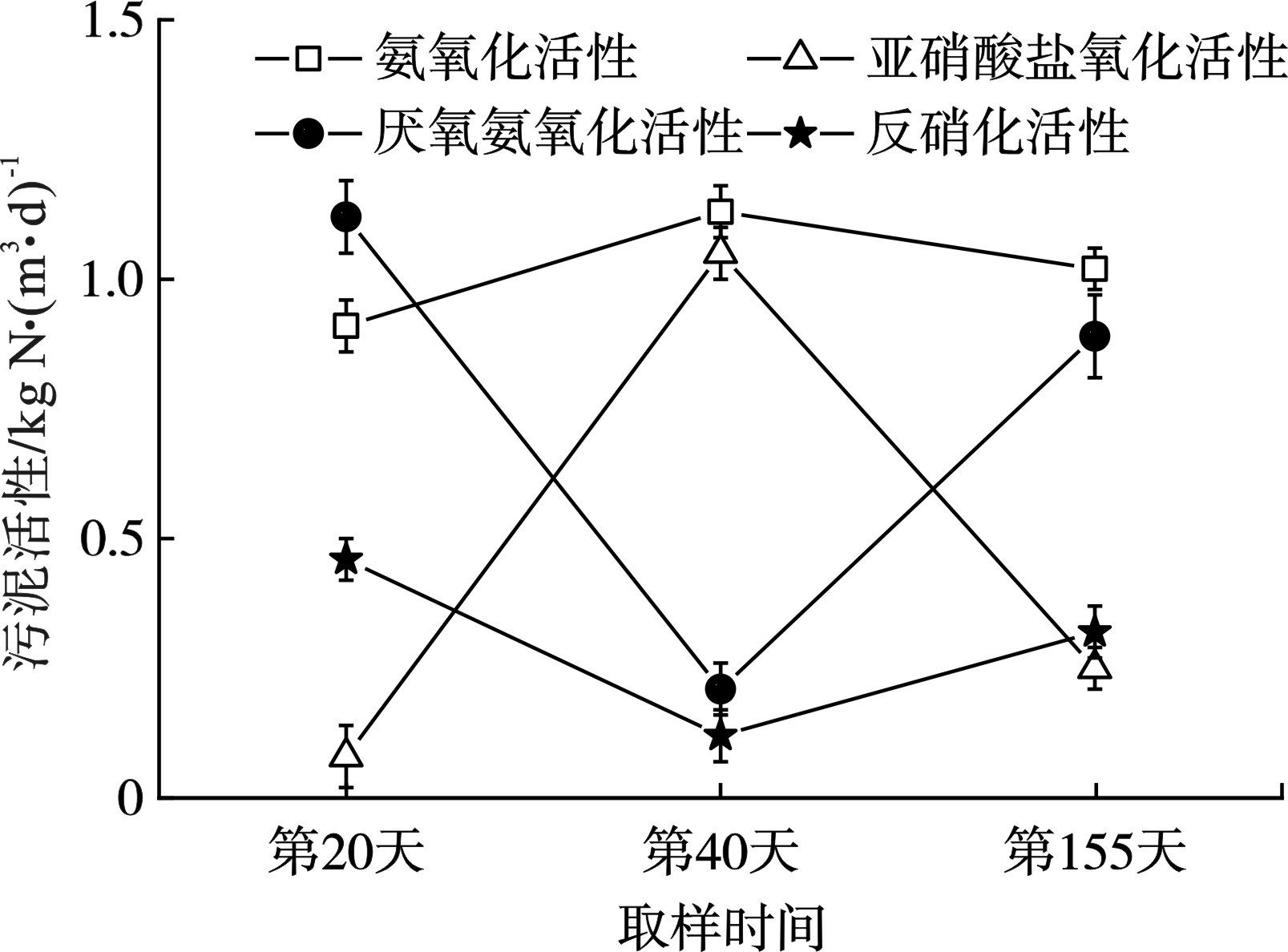
工艺的脱氮性能与污泥活性密切相关,由污泥浓度和活性共同决定[10-11],各阶段污泥活性变化,见图6。
在阶段Ⅱ中,过量曝气和高溶解氧浓度极大地促进了硝化反应,同时抑制了厌氧氨氧化反应和反硝化活性。氨氧化活性和亚硝酸盐氧化活性由0.91和0.08 kg N/m3·d增长至1.13和1.05 kg N/m3·d;而厌氧氨氧化活性和反硝化活性降低至0.21和0.12 kg N/m3·d。这也与2.1节脱氮性能的变化相一致,污泥活性的变化影响了工艺的宏观脱氮性能。随着恢复阶段的曝气调控,氨氧化活性略微下降,厌氧氨氧化活性恢复至0.89 kg N/m3·d,而亚硝酸盐氧化活性得到了抑制。结果表明,适宜曝气调控不仅能够提高污泥浓度,同时可以强化功能反应的活性;氨氧化反应活跃、厌氧氨氧化反应主导和亚硝酸盐氧化反应抑制是主流PNA体系脱氮性能提升和恢复的关键。
-
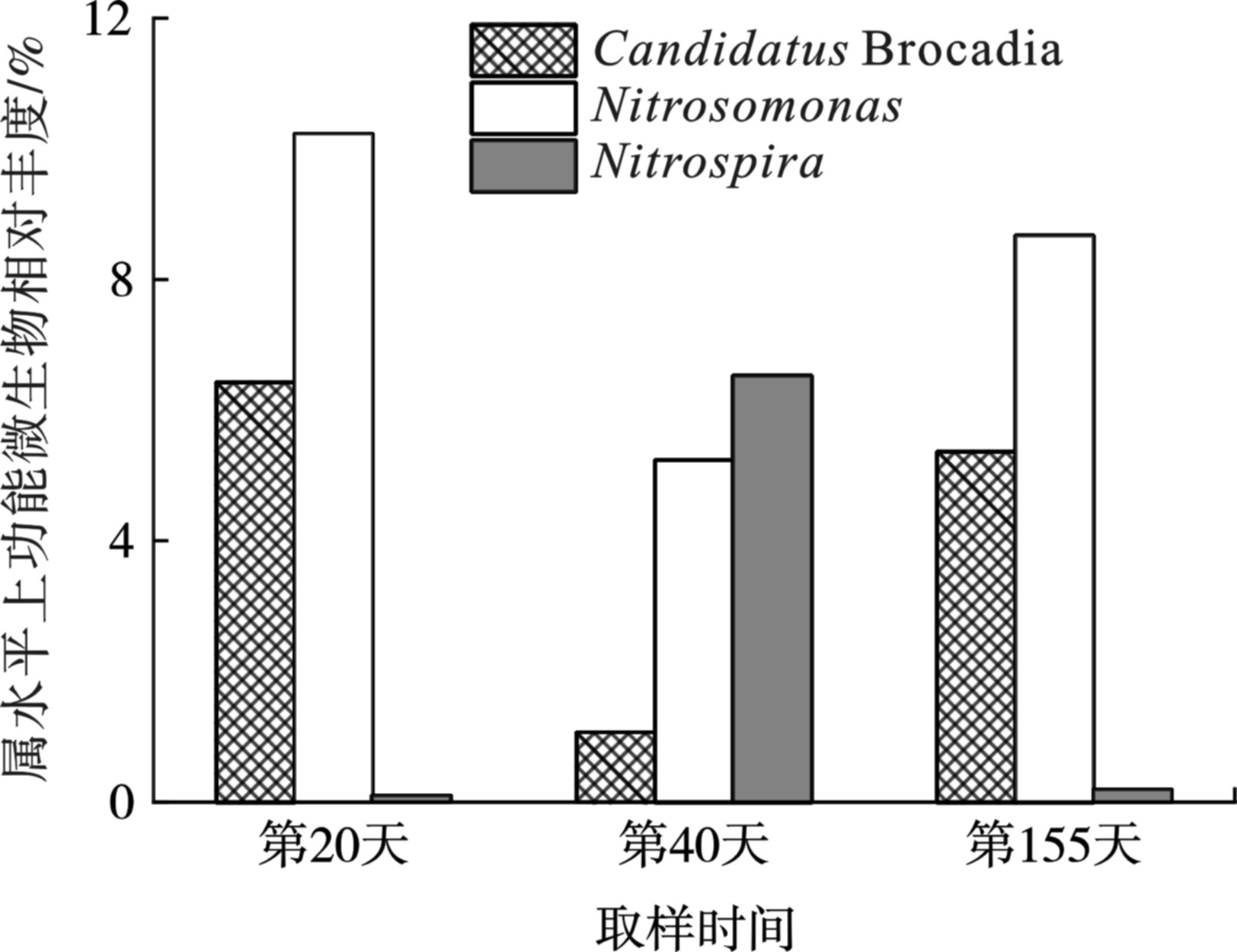
氨氧化菌和厌氧氨氧化菌是PNA工艺中的脱氮功能微生物,亚硝酸盐氧化菌属于干扰菌群[1]。各阶段污泥样品中功能微生物在属水平上的相对丰度,见图7。
整个过程中,检出的厌氧氨氧化菌为Candidatus Brocadia属,氨氧化菌为Nitrosomonas属,亚硝酸盐氧化菌为Nitrospira属。当工艺启动达到稳定阶段时,Candidatus Brocadia属和Nitrosomonas属的相对丰度达到6.4%和10.2%,Nitrospira属几乎未检出。在阶段Ⅱ中,过量曝气和高溶解氧抑制了厌氧氨氧化菌的生长(1.1%),使得Nitrospira属过度增殖(6.5%),这也是性能失稳后出水中出现硝氮积累的原因。但随着恢复操作的实施,Candidatus Brocadia属和Nitrosomonas属的相对丰度恢复至5.3%和8.7%,Nitrospira属的相对丰度减少至0.2%。结果表明,适宜的曝气调控可以抑制亚硝酸盐氧化菌的生长,促进氨氧化菌和厌氧氨氧化菌的富集,能够优化主流PNA体系中功能菌群结构,从而使得工艺性能得到改善甚至恢复。
-
针对脱氮性能失稳的PNA工艺,通过适宜的原位曝气调控,实现了主流条件下PNA工艺失稳后性能的恢复。在进水氮浓度为(50±1.81) mg/L、曝气速率为0.30 L/min的条件下,总氮去除率达到74.8%,氮去除速率达到0.46 kg N/m3·d。
适宜的曝气调控能够有效地提升污泥浓度和促进颗粒化的形成,使得系统内恢复并维持较高的生物量;此外,曝气调控能够强化氨氧化反应和厌氧氨氧化反应、提高功能菌群的丰度水平,抑制亚硝酸盐氧化菌的过度增殖。
本研究验证了曝气调控原位恢复主流PNA工艺脱氮性能的可行性,适宜的曝气调控是PNA工艺性能恢复和提升反应速率及污泥丰度的关键要素,这为厌氧氨氧化工艺在主流条件下的应用提供了策略。
曝气调控恢复主流自养脱氮性能及脱氮菌群特性研究
Recovery performance of mainstream autotrophic nitrogen removal and characteristics of functional microbes under aeration control
-
摘要: 针对主流条件下部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化(PNA)工艺难以维持长期稳定运行的问题,采用气升式内循环反应器构建一段式反应系统,探究高溶解氧浓度导致工艺脱氮性能失稳后,原位恢复工艺脱氮性能的可行性及调控策略。结果表明,仅通过适宜的曝气调控,主流PNA工艺的脱氮性能可以实现原位恢复。在进水氨氮浓度为(50±1.81) mg/L、曝气速率为0.30 L/min的条件下,工艺的氮去除率可恢复至74.8%,氮去除速率达0.46 kg N/m3·d。此外,曝气调控能够提高胞外聚合物中蛋白质的含量,从而提升污泥浓度和促进污泥颗粒化;氨氧化活性和厌氧氨氧化活性得到了增强,亚硝酸盐氧化活性得到了有效的控制。在恢复策略的实施下,Candidatus Brocadia属和Nitrosomonas属的相对丰度恢复至5.3%和8.7%,Nitrospira属的相对丰度减少至0.2%。研究结果为厌氧氨氧化技术在主流条件下的应用提供理论指导和技术支持。
-
关键词:
- 部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化 /
- 主流 /
- 性能恢复 /
- 曝气调控 /
- 氮去除
Abstract: To solve the stability of partial nitrification-anammox process (PNA) under mainstream conditions, a one-stage PNA system was constructed by an airlift internal circulation reactor. The feasibility of the in-situ recovery and the control strategy of PNA process were explored under an instability condition of nitrogen removal by a high concentration dissolved oxygen. The results showed that the performance of the PNA process could be recovered under an appropriate aeration control. The nitrogen removal efficiency reached 74.8% and the nitrogen removal rate reached 0.46 kg N/m3·d with the influent concentration of (50 ±1.81) mg/L and the aeration rate of 0.30 L/min. Furthermore, aeration control could improve the protein contents and enhance the sludge concentration. It also promoted the sludge granulation. The specific activity of ammonia oxidation and anammox were enhanced, and the specific activity of nitrite oxidation was inhibited. With the implementation of recovery strategy, the relative abundance of Candidatus Brocadia and Nitrosomonas returned to 5.3% and 8.7%, and the Nitrospira abundance decreased to 0.2%. This study provided a scientific basis for the application of the mainstream anammox process.-
Key words:
- partial nitrification-anammox /
- mainstream /
- performance recovery /
- aeration control /
- nitrogen removal
-
表 1 工艺操作条件
阶段 t/d 曝气速率/L·min−1 溶解氧/mg·L−1 进水氨氮/mg·L−1 进水氮负荷/kg N·(m3·d)−1 Ⅰ 1~25 0.20 0.10~0.25 50±1.81 0.60±0.02 Ⅱ 26~40 1.00 0.85~1.05 Ⅲ 41~64 0.10 0.05~0.10 65~110 0.20 0.10~0.15 111~134 0.30 0.25~0.30 Ⅳ 135~160 0.30 0.25~0.30 -
[1] 夏琼琼, 张文安, 王雅雄, 等. 污水处理厌氧氨氧化工艺研究与应用进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(5): 1 − 5. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2019.05.001 [2] 韩晓宇, 黄京, 刘新春, 等. 厌氧氨氧化技术处理热水解消化液的实验研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(7): 2542 − 2549. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.07.016 [3] 赵晴, 刘梦莹, 吕慧, 等. 耦合短程硝化反硝化的垃圾渗滤液厌氧氨氧化处理系统构建及微生物群落分析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4195 − 4201. [4] CHEN H, WANG H, YU G, et al. Key factors governing the performance and microbial community of one-stage partial nitritation and anammox system with bio-carriers and airlift circulation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 324: 124668. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124668 [5] CHEN H, WANG H, CHEN R, et al. Unveiling performance stability and its recovery mechanisms of one-stage partial nitritation-anammox process with airlift enhanced micro-granules[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 330: 124961. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124961 [6] 刘珂, 吴莎, 陈婧, 等. 新型单级强化自养脱氮系统关键因子优化研究[J]. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 19(2): 28 − 36. [7] CHEN R, JI J, CHEN Y, et al. Successful operation performance and syntrophic micro-granule in partial nitritation and anammox reactor treating low-strength ammonia wastewater[J]. Water Research, 2019, 155: 288 − 299. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.041 [8] 李权, 王少坡, 李博洋, 等. 厌氧氨氧化菌种类及其与各类功能菌在ANAMMOX系统内的协作[J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(7): 10 − 16. [9] LI X Y, YANG S F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(5): 1022 − 1030. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.037 [10] 宋培圆, 张亮, 杨慎华, 等. 生物膜强化推流式颗粒污泥自养脱氮反应器启动[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(6): 2595 − 2601. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.06.012 [11] 赵婉情, 李柏林, 王伟, 等. 颗粒-絮状污泥耦合单级自养脱氮系统的脱氮性能分析[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(9): 43 − 47. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202009007 -





 下载:
下载: