-
黄河是中华民族的发源地,中华文明的孕育者[1]。习近平总书记指出,“保护黄河是事关中华民族伟大复兴和永续发展的千秋大计”。黄河流域环境稳定向好发展事关中华民族伟大复兴,保护黄河生态环境为基本国策[2]。目前有关黄河流域环境领域的研究多以文献综述为主,但文献综述存在可视化程度低、时间跨度短和覆盖范围小等问题,难以准确把握所研究领域知识网络。因此,为弥补传统文献综述局限性,明确黄河流域环境方向研究进展,本文采用文献计量学的方法进行文献分析,以达到全面直观了解该领域研究脉络及热点动态的目的,以期为黄河流域环境研究和污染防控提供数据参考,为《黄河流域生态环境保护规划》提供理论依据,配合黄河保护法立法工作。
文献计量学集数学、统计学和文献学为一体,可客观反映研究领域发展特点[3]。2004年,美国德雷塞尔大学英籍华裔陈超美教授基于Java环境,开发Citespace可视化分析软件。该软件可对科学研究的发展规律和分布情况准确全面地可视化描述,目前将此类方法分析所得可视化图形称为“科学知识图谱”[4]。张胤杰等[5]利用Citespace软件对Web of Science文献检索平台中检索数据进行处理,探明该领域研究演变发展,明晰当前研究进展和热点前沿并提出未来研究方向;何思笑等[6]运用CiteSpace软件对我国城市绿地健康效应相关研究进行分析。然而遗憾的是目前运用 Citespace可视化分析软件探讨黄河流域环境领域的研究尚未报道,且基于文献及发文量调查,2001年前该领域研究较为零星松散,研究价值较低,2001~2020年黄河流域环境领域急速发展,形成较为完整理论体系,故本研究利用Citespace软件对Web of Science核心数据库中2001~2020年黄河流域环境方向研究论文与综述进行可视化分析,全面分析该领域研究热点及趋势,旨在为为黄河流域污染治理提供数据参考。
-
本文使用Citespace进行文献数据挖掘和可视化分析。以Web of Science核心数据库为文献检索数据源,以TS=("Yellow River" AND environment)、时间2001~2020年为检索条件进行高级检索,并将其文献类型精炼为文章和综述,2020年7月23日检索所得文献798篇。经Citespace软件去重、设置参数后,对黄河流域环境研究进行科学计量审查与分析,再经可视化分析对已有研究结果进行总结。
-
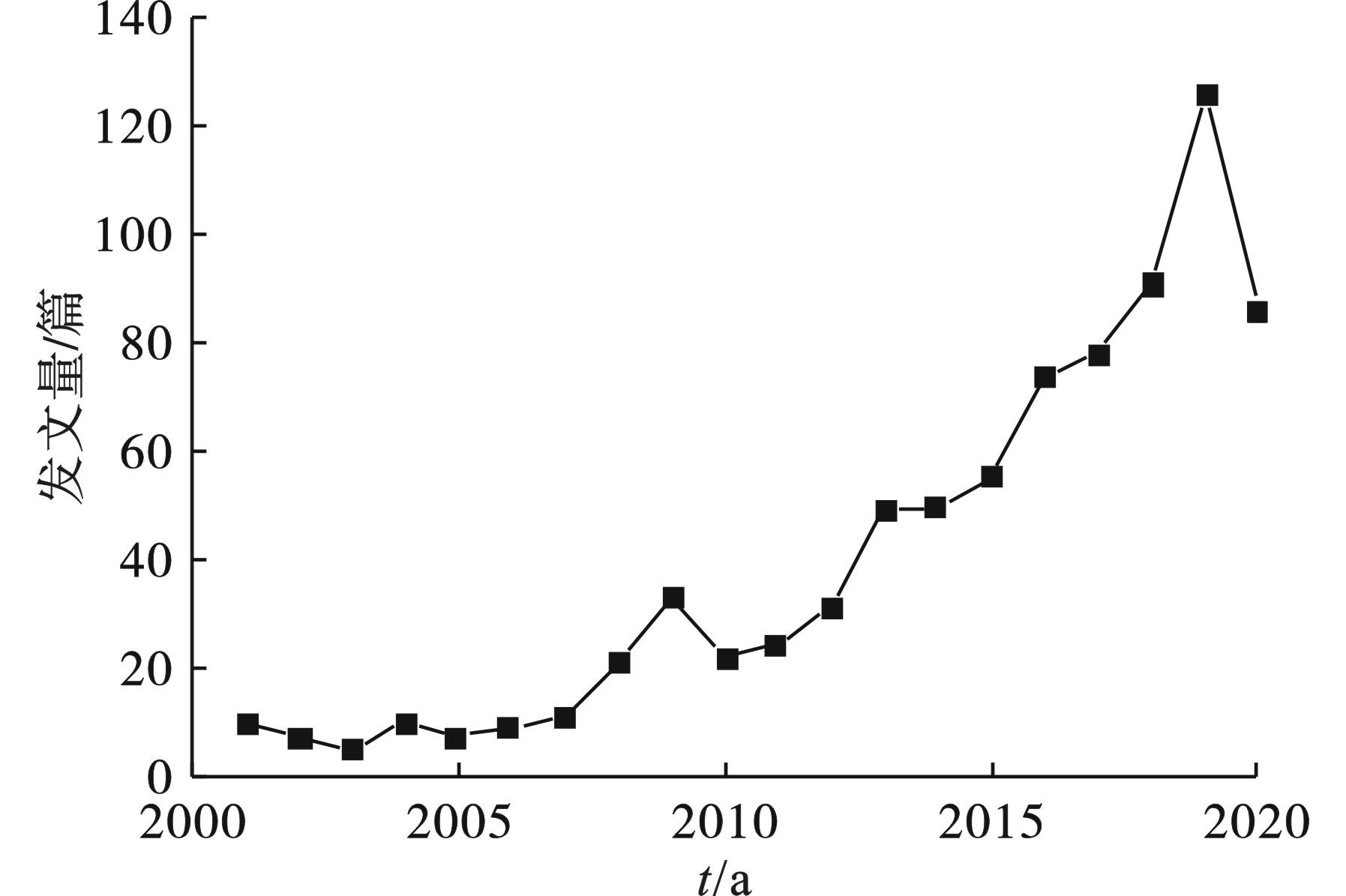
黄河流域环境领域年发文数量的变化,见图1。
图1可知,2001~2020年黄河流域环境方面的发文量总体呈上升趋势,表明国内外对该领域的关注度逐步提高。其次,基于黄河流域环境方面的发文量逐年变化趋势不同,研究趋势整体分为2个阶段。
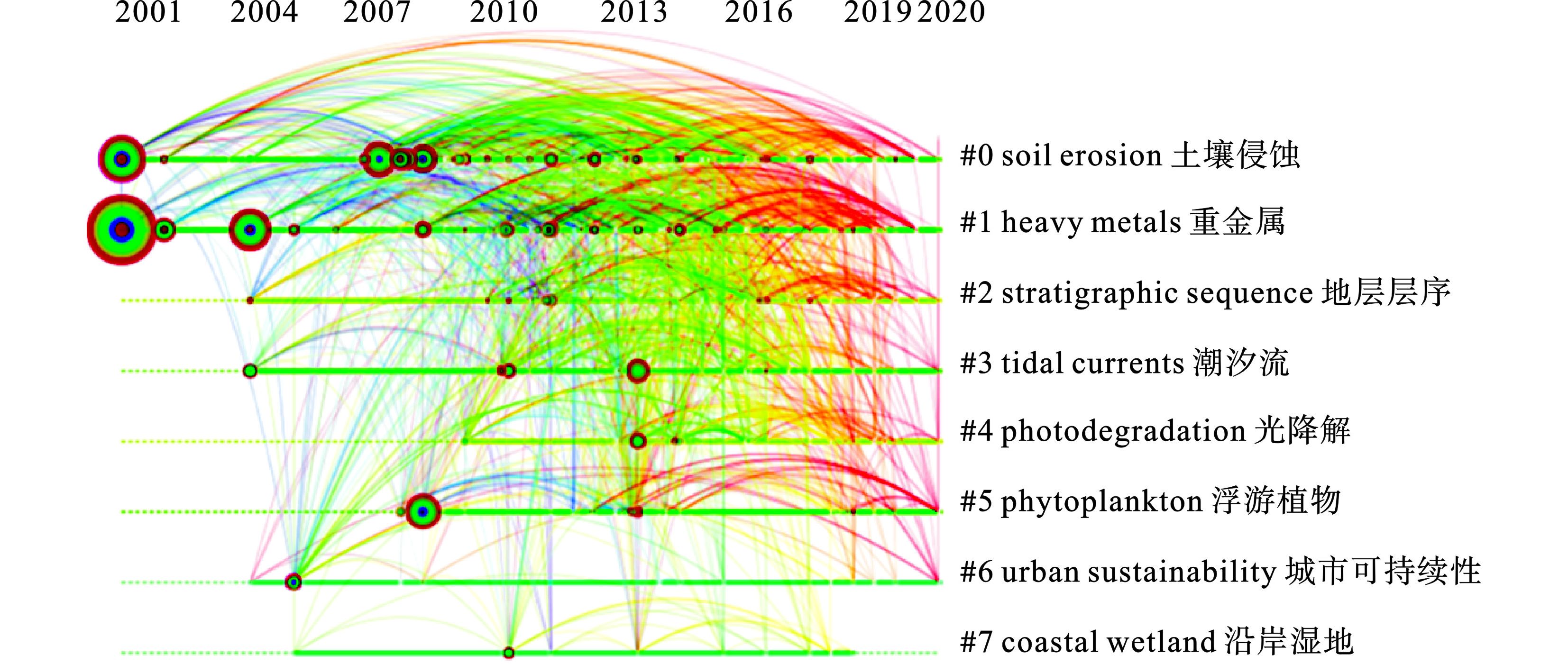
(1) 2001~2007年为研究初期阶段,发文量较少,上升趋势较缓,年均发文量在10篇以下,主要围绕 0#“soil erosion”以及1#“heavy metals”2个主题聚类进行研究,见图2。降雨引起的水力土壤侵蚀,早年已引起科研人员的广泛关注。金鑫等[7]构建了逐网格汇沙的土壤侵蚀模型,通过水文和土壤侵蚀模型的有机耦合, 实现了泥沙产生和汇集的分布式计算。通过研究该主题相关文献,明确该阶段主要集中于污染物排放对黄河水环境的影响以及黄河水环境与沿岸土壤环境、大气环境的相互影响研究。该阶段发表文章中被引频次最高的论文来自于日本地质调查局 SAITO et al[8],研究了人类活动对黄河的长期影响,总结了黄河演化和泥沙排放特征。
(2)2008~2020年黄河流域环境方面研究进入快速发展阶段,发文量大致呈线性增长趋势,该阶段除延续前阶段研究内容外,还围绕 3#“tidal currents”、 4#“phytoplankton”两个主题聚类进行研究,见图2。浮游植物在水生生态系统的物质循环中起着至关重要的作用,对水动力和理化环境变化敏感,常被用作水生生态系统监测中的重要环境指标,如强烈的环境变化将影响浮游植物的生理特性、生物量和群落。LIU et al[9]利用2008~2009年间进行的生物地球化学观测,报道了人类活动对黄河养分运输的影响等。根据目前对于现有论文的分析,可以预估,关于黄河流域环境领域相关研究将在较长的时间内被广泛关注。
-
通过 Citespace软件,以 TOP50 为阈值筛选出 169位作者,呈现黄河环境领域研究作者共现图谱。该共现图谱密度值(Density)仅为 0.0158,表明作者间整体联系较为松散,可见各科学研究团队之间合作较少,且研究人员以国内研究学者为主,国外研究学者较少,呈现出较大的对比度。在所检索文章中,LIU et al[10]共贡献12篇,发表于Quaternary Science Reviews的一篇文章引起了较为广泛的关注。从研究作者共现图谱可知,目前黄河环境领域研究体系化较为薄弱,各研究团队合作尚且不足,有望在未来实现学术间紧密沟通。
-
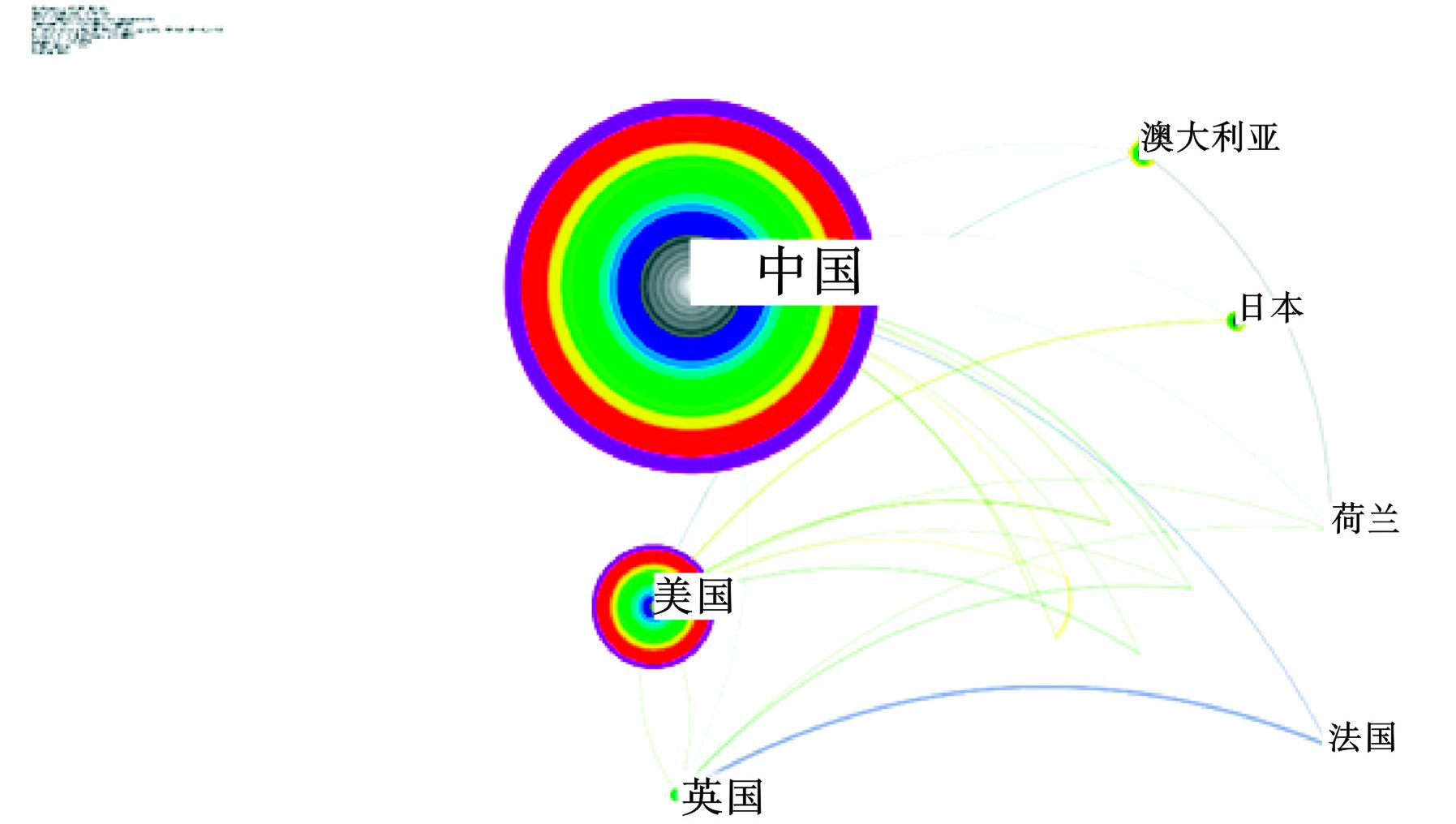
2001~2020年黄河环境领域发文量排前10的国家,基本呈现出“部分集中、整体分散”的特征,见表1。
中国发文量远高于其余各国,占总发文量91.89%,可归因于黄河位于中国境内,且中国近年来对环境重视,发布了一系列相应规范及标准,开展了多项围绕黄河环境领域的项目。以 TOP30 为阈值对国家与机构分别进行筛选,得到研究国家共现图谱与研究机构共现图谱,见图3~4。
图3 可知,知识网络密度值(Density)为 0.2967,表明各国对该领域合作结构较为紧密。
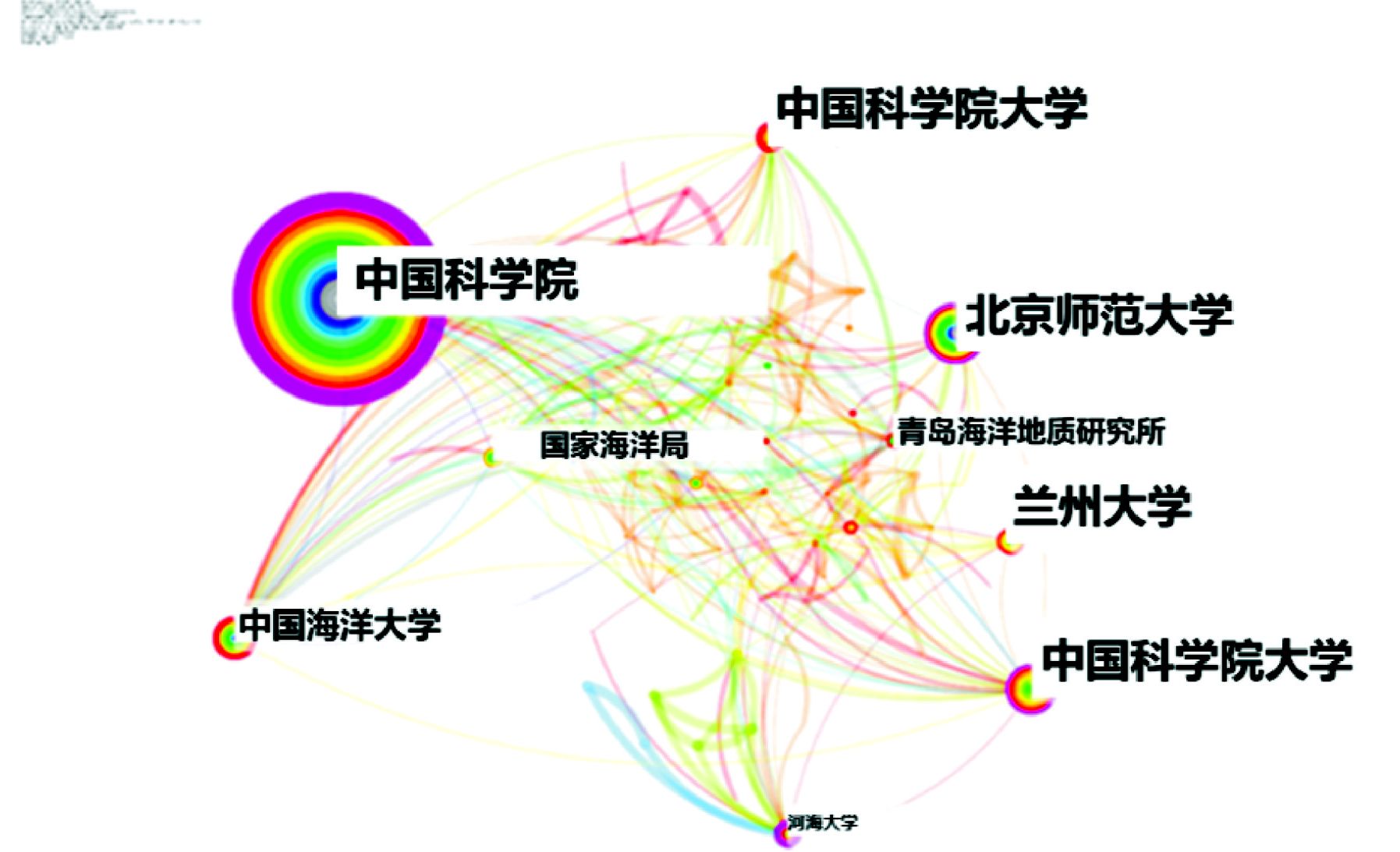
图4可知,最大发文从属机构聚类群是中国科学院(Chinese Academy of Sciences),其次为北京师范大学(Beijing Normal University)、美国农业部农业工程应用技术研究所(Agricultural Research ServiceU. S. Department of Agriculture)、中国科学院大学(University of Chinese Academy of Sciences)、中国海洋大学(Ocean University of China)。中国科学院的中心性最强(0.80),表明其在该领域研究中具有不可或缺的作用。中国科学院位于中国,对黄河流域环境的研究由来已久,受到国内外学者广泛关注[11-13]。
-
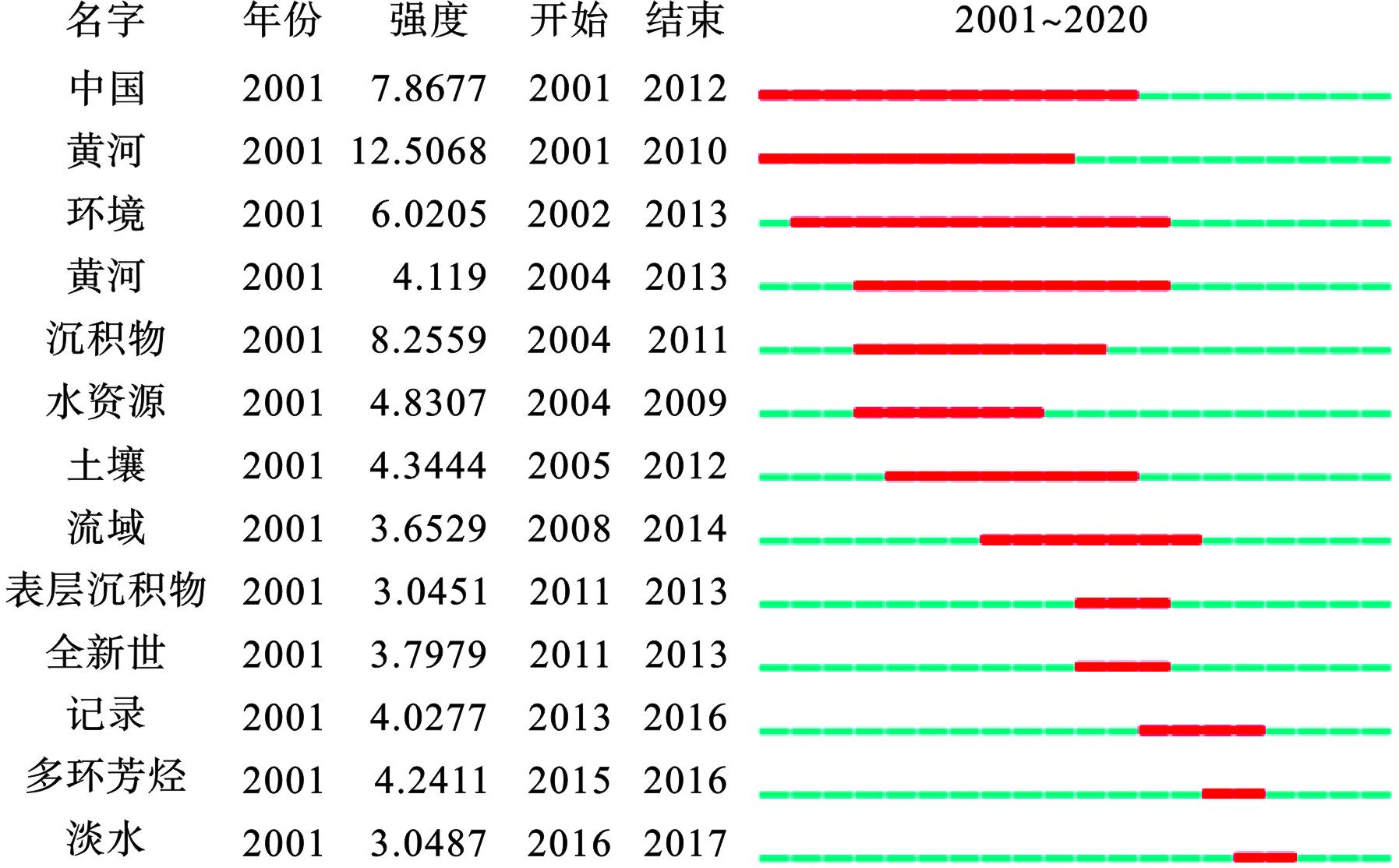
为分析黄河流域环境研究的现状与态势,把握国内外研究人员的研究热点及历程,对关键词共现分析,通过关键词了解该研究基本概貌并进行热点关键词分析。将Citespace软件的时间范围设置为“2001~2020”,“节点类型属性”设置为“关键词”,生成358个节点,700条连线的关键词共现谱图,见图5。在此基础上,设置数量为10个,生成黄河流域环境研究突现词分布,见图6。
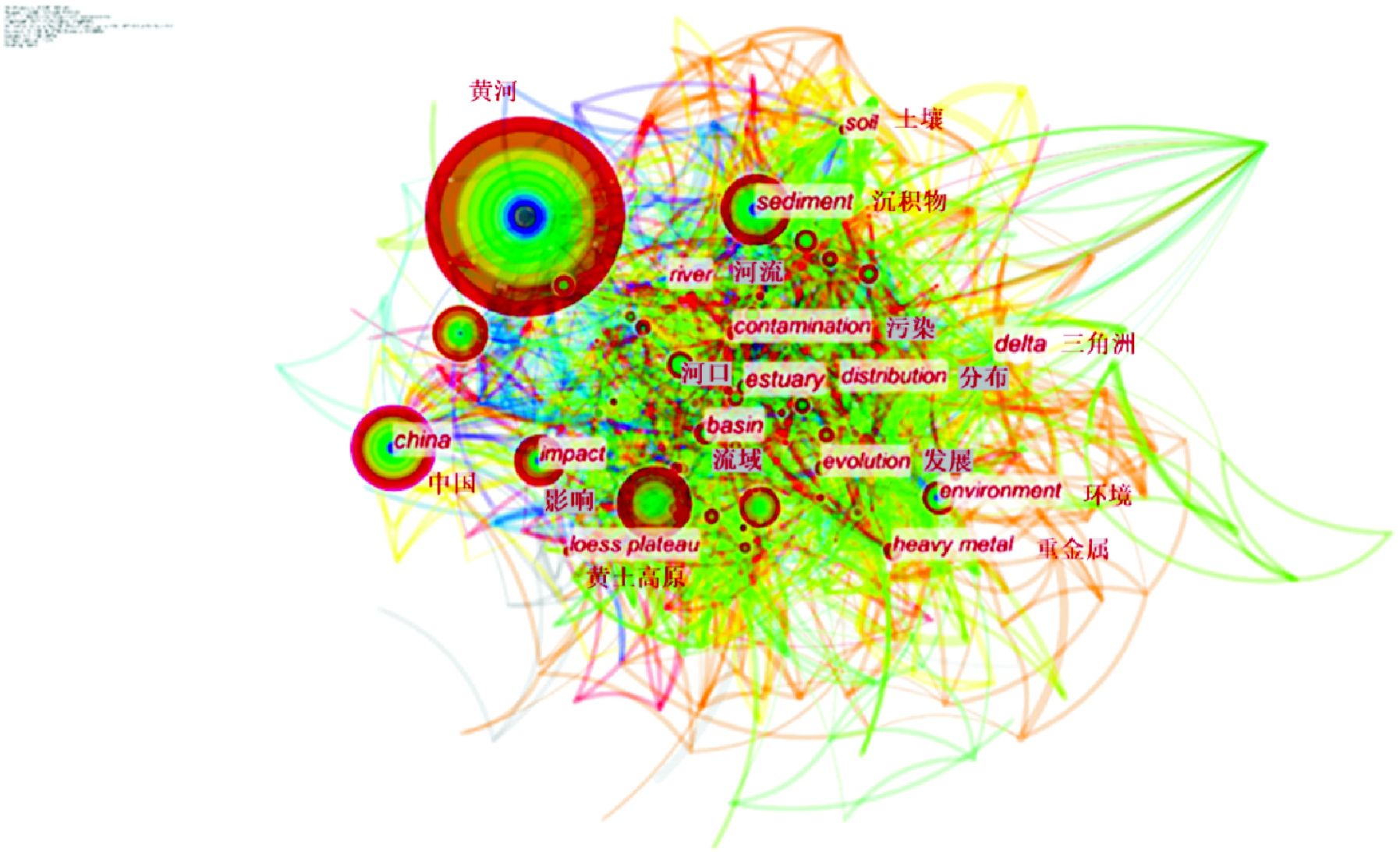
图5可知,该研究领域高频关键词为黄河(227 次)、中国(114 次)、沉积物(96 次)、气候变化(91 次)、水(80 次)、影响(73 次)。在前 20 位高频关键词中,高中心性的关键词有三角洲(0.12)、中国(0.11)、流域(0.09)、河口(0.09)、黄土高原(0.07)。
黄河共现节点最大,且突显词强度最强,其突显性表现为2001~2009年研究较为集中,与国家政策时段大致吻合。1997年,江泽民总书记《关于陕北地区治理水土流失、建设生态农业的调查报告》上作出重要批示,黄河流域的环境保护迈入了新的时期[14]。全国“八大片”治理、“三北”防护林建设等环境保护工作的进行也推动了黄河流域环境研究。2004年10月10日水利部部务会议审议通过《黄河河口管理办法》,2008年党的十七届三中全会要求切实加强节能减排和生态环境保护,2009年12月1日,中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会印发《黄河三角洲高效生态经济区发展规划》。因此,在此阶段,为响应国家号召,科研人员在黄河流域环境领域投入大量心血,表现出论文数量较多的特点。
近年黄河流域多环芳烃(PAHs)污染相关研究越来越得到重视,呈现出较为活跃的态势。PAHs为环境中广泛存在的有机污染物,具有致癌和诱变作用,并有生物积累现象[15]。2006年黄河流域兰州河段PAHs平均浓度达到18 663 ng/L,为世界上多环芳烃污染严重河流之一[16];2016年,中国由于燃料不完全燃烧而排放的PAHs约为32 720 t[17]。因此,由于PAHs污染严重性,黄河流域PAHs污染相关研究引起了国内外科研人员的广泛关注。
气候变化主要以降水、气温等因素影响黄河,对黄河流域的生态安全产生深远影响。2019年9月18日,习近平总书记在黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展座谈会上强调,要坚持生态优先、绿色发展,以水而定、量水而行,因地制宜、分类施策,着力加强生态保护治理和高质量发展[18]。在气候变化和人类活动共同作用下,黄河流域出现水资源总量下降、洪涝灾害频发、生物多样性减少、黄河上游冻土融解、湿地生态系统功能下降、土地荒漠化形势严峻、水土流失加剧和极端天气增多等一系列生态环境问题[19-21]。因此,为解决已出现问题及预防未来气候变化对黄河流域生态环境的不利影响,近年关于黄河流域气候变化的科学研究增多。在全球变暖和极端天气频发的大背景下,提升气候变化风险管理能力和多部门联合协作共同应对气候变化带来的生态安全风险将依然为热点问题。
通过Web of Secience黄河环境研究领域关键词共现分析,阅读国内外相关文献,总结归纳出未来黄河流域环境领域的研究可能有3大趋势。
(1)分析研究新型污染物在黄河流域的来源、分布和潜在毒性。除图6所示多环芳烃(Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons)外,多种新型污染物,如人用和兽用药物制剂、全氟有机化合物、溴化阻燃剂和汽油添加剂等由于其尚无完善的法律法规予以规定且具有生态危害性的新型污染物已引起了国内外科研人员的广泛关注。
抗生素由于其广泛生产及频繁使用并进入环境,导致形成“假持续”现象,进而对人体健康及整个生态系统构成长期潜在危害[22]。ZHOU et al [23]应用快速分辨率液相色谱-串联质谱法检测出黄河中7种抗生素,结果发现2008年11月位于兰州市下游站点的沉积物中土霉素、诺氟沙星和氧氟沙星的浓度分别达到184、142和124 ng/g。多溴二苯醚为溴化阻燃剂中一大类阻燃物质,广泛应用于电子设备、纺织品等产品[24]。其具有一定的挥发性且化学性质稳定,可妨碍人类和动物脑部与中枢神经系统的正常发育,在暴露于紫外线或高温条件下,可能生成致癌物多溴二苯并呋喃等[25]。PEI et al[26]对黄河沿岸14种多溴二苯醚进行了多阶段研究,结果表明工业活动引起多溴二苯醚浓度在黄河中下游处于较高水平。
由此可见,新型污染物在黄河流域中已有检出,且存在生态毒性,因此,在未来研究中应针对新型污染物深入研究。
(2)研究黄河三角洲生态系统及修复路径。黄河三角洲为我国海陆交界、咸淡水交汇的地带,在水陆交互作用以及人为扰动的影响下造就了其复杂多样的环境特征[27]。黄河三角洲可淤积土地,提高黄河防洪强度,还可形成可供开发的土地,为农业以及生态保护提供宝贵的土地资源。但由于河流断流,泥沙淤积降低、石油烃等污染和土地过度开发等问题造成黄河三角洲动态平衡受到威胁。
WANG et al[28]曾在Nature Geoscience报道黄河潼关站输沙量由20世纪70年代每年近16亿t剧减为3亿t,研究组通过对黄土高原降水、径流及泥沙数据推测黄河输沙量的减少的主要原因为产流能力的降低。XIE et al[29]报道黄河三角洲周围环境变化性大,且由于水文连通性的下降,黄河三角洲将面临不断退化的风险。ZHANG et al[30]提出了一种用于生态系统脆弱性评估的压力-支持-状态-响应模型(PSSR),并用该模型评价黄河三角洲湿地生态系统脆弱性。研究结果表明,2005~2009年,黄河三角洲湿地生态系统脆弱性为0.62,2010~2014年下降为0.68。生态脆弱性的下降证明了黄河三角洲亟待生态保护,应防止环境恶化以及湿地退化。因此,黄河三角洲的生态保护迫在眉睫,在未来国内外科研人员应关注黄河三角洲生态安全以及黄河三角洲稳定发展。
(3)结合多学科,产学研用融合,探究黄河流域生态保护高质量发展道路。黄河流域环境研究具有多元且复杂的特点,需要加强多学科交叉,理论与实践并行,鼓励支持科研、学术团队的合作,实现黄河环境领域研究由理论走向实践工程并形成系统方法的完整体系。2020年4月,WU et al[31]基于沉积记录和水文调查,研究了黄河沿岸遗弃河道,发现侵蚀的沉积物的一部分可以被潮汐运入废弃的河道,有助于废弃河道充填和发育。LIE et al[32]构建了一个氮代谢网络模型,整合黄河三角洲生态和社会经济网络,弥补了之前城市代谢研究中生态部分的漏洞,对湿地恢复和产业结构调整提供了一定的理论基础。可见,强调学术交叉、推动国际合作、促进学术交流是未来黄河流域环境研究的发展特点。
-
本研究对2001~2020年 Web of Science 文献检索平台中核心数据库中黄河环境研究论文与综述文献进行检索筛选;利用 Citespace 可视化软件对其进行计量学和可视化分析;通过分析结果,梳理归纳黄河流域环境研究现状与发展历程、研究热点与趋势,并对该研究领域未来发展方向做出预测。
(1)黄河流域环境研究从发文量看正处于快速发展阶段,作者间学术合作较少,整体联系较为松散,以国内研究为主,中国科学院为主要科研机构。
(2)研究热点主要集中于黄河流域环境污染修复。黄河共现节点最大,且突显词强度最强,与国家政策时段大致吻合,PAHs污染相关研究近年来越来越得到重视,呈现出较为活跃的态势。
(3)黄河流域环境研究还需进一步分析,如人用和兽用药物制剂、全氟有机化合物、溴化阻燃剂和汽油添加剂等新型污染物在黄河流域的来源、分布以及潜在毒性;研究黄河三角洲生态系统及修复路径,为黄河三角洲稳态发展提供理论基础;加强多学科联合,产学研用结合,在理论研究的同时,满足产业化的需求,形成合理高效的研究体系。
基于知识图谱的黄河流域环境研究进展分析
Development of environmental research of Yewllow River by bibliometrics analysis
-
摘要: 黄河流域环境领域研究众多,以文献综述为主的文献分析存在可视化程度低、时间跨度短和覆盖范围小等问题。针对文献综述局限性,以明确黄河流域环境方向研究进展为目的,采用文献计量学的方法,以Web of Science核心数据库中2001~2020年黄河流域环境方向研究论文与综述进行科学计量审查,利用Citespace软件进行可视化分析。研究表明:黄河流域环境研究关注度逐步提高但体系化较为薄弱,各研究团队合作尚且不足;研究热点主要集中于黄河流域环境污染修复等方向;经分析预测未来该领域将以新型污染物、三角洲生态系统、多学科联合为主要研究趋势。本文通过明晰该领域研究热点及趋势,以期为黄河流域环境研究和污染防控提供数据参考,为《黄河流域生态环境保护规划》提供理论依据,推动黄河流域环境领域高质量发展,配合黄河保护法立法工作。Abstract: There are many types of researches in the environmental field about the Yellow River Basin. However, there are several problems in the present literature review, such as the low visualization, the short period, and a small coverage of the literatures, etc. Considering the limitations and in order to clarify the environmental research progress of the Yellow River, this study searches the WOS Core Collection database from 2001 to 2020, uses Citespace software to realize the function of visible analysis, clarifies the research hotspots and trends in this field and provides the basic data for environmental research and pollution prevention in the Yellow River Basin. The research shows a gradually increased attention of the environmental research in the Yellow River Basin with a relatively poor systematization. In addition, the cooperation of various research teams is still insufficient. The research hotspots are mainly concentrated in the environmental pollution restoration in the Yellow River Basin. It is predicted that the new pollutants and delta ecosystems as well as the multidisciplinary cooperation will be the main research trends in the future. By clarifying the research hotspots and trends in this field, this paper aims to provide a reference for the environmental research and pollution prevention and control in the Yellow River Basin, also provide a theoretical basis for “Yellow River Basin Ecological Environment Protection Plan”, thus promoting the high-quality development of the environmental field in the Yellow River Basin, and cooperating with the legislative work of the Yellow River Protection Law.
-
Key words:
- Yellow River's environment /
- Citespace /
- bibliometrics method /
- knowledge map /
- frontier hotspots
-
面对日益严重的水资源紧缺以及水体富营养化等问题,世界各国对直接排入河流及地下水的处理出水水质标准正在进一步提高。为满足不断提高的污水排放标准,污水处理厂提标改造势在必行。膜生物反应器由于其具有容积负荷高、抗冲击性强、出水水质好等优点,十分适用于出水要求较高或土地资源紧张的现有污水处理工艺的提标改造[1]。此前,有研究[2-4]分别尝试了将膜组件与氧化沟、序批式反应器等组合以提高相应工艺的处理效能和出水水质,其运行结果均表明出水水质有明显的提升,均实现了扩能提标的目标,且土地利用效率高,这说明膜组件应用于污水处理厂的提标扩容改造是较为可行的选择。在实际工程运用中,A2O工艺是污水处理厂应用最广泛的工艺,脱氮除磷中存在的基质竞争、泥龄不同的矛盾和反硝化碳源不足等缺点使其处理效率相对较低,其与膜组件的结合对于现有A2O工艺的提标改造受到广泛关注[5-9]。然而,无论是与何种工艺结合,膜组件应用的单元及由此引发的膜通量降低、使用寿命下降一直是限制膜组件广泛运用的主要瓶颈。
已有研究[10]表明,将膜组件运用于A2O工艺不同工段时,其膜污染特性可能存在显著差异。为此,本研究采用三维荧光光谱、红外光谱、分子排阻色谱和恒压膜过滤装置分析了A2O工艺不同阶段混合液的膜污染特性,揭示了不同阶段混合液中悬浮物和溶解性有机物对膜组件的污染机制,为膜组件运用于现有A2O工艺提标改造提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
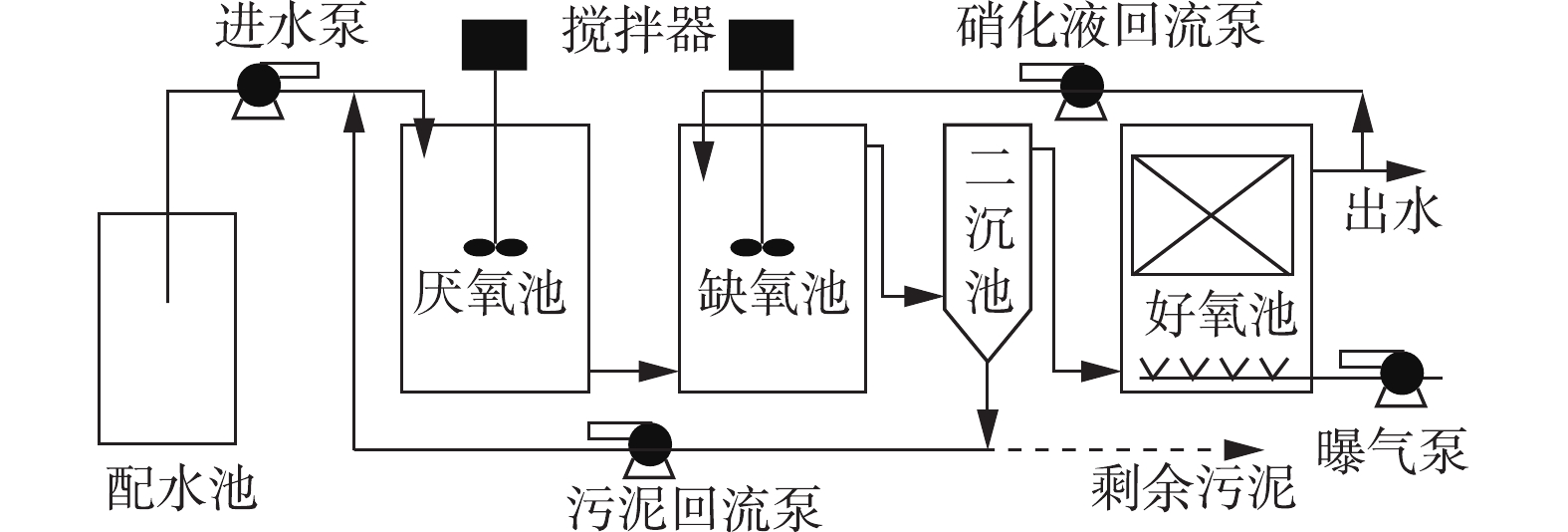
实验室A2O工艺小试装置流程如图1所示。原水依次经厌氧池、缺氧池处理后进入二沉池,经二沉池泥水分离后污泥回流至厌氧池,上清液溢流进入好氧池;好氧池设置有膜组件,利用硝化液回流泵将分离的硝化液回流至缺氧池。厌氧、缺氧和好氧单元的有效容积分别为3、6、12 L,厌氧和缺氧池设置有搅拌器,好氧池配置有曝气装置。
1.2 运行条件
实验所用污泥取自上海闵行区江川水质净化厂,进水按照葡萄糖150 mg·L−1、蛋白胨30 mg·L−1、NH4Cl 80 mg·L−1、KH2PO4 5 mg·L−1配制,以模拟生活污水。定期采集配水和厌氧、缺氧、好氧单元混合液进行恒压膜过滤分析,用于水质检测的水样采样后立即用0.45 μm的有机水系膜过滤,并于4 ℃低温保存。
1.3 水样膜污染特性测定
膜通量的大小可以作为衡量膜污染程度的重要指标之一。在恒定压力下,水样的膜通量越小,表明其膜过滤阻力越大,更容易造成膜污染。本实验利用隔膜真空泵,在恒定压力20 kPa下抽滤水样,依据水样在一定时间内透过滤膜的水量来评估各水样的膜污染潜力。滤膜为混合纤维素MCE膜,平均孔径为0.45 μm,有效膜直径为4 cm。膜通量的计算方法见式(1)。
J=V/At (1) 式中:J为膜通量,L·(m2·h)−1;A为有效膜面积,m2;t为过滤时间,h;V为时间t时过滤的水样体积,L。
1.4 荧光光谱分析
采用HITACHI F-7000FL型荧光光度计测定水样的三维荧光光谱,激发波长为200~550 nm,发射波长为200~550 nm,扫描速度为12 000 nm·min−1,激发与发射的步长和狭缝均为5 nm,光电倍增管的电压为400 V,响应时间为自动。以去离子水为空白样品,进行荧光扫描,减少拉曼散射的影响,再利用Matlab 2014a自动去除三维荧光光谱中的拉曼和瑞利散射,并通过插值算法补齐缺失的光谱。
利用荧光区域积分法对所得的荧光光谱数据进行分析。荧光区域积分法根据溶解性有机物化学基团的荧光特性按不同的激发/发射波长主要划分为5个区域:区域Ⅰ(Ex/Em =(200~250) nm/(280~330) nm)表征酪氨酸类蛋白质;区域Ⅱ(Ex/Em =(200~250) nm/(330~380) nm)表征色氨酸类蛋白质;区域Ⅲ(Ex/Em =(200~250) nm/(380~550) nm)表征富里酸类物质;区域Ⅳ(Ex/Em =(250~400) nm/(280~380) nm)表征溶解性微生物代谢蛋白质;区域Ⅴ(Ex/Em =(250~400) nm/(380~550) nm)表征腐殖酸类物质。对各荧光区域的响应值进行体积积分计算,归一化处理后,分析各荧光区域的荧光强度变化[11]。
1.5 有机物的分子质量分布
凝胶渗透色谱法(gel permeation chromatography, GPC)是依据分子筛效应,利用各物质分子大小和凝胶孔洞的差别而对其进行分离,广泛用于测定有机物相对分子质量和相对分子质量的分布。本实验采用Waters 1515-2414仪器,色谱柱为UltrahydrogelTM Linear柱(7.8 mm×300 mm),流动相为超纯水溶液,流速1 mL·min−1,采用示差折光检测器,柱温40 ℃,进样量20 μL。以保留时间为横坐标,以相对强度为纵坐标,绘制相对分子质量分布曲线。
1.6 傅里叶红外光谱分析
傅里叶变换红外光谱一般用于分析化合物官能团信息,在研究中,用其对水样中溶解性有机物进行定性分析。将水样经真空冷冻干燥机干燥后获得的固体样品与溴化钾以大约 1∶100 的比例混合,研磨均匀、压片制成透明薄片后进行测定,分辨率为4 cm−1,测定时采用的红外波段为400~4 000 cm−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 各反应器出水膜污染特性分析
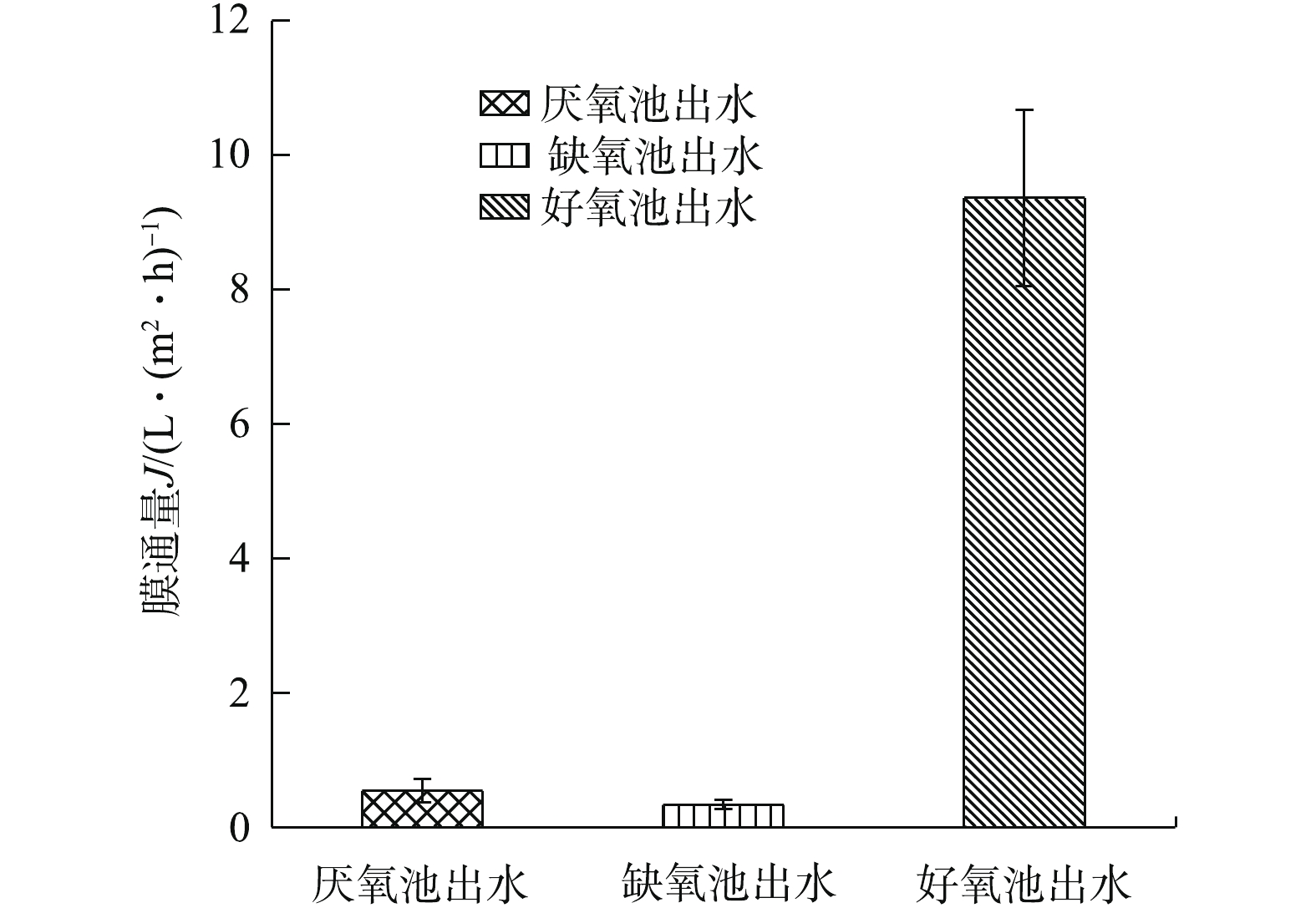
膜污染是指污水中的污泥絮体、胶体粒子、无机溶质或有机物等在膜表面或膜孔中沉积堵塞、吸附沉积,从而导致跨膜压力增加或渗透通量降低的现象[12]。当系统在恒定压力下运行时,膜污染表现为通量的降低。在实验中,依据A2O各阶段混合液恒压过滤下的膜通量大小,可分析其水样对膜污染的潜力。选取各阶段混合液的3次水样进行恒压过滤实验结果见图2。可以看出,好氧阶段的混合液膜通量远大于厌氧和缺氧阶段的混合液,厌氧阶段混合液的膜通量略大于缺氧阶段混合液的膜通量。与厌氧和缺氧段相比,好氧段的混合液膜污染潜力较小,好氧段更适合与膜组件结合,且可作为最终出水的固液分离单元,可以大幅降低出水的SS。
2.2 各反应器出水的三维荧光光谱分析
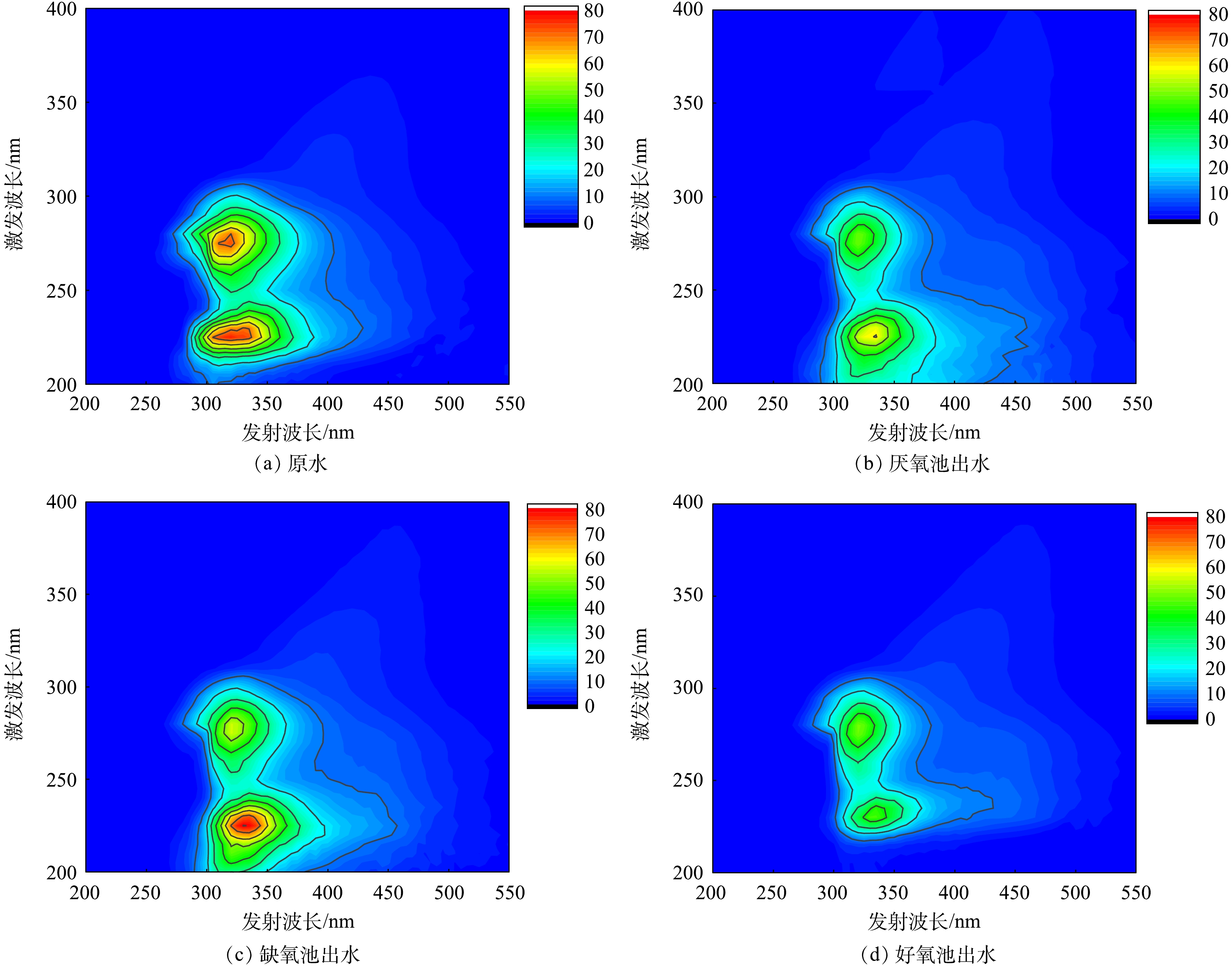
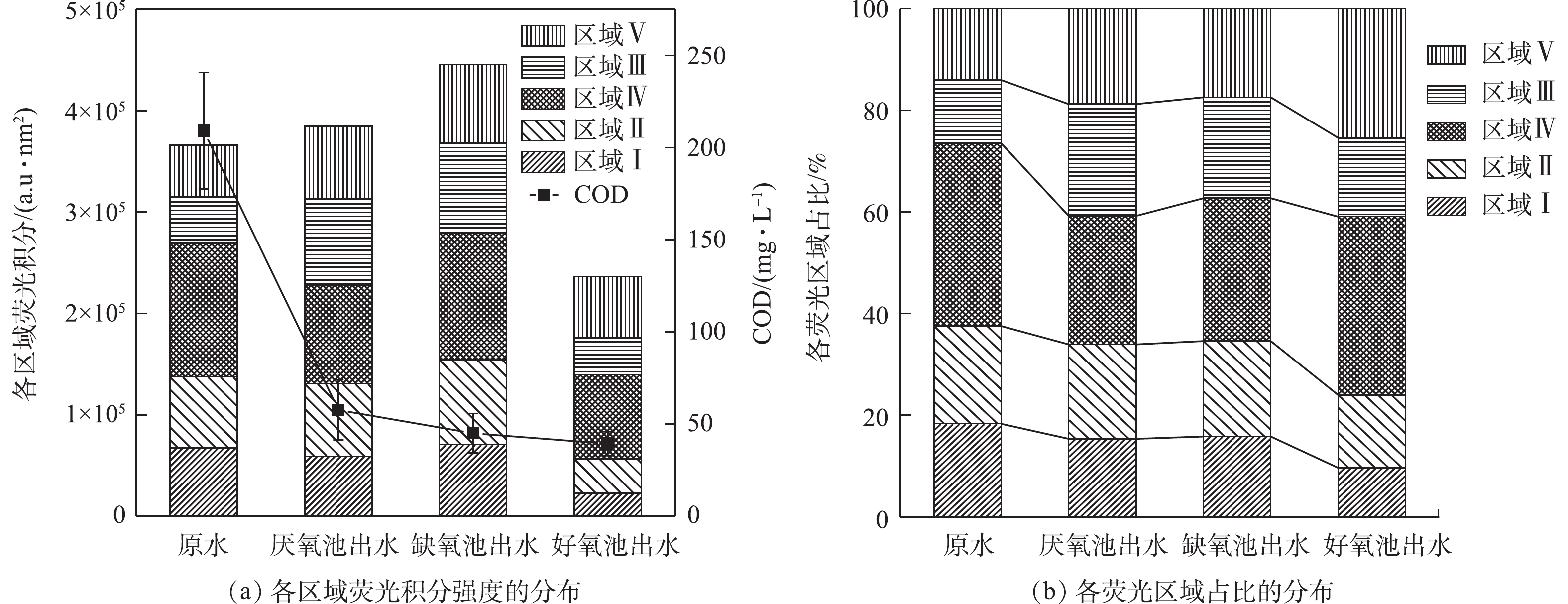
三维荧光光谱能够较好地揭示水体中溶解性有机物组分。如图3所示,A2O工艺沿程各段水样的三维荧光特征总体相似,主要有2个较为明显的荧光峰。其中,位于区域Ⅰ和区域Ⅱ荧光峰(Ex/Em =225 nm/335 nm)属于酪氨酸、色氨酸类蛋白质;位于区域Ⅳ的荧光峰(Ex/Em =230 nm/410 nm)代表微生物代谢蛋白质。这说明A2O工艺各段水样含有的荧光类有机物主要为蛋白质类物质。依据进水和A2O各阶段混合液的5个荧光区域强度及各区域的积分体积占比,进一步分析了各反应器出水的溶解性有机物质的变化(图4)。相对于原水,厌氧池出水的区域Ⅰ、Ⅳ的积分值和组分占比均有所减少,而区域Ⅲ、Ⅴ反而增加,区域Ⅱ的积分强度虽然增加,但其占比却下降。这意味着原水中大量易降解的酪氨酸、微生物代谢蛋白质被微生物分解利用,促进自身繁殖,并合成结构复杂的富里酸、腐殖酸物质。当进入缺氧段后,混合液各区域荧光强度均有所上升,类富里酸和腐殖质组成有所减少,而酪氨酸、溶解性微生物代谢蛋白质反而增加。区域Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅳ属于类蛋白质物质,区域Ⅲ、Ⅴ属于类腐殖质物质,而一般认为区域(Ⅰ+Ⅱ+Ⅳ)/(Ⅲ+Ⅴ)荧光强度的比值可表征有机物的可生物降解性[13],由此表明,缺氧池出水的可生物降解性大于厌氧池出水。然而,类蛋白质属于疏水性物质,分子质量大,容易被膜截留,其对膜污染的贡献大,是造成膜污染的主要物质[14]。胡以松[15]对A2O-MBR污水处理系统中膜污染行为的研究也发现,尽管蛋白质类物质可生物降解,但易在膜表面沉积黏附,对膜污染的贡献大于腐殖酸类物质,由此导致缺氧池出水比厌氧池出水的过滤性更差。
进入好氧段处理单元后,出水的总荧光强度和各区域荧光强度明显低于厌氧和缺氧池出水,表明好氧池出水的溶解性有机物含量相对较少,这与胡以松[15]对A2O-MBR污水处理系统分析溶解性有机物沿程变化时,好氧池有机物质各峰的荧光强度最小的结果一致。相比厌氧和缺氧池出水,好氧池出水类蛋白物质的占比明显减少,但微生物代谢蛋白质和腐殖质占比相对增加。这说明在好氧段微生物代谢旺盛,水溶性色氨酸、酪氨酸和富里酸等有机物被大量去除,而腐殖酸和微生物代谢蛋白质作为微生物代谢过程产生的主要物质,其组分占比明显增加。好氧段对各区域荧光物质均有很好的去除效果,剩余有机物主要是腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物,且总含量较少,从而使其膜污染潜力最小。
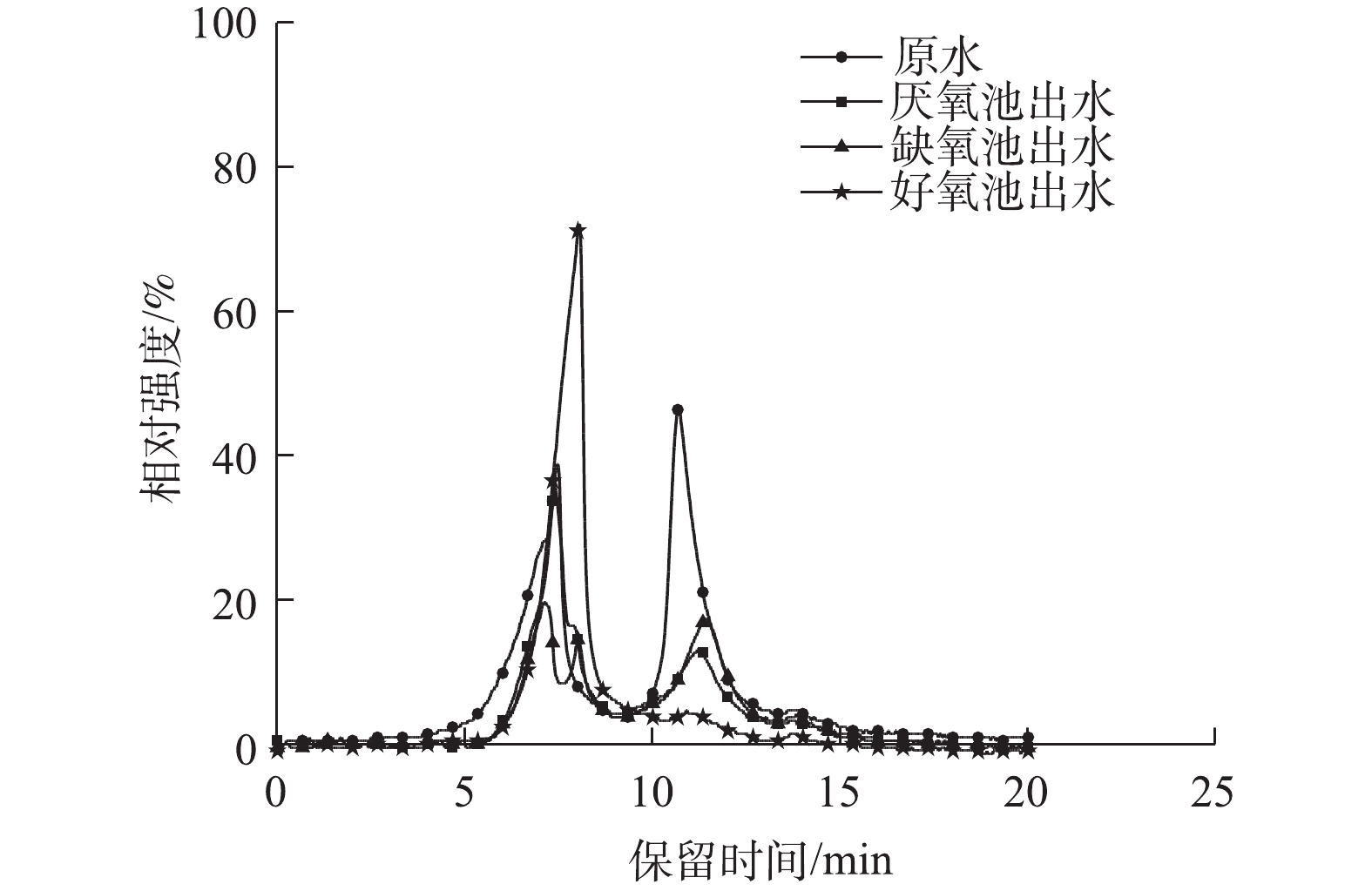
2.3 A2O各反应器出水的有机物分子质量分布
凝胶色谱图可用于分析有机溶剂可溶物的相对分子质量分布,常用于表征膜污染物的特征分子质量。在本研究中,A2O各阶段水样的溶解性有机物分子质量分布情况如图5所示。原水经厌氧段后,去除了大部分的小分子有机物质和小部分大分子物质,经缺氧处理后,大分子物质进一步减少,小分子物质组成增多,这与缺氧池提高了污水的可生物降解性结论相一致。好氧池混合液只有一个窄峰,其有机物主要集中在>23 000 Da的分子质量范围内,基本不含小分子物质。好氧池混合液的三维荧光光谱分析结果与此相一致,即残留的溶解性有机物为腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物类大分子有机物。一般认为,小分子质量有机物在膜孔中吸附造成膜孔堵塞或使膜孔变小[16],大分子有机物则倾向于在膜表面形成滤饼层[17],不同分子质量的有机物共同作用会加快膜污染的发生[18]。综上所述,好氧池混合液由于有机物含量少,且主要为是腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物的大分子物质,因此,其具有较小的膜污染潜力。
2.4 红外光谱分析
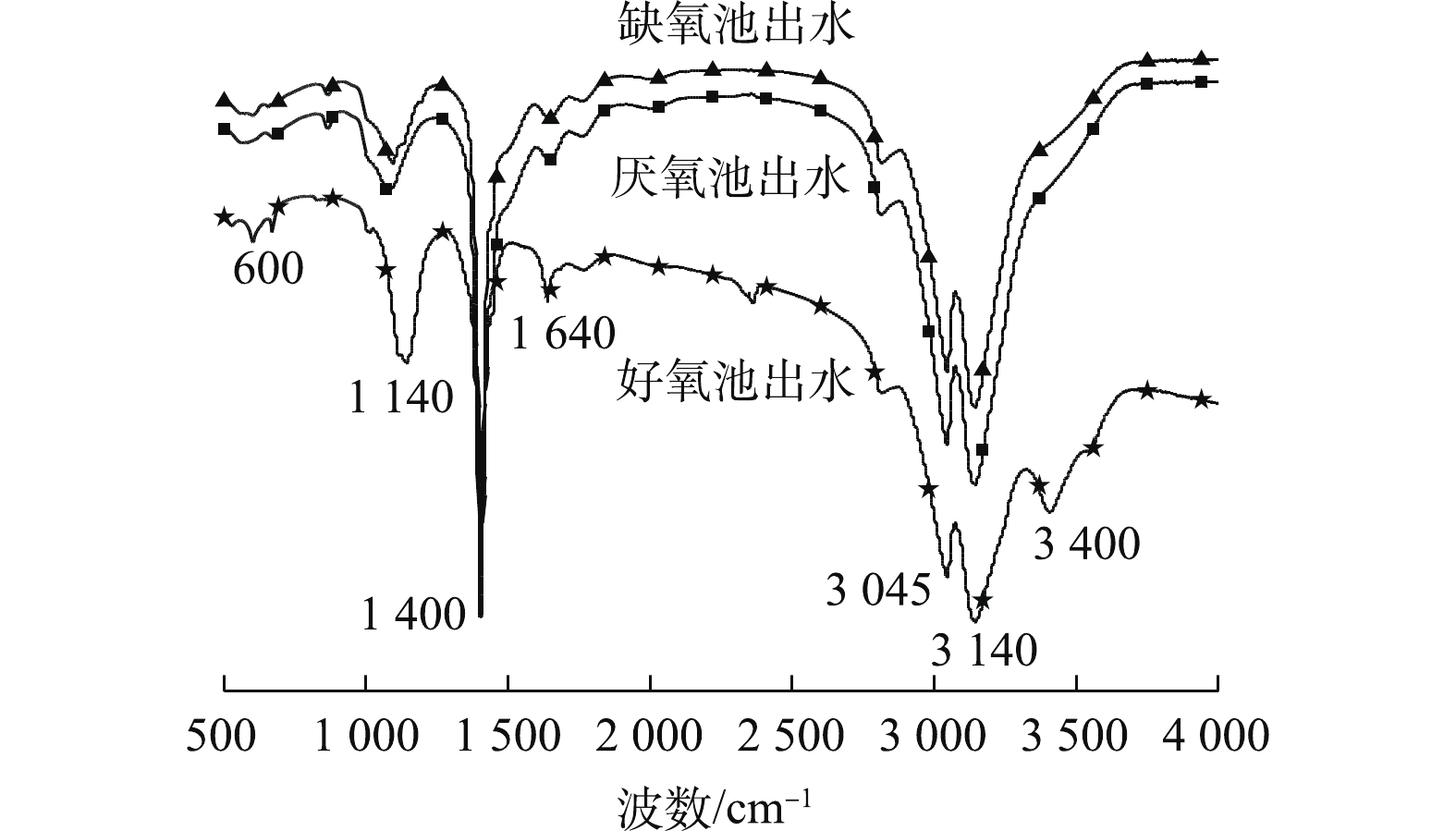
红外光谱分析主要是利用化合物分子对红外光谱特征吸收定性检测其化学键的方法,一般可将红外吸收光谱分为400~1 350 cm−1的指纹区和1 350~4 000 cm−1的官能团区。对比厌氧、缺氧和好氧段上清液的红外光谱图发现,厌氧和缺氧段的红外光谱的峰形状和峰位置等基本相似,主要以1 400 cm−1的芳香族羧基峰、3 045 cm−1和3 140 cm−1的不饱和碳氢峰为主。在好氧段的红外光谱中,除了含有上述代表性官能团之外,在1 640 cm−1、1 140 cm−1处的峰明显增强,且在高频3 400 cm−1处存在独有的特征峰。3 400 cm−1处的特征峰可能是酚类、羟基和羧基的O—H伸缩振动峰[19],在1 640 cm−1区域的吸收峰可能是酰胺I带羰基C=O伸缩振动或氨基酸
NH+3 不对称变角和NH+2 变角振动[20],而1 140 cm−1处为糖类C—O—C键伸缩振动和O—H面内弯曲振动[21]。这表明好氧池出水的不饱和结构化合物组分增加,氧化聚合度增加,这与好氧池出水的荧光峰较厌、缺氧出水出现红移的现象一致。基于如上分析,通过对A2O工艺各阶段混合液的恒压膜通量测试,以及混合液中溶解性有机物的三维荧光光谱、分子排阻色谱和红外光谱分析表明,厌氧和缺氧段混合液中含有大量溶解性蛋白质类物质,且总体有机物含量较高,具有较强的膜污染潜力;而好氧段混合液中有机污染明显降低,且主要是大分子的腐殖酸和微生物代谢产物,膜污染潜力较小。因此,在A2O工艺与膜组件结合时,建议将膜组件用于好氧段泥水分离,从而有效提高出水水质并延长膜使用寿命。
3. 结论
1)恒压膜通量的测试结果表明,A2O工艺好氧段混合液的膜通量分别是厌氧段和缺氧段混合液的17倍和28倍,说明好氧段混合液发生膜污染的潜力最小。
2)三维荧光光谱分析结果表明,厌氧池和缺氧池中有机物的荧光积分强度分别为好氧池出水的1.63倍和1.88倍,且主要是酪氨酸、色氨酸类蛋白质物质;而凝胶色谱分析结果表明,好氧池出水中有机物主要是分子质量大于23 000 Da的腐殖酸类微生物代谢产物,而非氨基酸类蛋白质物质,故导致其膜污染潜力较小。
3)根据A2O工艺以及各阶段混合液的恒压膜通量和所含有机物的组成特性,建议在对A2O工艺进行提标改造时,宜将膜组件用于好氧段泥水分离,以缓解膜污染,降低污水处理成本。
-
表 1 2001~2020年黄河环境领域发文量前10的国家
排名 国家 频数 百分比/% 1 中国 734 91.98 2 美国 102 12.78 3 日本 29 3.63 4 英国 27 3.38 5 澳大利亚 24 3.00 6 德国 16 2.00 7 荷兰 16 2.00 8 加拿大 13 1.63 9 印度 8 1.00 10 意大利 8 1.00 -
[1] 黄喜峰, 苏志诚. 黄河生态治理与开发管理研究——评《变化环境下黄河上游河道生态效应模拟研究》[J]. 人民黄河, 2020, 42(7): 167. [2] 王镇环. 加强黄河流域生态环境治理[J]. 中国人大, 2018(1): 47 − 48. [3] LI Y X, WANG Y, RUI X, et al. Sources of atmospheric pollution: A bibliometric analysis[J]. Scientometrics, 2017, 112(2): 1025 − 1045. doi: 10.1007/s11192-017-2421-z [4] 安显金, 李维. 基于CNKI的我国生物炭研究趋势文献计量学分析[J]. 农业环境与发展, 2018, 35(6): 483 − 491. [5] 张胤杰, 赵越, 孙宏亮, 等. 基于知识图谱的河流面源污染国际研究与前沿分析 [C]//中国环境科学学会环境工程分会. 2019年科学技术年会——环境工程技术创新与应用分论坛论文集(四). 西安: 2019. [6] 何思笑, 张建国, 张明如. 基于知识图谱法的国内城市绿地健康效应研究进展[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 46(3): 152 − 163. [7] 金鑫, 郝振纯, 张金良, 等. 黄河中游分布式水沙耦合模型研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2006(12): 11 − 15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2006.12.004 [8] SAITO Y, YANG Z, HORI K, et al. The Huanghe (Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River) deltas: A review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene[J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2): 219 − 231. [9] LIU S M, LI L W, ZHANG G, et al. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) estuary[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 430-431: 103 − 110. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.005 [10] LIU J, SAITO Y, KONG X H, et al. Sedimentary record of environmental evolution off the Yangtze River estuary, East China Sea, during the last 13, 000 years, with special reference to the influence of the Yellow River on the Yangtze River delta during the last 600 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(17-18): 2424 − 2438. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.06.016 [11] ZHAO G, MU X, WEN Z, et al. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the loess plateau of china[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 2013, 24(5): 499 − 510. [12] FU G B, CHEN S L, LIU C M, et al. Hydro-climatic trends of the Yellow River basin for the last 50 years[J]. Climatic Change, 2004, 65(1): 149 − 178. [13] ZHAO M M, CHEN Y, XUE L, et al. Greater health risk in wet season than in dry season in the Yellow River of the Lanzhou region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644(10): 873 − 883. [14] 刘正杰. 黄河流域水土保持工作的特点与经验[J]. 中国水土保持, 2001(12): 10 − 11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2001.12.005 [15] MOJIRI A, ZHOU J L, OHASHI A, et al. Comprehensive review of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water sources, their effects and treatments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 696(15): 133971. [16] HAN D M, CURRELL M. Persistent organic pollutants in China's surface water systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 580(15): 602 − 625. [17] HAN J, LIANG Y S, ZHAO B, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) geographical distribution in China and their source, risk assessment analysis[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 251: 312 − 327. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.022 [18] 习近平. 在黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展座谈会上的讲话[J]. 中国水利, 2019(20): 1 − 3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2019.20.006 [19] 肖风劲, 徐雨晴, 黄大鹏, 等. 气候变化对黄河流域生态安全影响及适应对策[J]. 人民黄河, 2021, 43(1): 10 − 14+52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.01.003 [20] 黄建平, 张国龙, 于海鹏, 等. 黄河流域近40年气候变化的时空特征[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51(9): 1048 − 1058. [21] 张镭, 黄建平, 梁捷宁, 等. 气候变化对黄河流域的影响及应对措施[J]. 科技导报, 2020, 38(17): 42 − 51. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2020.17.004 [22] ZHANG Q Q, YING G G, PAN C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6772 − 6782. [23] ZHOU L J, YING G G, ZHAO J L, et al. Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(7): 1877 − 1885. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.03.034 [24] LI W L, MA W L, JIA H L, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface soils across five Asian countries: Levels, spatial distribution, and source contribution[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(23): 12779 − 12788. [25] CHRISTOPH, K, BERND S. Degradation of brominated polymeric flame retardants and effects of generated decomposition products.[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 227: 329 − 333. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.052 [26] PEI J, YAO H, WANG H, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in water, surface sediment, and suspended particulate matter from the Yellow River, China: Levels, spatial and seasonal distribution, and source contribution[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 129(1): 106 − 113. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.017 [27] 高吉喜, 李政海. 黄河三角洲生态保护面临的问题与建议[C]// 中国水利学会、黄河研究会. 黄河河口问题及治理对策研讨会专家论坛文集. 中国水利学会、黄河研究会: 中国水利学会, 2003: 60-66. [28] WANG S, FU B J, PIAO S L, et al. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2016, 9: 38 − 41. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2602 [29] XIE C J, CUI B S, XIE T, et al. Hydrological connectivity dynamics of tidal flat systems impacted by severe reclamation in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 739(15): 139860. [30] ZHANG X Q, WANG L K, FU X S, et al. Ecological vulnerability assessment based on PSSR in Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 167(20): 1106 − 1111. [31] WU X, WANG H J, BI N S, et al. Evolution of a tide-dominated abandoned channel: A case of the abandoned Qingshuigou course, Yellow River[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 422: 106116. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106116 [32] ZHI L H, LI X W, BAI J H, et al. Integrating ecological and socioeconomic networks using nitrogen metabolism in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 162: 105012. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105012 -






 下载:
下载: