-
膜生物反应器(membrane bioreactor, MBR)作为一种高效污水处理技术,相较传统活性污泥法,MBR通过高效的固液分离,具有混合液微生物浓度高、反应器占地面积小、污泥产量低和更高出水水质等优势[1-2]。但膜污染仍是MBR进一步发展应用的最大阻碍。早期研究认为活性污泥混合液是膜污染的直接来源,其中微生物代谢产物,即胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)与溶解性微生物产物(soluble microbial products,SMP)是MBR主要的污染物质,根据LASPIDOU的统一理论,EPS和SMP之间存在一定的转化关系。有研究[3]表明,EPS含量可以作为膜污染的指数,但由于污泥特性复杂以及相互作用,至今还没有系统性的研究定论。
众多膜污染控制策略相继提出,包括改性膜材料[4]、优化操作条件[5]和改善混合液特性等[6-8]。相关的研究主要集中在改性膜材料和投加新物质改善混合液特性方面。但从经济角度出发,优化操作条件无疑是更好的选择。相关的研究已有很多,包括曝气量、水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time, HRT)、污泥停留时间、有机负荷率等。其中,HRT被认为是优化MBR膜污染的重要操作参数[9],该参数能有效调节进水中有机物与微生物的接触时间,并改变EPS和SMP等混合液特性[10-11],同时影响活性污泥颗粒粒度、Zeta电位与黏度等混合液特性参数的变化[12]。MBR工艺处理可生化性较好的污水时,过低HRT(1.2 h)会促使MBR混合液中碳水化合物积累,同时对有机碳去除贡献也小,促使膜的清洗频率和不可逆污染均增高[13]。由此可见,针对不同水质,HRT参数的选取具有差异性,所以,对MBR处理生化尾水中HRT的合理选取需进一步的探讨。
因此,基于上述研究结果,本实验从强化现有工艺处理能力出发,针对兰州某生活污水处理厂出水水质超标问题,构建处理生化尾水MBR工艺,现场开展相关实验研究,梳理运行参数HRT与混合液特性参数间相关性,以寻求适宜的HRT,从而实现对MBR膜污染控制的工程调控。
全文HTML
-
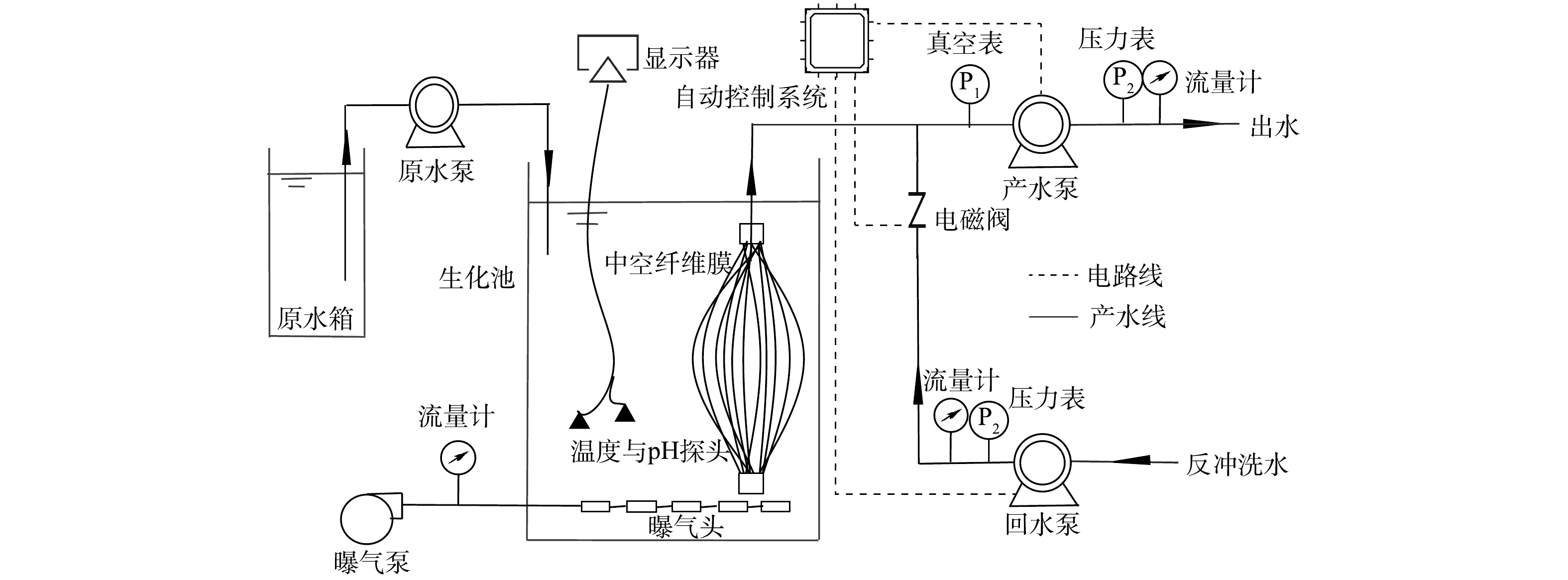
实验用水来自兰州市某生活污水处理厂实际现场,前期经过厌氧-缺氧-好氧生物脱氮除磷工艺生物处理,生化尾水直接接入中空纤维膜组件小试装置。如图1所示,小试装置生化池有效容积95 L(285 mm×500 mm×670 mm),膜池有效容积13 L(40 mm×500 mm×670 mm),产水池有效容积为25 L(75 mm×500 mm×670 mm)。其中,膜材料选用聚偏氟乙烯,平均孔径0.05 µm,膜片有效面积为1 m2,运行最高压力0.03 MPa。
-
实验装置采用自动控制,MBR的产水模式采用间歇式(运行10 min,暂停2 min)产水,产水泵工作4 h后,进行1次清水反冲洗,反洗时间为3 min,膜通量为15 L·(m2·h)−1。实验温度控制在(20±1) ℃,pH为7.0~7.5。为考察HRT对MBR体系内的混合液特性、处理效率以及膜污染的影响,根据已有的实验研究[14],通过调节混合液在反应器中的容量,先后于6、8和12 h下考察HRT对MBR的影响,整个运行过程中污泥质量浓度基本保持在4 000 mg·L−1左右。
-
总氮(total nitrogen, TN)、总磷(total phosphorus, TP)、化学需氧量(chemical oxygen demand, COD)、氨氮(ammonia nitrogen,
NH+4 -N)和浊度等采用《水和废水监测分析方法》中规定的标准方法检测。EPS分为松散附着性胞外聚合物(loosely bound EPS, LB-EPS) 和固着性胞外多聚物(tightly bound EPS, TB-EPS),均采用热提取法提取。多糖采用蒽酮-硫酸比色法测定,蛋白质采用LOWRY法测定,其中分光光度计使用尤尼柯UV-2800A紫外-可见光分光光度计。EPS分子质量大小通过岛津LC20凝胶渗透色谱进行表征,红外光谱测定使用Niolet IS10傅里叶红外光谱仪(美国尼高力公司)测定,污泥粒径测定使用Mastersizer 2000激光粒度仪(英国马尔文公司),Zeta电位测定使用Zetasizer Nano ZS90仪(美国赛默飞公司),黏度测定使用NDJ-1旋转黏度计(深圳德卡精密量仪有限公式),TMP通过真空表表征。
1.1. 实验装置
1.2. 实验运行条件
1.3. 分析方法
-
考察了不同HRT条件下MBR运行水质变化,结果见表1。如表1所示,随着HRT的增加,COD、TP与浊度的出水数值相应增高,但TN的出水质量浓度在6 h与8 h时变化不大。当HRT为6 h时,出水中COD、TP和浊度的数值最低,分别为29.0 mg·L−1、0.22 mg·L−1和0.9 NTU。随着HRT延长,出水中污染物质量浓度略有增高。这可能是由于随着HRT的延长,混合液中以多糖为主的SMP含量增加致使出水中有机物质量浓度也随之增加[15]。上清液浊度的增加可能与污泥的絮凝有关,这会对膜污染和去除性能产生影响[16],但出水水质基本均达到一级A水质排放标准。
-
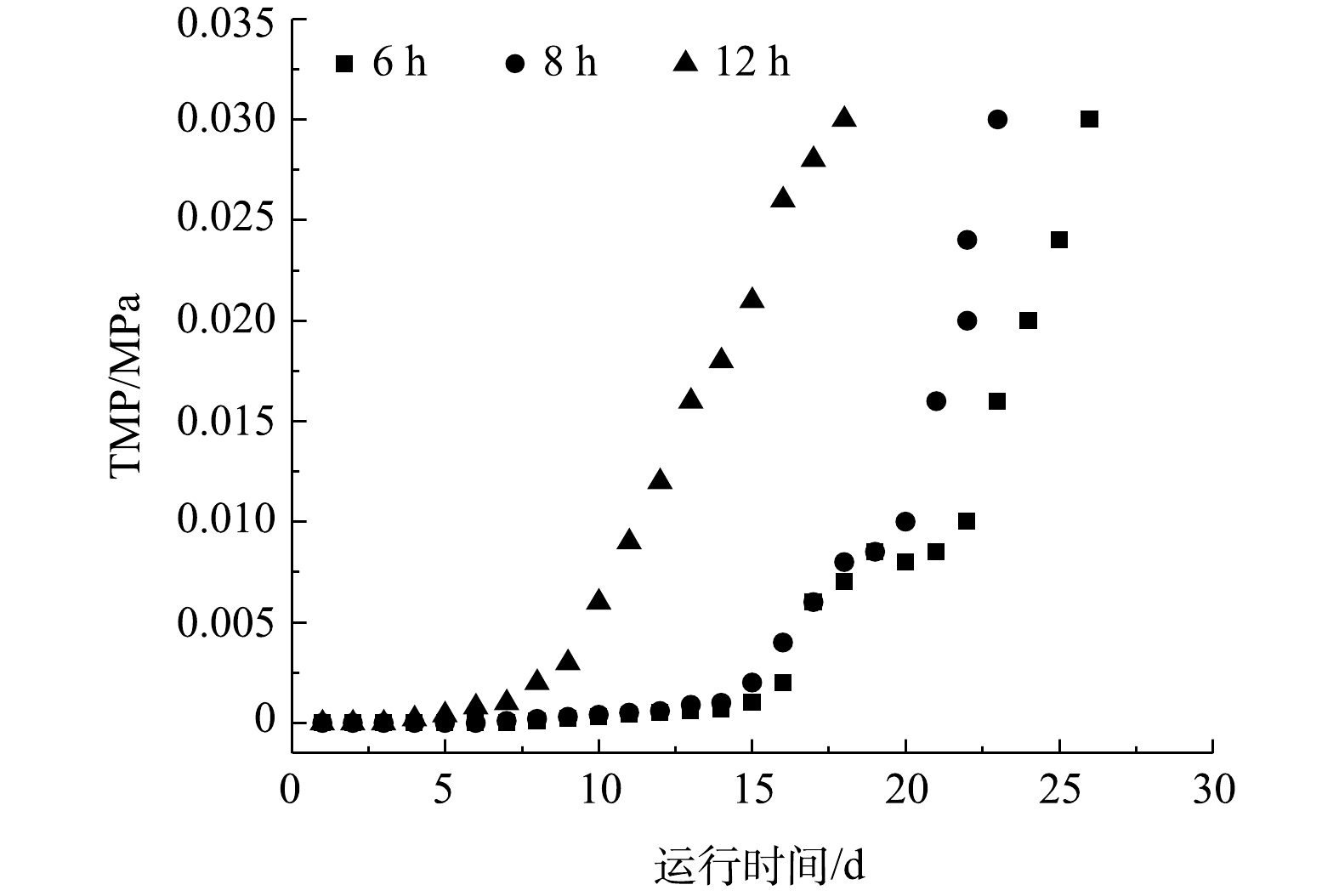
由图2可知,当HRT为6 h时,膜运行时间最长,在运行27 d后达到0.03 MPa。随HRT的升高,膜组件运行时间降低,导致TMP快速增大,从而加快了膜污染的进程。这也从侧面说明微生物代谢产物对污泥特性起主要作用,是研究膜污染机制的关键[1, 12, 17-18]。EPS是微生物在生长过程中向其外部分泌的一种物质,对维持活性污泥稳定性具有重要作用[11],但同时也是造成膜污染的主要原因[2]。从结构上区分,TB-EPS为紧密附着在细胞壁上的胞囊聚合物,LB-EPS为以胶体或溶解松散态物质存在于液相主体中的黏性聚合物,而SMP是在微生物降解基质和内源呼吸过程中产生的。以上3个指标是影响膜污染的重要指标。
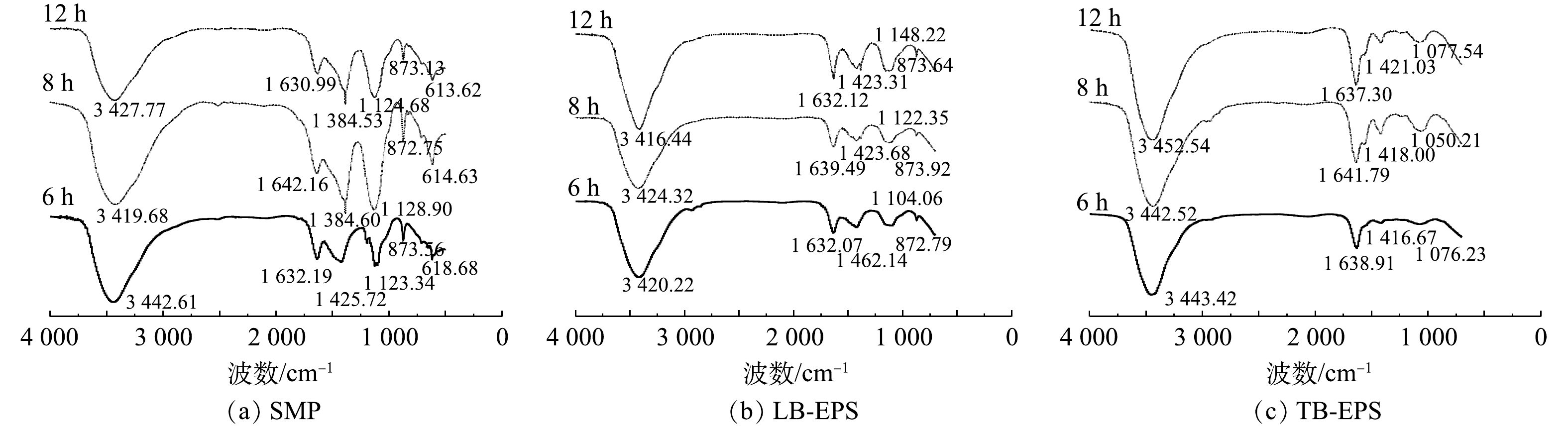
因此,检测了不同HRT(6、8和12 h)下SMP、LB-EPS和TB-EPS含量的变化,结果如图3和图4所示。由图3可见,SMP、LB-EPS和TB-EPS的特征吸收峰的变化相似,且HRT越大,三者的特征吸收峰强度越高。且TB-EPS的吸收峰强度大于SMP的吸收峰强度。在EPS的FTIR光谱3 300~3 500 cm−1处出现了6N—H与O—H振动[11, 19],同时在1 020~1 120 cm−1处出现代表多聚糖的C—O—C伸缩振动[11, 20],1 416 cm−1附近出现CH2伸缩振动,1 050~1 650 cm−1为蛋白质肽键对应的伸缩振动峰,在613.62 cm−1处的吸收峰表明有类似腐殖酸等化合物[19]。
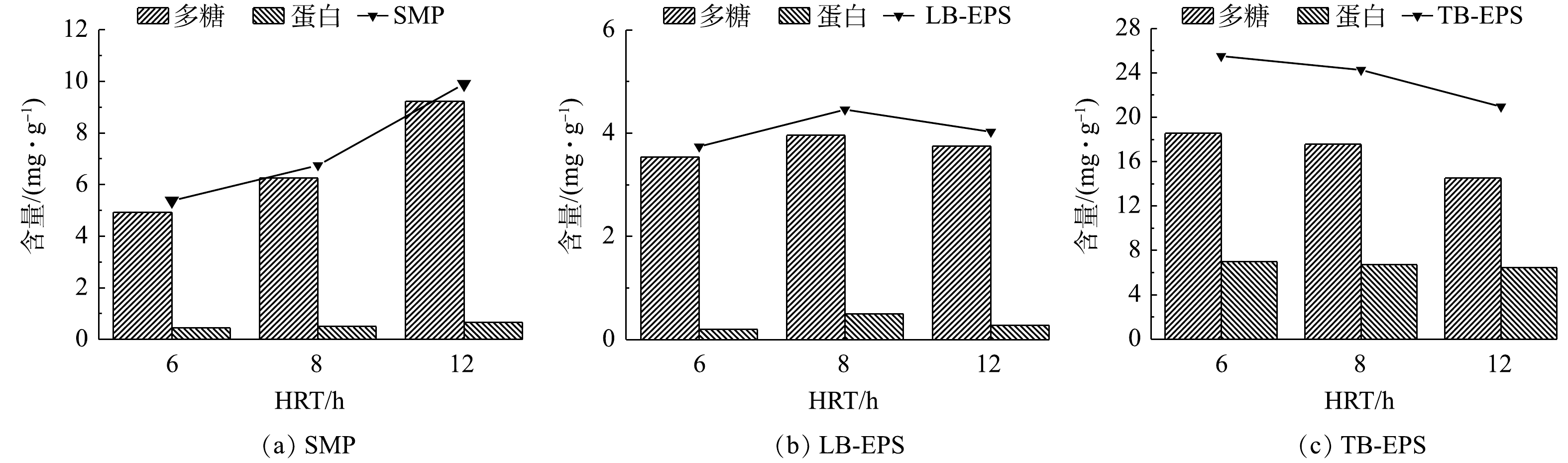
由图4可以看出,EPS中主要成分为多糖,同时在TB-EPS中含有部分蛋白,而SMP的主要成分为多糖,蛋白含量极少。由图4(a)可见,SMP含量随着HRT的增加呈现上升趋势,这与有的研究成果不一致[4]。HRT为12 h时的SMP含量要比6 h时平均高出78.2%左右。这是因为,在保证一定进水营养物质前提下,当HRT较长时,反应器能充分降解营养物质,但同时也有可能发生内源呼吸而发生SMP的累积。SMP中多糖含量呈上升趋势,HRT为12 h时的SMP多糖含量要比6 h时平均高出80%左右。这是由于反应器运行延长,微生物不断繁殖代谢能力升高,在进水碳源相对充足的情况下,SMP中多糖不断累积。SMP中蛋白质含量呈缓慢上升趋势,HRT为12 h时SMP蛋白质含量要比6 h时平均高出50.2 mg·g−1。这是由于反应器运行延长,在不能很好满足脱氮反硝化条件下,导致氮源降解受阻,SMP中蛋白质也不能作为氮源所消耗,因此,蛋白质含量升高。
由图4(b)和图4(c)可见,LB-EPS中多糖和蛋白质含量随HRT增加呈先上升后下降趋势,TB-EPS中多糖含量随着HRT的增加不断降低,蛋白含量基本保持不变。这是由于伴随着反应器的运行,微生物不断繁殖代谢增强,向体外分泌物增多,可利用营养物水平降低导致将EPS中多糖和蛋白质作为碳源和氮源消耗。而且,EPS与SMP之间存在相互转化、吸附与被吸附的关系[21],二者转化主要成分为多糖。从实验结果得出,微生物优先以EPS作为微生物的营养物来源,因此,SMP应为最主要的膜污染因素[22]。
-
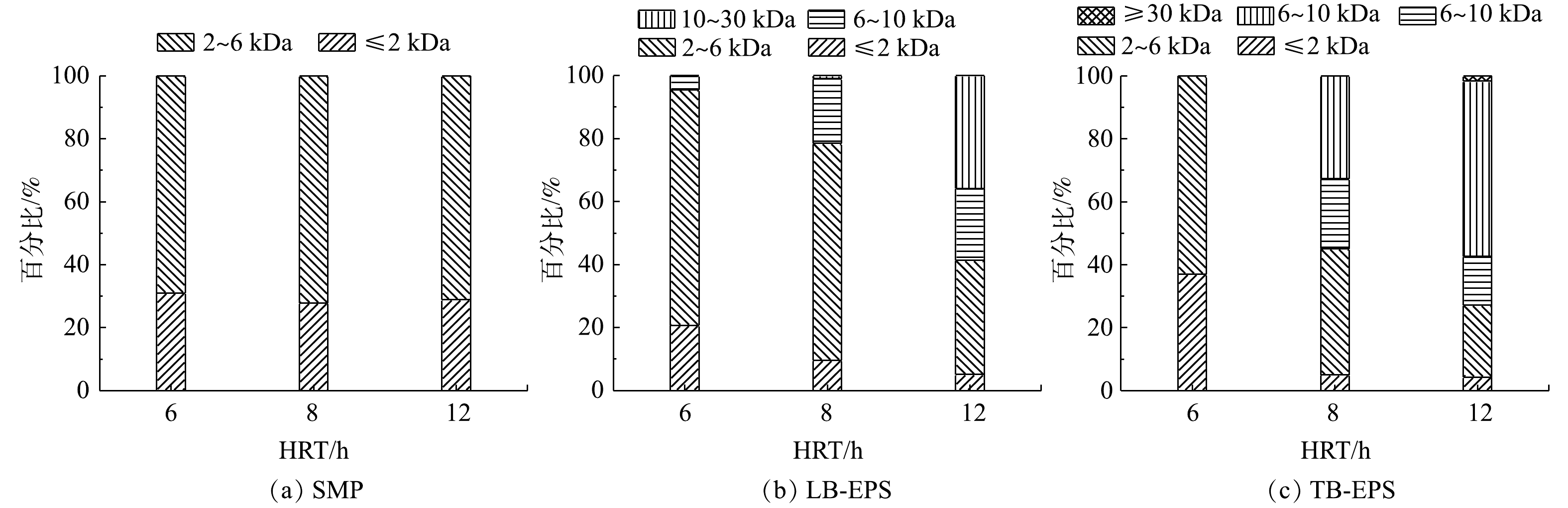
检测了不同HRT下SMP、LB-EPS与TB-EPS中颗粒物的分子质量分布。由图5可知,EPS中颗粒物主要分布在2~30 kDa,这与LIN等[23]的研究结果相似。结果显示,在不同HRT下,SMP、LB-EPS与TB-EPS三者中颗粒物的分子质量分布呈现不同的变化趋势,SMP中颗粒物的分子质量分布受HRT的影响不显著,而HRT对LB-EPS与TB-EPS中颗粒物的分子质量分布与转化具有重要作用。当HRT增至8 h,分子质量在6 kDa以下的颗粒物占比降低,分子质量在6~10 kDa的颗粒物占比约为20%,同时TB-EPS中出现30%左右的分子质量在10~30 kDa的颗粒物;当HRT为12 h时,分子质量在6~10 kDa的颗粒物占比基本未发生变化,分子质量在6 kDa以下的颗粒物占比降低至30%,同时分子质量在10~30 kDa的颗粒物占比增长30%左右。有研究表明,大分子质量物质对膜污染的贡献更高[24],结合上述实验结果,所以建议HRT控制在8 h以内。
-
1) HRT对污泥粒径的影响。由图6可见,3种HRT运行下,污泥粒径分布均表现出相似规律,污泥粒径主要分布在0.4~200 μm。随HRT的增大,混合液中污泥粒径呈现逐渐降低的趋势。污泥粒径小于10 μm的颗粒被认为是造成膜污染的最主要颗粒成分[17],因为污泥粒径越小,污泥颗粒沉积在膜表面,形成泥层的孔隙率低阻力大,膜污染增大[17]。当HRT为6 h和8 h时,污泥粒径小于10 μm的占比分别为14.46%和16.51%;而当HRT为12 h时,污泥粒径小于10 μm的占比为48.7%。这是由于EPS中多糖量与颗粒污泥大小成正相关[4, 11],这从图4的结果中也可以得到验证,即当HRT为12 h时,TB-EPS中多糖含量最低。EPS含量越低,污泥聚集性能越差,污泥粒径越小。
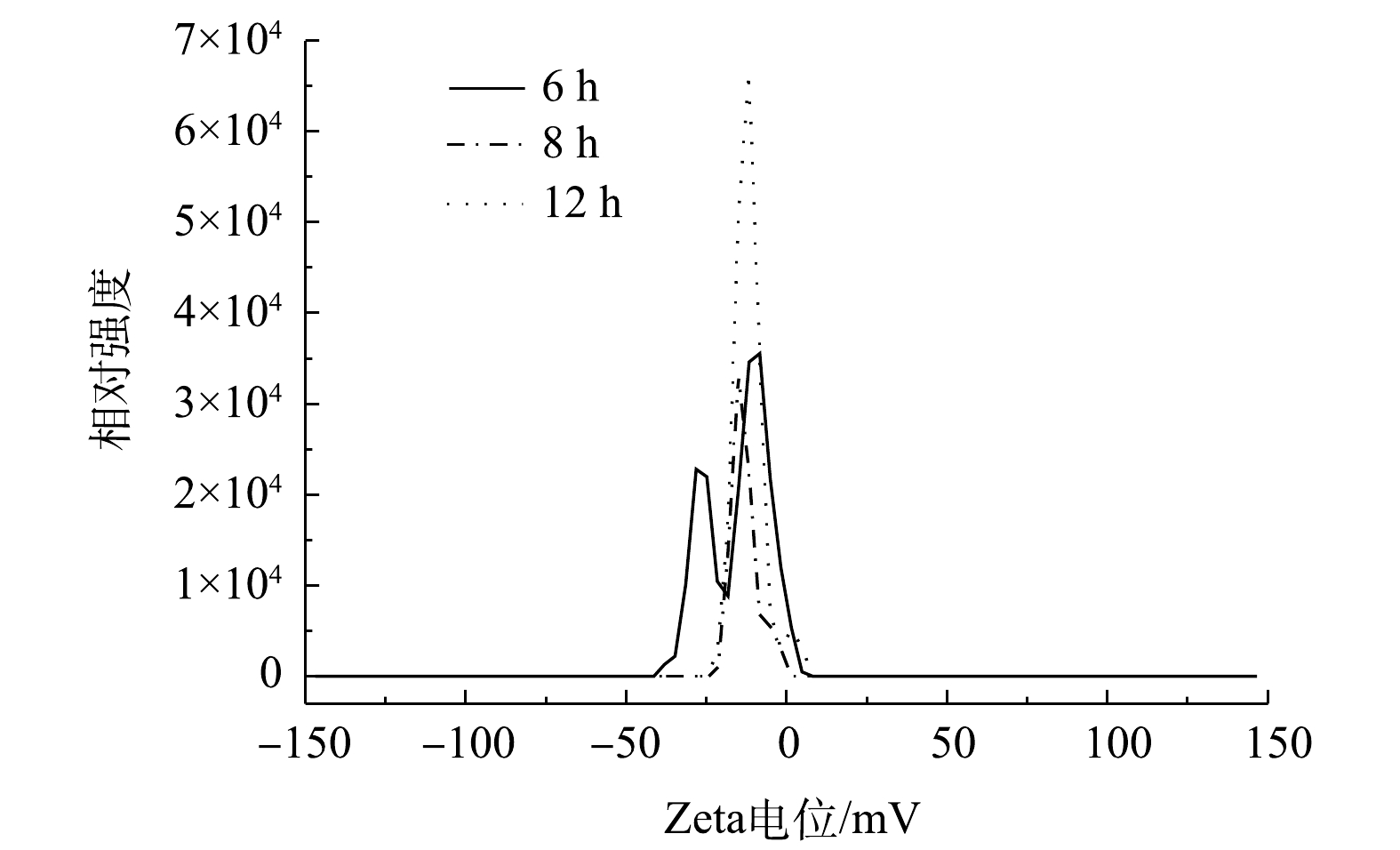
2) HRT对污泥Zeta电位和黏度的影响。由图7可知,当HRT为6 h时,Zeta电位范围最宽,为−38.11~4.77 mV;当HRT为8 h时,Zeta电位值最小,为−16.79~−0.27 mV,污泥颗粒最为稳定。这从侧面也反映出HRT使混合液中EPS的含量发生变化,部分EPS会作为底物被微生物利用[25]。Zeta电位的变化与微生物新陈代谢所产生的EPS有直接关系,EPS带有大量带负电荷的官能团,其含量与Zeta电位成正相关[26],但与膜阻力成负相关[18]。
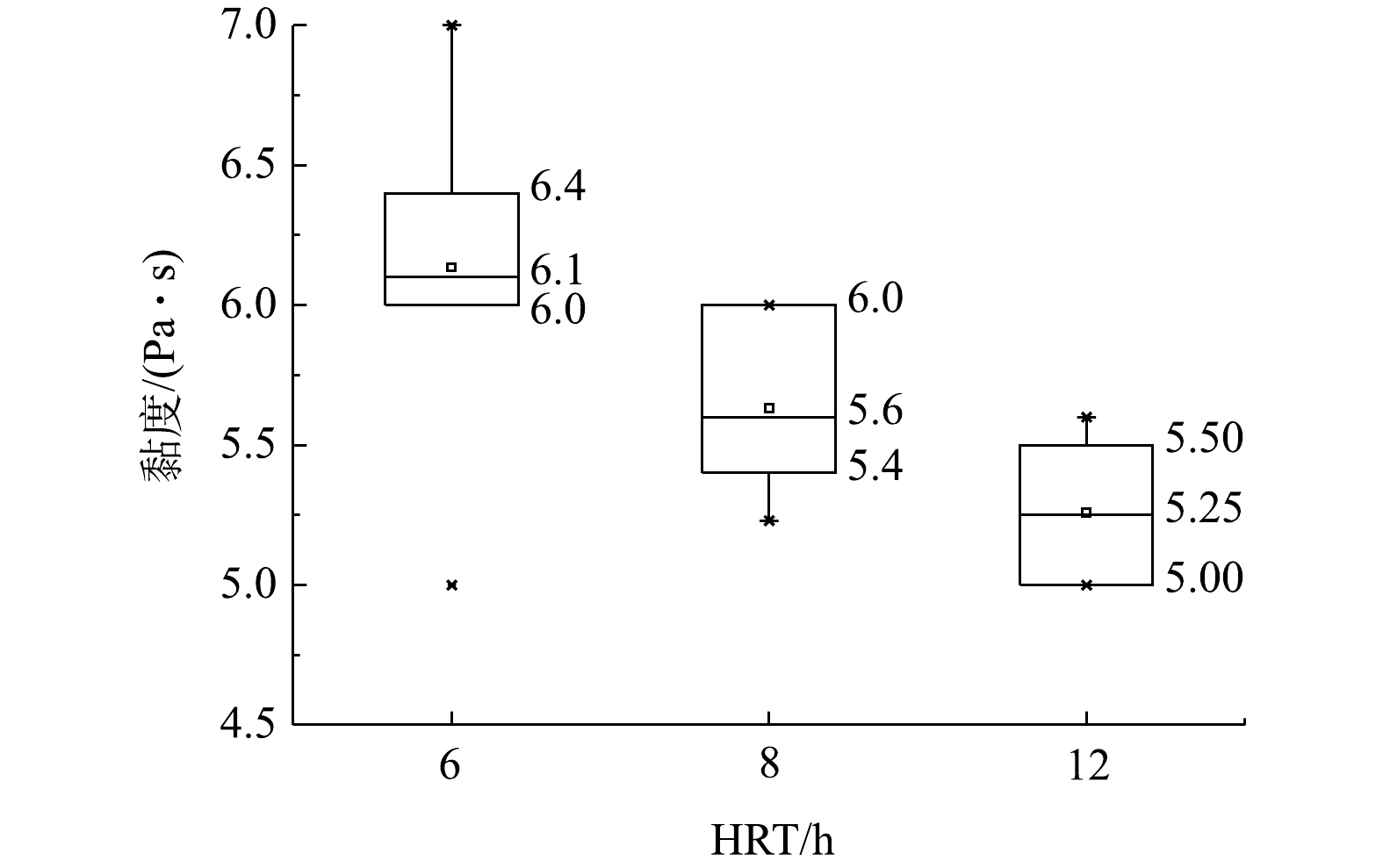
由图8可知,当HRT为6 h时,混合液黏度最高,保持在6~6.5 Pa·s;随着HRT的延长,混合液的黏度降低,当HRT为12 h时,混合液黏度最低,为5~5.25 Pa·s。这可能是由于低HRT促使丝状菌增长,从而导致黏度较高[13],微生物会产生更多的多糖和蛋白等,也可导致混合液黏度增高[18],因此,黏度可从侧面反映混合液对膜污染的影响程度。
2.1. HRT对出水水质影响
2.2. HRT对微生物代谢产物含量的影响
2.3. HRT对微生物代谢产物中颗粒物的分子质量分布的影响
2.4. HRT对混合液中污泥的影响
-
1) 在HRT为6 h、膜通量15 L·(m2·h)−1、污泥质量浓度为4 000 mg·L−1条件下,MBR处理生化尾水可以获得较好的混合液特性和处理效果。
2)随着HRT的逐渐延长,会使膜组件运行时间缩短,从而影响微生物代谢行为,微生物代谢产物的大分子质量颗粒物的比例和SMP含量随之增加,EPS多糖含量和污泥粒径的降低共同作用于膜阻力,导致TMP快速增大,加快膜的污染进程。
3)污泥Zeta电位的升高和污泥黏度的降低导致污泥凝聚力和传质能力变弱,从而降低了其处理效果。
4) HRT对微生物代谢和膜污染进程有着重要调控作用,通过优化HRT可以较为简便地改善膜污染程度。



 下载:
下载: