-
生活污水中的表面活性剂通常由洗手液、洗涤剂残液成分带入,是两端分别由疏水基团与亲水基团所形成的两性结构化合物[1]。由于表面活性剂在污水中含量通常较低,故长期以来未能引起污水处理行业的关注。2020年新型冠状病毒疫情爆发导致洗手液使用量急剧增加,进而致使生活污水中表面活性剂质量浓度升高[2]。这使得表面活性剂对污水、污泥处理的影响应受到业界重视。表面活性剂具有较强吸附性能,故可能会对污水处理效率产生负面影响[3],而进入剩余污泥中的表面活性剂又会对污泥脱水等预处理产生正面影响[4]。
本文梳理了表面活性剂的来源及其在污水中的演变,对其进入污水生物处理系统产生的负面影响进行了概括、剖析,以提出可能的运行应对措施;最后,归纳、分析表面活性剂在污泥处理、处置中的正面作用,厘清在工程应用中的应对策略。
全文HTML
-
根据表面活性剂基团类型,可将其分为阴离子型、阳离子型、非离子型及两性离子型。阴离子型按其亲水基团结构包括磺酸盐与硫酸酯盐型;阳离子型主要包含胺盐类与季氨盐类;非离子型中典型的是以烷基酚为基团的聚氧乙烯醚和脂肪醇聚氧乙烯醚;两性离子型含有的阴离子部分为羧酸基类,而阳离子部分是氨基酸型与甜菜碱型。非离子型和阴离子型表面活性剂的使用量最大,分别占比56.1%和36.8%。
生活污水中表面活性剂的质量浓度通常为5~20 mg·L−1,而掺杂工业废水后的市政污水中,质量浓度可能高达300 mg·L−1[5]。2020年1—2月,除春节期间减产、甚至停工影响外,其他合成洗涤剂产量较2019年同期均有较大幅度提升,平均每天多产3.33×103 t·d−1,涨幅为10%~15%。据供求关系推测,市场需求量的增加会导致进入污水处理厂的表面活性剂增加至少10%,从而使得其在市政污水处理厂中的质量浓度会超过10 mg·L−1。
表面活性剂的主要成分为有机物[6]。难生物降解和不可生物降解的表面活性剂绝大部分会被污泥吸附,并随剩余污泥排出系统,只有很少部分溶解态的表面活性剂会随出水排放(监测中会计入COD)。因此,应该重点关注污水中的可生物降解表面活性剂。
直链烷基苯磺酸盐(linear alkylbenzene sulfonates,LAS)应用广泛,是一种典型阴离子表面活性剂,在生活污水中的质量浓度一般为 3~20 mg·L−1。有研究表明,在污水处理过程中LAS会被一定程度地降解,但受自身结构及所处环境(好氧或厌氧)影响,其降解程度不一[7]。LAS的生物降解需满足以下条件:1)特定微生物种群协同作用,需有假单胞杆菌、芽孢杆菌、大孢子虫和弧菌等共同参与,而非单一细菌可完成;2)较高的溶解氧(DO)水平;3)较长的水力停留时间(HRT)[7]。
很显然,LAS降解所需条件较为严格,代价可能是增加能耗与运行成本。即使满足上述条件,进水中LAS也只有80%~90%可以降解,其余大部分都残留于污泥之中(1%随出水排放)[7]。LAS在污水处理过程中的固-液分配系数(Kd,表示单位质量固相污泥吸附LAS的质量(mg·kg−1)与液相水溶液中残留的LAS的质量浓度(mg·L−1)的比值,单位为L·kg−1)为:初沉污泥Kd=13 211 L·kg−1;剩余污泥Kd=13 316 L·kg−1[8]。
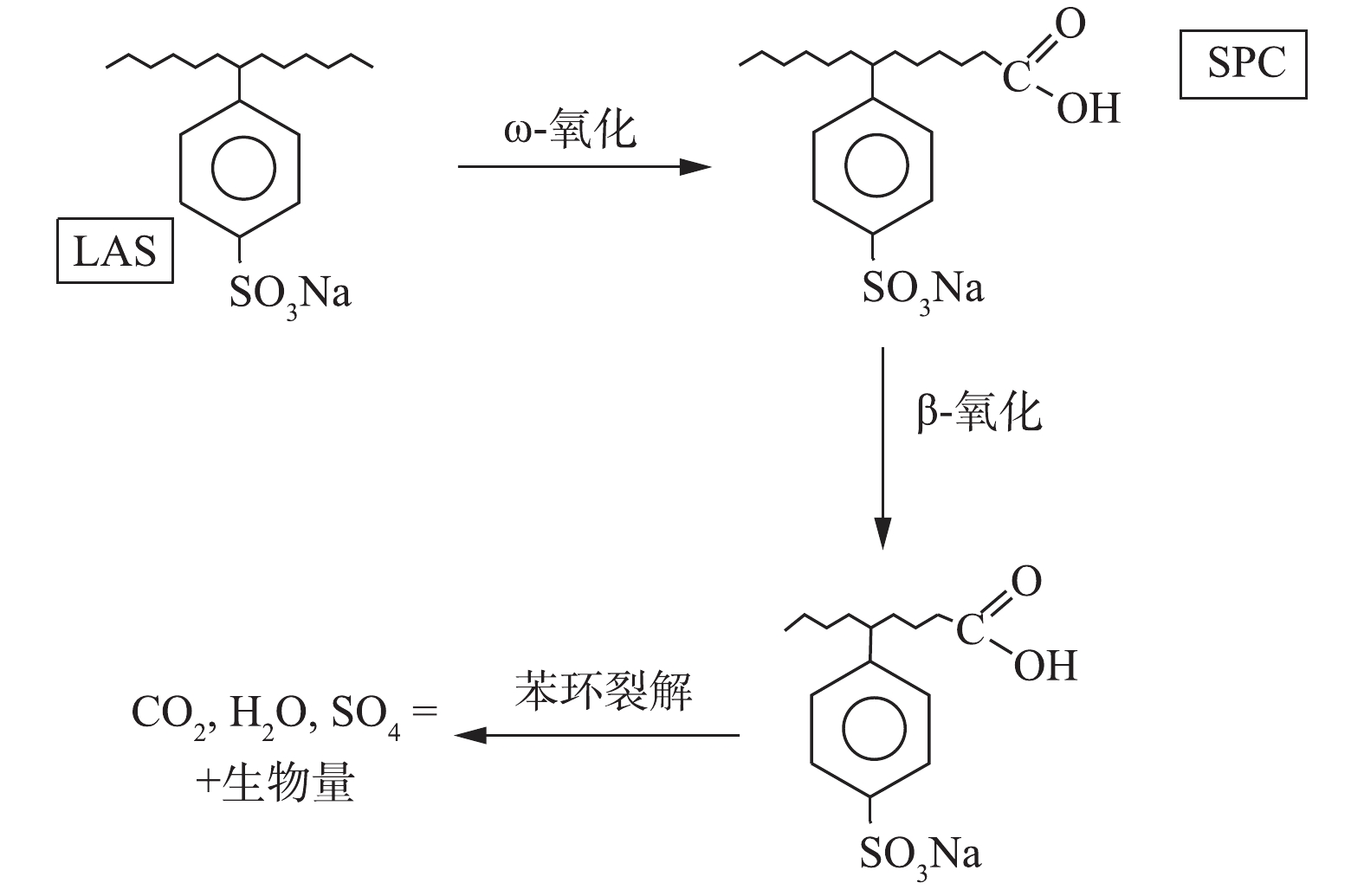
深入研究可发现,LAS降解并非直接被氧化至CO2,而要经历一定的中间代谢过程[7](见图1)。LAS生物降解是伴随烷基链ω氧化开始,即乙氧基链初步氧化,末端甲基氧化成羧基,进而连续裂解2个碳原子片段后发生β氧化(烷基链缩短);ω和β氧化过程会产生硫苯基羧酸盐(SPCs),这一过程导致活性剂界面活性与毒性一并丧失,完成无毒化转变;最后,SPCs芳香环继续裂解,彻底矿化为CO2和H2O[7]。
然而,非离子表面活性剂的生物降解效果远不如LAS,如壬基酚乙氧基酸盐(NPEO)。有研究表明[9],芽孢杆菌(Bacillus sp. LY)在3 d内仅可去除60%的NPEO(初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1)。分析其原因,NPEO中间体壬基酚(nonyl phenol,NP)本身就难生物降解,且其毒性大概是母体NPEO的10倍;这些中间体还会抑制异养反硝化菌对NPEO进行生物降解,最终导致NPEO生物降解率变低[10]。
综上所述,即使是可生物降解表面活性剂,其在生物处理过程中能真正实现降解也并非易事,不仅会造成能耗与成本增加,而且多数情况下降解也只是发生母体降解表象,其代谢中间产物的毒性甚至可能比母体还高。
-
表面活性剂进入污水后,在污水生物处理过程中会对曝气、生物反应等产生负面影响,且浓度越高其影响越大。因此,有必要关注新冠疫情时期表面活性剂因使用量增加,进而给污水处理系统带来的负面影响。
有学者研究了SBR反应器中阴离子表面活性剂十二烷基磺酸钠(sodium laurylsulfonate,SDS)对污水处理过程的影响,发现SDS对脱氮除磷均有明显影响。当SDS=5 mg·L−1时,TP去除率为85.8%;但当SDS≥10 mg·L−1时,TP去除率则明显下降,从73.2%降至50.8%;同时,
NH+4 去除率下降更为明显,从83.6%直接降至39.5%,降幅超过50%[11]。亦有学者观察到,SDS与十二烷基苯磺酸钠(sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate,SDBS)在高盐废水处理中会影响生物脱氮除磷效果。SDS的添加导致TP去除率从55.6%降至41.3%;SDBS的存在仅影响反应初期TP的去除效果,但经驯化培养后,TP去除率可恢复如初(55.1%);在SDS和SDBS各自单独存在情况下,NH+4 去除率分别从63.4%下降至42.6%和59.8%[12]。笔者在新冠疫情期间进行生物脱氮除磷的中试试验时发现,当进水掺混50%生活污水后,系统内硝化明显受到抑制;从原自来水配水时出水的
NH+4 接近0突然升至5 mg·L−1;而溶解态PO3−4 并未发生明显变化。好氧池DO检测发现,无论怎样增大曝气量,均难以提高DO。经文献调研及推理分析可认为,可能是进水中洗手液含量增多即表面活性剂增多,造成了这一结果,也因为如此,进水表面存在大量漂浮的泡沫。基于上述原因,以下将从氧传质、污泥絮体、微生物抑制等3方面进一步分析表面活性剂的影响及机理。
-
表面活性剂是微溶大有机分子物质,具有强亲水端和强疏水脂肪族/芳香端。曝气过程中,疏水端吸附在气液界面,而亲水端则延伸至本体溶液中,从而形成有序分子单层。分子单层结构会施加阻塞效应,增加界面粘度,从而降低空气与液相之间的氧传质效率[13]。但也有结果相反的研究结果,表明表面活性剂的分子晶格结构会阻碍氢键作用力,导致气泡体积变小,进而降低表面张力,使气泡均匀分布于气-液界面,致使液相含气率提高,即可改善氧的传质[14]。综合2种相左的作用,前者对液体传质的负面效应远远高于后者,最终表现为降低氧传质效率。亦有研究者发现,在较短污泥龄(sludge retention time,SRT)下,降低氧传质效率之负面影响表现更为突出。这是由于在长SRT运行状态下,可很大程度地降解表面活性剂,从而降低其对氧传质的不利影响[8]。
有学者用表面活性剂SDS研究好氧活性污泥对氧传质的影响时发现,SDS并没有降低液体氧转移效率(oxygen transfer efficiency,OTE),这可能是由于SDS进入反应器后会迅速被污泥絮体吸附并随后降解,导致液相中SDS浓度较低,从而对液相氧传质的影响变弱。传统观点认为,表面活性剂降低OTE往往忽略了生物体本身对表面活性剂的降解能力,这意味着较低浓度的表面活性剂存在时,而OTE可能会因生物降解表面活性剂或其裂解的EPS,从而加快氧传质效率[8]。进一步的研究表明,在高浓度表面活性剂存在情况下,表观黏度(μapp)与细胞碎片增加很可能是OTE降低的原因,同时污泥氧的转移性能主要取决于污泥形态参数,如MLSS、SV30、絮体直径和μapp等,而与进水表面活性剂关系不大[8]。
-
污泥絮体与表面活性剂结合会影响絮体的形态[8],导致絮体中结合松散的EPS(LB-EPS)破裂,进而影响紧密的EPS(TB-EPS)、甚至细胞结构[15]。还有研究者报道了表面活性剂会被生物絮体乃快速吸附而生物降解,因为活性污泥具有很高的吸附能力(每克MLSS会吸附70 mg LAS)[16]。当进水中LAS质量浓度<25 mg·L−1时,表面活性剂则迅速从溶液中消除,在15 min后便保持在0.1 mg·L−1不变[16]。也有研究结果[17]证实,吸附与生物降解是促进生物处理过程中表面活性剂去除的重要过程。
-
有学者在培养聚磷菌(phosphorus-accumulating bacteria,PAOs)时发现[18],当SDS=0.6~2.3 mg·L−1时,能抑制PAOs的菌落(CFUs)达50%;当SDS≥300 mg·L−1时,则对CFUs形成100%抑制作用;对CFUs的抑制会进一步降低PAOs对磷的摄取效率,且二者呈现线性相关关系(r=0.828,p<0.05)。同时发现,当阳离子表面活性剂十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide,HDTMA)的质量浓度>3.65 mg·L−1时,显示出特别毒性,对CFUs和磷摄取率均产生100%抑制作用。然而,实际污水中通常存在的阴、阳离子表面活性剂质量浓度分别为10 mg·L−1和5 mg·L−1[18]。这意味着表面活性剂对污水生物除磷系统的负面影响不容小觑。该结果表明,表面活性剂对PAOs增殖和磷摄取均存在抑制作用,而对PAOs增殖的抑制作用更为明显。进一步分析表面活性剂对PAOs的聚磷作用影响表明,表面活性剂会抑制PAOs对P的摄取和积累能力,表现为好氧吸磷效率低下,可降低EBPR系统除磷效率,并且在高浓度表面活性剂存在下直接导致细胞壁、膜结构破裂解体而表现为永久性释磷,导致后续无法完成好氧吸磷。污水中通常存在的阴、阳离子表面活性剂质量浓度分别为10 mg·L−1和5 mg·L−1[18],这种低浓度表面活性剂虽然会对微生物产生一定抑制作用,但因活性污泥絮体EPS等结构给细菌提供了某种保护,导致实际监测中其负面影响可能被忽视[19]。DERESZEWSKA等[16]发现,当每克DS中LAS的质量<3 mg时,其对污水处理基本没有负面影响,甚至可以提高污泥生物活性;但当每克DS中LAS的质量>15 mg时,则可观察到微生物新陈代谢呼吸作用减弱、且磷吸收机制被破坏,甚至直接影响活性污泥形态,导致絮体碎裂和原生动物细胞裂解;研究结果表明,低浓度LAS可改善厌氧条件下的P释放,而高浓度LAS则会阻碍P释放;但LAS无论浓度如何均会阻碍好氧磷吸收过程。
-
表面活性剂也会对污水处理脱氮相关细菌产生严重影响[20]。有研究者发现,进水中随LAS质量浓度增加,硝化过程逐渐受到抑制;当LAS的质量浓度为2 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1时,对硝化细菌抑制率高达50%和100%[16]。这一结果表明,即使进水中存在低浓度表面活性剂时,也会对硝化产生严重影响。这可能是因为,
NH+4 被氨单加氧酶所氧化,而表面活性剂存在时,则会对AMO产生毒害作用,从而抑制NH+4 氧化过程[21]。LUSSIER等[22]提出了另外一种抑制机制,即表面活性剂代谢中间产物(如烷基酚乙氧酸盐(alkyl phenol ethoxylate,APE)壬基酚(nonyl phenol,NP))是一种较强的内分泌干扰物,NP毒性大约是乙氧基化形式的10倍,会对NH+4 氧化产生较大抑制作用,即使在低浓度时也会影响微生物新陈代谢过程。OTHMAN等[23]则认为,LAS单体可与细胞壁结构直接反应,辅以细胞膜相互作用,使膜透性增加,从而导致离子梯度和膜电位耗散或基本细胞成分泄漏。同样的表面活性剂抑制现象也会发生在缺氧反硝化过程中。SDS浓度增加将会导致酶活性受到抑制,进而影响反硝化过程[24]。但有趣的是,低浓度表面活性剂亦可作为碳源被反硝化菌所利用,从而促进硝酸盐还原脱氮作用[24]。LU等[10]发现,非离子表面活性剂壬基酚乙氧基酸盐作为反硝化细菌碳源可促进反硝化脱氮过程,但当其他有机物存在的情况下,其降解过程明显变缓或停止。JIMÉNEZ-GONZÁLEZ等[25]认为,辛基酚乙氧基酸盐会影响反硝化颗粒污泥EPS,会将细胞壁和细胞膜蛋白溶解,但这种作用并没有对整体脱氮过程产生较大影响。此外,表面活性剂还会抑制相关酶活性,从而对厌氧氨氧化(ANAMMOX)过程产生负面影响[26]。
综上所述,表面活性剂对污水处理涉及微生物影响包括4个方面。1)低浓度时可用作碳源,在一定程度可助厌氧释磷或反硝化;而高浓度表面活性剂则会对微生物产生毒性作用[16, 24]。2)对微生物细胞膜等结构产生破坏作用,而对膜电位影响可能改变代谢控制,甚至可能与细胞膜物质直接作用,导致细胞膜溶解,进而影响优势菌属类别以及菌属相对丰度[20]。3)通过静电或疏水相互作用与酶蛋白催化残基结合,导致酶活性降低[20]。4)表面活性剂作为一种活性基团,可与基质大分子(淀粉、蛋白质、肽和DNA等)结合,严重时会直接插入各种细胞结构片段(如细胞膜磷脂双分子层),进而导致功能失调[27]。
-
截至目前,似乎还未见到污水处理厂受表面活性剂影响导致出现运行问题的报道。也许这种影响尚未被察觉,如表面活性剂所导致的氧传质效率降低很容易与进水COD和
NH+4 负荷增高导致DO下降混为一谈。面对该问题,其实目前还没有现成的运行应对技术措施,尽管存在一些实验控制或消除手段,例如吸附法、泡沫分离法、混凝法等可将表面活性剂从污水中分离出去,而微电解或催化氧化法可实现表面活性剂的降解或彻底去除[28]。然而,研究中的实验方法目前显然难以在实际运行中被直接采用,实际有效的方法是需要及时调整运行参数来尽可能抵消表面活性剂带来的负面影响。如对氧传质的降低问题,可以通过加大曝气量来得到一定程度地缓解;对污泥絮体的影响可以通过加大污泥回流量来保证系统内具有足够有效的生物量;对微生物的影响则需要进一步提供稳定的运行环境(如保证足够碳源、pH和环境温度等),以实现微生物稳定增殖和新陈代谢。
2.1. 对氧传质效率的影响
2.2. 对污泥絮体的影响
2.3. 对微生物活性的影响
2.3.1. 对聚磷菌的抑制作用
2.3.2. 对生物脱氮相关细菌的抑制作用
2.4. 应对策略
-
虽然表面活性剂的存在会对污水处理产生负面影响,但文献调研发现,其对污泥处理、处置过程却可能有正面作用[4]。移至剩余污泥(10%~20%)的表面活性剂作为一种有机物成分,与污泥有机质相比微不足道。事实上,有很多进行污泥处理、处置的研究,都采用投加表面活性剂的作法来提高处理效果或提高效率,其作用原理主要体现在3个方面:1)污泥脱水预处理;2)厌氧消化;3)污泥资源化。
-
剩余污泥的含水率高达99%,且体积庞大,故脱水时添加一定量的表面活性剂以实现高效、节能的效果。有研究表明,表面活性剂具有与聚丙烯酰胺相类似的功能,可以用作脱水助剂,能大幅度降低滤饼水分含量[4]。表面活性剂的加入伴随着皂化现象发生,导致污泥絮体直径快速减小,从而影响絮体形态[4]。具体来说,表面活性剂亲水基团会与蛋白质结合,从而损害生物膜功能性和完整性;而疏水基团与脂质结合,可导致膜液化、损害其屏障特性[4]。与此同时,表面活性剂(如十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(cetyltrimethylammonium bromide,CTAB))携带的电荷效应会在一定程度上中和污泥表面电荷,降低污泥之间静电斥力,使污泥絮体变得松散[4];表面活性剂也会增加细胞疏水性,促进细胞与细胞之间的相互作用,进一步诱导污泥絮体从亲水性液相中脱出,从而提高沉降速率和脱水性能[4]。该研究亦表明,SDS和曲拉通(TritonX-100)对污泥EPS的增溶作用会导致污泥基质破裂,使更多污泥内蛋白和多糖释放,引起粘度增加,反而会恶化污泥的脱水性能[4]。
-
1)促进水解酸化。表面活性剂会对污泥厌氧消化产生一定影响,不同厌氧消化阶段产生的影响作用不尽相同。众所周知,污泥厌氧消化能源转化效率不高的主要原因在于污泥水解过程困难而缓慢。有研究表明,表面活性剂可以促进污泥水解,其作用机理[29]包括:1)增溶;2)酶释放(如图2所示)。表面活性剂可通过降低表面张力或形成胶束来增强颗粒的溶解度,引起污泥物质分解,特别是EPS会释放更多蛋白质和碳水化合物,表现为聚集态大分子有机物转化为小分子或溶解态物质,增加厌氧消化产甲烷阶段可利用的底物浓度[4]。另一方面,酶和EPS之间由于存在静电相互作用,可形成稳定的EPS-酶复合物,EPS释放也意味着水解酶可以从污泥中释放出来,从而可提高水解效率。也有研究表明,SDS和SDBS均可以刺激或增加蛋白酶和淀粉酶活性[29]。但是,表面活性剂是否存在刺激酶活性等影响机理还有待于进一步研究。
表面活性剂还可以促进酸化。除上述增加溶解态底物浓度和加速水解造成间接酸化提高外,更重要的是其官能团可作为电子中间转移体加速电子转移,从而促进酸化。另有研究者发现[30],SDS可提高SCFA产率。文献[29]亦进一步揭示,当每克DS中含有SDS质量为100 mg时,SCFA质量浓度(以COD计)接近2 243 mg·L−1,而空白对照组仅为191 mg·L−1。然而,过高的SDS含量将会产生负面影响,这可能是由于微生物蛋白质结构被破坏或积累了部分有毒副产物[29]。
2)抑制产甲烷。有研究结果显示,表面活性剂也会抑制厌氧消化产甲烷菌活性。具有芳香和环状结构的表面活性剂(如SDBS)被认为是厌氧消化过程中嗜乙酸产甲烷菌最危险的化合物;而直链SDS则是产甲烷菌毒性最小的表面活性剂之一[29]。有研究者发现,随着SDS含量从每克DS中20 mg提高至300 mg,产甲烷抑制率可从3%提高至100%[29]。厌氧消化系统中表面活性剂抑制产甲烷可能与2个原因密切相关:1)直接抑制产甲烷,阻断转化途径;2)抑制产甲烷菌群,破坏不同厌氧种群之间存在的共营养关系,导致系统失衡[31]。
-
剩余污泥EPS具有高值回收潜力,而表面活性剂有助于EPS与细胞分离,在EPS提取与回收中发挥事半功倍的效果。以淀粉样蛋白提取分离为例,常规方法并不能有效溶解和分离这种结构性聚合物[32-33],但在碱性条件下投加仅0.1%的SDS便可实现固体颗粒完全溶解,最终从回收萃取物(每克挥发性悬浮固体(VSS))中提取出(480±90) mg EPS[34]。分析这种淀粉样蛋白质难以在普通条件下分离的原因,发现其化学和热稳定性都极强,即使在强变性试剂(2 mol·L−1的硫脲+8 mol·L−1的尿素+3%的SDS)中煮沸60 min也只能分解部分蛋白质,而表面活性剂的参与能部分剥离蛋白质四级和三级结构,从而实现EPS分离提取。
表面活性剂不仅可实现物质分离,也可以实现提取物质增产。王欣[35]通过添加CTAB和SDS辅助超声波法提取EPS,结果表明,较单一超声波法提取量分别提高了76.5%和53.1%。经分析提取物成分发现,EPS组分多糖和蛋白质并未发生明显变化;而从EPS粒径发现,添加表面活性剂后EPS粒径明显减小。这意味着表面活性剂可能仅仅是整体促进了EPS溶出或溶解过程,而提高了EPS产量[35]。不同种类表面活性剂的提高效果不同,这表明表面活性剂因自身结构不同亦会产生独特的增产机理,如CTAB自身线性烃链形成胶束,通过互溶原理能加速EPS释放[36]。
3.1. 对污泥脱水预处理的影响
3.2. 对厌氧消化的影响
3.3. 污泥资源化
-
1)新冠疫情强化了人们的卫生习惯,同时也造成污水处理厂进水中表面活性剂含量升高(10~30 mg·L−1)。表面活性剂对污水生物处理过程的影响贯穿始终,在低浓度时可以作为碳源被降解,而在高浓度时会影响曝气,进而影响脱氮除磷效果。
2)表面活性剂在生物处理过程会降低氧传质、破坏污泥絮体结构以及影响脱氮除磷微生物活性与丰度,其负面影响不容小觑。尽管一些常规方法,理论上可以以预处理方式去除表面活性剂,如物理吸附法、混凝法,化学微电解法、催化氧化法等,但对已有污水处理工艺来说似乎是纸上谈兵。现实中,恐怕只有通过适当调整运行参数(加大曝气与回流量等)短时予以应对,尚无长远之计。因此,需要就此开展相应的研究。
3)表面活性剂仅约1%会随出水流出,而有10%~20%进入剩余污泥。然而,进入污泥的表面活性剂对污泥处理、处置似乎有正面影响,这主要是因为它们能够对污泥絮体脱水、解体与增溶产生正面效果。除提高污泥脱水效率外,表面活性剂亦可促进厌氧消化水解酸化过程,但对产甲烷过程却有抑制作用。




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: