-
矿山开采、冶炼、电镀与金属加工等工业活动引发了一系列的水体重金属污染问题,形势严峻,亟待解决[1]。铜是常见重金属污染物之一,经食物或饮用水摄入过量的铜,将导致人体肝脏损害、急性中毒和造血功能失常[2]。因此,寻求一种高效便捷的除铜的方法势在必行。
目前,水体重金属治理的方法主要囊括了电化学、吸附、膜分离以及化学沉淀等技术[3-4]。其中吸附法因其吸附剂原料易得、操作简便及高效利用的优点,受到了科研工作者的高度关注[5]。海藻酸钠(SA)是一种二元线性多糖类聚合物,其具有生物降解性和非生物毒性的优点,被认为是环境友好型的重金属吸附剂[6]。其分子链上含有丰富的羟基(—OH)和羧基(—COOH)[7]。对pH具有高度敏感性的羧基(—COOH)基团能在合适的pH条件下,迅速与钙离子配位,形成网状结构的海藻酸钙凝胶球[8]。这种结构能有效固定小颗粒磁性物质,同时也相应地削弱吸附剂的吸附能力。L-半胱氨酸(L-Cys)是一种人体常见的非必需氨基酸,具有氨基、羧基和巯基官能团,颇具重金属富集潜力[9]。在海藻酸钠中引入这部分基团,将有望提高其对重金属的吸附能力。
但在吸附过后,吸附剂难与水媒介分离,从而导致二次污染。有研究[10-11]表明,将吸附剂赋予磁性后进行高效吸附,且利用其磁性进行快速分离是一种有效的解决办法。因此,本研究把L-Cys、磁性物质Fe3O4和SA通过钙离子交联,制备得到了一种环保型磁性复合材料,旨在进一步改善其吸附能力和磁响应性。以中山市某工业园含铜电镀废水为对象,验证了该磁性复合材料在实际水处理中的吸附效能,重点考察了pH、共存离子和吸附时间对铜吸附效果的影响。分析了其吸附动力学、吸附等温模型以及热力学过程,并采用SEM-EDS、PPMS以及XPS分析手段探索了可能的吸附机理。
全文HTML
-
1)仪器试剂:实验所用SA、L-Cys购自上海阿拉丁公司;HCl和NaOH采购自广州化学试剂厂;CaCl2、CuSO4·5H2O、FeCl2·4H2O、FeCl3·6H2O和NH3·H2O试剂采购于天津市大茂化学试剂厂。实验涉及所有试剂纯度等级为分析纯,实验用水为去离子水。本研究所涉及的仪器包括PHS-3S型pH计、D2010W电动搅拌器、DHG-9075A电热鼓风恒温干燥箱、XTLZ多用真空过滤机、SHA-B型恒温水浴振荡器、WFX-110B型原子吸收分光光度计。
2)磁性复合材料的制备。将质量比为3∶1的FeCl3·6H2O和FeCl2·4H2O配制成100 mL混合溶液,置于三口烧瓶中氮气吹扫30 min。在氮气保护下,用NH3·H2O调节溶液pH至10,升温至80 ℃继续反应30 min。反应完毕,用磁铁分离混合液中的黑色Fe3O4颗粒,用蒸馏水冲洗3~5次,50 ℃烘干备用。然后将SA、L-Cys、Fe3O4按一定的质量比添加到50 mL的蒸馏水中,以180 r·min−1的转速搅拌2 h。最后将上述均匀混合液滴加到确定质量分数的CaCl2溶液中,固化12 h,干燥得最终产品SA@L-Cys@Fe3O4磁性复合材料(MSAL)。
-
采用单因素实验考察了SA、L-Cys、Fe3O4以及CaCl2浓度4个因素对溶液中Cu(Ⅱ)吸附性能的影响。实验在100 mL Cu(Ⅱ)溶液中进行吸附,其条件为:吸附温度(25 ℃)、吸附时间(2 h)、MSAL投加量(0.75 g·L−1)、Cu(Ⅱ)初始浓度(100 mg·L−1)。吸附完毕,取上清液过0.45 μm滤膜,采用型原子吸收分光光度计测定溶液剩余Cu(Ⅱ)浓度。每组实验重复3次,取平均值为最终结果。
-
鉴于pH约为5.5时,Cu(Ⅱ)溶液已经出现轻微浑浊,Cu(Ⅱ)去除率不完全由吸附贡献,因此,调节最大pH=5.0。在250 mL锥形瓶中加入100 mL CuSO4·5H2O溶液,用0.1 mol·L−1的HCl分别调节pH至2.5、3.0、3.5、4.0、4.5、5.0,置于25 ℃水浴恒温振荡器内,吸附2 h。实验平行3次,取其平均值作最后结果。
-
实验选取Ni2+、Zn2+、Cr6+、
SO2−4 、PO3−4 、Cl−共6种共存离子,离子浓度为50 mg·L−1。将共存离子分别加入到100 mg·L−1的铜溶液中,使其形成相应的二元体系,振荡吸附120 min。 -
为探究MSAL对溶液中Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附行为,用准一级和准二级动力学模型对吸附数据进行拟合。其计算方法[12-13]如式(1)和式(2)所示。
式中:t为吸附时间,min;Qt为t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;Qe为平衡时吸附量,mg·g−1;k1为准一级动力学吸附速率常数,min−1;k2为准二级动力学吸附速率常数,g·(mg·min)−1。
-
在固-液吸附体系中,Langmuir或Freundlich吸附模型通常用于解释等温吸附过程。Langmuir方程假设吸附过程为单层吸附,Freundlich方程是基于非均相表面吸附的经验公式,分离因子RL用于判别吸附性质,其线性表达式[14-15]分别如式(3)~式(5)所示。
式中:Qe为平衡时吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为吸附平衡时Cu(Ⅱ)浓度,mg·L−1;Qmax为最大吸附量,mg·g−1;kL为Langmuir平衡常数,L·mg−1;kF为与MSAL吸附容量有关的常数;n为吸附强度特征常数。
为了进一步了解MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)的行为,对不同温度(25~40 ℃)下的吸附数据进行了热力学参数计算,计算公式如式(6)~式(8)所示。
式中:ΔG为吉布斯自由能,kJ·mol−1;ΔS为吸附熵变,kJ·(mol·K)−1;ΔH为吸附焓变,kJ·mol−1;kF为吸附平衡常数,由Freundlich吸附等温式中的吸附常数kF确定;T为热力学温度,K;R为气体常数,取值8.314
× 10−3 kJ·(mol·K)−1。 -
吸附脱附实验共重复5次,将已吸附Cu(Ⅱ)的MSAL加入到100 mL的0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液中,搅拌60 min后过滤,再经超纯水洗涤。将脱附后的MSAL置于含有100 mL的100 mg·L−1 Ca2+溶液中,以重新固化MSAL。
-
本实验含铜废水为广东省中山市某工业园电镀综合废水。该废水水质情况为:铜、锌、镍和铬浓度分别为(23.1±0.6)、(177.5±1.5)、(13.3±0.9)和(5.7±0.5) mg·L−1;SS值为(2 147.2±26) mg·L−1;pH=1.7。针对复杂的水质状况,采用MSAL吸附联合聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)絮凝工艺,考察了MSAL用量(1.0~5.0 g·L−1)、pH (1.7~5.2)对含铜废水污染物的去除率以及MSAL回收率的影响。
-
采用美国Quantum Design公司生产的PPMS-9型综合物性测量系统分析了Fe3O4和磁性MSAL的磁学性能;采用Quanta 650环境电子扫描显微镜对MSAL的形貌进行分析,利用仪器自带的EDS采集了MSAL元素信息;采用美国Thermo Fischer Scientific K-Alpha型号分析仪分别对MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)前后的XPS进行分析。
1.1. 材料与制备
1.2. 制备条件实验
1.3. pH对MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)的影响
1.4. 共存离子对MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)的影响
1.5. 吸附动力学研究
1.6. 等温吸附与热力学
1.7. 吸附循环实验
1.8. 含铜电镀废水处理
1.9. 表征分析
-
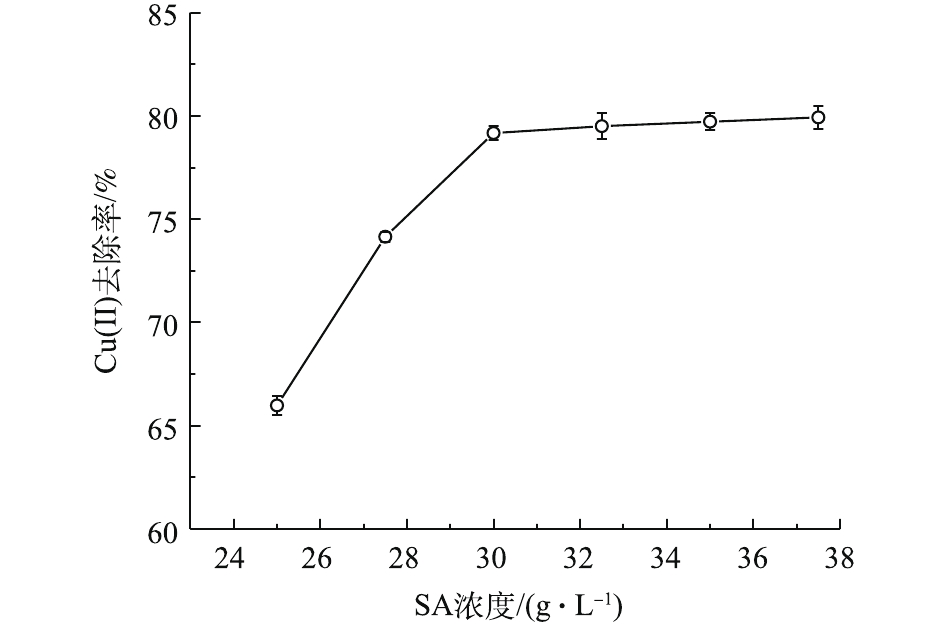
图1反映了SA浓度对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附性能的影响结果。在初始阶段,随着SA浓度的增加,MSAL对溶液中Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附能力逐渐提高,并在30.0 g·L−1时去除率达到最高。原因在于,逐渐增加的SA为Cu(Ⅱ)吸附提供充足位点[16]。在后期,随着SA浓度进一步升高,去除率缓慢上升。原因在于,MSAL外表面吸附位点有限,大部分内部的吸附位点则在高浓度SA作用下被紧密包裹于凝胶中,难以发挥作用。因此,本研究中的SA适宜浓度应为30.0 g·L−1。
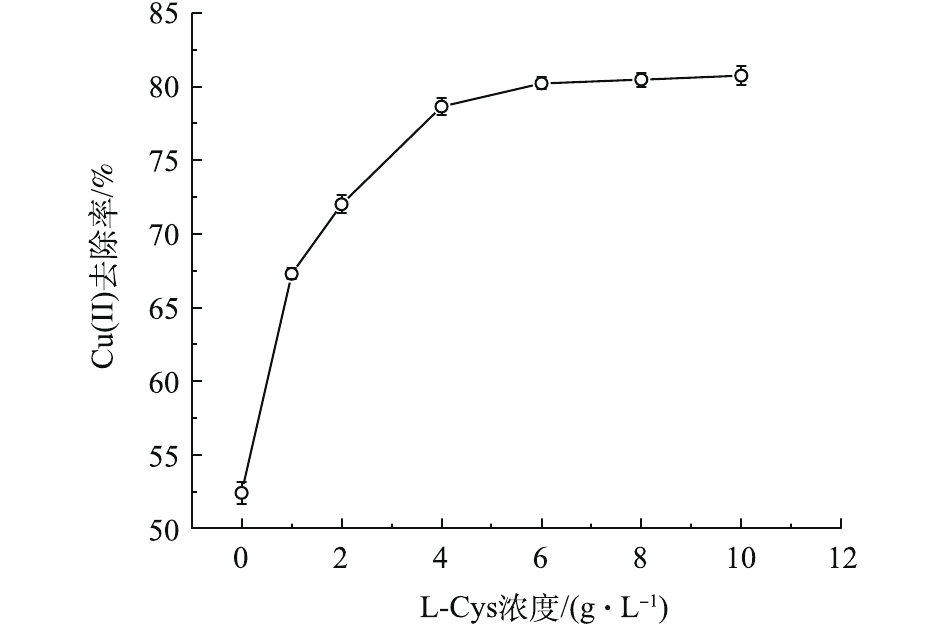
L-Cys内含有能与重金属络合的基团,因此,其浓度是影响吸附性能的重要因素[17]。由图2可见,随L-Cys浓度的增加,MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)去除率呈现快速提升而后趋于平缓的趋势。当L-Cys用量为6.0 g·L−1时,吸附趋于平衡,此时Cu(Ⅱ)去除率为80.23%,相比无添加L-Cys时高出27.81%。陶虎春等[16]的研究表明,壳聚糖/海藻酸钙复合凝胶球对初始浓度(25 mg·L−1) 相对较低的Cu(Ⅱ)的最大去除率为78.13%。综上可知,L-Cys的引入在一定程度上提高了MSAL的吸附能力。L-Cys上活泼的巯基基团容易与二价金属离子形成不溶性络合物,随L-Cys浓度的增加,随沉淀而固定下来的L-Cys越多,从而越有利于吸附[18]。但是这一特性也使得凝胶球交联更为紧密,内部空间变小,不利于Cu(Ⅱ)溶液进入凝胶网络[19],因此L-Cys浓度进一步增加,MSAL对铜去除率无明显的提升。综上所述,制备MSAL适宜的L-Cys浓度为6.0 g·L−1。
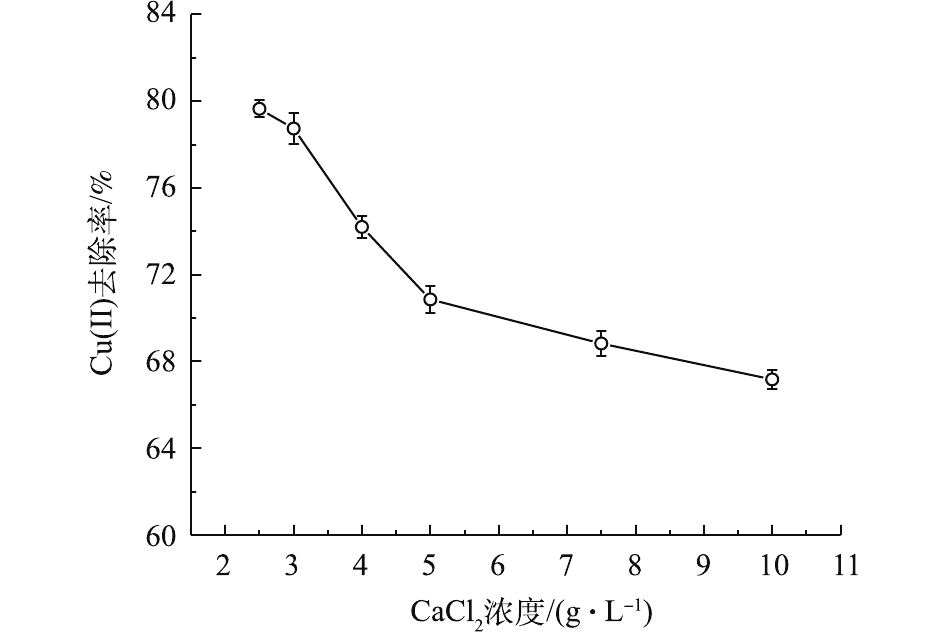
SA通过钙离子作用形成具有一定机械强度的凝胶球,进而将L-Cys和磁性物质包裹其中[20]。过低的CaCl2浓度影响海藻酸钙的成球性能,过高时过分紧密的包裹作用又会损失吸附位点,导致吸附能力下降。由图3可知,当CaCl2浓度为2.5~10.0 g·L−1时,Cu(Ⅱ)去除率由79.65%降低至67.17%。推测其原因可能是,过度的海藻酸钙包裹作用减少了有效吸附位点。在CaCl2浓度为2.5 g·L−1时,MSAL仍然具备较好的成球性。因此,2.5 g·L−1可作为后续实验的CaCl2浓度。
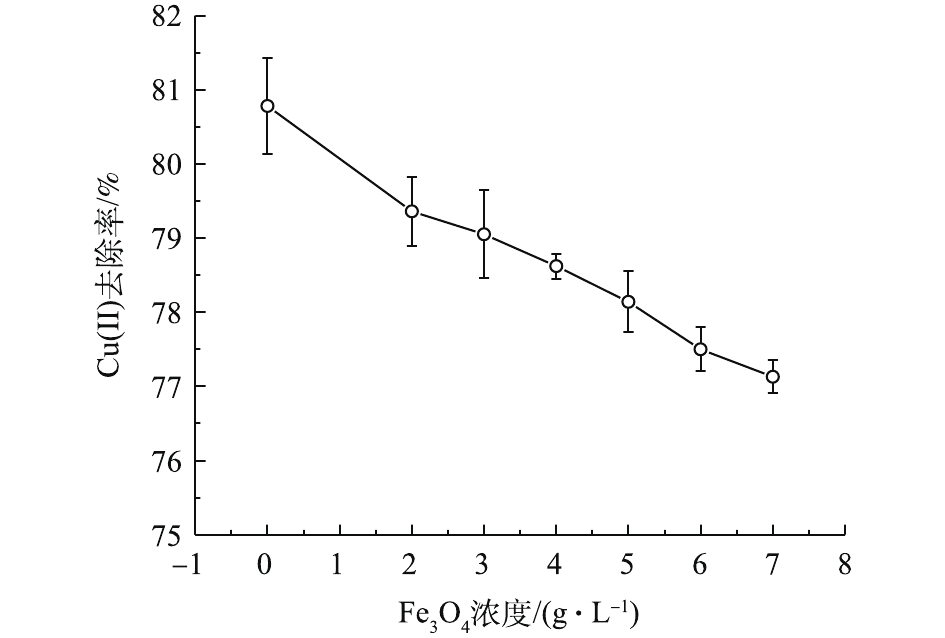
Fe3O4的引入赋予复合材料相应的磁学性能,只有当Fe3O4达到一定的浓度时,才能表现出良好的磁分离能力,实现MSAL与水媒介的快速分离。另一方面,Fe3O4浓度也在不同程度上影响着复合材料对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附性能。由图4可知,当Fe3O4浓度为0~7.0 g·L−1时,Cu(Ⅱ)去除率有所降低,下降幅度为3.65%。这是因为加入的纳米Fe3O4占据了原水分子应有的空间,使MSAL更加致密,从而一定程度上削弱了其吸附能力[8]。因此,在保证复合材料磁分离能力的前提下,尽量降低Fe3O4浓度,以便有利于吸附进行。当Fe3O4添加量为2.0 g·L−1时,MSAL已具备良好的磁分离效果,因此,本研究选择2.0 g·L−1为最佳Fe3O4添加量。
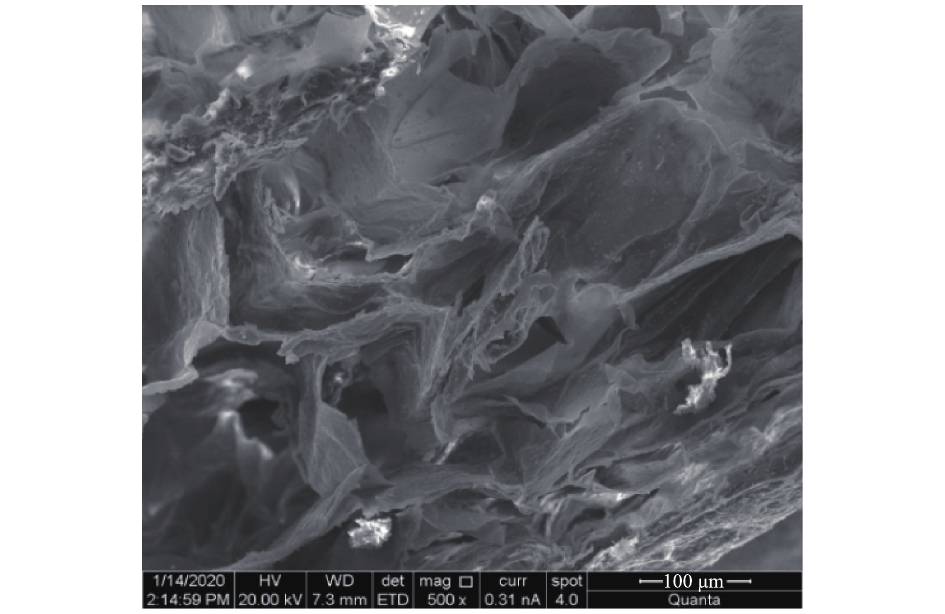
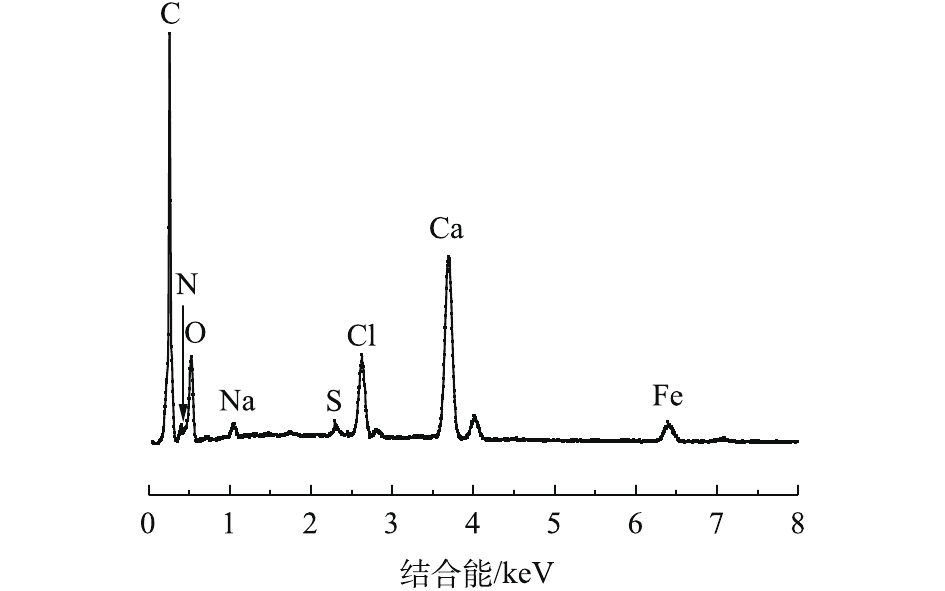
MSAL内部结构放大500倍后的形貌如图5所示。由图5可见,MSAL内部形成了海绵网络空隙结构,增大了其比表面积,为Cu(Ⅱ)吸附提供了丰富的附着位点。MSAL内部片层明显,且可见大量的细小颗粒Fe3O4被固定在片层中,为MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)并从水媒介中快速分离回收提供了可能性。对MSAL进行了EDS分析,结果如图6所示。在EDS图谱中,发现L-Cys的特征元素N和S以及Fe3O4的特征元素Fe对应的特征峰,这说明MSAL已成功加载L-Cys和Fe3O4。
图7为Fe3O4和MSAL的磁滞回线。由图7可见,二者均为S型磁滞回线,且无明显滞后环的出现,矫顽力和剩磁均接近于零。Fe3O4和MSAL的饱和磁化强度分别为50.7 emu·g−1和23.6 emu·g−1。尽管经海藻酸钙的包裹后,MSAL的磁学性能有一定程度的削弱,但仍维持在允许范围内。可见MSAL拥有良好的磁响应性,能够在超磁分离装备的磁场作用下实现快速的磁分离[21],有利于MSAL的回收利用,避免二次污染,从而可降低成本。
-
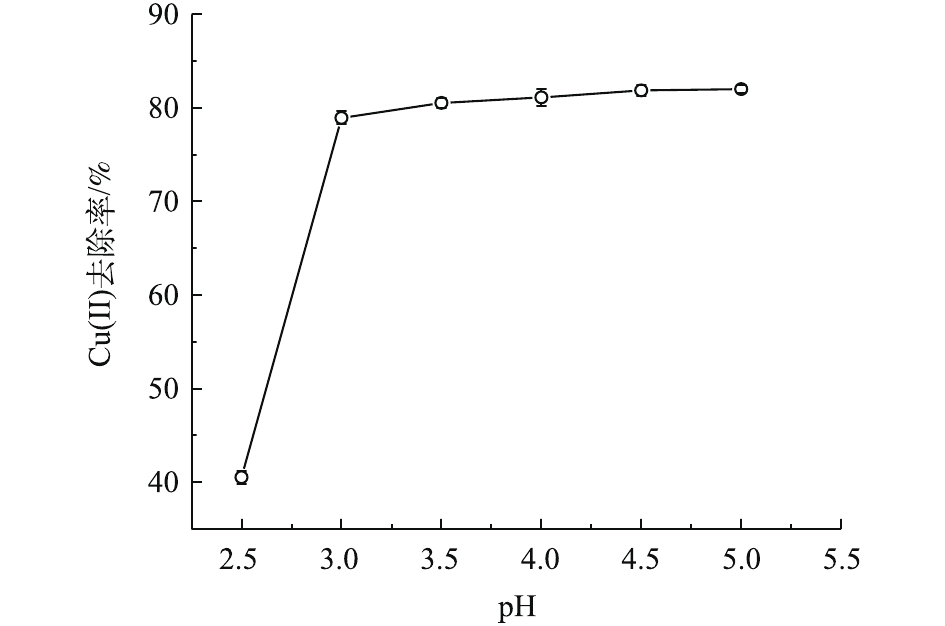
pH是影响吸附性能的一个重要因素,其不仅影响金属离子的离子化程度,还可影响MSAL官能团的存在形态。由图8可知,MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)去除率随pH变化可分为2个阶段。在第1阶段,pH=2.5,溶液中存在大量的H+与Cu(Ⅱ)竞争吸附位点,使得自由氨基和羧基数量有所减少,导致其吸附能力明显较低。此外,在强酸性条件下,质子化严重,加大了MSAL与Cu(Ⅱ)间的静电斥力,不利于吸附进行,去除率仅为40.53%。在第2阶段,随着pH的升高,去除率先迅速提高至68.94%,而后在一个较宽的范围(pH=3.0~5.0)内,维持着较高的去除率。这是因为H+在竞争吸附中逐渐失去优势,质子化削弱,氨基和羧基等吸附位点重新暴露[22]。而在实际应用中,Cu(Ⅱ)污染废水的pH通常为3~6。因此,体系中pH为3.0~5.0均可作为溶液Cu(Ⅱ)吸附条件,为方便实验室调节pH,后续可选择pH=5为宜。
-
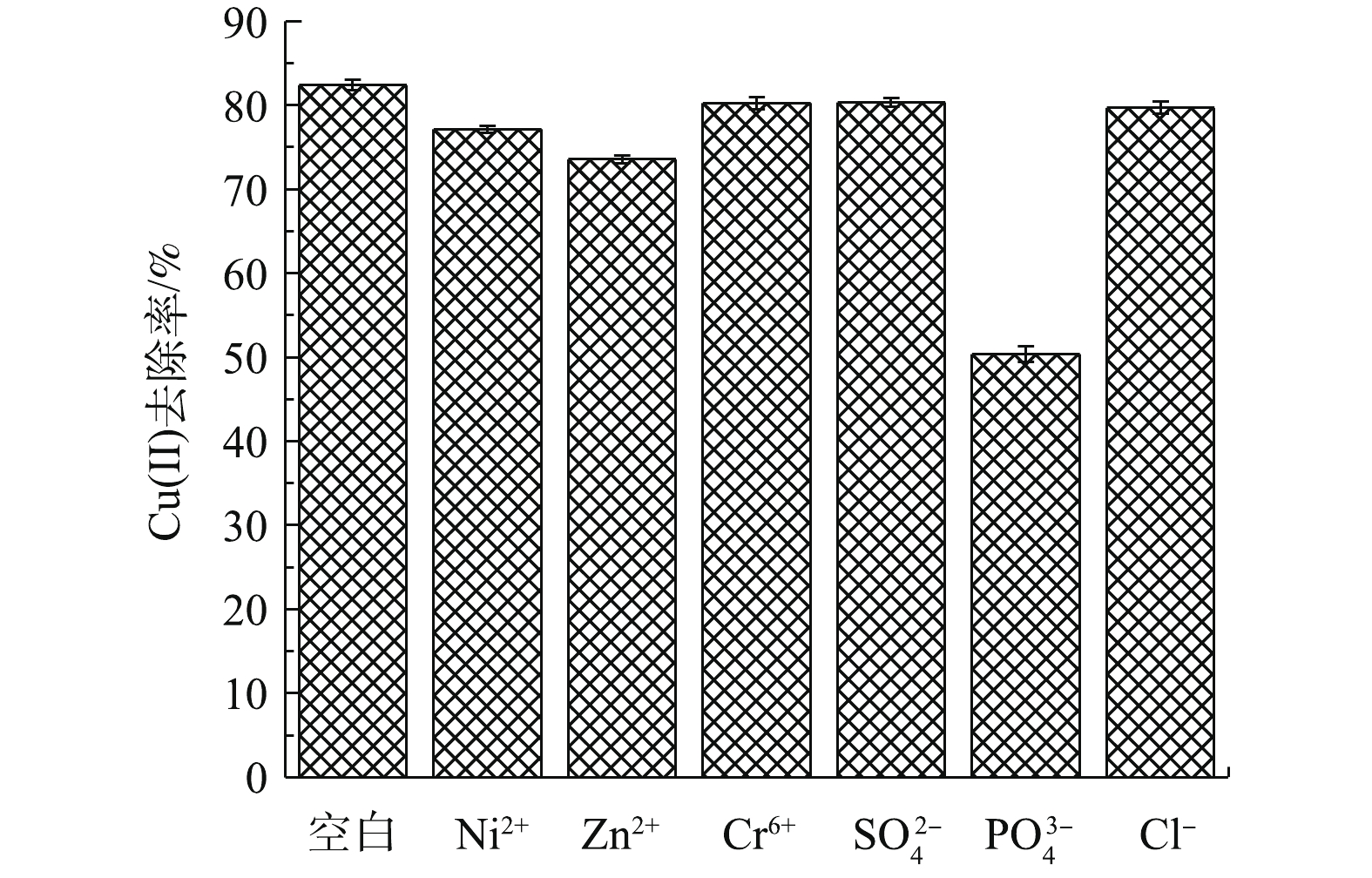
受水体共存离子的影响,水体中金属离子存在形式不尽相同,最终导致吸附效果也有所差别。如图9所示,受共存Zn2+和Ni2+竞争吸附影响,MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附能力有所下滑。在阴离子方面,受
SO2−4 和Cl−影响,MSAL吸附性能基本保持不变;受共存PO3−4 离子影响,MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)去除率下降至50.36%。原因是PO3−4 的引入使其形成了复杂的络合阴离子Cu(P2O7),不利于MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)。 -
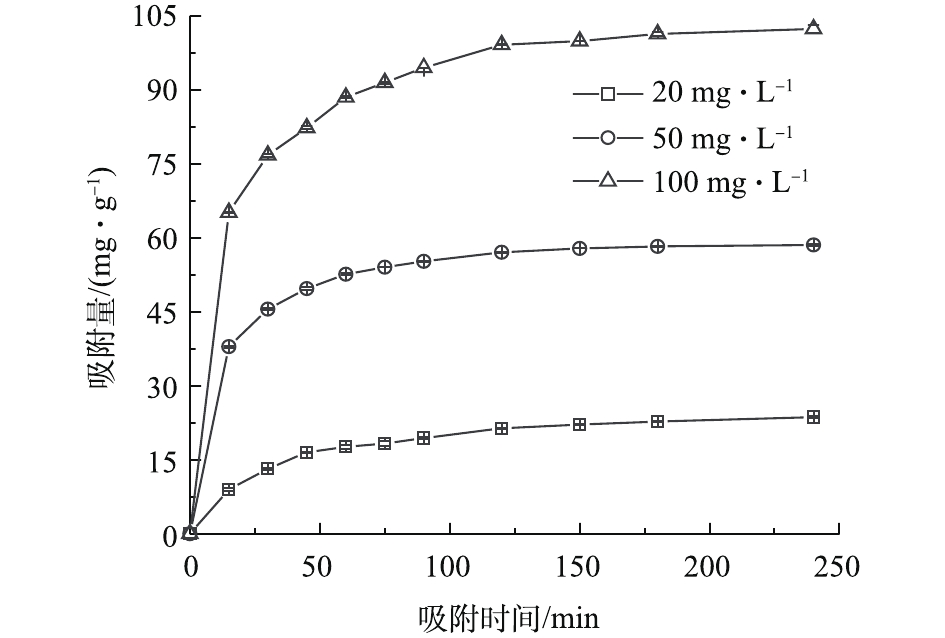
图10反映了0~240 min内MSAL对溶液中Cu(Ⅱ)吸附量的影响。由图10可见,吸附主要发生在0~120 min内,120 min达到吸附平衡,当Cu(Ⅱ)初始浓度为20、50和100 mg·L−1时,其所对应的Cu(Ⅱ)平衡吸附量分别为23.66、58.57和102.37 mg·g−1。在吸附初期,吸附量随时间增长而迅速升高。这是因为,在吸附初期MSAL表面提供了充足的吸附位点,两相之间的Cu(Ⅱ)浓度差为溶液中Cu(Ⅱ)移动提供了足够的传质动力[23],Cu(Ⅱ)能够快速被吸附到MSAL表面。吸附后期,大量的Cu(Ⅱ)占据了活性基团,活性基团数量逐渐减少,吸附量缓慢提升直至平衡。表1为准一级动力学模型和准二级动力学模型的线性回归拟合结果。可以看出,Cu(Ⅱ)初始浓度为20、50和100 mg·L−1条件下,准二级动力学模型获得的Qe与实测值较为接近,可决系数R2分别为0.999 2、0.999 9和0.999 6,更接近于1,表明吸附过程遵从准二级动力学模型。根据准二级动力学模型的前提假设条件,可推测化学吸附是速率控制步骤[23]。
-
本研究采用Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型对MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)实验数据进行拟合,结果见表2。可以看出,Langmuir模型得到的可决系数R2优于Freundlich模型,表明吸附过程更倾向于单分子层吸附。在温度由25 ℃上升至40 ℃的过程中,kF逐渐升高,这说明温度的升高有利于吸附的进行。由表2可见,不同浓度下的RL值均为0~1,这说明其属于优惠吸附,对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附是容易进行的[24]。在Freundlich模型中n值也通常用于判断吸附性能强弱,n值越大,说明吸附质更倾向于被吸附剂吸附。由n = 2.879 8>1,可判定其属于优惠吸附,这一结论与Langmuir模型结果[25]相一致。
利用等温吸附数据、吉布斯函数和范特霍夫方程进行热力学计算分析,结果如表3所示。当温度在25~40 ℃时,ΔG<0,表明MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附过程时自发进行的;ΔS>0,说明吸附过程为一个熵增过程,体系内混乱度增加;ΔH>0,这说明吸附为一个吸热反应过程,提高温度有利于Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附,这与吸附等温模型反应的结论相符。
-
循环使用能力是评价一种吸附材料实用性的关键指标。实验结果表明,经5次吸附/脱附循环以后,对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附容量维持在(105±3) mg·g−1。当pH=5时,吸附水样中铁浓度为(0.28±0.05) mg·L−1,铁的溶出损失量占MSAL中铁总量的0.93%;再生水样中铁浓度为(0.10±0.07) mg·L−1,铁的溶出损失率为0.33%。上述结果表明,MSAL在Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附/脱附过程中结构较稳定,不容易产生二次污染。
-
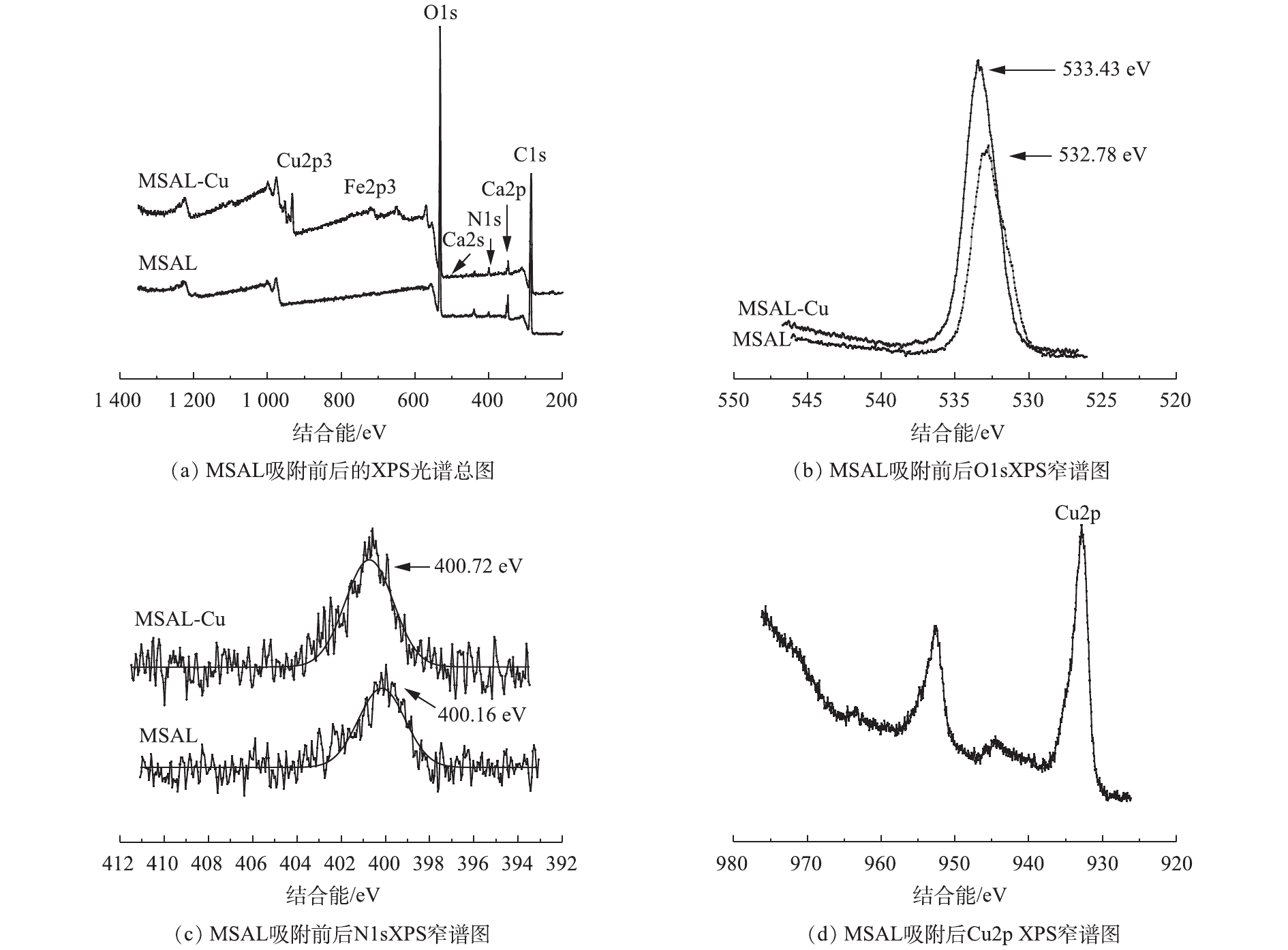
图11为MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)前后X射线光电子能谱分析结果。由图11(a)可以看出,在MSAL吸附Cu(Ⅱ)后,Ca2s峰的强度几乎消失,Ca2p峰强度明显变弱,同时出现了新的Cu(Ⅱ)特征峰Cu2p3。这些变化表明,系统中存在MSAL上的钙离子与溶液中的Cu(Ⅱ)之间的离子交换作用[26]。为了进一步揭示Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附机理,还考察了Cu(Ⅱ)吸附前后的O1s峰和N1s峰(图11(b)和图11(c))的变化情况。C—O基团的结合能从532.78 eV转移到533.43 eV。N1s的核心能级谱表明,C—N基团的特征结合能在吸附铜后由400.16 eV移至400.72 eV。这些变化可能是O和N的孤电子对向Cu(Ⅱ)转移,从而降低了O和N的电子云密度,并增加了系统的结合能所造成的[27]。如图11(d)所示,在933.1 eV和952.5 eV处检测到了Cu2p3的结合能,这意味着MSAL与Cu(Ⅱ)之间可能形成了Cu—O/Cu—N配位键。由此可见,吸附过程主要受Ca2+和Cu(Ⅱ)之间的离子交换以及—COO,—NH2 和Cu(Ⅱ)之间的配位作用影响。
-
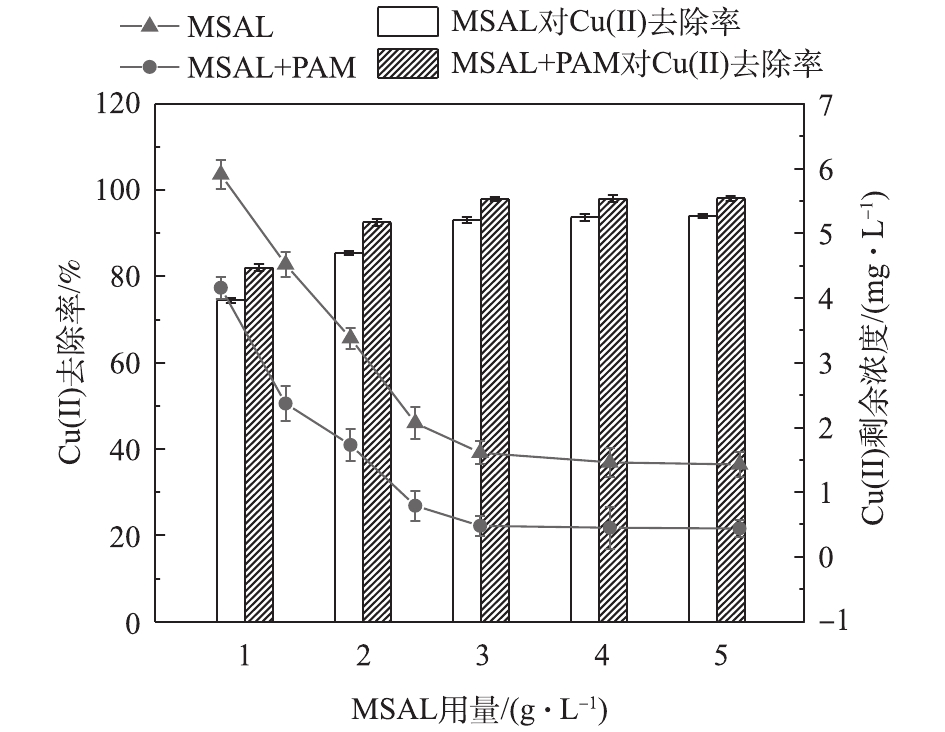
如图12所示,无论是MSAL吸附超磁分离工艺或者是MSAL+PAM超磁分离工艺,Cu(Ⅱ)的去除率随MSAL用量增加均有明显提高。任意MSAL用量条件下,MSAL+PAM工艺中Cu(Ⅱ)去除率比MSAL工艺高出近4%。当MSAL用量为5 g·L−1时,在经MSAL和MSAL+PAM超磁分离工艺处理后,Cu(Ⅱ)去除率分别达到94.02%和98.09%,而废水中残留Cu(Ⅱ)含量分别为1.43 mg·L−1和0.44 mg·L−1。此外,MSAL对废水中共存的锌和铬去除率可高达94.48%和93.15%,而对镍吸附效果则稍显逊色,去除率仅为51.13%。以上结果表明,MSAL能够高效吸附电镀废水中的铜、锌和铬,投加适量的PAM则能够低于电镀污染物铜排放阈值要求。
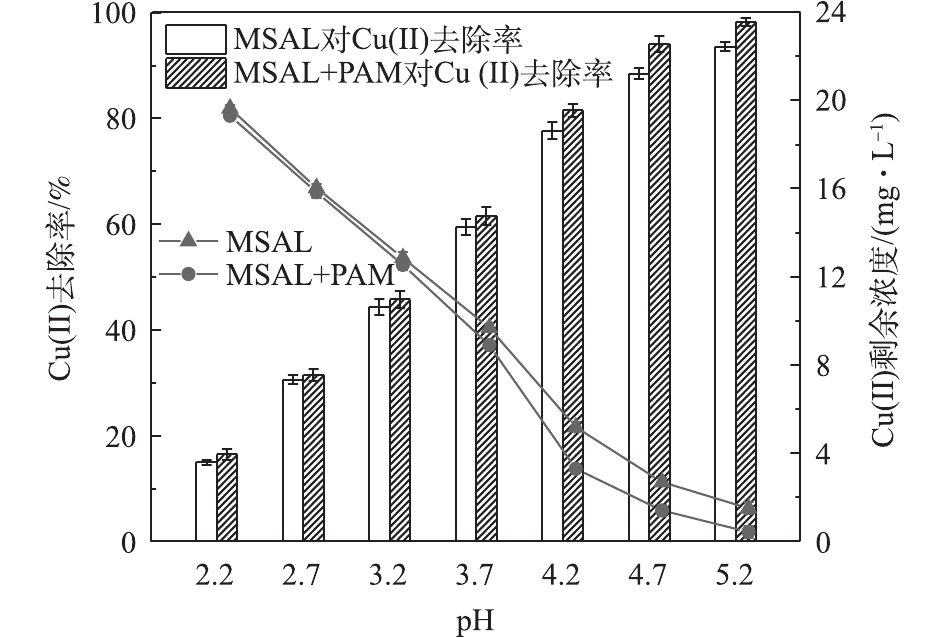
图13反映了MSAL用量为3.0 g·L−1时,pH对电镀废水除Cu(Ⅱ)的影响。废水中Cu(Ⅱ)去除率随pH的增大逐渐有所提高。其原因为:1)去质子化作用为MSAL提高了竞争吸附能力;2)受多金属共存条件下共沉淀作用的影响;3)受PAM絮凝沉淀作用影响。总体而言,MSAL在电镀废水处理中,Cu(Ⅱ)去除率可达到约94%,与PAM联合处理将进一步提高其去除率,实现废水中铜的达标处理。
2.1. MSAL的制备与表征
2.2. pH对吸附性能的影响
2.3. 共存离子对吸附性能的影响
2.4. 吸附时间的影响及动力学模型
2.5. 等温吸附与热力学
2.6. 循环使用性能
2.7. 机理分析
2.8. 含铜电镀废水处理
-
1) MSAL的最佳制备条件为 30.0 g·L−1 SA、6.0 g·L−1 L-Cys、2.5 g·L−1 CaCl2、2.0 g·L−1 Fe3O4。该条件下制备的MSAL具有较大的比表面积,结构稳定,可多次回用,拥有良好的磁响应性,使其能高效吸附并与水媒介快速分离。
2) MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附性能随pH的增大明显提高,在pH=3.0~5.0时,可维持高的去除率。吸附为自发的吸热反应过程,吸附量随温度的增加缓慢提高。吸附数据符合准二级动力学模型,表明吸附过程受化学吸附控制。Langmuir模型更适合描述MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附过程,可推断吸附过程为単分子层吸附。该磁性材料对Cu(Ⅱ)的最大吸附容量可达到175.45 mg·g−1。
3) MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附机制有2种可能:第1种是溶液中的Cu(Ⅱ)与该材料中的钙离子发生了离子交换;第2种是MSAL中O和N孤对电子转移至Cu(Ⅱ)上,电子云密度降低,形成了Cu—O 和 Cu—N之间的配位作用。
4)在pH=5下,受电镀废水复杂的水质情况影响,MSAL对Cu(Ⅱ)去除率仍高达94.02%。当投入0.3 mg·L−1 PAM时,废水中Cu(Ⅱ)的去除率可进一步提升至98.09%,废水中Cu(Ⅱ)残留量为0.44 mg·L−1,低于(GB 21900-2008)中关于新建企业水污染物排放限值(0.5 mg·L−1)。



 下载:
下载: