-
印染废水具有水量大、有机污染物负荷高、可生化性差等特点[1-2]。目前,国内外处理印染废水的方法主要有物理法[3-4]、生物法[5-6]和高级氧化法(advanced oxidation processes, AOPs)[7-8]等。作为AOPs之一的非均相光芬顿(Fenton)技术,因其具有pH适用范围广、不产生铁泥、较高的Fe3+/Fe2+循环效率等优势,从而得到了广泛的关注[9-11]。然而,非均相光Fenton技术仍然面临催化效率低、催化剂稳定性差、需要紫外光介入等问题。因此,开发高效、稳定、能以可见光或天然日光作为驱动光源的非均相光Fenton技术具有重要的意义。
针铁矿(α-FeOOH)作为一种天然矿物,因化学性质稳定、环境友好、低毒、廉价等优势而被广泛应用于光Fenton/类光Fenton中[12-14]。最近的研究[15-16]表明,Cu、Ni等金属元素掺杂可以进一步提高FeOOH的催化效率。相比于Cu、Ni,Co不仅能够分解H2O2产生·OH,而且多价态的Co以及Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)之间的标准电势,有利于Co与Fe之间形成协同作用,进而提高催化效率和催化剂的稳定性。然而,较低的Fe(III)/Fe(II)循环效率及必要的紫外光诱导仍然是亟待解决的问题。石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)是一种不含金属元素的可见光催化剂[17-18]。将g-C3N4与FeOOH复合,利用g-C3N4被可见光激发产生的光生电子(e−)可以有效促进Fe(III)/Fe(II)的还原,从而提高催化效率[19-21]。
综上所述,本研究拟通过化学浴沉淀法制备Co掺杂的FeOOH与g-C3N4复合催化剂(Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4),并构建可见光驱动的非均相光芬顿反应体系。在该体系中,利用可见光激发g-C3N4产生光生e−和空穴(h+),光生e−从g-C3N4迁移至Co-FeOOH,一方面促进Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)的循环,加速催化H2O2产生·OH,另一方面,光生e−和h+的有效分离强化了h+的直接氧化作用,从而使催化效率得到提高。本研究考察了各影响因素对该体系催化效率的影响规律,优化了反应参数;在最佳反应条件下,考察了Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4/H2O2体系在天然日光辐照下对高浓度染料废水脱色及化学需氧量(COD)的去除性能。
全文HTML
-
采用热聚合三聚氰胺法[22]制备了g-C3N4。将500 mg的g-C3N4溶于40 mL乙醇中,加入1 mmol FeCl3·6H2O和一定量Co(NO3)3·6H2O(Co分别占Fe的物质的量的0、10%、15%、20%、30%,并表示为XCo-FeOOH/g-C3N4),搅拌10 min,再加入3 mmol NH4HCO3,持续搅拌8 h。将所得的悬浊液离心,用无水乙醇洗涤数次,在40 ℃下干燥,即得到Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4样品。Co-FeOOH采用相同的制备方法,但反应体系中不加入g-C3N4。
-
称取0.1 g Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4,加入100 mL浓度为10 mg·L−1的RhB溶液中,在暗态下搅拌30 min,达到吸附-解吸平衡,然后加入2 mmol浓度为30%的H2O2,在可见光照射下开始反应(500 W氙灯,用400 nm滤光片滤掉光源中的紫外光部分)。每间隔15 min取样,经离心后取上清液测试溶液的吸光度。反应后体系中残留的H2O2通过硫酸氧钛/硫酸-紫外分光光度法检测。
-
配制1 L浓度为800 mg·L−1的RhB,将其放置在太阳光下(平均辐照强度为800 W·m−2),加入1.0 g催化剂,2.0 mL H2O2(摩尔比H2O2∶RhB约为12.5∶1),每间隔1 h取样,使用MnO2分解掉残余的H2O2后,采用重铬酸钾法(GB 11914-1989)测定染料废水中的COD。
1.1. g-C3N4和Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4的制备
1.2. 光芬顿实验
1.3. 天然日光驱动Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4/H2O2体系处理高浓度染料废水实验
-
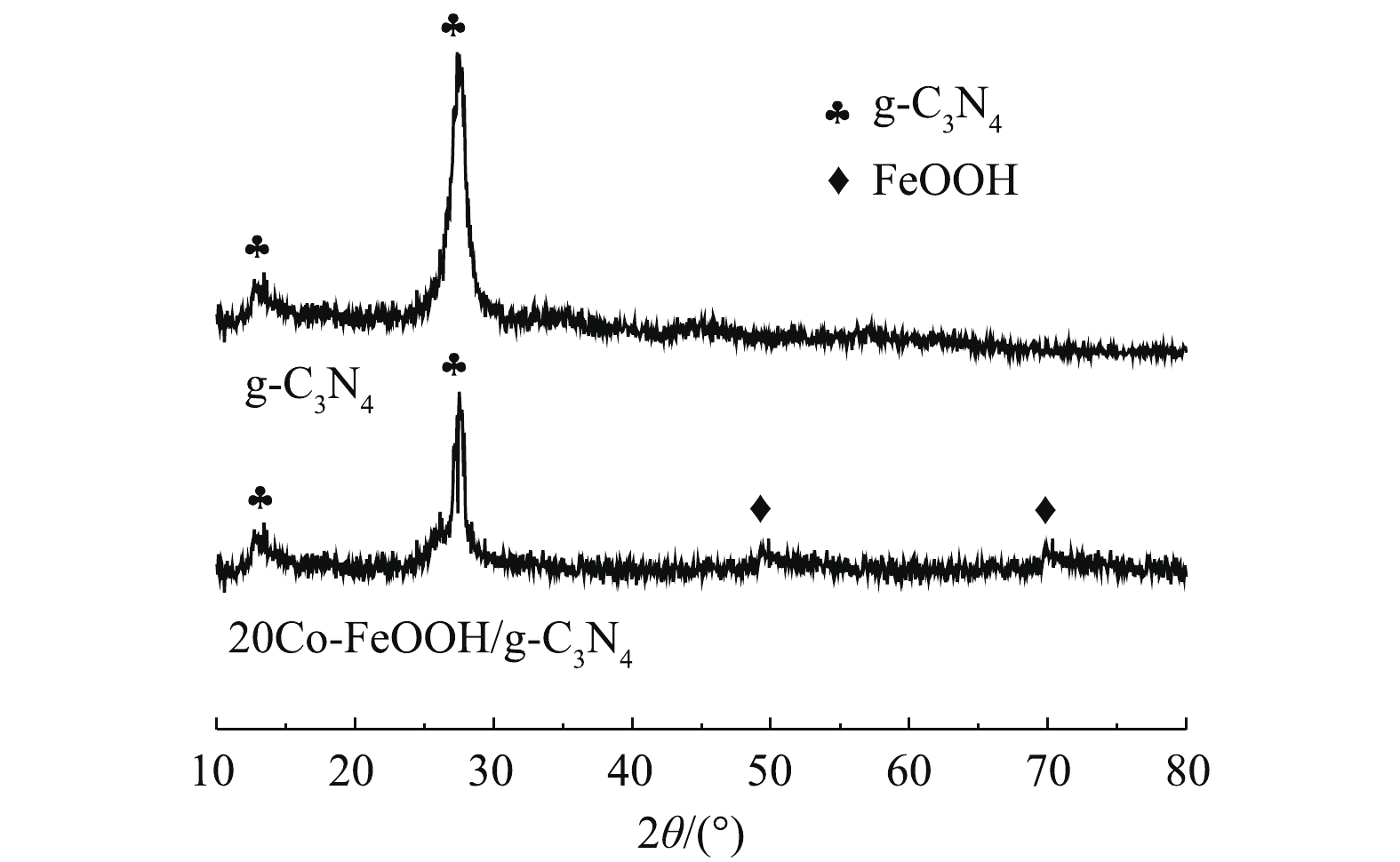
由XRD图谱(图1)可见,在2θ=12.8°和27.2°处有2个明显的衍射峰,分别归属于g-C3N4的(100)和(002)面[23]。对于20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合材料,在2θ=50.0°和71.1°处出现FeOOH的特征峰(JCPDS NO.290-713)。而在图谱中没有出现Co或其氧化物的衍射峰,这可能是由于Co在样品中含量较少,以高度分散的状态存在或者其与Fe形成非晶态结构的复合氧化物所导致[13]。
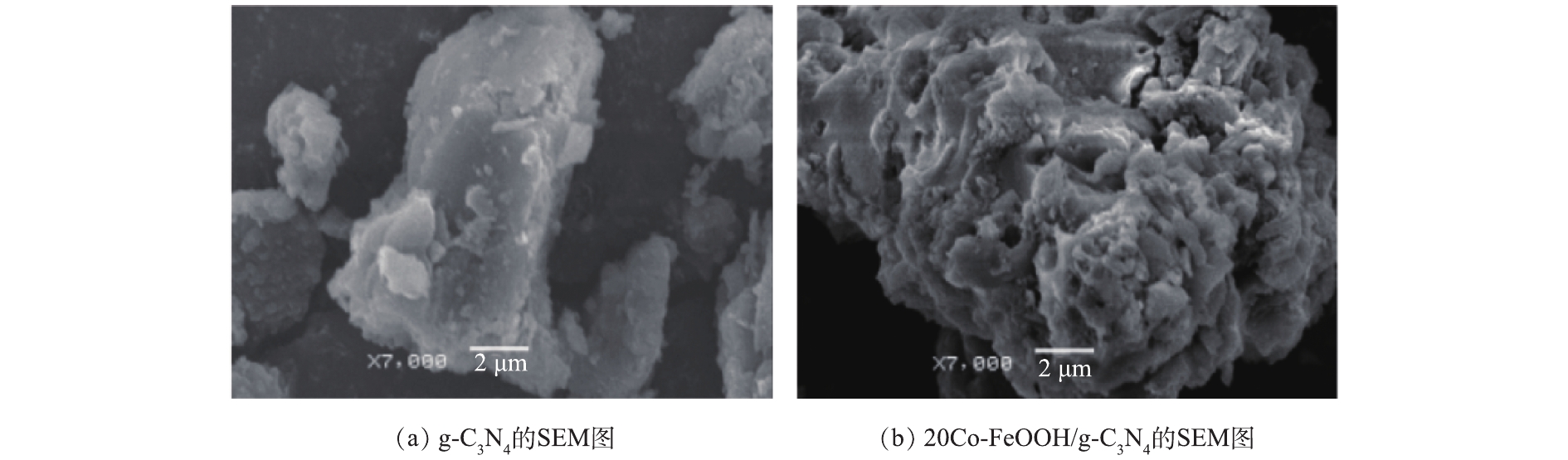
g-C3N4和20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4的扫描电子显微镜(SEM)分析结果见图2。由图2(a)可以看出,g-C3N4样品呈现出不规则的块状结构。和g-C3N4相比,Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合催化剂表面粗糙,化学浴沉淀过程生成的颗粒状Co-FeOOH均匀附着在g-C3N4表面。
-
不同反应体系下催化处理RhB的结果如图3所示。由图3可见,在可见光/H2O2催化体系中,RhB转化率不足10%,这表明可见光无法激发H2O2产生自由基。在可见光/催化剂/H2O2体系中,RhB转化率显著提高,20Co-FeOOH、g-C3N4、20Co-FeOOH +g-C3N4机械混合和20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合催化剂对RhB的转化率分别为23.7%、59.6%、60.0%和91.5%,这表明复合催化剂具有最高的催化活性,且20Co-FeOOH与g-C3N4之间复合后相比于简单的机械混合产生了耦合作用。对于20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合催化剂,在可见光催化、H2O2催化氧化和可见光/H2O2光Fenton作用下,RhB的转化率分别为35.6%、38.9%和91.5%。光Fenton体系下的去除率远高于两者单独作用之和。进一步对反应进行动力学拟合,发现反应过程符合准一级动力学方程(式(1))。
式中:k为一级动力学常数,min−1;t为反应时间,min;C0为RhB溶液的初始浓度,mol·L−1;C为RhB溶液反应t时间后的浓度,mol·L−1。可见光催化、H2O2催化氧化和光Fenton作用下的动力学常数分别为0.004 7、0.004 9和0.027 2 min−1。RhB的去除率和动力学常数计算结果表明,光Fenton作用下,20Co-FeOOH与g-C3N4之间产生了显著的协同效应。这种协同效应的产生是由于在复合催化剂中,g-C3N4在可见光激发下,产生光生e−和h+,e−从g-C3N4迁移到Co-FeOOH表面。这一过程不仅加速了Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)的还原过程,提高了对H2O2的催化效率,而且促进了e−与h+的分离,提高了h+对RhB的直接氧化效率,从而产生协同效应,使光Fenton体系对RhB的处理效率显著提高,表现出去除率及动力学常数均大于光催化与H2O2催化氧化两者之和的现象。
在复合催化剂中,Co的掺杂量会影响体系对RhB的去除效果,结果如图4所示。复合催化剂中当Co的掺杂量为0、10%、15%、20%和30%时,反应90 min后,RhB的转化率分别为51.16%、52.87%、77.64%、91.45%和66.02%。结果表明,在掺杂Co后,催化剂的催化活性得到提高,这主要归于以下3点原因:1) Co2+和Fe2+均能够活化H2O2产生·OH;2) g-C3N4的导带电位为-1.12 V(vs NHE)低于Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ) (0.77 V)和Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ) (1.82 V),g-C3N4导带产生的光生e−可以分别还原Co(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅲ)为Co(Ⅱ)、Fe(Ⅱ),加速Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)的循环过程;3) Co(Ⅲ)可以氧化Fe(Ⅱ)为Fe(Ⅲ),减少反应过程中过量的Fe(Ⅱ)对·OH的消耗(Fe2++·OH
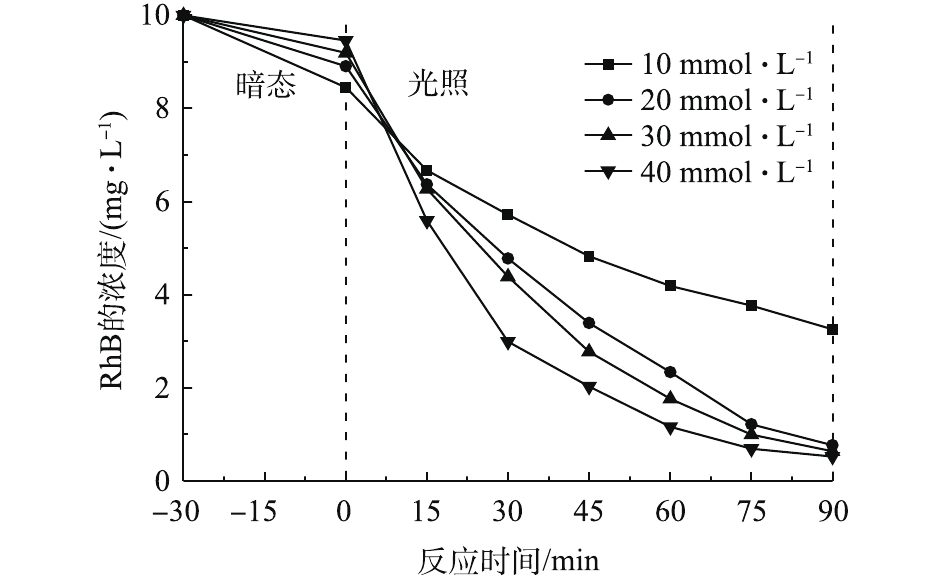
→ Fe3++OH−),因此,Co掺杂能够提高催化活性。然而对于Fenton反应,Fe的活性大于Co,在催化剂中金属总量不变的情况下,Co的含量增加可使得Fe的含量会相对减少,导致Fe可提供的活性位点减少,使催化剂整体活性下降。综上所述,本研究确定Co的最佳掺杂量为20%。H2O2的浓度是影响RhB去除效果的因素之一,实验结果如图5所示。由图5可知,当H2O2的浓度为10、20、30和40 mmol·L−1时,RhB的转化率分别为61.5%、91.4%、93.1%和94.4%。这表明RhB的转化率随着H2O2浓度的升高而提高,但当H2O2浓度大于20 mmol·L−1时,继续增加H2O2对RhB转化率提高并不明显。这是因为过量的H2O2会与·OH发生淬灭反应(H2O2+·OH
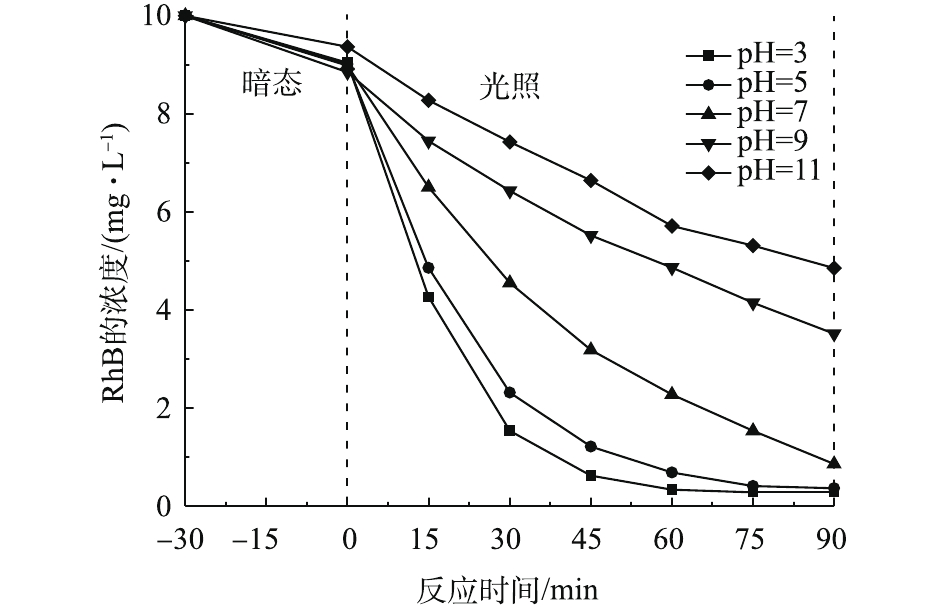
→ H2O+·O2H,·OH +·O2H→ H2O+O2),从而影响反应体系的降解效果。此外,通过测试反应后H2O2残留量,计算出H2O2的利用率。当浓度为10、20、30和40 mmol·L−1时,其利用率分别为67%、42%、27%和14%。这表明随着H2O2剂量的增加,其利用率逐步下降。考虑光Fenton过程的经济性,在后续实验中H2O2添加量均为20 mmol·L−1。pH对催化反应的影响情况如图6所示。由图6可知,酸性条件下的处理效率优于碱性条件。在酸性条件下,反应90 min后,RhB的转化率达到96%,中性条件下RhB的转化率能达到91.5%。与传统的Fenton方法相比(pH仅为2~4),该体系拓宽了反应的pH适用范围。
反应温度对RhB去除效果的影响如图7所示。结果表明,随着反应温度的升高,反应速率加快。根据一级动力学方程,可计算20、30、40、50 ℃下的动力学常数,分别为0.027 2、0.032 3、0.038 4、0.043 8 min−1。根据阿伦尼乌斯方程(式(2)),计算出反应活化能Ea为12.8 kJ·mol−1,远低于断裂H2O2分子中O—O键形成·OH所需的键能(126.6 kJ·mol−1)[24],这表明光Fenton体系大幅降低了反应所需的活化能,从而有利于提高反应速率。
式中:R为常数,取值8.314 J·(mol·K)−1;T为热力学温度,K;lnA为截距。
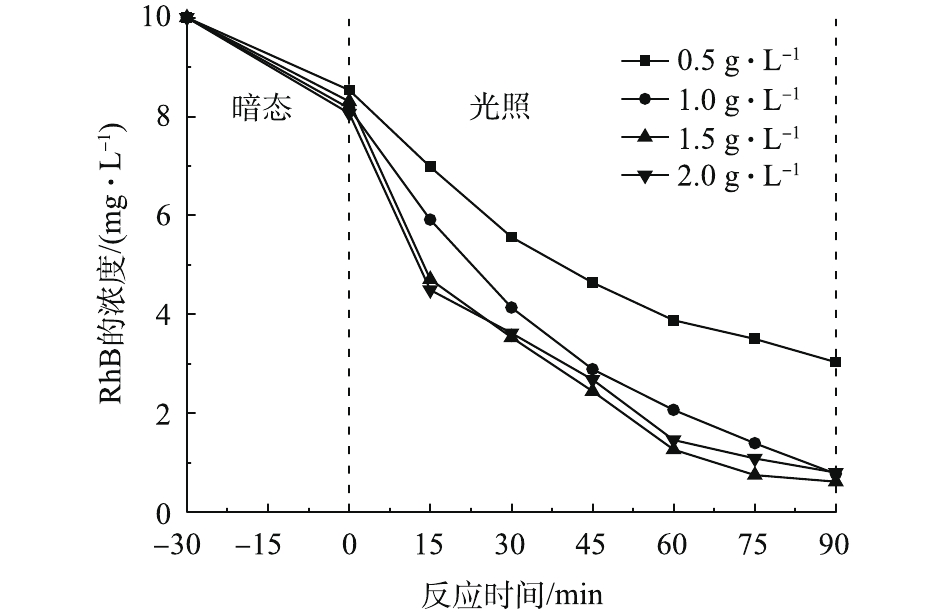
催化剂的投加量在对RhB的处理中也起到了重要作用,结果如图8所示。当催化剂的投加量由0.5 g·L−1增加至1.5 g·L−1时,反应速率随之提高。这是因为增加催化剂的投加量能够提供更多的活性位点,进而加速分解RhB。但是,当催化剂投加量进一步增加至2.0 g·L−1时,RhB的转化率有轻微降低。这是由于粉体催化剂投加量过大,降低了溶液的透光性,影响了催化剂的光吸收,导致RhB转化率下降。因此,确定催化剂的最佳投加量为1.0 g·L−1。
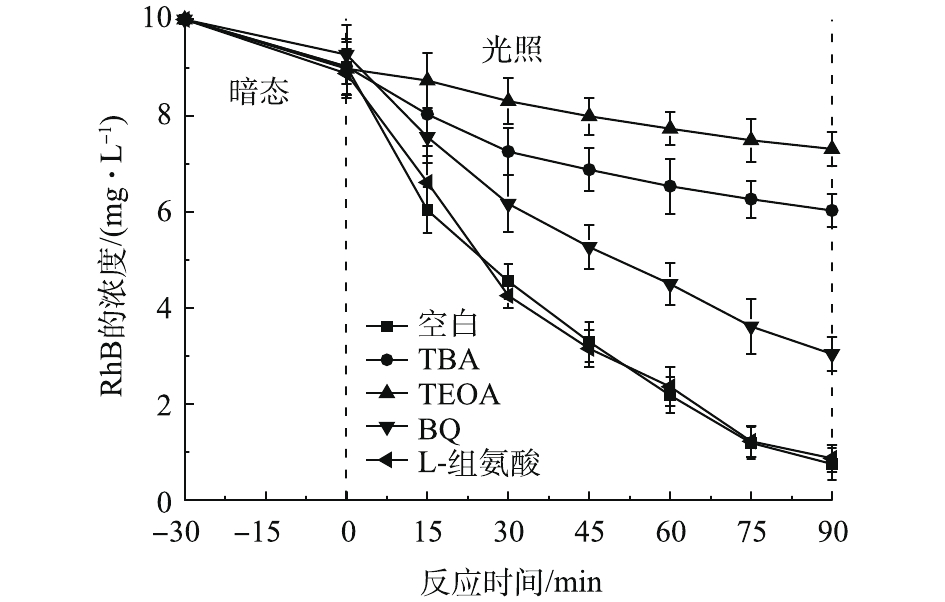
为进一步确定光Fenton过程中的主要活性物种,本研究进行了自由基捕获实验。分别以叔丁醇(TBA)、三乙醇胺(TEOA)、对苯醌(BQ)和L-组氨酸分别作为·OH、h+、超氧自由基(·O2-)和单线态氧(1O2)的捕获剂,实验结果如图9所示。在反应过程中加入TBA后,RhB的转化率由91.5%降至33.1%,说明光Fenton体系中·OH对RhB转化起到主要作用。·OH一部分来源于Fe、Co诱导的H2O2分解,一部分是光生e−与O2分子反应经过·O2-最终形成的(g-C3N4价带位置决定光生h+无法直接氧化H2O产生·OH)。在反应体系中加入BQ后,RhB的转化率由91.5%降至67.1%,这说明转化RhB的·OH大部分来源于H2O2,少部分来自于光生e−还原O2。在反应中加入TEOA后,RhB的转化率降低至18.6%,说明光生h+的直接氧化作用也是RhB转化的重要原因。此外,L-组氨酸对反应体系几乎没有影响,这说明1O2不是反应过程中起主要作用的活性物种。
-
通过5次循环实验考察了催化剂的稳定性,结果如图10所示。催化剂在5次的连续反应中对RhB的去除率分别为91.5%、90.5%、89.0%、88.6%和87.2%,证明催化剂具有良好的稳定性。通过原子吸收光谱测定反应后溶液中铁离子的浓度为0.9 mg·L−1,仅占催化剂总铁量的0.36%,溶出的铁离子浓度低于欧盟和美国规定的最高排放标准(2.0 mg·L−1)[25]。反应后溶液中Co离子浓度未检出,说明反应过程中金属离子的溶出量较低,不会造成二次污染。
-
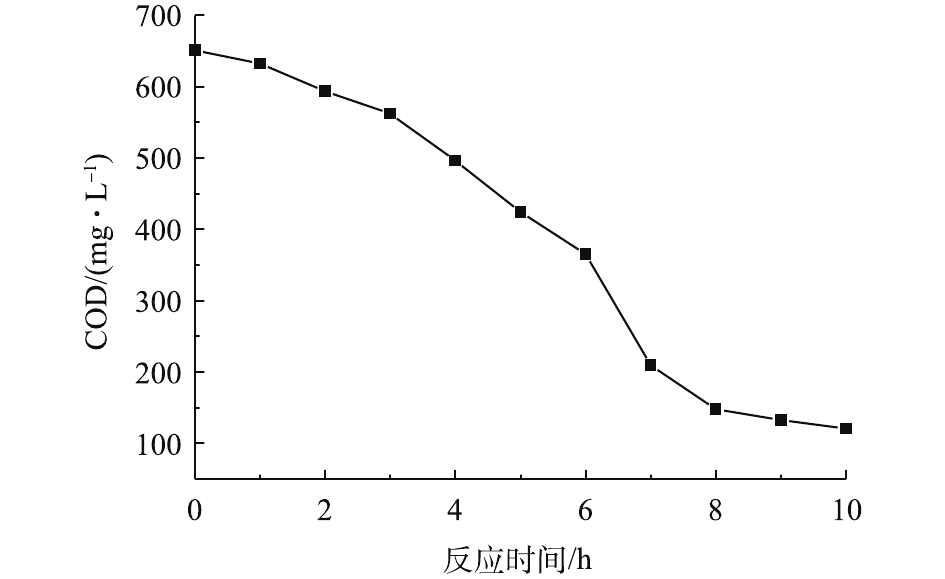
实际染料废水普遍具有高浓度、高色度的特点,不利于光线在水体中的传播。此外,光Fenton体系中的人造光源能耗较高,这些因素严重制约了光Fenton技术在实际中的应用。为了考察20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合催化剂的实用性,本研究构建了以天然日光驱动的光Fenton体系,考察了催化剂对高浓度(800 mg·L−1)染料废水的处理性能,结果如图11和图12所示。在天然日光的照射下,该体系6 h可使废水脱色率达到100%,此时废水的COD由初始的651.5 mg·L−1降低至365.5 mg·L−1,COD去除率达到43.9%。继续延长反应时间至10 h时,废水的COD的去除率可进一步达到81.6%。上述结果表明,在反应过程中,·OH和光生h+首先破坏了染料分子的发色基团导致脱色,然后再进一步将染料分子分解为CO2和H2O等无机物,使COD得到去除。
2.1. Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4催化剂的表征
2.2. Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4的光Fenton催化性能
2.3. 催化剂稳定性评价
2.4. 太阳光驱动光Fenton处理高浓度染料废水
-
1)由可见光/20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4/H2O2构成的光Fenton体系,对RhB的处理效果最好,最佳反应条件下的去除率可达91.5%。催化剂具有良好的稳定性。
2) 20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合催化剂良好的催化性能主要归因于20Co-FeOOH和g-C3N4之间的协同作用。g-C3N4受到可见光激发产生e−和h+,其中e−转移至20Co-FeOOH表面,提高Fe(Ⅲ)/Fe(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)的循环率。同时也降低了e−/h+的复合率,从而提高了复合催化剂的催化效率。
3)在天然日光驱动下,20Co-FeOOH/g-C3N4复合催化剂对高浓度染料废水的脱色率可达100%,COD去除率可达81.6%,具有一定的实用性。





 下载:
下载: