-
斑石鲷(Oplegnathus punctatus)为石鲷科石鲷属的一种鱼类,具有重要的实用价值和市场前景[1]。我国在斑石鲷养殖方面起步较晚,目前,主要采用工厂化流水养殖,而采用循环水系统养殖斑石鲷的技术尚未被大规模推广。同时,对于斑石鲷循环水养殖系统中的各级生物滤池的水处理效果以及微生物群落对养殖过程中水质的动态响应的研究尚鲜见报道。生物滤池的水处理效果与微生物群落结构变化密切相关,当群落结构变化时,养殖环境水质会产生相应的变化[2]。在研究微生物群落结构的方法中,高通量测序技术近年来应用较为广泛,其测序手段更为先进,能够同时对几百万条核酸分子进行测序,可全面精准地分析不同领域中的细菌[3]。吴越等[4]运用16S rRNA高通量测序手段研究石斑鱼循环水养殖系统水体中微生物种群结构,发现从养殖塘到补氧池细菌多样性指数先降低后升高, 在生物滤池中达到最高值。张海耿等[3]运用高通量测序技术研究了生物流化床挂膜期和稳定期的细菌群落,发现流化床的硝化作用主要发生于床层下部。
为了解各级生物滤池的净水机制,得到优化生物滤池运行参数的基础数据,为斑石鲷循环水养殖系统的高效运作提供一定的技术支持,本研究运用高通量测序技术考察了斑石鲷循环水养殖系统生物滤池内部微生物群落结构的变化及其与水质变化的关系,结合水质指标检测,得到生物群落变化对水质的动态响应规律,为斑石鲷及其他同类海水名贵鱼循环水养殖污水处理提供参考。
全文HTML
-
斑石鲷循环水养殖系统建于山东省莱州明波水产有限公司“循二”养殖车间,水处理系统由养殖池、弧形筛、生物滤池、臭氧发生器、蛋白质分离器、紫外线消毒、液氧罐等单元组成(见图1)。在系统稳定运行的过程中,总水量约为320 m3,日换水量占总水量的5%,循环频率为16 次·d−1。生物过滤单元为3级浸没式生物滤池。第1级为弹性生物滤料,比表面积为296 m2·m−3;第2级为丹麦生物包,比表面积为200 m2·m−3;第3级为网状生物包,比表面积为380 m2·m−3。该系统生物滤池采用自然挂膜。2018年3月开始养殖斑石鲷,养殖过程中投喂斑石鲷配合饲料(海童高效优食EP饲料),初始密度为20 kg·m−3,每天07:30和16:30各投喂1 次, 投喂量为鱼体质量的 4%,鱼体生长情况良好。
-
在生物膜取样期间,每15 d测定1次各级生物滤池内的水温、溶解氧、pH,每3 d测定1次生物滤池进出水口的总氨氮、亚硝态氮、硝态氮、化学需氧量。实验方法根据《海洋监测规范第4部分:海水分析》(GB 17378.4-2007)操作,水温、溶解氧、pH 现场检测, 其他指标在水样运回实验室后立即检测。每个指标重复测定3次, 结果取平均值。水温、溶解氧、pH采用YSI 多参数水质分析仪进行测定;总氨氮采用次溴酸盐氧化法进行测定;亚硝态氮采用萘乙二胺分光光度法进行测定;硝态氮采用锌镉还原法进行测定;化学需氧量采用碱性高锰酸钾法进行测定。
-
将3级浸没式生物滤池按水流方向顺序标为第1、2、3级生物滤池。分别从3个滤池中取生物膜样品,在每个滤池中选取5个采样点(滤池4个角和中心点)剪取滤料样品,每个混合样品约15 g,编号放入50 mL取样管,放入液氮中保存。在2个月内,每15 d取生物膜样品,取样时间为实验开始的第1、16、31、46、61天,共取5次,得到15个样品。把第1级生物滤池5个时间点的生物膜样品按取样时间先后顺序编号为a1、a2、a3、a4、a5,第2级生物滤池的样品编号为b1、b2、b3、b4、b5,第3级生物滤池的样品编号为c1、c2、c3、c4、c5。样品采集完成后,全部放入液氮中保存。在DNA提取之前,取10 g样品置于100 mL无菌生理盐水中,加入100 μL 吐温80洗涤剂溶液,涡旋振荡10 min后,将样品于聚碳酸酯过滤器(0.22 μm,Millipore,MA,U.S.)过滤,将样品中微生物抽滤于聚碳酸酯滤膜上,以进行后续的DNA提取。使用E.Z.N.A. DNA 试剂盒(Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, U.S.)进行样本基因组DNA提取,所提取DNA通过1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测质量。
-
采用细菌通用引物338F(5'-GTACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3')和806R(5'- GTGGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3') 对样品16S rRNA的V3~V4区域进行PCR扩增。PCR扩增体系为25 μL,反应条件:94 ℃预变性5 min,94 ℃变性30 s,50 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸60 s,25个循环,72 ℃延伸7 min,冷却至4 ℃。使用AxyPrep DNA凝胶回收试剂盒(AXYGEN公司)对PCR产物进行回收,Tris_HCl洗脱。将扩增产物使用2%琼脂糖电泳检测分析,检查扩增效果。将扩增产物送至北京奥维森科技有限公司在Illumina-MiSeq平台上进行测序分析。
-
采用 Microsoft Excel 软件对水质数据进行统计分析,使用 SPSS 22.0 软件进行单因素方差分析,分析其显著性差异(α取0.05)。根据 Index 序列区分各样本的数据,将其以fastq格式保存,利用Qiime (version 1.8)对数据进行检测并去除嵌合体序列[5]。利用Uparse软件(version 10.0.240)按照97%相似性序列,进行OTUs聚类(不含单序列),得到代表序列,再将其全部序列按照97%相似度映射到OTUs上,形成OTUs列表[6]。用RDP Classifier算法对OTUs代表序列进行比对分析,并在各水平注释其群落的物种信息[7]。
基于OTU聚类结果,利用mothur做稀释性曲线(rarefaction)分析,利用R语言工具制作曲线图[8]并计算Shannon和Chao1指数[9]。Venn图用R语言工具统计和作图[10]。使用Qiime平台计算Unifrac距离,构建UPGMA样品聚类树。
1.1. 养殖系统
1.2. 水质监测方法
1.3. 样品采集和DNA提取
1.4. PCR扩增和高通量测序
1.5. 数据处理分析
-
在斑石鲷养殖系统运行期间,此3 级浸没式生物滤池可以有效地维持系统稳定运行。取生物膜样品期间的相关水质参数(如表1和表2所示),氨氮、亚硝态氮和化学需氧量的去除率分别达到68.9%、48.9%和15.9%,经过生物滤池处理后的水质完全符合斑石鲷的养殖要求。
-
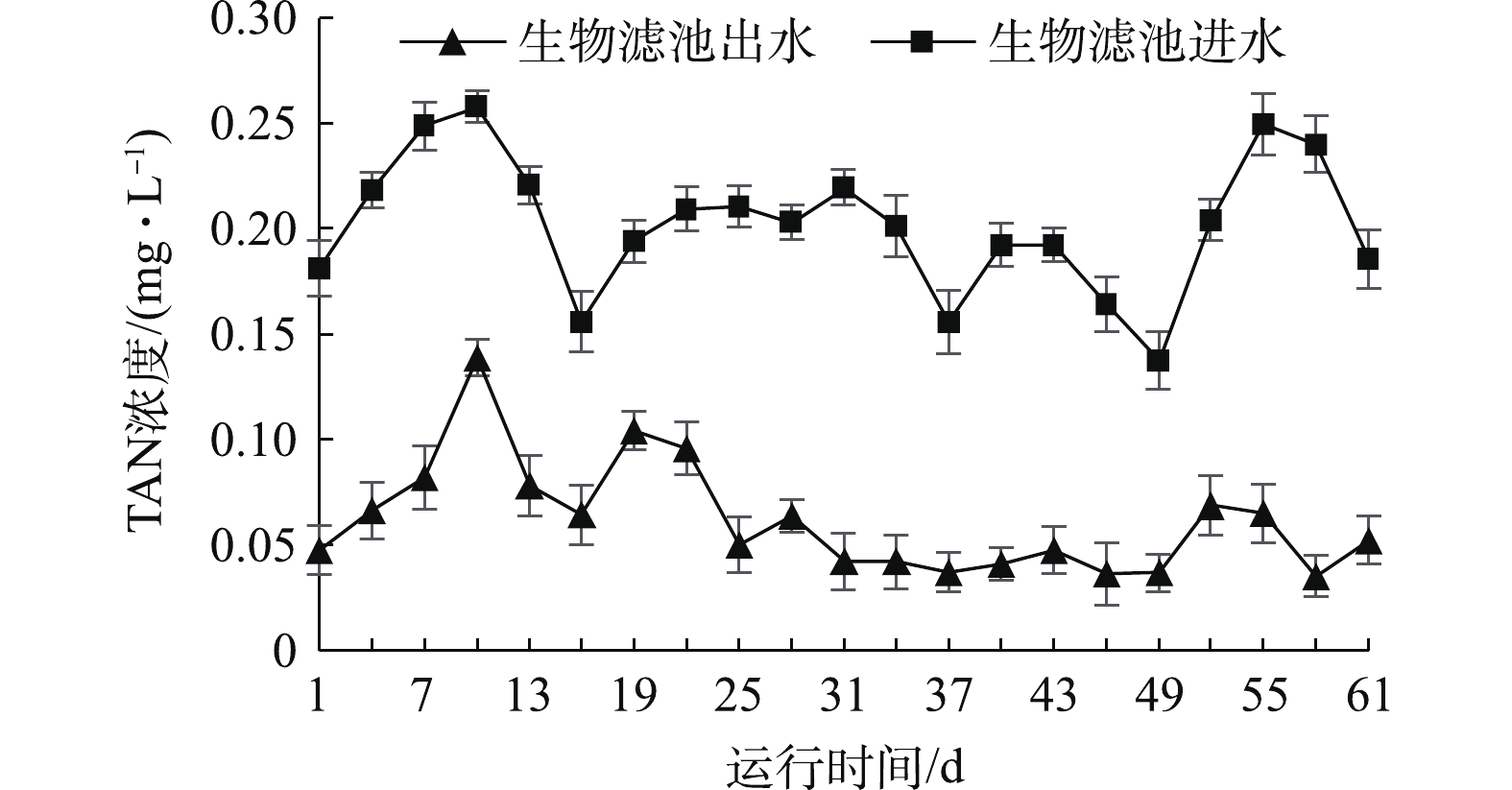
由表2可知,水温、溶解氧和pH在实验第1、46、61天较高,在第16、31天较低,这可能是受养殖过程中海水水温、充氧量、pH缓冲液调控的影响。由图2可知,生物滤池进水和出水氨氮浓度差异显著(P<0.05);生物滤池进水氨氮浓度较高,为0.137~0.257 mg·L−1,经处理后,生物滤池出水氨氮降至较低的水平,浓度为0.035~0.139 mg·L−1。鱼体内氨氮浓度过高,会导致其离子调节失去平衡,引起鱼惊厥、抽搐甚至死亡[11]。魏晓安等[12]使用曝气生物滤池工艺处理珠江原水,对氨氮的平均去除率可达81.2%。本实验的结果表明,该水处理系统可有效去除养殖水中的氨氮,且水质保持稳定。
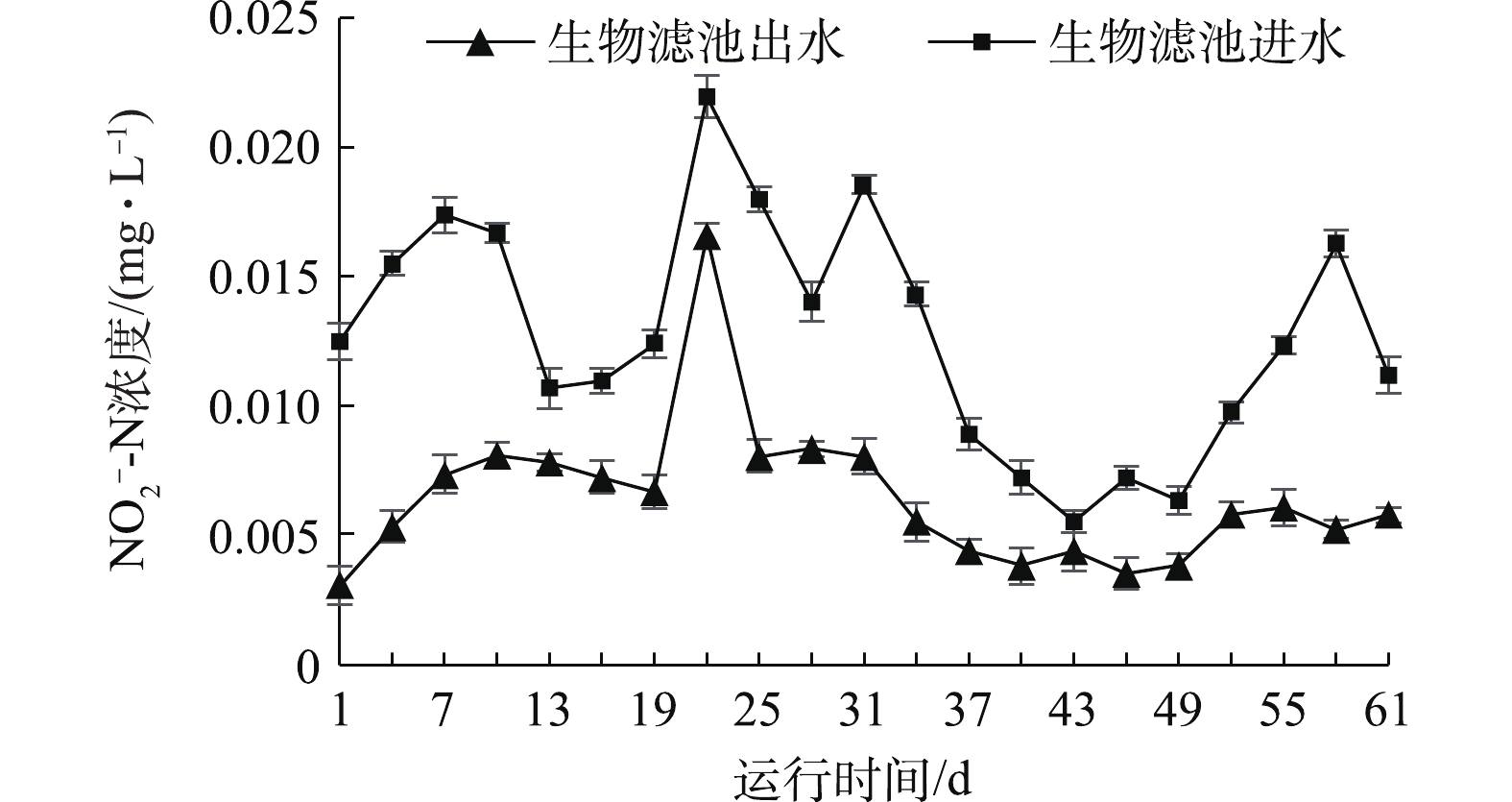
由图3可知,实验过程中进水亚硝态氮浓度最高值为0.022 mg·L−1,最低值为0.005 mg·L−1; 生物滤池进水经处理后,整体上出水的亚硝态氮浓度低于进水。出水亚硝态氮浓度最高值为0.017 mg·L−1,最低值为0.003 mg·L−1。高浓度的亚硝态氮会将鱼体血液中的血红蛋白转化成高铁血红蛋白,导致鱼类缺氧,进而引起代谢紊乱等生理变化,最终导致鱼类死亡[13]。生物滤池对亚硝态氮的去除效果较好。钟惠舟等[14]使用活性无烟煤生物滤池去除亚硝态氮,平均去除率达到87.02%。本实验的结果表明,该循环水生物滤池对亚硝态氮有较好的去除效果。
由图4可知,硝态氮生物滤池进出水浓度整体上呈上升趋势。硝态氮作为硝化反应的最终产物,在利用自养硝化过程控制氨氮的封闭式循环水养殖系统中常有积累[15]。这说明该循环水养殖系统出现了一定程度的硝态氮积累,其反硝化作用不明显。
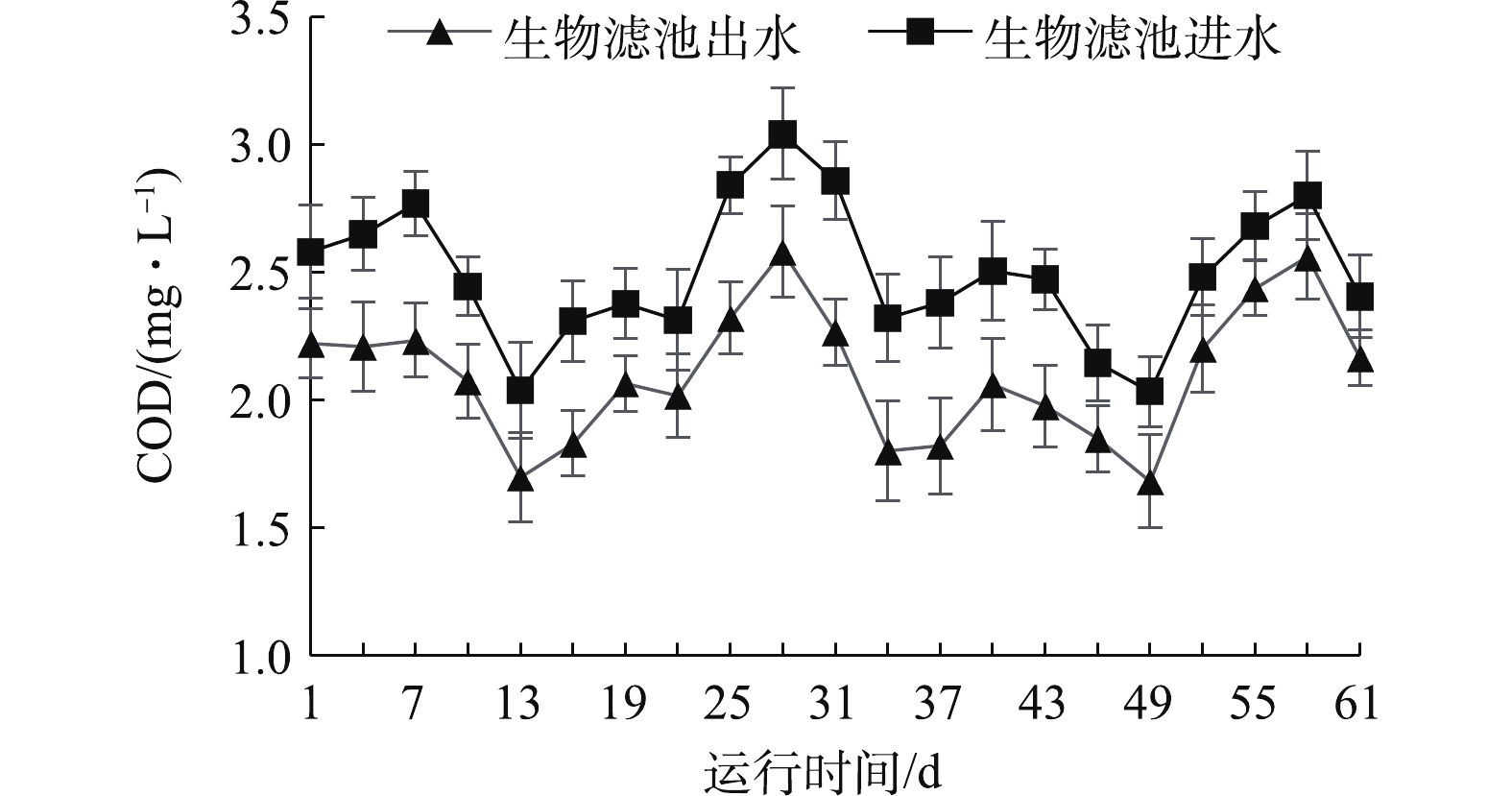
在系统运行中,生物滤池的COD进出水变化趋势如图5所示。进水COD为2.03~3.23 mg·L−1,出水COD为1.68~2.58 mg·L−1。进出水口COD有显著差异(P<0.05),COD去除率为15.9%。曹文平[16]探究了水力负荷对生物反应器去除COD的影响,发现当水力负荷增加时,COD去除率先升高再降低。本实验的结果表明,进入生物滤池的水经生物过滤后对COD的去除有一定作用,去除率较低可能是由水力负荷较低导致的。
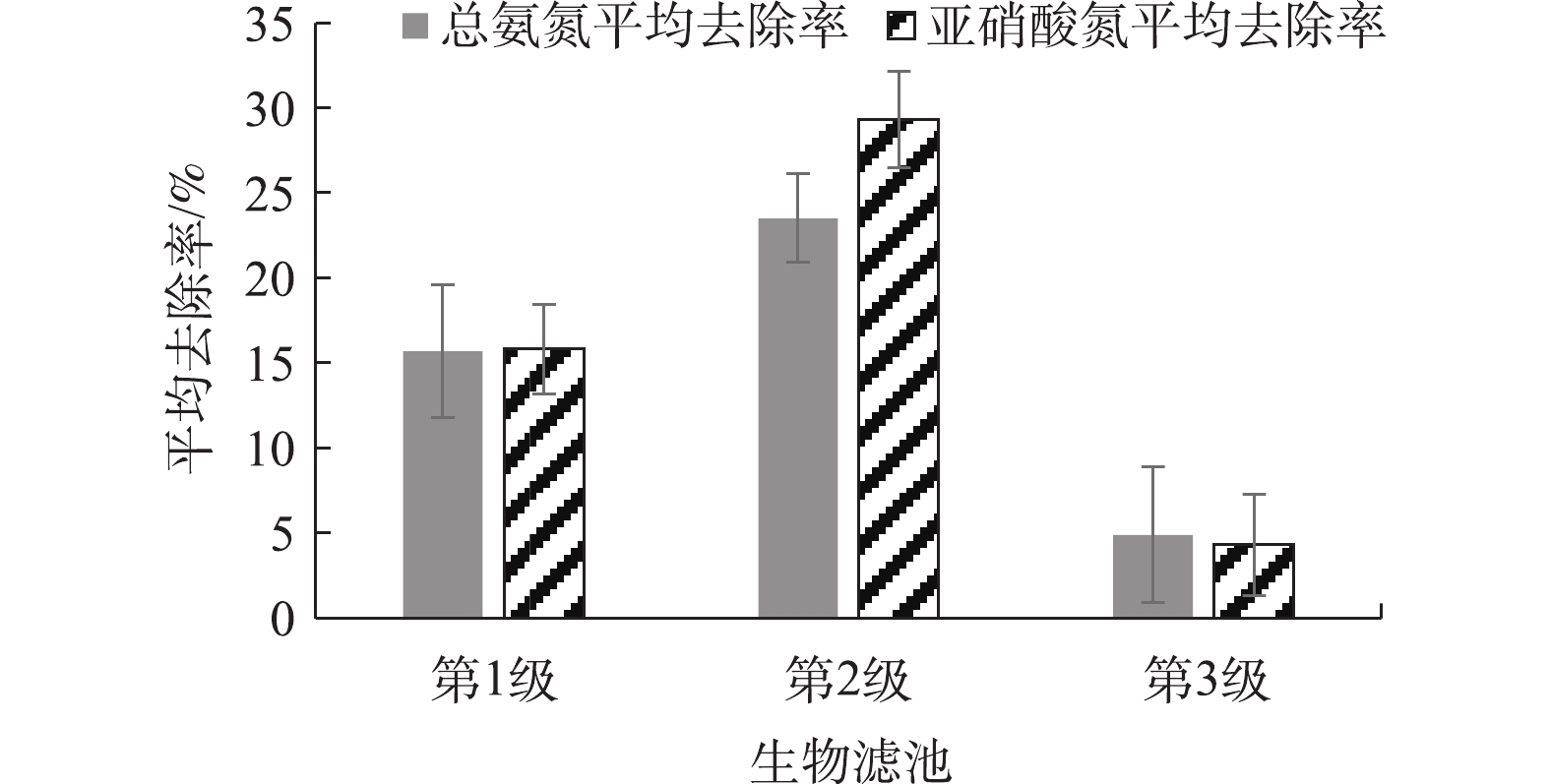
由图6可知,第1级生物滤池的总氨氮和亚硝态氮平均去除率是15.0%左右,第2级生物滤池的总氨氮平均去除率是23.5%,亚硝态氮平均去除率是29.3%。第3级生物滤池去除总氨氮和亚硝态氮的去除率不高于5%,显著低于第1级和第2级的(P<0.05)。原因可能是污染物在经第1级和第2级生物滤池处理后,氨氮和亚硝态氮负荷已较低,导致第3级生物滤池的硝化作用不明显。
-
对各样品所测结果整理分析发现,样品的优质序列大于35 000条,有效OTUs为947~1 749个。15个生物膜样品分别得到原始序列和有效OTUs数如表3所示。由表3可知,样本数量OTUs从大到小的顺序为c1、c5、b1、c4、a2、b5、c3、b4、a3、a1、c2、b3、b5、b2、a4。总体来说,相比于第1级和第2级生物滤池,在5个时间点对应的第3级生物滤池的群落OTUs数处于较高的水平。而且,通过比较5个时期3个生物滤池的Chao1指数、Shannon指数也能发现,第3级生物滤池整体微生物群落丰富度和多样性均高于第1级和第2级生物滤池。
由表3中的Shannnon指数可知,微生物群落多样性表现为第2级和第3级生物滤池微生物丰富度和多样性在第1个和第4、5个时间点较高,其他时间点相对较低。这可能是由于水温、溶解氧、pH在第1个和第4、5个时间点偏高(表2)导致的。BOUWER[15]的研究发现,硝化细菌的最佳适宜温度为30~35 ℃,温度适当升高,有利于硝化细菌的繁殖。秦宇等[17]通过研究溶解氧及曝停比对单级自养脱氮系统微生物群落结构的影响,发现较高溶解氧会对厌氧菌的代谢产生抑制, 而低溶解氧将影响好氧菌的活性。王新为等[18]通过人工调节液体培养基的 pH,检测氨氮和亚硝态氮氮转化率后发现,氨氧化细菌对碱性环境要求较高,液体培养基若存在于较高pH的环境下,则有利于促进氨氧化细菌氧化氨氮。以上的研究结果与本研究结果基本一致。对于第1级生物滤池在第2个时间点的群落丰富度和多样性为最高的现象,分析其原因,可能是其在第2个时间点的环境条件发生了波动,但这种波动并没有影响第2级和第3级生物滤池。
-
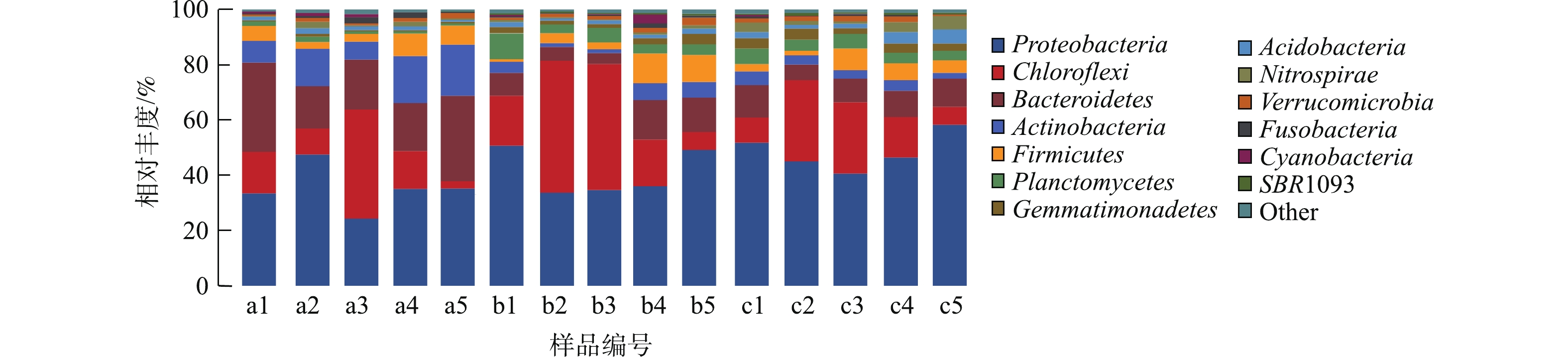
图7显示了不同样品细菌群落门水平的变化,15个样品中微生物群落结构组成相似,但每种微生物所占比例略有不同。样品中微生物主要隶属于14个门,其中变形菌门(Proteobacteria,24.3%~58.3%)占主要优势。其他优势菌门分别为Chloroflex (绿弯菌门,25.4%~47.7%)、Bacteroidetes(拟杆菌门, 3.9%~32.3%)、Actinobacteria(放线菌门,1.3%~18.6%)、Firmicutes(厚壁菌门,1.1%~10.9%)、Planctomycetes(浮霉菌门,0.7%~9.2%)、Gemmatimonadetes(芽单胞菌门,0.42%~4.0%)、Acidobacteria(酸杆菌门,0.75%~5.14%)、Nitrospirae(硝化螺旋菌门,0.32%~4.79%)。各生物滤池中载体生物膜的微生物在门水平上的组成分布与先前报道的结果[13-15]相似。生物滤池在运行过程中,各个时期的细菌种群有一定的变化,如变形菌门(Proteobacteria)在同一个生物滤池的5个时间点的细菌种群呈现波动起伏的趋势,绿弯菌门(Chloroflex)在第1级生物滤池第3个时间点以及第2和第3级生物滤池的第2、3个时间点的比例显著高于其他时间点。不同级别的生物滤池载体细菌种群所占比例也有区别,如第2级和第3级生物滤池的变形菌门(Proteobacteria)细菌种群多于第1级,硝化螺旋菌门(Nitrospirae)的第3级生物滤池区域细菌种群多于第1级和第2级生物滤池。
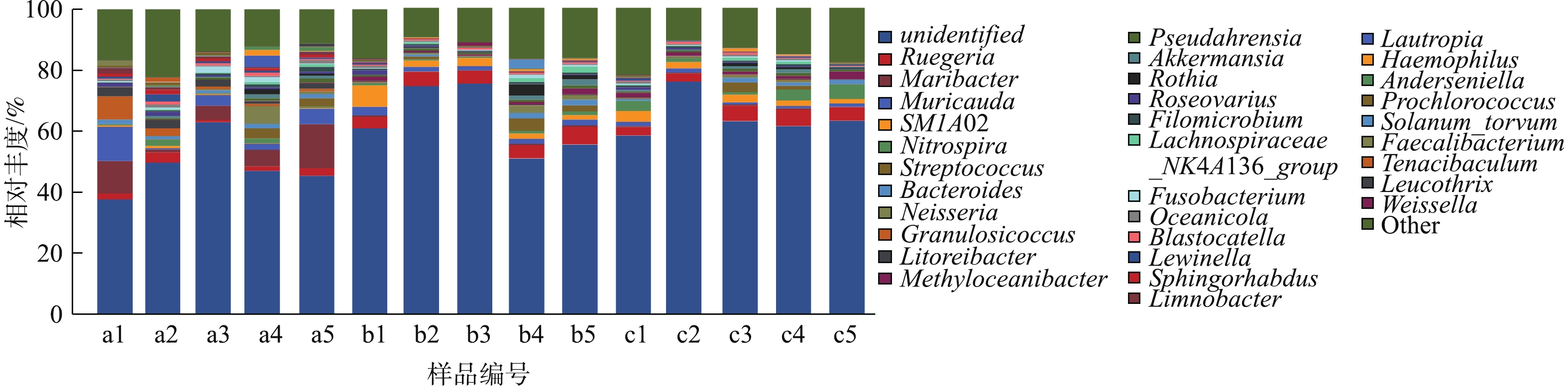
图8为15个样品表现物种占比大于1%的属水平分析。占优势的菌属分别为Ruegeria(鲁杰式菌属,0.71%~5.79%)、Maribacter(栖海杆菌属,0.14%~14.4%)、Muricauda(0.42%~11.3%)、SMA102(0.14%~7.06%)、Nitrospira(硝化螺菌属,0.27%~4.78%)、Streptococcus(链球菌属,0.019%~4.12%)、Bacteroides(拟杆菌属,0.033%~1.81%)。其中Ruegeria属于α-变形亚门的红杆菌科 Rhodobacteraceae,是一类紫色非硫细菌,可以利用养殖水体中的多种有机碳源进行异氧代谢反应[19]。Muricauda和Maribacter为拟杆菌门的黄杆菌科Flavobacteriaceae,一般为兼性厌氧细菌,可以利用硝态氮作为电子受体进行无氧呼吸,即异化性硝态氮还原作用,这说明滤池中存在反硝化过程[20]。此外,还筛选出一批丰度不高,但在水处理过程中起重要作用的功能性细菌,如Nitrosomonas(亚硝化单胞菌属,0.08%~0.93%)、Bacillus(芽孢杆菌属,0~0.27%)。生物滤池中起硝化作用的细菌是氨氧化细菌和亚硝酸盐氧化细菌,样品中相关细菌有硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)和亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)[21]。硝化螺旋菌对环境中的亚硝态氮具有良好的去除作用,且对养殖废水的处理效果尤为显著[22]。
-
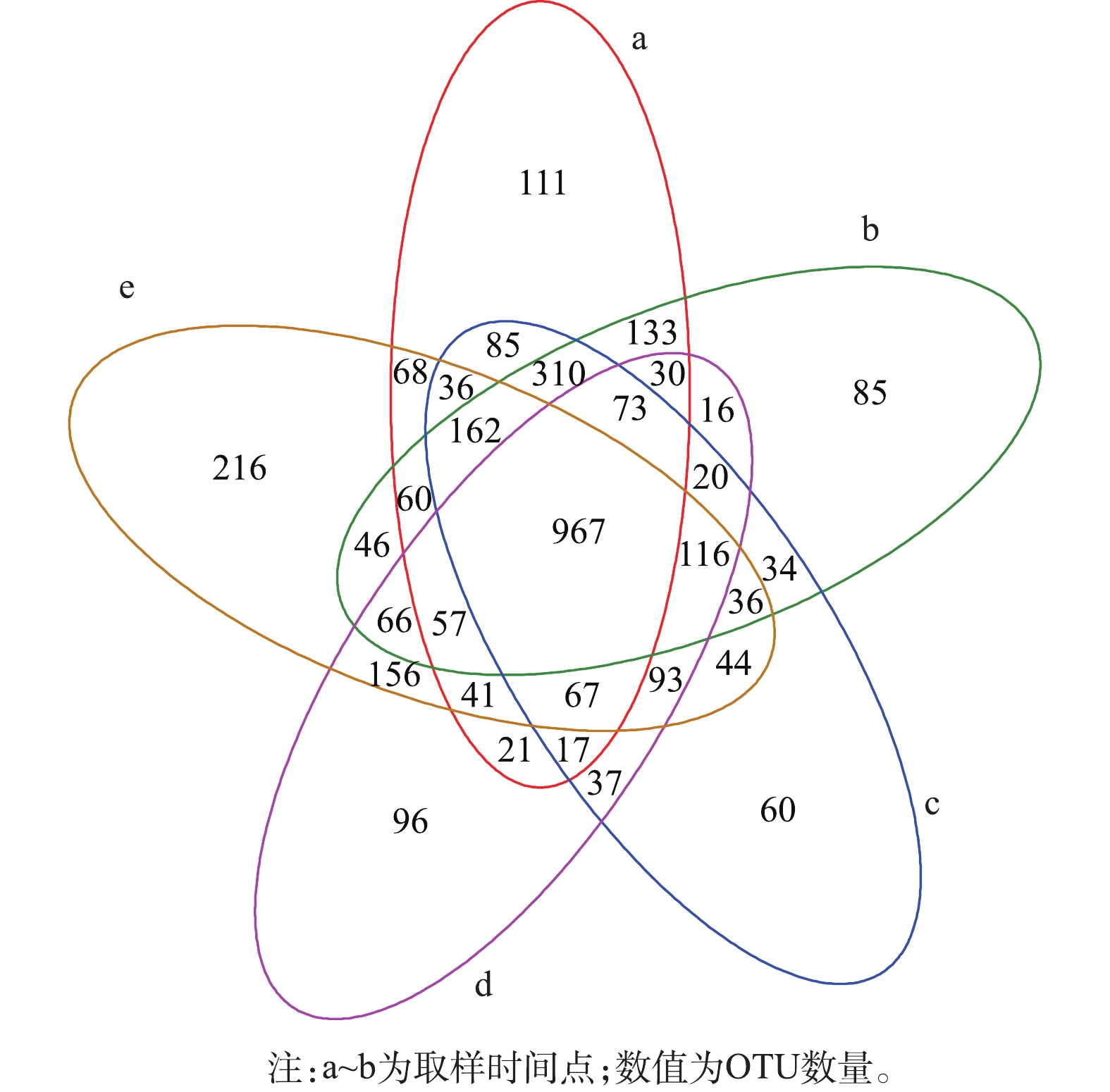
维恩图(图9)可直观地反映15个生物滤池样品的OTUs数目组成相似性及其重叠情况。5个时间点之间共有的OTUs共有967个,第1天样品独有的OTUs为111个,第16天独有OTUs为85个,第31天独有OTUs为60个,第46天独有OTUs为96个,第61天独有OTUs为216个。第31天独有的OTU数最少,第61天独有的OTU数最多。由此可见, 群落丰富度在稳定期的演替模式是先降低再升高。
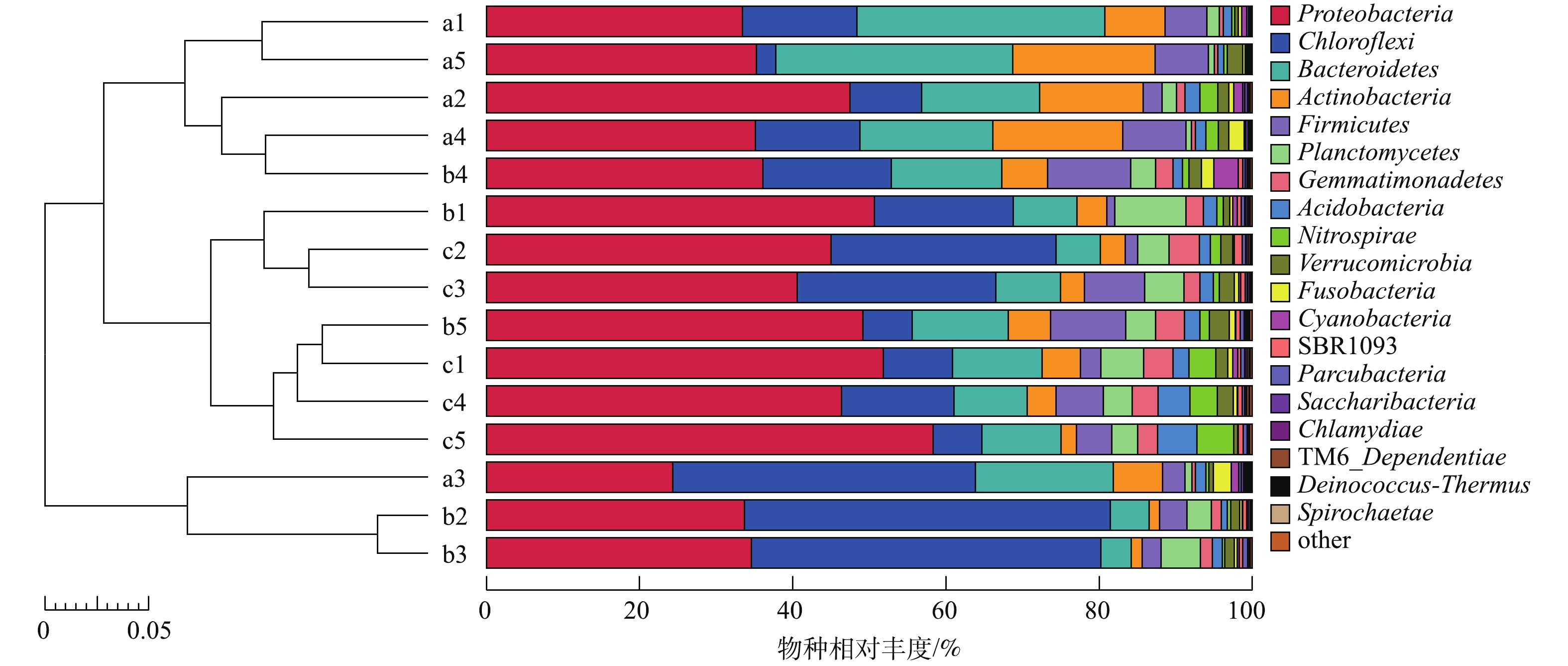
基于Unweighted Unifrac距离矩阵和UPGMA方法聚类建树,并将聚类结果与各样品在门水平上的物种相对丰度整合展示,结果见图10。按样品相似性程度较高的结果可分为5组:第1组(a1和a5);第2组(a2、a4和b4);第3组(b1、c2和c3);第4组(b5、c1、c4和c5);第5组(a3、b2和b3)。上述结果说明第2级和第3级生物滤池的微生物群落结构相似度较高,与第1级生物滤池内微生物群落结构相似度较低。第1级生物滤池的第1个和第5个时间点(a1和a5),第2个和第4个时间点(a2和a4)相似度较高,第2级生物滤池的第2个和第3个时间点(b2和b3)未发生显著的变化,第3级生物滤池的第1、第4和第5个时间点(c1、c4、c5)相似性较高。这可能是由于养殖过程中各级生物滤池氨氮、亚硝态氮、COD等参数的变化而导致的。
-
本实验把第1~16天记为第Ⅰ时期,第16~31天记为第Ⅱ时期,依此类推,分别对应4个时期。通过水化学检测分析,氨氮、亚硝态氮、COD在整个实验期内变化平稳,这表明整个实验期均处于生物滤池稳定运行期。
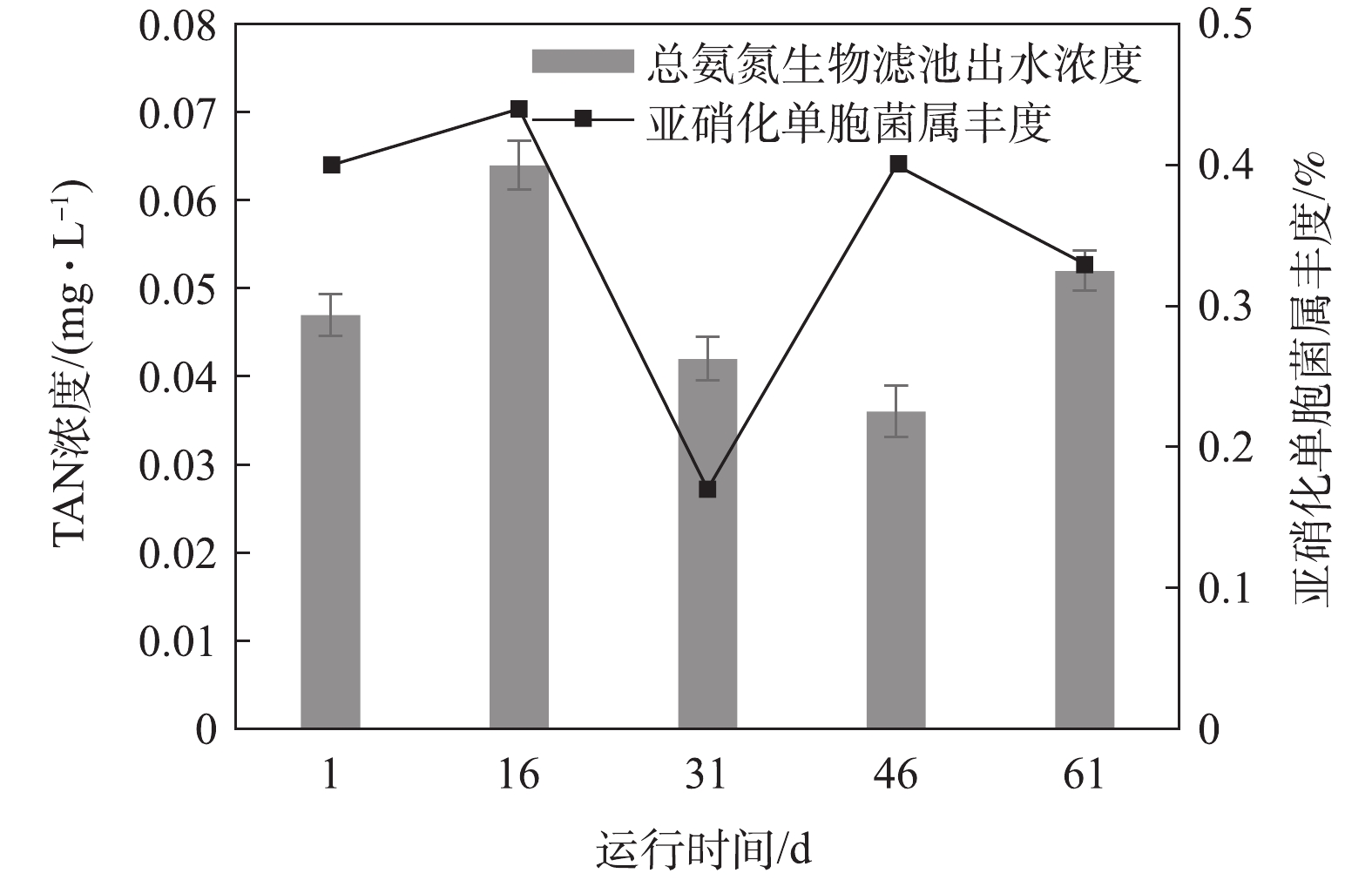
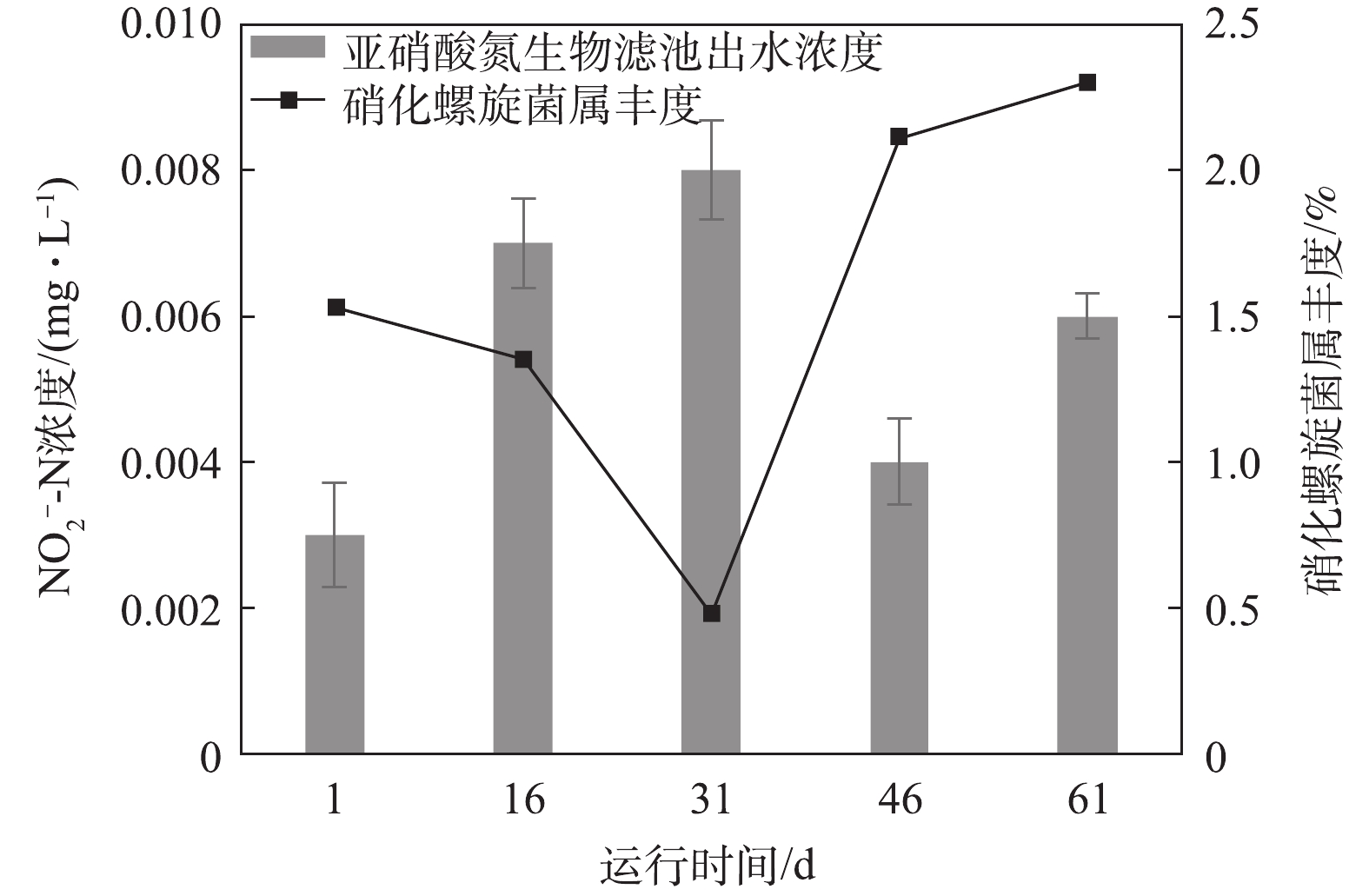
图11和图12分别显示了氨氮和亚硝态氮浓度变化对微生物群落变化的动态响应情况。氨氮和亚硝态氮是循环水养殖系统中残饵和粪便产生的主要代谢废物[23],循环水系统的生物滤池通过生物过滤作用普遍用来去除氨氮和亚硝态氮[19]。在硝化作用中,氨氮先被氨氧化细菌氧化成亚硝态氮,亚硝态氮被亚硝酸盐氧化菌氧化成毒性更小的硝态氮[24]。本次实验中发现的氨氧化细菌是亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas),亚硝酸盐氧化菌是硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)。一般来说,氨氧化细菌丰度和氨氮浓度,亚硝酸盐氧化菌丰度和亚硝态氮浓度成相互抑制的关系[24]。
氨氮和亚硝态氮浓度变化与Nitrosomonas和Nitrospira 2种菌属的丰度变化关系如图11和图12所示。在第Ⅰ时期,亚硝态氮的生物滤池出水浓度增加了0.004 mg·L−1,这可能是由于生物滤池内硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)丰度由1.5%下降至1.3%。在第Ⅱ时期,亚硝态氮的生物滤池出水浓度增加了0.001 mg·L−1,原因可能是硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)丰度由1.3%降低至0.5%。在第Ⅲ时期,氨氮浓度减少了0.006 mg·L−1,亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)的丰度由0.17%上升至0.4%;亚硝态氮浓度下降了0.005 mg·L−1,这可能是由硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)丰度升高了1.6%引起的。在第Ⅳ时期,氨氮的生物滤池出水浓度升高0.021 mg·L−1,这可能与亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)平均丰度由0.4%降低至0.33%相关。
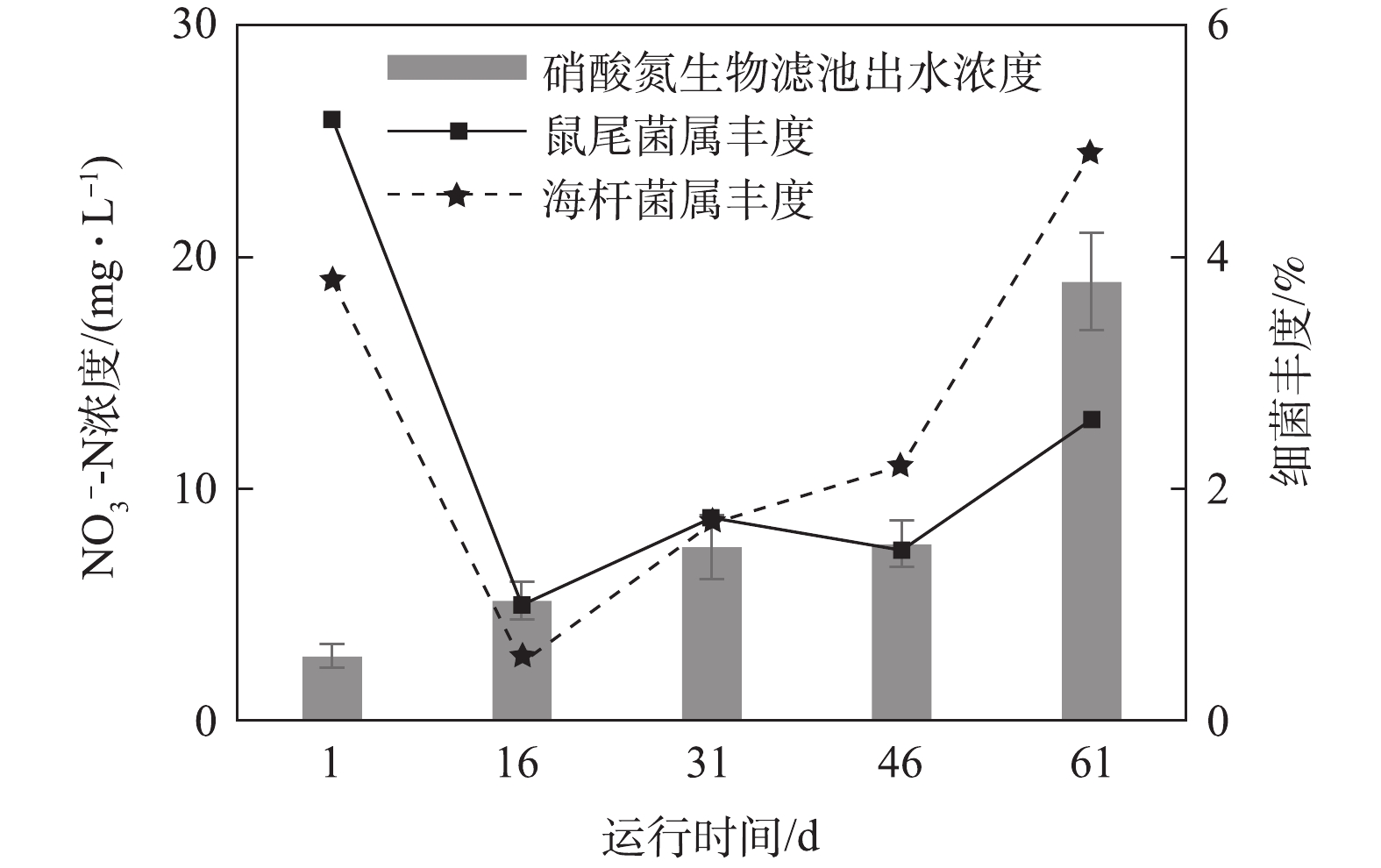
由图13可知,相比于氨氮和亚硝态氮,硝态氮在前2个时期有积累的过程,最高浓度达18.9 mg·L−1。硝态氮的去除大部分是通过兼性厌氧微生物的反硝化反应完成的[24],本实验筛选出具有反硝化作用的鼠尾菌属Muricauda、海杆菌属Maribacter为拟杆菌门的黄杆菌科Flavobacteriaceae,一般为兼性厌氧细菌,Muricauda和Maribacter的丰度在第Ⅰ时期减少,在第Ⅱ时期、第Ⅲ时期和第Ⅳ时期略微增加。但是,由于循环水系统的曝气环境,生物滤池内溶解氧浓度较高(>3.9 mg·L−1), 导致生物滤池的反硝化反应一定程度上被抑制,进一步造成硝态氮积累。
在生物过滤中,COD可以被异养生物去除[25]。在本研究中,COD生物滤池出水浓度在整个稳定运行期内变化平稳,其浓度的变化可能是由于各种异养细菌的群落演替引起的。本研究筛选出了鲁杰式菌属(Ruegeria)、海杆菌属(Maribacter)、鼠尾菌属(Muricauda)、链球菌属(Streptococcus)、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)等一系列异养细菌,其共同作用可影响生物滤池内COD值。
2.1. 3级生物滤池水处理性能分析
2.2. 3级生物滤池水质指标变化情况分析
2.3. 生物滤池群落多样性变化
2.4. 生物滤池微生物群落组成变化
2.5. 各样品细菌群落的相似性分析
2.6. 微生物群落结构对水质参数的动态响应
-
1)通过高通量测序,本实验共筛选 37 个门,513个细菌属。第3级生物滤池整体微生物群落丰富度和多样性均高于第1级和第2级,第2级和第3级的微生物群落相似性最高。在门水平上,细菌主要以变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)为主。本研究发现了与硝化作用有关的少量亚硝化单胞菌属Nitrosomonas和硝化螺菌属Nitrospira以及与COD去除相关的一系列异养细菌。本实验发现第3级生物滤池的氨氮和亚硝态氮的去除效果较低,可能与大量氨氮和亚硝态氮负荷已被前2级生物滤池处理有关,因此,第3级生物滤池可能存在功能上的浪费。
2)在微生物群落对水质的动态响应方面,亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)丰度在Ⅲ、Ⅳ时期,与氨氮的浓度变化呈相互抑制的关系;硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)在Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ时期对亚硝态氮的浓度变化呈相互抑制关系。Muricauda、Maribacter等反硝化细菌对降低硝态氮浓度的作用不明显;与COD去除有关的异养细菌种类较多,其共同作用可影响生物滤池内COD。
3)生物滤池微生物群落对水质变化有一定程度的动态响应,但不能完全控制水质变化,水质变化同样受外部条件的影响,如水温、溶解氧、pH、养殖物与饲料等。在实际生产中,调节生物滤池稳定运行期的群落结构,使多样性和丰富度长期处于较高水平,可能有利于增强生物滤池的水处理效果。




 下载:
下载: