-
A/A/O工艺是传统活性污泥工艺、生物硝化反硝化工艺和生物除磷工艺的结合体,具有强化生物脱氮和生物除磷的双重特点[1-2]。氧化沟工艺属于延时曝气活性污泥法,处理效果稳定[3]。A/A/O微曝氧化沟分为厌氧段、缺氧段和好氧段,3个区以隔墙分开来,形成较好的独立环境。池型为环形池形,兼有推流式和完全混流式的特点。A/A/O微曝氧化沟工艺作为一种现代化新型工艺,采用曝气和推流相分离的方式,具有流程简单、抗冲击能力强、出水水质稳定、能耗低和易操控等优点。同时,随着污水排放标准的提高,水质净化厂逐渐采用深度处理工艺,如V型滤池和高效纤维滤池等,以强化对污染物的去除。
目前,关于水质净化厂脱氮除磷的影响因素研究相对较多,但大多数基于实验室小试,且分析条件与内容单一[4-6]。同时,针对实际水质净化厂处理工艺进行污染物全程系统分析的研究亦相对较少。本研究以深圳某水质净化厂为例,以其A/A/O微曝氧化沟工艺和V型滤池为研究对象,分析了沿程污染物浓度和微生物活性,并结合物料平衡计算,探讨了该水质净化厂去除污染物的能力,寻找增强反应速率和水质净化厂系统稳定性的方法,以期为同类水质净化厂的出水达标提供参考。
-
该水质净化厂位于深圳市坪山区,进水以生活污水为主,设计总规模2×105 m3·d−1。生活污水经一级处理(粗格栅、细格栅、曝气沉砂池)后,进入二级处理系统(A/A/O微曝氧化沟工艺),流经二沉池再进入深度处理系统(V型滤池),出水经紫外消毒后排入坪山河,工艺流程如图1所示。
-
常规水质分析采用国家标准方法[7]:COD采用重铬酸钾法;BOD5采用稀释与接种法;TN采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法;
NH+4 -N采用纳氏分光光度法;TP采用钼酸铵分光光度法;SS采用滤膜法;DO和Eh采用哈希DO仪和哈希Eh仪测定。上述指标及处理水量每天检测至少一次,各指标以每月平均值和年平均值统计。 -
该水质净化厂2018年1—12月的进水水量和进、出水水质如表1和表2所示。2018年的年平均水量为15.57×104 m3;年平均进水COD为200.47 mg·L−1;年平均进水BOD5为64.53 mg·L−1;年平均进水
NH+4 -N为16.83 mg·L−1;年平均进水TN为24.2 mg·L−1;年平均进水TP为3.68 mg·L−1。全年范围内进水水量波动较大,丰水季水量较大。枯水季进水COD、BOD5、NH+4 -N、TN和TP浓度较大。年平均进水BOD5/COD为0.32,丰水季BOD5/COD偏低,可生化性一般;年平均进水BOD5/TN为2.67,丰水季BOD5/TN偏低,生物脱氮可行,基本不用外加碳源;年平均进水BOD5/TP为17.54,丰水季BOD5/TN偏低,生物除磷效果一般,需借助化学除磷增强除磷效果。2018年年平均出水COD为16.43 mg·L−1;年平均出水BOD5为2.50 mg·L−1;年平均出水
NH+4 -N为0.40 mg·L−1;年平均出水TN为10.56 mg·L−1;年平均出水TP为0.25 mg·L−1。各出水指标均达到一级A标准,COD、BOD5、NH+4 -N、TN和TP的去除率分别为91.80%、96.12%、97.62%、56.36%和93.21%。由此可知,该工艺对COD、BOD5、NH+4 -N和TP的去除效果明显,但对TN的去除效果较差,还有优化和提升的空间。 -
为分析工艺中沿程脱氮除磷效果,对水质净化厂的指标进行了长期监测。监测结果如下:生物池厌氧段DO为0.1 mg·L−1,Eh为−265 mV;缺氧段DO为0.4 mg·L−1,Eh为−105 mV;好氧段DO为3.5 mg·L−1,Eh为68 mV。生物池内回流比为100%,外回流比为50%,混合液悬浮固体浓度MLSS为4 348 mg·L−1,混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度MLVSS为1 261 mg·L−1,污泥体积指数SVI为21 mL·g−1,泥龄SRT为15.78 d,有机负荷率(以BOD5计)为0.024 kg·(kg·d) −1(以MLSS计)(有机负荷率F/M指单位重量的混合液悬浮固体浓度在单位时间内承受的有机物的数量)。沿程污染物浓度监测如图2所示。大部分有机物在厌氧段和缺氧段被去除,厌氧段和缺氧段对有机物的去除率分别为60.67%和18.20%,在好氧段中变化较小,可能的原因是,厌氧池和缺氧池生物代谢较快,大部分易降解的有机物被去除[8]。厌氧段、缺氧段和好氧段对
NH+4 -N的去除率分别为20.2%、15.13%和61.13%,所以好氧段对NH+4 -N的去除起主要作用。NO−3 -N浓度在缺氧段中有小幅度增加,在好氧段逐渐增加且趋于稳定,说明内回流和外回流比正常,生物池沿程脱氮效果良好。NO−2 -N浓度较小且沿程变化不大。厌氧池和好氧池对TP的去除率分别为23.8%和21.5%,缺氧池没有去除磷的能力,生物除磷效果明显低于郭玉梅等[9]研究的厌氧池和好氧池对磷的去除率。这说明生物系统中没有活性较强的聚磷菌,需要借助化学除磷手段进一步降低TP浓度,所以在生物池出水端和滤池前端投加化学除磷药剂。如图3所示,化学除磷药剂投加浓度为25.46~68.19 mg·L−1,投药浓度与进水BOD5/TP值变化趋势呈负相关,即进水BOD5/TP值较低时,需加大投药浓度,同时投加除磷药剂还起到吸附污泥颗粒加速沉淀作用从而使出水更清澈。由功能菌活性实验可以看出,厌氧段单位重量的混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度在单位时间内微生物释磷速率为1.83 mg·(g·h)−1(以MLVSS计),明显低于许德超等[10]得出的释磷速率12.86 mg·(g·h)−1,这进一步说明生物除磷效果较差,与沿程分析结果一致;缺氧段单位重量的混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度在单位时间内微生物的反硝化速率为3.87 mg·(g·h) −1;好氧段单位重量的混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度在单位时间内微生物的氨氧化速率为1.83 mg·(g·h) −1、亚硝酸盐氧化速率1.03 mg·(g·h) −1。经计算,假设硝化反应仅在好氧段进行,将进水
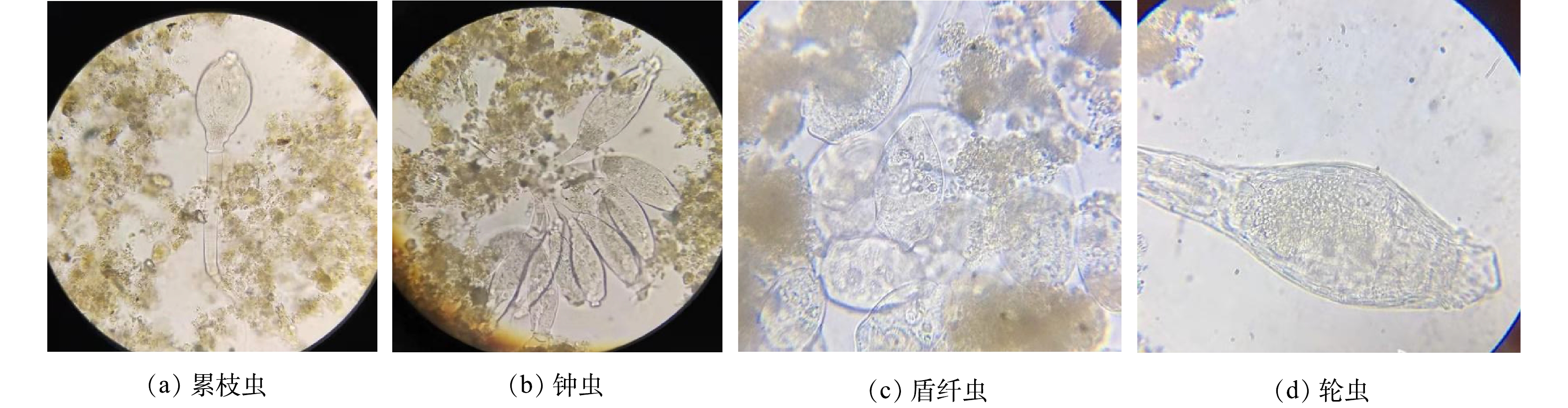
NH+4 -N(浓度为16.83 mg·L−1)完全转化为NO−3 -N所需的时间为7.29 h,该反应时间小于好氧段的水力停留时间(HRT为8.44 h),说明该水质净化厂能够满足硝化反应所需的水力停留时间。将NO−3 -N完全反硝化(假设NH+4 -N全转化为NO−3 -N)所需时间为4.96 h,因此,反硝化速率较低是反硝化脱氮的限制因素,可通过降低内回流DO和增加缺氧段碱度来提高微生物的反硝化速率。对生物池的活性污泥进行生物相镜检,结果如图4所示。生物池中有大量的累枝虫、钟虫、盾纤虫和轮虫,说明固着型纤毛虫数量较多,活性污泥正常,出水水质良好。轮虫是活性污泥处理污水效果较好的指示性生物,但有污泥老化的趋势,应适当排泥,降低有机负荷率F/M。活性污泥成熟期菌胶团数量较多,结构紧密。
-
二级出水和深度出水各项指标如表3所示。二级出水和深度出水的
NH+4 -N、TN和COD相差不大,而深度处理后的TP(滤池混合井投加除磷药剂)和SS浓度有明显降低,说明深度处理对有机物和氮素基本没有去除效果,对TP和SS的去除率分别为60.3%和33.71%。除磷效果明显高于郑育毅[11]用改性硅藻土深度处理城市污水厂出水的效果。其主要原因是,除磷药剂中Al3+和Fe3+与PO3−4 生成沉淀物,从而降低了TP。V型滤池对SS的去除效果略低于郭强[12]利用纤维转盘滤布滤池对SS的去除效果。 -
2018年平均处理水量为15.57×104 m3,污泥生成量为22.3 t·d−1。生物池混合液悬浮固体浓度MLSS为4 348 mg·L−1,混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度MLVSS为1 261 mg·L−1。1 mg混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度中氮含量为0.098 mg、磷含量为0.03 mg。经计算,该水质净化厂去除的总氮量为2.07 t·d−1,其中被微生物同化的氮含量为0.893 t·d−1,被同化的氮含量占43%,另外57%的氮通过反硝化作用被去除。磷主要通过剩余污泥的排放而得以去除[13]。该水质净化厂去除的总磷量为0.53 t·d−1,通过微生物合成和吸附被去除的磷含量和与除磷药剂形成化学沉淀的磷含量各占49.06%和50.94%。
-
综上所述,总氮去除率较低是水质净化厂存在的常见问题,可通过降低内回流DO、增加缺氧段碱度以及投加碳源等方式增加总氮的去除率。当生物除磷难以满足除磷要求时,应及时采用化学除磷方式,投药浓度与进水BOD5/TP变化趋势呈负相关,即进水BOD5/TP较低时需加大投药浓度,确保出水TP达标排放。
-
1)该水质净化厂进水水量有一定的季节变化,进水可生化性一般,生物脱氮可行,生物除磷效果有限,需借助化学除磷增强除磷效果。
2)大部分有机物在厌氧段和缺氧段被去除;好氧段微生物的氨氧化速率和亚硝酸盐氧化速率能满足硝化反应的正常进行;但缺氧段反硝化速率较低,是生物脱氮的限制因素,可通过降低内回流DO和增加缺氧段碱度来增强微生物的反硝化速率。生物池中有大量的累枝虫、钟虫、盾纤虫和轮虫,且成熟期菌胶团数量较多,结构紧密。
3)深度处理对有机物和氮素基本没有去除效果,对TP和SS的去除率分别为60.3%和33.71%。通过物料平衡计算,被同化的氮含量和反硝化的氮含量各占43%和57%。通过微生物合成和吸附被去除的磷含量和与除磷药剂形成化学沉淀的磷含量各占49.06%和50.94%。
4)通过对深圳某水质净化厂的深度脱氮除磷工艺效果分析,发现可通过降低内回流DO、增加缺氧段碱度以及投加碳源等方式增加总氮的去除率。同时,可采用化学除磷的方法增强总磷的去除率,投药浓度与进水BOD5/TP变化趋势呈负相关。
深圳某水质净化厂A/A/O微曝氧化沟深度脱氮除磷工艺效果分析
Effect analysis of deep removal of nitrogen and phosphorus by A/A/O micro-aeration oxidation ditch process in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Shenzhen, China
-
摘要: 为探究A/A/O微曝氧化沟深度脱氮除磷工艺的性能,根据深圳市某水质净化厂长期监测数据,分析了进水污染物浓度、生物池沿程脱氮除磷性能和微生物相。结果表明:进水可生化性一般,生物脱氮可行,但生物除磷效果有限,需借助化学除磷增强除磷效果,投药浓度与进水BOD5/TP值变化趋势呈负相关;生物池好氧段微生物的氨氧化速率和亚硝酸盐氧化速率能满足硝化反应的正常进行;但缺氧段反硝化速率较低,是生物脱氮的限制因素,可通过降低内回流DO和增加缺氧段碱度来增强微生物的反硝化速率;生物池中有大量的累枝虫、钟虫、盾纤虫和轮虫,且成熟期菌胶团数量较多,结构紧密;深度处理对TP和SS的去除率分别为60.3%和33.71%。物料平衡分析结果显示,被同化的氮含量和反硝化的氮含量各占43%和57%,通过微生物合成和吸附被去除的磷含量和与除磷药剂形成化学沉淀的磷含量各占49.06%和50.94%。本研究结果为水质净化厂深度脱氮除磷提供了思路,可为提高出水水质标准提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 污水处理 /
- A/A/O微曝氧化沟工艺 /
- 脱氮除磷 /
- 生物相 /
- 物料平衡
Abstract: In order to investigate the performance of A/A/O micro-aeration oxidation ditch process on deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal, based on the long-term monitoring data of a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Shenzhen, the concentration of influent pollutants, the performance of nitrogen and phosphorus removal along the A/A/O, and the biological phase were analyzed. The results showed the general biochemical properties for the influent, and feasible biological nitrogen removal effect, while the limited biological phosphorus removal effect. This indicated that the chemical phosphorus removal was needed to enhance the phosphorus removal effect. There are negative correlation between concentration of PAFC dosage and the BOD5/TP of influent. The ammonia oxidation rate and nitrite oxidation rate of the microorganisms in the aerobic section of A/A/O could meet the normal progress of the nitrification reaction. However, the low denitrification rate in the anoxic section of A/A/O was a limiting factor for biological denitrification. The denitrification rate of the microorganism could be enhanced by reducing the internal return DO and increasing alkalinity in this anoxic section. There were a large number of epistylis, vorticellas, aspidiscas and rotifers in the biological pool, and lots of bacterial micelles at the mature stage with compact strucuture. The removal rates of TP and SS by deep treatment process could reach 60.3% and 33.71%, respectively. Through the material balance analysis, the assimilated nitrogen content and denitrified nitrogen content accounted for 43% and 57%, respectively. The percent of phosphorus removed by microbial uptake and adsorption was 49.06%, and the percent of phosphorus formed as chemical precipitate of phosphorus and PAFC was 50.94%. The case provides ideas for deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal in municipal wastewater treatment plant, and provides reference for improving effluent water quality standards. -
抗生素作为一类新兴的药物和个人护理产品(pharmaceutical and personal care products,PPCPs)[1-2],被广泛用于治疗和预防人体、畜禽和水产品的疾病和细菌性病害。近年来,由于新兴冠状病毒肺炎(corona virus disease 2019,COVID-19)疫情的爆发,世界各地抗生素的使用急剧增加[3],由抗生素类毒物引起的水生环境污染问题也已成为全世界备受关注的问题[4]。
由于抗生素类药物分子结构稳定,被食用后不易被生物体完全吸收,会以代谢活性产物甚至原结构形式排出体外进而释放到环境中[5-6]。此外,未使用或过期的药物以及生产废水的不当处理使更多的抗生素进入自然水系统中,包括饮用水源[7-8]。据估计,2013年共有53 800 t抗生素被释放到中国的河流和水道中[9]。联合国的“2017年前沿报告”指出,水产养殖中75%的抗生素可能会流失到周围环境中[10],这对生态系统和人类健康均存在潜在的威胁[11-12]。因此,对水体中抗生素的去除很有必要。然而,常规水处理工艺对这类痕量污染物去除效果有限[13-14],一些深度处理技术例如膜处理技术、臭氧技术、吸附技术、电化学氧化技术等,在处理抗生素时虽然可以实现一定程度的降解[15],但存在着处理费用高、操作过程复杂、稳定性低、再循环能力差等问题,这也对世界各国抗生素污水的处理提出了新的挑战。
近年来,基于TiO2的光催化技术由于其有效性、低成本、高稳定性和环境友好性被广泛用于光催化降解含抗生素类废水。将TiO2纳米粒子通过水热处理制备得到的钛酸纳米材料(titanate nanomaterials,TNM)通常具有较大的比表面积和精细的纳米级结构,具有良好的去除多种污染物的性能[16]。但是,由于纳米TiO2光催化剂的带隙(Eg)(3.2~3.4 eV)较大,只对波长低于380 nm的紫外光有响应,以及快速的电子-空穴对复合速率,使得TiO2和TNM的可见光响应较弱,从而限制了其在太阳/可见光下的应用[17-18]。因此,开发新兴、高效的催化剂成为近年来研究的热点。研究人员利用将光催化剂与金属和非金属掺杂、设计和构建异质结等方法,合成了大量的TiO2基光催化材料[19],并应用于对水体中各类有机污染物的高效去除。
本研究中通过将铌酸盐作为光反应促进剂掺入钛酸盐中,水热法合成一类新型片状纳米复合材料-铌酸盐/钛酸钠米片(niobate/titanate nanoflakes,Nb-TiNFs),利用 XRD、XPS、FT-IR、SEM、TEM等多种手段对Nb-TiNFs材料进行表征和分析。选取氟喹诺酮类抗生素的代表环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin,CIP)作为目标污染物,探究了Nb-TiNFs在模拟日光下对水中CIP的光催化性能和机理,以期为光催化降解水中新兴有机污染物提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与仪器
试剂:二氧化钛(TiO2(P25),德国Degussa 公司)、五氧化二铌(Nb2O5,国药集团化学试剂有限公司)、环丙沙星(C17H18FN3O3,上海阿拉丁试剂)、对苯醌(C6H4O2,天津市清华津英科技有限公司)、碘化钾(KI,天津市北联精细化学品开发有限公司)、叔丁醇(C4H10O,天津市恒兴化学试剂制造有限公司)、呋喃甲醇(C5H6O2,上海吉至生化科技有限公司)、无水乙醇(CH3CH2OH,天津市富宇精细化工有限公司)、氢氧化钠(NaOH,上海阿拉丁试剂)、盐酸(HCl,国药控股有限公司),氯化钠(NaCl,天津市大茂化学试剂厂)、氯化钙(CaCl2,天津市恒兴化学试剂制造有限公司)、氯化铁(FeCl3,上海吉至生化科技有限公司)均为分析纯,乙腈(C2H3N,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司)、甲酸(CH2O2,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司)均为色谱纯。
仪器:电子分析天平(BSA224S,赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司),pH计(FE28,梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司),高速离心机(KH20R,湖南凯达科学仪器有限公司),磁力搅拌器(78-1,常州荣华仪器制造有限公司),电热鼓风干燥箱(GZX-9023MBE,上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂),300W氙灯弧光灯光源(Microsolar 300W 氙灯光源,泊菲莱),Zeta电位仪(Nano-ZS90,英国Malvern Instruments公司),X射线衍射仪(XRD)(D8 ADVANCE,德国Bruker公司),热场发射扫描电镜(SEM)(JSM-7001F,日本电子株式会社),高分辨透射电子显微镜(TEM)(JEM-2010,日本电子株式会社),X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)(Thermo Scientific K-Alpha),傅里叶红外光谱仪(IRTracer-100 光谱仪,日本岛津),高效液相色谱法(HPLC,Agilent 1260,美国)。
1.2 Nb-TiNFs纳米材料的制备
采用一步水热法合成Nb-TiNFs纳米材料,具体步骤为:首先将0.8 g TiO2和0.2 g Nb2O5投加到66.7 mL的NaOH (10.0 mol·L−1 ) 溶液中,于25 ℃下放置于磁力搅拌器(500 r·min−1)上搅拌12 h。接着将混合均匀的溶液移入到100 mL的聚四氟乙烯内衬中,随后放置于不锈钢反应釜中,并置于烘箱中 (130 °C) 进行水热处理。72 h后,将反应釜自然冷却至室温,用去离子水反复洗涤几次至生成物近中性,用无水乙醇将生成物分散后置于烘箱中80 °C烘干,研磨备用。
1.3 材料的表征
使用X射线衍射仪(XRD)对制备好的Nb-TiNFs进行晶体结构分析测定。将样品粉末用KBr压片法制成样品试片,在X射线衍射仪上检测产物的晶型,扫描范围2θ为10°~80°,扫描速度为4°·min−1。
使用扫描电镜(SEM)和透射电镜(TEM)对制备好的Nb-TiNFs进行形貌和微观结构分析;使用 X 射线光电子能谱法(XPS)表征表面化学组成,辐射源为单色 Al 的 Kl 射线,所有的结合能都以284.8 eV 的外来碳信号做内标进行校正以消除静电效应;使用傅里叶红外光谱仪测量样品的傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR),以 KBr 为背景,制样中 KBr 与样品质量比为 100∶1,扫描范围为 400~4 000 cm−1;使用Zeta电位仪测量不同pH下的Zeta电位,将样品按照0.2 g·L−1的比例投入超纯水中制成悬浊液,用0.1 mol·L−1 HCl或0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH调节溶液pH,将确定pH的悬浊液注入Zeta电位仪的测量池,进行测量。
1.4 环丙沙星(CIP)降解实验
环丙沙星光催化降解实验在300W氙灯弧光灯光源下模拟太阳光(AM1.5模式)进行。称量0.015 g的催化剂,将其分散于150 mL 10 mg·L−1环丙沙星溶液中,用0.1 mol·L−1氢氧化钠和盐酸溶液调整pH。首先,将混合溶液在避光条件下搅拌30 min,使CIP在光催化剂上达到吸附平衡。然后,将反应器置于氙灯光源下,在预设时间间隔取样,样品过 0.22 μm 尼龙滤膜,用高效液相色谱仪测定滤液中CIP浓度。整个实验过程中采用循环冷却水装置以控制反应器温度为(25±1) °C。此外,在高效液相色谱法中使用ZORBAX SB-C18柱(250 mm×4.6,5 µm),柱温40°C,荧光检测器激发波长280 nm,发射波长450 nm。流动相体积分数为85%甲酸水(甲酸比例为0.1%),15%乙腈,流动相流速为0.25 mL·min−1,反应时间为240 min。CIP的降解率根据式(1)进行计算。
D=C0−CtC0×100% (1) 式中:D为降解率,%;C0是CIP的初始浓度,mg·L−1;Ct是t时刻CIP的浓度,mg·L−1。
1.5 溶液pH的影响
配置初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1的环丙沙星溶液(150 mL),投加15 mgNb-TiNFs(催化剂质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1),用0.01 mol·L−1的 HCl 和 NaOH 溶液将反应体系的初始 pH 调节为2、4、6和8。经氙灯光源照射在预设时间间隔取样,过膜待测。
1.6 常规无机离子的影响
配置初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1的环丙沙星溶液(150 mL),加入不同浓度水中常见无机离子(Na+、Ca2+和Fe3+)溶液,投加15 mg Nb-TiNFs(催化剂质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1),调节溶液pH为6。氙灯光源照射过程中在预设时间间隔取样,过膜待测。其中,Na+、Ca2+浓度分别设0.5、1和1.5 mmol·L−1三个梯度,Fe3+浓度设0.5、1和1.5 µmol·L−1,总反应时长为180 min。
1.7 淬灭实验
利用对苯醌(BQ)、碘化钾(KI)、呋喃甲醇(FA)和树丁醇(TBA)分别作为超氧自由基(·O2-),空穴(h+),单线态氧(1O2)和羟基自由基(·OH)的淬灭剂 ,考察不同可能存在的活性物种对环丙沙星去除率和降解速率的影响。在光催化反应开始前,加入活性物种淬灭剂 (0.01 mol·L−1 ) ,在设定时间取样过膜后检测。
1.8 催化剂重复利用实验
配置环丙沙星初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1, Nb-TiNFs为0.1 g·L−1的溶液,调节pH为6,在氙灯光源照射下预设时间取样,过膜待测。180 min反应结束后,混合溶液经0.22 µm水系滤膜真空抽滤,将滤得的粉末纯水清洗、烘干后重复利用。通过 5 次连续循环实验探究材料的可重复利用性能。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 催化剂的表征与分析
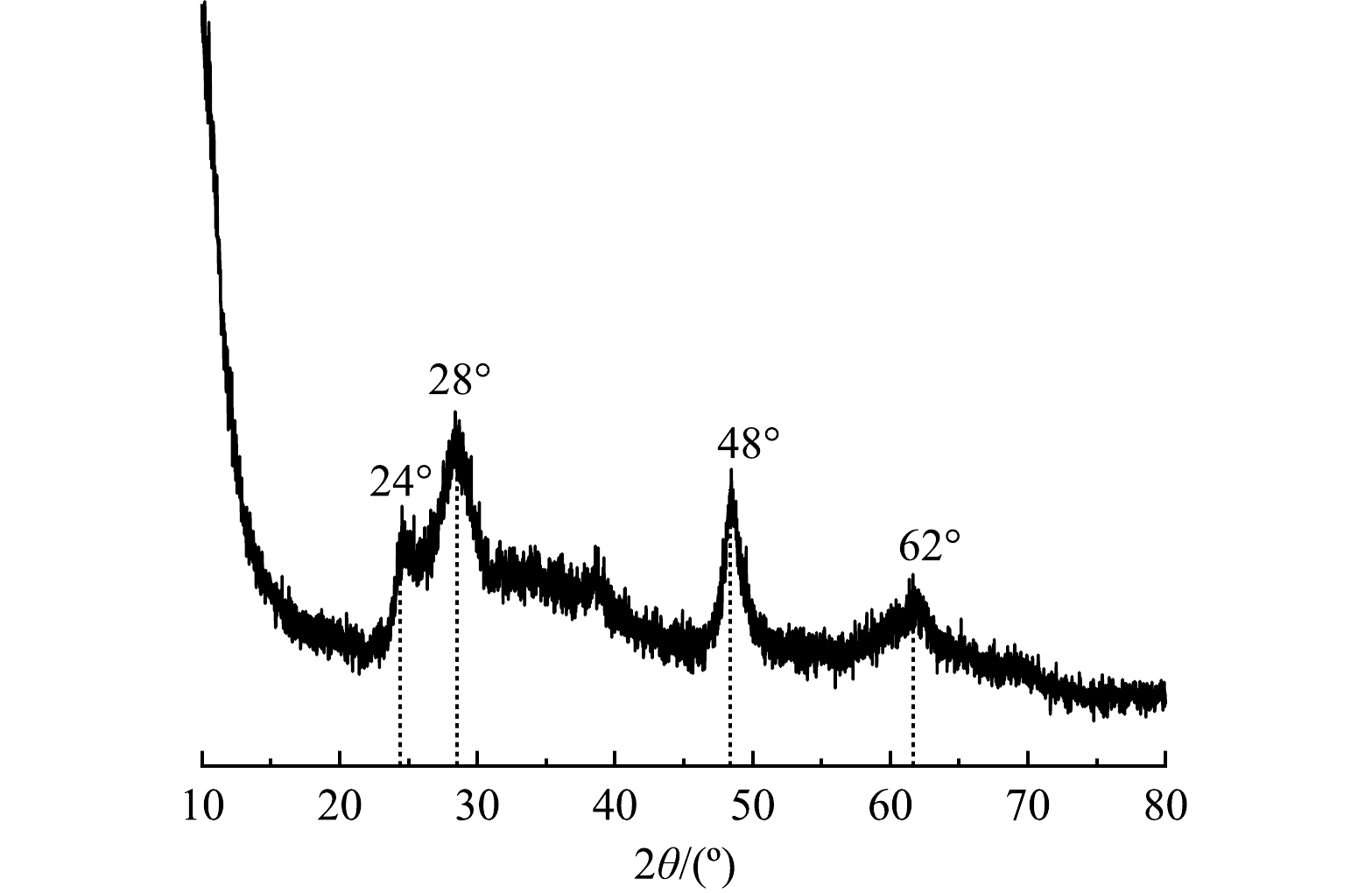
Nb-TiNFs的XRD表征结果如图1所示。可见,在2θ为24°、28°、48°、62°处的特征衍射峰说明Nb-TiNFs为钛酸钠的晶型,可用化学式Na2H2-xTi3O7 .n H2O表示(x取决于钠含量)[20]。因此,水热合成后生成的Nb-TiNFs主体为钛酸盐,该钛酸盐由三重的[TiO6]八面体(骨架)和层间可交换的Na+/H+组成[20-21]。另外,在Nb-TiNFs的XRD图谱中未检测到铌酸盐的特征峰。这可能是掺入铌的量较少,铌酸盐未形成晶体结构。
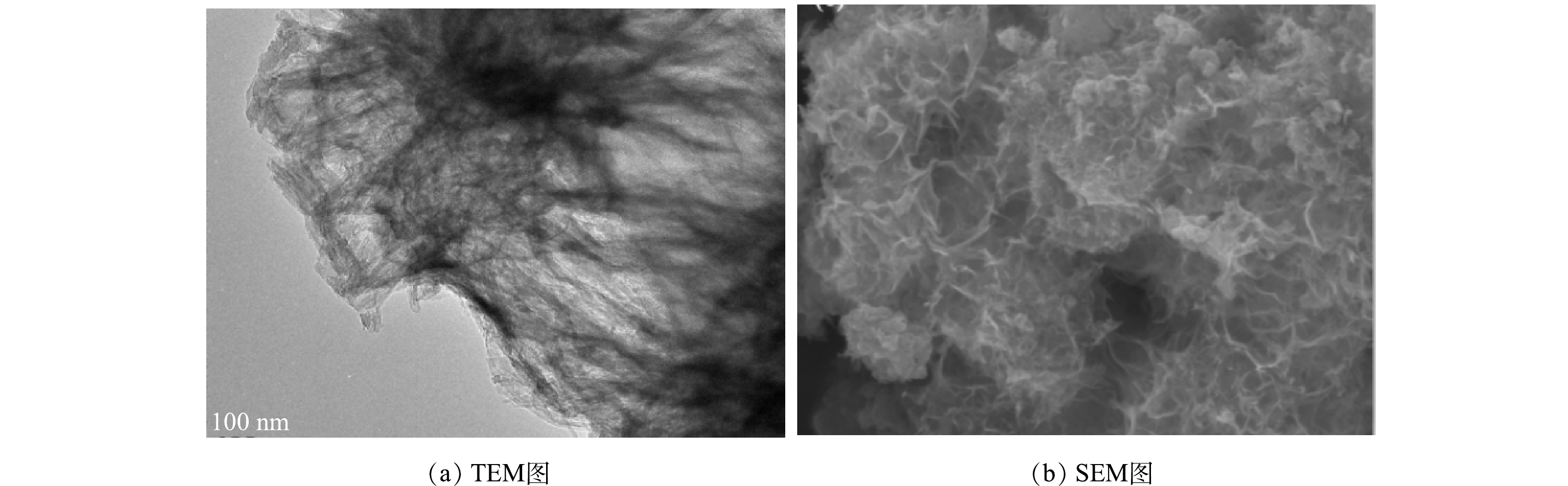
Nb-TiNFs的TEM和SEM表征结果分别如图2(a)和图2(b)所示。由图2(a)可以看出,复合材料呈现清晰的片状结构,可见其为钛酸钠米片结构。通常情况下,P25在130 °C和72 h的水热条件下可形成钛酸纳米管[22],而片状结构一般是形成管状结构前的中间产物。本研究中未成管的原因可能是Nb2O5的掺杂影响了复合材料的最终构型[23]。由图2(b)也可以看出,Nb-TiNFs呈片层无序堆叠形成的块状形态。
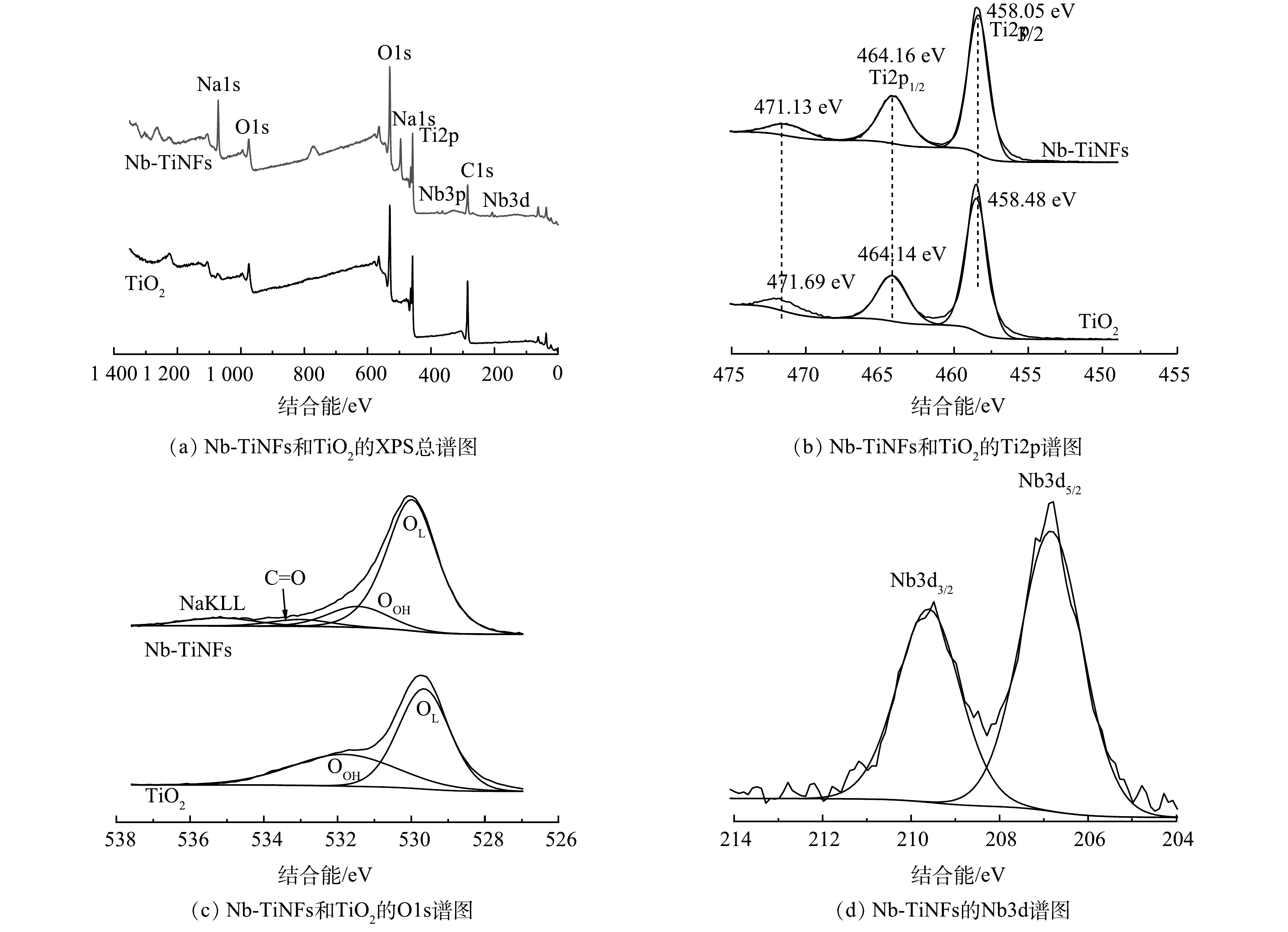
Nb-TiNFs和TiO2 的XPS谱图如图3所示,其中,图3(a)、图3(b)、图3(c)、图3(d)中的所有信号都经过了C1s校准。由XPS总谱(图3(a))中可以看出,Nb-TiNFs的主要元素是O(60.69%)、Ti(21.14%)、Na(17.23%)、Nb(0.95%),显然,在这种合成条件(130 ℃,72 h)下,钛酸盐的产率远远高于铌酸盐。在Ti2p谱图(图3(b))中,结合能分别位于458.05 eV和464.16 eV的 Ti2p3/2峰和 Ti2p1/2峰表明Nb-TiNFs中的Ti为Ti4+的特征[24]。在O1s谱图(图3(c))中,TiO2具有2个特征谱峰,其中,位于低结合能529.68 eV附近的信号峰对应于晶格氧(OL),位于高结合能531.82 eV附近的信号峰对应于材料表面吸附的羟基(·OH);Nb-TiNFs材料具有4个谱峰,其中低结合能530.0 eV附近处的信号峰对应于晶格氧(OL),高结合能531.4 eV附近的信号峰对应于材料表面吸附的羟基(·OH),533.0 eV处的信号峰对应C=O键的信号峰,535.2 eV处的信号峰对应NaKLL峰。在Nb3d谱图(图3(d))中,掺杂的Nb元素的Nb 3d3/2峰和Nb 3d5/2峰均以Nb5+的形式存在[25-28]。
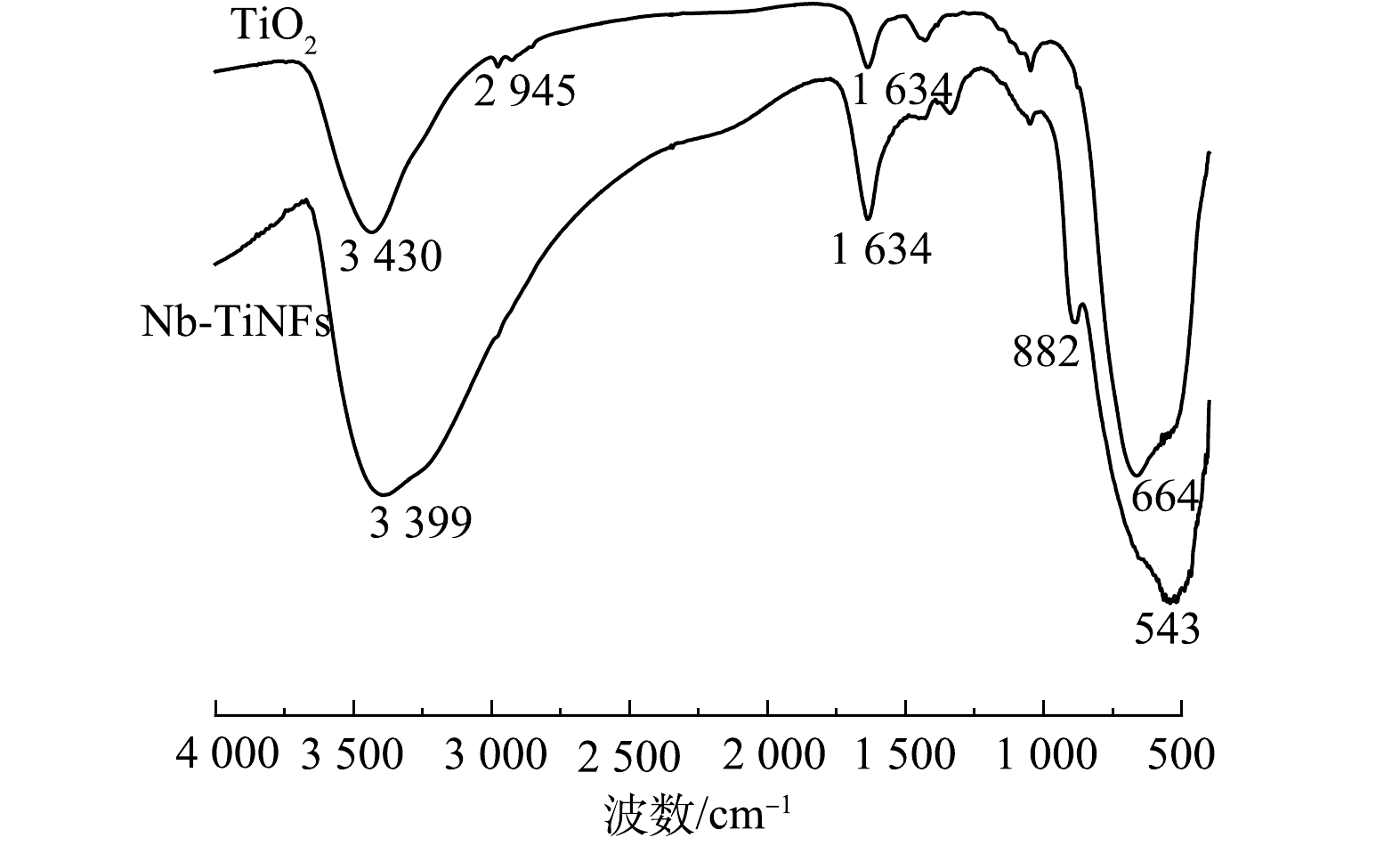
Nb-TiNFs和TiO2的红外图谱如图4所示,3 430 cm−1和3 399 cm−1附近的宽峰为 Ti-OH 及 吸 附 水 的—OH 伸缩振动峰,TiO2和Nb-TiNFs的峰有轻微偏移,可能是由于Nb的掺杂所导致。TiO2在2 945cm−1附近的峰为—CH2—的吸收峰,1 634 cm−1附近的峰为催化剂表面物理吸附水的H—O—H 弯曲振动峰,400~700 cm−1对应着金属氧化物键,664 cm−1 和 543 cm−1对应着Ti—O 键,882 cm−1处的峰对应着Nb—O键[29-30]。分析说明该催化剂表面存在较丰富的羟基官能团,而表面羟基有利于捕获光生空穴,生成强氧化性的羟基自由基,有利于光催化降解[31]。
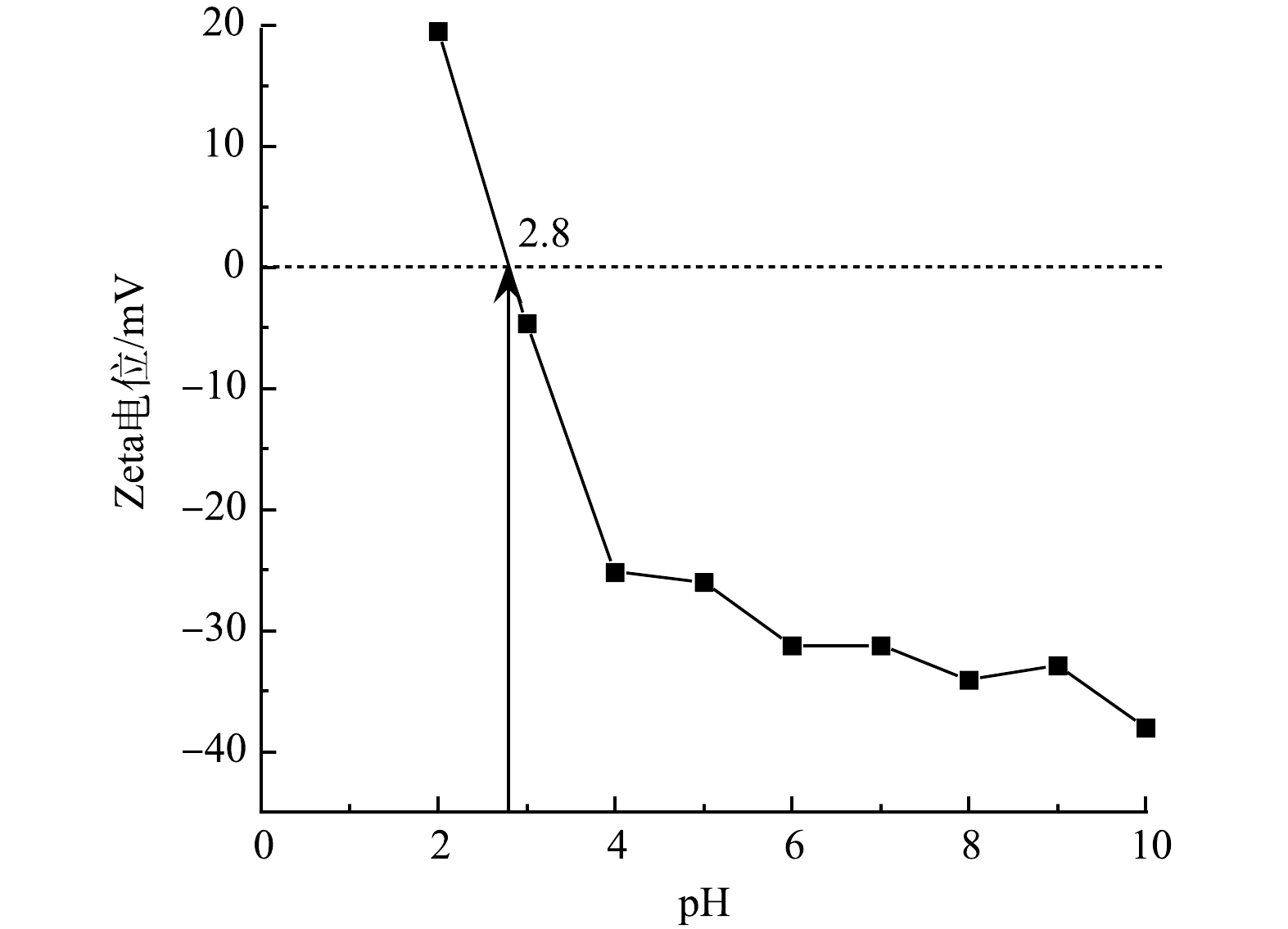
Nb-TiNFs在不同pH下的Zeta电位见图5。可见,Nb-TiNFs的等电点约为2.8。当溶液 pH 为2.8时,Nb-TiNFs所带电荷为零;当溶液pH 小于等电点时,导致碱性解离小于酸性解离, 则 Nb-TiNFs的 Zeta 电位为正值;当溶液pH 大于等电点时, 导致碱性解离大于酸性解离,则 Nb-TiNFs的 Zeta 电位为负值。因此,当pH<2.8时,Nb-TiNFs的表面带正电,当pH>2.8时,Nb-TiNFs的表面带负电。
2.2 光催化降解性能分析
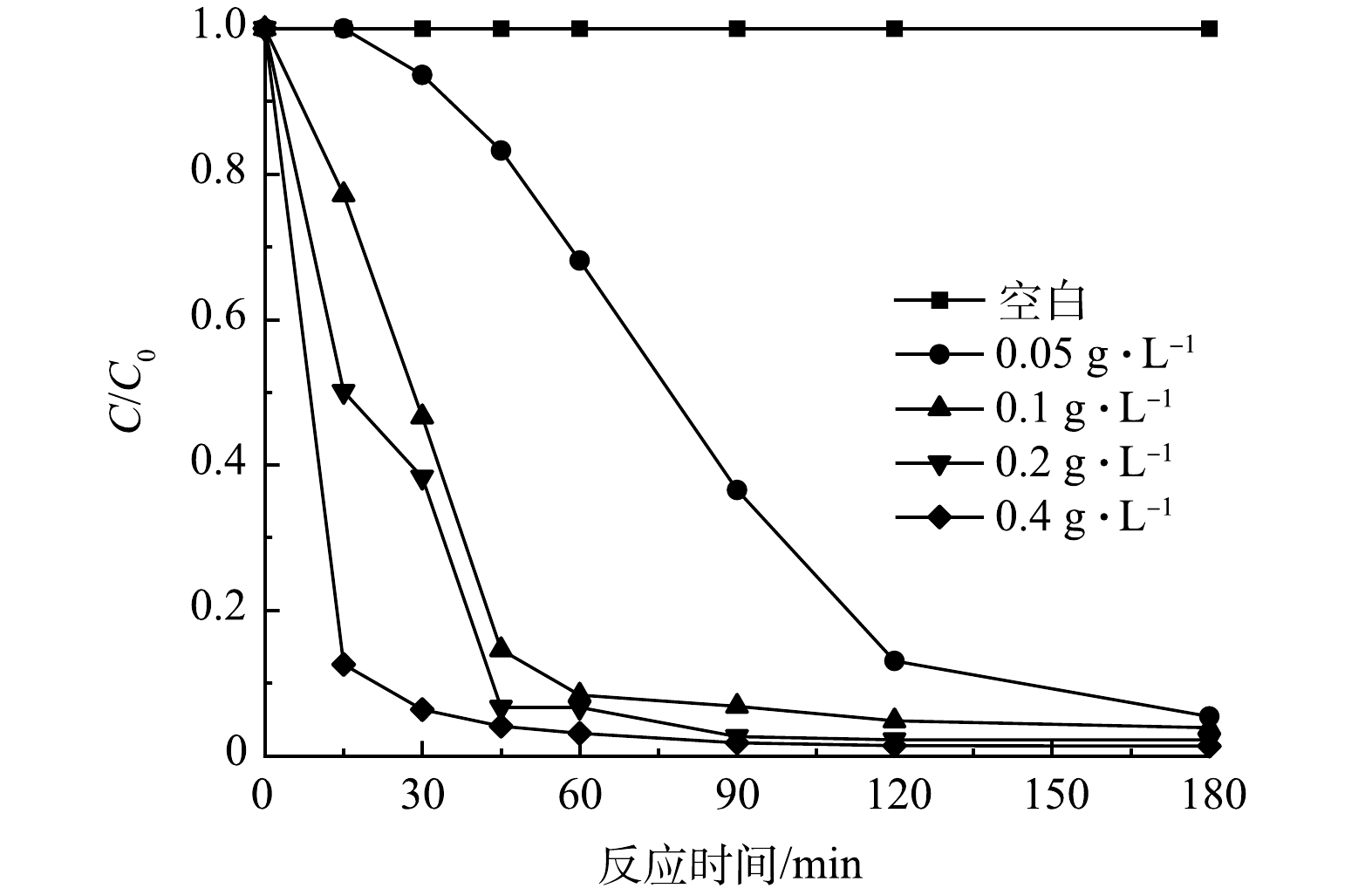
黑暗条件下的吸附预实验结果表明,CIP(初始质量浓度10 mg·L−1)在30min内达到吸附平衡,材料对CIP的吸附量为2.68%,可忽略不计。在光催化实验中,光催化剂的投加量是影响催化效率的1个重要因素[32]。图6反映了在CIP的初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,pH为6的条件下,催化剂质量浓度(0.05~0.4 g·L−1)对CIP降解的影响情况。结果表明,CIP的去除率随着光催化剂投加量的增加而升高,当催化剂质量浓度为0.05 g·L−1时,60 min内CIP的去除率为30.89%,催化剂质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1时,60 min左右CIP的去除率达到91.67%,催化剂的质量浓度增加到0.2 g·L−1和0.4 g·L−1时,60 min内去除率分别增至93.33%和96.92%。当催化剂为0.05、0.1、0.2 和0.4 g·L−1时,180 min后CIP的去除率分别为94.6%,96.1%,97.8%和98.7%。出于实际应用考虑, 0.1 g·L−1催化剂即可以满足应用需求,故之后的实验选用投加0.1 g·L−1光催化。
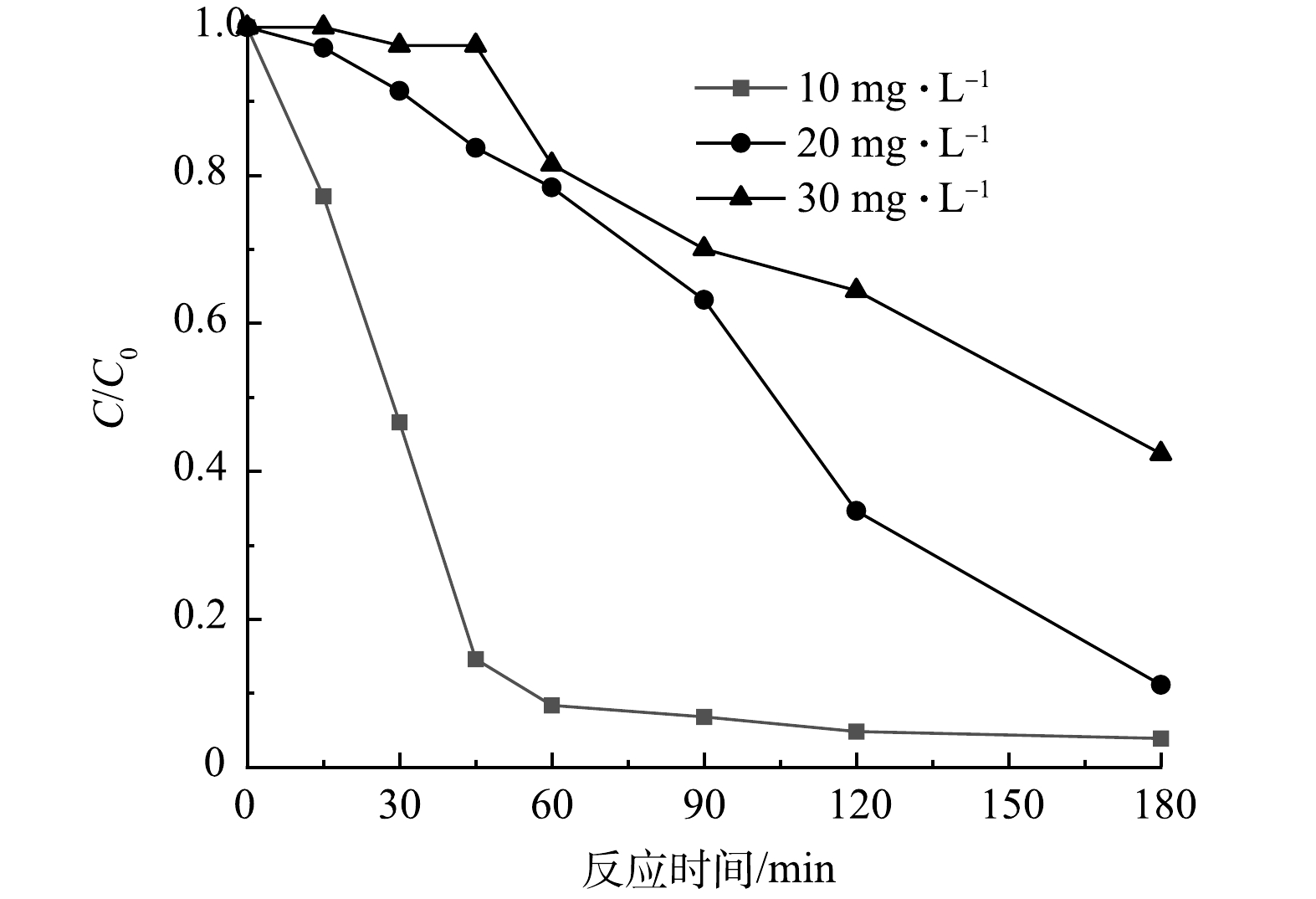
目标污染物的初始质量浓度也会对光催化剂的催化效率产生重要影响,为此,本研究考察了在相同催化剂浓度下不同初始质量浓度CIP的降解性能(图7)。如图7所示,当Nb-TiNFs为0.1 g·L−1、pH为6、CIP初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1时,起初CIP被迅速降解,60 min左右即达到平衡,3 h后降解率达96%。随着CIP初始质量浓度升高,其降解率逐渐下降,当CIP质量浓度为20 mg·L−1和30 mg·L−1时,3 h后降解率分别下降至92%和56%。
为探究Nb-TiNFs在可见光驱动(visible light drive,VLD)下的降解性能,本研究使用UV滤光片(<420 nm)滤掉紫外光以考察Nb-TiNFs在可见光下对CIP的降解性能。如图8所示,在CIP初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,Nb-TiNFs质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1,pH为6的条件下,当使用滤光片反应180 min后,CIP的去除率由96.1%降至46.1%。因此,在日光下,可见光CIP的去除贡献为46.1%,紫外光的去除贡献为50%。如前所述,TiO2基光催化剂只对紫外光响应[17-18],而Nb-TiNFs材料对CIP的降解过程中虽然紫外光仍起着重要作用,但结果表明,铌酸盐的掺入一定程度上增强了材料的可见光驱动性能。
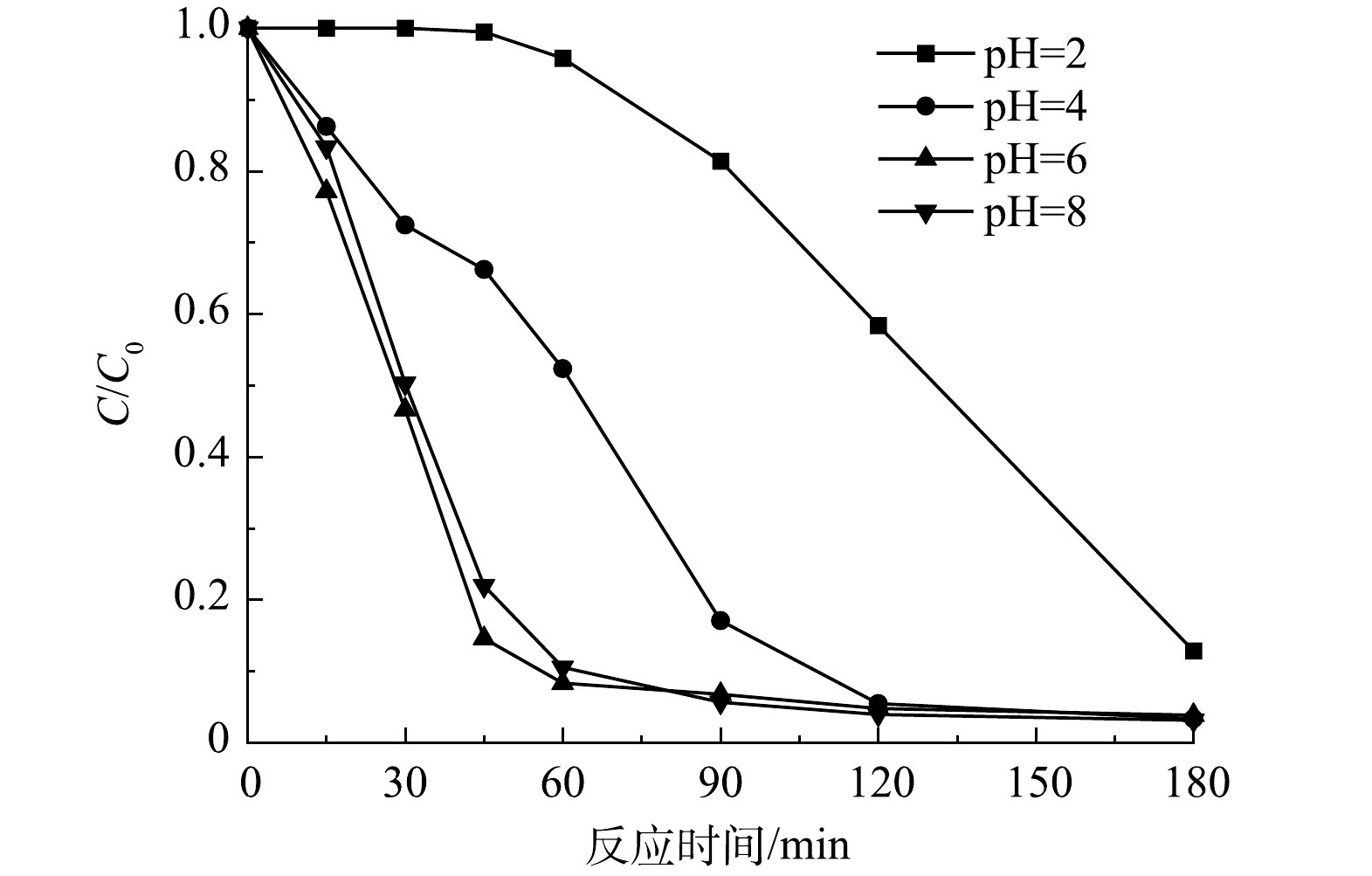
溶液 pH 在水处理过程中是不可忽略的因素。溶液的 pH 会影响催化剂的表面性质和污染物分子的形态分布,进而通过静电作用影响催化剂对污染物的去除[33]。同时,溶液 pH 也会影响光催化过程中活性氧物种的形成和活性,影响光催化体系的氧化能力。不同溶液 pH 对Nb-TiNFs光催化降解环丙沙星的影响情况见图9。结果表明,在CIP初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,Nb-TiNFs质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1的条件下,当溶液pH=2时,反应180 min后CIP的去除率最低,为87%,而当pH为4、6和8时,180 min后CIP的最终去除率分别为95.6%、96.1%、95.9%。有研究[34]表明,CIP作为一种可解离抗生素,由于其结构中的亚氨基-NH和羧基-COOH上的质子化和脱质子化过程,使其在不同的pH条件下呈现不同的存在形式,在 pH<8.7 的溶液中CIP表现为正电,在溶液 pH为 8.7~10.6 时CIP呈电中性,在溶液 pH>10.6 时CIP显示负电性。在本研究中,Nb-TiNFs的等电点为2.8,因此,溶液 pH为 2 时,Nb-TiNFs表面带正电,与CIP之间存在静电斥力,进而导致环丙沙星去除率的下降。而pH为4、6和8时,Nb-TiNFs表面带负电,CIP带正电,两者之间的静电吸引促使Nb-TiNFs能够捕获更多的CIP,从而进一步增强其降解效率。此外,随着 pH 的升高溶液中的氢氧根数量增多,为羟基自由基的产生提供了更多可能性,这也可能是引起环丙沙星去除效率升高的原因。
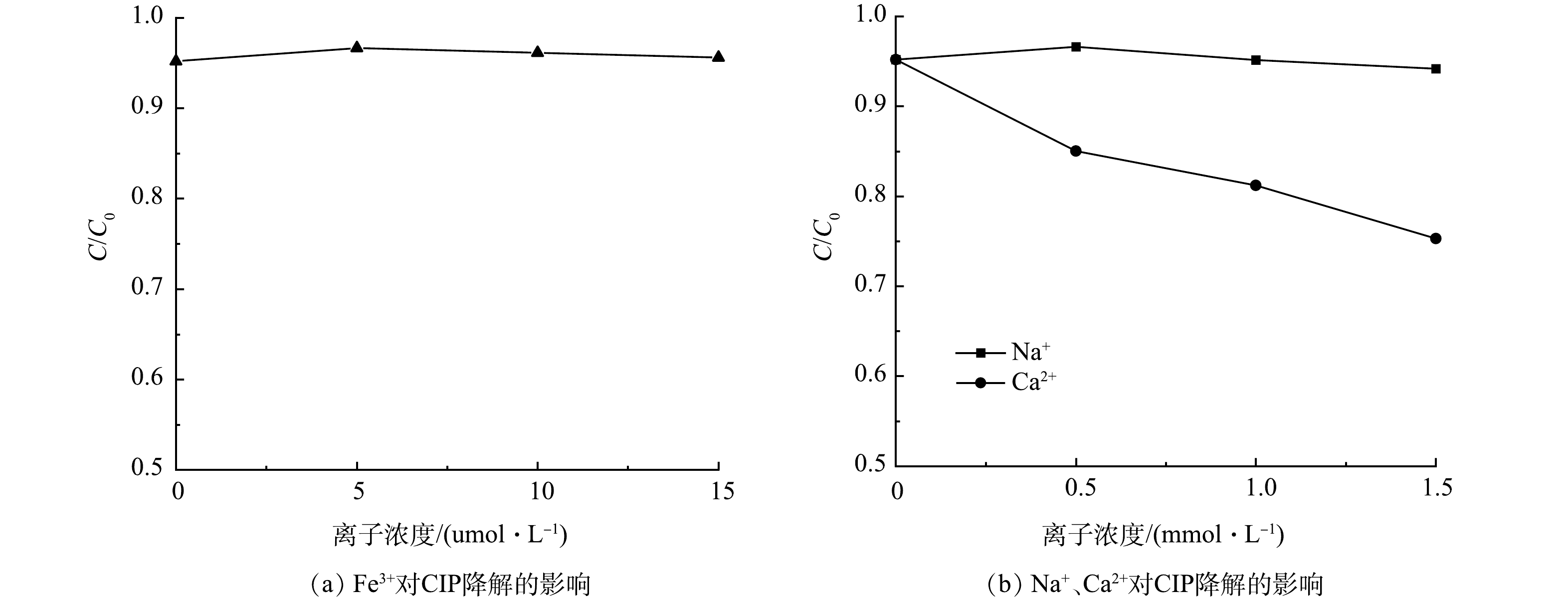
实际水体中普遍存在的无机阳离子可能对环丙沙星的去除产生影响[35]。本研究考察了在初始CIP质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,光催化剂质量浓度为0.1 g·L−1的条件下,水中典型Na+、Ca2+和Fe3+对Nb-TiNFs在可见光下降解CIP的影响(图10)。由图10可见,当Na+浓度在 0.5~1.5 mmol·L−1时,其对环丙沙星的光催化去除的影响微乎其微。当Na+浓度为 1.5 mmol·L−1 时,氙灯照射下120 min 后环丙沙星的去除率为 94.17%,比未加入Na+时仅降低了 1.02%。然而,当共存Ca2+浓度为0.5~1.5 mmol·L−1时,光催化120 min后,溶液中CIP降解率降低了10.2%~19.9%,抑制作用较为显著。这可能是由于带正电的 Ca2+与环丙沙星在催化剂表面竞争吸附位点,从而抑制了环丙沙星的去除。而当溶液中共存的阳离子浓度相同时, Ca2+的影响大于Na+,这可能是因为带正电的阳离子与环丙沙星在催化剂表面竞争吸附,二价阳离子的竞争力更强,此外,Ca2+与有机污染物的螯合能力较强,Ca2+可以与环丙沙星键合形成分子量较大的络合物,不利于环丙沙星在催化剂表面的吸附和光催化去除[36],考虑到常温下Fe(OH)3的溶度积Ksp为4×10−38,因此中性水体中存在的Fe3+浓度较小,故添加共存Fe3+浓度为5~15 µmol·L−1。少量共存的Fe3+可轻微促进CIP的光催化去除,当加入5 µmol·L−1 Fe3+时,可见光照射120 min后CIP的去除率由原来的95.19%升高至96.67%,这可能是因为 Fe3+的电子捕获作用进一步促进了电子和空穴的分离,有利于材料表面活性自由基的产生,但随着Fe3+浓度的增加,促进作用更加微弱,几乎可以忽略不计。
2.3 环丙沙星的降解机理及降解过程中的活性物种分析
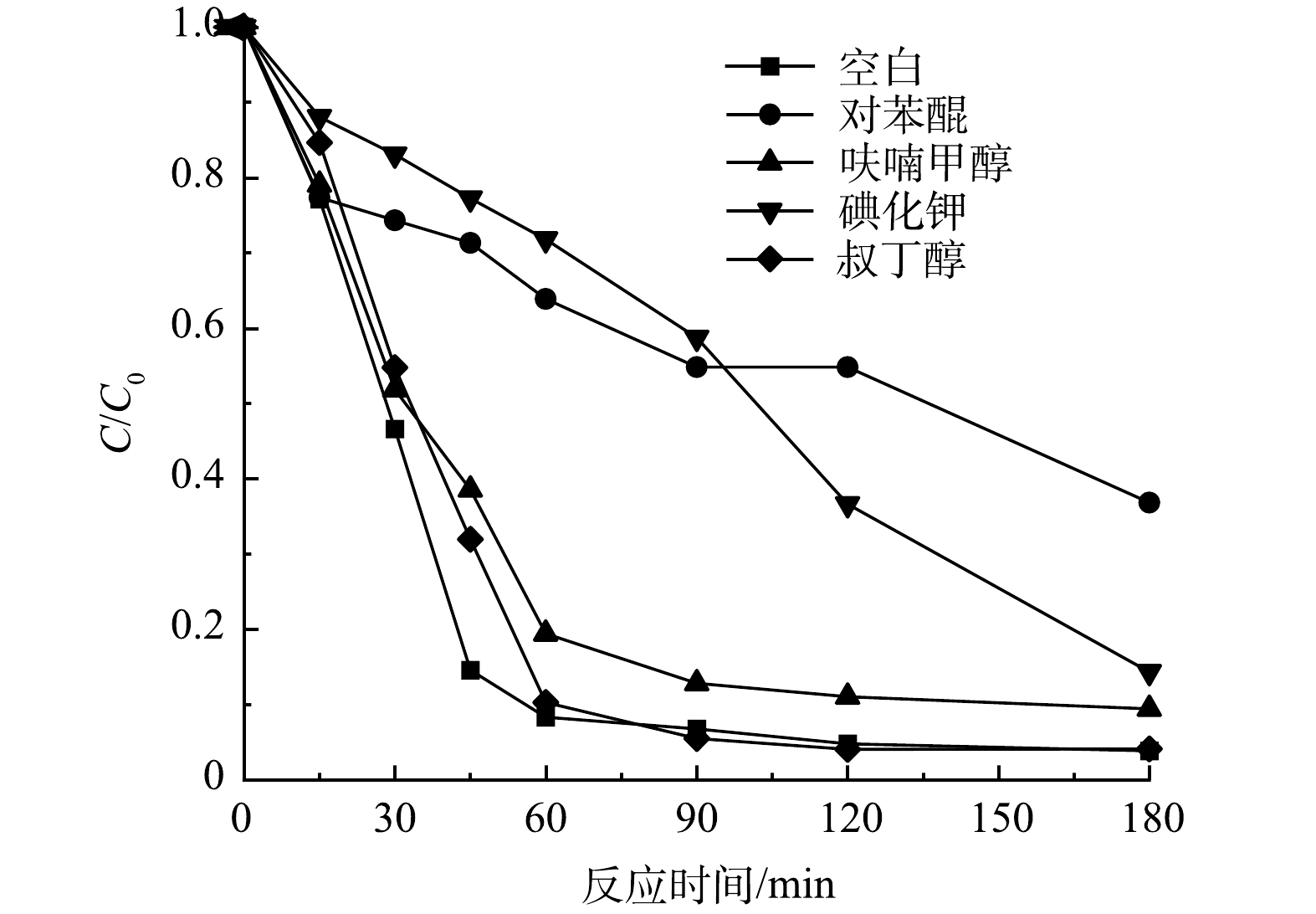
不同淬灭剂对环丙沙星降解速率的影响如图11所示。其中初始CIP质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,淬灭剂质量浓度为0.01 mol·L−1,pH为6。结果表明,在加入BQ、KI、FA和TBA后,光照60 min内CIP的去除率由 91.7%分别降至 36.1%、28.2%和 80.6%和89.7%,与未添加淬灭剂相比,去除率分别降低了 55.6%、63.5%和 11.1%和2%,180 min反应结束后,CIP的去除率由 96.2%分别降至 42.8%、85.6%和 90.6%和95.9%。结果表明,超氧自由基、空穴、单线态氧和羟基自由基在环丙沙星的降解过程中均发挥了作用,其中超氧自由基发挥的作用最显著。
根据以上结果推测在模拟日光下Nb-TiNFs光催化CIP的机理。经过水热处理,具有不同能带隙(Eg)的2种半导体材料可能形成异质结构。当太阳光照射时,钛酸盐和铌酸盐均可被激发,从而形成具有不同能带间隙的2种材料的导带(conduction band,CB)和价带(valence band,VB)(式(2)和式(3)),光子激发价带(VB)上的电子跃迁至导带(CB)形成光生电子,同时VB上留下光生空穴。通常情况下,产生的光生空穴-电子对(h+-e−)易发生复合而耗散能量,而由于Nb的掺杂和异质结构的形成,导致导带发生偏移,使得钛酸盐上生成的电子转移到铌酸盐的CB上(式(4))从而抑制了h+-e− 的复合,增加了载流子的分离效率。转移的e− 将被其他受体(氧气)捕获以形成·O2−(式(5)),并进一步产生·OH(式(6)),同时,空穴(h+)氧化H2O分子可产生·OH(式(7)),并且空穴也可以直接攻击CIP将其降解(式(9))。另一方面,O2受光能量激发后生成1O2(式(8))。CIP被生成的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)(·O2−、·OH、1O2)降解甚至矿化(式(10))。
钛酸盐+hv→e−Ti+h+Ti (2) 铌酸盐+hv→e−Nb+h+Nb (3) 铌酸盐+e−Ti→铌酸盐−e−Ti(电子转移) (4) O2+e−→·O−2 (5) ⋅O−2+2e−+2H+→⋅OH+OH− (6) H2O+h+→⋅OH (7) O2+hv→1O2 (8) CIP+h+→中间产物→CO2+H2O (9) CIP+ROS→中间产物→CO2+H2O (10) 2.4 光催化剂的重复利用性能
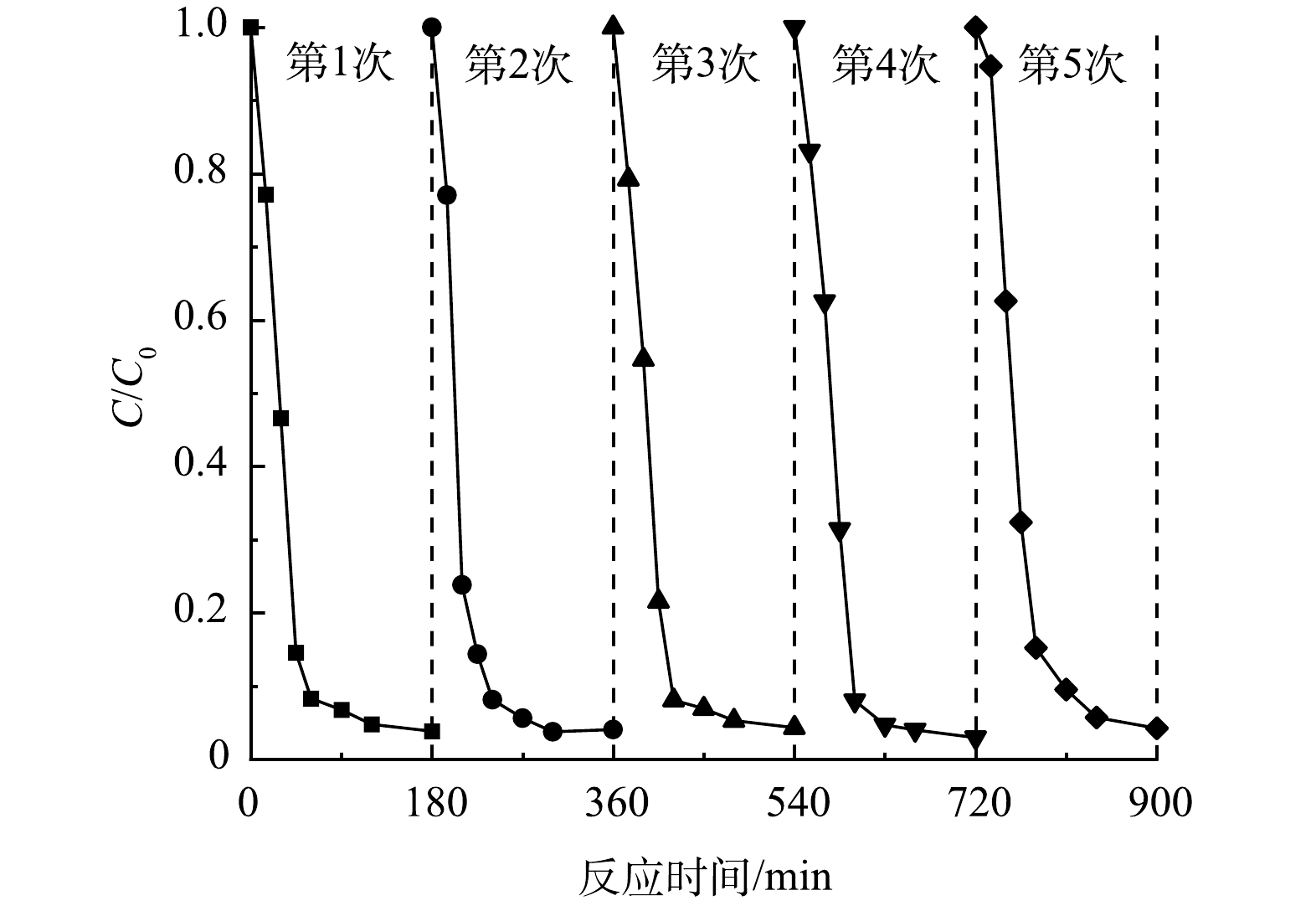
光催化剂的稳定性与其是否可以在实际工程中应用紧密相关,只有重复使用过程中性能稳定的催化剂才具备经济性,图12为Nb-TiNFs光催化剂的可重复利用性能测试结果,其中催化剂的质量浓度为 0.1 g·L−1,CIP溶液质量浓度为 10.0 mg·L−1, pH 为 6.0。结果表明,5次循环利用过程中,反应180 min后CIP的去除率没有显著下降,仅由 96.2%降低为 94.3%。说明 Nb-TiNFs催化剂在重复使用过程中具有较高的稳定性,并且保持着较高的活性,该催化剂具有实际应用的潜力。
3. 结论
1) Nb-TiNFs复合材料呈现出铌酸盐和钛酸盐的异质结构,其形貌为掺杂铌酸盐的钛酸纳米片。
2) Nb-TiNFs在模拟太阳光下可高效快速光催化降解水中新兴污染物CIP,在pH为6时,0.1 g·L−1 Nb-TiNFs光催化剂180min内对10 mg·L−1CIP的降解率可达96.2%。pH、共存离子等因素对Nb-TiNFs光催化降解水中CIP影响程度不同。
3) ROS(·O2−,·OH,1O2)在环丙沙星的降解过程中均发挥了作用,其中超氧自由基发挥的作用最显著。
4) 5轮光催化重复去除实验中,CIP的去除率由 96.2%降低为 94.3%,仅下降 1.9%。说明Nb-TiNFs催化剂具有较高的稳定性,具有实际应用前景。
5)钛酸盐和铌酸盐的异质结构导致带状复合材料的带隙偏移,便于转移激发电子从钛酸盐到铌酸盐,抑制电子-空穴对的复合,从而极大地促进了太阳光驱动的光催化活性。与基于TiO2的光催化剂相比,Nb-TiNFs不需要强制性的额外UV光源来激发反应过程,在太阳光下即可彻底反应。
-
表 1 2018年1—12月某水质净化厂进水水量与污染物浓度
Table 1. Wastewater inflow and pollutant concentration in the municipal wastewater treatment plantfrom January to December, 2018
月份 水量/(104 m3) COD/(mg·L−1) BOD5/(mg·L−1) NH4+-N/(mg·L−1) TN/(mg·L−1) TP/(mg·L−1) BOD5/COD BOD5/TN BOD5/TP 1 10.62 308.5 111.1 19.3 28.3 4.59 0.36 3.93 24.20 2 8.90 287.6 94.9 17.6 25.7 4.18 0.33 3.69 22.70 3 11.34 338.3 109.4 20 29.2 5.82 0.32 3.74 18.80 4 11.42 228.2 78.1 20.9 29.9 5.11 0.34 2.61 15.28 5 13.32 216.1 72.6 16.5 27.1 4.18 0.34 2.67 17.37 6 20.02 131.4 46.2 23.1 31.5 2.86 0.35 1.46 16.15 7 22.16 155.7 45.3 12.4 19.2 3.27 0.29 2.35 13.85 8 20.09 136.2 33.6 10.1 15.9 2.66 0.25 2.11 12.63 9 18.24 104.9 25.9 10.9 14.2 1.61 0.25 1.82 16.09 10 16.52 178.4 56.1 17.1 21.7 3.76 0.31 2.58 14.92 11 16.63 167.2 47.2 16.7 23.4 3.39 0.28 2.01 13.92 12 17.54 153.1 54 17.3 24.3 2.78 0.35 2.22 19.42 表 2 2018年1—12月某水质净化厂出水水质
Table 2. Analysis of effluent quality in the municipal wastewater treatment plant from January to December, 2018
mg·L−1 月份 COD BOD NH4+-N TN TP 1 21.73 3.50 0.68 12.60 0.33 2 17.19 3.51 0.63 11.83 0.29 3 19.33 2.83 0.46 12.91 0.34 4 19.90 2.52 0.54 11.82 0.27 5 15.44 2.31 0.36 12.00 0.26 6 13.41 2.33 1.00 14.90 0.17 7 14.28 2.18 0.14 7.27 0.21 8 14.42 2.03 0.20 6.37 0.20 9 13.84 2.19 0.17 6.32 0.14 10 17.51 2.13 0.16 9.30 0.26 11 15.62 2.32 0.27 11.10 0.25 12 14.45 2.18 0.23 10.27 0.28 表 3 二级出水和深度出水水质
Table 3. Effluent quality of secondary and advanced treatment processes
mg·L−1 水质来源 SS COD NH4+-N TN TP 进水 217.78 200.47 16.83 24.2 3.68 二级出水 6.11 16.52 0.40 10.93 0.63 深度出水 4.05 16.43 0.40 10.56 0.25 -
[1] 刘章富, 熊杨, 侯铁, 等. 同步生物除磷脱氮的几种实用新工艺[J]. 中国给水排水, 2002, 18(9): 65-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2002.09.022 [2] 李斯亮. A2O工艺处理东北小城镇污水的优化运行及效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016. [3] 冀宝友. Orbal氧化沟在小城镇污水处理厂中的调试运行研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011. [4] 赵维妍. SBR工艺处理生活污水同步脱氮除磷的效能研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2019. [5] POGNANI M, BARRENA R, FONT X, et al. A complete massbalance of a complex combined anaerobic/aerobic municipal source-separated waste treatment plant[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(7): 4646-4653. [6] 杨洋. 城市污水厂A2O工艺效能优化与应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013. [7] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1989. [8] 郑兴灿, 张昱. 城镇污水处理厂微量污染物的来源与控制途径[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 54(2): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2018.02.001 [9] 郭玉梅, 李志平, 王莹莹, 等. A2O与V型滤池组合工艺强化脱氮除磷性能分析[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(5): 11-15. [10] 许德超, 陈洪波, 李小明, 等. 静置/好氧/缺氧序批式反应器(SBR)脱氮除磷效果研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(1): 152-159. [11] 郑育毅. 改性硅藻土深度处理城市污水厂尾水的实验研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(7): 1527-1531. [12] 郭强. 城市污水处理厂升级改造工艺及运行研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2018. [13] 夏雪, 邵明非, 吕小梅, 等. 不同碳源驯化除磷污泥的除磷效果及菌群结构分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(8): 936-942. -




 下载:
下载: