-
水体富营养化是严重的水质污染问题,磷是导致水体富营养化的主要营养元素[1]。为抑制藻类生长,水体中磷浓度应控制在一个较低的范围内(<0.05 mg∙L−1)[2]。但A/A/O等污水处理工艺对磷的去除效果并不理想,出水磷浓度一般在0.5~2 mg∙L−1[3-4]。因此,需要深度除磷,以进一步降低水中的磷浓度。
吸附法是一种常用的水处理方法,与其他深度除磷方法(如纳滤/反渗透[5]、离子交换[6]和人工湿地[7]等)相比,具有操作简便、出水水质优和运行稳定等优势[8-10]。在除磷吸附剂中,金属复合吸附剂有较强的磷酸盐吸附特性[11-13],其可融合单金属的优势,且能够展现出不同于单金属的物理化学特性,如较大的比表面积和零电位点(pHpzc)等,在一定程度上提高了对磷酸盐的吸附性能[14-15]。LYU等[12]合成了Fe-Al-Mn复合吸附剂,他们在Fe-Mn的基础上引进了氧化铝,提高了吸附剂的pHpzc和除磷性能。HAO等[13]合成了La-Fe复合吸附剂,发现Fe的掺杂提高了吸附剂的除磷性能及其分离能力。
铈和锆基吸附剂具有环境友好、抗酸碱能力强、稳定性高等优势,其对磷酸盐具有优良的去除能力和较高的选择性[16-18]。SU等[18]制备的Ce-Zr复合吸附剂具有较佳的磷吸附容量和选择性,但其pHpzc仅为3.9,当pH接近中性时,磷的去除率急剧下降,最低降至55%,而水的pH通常为中性,影响其实际应用。ZnO是常用的金属氧化物,除磷性能良好,且具有高的零电位点(pHpzc=9.5)[19]。将ZnO掺杂至Ce-Zr中,可望有效改善吸附剂pHpzc,提高pH使用范围和除磷能力。因此,本研究制备了一种新型的Ce-Zr-Zn复合吸附剂,结合XRD、SEM、BET、XPS和FT-IR等分析表征手段,研究了其深度除磷的吸附性能和相关机理,旨在寻找一种理想的除磷吸附剂,并为该材料用于水体深度除磷提供参考。
-
磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、六水合硝酸铈(Ce (NO3)3·6H2O)、八水合氧氯化锆(ZrOCl2·8H2O)、六水合硝酸锌(Zn(NO3)2·6H2O)、氯化钠(NaCl)、硝酸钠(NaNO3)、硫酸钠(Na2SO4)和碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)等均为分析纯或优级纯,溶液配置均使用去离子水。
-
将Ce (NO3)3·6H2O、ZrOCl2·8H2O和Zn(NO3)2·6H2O以1∶1∶1的摩尔比溶解在200 mL去离子水中,混合均匀,使用氢氧化钠,缓慢调节溶液pH至10.8,再分别搅拌3 h和陈化24 h。多次水洗沉淀,收集沉淀,烘箱干燥12 h,随后在400 ℃焙烧2 h,研磨获得吸附剂。单一金属氧化物的制备方法和步骤与上述方法相同。
-
在进行吸附实验时,将磷溶液置于烧杯中,加入吸附剂并搅拌,间隔一定时间,采用钼酸铵分光光度法测定水中磷酸盐的浓度。除在pH对除磷效果影响的实验中调节了溶液pH外,其他实验均未对溶液的pH进行调节。实验均重复3次。
在进行除磷效果实验时,设置初始磷浓度分别为0.5、1和2 mg∙L−1,吸附剂投加量为0.5 g∙L−1,反应时间为6 h;在进行不同金属氧化物除磷效果实验时,调整初始磷浓度为2 mg∙L−1,吸附剂投加量为0.5 g∙L−1,反应时间为6 h;在进行吸附动力学实验时,调整初始磷浓度为2 mg∙L−1,吸附剂投加量为0.5 g∙L−1,测定不同时间间隔下的磷浓度;在进行等温线实验时,调整吸附剂投加量为0.2 g∙L−1,测定不同初始磷浓度(0.5~100 mg∙L−1)下的平衡磷浓度,并计算磷吸附量;在进行pH影响实验时,采用HNO3和NaOH调节溶液pH为3~11,初始磷浓度为2 mg∙L−1,吸附剂投加量为0.5 g∙L−1,反应时间为6 h;在进行离子影响实验时,选择4种典型离子(Cl−、
NO−3 、SO2−4 和HCO−3 ),每一种离子浓度分别0.1、1、10 mmol∙L−1,吸附剂投加量为0.5 g∙L−1,反应时间为6 h。 -
使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM, JSM-6301F, 日本)分析吸附剂形貌;使用比表面积及孔径分析仪(ASAP 2 460 analyzer,Mike, 美国)分析测定吸附剂比表面积;使用纳米粒度及Zeta电位仪(ZS90,中国)分析吸附剂的粒径;使用X射线衍射仪(XRD, D/max-2 500/PC, 日本)分析吸附剂的晶体结构;使用傅里叶红外变换光谱仪(FT-IR, X70, 德国)表征吸附剂表面的官能团;使用X射线光电子光谱(XPS,EScalab 250Xi,美国)定性分析吸附剂中元素;吸附剂零电位点的测定参照文献中的方法[20]。
-
图1(a)是Ce-Zr-Zn的XRD图谱,在衍射角2θ分别为31.73°、34.4°、36.2°、47.5°、56.5°、62.8°、66.3°、67.9°和69.0°出现吸附剂的特征衍射峰,与标准卡JCPDS NO. 80-0075的衍射峰一致,这说明在吸附剂中存在氧化锌。在XRD图谱中没有明显的铈和锆的衍射峰,这可能是由于含有铈和锆的化合物在吸附剂上是均匀分散或非晶体结构所致[8]。吸附剂表面粗糙不规则(图1(c)和图1(d)),其比表面积、孔容和孔径分别为65.769 m2∙g−1、0.065 cm3∙g−1和3.833 nm(图1(b))。吸附剂的比表面积均高于ZnO (25 m2∙g−1) [21]和ZrO2 (8.83 m2∙g−1)[22],这有利于吸附剂对磷酸盐的吸附。
-
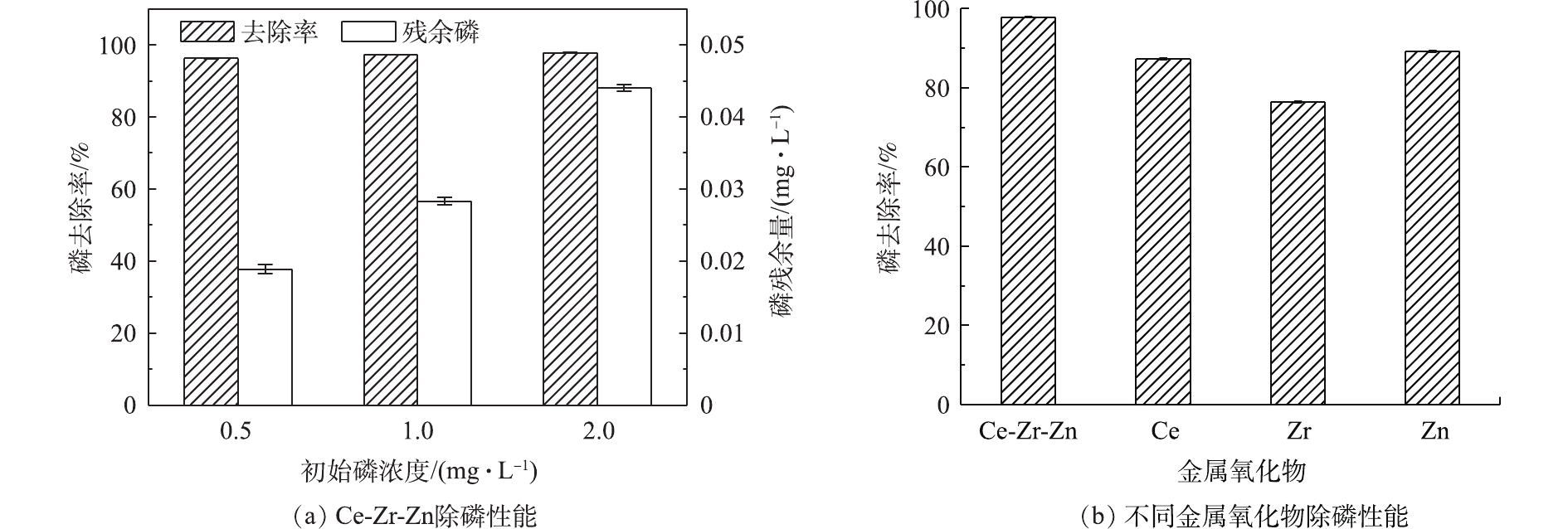
图2反映了Ce-Zr-Zn和不同金属氧化物的除磷效果。图2(a)为Ce-Zr-Zn的除磷效果。由图2(a)可知,当进水磷浓度低于2 mg∙L−1时,去除率高达96%,出水磷残余量小于0.045 mg∙L−1。但随着初始磷浓度的增加,出水磷浓度也会相应上升。SHI等[8]和SU等[18]也报道了类似的结果。图2(b)为不同金属氧化物的除磷性能,Ce-Zr-Zn的除磷性能优于单一的金属氧化物,其除磷性能由大到小为Ce-Zr-Zn>Zn>Ce>Zr。这表明金属复合物更利于提高吸附剂的除磷性能。
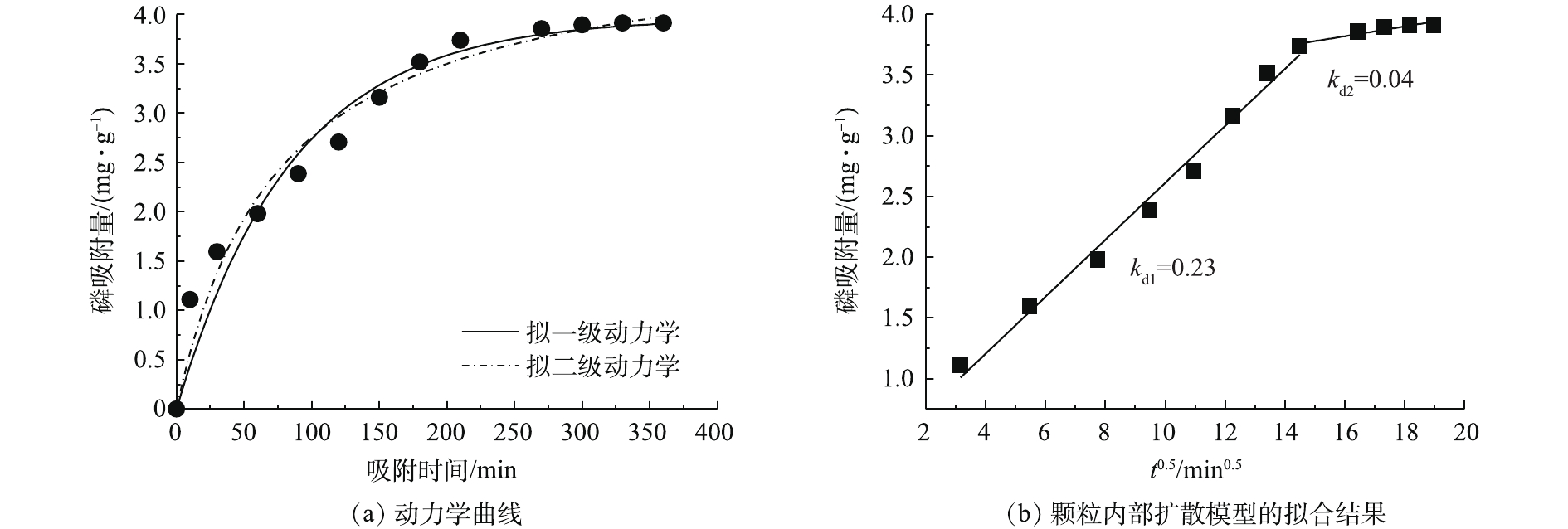
图3反映了Ce-Zr-Zn吸附磷酸盐的拟合结果。使用拟一级动力学模型和拟二级动力学模型[8]对吸附过程进行了拟合,得到图3(a)所示的拟合曲线。吸附剂吸磷初期速率快,随后进行吸附缓慢,直至6 h后达到平衡。动力学参数见表1,基于拟合的相关参数(R2),可判断该过程更符合拟二级动力学模型,速率常数为0.003 g∙(mg·min)−1,以化学吸附为主[23]。这与LYU等[12]的研究结果相似,Fe-Al-Mn的速率常数为0.004 g∙(mg·min)−1。
影响吸附速率的因素有很多,如吸附剂的比表面积、表面基团、表面电荷和孔结构等[8-10, 14]。为进一步研究吸附剂对磷吸附的机理,需要分析吸附过程的限速因素。采用颗粒内部扩散模型[8]对实验数据进行拟合,结果如图3(b)所示。发现吸附过程可分2个阶段:在第1阶段,Ce-Zr-Zn表层的吸附位点被迅速占用,此限速步骤为膜扩散[24];在第2阶段,随着Ce-Zr-Zn表层吸附位点达到饱和,磷酸根离子缓慢扩散至吸附剂内部位点完成吸附过程,吸附速率变得缓慢,此限速步骤为孔隙扩散[25],这与实验拟合结果是一致的(kd1>kd2)。
图4为Langmuir和Freundlich模型[8]拟合的结果,相关参数见表2。由表2中的R2可知,此过程更符合Freundlich模型,这表明吸附磷酸盐为多层吸附过程[17]。吸附剂饱和吸附容量为66.61 mg∙g−1,相比其他的吸附剂[12, 25-26],Ce-Zr-Zn具有更大的磷酸盐吸附量。
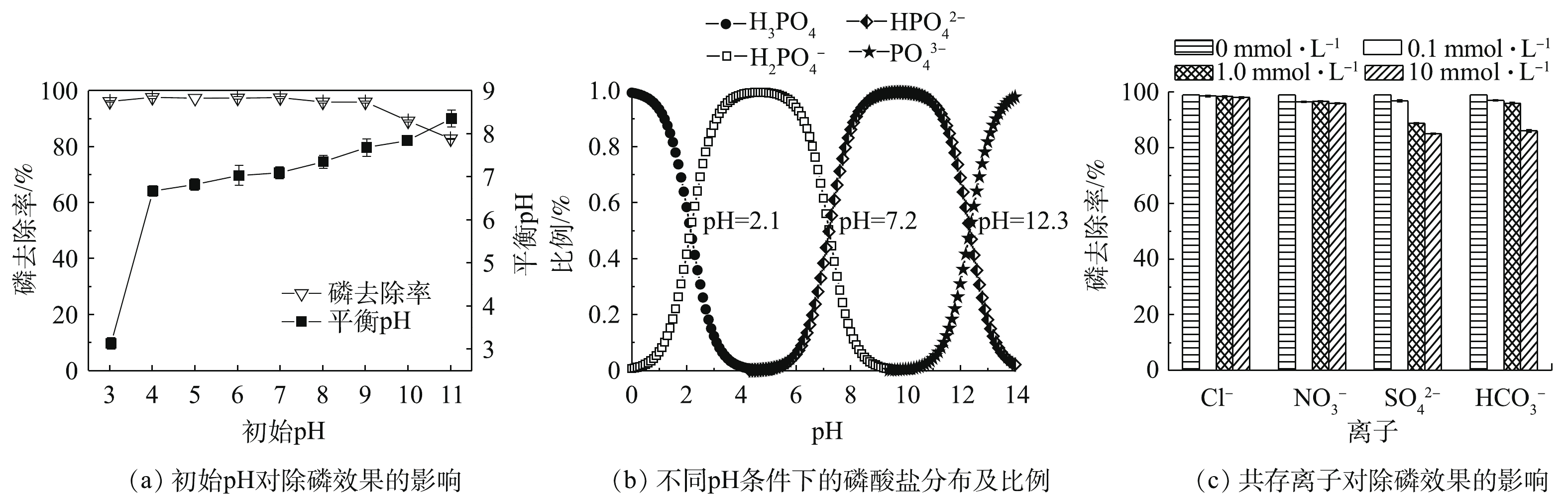
图5(a)为初始pH对磷去除效果的影响。在pH为3~9时,磷去除率基本不变,在96%以上;当pH为10和11时,磷的去除率有所下降,总体在80%以上。上述结果表明,Ce-Zr-Zn吸附剂有较宽的pH适用范围。据报道,在碱性条件下,许多吸附剂对磷的去除率会出现显著下降。SU等[18]合成的Ce0.8Zr0.2O2吸附剂,当溶液pH接近7时,磷去除率下降至50%左右;pH为10时,磷去除率仅有20%左右。HE等[24]合成了La-沸石吸附剂,当溶液pH一接近7时,磷去除率出现下降现象;pH为10时,磷去除率仅有20%左右。图5(b)为不同pH条件下的磷酸盐分布及比例。当pH为3~11时,磷酸盐在水中主要以
H2PO−4 和HPO2−4 为主。且H2PO−4 比HPO2−4 有更低的吸附自由能,因此,在水中H2PO−4 更容易被吸附剂吸附[8]。图5(c)为共存离子对磷去除效果的影响。当Cl−和NO−3 存在时,磷去除率在97%以上,Cl−和NO−3 对磷去除的影响可忽略不计;而当SO2−4 和HCO−3 存在时,磷酸盐去除率有所下降,这可能是由于离子会竞争磷酸根离子的吸附位点[8]。综上所述,当Cl−、NO−3 、SO2−4 和HCO−3 存在时,磷的去除率保持在85%以上,以上结果表明吸附剂具有较好的磷酸盐选择性。此外,考察了吸附剂循环再生能力,吸附剂用NaOH溶液(0.5 mol∙L−1)再生,磷酸盐的脱附率可以达到90%,表现出好的脱附性能,可以循环再生。
-
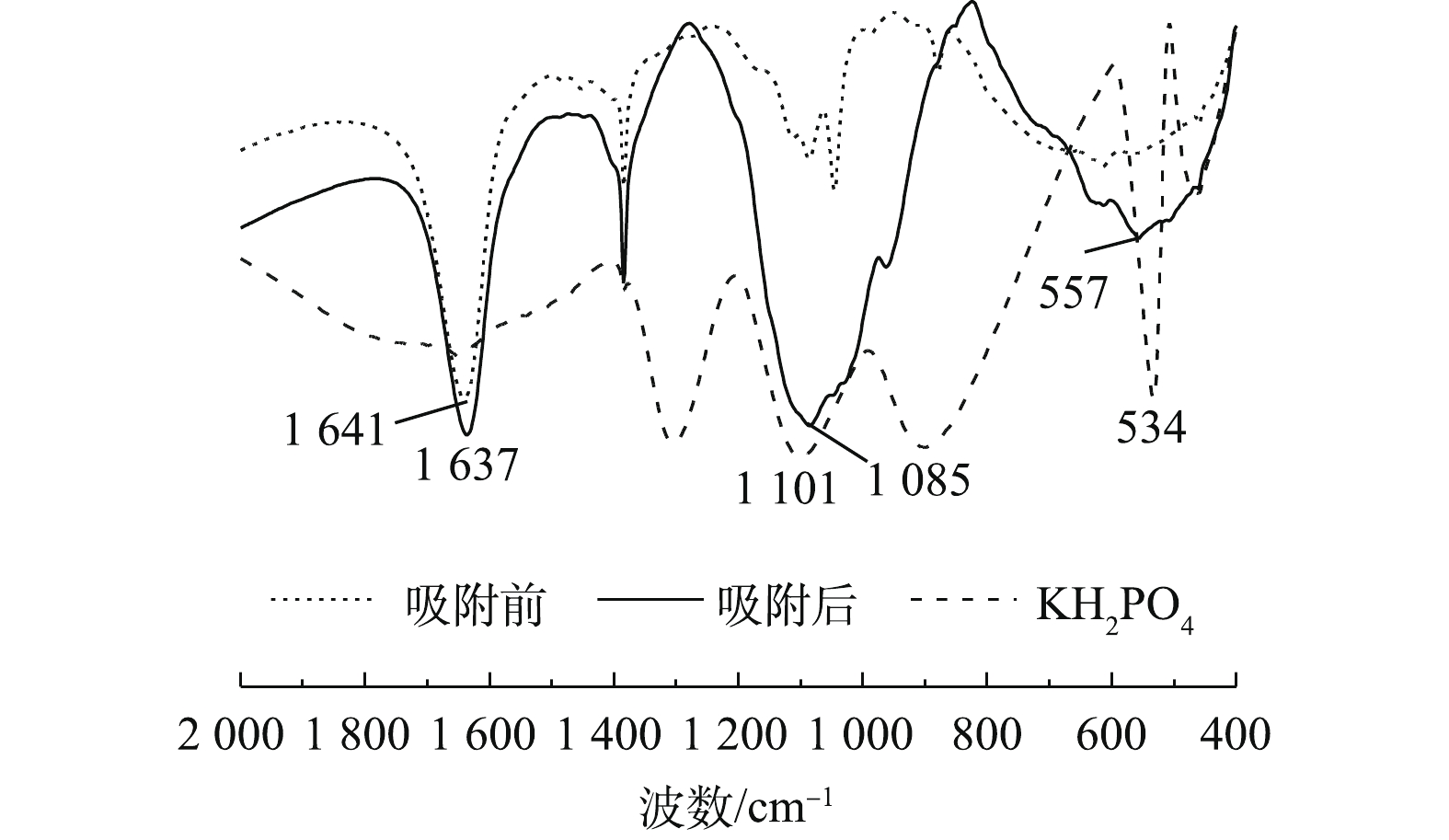
图6为Ce-Zr-Zn吸附磷酸盐前后的FT-IR谱图。1 641 cm−1和1 637 cm−1为水分子中H—O—H的弯曲振动峰[8]。在吸附磷酸盐后,在1 085 cm−1和557 cm−1处出现新峰,分别对应P—O的伸缩振动吸收峰和P—O—P的弯曲振动的吸收峰,表明磷酸盐被吸附在Ce-Zr-Zn表面;且相比KH2PO4标准的P—O的伸缩振动吸收峰(1 101 cm−1处)和P—O—P的弯曲振动的吸收峰(534 cm−1处),吸收峰频率发生了变化。分析原因是由于磷酸根离子在金属活性位点发生配位[8, 14]、表面羟基与磷酸盐发生配位体交换[16, 20, 24]所致。
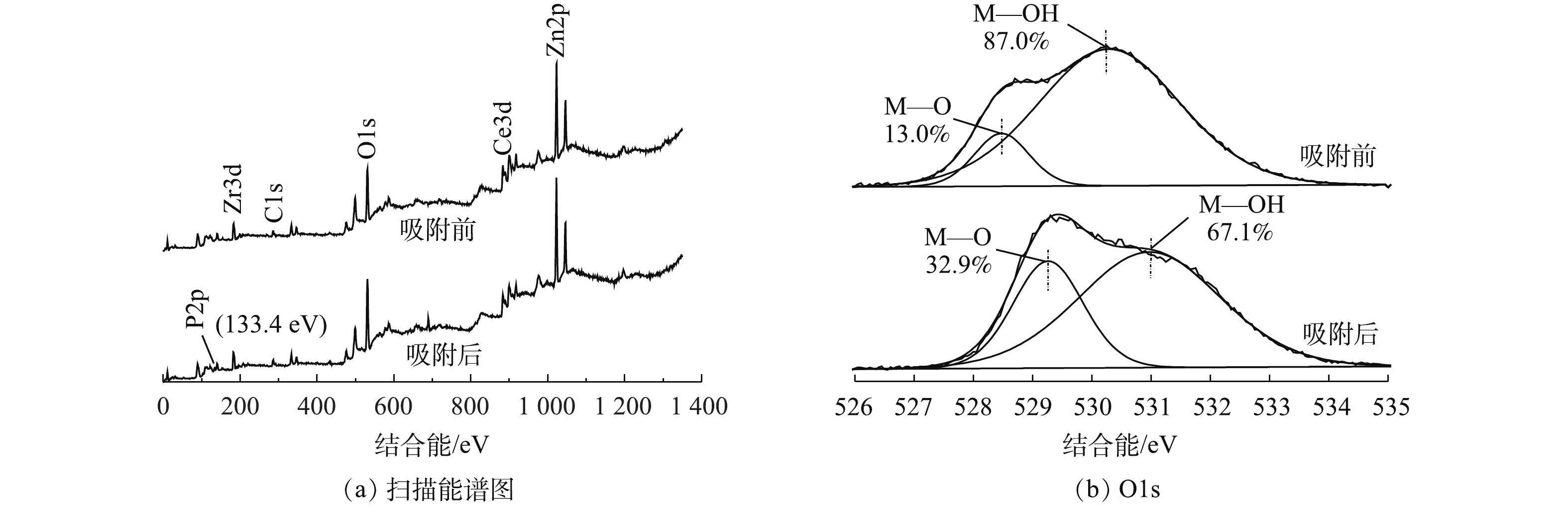
为进一步研究Ce-Zr-Zn复合吸附剂除磷机理,考察了吸附磷前后XPS能谱图。所有的峰基于C1s (284.6 eV处) 进行校正,结果如图7所示。由图7(a)可以看出,吸附剂包括Ce3d、Zr3d、Zn2p、C1s和O1s,在吸附磷酸盐后,在谱图133.4 eV处出现新峰,该峰属于P2p,这表明磷酸盐被吸附在吸附剂表面。相比KH2PO4的标准P2p峰(134.0 eV处),结合能迁移了0.6 eV,说明磷酸盐向更低的能量转换,这表明磷酸盐在吸附剂表面形成了复合物[8, 24]。
图7(b)为吸附剂吸附磷酸盐前后的O1s谱图。吸附前,O1s谱图可以分为金属氧化物(M—O)和金属表面羟基(M—OH)2个峰,结合能分别在529 eV和530.8 eV处[10],所占比例分别为13%和87%;吸附磷酸盐后,氧的峰面积比例发生变化,M—OH所占比例从87%下降至67.1%,M—O从13%上升至32.9%。M—OH比例下降,表明M—OH参与了吸附过程[8]。
FT-IR和XPS分析结果表明,Ce-Zr-Zn表面羟基参与了吸附磷酸盐吸附过程。推测其潜在机理方程如式(1)~式(3)所示。一般来说,当pH在3~11时,磷酸盐存在形式主要以
H2PO−4 和HPO2−4 为主,而水中的pH一般为6~9,磷酸盐主要以负电的形式存在。本研究中吸附剂pHpzc为8.3,当水中pH<8.3,Ce-Zr-Zn表面羟基质子化呈正电(式(1)),通过静电作用吸附磷酸盐(式(2)),表面羟基也可以与磷酸盐发生配位体交换置换至水中(式(3)),溶液pH上升(见图5(a));当pH>8.3, 吸附剂表面呈负电性,不利于吸附磷酸盐,且由于溶液中OH− 会磷酸盐竞争吸附位点,磷去除率有所下降,这与图5(a)得到的结果类似。其他研究也报道了类似的吸附机理[8, 14, 24]。 -
1)通过共沉淀法制备了一种新型的Ce-Zr-Zn复合吸附剂,且将其用于除磷(≤2 mg∙L−1),该吸附剂表现出优异的除磷效果(磷去除率>96%),出水磷酸盐残余量低于0.045 mg∙L−1,吸附剂投加量0.5 g∙L−1,反应时间6 h,不调pH。
2)吸附过程符合拟二级动力学模型,以化学吸附为主,膜扩散和孔隙扩散为主要的限速步骤。配位体交换和静电吸附是吸附剂去除磷酸盐的主要机理。
3)该吸附剂具有吸附容量大(66.61 mg∙g−1)、pH适用范围宽(3~9)和磷酸盐选择性好等优势。Ce-Zr-Zn复合吸附剂有着良好的应用前景。
三元复合吸附剂Ce-Zr-Zn对水中低浓度磷的吸附性能及其机理
Performance and mechanism of adsorption of low concentration phosphate in water by Ce-Zr-Zn ternary composite adsorbent
-
摘要: 为缓解水体富营养化问题,通过沉淀法合成了新型的三元复合吸附剂Ce-Zr-Zn,且将其用于除磷研究。结合XRD、SEM、BET、XPS和FT-IR表征分析,研究了其对水中低浓度磷的吸附性能及可能的吸附机理。结果表明:Ce-Zr-Zn具有优异的除磷特性,磷的去除率可高达96%,出水磷浓度低于0.045 mg·L−1;其对磷酸盐的最大吸附容量为66.61 mg·g−1,磷酸盐吸附过程符合拟二级动力学模型和Freundlich模型。此外,吸附剂具有较宽的pH适用范围(3~9)和良好的磷酸盐选择性。机理分析结果表明,配位体交换和静电吸附是该吸附剂除磷的主要原因。以上结果可为该材料用于水体深度除磷提供参考。Abstract: In order to alleviate the eutrophication problem, a novel Ce-Zr-Zn ternary composite adsorbent was synthesized by co-precipitation method for phosphate removal. The adsorption performance and proposed mechanisms of low concentration phosphate were investigated through the combination of XRD, SEM, BET, XPS and FT-IR characterization analysis. The results showed that the adsorbent had an excellent performance on phosphate removal with the removal rate above 96%, and the residual phosphate concentrations in the effluent were below 0.045 mg·L−1. The maximum phosphorus adsorption capacity was 66.61 mg·g−1. The phosphate adsorption process conforms to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Freundlich model. In addition, the adsorbent exhibited a wide pH range of 3~9 and a good selectivity toward phosphate. The mechanism analysis showed that ligand exchange and electrostatic interaction are the main phosphorus removal contributors. The above results can provide references for the application of this Ce-Zr-Zn ternary composite adsorbent to perform advanced phosphate removal in water.
-
Key words:
- phosphate removal /
- Ce-Zr-Zn /
- adsorption performance /
- mechanisms
-
江南平原河网地区地势平坦、水资源丰富、人类开发活动高度密集[1],是我国经济核心区域之一,同时也是河网最密集的地区之一[2]。近年来,随着经济迅速发展与城市化水平的提高,大量生活、工农业污染物进入水体,平原河流区域生态水平普遍降低,亟待治理[3]。
水环境容量是指在给定水文条件,确定排污方式和功能目标的前提下,水域所能容纳污染物的最大负荷量[4],这与国外使用的“Total maximum daily loads (TMDL) ” “Environment capacity”有着相似的含义[5]。早在20世纪70年代水环境容量概念引入中国,随着研究的不断深入,如今逐渐形成了公式法[6]、不确定分析法[7]、非均匀系数法[8]等计算方法,但具有一定局限性。随着水环境数学模型及计算机技术的发展,国内外学者大多基于SWMM[9-10]、SWAT[11-12]、EFDC[13]、WASP[14-15]、GIS[16]、MIKE[17-18]等模型,综合考虑实际水力学、地形地貌等自然因素,以模拟水体污染物的时空演变规律。江南平原河网水系具有水流方向不定、产流汇流过程复杂[19]、污染负荷高且分布分散等特点使水环境容量呈现动态变化,然而当前对这变化过程及变化幅度研究较少,传统水环境容量计算方法忽略了水文条件动态变化对水环境容量的影响,水环境容量的准确性不足,亟待开展基于水动力水质模型的动态水环境容量研究。
本研究选取江南平原河网地区典型代表宜兴市官林镇为研究对象,选取化学需氧量 (COD) 、氨氮 (NH3-N) 、总磷 (TP) 3个水质指标作为研究目标,基于MIKE11模型,构建官林镇平原河网水质模型,计算满足水质目标的官林镇各控制单元逐月动态水环境容量,为流域水环境保护与管理提供依据,同时选取控制单元代表河道,通过探究影响动态水环境容量的关键要素,旨在为江南平原地区类似流域水体污染治理提供技术支持和创新思路。
1. 研究区域概况
1.1 研究区域范围
官林镇 (北纬31°34’~31°24’,东经119°38’~119°47’) 位于宜兴西北部,是无锡地区首个千亿级涉农乡镇,工业发达、人口众多。其地处滆湖西畔,地势平坦,属于长江中下游水系的湖沼平原,区域内河流密布、湖荡相连,共有市级河道5条、镇级河道18条,村级河道241条,总长348.47 km,为典型的江南平原河网地区。
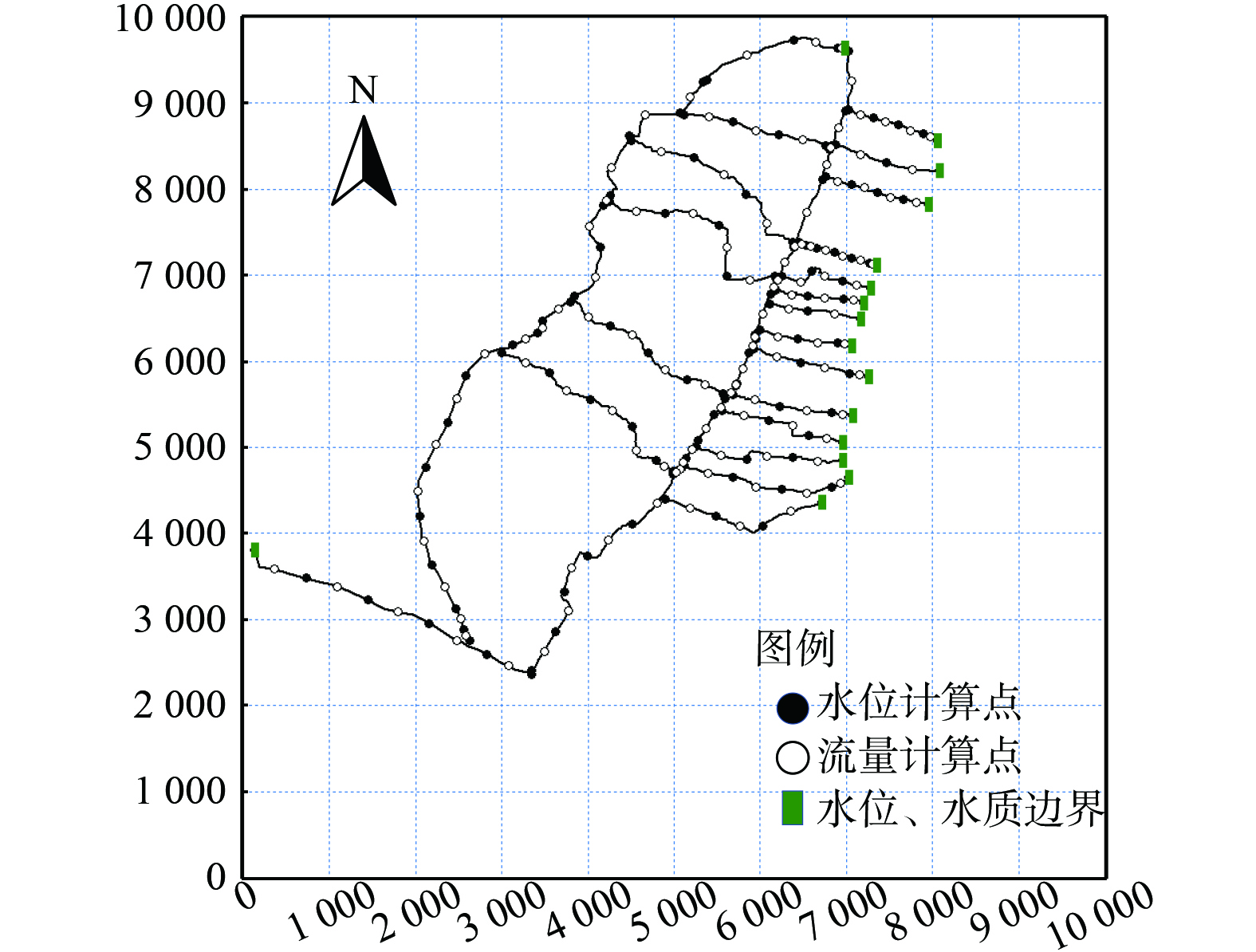
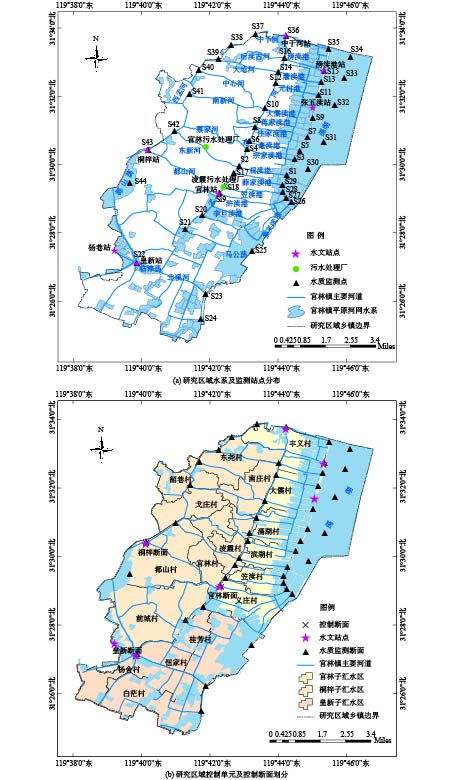
控制单元是我国流域空间管理的基础单位,本研究以水环境功能区划、行政区划及流域边界为基础,综合考虑水质监测断面设置、水文站点、点面源污染等因素,以村级行政区作为控制单元的基本组成,以官林、桐梓和皇新为控制断面,将官林镇河网分为官林、桐梓和皇新3个控制单元汇流区,其中桐梓控制单元水质要求达到地表水水质标准Ⅳ类,皇新和官林控制单元要求达到Ⅲ类水质标准。研究区域水系监测点及控制单元划分见图1、表1。
表 1 官林镇采样点坐标Table 1. The coordinates of sampling sites in Guanlin Township监测点位置 断面名称 断面坐标 水环境质量控制目标 经度°E 纬度°N 滆湖 S30 119°45′11.63″ 31°29′46.78″ Ⅲ类 S31 119°45′39.66″ 31°30′35.15″ S32 119°45′57.82″ 31°31′38.51″ S33 119°46′15.40″ 31°32′28.19″ S34 119°46′25.50″ 31°33′5.16″ 官林控制单元 S1 119°44′39.10″ 31°29′46.07″ Ⅲ类 S3 119°44′48.23″ 31°30′1.44″ S5 119°44′56.99″ 31°30′19.03″ S7 119°45′11.28″ 31°30′42.75″ S9 119°45′20.15″ 31°31′16.74″ 官林控制单元 S11 119°45′30.01″ 31°31′56.04″ Ⅲ类 S13 119°45′36.90″ 31°32′18.35″ S15 119°45′39.04″ 31°32′39.18″ S26 119°44′44.29″ 31°28′49.01″ S27 119°44′34.56″ 31°28′54.75″ S28 119°44′30.02″ 31°29′5.30″ S29 119°44′37.26″ 31°29′34.81″ S35 119°45′49.79″ 31°33′15.92″ 桐梓控制单元 S2 119°43′26.89″ 31°30′0.13″ Ⅳ类 S4 119°43′30.68″ 31°30′19.95″ S6 119°43′42.04″ 31°30′32.48″ S8 119°43′57.43″ 31°30′58.92″ S10 119°44′16.18″ 31°31′30.68″ S12 119°44′22.85″ 31°32′14.42″ S14 119°44′33.14″ 31°32′36.27″ S16 119°44′33.14″ 31°32′59.52″ S17 119°43′11.97″ 31°29′48.55″ S18 119°42′52.34″ 31°29′22.39″ S19 119°42′38.06″ 31°29′2.18″ S36 119°44′34.51″ 31°33′39.7″ S37 119°43′41.40″ 31°33′43.68″ S38 119°42′57.56″ 31°33′21.65″ S39 119°42′35.36″ 31°32′59.27″ S40 119°41′58.96″ 31°32′36.36″ S41 119°41′40.36″ 31°31′52.74″ S42 119°41′19.91″ 31°30′50.53″ S43 119°40′39.44″ 31°30′23.22″ S44 119°40′7.38″ 31°29′25″ S20 119°42′7.00″ 31°28′23.14″ S21 119°41′35.66″ 31°27′59.75″ 皇新控制单元 S22 119°40′12.27″ 31°27′1.26″ Ⅲ类 S23 119°42′11.51″ 31°26′3.74″ S24 119°42′6.55″ 31°24′56.52″ S25 119°43′32.29″ 31°27′22.72″ 1.2 流域水质现状
2022年官林镇水体水质监测显示,COD、NH3-N和TP平均浓度介于Ⅲ类水至劣Ⅴ类水之间,其中滆湖水质污染最严重,不满足Ⅲ类水质要求,TP最大超标倍数为12倍,断面超标率为93.75%,官林控制单元COD和TP断面超标率均超过40%。因此为更精确地对污染物总量排放进行控制,需对官林镇分区段计算水环境容量,研究区域水质现状见表2。
表 2 研究区域水质现状及水质目标Table 2. Status of water quality and water quality objectives in the research area污染物指标 统计值 滆湖 官林控制单元 桐梓控制单元 皇新控制单元 COD 浓度范围/(mg∙L−1) 2.07~25.80 7.20~38.02 4.83~70.95 6.86~67.60 平均值/(mg∙L−1) 22.18 26.03 24.37 21.38 水质目标/(mg∙L−1) ≤20 ≤20 ≤30 ≤20 断面超标率/% 52.08 44.79 19.05 26.71 NH3-N 浓度范围/(mg∙L−1) 0.02~2.84 0.02~1.99 0.04~2.53 0.01~2.24 平均值/(mg∙L−1) 0.63 0.82 0.97 0.73 水质目标/(mg∙L−1) ≤1 ≤1 ≤1.5 ≤1 断面超标率/% 33.33 27.78 14.88 11.13 TP 浓度范围/(mg∙L−1) 0.03~0.60 0.05~0.76 0.05~0.63 0.03~0.44 平均值/(mg∙L−1) 0.23 0.25 0.23 0.19 水质目标/(mg∙L−1) ≤0.05 ≤0.20 ≤0.30 ≤0.20 断面超标率/% 93.75 49.48 31.17 38.68 2. 数据与方法
2.1 采样及分析
为更好的分析官林镇平原河网整体水环境现状,水质监测点设置在滆湖及官林镇河网主干河道河口处,共计44个,于2022年每月开展监测。采样时为消除河道边际效应的影响,用有机玻璃采水器 (WB-PM,北京普力特仪器有限公司) 于河道中部水面下0.5 m处采集水样,分装500 mL于聚乙烯储存瓶保存,于24 h内完成水质测定。水体COD、NH3-N和TP分析方法参考国标进行测定,其中COD采用快速消解分光光度法 (HJ/T 399-2007) ,NH3-N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法 (HJ 535-2009) ,TP采用钼酸铵分光光度法 (GB/T 11893-1989) 。
2.2 数据来源
本研究水质目标来源于《江苏省水环境功能区划》,7个水文监测站点的逐时水位数据来源于宜兴市水利局和水文局,河道沿线排污口数据、点源与非点源污染的数据来源于宜兴市环境数据统计。
2.3 模型基本方程
水动力模块是MIKE11模型的核心模块,该模块建立在基于垂直积分的物质和动量守恒方程,即一维非恒定流圣维南方程的基础上。圣维南方程可以从物理机制上描述河流或河口的水文运动规律,其方程主要包括连续性方程与动量方程[20]见式(1)、式(2)。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 式中:x为空间变量;t为时间变量;Q为断面流量;h为水位;A为断面面积;R为水力半径;BS为水面宽度;q为旁侧入河流量;C为谢才系数;g为重力加速度;α为垂向速度分布系数。
MIKE11 AD模块是以水动力模块生成的水质流场条件为基础,通过求解水体中较大浓度梯度污染物的一维对流扩散方程模拟水质污染物迁移的模块。AD模块的一维对流扩散方程[21] 见式(3)。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) 式中:C为模拟的物质浓度;u为河段平均流速;Ex为扩散系数;K为模拟物质的衰减系数;x为空间变量;t为时间变量。
2.4 模型构建
1) 河网概化。河网概化的核心原则在于经过概化处理后的河网必须准确地体现自然河网的基本水力特征,这意味着概化后的河网输水过流能力与调蓄能力方面应与实际天然河网相一致[22]。根据研究区域的实际情况,以官林镇河网主干河道为主,不考虑水流量小且对河网影响小的支流,计算模型中共概化河道23条,河道断面间距取500 m,计算节点 (水位、流量计算点) 共314个。河道概化见图2。
2) 模型边界条件。模型的边界条件采用2022年中干河站、杨巷站、滂渎港站、张五渎站逐时水位数据;采用2022年官林镇各监测断面的实测水质数据作为水质边界条件。
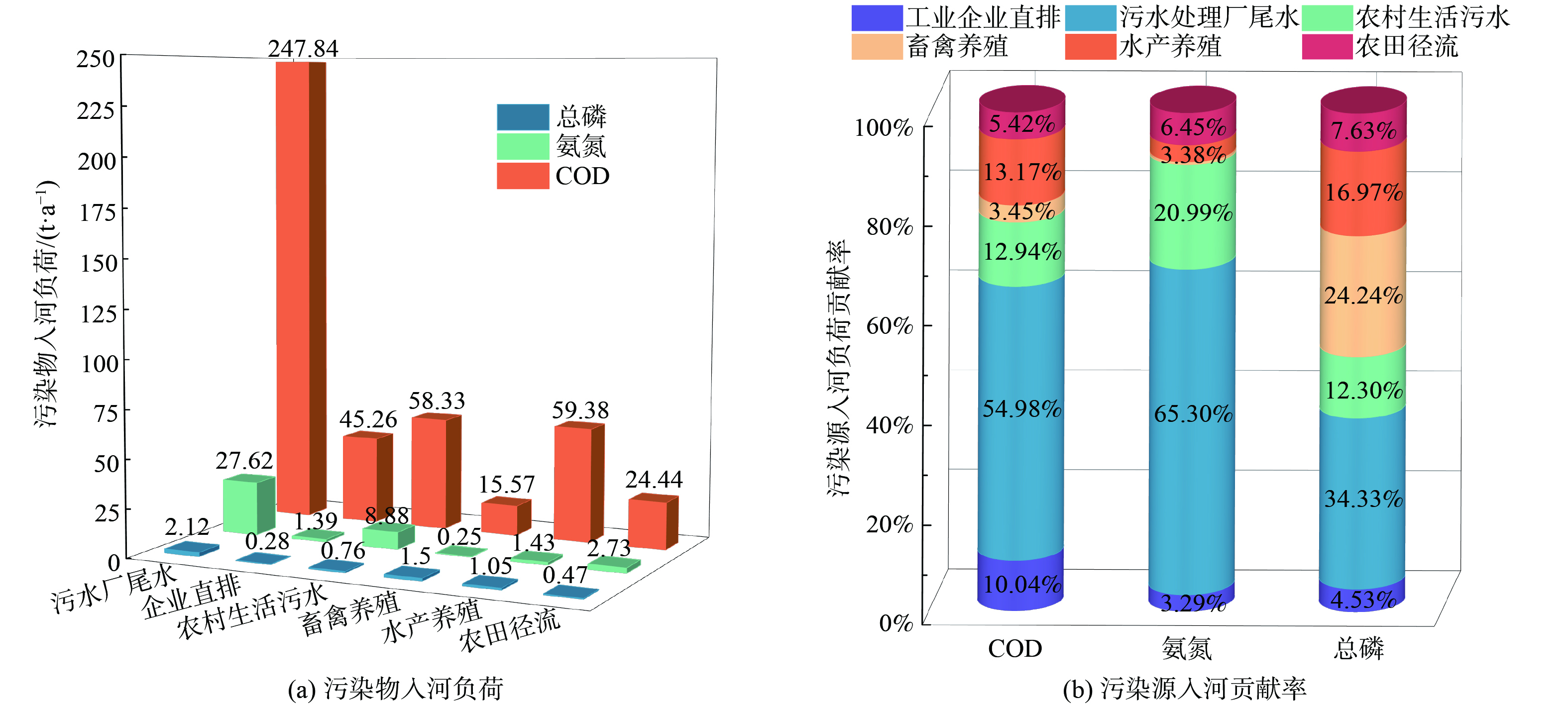
3) 研究区域污染负荷排放情况。根据宜兴市环境数据统计及Johns输出系数模型[23]估算官林镇污染负荷排放量。官林镇点源污染主要包括污水处理厂尾水及工业企业直排废水,其中COD入河量320.10 t∙a−1、NH3-N入河量29.01 t∙a−1、TP入河量2.40 t∙a−1。面源污染主要来源于农村生活污水、畜禽水产养殖污染以及农田径流带来的污染,其中COD入河量157.72 t∙a−1、NH3-N入河量13.29 t∙a−1、TP入河量3.78 t∙a−1,具体负荷分布占比见图3。
2.5 模型率定
依据2022年实测水文水质数据,运用经验法及人工试错法对研究区域河网的HD模块及AD模块进行率定,考虑到官林镇河网主干河道水文特征,将官林镇河网分为4个区段分别率定参数,使得模拟结果更符合实际水文情况。
2.6 水环境容量计算
传统一维水环境容量计算模型公式见式(4)[5]。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) 式中:Cs为水质目标浓度,mg∙L−1;C0为断面初始浓度,mg∙L−1;x为沿河段纵向距离,m∙s−1;ux为河段平均流速,m∙s−1;K1为污染物衰减系数,s−1;Q为断面流量,m3∙s−1;q为污水排放量,m3∙s−1;W为河段水环境容量,g∙s−1。Q一般取90%保证率下的最枯月平均流量,该方法计算简便但不能反映水环境容量的时空变化,因此本研究在一维水环境容量计算模型的基础上,提出基于MIKE11模型的动态水环境容量计算方法,能够更真实的反映实际水体水质的迁移转化规律,充分考虑污染物衰减作用,得到计算单元水环境容量计算公式(5)、(6)[5, 24]。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) 式中:
ˉQ ˉq ˉCm 3. 结果与讨论
3.1 参数率定结果
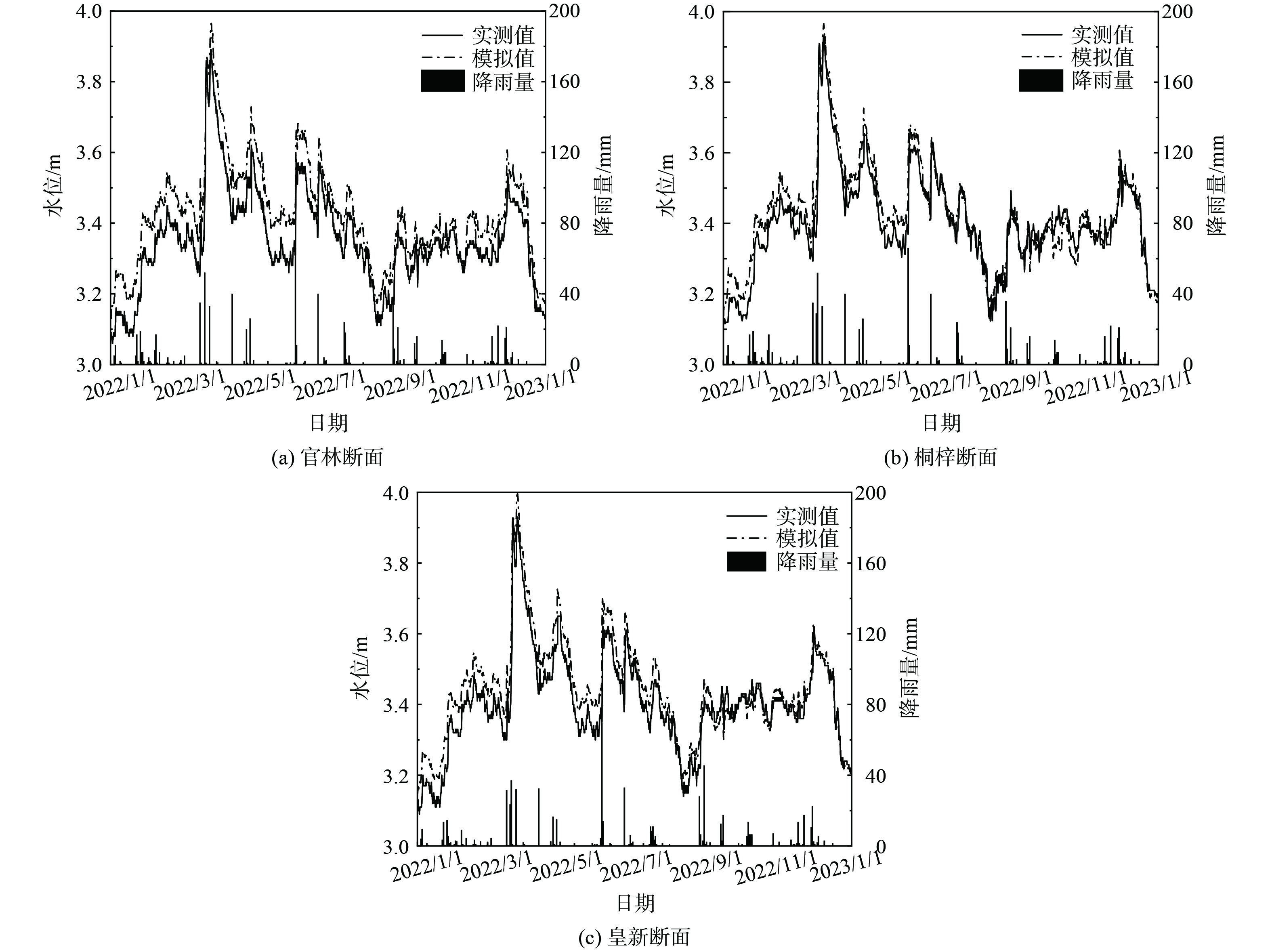
1) 水动力模块。水动力模块需要率定河床糙率,结果如表3所示。采用绝对误差Re、均方根误差RMSE、相关系数R2、Nash-Suttcliffe系数Ens来评价模型的准确性,一般认为Re≤20%,RMSE≤0.1,R2≥0.6,Ens≥0.5时,模型的模拟结果可接受[24-25]。官林、桐梓和皇新断面水位模拟结果见图4。
表 3 MIKE11模型参数率定结果Table 3. parameter calibration results of MIKE11河道名称 河床糙率n 对流扩散系数D/ (m2∙s−1) 综合降解系数K/d−1 COD NH3-N TP 孟津河 0.030 10 0.12 0.09 0.10 西孟河、北溪河、中干河 0.028 8 0.10 0.08 0.09 大埝河、中心河等孟津河支流 0.033 5 0.09 0.08 0.06 滂渎港、灌渎港等入滆湖河道 0.035 3 0.08 0.06 0.06 从图4的模拟结果来看,模拟水位与实测水位拟合情况良好,官林水位的绝对误差Re为2.17%,均方根误差RMSE为0.083,相关系数R2为0.968,Nash-Suttcliffe系数Ens为0.643;桐梓水位的绝对误差Re为1.12%,均方根误差RMSE为0.061、相关系数R2为0.957,Nash-Suttcliffe系数Ens为0.892;皇新水位的绝对误差Re为1.39%,均方根误差RMSE为0.056,相关系数R2为0.962,Nash-Suttcliffe系数Ens为0.832。造成水位误差的原因可能是河网概化时,忽略了水量较小的支浜来水,同时部分排污口流量采用恒定流概化值,导致断面水位偏大。总体而言,模型可以较好的反应官林镇平原河网水动力学变化过程,为进一步与对流扩散模块耦合奠定基础。
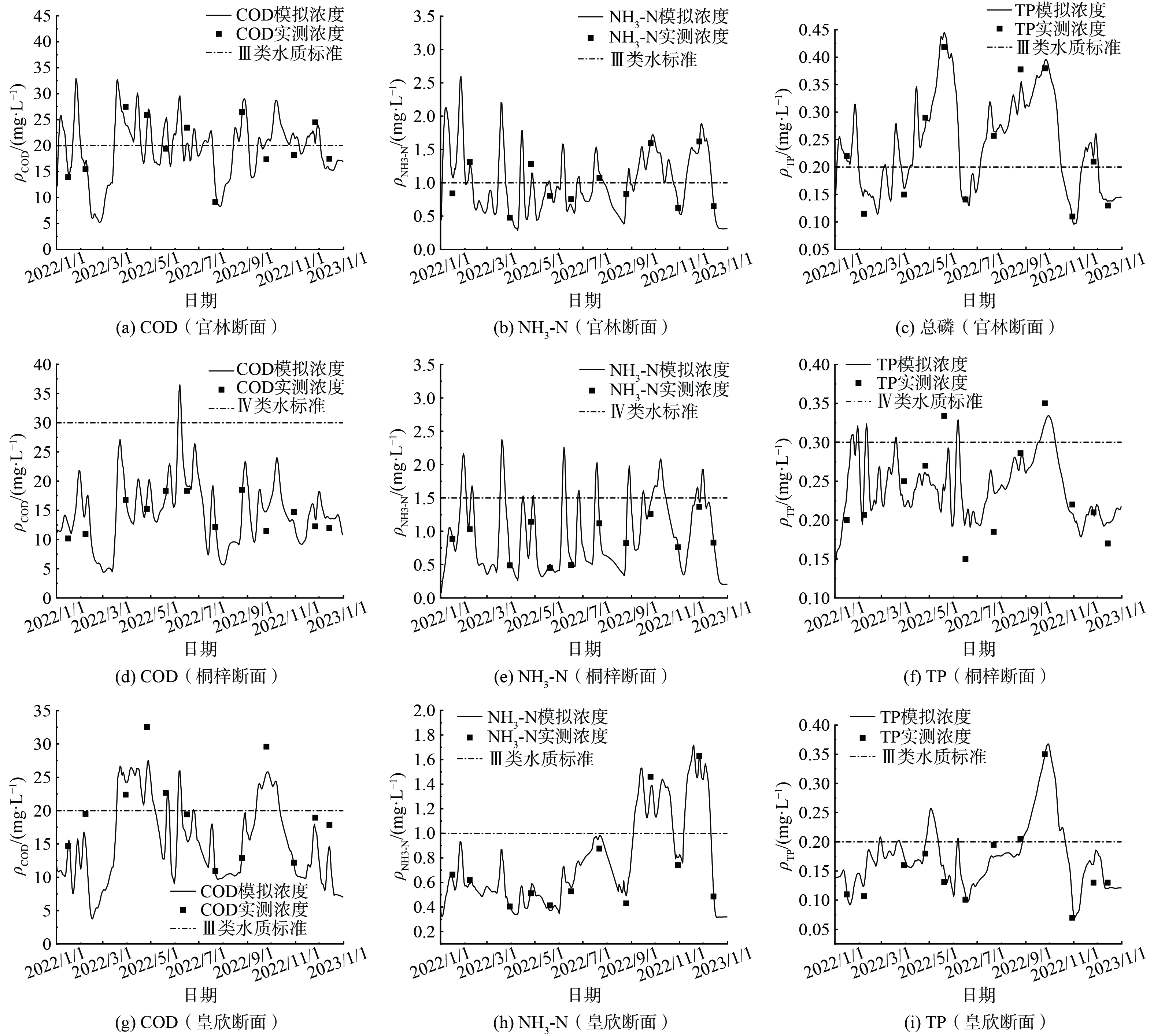
2) 对流扩散模块。对流扩散模块主要率定的参数为纵向扩散系数D和综合衰减系数K,鉴于研究区域污染源及水质污染特征,选择COD、氨氮和TP作为水质模拟污染因子,以官林、桐梓和皇新断面2022年水质监测数据进行率定,参数率定结果见表3,率定断面污染物模拟结果如图5所示。
从图5水质拟合结果可看出该模型基本可以反应研究区域水质变化状况,其中官林断面处COD、NH3-N、TP模拟值与实测值之间的平均相对误差分别为15.19%、10.07%、7.23%;桐梓断面处COD、NH3-N、TP模拟值与实测值之间的平均相对误差分别为14.69%、8.59%、14.38%;皇新断面处COD、NH3-N、TP模拟值与实测值之间的平均相对误差分别为13.21%、7.24%、13.62%,造成误差的原因可能是月际采样只能描述断面水质总体变化趋势,不能真实反应污染物沉积降解过程,同时监测时段可能存在排污口集中排放、偷排等现象,导致实测值显著增大。总体而言,污染物衰减系数及对流扩散系数取值合理,模拟值与实测值之间的拟合程度较高,模型能较好的模拟研究区域的水动力和水质的时空变化,其结果可应用于动态水环境容量的研究。
3.2 水环境容量计算结果
采用MIKE11模型法计算官林镇各控制单元水环境容量,计算公式见(6),水环境容量安全容量取10%,具体计算结果见表4,官林镇剩余水环境容量见表5,各控制单元水环境容量月均变化见图6所示。
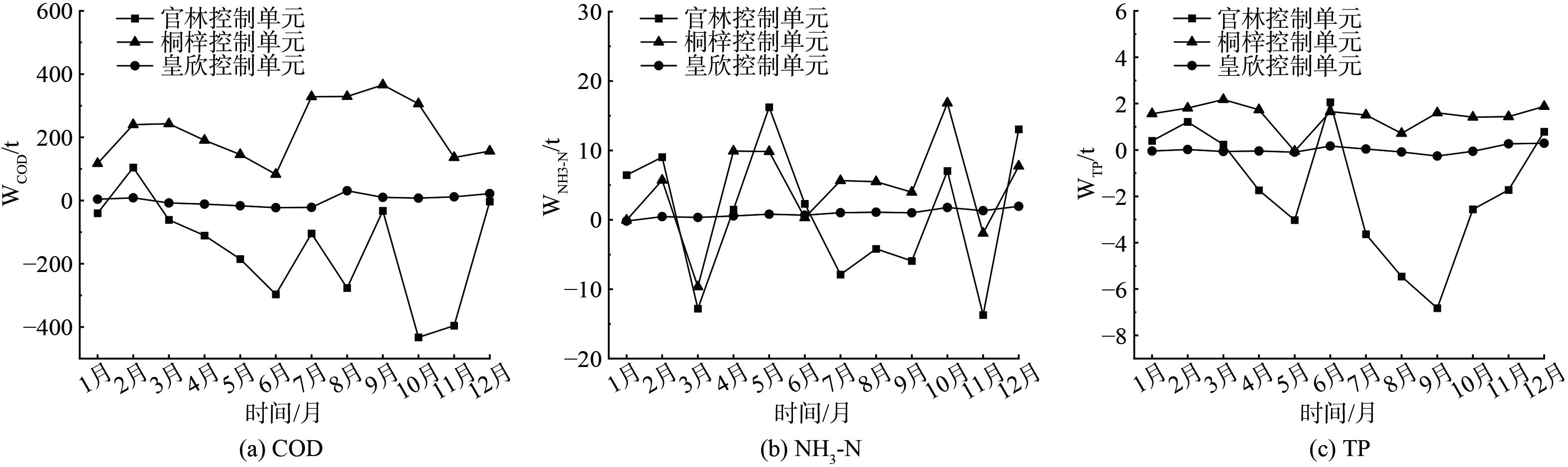
表 4 官林镇各控制单元水环境容量月均值Table 4. Monthly average values of water environment capacity of each control unit in Guanlin Townshipt 控制单元 COD NH3-N TP 考虑安全余量 未考虑安全余量 考虑安全余量 未考虑安全余量 考虑安全余量 未考虑安全余量 官林 −152.80 −137.52 0.92 0.83 −1.69 −1.52 桐梓 220.23 198.21 4.49 4.04 1.45 1.31 皇新 15.42 13.88 0.90 0.81 0.14 0.13 表 5 官林镇剩余水环境容量Table 5. The remaining water environment capacity of Guanlin Townshipt∙a−1 污染物 水环境容量 污染物入河量 剩余水环境容量 COD 994.2 477.82 516.38 NH3-N 75.72 42.30 33.42 TP -1.20 6.18 -7.38 在空间尺度上,由表4可知,水环境容量在不同控制单元呈现出明显的动态分布。官林、桐梓与皇新COD环境容量之比为−1︰1.44︰0.10,NH3-N环境容量之比为1︰4.86︰0.98,TP环境容量比值为−1︰0.8︰0.08,说明官林镇水环境容量分布不均匀,且COD分布均匀性更差。其中官林镇临滆湖区域官林控制单元水环境容量小于桐梓与皇新控制单元,且COD、TP水环境容量出现负值。主要是因为官林控制单元人口密度较大,同时伴有水产养殖、畜禽养殖等人为活动,水产养殖以池塘高密度养殖为主,粗放养殖模式下养殖尾水直接排放至河道当中,导致河道淤泥与污染物沉淀严重,水体自净能力显著下降,同时入湖河道水质目标要求较高,河道上下游来水为孟津河与滆湖,水质介于Ⅲ类水与劣Ⅴ类水之间,在部分月份未能满足水功能区划要求;桐梓控制单元内河道本底水质基本满足水质目标,河道常流量较大,稀释容量较高,水环境容量仍有较多剩余;皇新控制单元汇水面积较少,水质在Ⅲ类水上下波动,剩余容量较少。
在时间尺度上,从图6可以看出,各控制单元水环境容量计算结果有明显的动态变化。各污染物水环境容量变化趋势基本相同,进一步对比各月份不同控制单元水环境容量可以看出各控制单元的水环境容量5月至9月变化幅度较大,主要是因为5月开始官林镇河网进入丰水期,受春夏交际“梅雨期”影响,降雨量增大,河道流量增大的同时上游入流水质、污染物入河量也随之变化,同时伴有鱼塘换水及农田灌溉排水等人为活动,导致水环境容量波动明显。
从表5可知,官林镇COD、NH3-N和TP剩余水环境容量分别为516.38、33.42和-7.38 t∙a−1,水环境容量差距悬殊,这与水质标准限值、河网水文条件有关,因此TP水环境容量敏感性最高。官林镇平原河网TP水环境容量超出阈值,需进行污染物削减,COD、NH3-N水环境容量仍有剩余,但官林控制单元水体污染严重,现状条件下几乎没有可利用的水环境容量,需进一步对流域农田径流、畜禽水产养殖等含磷污染源进行管控,采取河道环保疏浚、鱼塘升级改造等科学合理的治理措施,改善水环境质量。
3.3 代表河道水环境容量影响因素分析
由公式(4)可知,水质目标要求、水体平均流速、上游断面来水水质、污染物综合降解系数、非点源污染的时空变化性等都是影响水环境容量的重要影响因素。显而易见,水环境容量与污染物综合降解系数呈正相关,而流速与水环境容量的关系则复杂多变,当流速
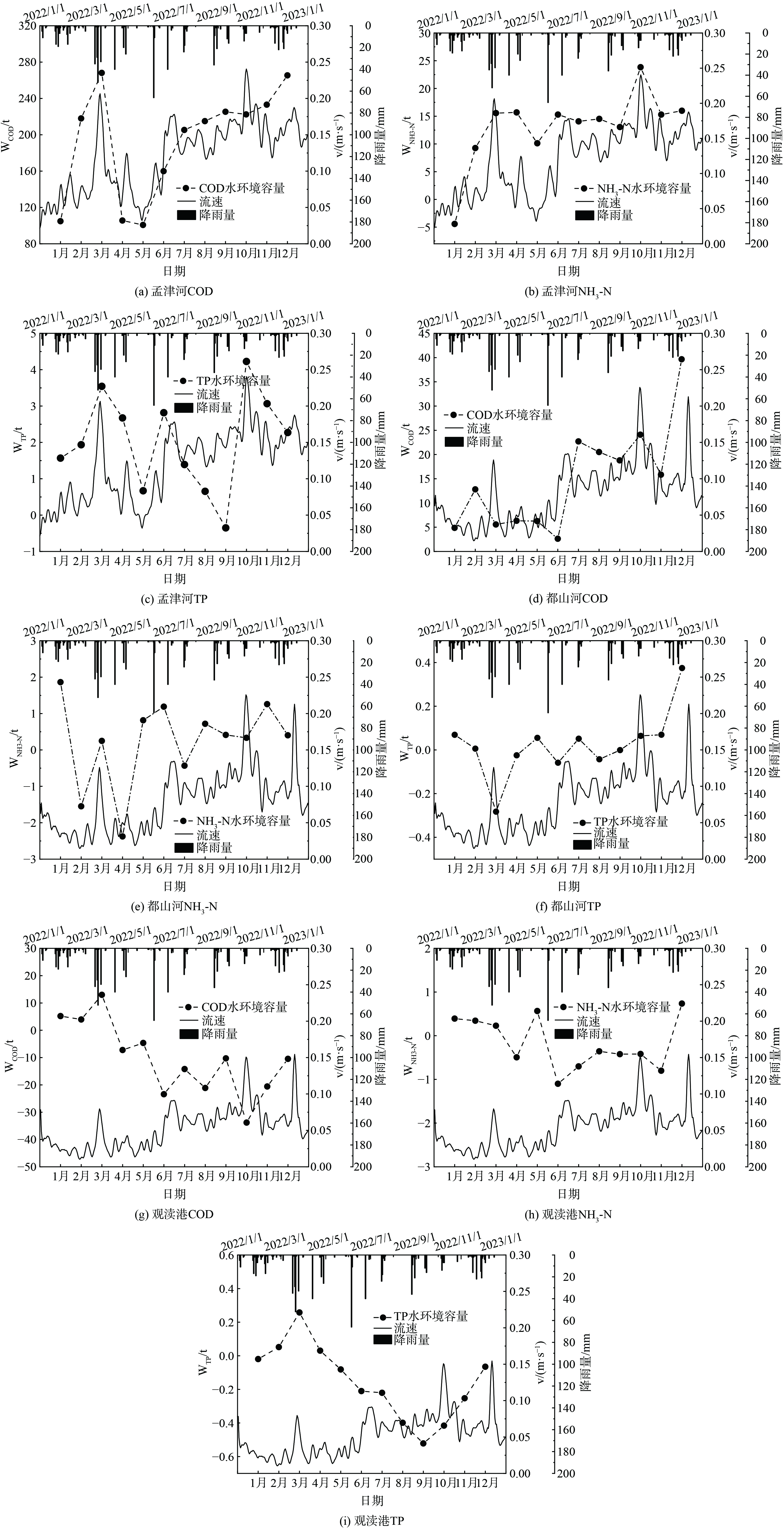
ux=−K1x/ln(cs/c0) 由图7可知孟津河COD、NH3-N、TP水环境容量月均值分别为 (193.65±58.22) 、 (13.18±6.31) 、 (2.03±1.27) t;都山河COD、NH3-N、TP水环境容量月均值分别为 (15.00±10.39) 、 (0.24±1.14) 、 (0.02±0.14) t;观渎港COD、NH3-N、TP水环境容量月均值分别为 (−10.31±12.87) 、 (−0.17±0.57) 、 (−0.15±0.21) t,总体来看孟津河整体水环境状况良好,水环境容量基本满足水功能区划要求;都山河整体水环境容量仍有剩余,但出现部分月超标现象;观渎港水环境容量变化范围并不理想,均处于超标情况,由此可见随着河道平均流速的增大,水环境容量也随之增大,水环境容量达标率也逐步提高。由表6河道平均流速与水环境容量相关性可知,孟津河、都山河水环境容量变化与河道平均流量呈正相关,原因为孟津河、都山河上游来水基本满足水质目标要求,随着河道进入丰水期流速增加,微生物活性与生化反应速率提高,有利于水体污染物降解,汛期河道水质提高,导致水环境容量随着流速的增大而增大,呈现正相关性。而观渎港水环境容量变化与河流流量呈负相关,这与普遍认知的丰水期河道纳污能力强有所差别,原因可能是观渎港上游来水水质不满足水质目标要求,随着丰水期河道流速增大,水体交换和流动能力增强,水体自净能力虽有所增强,但河流常流量较小,受丰水期强降雨及上下游季节性河道水质影响较大,入河污染物量超出自净能力范围,汛期河道水质反而降低,导致平均流速越大,水环境容量越差,呈现负相关性。综上所述,官林镇平原河网中孟津河、都山河等水质整体达标河道水环境容量的变化大小与河流流速呈现正相关特征,而观渎港等水质整体不达标河道水环境容量的变化大小与河流流速呈现负相关特征。
表 6 代表河道平均流速与水环境容量相关性Table 6. Correlation between mean flow velocity and water environment capacity of representative stream channels河道 平均流量/ (m3∙s−1) 平均流速/ (m∙s−1) 水环境容量与平均流速相关性 COD NH3-N TP 孟津河 7.64 0.118 0.719 0.749 0.203 都山河 0.94 0.078 0.695 0.306 0.312 观渎港 0.59 0.052 -0.347 -0.511 -0.119 4. 结论
1) 利用MIKE11构建官林镇平原河网一维水环境模型,并依据2022年实测水文水质数据率定模型参数,官林镇平原河网河床糙率为0.028~0.035;纵向扩散系数为3~10 m·s−1;COD综合衰减系数为0.08~0.12 d−1;NH3-N综合衰减系数为0.06~0.09 d−1;TP综合衰减系数为0.06~0.10 d−1,其模拟水质变化趋势与实测值拟合程度较高,所确定的参数基本能反映河网水质时空演变规律。
2) 官林镇水环境容量计算结果显示,桐梓、皇新控制单元水环境容量仍有剩余;官林控制单元污染物排放量超出水体纳污能力,水环境容量存在数月超标现象,需进一步落实官林控制单元入湖河道清淤和滆湖水产养殖围网综合整治工作。
3) 孟津河、都山河等水质整体达标的河道水环境容量的变化趋势与各月流量和流速的变化趋势一致,呈正相关;观渎港等水质整体未达标的河道水环境容量与各月流量和流速呈负相关,说明水环境容量的大小受水量和水体流速等水文参数的影响较大。
-
表 1 磷吸附动力学参数
Table 1. Kinetic parameters for phosphate adsorption
拟一级动力学 拟二级动力学 k1/min−1 qe/ (mg∙g−1) R2 k2/ (g∙(mg·min)−1) qe /(mg∙g−1) R2 0.012 3.96 0.956 0.003 4.79 0.968 表 2 磷吸附等温线拟合参数
Table 2. Isotherm parameters for phosphate adsorption
Langmuir模型 Freundlich 模型 KL/(L∙mg−1) qm /(mg∙g−1) R2 KF n R2 0.60 66.61 0.860 38.10 7.24 0.977 -
[1] ZAMPARAS M, ZACHARIAS I. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 496: 551-562. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.076 [2] GENZ A, KORNMÜLLER A, JEKEL M. Advanced phosphorus removal from membrane filtrates by adsorption on activated aluminium oxide and granulated ferric hydroxide[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38: 3523-3530. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.006 [3] MULKERRINS D, DOBSON A D W, COLLERAN E. Parameters affecting biological phosphate removal from wastewaters[J]. Environment International, 2004, 30: 249-259. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00177-6 [4] IFTEKHAR S, KÜÇÜK M E, SRIVASTAVA V, et al. Application of zinc-aluminium layered double hydroxides for adsorptive removal of phosphate and sulfate: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 209: 470-479. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.115 [5] DOLAR D, KOŠUTIĆ K, VUČIĆ B. RO/NF treatment of wastewater from fertilizer factory: Removal of fluoride and phosphate[J]. Desalination, 2011, 265: 237-241. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.057 [6] KIM H C. High-rate MIEX filtration for simultaneous removal of phosphorus and membrane foulants from secondary effluent[J]. Water Research, 2015, 69: 40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.012 [7] PARK J H, WANG J J, KIM S H, et al. Phosphate removal in constructed wetland with rapid cooled basic oxygen furnace slag[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 327: 713-724. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.155 [8] SHI W, FU Y, JIANG W, et al. Enhanced phosphate removal by zeolite loaded with Mg-Al-La ternary (hydr)oxides from aqueous solutions: Performance and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 357: 33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.003 [9] CHEN L, LI Y, SUN Y, et al. La(OH)3 loaded magnetic mesoporous nanospheres with highly efficient phosphate removal properties and superior pH stability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 342-348. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.234 [10] GU W, XIE Q, QI C, et al. Phosphate removal using zinc ferrite synthesized through a facile solvothermal technique[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 301: 723-729. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.07.015 [11] 雷行, 杨雪, 刘婷, 等. 锆改性铝氧化物对水中磷的吸附特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1389-1396. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201710107 [12] LYU J, LIU H, LIU R, et al. Adsorptive removal of phosphate by a nanostructured Fe-Al-Mn trimetal oxide adsorbent[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 233: 146-154. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.024 [13] HAO H, WANG Y, SHI B. NaLa(CO3)2 hybridized with Fe3O4 for efficient phosphate removal: Synthesis and adsorption mechanistic study[J]. Water Research, 2019, 155: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.01.049 [14] LIU R, SUI W Y, WANG Y, et al. Review of metal (hydr)oxide and other adsorptive materials for phosphate removal from water[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2018, 6: 5269-5286. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.008 [15] REN Z, SHAO L, ZHANG G. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution using an iron-zirconium binary oxide sorbent[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2012, 223: 4221-4231. doi: 10.1007/s11270-012-1186-5 [16] LIU T, ZHENG S, YANG L. Magnetic zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks for selective phosphate adsorption from water[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2019, 552: 134-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.022 [17] WANG L, WANG J, HE C, et al. Development of rare earth element doped magnetic biochars with enhanced phosphate adsorption performance[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2019, 561: 236-243. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.10.082 [18] SU Y, YANG W, SUN W, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous cerium-zirconium binary oxide nanoadsorbents by a solvothermal process and their effective adsorption of phosphate from water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 268: 270-279. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.070 [19] DEGEN A, KOSEC M. Effect of pH and impurities on the surface charge of zinc oxide[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20: 667-673. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(99)00203-4 [20] MITROGIANNIS D, PSYCHOYOU M, BAZIOTIS I, et al. Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto Ca(OH)2 treated natural clinoptilolite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 320: 510-522. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.063 [21] LIU X, HU Q, WU Q, et al. Aligned ZnO nanorods: A useful film to fabricate amperometric glucose biosensor[J]. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2009, 74: 154-158. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.07.011 [22] LIU H, SUN X, YIN C, et al. Removal of phosphate by mesoporous ZrO2[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 151: 616-622. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.033 [23] FU H, YANG Y, ZHU R, et al. Superior adsorption of phosphate by ferrihydrite-coated and lanthanum-decorated magnetite[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2018, 530: 704-713. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.025 [24] HE Y, LIN H, DONG Y, et al. Preferable adsorption of phosphate using lanthanum-incorporated porous zeolite: Characteristics and mechanism[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 426: 995-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.272 [25] KUROKI V, BOSCO G E, FADINI P S, et al. Use of a La(III)-modified bentonite for effective phosphate removal from aqueous media[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 274: 124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.023 [26] FANG L, LIU R, LI J, et al. Magnetite/lanthanum hydroxide for phosphate sequestration and recovery from lake and the attenuation effects of sediment particles[J]. Water Research, 2018, 130: 243-254. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.008 -




 下载:
下载: