-
随着我国对水环境质量要求的提高,废水的排放标准也日益严格,从一级A到各地方标准、从日均值达标到时时达标,都对污水处理工艺以及运行提出了严格的要求。但随着人们生活水平的不断提高,污水厂进水管控不严格,常常出现进水水质超过设计标准的情况,尤其是有机物浓度,对于污水厂的正常运行和出水造成了恶劣的影响,所以改善污水厂运行工艺,提高其抗冲击性能,对于保障污水厂的正常运行具有重要意义。
目前,活性污泥法在我国应用较为普遍,其结构简单、形式多样、运行管理方便,但进水水质波动会对处理过程产生冲击,使生化系统C/N/P营养比例失衡,在冲击来临时,常面临出水不达标的问题;同时污泥中的硝化菌丰度会伴随冲击过程逐步降低,导致出水氨氮恢复较慢,严重影响出水水质[1]。因此,需要通过工艺改善来保障污染物稳定达标。吴成强等[2]采用深度水解/MBR工艺处理高COD、高氨氮废水,工程运行结果表明,该工艺抗冲击负荷能力强,出水氨氮稳定低于1 mg·L−1。移动床生物膜反应器(moving bed biofilm reactor, MBBR)兼具生物接触氧化和生物流化床的优点[3],属于典型的生物膜法。工程实践表明,MBBR工艺具有很强的抗冲击负荷能力。如在北方某污水厂实施Bardenpho-MBBR工艺改造后[4],进水COD波动频繁的情况下,出水水质稳定达标,且系统可稳定运行;李新利等[5]采用MBBR工艺处理皮革废水,常规活性污泥法氨氮容积负荷为0.21 kg·(m3·d)−1,而采用MBBR工艺后,容积负荷为0.53 kg·(m3·d)−1,MBBR工艺硝化负荷提升1.5倍,从而保障了氨氮稳定达标。
本研究通过向活性污泥系统中投加悬浮载体,形成泥膜复合的MBBR工艺,依靠悬浮载体对于微生物的富集筛选作用抵抗进水冲击,以期达到抗水质冲击的效果,保障水厂稳定达标;通过实际工程的运行效果,判定宏观上MBBR工艺的抗冲击性能,然后通过硝化小试实验和生化段沿程的测定,分析了活性污泥和悬浮载体的抗冲击性能;通过高通量测序,从微生物角度探究了活性污泥和悬浮载体对于硝化细菌的富集能力;从宏观和微观上分析了MBBR工艺的抗冲击性能,为污水厂的抗冲击提供稳定运行工艺以及理论指导,为类似工程的运行提供数据指导。
全文HTML
-
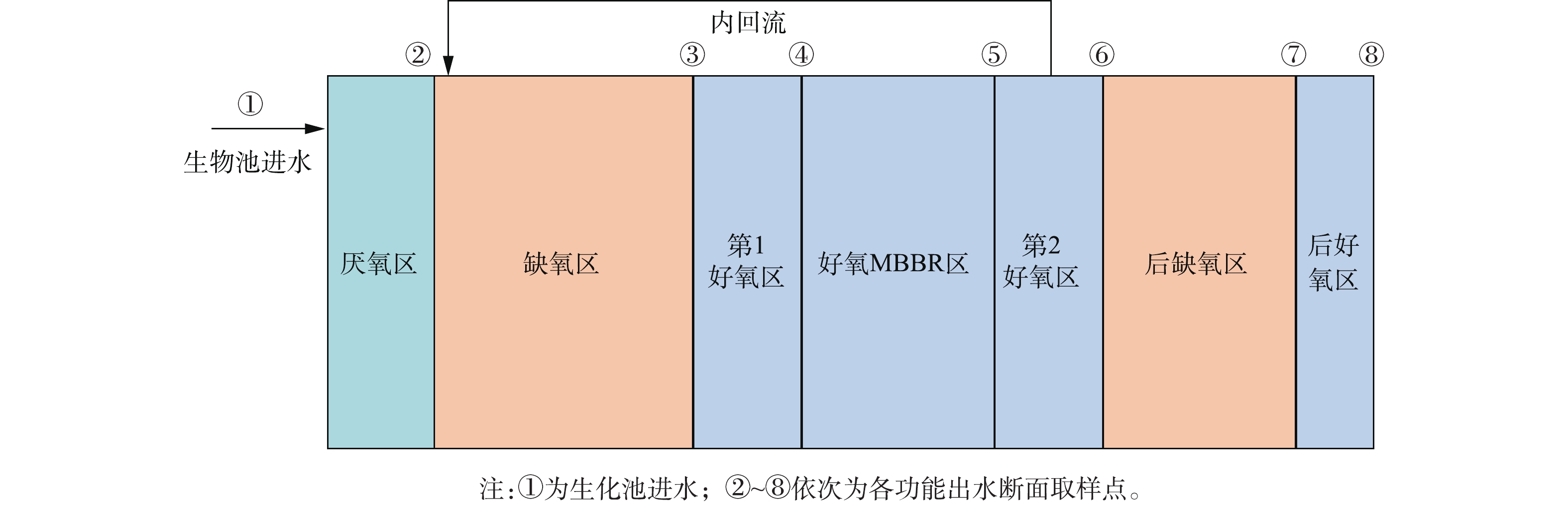
该污水厂生化池采用Bardenpho (A2/O+A/O)-MBBR工艺,总HRT为19.33 h,其中前厌氧区和缺氧区HRT为7.06 h、好氧区为8.42 h (MBBR区HRT为4.93 h),后缺氧区HRT为2.80 h,后好氧区HRT为1.05 h。污泥浓度为4 g·L−1,污泥龄为16 d,内回流比为100%~300%,外回流比为50%~150%。
MBBR区投加悬浮载体为新型悬浮载体SPR-III,悬浮载体直径为(25±0.5) mm,高为(10±1) mm,挂膜后比重与水接近,有效比表面积大于800 m2·m−3,符合《水处理用高密度聚乙烯悬浮载体填料》(CJ/T 461-2014)行业标准。好氧内回流硝化液全部进入前缺氧区,在强化TN去除的同时也提高了原水碳源的利用率。此外,后缺氧区作为后置反硝化区,可通过碳源外部投加或內源呼吸对硝酸盐氮进一步去除,从而保障TN的去除不受回流比的限制,强化TN去除。生化处理段末端的好氧区保证了有机物去除及生物池出水中一定的溶解氧浓度,防止二沉池污泥上浮。
-
为了解生化段对污染物质的去除情况,对生化段各功能区进行了沿程分析,取样点包括生化池进水、 厌氧区出水 、缺氧区出水、第1好氧区出水、好氧MBBR区出水、第2好氧区出水、后缺氧区出水和后好氧区出水,共8个取样点,具体取样点均位于各功能区出水断面,分布如图1所示。每间隔2~3 h取样,所有样品先快速沉淀后取上清液,取回后及时进行预处理,将3次样品等量混合均匀后,分别进行氨氮、硝氮、TN、COD的测定。
-
对悬浮载体和活性污泥的硝化性能进行测定,实验用水采用缺氧区出水经沉淀后的上清液。实验温度为13 ℃,纯活性污泥实验控制污泥浓度为4.4 g·L−1,纯膜系统控制悬浮载体填充率为33%。
-
沿程样及硝化小试的常规指标测定方法如下:氨氮采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定,硝氮采用紫外分光光度法测定,TN采用过硫酸钾氧化紫外分光光度法测定,COD采用重铬酸钾法测定;pH、DO采用WTW Multi-3430i离线测定。
-
高通量测序通过试剂盒(E.Z.N.A Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit,OMEGA)提取微生物基因组DNA,通过1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测抽提基因组的完整性,利用Qubit 3.0 DNA试剂盒检测基因组DNA浓度。PCR扩增所用引物为341F/805R。对PCR产物进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳,并通过DNA胶回收试剂盒(SanPrep)对PCR产物进行回收,利用Qubit3.0 DNA检测试剂盒对回收的DNA精确定量,按照1∶1的等量混合后测序,等量混合时,每个样品DNA量取10 ng,最终上机测序浓度为20 pmol,通过Illumina Miseq测序平台完成对样品的高通量测序。
采用UPARSE 7.1软件根据97%的相似度进行OTU聚类;使用UCHIME软件剔除嵌合体;利用RDPclassifier对每条序列进行物种分类注释,比对Silva数据库(SSU123),设置比对阈值为70%。
1.1. 沿程实验
1.2. 硝化小试实验
1.3. 指标测试
1.4. 高通量测序
-
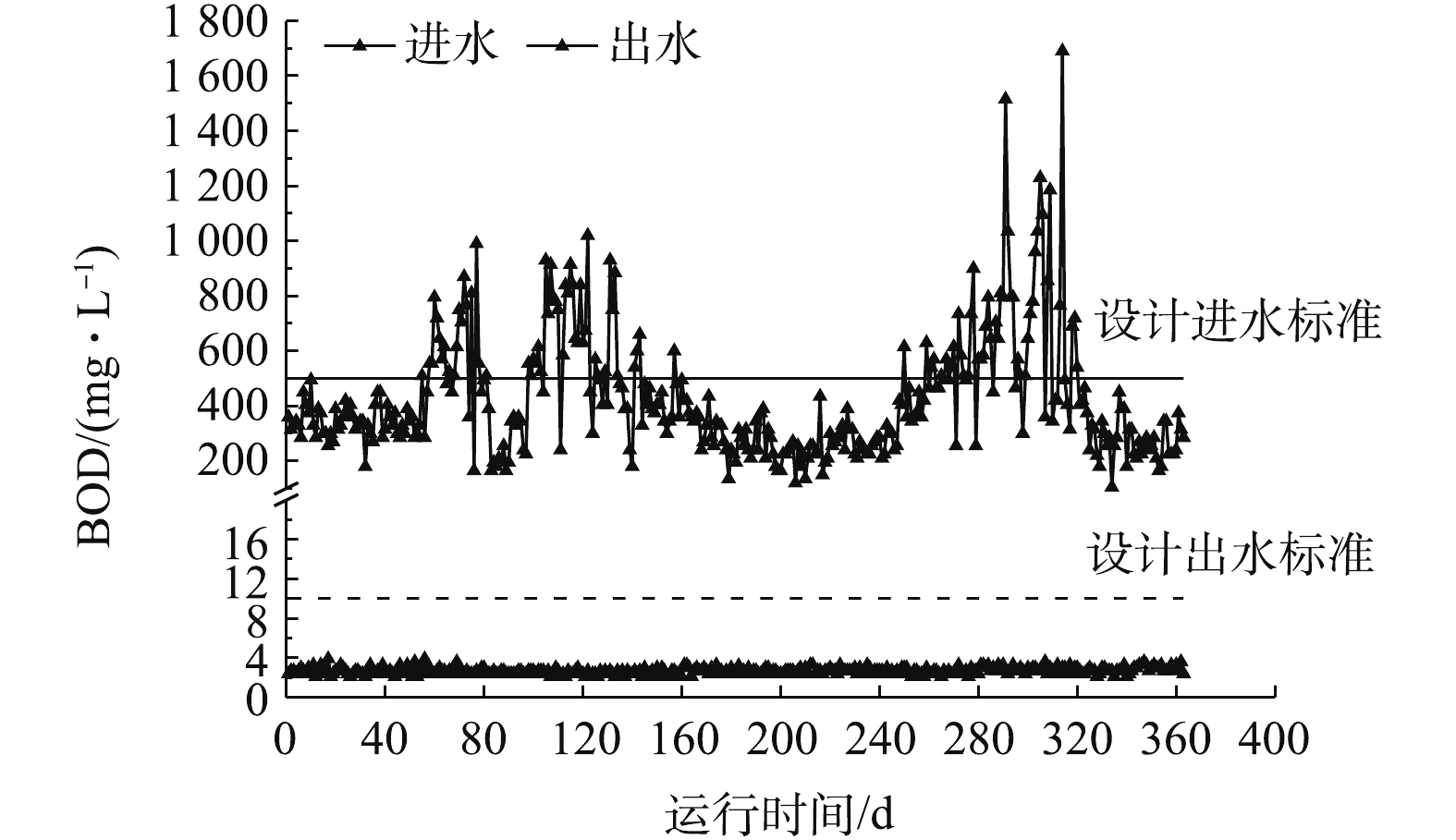
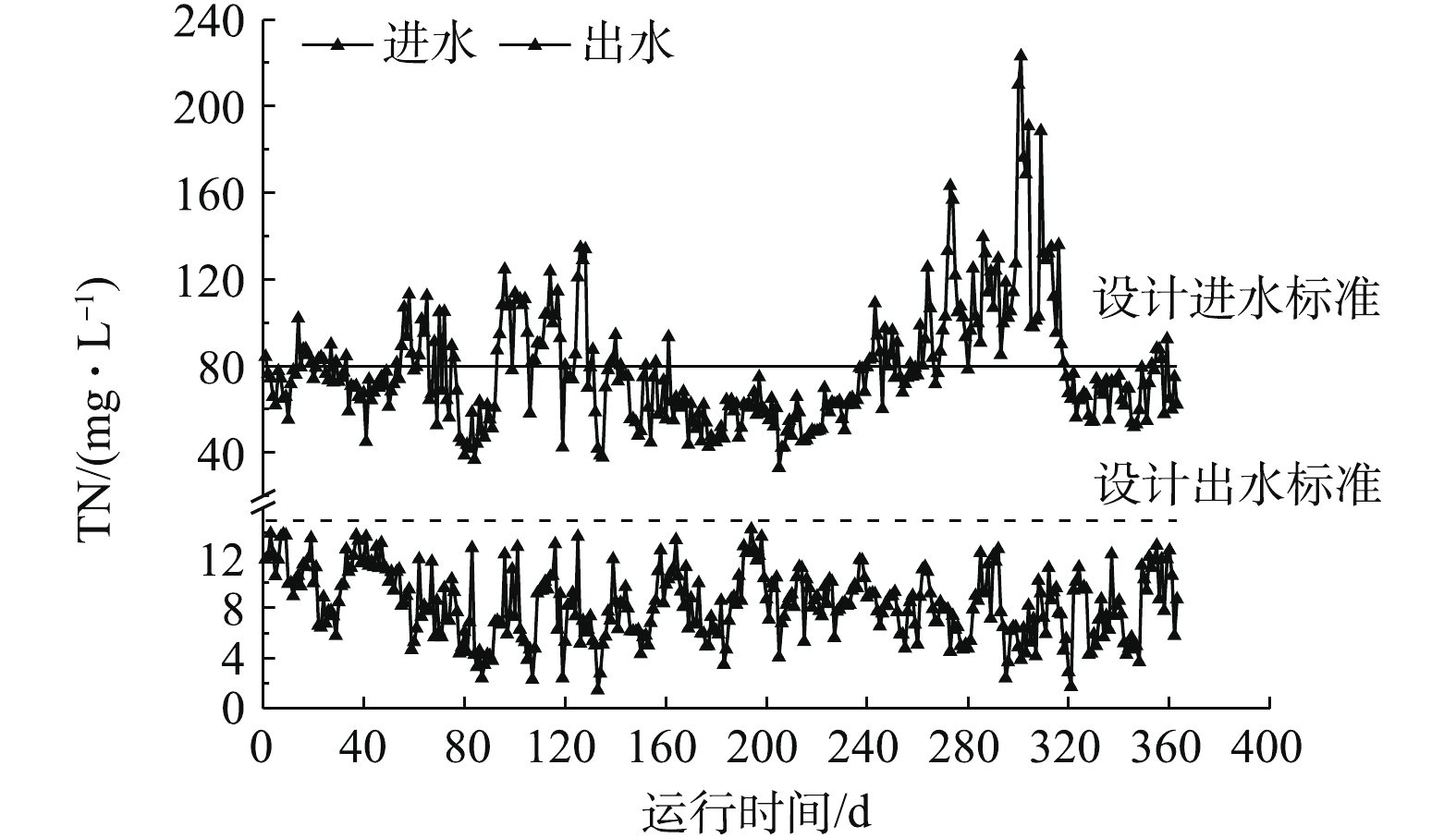
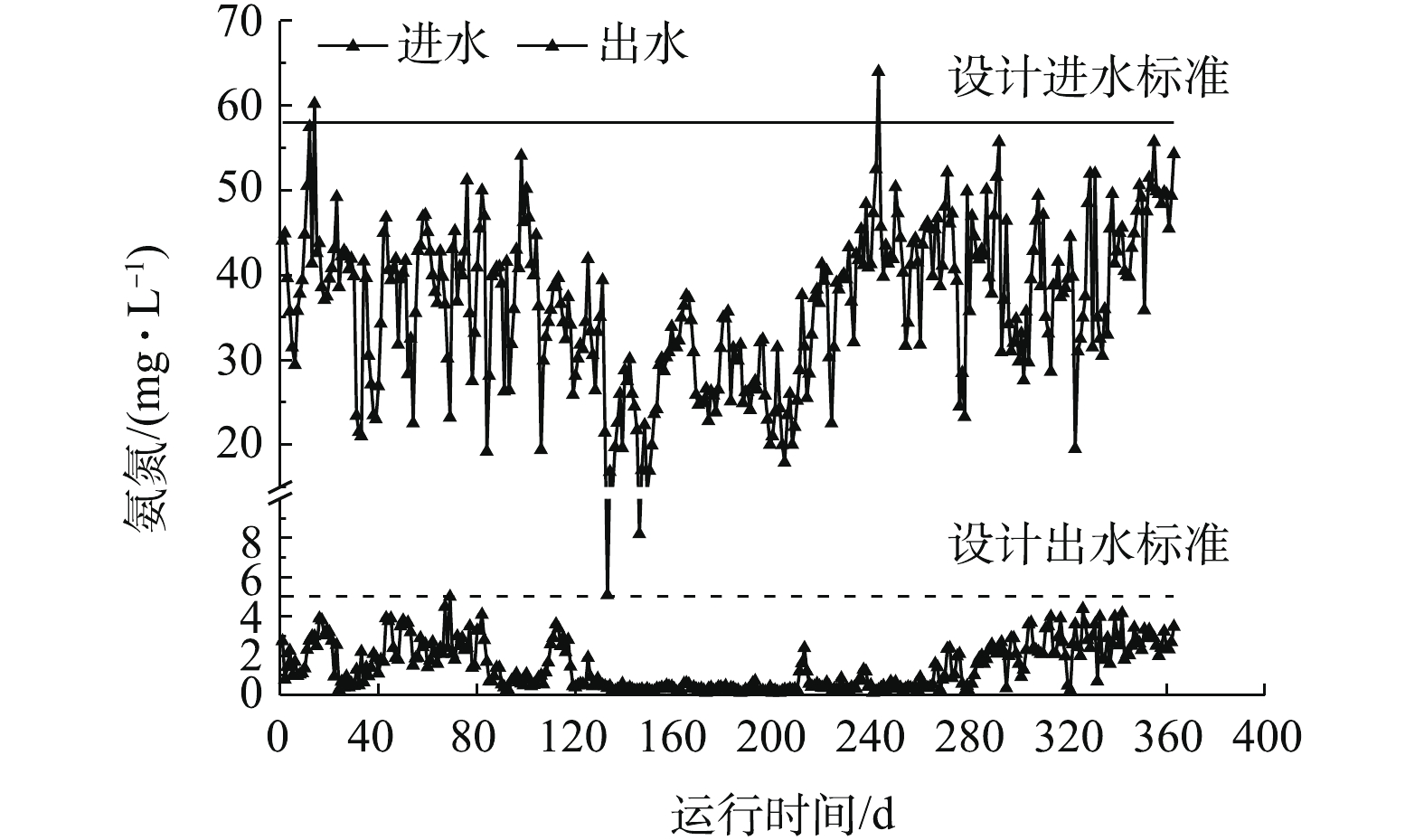
图2、图3和图4分别为该水厂2018年2月27日至2019年2月26日的BOD、TN和氨氮的运行数据。从图2和图3中可以看出,一年中进水存在2次严重超标,主要是TN、BOD,进水C/N(五日生化需氧量/总氮)为5.57±2.61。一年中进水有机负荷超过设计值(1.23 kg·(m3·d)−1)的时间达到了111 d,占30%。虽然进水氨氮不超标,但是TN超标,进水TN超标天数达到137 d,超标率为38%。由于TN的去除仍以硝化反硝化为主,故实际硝化的氮高于设计值,TN的超标间歇性地导致了氨氮的超标。
由图2、图3可知,在进水BOD、TN超标的状态下,出水稳定达标,出水BOD均值为(2.82±0.34) mg·L−1,已经稳定达到了地表Ⅳ类水标准。出水TN均值为(7.75±2.67) mg·L−1,低于10 mg·L−1的时间为262 d,达到72%,低于12 mg·L−1的时间为332 d,达到91%,说明脱氮效果良好。
由图4可知,一年出水氨氮均值为(2.43±1.04) mg·L−1。正常情况下,出水氨氮可以稳定小于1.5 mg·L−1,但是在进水BOD和TN超标时,出水氨氮有所提升,但仍小于5 mg·L−1。分析其原因主要为2点:1) TN超标间接导致氨氮超标,从而导致出水氨氮偏高;2) 进水BOD超标,由于异养菌对于溶解氧的竞争能力强于自养菌,所以一旦有机物浓度过高,在好氧池就会优先发生异养菌好氧脱碳过程,从而导致硝化菌可利用溶解氧不足,致使出水氨氮浓度升高[6-7]。但即使出现了间接的TN和BOD超标,出水氨氮仍可稳定达到一级A标准。
该污水厂生化段采用Bardenpho镶嵌MBBR工艺进行改造。首先,增设前缺氧和后缺氧区,其中,前缺氧区通过内回流过程充分利用原水碳源进行反硝化脱氮,后缺氧区通过投加碳源进一步进行反硝化脱氮,两大缺氧区共同保障了TN的去除效果,生化池出水硝氮最低可达到1 mg·L−1。其次,在前好氧区投加了悬浮载体,悬浮载体生物膜为长泥龄,这就为长泥龄菌尤其是硝化细菌的高效附着提供了场所。此外,由于悬浮载体专性在好氧区,所以即使有冲击来临,也能保障悬浮载体在好氧区内的持留,从而保障硝化效果。综上所述,采用Bardenpho镶嵌MBBR工艺可强化硝化和反硝化过程,抗冲击能力强,从而达到出水稳定达标的目的[8-10]。
-
为验证MBBR工艺在有机物冲击情况下对系统的处理情况,进行悬浮载体及活性污泥硝化小试并对污水厂生化段各功能区的沿程水样进行检测分析。
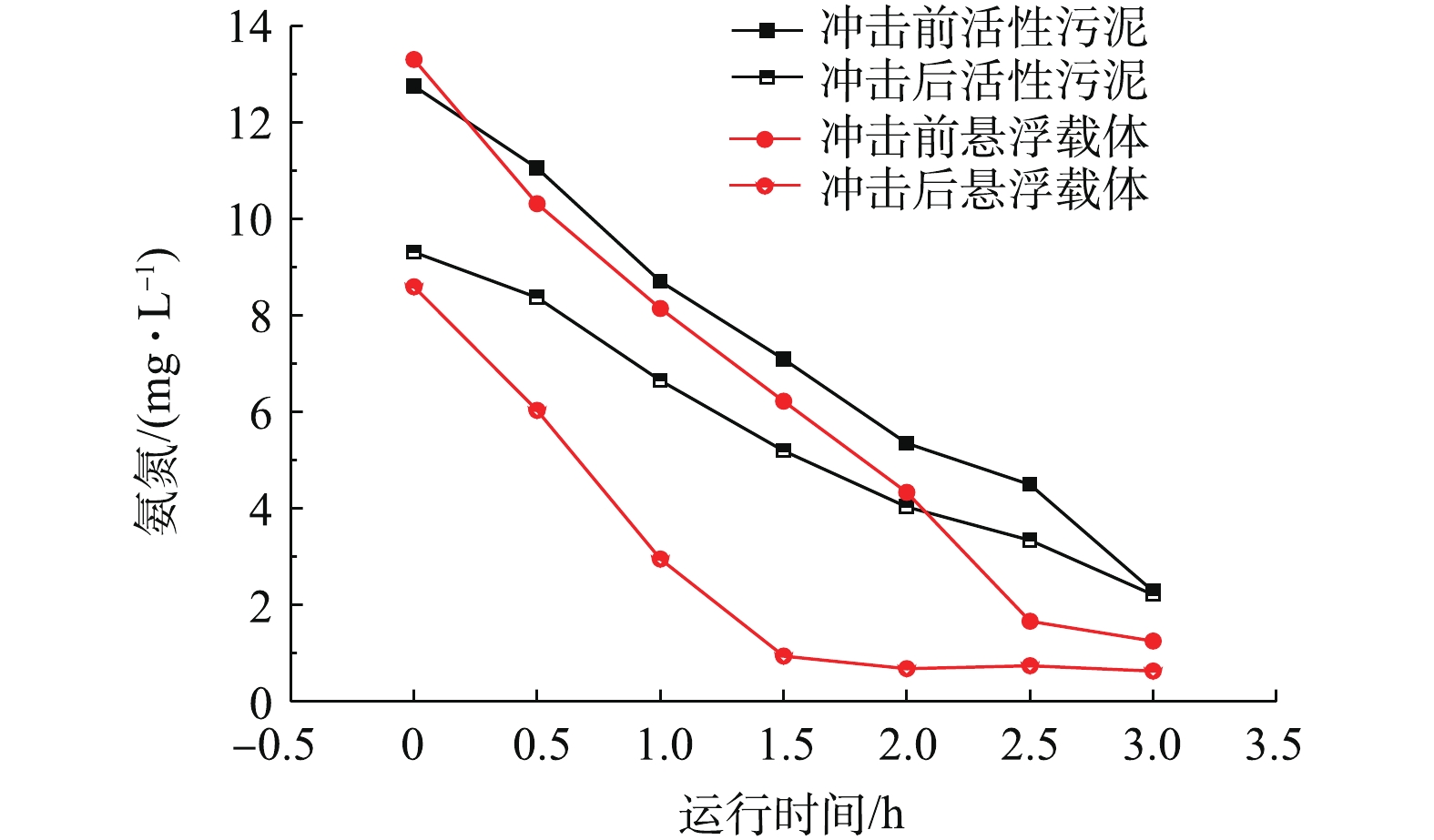
在对悬浮载体及污泥硝化性能进行对比时,根据MBBR区实际情况,分别在有机物冲击前后对好氧池内挂膜成熟的悬浮载体和活性污泥进行硝化小试实验,测定悬浮载体及活性污泥的硝化速率。硝化小试实验条件和所得的结果见表1和图5。活性污泥浓度和悬浮载体填充率为实验时生化池内实时值,实验温度为13 ℃。由表1可知,不论是在冲击前还是冲击后,悬浮载体的硝化速率均高于活性污泥。冲击前,悬浮载体的硝化性能是活性污泥的1.4倍,冲击后则增大至1.9倍。从有机物冲击对悬浮载体及活性污泥的硝化性能影响方面看,虽然冲击后生物池污泥浓度升高,但是污泥的硝化负荷有所降低,容积负荷由0.076 kg·(m3·d)−1降至0.057 kg·(m3·d)−1,降低了25%,污泥的硝化负荷由0.018 kg·(kg·d)−1降至0.010 kg·(kg·d)−1,降低了44%。而对于悬浮载体,冲击前后容积负荷未发生变化,这说明有机物的冲击并没有影响悬浮载体的硝化性能。
进水有机物浓度过高会导致异养菌繁殖过快,从而引起污泥浓度的升高。此外,由于自养菌对于溶解氧的争夺处于劣势,繁殖速率降缓,且随着污水厂剩余污泥排放量的增大,最终导致了硝化菌在活性污泥中的占比降低,从而导致污泥的硝化性能下降。而对于悬浮载体,由于硝化菌附着于悬浮载体表面,且悬浮载体专性在好氧区,即使在有机物冲击的条件下,悬浮载体也不会流失,生物膜的高效附着有效地持留了硝化菌,从而保障了悬浮载体的硝化性能不受影响,抗冲击能力强[11-13]。
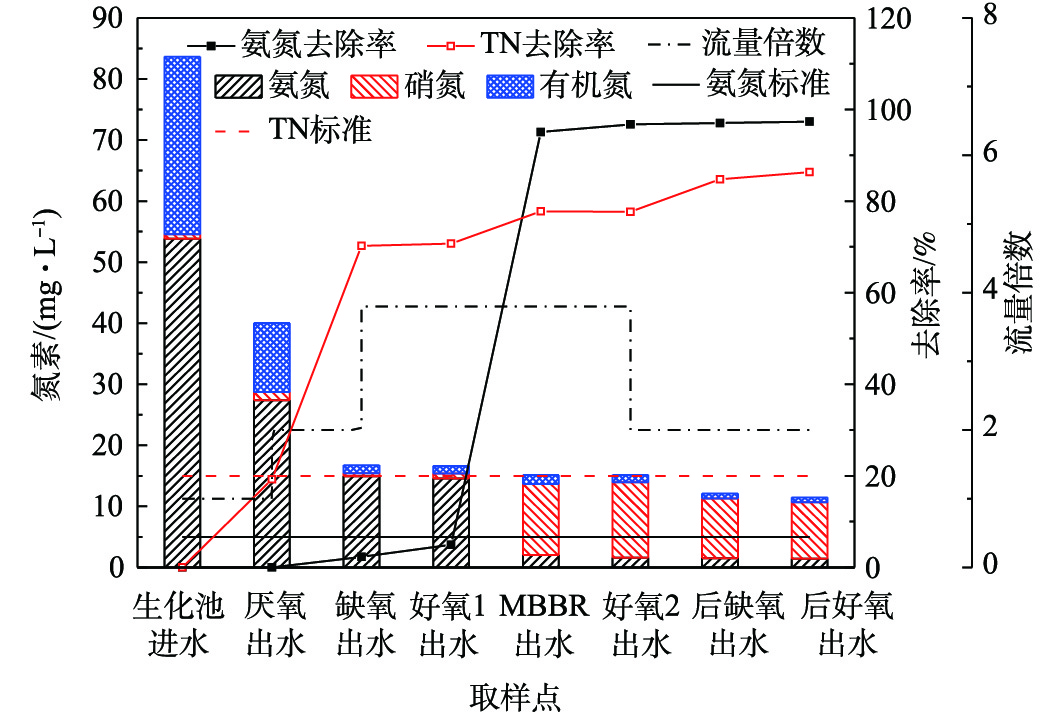
为分析有机物冲击情况下生化系统各功能区对氮素的处理情况,对生化段各功能区进行取样检测,生化池氮素浓度沿程变化如图6所示。由图6可知,生化系统进水氨氮接近设计值,在TN超标的情况下,出水氨氮为1.42 mg·L−1,出水TN为11.48 mg·L−1,均优于设计标准。对于硝化过程,由于进水有机物超标,故在好氧1区内基本无硝化发生,氨氧化率仅为2.66%,硝化容积负荷为0.029 kg·(m3·d)−1。而在好氧MBBR区内,氨氧化率则达到90%以上,硝化容积负荷达到0.192 kg·(m3·d)−1,硝化速率是好氧1区的6.6倍,从而保障了好氧MBBR区出水氨氮稳定达标。对于反硝化过程,厌氧区和前缺氧区对TN的去除率达到了70.22%,并且前缺氧区出水硝氮基本为零,这说明厌氧区和缺氧区脱氮效果良好,充分利用了原水碳源。值得注意的是,在好氧MBBR区也有7%的TN去除,推测可能是发生了同步硝化反硝化(SND)过程。基质(有机物、硝态氮等)以及DO在悬浮载体生物膜内部存在传质梯度并且各类微生物的代谢活动及其相互作用所形成的微环境是引起同步硝化反硝化(SND)的主要因素。此外,由于生物膜分层分布的特点,使其存在典型的缺/好氧微环境,进而形成功能菌群分置。生物膜外层形成好氧生物膜,硝化菌群得以附着并氧化氨氮;内层则形成缺氧生物膜,具备反硝化功能的菌群能够得以生长并将氨氮的氧化产物还原为氮气实现脱氮[14]。好氧MBBR区出水TN已经降低至15.12 mg·L−1,通过在后缺氧区投加碳源,使出水TN进一步降低,最终达到11.48 mg·L−1。
从沿程氮素去除效果来看,在受进水有机物冲击的情况下,系统仍能保持较好的处理效果,结合硝化小试及沿程数据可知,MBBR工艺为系统抗冲击性能提供了保障。一方面通过悬浮载体的投加,为硝化菌的大量生长提供了附着条件,易受冲击的硝化菌群主要附着在悬浮载体上,在进水存在负荷冲击时,MBBR抗冲击能力强,减轻了系统受冲击负荷的影响;另一方面,采用MBBR工艺进行改造,增大了缺氧区的停留时间,尤其是增加了后缺氧区,破除了回流比对TN去除的限制,可控性强。当MBBR区出水TN达标时,后缺氧区可不投加碳源,利用原水碳源或者内碳源进行反硝化可去除少量的TN,而一旦进水TN超标,导致MBBR区出水TN偏高时,则可通过在后缺氧区投加碳源,从而保障生化池出水TN达标[14-15]。
-
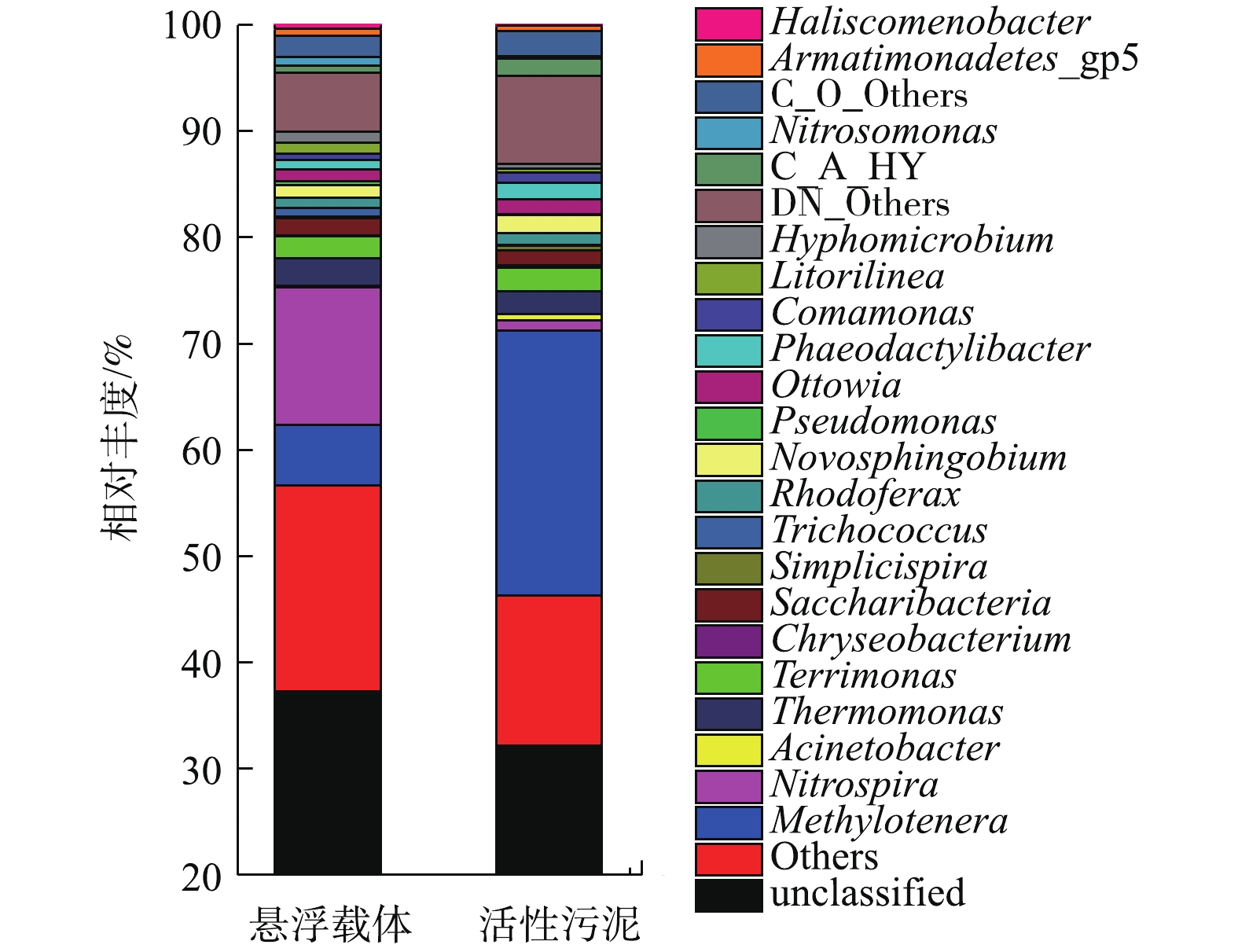
为从微观层面进一步分析系统抗冲击负荷的原因,对该污水厂活性污泥以及悬浮载体进行了基于16S rRNA扩增子高通量测序,各样品属水平物种相对丰度如图7所示。MBBR悬浮载体中优势菌群主要包括Nitrospira(硝化螺旋菌属)、Acinetobacter(不动杆菌属)、Nitrosomonas(亚硝化单胞菌属)等;污泥中优势菌群主要包括Nitrosomonas(亚硝化单胞菌属)、Thermomonas(热单胞菌属)、Nitrospira(硝化螺旋菌属)。系统中AOB主要为Nitrosomonas(亚硝化单胞菌属),在悬浮载体生物膜和活性污泥上的丰度分别为1.46%和1.08%,占比较少。Nitrospira是主要的NOB菌属,在悬浮载体生物膜和活性污泥上的丰度分别为12.94%和1.01%。研究发现,Nitrospira更容易以附着态形式存在,因此,在悬浮载体中的丰度较大;Nitrospira在污泥中的丰度也高于传统污水厂,这可能是由于悬浮载体生物膜脱落后,对污泥进行了接种,使之在污泥中也能够维持一定的比例。有研究[16]发现,Nitrospira兼具AOB和NOB功能,另外,该菌属适宜生存在低氨氮环境中,可以作为出水水质较好和稳定的指示性微生物。因此,Nitrospira作为硝化菌中优势种属也反映了水厂处理效果较为良好。
取样时,系统内污泥浓度为4.86 g·L−1,VSS/SS=0.51,悬浮载体上污泥量为9.07 g·m−2,VSS/SS=0.89。在好氧系统中,结合池容、悬浮载体填充率等进行计算发现,悬浮载体提供83%的硝化菌,是活性污泥的5倍,由此可见,悬浮载体保障了系统硝化的进行。
值得注意的是,冲击过后,同样对活性污泥和悬浮载体进行了高通量测定,与冲击前相比,两者的硝化菌属均未发生改变,仍以Nitrospira为主,兼具Nitrosomonas,但冲击过后活性污泥中硝化菌属的丰度均明显降低,Nitrospira由1.01%降低至0.84%,Nitrosomonas由1.08%降低至0.61%。相比而言,悬浮载体的硝化菌属丰度并未发生明显改变,Nitrosomonas的丰度为1.52%,Nitrospira的丰度为12.06%。从微生物的角度进一步证明了MBBR工艺良好的抗冲击性能。
2.1. 水厂运行效果
2.2. 硝化性能研究
2.3. MBBR系统微生物分析
-
1)通过向活性污泥系统中投加悬浮载体形成泥膜复合MBBR工艺,强化了系统的抗冲击能力,在进水TN、BOD超标的情况下,出水TN、BOD、氨氮分别为(7.75±2.67)、(2.82±0.34)、(2.43±1.04) mg·L−1,稳定达到一级A标准。
2) Bardenpho工艺通过后缺氧的设置,破除了回流比对TN去除的限制,使系统在进水TN超标的情况下同样能够稳定达标,可控性强。
3)悬浮载体生物膜长泥龄、专性培养的特点使其能够对硝化细菌实现高效的筛选富集和持留,保障了在有机物冲击前后,悬浮载体的硝化性能不受影响。
4)悬浮载体和活性污泥的高通量结果显示,悬浮载体上优势硝化菌为硝化螺旋菌,其丰度是活性污泥的5倍,高效的硝化细菌保障了工程中氨氮的稳定达标。
5)工程实践表明,MBBR工艺抗冲击能力较强,出水各指标稳定达标,适用于污水厂在高排放标准下的应用。








 下载:
下载: