-
印染废水具有高化学需氧量、高色度的特点,含有大量“三致”毒性的难降解有机污染物,是一种很难处理的废水[1]。现阶段,国内外处理印染废水的方法有吸附法、高级氧化法和膜过滤等[2]。纳米氧化锰八面体分子筛(manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve,OMS-2)含有不同价态的Mn 离子,结构上又是多孔形貌,具备良好的离子交换性[3],作为高级氧化技术中的一种,纳米催化剂在近年获得广泛的关注[4];DUAN 等[5]采用OMS-2/PMS 体系,研究酸性橙II(AO7)在可见光下的降解,发现OMS-2/PMS能明显提高印染废水的脱色率。喻阳等[2]采用磁性OMS-2/SBR耦合处理活性染料X-3B废水发现,发现处理磁性OMS-2在酸性条件下,催化PMS氧化去除X-3B的效果较好。
但是,纳米OMS-2这一类人工纳米材料(manufactured nanomaterials,MNMs)释放到水体后,在水环境中会发生一系列的行为变化,如分散-团聚-沉降-再悬浮、吸附-解吸-被吸附、生物黏附-吞食-累积-放大等[6]。微生物在城市污水处理厂(wastewater treatment plants,WWTPs)的污水生物处理系统中发挥着至关重要的作用,WWTPs的处理效率很大程度上取决于微生物群落的组成和活性。现阶段,已有研究表明,在WWTPs中检出了纳米TiO2[7],这些MNMs独特的物理化学属性可能给污水生物处理的效果带来难以预料的影响,其与污泥的相互作用可能会对污水处理效能和微生物特性产生影响。CHEN等[8]发现,暴露于50 mg·L−1纳米Al2O3颗粒后,大量吸附于活性污泥表面的纳米Al2O3颗粒降低了反硝化菌的数量。LIANG等[9]发现,经过纳米Ag颗粒的冲击负荷后,氨氧化菌和亚硝化菌的数量均出现降低,而硝化菌则完全消失。SIMONIN等[10]研究发现,纳米TiO2能显著影响硝化菌及反硝化菌的活性及丰度,而亚硝酸盐氧化菌的活性则基本不受纳米TiO2投加量的影响。
本研究在前期研究的基础上,针对纳米材料残留对污水生物处理系统混合菌群影响尚未明确的问题,将不同浓度的纳米OMS-2混入序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor,SBR)中,探讨纳米OMS-2对SBR运行情况和活性污泥微生物菌群的影响,为MNMs的实际应用和环境风险的研究提供参考。
全文HTML
-
试剂:过硫酸氢钾(PMS)为进口分析纯(购自美国Aladdin Industrial Corporation),高锰酸钾、硫酸锰、氢氧化钠、浓盐酸等均为国产分析纯,活性艳红X-3B为国产化学纯。
纳米氧化锰八面体分子筛(OMS-2)采用回流法[11]制备:在30 mL去离子水中加入60 mmol MnSO4 和 3 mL 硝酸制成溶液1,将38 mmol KMnO4溶解在 100 mL去离子水中制成溶液2;将溶液2逐滴加入溶液1中,持续搅拌,在温度为110 ℃的条件下,获得暗棕色沉淀;然后,将沉淀在回流温度下保温过夜,用去离子水多次洗涤;最后,在120 ℃的条件下,干燥12 h,获得纳米OMS-2。
-
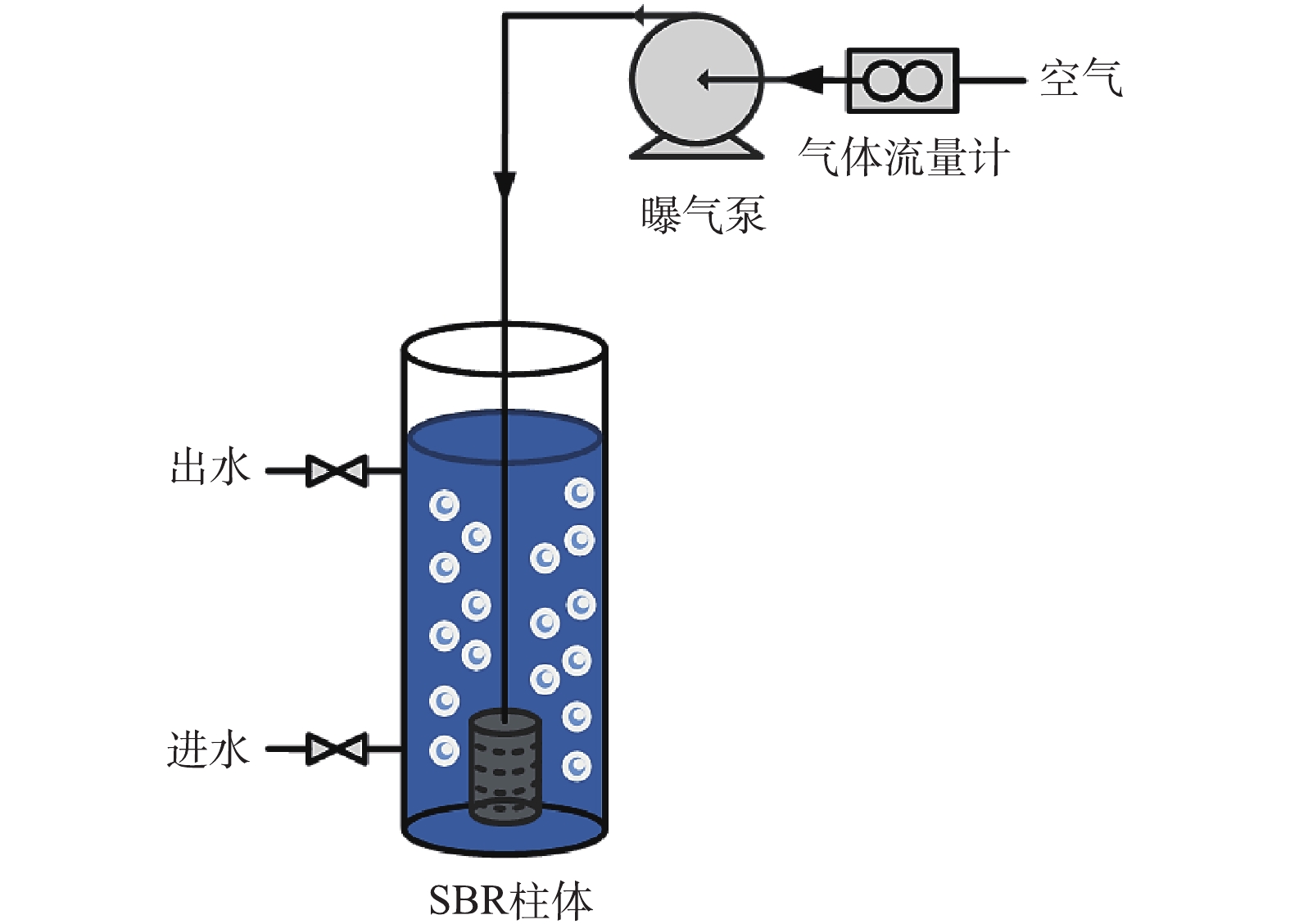
为了研究OMS-2对SBR系统微生物群落结构的影响,分别取0.05、0.25和1.25 g·L−1浓度梯度的OMS-2,加入3个不同有机玻璃序批式反应器(SBR)中,并设置1组SBR装置作为空白对照(不添加OMS-2),相关SBR对应编号为S0(空白)、S1(含0.05 g·L−1的OMS-2)、S2(含0.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)和S3(含1.25 g·L−1的OMS-2);实验装置如图1所示,反应器的容积均为2 L,将相同规格的曝气头置于SBR中,并用硅胶管将其与曝气泵连接,水中溶解氧浓度由流量计来控制。
SBR 运行参数:水力停留时间为20 h,循环时间为12 h(曝气11.5 h,进水和放水时间0.5 h),空气流速为1.5 L·min−1,交换率为60%,污泥停留时间为5 d;反应器的进水以葡萄糖为碳源,NH4Cl和KH2PO4分别为氮源和磷源,进水参数为X-3B 50 mg·L−1,COD 800 mg·L−1,pH 6.8~7.2。测定不同浓度OMS-2条件下连续30 d对SBR降解X-3B和COD指标的变化情况。
反应器接种污泥取自武汉纺织大学污水处理站好氧消化池污泥,该污泥经70 d驯化后,具有良好的降解X-3B废水的能力;污泥相关参数为:pH 6.8~7.2,MLSS 4 098 mg·L−1,MLVSS 2 665 mg·L−1。
-
在4个SBR运行30 d后,采集活性污泥样品。首先,采用OMEGA土壤基因组DNA提取试剂盒进行DNA提取[12]。PCR扩增区域选择活性污泥样品16S rRNA的V4区域,合成融合引物,引物PAGE纯化,其引物序列为F:5'-AYTGGGYDTAAAGNG-3';R:5'-TACNVGGGTATCTAA TCC-3'。PCR反应体系以20 ng·μL−1 RNA为模板,PCR的扩增条件[4]为:98 ℃预变性30 s后,27个PCR循环(98 ℃变性30 s,50 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s),72 ℃延伸5 min,最后保持在4 ℃条件下。0.8% 琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,切割回收,使用DNA胶回收试剂盒回收。采用BioTek酶标仪对各个样品定量。接着构建DNA文库,使用Agilent 2100对PCR富集片段进行质量控制,验证DNA文库的片段大小及分布。最后采用Illumina MiSeq高通量测序平台进行基因测序。
在Illumina MiSeq平台测序完成后,根据序列的相似度,应用Qiime,将序列归为多个操作分类单元(operational taxonomic units,OTU),OTU的相似性水平是97%。根据获得的OTU数据,做出每个样品的稀释曲线,对OTU列表中获得的分类信息与丰度进行整理,在属层次下对各样品进行物种丰度统计、聚类分析等数据分析。
-
利用SEM、XRD、XPS等测试方法对OMS-2进行表征,采用紫外分光光度法[2]测定538 nm处吸光度值,确定模拟印染废水中X-3B浓度。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 实验装置和方法
1.3. DNA的提取和PCR扩增及其微生物多样性分析
1.4. 分析方法
-
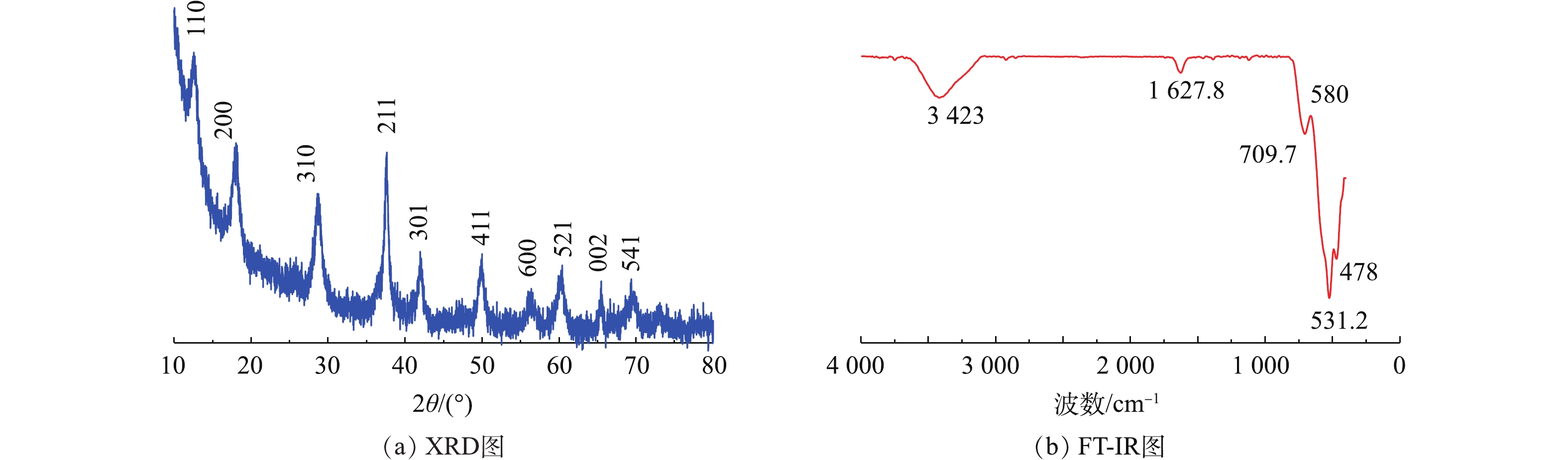
对OMS-2样品的结构进行分析,所得X射线衍射分析(XRD)结果见图2(a),所得傅氏转换红外线光谱(FT-IR)分析结果见图2(b);样品XRD图谱与标准品(JCPDS29-1020)比对[3],所有的特征峰都吻合,说明本实验制备的样品是OMS-2。样品微观形貌的扫描电镜分析结果见图3。
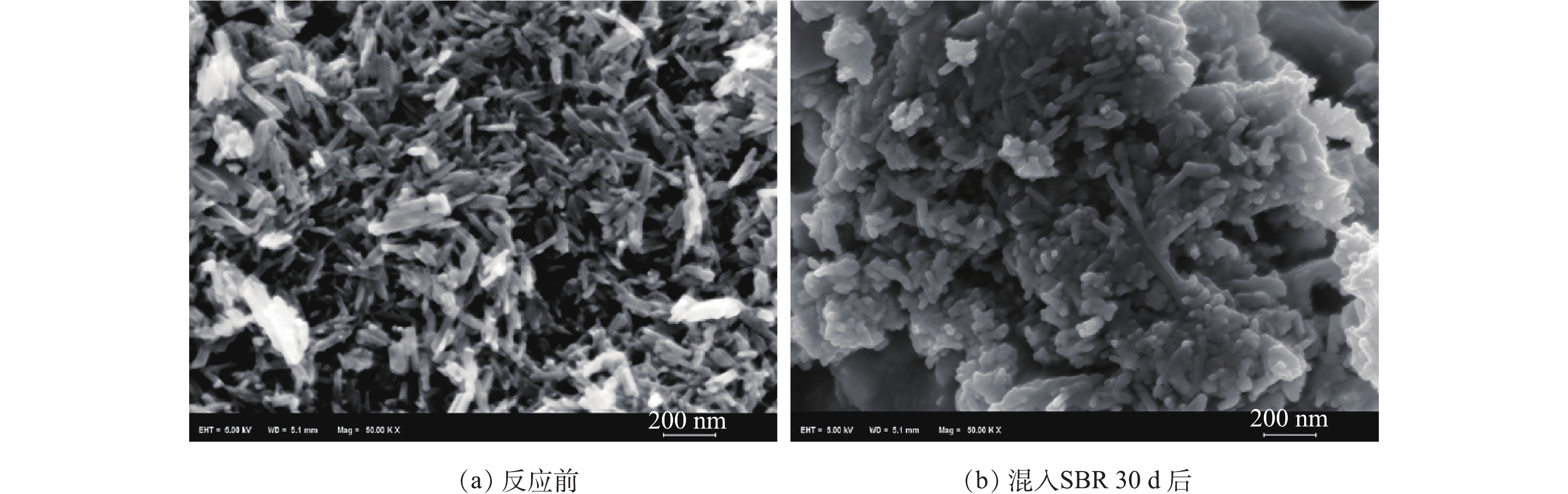
由图3(a)可知,OMS-2为柱状纳米颗粒,粒径为(40~60 nm)×(150~300) nm;图3(b)是将OMS-2以0.25 g·L−1的浓度与活性污泥反应30 d后的扫描电镜图片,由图3(b)可看出,OMS-2已经被SBR中活性污泥包裹起来,说明活性污泥和OMS-2紧密结合。
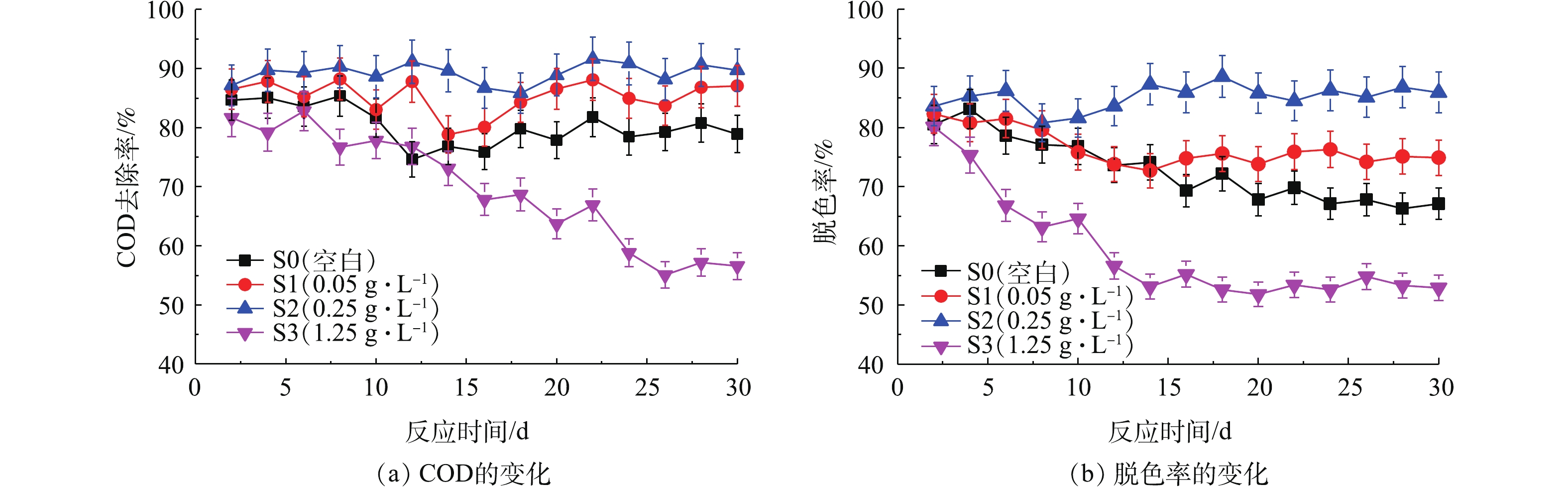
OMS-2对SBR的影响如图4所示。不同浓度的OMS-2投入到SBR后,其对COD去除率和脱色率的影响呈先促进后抑制的变化趋势:当OMS-2浓度不超过0.25 g·L−1时,SBR中的COD去除率和脱色率可以提高;但当OMS-2的浓度超过0.25 g·L−1时,OMS-2会抑制COD的去除和脱色。有研究表明,多孔结构物质有利于污泥中菌体的附着生长,加速活性污泥颗粒的形成[2];OMS-2长时间置于SBR中,会释放少量的锰离子,有利于激活污泥中某些菌体的胞外酶活性[4],从而可以提高SBR去除COD和降解X-3B的效果。但是,如果水中锰离子的浓度过高,就会抑制污泥中菌体的生长[13],从而抑制活性污泥的形成和降低SBR的运行效果。
-
4个SBR中活性污泥菌群经过Illumina MiSeq高通量测序平台进行基因测序后,共获得171 345条有效序列,表1为不同SBR中菌群的有效序列分布情况。ACE指数、Chao1指数是生态学上用于表明微生物群落丰富度的指数,数值越大,表明群落丰富度越高[14]。Shannon指数和Simpson指数是生态学上用于表征微生物群落多样性的指数,Shannon值越大,说明群落多样性越高[11],Simpson值越大,说明优势微生物占微生物群落总生物量越高[15]。
由表1可知,随着OMS-2浓度的增加,SBR中ACE指数和Chao1指数呈先增加后降低的变化趋势;以Chao1指数为例,OMS-2的浓度由S1(0.05 g·L−1的OMS-2)提升到S2(0.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)时,Chao1指数相对于S0(空白)上升的幅度分别是6.03%和78.79%;但是OMS-2的浓度继续上升到S3(含有1.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)时,Chao1指数则相对于S0下降了13.17%。ACE指数和Shannon指数的变化趋势与Chao1指数基本一致。Simpson指数随着OMS-2浓度的增加,也呈先增加后降低的变化趋势;Simpson指数相对于S0(空白),首先上升了3.26%(S1)和4.35%(S2),然后下降了35.87%(S3),这说明低浓度OMS-2有利于提升SBR中优势微生物种群占总生物量的比例,高浓度OMS-2则会降低优势微生物种群占总生物量的比例。
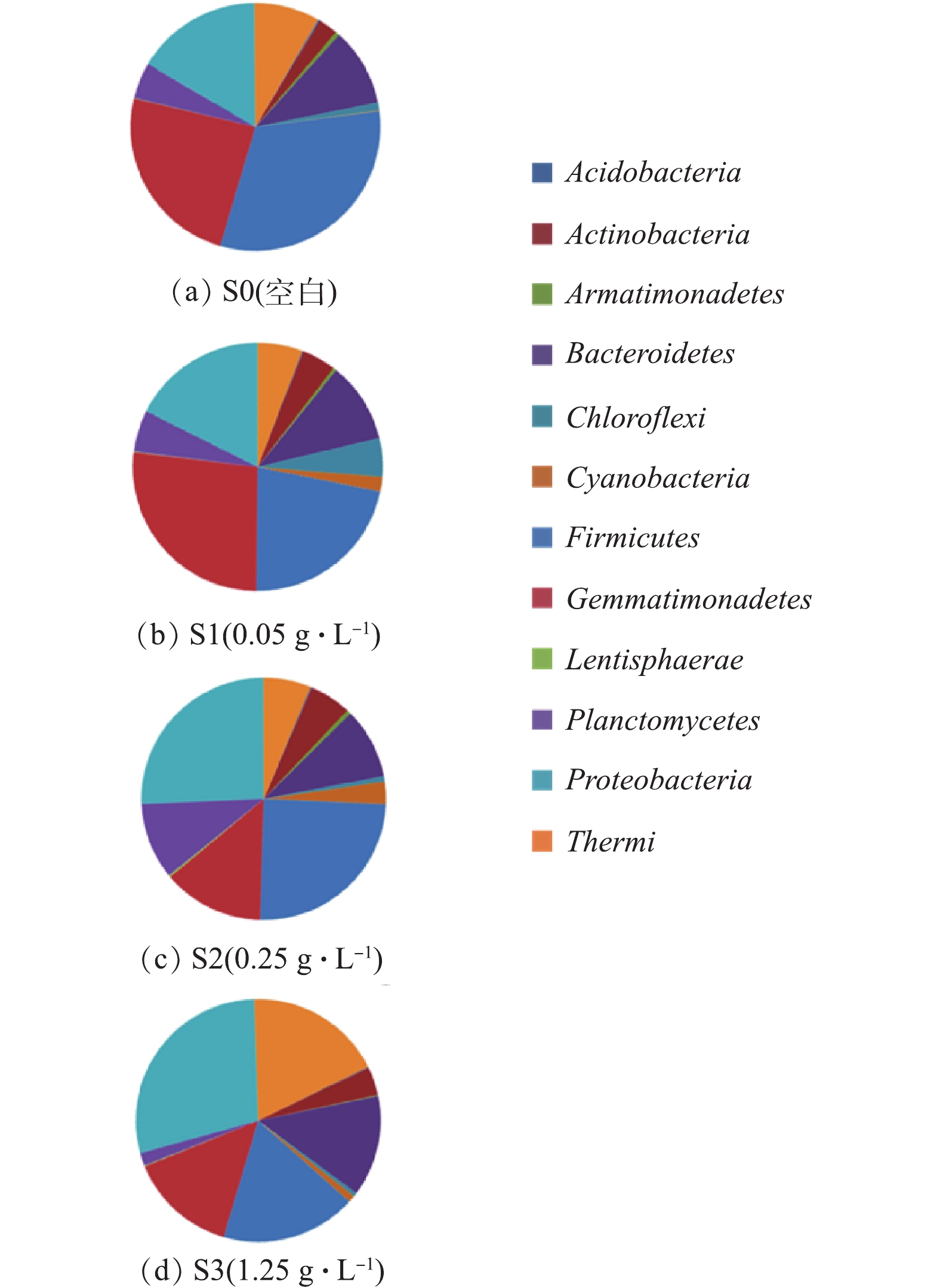
将SBR中获取的活性污泥菌群DNA序列与Greengenes OTU数据库进行比对,获知SBR中菌群主要由12个门的微生物组成,如图5所示。反应器中微生物可以分为酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、装甲菌门(Armatimonadetes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)、蓝藻菌门(Cyanobacteria)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、芽单胞菌门(Gemmatimonadetes)、黏胶球形菌门(Lentisphaerae)、浮霉菌(Planctomycetes)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和栖热菌门(Thermi)等12个门。由图5可知,随着OMS-2浓度的增加,不同微生物的数量呈现不同的变化情况。其中:有的微生物在不同OMS-2浓度的情况下,数量基本上一直保持不变,如酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria);有的微生物随着OMS-2浓度的增加,数量呈现先增加后下降的变化趋势,如放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、装甲菌门(Armatimonadetes)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)、芽单胞菌门(Gemmatimonadetes)、蓝藻菌门(Cyanobacteria)、黏胶球形菌门(Lentisphaerae)和浮霉菌门(Planctomycetes);有的微生物在较低浓度OMS-2的情况下,数量基本不变,较高浓度OMS-2(1.25 g·L−1)的情况下,数量明显变化,如厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和栖热菌门(Thermi);有的微生物随着OMS-2浓度的增加,数量呈先增加后下降,接着又增加的波浪变化趋势,如相对于S0,在S1、S2和S3中,拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)菌种OTU数量分别增加了45.0%、16.8%和70.0%;有的微生物随着OMS-2浓度的增加,数量也一直保持增加,如相对于S0,在S1、S2和S3中,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)菌种OTU数量分别增加了50.8%、96.4%和126.2%。
浮霉菌门(Planctomycetes)和变形菌门(Proteobacteria)是具有脱氮功能的微生物[16],这2类菌种数量的增加有利于提升SBR的脱氮能力;拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)数量的增加有利于缓解菌群的代谢紊乱并提升菌群的新陈代谢水平[17]。拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和变形菌门(Proteobacteria)都可以强化SBR降解有机污染物的能力[18-19]。绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)是一类构成污泥菌胶团絮状体的重要菌种,普遍存在于污水处理厂中[20],该菌可以将CO2转变为丙酮酸而具有固碳的作用。有研究[21]表明,绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)也可以提升污水反应器降解污染物的能力。因此,OMS-2加入SBR后,在低浓度下强化了SBR处理污染物的能力,这一点和图4中COD和脱色率的变化情况是一致的。
-
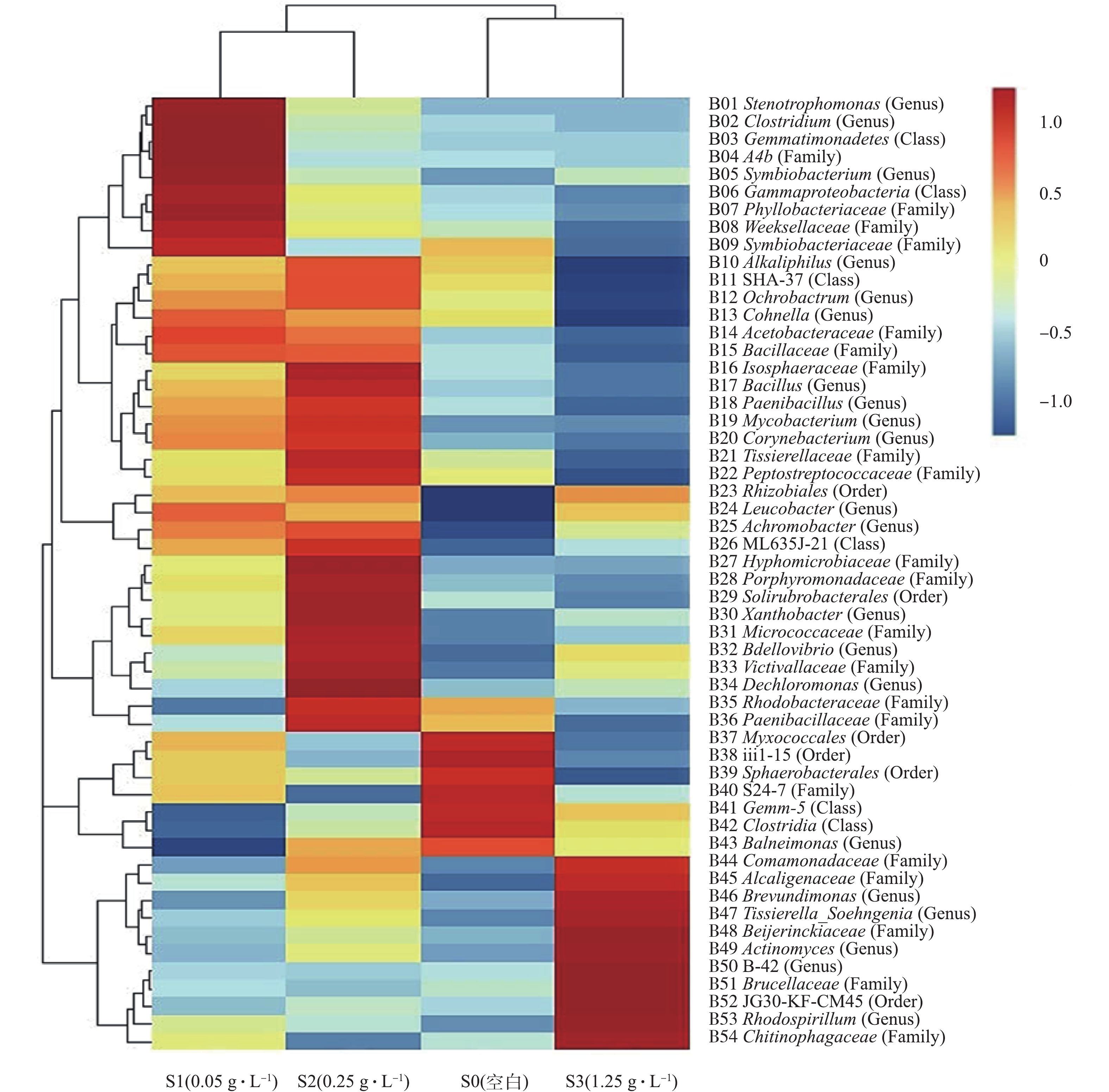
通过Illumina MiSeq高通量测序,鉴定出SBR中54种丰度大于0.2%的菌种,菌群的热图分析结果如图6所示。热图是在菌种属的分类水平进行聚类后,依据高丰度和低丰度的菌种分块聚集,通过颜色梯度和相似度,在菌种属的分类水平反映菌落结构的差异性[22]。由图6可知,在S0(空白)、S1(0.05 g·L−1的OMS-2)、S2(0.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)和S3(1.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)的浓度梯度下,SBR中菌群结构发生了明显的变化。根据菌群结构变化规律,54种菌种可以分为4个集群,第1个集群从B01寡养单胞菌属(Stenotrophomonas)到B25无色杆菌属(Achromobacter),这25种是S1条件下(0.05 g·L−1的OMS-2)的高丰度微生物;第2个集群从B10嗜碱菌属(Alkaliphilus)到B36类芽孢杆菌科(Paenibacillaceae),这27种是S2条件下(0.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)的高丰度微生物;第3个集群从B37黏球菌目(Myxococcales)到B43甲基杆菌属(Balneimonas),这7种是S0条件下(空白)的高丰度微生物;第4个集群从B44丛毛单胞菌科(Comamonadaceae)到B54丝状菌科(Chitinophagaceae),这11种是S3条件下(1.25 g·L−1的OMS-2)的高丰度微生物。
有研究[4]表明,低浓度的OMS-2有利于提升菌群的新陈代谢水平和强化菌群降解有机物污染物的能力,而在高浓度下则具有抑制作用。S1和S2条件下高丰度的菌种数量明显高于S0和S3条件下的,说明低浓度OMS-2可以提升菌群中高丰度菌种的数量,这个结果与已有研究结果[11]一致。
-
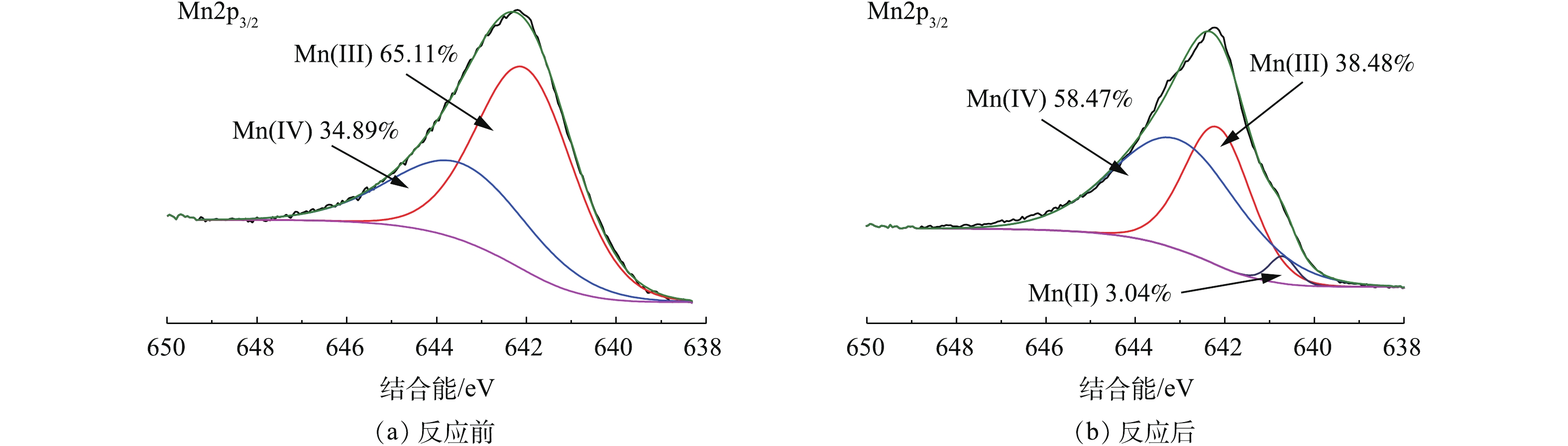
OMS-2中含有不同的锰氧化态(如Mn(Ⅳ)、Mn(Ⅲ)和Mn(Ⅱ))。Mn(Ⅲ)/Mn(Ⅳ)氧化物稳定且相对不溶,而Mn(Ⅱ)氧化物可以在酸性条件下溶解。为了研究OMS-2中Mn氧化态物质的变化,在进行SBR实验前后,分别测量OMS-2的XPS光谱。对于OMS-2的Mn2p3/2光谱,发现在642.0 eV和643.8 eV处具有65.11∶34.89的峰面积比的2个峰(图7(a)),并且这些峰可以被认为是Mn(Ⅲ)和Mn(Ⅳ)氧化态。在进行SBR实验后,在OMS-2中鉴定出Mn(Ⅱ)氧化态的第3个峰,测定其峰面积比为58.47∶38.48∶3.04(Mn(Ⅳ)∶Mn(Ⅲ)∶Mn(Ⅱ))(图6(b))。XPS的结果表明,在SBR中,OMS-2中锰氧化态分布发生了明显的变化,说明Mn(Ⅳ)/ Mn(Ⅲ)发生了氧化还原反应。
通常情况下,异构Mn(Ⅳ)还原微生物包含2个主要部分[11]:1)Mn(Ⅳ)-微生物(FMR),它通过保存从电子转移到Mn(Ⅳ)的能量而支持生长;2)非Mn(Ⅳ)-微生物(Non-FMR),FMR广泛分布在细菌和古菌以及生长过程通过氧化有机化合物、氢或单质硫来还原Mn(Ⅳ)的微生物中。
锰离子可以作为细菌体内各种氧化酶、DNA聚合酶的辅助因子,与细胞的生长、代谢以及毒力密切相关[23]。Illumina MiSeq高通量测序结果表明,低浓度的OMS-2可以提高芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)等锰氧化还原菌在微生物群落中的丰度;有研究[24]表明,锰氧化还原菌可以和锰离子反应,生成具有高的催化氧化能力和比表面积的生物氧化锰,进而通过吸附和氧化作用去除污水中的污染物。这可能与OMS-2混入SBR系统后改变了COD和色度的去除效果有关。
2.1. OMS-2对SBR运行情况的影响
2.2. 微生物多样性分析
2.3. 样品的聚类分析和热图
2.4. OMS-2变化机理分析
-
1) OMS-2添加到SBR中,与对照实验相比,在OMS-2浓度为0.05~0.25 g·L−1时,脱色率增大,在浓度为0.25~1.25 g·L−1时,脱色率降低,但总体上来说,添加OMS-2能提高脱色率。
2)不同浓度的OMS-2改变了菌群的多样性和结构,低浓度的OMS-2(0.05~0.25 g·L−1)可以提升微生物菌群的多样性和改变菌群的结构。
3)在污水生物处理过程中,OMS-2中Mn(Ⅳ)/Mn(Ⅲ)具有很好的氧化还原活性,该过程可能影响了菌群的组成。



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: