城市生活污水短程硝化系统的恢复与启动
Biological activity recovery and start-up of mainstream shortcut nitrafication system
-
摘要: 为了实现主流的短程硝化反硝化和厌氧氨氧化,设计了基于pH-DO和阀ON-OFF间歇曝气的在线控制系统,搭建了中试级别的短程硝化SBR,在高DO条件下基于城市生活污水恢复种泥活性后,加入反硝化稳定短程,最后接入厌氧氨氧化滤池实现全过程自养脱氮。将脱氮率、NO2--N积累率等作为考察指标,研究了系统的启动过程和稳定性。结果表明:控制SBR(sequencing batch reactor)中DO=2~2.5 mg·L-1、HRT=8~10 h、SRT=4~5 d、T=25℃,启动恢复3个月后,系统能保持90%以上的NO2--N积累率、NO2--N/NH4+-N=0.96±0.18;短程硝化反硝化能达到50%左右的NH4+-N去除率,60%左右的TIN去除率;短程硝化接厌氧氧氨氧化能保证90%左右的NH4+-N去除率和TIN去除率,出水达一级A标准。由实验结果分析,系统在高DO条件下能恢复短程硝化污泥的活性,基于pH-DO和阀ON-OFF间歇曝气的在线控制系统稳定性高,能保证短程硝化系统的稳定运行;恢复活性后,后接厌氧氨氧化滤池能实现中试级别的全过程自养脱氮。Abstract: In order to achieve the mainstream shortcut nitrification-denitrification and nitritation-ANAMMOX, an online pH-DO control mainstream nitritation system was built, which in a pilot SBR. After recovering the activity of seed sludge under high DO and municipal wastewater, denitrification was added to stabilize shortcut nitrification. At last,ANAMMOX was connected with SBR to realize auto trophic nitrogen removal.The nitrogen removal rate, nitrite accumulation rate during start-up process was investigated to characterize the stabilization of system. The results showed that when control the DO of SBR reactor at 2 to 2.5 mg·L-1, HRT from 8 to 10 h, SRT from 4 to 5 d, and T=25℃,the nitrite accumulation rate can keep 90%, and NO2--N/NH4+-N=0.96±0.18. The nitrogen removal rate of shortcut nitrification-denitrification can reach 50% and TIN removal rate can reach 60% after 3 months. The nitrogen removal rate and TIN removal rate of nitritation-ANAMMOX can achieve 90%, and the effluent can reach primary discharging standard A. Our study shows that shortcut nitrification system can be start-up under high DO successfully, and the online pH-DO control system play an important role in the stability of nitritation. Nitritation-ANAMMOX can realize autotrophic nitrogen removal.
-
Key words:
- online control /
- pH /
- DO /
- shortcut nitrification /
- ANAMMOX /
- autotrophic nitrogen removal
-
市政污泥是城市污水处理过程中不可避免的副产物,其含水率高、有机质含量高、成分复杂,并且含有大量的寄生虫卵、病原微生物和一定量的重金属[1]。近年来,市政污泥的产量也在不断增加,预计2025年我国污泥年产量将突破9×107 t,污泥处理处置已成为一项亟待解决的难题[2]。污泥的主要处置方式包括卫生填埋、农业利用、干化焚烧、建筑材料利用等,我国较大部分污泥采用填埋方式,约占我国污泥总处置量的65%[3]。
由于我国早期污水处理厂存在着“重水轻泥”的现象,导致已填埋污泥的含水率过高,力学性质较差。而填埋场的库容有限,随着污泥产量的逐年增加,目前国内许多城市的填埋场,例如上海老港、成都长安、深圳下坪、杭州天子岭的填埋场的库容已经严重不足[4-5],为此,许多填埋场要求将填埋污泥的含水率从80%降低至60%以下,这样可以增加至少50%的填埋库容[6]。但是,由于污泥有机质含量高、结合水含量高、亲水性强,单一的机械处理很难将污泥含水率降低至60%以下,需结合一定的预处理方法将污泥的胞外聚合物(EPS)破解,释放出自由水后再进行脱水减量处理[7]。当前填埋污泥的深度脱水通常采用“化学调理+板框压滤”的方法[8],该方法需将污泥从填埋库中挖出,运输到指定场地后再进行处理,存在着成本高、易对环境造成二次污染的问题,因此,需寻找一种高效、环保的污泥原位处理方法。
真空预压法具有施工工艺简单、成本低等优点,是软土地基原位处理的一种有效方法[9-11]。近年来,将化学预调理与真空预压相结合的工艺已逐渐被应用于填埋污泥原位处理[3,8,12-16],该工艺在一定程度上能够实现污泥的原位减量,但是仍存在易产生臭气污染、难以保证药剂调理均匀等问题。为了寻找更加环保高效的填埋污泥原位处理方法,有研究者提出了冻融联合真空预压填埋污泥原位处理技术[17-18]。冻融的原理是污泥被冷冻时,冷冻过程中不断生长的冰晶会破坏污泥细胞膜的完整性,使细胞脱水、收缩或溶解,使胞外聚合物释放到上清液中[19];同时,冻融后污泥中小颗粒团聚成大颗粒,能显著提高污泥的脱水性能,而且冻融循环可显著提高污泥的渗透系数[20-21]。
有研究表明,采用冻融联合真空预压法处理填埋污泥时,在出水量、出水速率、沉降量、减量比、含水率均优于药剂预调理方法[18],但其在实验过程中并没有使用实际真空预压过程中的塑料排水板;塑料排水板作为真空预压的负压传递通道和排水通道,其性能对真空固结效率和效果有着显著影响[22]。根据芯板与滤膜的复合方式不同,目前工程界常采用分离式和整体式2种塑料排水板,在普通土体真空预压中,已有这2种排水板类型的对比研究[10, 23-24]。但是,污泥作为一种胶体状生物固体,其工程性质显著不同于软土和吹填土,但目前鲜有考察不同排水板类型对填埋污泥真空固结效果的研究。
本研究开展了不同排水板类型填埋污泥冻融-真空对比研究。首先,对填埋污泥进行冻融预处理;随后进行室内真空预压模型实验,分别设置分离式排水板(SPVD)与整体式排水板(IPVD)对照组;最后,通过对比出水量、减量比、含水率等数据,探究该法处理填埋污泥的宏观效果,并且通过压汞、电镜扫描等微观实验,探究冻融后污泥在真空预压过程中微观结构变化特性。
1. 实验方案
1.1 实验污泥
供试污泥取自上海市某污泥填埋库区,污泥填埋龄期约为12 a,占用了大量土地和地下空间,亟需对填埋库中的污泥进行原位脱水减量处理。填埋污泥的基本物理性质如表1所示。可以看出,填埋污泥含水率高,有机质含量比新鲜污泥(60%左右)有所降低。这是因为,填埋污泥受填埋龄期及厌氧消化影响,发生了一定程度的降解。填埋污泥的液塑限较大,按照细粒土的分类应为高液限有机质粉土。
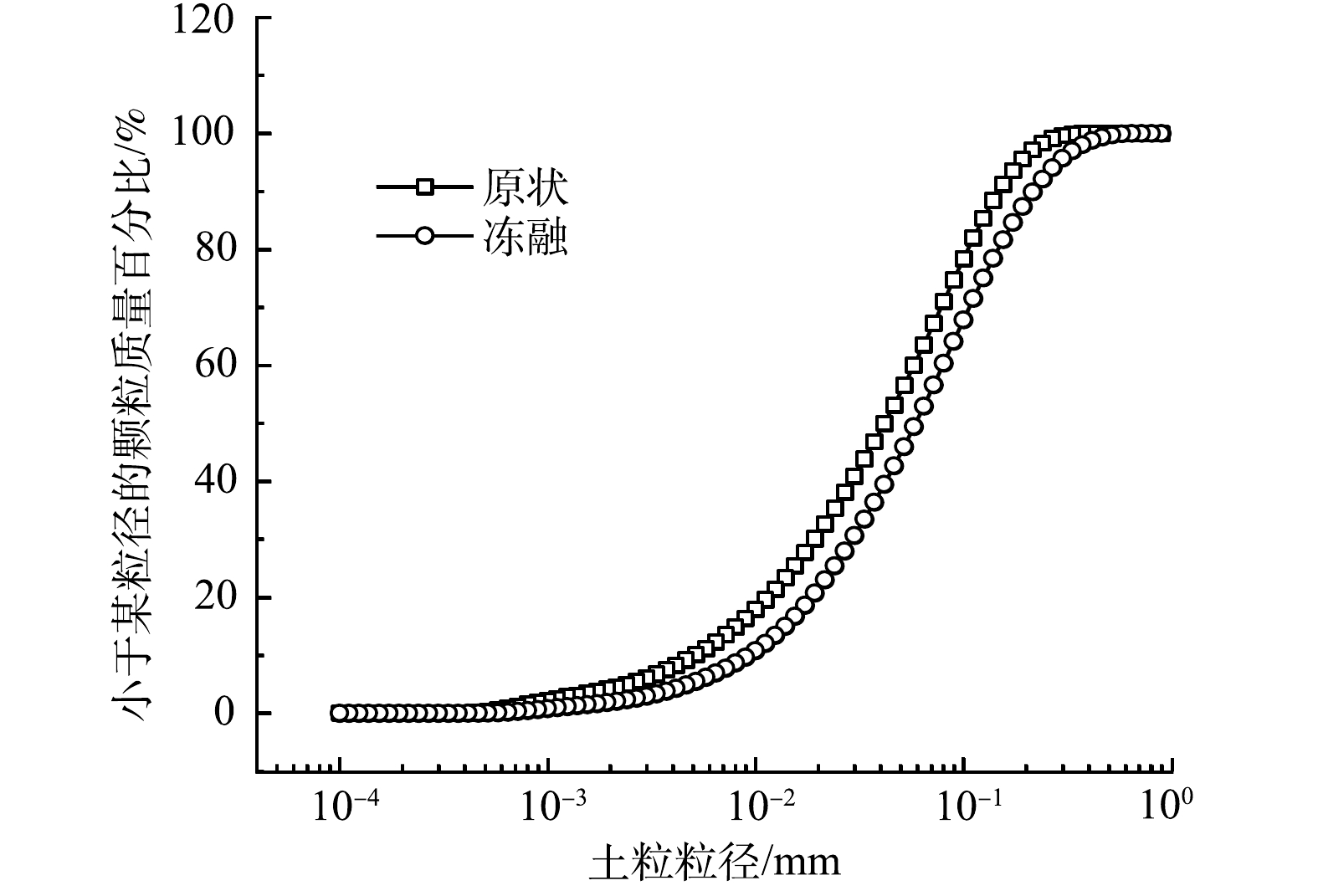
表 1 污泥基本物理指标Table 1. Basic physical indexes of sludge比重 含水率/% 密度/(g·cm−3) 有机质/% 液限/% 塑限/% 1.8 86 1.13 40 184 111 采用Mastersize2000激光粒度仪对原状填埋污泥及冻融后污泥进行了粒度分布测试,粒径分布曲线如图1所示。原状污泥d90为169.5 μm、d50为47.28 μm,而冻融后污泥d90为241.6 μm、d50为65.68 μm,经冻融后,污泥颗粒粒径显著增大。这主要是因为:在冻结过程中,污泥中的小颗粒被不断生长的冰晶推挤压密,污泥小颗粒团聚为大颗粒,显著提高了其脱水沉降能力。
1.2 真空预压模型实验
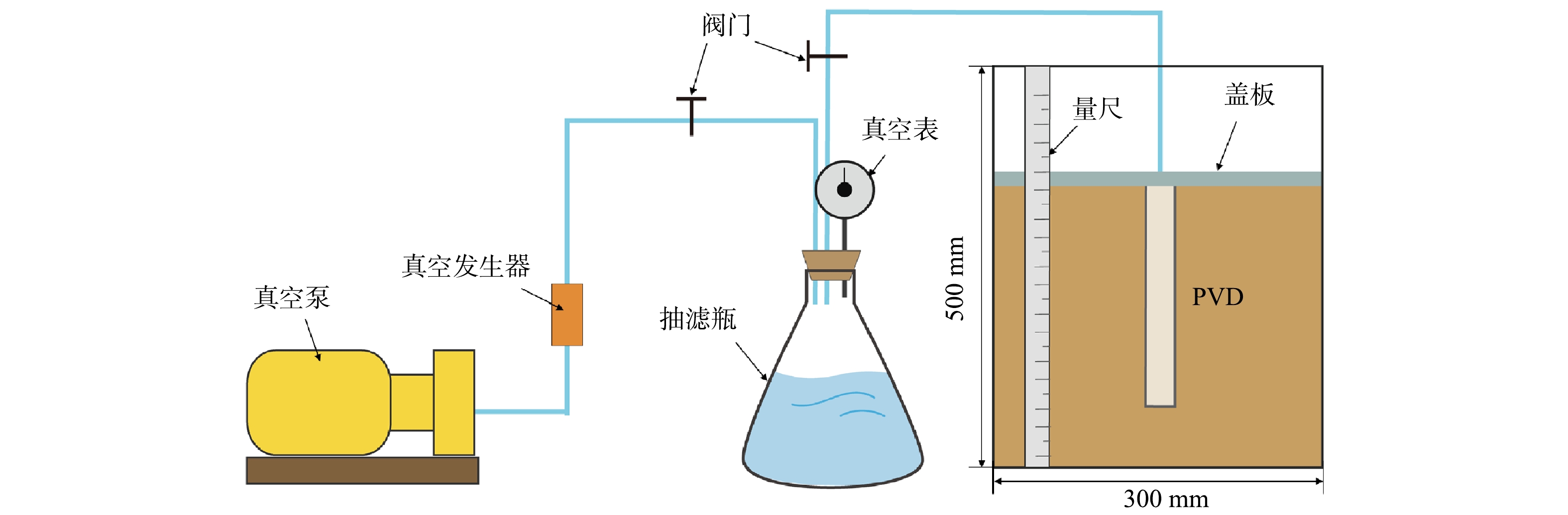
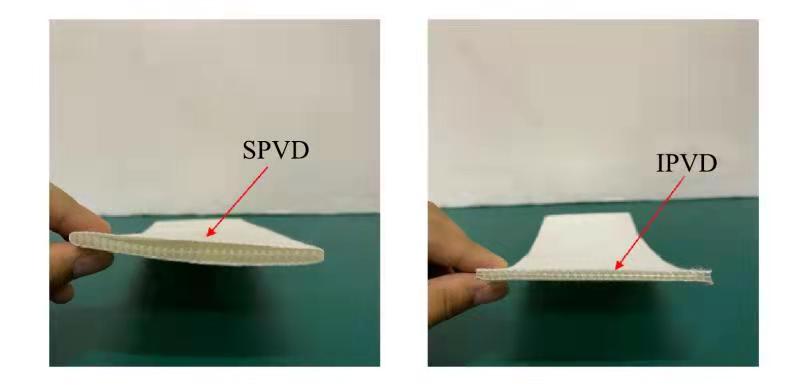
真空预压实验装置由真空泵、抽滤瓶、排水板和模型箱组成,具体如图2所示。模型箱由有机玻璃桶及密封盖组成,玻璃桶高500 mm、外径320 mm、内径300 mm,密封盖为20 mm厚的有机玻璃盖板。分别采用如图3所示的分离式排水板和整体式排水板,排水板通过土工布与排水管绑扎。分离式排水板属于分体式十字型塑料排水板,排水板滤膜包裹在塑料芯板的外侧,与芯板不黏接,滤膜被制作成略大于芯板尺寸的土工织布常套包裹于芯板四周,滤膜等效孔径为75 μm;整体式排水板芯板与滤膜通过热合紧贴在一起,两者间不可作相对移动,滤膜等效孔径为120 μm。
采用冰柜对污泥进行冻融处理,冻结温度设置为−15 ℃,待达到冻结温度后将污泥取出于室温(22 ℃)融化。每个模型箱污泥用量为约16 kg。整个实验期间真空度保持在85 kPa左右,实验过程中对累计出水量、累计沉降量以及真空度进行监测记录,实验完成后对模型箱内污泥取样测定含水率及取样进行压汞、电镜扫描微观测试。
2. 实验结果及分析
2.1 累积出水量
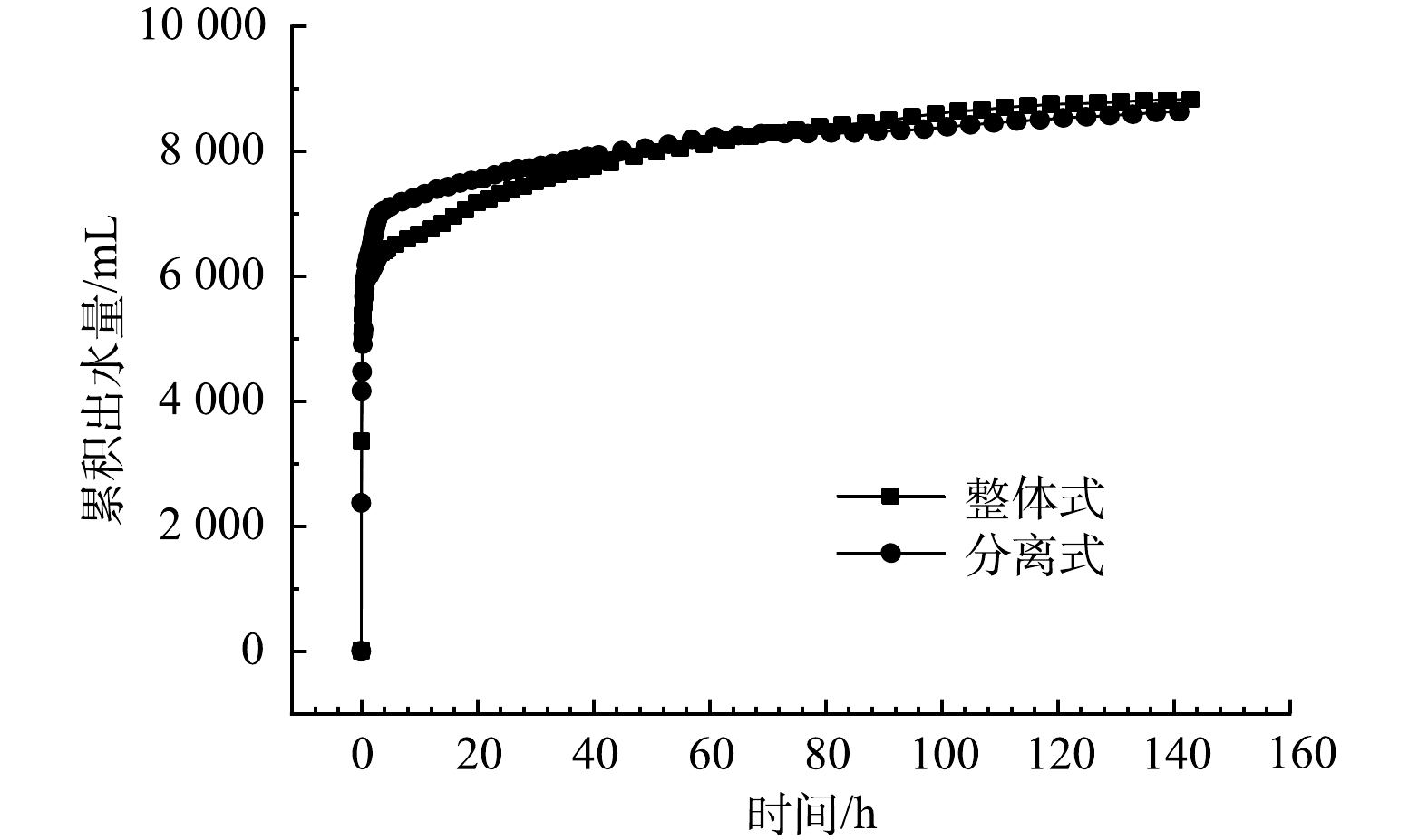
由累计出水量变化曲线(图4)可以看出,分离式排水板和整体式排水板两者最终出水量差别不大。整体式排水板的最终出水量为8 830 mL,而分离式排水板的最终出水量为8640 mL,二者仅相差190 mL。在实验初期,分离式排水板与整体式排水板的出水速率都很高,在前4 h的出水量可达总出水量的70%以上。这可能是因为污泥经冻融后,污泥细胞内外不断生长的冰晶使得污泥细胞破裂,导致污泥细胞膜的完整性被破坏,EPS被破解,从而释放细胞内外的物质,导致污泥絮体结构被破坏,释放出大量的结合水和间隙水,进而大幅提高了污泥的脱水性能[19]。冻融后污泥中含有大量的自由水,这导致前期出水速率及出水量都很高。
在前4 h,分离式排水板的累计出水量达7 050 mL,占总出水量的81.5%,而后出水速率突然变缓,后139 h的出水量仅为1 590 mL;而整体式排水板在前4 h累计出水量为6 410 mL,后139 h的出水量为2 420 mL。造成后期出水量差异的可能原因为,分离式排水板的等效滤膜孔径为75 μm,而整体式排水板的滤膜孔径为120 μm,在真空排水固结前期,渗流通道尚未形成,污泥颗粒在真空负压及孔隙水压力的作用下不断向排水板附近运移,由于分离式排水板等效滤膜孔径过小,部分细小颗粒未能穿过滤膜,从而影响排水板附近的渗流通道的通畅性,造成一定的淤堵。这也与已有研究[10, 25]的结果一致。但由于冻融后污泥颗粒粒径增大,小颗粒含量少,只造成部分淤堵,大部分排水通道仍保持通畅,所以二者最终出水量差异不大。
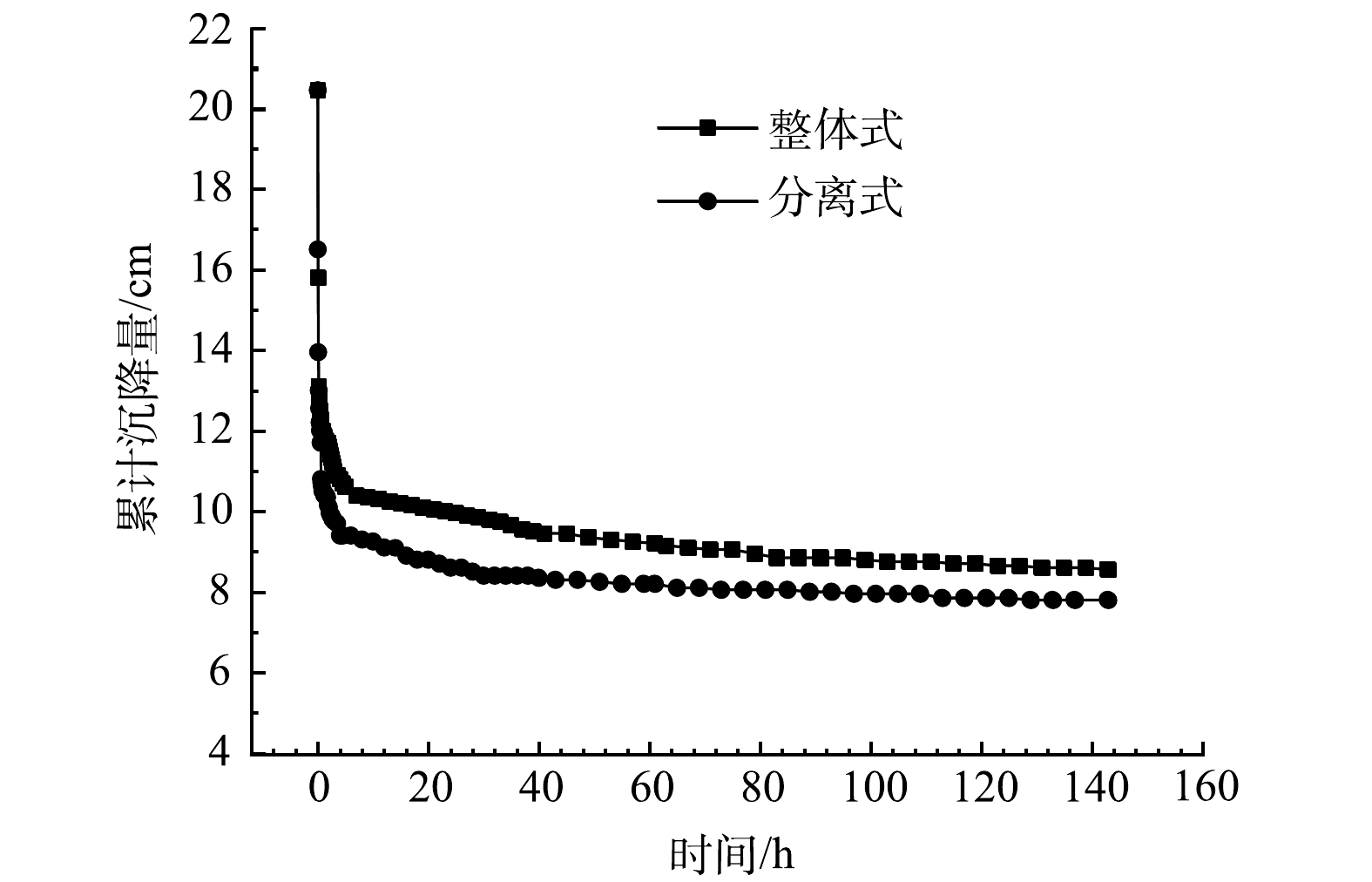
2.2 累计沉降量与减量比
由累计沉降量变化曲线(图5)可以看出,冻融污泥原始高度为20.5 cm,分离式排水板的最终高度为7.8 cm,整体式排水板的最终高度为8.55 cm,二者均下降50%以上。污泥在冻融时,污泥颗粒被不断生长的冰晶推挤压密,污泥小颗粒得以团聚为大颗粒,并显著提高了大中孔隙的分布,在真空预压固结时显著提高了其渗透固结性,从而提高了污泥的固结度。与分离式排水板相比,整体式排水板的高度变化却相对较小。这可能是因为:本次实验高度测量仅取实验模型箱两侧高度变化平均值记录,而取样后发现,整体式排水板处理后污泥在侧壁附近发生了1 cm左右的径向收缩,若考虑径向收缩的变化来计算实验后污泥体积,则分离式排水板污泥的最终体积为5 510 cm3,而整体式排水板最终体积为5 262 cm3,相比分离式排水板体积变化更大,这也与累计出水量变化规律相互印证。而整体式排水板最终出现了径向收缩现象,径向收缩是因为在真空排水固结过程中,在排水板远端的土颗粒在水力梯度的作用下不断向排水板中心处运移[26]。这也说明采用整体式排水板后冻融污泥整体的排水固结效果较好,整体渗流通道顺畅,真空负压影响范围可覆盖到远端土体,污泥整体固结度较好。
经计算,两种不同类型排水板的最终减量比均在60%以上,整体式排水板的减量比为63.6%,分离式排水板的减量比为61.9%。这表明整体式排水板减量比略优于分离式排水板,冻融联合真空预压法可有效实现填埋污泥的原位减量。
2.3 含水率
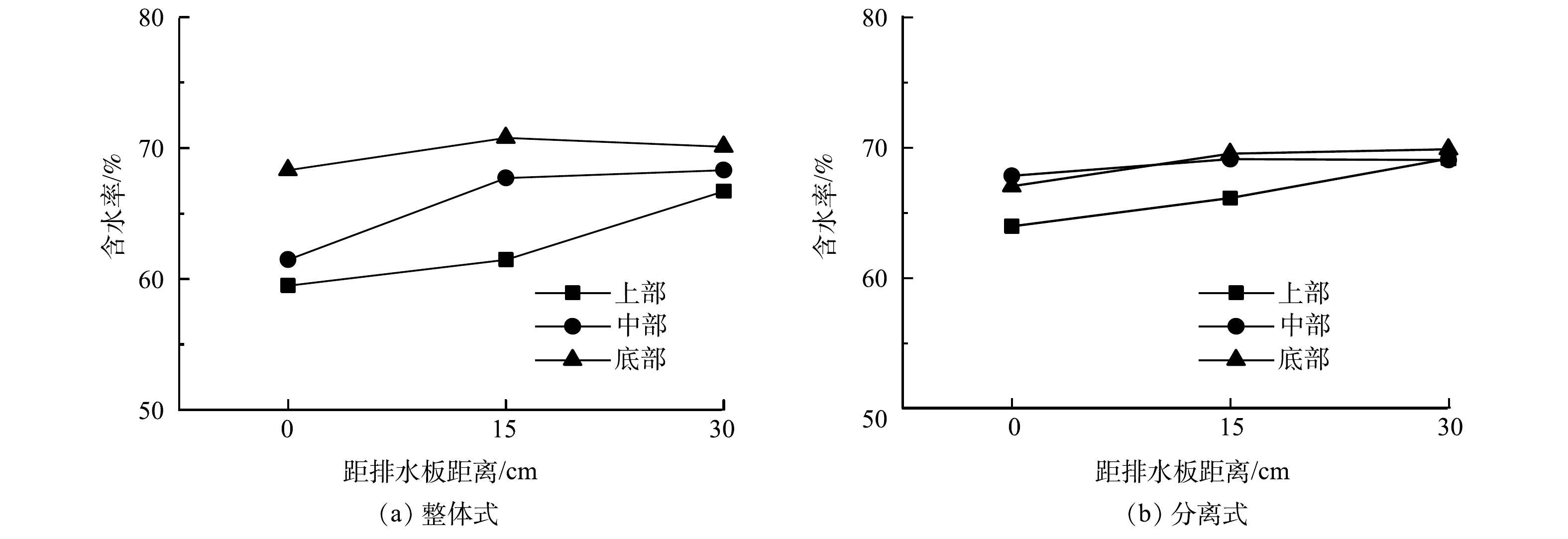
实验结束后,从排水板中心处开始,沿径向在0、15、30 cm处取污泥上、中、下3个位置,每个位置取3个样对照,测定不同位置处的含水率,结果如图6所示。
1) 原始污泥含水率为86%,经冻融联合真空预压处理后,其含水率大幅度下降,含水率最低可降至59.5%。
2) 沿半径方向污泥整体含水率分布呈现出逐渐增加的变化规律。径向上的差异主要是由于:离开排水板中心的距离和水力梯度的差异,排水板附近水力梯度大,水更容易渗流排出,而距离排水板较远处水力梯度小,水不易排出,所以靠近排水板中心处含水率更低。
3) 沿深度方向呈现出上部含水率低、底部含水率高的分布规律。这是因为:真空负压强度沿着排水板衰减,排水板周围土体水力梯度逐渐减小,对排水板的影响范围逐渐减小,影响范围沿着排水板呈现出倒锥形逐渐减小的趋势[24],这导致上部由于真空负压强度高,水力梯度大,水容易排出,而底部由于真空强度衰减,水力梯度减小,故形成底部含水率高、上部含水率低的分布规律。
4) 整体式排水板上部含水率在60%左右分布,中部在65%左右分布,底部在70%左右分布;而分离式排水板的上、中、下部均在65%~70%左右分布。可见,整体式排水板的整体处理效果更好,且靠近上、中部含水率明显优于分离式排水板。这可能是因为:一方面,分离式排水板滤膜孔径较小,易造成小颗粒淤堵,从而影响排水固结效果;另一方面,由于分离式排水板芯板是内包于滤膜的,在土体压力下不可避免地出现滤膜“陷入”排水通道的情况,从而减少排水面积,而整体式排水板滤膜是胶结于芯板竖齿上的,滤膜始终是“紧绷”状态,在土体压力下变形较小[27],从而造成含水率分布的差异。
2.4 压汞实验
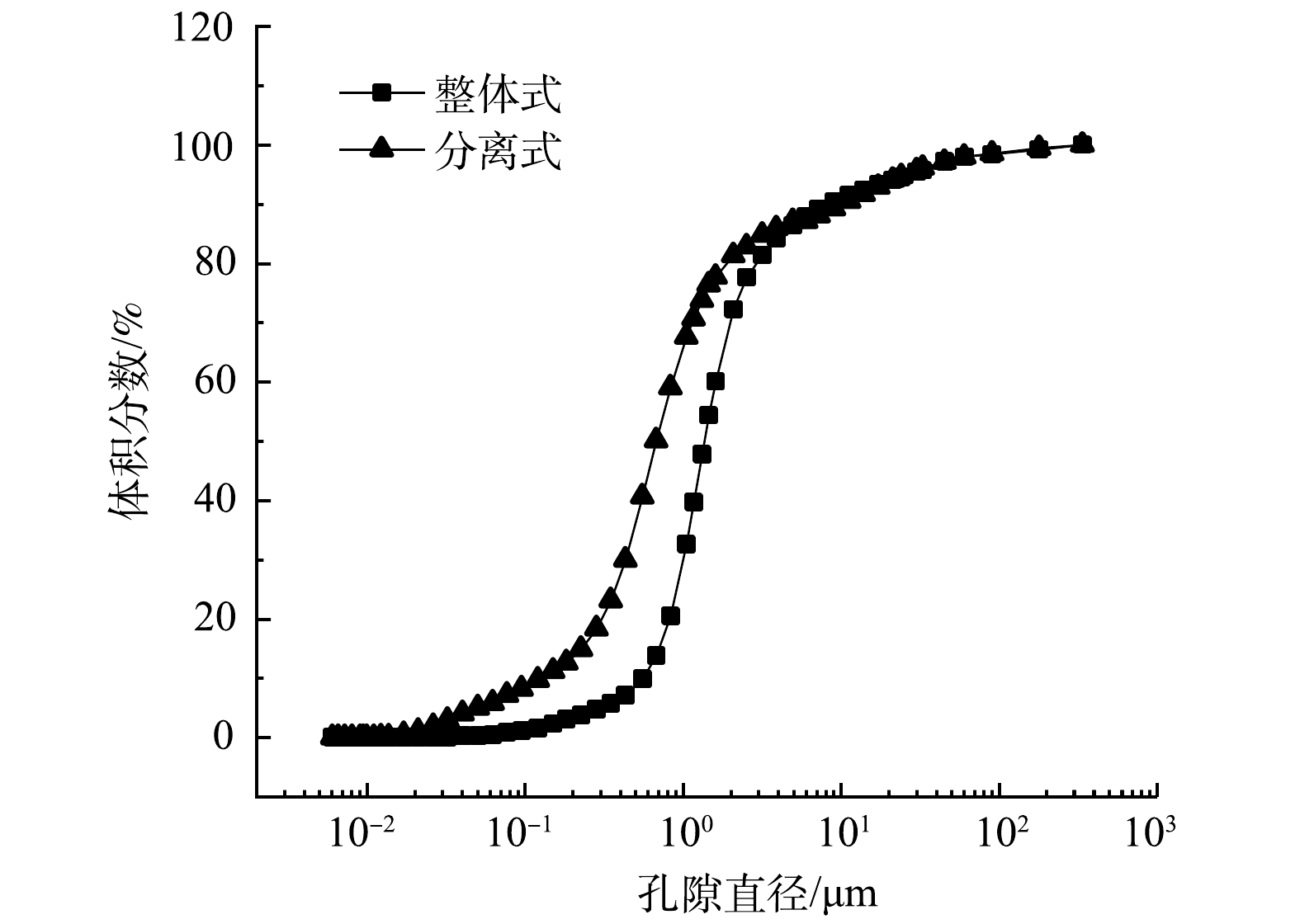
实验结束后,分别在整体式排水板、分离式排水板模型箱中心位置处取样进行压汞(MIP)实验,分析不同冻结条件下冻融污泥径向真空排水的固结孔径的大小分布规律,结果如图7、图8所示。
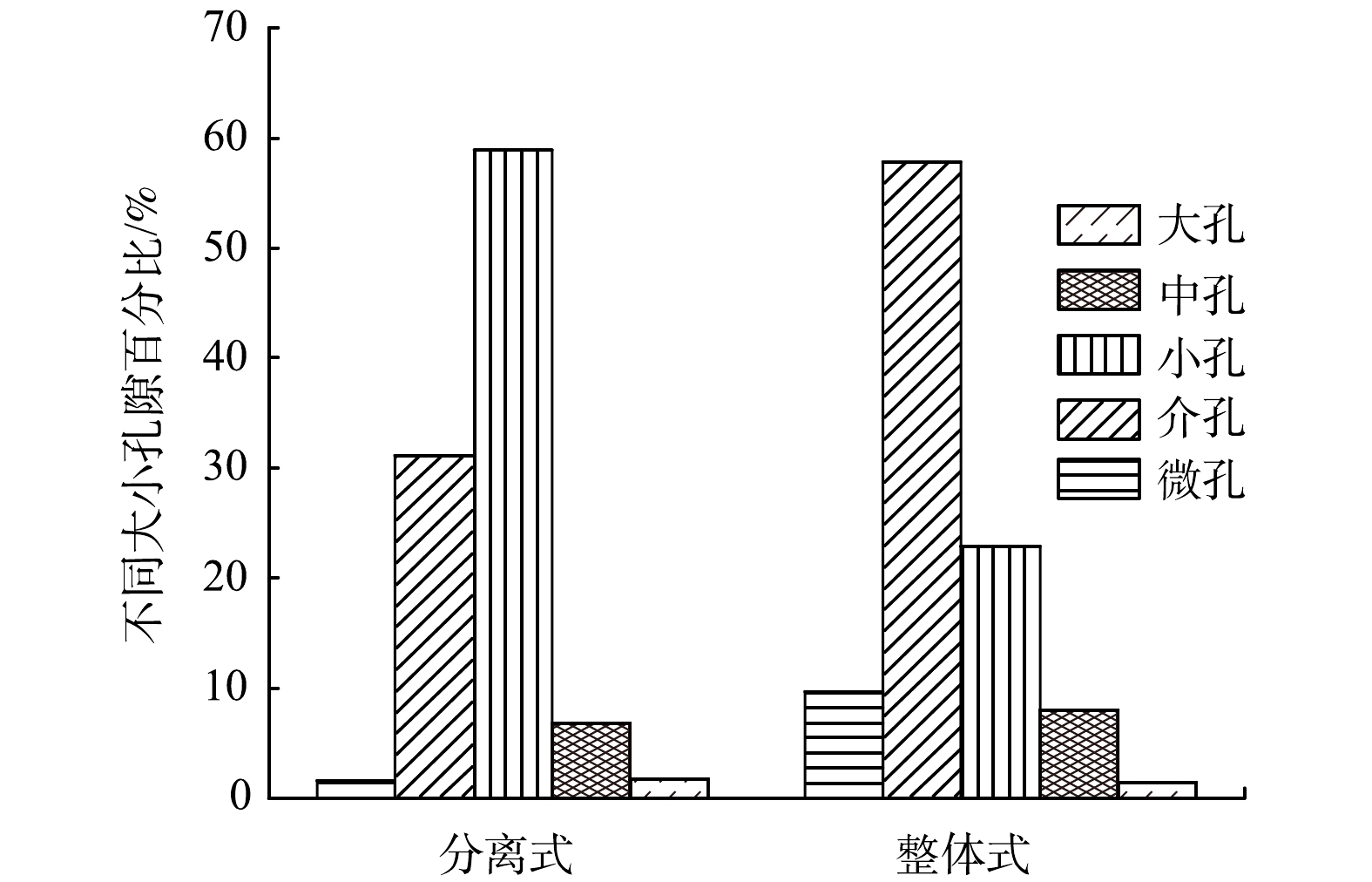
整体式排水板与分离式排水板孔径分布有明显差异:分离式排水板主要以小孔分布为主,即以团粒内孔隙分布为主;而整体式排水板主要以微孔和介孔分布为主,即以颗粒间孔隙为主。其原因是,在真空预压过程中,真空度不断向污泥深度处传递,并以排水板为中心的径向上形成真空负压梯度,在该真空负压梯度的作用下形成真空渗流场[28]。排板周围土体首先开始渗流出水,孔隙水在负压的作用下不断向排水板方向渗流,而此时污泥中的细小颗粒也在渗流力的作用下不断向排水板中心运移,使得排水板附近土体渗透系数不断降低,使排水板中心处的土体首先发生径向固结,土体发生压缩。
污泥经冻融后,污泥大中孔隙数量分布大幅度提高,小、微孔隙数量减少;而在真空排水固结时,较大孔隙先被压缩成较小孔隙,较小孔隙后被压缩[29]。整体式排水板由于不易淤堵,在真空排水固结时渗流通道顺畅,固结程度高,大、中孔隙先不断被压缩为小孔隙,而后小孔隙被压缩为更小的介孔;而分离式排水板由于发生了部分淤堵,从而导致排水板中心处污泥固结程度对比整体式排水板低,主要以大、中孔隙压缩为小孔为主。这也与含水率分布规律互相印证,即整体式排水板由于固结程度高,在贴近排水板处污泥含水率低于分离式排水板。
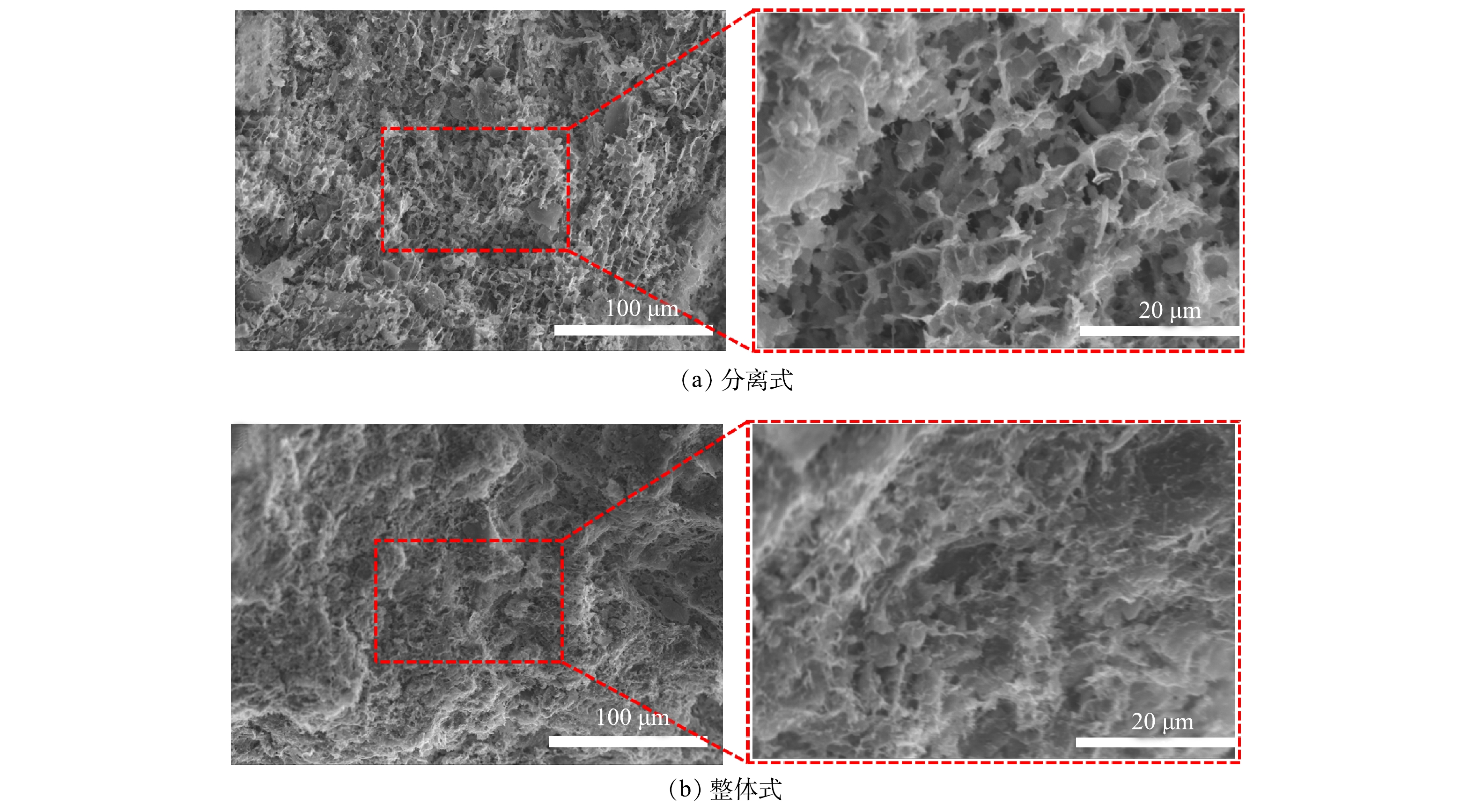
2.5 电镜扫描
实验完成后,对不同排水板径向真空排水固结后靠近排水管中心处的污泥取微观样进行电镜扫描实验(SEM),观察其微观结构特性,如图9所示。可以看出,整体式排水板与分离式排水板真空排水固结后污泥整体结构致密均匀,呈现出有规律的网状结构。但整体式排水板对比分离式排水板结构更加致密,固结程度高,以颗粒间孔隙分布为主;而分离式排水板固结程度低,孔径相对更大,以团粒内孔隙为主。这也与MIP实验结果相印证。
3. 结论
1)分离式排水板和整体式排水板两者的最终出水量差别不大。两种不同类型排水板的最终减量比均在60%以上,整体式排水板的减量比为63.6%,分离式排水板的减量比为61.9%,整体式排水板减量比略优于分离式排水板。
2)原始污泥含水率为86%,经冻融联合真空预压处理后,其含水率大幅度下降,含水率最低可降至59.5%,符合我国填埋污泥的规范要求;其中,整体式排水板的整体处理效果更好。沿半径方向,污泥整体含水率分布呈现出逐渐增加的变化规律;沿深度方向,呈现出上部含水率低,底部含水率高的分布规律。
3)整体式排水板与分离式排水板孔径分布具有明显差异。分离式排水板主要以小孔分布为主,即以团粒内孔隙分布为主;而整体式排水板主要以微孔和介孔分布为主,即以颗粒间孔隙为主。整体式排水板对比分离式排水板结构更加致密,固结程度高,以颗粒间孔隙分布为主;而分离式排水板固结程度低,孔径相对更大,以团粒内孔隙为主。
-
[1] TURK O, MAVINIC D S. Maintaining nitrite build-up in a system acclimated to free ammonia[J]. Water Research, 1989, 23(11):1383-1388 [2] FDZ F. Nitrite accumulation in submerged biofilters:Combined effects[J]. Water Science & Technology, 1996, 34(3/4):371-378 [3] HELLINGA C, SCHELLEN A A J C, MULDER J W, et al. The SHARON process:An innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonium-rich wastewater[J]. Water Science & Technology, 1998, 37(9):135-142 [4] YOO H, AHN K H, LEE H J, et al. Nitrogen removal from synthetic wastewater by simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) via nitrite in an intermittently-aerated reactor[J]. Water Research, 1999, 33(1):145-154 [5] RUIZ G, JEISON D, CHAMY R. Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(6):1371-1377 [6] THAMDRUP B, DALSGAARD T. Production of N2 through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction in marine sediments[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(3):1312-1318 [7] PICIOREANU C, LOOSDRECHT C M V M, HEIJNEN J J. Modelling the effect of oxygen concentration on nitrite accumulation in a biofilm airlift suspension reactor[J]. Water Science & Technology, 1997, 36(1):147-156 [8] RATHNAYAKE R M L D, OSHIKI M, ISHⅡ S, et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen and pH on nitrous oxide production rates in autotrophic partial nitrification granules[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 197:15-22 [9] LAW Y, LANT P, YUAN Z. The confounding effect of nitrite on N2O production by an enriched ammonia-oxidising culture.[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(13):7186-7194 [10] TIAN W D, KYOUNG J A, MA C, et al. Partial nitritation for subsequent Anammox to treat high-ammonium leachate[J]. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34(8):1063-1068 [11] ISAKA K, KIMURA Y, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Complete autotrophic denitrification in a single reactor using nitritation and anammox gel carriers[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 147(8):96-101 [12] JIN R C, XING B S, NI W M. Optimization of partial nitritation in a continuous flow internal loop airlift reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 147(11):516-524 [13] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版.北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2002 [14] 高大文, 彭永臻, 郑庆柱. SBR工艺中短程硝化反硝化的过程控制[J]. 中国给水排水, 2002, 18(11):13-18 [15] 周丹丹, 马放, 董双石,等. 溶解氧和有机碳源对同步硝化反硝化的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2007, 1(4):25-28 [16] REGMI P, MILLER M W, HOLGATE B, et al. Control of aeration, aerobic SRT and COD input for mainstream nitritation/denitritation[J]. Water Research, 2014, 57(5):162-171 [17] 张立成, 党维, 徐浩,等. SBR快速实现短程硝化及影响因素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(5):2272-2276 [18] TANG X, YANG Q, LI J, et al. Semi-nitritation process producing optimum influent for anammox process in treatment of domestic wastewater[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 152:55-61 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 付文娟,汪启源,朱英卓,高仕,赖幼纯,李绪锐,陈韵琪,袁景欣,李红梅,李月婷,王庆. 间型脉孢菌JY-05211固态发酵玉米秸秆条件优化. 嘉应学院学报. 2024(06): 30-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2778
- HTML全文浏览数: 2274
- PDF下载数: 530
- 施引文献: 3





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: