5种水生植物的脱氮除磷效果及其对水体胞外酶活的影响
Efficiency of removing nitrogen and phosphorous and effects on extracellular enzyme activity in water body by five hydrophytes
-
摘要: 利用静态小区实验研究了菱角(Trapa quadrispinosa Roxb.)、凤眼莲(Eichhornia crassipes.)、水鳖(Hydrocharis dubia(Bl.)Backer)、空心菜(Ipomoea aquatica Forsk)和青萍(Lemna minor L.)5种不同植物对富营养水体的净化效果及对水体胞外酶活性的影响。研究结果表明,5种植物对水体总氮(TN)的去除率依次为凤眼莲(81.6%) > 空心菜(72.2%) > 水鳖(68.4%) > 菱角(65.8%) > 青萍(60.2%),对总磷(TP)的去除率为凤眼莲(95.0%) > 空心菜(89.7%) > 水鳖(78.4%) > 菱角(77.3%) > 青萍(70.5%);5种植物的种植均能大幅提高水体胞外酶活性,其中凤眼莲处理的效果最好,其脲酶活性(UA)峰值和极差值分别为19.70和10.33 μg·mL-1,碱性磷酸酶活性(APA)峰值和极差值分别为8.12和5.95 μg·mL-1,空心菜处理次之;各处理水体脲酶活性和碱性磷酸酶活性分别与水体氨态氮(NH4+-N)和溶解性活性磷(SRP)浓度均存在显著的负相关关系,其相关系数r分别在-0.853~-0.992和-0.813~-0.994之间。综合可知,凤眼莲和空心菜较菱角、水鳖和青萍修复能力更强,可更好的修复富营养水体。Abstract: To investigate the role of hydrophytes in the purification of eutrophic water bodies,Trapa quadrispinosa Roxb.,Eichhornia crassipes,Hydrocharis dubia (Bl.) Backer,Ipomoea aquatica Forsk, and Lemna minor L.were planted in treated water to compare their effects on purification and their influence on extracellular enzyme activity.The results showed that all hydrophytes performed well during the purification process.For total nitrogen (TN),the order of removal efficiency was Eichhornia crassipes (81.6%) > Ipomoea aquatica Forsk (72.2%) > Hydrocharis dubia (Bl.) Backer (68.4%) > Trapa quadrispinosa Roxb.(65.8%) > Lemna minor L.(60.2%),and for total phosphorous (TP) removal,the order was Eichhornia crassipes (95.0%) > Ipomoea aquatica Forsk (89.7%) > Hydrocharis dubia (Bl.) Backer (78.4%) > Trapa quadrispinosa Roxb.(77.3%) > Lemna minor L.(70.5%).All five hydrophytes could enhance the activity of extracellular enzymes,and the treatment involving E.crassipes showed the maximum range and peak urease activity (UA) and alkaline phosphatase activity (APA).The range and peak UA were 19.70 μg·mL-1 and 10.33 μg·mL-1,respectively,and for APA,they were 8.12 μg·mL-1 and 5.95 μg·mL-1.The range and peak UA and APA for Ipomoea aquatica Forsk were the next highest.UA and APA were significantly negatively correlated with the concentrations of both NH4-N and dissolved active phosphorus (SRP),and the correlations were between -0.853 and -0.992 and -0.813 and -0.994,respectively.Eichhornia crassipes and Ipomoea aquatica Forsk may work better than Trapa quadrispinosa Roxb,Hydrocharis dubia (Bl.) Backer and Lemna minor L.,and have potential for application in the purification of eutrophic water bodies.
-
Key words:
- hydrophyte /
- removal of nitrogen and phosphorus /
- extracellular enzyme
-
锑(Sb)和砷(As)及其化合物因其强生物毒性和潜在的致癌性而受到广泛关注和重视,许多国家与组织已将他们列为优先控制污染物,并对其在饮用水中的浓度进行了限定。世界卫生组织规定饮用水中锑、砷的最大质量浓度分别为0.01 mg∙L−1和0.02 mg∙L−1[1]。此外,由于锑和砷的地球化学行为和理化性质的相似性[2],加之目前许多地区对工业废水进行集中化处理[3],导致了废水水体中他们的共存。例如,国内湖南锡矿山和广西大厂等矿山附近水体以及贵州省独山县某厂的冶炼废水中均同时检测到了较高浓度的Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ),尤其是锡矿山周围水体中锑和砷的质量浓度可达10.09 mg∙L−1和1.62 mg∙L−1[4-6]。而当Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)共存时,不仅会对生态环境造成更大的威胁,对其处理也提出更高要求。由此,选择一种合适的工艺处理复合重金属废水对实际废水治理具有重要实际意义。
在众多处理工艺中,吸附法因操作简单、效率高、经济适用等优势被广泛采用。开发高性能吸附剂成为当前的研究热点。目前,众多吸附剂被开发用于处理Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)废水,包括铁氧(氢氧)化物、活性氧化铝、沸石、阴离子粘土矿物[7]等。其中,水滑石(layered double hydroxides, LDHs)作为一种新型环境功能材料,因其比表面积大、阴离子交换容量大、热稳定性好等优点被广泛应用于去除Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)等离子污染物[8]。李杨等[9]研究表明,MgAl LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)的最大吸附量可达50.52 mg∙g−1;ARDAU等[10]研究表明,ZnAl LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)的最大离子交换容量为30.3 mg∙g−1。郭亚祺等[11]研究表明,煅烧水滑石在共存氟砷的水体中对砷的最大吸附量为51.02 mg∙g−1;VIOLANTE等[12]通过共沉淀法制备的LDHs对AsO4的吸附量为52.58 mg∙g−1。然而,LDHs材料对2种污染物的去除效果仍然有限,且鲜有关于二者共存体系的去除研究。
LDHs具有高度可变的矿物结构,LDHs板层结构类似水镁石Mg(OH)2的正八面体,可以看作是Mg2+离子通过类质同象作用部分地被M3+离子取代。为了中和M3+/Mg2+的正电荷,需要更多的阴离子达到电荷平衡。因此,其层间阴离子具有可交换性,为含有功能基团的有机分子插入层间来改性LDHs增强其吸附性能提供了可行性[13-14]。氨基酸是蛋白质的基本组成单元,通常以兼性离子的形式存在于水溶液中。在碱性环境中,其可以电离成阴离子,呈现出负电性,通过与LDHs主层板间的静电吸引、氢键等作用插入LDHs层间[15]。使用氨基酸作为客体阴离子改性LDHs时,其中所含的氮、氧等官能团均对Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)这类重金属离子有着较强的络合作用。此外,氨基酸属于环境友好的生物大分子,对环境没有任何危害。因此,利用氨基酸改性来提升LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)去除性能的潜力巨大[16]。在众多氨基酸中,甲硫氨酸(Methionine, Met)作为功能基团丰富的代表已经被用于改性环境材料以提升污染物的去除性能。例如,甲硫氨酸改性的蒙脱石和纤维素对Pb2+和氨基黑10B的吸附量分别提高了16.5%和400%[17-18]。基于此,本研究选择甲硫氨酸作为模型分子,采用共沉淀法合成了改性水滑石(Met/LDHs),通过XRD、FTIR、XPS等多种分析测试手段对合成产物的物相组成、表面官能团等进行了表征和分析;采用静态批处理法考察了Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附能力,且探究了其对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附机制,以期为废水去除含锑、砷治理技术提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验试剂及仪器
主要试剂有六水合硝酸镁(Mg(NO3)2∙6H2O)、九水合硝酸铁(Fe(NO3)3∙9H2O)、焦锑酸钾(KSbO6H6)、砷酸钠(Na3AsO4)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、硝酸(HNO3)、无水乙醇(C2H6O)和甲硫氨酸(C5H11O2NS),以上试剂均为分析纯级别;实验用水为去离子水,电阻率为18.25 MΩ∙cm−1。主要仪器有pH计(SevenMulti S40,美国 梅特勒-托利公司)、蠕动泵(BT100L,保定雷弗流体科技有限公司)、恒温摇床(TS-2102C,常州 恩培仪器制造有限公司)。
1.2 吸附剂制备
首先将0.02 mol Mg(NO3)2∙6H2O和0.01 mol Fe(NO3)3∙9H2O溶解于150 mL去离子水中,再与1 mol∙L−1 NaOH溶液同时通过蠕动泵滴入已含有150 mL去离子水的圆底烧瓶中,并于室温下保持匀速地搅拌,控制溶液pH在9.5~10,整个反应过程在N2保护下进行,再将所得悬浮液置于80 ℃晶化12 h,最后用去离子水和无水乙醇离心洗涤5次,干燥后研磨得到LDHs样品。称取0.02 mol甲硫氨酸搅拌溶解于150 mL的去离子水中,用NaOH调节pH至10置于圆底烧瓶中,其余步骤同上,制得甲硫氨酸改性的LDHs,记为Met/LDHs。
1.3 实验方法
采用静态批处理法开展吸附实验。典型步骤是称取0.01 g吸附剂加入到20 mL装有一定浓度的Sb(Ⅴ)或As(Ⅴ)溶液的锥形瓶中,再将其置入转速为150 r∙min−1、温度为25 ℃的恒温摇床中进行反应,待到指定时间后取出锥形瓶,并用0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤悬浮液,所得清液用ICP-AES进行浓度测试。分别考察吸附时间、吸附质的初始浓度、初始pH、共存体系以及解吸循环对吸附性能的影响。
1)接触时间。在Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)初始质量浓度分别为50 mg∙L−1、初始pH=5.0±0.1的条件下,研究了LDHs和Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附过程与接触时间的关系。
2)吸附质的初始浓度。在溶液初始pH=5.0±0.1,接触时间为12 h的条件下,研究LDHs和Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附等温线。
3)初始pH。设定初始pH在3~10,初始质量浓度为50 mg∙L−1,接触时间为12 h,考察了pH对Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)效果的影响。
4)共存体系。设定一种重金属离子的初始质量浓度为0~200 mg∙L−1,在其中投加0~50 mg∙L−1另一种重金属离子,并在初始pH为5.0±0.1,接触时间为12 h的条件下考察了在Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)共存体系中Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附性能。
5)解析循环。在Met/LDHs分别对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)吸附饱和后,选用0.1 mol∙L−1 NaOH为解吸剂,考察了Met/LDHs在吸附-解吸循环过程中对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的去除性能。
1.4 表征方法
采用X-射线衍射仪(Ultima IV,日本理学公司)分析产物的物相组成及晶体结构;使用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Spectrum One,美国铂金埃尔默公司)测定吸附剂的官能团;使用X射线光电子能谱仪(Thermo Escalab 250Xi,美国赛默飞世尔公司)测定样品表面的元素组成;使用Zeta电位分析仪(Zetasize Nano 250Xi,英国马尔文公司)测定样品表面电位;使用电感耦合等离子发射光谱仪(iCAP 6500,美国赛默飞世尔公司)测定吸附后Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的质量浓度。
1.5 数据处理方法
1)实验中Met/LDHs分别对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附量和去除率分别根据式(1)和式(2)计算。
qe=(Co−Ce)Vm (1) R=Co−CeCo×100% (2) 式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg∙g−1;Co和Ce分别为Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)溶液的起始浓度和平衡浓度,mg∙L−1;V为溶液体积,mL;m为吸附剂质量,mg;R为表示去除率,%。
2)为评估吸附系统的质量传递过程,采用拟一级动力学(式(3))和拟二级动力学模型(式(4))拟合实验结果。
ln(qe−qe)=lnqe−k1t (3) tqt=1k2q2e+1qtt (4) 式中:qe为平衡吸附容量,mg∙g−1;qt为t时刻吸附容量,mg∙g−1;k1为拟一级动力学吸附速率常数,h−1;k2为拟二级动力学吸附速率常数,g∙(mg∙h) -1;t为吸附时间,h。
3)并对吸附数据应用Langmuir等温线模型(式(5))和Freundlich等温线模型(式(6))进行拟合。
qe=qmKLCe1+KLCe (5) qe=KFC1ne (6) 式中:Ce为平衡浓度,mg∙L−1;qm为饱和吸附量,mg∙g−1;KL为Langmuir常数;n,KF为Freundlich常数。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 材料的表征
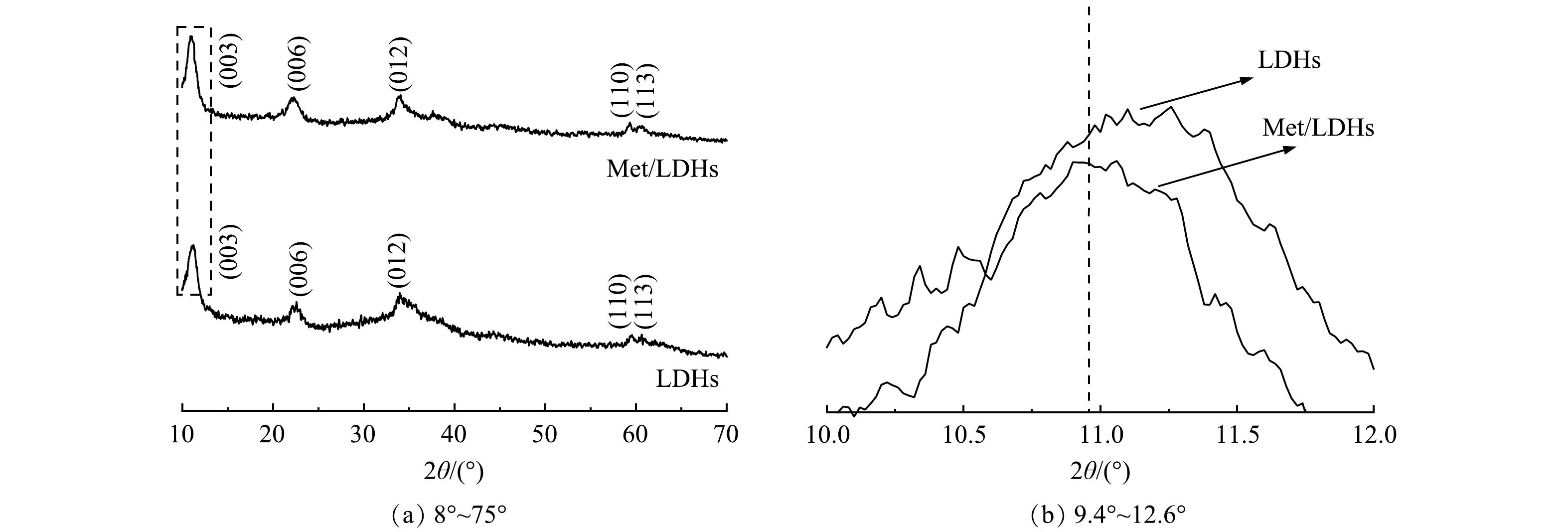
1) XRD分析。样品LDHs和Met/LDHs的XRD图谱如图1(a)所示。由图1(a)可知,2种材料的全部衍射峰均能与水滑石相对应,未见杂峰,并且基线平稳,说明实验制备得到了结晶度较好的纯相水滑石。与LDHs相比较而言,Met/LDHs的(003)晶面的向低衍射角度的方向偏移(图1(b)),表明其层间距发生变化。根据布拉格方程可以进一步地计算出甲硫氨酸分子改性后的水滑石(003)晶面对应的基底间距值(d003)由0.776 nm增大到0.801 nm,表明甲硫氨酸分子成功插入到LDHs层间,并与LDHs主层板平行排列[16, 19]。
2)FTIR和XPS分析。样品LDHs和Met/LDHs的FTIR光谱如图2(a)所示。可见,未改性镁铁水滑石在3 438 cm−1和1 632 cm−1附近的吸收峰对应于—OH的伸缩振动和弯曲振动;1 384 cm−1处的吸收峰归属于NO3−的伸缩振动,而在500~1 010 cm−1处出现的吸收峰则来源于LDHs层板中M—O、O—M—O和M—O—M的晶格振动(M指的是Mg或者Fe[20])。合成过程中加入甲硫氨酸分子后,样品在2 920 cm−1附近新增了对应—CH2的伸缩振动,在1 500 cm−1处新增了对应于—COO−的伸缩振动峰。而且,—OH对应吸收峰偏移至3 432 cm−1和1 624 cm−1,表明插入分子可能与水滑石发生氢键作用[21]。利用XPS技术对Met/LDHs进行了进一步分析如图2(b)所示。结果表明,Met/LDHs光谱中位于163.29 eV峰与C—S相对应,进一步表明材料中具有甲硫氨酸分子[22]。上述结果表明,在合成中引入甲硫氨酸分子可以丰富镁铁水滑石的功能基团。
2.2 吸附动力学分析
接触时间对LDHs和Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)性能影响见图3(a)~(b)。由图3(a)~(b)可见,2种材料对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附量随时间呈相同变化趋势,即在前2 h的吸附速率较快,之后则以较慢的速度进行,约在12 h时达到吸附平衡。在吸附初始阶段,快速的吸附速率可能是由于吸附剂表面存在大量的活性位点;而随着Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)不断占据这些活性位点,吸附质需进入吸附剂内部反应,需要克服更大的空间位阻,从而导致吸附速率的降低[1]。为了分析吸附机制,进一步对实验结果进行了吸附动力学模拟,结果见图3和表1。结果表明,LDHs和Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附数据使用拟二级动力学模型模拟的相关系数更高,这表明限制反应速率的主要步骤为化学吸附[23]。
表 1 吸附动力学参数Table 1. Adsorption kinetic parameters吸附剂 吸附质 拟一级动力学参数 拟二级动力学参数 qe k1 R2 qe k2 R2 LDHs Sb(V) 17.58 10.65 0.978 5 18.09 1.26 0.993 6 Met/LDHs Sb(V) 24.75 8.79 0.979 8 25.59 0.68 0.997 0 LDHs As(V) 35.36 6.58 0.991 0 36.37 0.35 0.995 9 Met/LDHs As(V) 39.17 6.63 0.967 9 40.46 0.30 0.989 5 2.3 吸附等温线分析
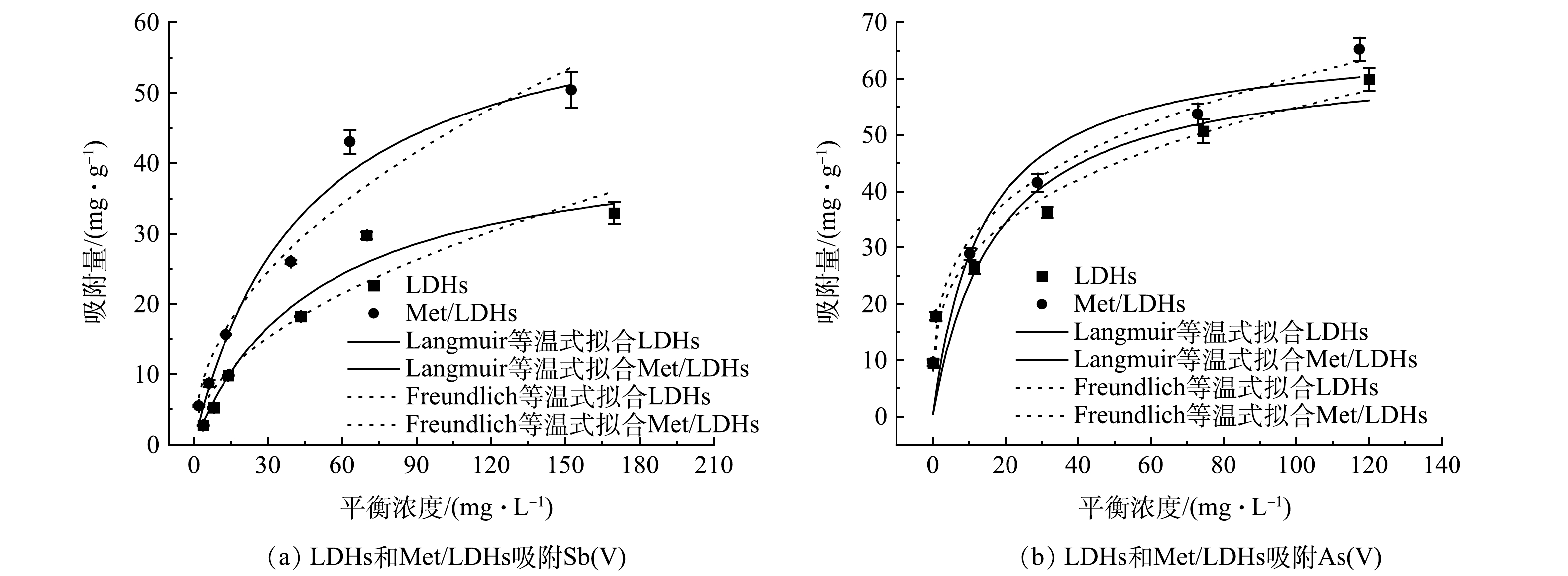
在不同起始浓度条件下的实验研究了LDHs和Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附等温式,并用Langmuir及Freundlich模型对实验数据进行了拟合,结果如图4和表2所示。结果表明,LDHs和Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附数据用Langmuir等温线模型拟合相关系数更高,表明改性前后的吸附剂对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附均为单分子层吸附;而对As(Ⅴ)的吸附行为更为适用Freundlich等温线模型描述,表明他们对As(Ⅴ)的去除可能是物理和化学吸附综合作用的结果。根据Langmuir等温线模型的拟合结果,甲硫氨酸改性后水滑石对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的最大吸附量分别由改性前的44.32 mg∙g−1和64.23 mg∙g−1提升至66.23 mg∙g−1和67.20 mg∙g−1,说明Met/LDHs具有更强的对污染物的去除能力。对比其他类型材料的吸附量可以发现,Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)的最大吸附量高于针铁矿(0.186 mg∙g−1)和高岭石(59 mg∙g−1),对As(Ⅴ)的最大吸附量高于纳米磁铁矿(13.2 mg∙g−1)和人造沸石(35.8 mg∙g−1)[24-25]。
表 2 吸附等温线参数Table 2. Adsorption isotherm parameters吸附剂 吸附质 Langmuir等温线参数 Freundlich等温线参数 qm KL R2 n KF R2 LDHs Sb(V) 44.32 0.020 0.964 0 2.01 2.80 0.895 3 Met/LDHs Sb(V) 66.23 0.022 0.962 4 2.08 4.78 0.936 2 LDHs As(V) 64.23 0.058 0.775 9 3.43 14.36 0.975 4 Met/LDHs As(V) 67.20 0.074 0.820 1 3.50 16.15 0.988 3 2.4 初始pH对吸附行为的影响
污染体系初始pH与Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)形态及吸附剂表面电性密切相关,因此重点研究了pH对Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)吸附行为的影响。由图5(a)可知,在初始pH为3时,Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附量最大,这可能是由于吸附剂表面发生质子化,产生大量正电荷,对Sb(OH)6−有较强的静电吸引作用;在pH为4~10范围内,其吸附量略有降低,可归因于溶液中OH−与吸附质之间的竞争作用,此外,由于Met/LDHs具有良好的pH缓冲作用且Sb(Ⅴ)的存在形态稳定[26],使得其吸附量在此区间保持稳定;在pH为3~7时,其对As(Ⅴ)的吸附量变化与Sb(Ⅴ)相似,而当pH>7时,As(Ⅴ)主要以HAsO42-的形式存在[27],与去质子化表面存在较强的静电排斥作用,导致其吸附量显著降低。吸附剂表面的电性对污染物的去除有重要影响。Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)吸附前后的Zeta电位变化如图5(b)所示,分析发现,在Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)后,等电点(pHPZC)从9.4分别降低至4.38和4.05。有研究表明[27],当吸附质以内球表面络合的形式被吸附时,与吸附剂表面的羟基结合成键,才会导致pHPZC发生变化。据此推测Met/LDHs可能与Sb(Ⅴ)、 As(Ⅴ)之间形成络合物。
2.5 共存体系的吸附性能分析
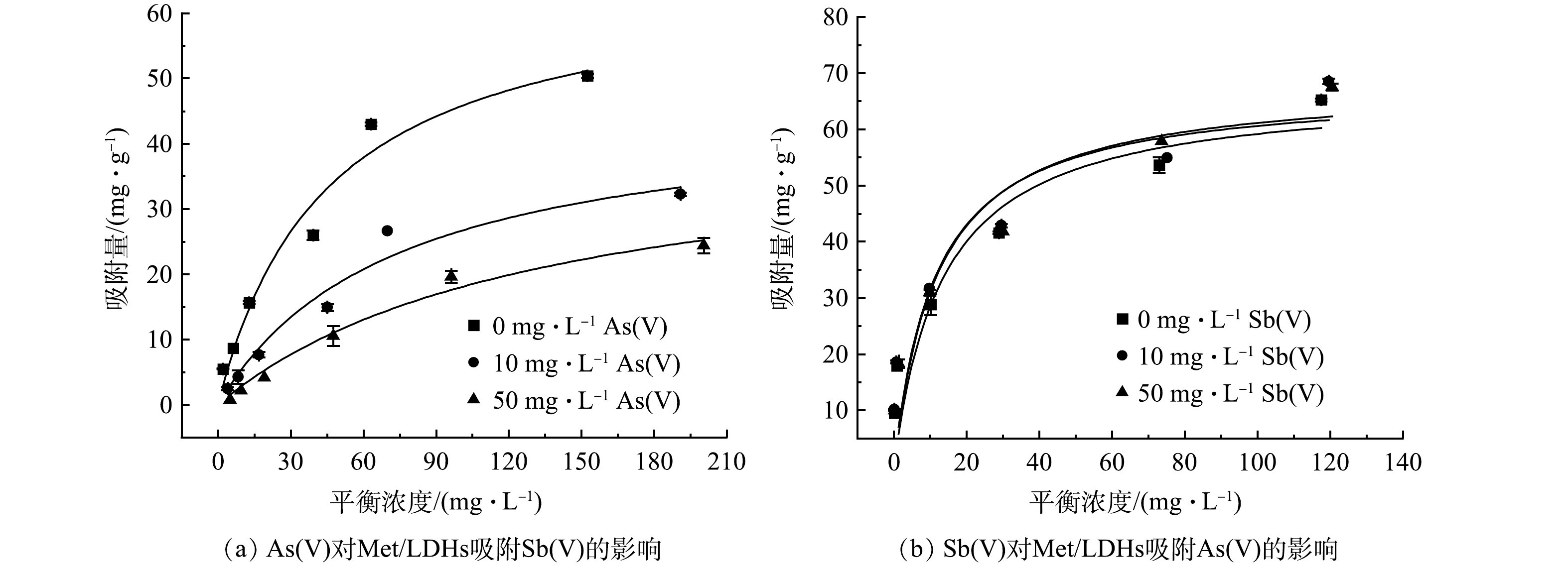
鉴于在实际废水中已经发现Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)有共存情况,故设计二者共存的模拟体系进行Met/LDHs吸附性能的研究,结果如图6(a)~(b)和表3所示。由图6(a)~(b)可知,在分别含有10 mg∙L−1和50 mg∙L−1的As(Ⅴ)体系中,Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)的最大吸附量将分别降低至46.11 mg∙g−1和42.09 mg∙g−1;然而,当溶液中共存一定浓度Sb(Ⅴ)时,Met/LDHs对As(Ⅴ)的吸附效果保持稳定。说明Met/LDHs倾向于优先吸附As(Ⅴ)。这可能是由于As(Ⅴ)的离子半径更小,易与Met/LDHs发生层间阴离子交换,这与吸附动力学中所得结论一致[28]。
表 3 共存体系中的Langmuir吸附等温线参数Table 3. Langmuir adsorption isotherm parameters in the coexisting system处理离子浓度/(mg∙L−1) 掺入离子浓度/(mg∙L−1) Langmuir等温线参数 qm KL R2 Sb(Ⅴ)/(0~200) As(Ⅴ)/0 66.23 0.022 0.962 4 As(Ⅴ)/10 46.11 0.014 0.956 5 As(Ⅴ)/50 42.09 0.007 0.980 9 As(Ⅴ)/(0~200) Sb(Ⅴ)/0 67.20 0.074 0.820 1 Sb(Ⅴ)/10 68.47 0.083 0.853 2 Sb(Ⅴ)/50 67.50 0.088 0.799 0 2.6 解吸循环分析
为了进一步探究Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的重复利用的性能,进行了5次解吸循环实验结果如图7所示。结果表明,在经过第2次循环后,Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)的去除率分别降低了41.4%、37.5%,并在后几次的吸附-解吸循环中,去除率保持稳定。这可能是由于经过Met/LDHs吸附后,部分Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)能够牢固地附着在吸附剂上,难以被解吸释放,随着吸附位点的减少,导致后续循环过程中去除率的降低。若Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)仅通过物理吸附或表面静电作用被Met/LDHs去除,则吸附质的选择性较小,容易被释放到溶液中[29]。由此,可以推断Met/LDHs与Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)之间存在一些化学作用[30]。
2.7 吸附机理
为了更深入分析Met/LDHs去除污染物的作用机理,本文首先对比了其吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)前后的XRD图谱。如图8(a)所示,Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)后仍具备典型类水滑石特征峰,表明其结构并未受到破坏。然而,吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)后Met/LDHs基底间距值d003由0.801 nm分别减小到0.777 nm和0.786 nm,表明这2种污染物可能与层间阴离子发生交换而被去除[31-32]。此外,由图8(b)可见,Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)后其中羟基对应伸缩振动峰由3 432 cm−1减小到3 417 cm−1和3 406 cm−1,弯曲振动峰从1 624 cm−1偏移至1 632 cm−1和1 632 cm−1。说明吸附剂中的羟基可能与Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)之间存在氢键作用[33]。而且,位于1 384 cm−1处硝酸根的伸缩振动峰强度明显减弱[34-35],表明Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)与Met/LDHs层间的硝酸根之间发生了离子交换,这与XRD分析结果相对应。另外,在Met/LDHs吸附As(Ⅴ)后,856 cm−1附近出现新的吸收峰,其对应于As—O[36],说明As(Ⅴ)与Met/LDHs之间可能发生内球表面络合反应[37]。而在吸附Sb(Ⅴ)后,FTIR谱图中无法区分特定的Sb—O吸收峰,这可能是由于Met/LDHs层板中的M—O晶格振动与Sb—O的振动峰重合而不易区别[38]。处于437~587 cm−1内的振动峰未发生明显变化,表明在Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附过程中,其主体层板没有改变。
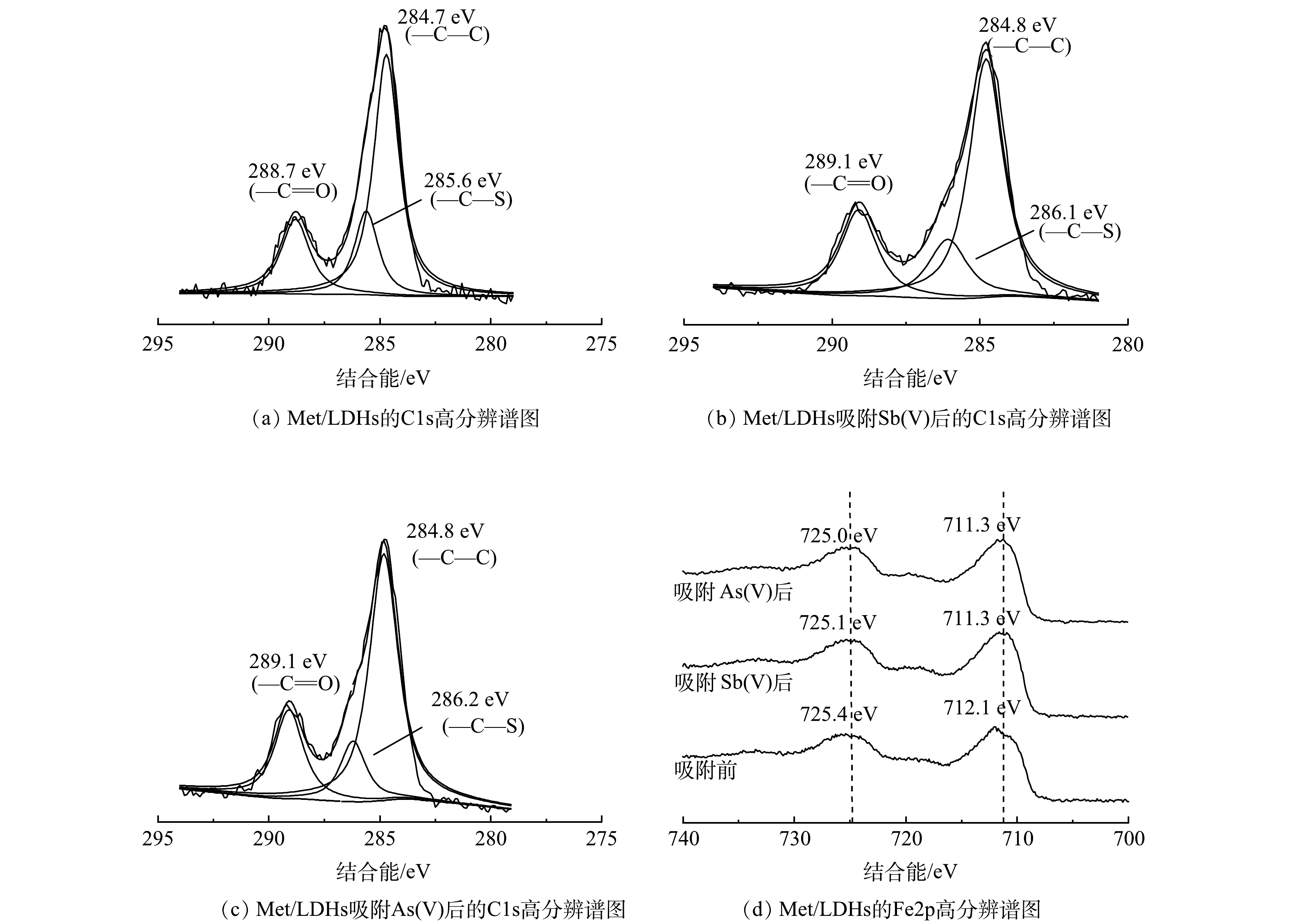
Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)前后的高分辨C1s XPS图谱如图9(a)~(c)所示。由图9(a)~(c)可知,位于284.7 eV处的—C—C特征峰在吸附前后未发生位移。这说明吸附过程没有改变甲硫氨酸的主碳链的碳原子的化学状态;在吸附Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)后,结合能为285.6 eV对应的—C—S特征峰偏移了0.5 eV和0.6 eV,说明—C—S中碳原子周围电子密度改变。这可归因于Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)与—C—S之间的氢键作用[22]。与此同时,—C=O的结合能均增加了0.4 eV,表明其化学环境发生变化。这可能是由于—C=O中氧原子上的电子转移到了Sb(OH)6−或H2AsO4−的羟基中形成氢键[39-40]。图9(d)为Met/LDHs吸附Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)前后Fe2p高分辨XPS图谱。如图9(d)所示,在吸附Sb(Ⅴ)、As(Ⅴ)后,Fe2p的特征峰均向更低电子结合能方向移动。结合FTIR分析结果推测,这可能是因为Sb(Ⅴ)或As(Ⅴ)与Met/LDHs中的Fe原子发生了内球表面络合反应[26, 41]。综上所述,推测Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附主要包括层间阴离子交换、氢键作用以及内球表面络合反应。
3. 结论
1)本研究通过共沉淀法成功将甲硫氨酸插入水滑石层间,得到具有羧基和甲巯基等基团的Met/LDHs吸附剂。
2) Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的吸附动力学符合拟二级动力学模型,对Sb(Ⅴ)的吸附数据更加符合Langmuir模型,对于As(Ⅴ)的吸附数据更适合用Freundlich等温线模型。在Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的二元体系中,Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)之间存在竞争吸附去除,Met/LDHs会优先吸附离子半径更小的As(Ⅴ)。
3)第1次经NaOH解吸后的Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)的去除率分别降低了41.4%和37.5%,但后续循环利用去除率稳定,说明在第1次吸附后有一部分Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)通过化学作用牢固附着在Met/LDHs上。
4) Met/LDHs对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)去除主要依靠层间阴离子交换、氢键作用以及内球表面络合反应。由此可见,甲硫氨酸改性镁铁水滑石可以提升对Sb(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅴ)去除率,具有良好的应用前景。
-
[1] 薛传东,杨浩,刘星.天然矿物材料修复富营养化水体的实验研究.岩石矿物学杂志,2003,22(4):381-385XUE Chuandong,YANG Hao,LIU Xing.An experimental application of natural mineral materials to the remedy of the eutrophic water.Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2003,22(4):381-385(in Chinese) [2] 陆开宏,晏维金,苏尚安.富营养化水体治理与修复的环境生态工程:利用明矾浆和鱼类控制桥墩水库蓝藻水华.环境科学学报,2002,22(6):732-737LU Kaihong,YAN Weijin,SU Shang'an.Environmental and ecological engineering on control and remediation of eutrophicated waterbodies:By using ameliorated alum plasma and fishes to control blue-green blooms of Qiaodun reservoir.Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2002,22(6):732-737(in Chinese) [3] 郑焕春,周青.微生物在富营养化水体生物修复中的作用.中国生态农业学报,2009,17(1):197-202ZHENG Huanchun,ZHOU Qing.Function of microorganism in bioremediation of eutrophic water.Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2009,17(1):197-202(in Chinese) [4] 王爽,赵兰坡.秸秆碳和硫酸铝对富营养化水体中氮磷的吸收去除效应及其影响因素.水土保持学报,2011,25(2):114-120WANG Shuang,ZHAO Lanpo.Adsorption and removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from eutrophic water by straw carbon and aluminum sulfate and influencing factors.Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,25(2):114-120(in Chinese) [5] 潘涌璋,吕雯岚,张娜,等.微生物菌剂净化富营养化景观水体的研究与应用.给水排水,2005,31(6):73-77PAN Yongzhang,LÜ Wenlan,ZHANG Na,et al.Study on purification of eutrophicated scenery water body by dominant bacterial agents.Water & Wastewater Engineering,2005,31(6):73-77(in Chinese) [6] BATTY L.C.,ATKIN L.,MANNING D.A.C.Assessment of the ecological potential of mine-water treatment wetlands using a baseline survey of macroinvertebrate communities.Environmental Pollution,2005,138(3):412-419 [7] SOOKNAH R.D.,WILKIE A.C.Nutrient removal by floating aquatic macrophytes cultured in anaerobically digested flushed dairy manure wastewater.Ecological Engineering,2004,22(1):27-42 [8] 汤坤贤,游秀萍,林亚森,等.龙须菜对富营养化海水的生物修复.生态学报,2005,25(11):3044-3051TANG Kunxian,YOU Xiuping,LIN Yasen,et al.A study on bioremediation of eutrophication of mariculture waters by Gracilaria lemaneaformis.Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005,25(11):3044-3051(in Chinese) [9] 曹银珠,刘树庆,石艳星.蔬菜对富营养化藕田水体的净化效应研究.水土保持学报,2013,27(6):97-102CAO Yinzhu,LIU Shuqing,SHI Yanxing.Study on purification effect of vegetable on eutrophication water in the artificial wetland of lotus.Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2013,27(6):97-102(in Chinese) [10] 童昌华,杨肖娥,濮培民.富营养化水体的水生植物净化试验研究.应用生态学报,2004,15(8):1447-1450 TONG Changhua,YANG Xiaoe,PU Peimin.Purification of eutrophicated water by aquatic plant.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2004,15(8):1447-1450(in Chinese) [11] 王超,张文明,王沛芳,等.黄花水龙对富营养化水体中氮磷去除效果的研究.环境科学,2007,28(5):975-981 WANG Chao,ZHANG Wenming,WANG Peifang,et al.Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in eutrophic water by Jussiaea stipulacea ohwi.Environmental Science,2007,28(5):975-981(in Chinese) [12] LI Mao,WU Yuejin,YU Zengliang,et al.Nitrogen removal from eutrophic water by floating-bed-grown water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.) with ion implantation.Water Research,2007,41(14):3152-3158 [13] 梁淑轩,张振冉,王云晓,等.白洋淀典型挺水植物净化水质效果.科学技术与工程,2013,13(11):3048-3052 LIANG Shuxuan,ZHANG Zhenran,WANG Yunxiao,et al.Purification of typical emergent aquatic plant on eutrophicated water in lake Baiyangdian.Science Technology and Engineering,2013,13(11):3048-3052(in Chinese) [14] 陈倩,晁建颖,张毅敏,等.底栖动物与挺水植物协同修复富营养化水体的研究.水处理技术,2011,37(8):61-63 CHEN Qian,CHAO Jianying,ZHANG Yimin,et al.Study on remediation in eutrophic waterbody by zoobenthos and emergent plants.Technology of Water Treatment,2011,37(8):61-63(in Chinese) [15] 姜义帅,陈灏,马作敏,等.利用沉水植物生长期收割进行富营养化水体生态管理的实地研究.环境工程学报,2013,7(4):1351-1358 JIANG Yishuai,CHEN Hao,MA Zuomin,et al.Field study on effect of harvesting submerged plant during growing season for ecological management of eutrophicated water.Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2013,7(4):1351-1358(in Chinese) [16] 吴振斌,邱东茹,贺锋,等.沉水植物重建对富营养水体氮磷营养水平的影响.应用生态学报,2003,14(8):1351-1353 WU Zhenbin,QIU Dongru,HE Feng,et al.Effects of rehabilitation of submerged macrophytes on nutrient level of a eutrophic lake.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2003,14(8):1351-1353(in Chinese) [17] 向律成,郝虎林,杨肖娥,等.多年生漂浮植物对富营养化水体的响应及净化效果研究.水土保持学报,2009,23(5):152-155 XIANG Lvcheng,HAO Hulin,YANG Xiaoe,et al.Response and purification of perennial floating plants in eutrophic waterbody.Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2009,23(5):152-155(in Chinese) [18] 娄敏,廖柏寒,刘红玉,等.3种水生漂浮植物处理富营养化水体的研究.中国生态农业学报,2005,13(3):194-195 LOU Min,LIAO Bohan,LIU Hongyu,et al.Study of three aquatic floating plants to treat the water eutrophication.Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2005,13(3):194-195(in Chinese) [19] 舒金华.我国主要湖泊富营养化程度的评价.海洋与湖沼,1993,24(6):616-620 SHU Jinhua.Assessment of eutrophication in main lakes of China.Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,1993,24(6):616-620(in Chinese) [20] 国家环境保护总局.水和废水监测分析方法.4版.北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002 [21] 李宏.多年生牧草与微生物联合作用对富营养化水体的修复效应研究.杭州:浙江大学硕士学位论文,2010 LI Hong.Remediation of eutrophic water by perennial grasses and microorganism integrated system.Hangzhou:Master Dissertation of Zhejiang University,2010(in Chinese) [22] 徐德福,徐建民,王华胜,等.湿地植物对富营养化水体中氮、磷吸收能力研究.植物营养与肥料学报,2005,11(5):597-601 XU Defu,XU Jianmin,WANG Huasheng,et al.Absorbability of wetland plants on N and P from eutrophic water.Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,2005,11(5):597-601(in Chinese) [23] DE MARINS J.F.,CARRENHO R.,THOMAZ S.M.Occurrence and coexistence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and dark septate fungi in aquatic macrophytes in a tropical river-floodplain system.Aquatic Botany,2009,91(1):13-19 [24] 张丽华,宋长春,王德宣,等.沼泽湿地生态系统呼吸与温度、氮素及植物生长的相互关系.环境科学,2007,28(1):1-8 ZHANG Lihua,SONG Changchun,WANG Dexuan,et al.Relationship of ecosystem respiration with temperature,nitrogen and plant in freshwater marshes.Environmental Science,2007,28(1):1-8(in Chinese) [25] GIFFORD R.M.Plant respiration in productivity models:Conceptualisation,representation and issues for global terrestrial carbon-cycle research.Functional Plant Biology,2003,30(2):171-186 [26] 李娟,王应军,金航标,等.包埋活性污泥和反硝化污泥全程硝化反硝化脱氮.环境工程学报,2013,7(1):196-200 LI Juan,WANG Yingjun,JIN Hangbiao,et al.Complete nitrification and denitrification using embedded mixed sludge.Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2013,7(1):196-200(in Chinese) [27] 王敏,唐景春,王斐.常见水生植物对富营养化和重金属复合污染水体的修复效果研究.水资源与水工程学报,2013,24(2):50-56 WANG Min,TANG Jingchun,WANG Fei.Remediation effect of common aquatic plants on the combined water pollution of eutrophication and heavy metals.Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2013,24(2):50-56(in Chinese) [28] KONG Ling,WANG Yubin,ZHAO Li'na,et al.Enzyme and root activities in surface-flow constructed wetlands.Chemosphere,2009,76(5):601-608 期刊类型引用(21)
1. 蔺星娜,李惋瑾,尹园丰,邵学新,吴明,张龙. 千岛湖坡地地表径流氮磷流失及生态拦截控制. 环境科学学报. 2024(03): 150-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 顾珉嘉,刘佳佳,张逸飞,李文润,刘雨佳. 不同水生植物对生活污水尾水净化能力对比研究. 广东化工. 2023(07): 178-180+202 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 崔建伟,李金凤,崔键,常雅军,刘晓静,王巍,姚东瑞. 6种水生植物去除污水中总磷的实验研究. 湿地科学. 2023(03): 430-438 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 田创,张择瑞,刘鑫,杨兰,胡淑恒. 4种浮床花卉植物及其混种对富营养化水体的净化效果. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(01): 99-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 谌宏伟,蔡雪璨,杨欣怡,辛龙,喻娓厚,周慧,于莎莎. 南方6类挺水植物净化污水氮素的对比试验研究. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(01): 34-44+114 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张忠武,黄琳,邓正春,王中美,胡超,蒋万,张洋,彭元群,王桢. 菱角净水功能及栽培技术研究进展. 农学学报. 2022(05): 37-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘沙沙,张剑文,梁敏诗,李文浩. 水生植物对污水中氮磷的去除效果研究. 山东化工. 2022(13): 195-197 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 程浩淼,季书,葛恒军,朱腾义,冯绍元. 生态沟渠对农田面源污染的消减机理及其影响因子分析. 农业工程学报. 2022(21): 42-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李文梦,张清东,苟俊莉,张思林. 模拟复合系统对富营养化水体的治理效果. 贵州农业科学. 2020(01): 142-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赵静岩,吴继业,王强强,葛利云,叶盛,彭路菊,鲍根莲,钟铭晨,邓欢欢. 植物对河滨人工护坡基质上生物膜酶活的影响. 浙江农业科学. 2020(10): 2081-2084+2087 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨勇,田昌,谢桂先,张玉平,宋海星,荣湘民. 生态沟渠吸收氮磷效果研究. 湖南农业科学. 2019(01): 39-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 万琼,雷茹,张波. 生物生态耦合系统对分散式农村生活污水的深度净化. 环境工程学报. 2019(07): 1602-1611 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 陈照方,陈凯,杨司嘉. 水生植物对淡水生态系统的修复效果. 分子植物育种. 2019(13): 4501-4506 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 林海,陶艳茹,董颖博,李冰. 基于妫水河水体水质净化的浮水植物优选. 安全与环境学报. 2019(05): 1685-1694 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 杨勇,田昌,谢桂先,张玉平,宋海星,荣湘民. 生态沟渠吸收氮磷效果研究(英文). Agricultural Science & Technology. 2019(05): 32-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 许永辉,崔正国,曲克明,王艳艳,王加鹏,李悦悦,胡清静. 不同耐盐植物人工湿地净化养殖外排水效果. 渔业科学进展. 2018(03): 80-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 司圆圆,卢王梯,关则智,陈兴汉,叶芬. 菱角与草鱼立体生态种养技术. 农业与技术. 2018(12): 110+167 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 司圆圆,卢王梯,陈兴汉,关则智,叶芬. 菱角对农村富营养化水体营养盐吸收的初步研究. 水生态学杂志. 2018(01): 32-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 李旭霞,荣湘民,谢桂先,张玉平,严红星,宋海星. 不同水生植物吸收地表水中氮磷能力差异及其机理. 水土保持学报. 2018(01): 259-263 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 王艳英,王晓磊,王成,董建华,刘晓双,郜爱玲. 基于净化城市河道功能的水培花卉的筛选研究. 热带作物学报. 2017(09): 1595-1600 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 张鹏飞,岳烨,侯嫔,严哲,林雷鸣. 人工湖水体富营养化的活性炭处理技术及生态修复建议. 水资源与水工程学报. 2017(02): 92-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(18)
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2774
- HTML全文浏览数: 2267
- PDF下载数: 463
- 施引文献: 39




 下载:
下载: