吸附-电化学氧化耦合处理对氯苯酚废水及动力学
Treatment and kinetics of p-chlorophenol wastewater by coupling electrochemical oxidation and adsorption
-
摘要: 以毡状活性炭纤维为阳极,不锈钢为阴极,吸附-电化学氧化耦合降解对氯苯酚废水进行了研究。考察了吸附或耦合电化学氧化过程、电流密度、支持电解质硫酸钠浓度和活性炭纤维重复使用对废水COD去除率的影响,结果表明,采用吸附-电化学氧化耦合方法,当电流密度7.6 mA/cm2 支持电解质(硫酸钠)浓度为1 g/L,处理时间为180 min,4-CP废水COD去除率可达97.09%。毡状活性炭纤维对4-CP的静态吸附过程符合Langmiu吸附等温方程。建立了吸附-电化学氧化COD去除动力学模型,动力学模型参数表明, 对于COD的去除,电化学氧化作用比吸附作用大。Abstract: The p-chlorophenol(4-CP)wastewater treatment by coupling adsorption with electrochemical oxidation degradation was investigated, using felty activated carbon fiber as positive electrode and stainless steel as negative electrode. The influences of adsorption or coupled with electrochemical oxidation process,current density,supporting electrolyte(Na2SO4)concentration and reusing of activated carbon fiber on the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) were studied. Base on the method of coupling adsorption with electrochemical oxidation degradation, under the following conditions: current density of 7.6 mA/cm2, supporting electrolyte (Na2SO4) of 1 g/L,reaction time of 180 min, the removal of COD was about 97.09%.The adsorption equilibrium of 4-CP onto activated carbon fiber was coincident with the Langermiu isotherm equilibrium. A kinetic model for COD removal was established based on the adsorption and electrochemical oxidation process. The parameters predicted from the kinetic model showed that electrochemical oxidation process contributed more than adsorption process to the removal of COD.
-
Key words:
- electrochemical oxidation /
- adsorption /
- p-chlorophenol /
- activated carbon fiber /
- kinetics
-
四溴双酚A(TBBPA)是一种溴代阻燃剂,由于其具有高阻燃性和低廉价格等特点,广泛应用于电子电器产品、家具、油漆、纺织品等日用品中. TBBPA在生产和使用过程中可通过多种途径进入环境. 研究表明,TBBPA具有持久性有机污染物的特征,具有生物累积性、高度亲脂性和难分解性,具有内分泌干扰效应、细胞和神经毒性、免疫毒性等,会对生态系统和人类健康构成严重的威胁[1-4]. TBBPA微溶于水且容易在土壤中聚集,土壤是TBBPA最重要的归宿之一. 近年来,如何有效降解和去除土壤中TBBPA的研究备受关注 .
目前,土壤有机污染物修复技术包括物理修复[5]、生物修复[6-8]和化学修复[9-10],其中化学修复因其低投资、高效率、实施周期短的优点应用广泛. 过硫酸盐(PS)高级氧化技术是最常用的一种化学氧化修复技术,该技术的关键是通过热[11]、紫外光[12]和通过添加过渡金属[13]等方式活化PS. 热活化PS体系中虽然操作简单,但能耗较高,不适用大规模的处理. 在过渡金属活化PS中,亚铁离子(Fe2+)和铁离子(Fe3+)由于含量丰富、环境友好、价格低廉而被广泛用于PS活化,然而Fe2+活化PS技术仍然有一些缺陷,过量的Fe2+会抑制PS的活化,Fe3+还原为Fe2+的速率较慢,难以控制氧化体系中的量[14].
为了提高PS活化性能,本文以典型溴代阻燃剂TBBPA为目标污染物,考虑将Fe2+活化与热活化结合,采用Fe2+耦合热活化PS处理土壤中TBBPA,考察温度、Fe2+初始浓度、PS浓度、初始pH、无机阴离子和其他金属离子对Fe2+/热/PS体系降解TBBPA的影响,以寻求土壤体系中TBBPA降解的最佳反应条件,为土壤中持久性有机污染物的修复提供依据.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 实验试剂
TBBPA购于上海麦克林生化科技有限公司,甲醇购于美国迈瑞达科技公司,过硫酸钠、五水合硫酸铜、七水合硫酸锌和六水合硫酸镍购于天津津科精细化工研究所,氯化钠、碳酸氢钠、氢氧化钠和七水合硫酸亚铁购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司,浓硫酸购于北京化工厂. 以上药品除甲醇为色谱纯外,其余药品均为分析纯. 实验溶液配制用水为去离子水,高效液相仪器用水为哇哈哈纯净水.
1.2 实验仪器
LC-20AT 高效液相色谱仪(日本Shimadzu公司);Optima-XPN PN-100 高速离心机(BECKMANCOULTER公司);S400-B多参数pH测试仪(梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司);FD-A10N-50冷冻干燥机(北京博医康实验仪器有限公司);HH-1-5L恒温水浴锅(江苏科析仪器有限公司);旋转蒸发仪(上海申生科技有限公司);SHA-2恒温振荡器(常州菲普实验仪器厂).
1.3 土壤的采集
供试土壤采自安徽省合肥市瑶海区某农田(117°21'53.424"E, 31°51'23.886"N),采集深度0—20 cm. 去除碎石、树枝杂质,经室内自然干燥,研磨后过60目筛网,储存于棕色玻璃瓶中密封保存. 经检验,土壤中无TBBPA检出. 该土壤基本理化性质见表1.
表 1 土壤基本理化性质Table 1. Basic physicochemical properties of soilpH 孔隙比 Porosity ratio 饱和度/% Saturation 颗粒成分组成/% Particle composition <0.005 mm 0.005—0.075 mm 0.075—0.25 mm 0.25—0.5 mm 7.10 1.50 95.1 13.3 17.7 47.7 21.3 1.4 污染土制备
TBBPA配制:精确称取0.250 g TBBPA粉末溶解于500 mL甲醇中,TBBPA浓度为500 mg·L−1.
TBBPA污染土:称取500 g未污染的土壤于2 L烧杯中,加入200 mL甲醇,玻璃棒搅拌均匀后,取30 mL TBBPA(500 mg·L−1)缓缓倒入烧杯中,边搅拌使之充分混匀,接着加甲醇直至液体浸没土壤表面,用玻璃棒搅拌20—30 min,使TBBPA在土壤中均匀混合,置于通风橱中自然风干、老化2周后备用(测定TBBPA约20 mg·kg−1).
1.5 实验方法
实验选用过硫酸钠(PS)氧化剂,过渡金属离子选用Fe2+,无机阴离子选用Cl−、
HCO−3 表 2 单因素实验参数变量Table 2. One-way experimental parameter variables单因素名称 Single factor name 参数变量 Parameter variable 温度/℃ 25 35 45 55 65 PS浓度/(mmol·L−1) 15 25 50 70 100 Fe2+浓度/(mmol·L−1) 15 25 50 70 100 初始pH 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 — PS与无机阴离子浓度摩尔比 1:0.1 1:1 1:2 — — Fe2+与其他金属离子浓度摩尔比 1:0.1 1:1 1:2 — — 称取2.000 g TBBPA污染土壤于30 mL棕色玻璃瓶中,加入2 mL去离子水和2 mL 25 mmol·L−1的硫酸亚铁溶液,再加入2 mL 50 mmol·L−1的PS储备溶液,使用1 mol·L−1稀硫酸和氢氧化钠溶液调节初始pH为3.0,随即用橡胶塞密封,置于温度55 ℃的恒温振荡器中(转速200 r·min−1)12 h. 预定时间间隔(0.05、0.25、0.5、1、2、4、6、8、12 h)取出放入冰水中(5 min)并加入0.2 mL甲醇,随后将样品放入-20 ℃的冰箱中冷冻4 h后放入冷冻干燥机中冷冻干燥48 h,经预处理,测定土壤中TBBPA浓度.
1.6 土壤样品的预处理
将10 mL甲醇溶剂加入待测棕色玻璃瓶中,置于25 ℃恒温振荡器中振荡8 h后,在剩余土壤中加入10 mL甲醇超声辅助萃取,萃取1 h,转移至离心管分离土壤与上清液. 随后,将离心管中的上清液经滤纸自然过滤转移至茄形烧瓶中,利用旋转蒸发仪将烧瓶中的萃取液旋转蒸发至1 mL,再用甲醇溶液重复多次提取至5 mL容量瓶,定容到刻度线,摇晃均匀,将容量瓶中的液体通过孔隙为0.22 μm的有机滤膜过滤,收集1.5 mL滤液于棕色进样瓶瓶中,用HPLC进行定量分析.
1.7 分析方法
(1) TBBPA的测定
本实验采用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC)测定土壤中的TBBPA. HPLC分析条件为:Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18色谱柱(5 μm,250 mm×4.6 mm),流动相为甲醇:超纯水=85:15,检测波长为230 nm,流速为1.0 mL·min−1,进样体积为10 μL,柱温35 ℃. 对标样进行定性分析,TBBPA在该分析条件下的保留时间为(5.5±0.2) min[10].
(2) 数据分析方法
降解率W计算公式如下所示(公式1),采用准一级反应动力学和二级反应动力学模型(公式2、3)对TBBPA降解进行分析拟合.
W=(1−CtC0)×100% (1) lnCtC0=−kt (2) 1Ct−1C0=kt (3) 式中,t为反应时间(h),C0与Ct分别表示0 h和t h时TBBPA的浓度(mg·kg−1),k为拟合得到的反应动力学常数(h−1).
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 Fe2+耦合热活化PS降解TBBPA
比较了加热、热/Fe2+、热/PS、Fe2+/PS和Fe2+/热/PS体系对土壤中TBBPA降解效果的影响(图1),TBBPA在加热、热/Fe2+、热/PS和Fe2+/PS体系中12 h内的降解率分别为25.0%、32.0%、47.3%和89.9%. 由图可以看出,升高温度对土壤中TBBPA有一定的影响;在热/Fe2+的体系下,TBBPA降解速率小;热/PS和Fe2+/PS体系下TBBPA降解速率有进一步提升,原因主要是热和Fe2+都能活化PS产生较多的
SO·−4 2.2 TBBPA在Fe2+/热/PS体系中降解的影响因素
(1) 温度
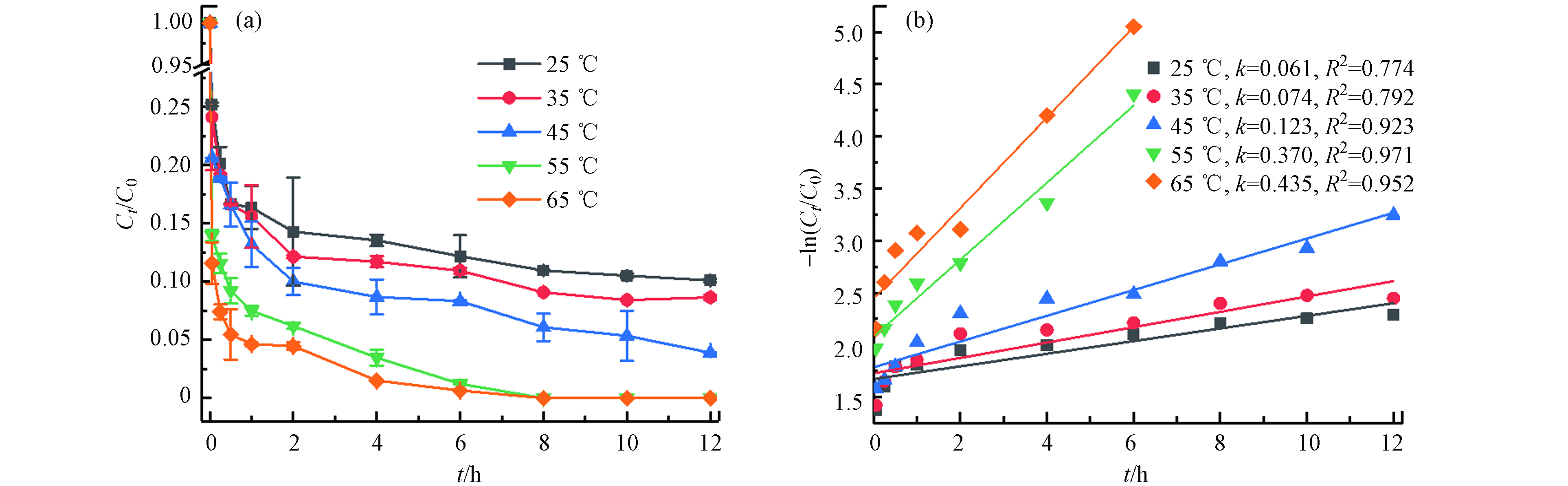
不同温度(25 ℃、35 ℃、45 ℃、55 ℃、65 ℃)对TBBPA在Fe2+/热/PS体系中降解的影响(如图2). 结果表明,TBBPA的降解效率随温度的升高而显著增加,在12 h内25 ℃、35 ℃、45 ℃时TBBPA的降解率分别为89.91%、91.35%、96.10%,55 ℃和65 ℃时降解率则在8 h已经达到100%. 这是由于在Fe2+活化过硫酸盐产生
SO·−4 SO·−4 SO·−4 Fe2++S2O2−8→Fe3++SO2−4+SO•−4 (4) S2O2−8+heat→2SO•−4 (5) (2) Fe2+初始浓度
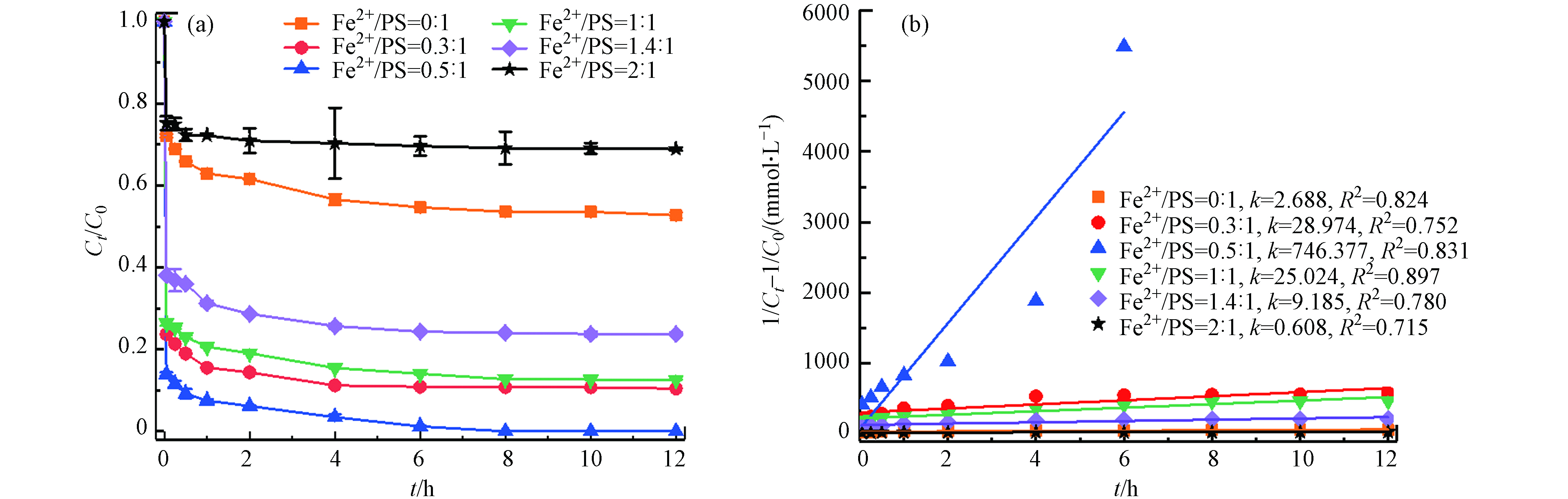
在温度55 ℃、PS浓度为50 mmol·L−1、pH=3的条件下,考察不同初始Fe2+浓度(0、15、25、50、 70、100 mmol·L−1)对土壤中TBBPA降解的影响. 如图3所示,未投加Fe2+时,此时反应仅是热活化反应降解,12 h内TBBPA降解率为47.3%,当Fe2+与PS摩尔比从0.3:1增加到0.5:1,TBBPA降解率从89.6%增加到100%;而继续增大Fe2+与PS摩尔比至2:1,TBBPA的降解效率开始下降,反应结束时仅有31.1%. 由图3(b)可以看出,TBBPA的降解较好拟合二级反应动力学,降解速率常数先增大,然后逐渐减小. 可见,添加Fe2+能够有效活化PS降解土壤中的TBBPA,在Fe2+浓度一定范围内,适当提高Fe2+浓度,能加速TBBPA的降解,在Fe2+与PS摩尔比为0.5:1,降解率最大,随着Fe2+浓度增加,过量的Fe2+也能分解
SO·−4 Fe2++SO•−4→Fe3++SO2−4 (6) (3) PS浓度
在温度55 ℃、Fe2+浓度为25 mmol·L−1、pH=3的条件下,考察不同PS浓度(15、25、50、70、100 mmol·L−1)对土壤中TBBPA降解的影响. 如图4所示,随着PS浓度的增加,12 h内TBBPA的去除效率从50.1%提高到100%,降解速率常数也从0.014 h−1增至1.135 h−1;TBBPA完全去除所需的时间随PS浓度的增大而缩短,PS浓度50 mmol·L−1、70 mmol·L−1和100 mmol·L−1降解率达到100%的时间分别为8 h、6 h和4 h. 由此可见,增加PS浓度对TBBPA的降解有促进作用. 有研究表明,过量的PS会抑制污染物的降解[18],因为是过量
S2O2−8 SO·−4 SO·−4 SO•−4+S2O2−8→•S2O2−8+SO2−4 (7) SO•−4+SO•−4→S2O2−8 (8) (4) 初始pH值
在温度55 ℃,Fe2+与PS最佳摩尔比0.5:1条件下,进一步研究了不同初始pH值(3.0、5.0、7.0和9.0)对Fe2+耦合热活化PS体系降解TBBPA的影响. 如图5所示,当初始pH分别为3.0、5.0、7.0和9.0时,反应12 h后,TBBP降解率分别为100%、99.62%、99.68%和99.66%,随着pH从3增加到9,反应速率常数从0.370 h−1减小到0.316 h−1,酸性条件下的降解率略高于中性和碱性条件,初始pH为5.0、7.0和9.0时降解效率之间相差不大. 出现这种趋势的原因是,在酸性条件下存在一定的酸催化效应(公式9、10)[19];硫酸亚铁溶液和过硫酸盐溶液自身呈酸性;两者在反应开始前3 min时较为迅速,PS很容易氧化Fe2+成为Fe3+,Fe3+水解也会使pH值降低. 总体来说,Fe2+耦合热活化PS体系具有良好的pH适应性,pH=3.0时最为合适.
S2O2−8+H+→HS2O−8 (9) HS2O−8→SO2−4+SO•−4+H+ (10) 2.3 无机阴离子在Fe2+/热/PS体系中的影响
在场地土壤和地下水的复杂系统中,可能存在无机阴离子对过硫酸盐降解污染物的过程产生一定制约[20]. 因此我们选取氯化钠和碳酸氢钠分别作为Cl−和
HCO−3 HCO−3 (1) Cl−
在最佳反应条件下(温度55 ℃、Fe2+浓度25 mmol·L−1、PS浓度50 mmol·L−1、pH=3),不同浓度的Cl−(0、5、50、100 mmol·L−1)对TBBPA降解的影响(如图6). 反应至4 h时,TBBPA的降解率分别为96.5%、96.2%、98.4%和99.4%;反应至12 h时,降解率分别为100%、99.7%、100%和100%,随着Cl−浓度从0 mmol·L−1增加至100 mmol·L−1,TBBPA完全去除所需时间缩短了2 h. 由图6(b)所示,反应符合准一级动力学模型,其对应的反应动力学常数分别为0.369 h−1、0.367 h−1、0.491 h−1和0.707 h−1. 当Cl−浓度较低时,Cl−与
SO·−4 SO•−4+Cl−→Cl•+SO2−4 (11) (2)
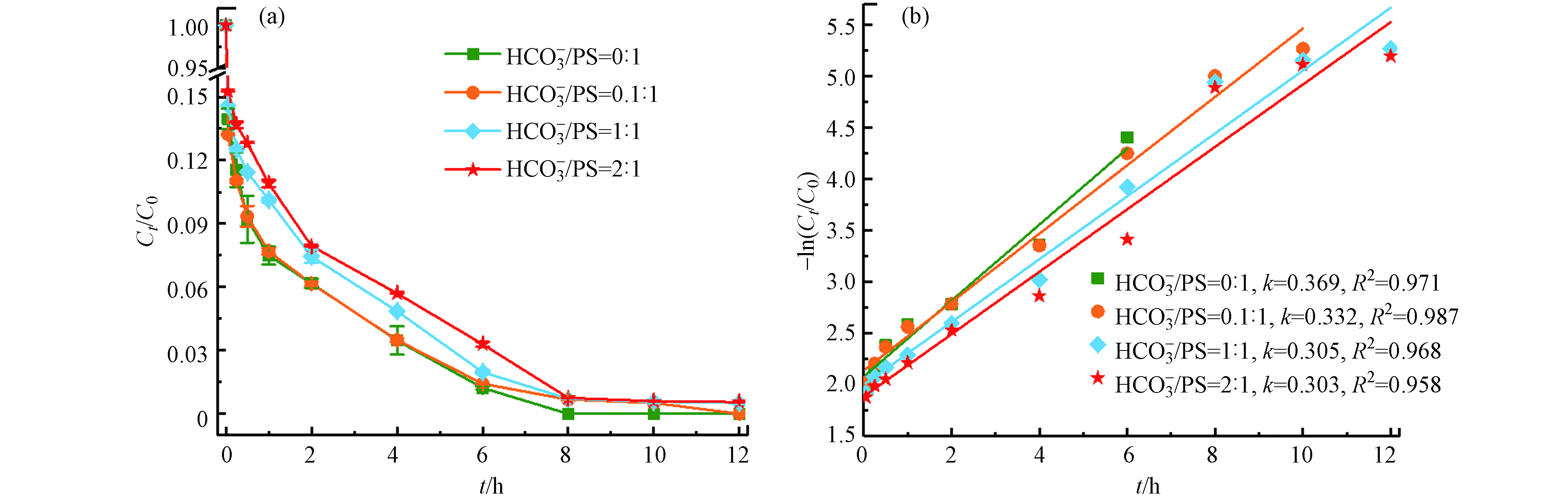
HCO−3 在最佳反应条件下(温度55 ℃、Fe2+浓度25 mmol·L−1、PS浓度50 mmol·L−1、pH=3),不同浓度的
HCO−3 随着
HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 CO2−3 SO⋅−4 HCO⋅3 CO⋅−3 HCO−3 HCO−3→CO2−3+H+ (12) SO⋅−4+HCO−3→SO2−4+HCO⋅3 (13) SO⋅−4+CO2−3→SO2−4+CO⋅−3 (14) 2.4 金属离子Cu2+、Zn2+、Ni2+对Fe2+/热/PS体系催化活性的影响
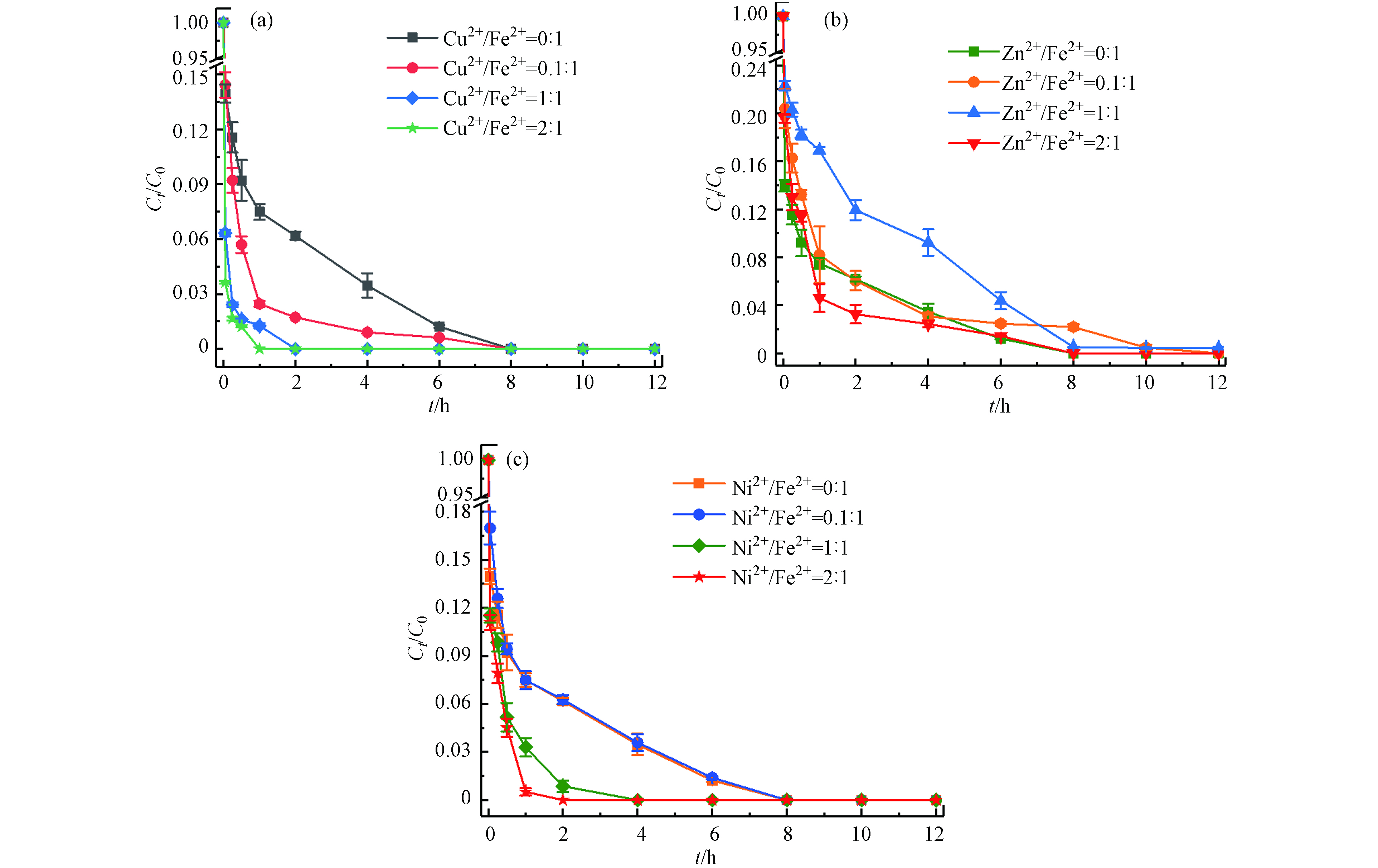
土壤中存在着大量的金属矿物,多种金属的存在也是影响应用的重要因素[23-24]. 本文选择土壤中的几种过渡金属(Cu2+、Zn2+、Ni2+)考察其对Fe2+/热/PS体系降解土壤中TBBPA的影响. 在体系最佳反应条件下(温度55 ℃、Fe2+浓度25 mmol·L−1、PS浓度50 mmol·L−1、pH=3),分别加入M2+/Fe2+摩尔比为0:1、0.1:1、1:1、2:1(M=Cu、Zn、Ni)的过渡金属离子,反应12 h后计算TBBPA降解效率. 结果如图8所示,Cu2+对Fe2+/热/PS体系表现出较好的促进作用,且随着Cu2+浓度的增大,TBBPA完全去除所需的时间从8 h(Cu2+/Fe2+摩尔比0:1)缩短到1 h(Cu2+/Fe2+摩尔比2:1);当增加Ni2+与Fe2+的摩尔比时,Ni2+显现出的促进作用由弱变强;而逐渐增大Zn2+与Fe2+的摩尔比时,对反应速率的影响出现由抑制转变成促进的双重作用. 这可能与M2+/M3+的氧化还原电位有关,△Ep(Cu2+/Cu3+)<△Ep(Ni2+/Ni3+)<△Ep(Zn2+/Zn3+),电位越低意味着催化剂越容易得到电子,有利于PS的活化[25];同时由于金属离子的氧化性Cu2+>Ni2+>Fe2+>Zn2+,Cu2+和Ni2+则更容易促使PS产生更多
SO⋅−4 3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)Fe2+耦合热活化过硫酸盐的方法能高效降解土壤中TBBPA. Fe2+耦合热活化过硫酸盐降解土壤中TBBPA相比于单一热活化和Fe2+活化方式,降解率分别提升52.7%和10.1%.
(2)对Fe2+耦合热活化PS降解TBBPA的影响因素研究表明,TBBPA的降解率随着温度的增加而升高;增大亚铁离子浓度,TBBPA的降解速率呈现出先增加后降低的趋势,Fe2+与PS的最佳摩尔比为0.5:1;增大PS浓度能够显著提高TBBPA的降解率,缩短TBBPA去除时间;Fe2+耦合热活化PS体系具有较宽的pH应用范围且在酸性条件下更有利于降解. 最优条件:温度55 ℃、Fe2+浓度25 mmol·L−1、PS浓度50 mmol·L−1、pH=3.
(3)较高浓度的Cl-对Fe2+/热/PS体系中TBBPA的降解起促进作用,而HCO3-在研究浓度范围内均呈现抑制作用;Cu2+和Ni2+促进Fe2+/热/PS体系对TBBPA的降解,而随着Zn2+浓度的增加,TBBPA的降解速率呈现出先减小后增大的变化.
-
[1] Sofia A.C. Lima, M.Filomena J. Raposo, Paula M.L., et al. Biodegradation of p-chlorophenol by a microalgae consortium.Water Research, 2004, 38(1):97-102 [2] Czaplicka M. Sources and transformations of chlorophenols in the natural environment. Sci.Total Environ., 2004,322(1-3):21-39 [3] Dabo D.,Cyr A.,Laplante F.,et al. Electrocatalytic dehydrochlorination of pentachlorophenol to phenol or cyclohexanol. Environmental Science & Technology,2000,34(7):1265-1268 [4] Ayse Kuleyin. Removal of phenol and 4-chlorophenol by surfactant-modified natural zeolite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007,144(1-2):307-315 [5] Fikret Kargi, Serkan Eker. Toxicity and batch biodegradation kinetics of 2,4 dichlorophenol by pure pseudomonas putida culture. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,2004,35(5-6): 424-428 [6] F.Kargi,S.Eker.Removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol and toxicity from synthetic wastewater in a rotating perforated tube biolm reactor. Process Biochemistry,2005,40(6):2105-2111 [7] Jun Shan,Jun Xu,Zhou Wenqiang,et al. Enhancement of chlorophenol sorption on soil by geophagous earthworms (Metaphire guillelmi). Chemosphere,2011,82(2):156-162 [8] Jung M.W.,Ahn K.H.,Lee Y., et al. Adsorption characteristics of phenol and chlorophenols on granular activated carbons(GAC). Microchem. J.,2001,70 (2): 123-131 [9] Akhtar M.,Bhanger M.I.,Iqbal S., et al.Sorption potential of rice husk for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol from aqueous solutions: Kinetic and thermodynamic investigations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006,128(1):44-52 [10] Yan F.,Urmila M.D. Cost effective environmental control technology for utilities,J.Adv. Environ.Res.,2004,8(2):173-196 [11] Akn Karci,Idil Arslan-Alaton,Tugba Olmez-Hanci, et al. Transformation of 2,4-dichloro-phenol by H2O2/UV-C,Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation products and toxicity evolution processes.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,2012, 230(1):65-73 [12] Jingjing Li,Yang Hu,Wenhui Liu,et al.Efficient oxidative degradation of 2-chlorophenol and 4-chlorophenol over supported CuO-based catalysts.Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry,2011,20(5):493-497 [13] 周剑,丁燕燕.电化学氧化法处理酸性染料废水的试验研究.工业用水与废水, 2011,42(6):37-39 Zhou J.,Ding Y.Y.Experimental study on acid dye wastewater treatment by electro-chemical oxidation. Industrial Water &Wastewater,2011,42(6):37-39(in Chinese) [14] Zhou M H,He J J.Degradation of cationic red X-GRL by electrochemical oxidation on modified PbO2 electrode. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2008,153(1-2):357-36 [15] Yang J.,Jia J. P.,Liao J.,et al.Removal of fulvic acid from water electrochemically using active carbon fiber electrode. Water Research,2004,38(20):4353-4360 [16] Tsai Jiunhorng,Chiang Hsiumei,Huang Guanyinag,et al.Adsorption characterristics of acetone,chloroform and acetonitrile on sludgederived adsorbent,commercial granular activeted carbon and activated carbon fibers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(1-3):1183-1191 [17] Shen Z. M., Wang W. H., Jia J. P., et al.Degradation of dye solution by an activated carbon fiber electrode electrolysis system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2001, 84(1):107-116 [18] 马淳安.有机电化学合成导论.北京:科学出版社,2002.161 [19] Mathialagan T.,Viraraghavan T. Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution by perlie.Journal of hazardous malterials,2002,94(3):291-303 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 1890
- HTML全文浏览数: 998
- PDF下载数: 972
- 施引文献: 0



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: