厌氧活性污泥处理废水中的U(Ⅵ)
U(Ⅵ) removal from wastewater by anaerobic sludge
-
摘要: 用人工驯养的厌氧污泥进行除铀实验,探讨了微生物投加量(VSS)、pH值、U(Ⅵ)初始浓度、外加电子供体和污泥重复利用等对污泥处理U(Ⅵ)的影响,并进行了相关机理分析。实验结果表明,在适当的pH范围内(5.2~6.6),厌氧污泥对铀保持较长时间的高效去除率;当以还原铁粉和无水乙醇作电子供体时,U(Ⅵ)去除率保持在95%以上的时间为未加电子供体时的2倍。U(Ⅵ)去除速度与VSS投加量成正比关系,U(Ⅵ)初始浓度对去除效果的影响不大,厌氧污泥可以长期使用。pH值的影响最关键,其次是外加电子供体。厌氧污泥除U(Ⅵ)机理为氧化还原和吸附的共同作用。Abstract: This paper focused on the bioremediation ability of anaerobic sludge which artificially domesticated. The affecting factors such as different VSS dosages, pH, U(Ⅵ) initial concentration, addition of electron donors, reuse of anaerobic sludge were studied by batch experiments and the mechanisms for U(Ⅵ) removal were discussed. The results showed that pH is one of the key factors which influenced the experiment. High U(Ⅵ) removal rate could be reached only under proper pH(5.2~6.6). Batch experiment which added zero-valent iron or ethanol as electron donors showed 2 times longer time lasted with high U(Ⅵ) removal ratio of 95%. The speed of U(VI) removal was in proportion to the VSS dosage. Different initial U(Ⅵ) concentrations have little influence on U(Ⅵ) removal rate. The anaerobic sludge can be reused and the mechanisms for U(Ⅵ) removal are redox and adsorption.
-
Key words:
- U(Ⅵ) /
- anaerobic sludge /
- adsorption /
- redox /
- uranium wastewater
-
随着电子产品更新速度的加快,导致其使用周期缩短,产生了大量的电子垃圾。据统计,2020年全球产生了5.36×107 t电子垃圾,比上一年增加近2×106 t,电子废弃物已成为世界上增长最快的固体废物;预计到2030年将达7.4×107 t,2050年增至1.2×108 t [1]。手机的平均使用寿命约为2~3 a,2020年中国废旧手机已超过5×108 台[2]。线路板是手机中核心部件之一,废旧手机的产生伴随着大量的废手机板(Waste Printed Circuit Boards of Mobile Phones, WPCB-MPs)。WPCB-MPs中含有大量的铜、锡、铅、镍等有色金属,是手机元器件中最具价值的二次资源[3]。因此,WPCB-MPs中金属的回收一直是研究的热点。
目前,WPCB-MPs金属回收方法主要有机械物理法、生物冶金、湿法冶金等[4]。机械物理法包括WPCB-MPs的拆解、破碎、分选等,一般可作为其他处理方式的预处理[5]。生物冶金法是利用某些微生物或其代谢产物与电子废弃物中的金属发生作用,产生氧化、还原、溶解、配位等反应,从而实现电子废弃物中有价金属(尤其是贵金属)的回收[6]。传统湿法冶金主要是利用强酸或强碱浸出废线路板中的金属,然后再对浸出液进行分离和除杂,利用净化、沉淀、过滤、萃取、离子交换等方法得到目标金属[7-8]。
矿浆电解不同于传统的湿法冶金,它是指在一个装置中同时实现金属浸出、部分溶液净化及电沉积的技术,因此具有流程短、能耗低、金属分离效果好、环保等优势。在我国,利用矿浆电解法第一次成功实现分离的是金属铋,并且阴极上析出的金属锑纯度可达99%以上,含铅小于0.04%,首次实现了矿浆电解工业化[9-10]。近年来,矿浆电解法也逐步用于电子垃圾资源化。例如,在酸性条件下,利用矿浆电解法回收废弃CPU插槽中的金属,在最佳实验条件下,总金属的分离率可高达93%以上[11]。随后,为了促进其工业应用,进行了5 000 mL规模实验,铜的回收率达94.5%[12-13];此外,还证实了酸性体系下矿浆电解液循环使用的可行性[14]。虽然这些研究可以获得较高的铜回收率,但其他金属,如Fe、Al等也存在于电解质和阴极产物中,因而降低了电流效率和产物纯度[15]。有研究发现,在氨-氯化铵碱性矿浆电解体系中,Cu可以形成低价态的[Cu(NH3)]+铜氨络合物从而在阴极沉积,而铁和锰等金属几乎不能形成此类络合物,这有助于提高电流效率和铜纯度[16]。实验结果显示,在最佳条件下,WPCB-MPs中铜的回收率为97.48%、纯度为99.992 1%,电流效率达106.76%[17]。
电解液循环可以降低化学试剂的使用量以及减少废液的产生,节约成本、保护环境,对工业化生产有着重要作用。因此,在前期氨-氯化铵碱性矿浆电解体系的研究基础上,探讨电解液循环对Cu的回收率、电流效率和纯度以及Cu和Ni、Zn、Pb等金属迁移转化的影响,以期为后期工业化应用奠定基础。
1. 实验部分
1.1 实验材料与试剂
本实验所使用的WPCB-MPs已拆除元器件,经切割式破碎机破碎(BR20,中科骏驰精密仪器(北京)有限公司),过40目筛,得到粒径<0.45 mm的WPCB-MPs粉。
采用HCl-HNO3-HClO4-HF[18]对样品进行消解,通过电感耦合等离子体光学发射光谱法(ICP-OES,Optima 8300,美国PerkinElmer公司)测定其金属的质量分数,结果如表1所示。WPCB-MPs中最主要元素是Cu,其质量分数达到34.30%;其次是Ba、Fe、Al、Ni,质量分数分别为2.40%、1.59%、1.40%、1.42%;然后是Zn、Pb、Sn、Mg、Cr,质量分数均低于1%,共计为2.69%,远低于铜。
表 1 废手机板主要成分Table 1. Main compositions of WPCB-MPsCu Ba Fe Al Ni Zn Pb Sn Mg Cr 34.30% 2.40% 1.59% 1.40% 1.42% 0.89% 0.55% 0.73% 0.28% 0.24% 本实验所用氨水(NH3·H2O)、五水硫酸铜(CuSO4·5H2O)、氯化铵(NH4Cl)、氯化钠(NaCl)皆为分析纯,实验用水为超纯水。
1.2 实验装置与方法
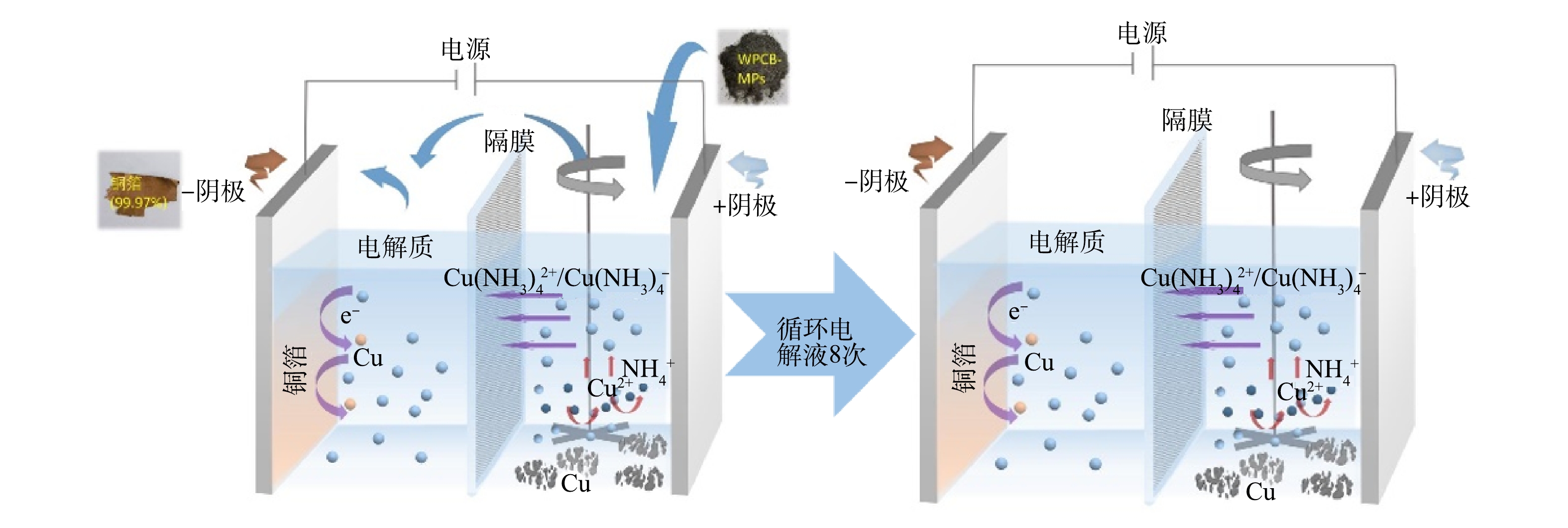
实验采用自制的聚四氟乙烯槽(10 cm×6 cm×7 cm),如图1所示。耐酸碱的滤布分隔成阴极区和阳极区,阴极区宽4.5 cm,阳极区宽5.5 cm。阳极使用钛表面镀钌铱电极,阴极为钛板,极板的尺寸为6.95 cm×6.5 cm×0.2 cm。反应时采用精密增力电动搅拌器(JJ-1,江苏金怡仪器科技有限公司,中国)在阳极区进行机械搅拌,使线路板粉与电解液充分接触。
首次电解时电解液200 mL,0.5 mol∙L−1 NaCl、0.5 mol∙L−1 NH4Cl、4 mol∙L−1 NH3∙H2O、20 g∙L−1 Cu2+(CuSO4∙5H2O)。将6 g WPCB-MPs粉末添加到阳极室中,搅拌,20 mA·cm−2下电解3 h。电解完成后,收集阴极区的铜箔,用1∶2的氨水混合液反复冲洗以洗去铜箔表面的铜氨络合物,洗净后于60 ℃下干燥至恒重。浆料通过0.45 μm的多孔滤膜进行抽滤,阳极渣60 ℃下干燥至恒重,分离后的电解液则用于第2次循环。第2次电解,使用第1次电解后的剩余电解液,用氨水调节电解液的pH至9.90左右,同时,用NH4Cl适当调节电解液NH4+物质的量浓度,在相同的Cu2+质量浓度、电流密度、固液比和电解时间下进行第2次实验。反应结束后,收集阴极产物、阳极渣以及电解液。重复该过程7次,具体如表2所示。
表 2 电解液循环体系实验安排Table 2. Experimental arrangements of the electrolyte circulation system循环次数 电流密度/(mA∙cm−2) 固液比/(g∙L−1) 时间/h 调节前电解液中Cu2+质量浓度/(g∙L−1) 调节后电解液中Cu2+质量浓度/(g∙L−1) 反应前pH 反应后pH 电解液/mL 氨水加入量/mL 1 20 30 3 − 20 10.20 9.5 200 − 2 20 30 3 20.75 20 10.00 9.2 205 19 3 20 30 3 21.63 20 9.90 9.10 210 28 4 20 30 3 20.47 20 9.90 9.10 209 18 5 20 30 3 20.34 20 9.90 9.10 200 15 6 20 30 3 19.63 20 9.90 9.00 200 20 7 20 30 3 21.08 20 9.90 9.30 208 17 8 20 30 3 20.47 20 9.90 9.10 206 13 注:“−”表示该数值不存在。 每次电解之后,分别收集阳极渣、阴极产物、电解液。阴极产物和阳极渣在HCl-HNO3-HClO4-HF体系[18]下进行消解。消解液和电解液中铜浓度采用紫外分光光度法(730 nm)测定[19],其他金属则使用ICP-OES测定。阴极产物的物相及微观形态分别通过X射线衍射仪(XRD,Japan Rigaku, 29 /Ultima IV)和扫描电子显微镜(SEM, Cari Zeiss, UItra55, Heidenheim ,德国)进行表征。
Cu回收率、阴极产物纯度、Cu的电流效率、金属在阳极渣、阴极产物、电解液中的分布率计算方法如式(1)~式(4)所示。
Cu回收率=100%−m1w1m2w2 (1) 式中:m1为阳极渣质量,g;w1为阳极渣中金属的质量分数;m2为WPCB-MPs粉质量,g;w2为WPCB-MPs粉中金属的质量分数。
阴极产物铜纯度=100%−其他金属的质量分数 (2) 铜的电流效率=m3m4×100% (3) 式中:m3为实际得到的阴极铜的质量,g;m4为根据法拉第定律计算得到的理论阴极铜的质量,g。
m4=MCuItZCuF (4) 式中:MCu为Cu的相对分子质量,63.54 g∙mol−1;I为通过的电流,A;t为电解反应的时间,h;ZCu为铜的价态,2;F为法拉第常数,F=96 485.3 C∙mol−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 电解液循环对Cu回收率、纯度、电流效率的影响
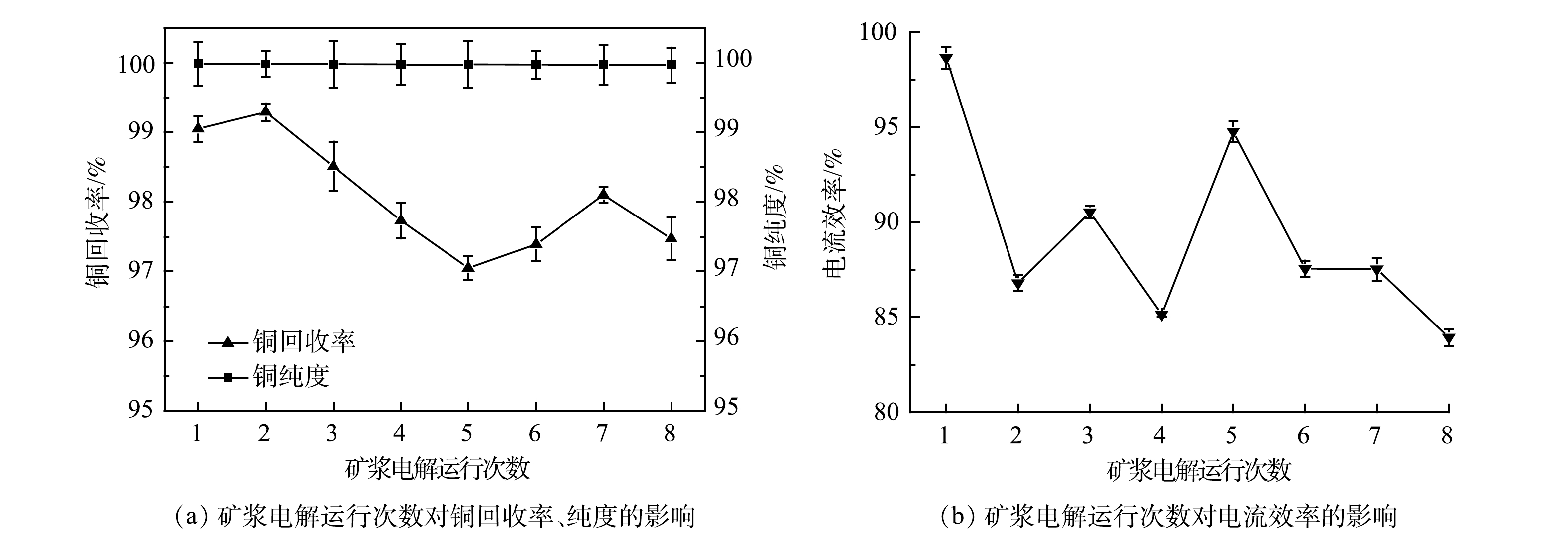
阴极铜的纯度和电流效率是金属回收率的重要指标[20]。因此,通过阴极铜回收率、纯度和电流效率,分析了矿浆电解回收过程中电解液重复使用对铜的影响(图2)。结果表明,初次运行时,阴极铜的纯度、电流效率和回收率分别为99.98%、98.63%和99.05%。随着电解液的重复使用,阴极铜的纯度与回收率波动较小,尤其是纯度,达到99.9%以上。这是因为,在该系统中,WPCB-MPs中的Cu可形成可溶性氨络合物被选择性浸出,而Fe和Mn等金属几乎不形成此类络合物[21],这极大提高了阴极铜纯度。另外,铜回收率的变化也较小,高于95%(如图2(a))。铜的电流效率变化幅度较大,但均在83%以上(如图2(b)),远高于铜电解精炼的电流效率(60%~70%)。其原因可能是,WPCB-MPs中的Cu能直接一步溶解生成一价或二价铜氨络合物,二价铜氨络合物又能与金属铜反应生成一价铜氨,最终使溶液中的部分铜以一价铜的形式沉积,从而提高了电流效率(式(5)~式(9))[22]。氨水容易挥发,易有挥发性气体NH3生成,由此可见,消耗的氨水中N的去向主要以Cu(NH3)42+、Cu(NH3)2+、NH3、NH3·H2O、NH4+形式存在。
Cu+2NH3⋅H2O→Cu(NH3)+2+2H2O+e (5) Cu+4NH3⋅H2O→Cu(NH3)2+4+4H2O+2e (6) Cu(NH3)2+4+Cu→2Cu(NH3)+2 (7) 2Cu(NH3)2+4+6H++3e→Cu(NH3)+2+Cu+6NH+4 (8) Cu(NH3)+2+2H++e→Cu+2NH+4 (9) 2.2 电解液循环对Cu分布的影响
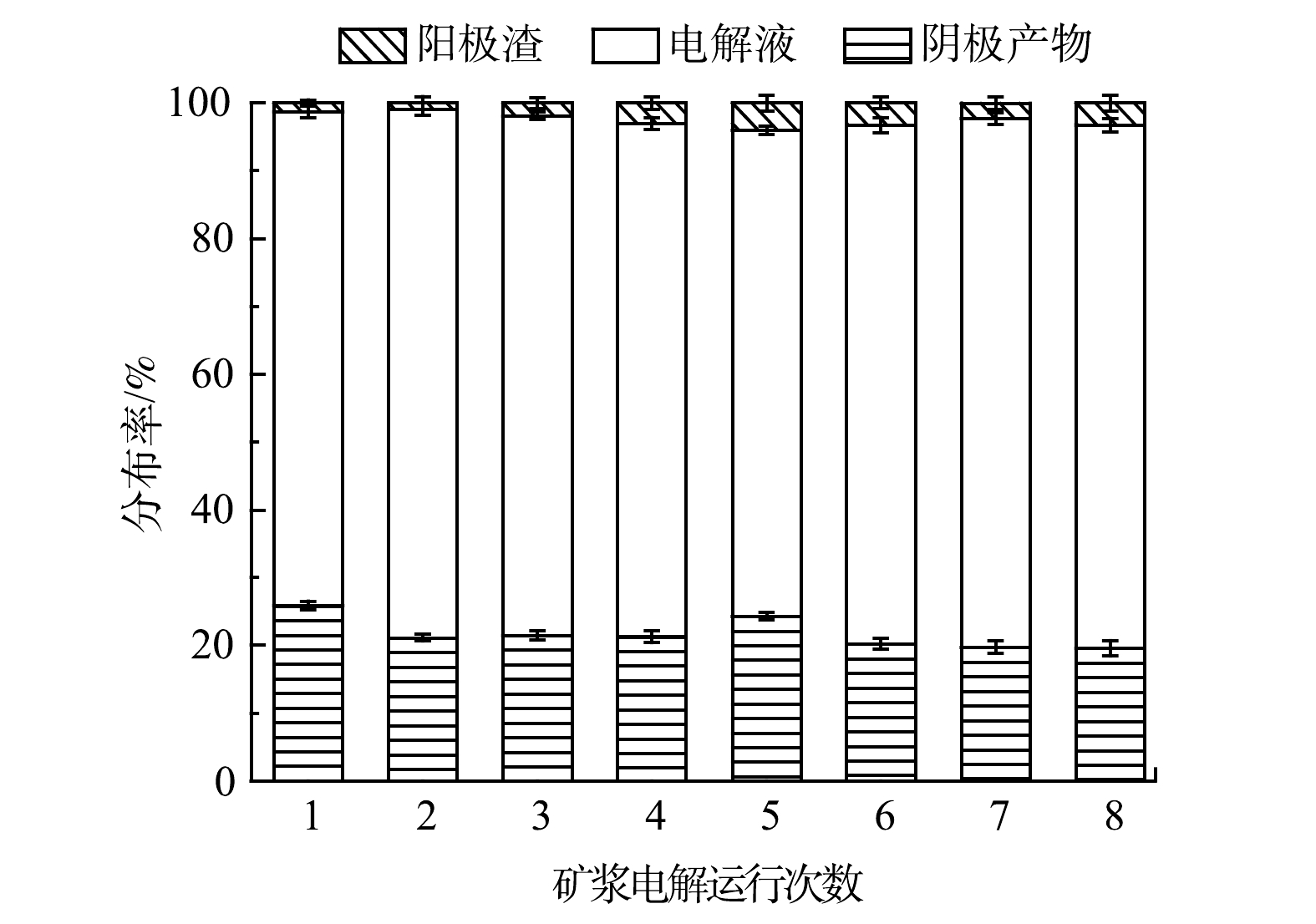
在电解液循环过程中,为探索各金属的变化规律,可通过各金属在阳极渣、阴极产物、电解液中的分布率来表示。矿浆电解运行次数对铜在阳极渣、电解液、阴极产物中分布的影响如图3所示。首次电解后,Cu在电解液与阴极产物中的分布率分别为72.87%和25.86%,仅有1.27%的Cu存在于阳极渣中。首次矿浆电解反应后剩余电解液中Cu的分布率远高于阴极产物,且剩余电解液中Cu的质量浓度(20.75 g∙L−1)与矿浆电解前电解液中Cu的质量浓度(20 g∙L−1)相近,适合再次循环。第8次电解之后,Cu在电解液中的分布率依旧较高,为77.19%。在8次实验中,阳极渣中Cu的分布率呈现小幅度波动性变化规律,在第2组实验达到最低,为0.89%。这表明,电解液重复使用的次数对WPCB-MPs中Cu的回收影响很小,几乎所有的Cu都以金属箔片的形式沉积在阴极或浸出到电解液中[23]。另外,Cu在电解液与阴极产物中的分布率变化幅度较小,但其在电解液中的分布率始终高于阴极产物,这可能是由于阴极Cu的沉积速率始终小于阳极Cu的浸出速率,从而使电解液中的Cu累积增加。
2.3 电解液循环对Al、Fe、Ba、Ni、Zn、Pb分布的影响
电解液重复使用对Al、Fe、Ba、Ni、Zn、Pb分布的影响如图4所示。首先,在8次运行中,Al在电解液中的分布率从21.55%逐渐增加至69.35%,在阳极渣中的分布率从78.42%逐渐降低至30.59%(如图4(a))。这说明,碱性矿浆电解体系可以使WPCB-MPs中的Al浸出在电解液中得到富集。在8组实验的阴极产物中,未检测到Al。这是因为,Al具有较低的浓度和还原电位(−1.676 V),从而不能在阴极沉积[24]。具有相同变化趋势的还有Ba与Ni,其在电解液中的分布率均逐渐增加(如图4(c)~图4(d)),但Ni在电解液中的分布率始终大于Ba。其原因可能是Ni能与氨水进行络合,生成[Ni(NH3)4]2+,而Ba很难在该体系中反应。
Fe大部分存在于阳极渣中。例如,在第7组实验中,阳极渣中Fe的分布率达到最大,为99.93%;在第2组实验中,Fe在阳极渣中分布最少但也高达81.28%(如图4(b))。8组实验的阴极产物中均未检测到Fe。表明在该体系中,WPCB-MPs中的Fe很难浸出到电解液中。这是因为WPCB-MPs中的Fe一般不会与氨水发生氧化还原反应,即使将Fe置于浓氨水中也不发生络合反应生成铁氨络合物。Pb因其具有两性的特征,既可与碱反应生成铅酸盐,又能与酸作用生成PbCl2和PbSO4的表面膜,因此,在电解液中的存在是不稳定的(如图4(f))。LI等[25]采用火法与湿法相结合的“湿-火-湿”回收工艺对废铅酸蓄电池进行回收,得到了一种高纯度大于99%、回收率为93.1%的有用的碘化铅资源,这对铅的再利用有很大帮助。
Zn在阳极渣中的分布率普遍很低。例如,在第8组实验中,Zn在阳极渣中的分布率为2.03%,高达97.97%的Zn分布于电解液中(如图4(e))。这表明,碱性矿浆电解法可以将大部分Zn从WPCB-MPs中浸出。其原因可能是,WPCB-MPs中的Zn与水生成Zn(OH)2和H2,Zn(OH)2又溶于氨水,反应不断进行,生成[Zn(NH3)4](OH)2络合物(式(10)~式(11))。由于该物质只能在酸性体系中电离沉积,因此,随着循环的进行,在阴极产物中未检测到Zn的存在[26]。
Zn+2H2O→Zn(OH)2+H2 (10) Zn(OH)2+4NH3⋅H2O→[Zn(NH3)4](OH)2+4H2O (11) 从电解液循环对Cu、Al、Fe、Ba、Ni、Zn、Pb分布的影响可以看出,随着循环的进行,金属在电解液中的分布率在整体上呈现逐渐增加的趋势。这意味着溶液中的总金属浓度越来越高,呈金属富集现象。结合阴极产物Cu的纯度分析,8组实验中其纯度维持在99.9%以上,这表明,电解液中金属的累积不会给阴极铜的纯度带来不利影响。另外,对于电流效率,虽然Al、Fe、Ba、Ni、Zn、Pb等金属在电解液中的转移引起电能损失,但由于这些金属在原样中的量很少且很难沉积,因此对电流效率影响很小。
2.4 阴极产物特性分析
阴极产物中主要金属的质量分数变化如表3所示。结果表明,随着循环的进行,阴极产物中Cu的质量分数均达到了99.9%以上。这说明,电解液重复使用的频率几乎不会影响阴极铜的纯度。另外,Fe、Ni、Zn、Mg、Cr在8组实验的阴极产物中均未检测到,说明这些金属均不会以电沉积的方式进行回收。Pb与Sn的质量分数缓慢增多,但是总量依然很少。相较之下,Pb的质量分数高于Sn。这是由于Pb电解反应的标准电极电位为−0.126 V,是金属电解反应中最接近于Cu(+0.342 V)的一类金属,因此,在过电位条件下,相邻近的金属Pb也会随之沉积[27]。
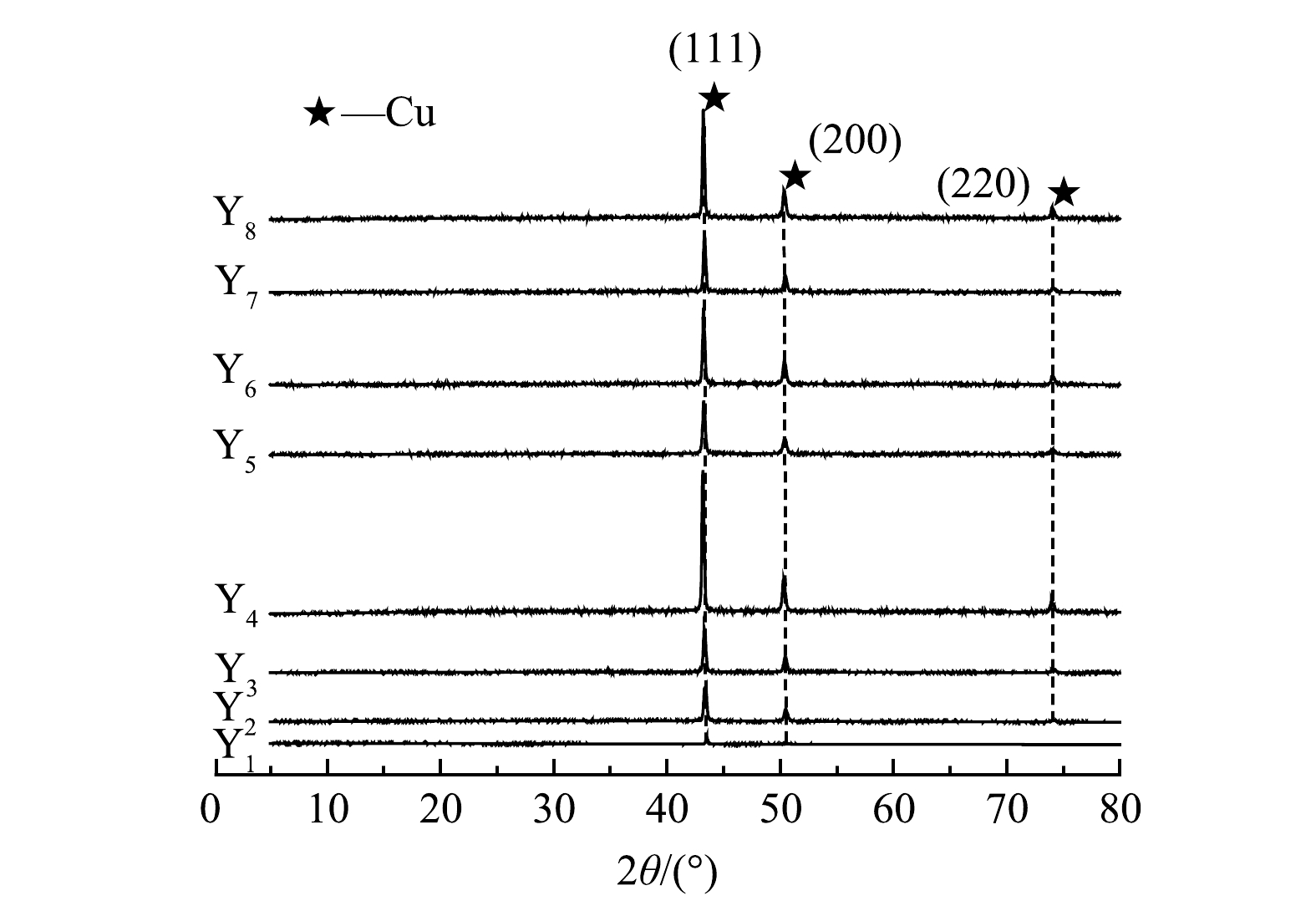
表 3 阴极产物主要金属的质量分数Table 3. Cathode products mass fraction of major metals阳极产物 Cu Fe Ni Zn Pb Mg Sn Cr Y1 99.984 0% ND ND ND 0.016 0% ND ND ND Y2 99.981 8% ND ND ND 0.018 1% ND 0.000 1% ND Y3 99.980 1% ND ND ND 0.019 7% ND 0.000 2% ND Y4 99.976 9% ND ND ND 0.022 0% ND 0.001 1% ND Y5 99.976 2% ND ND ND 0.022 4% ND 0.001 4% ND Y6 99.971 7% ND ND ND 0.026 4% ND 0.001 9% ND Y7 99.969 9% ND ND ND 0.027 4% ND 0.002 7% ND Y8 99.968 0% ND ND ND 0.029 0% ND 0.003 0% ND 注:ND表示未检出;Y1~Y8分别表示第1组~第8组电解得到的阴极产物。 将8组实验中阴极得到的铜箔进行XRD扫描分析,结果如图5所示。由图可以看出,8组阴极铜箔在2θ角为43.316°、50.448°和72.124°处都出现明显的衍射峰,与Cu的JCP-DS 标准卡片的(JCPDS No.36-1450)的(111)、(200)、(220)特征衍射峰的峰位置一一对应,且衍射图谱中没有出现其他峰。这充分说明,在碱性矿浆电解液循环实验下得到的阴极铜纯度很高,这与消解的结果一致。
由Scherrer公式(D=kλ/Bcosθ)[28]计算晶粒尺寸大小,结果见表4。由衍射图谱可知,8组样品的(111)晶面衍射强度最强。第一组循环的阴极铜箔沿(111)晶面的平均晶粒大小为44.189 nm,随着循环的进行,阴极铜箔的晶粒尺寸总体上小幅度降低,但基本维持在31 nm以上。这表明多次循环后生成的铜箔致密,稳定,纯度高。另外,已有文献报道[29],织构(111)可提升铜箔的抗拉强度,织构(220)可提高铜箔的伸长率,但会降低铜箔的抗拉强度,因此该阴极铜箔可能具有较高的抗拉强度。
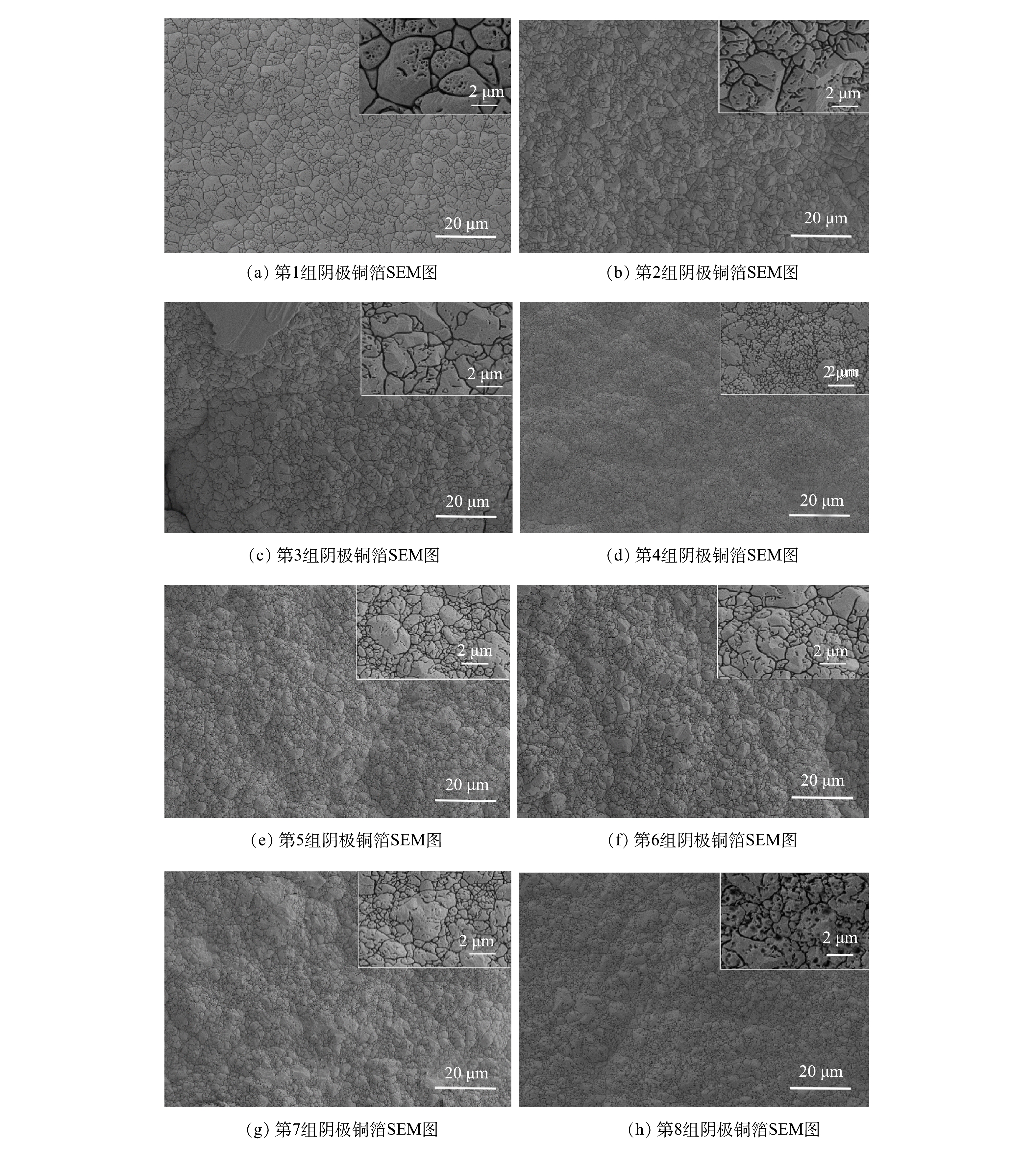
表 4 阴极产物最强峰的半峰宽、晶粒尺寸Table 4. Half peak width and grain size of the strongest peak of the cathode product阴极产物 Cu(111)晶面半峰宽/(°) 晶粒尺寸/nm Y1 0.181 44.189 Y2 0.301 26.572 Y3 0.253 31.613 Y4 0.215 37.201 Y5 0.253 31.614 Y6 0.216 37.029 Y7 0.232 34.475 Y8 0.207 38.639 注:Y1~Y8分别表示第1组~第8组电解得到的阴极产物。 将8组实验后所得阴极铜箔毛面(铜箔具有2个形貌完全不同的面,一个是从阴极板剥离的铜箔光面,一个是与之对应的铜箔毛面)进行SEM扫描分析,观察其微观形貌,结果如图6所示。可以看出,所有铜箔均表面平整,外观无其他任何颗粒状枝晶,且Cu原子连接紧密,排列有序,这与XRD扫描结果一致。但这8组阴极铜箔的微观结构也存在变化,例如,从图6(a)~图6(h)可知,随着循环的进行,铜箔表面的凹坑逐渐增多。这可能是因为铜原子沉积速度过快,在铜箔上冲撞出许多的凹坑所致[30-31]。
3. 结论
1)基于碱性矿浆电解法对WPCB-MPs中的金属进行回收,电解液可以成功地重复使用7次。该工艺主要回收金属铜,其他金属如Zn、Ni等也可以富集在电解液中。
2)电解液重复使用对阴极产物铜回收率、纯度影响不大,分别维持在99.9%、90%以上。铜主要分布在电解液和沉积物中,其他金属则基本分布在电解液与阳极渣中。
3)阴极产物中Pb的质量分数较高,因此,如何通过改良工艺,使阴极产物Pb的质量分数降低,以符合A级铜标准是目前亟须解决的问题。
-
[1] Wang J., Chen C. Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae: A Review. Biotechnol. Adv., 2006,24(5):427-451 [2] Lovley D. R.,Phillips E. J. P.,Gorby Y. A.,et al. Microbial reduction of uranium. Nature, 1991,350(6317):413-416 [3] Lovley D. R.,Phillips E. J. P. Bioremediation of uranium contamination with enzymatic uranium reduction. Environ.Sci.Technol., 1992,26 (11):2228-2234 [4] Merroun M. L.,Selenska-Pobell S. Bacterial interactions with uranium: An environmental perspective. Contam. Hydrol., 2008,102(3):285-295 [5] Wall J. D.,Krumholz L. R. Uranium reduction. Annual Review of Microbiol., 2006,60:149-166 [6] Suzuki Y.,Suko T. Geomicrobiological factors that control uranium mobility in the environment: Update on recent advances in the bioremediation of uranium-contaminated sites. Mineral Petrol. Sci., 2006,101(6):299-307 [7] Fernandez N.,Diaz E. E.,Amils R.,et al. Analysis of microbial community during biofilm development in an anaerobic wastewater treatment reactor. Microbiol. Ecol.,2008,56(1):121-132 [8] Gonzalez-Gil G.,Lens P. N. L.,Van-Aelst A.,et al. Cluster structure of anaerobic aggregates of an expanded granular sludge bed reactor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2001,67(8):3683-3692 [9] Tapia-Rodriguez A.,Luna-Velasco A.,Field J. A.,et al. Anaerobic bioremediation of hexavalent uranium in groundwater by reductive precipitation with methanogenic granular sludge. Water Research, 2010,44(7):2153-2162 [10] Nancharaiah Y. V.,Joshi H. M.,Mohan T. K. V.,et al. Aerobic granular biomass: A novel biomaterial for efficient uranium removal. Current Science,2006,91(4):503-509 [11] 夏良树,王孟,邓昌爱,等. 榕树叶-活性污泥协同曝气处理含铀废水. 核化学与放射化学, 2006,28(4):231-235 Xia Liangshu, Wang Meng, Deng Changai, et al. Synergistic aeration biosorption of uranium containing wastewater by banyan leaves activated sludge. Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 2006,28(4):231-235 [12] Goncalves M. M. M.,Goncalves A. C. A.,Leite S. G. F.,et al. Heavy metal removal from synthetic wastewaters in an anaerobic bioreactor using stillage from ethanol distilleries as a carbon source. Chemosphere, 2007,69(11):1815-1820 [13] Nwyenys E.,Baeyens J.,Dewil R.,et al. Advanced sludge treatment affects extracellular polymeric substances to improve activated sludge dewatering. Hazard. Mat.,2004,106(2-3):83-92 [14] 谢冰,奚旦立,陈季华. 活性污泥工艺对重金属的去除及微生物的抵抗机制. 上海环境科学, 2003,22(4):283-288 Xie Bing, Xi Danli, Cheng Jihua. Mechanisms of removal heavy metals and resistance to microorganisms by activated sludge process. Shanghai Environmental Sciences, 2003,22(4):283-288 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2550
- HTML全文浏览数: 1478
- PDF下载数: 1304
- 施引文献: 0



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: