-
重金属具有毒性强、来源广、易富集且难降解等特征,对环境和人体健康有着间接和直接的危害,其在自然生态系统的分布、迁移转化和毒性效应一直是环境学科研究的前沿热点问题之一[1-5]. 重金属在自然生态系统的分布特征对于深入认知和评估其环境行为和生态效应具有重要的指示意义. 研究表明,沉积物作为水生态系统中重金属主要的汇,可以作为水生态系统中重金属污染程度的“指示剂”[6-8]. 沉积物中的重金属可通过多途径如水动力扰动、化学和生物方式释放至天然水环境中,对水生生物和人类健康造成潜在和直接的影响甚至是毒性效应 [9-10]. As、Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr、Cu 是《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T166-2004)中监测的重金属,研究表明,这6种金属所造成污染及潜在生态风险更为严重[11-12]. 沉积物中有机物和营养盐是沉积物中重要组成部分,其中有机质对沉积物中重金属及有毒化合物的毒性、环境迁移力及营养盐交换有重要的作用[13-14]. 氮和磷不仅可为水体中浮游生物提供养分,亦可在水体和沉积物中迁移转化,研究表明,沉积物是水体中氮和磷的重要内源[15]. 因此,探究和明确沉积物中重金属、有机质和营养盐的含量特征和潜在风险,将为湖泊水环境污染防控策略提供科学依据.
湖泊对于维护地区生态健康,调节气候并为人类社会提供多种服务,特别是生境脆弱的西北地区,具有重要的作用[16]. 半咸水湖泊,又称为微咸水湖,是指湖水矿化度在1—35 g·L−1的湖泊,半咸水湖泊中鱼类生物量相对淡水湖泊较低,浮游动物与浮游植物占比低于淡水湖泊[17]. 西北地区湖泊多以半咸水湖泊为主,水动力环境较为封闭,地下水排泄能力较弱,易受人类活动和气候变化的影响[18-19]. 宁夏沙湖地处西北内陆干旱荒漠区域,是宁夏最大的天然半咸水湖泊,对于宁夏的生态调控起着不可或缺的作用[20]. 沙湖水生态环境脆弱,具备半咸水湖泊鲜明的特点. 由于补水短缺、水产养殖与旅游开发不合理性等因素,导致过量营养盐进入宁夏沙湖,影响多种元素在沉积物-水界面的分布特性及生物有效性. 重金属吸附在沉积物表面,在特定条件下,会向水体中再度释放,成为潜在污染源,同时对底栖动物产生毒性,对湖泊生态系统产生影响. 当前,针对沙湖的相关研究主要集中于水环境和浮游动植物多样性方面[21-22],这对于评估重金属在典型湖泊湿地的分布特性及风险是不利的. 2014年王春霞等[23]对沉积物重金属分布特征分析,但研究时间较早且未对宁夏沙湖沉积物中重金属污染特征、潜在风险进行分析.
本研究通过监测沙湖表层沉积物的理化指标和重金属含量,分析理化指标和重金属的空间分布特征,运用单因子污染指数法、地积累指数法和潜在生态风险指数法等多种手段对沉积物重金属污染特征进行评价和分析,并通过相关性分析和主成分分析对沉积物中重金属与营养盐相关性及来源解析. 本研究对揭示宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属分布情况,强化污染防治具有重要指导意义.
-
宁夏沙湖自然保护区(E 106°19′6″—106°24′10″,N 38°45′17″—38°49′42″)位于银川平原中北部,贺兰山东麓的蝶型静水湖泊,堤岸分隔的6个小型湖沼. 水域总面积3498.39 hm2,海拔1093—1102 m. 气候属典型的大陆性半湿润半干旱气候,年平均气温为 9.75 ℃,年降水量为 174.7 mm,多集中在6—9月,年蒸发量为1400.0—1600.0 mm,平均水深2.2 m,最深处为4.0—6.0 m [20]. 宁夏沙湖自然保护区位于银川断陷盆地的中心地带,堆积了大量河湖物质,下伏地层为细沙、黏土和湖相地层. 地势低洼,地面高程1088—1110 m,坡度平缓,沟渠纵横,土壤沼泽化、潜育化和盐渍化现象普遍. 沙湖是具有构造湖和牛轭湖双重特征的湖泊,兼具生物多样性保护、水源涵养、治污纳污、调节绿洲生态和调蓄防洪等多种功能.
-
根据宁夏沙湖水域特点设置9个采样点:采样点1(S1,1号曝气机),采样点2(S2,2号曝气机),采样点3(S3,3号曝气机),采样点4(S4,新澄清池入水口),采样点5(S5,湖心),采样点6(S6,鸟岛),采样点7(S7,2号桥),采样点8(S8,假日酒店东侧),采样点9(S9,1号拦水坝北侧),如图1所示.
于2018年4月18日(春)、7月22日(夏)、10月25日(秋)、2019年1月23日(冬)使用彼得森采泥器(PSC-1,采泥面积1/40 m2)采集表层沉积物(深度约为25 cm),用GPS导航定位采样点,确保采样地点相同. 样品采集时间为早上8:00—11:00. 每个采样点采集3个平行样品,去除动植物残体及石块,混合后装入自封袋带回实验室,−20 ℃保存. 采集的沉积物置于阴凉通风的地方阴干、混匀,研磨后过100目筛后备用.
-
根据《土壤农化分析方法》[24] 中的方法,测定沉积物的 pH、有机质(OM)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)和总盐的含量. 重金属含量 (As、Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr、和 Cu)按照相关国家标准(GB15618-1995、GB/T17141-1997、HJ491-2019)测定.
-
基于单因子污染指数法评价不同采样点营养盐和重金属污染物超标情况. 公式为:
PIi是沉积物重金属i的污染指数;Ci是沉积物中重金属i的实测含量;Si 是重金属 i的评价标准含量,本研究采用宁夏沙湖沉积物元素平均值作为标准值[23](表1).
-
运用Muller[26]提出的地理累积指数(Geo - accumulate Index, Igeo)确定宁夏沉积物重金属污染的定量程度,如公式(1):
Ci是重金属含量的实测值;Cn是计算所需的背景值,本研究采用宁夏沙湖沉积物元素平均值作为背景值从而更加真实地反映其污染现状[23],k为1.5;按Igeo可将沉积物污染指数分为以下7类:Igeo<0,清洁;0 ≤ Igeo<1,轻度污染;1 ≤ Igeo<2中度污染;2 ≤ Igeo<3,偏重度污染;3 ≤ Igeo <4 ,重度污染;4 ≤ Igeo<5,严重污染;≥ 5极严重污染.
-
采用Hakanson[27]方法对沉积物重金属污染情况进行潜在生态风险评价,公式如(2)、(3):
其中,Eir是第i种元素潜在生态风险系数;RI是潜在生态风险指数;Tir 是第i种重金属的毒性系数;Ci为沉积物中第i种重金属的实测值;CBi为第i种重金属的背景值. 本研究所采用的重金属背景值和毒性系数见表1. 重金属潜在生态风险程度评价标准见表2.
-
数据统计和计算使用Excel 2020,显著性分析、相关性分析和主成分分析采用JMP Pro V13.2.0分析,采用Orgin 2021绘图.
-
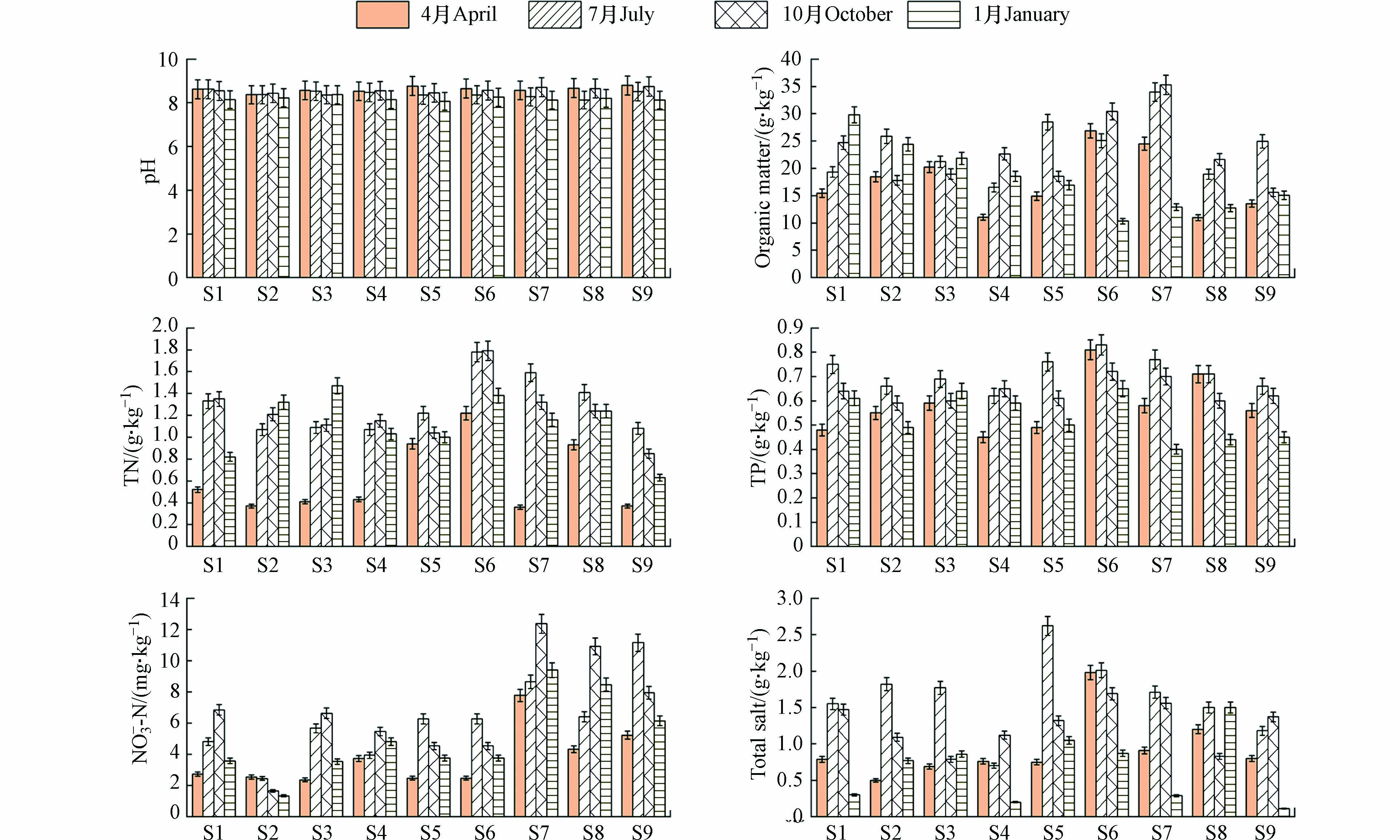
对宁夏沙湖各采样点沉积物理化性质进行分析(图2),结果表明,宁夏沙湖各采样点pH值范围为8.13—8.79,平均值为8.41,呈半碱性,各样点间pH无显著空间分布趋势,在不同季节间无明显差异,说明pH受外界影响较小,主要受湖泊自然运动与沉积作用影响.
OM是营养物质的载体,对氮、磷等营养元素在沉积物中的迁移、矿化起到重要作用[28]. 采样点沉积物中OM含量范围为10.34—35.27 g·kg−1,平均值为20.50 g·kg−1. S7各季节平均值最高,含量为26.66 g·kg−1,S8各季节平均含量最低,含量为16.06 g·kg−1。S7采样点分布大量水生植物,有利于OM富集. 夏季(7月)OM含量最高,含量为23.80 g·kg−1,春季(4月)含量最低,含量为17.34 g·kg−1,表明宁夏沙湖夏季沉积物营养物质丰富,肥力较高. TN变化范围在0.37—1.79 g·kg−1,TN全年平均值分别为1.06 g·kg−1,其中S6各季节平均含量最高,含量为1.54 g·kg−1,S9各季节平均值最低,含量为0.73 g·kg−1 .夏季(7月)TN含量最高为1.29 g·kg−1,春季(1月)含量最低为0.62 g·kg−1. TP范围在0.40—0.83 g·kg−1 之间,平均值为0.62 g·kg−1,其中S6各季节平均含量最高,含量为0.75 g·kg−1 ,S9各季节平均值最低,含量为0.57 g·kg−1. 夏季(7月)TP含量最高,含量为0.72 g·kg−1,春季(4月)含量最低,含量为0.53 g·kg−1. 沉积物中有机氮和有机磷主要来自水体中生物排泄物以及生物残体[28],S6位于鸟岛,生物排泄物较多,并且位于旅游区受人类活动影响较大,S6采样点各季节TN和TN平均值含量较高. 沉积物中OM、TN和 TP含量均在春季最低,夏季最高。因为夏季水温较高,水温是影响沉积物氮和磷释放的关键因素之一,随着夏季水温升高,底栖生物活动加强,增加对底泥扰动,通过发生硝化和反硝化等作用促进沉积物中生物残体向盐类物质转化[29]。在夏季宁夏沙湖有大量外源性氮磷营养盐会随着补水水源进入宁夏沙湖湖区内,而春季补水量减少,入湖外源性氮磷营养盐降低.
沉积物
NO−3 -N含量变化为1.34—12.36 mg·kg−1,平均值为5.8 mg·kg−1. 各采样点NO−3 -N含量差异较大,S2各季节平均值最低,含量为2.00 mg·kg−1,S7各季节平均值最高,含量为9.54 mg·kg−1. 主要是因为S7采样点邻近旅游区荷花邸和运河处,受人类活动干扰较大,而S2采样点离旅游区较远,人类活动对其干扰较小. 秋季(10月)NO−3 -N含量最高为7.58 g·kg−1,冬季(1月)含量最低为3.91 g·kg−1. 冬季补水较少,入湖携带外源输入的污染物较少,加之冬天温度最低,沉积物中硝化细菌的硝化作用减弱,导致沉积物NO−3 -N含量较低. 夏季气温升高降水增多,湖磷污染物增加,使NO−3 -N含量升高.根据卞培旺等的研究结果,全盐量越高,腐蚀速率越大[30]. 宁夏沙湖沉积物全盐含量变化范围为0.11—2.62 g·kg−1,平均值为1.12 g·kg−1,S5和S6采样点全盐含量高于其他采样点,分别为1.64 g·kg−1、1.44 g·kg−1,表明该区域底质环境具有一定的腐蚀性. 夏季(7月)全盐含量最高,含量为1.65 g·kg−1,冬季(1月)含量最低,含量为0.66 g·kg−1.
Ji等的研究结果表明,同一湖泊中沉积物理化性质差异主要是受人类活动影响[31]. 本研究中人类活动较为密集的区域(S5、S6和S7)沉积物中OM、TN、TP和
NO−3 -N高于其他区域. 夏季、秋季沉积物OM、TN、TP、NO−3 -N和全盐含量较高,春季、冬季含量较低,主要是因为夏季和秋季补水增加,入湖携带污染物增加,并通过沉积物和悬浮物中自然胶体的吸附作用絮凝沉降,且水温较高,底栖生物活动加强,对底泥的扰动增加,有助于沉积物中生物残体发生硝化和反硝化等作用向盐类物质转化[29],促使 OM、TN、TP和NO−3 -N含量升高,春季和冬季补水少,入湖携带外源污染物少,且水温较低,抑制氮、磷营养盐释放. 因此,水温和外源营养盐输入是影响宁夏沙湖沉积物营养盐含量重要因素. -
宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属含量特征如表3所示. 所有采样点中,仅S3和S4采样点As含量超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值,分别是宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值的1.01倍和1.08倍. S3、S4、S5和S6采样点As含量超过宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. 所有采样点中Pb和Cd含量都较高,均超过中国土壤元素背景值和宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值[32-33],但所有采样点中Pb低于宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值,S2、S4、S5、S6和S8采样点中Cd含量超过宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. S1、S7和S8采样点中Hg含量超过中国土壤元素背景值,分别是中国土壤Hg含量背景值的1.23、1.08和1.08倍. S1、S5、S7、S8和S9采样点中Hg含量超过超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值和宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. 在所有采样点的沉积物中,Cr均未超过中国土壤元素背景值,仅S1、S3、S6和S8采样点超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值,S1、S2、S3、S5、S6、S7和S8超过宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. 所有采样点中只有S3采样点Cu含量超过中国土壤元素背景值,S1、S2、S3和S8采样点Cu含量超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值,分别是宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值的1.19、1.09、1.3、1.24倍. 各个采样点沉积物中6种重金属含量均未超过土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB15618-2018,pH >7.5,田地性质为其他),说明宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属污染程度较轻. S1沉积物中的Hg显著高于其他采样点,S3沉积物中的Cr和Cu显著高于其他采样点,S6沉积物中的Cd显著高于其他采样点(P < 0.05). 整体上看,受人类活动干扰较多的区域S1、S6重金属含量相对较高,王春霞对宁夏沙湖2014年沉积物重金属分布研究结果也支持了本文研究结论[23] .
湖泊自身环境的差异,加上人类活动干扰等因素影响,不同区域重金属存在一定差异性[34-35] . 结果表明,S1采样点中As的差异性最大,变异系数为46.15%;S2、S3、S4、S7和S8采样点中Cd的差异性最大,变异系数分别为86.15%、55.03%、72.83%、85.22%和66.18%;S2、S4和S9采样点中Hg的差异性最大,变异系数分别为66.67%、59 .98%和81.86%. As、Hg和Cd变异系数较高,说明在空间上分布不均匀[36-37].
宁夏沙湖沉积物中6 种重金属含量均值由高到低顺序为 Cr > Cu > Pb > As > Cd > Hg( 表4) . 沉积物中重金属含量受沉积物理化性质(如:OM、TN、TP、粒径等因素)以及温度等多种因素影响[38]. 结果表明:夏季(7月)和秋季(10月)沉积物中Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr和Cu的平均浓度高于春季(4月)和冬季(1月). 夏季和秋季温度较高,温度较高时加速了沉积物中重金属释放速度. 研究表明OM和TP含量与重金属含量呈正相关[39],但TN含量高时,沉积物吸附重金属量降低. 图2表明沉积物中OM、TN和TP在夏季和秋季含量较高,但TN含量较高时,并没有使得沉积物中重金属吸附能力降低,这可能时因为湖泊之间因所处地理环境存在一定差异. 因此,宁夏沙湖重金属含量呈现不同季节差异与水温、OM、TN和TP有关. 从变异系数来看,春季和夏季变异系数最高的是Cd,其次是Hg,最小的是Cr,表明Cd和Hg含量在春季和夏季沉积物中差异较大. 秋季和冬季变异系数最高的是Cd,其次是Hg,最小的是Cr,表明Hg和Cd含量在秋季和冬季沉积物中差异较大.
-
运用单因子污染指数法,对宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属评价,结果显示(见表5),各采样点6种重金属元素单因子污染指数均小于1,表明沙湖沉积物质量状况良好. 各采样点6种重金属单因子污染指数排序为 Cr > As > Pb > Cd > Cu > Hg,其中Cr的单因子污染指数最大,平均值达到0.89,其次为As和Pb,平均值分别为0.71和0.70,其余重金属单因子污染指数均小于0.7. Cr、Pb和As的单因子污染指数较高,应引起足够重视,加强此类沉积物重金属元素监测.
-
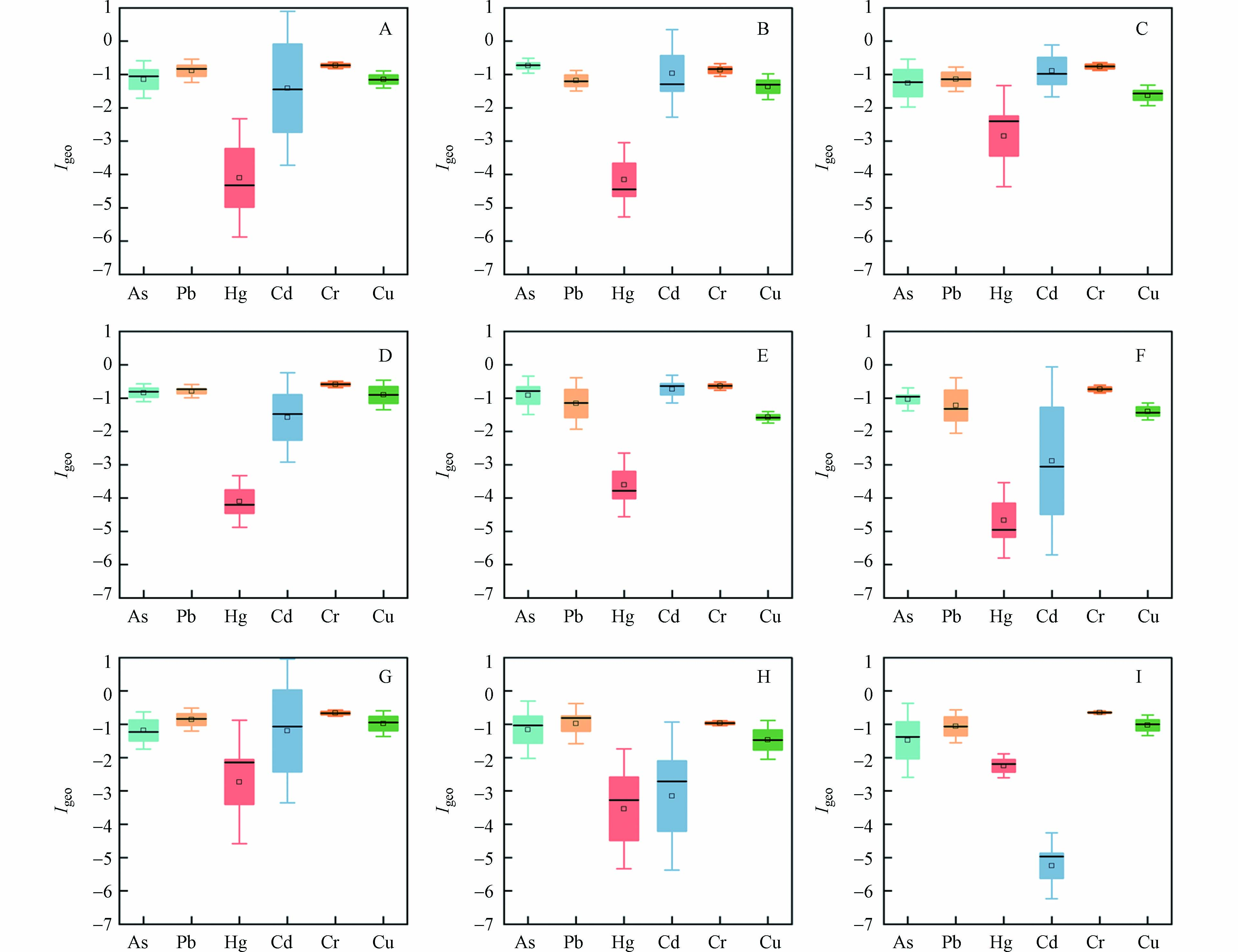
地积累指数对宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属的污染程度进行了评价(图3). S1采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Hg > Cr > Cu > Pb > As > Cd;S2采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Cd > Pb > Cu >As > Hg;S3采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Pb > As > Cu > Cd > Hg;S4采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cd > As > Cr > Pb > Cu > Hg;S5和S6采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Cd > Hg > Pb >As > Cu,Cr > Cd > As > Pb >Hg > Cu;S7采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > As >Pb > Cu > Cd > Hg;S8采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Cd > Hg > Cu > Pb >As;S9采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Pb > As > Cu > Hg > Cd. 所有地积指数均小于0,污染等级为清洁. 重金属年均值从大到小为 Cr > As > Pb > Cu > Cd > Hg,其中,Cr 地累积指数(-0.76)最大,在宁夏沙湖环境监测工作中需重点关注此金属元素.
空间分布结果为S8(−0.89) > S5(−1.11) > S9(−1.14) > S2(−1.16)> S4(−1.18) > S7(−1.49) > S1(−1.66) > S3(−2.09). S2、S3、S5、S7、和S8沉积物各采样点地积指数差异较小,可以推断,S2、S3、S5、S7、和S8采样点沉积物中的重金属来源相似,其余采样点沉积物中重金属地积指数差别较大,表明重金属来源有所不同.
-
潜在生态风险系数(Er)分析结果(表6),可以看出宁夏沙湖沉积物中Cd和Hg的风险等级最高,Cd处于中等生态风险(40 ≤ Er﹤80),Hg处于强生态风险(80 ≤ Er﹤160),Cd和Hg潜在生态风险系数分别在5.07—108.93和45.83—159.38之间,均值达到了74.98和83.76,其中Cd波动较大. S1和S9采样点中金属Cd潜在生态风险系数指数低于40,处于轻微生态风险(Er < 40),S3和S7处于中等生态风险(40 ≤ Er < 80),S2、S4、S5、S6和S8处于强生态风险. S7采样点中金属Hg潜在生态风险系数指数低于40,处于轻微生态风险,S2、S3、S4和S6处于中等生态风险,S1、S5、S8和S9处于强生态风险. 金属AS、Pb、Cr和Cu处于轻微生态风险(Er﹤40).
潜在生态风险指数(RI)结果可以得出(表6),宁夏沙湖沉积物中重金属RI值范围为167.04—311.45,均值为 222.81,所有采样点RI值均未超过600,采样点S7处于轻微生态风险(RI < 150),采样点S8处于强生态风险(300 ≤ RI < 600),其余采样点处于中等生态风险(150 ≤ RI < 300).
此外,表层沉积物中重金属Hg和Cd是重金属潜在生态风险的主要来源,贡献率分别达到了37.59%和33.65%. As贡献率达到了12.83%,Pb和Cu贡献了分别为6.23%和6.58%,Cr总贡献率低于4.00%. 在其他湖泊、水库和湿地也发现了类似结果[40-42]. 因此,未来应对宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属污染提高重视,特别是重金属Hg和Cd.
有研究表明采用多种评价方法评价沉积物重金属,能够更好说明沉积物中重金属复合污染特征[43],本研究采用单因子污染指数、地积指数和潜在风险指数综合地积累指数,评价宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属污染级别,整体来看,宁夏沙湖沉积物状态良好,其中Cr、As和Pb单因子污染指数和地积指数相对较高,而潜在风险指数结果与单因子污染指数和地积指数评价略有不同,Cd、Hg和As潜在风险指数较高,已往研究结果也呈现出潜在风险指数评价与单因子污染指数和地积指数评价结果略有不同[11,40,44]. 从空间上来看,三种评价方法均显示S8和S5采样点沉积物中重金属污染指数相对较高.
-
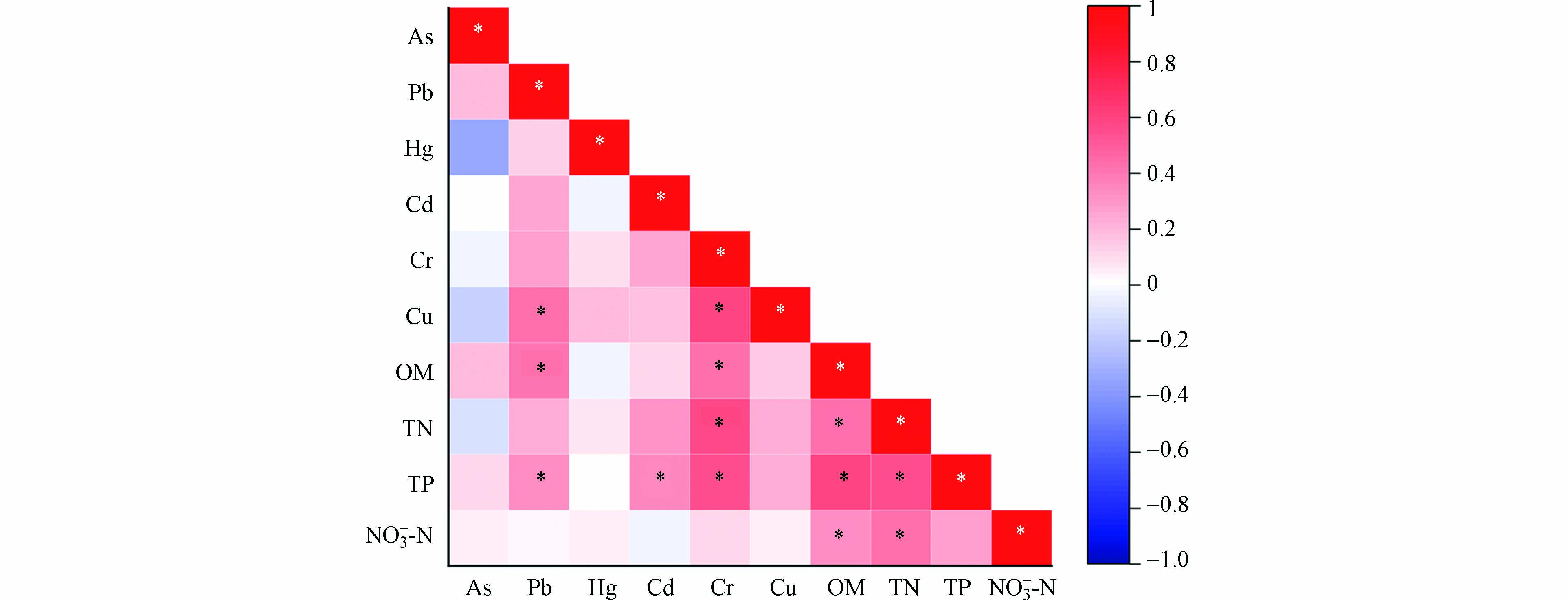
Pearson相关性分析结果如图4所示,结果表明 Cr 与 Cu、OM、TN、TP呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),Cr 与 Cu、OM、TN、TP具有相似的污染来源或产生了复合污染. OM与TN、TP和NO3−-N呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),说明沉积物OM的降解和释放对宁夏沙湖TN、TP和NO3−-N具有重要影响. TP与TN呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),说明TN和TP来源相同. As和Hg与其他元素的相关性都不高. 这表明 Pb、Cd、Cr、Cu、OM、TN、TP 具有相似的污染来源,而As和Hg的污染来源特征可能与自身的物理化学性质以及沉积物中含沙量有关[45].
-
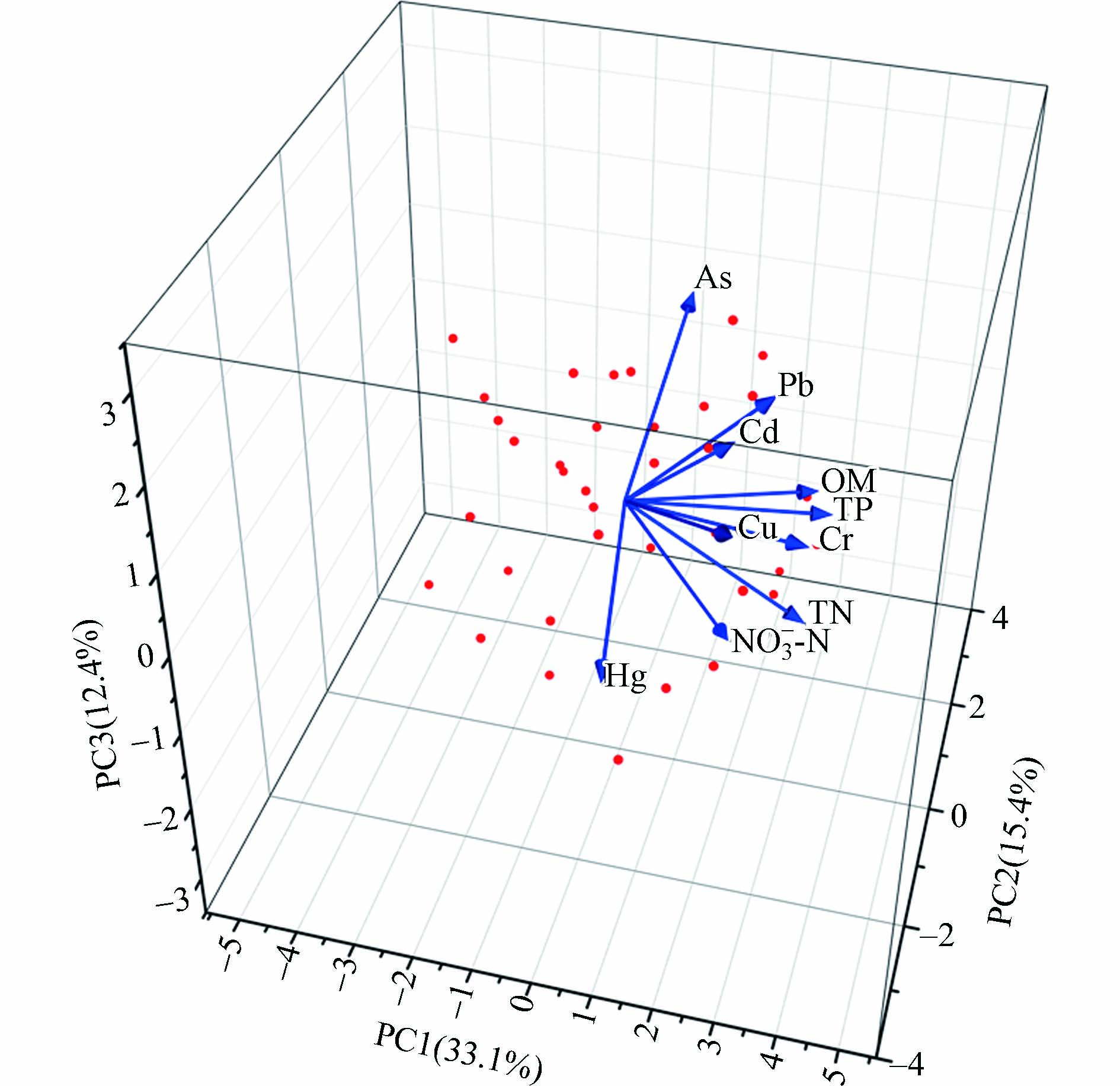
宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属主成分分析结果见表7和图5,前3个成分的方差累积贡献率达60.86%. 主成分1的贡献率是33.09 %,Cr与OM、TP和TN具有高正荷载(载荷 > 0.7),可推测Cr与OM、TP和TN具有强相关,这与Pearson相关性分析结果一致. Pb和Cu具有较高正载荷(载荷 > 0.5)推测这2种重金属具有相同的来源. 有研究表明重金属Pb和Cu含量主要来源于交通运输[46]和人类活动有关[47-48],沙湖大部分区域处于旅游区,交通和人类活动频繁,可能会造成沉积物中重金属Pb和Cu含量累积. 因此,重金属Pb和Cu主要来源于交通运输和人类活动. 宁夏沙湖中所有采样点Cr含量均低于中国土壤元素背景值,变异系数较低,且地累积指数处于清洁水平,推测宁夏沙湖沉积物中Cr可能与自身理化性质有关,属于自然来源. 因此在本研究中主成分1代表该轴的重金属主要来源于人类活动和自然来源. 主成分2的贡献率是15.40%,其中As具有高载荷(> 0.7),地累积指数评价结果显示宁夏沙湖沉积物的重金属As处于清洁水平,推测As属于重金属的自然来源,成分2重金属也来源于自然来源. 主成分3的贡献率12.37%,所有元素载荷均小于0.5.
-
(1)宁夏沙湖的OM、TN、TP、NO3−-N和全盐年平均值分别为20.50 g·kg−1、1.06 g·kg−1、0.62 g·kg−1、5.8 mg·kg−1和1.12 g·kg−1. 在人类活动密集区(S5、S6和S7)沉积物中有机质和营养盐高于其他区域,人类活动影响宁夏沙湖沉积物有机质和营养盐的空间分布. 全盐含量在夏季最高,冬季最低,夏季OM、TN和TP含量最高,春季含量最低,NO3−-N含量在秋季含量最高,春季最低. 水温和外源营养盐输入对宁夏沙湖沉积物有机质和营养盐含量具有重要的调节作用.
(2)单因子污染指数评价结果表明沙湖沉积物质量状况良好,单因子污染指数排序为 Cr > As > Pb > Cd > Cu > Hg,其中Cr单因子污染指数最高,应引起重视并加强日常监测.
(3)沉积物中6种重金属元素年地累积指数值均小于0,污染等级为清洁. 单个重金属年均值从大到小为 Cr > As > Pb > Cd > Cu > Hg,其中Cr 地累积指数最大.
(4)宁夏沙湖沉积物中Cd和Hg的风险等级最高,其中Cd和Cu是造成宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属生态风险的主要重金属. 宁夏沙湖积物中重金属RI值均值为222.81,采样点S7处于轻微生态风险,采样点S8处于强生态风险,其余采样点处于中等生态风险.
(5)相关分析结果表明:Pb、Cd、Cr、Cu、OM、TN、TP 具有相似的污染来源,主要来源是人为来源和自然来源.
(6)生态风险较高的区域主要位于人类活动较密集区域,应加强该区域监测,关注Cr、Pb、Hg和As监测.
半咸水宁夏沙湖沉积物中重金属的分布特征、潜在生态风险及来源解析
Distribution characteristics, potential ecological risk and source analysis of heavy metals in the sediments of the brackish-water lake Ningxia Sand Lake
-
摘要: 为揭示和明确半咸水湖泊湿地的重金属污染状况,以宁夏沙湖为例,于2018年4月(春)、7月(夏)、10月(秋)、2019年1月(冬),对沙湖湿地9个采样点沉积物中有机质(OM)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)、全盐和6种对环境影响较大的有毒有害重金属(As、Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr、Cu)的含量进行了定量分析并运用多种手段进行风险评估. 结果表明,人类活动密集区(湖心、鸟岛和2号桥)沉积物中OM和营养盐含量高于其他区域. 全盐含量在夏季最高,冬季最低;OM、TN和TP含量在夏季最高,春季最低;NO3--N含量在秋季含量最高,冬季最低. 宁夏沙湖沉积物中As、Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr、Cu含量分别在 8.83—13.55 mg·kg−1,16.61—21.71 mg·kg−1,0.02—0.08 mg·kg−1,0.02—0.46 mg·kg−1,51.16—66.54 mg·kg−1,14.67—24.42 mg·kg−1之间,其中Pb和Cd含量均超过背景值. 6种重金属单因子污染指数均小于1,地累积指数(Igeo)均小于0,表明宁夏沙湖沉积物质量状况良好,其中Cr、As和Pb 单因子污染指数和Igeo指数较大,空间分布为假日酒店、湖心相对较高,需在今后监测工作中重点关注. 潜在重金属生态风险为中等污染,仅Hg和Cd出现强和中等的生态危害程度,表明宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属生态风险主要由Hg和Cd造成,生态风险较高的区域主要位于假日酒店、湖心等区域. 相关性分析和主成分分析揭示Pb、Cd、Cr、Cu、OM、TN、TP 具有相似的污染来源,主要来源是人为来源和自然来源. 本研究将为半咸水湖泊重金属污染状况及潜在生态风险提供数据支撑,也将为水环境污染防控提供科学依据.Abstract: To reveal and clarify the heavy metal pollution status of brackish-water lake wetlands, we measured and analyzed the organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), total salt, and six types of environmentally relevant toxic and harmful heavy metals (As, Pb, Hg, Cd, Cr, Cu) from 9 sampling sites in April (spring), July (summer), and October (autumn) and January (winter) 2018. The results showed that content of OM and nutrient salts in sediments were larger in locations with substantial human activity (Lake Center, Bird Island, and Bridge #2) than that of other regions, revealing that human activities impacted the spatial distribution of nutritional salts. Summer had the highest levels of total salt, whereas winter had the lowest levels. The OM, TN, and TP levels were highest in summer but lowest in spring, whereas the NO3−-N values were highest in fall but lowest in winter. As, Pb, Hg, Cd, Cr and Cu in the sediments of Ningxia Sand Lake ranged from 8.83—13.55 mg·kg−1, 16.61—21.71 mg·kg−1, 0.02—0.08 mg·kg−1, 0.02—0.46 mg·kg−1, 51.16—66.54 mg·kg−1, 14.67—24.42 mg·kg−1, among which Pb and Cd were above the background values. The single-factor pollution index of six heavy metals was all less than 1, and the ground accumulation (Igeo) index of six heavy metals was all less than 0, suggesting that the sediment quality was satisfactory. While the single-factor pollution index and Igeo index of Cr, As, and Pb were higher, and the geographical distribution was quite high for Holiday Inn, Lake Center, which required further attention in monitoring work. The potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of the study area was all medium, whereas some Hg and Cd sites showed strong and medium ecological risk. These results indicated that the ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of Sand Lake was mainly caused by Hg and Cd, and the high ecological risk areas are mainly located in Holiday Inn, Lake Center. Correlation analysis and principal component analysis revealed that the pollution sources of Pb, Cd, Cr, Cu, OM, TN, and TP were similar, and the main sources were anthropogenic and natural sources. The anthropogenic and natural sources mainly contributed to the main sources of heavy metals in the sediments. This study will support the pollution status and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in semi-saline lakes and provide a scientific basis for water pollution control.
-
Key words:
- Ningxia Sand Lake /
- sediments /
- nutrients /
- heavy metal /
- risk evaluation
-
重金属具有毒性强、来源广、易富集且难降解等特征,对环境和人体健康有着间接和直接的危害,其在自然生态系统的分布、迁移转化和毒性效应一直是环境学科研究的前沿热点问题之一[1-5]. 重金属在自然生态系统的分布特征对于深入认知和评估其环境行为和生态效应具有重要的指示意义. 研究表明,沉积物作为水生态系统中重金属主要的汇,可以作为水生态系统中重金属污染程度的“指示剂”[6-8]. 沉积物中的重金属可通过多途径如水动力扰动、化学和生物方式释放至天然水环境中,对水生生物和人类健康造成潜在和直接的影响甚至是毒性效应 [9-10]. As、Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr、Cu 是《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T166-2004)中监测的重金属,研究表明,这6种金属所造成污染及潜在生态风险更为严重[11-12]. 沉积物中有机物和营养盐是沉积物中重要组成部分,其中有机质对沉积物中重金属及有毒化合物的毒性、环境迁移力及营养盐交换有重要的作用[13-14]. 氮和磷不仅可为水体中浮游生物提供养分,亦可在水体和沉积物中迁移转化,研究表明,沉积物是水体中氮和磷的重要内源[15]. 因此,探究和明确沉积物中重金属、有机质和营养盐的含量特征和潜在风险,将为湖泊水环境污染防控策略提供科学依据.
湖泊对于维护地区生态健康,调节气候并为人类社会提供多种服务,特别是生境脆弱的西北地区,具有重要的作用[16]. 半咸水湖泊,又称为微咸水湖,是指湖水矿化度在1—35 g·L−1的湖泊,半咸水湖泊中鱼类生物量相对淡水湖泊较低,浮游动物与浮游植物占比低于淡水湖泊[17]. 西北地区湖泊多以半咸水湖泊为主,水动力环境较为封闭,地下水排泄能力较弱,易受人类活动和气候变化的影响[18-19]. 宁夏沙湖地处西北内陆干旱荒漠区域,是宁夏最大的天然半咸水湖泊,对于宁夏的生态调控起着不可或缺的作用[20]. 沙湖水生态环境脆弱,具备半咸水湖泊鲜明的特点. 由于补水短缺、水产养殖与旅游开发不合理性等因素,导致过量营养盐进入宁夏沙湖,影响多种元素在沉积物-水界面的分布特性及生物有效性. 重金属吸附在沉积物表面,在特定条件下,会向水体中再度释放,成为潜在污染源,同时对底栖动物产生毒性,对湖泊生态系统产生影响. 当前,针对沙湖的相关研究主要集中于水环境和浮游动植物多样性方面[21-22],这对于评估重金属在典型湖泊湿地的分布特性及风险是不利的. 2014年王春霞等[23]对沉积物重金属分布特征分析,但研究时间较早且未对宁夏沙湖沉积物中重金属污染特征、潜在风险进行分析.
本研究通过监测沙湖表层沉积物的理化指标和重金属含量,分析理化指标和重金属的空间分布特征,运用单因子污染指数法、地积累指数法和潜在生态风险指数法等多种手段对沉积物重金属污染特征进行评价和分析,并通过相关性分析和主成分分析对沉积物中重金属与营养盐相关性及来源解析. 本研究对揭示宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属分布情况,强化污染防治具有重要指导意义.
1. 材料与方法 (Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区域
宁夏沙湖自然保护区(E 106°19′6″—106°24′10″,N 38°45′17″—38°49′42″)位于银川平原中北部,贺兰山东麓的蝶型静水湖泊,堤岸分隔的6个小型湖沼. 水域总面积3498.39 hm2,海拔1093—1102 m. 气候属典型的大陆性半湿润半干旱气候,年平均气温为 9.75 ℃,年降水量为 174.7 mm,多集中在6—9月,年蒸发量为1400.0—1600.0 mm,平均水深2.2 m,最深处为4.0—6.0 m [20]. 宁夏沙湖自然保护区位于银川断陷盆地的中心地带,堆积了大量河湖物质,下伏地层为细沙、黏土和湖相地层. 地势低洼,地面高程1088—1110 m,坡度平缓,沟渠纵横,土壤沼泽化、潜育化和盐渍化现象普遍. 沙湖是具有构造湖和牛轭湖双重特征的湖泊,兼具生物多样性保护、水源涵养、治污纳污、调节绿洲生态和调蓄防洪等多种功能.
1.2 样点的布设和样品采集
根据宁夏沙湖水域特点设置9个采样点:采样点1(S1,1号曝气机),采样点2(S2,2号曝气机),采样点3(S3,3号曝气机),采样点4(S4,新澄清池入水口),采样点5(S5,湖心),采样点6(S6,鸟岛),采样点7(S7,2号桥),采样点8(S8,假日酒店东侧),采样点9(S9,1号拦水坝北侧),如图1所示.
 图 1 宁夏沙湖采样点分布[20]Figure 1. Locations of sampling sites in Sand Lake of Ningxia
图 1 宁夏沙湖采样点分布[20]Figure 1. Locations of sampling sites in Sand Lake of Ningxia于2018年4月18日(春)、7月22日(夏)、10月25日(秋)、2019年1月23日(冬)使用彼得森采泥器(PSC-1,采泥面积1/40 m2)采集表层沉积物(深度约为25 cm),用GPS导航定位采样点,确保采样地点相同. 样品采集时间为早上8:00—11:00. 每个采样点采集3个平行样品,去除动植物残体及石块,混合后装入自封袋带回实验室,−20 ℃保存. 采集的沉积物置于阴凉通风的地方阴干、混匀,研磨后过100目筛后备用.
1.3 检测方法
根据《土壤农化分析方法》[24] 中的方法,测定沉积物的 pH、有机质(OM)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)和总盐的含量. 重金属含量 (As、Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr、和 Cu)按照相关国家标准(GB15618-1995、GB/T17141-1997、HJ491-2019)测定.
1.4 评价方法
1.4.1 单因子污染指数
基于单因子污染指数法评价不同采样点营养盐和重金属污染物超标情况. 公式为:
PIi=Ci/Si PIi是沉积物重金属i的污染指数;Ci是沉积物中重金属i的实测含量;Si 是重金属 i的评价标准含量,本研究采用宁夏沙湖沉积物元素平均值作为标准值[23](表1).
Table 1. Soil background value and toxicity coefficient of heavy metal elements项目Items As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu 背景值/(mg·kg−1)Background value 11.40 27.10 0.04 0.35 58.10 22.70 毒性系数Toxic coefficient 10 5 40 30 2 5 1.4.2 地积指数评价
运用Muller[26]提出的地理累积指数(Geo - accumulate Index, Igeo)确定宁夏沉积物重金属污染的定量程度,如公式(1):
Igeo=log2[Ci/k×Cn] (1) Ci是重金属含量的实测值;Cn是计算所需的背景值,本研究采用宁夏沙湖沉积物元素平均值作为背景值从而更加真实地反映其污染现状[23],k为1.5;按Igeo可将沉积物污染指数分为以下7类:Igeo<0,清洁;0 ≤ Igeo<1,轻度污染;1 ≤ Igeo<2中度污染;2 ≤ Igeo<3,偏重度污染;3 ≤ Igeo <4 ,重度污染;4 ≤ Igeo<5,严重污染;≥ 5极严重污染.
1.4.3 潜在生态风险评价方法
采用Hakanson[27]方法对沉积物重金属污染情况进行潜在生态风险评价,公式如(2)、(3):
Er=Tir×Ci/CiB (2) RI=n∑i=1Eir (3) 其中,Eir是第i种元素潜在生态风险系数;RI是潜在生态风险指数;Tir 是第i种重金属的毒性系数;Ci为沉积物中第i种重金属的实测值;CBi为第i种重金属的背景值. 本研究所采用的重金属背景值和毒性系数见表1. 重金属潜在生态风险程度评价标准见表2.
表 2 沉积物重金属潜在生态风险程度评价标准Table 2. Potential ecological risk assessment indicators and classification in sediment风险指数 Risk index 轻微 Slight 中等 Medium 强 Strong 很强 Very strong 极强 Pole-strength 危害系数(Er) Er﹤40 40 ≤ Er﹤80 80 ≤ Er ﹤160 160 ≤ Er﹤320 Er ≥ 320 生态风险指数(RI) RI﹤150 150 ≤ RI﹤300 300 ≤ RI﹤600 600 ≤ RI﹤1200 RI ≥1200 1.5 数据分析
数据统计和计算使用Excel 2020,显著性分析、相关性分析和主成分分析采用JMP Pro V13.2.0分析,采用Orgin 2021绘图.
2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 沉积物理化特征
对宁夏沙湖各采样点沉积物理化性质进行分析(图2),结果表明,宁夏沙湖各采样点pH值范围为8.13—8.79,平均值为8.41,呈半碱性,各样点间pH无显著空间分布趋势,在不同季节间无明显差异,说明pH受外界影响较小,主要受湖泊自然运动与沉积作用影响.
OM是营养物质的载体,对氮、磷等营养元素在沉积物中的迁移、矿化起到重要作用[28]. 采样点沉积物中OM含量范围为10.34—35.27 g·kg−1,平均值为20.50 g·kg−1. S7各季节平均值最高,含量为26.66 g·kg−1,S8各季节平均含量最低,含量为16.06 g·kg−1。S7采样点分布大量水生植物,有利于OM富集. 夏季(7月)OM含量最高,含量为23.80 g·kg−1,春季(4月)含量最低,含量为17.34 g·kg−1,表明宁夏沙湖夏季沉积物营养物质丰富,肥力较高. TN变化范围在0.37—1.79 g·kg−1,TN全年平均值分别为1.06 g·kg−1,其中S6各季节平均含量最高,含量为1.54 g·kg−1,S9各季节平均值最低,含量为0.73 g·kg−1 .夏季(7月)TN含量最高为1.29 g·kg−1,春季(1月)含量最低为0.62 g·kg−1. TP范围在0.40—0.83 g·kg−1 之间,平均值为0.62 g·kg−1,其中S6各季节平均含量最高,含量为0.75 g·kg−1 ,S9各季节平均值最低,含量为0.57 g·kg−1. 夏季(7月)TP含量最高,含量为0.72 g·kg−1,春季(4月)含量最低,含量为0.53 g·kg−1. 沉积物中有机氮和有机磷主要来自水体中生物排泄物以及生物残体[28],S6位于鸟岛,生物排泄物较多,并且位于旅游区受人类活动影响较大,S6采样点各季节TN和TN平均值含量较高. 沉积物中OM、TN和 TP含量均在春季最低,夏季最高。因为夏季水温较高,水温是影响沉积物氮和磷释放的关键因素之一,随着夏季水温升高,底栖生物活动加强,增加对底泥扰动,通过发生硝化和反硝化等作用促进沉积物中生物残体向盐类物质转化[29]。在夏季宁夏沙湖有大量外源性氮磷营养盐会随着补水水源进入宁夏沙湖湖区内,而春季补水量减少,入湖外源性氮磷营养盐降低.
沉积物
NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 根据卞培旺等的研究结果,全盐量越高,腐蚀速率越大[30]. 宁夏沙湖沉积物全盐含量变化范围为0.11—2.62 g·kg−1,平均值为1.12 g·kg−1,S5和S6采样点全盐含量高于其他采样点,分别为1.64 g·kg−1、1.44 g·kg−1,表明该区域底质环境具有一定的腐蚀性. 夏季(7月)全盐含量最高,含量为1.65 g·kg−1,冬季(1月)含量最低,含量为0.66 g·kg−1.
Ji等的研究结果表明,同一湖泊中沉积物理化性质差异主要是受人类活动影响[31]. 本研究中人类活动较为密集的区域(S5、S6和S7)沉积物中OM、TN、TP和
NO−3 NO−3 NO−3 2.2 重金属分布特征及污染评价
2.2.1 沉积物重金属的含量分析
宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属含量特征如表3所示. 所有采样点中,仅S3和S4采样点As含量超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值,分别是宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值的1.01倍和1.08倍. S3、S4、S5和S6采样点As含量超过宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. 所有采样点中Pb和Cd含量都较高,均超过中国土壤元素背景值和宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值[32-33],但所有采样点中Pb低于宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值,S2、S4、S5、S6和S8采样点中Cd含量超过宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. S1、S7和S8采样点中Hg含量超过中国土壤元素背景值,分别是中国土壤Hg含量背景值的1.23、1.08和1.08倍. S1、S5、S7、S8和S9采样点中Hg含量超过超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值和宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. 在所有采样点的沉积物中,Cr均未超过中国土壤元素背景值,仅S1、S3、S6和S8采样点超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值,S1、S2、S3、S5、S6、S7和S8超过宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值. 所有采样点中只有S3采样点Cu含量超过中国土壤元素背景值,S1、S2、S3和S8采样点Cu含量超过宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值,分别是宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值的1.19、1.09、1.3、1.24倍. 各个采样点沉积物中6种重金属含量均未超过土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB15618-2018,pH >7.5,田地性质为其他),说明宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属污染程度较轻. S1沉积物中的Hg显著高于其他采样点,S3沉积物中的Cr和Cu显著高于其他采样点,S6沉积物中的Cd显著高于其他采样点(P < 0.05). 整体上看,受人类活动干扰较多的区域S1、S6重金属含量相对较高,王春霞对宁夏沙湖2014年沉积物重金属分布研究结果也支持了本文研究结论[23] .
表 3 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属含量特征Table 3. Characteristics of the amount of heavymetals in Ningxia Sand Lake采样点Site 指标Index As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu S1 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 8.83 18.32 0.08a 0.02 63.74ab 22.21abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 4.07 4.14 0.01 0.01 1.34 3.11 变异系数/% 46.15 22.59 16.01 35.73 2.10 14.00 S2 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.38 20.46 0.03ab 0.41 60.39ab 20.42abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.52 3.15 0.02 0.36 2.72 2.42 变异系数 /% 24.29 15.40 66.67 86.15 4.50 11.85 S3 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 12.65 21.71 0.02b 0.27 66.54a 24.42a 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 1.52 1.91 0.01 0.16 3.09 4.97 变异系数 /% 11.98 8.82 38.78 55.03 4.64 20.36 S4 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 13.55 16.61 0.02b 0.45 54.92cd 17.66abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 1.38 2.38 0.01 0.33 4.73 2.99 变异系数 /% 10.17 14.30 59.98 72.83 8.61 16.93 S5 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 9.81 17.17 0.06ab 0.42 59.06bc 14.67c 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.15 2.87 0.03 0.16 3.30 1.98 变异系数/% 32.07 16.74 47.76 37.76 5.58 13.47 S6 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 12.20 17.57 0.02ab 0.46a 64.22ab 15.13c 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.91 6.07 0.01 0.18 3.68 1.21 变异系数 /% 23.84 34.52 47.94 17.67 5.73 8.00 S7 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 11.52 16.92 0.07b 0.19 60.70ab 17.44abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.03 6.73 0.04 0.16 2.86 1.79 变异系数/% 17.65 39.77 54.82 85.22 4.72 10.25 S8 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.14 20.88 0.07ab 0.45 63.09ab 23.10ab 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.61 3.28 0.04 0.30 5.40 3.32 变异系数 /% 25.78 15.72 54.82 66.18 8.56 14.38 S9 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.61 19.55 0.04ab 0.11 51.16d 16.70bc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.74 4.71 0.03 0.078 1.77 4.48 变异系数 /% 35.19 24.08 81.86 68.47 3.46 26.84 中国土壤元素背景值[32] 9.7 7.9 0.065 0.103 66.6 24.1 宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值[33] 12.5 11.4 0.032 0.105 61.2 18.7 GB15618-2018 1 20 240 1.0 0.8 350 100 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值[23] 11.4 27.1 0.04 0.35 58.1 22.7 注:同列平均数后的小写字母不同表示同一种重金属元素在采样点之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05).Different lowercase letters after the mean in the same column indicate significant differences between sampling sites for the same heavy metal element (P < 0.05). 1表示《土壤环境质量标准 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB15618-2018),pH >7.5,田地性质为其他.Indicates Soil Environmental Quality Standard Soil Contamination Risk Control Standard for Agricultural Land (GB15618-2018), pH > 7.5, and the field nature is other. 湖泊自身环境的差异,加上人类活动干扰等因素影响,不同区域重金属存在一定差异性[34-35] . 结果表明,S1采样点中As的差异性最大,变异系数为46.15%;S2、S3、S4、S7和S8采样点中Cd的差异性最大,变异系数分别为86.15%、55.03%、72.83%、85.22%和66.18%;S2、S4和S9采样点中Hg的差异性最大,变异系数分别为66.67%、59 .98%和81.86%. As、Hg和Cd变异系数较高,说明在空间上分布不均匀[36-37].
宁夏沙湖沉积物中6 种重金属含量均值由高到低顺序为 Cr > Cu > Pb > As > Cd > Hg( 表4) . 沉积物中重金属含量受沉积物理化性质(如:OM、TN、TP、粒径等因素)以及温度等多种因素影响[38]. 结果表明:夏季(7月)和秋季(10月)沉积物中Pb、Hg、Cd、Cr和Cu的平均浓度高于春季(4月)和冬季(1月). 夏季和秋季温度较高,温度较高时加速了沉积物中重金属释放速度. 研究表明OM和TP含量与重金属含量呈正相关[39],但TN含量高时,沉积物吸附重金属量降低. 图2表明沉积物中OM、TN和TP在夏季和秋季含量较高,但TN含量较高时,并没有使得沉积物中重金属吸附能力降低,这可能时因为湖泊之间因所处地理环境存在一定差异. 因此,宁夏沙湖重金属含量呈现不同季节差异与水温、OM、TN和TP有关. 从变异系数来看,春季和夏季变异系数最高的是Cd,其次是Hg,最小的是Cr,表明Cd和Hg含量在春季和夏季沉积物中差异较大. 秋季和冬季变异系数最高的是Cd,其次是Hg,最小的是Cr,表明Hg和Cd含量在秋季和冬季沉积物中差异较大.
表 4 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属含量季节变化特征Table 4. Seasonal variation characteristics of heavy metal content in sediment of Sand Lake in Ningxia季节 Season 指标 Index As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu 春季 Spring 最大值 14.60 24.48 0.07 0.64 63.20 20.40 最小值 7.66 11.30 0.01 0.02 49.00 11.90 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 12.10 18.0 0.03 0.30 57.80 16.00 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.60 3.80 0.0 0.20 5.50 3.10 变异系数 /% 20% 20% 60% 80% 10% 20% 夏季 Summer 最大值 14.01 24.48 0.08 0.94 68.29 29.1 最小值 4.14 14.69 0.01 0.03 50.30 15.80 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.78 20.29 0.05 0.50 62.68 21.43 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.20 3.60 0.0 0.30 5.50 4.80 变异系数 /% 30% 20% 60% 60% 10% 20% 秋季 Autumn 最大值 13.61 25.39 0.09 0.77 70.10 28.4 最小值 7.19 13.96 0.01 0.02 62.07 15.20 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.90 20.10 0.04 0.30 62.60 21.50 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.90 2.90 3.80 0.0 0.20 4.70 变异系数 /% 30% 20% 70% 70% 10% 20% 冬季 Winter 最大值 13.73 22.88 0.09 0.34 65.9 20.8 最小值 5.80 11.23 0.01 0.01 51.96 14.6 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.58 16.82 0.04 0.15 58.60 17.39 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.00 3.00 4.90 0.0 0.10 4.40 变异系数 /% 30% 30% 80% 90% 10% 20% 2.2.2 沉积物重金属单因子污染指数法评价
运用单因子污染指数法,对宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属评价,结果显示(见表5),各采样点6种重金属元素单因子污染指数均小于1,表明沙湖沉积物质量状况良好. 各采样点6种重金属单因子污染指数排序为 Cr > As > Pb > Cd > Cu > Hg,其中Cr的单因子污染指数最大,平均值达到0.89,其次为As和Pb,平均值分别为0.71和0.70,其余重金属单因子污染指数均小于0.7. Cr、Pb和As的单因子污染指数较高,应引起足够重视,加强此类沉积物重金属元素监测.
表 5 宁夏沙湖重金属单因子污染指数Table 5. Single-factor standard index for heavy metals in Ningxia Sand Lake采样点Site As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu S1 0.57 0.68 0.32 0.04 0.96 0.74 S2 0.67 0.82 0.11 0.83 0.91 0.68 S3 0.82 0.80 0.27 0.57 0.98 0.83 S4 0.87 0.61 0.29 0.98 0.81 0.60 S5 0.63 0.63 0.75 0.85 0.87 0.50 S6 0.79 0.65 0.42 0.92 0.94 0.51 S7 0.74 0.62 0.25 0.38 0.89 0.59 S8 0.65 0.77 0.86 0.91 0.93 0.79 S9 0.93 0.72 0.81 0.32 0.88 0.74 平均值 0.71 0.70 0.42 0.65 0.89 0.64 2.2.3 沉积物重金属地积指数法评价
地积累指数对宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属的污染程度进行了评价(图3). S1采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Hg > Cr > Cu > Pb > As > Cd;S2采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Cd > Pb > Cu >As > Hg;S3采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Pb > As > Cu > Cd > Hg;S4采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cd > As > Cr > Pb > Cu > Hg;S5和S6采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Cd > Hg > Pb >As > Cu,Cr > Cd > As > Pb >Hg > Cu;S7采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > As >Pb > Cu > Cd > Hg;S8采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Cd > Hg > Cu > Pb >As;S9采样点重金属地积指数排序依次为:Cr > Pb > As > Cu > Hg > Cd. 所有地积指数均小于0,污染等级为清洁. 重金属年均值从大到小为 Cr > As > Pb > Cu > Cd > Hg,其中,Cr 地累积指数(-0.76)最大,在宁夏沙湖环境监测工作中需重点关注此金属元素.
空间分布结果为S8(−0.89) > S5(−1.11) > S9(−1.14) > S2(−1.16)> S4(−1.18) > S7(−1.49) > S1(−1.66) > S3(−2.09). S2、S3、S5、S7、和S8沉积物各采样点地积指数差异较小,可以推断,S2、S3、S5、S7、和S8采样点沉积物中的重金属来源相似,其余采样点沉积物中重金属地积指数差别较大,表明重金属来源有所不同.
2.2.4 沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数法评价
潜在生态风险系数(Er)分析结果(表6),可以看出宁夏沙湖沉积物中Cd和Hg的风险等级最高,Cd处于中等生态风险(40 ≤ Er﹤80),Hg处于强生态风险(80 ≤ Er﹤160),Cd和Hg潜在生态风险系数分别在5.07—108.93和45.83—159.38之间,均值达到了74.98和83.76,其中Cd波动较大. S1和S9采样点中金属Cd潜在生态风险系数指数低于40,处于轻微生态风险(Er < 40),S3和S7处于中等生态风险(40 ≤ Er < 80),S2、S4、S5、S6和S8处于强生态风险. S7采样点中金属Hg潜在生态风险系数指数低于40,处于轻微生态风险,S2、S3、S4和S6处于中等生态风险,S1、S5、S8和S9处于强生态风险. 金属AS、Pb、Cr和Cu处于轻微生态风险(Er﹤40).
表 6 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数值及污染等级Table 6. Potential ecological risk index values and pollution levels of heavy metals in sediment of Ningxia Sand Lake采样点Site Er RI 危害程度Hazard level As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu S1 22.77 13.52 159.38 5.07 7.48 15.11 223.32 中等 S2 26.78 15.10 56.93 99.16 7.08 27.78 232.84 中等 S3 32.64 16.03 45.83 68.66 7.81 16.61 187.58 中等 S4 34.96 12.26 46.92 108.12 6.44 12.01 220.72 中等 S5 25.32 12.67 120.36 101.98 6.93 9.98 277.24 中等 S6 31.49 12.97 66.77 109.87 7.53 10.30 238.93 中等 S7 29.74 12.49 39.24 45.71 7.12 11.863 146.17 轻微 S8 26.17 15.41 137.83 108.93 7.40 15.71 311.45 强 S9 27.39 14.43 80.56 27.29 6.00 11.36 167.04 中等 平均值 28.58 13.88 83.76 74.98 7.09 14.52 222.81 中等 贡献率/% 12.83 6.23 37.59 33.65 3.18 6.52 潜在生态风险指数(RI)结果可以得出(表6),宁夏沙湖沉积物中重金属RI值范围为167.04—311.45,均值为 222.81,所有采样点RI值均未超过600,采样点S7处于轻微生态风险(RI < 150),采样点S8处于强生态风险(300 ≤ RI < 600),其余采样点处于中等生态风险(150 ≤ RI < 300).
此外,表层沉积物中重金属Hg和Cd是重金属潜在生态风险的主要来源,贡献率分别达到了37.59%和33.65%. As贡献率达到了12.83%,Pb和Cu贡献了分别为6.23%和6.58%,Cr总贡献率低于4.00%. 在其他湖泊、水库和湿地也发现了类似结果[40-42]. 因此,未来应对宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属污染提高重视,特别是重金属Hg和Cd.
有研究表明采用多种评价方法评价沉积物重金属,能够更好说明沉积物中重金属复合污染特征[43],本研究采用单因子污染指数、地积指数和潜在风险指数综合地积累指数,评价宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属污染级别,整体来看,宁夏沙湖沉积物状态良好,其中Cr、As和Pb单因子污染指数和地积指数相对较高,而潜在风险指数结果与单因子污染指数和地积指数评价略有不同,Cd、Hg和As潜在风险指数较高,已往研究结果也呈现出潜在风险指数评价与单因子污染指数和地积指数评价结果略有不同[11,40,44]. 从空间上来看,三种评价方法均显示S8和S5采样点沉积物中重金属污染指数相对较高.
2.3 重金属、营养盐沉积物来源分析
2.3.1 沉积物重金属、营养盐相关分析
Pearson相关性分析结果如图4所示,结果表明 Cr 与 Cu、OM、TN、TP呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),Cr 与 Cu、OM、TN、TP具有相似的污染来源或产生了复合污染. OM与TN、TP和NO3−-N呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),说明沉积物OM的降解和释放对宁夏沙湖TN、TP和NO3−-N具有重要影响. TP与TN呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),说明TN和TP来源相同. As和Hg与其他元素的相关性都不高. 这表明 Pb、Cd、Cr、Cu、OM、TN、TP 具有相似的污染来源,而As和Hg的污染来源特征可能与自身的物理化学性质以及沉积物中含沙量有关[45].
2.3.2 沉积物重金属、营养盐主成分分析
宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属主成分分析结果见表7和图5,前3个成分的方差累积贡献率达60.86%. 主成分1的贡献率是33.09 %,Cr与OM、TP和TN具有高正荷载(载荷 > 0.7),可推测Cr与OM、TP和TN具有强相关,这与Pearson相关性分析结果一致. Pb和Cu具有较高正载荷(载荷 > 0.5)推测这2种重金属具有相同的来源. 有研究表明重金属Pb和Cu含量主要来源于交通运输[46]和人类活动有关[47-48],沙湖大部分区域处于旅游区,交通和人类活动频繁,可能会造成沉积物中重金属Pb和Cu含量累积. 因此,重金属Pb和Cu主要来源于交通运输和人类活动. 宁夏沙湖中所有采样点Cr含量均低于中国土壤元素背景值,变异系数较低,且地累积指数处于清洁水平,推测宁夏沙湖沉积物中Cr可能与自身理化性质有关,属于自然来源. 因此在本研究中主成分1代表该轴的重金属主要来源于人类活动和自然来源. 主成分2的贡献率是15.40%,其中As具有高载荷(> 0.7),地累积指数评价结果显示宁夏沙湖沉积物的重金属As处于清洁水平,推测As属于重金属的自然来源,成分2重金属也来源于自然来源. 主成分3的贡献率12.37%,所有元素载荷均小于0.5.
表 7 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属主成分载荷分布Table 7. Principal component load distribution of heavy metals of Ningxia Sand Lake元素Elements 因子载荷Factor loadings 因子1 Factor 1 因子2 Factor 2 因子3 Factor 3 As 0.0468 0.7579 0.3455 Pb 0.5755 0.0071 0.4928 Hg 0.1248 −0.6738 −0.1809 Cd 0.4328 −0.0163 0.3106 Cr 0.7798 −0.2011 0.0990 Cu 0.5531 −0.5078 0.3273 OM 0.7060 0.3543 −0.0946 TN 0.7545 −0.0064 −0.3676 TP 0.7959 0.1970 −0.0640 NO3−−N 0.3967 0.2198 −0.6927 特征值 3.3088 1.5396 1.2371 贡献率/% 33.0881 15.3964 12.3712 累计贡献率/% 33.0881 48.4844 60.85559 3. 结论 (Conclusion)
(1)宁夏沙湖的OM、TN、TP、NO3−-N和全盐年平均值分别为20.50 g·kg−1、1.06 g·kg−1、0.62 g·kg−1、5.8 mg·kg−1和1.12 g·kg−1. 在人类活动密集区(S5、S6和S7)沉积物中有机质和营养盐高于其他区域,人类活动影响宁夏沙湖沉积物有机质和营养盐的空间分布. 全盐含量在夏季最高,冬季最低,夏季OM、TN和TP含量最高,春季含量最低,NO3−-N含量在秋季含量最高,春季最低. 水温和外源营养盐输入对宁夏沙湖沉积物有机质和营养盐含量具有重要的调节作用.
(2)单因子污染指数评价结果表明沙湖沉积物质量状况良好,单因子污染指数排序为 Cr > As > Pb > Cd > Cu > Hg,其中Cr单因子污染指数最高,应引起重视并加强日常监测.
(3)沉积物中6种重金属元素年地累积指数值均小于0,污染等级为清洁. 单个重金属年均值从大到小为 Cr > As > Pb > Cd > Cu > Hg,其中Cr 地累积指数最大.
(4)宁夏沙湖沉积物中Cd和Hg的风险等级最高,其中Cd和Cu是造成宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属生态风险的主要重金属. 宁夏沙湖积物中重金属RI值均值为222.81,采样点S7处于轻微生态风险,采样点S8处于强生态风险,其余采样点处于中等生态风险.
(5)相关分析结果表明:Pb、Cd、Cr、Cu、OM、TN、TP 具有相似的污染来源,主要来源是人为来源和自然来源.
(6)生态风险较高的区域主要位于人类活动较密集区域,应加强该区域监测,关注Cr、Pb、Hg和As监测.
-
图 1 宁夏沙湖采样点分布[20]
Figure 1. Locations of sampling sites in Sand Lake of Ningxia
Table 1. Soil background value and toxicity coefficient of heavy metal elements
项目Items As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu 背景值/(mg·kg−1)Background value 11.40 27.10 0.04 0.35 58.10 22.70 毒性系数Toxic coefficient 10 5 40 30 2 5 表 2 沉积物重金属潜在生态风险程度评价标准
Table 2. Potential ecological risk assessment indicators and classification in sediment
风险指数 Risk index 轻微 Slight 中等 Medium 强 Strong 很强 Very strong 极强 Pole-strength 危害系数(Er) Er﹤40 40 ≤ Er﹤80 80 ≤ Er ﹤160 160 ≤ Er﹤320 Er ≥ 320 生态风险指数(RI) RI﹤150 150 ≤ RI﹤300 300 ≤ RI﹤600 600 ≤ RI﹤1200 RI ≥1200 表 3 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属含量特征
Table 3. Characteristics of the amount of heavymetals in Ningxia Sand Lake
采样点Site 指标Index As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu S1 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 8.83 18.32 0.08a 0.02 63.74ab 22.21abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 4.07 4.14 0.01 0.01 1.34 3.11 变异系数/% 46.15 22.59 16.01 35.73 2.10 14.00 S2 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.38 20.46 0.03ab 0.41 60.39ab 20.42abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.52 3.15 0.02 0.36 2.72 2.42 变异系数 /% 24.29 15.40 66.67 86.15 4.50 11.85 S3 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 12.65 21.71 0.02b 0.27 66.54a 24.42a 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 1.52 1.91 0.01 0.16 3.09 4.97 变异系数 /% 11.98 8.82 38.78 55.03 4.64 20.36 S4 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 13.55 16.61 0.02b 0.45 54.92cd 17.66abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 1.38 2.38 0.01 0.33 4.73 2.99 变异系数 /% 10.17 14.30 59.98 72.83 8.61 16.93 S5 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 9.81 17.17 0.06ab 0.42 59.06bc 14.67c 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.15 2.87 0.03 0.16 3.30 1.98 变异系数/% 32.07 16.74 47.76 37.76 5.58 13.47 S6 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 12.20 17.57 0.02ab 0.46a 64.22ab 15.13c 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.91 6.07 0.01 0.18 3.68 1.21 变异系数 /% 23.84 34.52 47.94 17.67 5.73 8.00 S7 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 11.52 16.92 0.07b 0.19 60.70ab 17.44abc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.03 6.73 0.04 0.16 2.86 1.79 变异系数/% 17.65 39.77 54.82 85.22 4.72 10.25 S8 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.14 20.88 0.07ab 0.45 63.09ab 23.10ab 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.61 3.28 0.04 0.30 5.40 3.32 变异系数 /% 25.78 15.72 54.82 66.18 8.56 14.38 S9 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.61 19.55 0.04ab 0.11 51.16d 16.70bc 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.74 4.71 0.03 0.078 1.77 4.48 变异系数 /% 35.19 24.08 81.86 68.47 3.46 26.84 中国土壤元素背景值[32] 9.7 7.9 0.065 0.103 66.6 24.1 宁夏省潮土土壤重金属背景值[33] 12.5 11.4 0.032 0.105 61.2 18.7 GB15618-2018 1 20 240 1.0 0.8 350 100 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属平均值[23] 11.4 27.1 0.04 0.35 58.1 22.7 注:同列平均数后的小写字母不同表示同一种重金属元素在采样点之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05).Different lowercase letters after the mean in the same column indicate significant differences between sampling sites for the same heavy metal element (P < 0.05). 1表示《土壤环境质量标准 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB15618-2018),pH >7.5,田地性质为其他.Indicates Soil Environmental Quality Standard Soil Contamination Risk Control Standard for Agricultural Land (GB15618-2018), pH > 7.5, and the field nature is other. 表 4 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属含量季节变化特征
Table 4. Seasonal variation characteristics of heavy metal content in sediment of Sand Lake in Ningxia
季节 Season 指标 Index As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu 春季 Spring 最大值 14.60 24.48 0.07 0.64 63.20 20.40 最小值 7.66 11.30 0.01 0.02 49.00 11.90 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 12.10 18.0 0.03 0.30 57.80 16.00 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.60 3.80 0.0 0.20 5.50 3.10 变异系数 /% 20% 20% 60% 80% 10% 20% 夏季 Summer 最大值 14.01 24.48 0.08 0.94 68.29 29.1 最小值 4.14 14.69 0.01 0.03 50.30 15.80 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.78 20.29 0.05 0.50 62.68 21.43 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.20 3.60 0.0 0.30 5.50 4.80 变异系数 /% 30% 20% 60% 60% 10% 20% 秋季 Autumn 最大值 13.61 25.39 0.09 0.77 70.10 28.4 最小值 7.19 13.96 0.01 0.02 62.07 15.20 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.90 20.10 0.04 0.30 62.60 21.50 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 2.90 2.90 3.80 0.0 0.20 4.70 变异系数 /% 30% 20% 70% 70% 10% 20% 冬季 Winter 最大值 13.73 22.88 0.09 0.34 65.9 20.8 最小值 5.80 11.23 0.01 0.01 51.96 14.6 平均值 /(mg·kg−1) 10.58 16.82 0.04 0.15 58.60 17.39 标准差 /(mg·kg−1) 3.00 3.00 4.90 0.0 0.10 4.40 变异系数 /% 30% 30% 80% 90% 10% 20% 表 5 宁夏沙湖重金属单因子污染指数
Table 5. Single-factor standard index for heavy metals in Ningxia Sand Lake
采样点Site As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu S1 0.57 0.68 0.32 0.04 0.96 0.74 S2 0.67 0.82 0.11 0.83 0.91 0.68 S3 0.82 0.80 0.27 0.57 0.98 0.83 S4 0.87 0.61 0.29 0.98 0.81 0.60 S5 0.63 0.63 0.75 0.85 0.87 0.50 S6 0.79 0.65 0.42 0.92 0.94 0.51 S7 0.74 0.62 0.25 0.38 0.89 0.59 S8 0.65 0.77 0.86 0.91 0.93 0.79 S9 0.93 0.72 0.81 0.32 0.88 0.74 平均值 0.71 0.70 0.42 0.65 0.89 0.64 表 6 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数值及污染等级
Table 6. Potential ecological risk index values and pollution levels of heavy metals in sediment of Ningxia Sand Lake
采样点Site Er RI 危害程度Hazard level As Pb Hg Cd Cr Cu S1 22.77 13.52 159.38 5.07 7.48 15.11 223.32 中等 S2 26.78 15.10 56.93 99.16 7.08 27.78 232.84 中等 S3 32.64 16.03 45.83 68.66 7.81 16.61 187.58 中等 S4 34.96 12.26 46.92 108.12 6.44 12.01 220.72 中等 S5 25.32 12.67 120.36 101.98 6.93 9.98 277.24 中等 S6 31.49 12.97 66.77 109.87 7.53 10.30 238.93 中等 S7 29.74 12.49 39.24 45.71 7.12 11.863 146.17 轻微 S8 26.17 15.41 137.83 108.93 7.40 15.71 311.45 强 S9 27.39 14.43 80.56 27.29 6.00 11.36 167.04 中等 平均值 28.58 13.88 83.76 74.98 7.09 14.52 222.81 中等 贡献率/% 12.83 6.23 37.59 33.65 3.18 6.52 表 7 宁夏沙湖沉积物重金属主成分载荷分布
Table 7. Principal component load distribution of heavy metals of Ningxia Sand Lake
元素Elements 因子载荷Factor loadings 因子1 Factor 1 因子2 Factor 2 因子3 Factor 3 As 0.0468 0.7579 0.3455 Pb 0.5755 0.0071 0.4928 Hg 0.1248 −0.6738 −0.1809 Cd 0.4328 −0.0163 0.3106 Cr 0.7798 −0.2011 0.0990 Cu 0.5531 −0.5078 0.3273 OM 0.7060 0.3543 −0.0946 TN 0.7545 −0.0064 −0.3676 TP 0.7959 0.1970 −0.0640 NO3−−N 0.3967 0.2198 −0.6927 特征值 3.3088 1.5396 1.2371 贡献率/% 33.0881 15.3964 12.3712 累计贡献率/% 33.0881 48.4844 60.85559 -
[1] ZHANG A G, WANG L L, ZHAO S L, et al. Heavy metals in seawater and sediments from the northern Liaodong Bay of China: Levels, distribution and potential risks [J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2017, 11: 32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2017.02.002 [2] VARDHAN K H, KUMAR P S, PANDA R C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 290: 111197. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111197 [3] LIU L W, LI W, SONG W P, et al. Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: Principles and applicability [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 206-219. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161 [4] MANIRETHAN V, RAVAL K, RAJAN R, et al. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by melanin nanopigment obtained from marine source: Pseudomonas stutzeri [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 214: 315-324. [5] XIANG M T, LI Y, YANG J Y, et al. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 278: 116911. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116911 [6] MARIYANTO M, AMIR M F, UTAMA W, et al. Heavy metal contents and magnetic properties of surface sediments in volcanic and tropical environment from Brantas River, Jawa Timur Province, Indonesia [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 675: 632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.244 [7] LI X C, BING J P, ZHANG J H, et al. Ecological risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of a river-reservoir system [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 842: 156683. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156683 [8] LIU R, JIANG W W, LI F J, et al. Occurrence, partition, and risk of seven heavy metals in sediments, seawater, and organisms from the eastern sea area of Shandong Peninsula, Yellow Sea, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 279: 111771. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111771 [9] LIU Q, YANG P P, HU Z, et al. Identification of the sources and influencing factors of the spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments along the northern Jiangsu coast [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 137: 108716. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108716 [10] PAUL V, SANKAR M S, VATTIKUTI S, et al. Pollution assessment and land use land cover influence on trace metal distribution in sediments from five aquatic systems in southern USA [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128243. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128243 [11] FANG X H, PENG B, WANG X, et al. Distribution, contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 689: 557-570. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.330 [12] ZHANG P Y, QIN C Z, HONG X, et al. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 1136-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.228 [13] HORPPILA J. Sediment nutrients, ecological status and restoration of lakes [J]. Water Research, 2019, 160: 206-208. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.074 [14] ZHAO H C, ZHAO H X, WANG S R, et al. Coupling characteristics and environmental significance of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic carbon in the sediments of Erhai Lake [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(16): 19901-19914. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08120-9 [15] LIANG G N, ZHANG B, LIN M, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal mobilization in creek sediment: Influence of RAC values and ambient environmental factors [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 607/608: 1339-1347. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.238 [16] HAN Q, TONG R Z, SUN W C, et al. Anthropogenic influences on the water quality of the Baiyangdian Lake in North China over the last decade [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 701: 134929. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134929 [17] 王苏民, 窦鸿身. 中国湖泊志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. WANG S M, DOU H S. China Lakes Journal[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998 (in Chinese).
[18] LI W Q, QIAN H, XU P P, et al. Distribution characteristics, source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yellow River, China [J]. Catena, 2022, 216: 106376. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2022.106376 [19] REN J, HAO J X, TAO L. Concentrations, spatial distribution, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surficial sediments from upstream of Yellow River, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(3): 2904-2913. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10349-3 [20] 王燕, 刘彦斌, 赵红雪, 等. 宁夏沙湖水质评价及水污染特征 [J]. 湿地科学, 2020, 18(3): 362-367. doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2020.03.014 WANG Y, LIU Y B, ZHAO H X, et al. Water quality assessment and characteristics of water pollution of sand lake in Ningxia [J]. Wetland Science, 2020, 18(3): 362-367(in Chinese). doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2020.03.014
[21] 璩向宁, 曹园园, 刘文辉, 等. 宁夏沙湖主湖区水环境变化特征 [J]. 湿地科学, 2017, 15(2): 200-206. doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2017.02.006 QU X N, CAO Y Y, LIU W H, et al. Change characteristics of water environment of main lake area of Shahu lake in Ningxia [J]. Wetland Science, 2017, 15(2): 200-206(in Chinese). doi: 10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2017.02.006
[22] 翟昊, 刘曼红, 明霄阳, 等. 宁夏沙湖生态修复前后浮游植物群落结构变化与水质评价 [J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(8): 84-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2021.08.016 ZHAI H, LIU M H, MING X Y, et al. Variation of phytoplankton community structure before and after ecological restoration and water quality assessment in Shahu Lake, Ningxia [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(8): 84-89(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2021.08.016
[23] 王春霞, 王英超. 沙湖沉积物中重金属污染的分布特征及生态安全评价[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2017, 27(S2): 115-118. WANG C X, WANG Y C. Distribution characteristics of heavy metal pollution and evaluation of ecological risk in the sediments of Shahu Lake[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2017, 27(Sup 2): 115-118(in Chinese).
[24] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. BAO S D. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000(in Chinese).
[25] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2): 112-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030 XU Z Q, NI S J, TUO X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(2): 112-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
[26] MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2: 108-118. [27] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [28] 刘永九, 黄素珍, 张璐, 等. 洪湖国际重要湿地沉积物磷空间分布特征及释放风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3198-3205. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202009090 LIU Y J, HUANG S Z, ZHANG L, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of Phosphorus fractions and release risk in sediments of Honghu international importance wetland [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(7): 3198-3205(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202009090
[29] 王书锦, 刘云根, 张超, 等. 洱海流域入湖河口湿地沉积物氮、磷、有机质分布及污染风险评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(1): 69-77. doi: 10.18307/2017.0108 WANG S J, LIU Y G, ZHANG C, et al. Distribution and pollution risk assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in inlet rivers of Erhai Basin [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(1): 69-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2017.0108
[30] 卞培旺, 陈法锦, 张叶春, 等. 海底表层沉积物腐蚀性环境特征与评估: 以三亚湾为例 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020, 39(4): 563-569. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190010 BIAN P W, CHEN F J, ZHANG Y C, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of corrosive environment of surface sediments: A case study of the Sanya Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020, 39(4): 563-569(in Chinese). doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190010
[31] JI Z H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Fraction spatial distributions and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 174: 417-428. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.062 [32] 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990(in Chinese).
[33] 朱嵬, 李志刚, 李健, 等. 宁夏黄河流域湖泊湿地底泥重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(35): 281-288. ZHU W, LI Z G, LI J, et al. Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the lake wetlands in the Yellow River valleys of Ningxia [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(35): 281-288(in Chinese).
[34] BING H J, ZHOU J, WU Y H, et al. Current state, sources, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 214: 485-496. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.062 [35] LIU M, CHEN J B, SUN X S, et al. Accumulation and transformation of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary to the East China Sea shelf [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 245: 111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.128 [36] 邓海, 王锐, 严明书, 等. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属污染风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1127-1137. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071601 DENG H, WANG R, YAN M S, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil around mining area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1127-1137(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071601
[37] BENSON N U, ADEDAPO A E, FRED-AHMADU O H, et al. New ecological risk indices for evaluating heavy metals contamination in aquatic sediment: A case study of the Gulf of Guinea [J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2018, 18: 44-56. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2018.01.004 [38] 王钦, 丁明玉, 张志洁, 等. 太湖不同湖区沉积物重金属含量季节变化及其影响因素 [J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(4): 1362-1368. WANG Q, DING M Y, ZHANG Z J, et al. Seasonal varieties and influential factors of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008, 17(4): 1362-1368(in Chinese).
[39] BERTIN C, BOURG A C M. Trends in the heavy metal content (Cd, Pb, Zn) of river sediments in the drainage basin of smelting activities [J]. Water Research, 1995, 29(7): 1729-1736. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(94)00327-4 [40] 尹宇莹, 彭高卓, 谢意南, 等. 洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养元素、重金属的污染特征与评价分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2399-2409. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020042401 YIN Y Y, PENG G Z, XIE Y N, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2399-2409(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020042401
[41] 陈姗, 许凡, 谢三桃, 等. 合肥市十八联圩湿地表层沉积物营养盐与重金属分布及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 4932-4943. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201903184 CHEN S, XU F, XIE S T, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in surface sediments from shibalianwei wetland in Hefei, Anhui Province, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(11): 4932-4943(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201903184
[42] ZHANG J H, LI X C, GUO L Q, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and water quality characteristics of the reservoir control reaches in the middle Han River, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 799: 149472. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149472 [43] MIRANDA L S, WIJESIRI B, AYOKO G A, et al. Water-sediment interactions and mobility of heavy metals in aquatic environments [J]. Water Research, 2021, 202: 117386. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117386 [44] 许艳, 王秋璐, 曾容, 等. 渤海湾表层沉积物重金属污染状况及年际变化分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(9):4255-4263. XU Y, WANG Q L, ZENG R, et al. Pollution status and the annual variations of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Bohai Bay [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(9): 4255-4263(in Chinese)
[45] MA L, XIAO T F, NING Z P, et al. Pollution and health risk assessment of toxic metal(loid)s in soils under different land use in sulphide mineralized areas [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 724: 138176. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138176 [46] 历军, 赵伟强, 俞龙生, 等. 珠江三角洲某河流型饮用水源地的土壤重金属污染源解析和风险评价 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(12): 1511-1514, 1522. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.12.014 LI J, ZHAO W Q, YU L S, et al. Pollution source analysis and risk evaluation of heavy metals in soil of a river drinking water source in Pearl River Delta [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(12): 1511-1514, 1522(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.12.014
[47] 杜彩丽, 黎佳茜, 李国文, 等. 乌梁素海表层沉积物中营养盐和重金属分布特征以及风险评价[J]. 环境科学,2022,43(12): 5598-5607. DU C L, LI J Q, LI G W, et al. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and heavy metals in surface sediments of the Wuliang Su Sea and risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science,2022,43(12): 5598-5607 (in Chinese).
[48] 江涛, 林伟稳, 曹英杰, 等. 梅江流域清凉山水库沉积物重金属污染、生态风险评价及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5410-5418. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202003018 JIANG T, LIN W W, CAO Y J, et al. Pollution and ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments of Qingliangshan Reservoir in the Meijiang Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5410-5418(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202003018
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孙玉芳,金晓媚,雪彦宏,张勃,朱薇,徐兆祥. 宁夏平原鸣翠湖地表水与地下水转化关系. 现代地质. 2024(03): 744-754 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张永江,李希希,邓茂,吴丽君,马双,周洵平. 典型锰矿区河流沉积物重金属分布特征、来源解析及生态风险评价. 中国环境监测. 2024(04): 183-194 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 栗浩亮,徐继伟,王传澍,周睿,姚倩玉,张勇,徐锐. 校园人工湖泊表层沉积物重金属分布特征及生态风险评价. 环境污染与防治. 2024(11): 1639-1647 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)
-






 下载:
下载: