-
在国务院“水十条”对矿井水的最新定位下,煤炭开采形成的矿井水资源保护与综合利用成为实现我国煤炭工业绿色发展和生态文明建设中的重大关键问题[1]. 据统计我国吨煤开采产生矿井水为1.87 m3,矿井水产出量为每年6.88×109 m3,平均利用率约为35%[2-3],主要原因是矿井水水质差,导致不能直接利用,需要进行不同程度的预处理或深度处理,而高额的处理成本限制了综合利用[4-7].
近年来,国内外学者在地下水、地表水的水化学特征方面取得了一系列成果[8-12], 如探讨了神东矿区的高氟矿井水分布特征及形成机制[13];研究了辛置井田地下水的水化学特征和水-岩作用机理[14];系统分析了伊敏矿区地下水的水化学特征与其控制因素[15];对郭家湾煤矿井田内不同区域水化学特征进行差异性分析和水质综合评价[16];研究了高铁锰矿井水的水化学特征与其净化机制[17]. 研究主要侧重矿区水文地球化学特征及形成机制,而对干旱区矿井水综合利用于农田灌溉的相关评价相对较少.
我国西部煤炭资源丰富,占全国总量的70%以上,水资源匮乏,生态环境脆弱[18-20]. 在国家“以水定产,以环境承载力定产”煤炭工业发展理念下,矿井水综合利用成为西部矿区高质量快速发展的卡脖子问题. 因此,在地处干旱半干旱区的煤矿矿井水综合利用相关研究显得尤为重要. 新上海一号煤矿地处毛乌素沙漠边缘,属半干旱半沙漠大陆性气候,干旱少雨[21]. 矿井水若能有效的综合利用于农田灌溉,可有效降低矿井水综合利用成本,实现社会-经济-环境的高质量协同发展.
本研究拟对以新上海一号井田为例,针对各含水层矿井水形成作用进行研究,并对各含水层矿井水的灌溉适宜性进行评价,可为干旱半干旱区矿井水综合利用工作提供依据.
-
研究区为新上海庙一号矿井田,其自上而下地层主要有:新生界第四系(Q)和古近系(E);白垩系志丹群(K1zd);侏罗系直罗组(J2z);含煤岩系侏罗系延安组(J2y);三叠系延长组(T3y),其赋存的含水层依次命名为:新生界、白垩系、直罗组、煤系间、宝塔山、三叠系含水层[22]. 研究区内有21条断层,其中F2、FD5和DF20是导水断层.
研究区内井筒掘进和工作面推进过程中的直接充水水源为直罗组、煤系间、延安组和三叠系含水层,间接充水水源为新生界含水层. 为实现矿井水防控,在采掘活动前需要对相应充水含水层进行疏放工程,因此以上述充水含水层为对象进行水化学特征和矿井水综合利用模式研究.
-
采样分为4个阶段:2006年煤层顶板含水层勘探阶段;2012年近煤层含水层水文地质补充勘探阶段;2016年和2019年各个含水层水文地质补充勘探阶段. 各主要含水层共采集55组样品,检测项目包括K++Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42−、HCO3−、CO32−、pH和TDS,取样点信息详见表1.
-
利用Matlab对矿井水水化学数据进行整理统计和计算,利用Piper图分析地下水水化学类型,利用SPSS软件进行各离子与TDS的相关性分析,通过Gibbs图、氯碱指数图、脱硫酸系数图、离子比值图、水力联系度及矿井水盐碱害分类探讨矿井水水化学特征成因及灌溉适宜性.
-
根据研究区内所采集的矿井水样检测结果分析可得,各含水层矿井水的pH值为7.58—12.06,均呈碱性. TDS为466.00—7624.90 mg·L−1,除了新生界,其余均为高矿化度矿井水,而且从新生界到三叠系,埋深越大,越不易接受第四系含水层的补给,因此TDS逐渐增大. 水中主要离子组成变化及不同水样化学组成类型特征采用Piper三线图(图1)分析[23],K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−明显占优势. 由白垩系含水层至三叠系含水层矿井水化学类型由SO4·Cl-Na逐渐过渡为Cl SO4-Na,新生界含水层水化学类型较为多样.
-
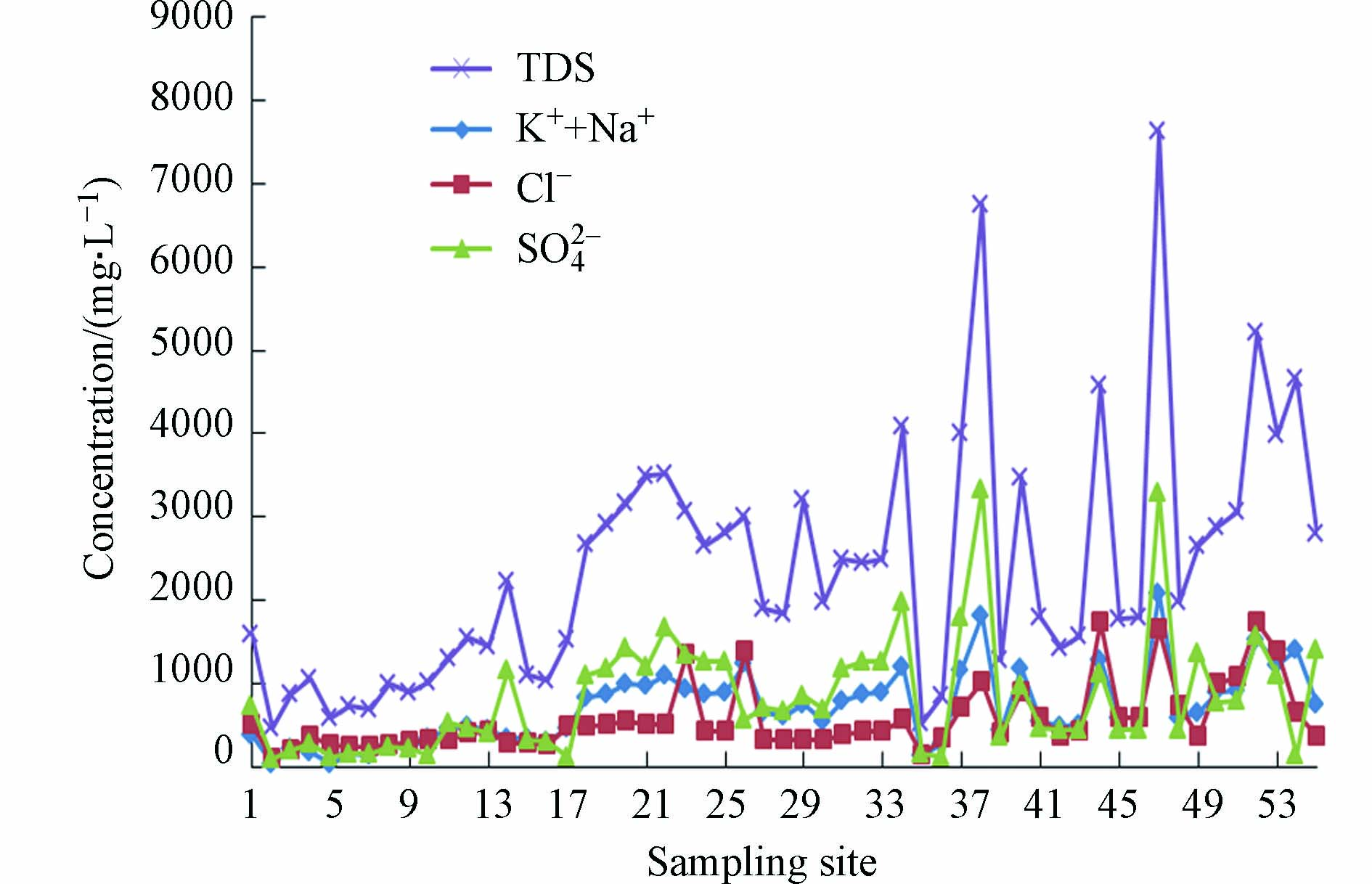
TDS可以来描述离子特征,利用SPSS软件计算得到Pearson相关性系数矩阵(见表2),可以看出除pH外,TDS与各离子均呈显著相关性[24]. 根据相关性分析结果,TDS与K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−呈显著正相关(P<0.01),相关系数分别为0.973、0.868和0.757,从图2可知,TDS、K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−变化趋势相同,说明K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−是TDS的主要来源.
-
Gibbs可有效揭示水化学组分的形成机制,在水化学分析中得到广泛应用[25]. Gibbs图横坐标为阴离子或阳离子质量浓度比,纵坐标为TDS质量浓度,判别方法见表3.
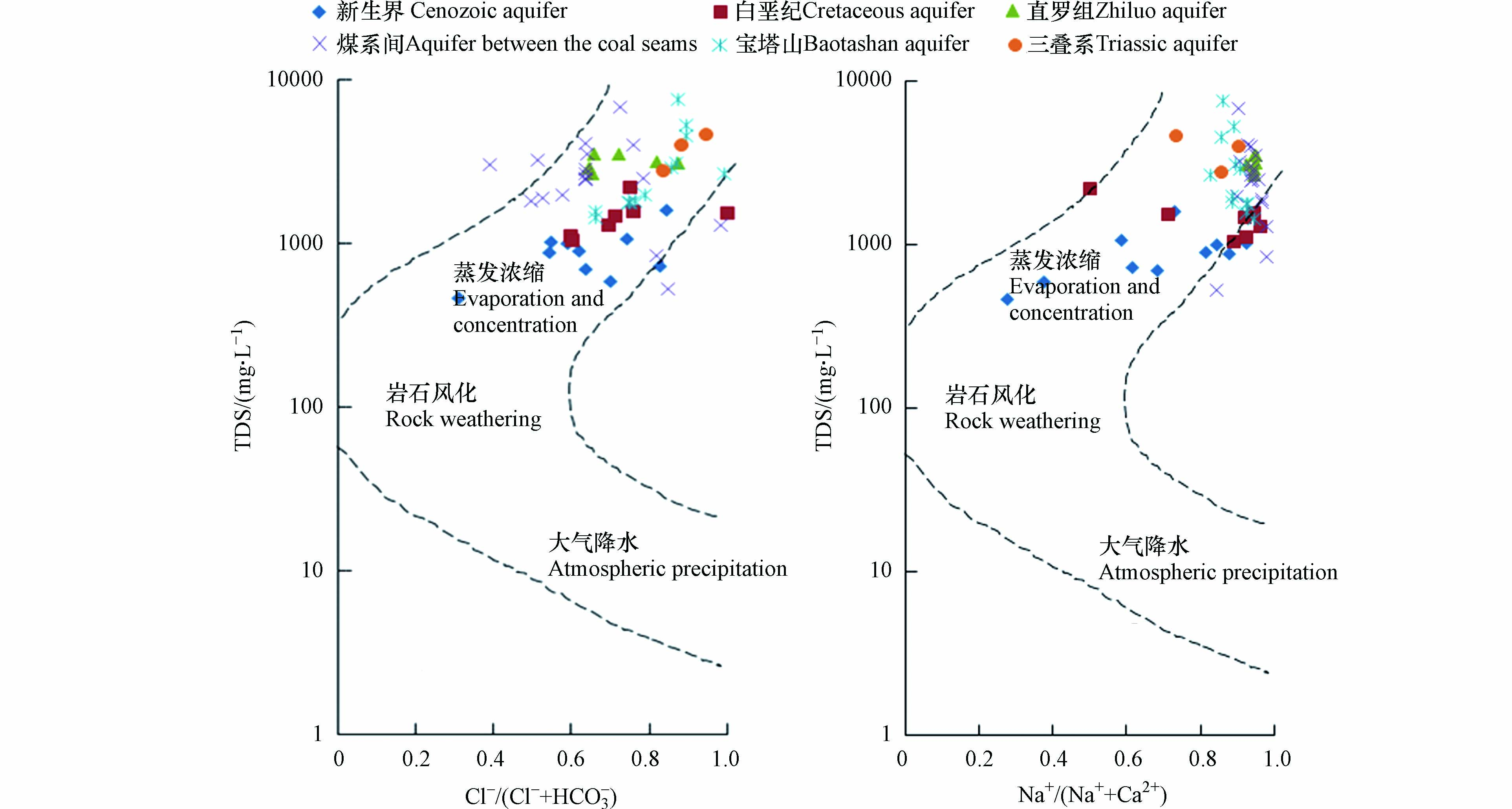
从图3可知,研究区内绝大部分水样分布在Gibbs图右上部,即TDS在1000—7625 mg·L−1之间,Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)或Na+/(Na++Ca2+)接近1,说明矿井水的水化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩影响.
-
阳离子交替吸附作用是由于Ca2+、Mg2+吸附能力较大,可置换岩土颗粒表面的Na+,使其在水中的含量降低[27]. 为了定量分析其作用的方向与强度,可以绘制研究区矿井水氯碱指数图,其中横坐标为CAI1,纵坐标为CAI2,计算公式如下:
式中,c表示毫摩尔浓度,单位为mmol·L−1. 若CAI1和CAI2均<0,则阳离子交替吸附作用较高;反之,若CAI1和CAI2均>0,则阳离子交替吸附作用较差[27].
从图4可知,各含水层矿井水均存在不同程度的阳离子吸附作用,由新生界至三叠系含水层,氯碱指数逐渐减小,随着阳离子交替吸附作用不断加强,Ca2+、Mg2+含量不断下降.
-
脱硫酸作用指的是水中的SO42−被还原,导致水中的SO42−含量下降,同时HCO3−含量升高的过程,其主要化学方程式为:
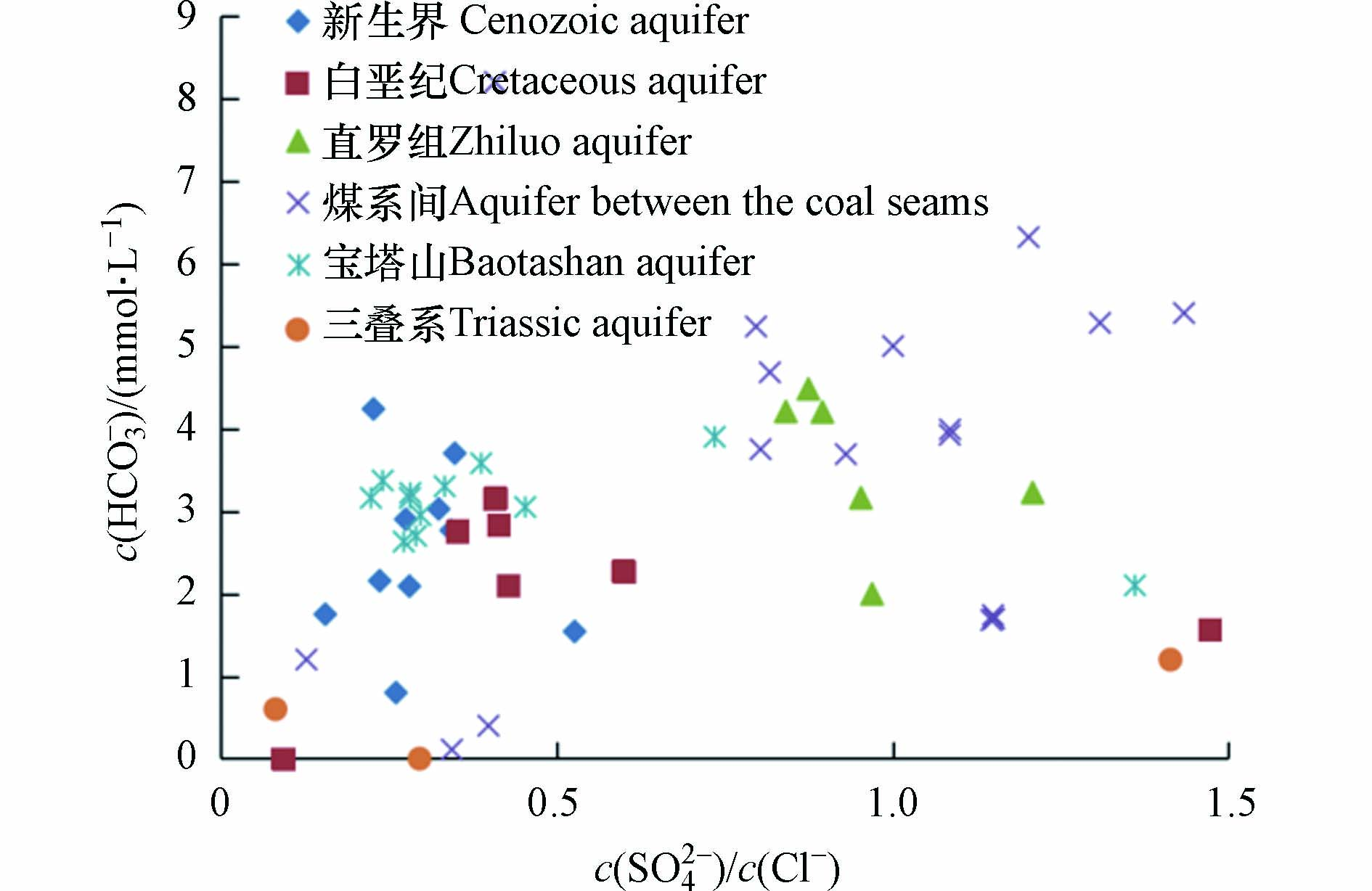
脱硫酸作用强度的主要评价指标是脱硫酸系数c(SO42−)/c(Cl−)[28],脱硫酸系数图中横坐标为SO42−与Cl−的摩尔浓度比,纵坐标为HCO3−的摩尔浓度. 从图5可知,研究区各含水层矿井水c(SO42−)/c(Cl−)数值较小,一般小于0.5,各个含水层存在不同程度的脱硫酸作用. 其中煤系间和直罗组含水层c(SO42−)/c(Cl−)一般为0.5—1.5,其受脱硫酸作用的影响较小. HCO3−在图中相关性不明显,说明HCO3−的唯一来源并不是脱硫酸作用.
-
离子比值分析是用于揭示水化学组成及离子来源常用的方法[29]. 岩盐溶解产生的Na+和Cl−物质量的比值为1,所以c(Na+)/c(Cl−)常被用来解释水中Na+的来源[30].
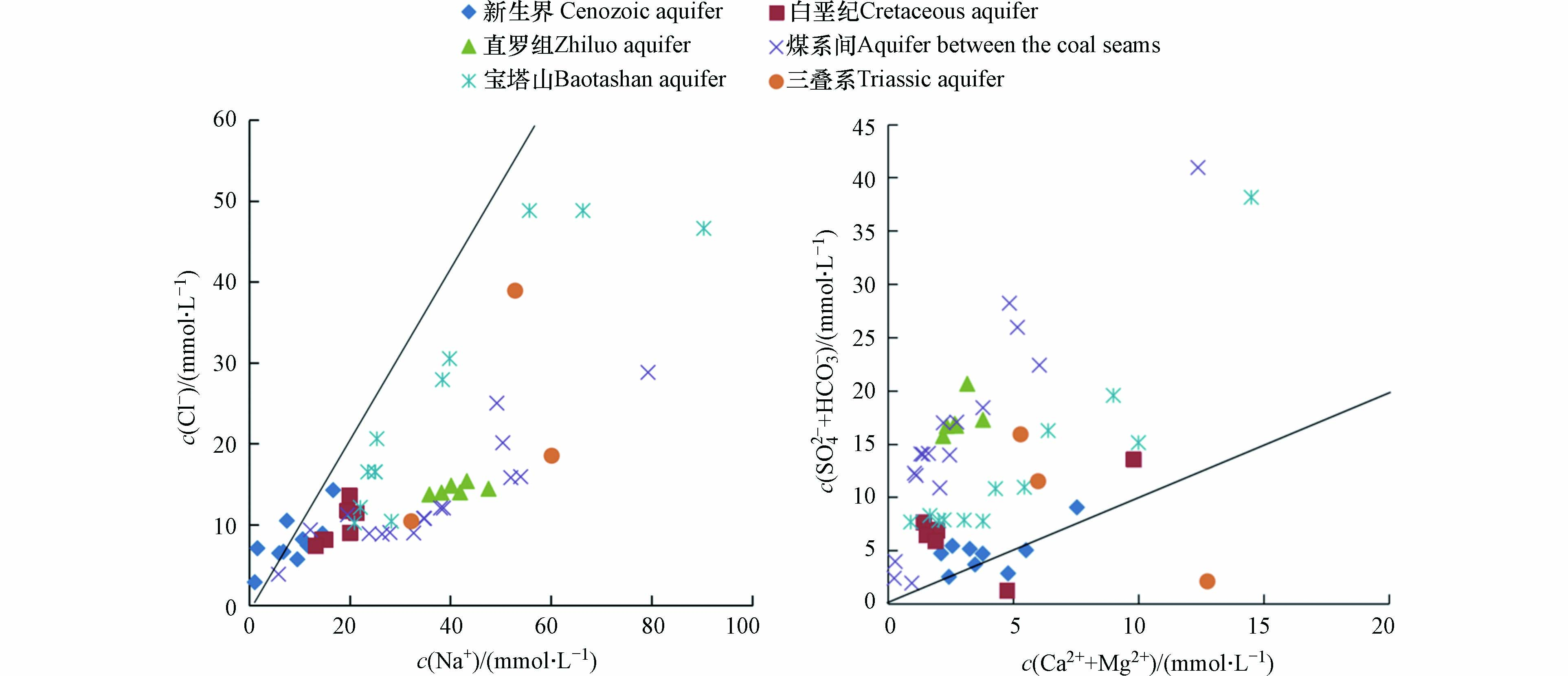
从图6可知,研究区新生界含水层水样的c(Na+)/c(Cl−)等于1,其他含水层水样的比值大于1. 以上情况说明,新生界含水层水样中Na+的唯一来源是钠盐溶解;其他含水层水样中相对Cl−偏高的Na+可能与硅酸盐的风化有关(2NaAlSi3O8+2CO2+11H2O→Al2Si2O5(OH)4+2HCO3−+2Na++4H4SiO4),同时存在其他含钠矿物的溶解[31]. 井田内含水层岩性以砂岩为主,矿物成分多为长石等硅酸盐类矿物,Na+偏高的原因可能是硅酸盐类矿物的溶解作用和阳离子交替吸附作用,使水中的Ca2+和Mg2+被吸附,释放的Na+也是导致Na+含量升高的一个原因. 当水中c(Ca2++Mg2+)/c(SO42−+HCO3−)=1时,代表Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐和硫酸盐的溶解[32-35].
从图6可知,研究区内仅有新生界含水层水样c(Ca2++Mg2+)/c(SO42−+HCO3−)基本等于1,其他含水层水样小于1. 说明新生界含水层水样中的Ca2+和Mg2+来自于碳酸盐及其溶解作用,其他含水层水样中的Ca2+和Mg2+来源有限(含水层多为砂岩),煤系间及其顶底板含水层存在大量的S2−氧化也会导致SO42−增加.
相关研究表明,研究区内除新生界之外的深部含水层相对封闭,径流缓慢,水岩作用较弱,其离子含量较高,矿化度较大[36]. 矿井水的水化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩作用影响,同时阳离子交替吸附作用随着埋深增大不断加强,Ca2+、Mg2+含量不断下降,并受到不同程度脱硫酸作用的影响.
-
从前面的分析可知Cl−是研究区各含水层中含量较高的离子,由于其浓度一般仅受到含水层的影响,受其他因素影响较小,故可以利用各含水层的Cl−浓度来判断含水层之间的水力联系紧密程度. 含水层间水力联系度K计算公式为:
式中,Cl−1和Cl−2分别代表不同含水层中Cl−的平均质量浓度.
当K<0.2,表示两个含水层之间水力联系强;当0.2<K<0.4,说明两个含水层之间水力联系中等;当K>0.4,说明两个含水层之间水力联系弱. 根据研究区水化学数据,分别计算了6个含水层之间的水力联系度. 由表4可知,研究区个含水层之间水力联系度K均小于0.2,说明各含水层之间均存在紧密的水力联系,这与研究区东西两侧的F2和DF20断层具有良好的导水性有关.
相关研究表明,研究区内断层附近的各含水层之间存在水力联系[36],这也导致其水文地球化学特征与周边同层含水层具有显著差异.
-
新上海一号井田地处干旱半干旱地区,水资源相当匮乏. 通过上述综合分析可知,由于矿井水的矿化度高,深度处理成本高,不适宜综合利用于生活饮用水. 随着矿井水综合利用于农田灌溉的需求越来越大,迫切需要开展矿井水灌溉适宜性评价方法研究.
灌溉水源直接影响农作物生长的评价指标是盐碱害[37]. 盐害常用电导率(EC)表征[38],碱害常用钠吸附比(SAR)和钠百分含量(SC)表征(表5),其计算公式(4)—(5)[39],公式中离子浓度单位均为mmol·L−1.
根据表5灌溉水水质分类标准可以进行矿井水灌溉的适宜性评价. 从图7(a)可知,研究区内矿井水的EC值和SAR值普遍较大,45%的矿井水EC值大于2250,位于盐害极高(C4)范围内;70%的矿井水SAR值大于18,位于碱害极高(S3)范围内;10%的矿井水SAR值大于26,位于碱害极高(S4)范围内;即研究区内除新生界和白垩系矿井水的盐碱害较严重(C4S3或C4S4区域),未经深度处理不适宜用于农田灌溉. 从图7(b)可知,73%的矿井水中SC值大于80,不适宜直接用于农田灌溉.
从图7可知,整体而言自上而下含水层的矿井水灌溉适宜性逐渐降低,新生界和白垩系含水层的矿井水基本适宜农田灌溉;而直罗组、宝塔山和三叠系含水层的矿井水适宜性一般为不确定-不适宜,不适宜直接用于农田灌溉,若达到农田灌溉水质要求,其矿井水深度处理成本相对较高. 因此,针对井田内矿井水的综合利用应采取“分层分质综合利用”的原则,可有效降低矿井水综合利用成本,实现社会-经济-环境的高质量协同发展.
-
(1)研究区阳离子以K++Na+为主,阴离子以SO42−和Cl−为主,新生界含水层水化学类型较为多样,由白垩系含水层至三叠系含水层矿井水化学类型由SO4·Cl-Na逐渐过渡为Cl·SO4-Na;TDS与K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−相关性最为显著,相关系数分别为0.973、0.868和0.757.
(2)研究区矿井水的水化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩影响,各含水层矿井水均存在不同程度的阳离子吸附作用,由新生界至三叠系含水层,阳离子交替吸附作用不断加强;新生界、白垩系、宝塔山和三叠系含水层受到不同程度脱硫酸作用影响,煤系间和直罗组含水层矿井水受脱硫酸作用影响较小.
(3)新生界含水层矿井水中Na+的唯一来源是岩盐溶解;其他含水层矿井水中相对Cl−偏高的Na+可能受硅酸盐的风化和其他含钠矿物的溶解影响;新生界含水层矿井水中的Ca2+和Mg2+来自于碳酸盐和硫酸盐的溶解,其他含水层矿井水中的Ca2+和Mg2+来源有限,煤系间及其顶底板含水层矿井水存在大量的S2−氧化也会导致SO42−增加;各含水层之间存在紧密的水力联系,这与断层具有导水性有关.
(4)研究区内45%的矿井水EC值大于2250,70%的矿井水SAR值大于18,73%的矿井水中SC值大于80,大部分矿井水不适宜直接用于农田灌溉. 新生界和白垩系含水层的矿井水基本适宜农田灌溉,而直罗组、宝塔山和三叠系含水层的矿井水不适宜用于农田灌溉,因此研究区内矿井水宜实施“分层分质综合利用”.
煤矿矿井水水化学形成作用与灌溉适宜性评价
Hydrogeochemical processes and irrigation applicability of mine water in coal mine
-
摘要: 矿井水的综合利用方式取决于其水化学特征. 以地处我国典型干旱区的新上海一号井田为研究区,从不同含水层采集55组矿井水样品分析其水化学形成作用,采用电导率(EC)、钠吸附比(SAR)、钠百分含量(SC)的3个指标对不同含水层的矿井水进行了灌溉适宜性评价. 结果表明,各含水层矿井水均呈碱性,总矿化度(TDS)普遍较高. 新生界含水层水化学类型较为多样,由白垩系至三叠系含水层水化学类型由SO4·Cl-Na逐渐过渡为Cl·SO4-Na. 矿井水TDS的主要来源为K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−. 矿井水的化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩影响. 各含水层矿井水均存在不同程度的阳离子交替吸附和脱硫酸作用,由新生界至三叠系含水层,随着阳离子交替吸附作用加强,Ca2+、Mg2+含量不断下降. 研究区内新生界和白垩系含水层的矿井水基本适宜农田灌溉,而直罗组、宝塔山和三叠系含水层的矿井水不适宜直接用于农田灌溉,提出矿井水“分层分质综合利用方法”.Abstract: Comprehensive utilization of mine water depends on its hydrochemical characteristics. The Xinshanghai No.1 coal field, located in typical arid area of China, was employed as the research area. 55 groups of mine water samples in different aquifers were collected and the hydrogeochemical processes of these samples were investigated. Three factors including electrical conductivity (EC), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) and sodium concentration (SC) were applied to evaluate the irrigation suitability of mine water in each aquifer. The results showed that the mine water was alkaline and total dissolved solids (TDS) was generally high in all aquifers. The hydrochemical types in Cenozoic aquifer were diverse. the mine water chemical types in Cretaceous aquifer were SO4·Cl-Na, which gradually became to Cl·SO4-Na in Triassic aquifer. The main TDS sources of mine water were K+, Na+, SO42−, and Cl−. The chemical composition of mine water was mainly affected by evaporation and concentration. Ex-change adsorption of anions and desulphurization existed in all aquifers with varying degree. From Cenozoic to Triassic aquifer, the contents of Ca2+ and Mg2+ decreased with the enhancement of ex-change adsorption. The mine water in Cenozoic and Cretaceous aquifers were basically suitable for farmland irrigation, while the mine water in Zhiluo、Baotashan and Triassic aquifers were not suitable for farmland irrigation. Therefore, a “stratified and qualitative method” was proposed for comprehensive utilization of mine water.
-
在国务院“水十条”对矿井水的最新定位下,煤炭开采形成的矿井水资源保护与综合利用成为实现我国煤炭工业绿色发展和生态文明建设中的重大关键问题[1]. 据统计我国吨煤开采产生矿井水为1.87 m3,矿井水产出量为每年6.88×109 m3,平均利用率约为35%[2-3],主要原因是矿井水水质差,导致不能直接利用,需要进行不同程度的预处理或深度处理,而高额的处理成本限制了综合利用[4-7].
近年来,国内外学者在地下水、地表水的水化学特征方面取得了一系列成果[8-12], 如探讨了神东矿区的高氟矿井水分布特征及形成机制[13];研究了辛置井田地下水的水化学特征和水-岩作用机理[14];系统分析了伊敏矿区地下水的水化学特征与其控制因素[15];对郭家湾煤矿井田内不同区域水化学特征进行差异性分析和水质综合评价[16];研究了高铁锰矿井水的水化学特征与其净化机制[17]. 研究主要侧重矿区水文地球化学特征及形成机制,而对干旱区矿井水综合利用于农田灌溉的相关评价相对较少.
我国西部煤炭资源丰富,占全国总量的70%以上,水资源匮乏,生态环境脆弱[18-20]. 在国家“以水定产,以环境承载力定产”煤炭工业发展理念下,矿井水综合利用成为西部矿区高质量快速发展的卡脖子问题. 因此,在地处干旱半干旱区的煤矿矿井水综合利用相关研究显得尤为重要. 新上海一号煤矿地处毛乌素沙漠边缘,属半干旱半沙漠大陆性气候,干旱少雨[21]. 矿井水若能有效的综合利用于农田灌溉,可有效降低矿井水综合利用成本,实现社会-经济-环境的高质量协同发展.
本研究拟对以新上海一号井田为例,针对各含水层矿井水形成作用进行研究,并对各含水层矿井水的灌溉适宜性进行评价,可为干旱半干旱区矿井水综合利用工作提供依据.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区概况
研究区为新上海庙一号矿井田,其自上而下地层主要有:新生界第四系(Q)和古近系(E);白垩系志丹群(K1zd);侏罗系直罗组(J2z);含煤岩系侏罗系延安组(J2y);三叠系延长组(T3y),其赋存的含水层依次命名为:新生界、白垩系、直罗组、煤系间、宝塔山、三叠系含水层[22]. 研究区内有21条断层,其中F2、FD5和DF20是导水断层.
研究区内井筒掘进和工作面推进过程中的直接充水水源为直罗组、煤系间、延安组和三叠系含水层,间接充水水源为新生界含水层. 为实现矿井水防控,在采掘活动前需要对相应充水含水层进行疏放工程,因此以上述充水含水层为对象进行水化学特征和矿井水综合利用模式研究.
1.2 样品采集与测试
采样分为4个阶段:2006年煤层顶板含水层勘探阶段;2012年近煤层含水层水文地质补充勘探阶段;2016年和2019年各个含水层水文地质补充勘探阶段. 各主要含水层共采集55组样品,检测项目包括K++Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42−、HCO3−、CO32−、pH和TDS,取样点信息详见表1.
表 1 研究区采样点信息表Table 1. The mine water sampling points of the study area采样时间Sampling time 采样含水层Sampling aquifer 采样钻孔编号Sampling borehole number 样品组数Number of samples 2006 新生界 W1、W3、W7、W11、W17、W21、W22、W25、W28、W32 10 白垩系 1604、1202 2 煤系间 2403(上段)、1602(上段)、1202、2403(下段)、1602(下段) 5 2012 白垩系 Z1、Z8 2 直罗组 Z1、Z2、Z3、Z8、Z10 5 煤系间 Z4、Z5、Z6、Z7、Z12、Z13、Z14、Z16 8 2016 白垩系 B3、B5、B9 3 直罗组 B10 1 煤系间 B1、B13、B35、B38 4 宝塔山 B2、B4、B6、B7、B8、B12、B14、 7 三叠系 B36 1 2019 宝塔山 B15、B37、B44、B45、B47 5 三叠系 B39、B46 2 合计 55 1.3 数据分析方法
利用Matlab对矿井水水化学数据进行整理统计和计算,利用Piper图分析地下水水化学类型,利用SPSS软件进行各离子与TDS的相关性分析,通过Gibbs图、氯碱指数图、脱硫酸系数图、离子比值图、水力联系度及矿井水盐碱害分类探讨矿井水水化学特征成因及灌溉适宜性.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 水化学分析
根据研究区内所采集的矿井水样检测结果分析可得,各含水层矿井水的pH值为7.58—12.06,均呈碱性. TDS为466.00—7624.90 mg·L−1,除了新生界,其余均为高矿化度矿井水,而且从新生界到三叠系,埋深越大,越不易接受第四系含水层的补给,因此TDS逐渐增大. 水中主要离子组成变化及不同水样化学组成类型特征采用Piper三线图(图1)分析[23],K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−明显占优势. 由白垩系含水层至三叠系含水层矿井水化学类型由SO4·Cl-Na逐渐过渡为Cl SO4-Na,新生界含水层水化学类型较为多样.
2.2 相关性分析
TDS可以来描述离子特征,利用SPSS软件计算得到Pearson相关性系数矩阵(见表2),可以看出除pH外,TDS与各离子均呈显著相关性[24]. 根据相关性分析结果,TDS与K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−呈显著正相关(P<0.01),相关系数分别为0.973、0.868和0.757,从图2可知,TDS、K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−变化趋势相同,说明K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−是TDS的主要来源.
表 2 TDS与各离子之间的相关系数矩阵Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix among TDS and ions项目 Item K++Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− CO32− pH TDS K++Na+ 1.000 Ca2+ 0.481 1.000 Mg2+ 0.353 0.178 1.000 Cl− 0.778** 0.433 0.555* 1.000 SO42− 0.820** 0.322 0.433 0.526* 1.000 HCO3− 0.292 −0.080 0.075 0.331 0.082 1.000 CO32− 0.246 0.619 −0.083 0.073 −0.146 0.070 1.000 pH −0.184 −0.057 −0.177 −0.207 −0.261 −0.187 0.078 1.000 TDS 0.973** 0.580* 0.389 0.757** 0.868** 0.174 0.213 −0.216 1.000 *表示在置信度0.05时相关性显著;**表示在置信度0.01时相关性显著. 2.3 水化学形成作用
2.3.1 水化学演化特征
Gibbs可有效揭示水化学组分的形成机制,在水化学分析中得到广泛应用[25]. Gibbs图横坐标为阴离子或阳离子质量浓度比,纵坐标为TDS质量浓度,判别方法见表3.
表 3 基于Gibbs图的水化学组成形成作用判别方法[26]Table 3. Determination method of formation of water chemical composition based on Gibbs diagram[26]判别指标 Discriminative index 判别依据 Discrimination on the basis of 阴离子质量浓度比值Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−) 0.5—1 <0.5 0.5—1 阳离子质量浓度比值Na+/(Na++Ca2+) 0.5—1 <0.5 0.5—1 TDS 较高(>1000) 中等(75—1000) 较低(<75) 主要形成作用 蒸发浓缩作用 岩石风化作用 大气降水作用 从图3可知,研究区内绝大部分水样分布在Gibbs图右上部,即TDS在1000—7625 mg·L−1之间,Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)或Na+/(Na++Ca2+)接近1,说明矿井水的水化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩影响.
2.3.2 阳离子交替吸附作用
阳离子交替吸附作用是由于Ca2+、Mg2+吸附能力较大,可置换岩土颗粒表面的Na+,使其在水中的含量降低[27]. 为了定量分析其作用的方向与强度,可以绘制研究区矿井水氯碱指数图,其中横坐标为CAI1,纵坐标为CAI2,计算公式如下:
CAI1=c(Cl−)−c(Na++K+)c(Cl−) (1) CAI2=c(Cl−)−c(Na++K+)2×c(SO42−)+c(HCO3−) (2) 式中,c表示毫摩尔浓度,单位为mmol·L−1. 若CAI1和CAI2均<0,则阳离子交替吸附作用较高;反之,若CAI1和CAI2均>0,则阳离子交替吸附作用较差[27].
从图4可知,各含水层矿井水均存在不同程度的阳离子吸附作用,由新生界至三叠系含水层,氯碱指数逐渐减小,随着阳离子交替吸附作用不断加强,Ca2+、Mg2+含量不断下降.
2.3.3 脱硫酸作用
脱硫酸作用指的是水中的SO42−被还原,导致水中的SO42−含量下降,同时HCO3−含量升高的过程,其主要化学方程式为:
SO42−+2C+2H2O→H2S+2HCO3− 脱硫酸作用强度的主要评价指标是脱硫酸系数c(SO42−)/c(Cl−)[28],脱硫酸系数图中横坐标为SO42−与Cl−的摩尔浓度比,纵坐标为HCO3−的摩尔浓度. 从图5可知,研究区各含水层矿井水c(SO42−)/c(Cl−)数值较小,一般小于0.5,各个含水层存在不同程度的脱硫酸作用. 其中煤系间和直罗组含水层c(SO42−)/c(Cl−)一般为0.5—1.5,其受脱硫酸作用的影响较小. HCO3−在图中相关性不明显,说明HCO3−的唯一来源并不是脱硫酸作用.
2.3.4 离子比值分析
离子比值分析是用于揭示水化学组成及离子来源常用的方法[29]. 岩盐溶解产生的Na+和Cl−物质量的比值为1,所以c(Na+)/c(Cl−)常被用来解释水中Na+的来源[30].
从图6可知,研究区新生界含水层水样的c(Na+)/c(Cl−)等于1,其他含水层水样的比值大于1. 以上情况说明,新生界含水层水样中Na+的唯一来源是钠盐溶解;其他含水层水样中相对Cl−偏高的Na+可能与硅酸盐的风化有关(2NaAlSi3O8+2CO2+11H2O→Al2Si2O5(OH)4+2HCO3−+2Na++4H4SiO4),同时存在其他含钠矿物的溶解[31]. 井田内含水层岩性以砂岩为主,矿物成分多为长石等硅酸盐类矿物,Na+偏高的原因可能是硅酸盐类矿物的溶解作用和阳离子交替吸附作用,使水中的Ca2+和Mg2+被吸附,释放的Na+也是导致Na+含量升高的一个原因. 当水中c(Ca2++Mg2+)/c(SO42−+HCO3−)=1时,代表Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐和硫酸盐的溶解[32-35].
从图6可知,研究区内仅有新生界含水层水样c(Ca2++Mg2+)/c(SO42−+HCO3−)基本等于1,其他含水层水样小于1. 说明新生界含水层水样中的Ca2+和Mg2+来自于碳酸盐及其溶解作用,其他含水层水样中的Ca2+和Mg2+来源有限(含水层多为砂岩),煤系间及其顶底板含水层存在大量的S2−氧化也会导致SO42−增加.
相关研究表明,研究区内除新生界之外的深部含水层相对封闭,径流缓慢,水岩作用较弱,其离子含量较高,矿化度较大[36]. 矿井水的水化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩作用影响,同时阳离子交替吸附作用随着埋深增大不断加强,Ca2+、Mg2+含量不断下降,并受到不同程度脱硫酸作用的影响.
2.3.5 含水层之间水力联系
从前面的分析可知Cl−是研究区各含水层中含量较高的离子,由于其浓度一般仅受到含水层的影响,受其他因素影响较小,故可以利用各含水层的Cl−浓度来判断含水层之间的水力联系紧密程度. 含水层间水力联系度K计算公式为:
K=0.5×Cl−1−Cl−2Cl−1+Cl−2 (3) 式中,Cl−1和Cl−2分别代表不同含水层中Cl−的平均质量浓度.
当K<0.2,表示两个含水层之间水力联系强;当0.2<K<0.4,说明两个含水层之间水力联系中等;当K>0.4,说明两个含水层之间水力联系弱. 根据研究区水化学数据,分别计算了6个含水层之间的水力联系度. 由表4可知,研究区个含水层之间水力联系度K均小于0.2,说明各含水层之间均存在紧密的水力联系,这与研究区东西两侧的F2和DF20断层具有良好的导水性有关.
表 4 各含水层之间水力联系程度Table 4. Hydraulic connection between each aquifer含水层Aquifer Cl−平均浓度/(mg·L−1)Mean concentration of Cl− 水力联系度KDegree of hydraulic connection K 水力联系程度Degree of hydraulic connection 新生界 275.76 — — 白垩系 351.36 0.06(与新生界) 强 直罗组 564.66 0.12(与白垩系) 强 煤系间 517.10 0.02(与直罗组) 强 宝塔山 902.28 0.14(与煤系间) 强 三叠系 801.18 0.03(与宝塔山) 强 相关研究表明,研究区内断层附近的各含水层之间存在水力联系[36],这也导致其水文地球化学特征与周边同层含水层具有显著差异.
2.4 灌溉适宜性评价
新上海一号井田地处干旱半干旱地区,水资源相当匮乏. 通过上述综合分析可知,由于矿井水的矿化度高,深度处理成本高,不适宜综合利用于生活饮用水. 随着矿井水综合利用于农田灌溉的需求越来越大,迫切需要开展矿井水灌溉适宜性评价方法研究.
灌溉水源直接影响农作物生长的评价指标是盐碱害[37]. 盐害常用电导率(EC)表征[38],碱害常用钠吸附比(SAR)和钠百分含量(SC)表征(表5),其计算公式(4)—(5)[39],公式中离子浓度单位均为mmol·L−1.
参数Parameter 分级标准Classification standard 参数Parameter 分级标准Classification standard 参数Parameter 分级标准Classification standard EC/(μs·cm−1) <250 适宜(C1) SAR/(mmol·L−1)1/2 <10 非常适宜(S1) SC/% <20 非常适宜 250—750 允许的(C2) 10—18 适宜(S2) 20—40 适宜 750—2250 不确定(C3) 18—26 允许的(S3) 40—60 允许的 >2250 不适宜(C4) >26 不适宜(S4) 60—80 不确定 >80 不适宜 注:C代表盐化级别,S代表碱化级别,1、2、3、4分别代表低、中、高、极高四个等级. SAR=c(Na+)+c(K+)√c(Ca2+)+c(Mg2+) (4) SC=c(Na+)+c(K+)c(Na+)+c(K+)+2×c(Ca2+)+2×c(Mg2+)×100 (5) 根据表5灌溉水水质分类标准可以进行矿井水灌溉的适宜性评价. 从图7(a)可知,研究区内矿井水的EC值和SAR值普遍较大,45%的矿井水EC值大于2250,位于盐害极高(C4)范围内;70%的矿井水SAR值大于18,位于碱害极高(S3)范围内;10%的矿井水SAR值大于26,位于碱害极高(S4)范围内;即研究区内除新生界和白垩系矿井水的盐碱害较严重(C4S3或C4S4区域),未经深度处理不适宜用于农田灌溉. 从图7(b)可知,73%的矿井水中SC值大于80,不适宜直接用于农田灌溉.
从图7可知,整体而言自上而下含水层的矿井水灌溉适宜性逐渐降低,新生界和白垩系含水层的矿井水基本适宜农田灌溉;而直罗组、宝塔山和三叠系含水层的矿井水适宜性一般为不确定-不适宜,不适宜直接用于农田灌溉,若达到农田灌溉水质要求,其矿井水深度处理成本相对较高. 因此,针对井田内矿井水的综合利用应采取“分层分质综合利用”的原则,可有效降低矿井水综合利用成本,实现社会-经济-环境的高质量协同发展.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)研究区阳离子以K++Na+为主,阴离子以SO42−和Cl−为主,新生界含水层水化学类型较为多样,由白垩系含水层至三叠系含水层矿井水化学类型由SO4·Cl-Na逐渐过渡为Cl·SO4-Na;TDS与K++Na+、SO42−和Cl−相关性最为显著,相关系数分别为0.973、0.868和0.757.
(2)研究区矿井水的水化学组分主要受蒸发浓缩影响,各含水层矿井水均存在不同程度的阳离子吸附作用,由新生界至三叠系含水层,阳离子交替吸附作用不断加强;新生界、白垩系、宝塔山和三叠系含水层受到不同程度脱硫酸作用影响,煤系间和直罗组含水层矿井水受脱硫酸作用影响较小.
(3)新生界含水层矿井水中Na+的唯一来源是岩盐溶解;其他含水层矿井水中相对Cl−偏高的Na+可能受硅酸盐的风化和其他含钠矿物的溶解影响;新生界含水层矿井水中的Ca2+和Mg2+来自于碳酸盐和硫酸盐的溶解,其他含水层矿井水中的Ca2+和Mg2+来源有限,煤系间及其顶底板含水层矿井水存在大量的S2−氧化也会导致SO42−增加;各含水层之间存在紧密的水力联系,这与断层具有导水性有关.
(4)研究区内45%的矿井水EC值大于2250,70%的矿井水SAR值大于18,73%的矿井水中SC值大于80,大部分矿井水不适宜直接用于农田灌溉. 新生界和白垩系含水层的矿井水基本适宜农田灌溉,而直罗组、宝塔山和三叠系含水层的矿井水不适宜用于农田灌溉,因此研究区内矿井水宜实施“分层分质综合利用”.
-
表 1 研究区采样点信息表
Table 1. The mine water sampling points of the study area
采样时间Sampling time 采样含水层Sampling aquifer 采样钻孔编号Sampling borehole number 样品组数Number of samples 2006 新生界 W1、W3、W7、W11、W17、W21、W22、W25、W28、W32 10 白垩系 1604、1202 2 煤系间 2403(上段)、1602(上段)、1202、2403(下段)、1602(下段) 5 2012 白垩系 Z1、Z8 2 直罗组 Z1、Z2、Z3、Z8、Z10 5 煤系间 Z4、Z5、Z6、Z7、Z12、Z13、Z14、Z16 8 2016 白垩系 B3、B5、B9 3 直罗组 B10 1 煤系间 B1、B13、B35、B38 4 宝塔山 B2、B4、B6、B7、B8、B12、B14、 7 三叠系 B36 1 2019 宝塔山 B15、B37、B44、B45、B47 5 三叠系 B39、B46 2 合计 55 表 2 TDS与各离子之间的相关系数矩阵
Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix among TDS and ions
项目 Item K++Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− CO32− pH TDS K++Na+ 1.000 Ca2+ 0.481 1.000 Mg2+ 0.353 0.178 1.000 Cl− 0.778** 0.433 0.555* 1.000 SO42− 0.820** 0.322 0.433 0.526* 1.000 HCO3− 0.292 −0.080 0.075 0.331 0.082 1.000 CO32− 0.246 0.619 −0.083 0.073 −0.146 0.070 1.000 pH −0.184 −0.057 −0.177 −0.207 −0.261 −0.187 0.078 1.000 TDS 0.973** 0.580* 0.389 0.757** 0.868** 0.174 0.213 −0.216 1.000 *表示在置信度0.05时相关性显著;**表示在置信度0.01时相关性显著. 表 3 基于Gibbs图的水化学组成形成作用判别方法[26]
Table 3. Determination method of formation of water chemical composition based on Gibbs diagram[26]
判别指标 Discriminative index 判别依据 Discrimination on the basis of 阴离子质量浓度比值Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−) 0.5—1 <0.5 0.5—1 阳离子质量浓度比值Na+/(Na++Ca2+) 0.5—1 <0.5 0.5—1 TDS 较高(>1000) 中等(75—1000) 较低(<75) 主要形成作用 蒸发浓缩作用 岩石风化作用 大气降水作用 表 4 各含水层之间水力联系程度
Table 4. Hydraulic connection between each aquifer
含水层Aquifer Cl−平均浓度/(mg·L−1)Mean concentration of Cl− 水力联系度KDegree of hydraulic connection K 水力联系程度Degree of hydraulic connection 新生界 275.76 — — 白垩系 351.36 0.06(与新生界) 强 直罗组 564.66 0.12(与白垩系) 强 煤系间 517.10 0.02(与直罗组) 强 宝塔山 902.28 0.14(与煤系间) 强 三叠系 801.18 0.03(与宝塔山) 强 参数Parameter 分级标准Classification standard 参数Parameter 分级标准Classification standard 参数Parameter 分级标准Classification standard EC/(μs·cm−1) <250 适宜(C1) SAR/(mmol·L−1)1/2 <10 非常适宜(S1) SC/% <20 非常适宜 250—750 允许的(C2) 10—18 适宜(S2) 20—40 适宜 750—2250 不确定(C3) 18—26 允许的(S3) 40—60 允许的 >2250 不适宜(C4) >26 不适宜(S4) 60—80 不确定 >80 不适宜 注:C代表盐化级别,S代表碱化级别,1、2、3、4分别代表低、中、高、极高四个等级. -
[1] 顾大钊, 李井峰, 曹志国, 等. 我国煤矿矿井水保护利用发展战略与工程科技 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(10): 3079-3089. GU D Z, LI J F, CAO Z G, et al. Technology and engineering development strategy of water protection and utilization of coal mine in China [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(10): 3079-3089(in Chinese).
[2] 顾大钊, 张勇, 曹志国. 我国煤炭开采水资源保护利用技术研究进展 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(1): 1-7. GU D Z, ZHANG Y, CAO Z G. Technical progress of water resource protection and utilization by coal mining in China [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(1): 1-7(in Chinese).
[3] 顾大钊, 李庭, 李井峰, 等. 我国煤矿矿井水处理技术现状与展望 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(1): 11-18. GU D Z, LI T, LI J F, et al. Current status and prospects of coal mine water treatment technology in China [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(1): 11-18(in Chinese).
[4] 孙亚军, 陈歌, 徐智敏, 等. 我国煤矿区水环境现状及矿井水处理利用研究进展 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(1): 304-316. SUN Y J, CHEN G, XU Z M, et al. Research progress of water environment, treatment and utilization in coal mining areas of China [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1): 304-316(in Chinese).
[5] 孙亚军, 徐智敏, 李鑫, 等. 我国煤矿区矿井水污染问题及防控技术体系构建 [J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(5): 1-16. SUN Y J, XU Z M, LI X, et al. Mine water drainage pollution in China's coal mining areas and the construction of prevention and control technical system [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(5): 1-16(in Chinese).
[6] 孙亚军, 张梦飞, 高尚, 等. 典型高强度开采矿区保水采煤关键技术与实践 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(1): 56-65. SUN Y J, ZHANG M F, GAO S, et al. Water-preserved mining technology and practice in typical high intensity mining area of China [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(1): 56-65(in Chinese).
[7] 孙亚军, 张莉, 徐智敏, 等. 煤矿区矿井水水质形成与演化的多场作用机制及研究进展 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(1): 423-437. SUN Y J, ZHANG L, XU Z M, et al. Multi-field action mechanism and research progress of coal mine water quality formation and evolution [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 423-437(in Chinese).
[8] 王建, 韩海东, 许君利, 等. 塔里木河流域出山径流水化学特征研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(4): 1576-1587. WANG J, HAN H D, XU J L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of the mountain runoff in Tarim River Basin, China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(4): 1576-1587(in Chinese).
[9] 罗珍, 仁增拉姆, 陈虎林, 等. 西藏巴松措冷季水化学特征及其影响因素 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(9): 4263-4270. LUO Z, REN Z, CHEN H L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and its controlling factors of Basong Lake in cold season in Tibet [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(9): 4263-4270(in Chinese).
[10] 刘鑫, 向伟, 马小军, 等. 黄土高原中部浅层地下水化学特征及影响因素 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(11): 5201-5209. LIU X, XIANG W, MA X J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of shallow groundwater in the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(11): 5201-5209(in Chinese).
[11] 刘敏, 赵良元, 李青云, 等. 长江源区主要河流水化学特征、主要离子来源 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(3): 1243-1254. LIU M, ZHAO L Y, LI Q Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics, main ion sources of main rivers in the source region of Yangtze River [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(3): 1243-1254(in Chinese).
[12] 郝春明, 张伟, 何瑞敏, 等. 神东矿区高氟矿井水分布特征及形成机制 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(6): 1966-1977. HAO C M, ZHANG W, HE R M, et al. Formation mechanisms for elevated fluoride in the mine water in Shendong coal-mining district [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(6): 1966-1977(in Chinese).
[13] 赵峰华, 郭元, 孙红福, 等. 辛置煤矿主要含水层的自由排水柱淋滤实验与水岩作用机理 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(4): 1207-1215. ZHAO F H, GUO Y, SUN H F, et al. Free draining column leaching experiment and mechanism of water-rock interaction in main aquifer of Xinzhi coal mine [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(4): 1207-1215(in Chinese).
[14] WANG T T, JIN D W, YANG J, et al. Assessing mine water quality using a hierarchy fuzzy variable sets method: A case study in the Guojiawan mining area, Shaanxi Province, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(8): 264. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8216-1 [15] 王甜甜, 张雁, 赵伟, 等. 伊敏矿区地下水水化学特征及其形成作用分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(5): 1480-1489. WANG T T, ZHANG Y, ZHAO W, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation process of groundwater in Yimin mining area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(5): 1480-1489(in Chinese).
[16] 李福勤, 杨静, 何绪文, 等. 高铁高锰矿井水水质特征及其净化机制 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2006, 31(6): 727-730. LI F Q, YANG J, HE X W, et al. Characteristics and treatment mechanism of mine water with high concentration of iron and manganese [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2006, 31(6): 727-730(in Chinese).
[17] 王双明, 段中会, 马丽, 等. 西部煤炭绿色开发地质保障技术研究现状与发展趋势 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(2): 1-6. WANG S M, DUAN Z H, MA L, et al. Research status and future trends of geological assurance technology for coal green development in Western China [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(2): 1-6(in Chinese).
[18] 姚峰, 古丽·加帕尔, 包安明, 等. 基于遥感技术的干旱荒漠区露天煤矿植被群落受损评估 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(4): 707-713. YAO F, GULI·J, BAO A M, et al. Damage assessment of the vegetable types based on remote sensing in the open coalmine of arid desert area [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(4): 707-713(in Chinese).
[19] 马超, 田淑静, 邹友峰, 等. 神东矿区AVHRR/NDVI的时空、开采强度和气候效应 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(9): 2749-2756. MA C, TIAN S J, ZOU Y F, et al. Dynamic responses of the coalfield ecosystem to mining intensity, spatio-temporal variation, and climate change derived from AVHRR/NDVI in Shendong coalfield [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(9): 2749-2756(in Chinese).
[20] 赵河聚, 成龙, 贾晓红, 等. 高寒沙区生物土壤结皮覆盖土壤碳释放动态 [J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(18): 6396-6404. ZHAO H J, CHENG L, JIA X H, et al. The dynamics of soil carbon release covered with biological soil crusts in Alpine sand area [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(18): 6396-6404(in Chinese).
[21] 张泽源. 新上海一号煤矿宝塔山砂岩含水层地下水疏降优化研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2021. ZHANG Z Y. Study on Groundwater Drainage Technology of Baotashan Sandstone Aquifer in New Shanghai No. 1 Coal Mine[J]. Beijing: China Coal Reasearch Institute, 2021.
[22] 吕玉广, 肖庆华, 程久龙. 弱富水软岩水-沙混合型突水机制与防治技术: 以上海庙矿区为例 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(10): 3154-3163. LÜ Y G, XIAO Q H, CHENG J L. Mechanism and prevention of water-sand inrush in soft rock with weakly abundant water: A case study in Shanghai temple mining area [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(10): 3154-3163(in Chinese).
[23] HAN G L, LIU C Q. Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: A study of the river waters draining Karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 204(1/2): 1-21. [24] 杨婷婷, 许光泉, 余世滔, 等. 煤层下部太原组岩溶水化学组分特征及其成因分析 [J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(2): 100-108. YANG T T, XU G Q, YU S T, et al. An analysis of the chemical composition characteristics and formation of the Karst groundwater in the Taiyuan Group in the lower part of a coal seam [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(2): 100-108(in Chinese).
[25] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry [J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [26] GIBBS R J. Water chemistry of the Amazon River [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1972, 36(9): 1061-1066. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(72)90021-X [27] 刘江涛, 蔡五田, 曹月婷, 等. 沁河冲洪积扇地下水水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(12): 5428-5439. LIU J T, CAI W T, CAO Y T, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and the origin in alluvialproluvial fan of Qinhe River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(12): 5428-5439(in Chinese).
[28] SCHOELLER H. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources: methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development [J]. Water Research, 1965, 33: 5483-5516. [29] 李书鉴, 韩晓, 王文辉, 等. 无定河流域地表水地下水的水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 220-229. LI S J, HAN X, WANG W H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of surface water and groundwater in Wuding River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 220-229(in Chinese).
[30] 郑涛, 焦团理, 胡波, 等. 涡河流域中部地区地下水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2): 766-775. ZHENG T, JIAO T L, HU B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and origin of groundwater in the central guohe river basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2): 766-775(in Chinese).
[31] 陈陆望, 许冬清, 殷晓曦, 等. 华北隐伏型煤矿区地下水化学及其控制因素分析: 以宿县矿区主要突水含水层为例 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(4): 996-1004. CHEN L W, XU D Q, YIN X X, et al. Analysis on hydrochemistry and its control factors in the concealed coal mining area in North China: A case study of dominant inrush aquifers in Suxian mining area [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(4): 996-1004(in Chinese).
[32] 孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 等. 哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化 [J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6): 1128-1141. SUN H Y, MAO Q G, WEI X F, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami Basin [J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6): 1128-1141(in Chinese).
[33] XING L N, GUO H M, ZHAN Y H. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70/71: 250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.017 [34] ZHU B Q, YANG X P, RIOUAL P, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of three watersheds (the Erlqis, Zhungarer and Yili) in northern Xinjiang, NW China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(8): 1535-1548. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.018 [35] GAILLARDET J, DUPRÉ B, LOUVAT P, et al. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 159(1/2/3/4): 3-30. [36] 赵宝峰, 吕玉广. 新上海一号井田水文地球化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(3): 92-98. ZHAO B F, LV Y G. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and main controlling factors of Xinshanghai No. 1 coal field [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(3): 92-98(in Chinese).
[37] MAHATO M K, SINGH P K, SINGH A K, et al. Assessment of hydrogeochemical processes and mine water suitability for domestic, irrigation, and industrial purposes in east bokaro coalfield, India [J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2018, 37(3): 493-504. doi: 10.1007/s10230-017-0508-7 [38] SINGH A K, MONDAL G C, SINGH T B, et al. Hydrogeochemical processes and quality assessment of groundwater in Dumka and Jamtara districts, Jharkhand, India [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 67(8): 2175-2191. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1658-3 [39] 毛萌, 朱雪芹. 宣化盆地地下水化学特性及灌溉适用性评价 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(7): 142-149. MAO M, ZHU X Q. Chemical characteristics of groundwater in Xuanhua Basin and assessment of irrigation applicability [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(7): 142-149(in Chinese).
[40] SEN Z. Practical and Applied Hydrogeology[M]. Elsevier, 2015. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: