-
以太阳能为基础利用光催化技术在温和反应条件下进行清洁能源转化和环境污染物净化对人类社会可持续发展具有重要意义. 绿色高效光催化剂作为光催化反应的核心始终是科研工作者首先需要解决的问题. 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)作为典型非金属聚合物材料,因其结构稳定、合成简单、具有可见光吸收等优点已逐步成为新一代光催化剂的典型代表[1-3].
空心球结构在半导体光催化反应体系格外引人注意,因其结构稳定,可将其他功能性基团集成在球体内外形成复杂的纳米结构,同时也可以“笼”形方式在球体内部进行一系列反应形成特殊的核壳结构[4-7]. 2012年,Wang等以多孔二氧化硅球为模板制备出氮化碳空心球,具有显著增强的光解水制氢性能[8]. 自此,以牺牲模板法制备氮化碳空心球成为主要方法[9]. 然而,受限于高温热聚合过程中聚合物中空纳米结构容易发生塌陷和扭曲,限制了空心球聚合物半导体的有效结构调控. 溶剂热技术可以通过分子工程实现溶液中分子自组装进行产物结构和形貌的有效调控[10]. 本课题组前期研究结果表明,可以在较低的温度下通过直接溶剂热法制备氮化碳空心球,且通过调控合成参数可实现氮化碳空心球的光催化性能优化[11]. 但低温合成产物聚合度较低,限制了光生电荷在长程范围内的有效传输,因此其光催化性能还有待进一步提升.
分子共聚合改性是优化g-C3N4电子结构和光学性质的有效方法. 含芳环小分子化合物与g-C3N4共聚可构造给体-受体结构,增强特征sp2杂化π电子离域. 例如,将巴比妥酸、2-氨基苄腈等共轭分子嵌入g-C3N4骨架有助于提高产物光催化性能[12]. 与等电子体系的六元芳环相比,五元杂环化合物为富电子体系,共聚g-C3N4不仅影响半导体的电子结构和光学性质,还可以调控其氧化还原电位.
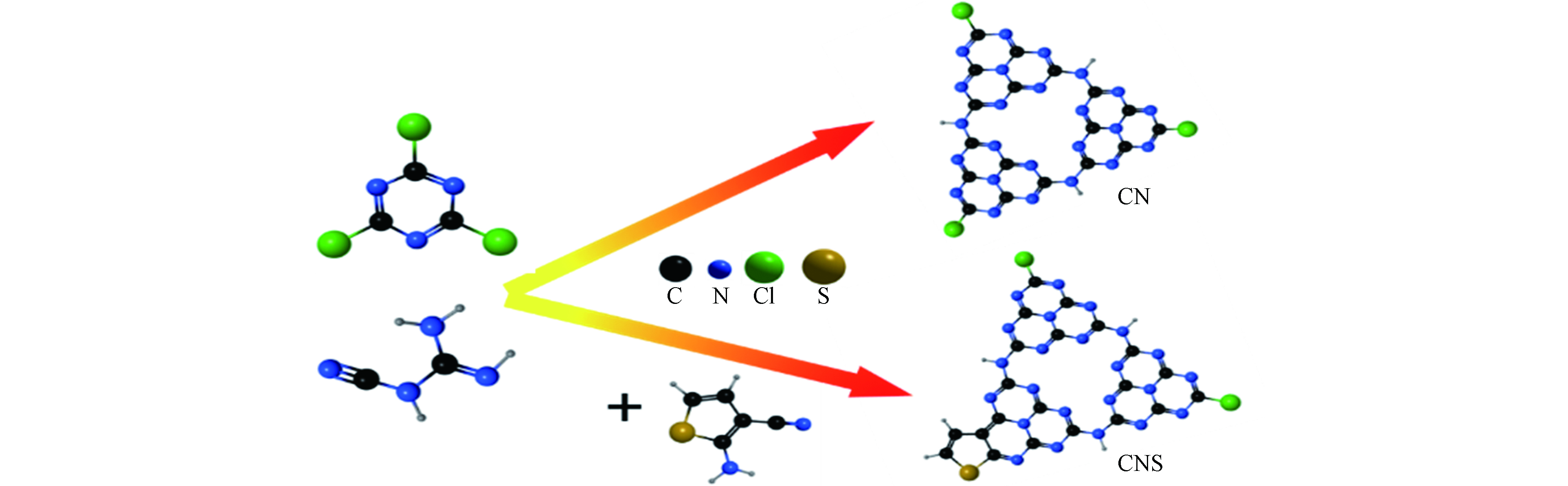
含S噻吩基团为典型的发色基团且具有强大的给电子能力,是优化半导体聚合物光电性能的有效基团,可在半导体内构建分子内电子给体,同时在费米能级上形成半占据杂质能级,降低半导体带隙[13]. 理论研究表明,噻吩基团修饰g-C3N4可引起光诱导电子的有效质量降低,光诱导电子-空穴的迁移率差异增大,从而降低电子-空穴复合率,同时修饰后产物结构畸变,可提高n-π*电子跃迁活性[14]. 截止目前,关于噻吩修饰g-C3N4的工作主要集中于高温热解共聚以及产物在光解水方面的应用,而针对低温合成条件下以含特殊基团分子为共聚体合成特定形貌的g-C3N4及其对光催化性能的影响研究工作还鲜少报道. 鉴于此,本工作以2-氨基噻吩-3甲腈(TPCN)为共聚合单体,一步溶剂热反应成功将噻吩环结构嵌入g-C3N4骨架中,制备出一系列具有宽可见光响应的氮化碳空心球(CNS). 采用多种表征技术对催化剂结构、组成、光电性质等进行分析,通过光催化还原水中Cr6+、光解水制氢以及降解甲基橙考察了催化剂的活性,并推测了相应的光催化反应机理,为低温合成高效g-C3N4基光催化剂提供实验基础.
-
本实验所用实验试剂均为AR级,去离子水为实验室自制. 主要试剂有:三聚氯氰(CC)、二聚氰胺(DCDA)、2-氨基噻吩-3甲腈(TPCN)、乙腈、甲基橙(MO)、重铬酸钾(K2Cr2O7)、三乙醇胺、氯铂酸(H2PtCl6·6H2O)、对苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、异丙醇(IPA).
-
将CC、DCDA和TPCN按一定物质的量比例分散于60 mL乙腈,常压下混合液中通氮气并连续搅拌30 min.将混合液转移入100 mL水热反应釜中,置于烘箱中180 ℃反应48 h. 自然冷却后将所得固体产物离心分离(转速8000 r·min−1,5 min),用乙腈和去离子水反复洗涤多次,置于烘箱中60 ℃干燥得到最终产物. 反应原料比例及产物命名列于表1,合成示意图见图1.
-
采用X-射线衍射仪(XRD,D/max 2500PC,日本理学株式会社)分析样品聚合结构;采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,SU-8010,日本日立公司)观察样品形貌;采用固体核磁(NMR,Agilent 600M,瑞士布鲁克公司)测定13C核磁谱图;采用紫外-可见分光光度计(UV-2550,日本岛津公司)表征样品的光吸收性质,BaSO4为标准物质;通过X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,ESCALAB 250,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司)测定材料表面电子性质;采用荧光光谱仪(PL,QuantaMasterTM40,美国PTI公司)考察催化剂的荧光发光性能;利用电化学工作站(CHI660E,上海辰华仪器有限公司)表征催化剂的光电化学性质. 具体测试方法:乙醇超声催化剂滴涂在FTO导电玻璃上作为工作电极,分别以铂片和饱和甘汞电极作为对电极和参比电极,电解液为 0.2 mol·L−1 Na2SO4溶液.
-
50 mg催化剂分散于100 mL K2Cr2O7溶液(含Cr6+ 10 mg·L−1),避光搅拌40 min,待达到吸附-脱附平衡后,300 W氙灯(CEL HXF300)进行光照(λ>420 nm,光强1.5 mW·cm2),每隔一段时间取反应液4 mL,经离心后取上清液,采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法测定吸光度.
-
50 mg催化剂分散于90 mL水,加入10 mL三乙醇胺和100 μL H2PtCl6·6H2O (0.04 g·mL−1). 搅拌30 min并抽真空后,300 W氙灯进行光照(同上). 通过气相色谱仪(GC7920,TCD检测器,N2作为载气)在线检测H2产量.
-
25 mg催化剂加入MO溶液中(20 mg·L−1),避光条件下搅拌30 min,以达到吸附平衡. 300 W氙灯进行光照(同上),每隔一段时间取反应液4 mL,经离心分离后用紫外可见分光光度计测定上清液吸光度.
-
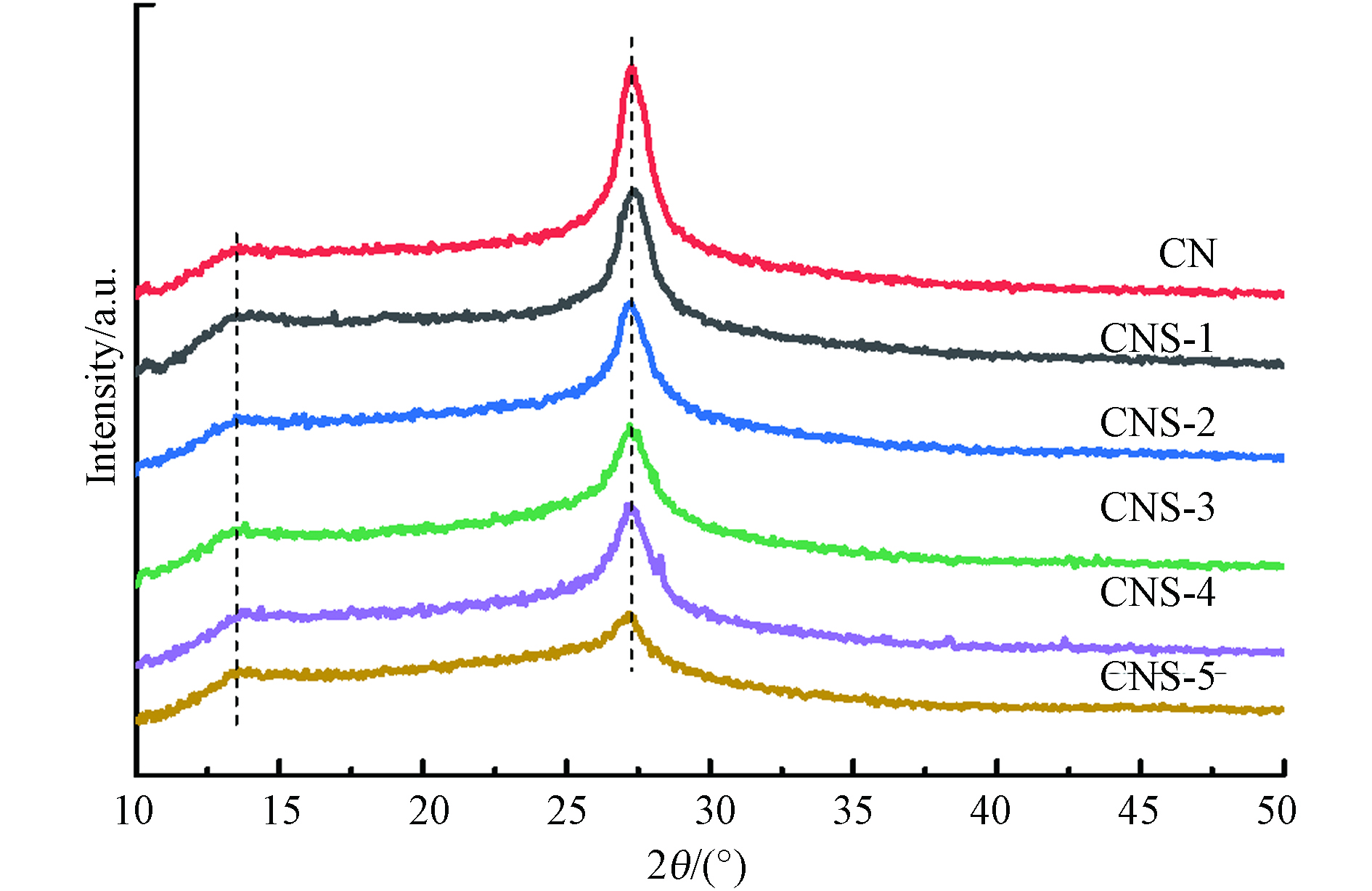
图2为合成催化剂的XRD图谱,CN及CNS样品均具有典型的石墨相结构. 27.3°强峰是石墨相材料典型的层间堆叠(002)峰,13.0°处的宽衍射峰对应氮化碳的(100)晶面,归属于氮化碳面内嗪环结构的重复排列[15]. 与CN相对比,CNS样品的XRD衍射峰位没有发生变化,说明噻吩环的引入没有破坏CN的基本聚合结构. 随着TPCN聚合量的增加,CNS样品的(002)衍射峰强度逐步降低,说明样品聚合结构的长程有序性降低.
通过SEM对CN和CNS样品(以CNS-2为例)的微观形貌进行表征,如图3所示. 图3中a—c和d—f分别为CN和CNS-2样品的SEM图. 低温溶剂热合成有利于CN聚合形成稳定的球状形貌,且呈空心态,平均尺寸约为1 μm. 低温自聚合形成空心球是溶剂热合成的典型合成路径[16]. 以TPCN为共聚合分子得到的CNS-2与CN相比,其形貌依然保持空心球结构,颗粒大小也无明显变化,但球体表面粗糙度增加. 这一结果表明,共聚分子的引入在一定程度上降低了产物聚合度,颗粒表面引入更多结构缺陷,在一定程度上增加了界面反应接触活性位.
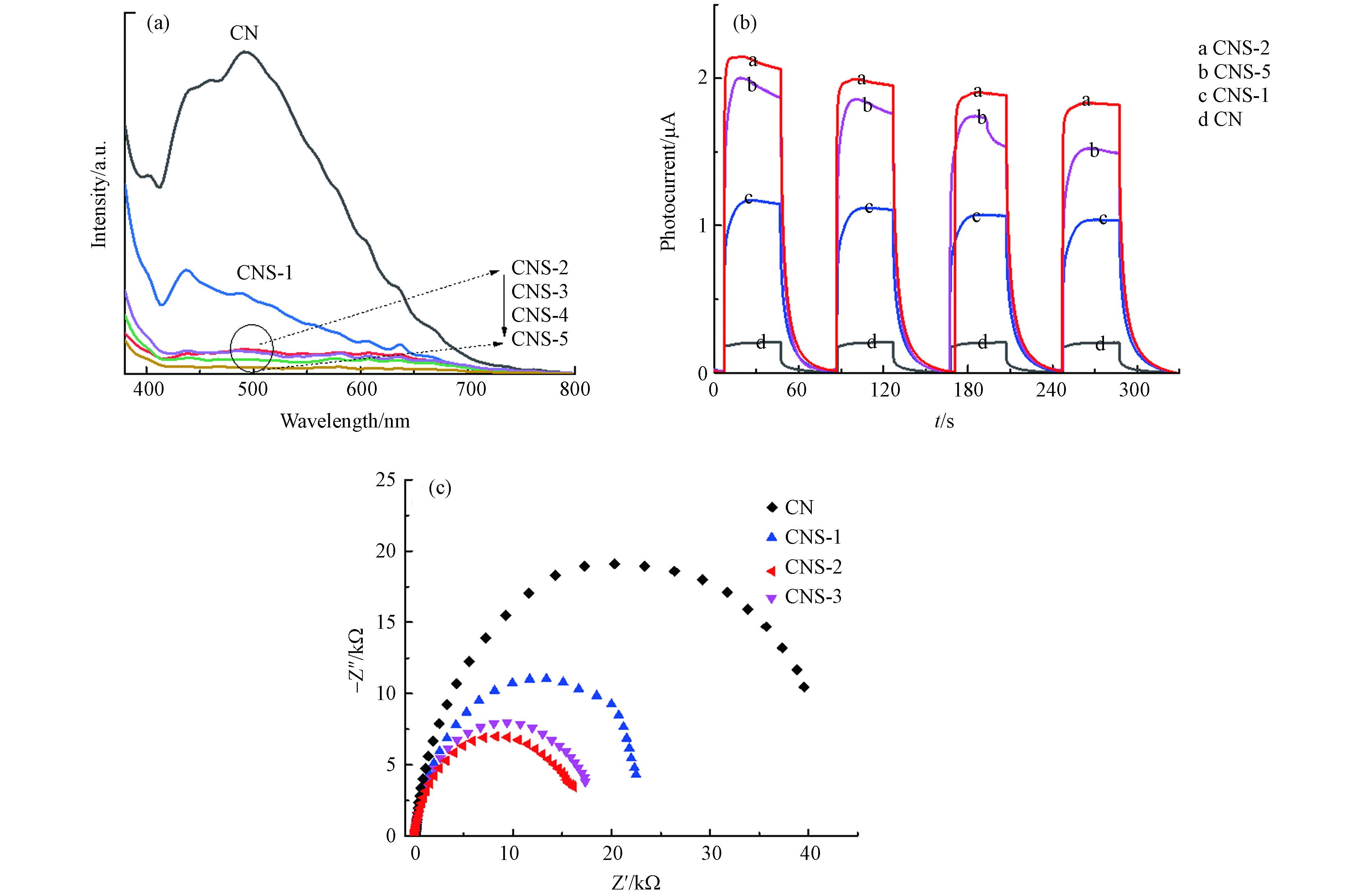
催化剂的光吸收谱图如图4a所示. 由图4可以看出,低温溶剂热法所合成产物具有较宽的可见光吸收范围,远大于常规高温煅烧法所制备的氮化碳产物(~ 460 nm). 相对于CN,CNS的光吸收带边均发生不同程度的红移,且随着噻吩环聚合量的增加而逐步扩展至~700 nm,样品颜色由橘红色过渡为暗红色,从光响应角度提升催化剂的光吸收至深可见区是光催化剂性能提升的重要因素. 通过Tauc曲线对样品的禁带宽度进行测算,如图4b所示,CN、CNS-2和CNS-5的带隙宽度分别为 2.0、1.92 eV和1.83 eV. 这一结果说明,噻吩环修饰共聚合有效拓展了CN的π共轭体系,窄化了带隙宽度,拓展了可见光的吸收范围,可显著提升对太阳光的吸收和利用. 图4c为CN和CNS-2的Mott-Schottky曲线. 曲线斜率均为正值说明样品为n型半导体,CN和CNS-2的平带电位分别位于−1.25 V和−1.15 V vs. NHE. 由于n型半导体平带电势接近导带电位,因此可以认为CN与CNS-2的平带电位分别位于−1.25 V和−1.15 V vs. NHE[17]. 与CN相比,尽管CNS-2的导带电位正移,但仍具有较强的还原电势,同时满足在含O2条件下超氧自由基(
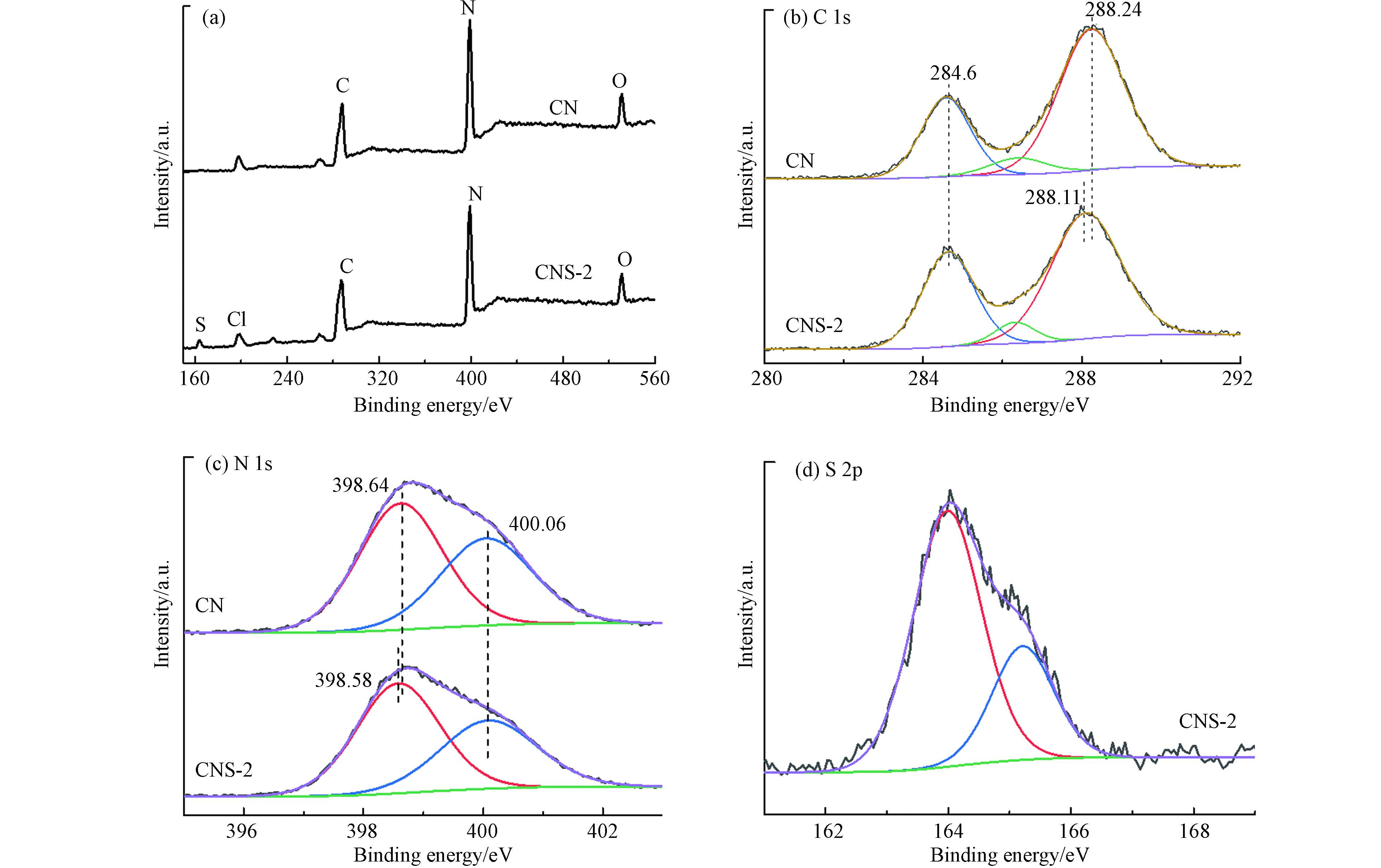
⋅O−2 )的生成(Eθ(O2/⋅O−2 ) = −0.33 V vs. NHE),因此在环境污染物降解方面具有潜在的应用价值[18].图5为CN和CNS-2的XPS谱图. 从总谱图5a中可以看出,CN及CNS样品主要由C、N和O元素组成,另外含有少量Cl元素,来源于三聚氯氰的末端不完全聚合. 与CN相比,CNS-2谱图中出现S元素,初步证明含S噻吩环分子结构共聚合嵌入CN共轭骨架. 图4b中 CN的C 1s谱曲线可以分别在284.60、286.30、288.24 eV处拟合3个峰,对应C—C/C=C键、少量C—O键和sp2杂化碳(N—C=N)[19]. CNS-2具有相似的C1s拟合曲线,但其sp2 C的峰向低位移动0.13 eV. 图4c中CN的N 1s可拟合为2条曲线,中心峰位分别为398.64 eV和400.06 eV,归因于共轭杂环中的sp2 N和桥连N原子N—(C)3[20]. CNS-2同样具有类似的N 1s谱线,但sp2 N峰位同样向低位偏移约0.06 eV. 图5为CNS-2样品的S 2p 高分辨XPS谱图,电子结合能分别位于164.0 eV和165.3 eV的两个峰来源于S 2p3/2和S 2p1/2. 这一结果与文献中报道的S掺杂的氮化碳中S的电子结合能(163.9 eV和168.5 eV)明显不同,而与噻吩化合物中S的电子结合能(163.8 eV和165.0 eV)相吻合,表明所得产物不是简单的S掺杂CN,有力地证实了噻吩环分子通过共聚合的方法成功地并入到了CN的分子结构中[21]. 图5b—d共同说明,CNS-2共轭结构中的sp2杂化C,N具有更高的电荷分布密度. 这是由于噻吩环为典型的供电子基团,共聚合嵌入CN共轭骨架能够拓展共轭杂化结构,拓展光吸收,同时使得产物CNS样品具有更高的不饱和电荷密度,有利于更多光生电荷的产生.
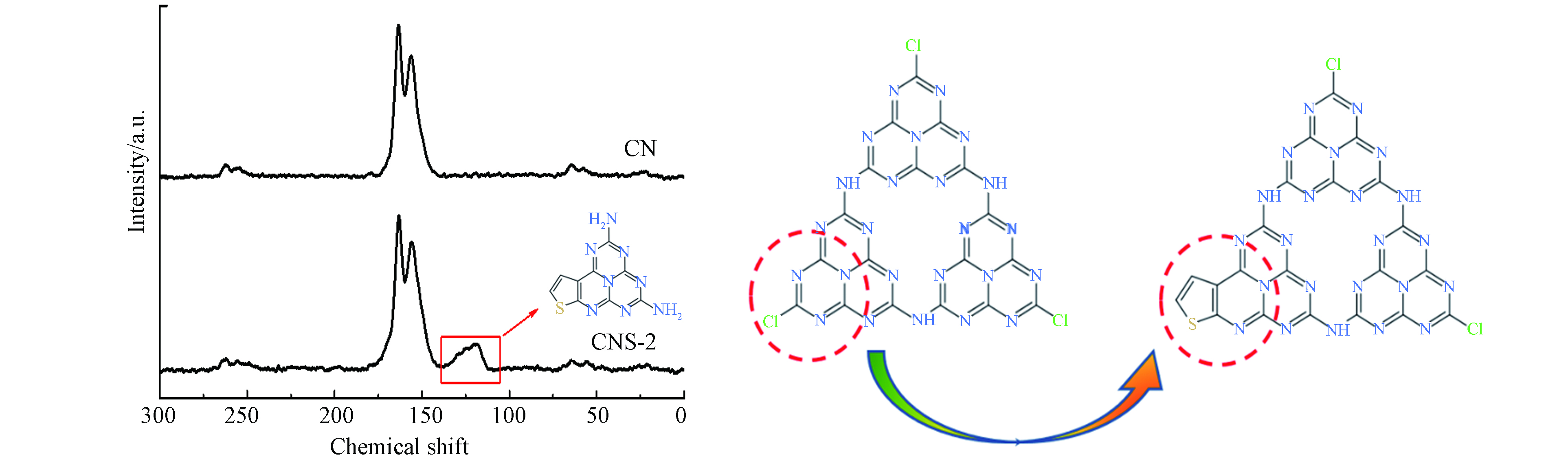
为了进一步证实噻吩环聚合嵌入CN骨架,采用固体13C NMR表征CN和CNS-2的化学结构变化,如图6所示. 可以看出,二者在化学位移155.6和164.3处均出现两个明显的核磁共振峰,归属于氮化碳共轭杂环C. 此外,CNS-2样品在化学位移110附近处出现一个新峰,由噻吩环分子中的C参与CN π共轭而引起,这表明噻吩环结构通过共聚合的方法成功嵌入到CN的组成结构中[22]. 结合XPS分析可推断,在热聚合过程中噻吩基团取代边缘N=C—Cl,从而实现将噻吩结构嵌入到CN分子骨架中.
光电响应性能是分析光催化剂的重要技术方法,可以直观的表明在光照条件下催化剂光生载流子的产生和分离. 图7a是催化剂的稳态PL光谱, 在360 nm光激发下,CN在500 nm附近处有较强的PL发射峰,来源于催化剂的π-π*电子激发跃迁[23],表明CN存在较强的光生电子-空穴复合. 当噻吩环嵌入后,CNS系列样品的PL发射峰强度骤然减弱. 除CNS-1仍出现较明显的发射峰外,其他样品PL发射峰几乎可忽略. 显著降低的PL发射峰强度表明CNS样品的光生电子-空穴复合率被明显抑制,具有增强的电子-空穴分离效率. 噻吩环的嵌入有利于优化电子结构,扩大共轭平面电荷离域性,增强电荷流动性. 图7b为采用三电极体系测得催化剂的I-t曲线. 在可见光照下(λ > 420 nm),CN及CNS样品均可以产生瞬时光电流,说明其良好的光电响应性能. 图中CN的光电流强度最弱,CNS样品均表现出显著增强的光电流强度,其中CNS-2的光电流强度最强,表明噻吩环结构聚合量影响CNS样品光电子的产生,其中CNS-2具有最强的光生电荷产生密度,具有最强的光电转换效率. 从暗态电化学阻抗测试(图7c)可以看出,与CN相比,CNS样品的Nyquist圆弧半径明显减小,其中CNS-2具有最小的Nyquist圆弧半径,说明适量的噻吩共聚合改性可以有效降低催化剂内部电荷传输阻力[24]. 从以上分析结果可以看出,噻吩共聚合嵌入CN共轭骨架,一方面拓展了CN的可见光吸收,另一方面增强了光生电荷的产生、传输和分离效率.
-
CN及CNS样品具有较强的还原电位,因此首先通过在室温下可见光还原Cr6+考察其光催化性能,结果如图8所示. 在K2Cr2O7溶液中(pH 6.7)经过40 min暗吸附处理,所有样品对Cr6+基本达到吸附-脱附平衡. 在可见光照下,高温煅烧法制备的纯C3N4对Cr6+几乎无去除效果,而CN及CNS样品均对Cr6+表现出不同程度的去除率. 光照2 h后,CNS-2对Cr6+具有最高的去除率,达55.7%,远高于CN对Cr6+的去除率37.9%. 而随着噻吩环聚合量的增加,CNS样品的催化活性反而下降,说明适量的噻吩环掺杂是优化CN光电性质的重要因素.
根据准一级动力学方程计算了催化剂的反应速率常数,如图8b所示. 可以看出,函数-ln(C/C0)与反应时间t呈较好的线性关系. CN、CNS-2、CNS-5的速率常数分别为0.00153、0.00388、0.00105 min−1. CNS-2的反应速率常数约是CN的2.5倍. 溶液pH是影响Cr6+还原的重要因素,图8c给出了在不同pH环境下CNS-2对Cr6+的还原活性. 可以看出,溶液pH对催化剂吸附性能影响并不明显. 在酸性环境中CNS-2具有显著增强的光还原Cr6+活性,当pH 1.8,光照反应90 min既可以完全去除溶液中Cr6+,而当pH 8.1,光反应2 h后去除率降低至30%. 这是由于溶液中Cr6+还原反应式为:
根据能斯特方程,
CrO2−7 还原为Cr3+在酸性环境中具有更低的电势值. 因此,在酸性及中性环境中,所制备CNS空心球表现出优异的光催化还原Cr6+活性,远高于常规氮化碳材料.光解水制H2是石墨相氮化碳半导体的重要研究方向. 图8d为在可见光下CN及CNS样品的分解水制H2活性速率. 同样的,CNS-2表现出最佳的制H2活性(2.72 μmol·h−1),约是CN活性的3.8倍. 尽管其产氢活性远低于高温热聚合法制备的常规氮化碳材料,但其较低的合成温度,灵活的形貌控制和改性途径仍然值得在清洁能源转化方向进一步深入研究.
尽管氮化碳半导体价带电位较低,通常不具有直接氧化分解有机污染物能力,但其合适的能带结构使得其在光激发下仍然能够生成具有较强氧化活性的氧自由基,同样具有光催化降解有机污染物的活性,在环境净化方面具有重要应用价值[25]. 采用可见光催化降解MO来评价催化剂对有机污染物的催化活性,结果如图9所示.
从图9a可以看出,经过30 min暗吸附,所有样品对MO基本达到吸附-脱附平衡,且吸附量相差不明显. 在光照反应中,相较于CN,适量噻吩共聚合改性后的CNS样品活性明显提升,经过2 h光照反应,CNS-2对MO的去除率达68.4%,远高于CN对MO的去除率50.5%. 对降解过程中MO溶液的pH进行监测,光照2 h后期pH变化仅为0.1,所以溶液pH变化对反应过程几乎无影响. 而随着噻吩环聚合量进一步增加,CNS的光催化活性降低,光照2 hCNS-5对MO的去除率仅为33.5%. 这可能是由于适量的噻吩环掺杂对催化剂电子结构调控提到积极作用,而过量噻吩环的嵌入容易引入更多的结构缺陷,而缺陷态往往是光生电荷复合中心,所以反而不利于光催化性能的进一步提升. 同样采用准一级动力学方程对CN和CNS光催化降解MO数据进行拟合计算催化反应速率常数. 由图9b可知,CNS-2具有最大的反应速率常数0.00934,约是CN(0.00594) 的1.6倍. 此活性测试结果趋势与上述Cr6+还原去除基本保持一致,说明CNS样品具有稳定的光催化应用活性. 同时考察了催化剂投加量对催化性能的影响,如图9c. MO分子较为稳定,在纯光解反应体系几乎不发生任何变化. 随着催化剂使用浓度的提升,光催化MO降解速率逐步提升,进一步证明了光催化剂在反应体系中的重要作用. 活性稳定性是评价催化剂应用性的重要指标. 对催化剂CN及CNS-2光催化降解MO进行反复试验,结果如图9d所示. 经连续5次循环使用后,催化剂依然保持相对稳定的催化活性.
-
为了深入验证CNS光催化降解MO过程中活性物种的产生,以异丙醇(IPA)、对苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、氮气(N2)分别作为羟基自由基(·OH)、超氧自由基(·O2-)、空穴(h+)捕获剂和溶解氧去除剂进行活性分析[26]. 如图10所示,与空白体系(无捕获剂)相对比, IPA和EDTA-2Na的加入对降解率影响不大,说明在反应过程中·OH和h+不是主要的活性物种. 反应溶液加入BQ后,CNS-2对MO的光降解率明显降低,这说明
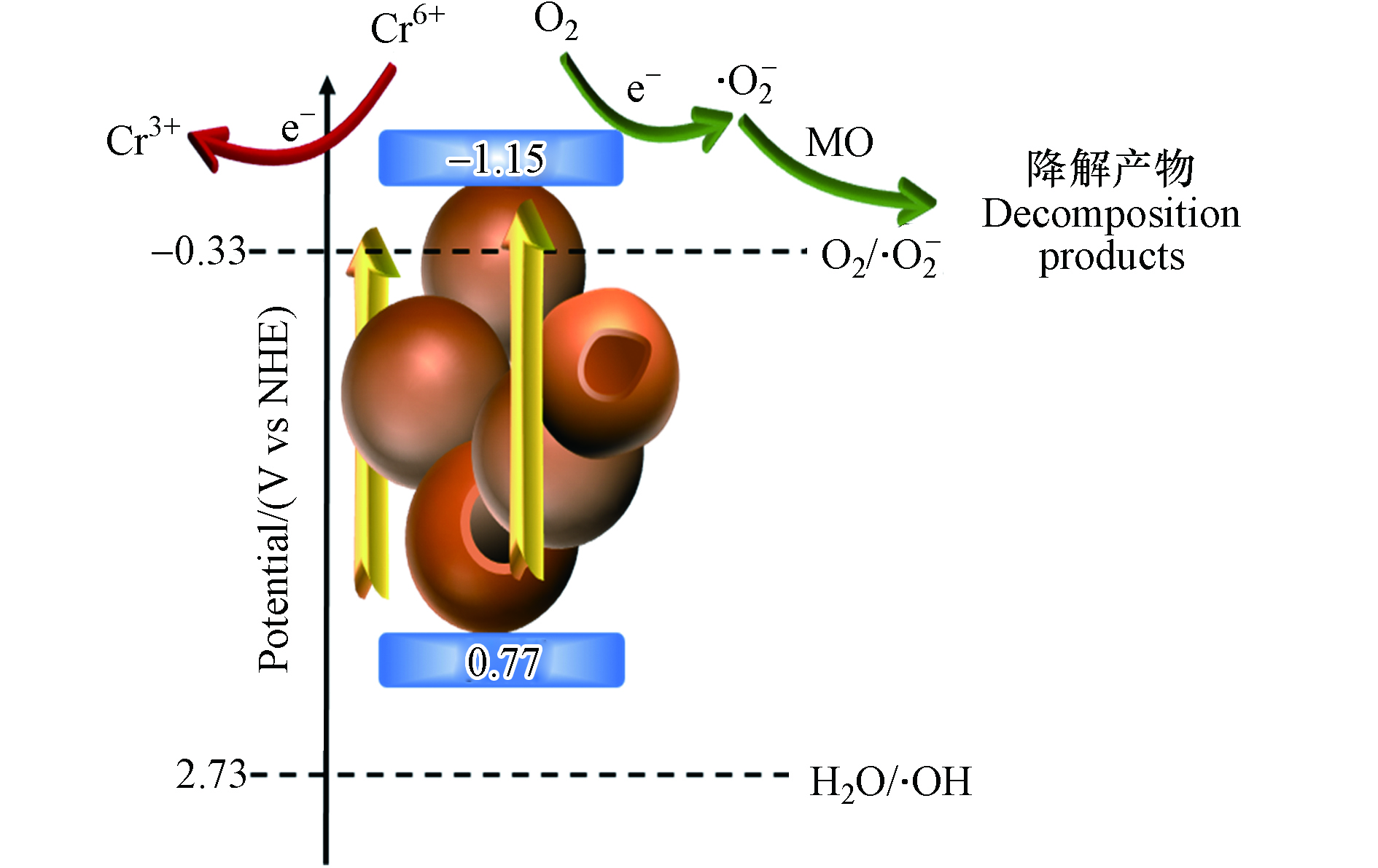
⋅O−2 是主要的活性物种. 向反应溶液中连续通入N2同样导致MO降解率显著下降,说明溶解氧在反应过程中起到重要作用,间接证明⋅O−2 来源于O2.由UV-vis所得带隙数据以及平带电势值可计算推断CNS-2的能带位置,如图11所示,其导带值为−1.15 V,在溶解氧存在环境中可利用光致电子转化生成·O2−. 其价带值为 0.77 V,远低于žOH的生成电势,因此不足以产生·OH. 在可见光照下,较低的带隙使得CNS容易被激发生成光生e−和h+,而光生e−可直接还原Cr6+,同时间接生成·O2−参与MO的催化降解. 为进一步验证此结论,对催化剂进行了难降解抗生素四环素(TC,20 mg·L−1)的光催化降解实验,CNS-2同样表现出最佳的降解活性,但经过2 h光照,对TC的去除率仅为36.5%. 较低的降解活性进一步证实CNS由于较低的氧化电位,不能生成强氧化性自由基.
-
(1) 以2-氨基噻吩-3甲腈为聚合分子,在低温溶剂热条件下可直接将噻吩环结构嵌入氮化碳分子骨架,实现分子聚合改性,所得产物CNS具有空心球形貌.
(2) 噻吩环分子嵌入使得CNS具有宽可见光吸收(~700 nm),且优化的电子结构使得CNS具有明显增强的光生电荷产生密度和电子-空穴分离效率.
(3) 调控噻吩环聚合量可优化催化剂光催化活性,使其具有显著提升的光催化还原Cr6+、光解水制H2以及MO降解活性. 其中,光生e−和间接生成的
⋅O−2 分别是还原反应和氧化降解反应的主要活性物种.
噻吩环修饰氮化碳空心球的制备及其可见光催化性能
Preparation and Photocatalytic performance of thiophene-ring modified carbon nitride hollow spheres
-
摘要: 以噻吩基团分子为聚合单体,低温溶剂热法一步合成噻吩环修饰的氮化碳空心球光催化剂. 采用XRD、SEM、XPS、UV-Vis DRS、PL等测试方法对催化剂的结构、形貌、光电响应等进行了表征. 结果表明,适量的噻吩环嵌入氮化碳骨架不影响产物空心球形貌,尽管降低了长程聚合度,但增加了球体表面缺陷,拓展了可见光吸收范围,缩小了带隙宽度,增强了光生电荷的产生密度并有效抑制了光生电子-空穴的复合,显著增强了光催化反应性能. 通过光催化还原水中Cr6+、光解水制氢和降解甲基橙的测试表明,噻吩环修饰后的CNS-2具有显著增强的光催化活性,其反应速率分别是未修饰氮化碳CN的2.5、3.8、1.6倍. 而光生e−和间接生成的
⋅O−2 分别是发生还原和氧化反应的主要活性物种.Abstract: Thiophene-ring modified carbon nitride hollow sphere photocatalysts (CNS) were synthesized by one-step low-temperature solvothermal method using thiophene group-containing molecules as monomers. The structure, morphology and optoelectronic properties of the catalysts were characterized by XRD, SEM, XPS, UV-Vis DRS, PL and others. The results show that appropriate amount of thiophene-rings embedded in the carbon nitride framework does not affect the hollow spherical morphology of the products, the long-range polymerization degrees of them are reduced, but it increases the surface defects of the spheres, expands the visible light absorption range, narrows the band gap, enhances the generation density of photogenerated charges and effectively inhibits the recombination of photogenerated electron-holes, therefore enhances the photocatalytic performances significantly. The photocatalytic reduction of Cr6+ in aqueous solution, water splitting for hydrogen production, and methyl orange degradation tests show that CNS-2 modified by thiophene-ring performs much enhanced photocatalytic activity, and its reaction rate was 2.5, 3.8 and 1.6 times that of unmodified carbon nitride (CN), respectively. Pphotogenerated e− and indirectly generated⋅O−2 are the main active species for reduction and oxidation reactions, respectively.-
Key words:
- carbon nitride /
- hollow sphere /
- thiophene-ring /
- photocatalysis.
-
以太阳能为基础利用光催化技术在温和反应条件下进行清洁能源转化和环境污染物净化对人类社会可持续发展具有重要意义. 绿色高效光催化剂作为光催化反应的核心始终是科研工作者首先需要解决的问题. 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)作为典型非金属聚合物材料,因其结构稳定、合成简单、具有可见光吸收等优点已逐步成为新一代光催化剂的典型代表[1-3].
空心球结构在半导体光催化反应体系格外引人注意,因其结构稳定,可将其他功能性基团集成在球体内外形成复杂的纳米结构,同时也可以“笼”形方式在球体内部进行一系列反应形成特殊的核壳结构[4-7]. 2012年,Wang等以多孔二氧化硅球为模板制备出氮化碳空心球,具有显著增强的光解水制氢性能[8]. 自此,以牺牲模板法制备氮化碳空心球成为主要方法[9]. 然而,受限于高温热聚合过程中聚合物中空纳米结构容易发生塌陷和扭曲,限制了空心球聚合物半导体的有效结构调控. 溶剂热技术可以通过分子工程实现溶液中分子自组装进行产物结构和形貌的有效调控[10]. 本课题组前期研究结果表明,可以在较低的温度下通过直接溶剂热法制备氮化碳空心球,且通过调控合成参数可实现氮化碳空心球的光催化性能优化[11]. 但低温合成产物聚合度较低,限制了光生电荷在长程范围内的有效传输,因此其光催化性能还有待进一步提升.
分子共聚合改性是优化g-C3N4电子结构和光学性质的有效方法. 含芳环小分子化合物与g-C3N4共聚可构造给体-受体结构,增强特征sp2杂化π电子离域. 例如,将巴比妥酸、2-氨基苄腈等共轭分子嵌入g-C3N4骨架有助于提高产物光催化性能[12]. 与等电子体系的六元芳环相比,五元杂环化合物为富电子体系,共聚g-C3N4不仅影响半导体的电子结构和光学性质,还可以调控其氧化还原电位.
含S噻吩基团为典型的发色基团且具有强大的给电子能力,是优化半导体聚合物光电性能的有效基团,可在半导体内构建分子内电子给体,同时在费米能级上形成半占据杂质能级,降低半导体带隙[13]. 理论研究表明,噻吩基团修饰g-C3N4可引起光诱导电子的有效质量降低,光诱导电子-空穴的迁移率差异增大,从而降低电子-空穴复合率,同时修饰后产物结构畸变,可提高n-π*电子跃迁活性[14]. 截止目前,关于噻吩修饰g-C3N4的工作主要集中于高温热解共聚以及产物在光解水方面的应用,而针对低温合成条件下以含特殊基团分子为共聚体合成特定形貌的g-C3N4及其对光催化性能的影响研究工作还鲜少报道. 鉴于此,本工作以2-氨基噻吩-3甲腈(TPCN)为共聚合单体,一步溶剂热反应成功将噻吩环结构嵌入g-C3N4骨架中,制备出一系列具有宽可见光响应的氮化碳空心球(CNS). 采用多种表征技术对催化剂结构、组成、光电性质等进行分析,通过光催化还原水中Cr6+、光解水制氢以及降解甲基橙考察了催化剂的活性,并推测了相应的光催化反应机理,为低温合成高效g-C3N4基光催化剂提供实验基础.
1. 实验部分(Experimental section)
1.1 实验试剂
本实验所用实验试剂均为AR级,去离子水为实验室自制. 主要试剂有:三聚氯氰(CC)、二聚氰胺(DCDA)、2-氨基噻吩-3甲腈(TPCN)、乙腈、甲基橙(MO)、重铬酸钾(K2Cr2O7)、三乙醇胺、氯铂酸(H2PtCl6·6H2O)、对苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、异丙醇(IPA).
1.2 催化剂制备
将CC、DCDA和TPCN按一定物质的量比例分散于60 mL乙腈,常压下混合液中通氮气并连续搅拌30 min.将混合液转移入100 mL水热反应釜中,置于烘箱中180 ℃反应48 h. 自然冷却后将所得固体产物离心分离(转速8000 r·min−1,5 min),用乙腈和去离子水反复洗涤多次,置于烘箱中60 ℃干燥得到最终产物. 反应原料比例及产物命名列于表1,合成示意图见图1.
表 1 样品合成原料比例Table 1. Raw materials ratio for samples synthesis样品Sample CC/mmol DCDA/mmol TPCN/mmol CN 10 7.5 0 CNS-1 10 7 1 CNS-2 10 6.5 2 CNS-3 10 6 3 CNS-4 10 5.5 4 CNS-5 10 5 5 1.3 催化剂表征
采用X-射线衍射仪(XRD,D/max 2500PC,日本理学株式会社)分析样品聚合结构;采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,SU-8010,日本日立公司)观察样品形貌;采用固体核磁(NMR,Agilent 600M,瑞士布鲁克公司)测定13C核磁谱图;采用紫外-可见分光光度计(UV-2550,日本岛津公司)表征样品的光吸收性质,BaSO4为标准物质;通过X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,ESCALAB 250,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司)测定材料表面电子性质;采用荧光光谱仪(PL,QuantaMasterTM40,美国PTI公司)考察催化剂的荧光发光性能;利用电化学工作站(CHI660E,上海辰华仪器有限公司)表征催化剂的光电化学性质. 具体测试方法:乙醇超声催化剂滴涂在FTO导电玻璃上作为工作电极,分别以铂片和饱和甘汞电极作为对电极和参比电极,电解液为 0.2 mol·L−1 Na2SO4溶液.
1.4 光催化活性测试
1.4.1 光催化还原Cr6+
50 mg催化剂分散于100 mL K2Cr2O7溶液(含Cr6+ 10 mg·L−1),避光搅拌40 min,待达到吸附-脱附平衡后,300 W氙灯(CEL HXF300)进行光照(λ>420 nm,光强1.5 mW·cm2),每隔一段时间取反应液4 mL,经离心后取上清液,采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法测定吸光度.
1.4.2 光解水制氢
50 mg催化剂分散于90 mL水,加入10 mL三乙醇胺和100 μL H2PtCl6·6H2O (0.04 g·mL−1). 搅拌30 min并抽真空后,300 W氙灯进行光照(同上). 通过气相色谱仪(GC7920,TCD检测器,N2作为载气)在线检测H2产量.
1.4.3 光催化降解MO
25 mg催化剂加入MO溶液中(20 mg·L−1),避光条件下搅拌30 min,以达到吸附平衡. 300 W氙灯进行光照(同上),每隔一段时间取反应液4 mL,经离心分离后用紫外可见分光光度计测定上清液吸光度.
2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 催化剂结构表征
图2为合成催化剂的XRD图谱,CN及CNS样品均具有典型的石墨相结构. 27.3°强峰是石墨相材料典型的层间堆叠(002)峰,13.0°处的宽衍射峰对应氮化碳的(100)晶面,归属于氮化碳面内嗪环结构的重复排列[15]. 与CN相对比,CNS样品的XRD衍射峰位没有发生变化,说明噻吩环的引入没有破坏CN的基本聚合结构. 随着TPCN聚合量的增加,CNS样品的(002)衍射峰强度逐步降低,说明样品聚合结构的长程有序性降低.
通过SEM对CN和CNS样品(以CNS-2为例)的微观形貌进行表征,如图3所示. 图3中a—c和d—f分别为CN和CNS-2样品的SEM图. 低温溶剂热合成有利于CN聚合形成稳定的球状形貌,且呈空心态,平均尺寸约为1 μm. 低温自聚合形成空心球是溶剂热合成的典型合成路径[16]. 以TPCN为共聚合分子得到的CNS-2与CN相比,其形貌依然保持空心球结构,颗粒大小也无明显变化,但球体表面粗糙度增加. 这一结果表明,共聚分子的引入在一定程度上降低了产物聚合度,颗粒表面引入更多结构缺陷,在一定程度上增加了界面反应接触活性位.
催化剂的光吸收谱图如图4a所示. 由图4可以看出,低温溶剂热法所合成产物具有较宽的可见光吸收范围,远大于常规高温煅烧法所制备的氮化碳产物(~ 460 nm). 相对于CN,CNS的光吸收带边均发生不同程度的红移,且随着噻吩环聚合量的增加而逐步扩展至~700 nm,样品颜色由橘红色过渡为暗红色,从光响应角度提升催化剂的光吸收至深可见区是光催化剂性能提升的重要因素. 通过Tauc曲线对样品的禁带宽度进行测算,如图4b所示,CN、CNS-2和CNS-5的带隙宽度分别为 2.0、1.92 eV和1.83 eV. 这一结果说明,噻吩环修饰共聚合有效拓展了CN的π共轭体系,窄化了带隙宽度,拓展了可见光的吸收范围,可显著提升对太阳光的吸收和利用. 图4c为CN和CNS-2的Mott-Schottky曲线. 曲线斜率均为正值说明样品为n型半导体,CN和CNS-2的平带电位分别位于−1.25 V和−1.15 V vs. NHE. 由于n型半导体平带电势接近导带电位,因此可以认为CN与CNS-2的平带电位分别位于−1.25 V和−1.15 V vs. NHE[17]. 与CN相比,尽管CNS-2的导带电位正移,但仍具有较强的还原电势,同时满足在含O2条件下超氧自由基(
⋅O−2 ⋅O−2 图5为CN和CNS-2的XPS谱图. 从总谱图5a中可以看出,CN及CNS样品主要由C、N和O元素组成,另外含有少量Cl元素,来源于三聚氯氰的末端不完全聚合. 与CN相比,CNS-2谱图中出现S元素,初步证明含S噻吩环分子结构共聚合嵌入CN共轭骨架. 图4b中 CN的C 1s谱曲线可以分别在284.60、286.30、288.24 eV处拟合3个峰,对应C—C/C=C键、少量C—O键和sp2杂化碳(N—C=N)[19]. CNS-2具有相似的C1s拟合曲线,但其sp2 C的峰向低位移动0.13 eV. 图4c中CN的N 1s可拟合为2条曲线,中心峰位分别为398.64 eV和400.06 eV,归因于共轭杂环中的sp2 N和桥连N原子N—(C)3[20]. CNS-2同样具有类似的N 1s谱线,但sp2 N峰位同样向低位偏移约0.06 eV. 图5为CNS-2样品的S 2p 高分辨XPS谱图,电子结合能分别位于164.0 eV和165.3 eV的两个峰来源于S 2p3/2和S 2p1/2. 这一结果与文献中报道的S掺杂的氮化碳中S的电子结合能(163.9 eV和168.5 eV)明显不同,而与噻吩化合物中S的电子结合能(163.8 eV和165.0 eV)相吻合,表明所得产物不是简单的S掺杂CN,有力地证实了噻吩环分子通过共聚合的方法成功地并入到了CN的分子结构中[21]. 图5b—d共同说明,CNS-2共轭结构中的sp2杂化C,N具有更高的电荷分布密度. 这是由于噻吩环为典型的供电子基团,共聚合嵌入CN共轭骨架能够拓展共轭杂化结构,拓展光吸收,同时使得产物CNS样品具有更高的不饱和电荷密度,有利于更多光生电荷的产生.
为了进一步证实噻吩环聚合嵌入CN骨架,采用固体13C NMR表征CN和CNS-2的化学结构变化,如图6所示. 可以看出,二者在化学位移155.6和164.3处均出现两个明显的核磁共振峰,归属于氮化碳共轭杂环C. 此外,CNS-2样品在化学位移110附近处出现一个新峰,由噻吩环分子中的C参与CN π共轭而引起,这表明噻吩环结构通过共聚合的方法成功嵌入到CN的组成结构中[22]. 结合XPS分析可推断,在热聚合过程中噻吩基团取代边缘N=C—Cl,从而实现将噻吩结构嵌入到CN分子骨架中.
光电响应性能是分析光催化剂的重要技术方法,可以直观的表明在光照条件下催化剂光生载流子的产生和分离. 图7a是催化剂的稳态PL光谱, 在360 nm光激发下,CN在500 nm附近处有较强的PL发射峰,来源于催化剂的π-π*电子激发跃迁[23],表明CN存在较强的光生电子-空穴复合. 当噻吩环嵌入后,CNS系列样品的PL发射峰强度骤然减弱. 除CNS-1仍出现较明显的发射峰外,其他样品PL发射峰几乎可忽略. 显著降低的PL发射峰强度表明CNS样品的光生电子-空穴复合率被明显抑制,具有增强的电子-空穴分离效率. 噻吩环的嵌入有利于优化电子结构,扩大共轭平面电荷离域性,增强电荷流动性. 图7b为采用三电极体系测得催化剂的I-t曲线. 在可见光照下(λ > 420 nm),CN及CNS样品均可以产生瞬时光电流,说明其良好的光电响应性能. 图中CN的光电流强度最弱,CNS样品均表现出显著增强的光电流强度,其中CNS-2的光电流强度最强,表明噻吩环结构聚合量影响CNS样品光电子的产生,其中CNS-2具有最强的光生电荷产生密度,具有最强的光电转换效率. 从暗态电化学阻抗测试(图7c)可以看出,与CN相比,CNS样品的Nyquist圆弧半径明显减小,其中CNS-2具有最小的Nyquist圆弧半径,说明适量的噻吩共聚合改性可以有效降低催化剂内部电荷传输阻力[24]. 从以上分析结果可以看出,噻吩共聚合嵌入CN共轭骨架,一方面拓展了CN的可见光吸收,另一方面增强了光生电荷的产生、传输和分离效率.
2.2 催化剂性能测试及分析
CN及CNS样品具有较强的还原电位,因此首先通过在室温下可见光还原Cr6+考察其光催化性能,结果如图8所示. 在K2Cr2O7溶液中(pH 6.7)经过40 min暗吸附处理,所有样品对Cr6+基本达到吸附-脱附平衡. 在可见光照下,高温煅烧法制备的纯C3N4对Cr6+几乎无去除效果,而CN及CNS样品均对Cr6+表现出不同程度的去除率. 光照2 h后,CNS-2对Cr6+具有最高的去除率,达55.7%,远高于CN对Cr6+的去除率37.9%. 而随着噻吩环聚合量的增加,CNS样品的催化活性反而下降,说明适量的噻吩环掺杂是优化CN光电性质的重要因素.
 图 8 不同催化剂在可见光下对Cr6+的光催化还原曲线(a)、动力学拟合曲线(b)、催化剂CNS-2在不同pH条件下对Cr6+的光催化还原曲线(c)和催化剂可见分解水制氢活性(d)Figure 8. Photocatalytic reduction curves (a), kinetic fitting curves (b) of Cr6+ by different catalysts under visible light, Photocatalytic reduction of Cr6+ by CNS-2 at different pH (c) and H2 evolution activity by visible light water splitting by catalysts (d)
图 8 不同催化剂在可见光下对Cr6+的光催化还原曲线(a)、动力学拟合曲线(b)、催化剂CNS-2在不同pH条件下对Cr6+的光催化还原曲线(c)和催化剂可见分解水制氢活性(d)Figure 8. Photocatalytic reduction curves (a), kinetic fitting curves (b) of Cr6+ by different catalysts under visible light, Photocatalytic reduction of Cr6+ by CNS-2 at different pH (c) and H2 evolution activity by visible light water splitting by catalysts (d)根据准一级动力学方程计算了催化剂的反应速率常数,如图8b所示. 可以看出,函数-ln(C/C0)与反应时间t呈较好的线性关系. CN、CNS-2、CNS-5的速率常数分别为0.00153、0.00388、0.00105 min−1. CNS-2的反应速率常数约是CN的2.5倍. 溶液pH是影响Cr6+还原的重要因素,图8c给出了在不同pH环境下CNS-2对Cr6+的还原活性. 可以看出,溶液pH对催化剂吸附性能影响并不明显. 在酸性环境中CNS-2具有显著增强的光还原Cr6+活性,当pH 1.8,光照反应90 min既可以完全去除溶液中Cr6+,而当pH 8.1,光反应2 h后去除率降低至30%. 这是由于溶液中Cr6+还原反应式为:
Cr2O2−7+14H++6e−→2Cr3++7H2O 根据能斯特方程,
CrO2−7 光解水制H2是石墨相氮化碳半导体的重要研究方向. 图8d为在可见光下CN及CNS样品的分解水制H2活性速率. 同样的,CNS-2表现出最佳的制H2活性(2.72 μmol·h−1),约是CN活性的3.8倍. 尽管其产氢活性远低于高温热聚合法制备的常规氮化碳材料,但其较低的合成温度,灵活的形貌控制和改性途径仍然值得在清洁能源转化方向进一步深入研究.
尽管氮化碳半导体价带电位较低,通常不具有直接氧化分解有机污染物能力,但其合适的能带结构使得其在光激发下仍然能够生成具有较强氧化活性的氧自由基,同样具有光催化降解有机污染物的活性,在环境净化方面具有重要应用价值[25]. 采用可见光催化降解MO来评价催化剂对有机污染物的催化活性,结果如图9所示.
 图 9 不同催化剂在可见光下对MO的光催化降解曲线(a)、动力学拟合曲线(b)、催化剂CNS-2对MO的光催化降解活性曲线(c)、CN和CNS-2对MO降解活性稳定性(d)Figure 9. Photocatalytic degradation curves (a), kinetic fitting curves (b) of MO by different catalysts under visible light, Photocatalytic degradation of MO by CNS-2 (c), degradation activity stability of MO by CN and CNS-2 (d)
图 9 不同催化剂在可见光下对MO的光催化降解曲线(a)、动力学拟合曲线(b)、催化剂CNS-2对MO的光催化降解活性曲线(c)、CN和CNS-2对MO降解活性稳定性(d)Figure 9. Photocatalytic degradation curves (a), kinetic fitting curves (b) of MO by different catalysts under visible light, Photocatalytic degradation of MO by CNS-2 (c), degradation activity stability of MO by CN and CNS-2 (d)从图9a可以看出,经过30 min暗吸附,所有样品对MO基本达到吸附-脱附平衡,且吸附量相差不明显. 在光照反应中,相较于CN,适量噻吩共聚合改性后的CNS样品活性明显提升,经过2 h光照反应,CNS-2对MO的去除率达68.4%,远高于CN对MO的去除率50.5%. 对降解过程中MO溶液的pH进行监测,光照2 h后期pH变化仅为0.1,所以溶液pH变化对反应过程几乎无影响. 而随着噻吩环聚合量进一步增加,CNS的光催化活性降低,光照2 hCNS-5对MO的去除率仅为33.5%. 这可能是由于适量的噻吩环掺杂对催化剂电子结构调控提到积极作用,而过量噻吩环的嵌入容易引入更多的结构缺陷,而缺陷态往往是光生电荷复合中心,所以反而不利于光催化性能的进一步提升. 同样采用准一级动力学方程对CN和CNS光催化降解MO数据进行拟合计算催化反应速率常数. 由图9b可知,CNS-2具有最大的反应速率常数0.00934,约是CN(0.00594) 的1.6倍. 此活性测试结果趋势与上述Cr6+还原去除基本保持一致,说明CNS样品具有稳定的光催化应用活性. 同时考察了催化剂投加量对催化性能的影响,如图9c. MO分子较为稳定,在纯光解反应体系几乎不发生任何变化. 随着催化剂使用浓度的提升,光催化MO降解速率逐步提升,进一步证明了光催化剂在反应体系中的重要作用. 活性稳定性是评价催化剂应用性的重要指标. 对催化剂CN及CNS-2光催化降解MO进行反复试验,结果如图9d所示. 经连续5次循环使用后,催化剂依然保持相对稳定的催化活性.
2.3 光催化机理研究
为了深入验证CNS光催化降解MO过程中活性物种的产生,以异丙醇(IPA)、对苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、氮气(N2)分别作为羟基自由基(·OH)、超氧自由基(·O2-)、空穴(h+)捕获剂和溶解氧去除剂进行活性分析[26]. 如图10所示,与空白体系(无捕获剂)相对比, IPA和EDTA-2Na的加入对降解率影响不大,说明在反应过程中·OH和h+不是主要的活性物种. 反应溶液加入BQ后,CNS-2对MO的光降解率明显降低,这说明
⋅O−2 ⋅O−2 由UV-vis所得带隙数据以及平带电势值可计算推断CNS-2的能带位置,如图11所示,其导带值为−1.15 V,在溶解氧存在环境中可利用光致电子转化生成·O2−. 其价带值为 0.77 V,远低于žOH的生成电势,因此不足以产生·OH. 在可见光照下,较低的带隙使得CNS容易被激发生成光生e−和h+,而光生e−可直接还原Cr6+,同时间接生成·O2−参与MO的催化降解. 为进一步验证此结论,对催化剂进行了难降解抗生素四环素(TC,20 mg·L−1)的光催化降解实验,CNS-2同样表现出最佳的降解活性,但经过2 h光照,对TC的去除率仅为36.5%. 较低的降解活性进一步证实CNS由于较低的氧化电位,不能生成强氧化性自由基.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1) 以2-氨基噻吩-3甲腈为聚合分子,在低温溶剂热条件下可直接将噻吩环结构嵌入氮化碳分子骨架,实现分子聚合改性,所得产物CNS具有空心球形貌.
(2) 噻吩环分子嵌入使得CNS具有宽可见光吸收(~700 nm),且优化的电子结构使得CNS具有明显增强的光生电荷产生密度和电子-空穴分离效率.
(3) 调控噻吩环聚合量可优化催化剂光催化活性,使其具有显著提升的光催化还原Cr6+、光解水制H2以及MO降解活性. 其中,光生e−和间接生成的
⋅O−2 -
图 8 不同催化剂在可见光下对Cr6+的光催化还原曲线(a)、动力学拟合曲线(b)、催化剂CNS-2在不同pH条件下对Cr6+的光催化还原曲线(c)和催化剂可见分解水制氢活性(d)
Figure 8. Photocatalytic reduction curves (a), kinetic fitting curves (b) of Cr6+ by different catalysts under visible light, Photocatalytic reduction of Cr6+ by CNS-2 at different pH (c) and H2 evolution activity by visible light water splitting by catalysts (d)
图 9 不同催化剂在可见光下对MO的光催化降解曲线(a)、动力学拟合曲线(b)、催化剂CNS-2对MO的光催化降解活性曲线(c)、CN和CNS-2对MO降解活性稳定性(d)
Figure 9. Photocatalytic degradation curves (a), kinetic fitting curves (b) of MO by different catalysts under visible light, Photocatalytic degradation of MO by CNS-2 (c), degradation activity stability of MO by CN and CNS-2 (d)
表 1 样品合成原料比例
Table 1. Raw materials ratio for samples synthesis
样品Sample CC/mmol DCDA/mmol TPCN/mmol CN 10 7.5 0 CNS-1 10 7 1 CNS-2 10 6.5 2 CNS-3 10 6 3 CNS-4 10 5.5 4 CNS-5 10 5 5 -
[1] WANG X C, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light [J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(1): 76-80. doi: 10.1038/nmat2317 [2] ONG W J, TAN L L, NG Y H, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis and environmental remediation: Are we a step closer to achieving sustainability? [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(12): 7159-7329. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00075 [3] HE D H, ZHANG C, ZENG G M, et al. A multifunctional platform by controlling of carbon nitride in the core-shell structure: From design to construction, and catalysis applications [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 258: 117957. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117957 [4] COOPER A I. Conjugated microporous polymers [J]. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(12): 1291-1295. doi: 10.1002/adma.200801971 [5] LI Q, GUO J N, ZHU H, et al. Space-confined synthesis of ZIF-67 nanoparticles in hollow carbon nanospheres for CO2 adsorption [J]. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2019, 15(8): e1804874. doi: 10.1002/smll.201804874 [6] HU J, CHEN M, FANG X S, et al. Fabrication and application of inorganic hollow spheres [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(11): 5472-5491. doi: 10.1039/c1cs15103g [7] LIU Z Y, BAI H W, SUN D. Facile fabrication of hierarchical porous TiO2 hollow microspheres with high photocatalytic activity for water purification [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2011, 104(3/4): 234-238. [8] SUN J H, ZHANG J S, ZHANG M W, et al. Bioinspired hollow semiconductor nanospheres as photosynthetic nanoparticles [J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 1139. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2152 [9] LUO L, MA J N, ZHU H X, et al. Embedded carbon in a carbon nitride hollow sphere for enhanced charge separation and photocatalytic water splitting [J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(13): 7339-7346. doi: 10.1039/D0NR00226G [10] NIU H J, CHEN H Y, WEN G L, et al. One-pot solvothermal synthesis of three-dimensional hollow PtCu alloyed dodecahedron nanoframes with excellent electrocatalytic performances for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 539: 525-532. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.12.066 [11] CUI Y J, LI M, WANG H, et al. In-situ synthesis of sulfur doped carbon nitride microsphere for outstanding visible light photocatalytic Cr(Ⅵ) reduction [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 199: 251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.037 [12] LI M, ZHANG S B, LIU X, et al. Polydopamine and barbituric acid co-modified carbon nitride nanospheres for highly active and selective photocatalytic CO 2 reduction [J]. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2019, 2019(15): 2014. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201900366 [13] ZHANG J S, ZHANG M W, LIN S, et al. Molecular doping of carbon nitride photocatalysts with tunable bandgap and enhanced activity [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 310: 24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.01.008 [14] ZHANG Y L, REN C J, ZHANG Y F, et al. Improvement of photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4 by five-membered heterocyclic small molecule modifications: A theoretical prediction [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 478: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.128 [15] WANG R R, YANG P J, WANG S B, et al. Regulating morphological and electronic structures of polymeric carbon nitrides by successive copolymerization and stream reforming for photocatalytic CO2 reduction [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(7): 2570-2576. [16] CUI Y J, TANG Y B, WANG X C. Template-free synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride hollow spheres for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants [J]. Materials Letters, 2015, 161: 197-200. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.106 [17] ZHANG F, ZHANG J H, WANG H F, et al. Single tungsten atom steered band-gap engineering for graphitic carbon nitride ultrathin nanosheets boosts visible-light photocatalytic H2 evolution [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 424: 130004. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130004 [18] ZHU Y X, CUI Y J, XIAO B B, et al. Z-scheme 2D/2D g-C3N4/Sn3O4 heterojunction for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2 evolution and degradation of ciprofloxacin [J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2021, 129: 105767. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2021.105767 [19] LIU S H, SONG X Z, LIU G C, et al. Synthesis of hollow donut-like carbon nitride for the visible light-driven highly efficient photocatalytic production of hydrogen and degradation of pollutants [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(28): 12247-12255. doi: 10.1039/D0NJ02244F [20] ZHU K, OU-YANG J, ZENG Q, et al. Fabrication of hierarchical ZnIn2S4@CNO nanosheets for photocatalytic hydrogen production and CO2 photoreduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 41(3): 454-463. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63494-7 [21] XU X L, ASHER S A. Synthesis and utilization of monodisperse hollow polymeric particles in photonic crystals [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(25): 7940-7945. doi: 10.1021/ja049453k [22] ZHENG D D, PANG C Y, LIU Y X, et al. Shell-engineering of hollow g-C3N4 nanospheres via copolymerization for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution [J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(47): 9706-9709. doi: 10.1039/C5CC03143E [23] DEIFALLAH M, MCMILLAN P F, CORÀ F. Electronic and structural properties of two-dimensional carbon nitride graphenes [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(14): 5447-5453. doi: 10.1021/jp711483t [24] PRAKASH K, SELVAM V, BABU S G, et al. Rational design of novel 3D flower-like praseodymium molybdate anchored graphitic carbon Nitride: An efficient and sustainable photocatalyst for mitigation of carcinogenic pollutants [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 569: 151104. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151104 [25] 郭桂全, 胡巧红, 王承林, 等. g-C3N4/RGO的制备、光催化降解性能及其降解机理 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(3): 808-817. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019092605 GUO G Q, HU Q H, WANG C L, et al. Preparation, photocatalytic degradation performance and degradation mechanism of g-C3N4/RGO [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(3): 808-817(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019092605
[26] KUMAR S, KAUSHIK R D, PUROHIT L P. ZnO-CdO nanocomposites incorporated with graphene oxide nanosheets for efficient photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A, thymol blue and ciprofloxacin [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127332. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127332 -








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: