-
垃圾焚烧飞灰(以下简称“飞灰”)和纳滤膜浓缩液均是生活垃圾无害化处理过程中产生的二次污染物,两者的无害化处置和资源化利用已成为当前环境主管部门需要迫切解决的难题. 飞灰通常含有高浸出浓度的重金属及痕量二噁英等污染物[1],已被列为危险废物. 飞灰若处置不当,会对环境和人体健康造成潜在危害[2-3]. 目前,我国飞灰主要处置方式是经过固化稳定化进入生活垃圾填埋场填埋,但重金属仍存在再度浸出的风险[4-5],而且北京、上海、江苏、浙江等经济发达省市诸多填埋场将面临封场,飞灰填埋面临着比较严峻的形势[6]. 而国内比较成熟的利用方式是水泥窑协同处置[7-8],但处置量有限,满足不了大量飞灰的消纳需求.
纳滤膜浓缩液是生活垃圾渗滤液膜法处理产生的高浓废水,其具有含盐量高、难降解有机物多、可生化性差等特点,难以生化处理[9-10]. 目前,纳滤膜浓缩液主要回灌生活垃圾填埋场[11],而深度处理技术包括高级氧化法[12]和蒸发[13]等,但这些技术的工业化应用多不能稳定运行,且产生二次固体废物也较难得到妥善处置,环境安全隐患仍较大. 鉴于此,本课题组利用飞灰比表面积大、吸附截留性能好的特性,结合热处理方法,提出了飞灰与纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤飞灰协同处置模式,通过协同处置去除纳滤膜浓缩液的色度、难生化降解有机污染物等特征污染物,实现了纳滤膜浓缩液从目前技术工艺“难处置的高浓度有机废水”变成“可处置的高盐废水”,同时去除了飞灰中可溶性氯盐,淋滤灰渣可经热处理后实现无害化与资源化利用[14]. 目前,国内外关于飞灰高温热处理过程中重金属的固化与挥发机制的研究报道很多[15-16],但关于纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤灰渣热处理过程中重金属的迁移特性尚无报道. 由于飞灰经纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤后去除了其中的Cl−,但增加了SO42−和PO43−等,可能影响后续热处理过程中重金属的迁移化特性.
飞灰中Pb含量通常较高,是一种典型的重金属,对人体会造成致癌健康风险[17]. 本课题组[18]前期研究表明,飞灰中Pb主要为PbO,少量以PbCl2形式存在,这些Pb在后续的热处理过程较易挥发. 孟棒棒[19]对膜浓缩液淋滤飞灰后灰渣进行热处理时发现,温度是影响重金属挥发率的重要因素,热处理温度高于800℃时,Pb的浸出浓度达到生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准(GB16889-2008)标准限值要求,但未对热处理过程中Pb的迁移转化机理进行深入探究. 为了解纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤对飞灰中重金属存在以及后续热处理过程中迁移转化的影响,本研究以Pb为例,探讨了淋滤过程、以及后续热处理不同温度下Pb的存在形态以及迁移转化特性,以期为探究飞灰协同处置纳滤膜浓缩液的可行性提供科学依据.
-
飞灰采集于北京某生活垃圾焚烧厂的布袋除尘器,外观呈灰色,该厂焚烧系统采用炉排炉技术,烟气处理系统采用炉内脱硝(SNCR)+半干法脱酸+干粉辅助脱酸+袋式除尘+炉外脱硝(SCR)的组合工艺. 其主要化学成分见表1.
纳滤膜浓缩液取自北京市某生活垃圾填埋场渗滤液的“厌氧+好氧+膜生物反应器(MBR)+纳滤(纳滤)+反渗透(RO)”组合处理工艺. 纳滤膜浓缩液主要特征污染物组成见表2.
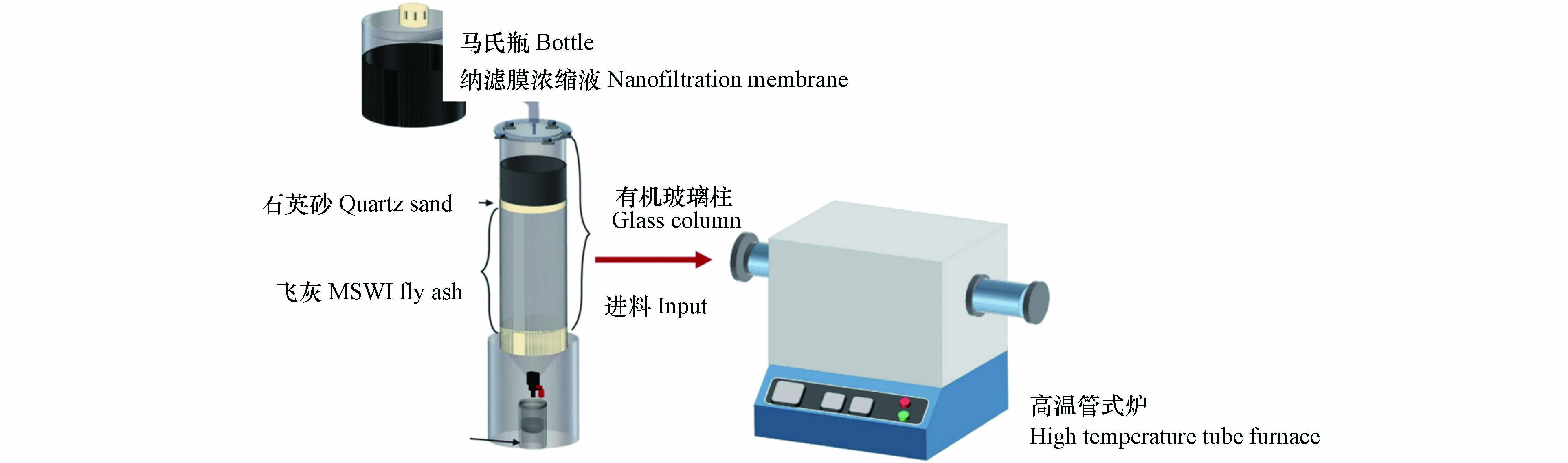
淋滤灰渣是将24 g PbO加入到2 kg飞灰中混匀并经纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤后得到的固体样品.
配比灰渣是按照淋滤灰渣主要成分比例,采用化学分析纯试剂进行配比得到固体样品,主要成分及百分质量比为:CaO(25%)、SiO2(25%)、Na2SO4(10%)、Al2O3(20%)和PbO(20%).
-
如图1所示,淋滤装置由马氏瓶和有机玻璃柱两部分组成,有机玻璃柱长80 cm、内径10 cm,顶部有均匀布水装置. 淋滤实验是将混匀后飞灰装填进入有机玻璃柱,前期根据氯离子最佳累积溶出量确定淋滤最佳条件为采用8 L纳滤膜浓缩液进行淋滤,并保持淋滤速度为60 mL·h−1,待纳滤膜浓缩液完全淋尽后,实验结束,将淋滤灰渣取出后进行干燥处理保存. 热处理实验采用高温管式炉装置,热处理温度分别为400、600、800、1000 ℃,热处理时间为60 min,采用空气作为载气,进气流量600 mL·min−1,尾气吸收装置采用2个装有浓度为5%HNO3和5%NaOH溶液的洗气瓶吸收处理. 实验时,先将炉温升至预设温度,再将淋滤灰渣20 g和配比灰渣10 g分别放置于坩埚内,缓慢推至恒温区,然后关闭进料阀门并通入空气. 60 min后,取出坩埚并放置于干燥器内冷却,称重记录.
-
采用飞利浦 X 射线荧光光谱仪PW-2404(XRF)分析实验样品的化学组成;采用岛津 X 射线衍射仪D/max-A(XRD)分析矿物相;采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法[20]分析重金属含量;采用Thermo Kalpha(XPS)分析重金属元素的价态;采用FactSage软件分析不同温度下Pb结合态的吉布斯自由能.
为更好的表达重金属的固化效果,特引入重金属固化率E定义,计算结果如下:
式中,
E 为重金属的固化率,%;ω1 为热处理后样品中Pb的含量,mg·kg−1;m1 为热处理后样品质量,g;ω 为热处理前样品中Pb的含量,mg·kg−1;m 为热处理前样品质量,g. -
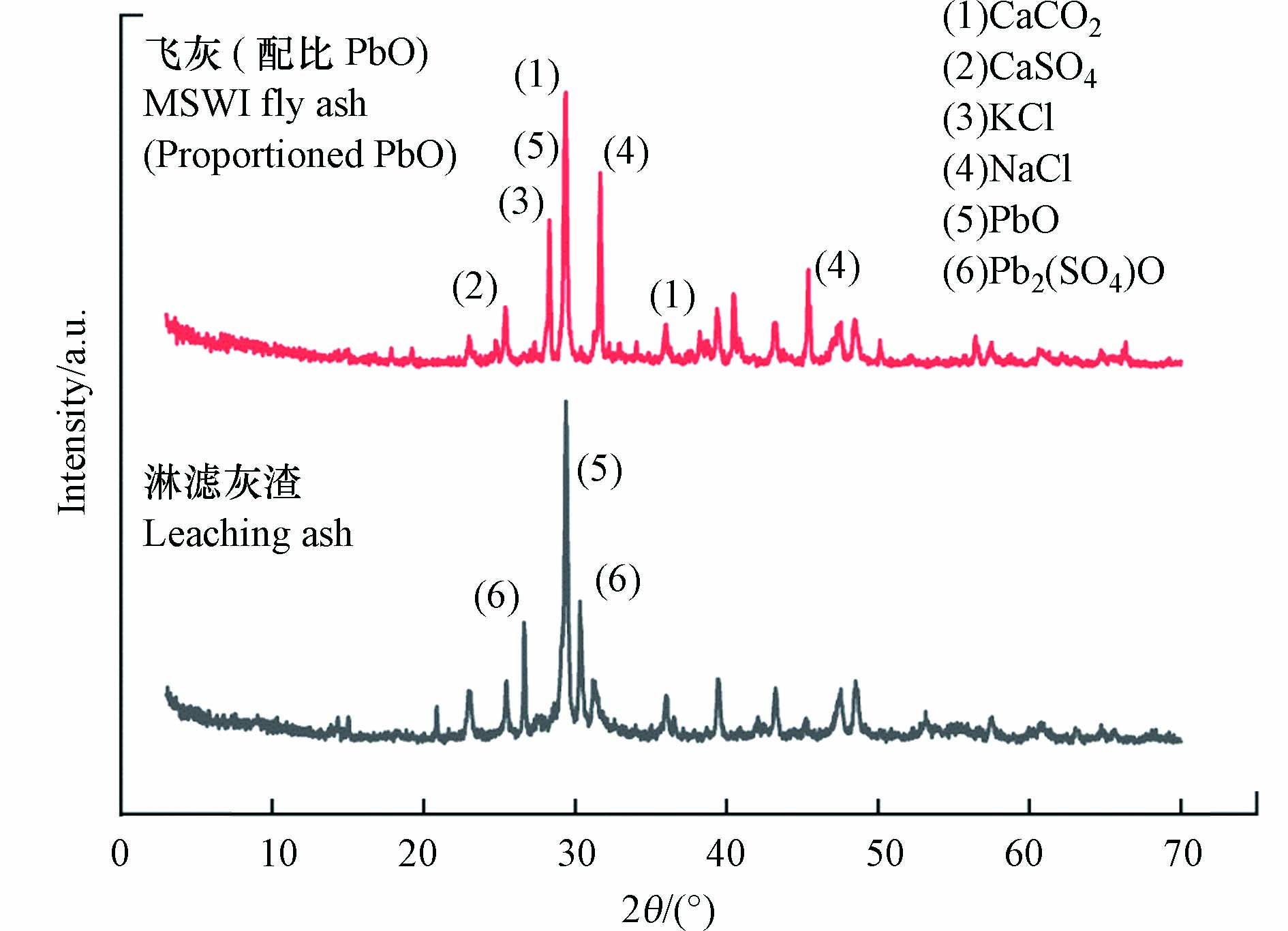
从图2可知,淋滤灰渣中除了PbO晶体外,同时检测到了铅黄Pb2(SO4)O,这说明纳滤膜浓缩液中SO42−与飞灰中PbO发生了反应(PbO+SO42−→PbO+PbSO4+PbO→Pb2(SO4)O). 经纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤后,PbO含量由1.30%上升至27.36%,其质量为546 g;将淋滤灰渣中含硫元素全部折算成硫酸根后,淋滤灰渣中硫酸根含量占比2.87%,其质量为58 g,计算可得PbO与硫酸根物质的量比为12:1,表明PbO和Pb2(SO4)O同时存在于淋滤灰渣中. 龚勋[21]用Visual MINTEQ淋滤粉煤灰,当6<pH<8时粉煤灰中可溶性Pb明显减少,推测可能生成了Pb2(SO4)O;当7<pH<8时PbO·PbSO4会逐渐分解,碱性环境下生成Pb(OH)2. 本实验采用的纳滤膜浓缩液pH为7.1,与龚勋研究结果基本相似.
从表3中可知,添加了PbO的飞灰经纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤后,组成成分发生了较大的变化,Cl含量由原飞灰的22.48%降至0.40%,飞灰中Cl的大量溶出使主要化学成分比例发生改变. 由表4和图2可知,淋出液中Cl−浓度高达3.2×105 mg·L−1,说明在纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤飞灰过程中,飞灰中Cl主要以NaCl、KCl等可溶性氯盐形式被洗脱到淋出液中. 在淋滤灰渣XRD中并未检出. 纳滤膜浓缩液中PO42−含量较SO42−和Cl−含量少,且飞灰中的P2O5含量仅占0.4%,推测淋滤灰渣中Pb的氯化物及磷酸盐结合态可能存在,但含量低于检出限值.
-
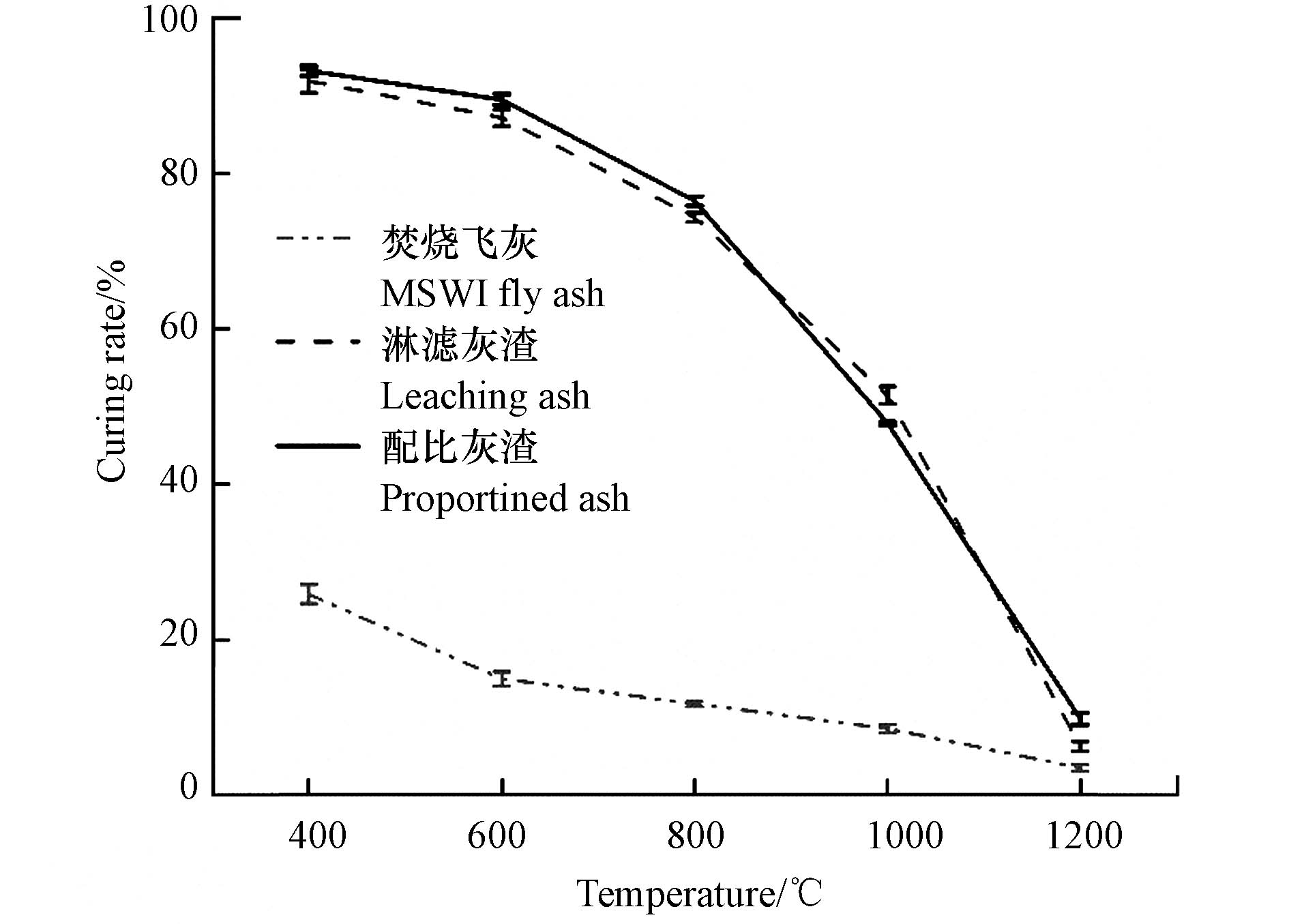
将飞灰与淋滤灰渣在400—1000 ℃下进行热处理. 从图3可知,淋滤灰渣中Pb的固化率比飞灰Pb的固化率高,增幅在30%—70%之间. 400 ℃下,淋滤灰渣中Pb的固化率最高,为96.87%. 随着温度的升高,固化率呈线性下降的趋势,800 ℃后下降更快. 随着温度的逐渐升高,淋滤灰渣中Pb的含量呈现先增加后减少的趋势,在800 ℃下达到最高为0.9%±0.02%. 这是因为在800 ℃左右,淋滤灰渣中有机质基本都焚毁,此时烧失率为20%,而温度又没有达到Pb可能存在氧化态(PbO熔点:886 ℃、沸点:1535 ℃),硫酸态(PbSO4熔点:1087 ℃)和磷酸态(Pb3(PO4)2熔点:1014 ℃)物质的熔沸点,Pb化合物的绝对质量变化较少,而相对质量含量小幅增加;当温度达到1000 ℃时,淋滤灰渣中Pb的含量下降至0.6%±0.02%,是由于在1000 ℃时,PbO开始挥发[22].
-
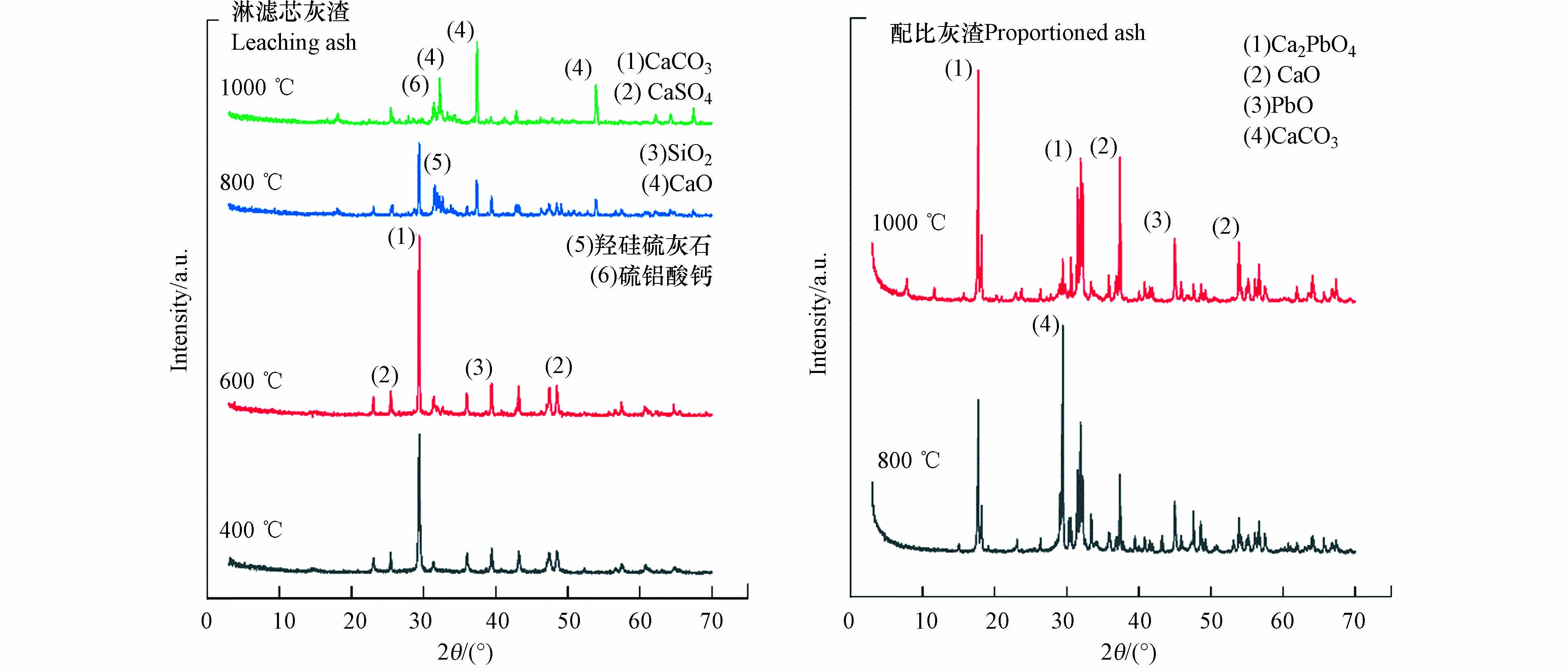
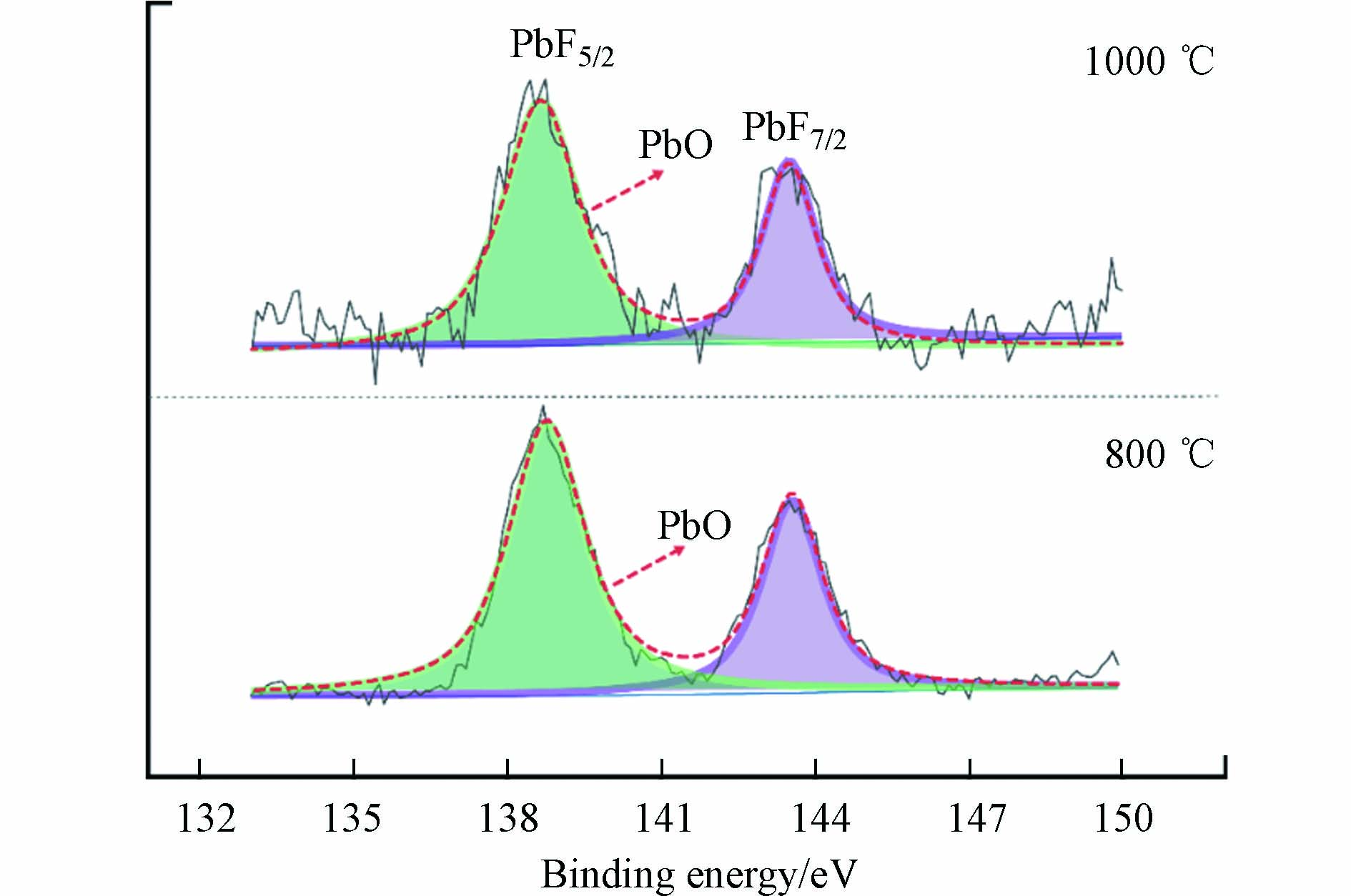
利用XRD分析了淋滤灰渣热处理产物的晶相成分. 从图4可知,400—1000 ℃过程中,淋滤灰渣中结合态Pb含量低于XRD检出限;但在800 ℃下,CaO与SiO2凝聚成新的矿物相Ca10[(SiO4)3(SO4)3]F2 (羟硅硫灰石);反应机理[23]可以描述为CaF2+SiO2+CaSO4→Ca10(SiO4)3(SO4)3F2+CaO+H2O;1000 ℃又出现了Ca5(SiO4)2(SO4)(硫铝酸钙),推测SiO2参与合成新的矿物相,表明800 ℃以上大部分化合物形态被破坏,发生了分子键的断裂和重新生成,以复合盐形式存在于淋滤灰渣中.
从图3可知,800—1000 ℃条件下,配比灰渣与淋滤灰渣中Pb的固化率有相似的趋势. 这虽不能完全断定淋滤灰渣的主要成分和重金属均以氧化物形式存在,但可以推测淋滤灰渣中Pb最初不是以氯化态形式存在,而且在热处理过程中会有挥发现象,最终多以氧化态形式参与反应并固化. 实验在800—1000 ℃对淋滤灰渣进行XPS分析,如图5可知,在淋滤灰渣中出现了Pb4f峰,表明Pb存在并以某种形式存在于淋滤灰渣中,而并未全部挥发. Pb4f峰根据自旋轨道分裂可以分为Pb4f5/2和Pb4f7/2,分别位于139 eV和144 eV,PbO的结合能在Pb4f5/2和Pb4f7/2谱峰下分别为138.85 eV和143.75 eV,表明PbO的拟合效果最好,Pb以PbO的形式参加反应. 为了能更好探索热处理过程中淋滤灰渣中Pb的固化机理,用化学药品PbO(分析纯)等按淋滤灰渣的主要成分比例进行人工配比实验,将复杂的热处理过程分解为几个过程来研究.
由图4可知,配比灰渣中出现了Pb的矿物相Ca2PbO4. 孙立等[24]研究表明,在800 ℃下,由于硅基物质含量的增加,重金属主要被固定在硅酸盐等结构中. Lu等[23]在使用密度泛函理论(DFT)来揭示飞灰中Pb在CaO表面转变的过程中发现,飞灰中的CaO能有效吸附PbO和PbCl2且PbO的电子离域更强,加速飞灰中Pb的富集,为重金属的原位固定提供了支持. 为验证配比灰渣中Pb的固化机理,借助FACT程序,通过平衡态稳定的Gibbs自由能判据来分析特定条件下Pb的结合态生成物的稳定性. ΔG<0,反应可以进行. ΔG越小,说明有利于反应的正向进行,生成的物质越稳定.
800 ℃下Ca2PbO4的合成反应更易发生,1000 ℃的Ca2PbO4晶格仍然存在. 从图4可知,800—1000 ℃过程中,配比灰渣中Ca2PbO4十分稳定且峰值明显增强,且生成量随着温度的升高而逐渐增大. 张芝昆[25]研究表明,碱度的增加会提高玻璃质熔渣的析晶能力. 由于CaCO3在800 ℃以上受热易分解为CaO和CO2,使得800 ℃后CaO的含量递增速度大,碱度增加使Ca2PbO4更易析出. Yang等[26]研究表明,800—1100 ℃中Ca2+会与硅氧四面体竞争更多的O2−,产生更多的活性位点,更易析出晶体. 推测Ca2+竞争位点后更易与Pb发生反应生成Ca2PbO4. 在1000 ℃下,PbSiO3的自由能小于Ca2PbO4的自由能,理论上会更易生成PbSiO3,但在XRD并未检出. 由于在1000 ℃下配比灰渣中大部分SiO2与Al2O3结合生成新的硅铝酸盐-八面沸石,推测只存在少部分SiO2与PbO结合生成了PbSiO3,但可能由于含量太低而未检出.
淋滤灰渣中增加了纳滤膜浓缩液中硫酸根、磷酸根等特征因子. 在热处理过程中,Pb仍会存硫酸盐、磷酸盐等形式,再次通过计算平衡态稳定的Gibbs自由能变量判据研究重金属Pb化合盐体系热分解或合成反应的可能性与进行程度.
由表5可知,400—1000 ℃过程中,PbSO4的热分解反应ΔG>+40 kJ·mol−1,反应不可自发进行;但对于PbSO4来说,其分解不直接发生此反应. 600 ℃后SO3的含量逐渐升高,是由于少量PbSO4在特定条件下分解成nPbO·PbSO4进而分解成PbO[27]. 由于Pb3(PO4)2的分解反应并不能自发进行且P2O5的含量随着温度的升高而增加,说明P2O5含量的升高与Pb的磷酸盐等化合物无影响. 淋滤灰渣中可能存在碱式碳酸盐其在热处理过程中机理与PbCO3类似,PbCO3在400 ℃可发生热分解反应[28],可说明Pb的碳酸盐形态受热不稳定易分解,实际上PbCO3的分解温度在225 ℃,首先分解为PbCO3·2PbO和CO2,然后PbCO3·2PbO分解成PbO和CO2. 由式(4)可知,PbSiO3的合成反应一直进行,800 ℃后出现了Ca10[(SiO4)3(SO4)3]F2(羟硅磷灰石)、Ca5(SiO4)2(SO4)(硫铝酸钙)等,使PbSiO3生成的量随温度升高而减小.
-
(1)纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤焚烧飞灰过程中,可溶性氯盐被大量溶出,Pb与SO42−结合形成Pb2(SO4)O(铅黄).
(2)随着温度的升高,淋滤灰渣中Pb的固化率较飞灰Pb的固化率高30%—70%.
(3)随着温度的升高,淋滤灰渣中碱式碳酸铅随着温度的升高逐渐被分解,400 ℃下完全分解;Pb以硫酸盐、磷酸盐形式稳定存在于灰渣中;当温度达到800 ℃以上时,Pb的氯化物挥发,Pb的硅酸盐含量随着温度升高逐渐降低;同时生成了新的矿物相Ca2PbO4,生成量随着温度的升高而逐渐增大,为淋滤灰渣在热处理过程中固化更多的Pb提供理论支撑.
焚烧飞灰在纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤及后续热处理中Pb的迁移转化
Migration and transformation of Pb in nanofiltration membrane leaching and incineration fly ash during heat treatment
-
摘要: 探究了纳滤膜浓缩液淋滤焚烧飞灰过程及淋滤灰渣在400—1000 ℃热处理过程中Pb的迁移转化特性. 结果表明,淋滤过程中飞灰中大部分氯盐被溶出,有新的矿物相Pb2(SO4)O出现. 后续的热处理中,在400—1000 ℃过程中Pb2(SO4)O分解成PbSO4,然后同Pb的磷酸盐稳定存在于灰渣中,碱式碳酸盐在400 ℃下完全分解. 当温度达到800 ℃以上,PbSiO3含量随着温度升高逐渐降低,生成了Ca2PbO4且生成量随着温度的升高而逐渐增大.Abstract: The leaching and incineration of fly ash from concentrated solution of nanofiltration membrane and the migration and transformation characteristics of Pb in leached ash during 400-1000℃ heat treatment were studied. The results showed that most of the chlorine salts in the fly ash were leached out during the leaching process, and a new mineral phase Pb2(SO4)O appeared. In the subsequent heat treatment, Pb2(SO4)O decomposed into PbSO4 at the temperature of 400—1000℃, and then the phosphate with Pb existed stably in the ash , and the alkali carbonate decomposed completely at 400℃. When the temperature reached above 800℃, the PbSiO3 content gradually decreased with the increase of temperature, and Ca2PbO4 was generated, and the amount generated gradually increased with the increase of temperature.
-
抗凝血灭鼠剂被广泛用于控制共生啮齿动物[1],其中杀鼠醚因其持久性、生物累积性和毒性,近年来引起了国际上多个组织的关注[2-3]. 暴露在水生环境中、饮用被污染的水或食用含有杀鼠醚残留的食物会对人体健康乃至整个生态系统产生不利影响. 目前,杀鼠醚的检测方法主要包括高效液相色谱法[3]、气相色谱法[4]、薄层色谱法[5]、高效液相色谱-质谱法[6]和电喷雾电离串联质谱法[7]. 然而,这些方法都有一定的局限性,对样品纯度有严格的要求,需要繁琐的前处理步骤,对操作人员的技能要求较高[8]. 同时由于仪器体积较大,不适用于现场分析[9]. 因此,迫切需要建立一种杀鼠醚的现场快速检测方法.
表面增强拉曼光谱(surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy,SERS)可以提供简单、快速和无损的检测,该技术具有高灵敏度和独特的光谱指纹,并且不受水分子的干扰,可以很好地适用于复杂的样品检测分析[10]. 目前,SERS技术已被应用于土壤[1]、水果和蔬菜[11]样品中的常规农药检测,但仍缺乏快速检测抗凝血杀鼠剂的相关报道.
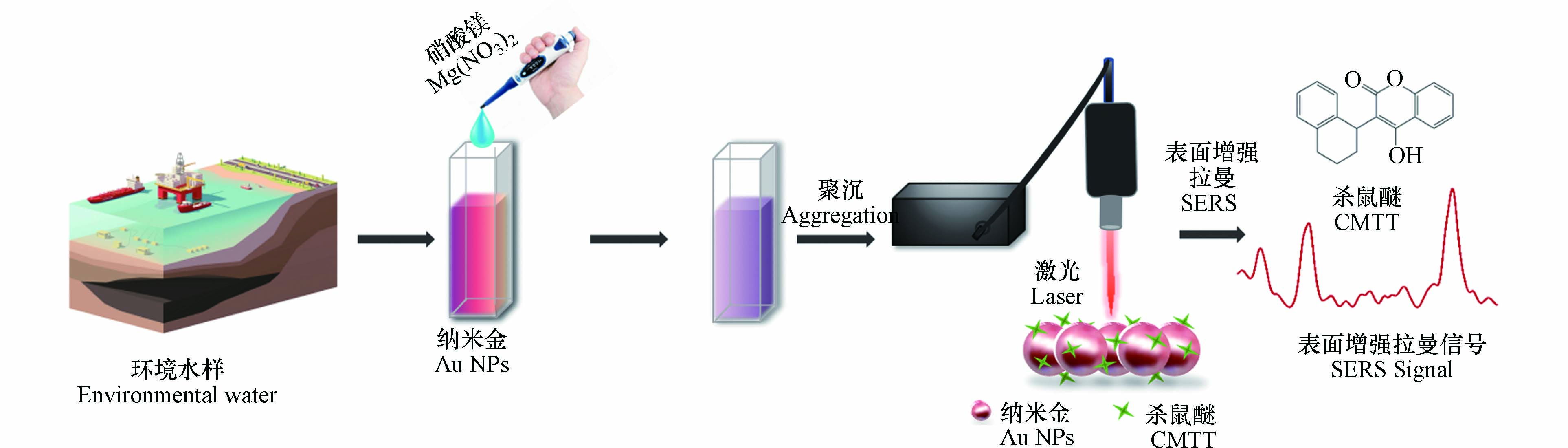
本文建立了一种简单快速的SERS方法,以纳米金作为活性基底,结合便携式拉曼光谱仪,实现了环境水中杀鼠醚的快速现场检测(图1). 与传统方法相比,该方法灵敏度高,检出限低,回收率良好,仅需3 min即可完成整个检测过程,有望成为现场应急分析的有效手段.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 材料和仪器
材料 氯金酸(99.99%)购自中国上海阿拉丁化工有限公司;柠檬酸三钠(99.99%)购自国药化学试剂(上海)有限公司;杀鼠醚(99.4%)购自Dr. Ehrenstorfer(中国北京);聚沉剂硫酸镁(99.7%)、氯化钙(99.7%)、氯化钾(99.8%)、氯化钠(99.7%)、硝酸铝(99.7%)、硝酸镁(99.7%)购自国药化学试剂有限公司;乙酸乙酯(99.9%)、二氯甲烷(99.5%)、乙腈(99.9%)、正己烷(99.5%)、环己烷(99.5%)购自天津科美尔化学试剂有限公司,三氯乙烷(95%)购自上海振兴第二化工厂;实验用水为经Milli-Q净化系统制备的去离子水(~18.2 MΩ cm). 环境水样采自济南市黑虎泉.
仪器 便携式拉曼光谱仪(QE Pro,海洋光学,美国);岛津2600紫外-可见光(UV-Vis)光谱仪(岛津株式会社,京都,日本);透射电子显微镜(TEM; JEM-CXII, JEOL Ltd.,东京,日本).
1.2 实验方法
纳米金的制备 根据先前的研究,用柠檬酸三钠化学还原氯金酸制备纳米金[12]. 将1 mL 1%的氯金酸加入到99 mL去离子水中,以600 r·min−1的转度搅拌,并加热至沸腾. 随后,加入1 mL 1%的柠檬酸钠溶液. 混合溶液在剧烈搅拌下继续煮沸35 min,使其发生反应,溶液很快变成黑色,然后逐渐合成为砖红色的纳米金胶体溶液.
杀鼠醚溶液的制备 将固体杀鼠醚溶解在乙醇中,配制2 mg·mL−1的杀鼠醚标准储备液. 然后用水稀释储备液配制成标准系列溶液,浓度分别为0.025、0.05、0.1、0.25、0.5、1、2.5、5 μg·mL−1. 杀鼠醚的环境水样采用标准添加法制备,浓度为0.025—5 μg·mL−1.
1.3 实验条件的优化
为了优化SERS信号,本研究并比较了6种盐(氯化钾、氯化钠、硝酸镁、硫酸镁、氯化钙和硝酸铝)对Au NPs的聚集效应. 首先,50 μL杀鼠醚水溶液(1 μg·mL−1)与940 μL Au NPs混合;然后加入10 μL的盐溶液,充分混合5 s,诱导聚沉. 使用配有785 nm波长激光器的便携式拉曼光谱仪采集信号,激光功率设置为500 mW,积分时间为20 s. 选择可以诱导最佳聚集效果的盐作为后续实验的聚沉盐. 通过比较不同浓度盐溶液(0.1、0.25、0.5、1、2 mol·L−1)对信号增强效果的影响,确定最佳聚沉条件. 随后采集连续60 min的SERS信号,选取信号强度稳定的时间点作为聚沉时间.
2. 结果和讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 纳米金的表征
透射电子显微镜结果显示,纳米金的粒径为45—60 nm(图2a).
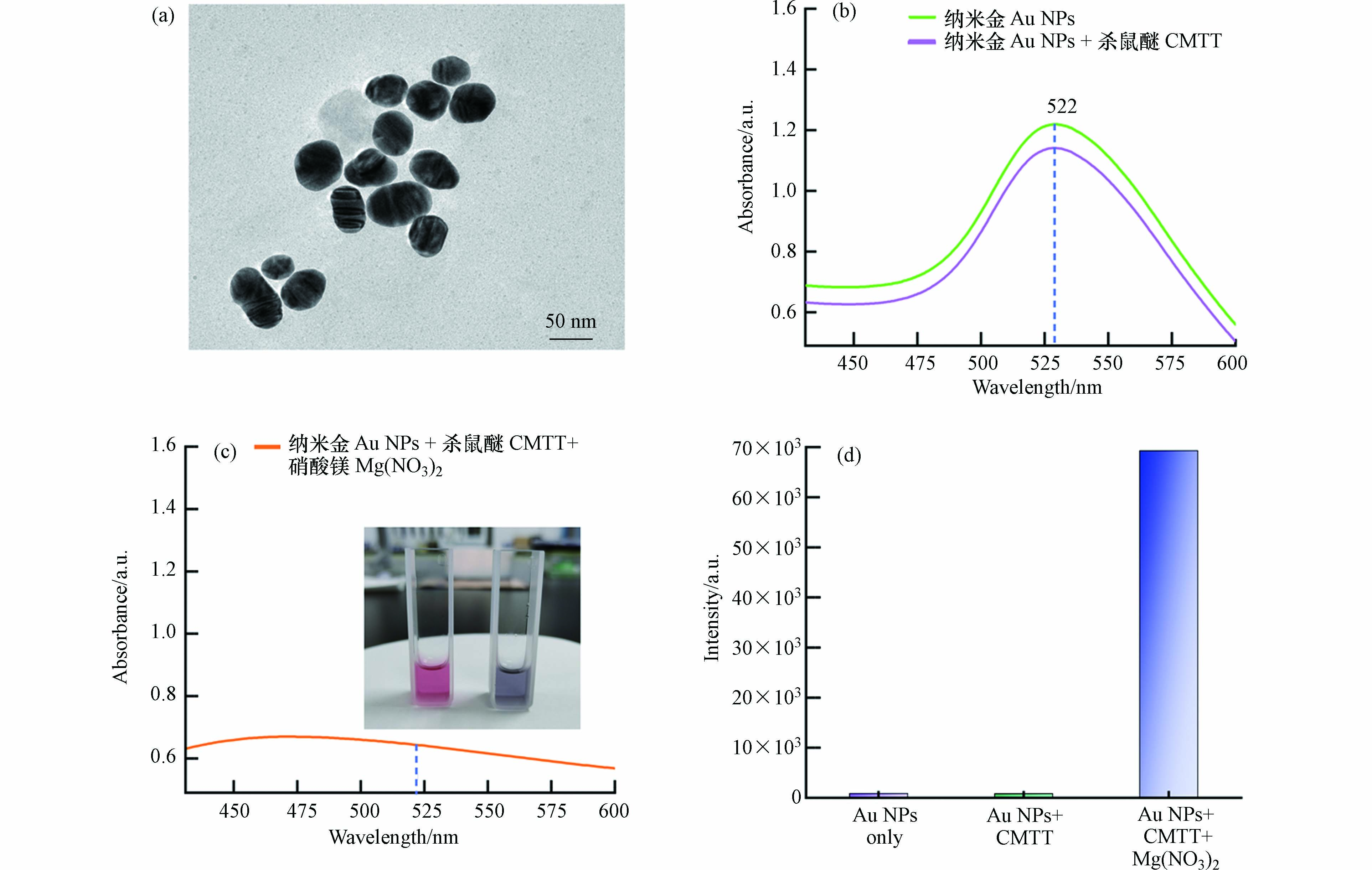 图 2 (a)本研究制备的纳米金透射电镜图;(b)纳米金、1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚混合纳米金的紫外-可见光谱;(c)将1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚与纳米金混合液加入硝酸镁聚沉后的紫外-可见光谱(插图显示纳米金胶体聚沉前后的颜色变化);(d) (b)和(c)对应溶液的SERS强度Figure 2. (a) TEM image of Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) prepared in this study; (b) UV-Vis spectra of colloidal Au NPs, Au NPs mixed with 1 μg·mL−1 CMTT; (c) UV-Vis spectra of aggregated Au NPs after adding 10 μL of 0.5 mol·L−1 Mg(NO3)2 (The inset shows the color change of Au NPs before and after aggregation); (d) SERS intensity of the solutions corresponding to (b) and (c)
图 2 (a)本研究制备的纳米金透射电镜图;(b)纳米金、1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚混合纳米金的紫外-可见光谱;(c)将1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚与纳米金混合液加入硝酸镁聚沉后的紫外-可见光谱(插图显示纳米金胶体聚沉前后的颜色变化);(d) (b)和(c)对应溶液的SERS强度Figure 2. (a) TEM image of Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) prepared in this study; (b) UV-Vis spectra of colloidal Au NPs, Au NPs mixed with 1 μg·mL−1 CMTT; (c) UV-Vis spectra of aggregated Au NPs after adding 10 μL of 0.5 mol·L−1 Mg(NO3)2 (The inset shows the color change of Au NPs before and after aggregation); (d) SERS intensity of the solutions corresponding to (b) and (c)紫外-可见光谱显示纳米金溶液的吸收峰位于522 nm(图2b). 将1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚加入50 μL溶液中,未见明显变化. 相比之下,加入10 μL 0.5 mol·L−1硝酸镁溶液会导致吸收峰显著下降,溶液颜色从砖红色变为紫灰色(图2c插图),表明纳米颗粒发生了团聚[13]. 紫外可见光谱对应的拉曼和SERS信号见图2c和图2d.
2.2 杀鼠醚的拉曼表征
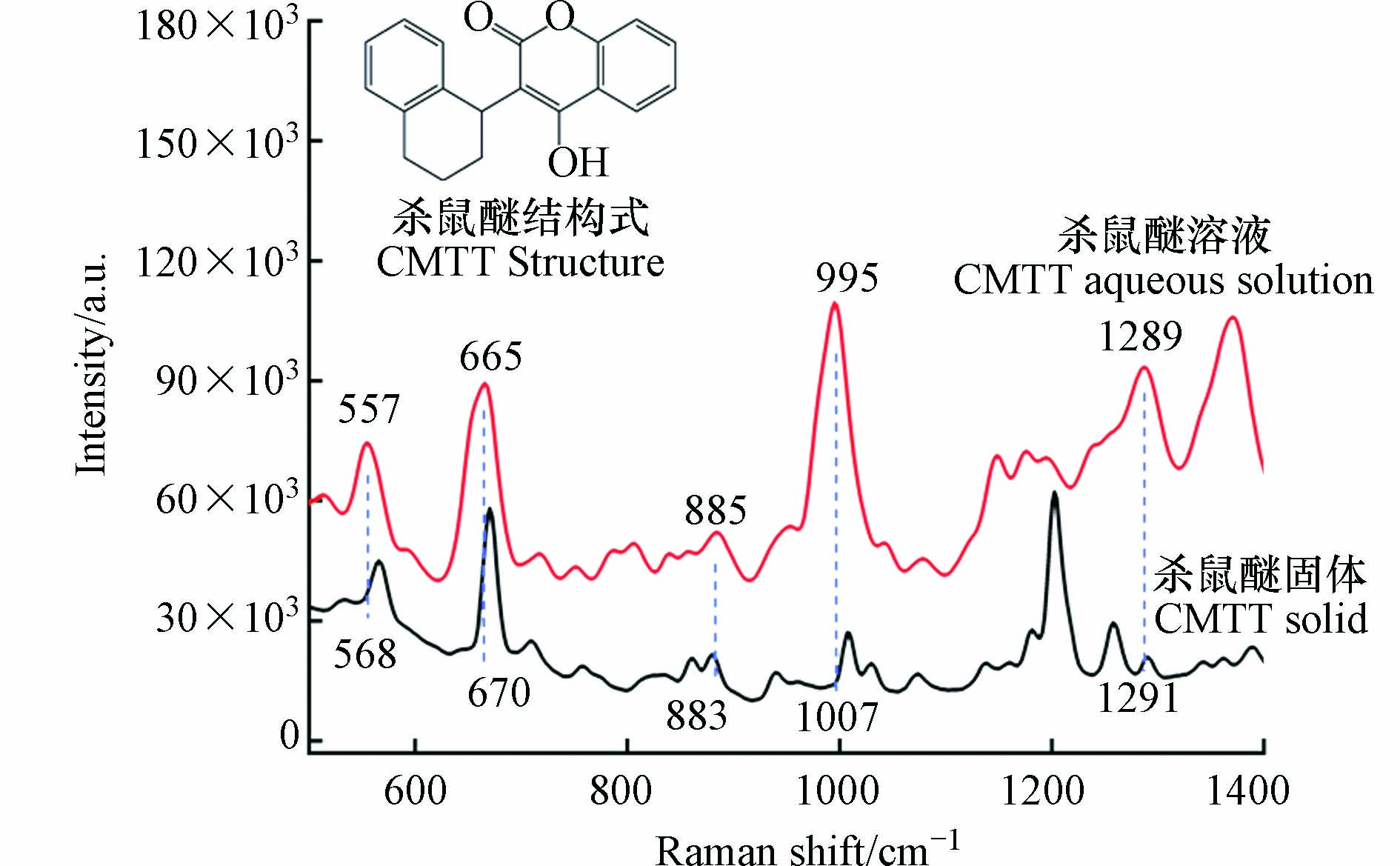
采用便携式拉曼光谱仪采集杀鼠醚固体的拉曼光谱和1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚溶液的SERS光谱. 杀鼠醚由香豆素与四水萘连接形成(图3结构式). 香豆素具有活性的羟基官能团,可以通过化学反应生成各种结构的衍生物. 且在杀鼠醚结构中存在着孤对电子,既能与金属离子配位,又能参与氢键的形成. 因此,环境变化也会引起杀鼠醚结构的轻微变化,图3显示了杀鼠醚固体及其溶液间的位移(图3). 在杀鼠醚溶液中,固体样品在670 cm−1和1007 cm−1处的两个不同的SERS光谱带分别移动到665 cm−1和995 cm−1. 其他几处特征峰也发生了变化,表明杀鼠醚在溶液中的构型发生了改变. 但几个特征峰的出现仍然表明杀鼠醚的存在. 665 cm−1处的特征峰归属于芳香环中的C—C—C[14],而995 cm−1处的特征峰由C—H振动引起[15],557 cm−1的SERS谱带主要与苯环呼吸模式有关[16],885 cm−1的SERS谱带归因于CH2模式[17],1289 cm−1处主要是由于C—H弯曲模式[16]. 在本研究中,选取SERS信号强度最佳、峰型独立且清晰的995 cm−1处的SERS信号作为定量信号.
2.3 聚沉条件
盐离子的加入导致纳米金聚沉,并在相邻纳米颗粒之间形成热点. 基底的性能往往会受到聚沉程度和聚沉时间的影响[18-19]. 为此,本研究对聚沉盐类型、聚沉盐浓度以及聚沉时间等实验参数进行了优化,以提高检测的灵敏性.
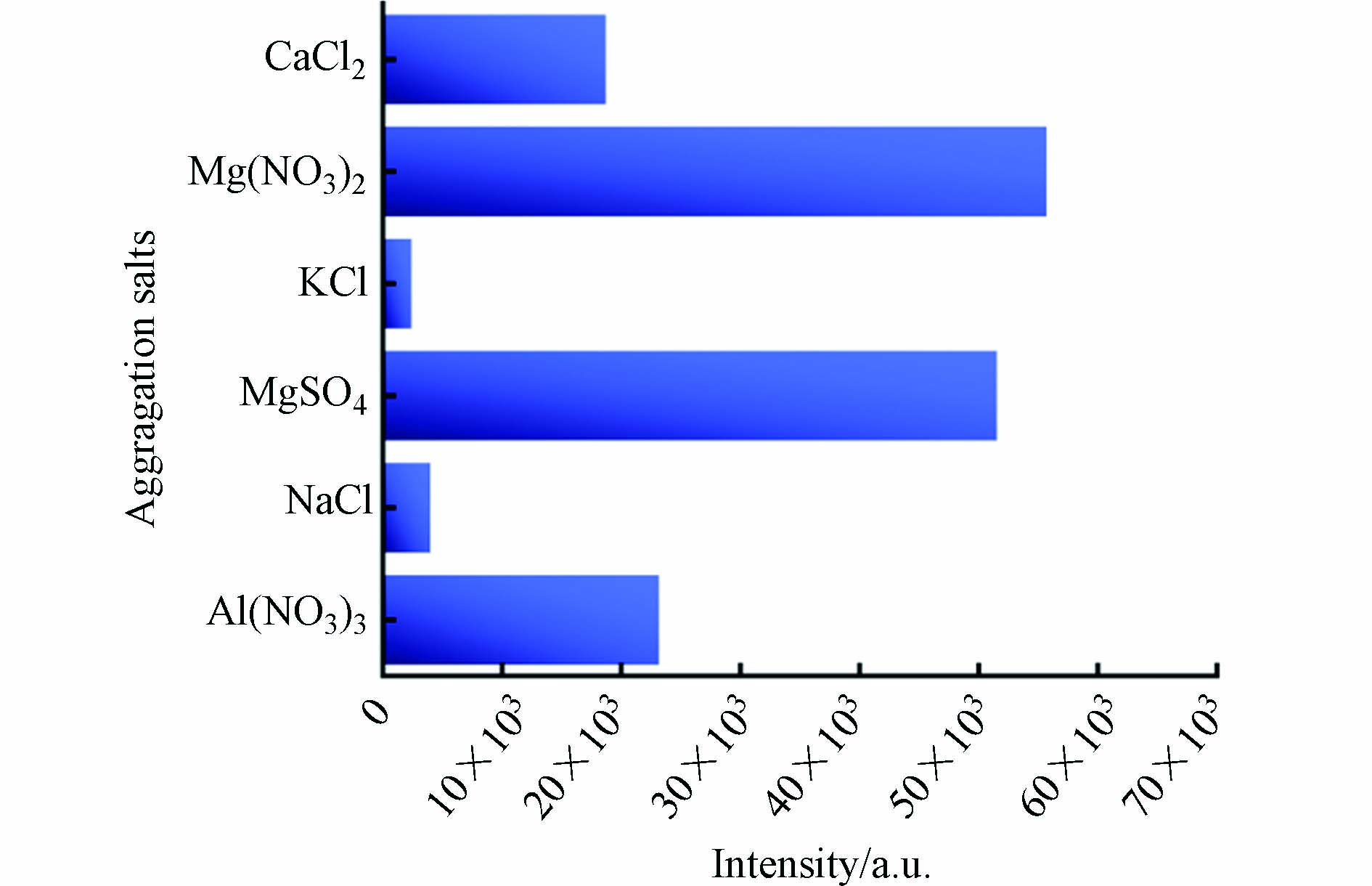
聚沉盐种类的影响 比较了6种浓度相同(0.5 mol·L−1)的聚沉盐对1 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚的SERS强度影响(995 cm−1). 结果表明,硝酸镁对信号的增强作用最为显著,其增强作用顺序为硝酸镁>硫酸镁>硝酸铝>氯化钙>氯化钠>氯化钾(图4). 先前的研究表明,二价和三价阳离子比一价阳离子能更有效地诱导纳米颗粒的聚沉[20]. 纳米金胶体溶液由于其表面电荷相同且相互排斥而保持稳定. 这种胶体粒子只能在吸附离子和组成吸附层的一些异性离子中带电并稳定. 当向胶体中加入盐时,阳离子或阴离子的浓度增加,导致最初分布在扩散层的异性离子被挤压到吸附层[21]. 这导致扩散层变薄,最终降低了zeta电位的稳定性[22]. 随后,粒子之间的斥力减弱从而引起团聚[23]. 当胶体粒子聚集成更大的粒子时,热点产生,导致表面增强共振,进一步增强拉曼信号[24-25]. 通过上述结果,本研究选择硝酸镁作为聚沉剂用于后续的实验.
聚沉盐浓度的影响 图5a—5d为不同浓度硝酸镁诱导纳米金聚沉后的TEM图像. 加入聚沉盐后,纳米颗粒间隙变小并融合、团聚. 且随加入聚沉剂浓度的增加,纳米颗粒团聚现象越明显. 如图所示,低浓度的硝酸镁导致纳米金聚集不足,而较高浓度的硝酸镁则会导致过度聚沉[26],这两者都会使得信号增强效果不佳.
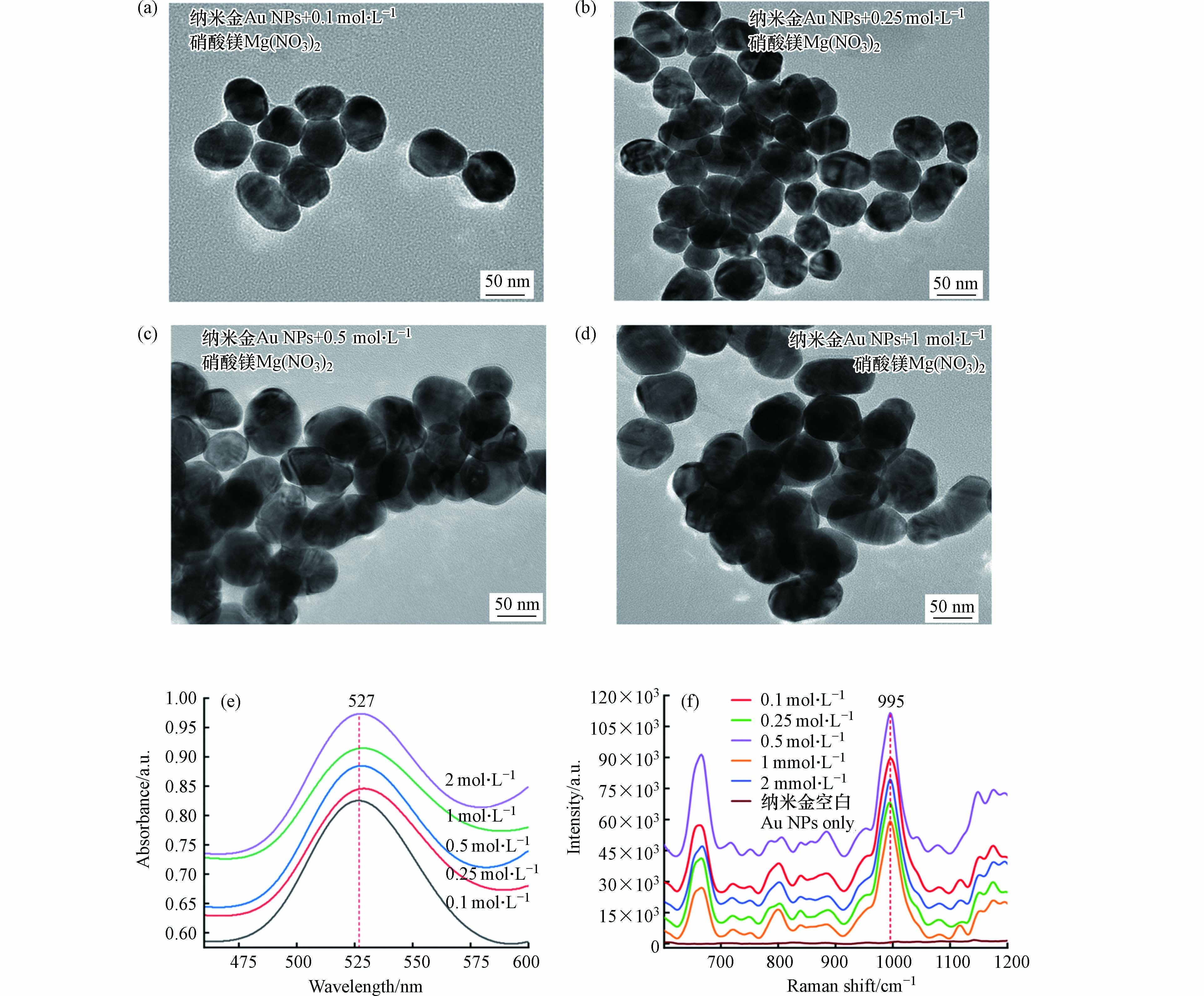 图 5 加入0.1 mol·L−1(a)、0.25 mol·L−1(b)、0.5 mol·L−1(c)、1 mol·L−1(d)硝酸镁聚沉后纳米金的TEM图像;(e) 加入不同浓度硝酸镁聚沉纳米金的紫外-可见光谱;(f)不同浓度的硝酸镁对995 cm−1处的SERS强度影响Figure 5. TEM image of Au NPs after adding 0.1 mol·L−1 (a), 0.25 mol·L−1 (b), 0.5 mol·L−1 (c) and 1 mol·L−1 (d) Mg(NO3)2; (e) UV-Vis spectra of Au NPs with different concentrations of Mg(NO3)2; (f) SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 induced by different concentrations of Mg(NO3)2
图 5 加入0.1 mol·L−1(a)、0.25 mol·L−1(b)、0.5 mol·L−1(c)、1 mol·L−1(d)硝酸镁聚沉后纳米金的TEM图像;(e) 加入不同浓度硝酸镁聚沉纳米金的紫外-可见光谱;(f)不同浓度的硝酸镁对995 cm−1处的SERS强度影响Figure 5. TEM image of Au NPs after adding 0.1 mol·L−1 (a), 0.25 mol·L−1 (b), 0.5 mol·L−1 (c) and 1 mol·L−1 (d) Mg(NO3)2; (e) UV-Vis spectra of Au NPs with different concentrations of Mg(NO3)2; (f) SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 induced by different concentrations of Mg(NO3)2本研究比较了5个浓度(0.1、0.25、0.5、1、2 mol·L−1)的硝酸镁对纳米金胶体溶液聚沉的程度,以及对995 cm−1处的特征峰信号强度信号增强的影响. 图5e显示了不同浓度的硝酸镁诱导纳米金聚沉后的紫外-可见光谱变化. 图5f显示,0.5 mol·L−1的硝酸镁可以诱导产生最强的SERS信号. 因此,本研究采用0.5 mol·L−1硝酸镁溶液作为聚沉剂.
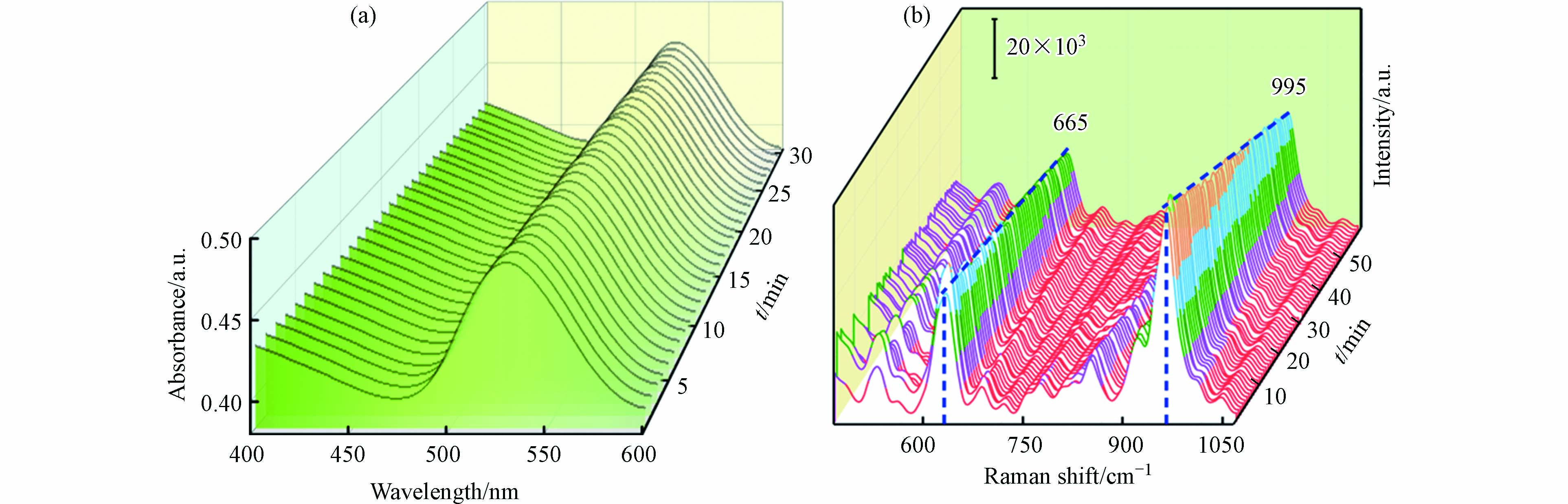
图6a记录了使用0.5 mol·L−1硝酸镁诱导聚沉后连续30 min的紫外-可见光谱变化图,从图中可以看出吸光度强度随时间变化不大,说明加入0.5 mol·L−1硝酸镁聚沉后,溶液体系较为稳定.
聚沉时间对SERS信号的影响 本研究记录了加入聚沉剂后的SERS信号时间变化趋势(60 min). 结果显示,SERS信号在1 min内即可达到最大值,随后缓慢下降,在第3—30 min保持相对稳定. 因此,以3 min为最佳聚沉时间(图6b). 根据之前的一项研究[27],在上述优化的条件下,平均增强因子计算为1.29×105. 具体计算公式如下:
AEF = (ISERS/CSERS)/(IRS/CRS)
其中,IRS代表的是非SERS条件下浓度为CRS的待测物溶液的拉曼强度,ISERS代表的是SERS基底上相同待测物的拉曼强度,浓度CSERS可能不同.
2.4 杀鼠醚溶液的测定
在纳米金中加入不同浓度梯度的杀鼠醚溶液,使用便携式拉曼光谱仪进行SERS检测. 图7a显示,杀鼠醚最显著的SERS峰位于995 cm−1处,该特征峰的强度随着浓度的增加显著增加. 图7b显示了995 cm−1处拉曼光谱强度与对数浓度的定量校准曲线. 在0.025—5 μg·mL−1范围内,杀鼠醚溶液浓度与SERS信号值呈明显的线性关系(R2 = 0.990),可以满足定量检测要求.
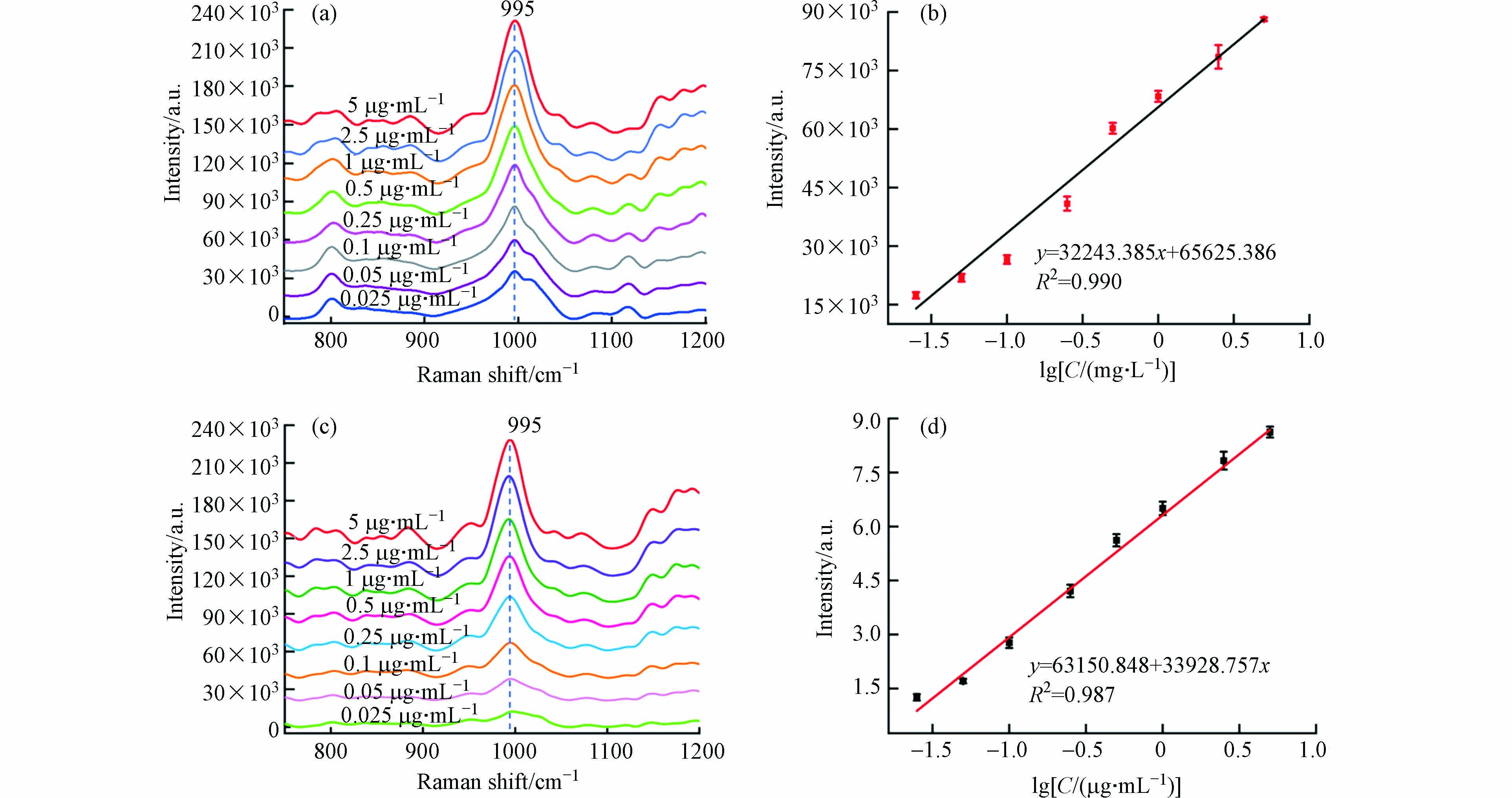 图 7 (a)不同浓度杀鼠醚溶液的SERS检测;(b)杀鼠醚SERS峰强度随浓度变化的曲线;(c)水样中不同浓度杀鼠醚的SERS检测;(d)水样中杀鼠醚SERS峰强度随浓度变化的曲线Figure 7. (a) SERS detection of CMTT aqueous solution with different concentrations; Calibration curve for different CMTT; (c) SERS detection of CMTT with different concentrations in water samples; Calibration curve for different CMTT in water samples
图 7 (a)不同浓度杀鼠醚溶液的SERS检测;(b)杀鼠醚SERS峰强度随浓度变化的曲线;(c)水样中不同浓度杀鼠醚的SERS检测;(d)水样中杀鼠醚SERS峰强度随浓度变化的曲线Figure 7. (a) SERS detection of CMTT aqueous solution with different concentrations; Calibration curve for different CMTT; (c) SERS detection of CMTT with different concentrations in water samples; Calibration curve for different CMTT in water samples2.5 环境水样的测定
为了验证所提出的SERS方法的可行性和实用性,在加标的真实环境水中进行了杀鼠醚检测. 使用便携式拉曼光谱仪可以直接采集杀鼠醚的信号,无需样品预处理,3 min内即可完成定性和定量检测. 995 cm−1处的SERS信号强度随着杀鼠醚浓度的增加而增加,与标准水溶液中的趋势相似(图7c),并且两者之间线性关系良好(图7d).
2.6 基底的重现性与重复性
获得重复稳定的SERS信号是评估基底性能的关键参数. 本研究选择浓度为0.05 μg·mL−1和1 μg·mL−1的杀鼠醚溶液,采用同批次的SERS基底,在不同时间内进行了21次平行实验. 由图8a和图8b可知,1 μg·mL−1和0.05 μg·mL−1对应的相对标准偏差(Relative standard deviation,RSD)分别为6.81%和9.00%. 这些结果表明,该基底可以提供高重复性的结果. 此外,为了确定所制备基底在实际加标水中的重现性,比较了8个不同批次和同一批次使用该基底的检测效果,发现RSD均在10%以内(图8c—8d),良好的重复性和重现性有助于保证该SERS方法的稳定性.
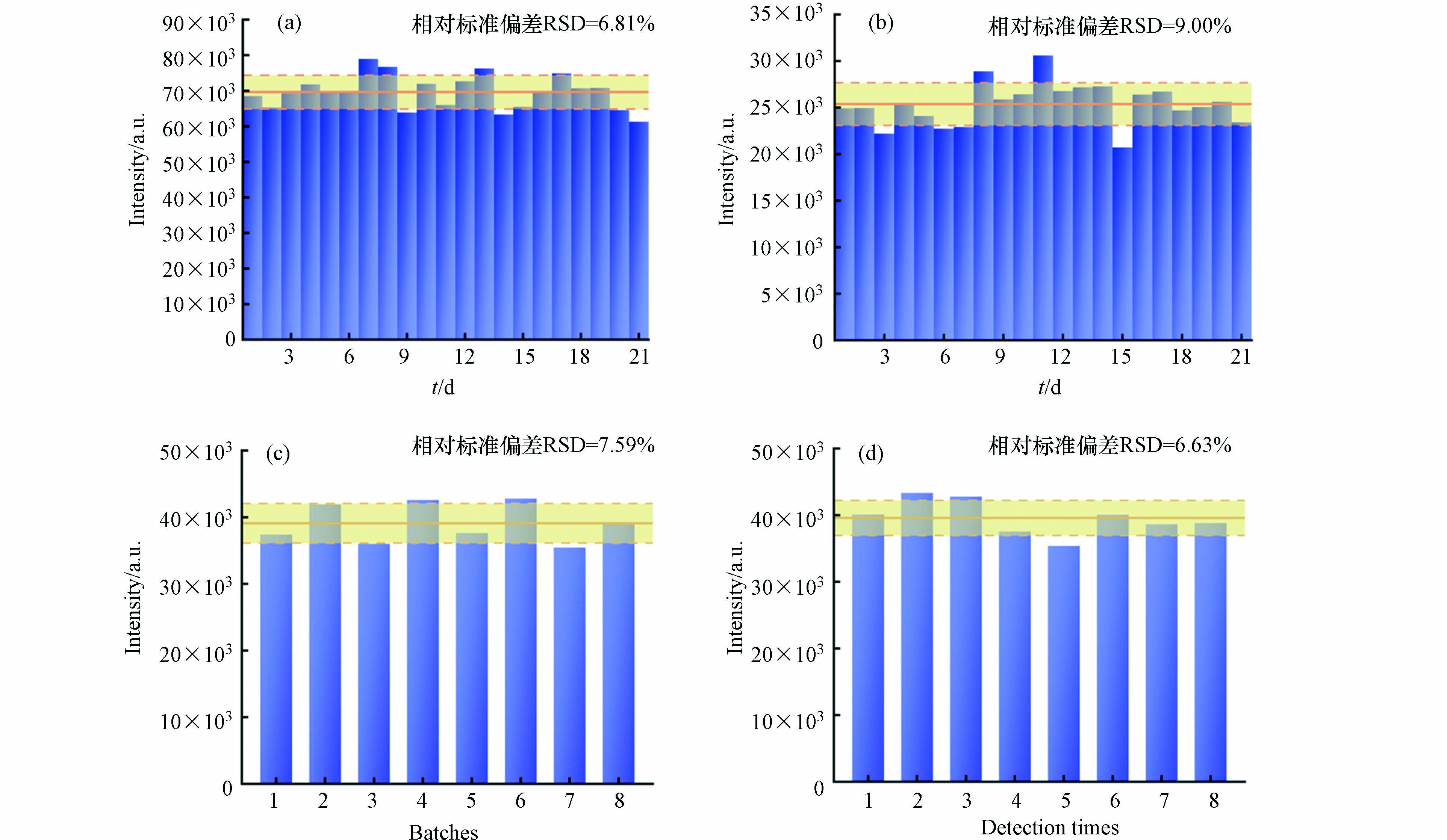 图 8 使用同批次纳米金在21 d内测定(a)1 μg·mL−1和(b)0.05 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚在995 cm−1处的SERS强度;(c)8个不同批次纳米金检测加标水样中0.25 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚在995 cm−1处的SERS强度;(d)同批次纳米金检测加标水样中0.25 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚在995 cm−1处的SERS强度Figure 8. SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 of (a) 1 and (b) 0.05 μg·mL−1 CMTT acquired over 21 d using the same batch of Au NPs; (c) SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 of 0.25 μg·mL−1 CMTT in spiked water using eight batches of Au NPs; (d) SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 of 0.25 μg·mL−1 CMTT in spiked water generated by the same batch of Au NPs
图 8 使用同批次纳米金在21 d内测定(a)1 μg·mL−1和(b)0.05 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚在995 cm−1处的SERS强度;(c)8个不同批次纳米金检测加标水样中0.25 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚在995 cm−1处的SERS强度;(d)同批次纳米金检测加标水样中0.25 μg·mL−1杀鼠醚在995 cm−1处的SERS强度Figure 8. SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 of (a) 1 and (b) 0.05 μg·mL−1 CMTT acquired over 21 d using the same batch of Au NPs; (c) SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 of 0.25 μg·mL−1 CMTT in spiked water using eight batches of Au NPs; (d) SERS intensity at 995 cm−1 of 0.25 μg·mL−1 CMTT in spiked water generated by the same batch of Au NPs2.7 加标回收率和检出限
用建立的SERS方法对环境水中杀鼠醚的加标回收率及检出限进行了测定. 制备已知浓度的加标杀鼠醚溶液,以模拟受污染水中杀鼠醚的含量. 测得水中平均回收率为90.2%—98.2%,相对标准偏差为2.69%—6.40% (n=8)(表1). 按照常规计算方法[28],计算出本方法在真实水样中的检出限为1.53 ng·mL−1. 结果表明,该方法可作为环境水中杀鼠醚现场检测的一种有效手段.
表 1 环境水中不同浓度杀鼠醚的平均回收率Table 1. Average recoveries of different CMTT concentrations in spiked environmental water加标量/(μg·mL−1)Added 回收量±标准差/(μg·mL−1)Found ± SD 回收率/%Recovery 相对标准偏差/%RSD 0.50 0.48 ± 0.12 96.4 6.40 1.00 0.90 ± 0.12 90.2 2.86 2.50 2.46 ± 0.36 98.2 2.69 2.8 方法的选择性
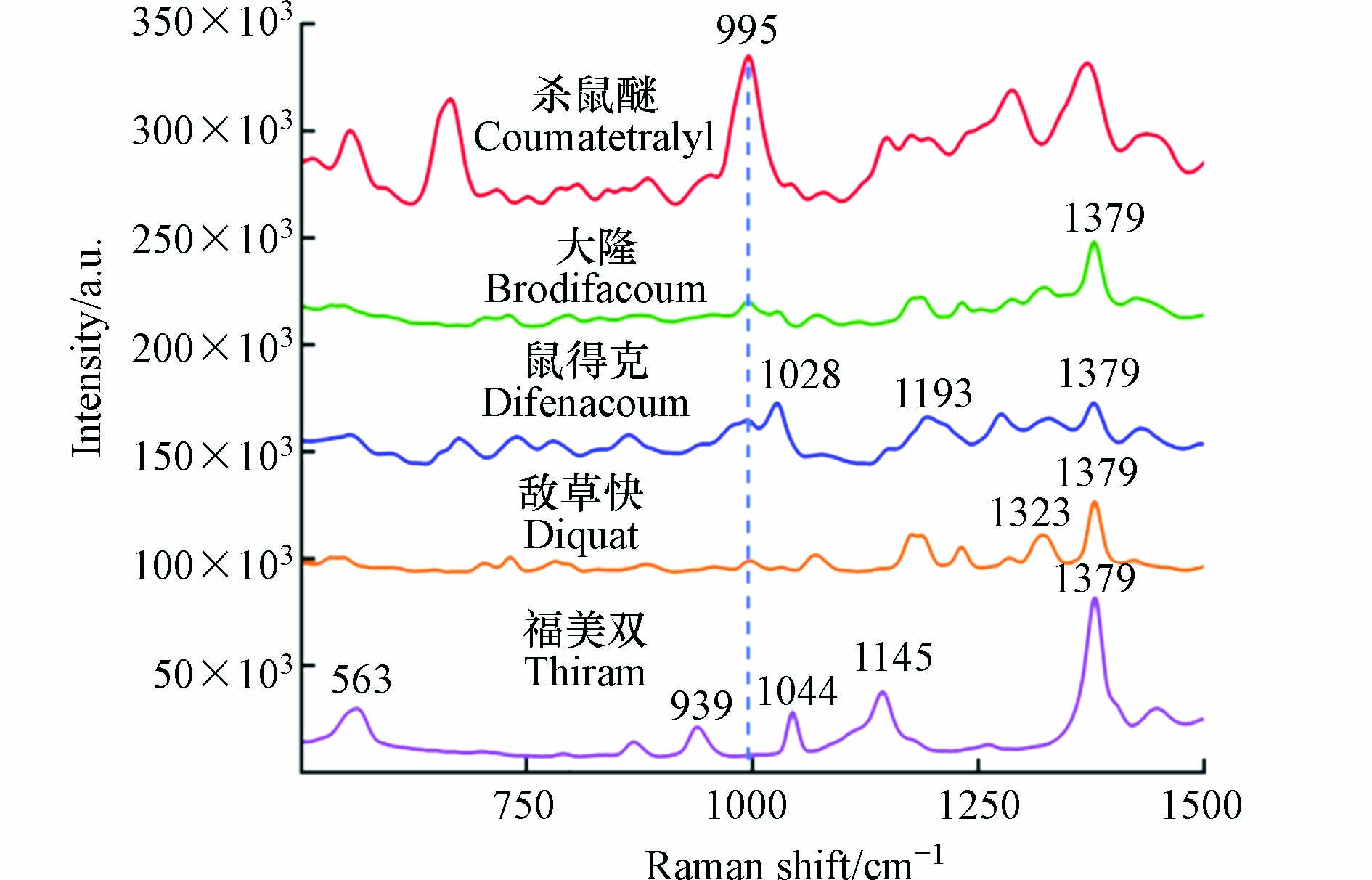
环境水中可能存在其他种类的混合农药残留,因此通过对几种潜在共存的农药(大隆、鼠得克、敌草快和福美双)进行SERS检测(图9),评估了在本方法对杀鼠醚的选择性. 结果显示,几类农药的SERS谱带各不相同,展示了拉曼技术获取化合物指纹谱的优点,信号来源如表2所示[29-30]. 同时,由于其他物质在995 cm−1处均未出现明显的SERS信号,因此不会对杀鼠醚的定量检测造成影响. 由于杀鼠醚所产生的SERS峰强度最高,说明本研究制备的纳米金基底对杀鼠醚具有良好的信号增强效果.
表 2 各农药对应SERS谱带的分配Table 2. The Assignation of SERS spectral bands corresponding to each pesticide表面增强拉曼光谱位移/cm−1SERS shift 归属结构Assignation 563 C—C—C弯曲振动 939 C—O/C—H弯曲振动 1028 C—O弯曲振动/C—C拉伸振动 1044 C—O弯曲振动/C—C拉伸振动 1145 H—C—H弯曲振动/CH2扭转 1193 C—H平面弯曲 1323 H—C—H/CH3/CH2/CH弯曲振动 1379 H—C—H/CH2扭转 3. 结论(Conclusion)
本文建立了一种快速的定性和定量检测环境水中杀鼠醚的SERS方法. 通过对实验条件进行优化,该技术测得环境水中的检出限为1.53 ng·mL−1,加标回收率为90.2%—98.2%,相对标椎偏差在2.69%—6.40%之间. 本方法简单、快速,仅需3 min即可完成检测,仪器可便携,不受场地限制. 此高灵敏度、高特异性的检测方法可以为杀鼠醚环境水污染事故的现场应急分析提供一种便捷的检测手段.
-
表 1 飞灰主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of MSWI fly ash and leached fly ash
主要成分 Ingredient 含量/ % Content 主要成分 Ingredient 含量/ % Content CaO 45.68±1.26 SiO2 2.72±0.19 Cl 22.75±0.28 ZnO 0.85±0.02 Na2O 12.17±0.12 Al2O3 0.81±0.10 SO3 6.16±0.11 P2O5 0.40±0.12 K2O 5.20±0.37 PbO 0.12±0.02 表 2 纳滤膜浓缩液水质参数(mg·L−1)
Table 2. Water quality parameters of nanofiltration membrane (mg·L−1)
污染物指标Pollutant index 化学需氧量Chemical oxygen demand 生化需氧量Biochemical oxygen demand 氨氮Ammonia nitrogen Cl− SO42− PO42− 纳滤膜浓缩液 2490±60 473±28 191±12 3420±38 249±18 5.88±0.37 表 3 淋滤前后飞灰主要化学成分(%)
Table 3. Main chemical constituents of fly ash before and after leaching
固体样品Solid samples CaO Cl SO3 SiO2 PbO P2O5 飞灰(加入PbO) 45.14±0.86 22.48±0.30 6.09±0.20 2.69±0.24 1.30±0.03 0.40±0.07 淋滤灰渣 33.63±0.56 0.40±0.08 2.39±0.23 1.52±0.05 27.36±0.22 0.19±0.08 表 4 淋滤前后纳滤膜浓缩液中主要离子指标
Table 4. Main ion indexes in nanofiltration membrane before and after leaching
液体样品 Liquid samples pH Cl-/(mg·L−1) SO42-/(mg·L−1) PO42-/(mg·L−1) 纳滤膜浓缩液 7.1±0.1 3.4×103±38.2 2.5×102±18.5 5.9±0.4 淋出液 13.5±0.1 3.2×105±1980.3 3.4×103±153.6 0.6×10−2±0.0 表 5 吉布斯反应自由能ΔG(kJ·mol−1)
Table 5. Gibbs reaction free energy energyΔG (kJ·mol−1)
温度/℃ Temperature 式(3) 式(4) 式(5) 式(6) 400 446.4 −12.6 454.0 −16.1 600 340.8 −39.6 447.5 −16.2 800 238.2 −64.4 435.8 −17.5 1000 138.5 −89.3 412.5 −21.3 -
[1] 杨凤玲, 李鹏飞, 叶泽甫, 等. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰组成特性及重金属熔融固化处理技术研究进展 [J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(1): 169-180. doi: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.20052801 YANG F L, LI P F, YE Z F, et al. Study progress on the composition characteristics of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration and treatment technology of heavy metal melting and solidification [J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(1): 169-180(in Chinese). doi: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.20052801
[2] HUBER F, LANER D, FELLNER J. Comparative life cycle assessment of MSWI fly ash treatment and disposal [J]. Waste Management, 2018, 73: 392-403. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.06.004 [3] SHARIFIKOLOUEI E, BAINO F, SALVO M, et al. Vitrification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: An approach to find the successful batch compositions [J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(6): 7738-7744. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.11.118 [4] LIU Z Y, YUE Y, LU M, et al. Comprehension of heavy metal stability in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with its compositional variety: A quick prediction case of leaching potential [J]. Waste Management, 2019, 84: 329-339. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.11.049 [5] 何品晶, 吴长淋, 章骅, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰及其稳定化产物的长期浸出行为 [J]. 环境化学, 2008, 27(6): 786-790. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2008.06.018 HE P J, WU C L, ZHANG H, et al. The long-term leaching behavior of air pollution control residues and its treatment products [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 27(6): 786-790(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2008.06.018
[6] HE H J, WU T, WANG X G, et al. Study on compressibility and settlement of a landfill with aged municipal solid waste: A case study in Taizhou [J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(9): 4831. doi: 10.3390/su13094831 [7] 田书磊, 王琪, 汪群慧, 等. 垃圾焚烧飞灰熔融过程中重金属固化特性 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2008, 40(10): 1576-1580. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2008.10.014 TIAN S L, WANG Q, WANG Q H, et al. Characterics of heavy metals during melting and solidification of MSWI fly ash [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008, 40(10): 1576-1580(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2008.10.014
[8] WU K, SHI H S, de SCHUTTER G, et al. Preparation of alinite cement from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2012, 34(3): 322-327. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.11.016 [9] 徐昌文, 王声东. 垃圾渗滤液及膜滤浓缩液处理技术探讨与分析 [J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2020, 45(5): 72-75. doi: 10.19758/j.cnki.issn1673-288x.202005072 XU C W, WANG S D. Discussion and analysis on treatment technology of leachate and membrane filtration concentrated solution [J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2020, 45(5): 72-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.19758/j.cnki.issn1673-288x.202005072
[10] 张睿涵. 阴极电Fenton法处理垃圾渗滤液浓缩液的研究及能耗评估[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2016: 2-11. ZHANG R H. Energy consumption evaluation of landfill leachate disposal using electro-Fenton[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2016: 2-11(in Chinese).
[11] 王晓青, 赵成云, 罗竞红. 回灌法处理反渗透浓缩液的试验研究 [J]. 环境科技, 2015, 28(4): 18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2015.04.004 WANG X Q, ZHAO C Y, LUO J H. Study on pilot experiment of recirculation treatment of concentrated liquor produced by reverse osmosis [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 28(4): 18-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2015.04.004
[12] JIA C Z, WANG Y X, ZHANG C X, et al. UV-TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of landfill leachate [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2011, 217(1/2/3/4): 375-385. [13] 王东梅, 刘丹, 龚正君, 等. Fenton氧化-絮凝-吸附法处理垃圾渗滤液反渗透浓缩液 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(18): 5423-5426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2013.18.065 WANG D M, LIU D, GONG Z J, et al. Treatment of landfill leachate reverse osmosis concentrate by Fenton oxidation-coagulation-adsorption [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2013, 13(18): 5423-5426(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2013.18.065
[14] 孟棒棒, 田书磊, 刘宏博, 等. 膜浓缩液淋滤飞灰后灰渣重金属热处理特性分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(4): 992-999. MENG B B, TIAN S L, LIU H B, et al. Analysis on heat treatment of heavy metal in residues from fly ash leaching process by membrane concentrated leachate [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 13(4): 992-999(in Chinese).
[15] 王琛, 许继云, 邵宁宁, 等. 危废焚烧过程中二噁英和颗粒物的生成机理以及重金属迁移特征探究 [J]. 环境卫生工程, 2020, 28(4): 111-112. WANG C, XU J Y, SHAO N N, et al. A field study of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans formation mechanism in a hazardous waste incinerator: Emission reduction strategies [J]. Environmental Sanitation Engineering, 2020, 28(4): 111-112(in Chinese).
[16] TIAN X, RAO F, LI C X, et al. Solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and immobilization of heavy metals using waste glass in alkaline activation system [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 283: 131240. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131240 [17] 刘丽君, 韩静磊, 钱益斌, 等. 利用靶器官毒性剂量法(TTD)和证据权重分析法(WOE)评估固化飞灰中重金属非致癌健康风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1014-1020. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018062002 LIU L J, HAN J L, QIAN Y B, et al. Assessment of heavy metal non-carcinogenic health risk in solidified fly ash using TTD and WOE methods [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1014-1020(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018062002
[18] TIAN S L, ZHU Y C, MENG B B, et al. Chemical speciation of lead in secondary fly ash using X-ray absorption spectroscopy [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 197: 362-366. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.026 [19] 孟棒棒. 利用生活垃圾焚烧飞灰协同处理膜浓缩液的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2018: 55-57. MENG B B. Study on the synergistic treatment of membrane concentrated leachate by MSWI fly ash[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2018: 55-57 (in Chinese)
[20] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 固体废物 金属元素的测定 电感耦合等离子体质谱法: HJ 766—2015[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2015. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Solid Waste-Determination of metals-Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): HJ 766—2015[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2015(in Chinese).
[21] 龚勋. 典型西部粉煤灰中重金属元素淋滤特性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2010: 82. GONG X. Leaching characteristics of heavy metal in the coal ash from West China[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2010: 82 (in Chinese)
[22] 田书磊. 垃圾焚烧飞灰重金属热分离工艺及挥发特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2007: 68-71. TIAN S L. Thermal-separation process and evaporation mechanism of heavy metal from MSWI fly ash[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007: 68-71 (in Chinese)
[23] LU Q, ZHOU X Y, WU Y W, et al. Migration and transformation of lead species over CaO surface in municipal solid waste incineration fly Ash: A DFT study [J]. Waste Management, 2021, 120: 59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.11.011 [24] 孙立, 吴新, 刘道洁, 等. 基于硅基的垃圾焚烧飞灰中温热处理重金属稳固化实验 [J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(9): 3514-3522. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017-0141 SUN L, WU X, LIU D J, et al. Stabilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash using thermal treatment with silica-based material [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(9): 3514-3522(in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017-0141
[25] 张芝昆. 油页岩复合灰制备微晶玻璃及其固化垃圾焚烧飞灰的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016: 37-40. ZHANG Z K. Preparation of glass-ceramics and solidification of solid waste incineration fly ash using oil shale fly ash-based composite ashes[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2016: 37-40 (in Chinese)
[26] YANG Z H, LIN Q, LU S C, et al. Effect of CaO/SiO2 ratio on the preparation and crystallization of glass-ceramics from copper slag [J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(5): 7297-7305. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.071 [27] LI Y, TASKINEN P, WANG Y J, et al. PbSO4 reduction mechanism and gas composition at 600–1000℃ [J]. JOM, 2021, 73(3): 881-891. doi: 10.1007/s11837-020-04551-4 [28] 刘敬勇, 孙水裕, 陈涛, 等. 污泥焚烧a过程中Pb的迁移行为及吸附脱除 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(2): 466-477. LIU J Y, SUN S Y, CHEN T, et al. Migration behavior of Pb and its vaporization control during sewage sludge incineration process [J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(2): 466-477(in Chinese).
-





 下载:
下载: