-
塑料因其重量轻、耐腐蚀、化学性质稳定等优点,被广泛应用于人类生产生活[1]. 目前所生产的塑料中,有近80%最终会成为塑料垃圾,被掩埋或堆积在环境中[2]. 环境里的塑料垃圾中有相当大的一部分是直径或长度小于5 mm的颗粒,也被称为微塑料[3]. 微塑料的来源包括较大尺寸塑料垃圾的分解、破碎,以及微米尺寸塑料颗粒的直接生产、使用和处置[4]. 目前针对环境微塑料污染的研究主要集中在陆地环境和水环境. 陆地环境中的微塑料主要来源于垃圾填埋场中塑料制品的破碎、污泥农用、农业地膜破碎和汽车轮胎磨损[5-6]. 水环境中的微塑料主要来源于污水处理厂排放、渔业活动以及船舶运输业释放[7-8]. 微塑料广泛分布在土壤、海洋、河流、湖泊等环境介质中,即便在偏远地区(如极地、高山、深海沉积物中)也均有检出[9-12]. 据估算,陆地环境中每年新增的微塑料超过43万吨[6],而海洋中至少漂浮着5.3万亿个微塑料颗粒[13]. 微塑料易被生物体吞食,诱导氧化应激和炎症反应进而引发颗粒毒性,从而造成肝脏、肾脏、胃肠道等器官损伤[14-15]. 同时,微塑料在生产过程中会混入大量添加剂,例如邻苯二甲酸酯、多溴联苯醚等;生物体摄食微塑料可导致添加剂在体内的释放和积累,进而引发化学毒性,显著抑制生物生长和早期发育[16-17]. 此外,微塑料粒径较小、比表面积较大,进入环境后可成为众多有机污染物、重金属以及微生物的载体,促进了这些污染物的生物富集,造成严重的生态和健康风险[18]. 因此,环境中微塑料的大量存在及其环境风险近年来已在全球范围内引起了广泛关注.
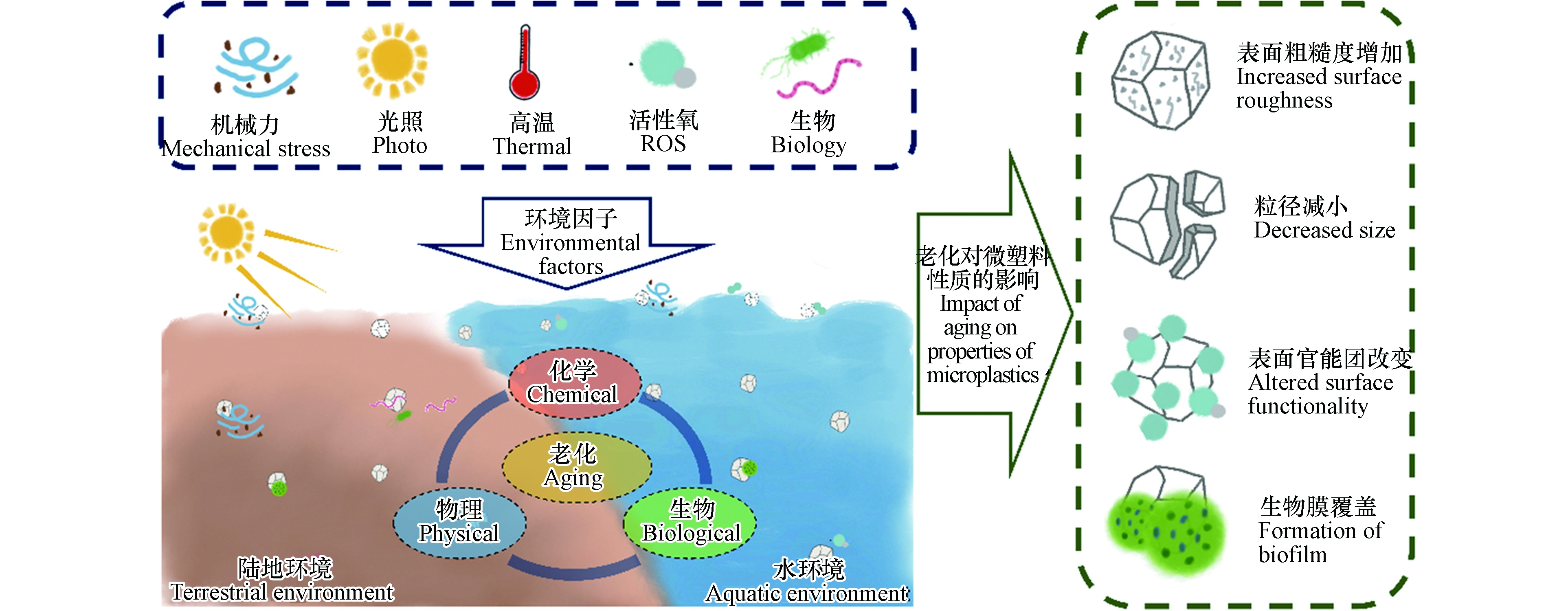
环境中的微塑料可在机械力、紫外线、高温、化学物质和生物等环境因素作用下发生一系列的物理、化学和生物老化[7, 19-22]. 环境老化使得微塑料表面形貌和理化性质发生改变,进而影响微塑料迁移和吸附污染物的能力,改变生物体摄入微塑料的方式和程度. 同时,老化增加了微塑料中添加剂向环境中释放的风险,增强了毒性效应[23-25]. 因此,研究微塑料的环境老化及由此产生的效应具有重要意义. 本文通过综述国内外微塑料环境老化研究的最新进展,总结了物理、化学和生物老化的主要过程与机制,分析了老化对微塑料的环境行为和效应的影响.
-
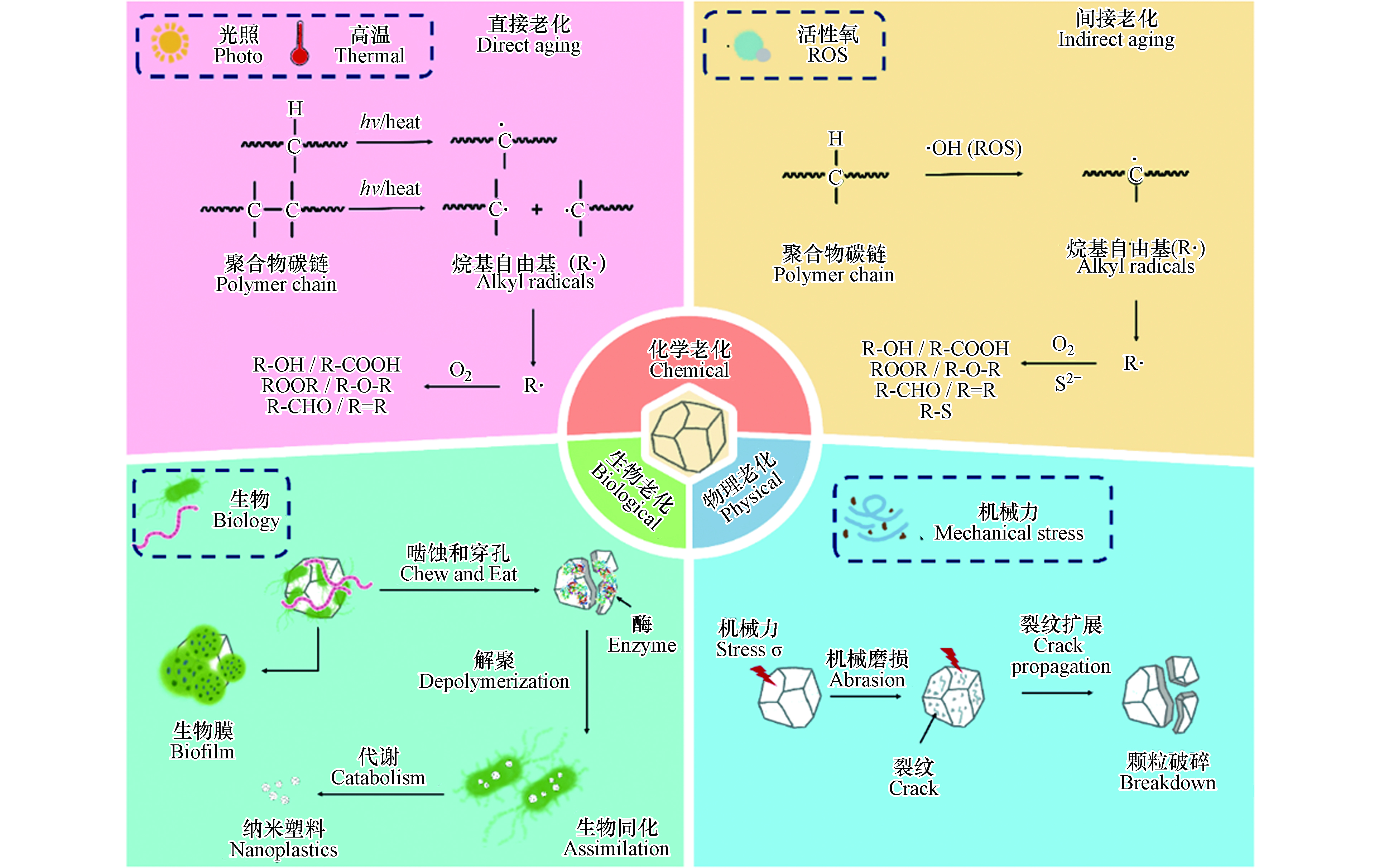
微塑料广泛分布在自然环境中,可在机械力、紫外光、高温、化学物质、生物等因素作用下发生老化,其表面形貌和理化性质均可发生变化(图1). 明确微塑料的老化机制对于理解其环境行为和风险至关重要. 本文从物理、化学和生物的3个方面阐述了微塑料在环境中的老化过程及机制(图2).
-
进入环境中的微塑料会受到周围环境力的机械作用,如湍流、波浪、沙砾或岩石碰撞及周围塑料碎片的碰撞等,从而发生表面开裂,破碎形成更多小尺寸的微塑料[26],所生成的塑料颗粒数量随尺寸的减小而增加[22]. 有研究显示,从磨砂膏中提取的粒径为398 nm的原生微塑料,可在模拟湍流作用下破碎为50 nm的微塑料颗粒,甚至出现了纳米塑料(<10 nm)[27]. 对海滩中采集到的塑料碎片进行分析发现,物理老化是微塑料表面纹理形成的主要原因,碰撞过程中塑料颗粒棱角会变成近圆形状,同时出现裂缝和凹坑[28]. 同时,已老化的塑料表面更易受沙子磨损等机械力作用而破裂[29]. 微塑料在机械力作用下表面产生裂纹,从而裂纹扩展,进而导致了微塑料颗粒的破碎[27, 30]. 相关研究使用Grady模型来描述微塑料在应力作用和裂纹扩展下的破碎,证明了裂纹在微塑料物理老化中发挥了决定性作用,裂纹越长,扩展时所需最小应力越低,因此,表面有裂纹的微塑料在剪切力的作用下更容易破碎、剥落成更小的颗粒[27]. 自然环境中的微塑料在土壤颗粒、沙砾磨损,海浪、潮汐碰撞等自然机械力作用下,原有的表面形貌被破坏、破碎并形成更多的裂缝,呈现更高的比表面积. 同时,物理老化有利于各种化学物质通过微塑料表面的孔隙和裂纹进入内部,并促进微塑料的进一步老化.
-
微塑料可在紫外线、高温、活性氧等作用下发生化学老化. 在实验室模拟或自然条件下,老化后微塑料的表面整体呈现粗糙度增加,出现裂纹和缝隙,伴随片状、颗粒状碎片脱落,粒径减小,孔隙度和比表面积增大. 老化后的微塑料往往表面羟基、羰基等含氧官能团含量增高,表面亲水性增强[3, 31-32]. 微塑料化学老化的作用机制可大致分为直接老化和间接老化:直接老化是指紫外光或高温作用使得微塑料聚合物碳键直接断裂及由此引发的一系列变化;间接老化是指活性氧物种等化学物质参与导致化学键断裂而发生的系列化学反应.
-
(1)光老化
光老化是微塑料环境老化最重要的过程[33]. 环境中微塑料的光老化本质上是聚合物碳链中的C—C、C—H等化学键吸收光能,从而直接断裂生成烷基自由基,随后引发的链式反应;光老化通过改变微塑料的化学结构和组成影响其极性、亲疏水性,并通过影响高分子链的排列改变微塑料的机械性能,诱导微塑料进一步破碎形成粒径更小的塑料颗粒,这也是环境中形成微塑料的重要途径. 光老化主要作用于微塑料表面,微塑料表面首先吸收紫外线,紫外线诱导聚合物链化学形态变化,导致链断裂和烷基自由基的形成,随后表面化学官能团解构和重组,从而分子量降低、表面氧化,最终形成惰性产物[3].
光老化过程通常分为3个步骤,分别是链引发、链传递和链终止(图2). 在链引发步骤中,C—C键(375 kJ·mol−1)和C—H键(420 kJ·mol−1)的键解离能相当于320 nm和290 nm处的紫外光能,因此,C—C和C—H键可以直接光解,生成烷基自由基(R· 初始自由基)[34]. 初始自由基(R·)一旦形成,就会迅速的增长、转移,进入链传递过程,而自氧化循环的传递反应对所有碳骨架聚合物都适用. 在链传递步骤中,R·首先与O2反应生成ROO·,ROO·从另一条聚合物链RH中提取氢原子生成氢过氧化物(ROOH),ROOH通过吸收光能裂解为·OH和RO·[35]. 随后RO·可以从RH中提取氢原子生成醇或者经电子离域β-裂解引起聚合物骨架链的断裂而生成酮[7, 34]. 在紫外线照射下,酮经过Norrish Ⅰ型反应生成R·和酰基(R—CO·)(自由基生成),或通过Norrish Ⅱ型反应生成末端羰基(R—CO—CH3)(链断裂)[23, 36]. 当双分子自由基结合或最终裂解形成酮、烯烃和醛等惰性产物时,链反应就会终止[37].
紫外线照射引发聚合物链骨架断裂并释放低分子量链片段,进而加速结构碎片化,导致介孔/微孔的产生和微塑料尺寸的减小[23]. 在半晶态聚合物中,光老化引发的断裂通常发生在无定形区域,导致老化后微塑料结晶度增加[38]. 此外,在模拟太阳光(光照强度分别比北纬0°和50°的自然太阳光高3倍和10倍)照射下,光老化可以使聚苯乙烯微塑料完全矿化成CO2[39].
(2)热老化
微塑料的热老化与光老化相似,都是聚合物链断裂后的氧化反应. 据估计,陆地环境中,深色干燥土壤的理论最高温度可达到90—100 ℃[40],在高温环境下,整个微塑料颗粒都会发生热老化,而光老化只发生在颗粒表面. 微塑料热老化的机制主要是高温有利于达到高分子化合物分子链间的化学键解离能,从而利于分子链的随机断裂和支链的脱落,生成烷基自由基(R·),随后进入自氧化循环(其过程类似于光老化)[7]. 温度是影响动力学反应速率的重要因素,高温可以加速微塑料的老化. 实验室人工老化箱模拟研究显示,随着温度的提高,微塑料薄膜的氧化程度更高,分子量、玻璃态转化温度和机械强度都显著下降,在60 ℃下,聚乳酸(PLA)薄膜的断裂伸长率在1周内便降低至初始值的一半,而在30 ℃下则需要15周[41]. 值得注意的是,自然界中的微塑料很少会经历单纯的高温热老化过程,热老化往往与光老化同时存在,温度的上升提高了紫外光照射下自由基类物质的生成速率,从而加速了微塑料的老化. 此外,自然界中普遍存在的干湿循环和冻融循环也伴随了热老化的过程,显著影响了微塑料的物理强度[42].
(3)其它因素导致的直接老化
环境中很多其它因素也会导致微塑料的直接老化,但相关研究较少. 例如环境中大量存在硫化物,硫离子可以与聚合物链中的C=C键发生亲核取代/加成反应,形成C—S键,进而硫化老化微塑料[43]. 此外,大气中臭氧会破坏不饱和聚合物的不饱和性,与聚合物碳链中C=C键、芳香环等直接加成,从而老化塑料[34]. 因此,即使臭氧浓度很低,也可能造成大气中微塑料的老化. 同时,在地下海底等极端环境中,高温高盐强酸强碱等作用可能导致微塑料的直接老化. 总的来说,目前对于这些环境因素导致微塑料直接老化机制的理解远远不及对光老化和热老化机制的认识,亟待进一步的研究.
-
水环境中,天然有机质(NOM)可在光照下与溶解氧反应生成大量活性氧(ROS,包括羟基自由基(·OH),超氧阴离子(O2·–)和单线态氧(1O2))[44],微塑料中的添加剂(塑料生产过程中会掺入光催化剂,以制备环境友好的可降解塑料)也会在光照下与氧气和水反应生成活性氧[45]. 活性氧具有强氧化能力,可通过与微塑料的作用,诱导微塑料聚合物碳链断裂,从而发生间接老化. 例如,羟基自由基(·OH)可进攻聚合物长链中叔碳原子上的C—H键(叔碳比伯碳和仲碳更活泼),生成烷基自由基(R·). 烷基自由基与氧气反应形成过氧自由基(ROO·)(R·与·OH的反应也可以形成ROO·,但与氧气的反应在热力学上更有利,因为与氧反应的活化能接近于零). 过氧自由基可以从聚合物分子(RH)中提取氢原子,形成氢过氧化物(ROOH)[36]. ROOH裂解脱去—OH生成烷氧基自由基(RO·)[34],RO·可以从聚合物分子(RH)中提取氢从而生成醇类化合物,或在电子离域作用下发生裂解,形成含有C=O和C=C键的化合物[23,36]. 研究显示,模拟太阳光照射下,微塑料的间接老化是导致其表面粗糙、粒径减小、生成大量含氧官能团的重要原因;在加入ROS淬灭剂抗坏血酸后,微塑料老化程度(以羰基指数作为老化程度指标)降低55.5%,老化作用被显著抑制,说明ROS在微塑料老化过程中起重要作用[46].
硫化物是一种亲核试剂和还原剂,生物硫酸盐还原和污水排放使得硫化物普遍存在于环境中[47-48]. 许多富含硫化物的环境(如河口、湖泊和河流沉积物)也是微塑料赋存的重要区域[11, 49-50].本课题组前期研究发现,硫化物诱导的老化是微塑料在自然环境中的重要老化途径[43]. 在中性pH值下,硫化物可在水溶液中自氧化形成超氧阴离子和过氧化氢[51-52]:
硫化物可以作为还原剂与H2O2反应,通过类芬顿反应生成·OH[53],从而促进了微塑料的表面氧化(图2). 硫化物诱导的间接老化可导致微塑料的脆化和开裂,颗粒粒径减小、比表面积的增加,硫化后热塑性聚氨酯(TPU)和聚苯乙烯(PS)的平均粒径分别降低了33.1%和27.3%,同时表面生成含氧官能团(C—O键、C=O键)和C—S键[43]. 有研究使用硫化钠处理聚酰胺(PA)、聚乙烯(PE)和聚苯乙烯(PS)3种微塑料,发现处理后的微塑料表面出现裂缝,比表面积和表面氧含量增加,其中处理后的PA和PS比表面积增加了3倍,PA羰基指数由0.05增长到0.14,3种材料玻璃态转化温度均降低[54],认为是其中硫化物诱导的间接老化起主要作用.
同时,本课题组发现,在硫化物诱导的老化过程中,自由基和小分子之间可能发生交联反应,这会导致聚合物分子量的增加[43]. 硫化体系中可能会出现多硫化物[55],多硫化物作为更强的还原剂,能促进分子氧的激活,加速老化反应. 微塑料硫化反应中C—S键的形成则是通过亲核取代/加成途径[56-57]. 微塑料首先被·OH氧化,在断链过程中生成C=C键,S2-或多硫化物作为亲核试剂进攻共轭双键形成巯基(图2)[43]. 与硫结合的氢原子比与碳结合的氢原子更倾向于与·OH反应[58],因此硫的加成进一步促进了聚合物的氧化.
-
生物作用是微塑料环境老化中的重要因素. 有关微塑料生物老化的研究目前主要集中在两个方面,一是微塑料被生物摄食后,生物体内特定的酶对微塑料的消化老化过程;二是微塑料进入自然环境后被水体中常见的生物质(如微生物群落、胞外聚合物等)覆盖形成生物膜的过程. 例如,用从蚯蚓肠道中分离出来的革兰氏阳性细菌与微塑料一起孵育21 d后,低密度聚乙烯(LDPE)的降解率可达60%,粒径从53.1—41.3 μm降至35.4—23.6 μm,甚至检测到纳米尺度颗粒[59]. 微生物定殖和生物膜的形成会改变微塑料的比表面积和含氧官能团(C—O和C=O)含量,进而影响其亲疏水性[60]. 微塑料表面生物膜的总量随其在水体中暴露时间显著增加,但随水深而减少[61].
-
微塑料被生物摄食进而被其体内的酶消化后,表面形貌、理化性质等会发生一系列的改变. 动物摄食过程中,微塑料会因动物咀嚼行为产生的物理应力而破碎,随后被吞食进入肠胃;某些动物的肠液、植物的根系中一些特定的酶能将微塑料作为其生长的能量基质进行消耗,使聚合物的分子链断裂、缩短、氧化(图2). 例如,南极磷虾可以通过咀嚼将摄入的微塑料(31.5 µm)破碎成直径小于1 µm的颗粒,并随粪便排出体内[62]. 黄粉虫可以啮食PS,并在24 h内将其降解矿化为CO2或同化为虫体脂肪[63]. 这一过程中,PS首先被黄粉幼虫咀嚼成细小碎片并摄入肠道中,所摄食的碎片在肠道微生物所分泌的胞外酶作用下,解聚成小分子产物,这些小分子产物在多种肠道细菌和黄粉幼虫自身酶的作用下,进一步降解并同化形成幼虫自身组织;残留的碎片与部分降解中间产物,混合肠道微生物,以虫粪的形态排泄出体内[64]. 100只黄粉虫每天可以摄入34—39 mg的PS,其中有47.7%被矿化为CO2,49.2%被老化为微纳米塑料并随粪便排出. 将PE与Zalerion maritimum(一种真菌)培养28 d后,微塑料表面出现不规则断裂,同时表面发生氧化反应,生成羟基羰基等含氧官能团,羟基含量(红外光谱3700—3000 cm−1处峰面积)由原始的1±1增长到了57±2,羰基含量(红外光谱1700—1500 cm−1处峰面积)由原始的0.2±0.3增长到了1±1[65].
-
为适应不同生存环境,微生物进化出了各种附着机制[66]. 微塑料具有较大的比表面积,微生物群落很容易在其表面附着增殖,黏附并形成生物膜[60, 67]. 微塑料表面的生物膜形成主要分为3个阶段:(1)环境中的生物质和生物群落在范德华力和静电引力的作用下吸附在微塑料的表面,形成微生物有机质层;(2)吸附在微塑料表面的微生物群落释放出胞外聚合物(EPS),形成对微生物群落具有保护效应的EPS层;(3)微塑料表面微生物群落大量增殖,形成复杂的生物膜结构[66]. 在微塑料表面形成生物膜的微生物群落(藻类、真菌、细菌)组成随水体环境条件(pH值、盐度、温度、营养元素)和微塑料表面性质(种类、颜色、粗糙度)的不同而不同,其中细菌是最常被观测到的微生物种类[68]. 例如,在盐度26‰的水体中,定殖在微塑料表面的弧菌丰度是海水和沉积物中的2—10倍,而在盐度小于18‰的水体中,微塑料表面、海水、沉积物中弧菌的丰度没有区别;同时,PS表面生物量显著高于PVC、PP、PE和TPU[69]. 生物膜的形成可显著改变微塑料的理化性质,包括:(1)改变其表面形貌,导致比表面积显著的增大,也可增加其表面的粗糙度;(2)改变其硬度和结晶度;(3)改变其密度,从而影响其在水体中的纵向分布;(4)改变其表面官能团,C—O、C=O含量上升,进而影响其亲疏水性[70]. 研究显示,在海水中原位老化6个月的4种微塑料纤维表面形成了生物膜,表面含氧官能团增多,并出现了多糖类化合物,其中PE的比表面积由(0.38±0.06) m2 g−1增加至(0.65±0.08) m2 g−1,微孔直径由0.76 nm增加至0.95 nm[60].
-
微塑料在进入环境后可能会经历其它老化过程,其中微塑料对腐殖质等天然有机质(NOM)的吸附受到了广泛关注. 微塑料可以通过疏水作用、静电作用、π-π相互作用等吸附水中的NOM[71],其作用机制和效应与微塑料对EPS的吸附类似. 微塑料吸附NOM后,表面形貌和理化性质显著改变,进而影响其环境效应. 原始PS微塑料颗粒表面光滑,NOM吸附后PS表面粗糙,粒径增大,表面含氧官能团增加[72]. 天然有机质包覆在微塑料表面后增加了微塑料表面电负性,从而加强静电斥力,增强了颗粒稳定性[73]. 一些综述也关注到了腐殖质对微塑料的老化[3,20],未来仍需进一步系统的探索不同类型微塑料与腐殖质不同组分之间的相互作用.
-
目前研究微塑料环境老化的手段主要有两种,一种是从环境中(如海滩[74]、农田[73]、河流[75]等)直接采集老化的微塑料颗粒开展研究,另一种是人工模拟老化过程,获得老化微塑料进行研究. 人工模拟老化又分为原位自然老化和实验室加速老化[19-20]:原位自然老化是指将购买或制备的微塑料颗粒置于特定自然环境中,老化后回收以进一步研究[60],例如有研究使用长江和太湖的天然水样制备微塑料悬浮液,将其置于屋顶暴露于阳光下5至11个月[45]. 实验室加速老化是指通过机械力磨损、紫外灯照射、化学氧化等方式加速老化微塑料. 例如,有研究将海滩沙砾与微塑料颗粒混合振荡两个月以模拟物理老化过程[22]. 大量研究选择氙灯、汞灯等光源模拟环境中微塑料的光老化[46, 76-77]. 也有很多研究利用Fenton反应和过氧化氢等高级氧化手段,模拟微塑料在活性氧作用下的化学老化[45, 78]. 近期一项研究对比了实验室加速老化与原位自然老化微塑料的性质差异,发现经过高温、紫外、臭氧和超声组合手段老化后的PS微塑料与在室外阳光照射老化11个月的微塑料颗粒表面形貌与理化性质相似,表明多种实验室加速老化手段的综合应用能够较好地评估环境中微塑料的老化过程[79].
-
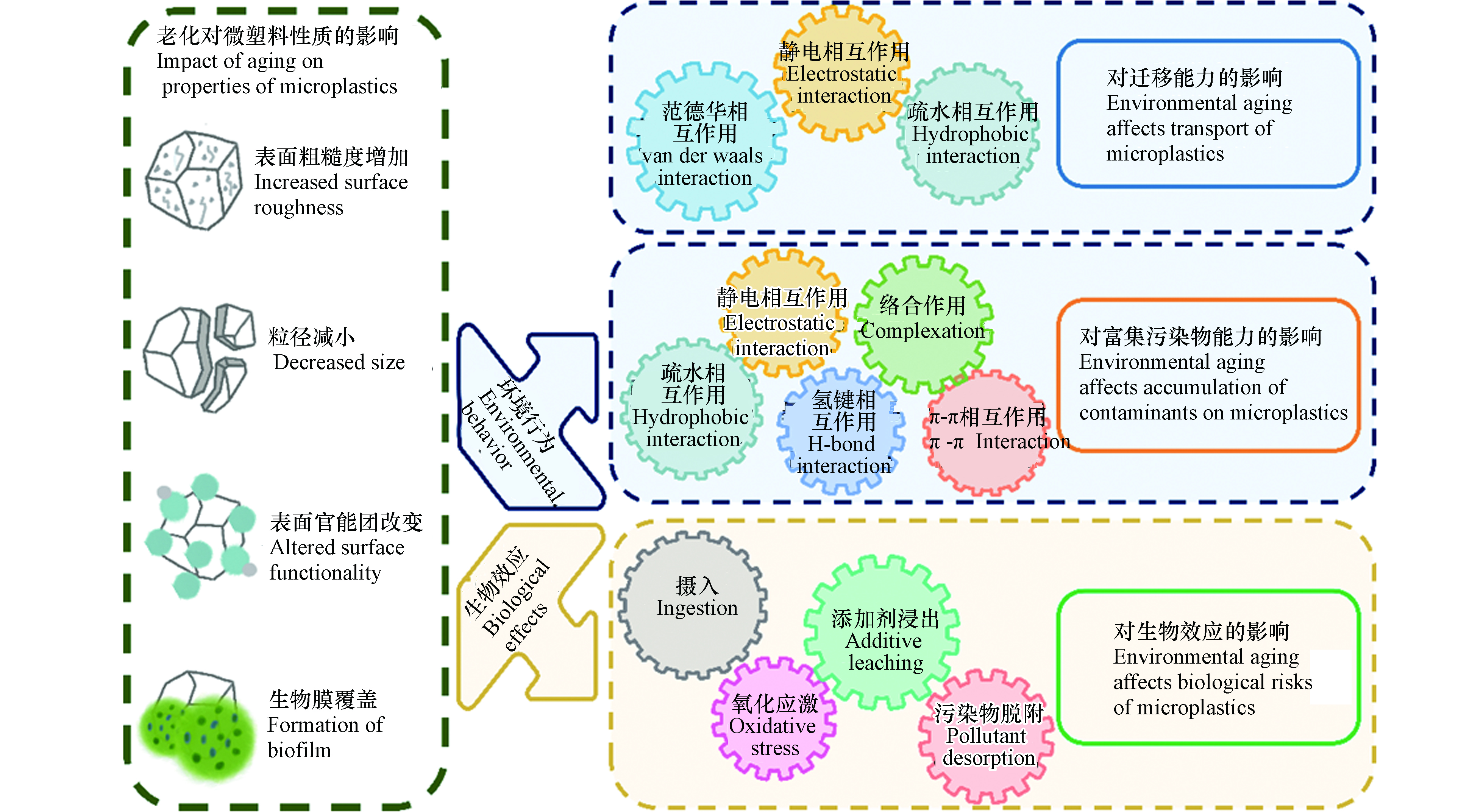
环境老化可改变微塑料的表观形貌、分子结构及化学组成等理化性质,从而显著影响其环境行为和生物效应(如图3所示).
-
微塑料可在环境中长期存在,具有较强的迁移能力. 环境老化过程会显著改变微塑料的物理化学性质,使得微塑料粒径减小、表面含氧官能团增加,影响了其与环境介质间的相互作用,进而显著影响了微塑料的迁移能力(图3). 老化后微塑料粒径的减小会削弱微塑料与多孔介质间的范德华力,微塑料在多孔介质中沉积减弱,迁移能力增强. 在农田自然老化所形成的小尺寸颗粒(15—30 µm)在天然土壤介质中具有更强的向下迁移能力[73]. 老化后微塑料表面含氧官能团含量增加,电负性增强,与带负电的多孔介质间的静电斥力增大,导致微塑料在多孔介质上的沉积减弱,有助于提升迁移能力. 例如,紫外老化的微塑料表面羧基官能团增加,羧基去质子化使其带有更多的负电荷,与带负电的石英砂介质之间静电斥力增大,迁移能力增强[80]. 此外,老化后微塑料表面含氧官能团的增加会显著增加微塑料的亲水性,进而影响其迁移行为. 例如,在背景溶液为0.5 mmol·L−1 NaCl中,原始PS最大穿透率约为43.3%,经紫外(UV)老化后的PS最大穿透率显著提高至90.7%;UV老化后的PS表面含氧官能团增加,这不仅增加了微塑料的表面电负性,还增强了其亲水性,亲水性的增强是老化PS迁移能力增强的关键因素[25]. 值得注意的是,老化后微塑料表面含氧官能团的增加也会导致其在Ca2+等阳离子条件中桥联作用的增加,这可能在一定程度上抑制老化微塑料的迁移能力.
-
老化过程可导致微塑料吸附污染物的能力发生明显变化. 老化后微塑料的表面更粗糙,出现裂缝和孔隙,粒径减小,比表面积增大;同时,生成的官能团改变了微塑料表面的电负性、极性和亲疏水性,从而影响了静电相互作用、疏水相互作用、π-π相互作用、氢键和络合作用等多种作用机制,进而改变了微塑料富集污染物的能力(图3). 首先,微塑料的吸附容量与比表面积呈正相关,老化后的微塑料产生裂纹或破碎为更小的碎片,粒径减小、比表面积增加,有效吸附位点增多从而具有更强的吸附能力. 例如,紫外照射导致PET微塑料比表面积增大,暴露出更多的有效吸附位点,对Cu2+的吸附能力是原始微塑料的2倍[81]. 其次,老化后微塑料表面生成了含氧官能团,表面氧碳比(O/C)增高,亲水性增加,这将抑制对疏水性污染物的吸附,增强对亲水性污染物的吸附[82-83]. 老化微塑料表面官能团的变化还会影响其与污染物之间的极性作用,增强氢键在吸附过程中的贡献从而改变微塑料的吸附能力. 例如,高温老化的PS表面因交联和断链产生的大量含氧官能团(羧酸、酮和内酯),增强了微塑料与抗生素之间的氢键作用,从而增加吸附容量;而老化后PS与周围的水分子间氢键作用的增强,降低了PS表面吸附位点的可利用性,极大地抑制了多环芳烃的吸附[84]. 在海水中原位老化6个月的微塑料纤维对铅(Pb2+)吸附能力增加4%—25%,这是由于老化后微塑料表面覆盖生物膜,生成的大量含氧官能团可以与Pb2+结合形成金属络合物,提高了吸附能力[60]. 一些带电污染物和微塑料之间的吸附主要由静电相互作用主导[85],老化过程增加了微塑料表面的负电荷,这将增强静电相互作用在吸附过程中的重要性[86]. 例如,自然老化的微塑料表面附着大量有机质,增强了微塑料表面负电荷,有利于对重金属阳离子Pb2+的静电吸引[86]. π-π相互作用是含有苯环的微塑料与芳香族化合物相互作用的主要机制,由于链断裂,老化过程可能会削弱π-π相互作用[3]. 例如,紫外照射后的PS聚合物链断裂、苯环脱落,导致π-π相互作用在PS和双酚A(BPA)的结合中减弱,老化PS对BPA的吸附能力下降[87]. 值得注意的是,微塑料吸附污染物的能力取决于不同吸附机制的整体贡献,而老化对不同机制的影响不尽相同,因此对于吸附的总体影响往往比较复杂[24],应进一步研究微塑料的结构、老化过程、老化程度对不同污染物的吸附贡献率,探明老化影响微塑料吸附行为的主控因子.
-
微塑料具有较强的胶体稳定性和迁移能力,因此,吸附了污染物之后,可作为载体促进污染物在环境中的运移[88-89]. 微塑料对污染物的载带能力主要取决于3个方面,一是微塑料自身的迁移能力,二是微塑料吸附富集污染物的能力,三是污染物在微塑料上发生不可逆吸附或解吸滞后的程度[90-91]. 前面已提到老化可显著影响微塑料的迁移能力和吸附污染物的能力[73, 92]. 与此同时,环境老化所引发的理化性质变化可显著影响微塑料上有机污染物的解吸行为,进而改变微塑料载带污染物迁移的能力. 首先,老化导致微塑料表面微裂纹、微孔体积增多,这一效应增强了非极性有机污染物在微塑料内部孔隙中的“孔填充”效应,不可逆吸附和解吸迟滞程度明显增强,更易于随微塑料迁移[25]. 其次,老化后微塑料表面羟基、羧基等表面含氧官能团的增多,可提升微塑料与极性有机污染物之间的氢键等极性相互作用,也会导致污染物的不可逆吸附程度的增强[25]. 上述两种效应均使得污染物与微塑料结合得更加紧密,更易随微塑料在环境中迁移.
-
作为一种新兴污染物,微塑料对环境中生物体影响越来越受到重视[93]. 环境老化后微塑料粒径减小,表面覆盖丰富的生物膜,可导致生物体摄入微塑料方式和数量的改变[3]. 塑料在制造过程中掺入了各种添加剂,相比于微塑料本身,添加剂的释放可能对生态安全构成更大的威胁[94],老化促进了微塑料内有毒添加剂的浸出,增强了其毒性效应. 同时,老化显著改变了微塑料富集污染物的能力,随着生物摄食行为,微塑料可将污染物载带至生物体中,促进了污染物的生物摄入.
许多生物体对食物选择有偏好,例如大小,形状等[95],老化后形成的较小的微塑料颗粒甚至是纳米塑料,更容易被生物体(尤其是贻贝和牡蛎幼虫等无脊椎动物)摄入[96]. 不同大小的PS微塑料在斑马鱼体内的摄取和积累位置不同,7 d暴露实验显示,直径为5 μm的PS主要积累在鱼的鳃、肝和肠中,而直径为20 μm的PS颗粒仅积累在鳃和肠道中;积聚在鱼肝中的较小的微塑料颗粒会诱导氧化应激和鱼肝脏代谢组学的改变[97]. 一般情况下,较小的微塑料颗粒更有可能被生物体摄入,并且在组织中分布更广,毒性更大[98]. 生物膜在微塑料上的形成可影响生物体的感知,在较低或较高的营养级,覆盖生物膜的微塑料的生物可利用性均更强,也更容易被生物体摄食[99-100]. 在海水中自然老化3周的微塑料,表面形成的生物膜掩盖了微塑料的惰性,并散发出化学信号使其更类似于食物颗粒,导致浮游动物对微塑料的摄入增加[99].
环境老化促进了微塑料中添加剂、中间体的浸出,增加了微塑料的生态风险[24, 101]. 例如,老化加速了商业微塑料中含有铬和铅的染料的释放,中性条件下在12 h内原始PE中Cr(Ⅵ)和Pb(Ⅱ)的浸出量分别为0.8 μg·g−1和1.7 μg·g−1,紫外老化后微塑料中两者的浸出量分别提高到了3.0 μg·g−1和11.9 μg·g−1. 相比于原始微塑料,老化微塑料的渗滤液更加抑制了铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)细胞生长和光合作用[101]. 另一研究表明,紫外线照射诱导了PS中的内源性污染物的浸出,原始PS的渗滤液中没有检测出添加剂,紫外线照射60 d后,老化PS渗滤液中检测到了邻苯二甲酸酯类化合物,其积聚在石斑鱼的肝脏脂肪中,造成了生长抑制和肝脏病变[23]. 老化后微塑料可富集更多污染物,增强了其毒性效应. 例如,在溪流中自然老化4周的PE微塑料,表面出现生物膜,对银离子(Ag)吸附量增加了44%;吸附到老化微塑料上的Ag在Steinberg培养基(通常用于培养淡水浮萍)中释放量为247.5 μg·L−1,显著高于原始微塑料(73.5 μg·L−1)[102]. 紫外老化微塑料吸附了更多的罗红霉素,使其在鲫鱼肠道内积累更多,进而导致了更严重的肠道内炎细胞浸润和纤毛受损,抑制了消化酶活性,并扰乱了肠道菌群,造成了代谢紊乱[103].
-
综上所述,微塑料在自然环境中会经历复杂的物理、化学和生物老化过程. 物理老化是机械力作用下微塑料表面裂纹的产生与扩展,从而导致颗粒破碎,有利于化学和生物因素的进一步作用. 化学老化是在紫外线、高温、活性氧等作用下,微塑料化学键断裂进而导致表面化学组成改变的过程. 生物老化是微塑料在生物作用下的破碎同化,微生物也可通过附着机制在其表面形成生物膜. 老化后微塑料的表面形貌、分子结构及化学组成等物理化学性质发生显著改变,不仅影响其自身环境行为,也改变了微塑料与环境介质中的生命和非生命体的相互作用. 因此,老化是评价微塑料环境行为和生物效应中不可忽视的重要因素.为了系统的认识与评价微塑料的环境老化过程和效应机制,亟需在以下几方面开展深入研究:(1)目前微塑料老化的实验研究中,主要是采用单一人工加速老化手段模拟自然老化过程,如机械研磨、紫外辐射、活性氧进攻等. 微塑料在真实环境中的老化,往往受到多种因素共同作用,单一老化手段可能不足以代表真实的环境老化过程. 因此,在实验室模拟老化研究中,更应关注多个老化过程对其的综合影响,缩小实验室模拟手段与环境自然老化过程之间的差距. (2)微塑料性质迥异,环境老化过程复杂,当前更多是定性研究老化机制,应进一步量化微塑料环境老化程度;明确老化微塑料性质变化对其环境行为的贡献,系统研究与开发微塑料不同类型-老化程度-性质变化-环境效应改变之间的关系曲线与预测模型,实现对微塑料的环境风险预测和评估. (3)微塑料与环境大分子如天然有机质、蛋白质、多糖和其他表面活性物质之间的相互作用值得关注,包括探究微塑料与天然有机质不同组分之间发生选择性吸附的作用机制和影响因素,以及微塑料-NOM复合物的环境行为和毒性机制. (4)目前实验室研究对象主要是微塑料颗粒和碎片,应加强对环境中大量检出的微塑料超细纤维和薄膜的老化过程及效应探索.(5)针对微塑料老化所引发的环境行为和效应变化的研究总体集中在光降解老化微塑料,应关注其他老化过程后所引起的效应变化与机制. (6)目前微塑料老化相关研究主要集中在天然水、土壤环境中,工程系统同样是微塑料的重要赋存环境,对于其中的老化过程,目前还鲜有研究. 因此应加强对污水处理厂和垃圾填埋场中微塑料老化的深入研究,例如水处理中的化学老化和固废处理中的热老化,以及自然条件下微塑料在垃圾渗滤液中的原位老化等.
微塑料的环境老化机制及效应研究进展
Environmental aging of microplastic: Processes, mechanisms and implications
-
摘要: 微塑料通常是指尺寸小于5 mm的塑料颗粒. 环境中微塑料的来源主要包括微米尺度塑料的直接排放,以及大块塑料制品的降解破碎. 微塑料在环境中的存在和富集对人体健康和生态环境产生严重危害,微塑料污染问题已在全球范围内引起广泛关注. 环境中的微塑料可在机械力、紫外线、高温、化学物质和生物等多种因素的作用下发生复杂的物理、化学和生物老化,导致微塑料表观形貌、分子结构及化学组成等理化性质的改变,进而显著影响其迁移特征、富集和载带污染物的能力,以及对生物体的毒性效应机制. 本文综述了微塑料在环境因子作用下可能发生的物理化学性质变化以及相应的老化机制,分析了老化对微塑料环境行为和效应的影响,指出了未来研究应更加关注微塑料在真实环境下的老化过程,量化老化程度,建立老化对微塑料环境效应影响的关系曲线并开发预测模型.Abstract: Microplastics, commonly referring to plastic particles ≤ 5 mm in size, can enter the environment either from direct release of micro-sized plastics contained in consumer products, or from the degradation and fragmentation of bulk plastic debris. The wide spread of microplastics in the environment poses serious risks to human health and ecological environment, and thus, has become an increasing environmental concern. In natural environments microplastics can undergo various chemical, physical and biological transformation, as affected by mechanical forces, ultraviolet irradiation, high temperature, as well as chemical and biological stresses. Environmental transformation can markedly affect the morphology, molecular structure and chemical compositions of microplastics, which in turn affect their transport, affinities for contaminants, and toxicity. In this paper we summarize the physicochemical changes of microplastics due to environmental aging processes, the underlying mechanisms, and the effects on their environmental behaviors and implications. We propose that future research should focus on understanding aging processes of microplastics in realistic environments, and on developing correlations and models for quantifying the extents of aging due to environmental stresses.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- aging /
- environmental implications /
- transport /
- contaminant accumulation /
- toxicity effects
-
塑料因其重量轻、耐腐蚀、化学性质稳定等优点,被广泛应用于人类生产生活[1]. 目前所生产的塑料中,有近80%最终会成为塑料垃圾,被掩埋或堆积在环境中[2]. 环境里的塑料垃圾中有相当大的一部分是直径或长度小于5 mm的颗粒,也被称为微塑料[3]. 微塑料的来源包括较大尺寸塑料垃圾的分解、破碎,以及微米尺寸塑料颗粒的直接生产、使用和处置[4]. 目前针对环境微塑料污染的研究主要集中在陆地环境和水环境. 陆地环境中的微塑料主要来源于垃圾填埋场中塑料制品的破碎、污泥农用、农业地膜破碎和汽车轮胎磨损[5-6]. 水环境中的微塑料主要来源于污水处理厂排放、渔业活动以及船舶运输业释放[7-8]. 微塑料广泛分布在土壤、海洋、河流、湖泊等环境介质中,即便在偏远地区(如极地、高山、深海沉积物中)也均有检出[9-12]. 据估算,陆地环境中每年新增的微塑料超过43万吨[6],而海洋中至少漂浮着5.3万亿个微塑料颗粒[13]. 微塑料易被生物体吞食,诱导氧化应激和炎症反应进而引发颗粒毒性,从而造成肝脏、肾脏、胃肠道等器官损伤[14-15]. 同时,微塑料在生产过程中会混入大量添加剂,例如邻苯二甲酸酯、多溴联苯醚等;生物体摄食微塑料可导致添加剂在体内的释放和积累,进而引发化学毒性,显著抑制生物生长和早期发育[16-17]. 此外,微塑料粒径较小、比表面积较大,进入环境后可成为众多有机污染物、重金属以及微生物的载体,促进了这些污染物的生物富集,造成严重的生态和健康风险[18]. 因此,环境中微塑料的大量存在及其环境风险近年来已在全球范围内引起了广泛关注.
环境中的微塑料可在机械力、紫外线、高温、化学物质和生物等环境因素作用下发生一系列的物理、化学和生物老化[7, 19-22]. 环境老化使得微塑料表面形貌和理化性质发生改变,进而影响微塑料迁移和吸附污染物的能力,改变生物体摄入微塑料的方式和程度. 同时,老化增加了微塑料中添加剂向环境中释放的风险,增强了毒性效应[23-25]. 因此,研究微塑料的环境老化及由此产生的效应具有重要意义. 本文通过综述国内外微塑料环境老化研究的最新进展,总结了物理、化学和生物老化的主要过程与机制,分析了老化对微塑料的环境行为和效应的影响.
1. 微塑料的环境老化机制(Mechanisms controlling environmental aging of microplastics)
微塑料广泛分布在自然环境中,可在机械力、紫外光、高温、化学物质、生物等因素作用下发生老化,其表面形貌和理化性质均可发生变化(图1). 明确微塑料的老化机制对于理解其环境行为和风险至关重要. 本文从物理、化学和生物的3个方面阐述了微塑料在环境中的老化过程及机制(图2).
1.1 物理老化
进入环境中的微塑料会受到周围环境力的机械作用,如湍流、波浪、沙砾或岩石碰撞及周围塑料碎片的碰撞等,从而发生表面开裂,破碎形成更多小尺寸的微塑料[26],所生成的塑料颗粒数量随尺寸的减小而增加[22]. 有研究显示,从磨砂膏中提取的粒径为398 nm的原生微塑料,可在模拟湍流作用下破碎为50 nm的微塑料颗粒,甚至出现了纳米塑料(<10 nm)[27]. 对海滩中采集到的塑料碎片进行分析发现,物理老化是微塑料表面纹理形成的主要原因,碰撞过程中塑料颗粒棱角会变成近圆形状,同时出现裂缝和凹坑[28]. 同时,已老化的塑料表面更易受沙子磨损等机械力作用而破裂[29]. 微塑料在机械力作用下表面产生裂纹,从而裂纹扩展,进而导致了微塑料颗粒的破碎[27, 30]. 相关研究使用Grady模型来描述微塑料在应力作用和裂纹扩展下的破碎,证明了裂纹在微塑料物理老化中发挥了决定性作用,裂纹越长,扩展时所需最小应力越低,因此,表面有裂纹的微塑料在剪切力的作用下更容易破碎、剥落成更小的颗粒[27]. 自然环境中的微塑料在土壤颗粒、沙砾磨损,海浪、潮汐碰撞等自然机械力作用下,原有的表面形貌被破坏、破碎并形成更多的裂缝,呈现更高的比表面积. 同时,物理老化有利于各种化学物质通过微塑料表面的孔隙和裂纹进入内部,并促进微塑料的进一步老化.
1.2 化学老化
微塑料可在紫外线、高温、活性氧等作用下发生化学老化. 在实验室模拟或自然条件下,老化后微塑料的表面整体呈现粗糙度增加,出现裂纹和缝隙,伴随片状、颗粒状碎片脱落,粒径减小,孔隙度和比表面积增大. 老化后的微塑料往往表面羟基、羰基等含氧官能团含量增高,表面亲水性增强[3, 31-32]. 微塑料化学老化的作用机制可大致分为直接老化和间接老化:直接老化是指紫外光或高温作用使得微塑料聚合物碳键直接断裂及由此引发的一系列变化;间接老化是指活性氧物种等化学物质参与导致化学键断裂而发生的系列化学反应.
1.2.1 直接老化
(1)光老化
光老化是微塑料环境老化最重要的过程[33]. 环境中微塑料的光老化本质上是聚合物碳链中的C—C、C—H等化学键吸收光能,从而直接断裂生成烷基自由基,随后引发的链式反应;光老化通过改变微塑料的化学结构和组成影响其极性、亲疏水性,并通过影响高分子链的排列改变微塑料的机械性能,诱导微塑料进一步破碎形成粒径更小的塑料颗粒,这也是环境中形成微塑料的重要途径. 光老化主要作用于微塑料表面,微塑料表面首先吸收紫外线,紫外线诱导聚合物链化学形态变化,导致链断裂和烷基自由基的形成,随后表面化学官能团解构和重组,从而分子量降低、表面氧化,最终形成惰性产物[3].
光老化过程通常分为3个步骤,分别是链引发、链传递和链终止(图2). 在链引发步骤中,C—C键(375 kJ·mol−1)和C—H键(420 kJ·mol−1)的键解离能相当于320 nm和290 nm处的紫外光能,因此,C—C和C—H键可以直接光解,生成烷基自由基(R· 初始自由基)[34]. 初始自由基(R·)一旦形成,就会迅速的增长、转移,进入链传递过程,而自氧化循环的传递反应对所有碳骨架聚合物都适用. 在链传递步骤中,R·首先与O2反应生成ROO·,ROO·从另一条聚合物链RH中提取氢原子生成氢过氧化物(ROOH),ROOH通过吸收光能裂解为·OH和RO·[35]. 随后RO·可以从RH中提取氢原子生成醇或者经电子离域β-裂解引起聚合物骨架链的断裂而生成酮[7, 34]. 在紫外线照射下,酮经过Norrish Ⅰ型反应生成R·和酰基(R—CO·)(自由基生成),或通过Norrish Ⅱ型反应生成末端羰基(R—CO—CH3)(链断裂)[23, 36]. 当双分子自由基结合或最终裂解形成酮、烯烃和醛等惰性产物时,链反应就会终止[37].
紫外线照射引发聚合物链骨架断裂并释放低分子量链片段,进而加速结构碎片化,导致介孔/微孔的产生和微塑料尺寸的减小[23]. 在半晶态聚合物中,光老化引发的断裂通常发生在无定形区域,导致老化后微塑料结晶度增加[38]. 此外,在模拟太阳光(光照强度分别比北纬0°和50°的自然太阳光高3倍和10倍)照射下,光老化可以使聚苯乙烯微塑料完全矿化成CO2[39].
(2)热老化
微塑料的热老化与光老化相似,都是聚合物链断裂后的氧化反应. 据估计,陆地环境中,深色干燥土壤的理论最高温度可达到90—100 ℃[40],在高温环境下,整个微塑料颗粒都会发生热老化,而光老化只发生在颗粒表面. 微塑料热老化的机制主要是高温有利于达到高分子化合物分子链间的化学键解离能,从而利于分子链的随机断裂和支链的脱落,生成烷基自由基(R·),随后进入自氧化循环(其过程类似于光老化)[7]. 温度是影响动力学反应速率的重要因素,高温可以加速微塑料的老化. 实验室人工老化箱模拟研究显示,随着温度的提高,微塑料薄膜的氧化程度更高,分子量、玻璃态转化温度和机械强度都显著下降,在60 ℃下,聚乳酸(PLA)薄膜的断裂伸长率在1周内便降低至初始值的一半,而在30 ℃下则需要15周[41]. 值得注意的是,自然界中的微塑料很少会经历单纯的高温热老化过程,热老化往往与光老化同时存在,温度的上升提高了紫外光照射下自由基类物质的生成速率,从而加速了微塑料的老化. 此外,自然界中普遍存在的干湿循环和冻融循环也伴随了热老化的过程,显著影响了微塑料的物理强度[42].
(3)其它因素导致的直接老化
环境中很多其它因素也会导致微塑料的直接老化,但相关研究较少. 例如环境中大量存在硫化物,硫离子可以与聚合物链中的C=C键发生亲核取代/加成反应,形成C—S键,进而硫化老化微塑料[43]. 此外,大气中臭氧会破坏不饱和聚合物的不饱和性,与聚合物碳链中C=C键、芳香环等直接加成,从而老化塑料[34]. 因此,即使臭氧浓度很低,也可能造成大气中微塑料的老化. 同时,在地下海底等极端环境中,高温高盐强酸强碱等作用可能导致微塑料的直接老化. 总的来说,目前对于这些环境因素导致微塑料直接老化机制的理解远远不及对光老化和热老化机制的认识,亟待进一步的研究.
1.2.2 间接老化
水环境中,天然有机质(NOM)可在光照下与溶解氧反应生成大量活性氧(ROS,包括羟基自由基(·OH),超氧阴离子(O2·–)和单线态氧(1O2))[44],微塑料中的添加剂(塑料生产过程中会掺入光催化剂,以制备环境友好的可降解塑料)也会在光照下与氧气和水反应生成活性氧[45]. 活性氧具有强氧化能力,可通过与微塑料的作用,诱导微塑料聚合物碳链断裂,从而发生间接老化. 例如,羟基自由基(·OH)可进攻聚合物长链中叔碳原子上的C—H键(叔碳比伯碳和仲碳更活泼),生成烷基自由基(R·). 烷基自由基与氧气反应形成过氧自由基(ROO·)(R·与·OH的反应也可以形成ROO·,但与氧气的反应在热力学上更有利,因为与氧反应的活化能接近于零). 过氧自由基可以从聚合物分子(RH)中提取氢原子,形成氢过氧化物(ROOH)[36]. ROOH裂解脱去—OH生成烷氧基自由基(RO·)[34],RO·可以从聚合物分子(RH)中提取氢从而生成醇类化合物,或在电子离域作用下发生裂解,形成含有C=O和C=C键的化合物[23,36]. 研究显示,模拟太阳光照射下,微塑料的间接老化是导致其表面粗糙、粒径减小、生成大量含氧官能团的重要原因;在加入ROS淬灭剂抗坏血酸后,微塑料老化程度(以羰基指数作为老化程度指标)降低55.5%,老化作用被显著抑制,说明ROS在微塑料老化过程中起重要作用[46].
硫化物是一种亲核试剂和还原剂,生物硫酸盐还原和污水排放使得硫化物普遍存在于环境中[47-48]. 许多富含硫化物的环境(如河口、湖泊和河流沉积物)也是微塑料赋存的重要区域[11, 49-50].本课题组前期研究发现,硫化物诱导的老化是微塑料在自然环境中的重要老化途径[43]. 在中性pH值下,硫化物可在水溶液中自氧化形成超氧阴离子和过氧化氢[51-52]:
HS−+O2→HS⋅+⋅O−2 (1) HS⋅+⋅O−2→S+HO−2 (2) HO−2+H+→H2O2 (3) 硫化物可以作为还原剂与H2O2反应,通过类芬顿反应生成·OH[53],从而促进了微塑料的表面氧化(图2). 硫化物诱导的间接老化可导致微塑料的脆化和开裂,颗粒粒径减小、比表面积的增加,硫化后热塑性聚氨酯(TPU)和聚苯乙烯(PS)的平均粒径分别降低了33.1%和27.3%,同时表面生成含氧官能团(C—O键、C=O键)和C—S键[43]. 有研究使用硫化钠处理聚酰胺(PA)、聚乙烯(PE)和聚苯乙烯(PS)3种微塑料,发现处理后的微塑料表面出现裂缝,比表面积和表面氧含量增加,其中处理后的PA和PS比表面积增加了3倍,PA羰基指数由0.05增长到0.14,3种材料玻璃态转化温度均降低[54],认为是其中硫化物诱导的间接老化起主要作用.
同时,本课题组发现,在硫化物诱导的老化过程中,自由基和小分子之间可能发生交联反应,这会导致聚合物分子量的增加[43]. 硫化体系中可能会出现多硫化物[55],多硫化物作为更强的还原剂,能促进分子氧的激活,加速老化反应. 微塑料硫化反应中C—S键的形成则是通过亲核取代/加成途径[56-57]. 微塑料首先被·OH氧化,在断链过程中生成C=C键,S2-或多硫化物作为亲核试剂进攻共轭双键形成巯基(图2)[43]. 与硫结合的氢原子比与碳结合的氢原子更倾向于与·OH反应[58],因此硫的加成进一步促进了聚合物的氧化.
1.3 生物老化
生物作用是微塑料环境老化中的重要因素. 有关微塑料生物老化的研究目前主要集中在两个方面,一是微塑料被生物摄食后,生物体内特定的酶对微塑料的消化老化过程;二是微塑料进入自然环境后被水体中常见的生物质(如微生物群落、胞外聚合物等)覆盖形成生物膜的过程. 例如,用从蚯蚓肠道中分离出来的革兰氏阳性细菌与微塑料一起孵育21 d后,低密度聚乙烯(LDPE)的降解率可达60%,粒径从53.1—41.3 μm降至35.4—23.6 μm,甚至检测到纳米尺度颗粒[59]. 微生物定殖和生物膜的形成会改变微塑料的比表面积和含氧官能团(C—O和C=O)含量,进而影响其亲疏水性[60]. 微塑料表面生物膜的总量随其在水体中暴露时间显著增加,但随水深而减少[61].
1.3.1 生物摄食消化
微塑料被生物摄食进而被其体内的酶消化后,表面形貌、理化性质等会发生一系列的改变. 动物摄食过程中,微塑料会因动物咀嚼行为产生的物理应力而破碎,随后被吞食进入肠胃;某些动物的肠液、植物的根系中一些特定的酶能将微塑料作为其生长的能量基质进行消耗,使聚合物的分子链断裂、缩短、氧化(图2). 例如,南极磷虾可以通过咀嚼将摄入的微塑料(31.5 µm)破碎成直径小于1 µm的颗粒,并随粪便排出体内[62]. 黄粉虫可以啮食PS,并在24 h内将其降解矿化为CO2或同化为虫体脂肪[63]. 这一过程中,PS首先被黄粉幼虫咀嚼成细小碎片并摄入肠道中,所摄食的碎片在肠道微生物所分泌的胞外酶作用下,解聚成小分子产物,这些小分子产物在多种肠道细菌和黄粉幼虫自身酶的作用下,进一步降解并同化形成幼虫自身组织;残留的碎片与部分降解中间产物,混合肠道微生物,以虫粪的形态排泄出体内[64]. 100只黄粉虫每天可以摄入34—39 mg的PS,其中有47.7%被矿化为CO2,49.2%被老化为微纳米塑料并随粪便排出. 将PE与Zalerion maritimum(一种真菌)培养28 d后,微塑料表面出现不规则断裂,同时表面发生氧化反应,生成羟基羰基等含氧官能团,羟基含量(红外光谱3700—3000 cm−1处峰面积)由原始的1±1增长到了57±2,羰基含量(红外光谱1700—1500 cm−1处峰面积)由原始的0.2±0.3增长到了1±1[65].
1.3.2 生物膜覆盖
为适应不同生存环境,微生物进化出了各种附着机制[66]. 微塑料具有较大的比表面积,微生物群落很容易在其表面附着增殖,黏附并形成生物膜[60, 67]. 微塑料表面的生物膜形成主要分为3个阶段:(1)环境中的生物质和生物群落在范德华力和静电引力的作用下吸附在微塑料的表面,形成微生物有机质层;(2)吸附在微塑料表面的微生物群落释放出胞外聚合物(EPS),形成对微生物群落具有保护效应的EPS层;(3)微塑料表面微生物群落大量增殖,形成复杂的生物膜结构[66]. 在微塑料表面形成生物膜的微生物群落(藻类、真菌、细菌)组成随水体环境条件(pH值、盐度、温度、营养元素)和微塑料表面性质(种类、颜色、粗糙度)的不同而不同,其中细菌是最常被观测到的微生物种类[68]. 例如,在盐度26‰的水体中,定殖在微塑料表面的弧菌丰度是海水和沉积物中的2—10倍,而在盐度小于18‰的水体中,微塑料表面、海水、沉积物中弧菌的丰度没有区别;同时,PS表面生物量显著高于PVC、PP、PE和TPU[69]. 生物膜的形成可显著改变微塑料的理化性质,包括:(1)改变其表面形貌,导致比表面积显著的增大,也可增加其表面的粗糙度;(2)改变其硬度和结晶度;(3)改变其密度,从而影响其在水体中的纵向分布;(4)改变其表面官能团,C—O、C=O含量上升,进而影响其亲疏水性[70]. 研究显示,在海水中原位老化6个月的4种微塑料纤维表面形成了生物膜,表面含氧官能团增多,并出现了多糖类化合物,其中PE的比表面积由(0.38±0.06) m2 g−1增加至(0.65±0.08) m2 g−1,微孔直径由0.76 nm增加至0.95 nm[60].
1.4 其它老化
微塑料在进入环境后可能会经历其它老化过程,其中微塑料对腐殖质等天然有机质(NOM)的吸附受到了广泛关注. 微塑料可以通过疏水作用、静电作用、π-π相互作用等吸附水中的NOM[71],其作用机制和效应与微塑料对EPS的吸附类似. 微塑料吸附NOM后,表面形貌和理化性质显著改变,进而影响其环境效应. 原始PS微塑料颗粒表面光滑,NOM吸附后PS表面粗糙,粒径增大,表面含氧官能团增加[72]. 天然有机质包覆在微塑料表面后增加了微塑料表面电负性,从而加强静电斥力,增强了颗粒稳定性[73]. 一些综述也关注到了腐殖质对微塑料的老化[3,20],未来仍需进一步系统的探索不同类型微塑料与腐殖质不同组分之间的相互作用.
1.5 微塑料环境老化的研究方法
目前研究微塑料环境老化的手段主要有两种,一种是从环境中(如海滩[74]、农田[73]、河流[75]等)直接采集老化的微塑料颗粒开展研究,另一种是人工模拟老化过程,获得老化微塑料进行研究. 人工模拟老化又分为原位自然老化和实验室加速老化[19-20]:原位自然老化是指将购买或制备的微塑料颗粒置于特定自然环境中,老化后回收以进一步研究[60],例如有研究使用长江和太湖的天然水样制备微塑料悬浮液,将其置于屋顶暴露于阳光下5至11个月[45]. 实验室加速老化是指通过机械力磨损、紫外灯照射、化学氧化等方式加速老化微塑料. 例如,有研究将海滩沙砾与微塑料颗粒混合振荡两个月以模拟物理老化过程[22]. 大量研究选择氙灯、汞灯等光源模拟环境中微塑料的光老化[46, 76-77]. 也有很多研究利用Fenton反应和过氧化氢等高级氧化手段,模拟微塑料在活性氧作用下的化学老化[45, 78]. 近期一项研究对比了实验室加速老化与原位自然老化微塑料的性质差异,发现经过高温、紫外、臭氧和超声组合手段老化后的PS微塑料与在室外阳光照射老化11个月的微塑料颗粒表面形貌与理化性质相似,表明多种实验室加速老化手段的综合应用能够较好地评估环境中微塑料的老化过程[79].
2. 老化对微塑料环境行为和生物效应的影响(Effects of aging on environmental processes and implications of microplastics)
环境老化可改变微塑料的表观形貌、分子结构及化学组成等理化性质,从而显著影响其环境行为和生物效应(如图3所示).
2.1 环境老化对微塑料迁移能力的影响
微塑料可在环境中长期存在,具有较强的迁移能力. 环境老化过程会显著改变微塑料的物理化学性质,使得微塑料粒径减小、表面含氧官能团增加,影响了其与环境介质间的相互作用,进而显著影响了微塑料的迁移能力(图3). 老化后微塑料粒径的减小会削弱微塑料与多孔介质间的范德华力,微塑料在多孔介质中沉积减弱,迁移能力增强. 在农田自然老化所形成的小尺寸颗粒(15—30 µm)在天然土壤介质中具有更强的向下迁移能力[73]. 老化后微塑料表面含氧官能团含量增加,电负性增强,与带负电的多孔介质间的静电斥力增大,导致微塑料在多孔介质上的沉积减弱,有助于提升迁移能力. 例如,紫外老化的微塑料表面羧基官能团增加,羧基去质子化使其带有更多的负电荷,与带负电的石英砂介质之间静电斥力增大,迁移能力增强[80]. 此外,老化后微塑料表面含氧官能团的增加会显著增加微塑料的亲水性,进而影响其迁移行为. 例如,在背景溶液为0.5 mmol·L−1 NaCl中,原始PS最大穿透率约为43.3%,经紫外(UV)老化后的PS最大穿透率显著提高至90.7%;UV老化后的PS表面含氧官能团增加,这不仅增加了微塑料的表面电负性,还增强了其亲水性,亲水性的增强是老化PS迁移能力增强的关键因素[25]. 值得注意的是,老化后微塑料表面含氧官能团的增加也会导致其在Ca2+等阳离子条件中桥联作用的增加,这可能在一定程度上抑制老化微塑料的迁移能力.
2.2 环境老化对微塑料富集污染物能力的影响
老化过程可导致微塑料吸附污染物的能力发生明显变化. 老化后微塑料的表面更粗糙,出现裂缝和孔隙,粒径减小,比表面积增大;同时,生成的官能团改变了微塑料表面的电负性、极性和亲疏水性,从而影响了静电相互作用、疏水相互作用、π-π相互作用、氢键和络合作用等多种作用机制,进而改变了微塑料富集污染物的能力(图3). 首先,微塑料的吸附容量与比表面积呈正相关,老化后的微塑料产生裂纹或破碎为更小的碎片,粒径减小、比表面积增加,有效吸附位点增多从而具有更强的吸附能力. 例如,紫外照射导致PET微塑料比表面积增大,暴露出更多的有效吸附位点,对Cu2+的吸附能力是原始微塑料的2倍[81]. 其次,老化后微塑料表面生成了含氧官能团,表面氧碳比(O/C)增高,亲水性增加,这将抑制对疏水性污染物的吸附,增强对亲水性污染物的吸附[82-83]. 老化微塑料表面官能团的变化还会影响其与污染物之间的极性作用,增强氢键在吸附过程中的贡献从而改变微塑料的吸附能力. 例如,高温老化的PS表面因交联和断链产生的大量含氧官能团(羧酸、酮和内酯),增强了微塑料与抗生素之间的氢键作用,从而增加吸附容量;而老化后PS与周围的水分子间氢键作用的增强,降低了PS表面吸附位点的可利用性,极大地抑制了多环芳烃的吸附[84]. 在海水中原位老化6个月的微塑料纤维对铅(Pb2+)吸附能力增加4%—25%,这是由于老化后微塑料表面覆盖生物膜,生成的大量含氧官能团可以与Pb2+结合形成金属络合物,提高了吸附能力[60]. 一些带电污染物和微塑料之间的吸附主要由静电相互作用主导[85],老化过程增加了微塑料表面的负电荷,这将增强静电相互作用在吸附过程中的重要性[86]. 例如,自然老化的微塑料表面附着大量有机质,增强了微塑料表面负电荷,有利于对重金属阳离子Pb2+的静电吸引[86]. π-π相互作用是含有苯环的微塑料与芳香族化合物相互作用的主要机制,由于链断裂,老化过程可能会削弱π-π相互作用[3]. 例如,紫外照射后的PS聚合物链断裂、苯环脱落,导致π-π相互作用在PS和双酚A(BPA)的结合中减弱,老化PS对BPA的吸附能力下降[87]. 值得注意的是,微塑料吸附污染物的能力取决于不同吸附机制的整体贡献,而老化对不同机制的影响不尽相同,因此对于吸附的总体影响往往比较复杂[24],应进一步研究微塑料的结构、老化过程、老化程度对不同污染物的吸附贡献率,探明老化影响微塑料吸附行为的主控因子.
2.3 环境老化对微塑料载带污染物能力的影响
微塑料具有较强的胶体稳定性和迁移能力,因此,吸附了污染物之后,可作为载体促进污染物在环境中的运移[88-89]. 微塑料对污染物的载带能力主要取决于3个方面,一是微塑料自身的迁移能力,二是微塑料吸附富集污染物的能力,三是污染物在微塑料上发生不可逆吸附或解吸滞后的程度[90-91]. 前面已提到老化可显著影响微塑料的迁移能力和吸附污染物的能力[73, 92]. 与此同时,环境老化所引发的理化性质变化可显著影响微塑料上有机污染物的解吸行为,进而改变微塑料载带污染物迁移的能力. 首先,老化导致微塑料表面微裂纹、微孔体积增多,这一效应增强了非极性有机污染物在微塑料内部孔隙中的“孔填充”效应,不可逆吸附和解吸迟滞程度明显增强,更易于随微塑料迁移[25]. 其次,老化后微塑料表面羟基、羧基等表面含氧官能团的增多,可提升微塑料与极性有机污染物之间的氢键等极性相互作用,也会导致污染物的不可逆吸附程度的增强[25]. 上述两种效应均使得污染物与微塑料结合得更加紧密,更易随微塑料在环境中迁移.
2.4 环境老化对微塑料生物效应的影响
作为一种新兴污染物,微塑料对环境中生物体影响越来越受到重视[93]. 环境老化后微塑料粒径减小,表面覆盖丰富的生物膜,可导致生物体摄入微塑料方式和数量的改变[3]. 塑料在制造过程中掺入了各种添加剂,相比于微塑料本身,添加剂的释放可能对生态安全构成更大的威胁[94],老化促进了微塑料内有毒添加剂的浸出,增强了其毒性效应. 同时,老化显著改变了微塑料富集污染物的能力,随着生物摄食行为,微塑料可将污染物载带至生物体中,促进了污染物的生物摄入.
许多生物体对食物选择有偏好,例如大小,形状等[95],老化后形成的较小的微塑料颗粒甚至是纳米塑料,更容易被生物体(尤其是贻贝和牡蛎幼虫等无脊椎动物)摄入[96]. 不同大小的PS微塑料在斑马鱼体内的摄取和积累位置不同,7 d暴露实验显示,直径为5 μm的PS主要积累在鱼的鳃、肝和肠中,而直径为20 μm的PS颗粒仅积累在鳃和肠道中;积聚在鱼肝中的较小的微塑料颗粒会诱导氧化应激和鱼肝脏代谢组学的改变[97]. 一般情况下,较小的微塑料颗粒更有可能被生物体摄入,并且在组织中分布更广,毒性更大[98]. 生物膜在微塑料上的形成可影响生物体的感知,在较低或较高的营养级,覆盖生物膜的微塑料的生物可利用性均更强,也更容易被生物体摄食[99-100]. 在海水中自然老化3周的微塑料,表面形成的生物膜掩盖了微塑料的惰性,并散发出化学信号使其更类似于食物颗粒,导致浮游动物对微塑料的摄入增加[99].
环境老化促进了微塑料中添加剂、中间体的浸出,增加了微塑料的生态风险[24, 101]. 例如,老化加速了商业微塑料中含有铬和铅的染料的释放,中性条件下在12 h内原始PE中Cr(Ⅵ)和Pb(Ⅱ)的浸出量分别为0.8 μg·g−1和1.7 μg·g−1,紫外老化后微塑料中两者的浸出量分别提高到了3.0 μg·g−1和11.9 μg·g−1. 相比于原始微塑料,老化微塑料的渗滤液更加抑制了铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)细胞生长和光合作用[101]. 另一研究表明,紫外线照射诱导了PS中的内源性污染物的浸出,原始PS的渗滤液中没有检测出添加剂,紫外线照射60 d后,老化PS渗滤液中检测到了邻苯二甲酸酯类化合物,其积聚在石斑鱼的肝脏脂肪中,造成了生长抑制和肝脏病变[23]. 老化后微塑料可富集更多污染物,增强了其毒性效应. 例如,在溪流中自然老化4周的PE微塑料,表面出现生物膜,对银离子(Ag)吸附量增加了44%;吸附到老化微塑料上的Ag在Steinberg培养基(通常用于培养淡水浮萍)中释放量为247.5 μg·L−1,显著高于原始微塑料(73.5 μg·L−1)[102]. 紫外老化微塑料吸附了更多的罗红霉素,使其在鲫鱼肠道内积累更多,进而导致了更严重的肠道内炎细胞浸润和纤毛受损,抑制了消化酶活性,并扰乱了肠道菌群,造成了代谢紊乱[103].
3. 结论与展望(Conclusions and prospects)
综上所述,微塑料在自然环境中会经历复杂的物理、化学和生物老化过程. 物理老化是机械力作用下微塑料表面裂纹的产生与扩展,从而导致颗粒破碎,有利于化学和生物因素的进一步作用. 化学老化是在紫外线、高温、活性氧等作用下,微塑料化学键断裂进而导致表面化学组成改变的过程. 生物老化是微塑料在生物作用下的破碎同化,微生物也可通过附着机制在其表面形成生物膜. 老化后微塑料的表面形貌、分子结构及化学组成等物理化学性质发生显著改变,不仅影响其自身环境行为,也改变了微塑料与环境介质中的生命和非生命体的相互作用. 因此,老化是评价微塑料环境行为和生物效应中不可忽视的重要因素.为了系统的认识与评价微塑料的环境老化过程和效应机制,亟需在以下几方面开展深入研究:(1)目前微塑料老化的实验研究中,主要是采用单一人工加速老化手段模拟自然老化过程,如机械研磨、紫外辐射、活性氧进攻等. 微塑料在真实环境中的老化,往往受到多种因素共同作用,单一老化手段可能不足以代表真实的环境老化过程. 因此,在实验室模拟老化研究中,更应关注多个老化过程对其的综合影响,缩小实验室模拟手段与环境自然老化过程之间的差距. (2)微塑料性质迥异,环境老化过程复杂,当前更多是定性研究老化机制,应进一步量化微塑料环境老化程度;明确老化微塑料性质变化对其环境行为的贡献,系统研究与开发微塑料不同类型-老化程度-性质变化-环境效应改变之间的关系曲线与预测模型,实现对微塑料的环境风险预测和评估. (3)微塑料与环境大分子如天然有机质、蛋白质、多糖和其他表面活性物质之间的相互作用值得关注,包括探究微塑料与天然有机质不同组分之间发生选择性吸附的作用机制和影响因素,以及微塑料-NOM复合物的环境行为和毒性机制. (4)目前实验室研究对象主要是微塑料颗粒和碎片,应加强对环境中大量检出的微塑料超细纤维和薄膜的老化过程及效应探索.(5)针对微塑料老化所引发的环境行为和效应变化的研究总体集中在光降解老化微塑料,应关注其他老化过程后所引起的效应变化与机制. (6)目前微塑料老化相关研究主要集中在天然水、土壤环境中,工程系统同样是微塑料的重要赋存环境,对于其中的老化过程,目前还鲜有研究. 因此应加强对污水处理厂和垃圾填埋场中微塑料老化的深入研究,例如水处理中的化学老化和固废处理中的热老化,以及自然条件下微塑料在垃圾渗滤液中的原位老化等.
-
-
[1] CHAE Y, AN Y J. Current research trends on plastic pollution and ecological impacts on the soil ecosystem: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 240: 387-395. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.008 [2] GEYER R, JAMBECK J R, LAW K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made [J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1700782. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700782 [3] LUO H W, LIU C Y, HE D Q, et al. Environmental behaviors of microplastics in aquatic systems: A systematic review on degradation, adsorption, toxicity and biofilm under aging conditions [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 423: 126915. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126915 [4] RICHARDSON S D, TERNES T A. Water analysis: Emerging contaminants and current issues [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(6): 2813-2848. doi: 10.1021/ac500508t [5] LI J, SONG Y, CAI Y B. Focus topics on microplastics in soil: Analytical methods, occurrence, transport, and ecological risks [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 257: 113570. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113570 [6] NIZZETTO L, FUTTER M, LANGAAS S. Are agricultural soils dumps for microplastics of urban origin? [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(20): 10777-10779. [7] DUAN J J, BOLAN N, LI Y, et al. Weathering of microplastics and interaction with other coexisting constituents in terrestrial and aquatic environments [J]. Water Research, 2021, 196: 117011. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117011 [8] 杨婧婧, 徐笠, 陆安祥, 等. 环境中微(纳米)塑料的来源及毒理学研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 383-396. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017071002 YANG J J, XU L, LU A X, et al. Research progress on the sources and toxicology of micro (nano) plastics in environment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 383-396(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017071002
[9] 郝爱红, 赵保卫, 张建, 等. 土壤中微塑料污染现状及其生态风险研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1100-1111. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020083102 HAO A H, ZHAO B W, ZHANG J, et al. Research progress on pollution status and ecological risk of microplastics in soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1100-1111(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020083102
[10] 仇付国, 童诗雨, 王肖倩. 水环境中微塑料赋存现状及生态危害研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(3): 221-228. QIU F G, TONG S Y, WANG X Q. Research progress on occurrence status and ecological hazards of microplastics in water environment [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(3): 221-228(in Chinese).
[11] SUN J, DAI X H, WANG Q L, et al. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal [J]. Water Research, 2019, 152: 21-37. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.050 [12] ROCHMAN C M. Microplastics research-from sink to source [J]. Science, 2018, 360(6384): 28-29. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7734 [13] ERIKSEN M, LEBRETON L C M, CARSON H S, et al. Plastic pollution in the world's oceans: More than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250, 000 tons afloat at sea [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(12): e111913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111913 [14] KOELMANS A A, MOHAMED NOR N H, HERMSEN E, et al. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality [J]. Water Research, 2019, 155: 410-422. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.054 [15] DENG Y, ZHANG Y, LEMOS B, et al. Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 46687. [16] CAPOLUPO M, SØRENSEN L, JAYASENA K D R, et al. Chemical composition and ecotoxicity of plastic and car tire rubber leachates to aquatic organisms [J]. Water Research, 2020, 169: 115270. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115270 [17] WARDROP P, SHIMETA J, NUGEGODA D, et al. Chemical pollutants sorbed to ingested microbeads from personal care products accumulate in fish [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(7): 4037-4044. [18] 陈雅兰, 孙可, 高博. 微塑料吸附机制研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2271-2287. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021031204 CHEN Y L, SUN K, GAO B. Sorption behavior, mechanisms, and models of organic pollutants and metals on microplastics: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2271-2287(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021031204
[19] ALIMI O S, CLAVEAU-MALLET D, KURUSU R S, et al. Weathering pathways and protocols for environmentally relevant microplastics and nanoplastics: What are we missing? [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 423: 126955. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126955 [20] SUN Y R, YUAN J H, ZHOU T, et al. Laboratory simulation of microplastics weathering and its adsorption behaviors in an aqueous environment: A systematic review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 114864. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114864 [21] KELKAR V P, ROLSKY C B, PANT A, et al. Chemical and physical changes of microplastics during sterilization by chlorination [J]. Water Research, 2019, 163: 114871. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.114871 [22] SONG Y K, HONG S H, JANG M, et al. Combined effects of UV exposure duration and mechanical abrasion on microplastic fragmentation by polymer type [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(8): 4368-4376. [23] WANG X, ZHENG H, ZHAO J, et al. Photodegradation elevated the toxicity of polystyrene microplastics to grouper (Epinephelus moara) through disrupting hepatic lipid homeostasis [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(10): 6202-6212. [24] LIU X L, GHARASOO M, SHI Y, et al. Key physicochemical properties dictating gastrointestinal bioaccessibility of microplastics-associated organic xenobiotics: Insights from a deep learning approach [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(19): 12051-12062. [25] LIU J, ZHANG T, TIAN L L, et al. Aging significantly affects mobility and contaminant-mobilizing ability of nanoplastics in saturated loamy sand [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(10): 5805-5815. [26] ENFRIN M, DUMÉE L F, LEE J. Nano/microplastics in water and wastewater treatment processes - Origin, impact and potential solutions [J]. Water Research, 2019, 161: 621-638. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.049 [27] ENFRIN M, LEE J, GIBERT Y, et al. Release of hazardous nanoplastic contaminants due to microplastics fragmentation under shear stress forces [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121393. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121393 [28] CORCORAN P L, BIESINGER M C, GRIFI M. Plastics and beaches: A degrading relationship [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 58(1): 80-84. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.08.022 [29] ANDRADY A L. Microplastics in the marine environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1596-1605. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030 [30] JULIENNE F, DELORME N, LAGARDE F. From macroplastics to microplastics: Role of water in the fragmentation of polyethylene [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 236: 124409. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124409 [31] WU X W, LIU P, SHI H H, et al. Photo aging and fragmentation of polypropylene food packaging materials in artificial seawater [J]. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116456. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116456 [32] MAO R F, LANG M F, YU X Q, et al. Aging mechanism of microplastics with UV irradiation and its effects on the adsorption of heavy metals [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 393: 122515. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122515 [33] ZHANG K, HAMIDIAN A H, TUBIĆ A, et al. Understanding plastic degradation and microplastic formation in the environment: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 274: 116554. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116554 [34] SINGH B, SHARMA N. Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation [J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2008, 93(3): 561-584. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.11.008 [35] TIAN L L, CHEN Q Q, JIANG W, et al. A carbon-14 radiotracer-based study on the phototransformation of polystyrene nanoplastics in water versus in air [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2019, 6(9): 2907-2917. doi: 10.1039/C9EN00662A [36] YOUSIF E, HADDAD R. Photodegradation and photostabilization of polymers, especially polystyrene: Review [J]. SpringerPlus, 2013, 2: 398. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-398 [37] GEWERT B, PLASSMANN M M, MACLEOD M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment [J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2015, 17(9): 1513-1521. [38] TYLER D R. Mechanistic aspects of the effects of stress on the rates of photochemical degradation reactions in polymers [J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part C, 2004, 44(4): 351-388. doi: 10.1081/MC-200033682 [39] WARD C P, ARMSTRONG C J, WALSH A N, et al. Sunlight converts polystyrene to carbon dioxide and dissolved organic carbon [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2019, 6(11): 669-674. [40] TANG C C, CHEN H I, BRIMBLECOMBE P, et al. Morphology and chemical properties of polypropylene pellets degraded in simulated terrestrial and marine environments [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 149: 110626. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110626 [41] COPINET A, BERTRAND C, GOVINDIN S, et al. Effects of ultraviolet light (315 nm), temperature and relative humidity on the degradation of polylactic acid plastic films [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 55(5): 763-773. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.038 [42] HESHMATI M, HAGHANI R, AL-EMRANI M. Durability of CFRP/steel joints under cyclic wet-dry and freeze-thaw conditions [J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2017, 126: 211-226. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.06.011 [43] ZHAO M T, ZHANG T, YANG X L, et al. Sulfide induces physical damages and chemical transformation of microplastics via radical oxidation and sulfide addition [J]. Water Research, 2021, 197: 117100. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117100 [44] YIN L J, ZHOU H X, LIAN L S, et al. Effects of C60 on the photochemical formation of reactive oxygen species from natural organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(21): 11742-11751. [45] LIU P, QIAN L, WANG H Y, et al. New insights into the aging behavior of microplastics accelerated by advanced oxidation processes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(7): 3579-3588. [46] ZHU K C, JIA H Z, SUN Y J, et al. Long-term phototransformation of microplastics under simulated sunlight irradiation in aquatic environments: Roles of reactive oxygen species [J]. Water Research, 2020, 173: 115564. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115564 [47] KENT R D, OSER J G, VIKESLAND P J. Controlled evaluation of silver nanoparticle sulfidation in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(15): 8564-8572. [48] RICKARD D, LUTHER G W I. Chemistry of iron sulfides [J]. ChemInform, 2007, 107(19): 514-562. [49] NIU L H, LI Y Y, LI Y, et al. New insights into the vertical distribution and microbial degradation of microplastics in urban river sediments [J]. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116449. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116449 [50] BRANDON J A, JONES W, OHMAN M D. Multidecadal increase in plastic particles in coastal ocean sediments [J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(9): eaax0587. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax0587 [51] TAPLEY D W, BUETTNER G R, SHICK J M. Free radicals and chemiluminescence as products of the spontaneous oxidation of sulfide in seawater, and their biological implications [J]. The Biological Bulletin, 1999, 196(1): 52-56. doi: 10.2307/1543166 [52] CHEN K Y, MORRIS J C. Kinetics of oxidation of aqueous sulfide by oxygen [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1972, 6(6): 529-537. [53] LOMBARDO S M, VINDEDAHL A M, ARNOLD W A. Determination of hydroxyl radical production from sulfide oxidation relevant to sulfidic porewaters [J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2020, 4(2): 261-271. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00297 [54] LI X W, LI M, MEI Q Q, et al. Aging microplastics in wastewater pipeline networks and treatment processes: Physicochemical characteristics and Cd adsorption [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 797: 148940. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148940 [55] FRANCOIS R. A study of sulphur enrichment in the humic fraction of marine sediments during early diagenesis [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(1): 17-27. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90003-2 [56] YU Z G, PEIFFER S, GÖTTLICHER J, et al. Electron transfer budgets and kinetics of abiotic oxidation and incorporation of aqueous sulfide by dissolved organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5441-5449. [57] PERLINGER J A, KALLURI V M, VENKATAPATHY R, et al. Addition of hydrogen sulfide to juglone [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(12): 2663-2669. [58] BUXTON G V, GREENSTOCK C L, HELMAN W P, et al. Critical Review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (·OH/·O− in Aqueous Solution [J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1988, 17(2): 513-886. doi: 10.1063/1.555805 [59] HUERTA LWANGA E, THAPA B, YANG X M, et al. Decay of low-density polyethylene by bacteria extracted from earthworm's guts: A potential for soil restoration [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 624: 753-757. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.144 [60] BHAGWAT G, TRAN T, LAMB D, et al. Biofilms enhance the adsorption of toxic contaminants on plastic microfibers under environmentally relevant conditions [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(13): 8877-8887. [61] TU C, CHEN T, ZHOU Q, et al. Biofilm formation and its influences on the properties of microplastics as affected by exposure time and depth in the seawater [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 734: 139237. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139237 [62] DAWSON A L", KAWAGUCHI S, KING C K", et al. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1001. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03465-9 [63] YANG Y, YANG J, WU W M, et al. Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms: Part 1. chemical and physical characterization and isotopic tests [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(20): 12080-12086. [64] YANG Y, YANG J, WU W M, et al. Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms: Part 2. role of gut microorganisms [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(20): 12087-12093. [65] PAÇO A, DUARTE K, da COSTA J P, et al. Biodegradation of polyethylene microplastics by the marine fungus Zalerion maritimum [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 586: 10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.017 [66] RUMMEL C D, JAHNKE A, GOROKHOVA E, et al. Impacts of biofilm formation on the fate and potential effects of microplastic in the aquatic environment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2017, 4(7): 258-267. [67] CHEN X C, XIONG X, JIANG X M, et al. Sinking of floating plastic debris caused by biofilm development in a freshwater lake [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 222: 856-864. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.015 [68] OBERBECKMANN S, LÖDER M G J, LABRENZ M. Marine microplastic-associated biofilms–a review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 12(5): 551. doi: 10.1071/EN15069 [69] LI W J, ZHANG Y, WU N, et al. Colonization characteristics of bacterial communities on plastic debris influenced by environmental factors and polymer types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(18): 10763-10773. [70] WANG J L, GUO X, XUE J M. Biofilm-developed microplastics as vectors of pollutants in aquatic environments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(19): 12780-12790. [71] ABDURAHMAN A, CUI K Y, WU J, et al. Adsorption of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on polystyrene microplastics in aquatic environments: Kinetic, isotherm and site energy distribution analysis [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 198: 110658. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110658 [72] CHEN W, OUYANG Z Y, QIAN C, et al. Induced structural changes of humic acid by exposure of polystyrene microplastics: A spectroscopic insight [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 233: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.027 [73] YAN X Y, YANG X Y, TANG Z, et al. Downward transport of naturally-aged light microplastics in natural loamy sand and the implication to the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 262: 114270. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114270 [74] BLANCHO F, DAVRANCHE M, FUMAGALLI F, et al. A reliable procedure to obtain environmentally relevant nanoplastic proxies [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2021, 8(11): 3211-3219. doi: 10.1039/D1EN00395J [75] WALDSCHLÄGER K, BORN M, COWGER W, et al. Settling and rising velocities of environmentally weathered micro- and macroplastic particles [J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 191: 110192. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110192 [76] RUMMEL C D, ESCHER B I, SANDBLOM O, et al. Effects of leachates from UV-weathered microplastic in cell-based bioassays [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(15): 9214-9223. [77] LIU Y J, HU Y B, YANG C, et al. Aggregation kinetics of UV irradiated nanoplastics in aquatic environments [J]. Water Research, 2019, 163: 114870. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.114870 [78] LANG M F, YU X Q, LIU J H, et al. Fenton aging significantly affects the heavy metal adsorption capacity of polystyrene microplastics [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 722: 137762. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137762 [79] SARKAR A K, RUBIN A E, ZUCKER I. Engineered polystyrene-based microplastics of high environmental relevance [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(15): 10491-10501. [80] XI X L, WANG L, ZHOU T, et al. Effects of physicochemical factors on the transport of aged polystyrene nanoparticles in saturated porous media [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133239. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133239 [81] WANG Q J, ZHANG Y, WANGJIN X X, et al. The adsorption behavior of metals in aqueous solution by microplastics effected by UV radiation [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 87: 272-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.07.006 [82] LIU P, ZHAN X, WU X W, et al. Effect of weathering on environmental behavior of microplastics: Properties, sorption and potential risks [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 242: 125193. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125193 [83] HÜFFER T, WENIGER A K, HOFMANN T. Sorption of organic compounds by aged polystyrene microplastic particles [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 218-225. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.022 [84] DING L, MAO R F, MA S R, et al. High temperature depended on the ageing mechanism of microplastics under different environmental conditions and its effect on the distribution of organic pollutants [J]. Water Research, 2020, 174: 115634. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115634 [85] GUO X T, PANG J W, CHEN S Y, et al. Sorption properties of tylosin on four different microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 209: 240-245. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.100 [86] FU Q M, TAN X F, YE S J, et al. Mechanism analysis of heavy metal lead captured by natural-aged microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270: 128624. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128624 [87] LIU X M, SUN P P, QU G J, et al. Insight into the characteristics and sorption behaviors of aged polystyrene microplastics through three type of accelerated oxidation processes [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 407: 124836. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124836 [88] ZHAO P, CUI L M, ZHAO W G, et al. Cotransport and deposition of colloidal polystyrene microplastic particles and tetracycline in porous media: The impact of ionic strength and cationic types [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 142064. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142064 [89] SATHICQ M B, SABATINO R, CORNO G, et al. Are microplastic particles a hotspot for the spread and the persistence of antibiotic resistance in aquatic systems? [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 279: 116896. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116896 [90] LING X, YAN Z H, LIU Y X, et al. Transport of nanoparticles in porous media and its effects on the co-existing pollutants [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 283: 117098. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117098 [91] LIU J, MA Y N, ZHU D Q, et al. Polystyrene nanoplastics-enhanced contaminant transport: Role of irreversible adsorption in glassy polymeric domain [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(5): 2677-2685. [92] SHI J H, WU D, SU Y L, et al. Selective enrichment of antibiotic resistance genes and pathogens on polystyrene microplastics in landfill leachate [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 765: 142775. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142775 [93] GE J H, LI H, LIU P, et al. Review of the toxic effect of microplastics on terrestrial and aquatic plants [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 791: 148333. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148333 [94] RIST S, CARNEY ALMROTH B, HARTMANN N B, et al. A critical perspective on early communications concerning human health aspects of microplastics [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 626: 720-726. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.092 [95] XIONG X, TU Y N, CHEN X C, et al. Ingestion and egestion of polyethylene microplastics by goldfish (Carassius auratus): Influence of color and morphological features [J]. Heliyon, 2019, 5(12): e03063. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03063 [96] COLE M, GALLOWAY T S. Ingestion of nanoplastics and microplastics by Pacific oyster larvae [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(24): 14625-14632. [97] LU Y F, ZHANG Y, DENG Y F, et al. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(7): 4054-4060. [98] 王英雪, 徐熳, 王立新, 等. 微塑料在哺乳动物的暴露途径、毒性效应和毒性机制浅述 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 41-54. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020053002 WANG Y X, XU M, WANG L X, et al. The exposure routes, organ damage and related mechanism of the microplastics on the mammal [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 41-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020053002
[99] VROOM R J E, KOELMANS A A, BESSELING E, et al. Aging of microplastics promotes their ingestion by marine zooplankton [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 987-996. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.088 [100] SAVOCA M S, WOHLFEIL M E, EBELER S E, et al. Marine plastic debris emits a keystone infochemical for olfactory foraging seabirds [J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(11): e1600395. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600395 [101] LUO H W, LI Y, ZHAO Y Y, et al. Effects of accelerated aging on characteristics, leaching, and toxicity of commercial lead chromate pigmented microplastics [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 257: 113475. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113475 [102] KALČÍKOVÁ G, SKALAR T, MAROLT G, et al. An environmental concentration of aged microplastics with adsorbed silver significantly affects aquatic organisms [J]. Water Research, 2020, 175: 115644. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115644 [103] ZHANG P, LU G H, SUN Y, et al. Metagenomic analysis explores the interaction of aged microplastics and roxithromycin on gut microbiota and antibiotic resistance genes of Carassius auratus [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 127773. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127773 -




 下载:
下载: