-
近年来,空气污染已成为一个严重的社会问题,而挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds, VOCs)是造成雾霾、臭氧(O3)和细颗粒物(PM2.5)等空气污染的重要前体物,因其对人体和环境的显著危害而备受关注[1]. 目前,VOCs的处理方法主要有吸附法[2]和催化燃烧法[3]. 吸附法主要是采用活性炭[4]、沸石分子筛[5-6]、高聚物吸附树脂[7]等吸附剂对VOCs进行吸附从而消除有害污染物,本质上是将低浓度VOCs富集为高浓度,仍需进一步处置. 催化燃烧法是使用催化剂降低VOCs的起燃温度而进行燃烧,具有高效率、低能耗、无二次污染的优点,但该方法对有机废气浓度有一定要求,过低浓度的VOCs无法维持催化反应的持续进行[8].
工业源有机废气大多为低浓度、大风量,应用单一处理技术受到若干实际因素限制且成本较高[9]. 吸附/催化双功能材料为VOCs处理技术的发展提供了新的动力,将高吸附容量的吸附材料和高催化活性的催化材料有机结合起来,一方面利用吸附材料富集VOCs为热催化过程提供所需浓度;另一方面利用热催化过程中的热量可以实现吸附材料的原位脱附再生[10-13]. 这种吸附/催化双功能材料因其在处理VOCs中的优越性而备受广大工作者的关注. Howard等[14]用金属Cr对ZSM-5沸石分子筛进行改性,以卤代VOCs为研究对象,发现这种材料在处理低浓度卤代VOCs时可节能93%. 孙静等[15]以USY分子筛作为吸附剂及载体,选用Co3O4作为催化剂,制备了具有吸附和催化氧化双重功能的Co3O4/USY,该材料具有较高的吸附容量,催化氧化甲苯活性也显著提升,Co3O4负载量越大,低温催化活性越好,CO2选择性越高. Wang等[16]对负载Ru的HZSM-5分子筛的吸附/催化性能进行了探讨,发现该催化剂对甲苯、邻二甲苯和三甲苯均表现出优异的吸附和催化氧化性能,且在吸附-催化循环过程中再生性良好.这些研究为吸附/催化双功能材料在VOCs处理中的应用提供了方向.
为了寻找更好的吸附/催化双功能材料,本研究选取具有独特三维孔道的ZSM-5沸石分子筛作为吸附剂及载体,以非贵金属中催化活性较高的MnOx为催化剂[17],采用柠檬酸络合法分别掺杂Cu、Co和Ni,制备了具有吸附和催化氧化双重功能的MnOx/ZSM-5、CuOx/ZSM-5、CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5和NiMnOx/ZSM-5催化剂,以常见污染物甲苯为处理对象,探讨了过渡金属Cu、Co和Ni掺杂对MnOx/ZSM-5吸附和催化氧化性能的影响。通过氮气吸脱附(brunauer-emmett-teller, BET)、X射线衍射(X-rays diffraction, XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)、H2程序升温还原(H2-temperature programmed reduction, H2-TPR)和X射线光电子能谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, XPS)对制备催化剂的物理结构性质及氧化还原性能进行了表征,并进一步评估了CuMnOx/ZSM-5的工业适用性,为VOCs常温吸附-低温催化氧化一体化技术的发展提供参考.
-
ZSM-5型沸石分子筛,n(Si)/n(Al)≈50,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;柠檬酸,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;无水乙醇、50%硝酸锰溶液、六水合硝酸钴,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;三水合硝酸铜,上海新宝精细化工厂;六水合硝酸镍,山东西亚化学工业有限公司.所用化学试剂均为分析纯.
-
采用柠檬酸络合法制备催化剂:称取2 g ZSM-5粉末,加入到一定浓度的Mn(NO3)2和Cu(NO3)2溶液中,保证金属元素理论负载量为10%wt,待搅拌均匀后,超声分散40 min.在磁力搅拌状态下向混合液中逐滴加入柠檬酸的乙醇溶液,其中n[柠檬酸]:n[金属离子]=1.2:1. 将搅拌均匀的混合物移至恒温水浴锅中,80 ℃下加热搅拌直至混合物呈干凝胶状. 105 ℃干燥过夜,研磨后在500 ℃马弗炉中煅烧5 h,得到催化剂CuMnOx/ZSM-5,筛分至40目—60目后待用.MnOx/ZSM-5、CuOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5和NiMnOx/ZSM-5的制备方法同上,其中Cu、Co和Ni元素的掺杂量均为5%wt.
-
吸附和催化氧化性能测试实验在固定床反应器中进行,反应器恒温区长度为60 cm,所用石英管内径为7 mm. 吸附实验在常温下(20 ℃)进行,石英管反应器中填充0.2 g(40目—60目)所制备的催化剂,甲苯浓度为400 mg·m−3,载气流量为100 mL·min−1,反应器出口甲苯浓度采用气相色谱(上海奇阳GC-9680-5C)在线分析,甲苯吸附容量用公式(1)计算.
式中,q为甲苯的吸附容量,mg·g−1;F为载气流量,mL·min−1;c0为进气甲苯浓度,mg·m−3;W为催化剂的装填量,g;ts为吸附平衡时间,min;ci为吸附i min后尾气中甲苯浓度,mg·m−3;t为吸附时间,min.
催化氧化性能测试采用带程序控制升温功能的管式炉控制催化床层温度,实验中甲苯浓度选用4000 mg·m−3,载气流量100 mL·min−1(GHSV=30000 mL·(g·h)−1),催化剂填充量0.2 g(40—60目),并在催化剂中添加石英砂以消除热效应. 为防止催化剂在初始阶段发生吸附现象导致出口甲苯浓度降低,催化氧化实验前先进行甲苯预吸附处理,待出口甲苯浓度稳定后再进行程序升温. 反应器出口甲苯浓度通过气相色谱仪(上海奇阳GC-9680-5C)在线分析,CO2浓度通过镍转化炉的氢火焰离子化检测器检测. 甲苯去除率及CO2选择性分别用公式(2)、(3)计算.
式中,η1表示甲苯去除率,%;η2表示CO2产率,%;cin表示进气甲苯浓度,mg·m−3;cout表示尾气中甲苯浓度,mg·m−3;cco2表示反应器出口CO2浓度,mg·m−3.
-
BET实验采用美国Micromeritics ASAP 2020比表面及孔径分析仪,对催化剂的比表面积和孔结构信息进行分析,分析前催化剂在300 ℃真空预处理2 h,以去除催化剂中吸附的水分. XRD实验采用日本理学公司Rigaku-Dmax-rA型固体衍射仪. 测试过程中使用的技术条件为:铜靶(λ=1.4818 nm),管压40 kV、管流30 mA,扫描范围为10°—60°,扫描速度为10°·min−1,扫描分辨率为0.02°. 采用日本日立公司Hitachi S-4800型场发射扫描电子显微镜对催化剂表面形貌进行了观察和分析,催化剂样品研磨成粉末后经过喷金处理,加速电场为20 kV. 采用FINETEC公司的FINESORB-3010化学吸附仪进行H2-TPR测试,测试样品约100 mg. 测试前在500℃ Ar气中预处理60 min,再以体积分数为10%的H2/Ar混合气对催化剂进行吹扫,待TCD基线走平后,以10 ℃·min−1升温至700 ℃进行程序升温还原. 采用日本Ulvac-Phi公司PHI 5000型X射线电子能谱仪对样品进行XPS分析,对催化剂表面的O种类和Mn、Cu价态进行定量和定性分析.
-
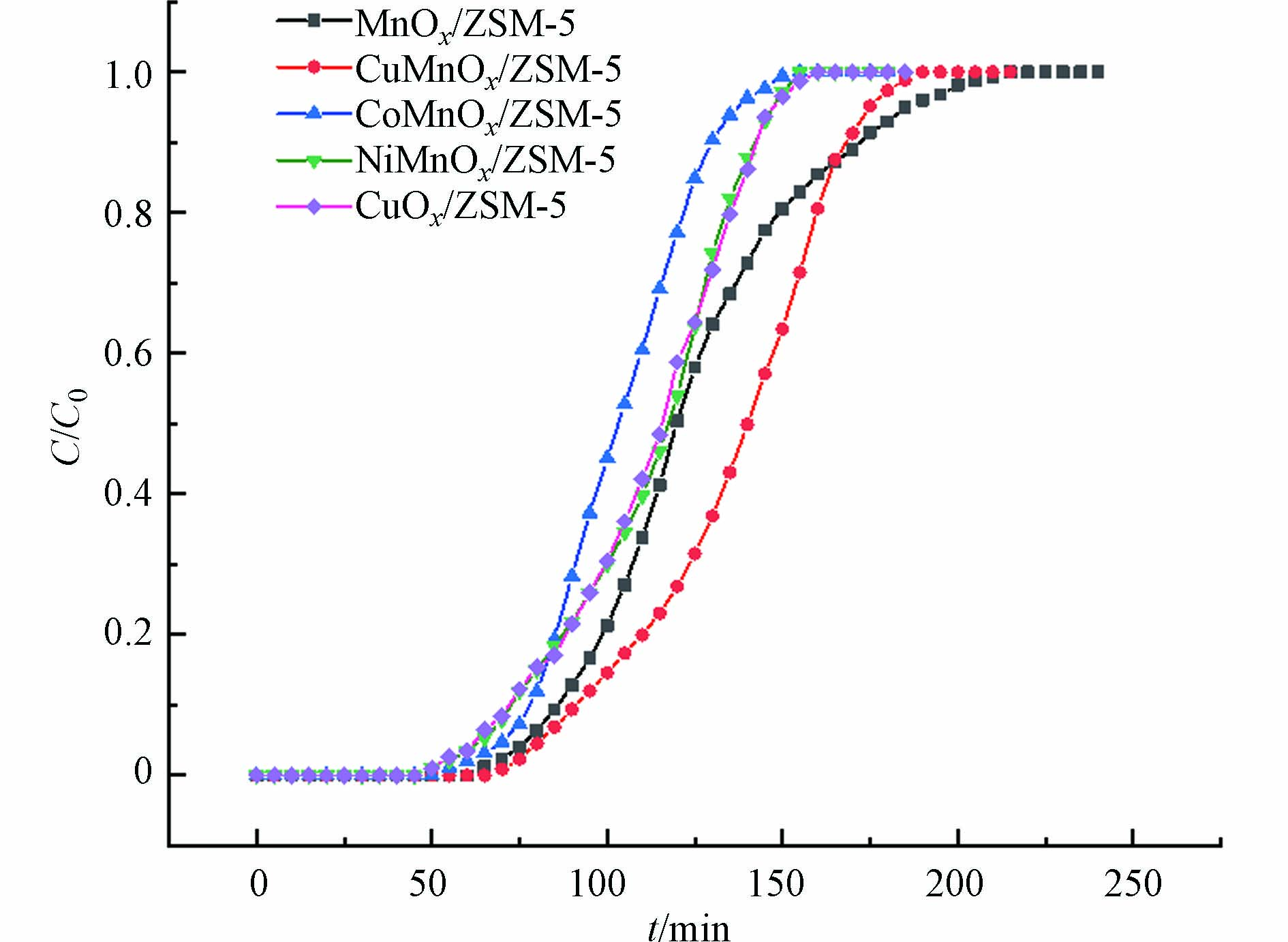
各催化剂的甲苯吸附穿透曲线如图1所示. 穿透时间是指从开始吸附到尾气浓度达到进气浓度5%时的时间[18]. 从表1中可以看出,MnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附在77 min时开始穿透,在215 min时达到平衡,甲苯的穿透吸附量为14.66 mg·g−1,平衡吸附量为24.01 mg·g−1. CuOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附在63 min时开始穿透,在160 min时达到平衡,甲苯的穿透吸附量为11.96 mg·g−1,平衡吸附量为21.30 mg·g−1. Cu、Co和Ni掺杂前后,MnOx/ZSM-5的吸附性能变化不大. CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附在81 min时开始穿透,在190 min时达到平衡,甲苯的穿透吸附量为15.44 mg·g−1,平衡吸附量为25.9 mg·g−1;CoMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附在70 min时开始穿透,在155 min时达到平衡,甲苯的穿透吸附量为13.31 mg·g−1,平衡吸附量为19.78 mg·g−1;NiMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附在64 min时开始穿透,在155 min时达到吸附平衡,甲苯的穿透吸附量为12.17 mg·g−1,平衡吸附量为21.38 mg·g−1. 各催化剂对甲苯均表现出较高的吸附容量,吸附量大小依次为:CuMnOx/ZSM-5>MnOx/ZSM-5>NiMnOx/ZSM-5≈CuOx/ZSM-5>CoMnOx/ZSM-5.
-
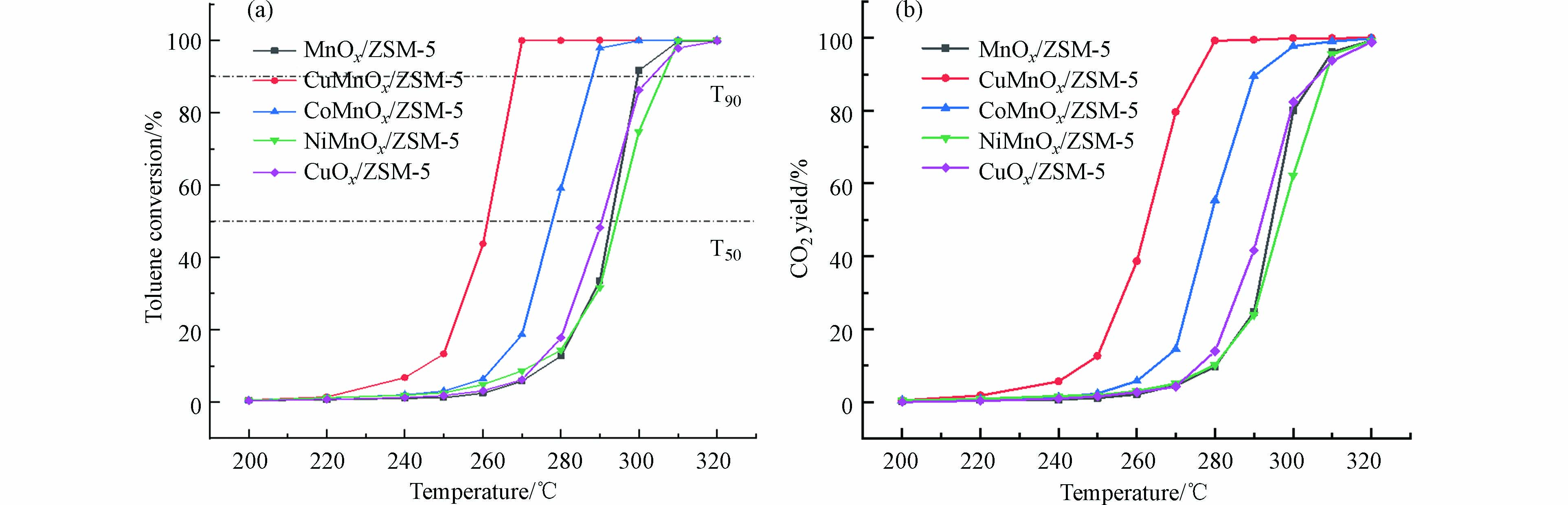
Cu、Co和Ni掺杂前后MnOx/ZSM-5在不同温度下的甲苯转化率如图2(a)所示. CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5、NiMnOx/ZSM-5、MnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的去除率为50%时的温度(T50)分别为261 ℃、278 ℃、294 ℃、293 ℃和290 ℃,相应的T90分别为268 ℃、288 ℃、306 ℃、300 ℃和303 ℃. 各个催化剂的CO2产率如图2(b)所示,说明甲苯反应后被转化成了CO2和H2O,具有良好的CO2选择性. 其中,CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5表现出较高的催化氧化活性.相比MnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的T50和T90均降低了30 ℃左右. CoMnOx/ZSM-5的T50和T90分别比MnOx/ZSM-5低15 ℃和12 ℃,Ni的掺入对MnOx/ZSM-5的催化活性影响不大.各催化剂均能以较低的温度去除甲苯,它们对甲苯的催化活性大小顺序依次为:CuMnOx/ZSM-5>CoMnOx/ZSM-5>MnOx/ZSM-5>CuOx/ZSM-5>NiMnOx/ZSM-5。
-
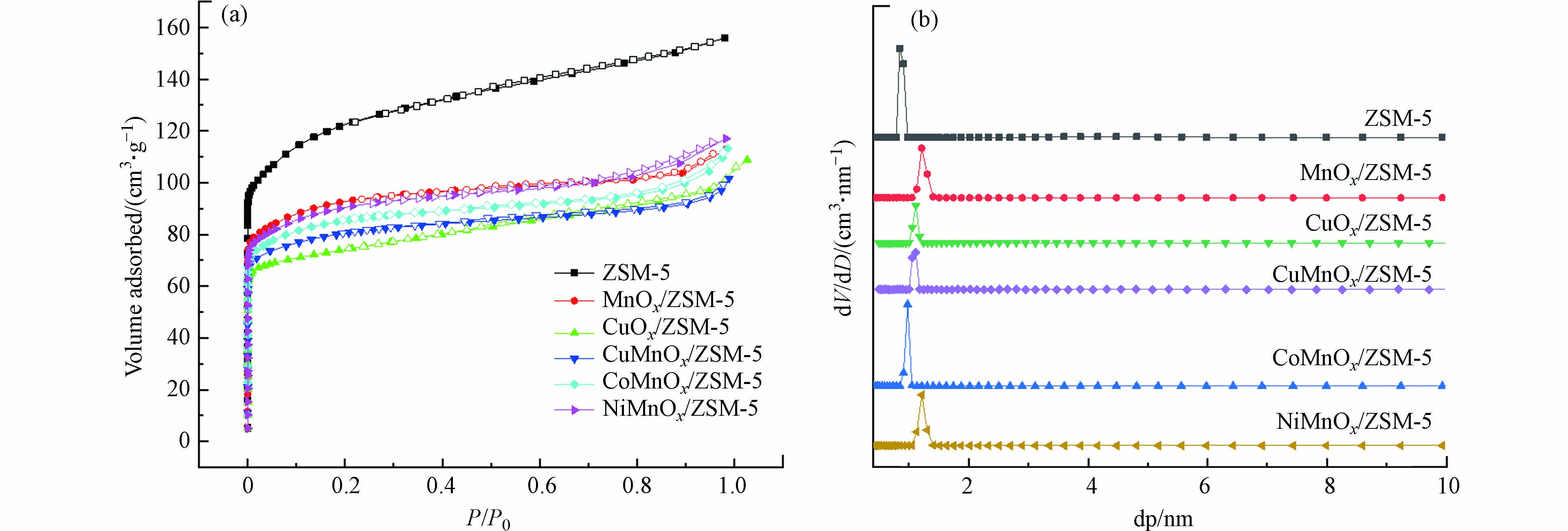
MnOx/ZSM-5、CuOx/ZSM-5、CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5、NiMnOx/ZSM-5和ZSM-5的比表面积及孔结构分析结果如图3和表2所示,各催化剂的比表面积大小顺序为:ZSM-5>MnOx/ZSM-5>NiMnOx/ZSM-5>CuMnOx/ZSM-5>CuOx/ZSM-5>CoMnOx/ZSM-5. 由图3(a)可知,过渡金属改性前后ZSM-5分子筛均表现为IUPAC分类中的Ⅰ型吸附等温线,在P/P0较低时发生单分子层吸附,相对压力P/P0达到0.45之后,氮气的吸附曲线和脱附曲线不重合,出现了较弱的H4型回滞环,结合图3(b)可知,各催化剂的孔道以1 nm左右微孔为主并存在一定介孔结构[19]. 甲苯分子的动力学直径为0.59 nm,研究表明在0.8—2.4 nm范围之间的孔最有利于甲苯的吸附,因此各催化剂对甲苯均表现出较高的吸附容量[20-21]. 过渡金属掺杂后,催化剂的比表面积和孔容有所降低,这是由于过渡金属氧化物进入到了ZSM-5的孔道中,导致部分孔道被堵塞[22].
结合表1、表2以及图2中数据可知,相对大的比表面积和孔容量可能有利于CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附和催化氧化,但各催化剂的比表面积以及孔容量并未与吸附容量和催化活性表现出直接的线性关系. 即使MnOx/ZSM-5表现出最高的比表面积,NiMnOx/ZSM-5具有最高的孔容量,但它们的吸附和催化氧化性能并非最优.
-
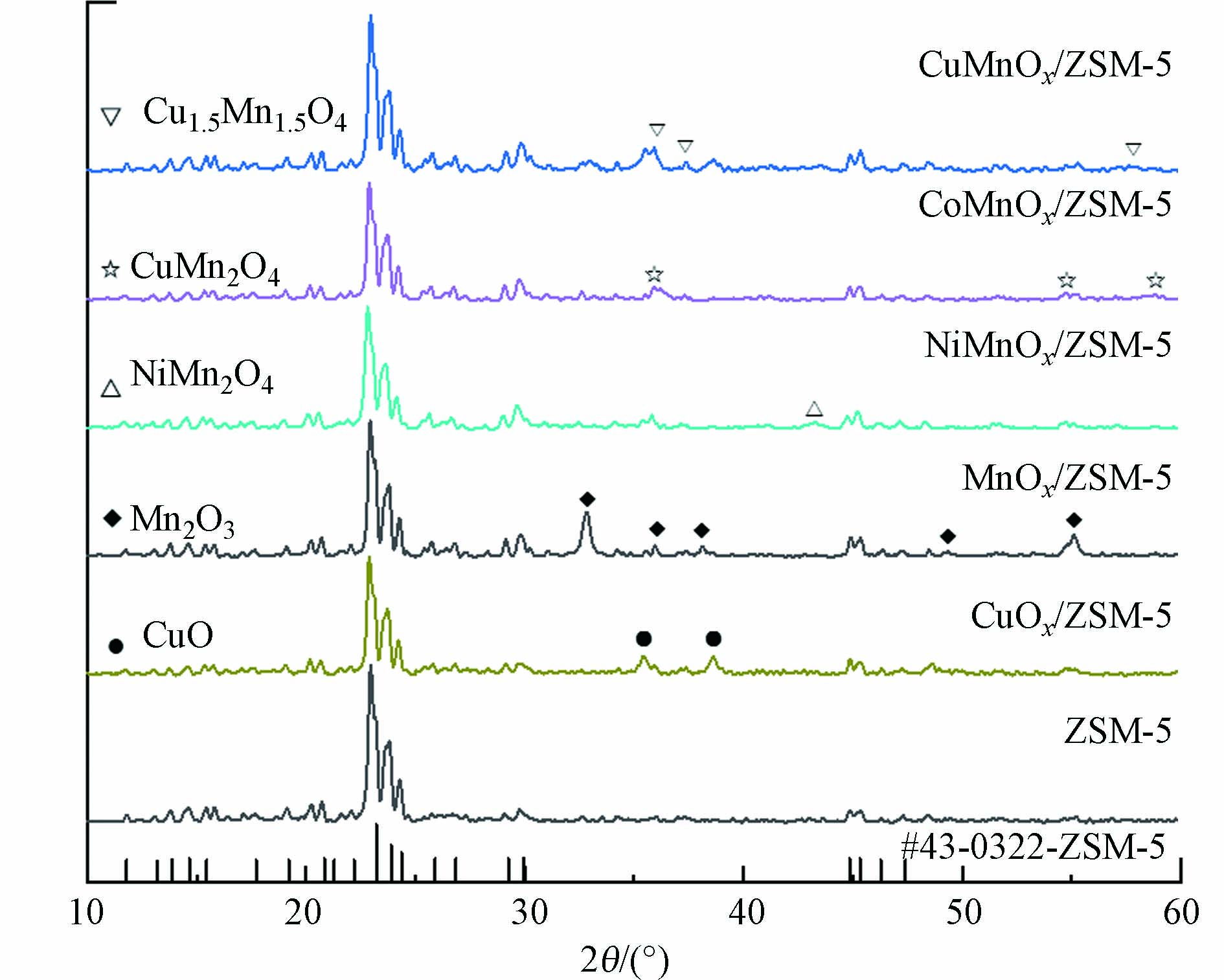
ZSM-5、MnOx/ZSM-5、CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5、NiMnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5的X射线衍射图谱如图4所示,图中对所制备催化剂的物相组成进行了分析. ZSM-5与ZSM-5沸石分子筛标准卡片JCPDS#43-0322的衍射峰吻合良好,所制备的MnOx/ZSM-5、CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5、NiMnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5也均保留了ZSM-5的主要衍射峰,表明过渡金属的掺入并未破坏分子筛载体的骨架结构. 在MnOx/ZSM-5图谱中的32.9°、36°、37.4°、49.3°、55.1°处观察到了Mn2O3(JCPDS#24-0508)的特征衍射峰,Cu、Co和Ni掺入后Mn2O3相关衍射峰明显变弱,这说明过渡金属掺杂能促进锰氧化物在载体上的分散,减少锰氧化物的团聚的发生[23-24]. 在CuMnOx/ZSM-5中,除在35.5°和38.8°观察到CuOx/ZSM-5中存在的CuO(JCPDS#45-0937)典型主峰外,还在36°、37.4°、57.8°处观察到Cu1.5Mn1.5O4(JCPDS#35-1171)的衍射峰. CoMnOx/ZSM-5和NiMnOx/ZSM-5中也分别出现了CoMn2O4(JCPDS#01-1126)和NiMn2O4(JCPDS#36-0083)的较弱衍射峰,这说明形成的金属氧化物高度分散且晶体尺寸较小[23, 25]. 有研究表明,Cu1.5Mn1.5O4和CoMn2O4中存在的Cu-O-Mn、Co-O-Mn架桥可以加快电子流动,从而大幅度提高催化氧化性能,这可能与CuMnOx/ZSM-5和CoMnOx/ZSM-5在催化氧化甲苯过程中表现出的良好催化活性有关[26-28].
-
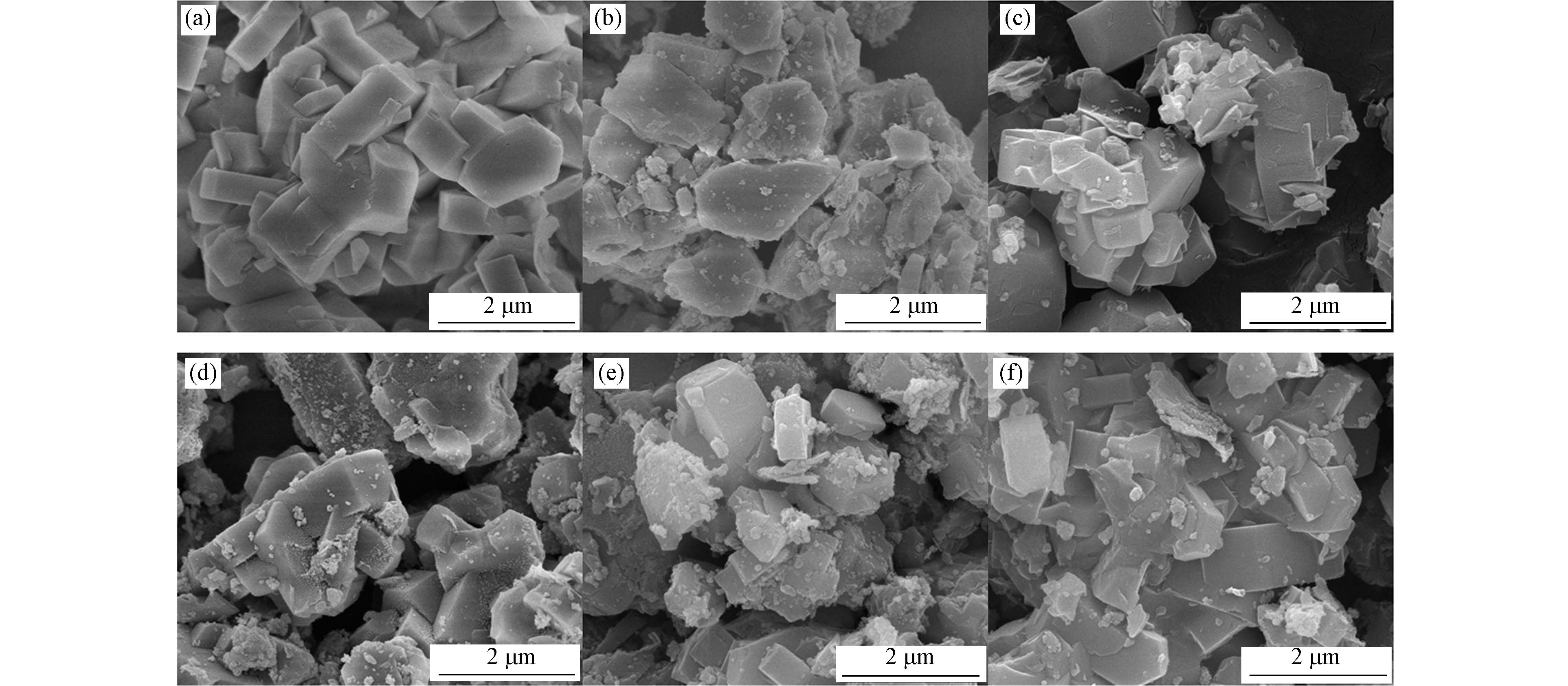
通过SEM观察到的ZSM-5、MnOx/ZSM-5、CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5、NiMnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5的形貌结构如图5所示.
未经改性的ZSM-5晶粒以棱柱状为主,形貌均一,表面光滑且晶体粒径较为均匀. 负载过渡金属后,各催化剂SEM图像中仍能观察到ZSM-5的棱柱状晶粒,说明负载过渡金属未改变分子筛载体的形貌结构,与XRD显示的结果一致. 此外,负载不同过渡金属的ZSM-5晶体表面出现了大小不一的团状和颗粒状物质,表面由光滑变得粗糙,说明过渡金属成功地负载到了ZSM-5载体表面. 其中,CuMnOx/ZSM-5和CoMnOx/ZSM-5载体表面的颗粒分布更加均匀且颗粒粒径更小. 结合XRD结果推断,Cu、Co引入后产生了高度分散且晶体尺寸更小的金属氧化物,这可能与Cu1.5Mn1.5O4、CoMn2O4的形成有关. 结合甲苯吸附和催化氧化结果可知,更加分散的金属氧化物颗粒为吸附和催化氧化甲苯提供了大量的反应活性位点,增大了活性位点利用率,从而使CuMnOx/ZSM-5表现出较好的吸附及催化氧化性能[22-23].
-
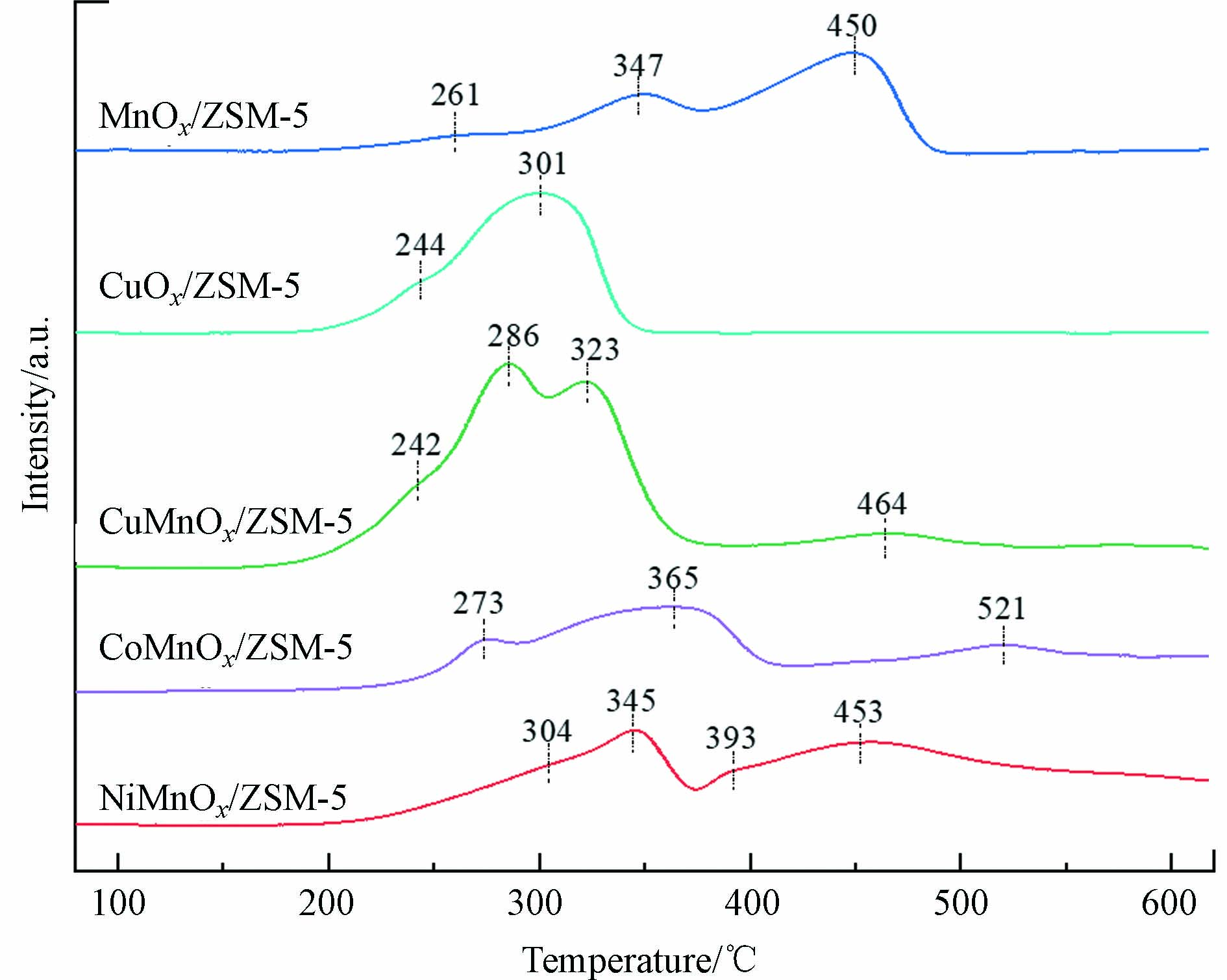
MnOx/ZSM-5、CuMnOx/ZSM-5、CoMnOx/ZSM-5、NiMnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5的H2-TPR曲线和耗氢量分别如图6和表2所示,各催化剂的耗氢量大小顺序依次为:CuMnOx/ZSM-5>CoMnOx/ZSM-5>NiMnOx/ZSM-5>MnOx/ZSM-5>CuOx/ZSM-5,与各催化剂催化氧化甲苯性能间有良好相关性.
MnOx/ZSM-5的H2-TPR曲线在261 ℃、347 ℃和450 ℃分别存在3个还原峰,其中处于261 ℃的较弱还原峰可能与Mn4+→Mn3+的还原过程有关,剩余的两个剧烈还原峰则对应Mn3+→Mn2+的还原过程[29-31]. Cu、Co掺杂明显降低了MnOx/ZSM-5的还原峰温度,CuMnOx/ZSM-5在242 ℃就表现出明显的还原峰,与MnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5相比还原峰面积更大;Co掺杂后,CoMnOx/ZSM-5的还原峰出现在273 ℃,结合XRD分析结果可知,Cu、Co掺杂后,生成了混合金属氧化物Cu1.5Mn1.5O4和CoMn2O4,不同金属氧化物间的强相互作用使晶格氧活动性增强,促进了氧化还原反应的进行[32-34]. NiMnOx/ZSM-5的还原峰位置与MnOx/ZSM-5相似,相比之下还原峰面积略有增加,结合甲苯催化氧化结果可知,Ni的掺杂对MnOx/ZSM-5的氧化还原能力影响不大.
-
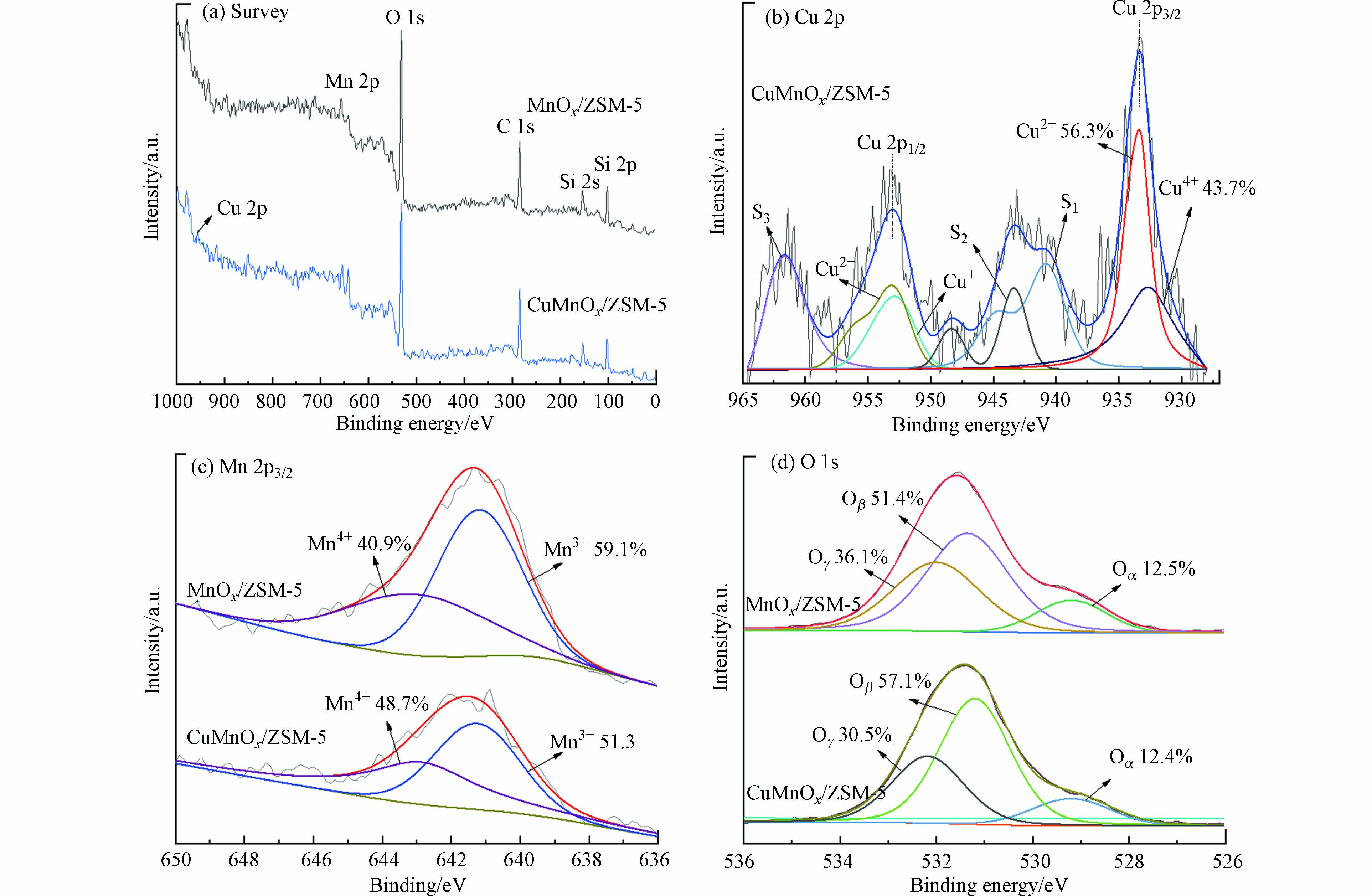
图7为MnOx/ZSM-5和CuMnOx/ZSM-5的XPS谱图. 在图7(a)可以观察到,MnOx/ZSM-5和CuMnOx/ZSM-5中均出现了对应于Si、O、C和Mn物种的峰,CuMnOx/ZSM-5在930 eV—960 eV额外出现了Cu 2p的峰,这表明Cu成功掺入到了MnOx/ZSM-5中[35]. 如图7(b)所示,位于932.7 eV和933.2 eV的两个峰分别归属于Cu+和Cu2+,表明Cu离子以Cu+和Cu2+混合价态形式存在[36-37].
此外,图7(b)中941.0 eV和961.65 eV处的S1和S3峰为Cu2+的卫星峰,943.36 eV处的S2峰为Cu+的卫星峰,Cu+/Cu2+的值为0.78,说明催化剂中Cu2+为Cu的主要价态[38]. Mn 2p3/2的XPS光谱如图7(c)所示,MnOx/ZSM-5和CuMnOx/ZSM-5催化剂在641.3 eV和642.7 eV左右的峰分别归属于Mn3+和Mn4+[38]. 与MnOx/ZSM-5相比(Mn3+/Mn4+=1.45),CuMnOx/ZSM-5中Mn3+与Mn4+的比值(1.05)明显降低,说明Cu掺杂使部分Mn3+向Mn4+转化.Mn4+物种可以在更低的温度下被还原,从而使CuMnOx/ZSM-5表现出更高的催化活性[23]. 如图7(d)所示,在529 eV、531 eV和532 eV附近O 1s的XPS光谱可以分解为3个峰,分别对应于晶格氧物种(Oα)、表面吸附氧物种(Oβ)和表面羟基与硅酸盐中的氧离子(Oγ)[24, 39]. 其中,Oβ与催化剂表面氧空位的存在密切相关,对甲苯的催化氧化具有促进作用[40]. MnOx/ZSM-5和CuMnOx/ZSM-5中Oβ/O的值分别为51.4%和57.1%,Cu引入后Oβ的数量明显增加,这可能是由于CuMnOx/ZSM-5中氧化还原电位的差异,使得Cu-Mn之间存在明显的电子相互作用,促进了电子迁移,导致催化剂表面电荷不平衡,出现了丰富的氧空位和不饱和化学键,产生了更多的Oβ,从而表现出更好的催化活性[41-43]. 结合XRD、H2-TPR、XPS分析和催化性能评价,证实了CuMnOx/ZSM-5中存在的Cu1.5Mn1.5O4对催化活性的提升有积极作用,更多的Mn4+和Oβ提高了CuMnOx/ZSM-5催化氧化甲苯的性能.
-
在上述研究中发现,Cu掺杂的MnOx/ZSM-5表现出了最高的吸附容量和催化活性,结合表征结果可知,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的吸附和催化氧化性能与其物理结构性质以及氧化还原性能之间有良好的相关性. 为进一步考察其工业应用前景,实验对不同空速和湿度条件下CuMnOx/ZSM-5吸附和催化氧化甲苯的性能进行了评估,同时考察了CuMnOx/ZSM-5的再生性和稳定性,为VOCs吸附/催化双功能材料的工业应用提供参考.
-
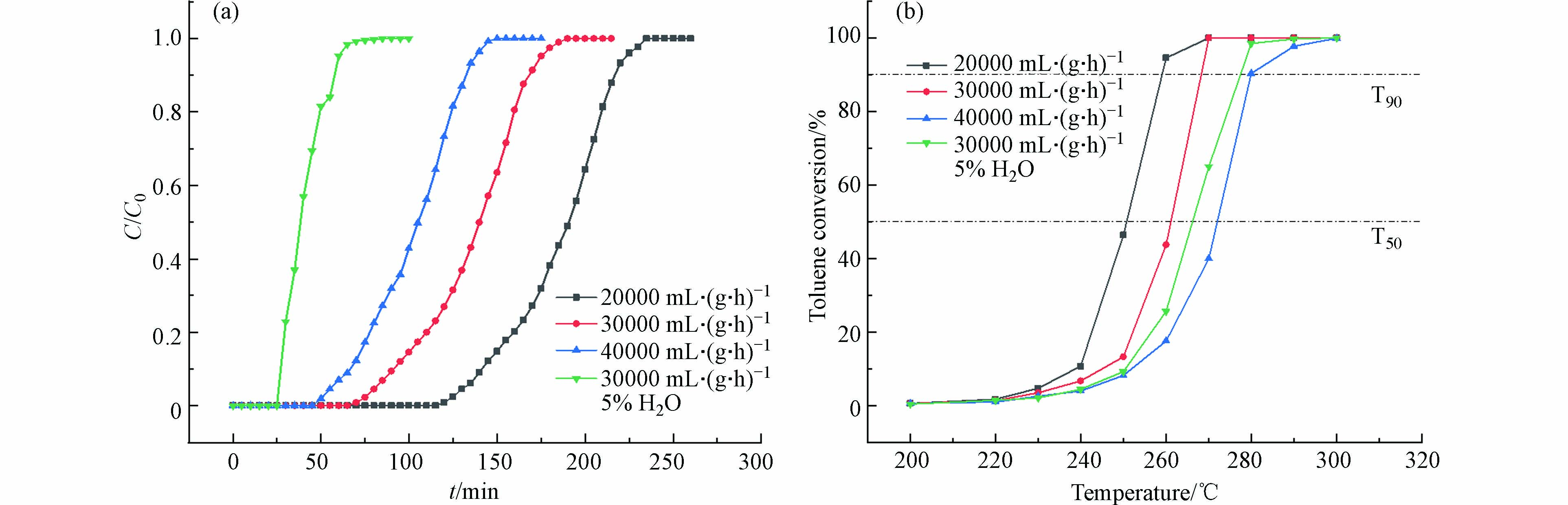
在不同空速下,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的吸附穿透曲线及吸附甲苯的性能如图8(a)、表3所示. 当空速为20000 mL·(g·h)−1时,CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附在131 min时开始穿透,在235 min时达到平衡,甲苯的穿透吸附量为15.39 mg·g−1,平衡吸附量为22.32 mg·g−1;当空速提升到30000 mL·(g·h)−1和40000 mL·(g·h)−1时,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的填充量相应减少,导致CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的穿透时间分别缩短至81 min和56 min,吸附平衡时间分别缩短至190 min和150 min,但单位质量催化剂的穿透吸附量和平衡吸附量仍然分别保持在14 mg·g−1和22 mg·g−1以上,说明催化剂在一定的空速范围内均能保持良好的吸附性能.
在不同空速下,CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的催化氧化活性如图8(b)所示. 随空速增大,催化剂对甲苯的催化活性逐渐降低. 当空速为20000 mL·(g·h)−1时,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的T50和T90值分别为251 ℃和259 ℃,而在空速提升到30000 mL·(g·h)−1和40000 mL·(g·h)−1时,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的T50分别上升为261 ℃和272 ℃,T90分别上升为268 ℃和280 ℃.这是由于空速较高时甲苯气体在催化剂床层中停留时间短,未能与催化剂充分接触氧化,导致催化活性下降. 但即便在较高空速下,CuMnOx/ZSM-5仍表现出良好的催化氧化性能,能以较低的温度去除甲苯.
-
在无水蒸气存在和引入5 vol.% H2O的条件下,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的吸附穿透曲线及吸附甲苯的性能如图8(a)、表3所示. 引入H2O后,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的穿透时间缩短至26 min,吸附平衡时间缩短至85 min,穿透吸附量和平衡吸附量也分别降低至4.97 mg·g−1和7.71 mg·g−1. 可见,湿度对CuMnOx/ZSM-5的吸附性能有一定的影响,这与水分子和甲苯在分子筛表面的竞争吸附密切相关[44].
CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的催化氧化性能如图8(b)所示. 引入5 %vol. H2O后,CuMnOx/ZSM-5的T50从261 ℃上升到了266 ℃,升高了5 ℃,T90从268 ℃上升到了277 ℃,升高了9 ℃. 这是由于水蒸汽使载气中氧气含量变低,导致催化剂表面接触氧浓度降低,影响了催化剂表面活性氧的循环再生;同时,水分子与甲苯在催化剂表面活性位上的竞争吸附阻碍了甲苯的催化反应[23]. 但所制备的CuMnOx/ZSM-5仍能以较低温度去除甲苯,对高湿环境表现出良好的适应性.
-
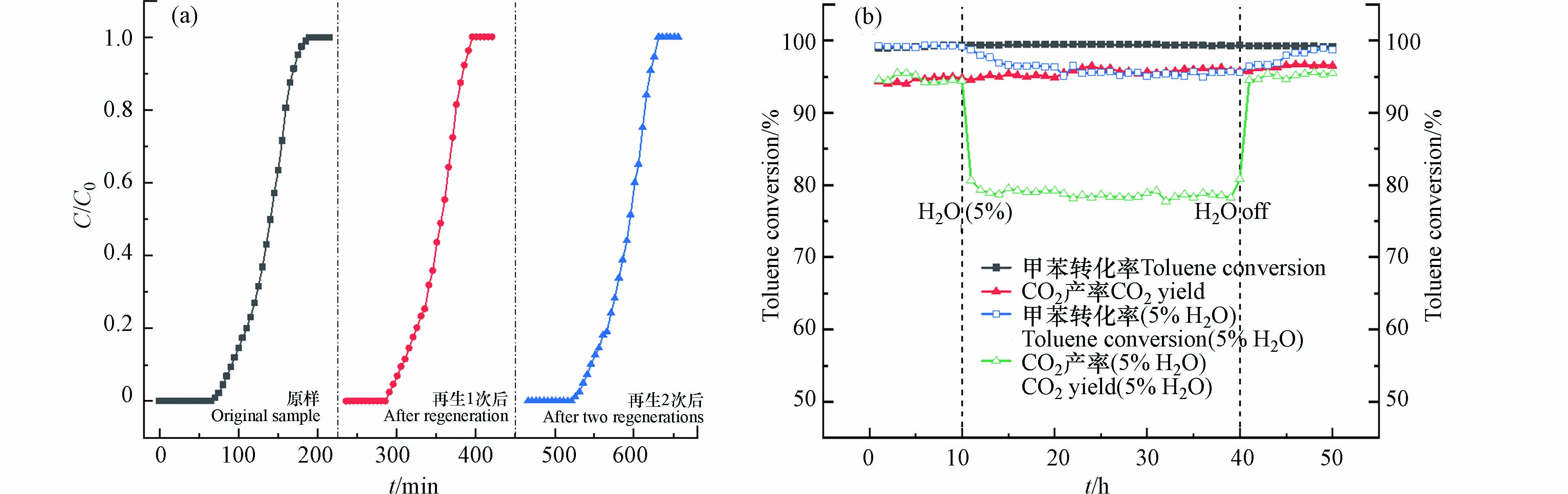
为探究CuMnOx/ZSM-5原位再生后的吸附性能变化,对催化剂进行了3次吸附与2次再生实验. 由图9(a)和表4可以看出,催化剂再生后的穿透时间分别缩短了15 min和6 min,吸附平衡时间分别缩短了25 min和20 min,吸附容量下降在3 mg·g−1以内,说明原位再生后CuMnOx/ZSM-5的吸附性能变化不大,具有良好的再生性. 在270 ℃对CuMnOx/ZSM-5进行了连续50 h的催化稳定性测试,结果如图9(b)所示. CuMnOx/ZSM-5在连续50h的催化氧化甲苯过程中表现出稳定的催化性能,对甲苯的去除率均在98%以上,CO2产率也均在94%以上,碳平衡值约为99%,说明该催化剂具有良好CO2选择性,无二次污染物产生. 在270 ℃条件下还对CuMnOx/ZSM-5催化剂进行了H2O(5% vol)稳定性试验. 研究发现,在固定床中通入5%vol H2O后CuMnOx/ZSM-5的甲苯转化率下降到95%,从进气中去除水蒸气后,甲苯转化率又恢复至原本的98%,这表明水蒸气的引入对催化剂的活性影响不大,而且这种影响是可逆的.这与CuMnOx/ZSM-5表面稳定的活性位点密切相关,说明CuMnOx/ZSM-5具备高效、稳定的催化性能,具有良好的工业应用前景.
此外,比较了相关文献和本文制备的CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯的吸附和催化氧化性能. 从表5可以看出,与相关文献中的实验数据相比,CuMnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯表现出更好的吸附性和催化氧化性能,在VOCs处理中具有一定的优势.
-
(1)过渡金属掺杂后,各催化剂对甲苯的吸附容量大小顺序依次为:CuMnOx/ZSM-5>MnOx/ZSM-5>NiMnOx/ZSM-5≈CuOx/ZSM-5>CoMnOx/ZSM-5,对甲苯的催化活性大小顺序依次为:CuMnOx/ZSM-5>CoMnOx/ZSM-5>MnOx/ZSM-5>CunOx/ZSM-5>NiMnOx/ZSM-5在所制备的催化剂中表现出最好的吸附和催化氧化性能.
(2)各催化剂的比表面积以及孔容量并未与其吸附容量和催化活性表现出直接的线性关系. Cu和Co的掺入产生了高度分散且晶体尺寸更小的金属氧化物,有利于催化氧化反应的发生. 其中,CuMnOx/ZSM-5中的Cu和Mn在甲苯吸附和催化氧化过程中产生强相互作用,使催化剂Mn4+以及Oβ物种量增多,提供了大量的活性位点,使CuMnOx/ZSM-5表现出较好的吸附和催化氧化性能. Ni的掺杂对MnOx/ZSM-5的催化活性影响不大.
(3)CuMnOx/ZSM-5在不同空速下均表现出良好的吸附和催化氧化性能,在高湿环境中吸附性能下降,但在催化氧化过程中仍能以较低温度去除甲苯,同时具有良好的再生性和稳定性,能够很好地实现再生和连续操作,具有良好的工业应用前景.
过渡金属掺杂MnOx/ZSM-5对甲苯吸附和催化氧化的影响
Effect of transition metal oxide doping MnOx/ZSM-5 on the adsorption and catalytic oxidation of toluene
-
摘要: 实验采用柠檬酸络合法制备了一系列过渡金属掺杂MnOx/ZSM-5的吸附/催化双功能材料,以甲苯为处理对象,探讨了过渡金属Cu、Co和Ni掺杂对MnOx/ZSM-5吸附和催化氧化性能的影响. 通过BET、XRD、SEM、H2-TPR和XPS对所制备催化剂进行了表征,并进一步评估了CuMnOx/ZSM-5的工业适用性. 结果显示,CuMnOx/ZSM-5在所有催化剂中表现出最好的吸附和催化氧化性能,对甲苯的平衡吸附量为25.90 mg·g−1,与MnOx/ZSM-5和CuOx/ZSM-5相比,其催化氧化甲苯的T50和T90均降低了30 ℃左右. 由表征结果可知,CuMnOx/ZSM-5中的Cu和Mn在甲苯吸附和催化氧化过程中产生强相互作用,使催化剂中Mn4+以及表面吸附氧(Oβ)物种量增多,提供了大量的活性位点,增强了其吸附和催化氧化性能. 此外,CuMnOx/ZSM-5在不同空速下均表现出良好的吸附和催化氧化性能,在高湿环境中吸附性能下降,但仍能对甲苯表现出良好的催化氧化性能,同时还具有良好的再生性和稳定性,可在吸附-催化氧化一体化技术处理工业VOCs中发挥重要作用.
-
关键词:
- 甲苯 /
- 过渡金属 /
- ZSM-5沸石分子筛 /
- 吸附 /
- 催化氧化.
Abstract: A series of transitional metal oxide doping MnOx/ZSM-5 were prepared via conventional citric acid complex method, and evaluated as adsorbent/catalyst bifunctional materials for VOCs elimination. The effects of transition metal Cu, Co and Ni doping on the adsorption and catalytic oxidation properties of MnOx/ZSM-5 were examined using toluene as representative molecules. Systematic structural/physicochemical characterizations such as BET, XRD, SEM, H2-TPR, XPS were also performed along with practical application tests under simulated industrial conditions. Results showed that the CuMnOx/ZSM-5 exhibited the best adsorption and catalytic oxidation performance among all the prepared catalysts. Compared with MnOx/ZSM-5 and CuOx/ZSM-5, the T50 and T90 of CuMnOx/ZSM-5 by toluene combustion were reduced by about 30°C with its equilibrium adsorption capacity of toluene above 25.90 mg·g−1. Characterization results suggested that strong interaction existed between Cu and Mn of CuMnOx/ZSM-5, which resulted in the formation of more Mn4+ and surface adsorbed oxygen(Oβ) species, providing more reactive sites and enhancing the adsorption and catalytic oxidation performance. In addition, practical application tests demonstrated that CuMnOx/ZSM-5 presented excellent tolerance to different space velocities turbulence, as well as good regeneration ability and long-term stability, although the high humidity environment could cause certain deterioration in adsorption performance. All the results suggested that CuMnOx/ZSM-5 could be promising candidates with practical potentials for the treatment of industrial VOCs by the integrated adsorption-catalytic oxidation technology.-
Key words:
- toluene /
- transition metal oxide /
- ZSM-5 zeolite molecular sieve /
- adsorption /
- catalytic oxidation.
-
磷是与能源和水并列的重要资源,具有单向流动和不可再生的特性[1-3]。依据美国地质调查局2010年数据,目前,磷矿资源可持续开采仅能维持50 a左右。一方面,由于磷矿不断受到镉、铀等放射性金属的污染以及富磷矿资源日益稀缺,致使开采难度逐年提高[4];另一方面,随着全球人口的增长以及社会经济的发展,对必须利用磷元素进行生产的产品需求也不断增大。磷矿的稀缺性和不可替代性使上述矛盾不断加剧,解决矛盾的方法之一就是从各种富磷废弃物中进行磷回收。
污泥磷回收技术主要是通过物理或化学的方法使污泥产生富磷上清液,通过投加金属盐类形成不溶性磷酸盐沉淀。磷的不同形态及其分布影响着污泥磷回收的效率。从污泥中回收磷的首要条件是污泥中的磷从固相转移到液相中[5]。目前,污泥磷溶出的方法主要有物理法、化学法和生物法等[6]。磷的溶出率基本上与其存在形态相关[7]。对于城市污泥中磷元素的研究,主要集中在污泥综合利用及其资源化利用等方面,包括农田林地应用和建筑材料应用等[8]。城市污泥中总磷含量为30 mg·g−1左右,大部分的磷随污泥进入填埋场所,仅有18.65%的磷被土地利用[9];同时,磷是水体富营养化的主要影响因子,水体中的磷含量增高易造成水华现象。因此,对污泥中磷的溶出过程进行研究十分必要。通过适当的提取方法,了解各形态磷占总磷的比例,对于研究污泥中磷的溶出规律以及污泥的资源化利用具有重要的意义。
自1990年起,化学连续提取法[10]在欧共体标准测量与检测局发起的欧洲标准测试计划框架下逐步发展,是一种标准化的沉积物磷形态分析方法。该方法操作简单,是目前广泛应用的磷形态连续分级提取方法[11],对污泥样品同样具有很好的实际操作性。该方法分3个步骤,采用盐酸和氢氧化钠进行提取,得到5种磷形态,包括总磷(TP)、无机磷(IP)、有机磷(OP)、非磷灰石无机磷(NAIP)和磷灰石无机磷(AP)[12]。
污泥磷溶出有多种方式,其中热解法和酸碱处理法是较为常用且高效的方法。热解法又分为高温预处理(一般温度高于100 ℃)[13]和低温预处理。考虑高温预处理成本较高,且pH对污泥磷溶出的影响一直是学者们的研究热点,而添加EDTA可以抑制金属离子在加热过程中对污泥磷溶出的影响,本研究通过SMT法提取污泥中不同形态的磷,分析磷的形态分布规律,并采用低温热解法、酸碱处理法和投加EDTA 3种方式研究北京市3座污水处理厂污泥中磷的溶出特性,为污泥资源化利用以及污泥磷回收提供技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
污泥为经污泥浓缩池处理后的脱水污泥。含水率低,易于储存,且含磷量较高。采自北京市高碑店(传统活性污泥法)、肖家河(A / O工艺)和清河(倒置A / A / O工艺)3座污水处理厂,含水率分别为36.48%、60.40%和74.42%。污泥样品在105 ℃下烘干12 h,经研磨后过 100 目筛,制成干污泥存于冰箱备用。
1.2 实验方法
1)污泥中磷的形态分析。以3座污水处理厂污泥中的磷为研究对象,应用SMT法[14]对污泥中各种形态的磷浓度进行检测,逐级提取,采用钼锑抗分光光度法对溶液中的磷进行测定。
2)污泥中磷的溶出实验。低温热解实验:分别取3种污泥0. 2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。将混合液置于恒温水浴锅中,温度分别控制在40、50、60和70 ℃,在中性pH条件下研究,低温热解6 h。投加酸碱实验:分别称取3种污泥0.2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。分别用浓度为1 mg·L−1的HCl和1 mg·L−1的NaOH调节溶液pH,pH分别控制为4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0和10.0,在常温条件下研究。反应24 h。投加EDTA实验:取3种污泥0.2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。添加0、5、10和15 mmol·L−1的EDTA,在常温条件下研究。反应24 h。
以上实验平行3次,实验数据取平均值。反应结束后均取上清液于2 000 r·min−1离心15 min后测量磷酸根和总磷的浓度。磷酸根和总磷的测定采用钼锑抗分光光度法。
1.3 试剂及仪器
试剂包括氢氧化钠、盐酸、磷酸二氢钾、抗坏血酸、钼酸铵、酒石酸锑钾和氯化钠等,均为分析纯。仪器包括恒温振荡器(HY-2B)、紫外可见分光光度计(UV-2102C型)、离心机(TGL-16D)、恒温水浴锅(HH-WO)和台式pH计(Ohaus STARTER 3C)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 污泥中磷的组成和形态
污泥中总磷和各形态磷含量的测定结果如表1所示。各形态磷占总磷的百分比见图1。在SMT分级法中,总磷为有机磷和无机磷的总和,无机磷为非磷灰石态无机磷和磷灰石态无机磷的总和,可将其分别表示为TP=OP+IP,IP=NAIP+AP[15]。结果表明,高碑店、肖家河和清河3座污水处理厂污泥的TP浓度分别为47.12、34.03、31.35 mg·g−1,IP依次占TP的89.3%、71.7%、74.7%,这表明污泥中的磷主要以IP的形态存在;而在IP中,NAIP是主要的存在形态;OP含量较低,仅为3%~10%。
表 1 3座污水处理厂污泥中各形态磷的浓度和占比Table 1. Concentrations and proportions of different phosphorus species in sludge from three different sewage treatment plants不同形态的磷 高碑店 肖家河 清河 浓度/(mg·g−1) 占比/% 浓度/(mg·g−1) 占比/% 浓度/(mg·g−1) 占比/% 有机磷 1.56±0.03 3.3 3.32±0.07 9.8 1.95±0.05 6.2 非磷灰石态无机磷 14.64±0.01 31.1 16.17±0.05 47.5 18.70±0.05 59.7 磷灰石态无机磷 13.62±0.02 28.9 7.89±0.05 33.2 2.41±0.01 7.7 其他的无机磷 13.85±0.00 29.3 0.35±0.10 1.0 2.30±0.08 7.3 其他形态的磷 3.467±0.09 7.4 6.30±0.02 18.5 5.98±0.06 19.1 由图1可知,高碑店和肖家河污水处理厂污泥中的AP占比较高,占TP的30%左右,而清河污水处理厂污泥中的AP含量很低,仅占TP的7.7%,这是因为污水处理厂来水组成不同,致使污泥中各形态磷的占比不同[16]。经调查可知,高碑店和肖家河污水处理厂来水中均含有工业废水,AP是工业废水中磷的主要存在形态,因此,其占比较高;而清河污水处理厂来水为生活污水,因此,其占比相对较低。
2.2 污泥中磷的溶出实验
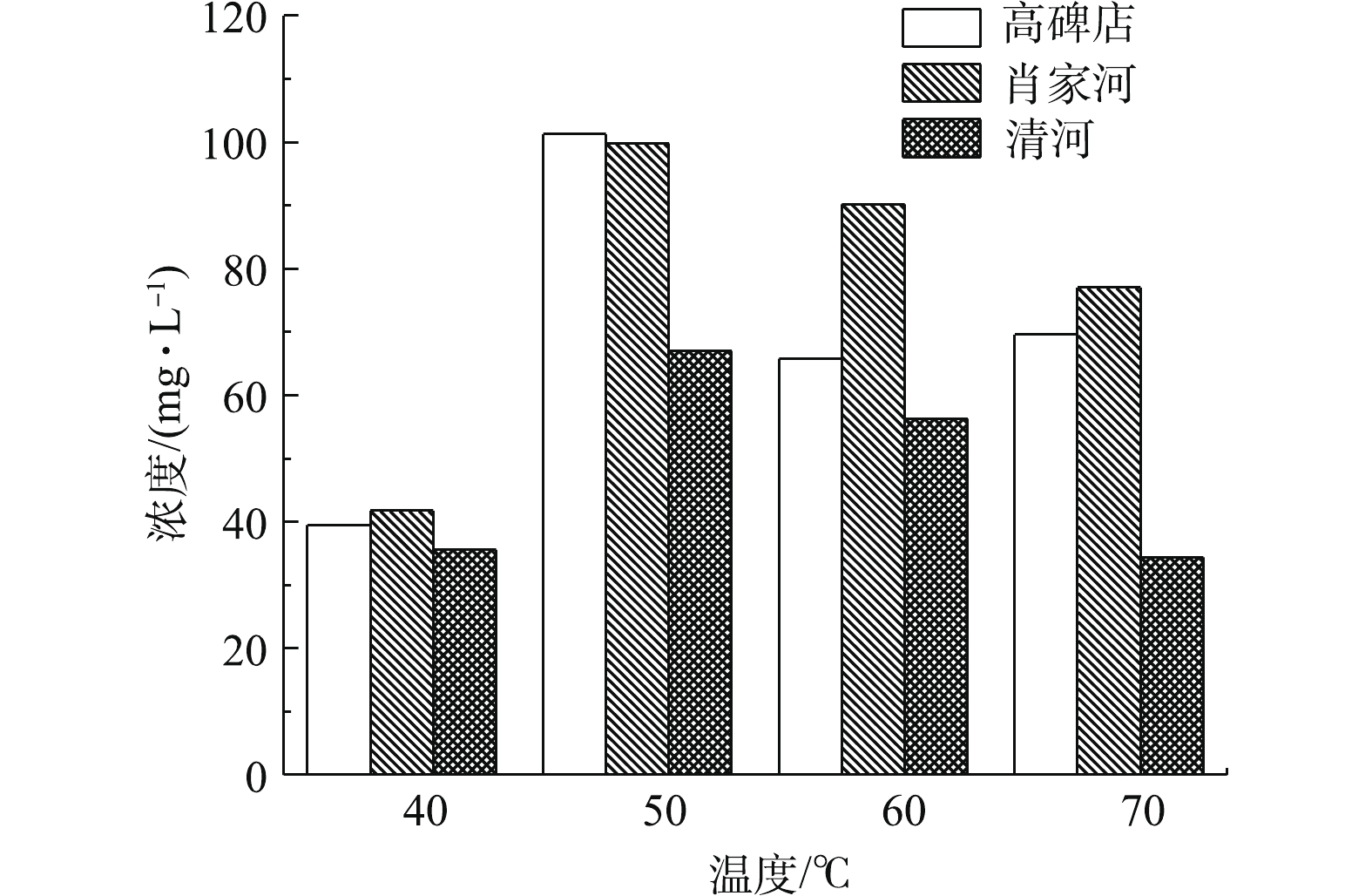
1)温度对污泥磷溶出的影响。经低温热解后,磷逐渐从污泥中溶出到上清液中,其中总磷浓度见图2。在不同温度下,3种污泥中的磷元素均有所溶出。这是由于升温破坏了污泥的表面结构,使污泥絮体分解,污泥中的大量磷得以溶出到上清液中。在50 ℃下,污泥总磷溶出率达到最高,此时高碑店污水处理厂、肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥上清液总磷浓度分别为101.24、99.80、67.02 mg·L−1,总磷溶出率分别为53.7%、73.3%、53.4%。
低温热解释放污泥中的磷,其原理是污泥细胞膜中的磷脂双分子层和细胞核中的DNA和RNA含有大量的磷元素,污泥絮体在加热过程中被破坏,可以有效地使其中的磷溶出[17]。因此,当温度从40 ℃升高到50 ℃时,污泥上清液中总磷的浓度升高;当温度从50 ℃升高到70 ℃时,污泥上清液总磷的浓度却呈下降趋势,这是因为温度升高致使污泥系统中的重金属不断释放,并与溶出的磷结合生成沉淀,导致污泥上清液总磷的浓度降低。
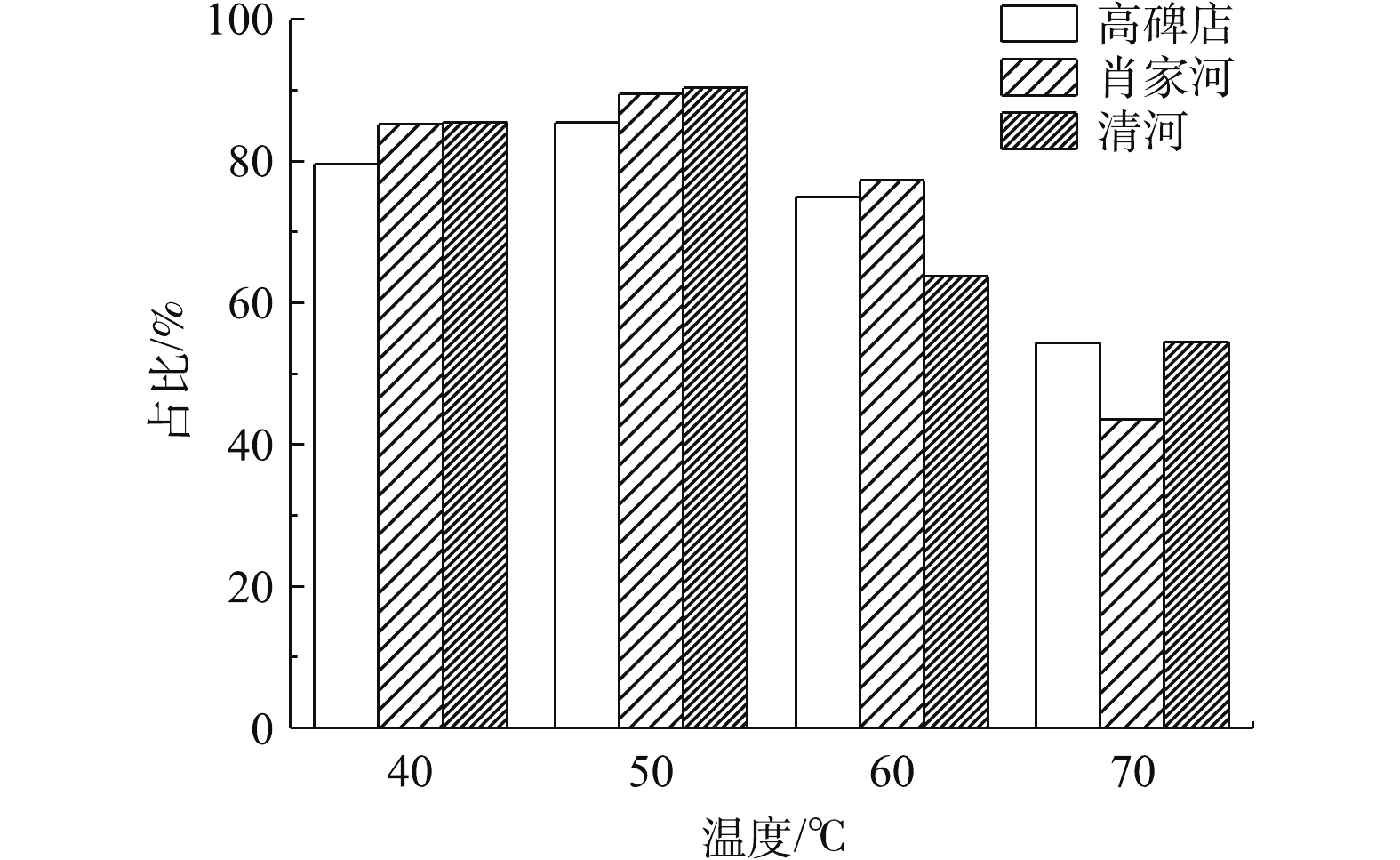
温度是影响污泥磷溶出的重要参数[18],温度过低时,污泥中的磷不能大量溶出;温度过高时,会影响污泥溶出的磷酸根占总磷的比例,而磷酸根的浓度占比越高,越有利于磷的回收[19]。由图3可知,低温热解实验中溶出来的磷以磷酸根为主,在不同温度条件下,3种污泥上清液中磷酸根占总磷的比例均在45%以上;当温度由50 ℃升高到70 ℃时,高碑店污水处理厂、肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥上清液中的磷酸根占总磷的比例均呈现下降的趋势,分别由86%下降到75%,89%下降到44%,90%下降到55%。这是因为污泥上清液中磷酸根占总磷的比例易受污泥中含有的重金属离子的影响,随着温度的升高,污泥中的重金属也不断溶出,从而与上清液中大量的磷酸根离子结合形成不溶性沉淀。
由于热解污泥时需要消耗大量能量,因此,从经济性和磷酸根的占总磷比例2方面进行考虑,在低温热解污泥时,温度并非越高越好。综上所述,确定低温热解温度为50 ℃。薛涛等[20]在处理污泥时,发现最佳的热处理温度为50 ℃,此时释放出来的总磷以磷酸根为主,约占95%。
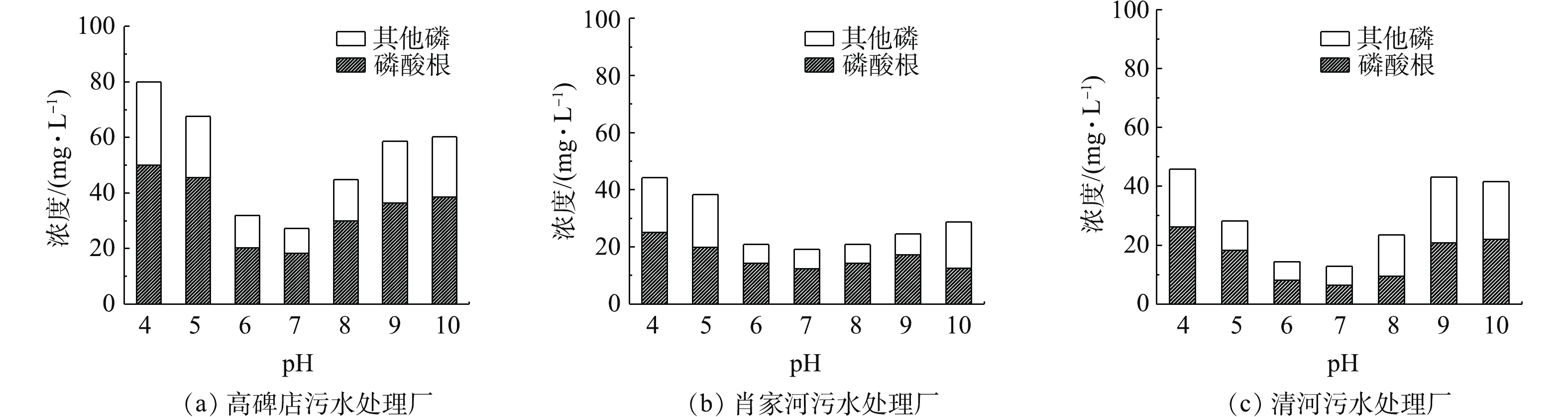
2) pH对污泥磷溶出的影响。pH是影响污泥中磷溶出的重要参数,同时改变磷酸盐沉淀的溶解状态,影响磷的溶解特性,从而改变磷的迁移转化过程[21]。污泥随着pH变化的磷溶出情况见图4,其中,柱状图表示总磷浓度变化,阴影部分为磷酸根浓度变化。结果表明,污泥中的磷在酸性、中性和碱性环境均有溶出。当pH小于7时,污泥上清液中磷的浓度均随着pH的增加而减小,当pH大于7时,污泥上清液中的磷浓度均随着pH的增加而增加。经酸碱处理后,污泥中的磷迅速溶出到上清液中,使磷酸根和总磷的浓度提高。在pH为4时,污泥中的磷达到了最大的溶出率。3种污泥上清液中的总磷含量分别为79.91、44.20、45.80 mg·L−1,总磷溶出率分别为42.4%、32.5%、33.6%。
在酸性条件下,由于酸的溶解作用[22],污泥中磷灰石态无机磷中的部分羟基磷灰石和弱吸附态磷迅速溶出,使得上清液中的磷浓度增加。且溶解作用随着酸性的增强而增强;在中性条件下,3种污泥上清液中的总磷含量最低;在碱性条件下,随着pH的升高,3种污泥上清液中的磷酸根浓度均有所下降,这是生成磷沉淀造成的[23]。
由图4可知,在碱性条件下(pH 8~10),清河污水处理厂污泥释放的总磷浓度均大于肖家河污泥,这是因为在pH较高的情况下,污泥中大部分非磷灰石态无机磷会大量溶出[24]。通过对污水处理厂污泥中的磷形态进行分析,清河污水处理厂污泥的AP含量较低,占污泥中TP的7.70%,而NAIP含量高,占污泥中TP的59.70%;肖家河污水处理厂污泥中AP含量高,占污泥中TP的33.20%,NAIP含量低,占污泥中TP的16.17%。NAIP主要是指铁结合态磷或铝结合态磷,是潜在的活性磷,不稳定,在碱性条件下易释放到水中[25]。AP主要是以钙的磷酸盐形式存在,常见于自然生长的磷灰石或湖泊沉积物中。其含量与陆源排放、沉积类型、沉积环境及间隙水中磷酸根含量等其他因素有关,钙结合态磷难溶于水,稳定性较高,只有在pH降低时有一小部分溶解[26]。因此,肖家河污水处理厂污泥在碱性条件下磷的溶出浓度要低于清河污水处理厂的污泥。
与中性pH条件下相比,投加酸或碱的污泥磷溶出效果均得到提高,且投加酸时的污泥磷释放效果优于投加碱时。综上所述,确定最佳pH为4。
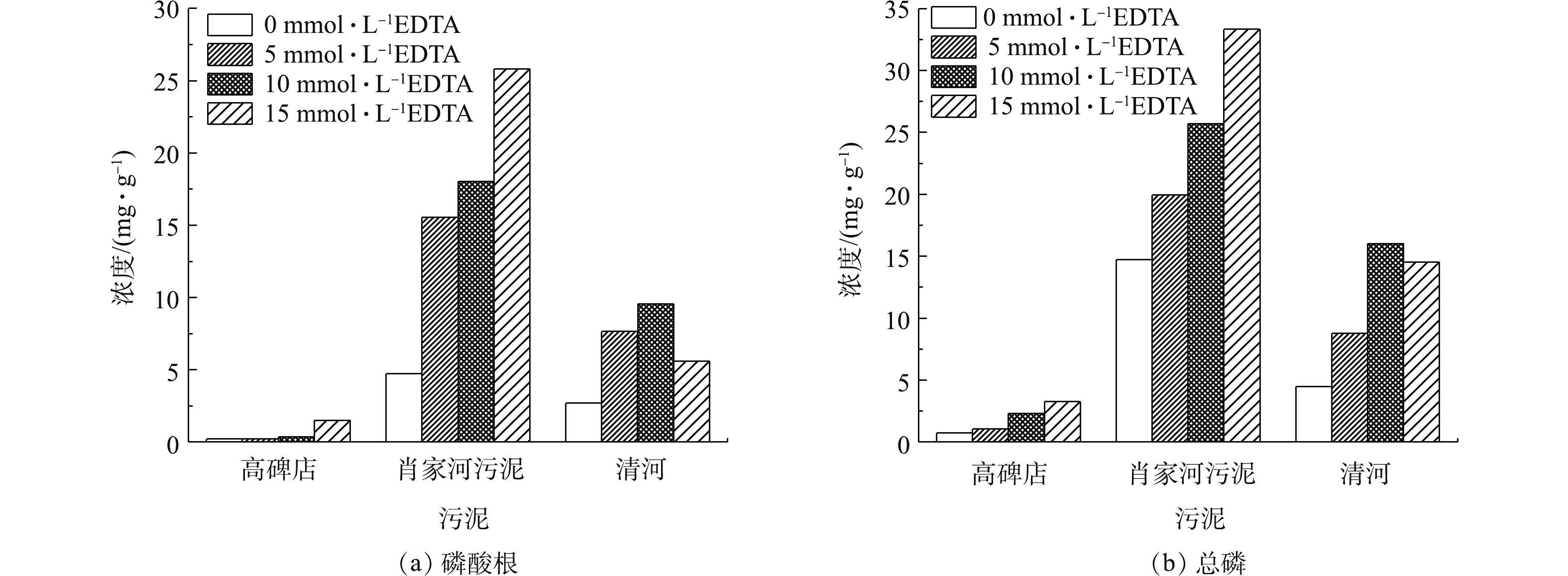
3) EDTA浓度对污泥磷溶出的影响。EDTA是一种重要的络合剂,易溶于水,可以与溶液中的金属离子络合形成稳定的水溶性化合物[27],因此,本研究通过添加EDTA来抑制金属离子对污泥磷溶出的影响。添加不同浓度的EDTA反应24 h后污泥中磷的溶出情况如图5所示。不添加EDTA时,有一部分总磷从污泥中释放出来,3种污泥总磷的溶出率分别为1.6%、43.3%、14.3%。EDTA均促进了污泥中磷的溶出,但对肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥磷的溶出效果明显[28],当EDTA的浓度达15 mmol·L−1时,肖家河污水处理厂污泥中的磷几乎全部溶出到液相中,总磷溶出率可达97.9%。这是由于当EDTA的添加量达到一定程度时,破坏了污泥的稳定结构,从而使污泥中的生物细胞的表面结构暴露出来。此时细胞壁和细胞膜表面上与脂多糖和蛋白质结合的Ca2+和Mg2+会被EDTA所络合,导致污泥细胞内的磷释放出来[29]。
添加EDTA后,高碑店水厂污泥磷的溶出量并没有明显提高。这是因为其采用了生物除磷法的同时,也投加了大量的铁、铝等金属盐类,使废水中的磷转化为不溶性磷酸盐沉淀,使用的除磷药剂主要为液态硫酸铝[30]。EDTA致使污泥分解,细胞内的磷元素释放出来,同时,污泥上清液中聚集了大量的游离Al3+离子,Al3+与水中的OH−易形成Al(OH)3絮状胶体[31],胶体具有巨大的比表面积,能强烈的吸附磷酸盐。也有研究发现,铁与磷的比值越大,磷的释放量越小[32]。HOLDREN等[33]的研究表明,如果铁、磷的原子数量比大于1.8,那么磷酸盐能够由铁离子的氧化物所固定。上述2点原因阻碍了高碑店污泥中磷的溶出,使污泥上清液中磷酸根的浓度偏低。
对比肖家河和清河2个污水处理厂,发现肖家河污水处理厂污泥上清液总磷的浓度要明显大于清河污水处理厂对应的总磷浓度,分析其原因是由于肖家河污水处理厂污泥AP含量较高,而清河污水处理厂污泥AP含量较低,在EDTA浓度相同的情况下,AP的溶出率大于NAIP[31]。EDTA对不同污水处理厂污泥中磷的溶出率差异可能和不同磷酸盐化合物中金属离子的结合能大小有关。综合考察药剂投加的成本等因素,确定最佳EDTA浓度为10 mmol·L−1。
3. 结论
1)3种污泥中的磷主要以IP的形态存在,IP占TP的71.7%~89.3%;而在IP中,NAIP是主要的存在形态。
2)在50 ℃条件下,3座污水处理厂污泥总磷溶出率达到最高。在从40 ℃升高到70 ℃的过程中,污泥上清液总磷的浓度先升高再下降。低温使磷大量溶出,温度过高则会导致溶出的磷酸根占总磷的比例下降,影响后续磷回收。
3)污泥磷在酸或碱条件下的溶出效果均优于中性条件,且酸性条件最优。在碱性条件下,清河污水处理厂污泥溶出的总磷含量均大于肖家河污泥。原因之一是清河污水处理厂厂非磷灰石态无机磷占比大,污泥中大部分非磷灰石态无机磷会大量溶出。
4) EDTA的添加能够明显促进肖家河水厂污泥磷的溶出。在EDTA浓度相同的情况下,磷灰石态无机磷的溶出率大于非磷灰石态无机磷。
5)磷的形态影响着污泥磷的溶出,不同形态的磷在相同实验条件下溶出规律不同,结合磷形态找出合理的释磷条件,有利于提高溶出效率及后续的磷回收。考虑后期磷回收的可行性以及药剂投加成本等因素,确定处理污泥的最佳条件:温度为50 ℃,pH为4,EDTA为10 mmol·L−1。
-
表 1 各催化剂对甲苯的吸附性能
Table 1. Adsorption property of catalysts for toluene
催化剂Catalyst 穿透时间/minPenetration time 穿透吸附量/(mg·g−1)Penetration adsorption capacity 吸附平衡时间/minAdsorption equilibrium time 平衡吸附量/(mg·g−1)Equilibrium adsorption capacity MnOx/ZSM-5 77 14.66 215 24.01 CuMnOx/ZSM-5 81 15.44 190 25.90 CoMnOx/ZSM-5 70 13.31 155 19.78 NiMnOx/ZSM-5 64 12.17 155 21.38 CuOx/ZSM-5 63 11.96 160 21.30 表 2 各催化剂的BET分析和耗氢量计算
Table 2. BET analysis and H2 consumption of catalysts
催化剂Catalyst 比表面积/(m2·g−1)SBET 微孔孔容/(m3·g−1)Micropore volume 总孔容/(m3·g−1)Total pore volume 平均孔径/nmMean pore diameter 耗氢量/(mmmol·g−1)H2 consumption ZSM-5 451.82 0.18 0.24 2.14 - MnOx/ZSM-5 347.60 0.14 0.17 2.01 0.38 CuOx/ZSM-5 303.71 0.12 0.16 2.07 0.36 CuMnOx/ZSM-5 322.15 0.13 0.18 2.18 0.85 CoMnOx/ZSM-5 295.01 0.11 0.16 2.24 0.42 NiMnOx/ZSM-5 338.26 0.14 0.18 2.14 0.41 表 3 CuMnOx/ZSM-5在不同空速、湿度下吸附甲苯的性能
Table 3. Adsorption property of CuMnOx/ZSM-5 under different space velocities and humidities for toluene
穿透时间/minPenetration time 穿透吸附量/(mg·g−1)Penetration adsorption capacity 吸附平衡时间/minAdsorption equilibrium time 平衡吸附量/(mg·g−1)Equilibrium adsorption capacity 20000 mL·(g·h)−1 131 15.39 235 22.32 30000 mL·(g·h)−1 81 15.44 190 25.90 40000 mL·(g·h)−1 56 14.22 150 25.97 30000 mL·(g·h)−15% vol. H2O 26 4.97 85 7.71 表 4 CuMnOx/ZSM-5的再生性能
Table 4. Reproducibility of CuMnOx/ZSM-5
再生次数Regeneration times 穿透时间/minPenetration time 穿透吸附量/(mg·g−1)Penetration adsorption capacity 吸附平衡时间/minAdsorption equilibrium time 平衡吸附量/(mg·g−1)Equilibrium adsorption capacity 0 81 15.44 190 25.90 1 66 12.57 165 23.01 2 75 14.29 170 24.58 表 5 不同催化剂对甲苯的吸附和催化氧化性能
Table 5. Adsorption and catalytic oxidation properties of toluene over various catalysts
-
[1] WU W J, ZHAO B, WANG S X, et al. Ozone and secondary organic aerosol formation potential from anthropogenic volatile organic compounds emissions in China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 53: 224-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.03.025 [2] ZHU L L, SHEN D K, LUO K H. A critical review on VOCs adsorption by different porous materials: Species, mechanisms and modification methods [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 122102. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122102 [3] KAMAL M S, RAZZAK S A, HOSSAIN M M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) - A review [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 140: 117-134. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.05.031 [4] YANG X, YI H H, TANG X L, et al. Behaviors and kinetics of toluene adsorption-desorption on activated carbons with varying pore structure [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 67: 104-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.06.032 [5] HU Q, LI J J, HAO Z P, et al. Dynamic adsorption of volatile organic compounds on organofunctionalized SBA-15 materials [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 149(1/2/3): 281-288. [6] POPOVA M, BOYCHEVA S, LAZAROVA H, et al. VOC oxidation and CO2 adsorption on dual adsorption/catalytic system based on fly ash zeolites [J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 357: 518-525. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.06.070 [7] 杨新玉, 史秋怡, 龙超. 吸附树脂吸附多组分VOCs的动力学特性及预测 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(5): 1830-1837. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.005 YANG X Y, SHI Q Y, LONG C. Adsorption kinetics and prediction of multicomponent VOCs on polymeric resins [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(5): 1830-1837(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.005
[8] LEE J E, OK Y S, TSANG D C W, et al. Recent advances in volatile organic compounds abatement by catalysis and catalytic hybrid processes: A critical review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719: 137405. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137405 [9] ZHANG Z X, JIANG Z, SHANGGUAN W F. Low-temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology and application: A state-of-the-art review [J]. Catalysis Today, 2016, 264: 270-278. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.10.040 [10] 刘秀珍. MnOX-CeO2/蜂窝沸石对甲苯的吸附—低温催化氧化一体化研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012. LIU X Z. The study of adsorption and low temperature catalytic oxidation of toluene on MnOX-CeO2/honeycomb zeolite[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012(in Chinese).
[11] DONG T, LIU W M, MA M D, et al. Hierarchical zeolite enveloping Pd-CeO2 nanowires: An efficient adsorption/catalysis bifunctional catalyst for low temperature propane total degradation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 393: 124717. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124717 [12] YU Q J, FENG Y C, TANG X L, et al. A novel ferrisilicate MEL zeolite with bi-functional adsorption/catalytic oxidation properties for non-methane hydrocarbon removal from cooking oil fumes [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 309: 110509. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110509 [13] BAEK S W, KIM J R, IHM S K. Design of dual functional adsorbent/catalyst system for the control of VOC's by using metal-loaded hydrophobic Y-zeolites [J]. Catalysis Today, 2004, 93/94/95: 575-581. [14] GREENE H L, PRAKASH D S, ATHOTA K V. Combined sorbent/catalyst media for destruction of halogenated VOCs [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 1996, 7(3/4): 213-224. [15] 孙静, 董一霖, 李法齐, 等. Co3O4改性USY分子筛吸附和催化氧化甲苯特性研究 [J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3306-3315. SUN J, DONG Y L, LI F Q, et al. Study on adsorption and catalytic oxidation characteristics of toluene on Co3O4 modified USY molecular sieve [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3306-3315(in Chinese).
[16] WANG Y, YANG D Y, LI S Z, et al. Ru/hierarchical HZSM-5 zeolite as efficient bi-functional adsorbent/catalyst for bulky aromatic VOCs elimination [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 258: 17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.08.052 [17] SIHAIB Z, PULEO F, GARCIA-VARGAS J M, et al. Manganese oxide-based catalysts for toluene oxidation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 209: 689-700. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.042 [18] 高君安, 王伟, 张傑, 等. 用于高湿度废气中甲苯吸附净化的疏水型ZSM-5分子筛的合成及其吸附性能研究 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 337-343. GAO J N, WANG W, ZHANG J, et al. Study on synthesis and adsorption performance of hydrophobic ZSM-5 zeolites for removal of toluene in high-humidity exhaust gas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(1): 337-343(in Chinese).
[19] ZHANG S, LI M, LI W, et al. Comparison and Analysis of Toluene Adsorption Properties of ZSM-5 Molecular Sieve Treated by Different Modification Methods: Adsorption Kinetic and Mechanism Studies [J]. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2021, 23(1): 76-87. [20] 刘伟, 李立清, 姚小龙, 等. 活性炭孔隙结构在其甲苯吸附中的作用 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(9): 3210-3218. LIU W, LI L Q, YAO X L, et al. Pore structure effects on activated carbon adsorption behavior for toluene [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(9): 3210-3218(in Chinese).
[21] WANG B D, GAN F L, DAI Z D, et al. Air oxidation coupling NH3 treatment of biomass derived hierarchical porous biochar for enhanced toluene removal [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123995. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123995 [22] CHAIHAD N, ANNIWAER A, KARNJANAKOM S, et al. In-situ catalytic upgrading of bio-oil derived from fast pyrolysis of sunflower stalk to aromatic hydrocarbons over bifunctional Cu-loaded HZSM-5 [J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 155: 105079. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105079 [23] LI X, WANG L J, XIA Q B, et al. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over copper and manganese based catalysts: Effect of water vapor [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2011, 14(1): 15-19. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.07.003 [24] LI J H, XIAO G F, GUO Z Y, et al. ZSM-5-supported V-Cu bimetallic oxide catalyst for remarkable catalytic oxidation of toluene in coal-fired flue gas [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 419: 129675. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129675 [25] PAPAVASILIOU J, AVGOUROPOULOS G, IOANNIDES T. Combined steam reforming of methanol over Cu-Mn spinel oxide catalysts [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 251(1): 7-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.07.025 [26] XIA G G, YIN Y G, WILLIS W S, et al. Efficient stable catalysts for low temperature carbon monoxide oxidation [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1999, 185(1): 91-105. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1999.2484 [27] 陆义媛, 孙敬雅, 宁欣, 等. 掺杂方法对Cu-OMS-2催化氧化甲苯性能的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(12): 2627-2633. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017040504 LU Y Y, SUN J Y, NING X, et al. Effect of doping methods of Cu-OMS-2 on catalytic oxidation of toluene [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 2627-2633(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017040504
[28] QU Z P, GAO K, FU Q, et al. Low-temperature catalytic oxidation of toluene over nanocrystal-like Mn-Co oxides prepared by two-step hydrothermal method [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2014, 52: 31-35. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2014.03.035 [29] CRACIUN R, NENTWICK B, HADJIIVANOV K, et al. Structure and redox properties of MnOx/Yttrium-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) catalyst and its used in CO and CH4 oxidation [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2003, 243(1): 67-79. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(02)00538-0 [30] LIANG S H, TENG F, BULGAN G, et al. Effect of phase structure of MnO2 nanorod catalyst on the activity for CO oxidation [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(14): 5307-5315. doi: 10.1021/jp0774995 [31] CAO H Y, LI X S, CHEN Y Q, et al. Effect of loading content of copper oxides on performance of Mn-Cu mixed oxide catalysts for catalytic combustion of benzene [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012, 30(9): 871-877. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60148-3 [32] LI W B, ZHUANG M, XIAO T C, et al. MCM-41 supported Cu–Mn catalysts for catalytic oxidation of toluene at low temperatures [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(43): 21568-21571. doi: 10.1021/jp063580g [33] LUO Y J, ZHENG Y B, ZUO J C, et al. Insights into the high performance of Mn-Co oxides derived from metal-organic frameworks for total toluene oxidation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 349: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.053 [34] CIAMBELLI P, CIMINO S, de ROSSI S, et al. AFeO3 (A=La, Nd, Sm) and LaFe1−xMgxO3 perovskites as methane combustion and CO oxidation catalysts: Structural, redox and catalytic properties [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2001, 29(4): 239-250. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00215-0 [35] MENG X L, MENG L K, GONG Y J, et al. Modifying Y zeolite with chloropropyl for improving Cu load on Y zeolite as a super Cu/Y catalyst for toluene oxidation [J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(59): 37528-37539. doi: 10.1039/D1RA06469J [36] LUO M M, CHENG Y, PENG X Z, et al. Copper modified manganese oxide with tunnel structure as efficient catalyst for low-temperature catalytic combustion of toluene [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 758-765. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.056 [37] LIU D J, ZHOU W G, WU J. Effect of Ce and La on the activity of CuO/ZSM-5 and MnOx/ZSM-5 composites for elemental mercury removal at low temperature [J]. Fuel, 2017, 194: 115-122. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.12.076 [38] LIU W, WANG S N, CUI R Y, et al. Enhancement of catalytic combustion of toluene over CuMnOx hollow spheres prepared by oxidation method [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 326: 111370. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111370 [39] BAI B Y, LI J H, HAO J M. 1D-MnO2, 2D-MnO2 and 3D-MnO2 for low-temperature oxidation of ethanol [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 164: 241-250. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.08.044 [40] XU Y, QU Z P, REN Y W, et al. Enhancement of toluene oxidation performance over Cu-Mn composite oxides by regulating oxygen vacancy [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 560: 149983. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149983 [41] MORALES M R, BARBERO B P, CADÚS L E. Evaluation and characterization of Mn-Cu mixed oxide catalysts for ethanol total oxidation: Influence of copper content [J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(7): 1177-1186. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.07.015 [42] MORALES M R, BARBERO B P, CADÚS L E. Total oxidation of ethanol and propane over Mn-Cu mixed oxide catalysts [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2006, 67(3/4): 229-236. [43] ZHANG X J, ZHAO H, SONG Z X, et al. Insight into the effect of oxygen species and Mn chemical valence over MnOx on the catalytic oxidation of toluene [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 493: 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.255 [44] KRAUS M, TROMMLER U, HOLZER F, et al. Competing adsorption of toluene and water on various zeolites [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 351: 356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.128 [45] KIM S C, SHIM W G. Catalytic combustion of VOCs over a series of manganese oxide catalysts [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 98(3/4): 180-185. [46] KIM S C, PARK Y K, NAH J W. Property of a highly active bimetallic catalyst based on a supported manganese oxide for the complete oxidation of toluene [J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 266: 292-298. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.06.049 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: