-
挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds,简称VOCs)大都具有刺激性和毒性,对人体眼睛、呼吸道和皮肤都具有很大的危害;当VOCs浓度过高时,会导致人体大脑、神经中枢、肾脏、肝脏等产生不可逆损害. 同时,VOCs在光照条件下还能发生光化学反应形成二次污染物[1]. 目前,吸收法、吸附法、燃烧法、光催化法、等离子体等技术在VOCs末端处理中都有应用[2],其中催化燃烧法因处理温度低、产物无毒无害而受到青睐[3].
分子筛具有独特孔道结构、高比表面积、酸性可调、热稳定性良好等特点[4],因此被广泛用于VOCs的催化氧化技术. 段明华等[5]以苯为探针反应物,将氧化钴负载至不同种类分子筛(MCM-41、MCM-48、SBA-15)上,发现孔径较大并且氧化还原性能较好的SBA-15载体呈现出更好的催化活性. 袁金芳[6]以Zr-Ce-SBA-15为载体,水热负载活性组分Cu—Mn,以甲苯为探针反应物,发现复合介孔载体能够综合微孔、介孔分子筛各自的孔道特点,从而促进活性组分在载体内部的分散,提高催化剂活性. He等[7]在研究不同分子筛载体对甲苯催化氧化活性时发现,微孔分子筛表面的酸性位是影响分子筛类催化剂催化活性的主要因素之一.
贵金属因其对H—H、C—H、C—O及O—H化学键具有较高的活化效果,常用做负载型催化剂的活性组分. 贵金属Ru作为铂系金属中的贵金属元素,其电子排布为4d75s1,氧化态较多,存在+2、+3、+4、+6等不同价态,因此能够构成多种配合物,并在许多反应中显示出独特性质.金属态的Ru呈六角密积的晶体结构,极易被氧化成RuO2. 相较于其余电子轨道,dn轨道上的电子更容易被还原,其轨道上的氧化物化学性质相较于d0轨道上的氧化物更加活跃. Ru(4+)的电子排布为4d4,因此其氧化物RuO2具有很强的活性,能加速催化反应进程[8]. Dai等[9]研究发现,相较于其余贵金属Au、Pt、Pd而言,Ru的催化活性差异不大,但价格相对低廉. Mitsui等[10]分别在CeO2上负载Ru、Pt、Pd、Rh,并以乙酸乙酯为探针反应物,发现Ru/CeO2的催化活性明显优于其他催化剂体系.
不同结构的分子筛对催化反应性能的影响较大,其具体作用机理仍需进一步研究;同时贵金属Ru化学性质活跃且价格相对低廉. 因此本研究选取不同结构的分子筛(β、MCM-41、Y、ZSM-5)为载体,通过浸渍法负载贵金属Ru,制备Ru/β、Ru/MCM-41、Ru/ZSM-5、Ru/Y催化剂,探究4种催化剂对甲苯的催化性能差异. 利用现代表征技术,从微观上对催化剂进行分析,构建催化剂物化结构与VOCs催化性能之间的构效关系,为分子筛类催化剂在VOCs废气治理的应用提供实验和理论依据.
-
Ru负载型催化剂的具体制备方法:按Ru质量负载量为0.6%,称取一定量β分子筛粉末,溶解于RuCl3的水溶液中,搅拌混合,并将混合液于烘箱中恒温烘干后置于马弗炉内,450 ℃高温焙烧得到所需Ru/β催化剂. 同理制得Ru/MCM-41、Ru/Y、Ru/ZSM-5催化剂.
-
催化剂的晶体结构由X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,XRD)进行表征,所用仪器为日产Rigaku D/MAXRAX射线多晶衍射仪,在40 kV和120 mA的条件下工作,扫描范围为5°—90°. 催化剂的比表面积以及介孔采用美国Quantachrome Instruments Quadrasorb EVO进行表征,微孔部分采用麦克默瑞提克ASAP2460 4MP进行表征.SEM表征使用日本日立公司生产的S4800冷场发射扫描电镜进行分析. 程序升温脱附(temperature programmed desorption,NH3-TPD)使用美国麦克AUTO Chem Ⅱ 2920仪器,用于表征催化剂表面酸性. 程序升温还原(temperature program reduction,H2-TPR)使用美国麦克AUTO Chem Ⅱ 2920,用于表征催化剂的氧化还原性能. X射线光电子能谱分析(X-ray photo electron spectroscopy,XPS)使用美国赛默飞世尔科技公司ESCALAB仪器,得到催化剂表面化学组成及其化学态的相关数据.
-
催化性能测试在实验室自主搭建的催化氧化装置上进行. 将甲苯、N2、O2通过流量计进入缓冲罐进行混合,混合气体进入反应炉,在装有催化剂的石英反应管中进行催化氧化,尾气由气相色谱在线检测.
本研究所采用的实验配气组成为总流量100 mL·min−1,其中1800 mg·m−3的甲苯,10%的O2,N2为平衡气体;反应温度为100—350 ℃. 将0.1 g催化剂与0.4 g石英砂均匀混合后置于反应管中部. T50和T90分别表示甲苯转化率为50%和90%时对应的温度.
甲苯的活性用甲苯的转化率表示,计算如式1所示:
式中,
CC7H8in 表示甲苯进口浓度,mg·m−3;CC7H8out 表示甲苯出口浓度,mg·m−3.CO2 选择性用CO2 的产率表示,计算如式2所示:式中,
CCO2 表示CO2 的浓度,mg·m−3;CCO 表示CO 的浓度,mg·m−3.反应中副产物的选择性用副产物的产率表示,计算如式3所示:
催化反应中的转化频率(Turnover Frequency, TOF)表示单位时间单个活性位点转化的反应物的量,以催化剂表面Ru原子数近似催化活性位点数,计算如式4所示:
式中,
XToluene 表示某一温度下甲苯的转化率;FToluene 表示甲苯气体摩尔速度,mmol·s−1;MRu 表示Ru的摩尔质量,101.07 g·mol−1;mCat 表示催化剂质量,g;XRu 表示催化剂Ru的负载量;DRu 表示Ru颗粒的分散度. -
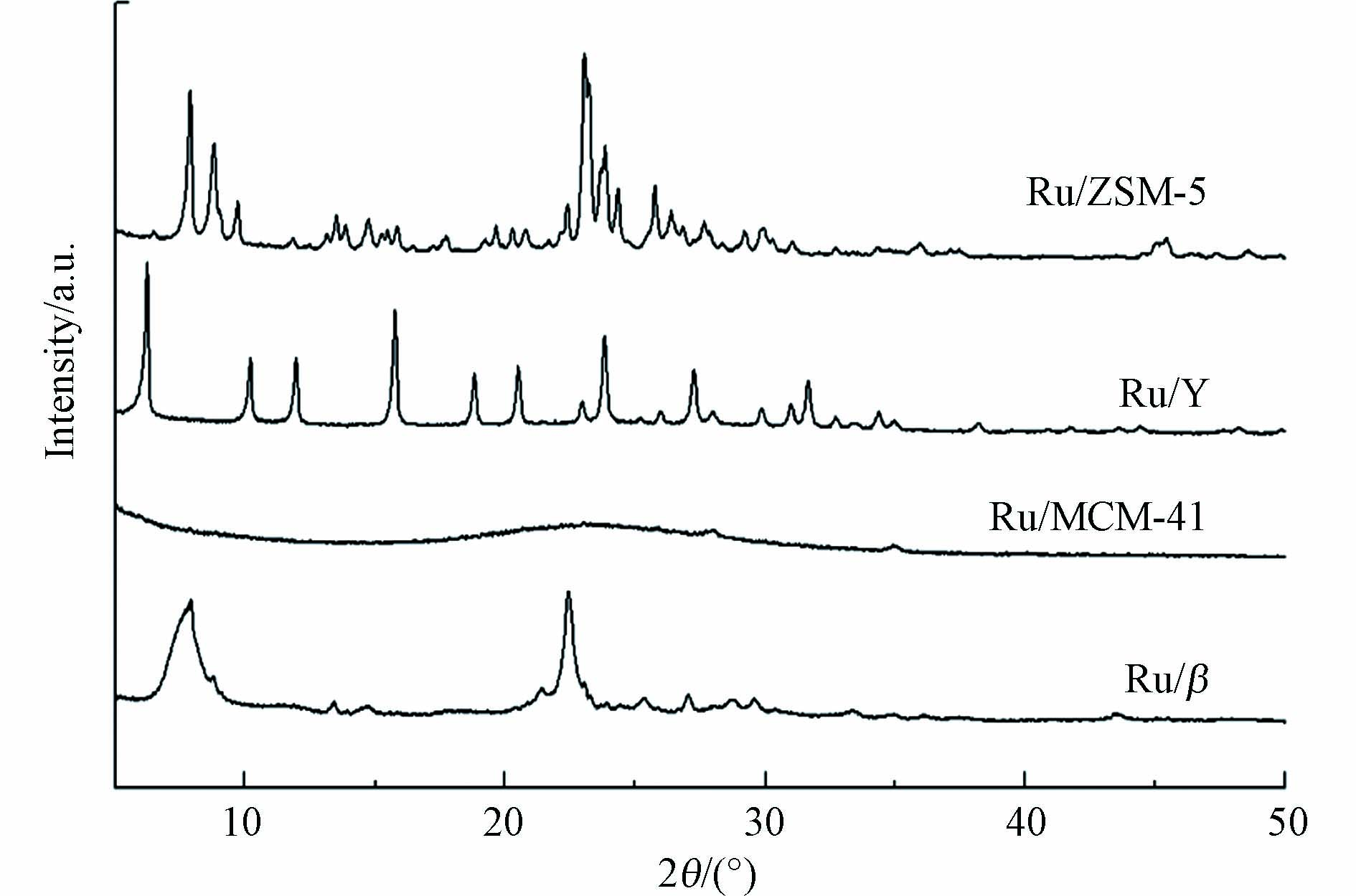
图1为4种催化剂的XRD衍射图谱. 其中Ru/β分子筛在7.9°、22.4°出现明显的BETA相特征衍射峰,与文献中报道的β分子筛XRD谱图一致[11]. Ru/MCM-41属于典型介孔材料,通常介孔材料的孔壁具有非晶态的结构,即广角XRD不具备其特征衍射峰,仅在20°—25°之间有一宽峰,归属于无定形SiO2的特征峰[12]. Ru/Y分子筛在6.3°、10.2°、12.1°、15.8°、18.7°、20.5°、23.8°、27.3°和31.6°出现明显的特征衍射峰,这归因于Y分子筛的FAU结构. Ru/ZSM-5分子筛在7.9°、8.8°、9.8°、23.1°、23.8°、24.3°和25.8°有明显的ZSM-5特征峰,与文献中报道的ZSM-5分子筛XRD谱图一致[13]. 同时,4种样品中均没有Ru金属单质或其氧化物的特征衍射峰,说明Ru在4种分子筛表面可能高度分散[14].
-
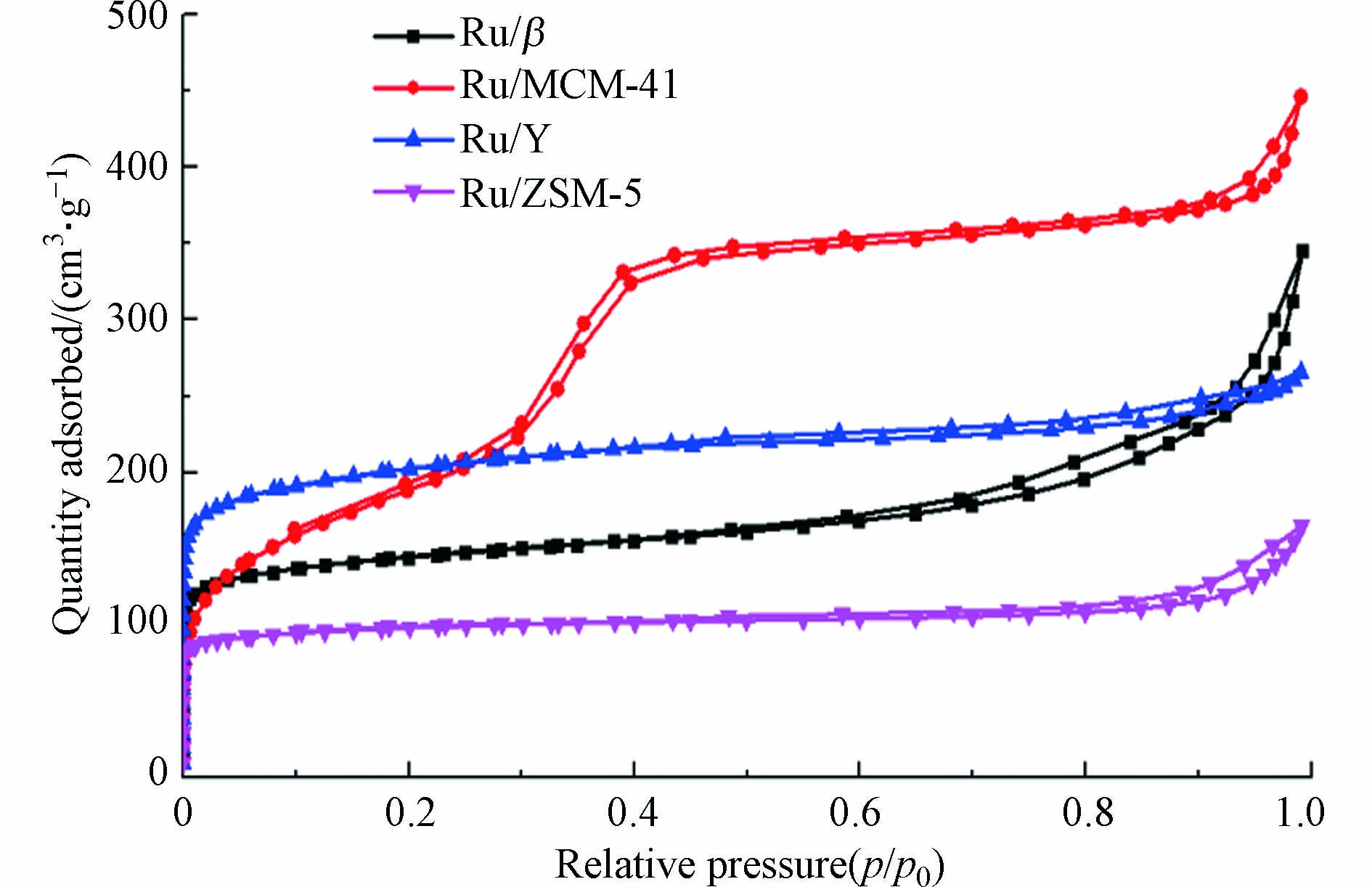
图2为Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的N2吸附-脱附等温线. Ru/Y与Ru/ZSM-5具备典型的Ⅰ型等温线的特点,在低压段出现N2吸附量的明显上升,这归属于微孔结构对于N2的吸附,由此推断两种催化剂具有一定的微孔结构;在高压段均出现H1型滞回环,其中Ru/Y的滞回环较Ru/ZSM-5而言更为明显,说明Ru/Y存在一定的介孔,而Ru/ZSM-5的介孔结构则相对较不显著.
Ru/MCM-41呈Ⅳ型等温线,为典型的介孔材料吸脱附曲线[15],与报道的MCM-41的吸脱附曲线较吻合. Ru/β同时具有Ⅰ型和IV型等温线的特点,低压段N2的吸附量明显上升,是由于微孔结构产生的吸附作用[16],说明Ru/β中存在较丰富微孔结构;高压段存在明显的H4型滞后环,表示Ru/β存在一定介孔结构[17].
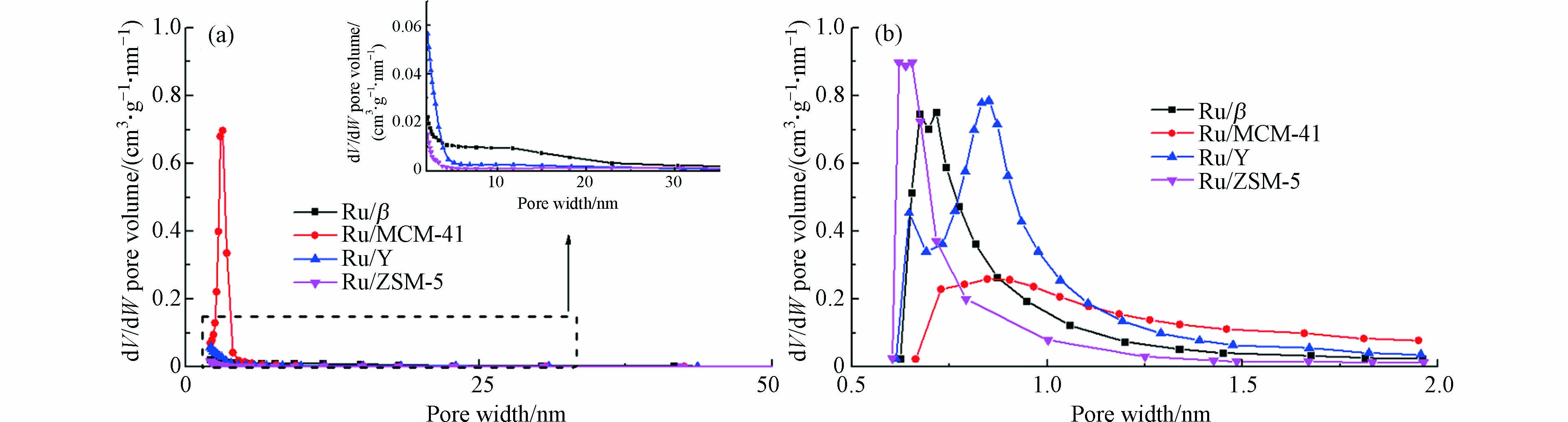
图3为Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的孔径分布曲线,其中为了更准确的表征样品的孔道特征,本研究采用BJH算法计算分析介孔孔径及分布,如图3(a)所示;采用HK算法计算分析微孔孔径及分布,如图3(b)所示.
由图3(b)可知,Ru/β在0.7 nm左右出现明显峰值,且该峰分布窄且峰强度高(约0.72 cm3·g−1·nm−1),因此可知其内部微孔结构以0.7 nm的微孔为主;而在图3(a)中的介孔分布曲线中,14.9 nm处出现较为平整的宽峰,推测是由纳米颗粒堆积形成的晶间介孔[17-18];同时,Ru/β介孔分布峰强度低(约0.022 cm3·g−1·nm−1)且分布宽泛,说明Ru/β的介孔孔径并不均一,在2—30 nm区间内变化.
根据图3(a),Ru/MCM-41孔径分布峰主要出现在2.7 nm处,孔径分布峰窄且强,因此推断其孔径分布较为集中,以2.7 nm的介孔结构为主;结合其微孔分布(图3(b)),发现Ru/MCM-41的微孔分布峰较宽且峰强度较低.
通过图3(b)可得,Ru/Y在0.65 nm和0.83 nm处出现明显峰值,表明其内部存在两种较为明显的微孔孔径;同时,结合图3(a),发现Ru/Y在2 nm左右出现明显峰且宽度较窄,说明存在一定数量2 nm左右的介孔结构.
如图3(b)所示,Ru/ZSM-5在0.65 nm处出现较强且分布较窄的峰,同时在其介孔分布曲线(图3(a))中可观察到2 nm左右出现较小的峰,证明Ru/ZSM-5为较典型的微孔结构,仅存在少量介孔.
Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的比表面积依次为Ru/Y>Ru/MCM-41>Ru/β>Ru/ZSM-5,其数值依次为764.44、686.72、547.45、381.66 m2·g−1. 通常而言,催化剂比表面积越大,有利于反应物分子的吸附与催化[19].
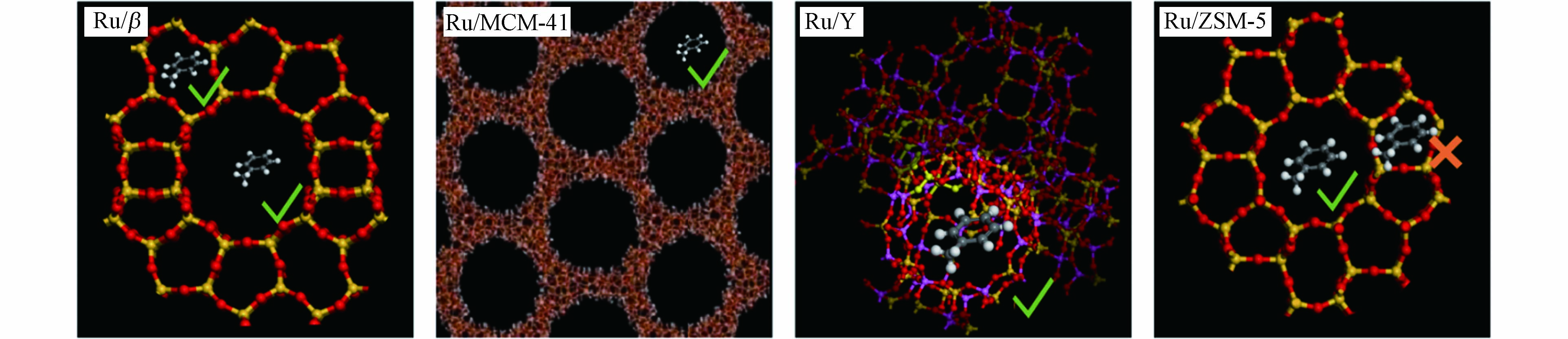
本研究以甲苯分子为反应物,为了更好的反应孔道尺寸对于催化性能的影响,本文构建了甲苯-催化剂孔道尺寸模型,将甲苯分子的动力学尺寸[17](0.67 nm)与分子筛的孔道尺寸进行对比,结果如图4所示. 通过图4,可以直观看出,Ru/β呈十二元环孔道结构,Ru/MCM-41呈六方有序孔道结构,Ru/Y呈立体笼状结构,Ru/ZSM-5呈十元环孔道结构. Ru/MCM-41孔道尺寸明显大于甲苯的分子直径,Ru/β与Ru/Y孔道尺寸与甲苯分子较为接近,而Ru/ZSM-5内部则存在大量小于甲苯分子尺寸的孔道结构.
-
图5为Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的扫描电镜图.
如图5(a)所示,Ru/β呈表面较为粗糙的不规则的球形状,球形颗粒互相交联形成网状结构,颗粒尺寸约为17 nm;同时存在较明显的团聚现象. 如图5(b)所示,Ru/MCM-41呈表面较为粗糙的珊瑚状,颗粒尺寸约为36 nm,颗粒之间的团聚现象较为严重,不利于催化降解[20]. 如图5(c)所示,Ru/Y颗粒呈表面光滑的规则立方形,颗粒相互交联形成多孔状结构,同时颗粒之间互相堆积形成明显介孔,颗粒尺寸约为9 nm. 如图5(d)所示,Ru/ZSM-5颗粒呈片层结构,颗粒尺寸约为17 nm,排列紧密,较少出现微孔堆积的情况,同时存在少量的明显大孔.
-
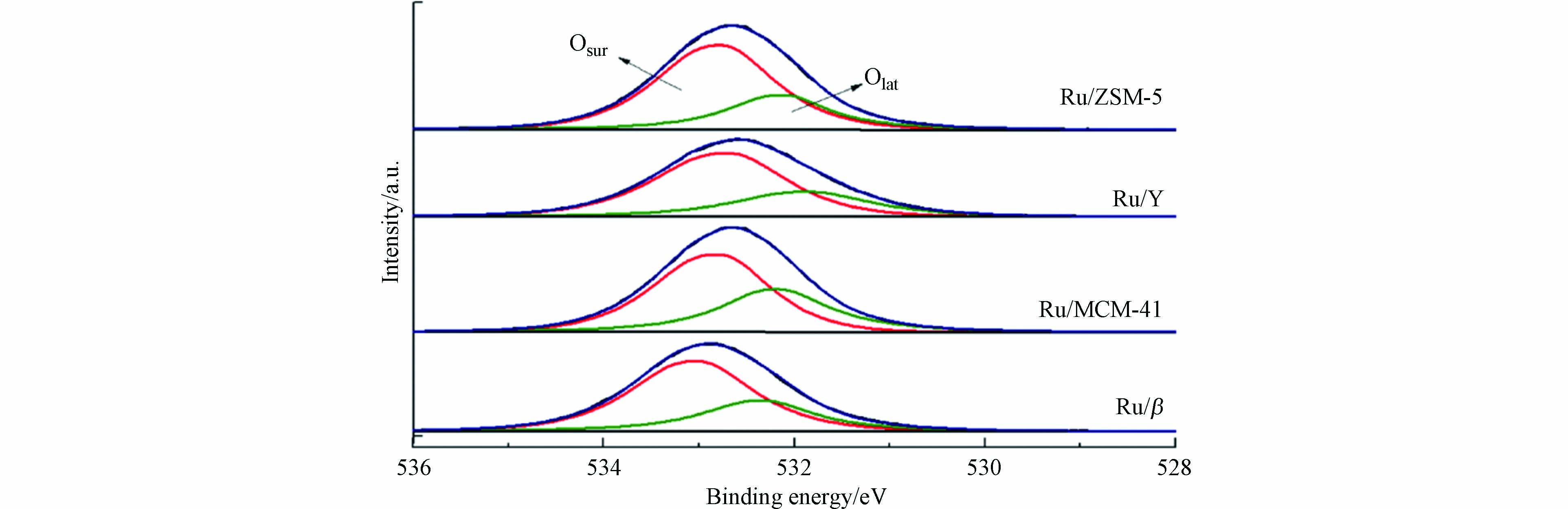
图6为Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的O1s的XPS图谱,O1s的XPS光谱主要分为2个峰,其中较高结合能的峰归属于表面吸附氧Osur,结合能较低的峰对应表面晶格氧Olat[21]. 4种催化剂的表面氧物种相对含量(Olat/Osur)比值按从大到小排序为Ru/MCM-41>Ru/β>Ru/Y>Ru/ZSM-5,如表1所示.
据研究表明[22-23],甲苯的氧化反应过程中同时存在Langmuir-Hinshelwood和Mars-van Krevelen两种反应机理;在低温阶段遵循Langmuir-Hinshelwood机理,该阶段以表面吸附氧直接参与甲苯氧化反应为主;随着温度升高,反应逐渐转为遵照Mars-van Krevelen机理,此阶段中,表面晶格氧为主要的活性氧物种,对甲苯氧化起重要作用.
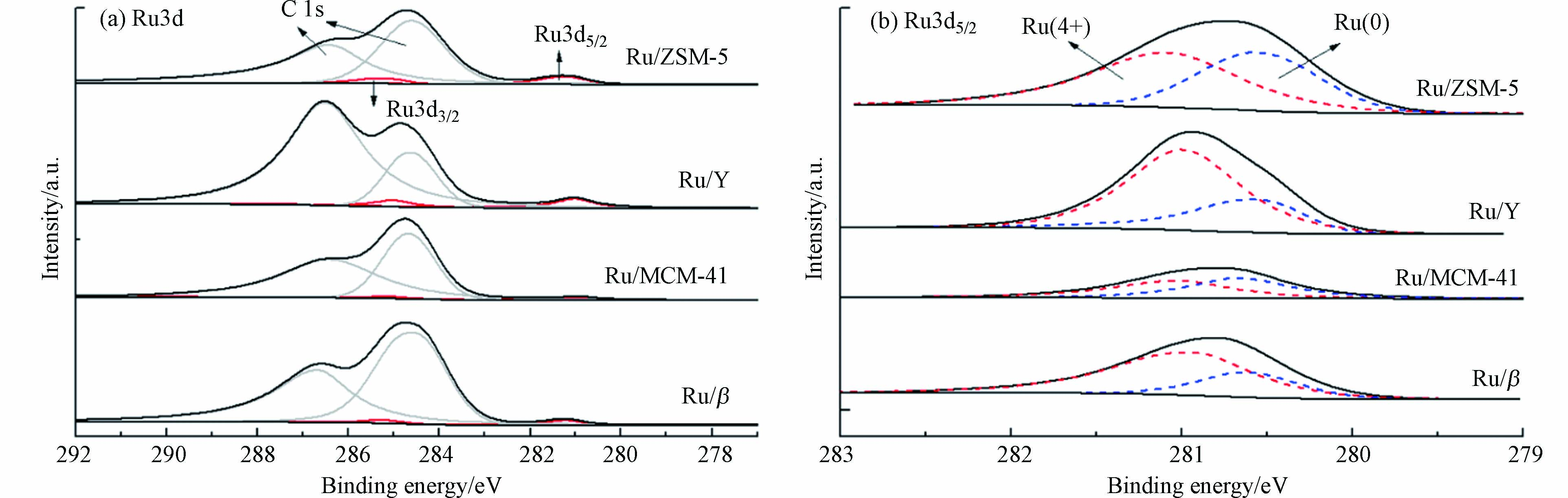
图7(a)为Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的Ru3d的XPS图谱.
由图7(a)所示,Ru3d3/2出峰位置在284.8 eV左右,与C1s重叠,因此选择Ru3d5/2作为研究对象,如图7(b)所示. Ru3d5/2在279—283 eV之间被分解为两个峰,分别归属于Ru(0)和Ru(4+),分别代表金属Ru和金属氧化物RuO2,Ru(0)的结合能相对Ru(4+)而言较低. 研究发现,RuO2呈现独特的金红石构型[24],为催化反应的还原中心,其浓度与催化活性呈正相关[25]. 在图7(b)中,Ru/Y的Ru(4+)特征峰最为明显,Ru/β和Ru/ZSM-5次之,Ru/MCM-41则较不明显.
-
催化剂的催化性能与其表面酸性位息息相关. 由于甲苯分子中的
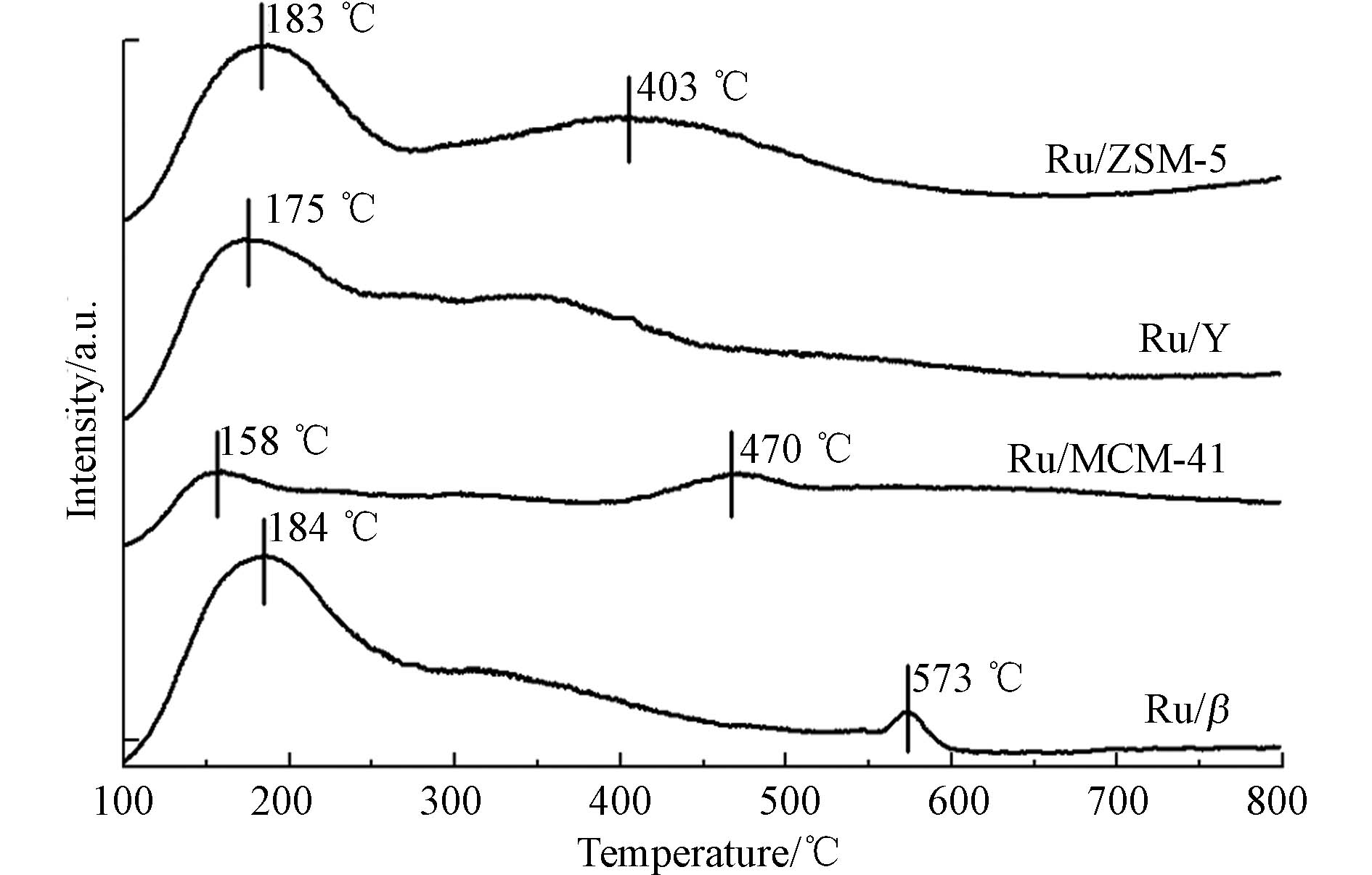
π66 键属于给电子体[26-27],而催化剂表面的酸性位表现出吸电子的特性,因而有利于二者之间发生相互作用,形成氢键,激活甲苯分子,促进甲苯分子的吸附[28],进而有利于其与催化剂活性组分发生反应,形成催化产物[29]. 肖丽[30]研究表明,针对甲苯分子的催化氧化而言,催化剂酸性与催化活性呈正相关,酸量越大代表能够给反应提供越多的酸性位[31],从而增强催化剂的催化氧化活性.NH3-TPD图谱一般用于表征催化剂的酸性,脱附温度越高,对应酸性位酸性越强;脱附峰面积越大,对应酸性位酸量越多.
由图8可得,Ru/β脱附峰集中出现在184 ℃附近,同时在573 ℃左右出现较小脱附峰,说明Ru/β具有较多弱酸位以及少量强酸位;Ru/MCM-41的脱附峰整体不显著,仅在158 ℃和470 ℃之间出现较小脱附峰,说明Ru/MCM-41表面酸性位少;Ru/Y仅在175 ℃处出现较明显脱附峰,说明Ru/Y以弱酸位为主;Ru/ZSM-5在183 ℃和403 ℃出现明显脱附峰,说明Ru/ZSM-5表面具有丰富弱酸位和强酸位. Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的总酸量排序依次为 Ru/Y>Ru/ZSM-5>Ru/β>Ru/MCM-41,其数值 对应为 59.22、55.26、41.94、35.20 mmol·g−1
-
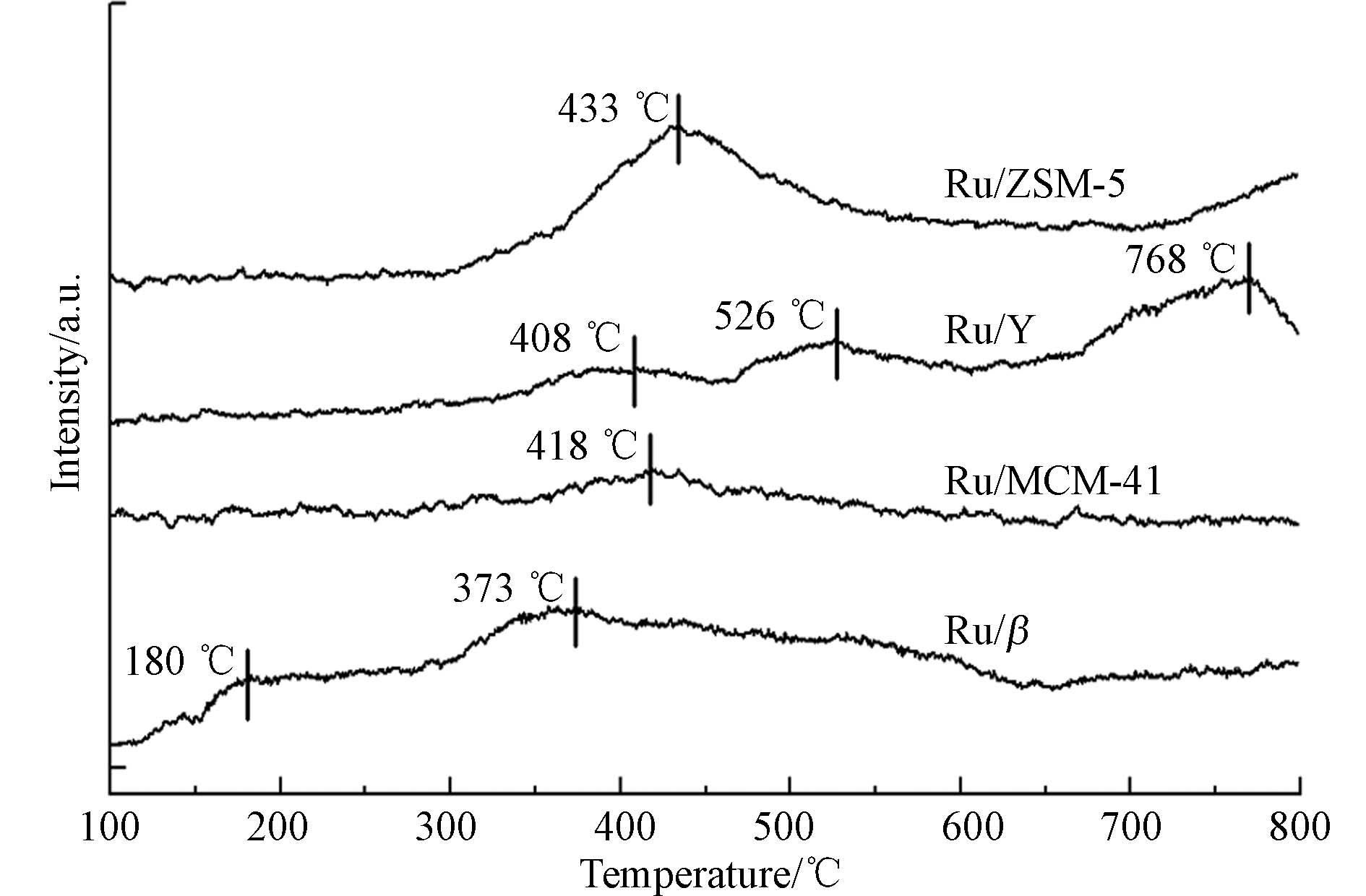
Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的H2-TPR结果见图9. 对于钌催化剂而言,一般的还原过程存在两种Ru物种的还原峰,其中,低温段对应的是催化剂表相的Ru物种(RuOx)或高度分散的Ru粒子的H2消耗峰,而高温段则对应了催化剂体相内的Ru粒子(RuO2)的还原[32-33].
由图9所示,Ru/β在180 ℃左右出现小的还原峰,对应的是Ru/β催化剂表面的表相Ru物种的还原,而Ru/Y、Ru/MCM-41、Ru/ZSM-5在低温段均未出现明显峰值,说明其催化剂表面表相Ru物种可能较少或是在催化剂表面高度分散[32-33]. 同时,4种分子筛在高温段(300—800 ℃)之间均出现了明显的H2还原峰,该峰归属于分子筛内部体相Ru物种的还原峰. Ru/β在373 ℃附近出现明显峰值较大的还原峰;而Ru/MCM-41整体曲线较平整,仅在418 ℃出现较小还原峰;Ru/Y的还原峰出现于408 ℃、526 ℃以及768 ℃,且3个还原峰的峰面积大小排序与其出峰位置温度高低排序保持一致;Ru/ZSM-5整体在中高温阶段出现面积较大的还原峰,基本集中于433 ℃附近.
H2-TPR的出峰位置及峰面积代表催化剂的氧化还原性能,出峰位置对应温度越低,还原峰峰面积越大,表明催化剂的氧化还原性能越好. 因此,4 种催化剂的氧化还原性能如下:Ru/β>Ru/Y>Ru/ZSM-5>Ru/MCM-41.
-
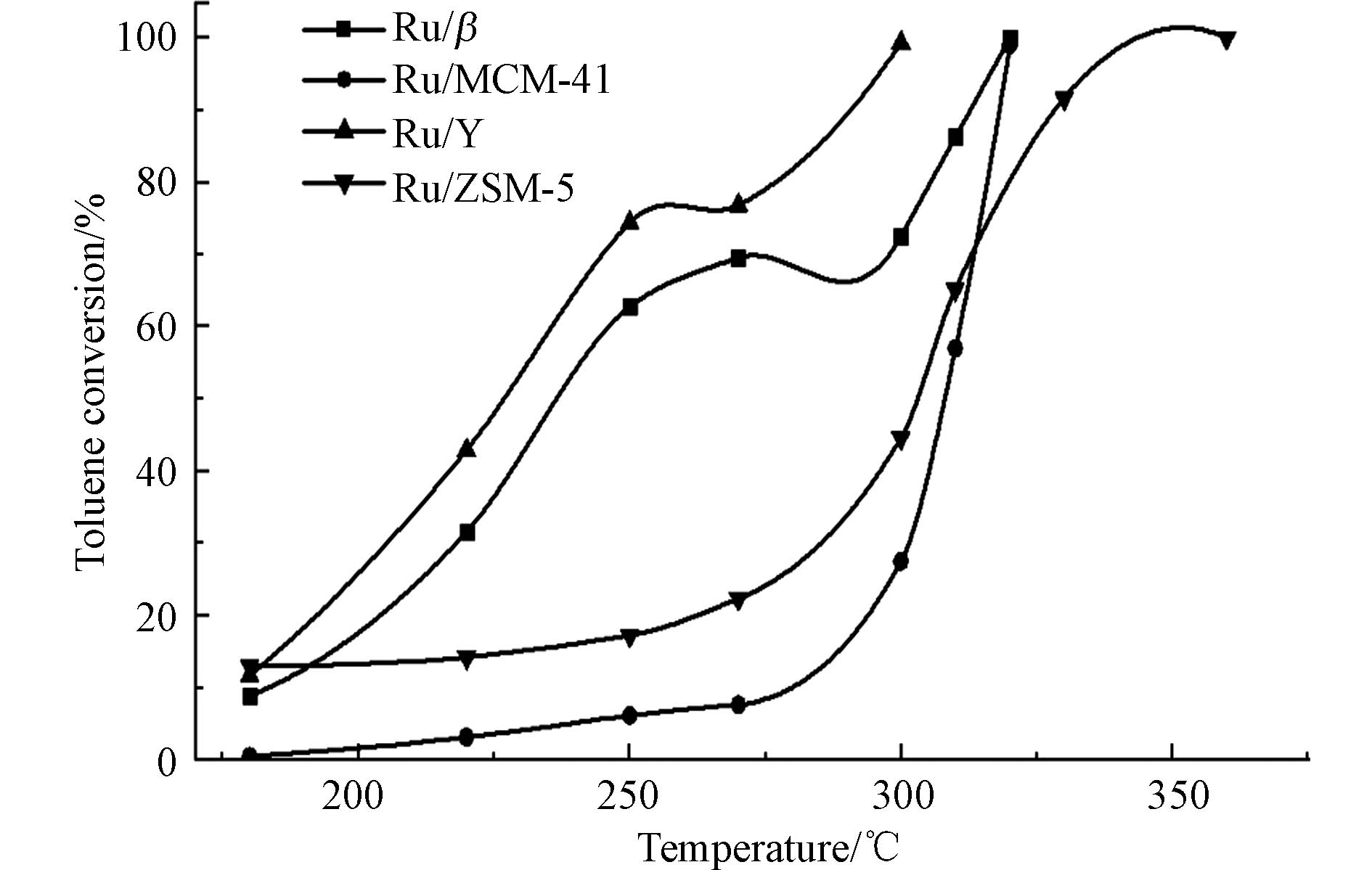
4种催化剂的表观催化活性如图10、表2所示,以Y为载体的催化剂对甲苯的表观催化活性最优,其T50和T90分别为227 ℃和290 ℃,在300 ℃左右甲苯基本完全降解. Ru/β次之,Ru/ZSM-5和Ru/MCM-41则相对较差.
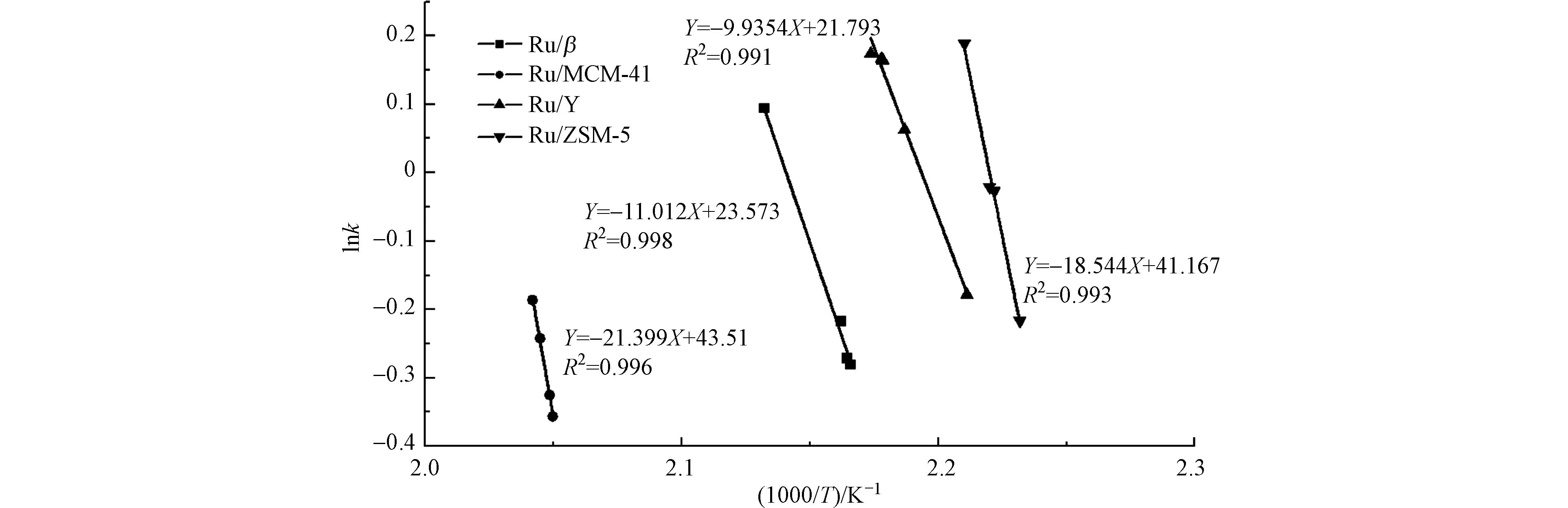
为探究4种催化剂催化氧化甲苯的本征活性,对其进行了动力学分析.在过氧条件下(本文中氧气占比10%),贵金属等催化材料上的甲苯催化燃烧反应为一级反应,通过对低转化率的条件下的实验数据进行线性计算,得到其反应活化能Ea以及转化频率TOF[34-35].
由图11和表2可知,4组数据线性拟合后R2值均大于0.99,说明拟合线性效果好,拟合数据可信度高.催化燃烧反应为放热反应,活化能越小越有利于反应的进行. 4种催化剂的反应活化能Ea大小为:Ru/Y<Ru/β<Ru/ZSM-5<Ru/MCM-41,与上述表观活性规律基本一致. 同时,4种催化剂的TOF值也表现出类似的规律:Ru/Y的TOF值最高,为5.71 mmoltoluene·molRu−1·s−1,说明其催化反应的速率最快,从而具有较好的催化活性;Ru/β次之,Ru/MCM-41和Ru/ZSM-5的较差.
-
Ru/Y的催化活性最好,起活温度在180 ℃左右,200—260 ℃之间,转化率迅速增加,300 ℃左右完全催化.根据XPS、NH3-TPD、H2-TPR的结果可知,Ru/Y具有最高的Ru(4+)/Ru(0)之比,较多酸性位和较好的氧化还原性能,可为反应提供充足的活性中心. 较大的比表面积可增加甲苯分子与催化剂的接触面积,促进活性组分的分散[6];同时丰富的微孔和介孔结构为甲苯的催化氧化提供良好的扩散条件[36]. 由图3可知,Ru/Y的微孔主要是0.65 nm和0.83 nm两种尺寸,并以0.83 nm的微孔为主,因此受甲苯分子(0.67 nm)择型限制较小[37]. 根据分子筛的“限域”效应[38],当分子筛的孔道尺寸与甲苯分子较为接近时,孔道内甲苯分子受“限域”效应影响,给电子能力得到提升,有利于其与催化剂表面酸性位点形成氢键,促进甲苯分子的吸附;同时“限域”效应还提高了反应过程中间过渡态的静电稳定性,降低反应活化能[39],有利于催化反应的进行,所以Ru/Y表现出最优的催化性能.
Ru/β的活性次于Ru/Y,200 ℃左右开始反应,320 ℃左右甲苯转化率达到99%以上. Ru/β具有较高的Ru(4+)/Ru(0)之比、最优的氧化还原性能和丰富的微孔结构. 其微孔孔径集中分布在0.7 nm左右,大于甲苯分子的动力学尺寸(0.67 nm),因而受择型催化的限制较小[37];同时,内部孔道尺寸与甲苯分子较为接近,限域效应显著[38],有效提升整体催化性能;但结合图8可知,Ru/β的整体酸量较Ru/Y而言较少,所以表现出Ru/β整体活性次于Ru/Y的情况.
Ru/MCM-41在280 ℃之前的转化率低于20%,低温催化活性差;300 ℃后转化率大幅上升,在320 ℃左右完全催化. Ru/MCM-41的整体酸量较少,无法为反应提供足够酸性位;同时,氧化还原性能较差、Ru(4+)/Ru(0)之比小,因此低温催化活性较差. 根据甲苯的催化氧化特性,其在高温阶段遵循Mars-van Krevelen 机理,以表面晶格氧为主要的活性氧物种,结合XPS表征结果可知,Ru/MCM-41的Olat/Osur比值较大,因此随着温度升高,其表面晶格氧的优势开始显现[22],加之孔道结构的特点以及较大的比表面积,有利于甲苯分子扩散,所以300 ℃后,Ru/MCM-41的催化活性开始增强.
Ru/ZSM-5在280 ℃之前的转化率低于20%,低温催化活性较差,但随着温度升高,活性缓慢上升,在350 ℃左右完全催化. 由图3和图4可知,Ru/ZSM-5以0.65 nm微孔为主,小于甲苯分子的动力学直径(0.67 nm),基于择型催化理论[37],甲苯分子难以进入孔道内部,限制了甲苯分子的催化. 300 ℃之后,由于温度升高,分子筛的骨架和反应物分子的伸缩、振动加快,传输阻力降低,加之二者均非刚性,因此动力学直径较孔径略大的反应物分子能在高温下顺利通过低温时无法通过的分子筛孔道[40]. 结合图8,Ru/ZSM-5酸量丰富,但受限于孔径尺寸,低温阶段难以发挥其优势;随着温度升高,传输阻力降低,甲苯分子顺利进入孔道内部,接触酸性位点,因此300 ℃后,Ru/ZSM-5酸性位的优势开始显现,催化活性得以提升.
由图10可知,Ru/Y与Ru/β在260—280 ℃之间均出现了明显的失活现象.结合图8,发现Ru/Y和Ru/β均具有丰富的酸性位. 据报道[40],酸中心不仅是催化反应的活性中心,同时也有利于分子筛上积炭反应的发生;催化剂的酸量越大,越容易导致积碳的生成并覆盖活性位点,阻碍其与反应物接触,导致活性下降,出现失活.由此可推测,两种催化剂的低温失活与积碳的生成密切相关. 280 ℃后,随反应温度升高,可促使易生成积炭的中间副产物高温分解,从而催化活性回升. Ru/MCM-41和Ru/ZSM-5均没有出现较为明显的失活现象,结合图3、图4和图8可知,Ru/MCM-41因整体酸量较少,不利于积碳的生成;而Ru/ZSM-5虽然酸性位多,但由于孔道尺寸的限制,低温阶段催化活性差,甲苯基本没有催化,因此积碳无法生成.
综上所述,催化剂的载体孔道结构和酸性位对催化性能影响相对较大. 在孔道结构方面,基于择型催化的限制,当甲苯分子的尺寸大于催化剂孔道尺寸时,难以进入孔道内部,反之则可以顺利通过;对于孔道内部的甲苯分子而言,当孔道尺寸与分子尺寸较为接近时,受限域效应影响,不仅可以增强甲苯分子给电子能力,还可以提高中间过渡体的静电稳定性,降低反应活化能,促进催化反应进行. 在酸性位方面,甲苯分子中的
π66 键易与催化剂表面的酸性位点形成氢键,有利于甲苯分子的吸附;但酸性位也会导致积碳的生成并覆盖活性位,造成低温阶段催化剂失活. 同时结合比表面积、氧化还原性能等因素,使得不同分子筛载体催化剂最终呈现出截然不同的催化性能. -
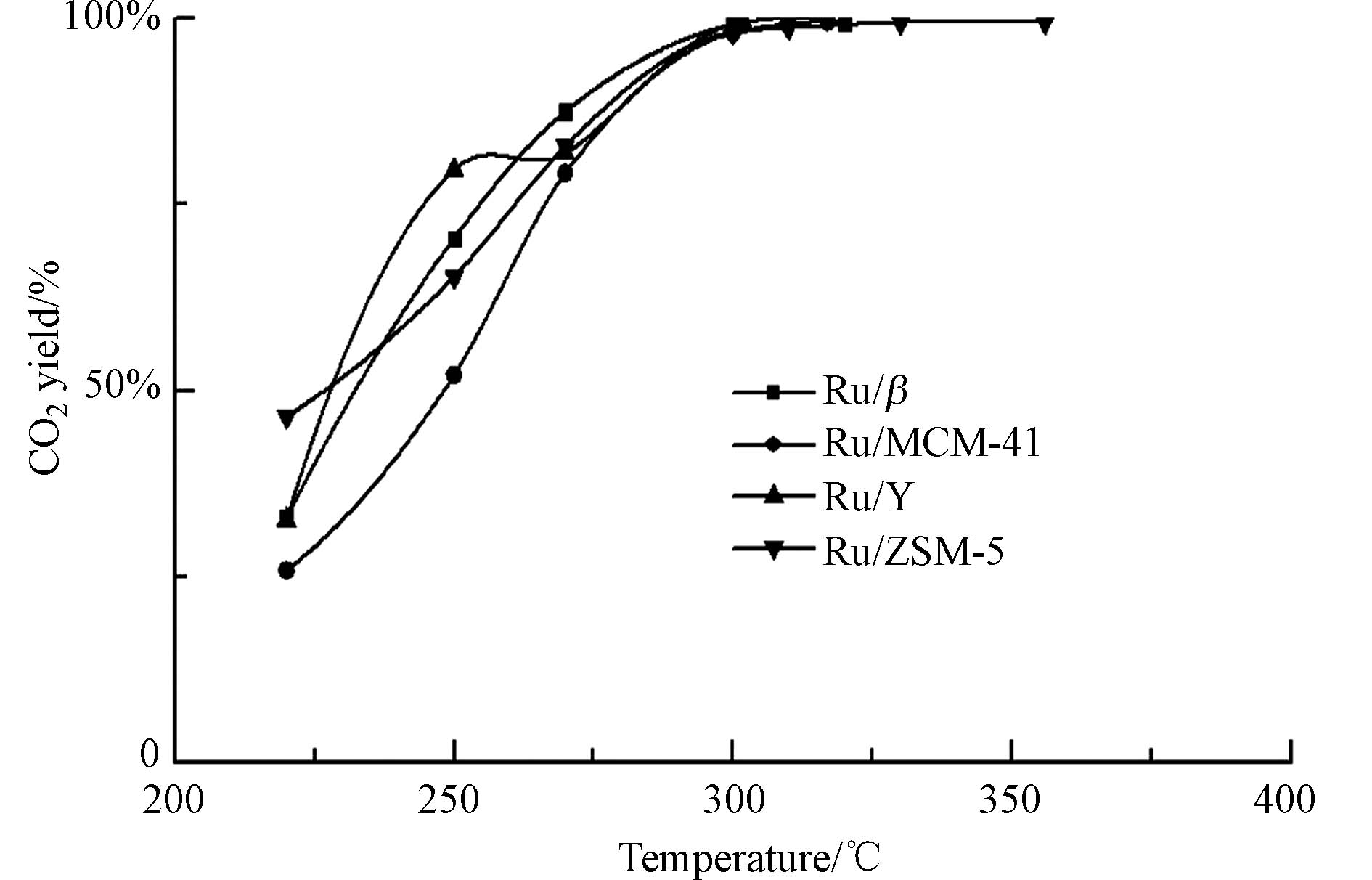
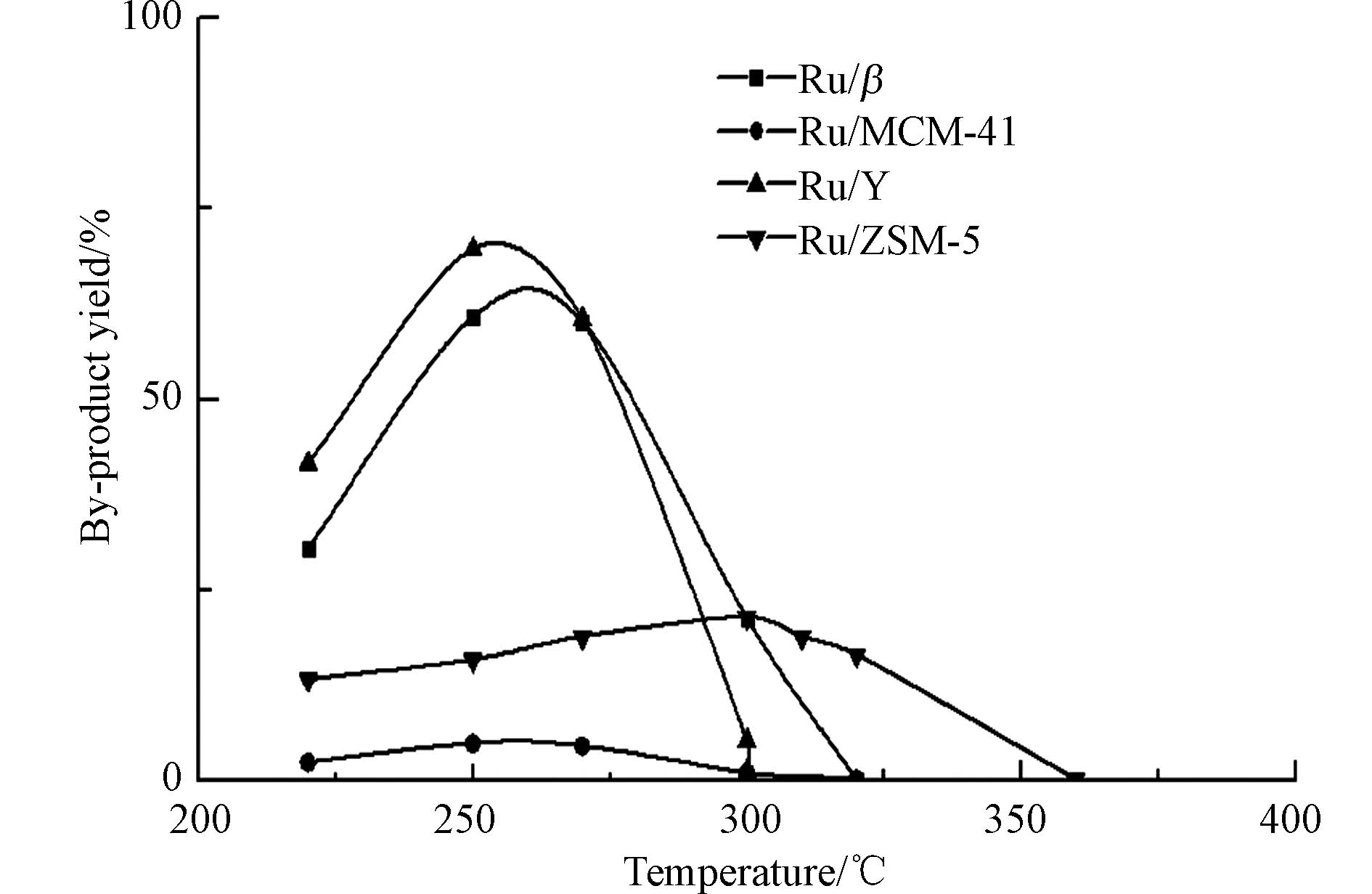
通过图12可以看出,4种催化剂的CO2选择性在320 ℃之后都能达到99%,即高温下,4种催化剂对于CO2的选择性均较好. 通过图13可以看出,Ru/ZSM-5和Ru/MCM-41副产物产量较少,均在20%以下. 而Ru/Y和Ru/β在280 ℃前有大量的副产物生成;280 ℃后副产物大幅减少,与图10中280—300 ℃催化活性回升相呼应,证明了催化剂的低温失活是由于积碳的生成;高温下副产物生成显著减少,从而活性回升;300 ℃以后副产物几乎为0,即高温下对于甲苯的催化均比较完全.
-
本文以4种不同分子筛为载体,浸渍法负载贵金属Ru,通过XRD、BET、XPS、NH3-TPD、H2-TPR等表征手段分析催化剂的物化性质,探究其与催化活性之间的构效关系,得出以下结论:
(1)载体的结构对于Ru催化剂的甲苯催化氧化性能影响较大,4种不同分子筛载体催化剂的催化性能依次为Ru/Y>Ru/β>Ru/MCM-41>Ru/ZSM-5. 以Y分子筛为载体的Ru催化剂催化活性明显高于其他载体,起活温度为180 ℃左右,200—260 ℃之间,转化率迅速上升,在260—280 ℃之间虽然出现失活,但高温下活性迅速恢复,并在300 ℃左右完全催化.
(2)甲苯催化氧化性能与催化剂的载体结构息息相关,其中孔道结构和酸性位影响最大. 孔道结构的影响主要体现在择型催化和限域效应上. 酸性位有利于甲苯的吸附催化,但过多的酸性位会导致低温阶段积碳的生成,造成催化剂的低温失活. 另外,较大的比表面积可增加甲苯分子与催化剂的接触面积,同时促进活性组分的分散,从而提高催化性能.高浓度的Ru(4+)能为催化反应提供更多还原中心,提升催化剂的氧化还原性能,有利于催化反应进行. 综上,具有较大比表面积、较高氧化还原性能、丰富酸性位以及孔径适中的Ru/Y催化剂表现出最优的催化性能.
负载型分子筛催化剂对甲苯的催化性能
Catalytic performance of supported molecular sieve catalysts for toluene
-
摘要: 采用不同类型分子筛浸渍负载活性组分Ru制备Ru/M(M=β、MCM-41、Y、ZSM-5)催化剂,考察其对甲苯的催化性能,并通过XRD、BET、SEM、XPS、H2-TPR、NH3-TPD等表征,分析催化剂的孔道结构、酸性位等物化结构对催化活性的影响.结果发现以贵金属Ru为活性组分,Y为载体的催化剂催化性能最优,在300 ℃左右,甲苯基本完全降解,CO2选择性接近99%,几乎无副产物生成.由此说明,适宜的孔径尺寸、丰富的酸性位、较好的氧化还原性能和较大的比表面积能有效促进分子筛催化剂对甲苯的催化氧化.Abstract: Ru/M (M=β, MCM-41,Y, ZSM-5) catalysts were prepared by impregnating the active component Ru with different types of molecular sieves to investigate their catalytic performance for toluene. The effect of physical and chemical structures such as pore structure and acid site on catalytic activity was analyzed by XRD, BET, SEM, XPS, H2-TPR and NH3-TPD.The results showed that the catalyst with precious metal Ru as the active component and Y as the carrier exhibited the best catalytic performance. At about 300 ℃, toluene was almost completely degraded, and the selectivity of CO2 was close to 99% with almost no by-product. This indicates that appropriate pore size, abundant acid sites, good redox performance and large specific surface area can effectively promote the catalytic oxidation of toluene by molecular sieve catalysts.
-
Key words:
- catalytic oxidation /
- toluene /
- molecular sieve /
- ruthenium /
- pore structure
-
随着我国纺织印染行业的高速发展,纺织印染废水已经成为重要的工业废水排放来源. 据统计,我国染料年产量达到77万—79万t,约占全世界总产量的2/3[1]. 印染纺织废水具有成分复杂、色度高、可生化性差等特性,成为难处理工业废水之一. 活性红3BS是一种典型偶氮染料被广泛的应用于纺织印染行业中,对水体中的各类生物具有强烈的毒害作用,经过食物链富集进入人体后可以引起人类恶性肿瘤病变,引发各种恶性疾病[2].
染料的降解工艺主要包括生物法、物理法和化学法. 生物法具有成本低、环境友好等优点,但微生物容易被染料的毒性抑制,对高浓度染料废水去除效果并不理想;物理法主要是利用吸附剂的高比表面积将液相中的污染物吸附至固体表面或内部孔道,对多种类型的染料具备处理能力,但没有实现从根本上消除污染物,吸附剂的再生和处置可能会造成二次污染等问题[3]. 因此,基于硫酸根盐自由基(SO4·−)的高级氧化技术因其能高效、快速降解水体各类高浓度染料而受到广泛关注与研究[4]. 一般而言,激活过一硫酸盐(PMS)产生SO4·−的方法包括超声、光辐射、紫外光等,耗能较大且对设备要求较高[5];而在均相反应中引入过渡金属虽然能够提高催化效果,但又易造成金属离子溶出形成污染[6]. 因此,制备碳基载铁改性材料作为非均相催化剂既可有效激活PMS增强降解效率[7],又能避免金属离子的二次污染. 除此之外,磁性生物炭的磁响应特征可以提高催化材料的可回收率[8],具有较高的应用研究价值.
本文通过生物沥滤将离子态铁负载到生物炭上,通过对铁负载材料进行二次热解改性制备出具有磁性的铁基生物炭(Fe3O4@BC)用于高浓度染料废水脱色研究. 生物沥滤驱动制备的磁性生物炭相较于传统方法简洁高效,为磁性生物炭的制备提供了新的的方法与路径.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and method)
1.1 实验材料与试剂
氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans,简称A.f 319)保存于武汉纺织大学微生物实验室. 使用改良后的9K培养基配方:KCL:0.1 g·L−1, (NH4)2SO4 :3 g·L−1 ,K2HPO4:0.5 g·L−1 ,MgSO4·7H2O :0.5 g·L−1,FeSO4·7H2O:40.0 g·L−1. 初始pH调至3.0. 实验所使用的活性红3BS、过一硫酸盐(PMS)、等试剂购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司. 生物炭材料来自湖北省通山县农业秸秆和木材气化副产物.
1.2 Fe3O4@BC的制备
将活化后的A.f 319添加入生物炭材料的9 K培养基中富集培养,60 h后抽滤分离,60 ℃烘干备用. 该生物炭材料命名为BBC. 将烘干后的BBC放入管式炉中热解,升温至700 ℃,全程氮气气氛保护,升温速率5 ℃·min−1,保温1 h. 温度降至室温后取出,使用去离子水反复清洗烘干备用,该材料标注为PBC.
1.3 碳材料表征
本实验使用扫描电子显微镜(Zeiss Gemini 300 ,德国Zeiss)分析材料的形貌特征;X射线衍射仪(Bruke D8 Advance ,德国Bruker )和傅立叶红外光谱仪(Thermo Scientific Nicolet 6700,美国)分析材料晶体结构和表面官能团;X射线光电子能谱技术(Thermo Scientific K-Alpha,美国 Thermo Scientific)分析材料表面元素及价态变化.
1.4 实验设计
染料浓度设置为200 mg·L−1,考察BC、BBC、PBC不同材料(添加量固定为1 g·L−1)对活性红3BS吸附实验;染料浓度设置为200 mg·L−1,考察BC、BBC、PBC不同材料(添加量固定为1 g·L−1)PMS(添加量固定为0.5 g·L−1)对活性红3BS的催化降解实验.
活性氧化物种猝灭实验是先将猝灭剂加入200 mg·L−1的活性红3BS的溶液中再进行催化降解实验. 选取甲醇(MeOH)、叔丁醇、对苯醌、L-组氨酸对·OH和SO4·−、·OH、·O2、1O2进行淬灭.
催化剂重复使用性能实验是在反应后进行固液分离,对分离出的催化剂使用超纯水多次冲洗,放入真空干燥箱干燥,循环5次.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 催化剂的表征结果
2.1.1 扫描电镜图(SEM)
图1(a)、(b)所示为黄钾铁矾负载于生物炭上的扫描电镜图. 结晶状的黄钾铁矾负载于生物炭上,结晶颗粒呈现不规则的块状,粒径大小从0.5—1 μm不等,经ICP测试载铁含量达到197.6 mg·g−1 . 生物沥滤将离子态铁负载到了生物炭上,可能的反应见式(1—3)[9]:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) 图1(c)、(d)为热解过后的生物炭,SEM可观察到黄钾铁矾的晶体形态发生了变化,晶体粒径变小,金属颗粒均匀的分散在生物炭上,以更加规整的圆形或椭圆形附着,无明显的团聚.
2.1.2 生物炭比表面积与孔径分布分析
用N2-BET对BC、BBC、PBC的比表面积和孔容孔径进行分析. 结果表明,PBC的比表面积(147.621 m2·g−1)相比BBC(52.743 m2·g−1)和BC(41.090 m2·g−1)显著提高(P<0.05),证明了Fe3O4负载于生物炭上可以提高材料的比表面积,增加有效的吸附点位,促进污染物在材料表面的吸附.
2.1.3 生物炭材料晶体结构分析
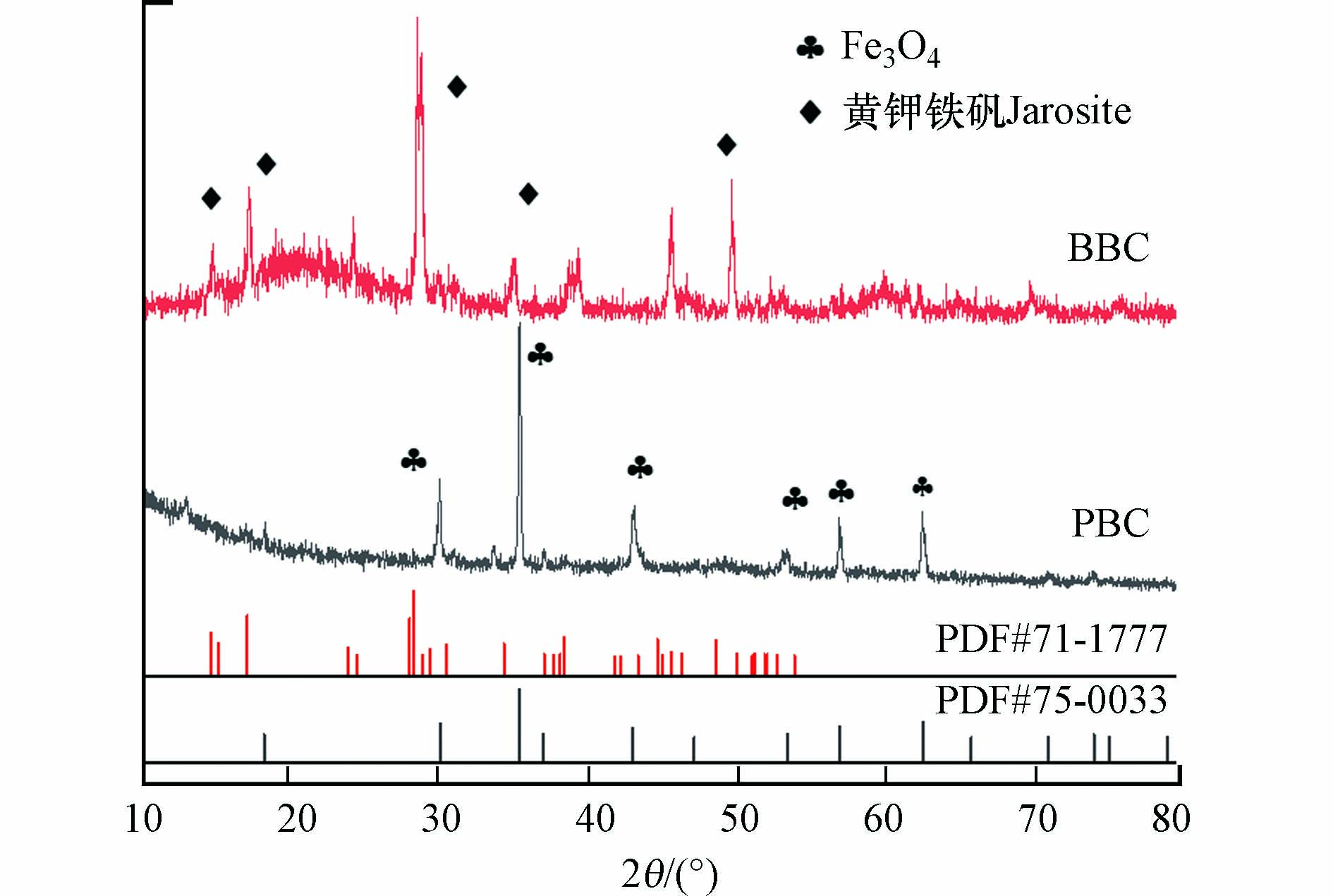
图2为负载黄钾铁矾的生物炭(BBC)与热解后的磁性生物炭(PBC)XRD图谱. BBC的主衍射峰与黄钾铁矾标准卡片PDF#71-1777中的17.4°、28.6°、28.9°、46.8°、49.9°高度吻合,表明黄钾铁矾被成功的负载于生物炭上. Fe3O4的衍射峰在29.9°、35.3°、43.1°、53.4°、57.2°和62.5°对应纯立方尖晶结构的(220)、(311)、(400)、(422)、(511)和(440)晶面,这些结果对应标准卡片PDF#75-0033,可以证明该材料为Fe3O4. 结合SEM图可以看出Fe3O4的比表面积明显大于热解前,暗示着在激活PMS产生自由基的催化反应中具有更好的活性位点[10].
2.1.4 傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)分析
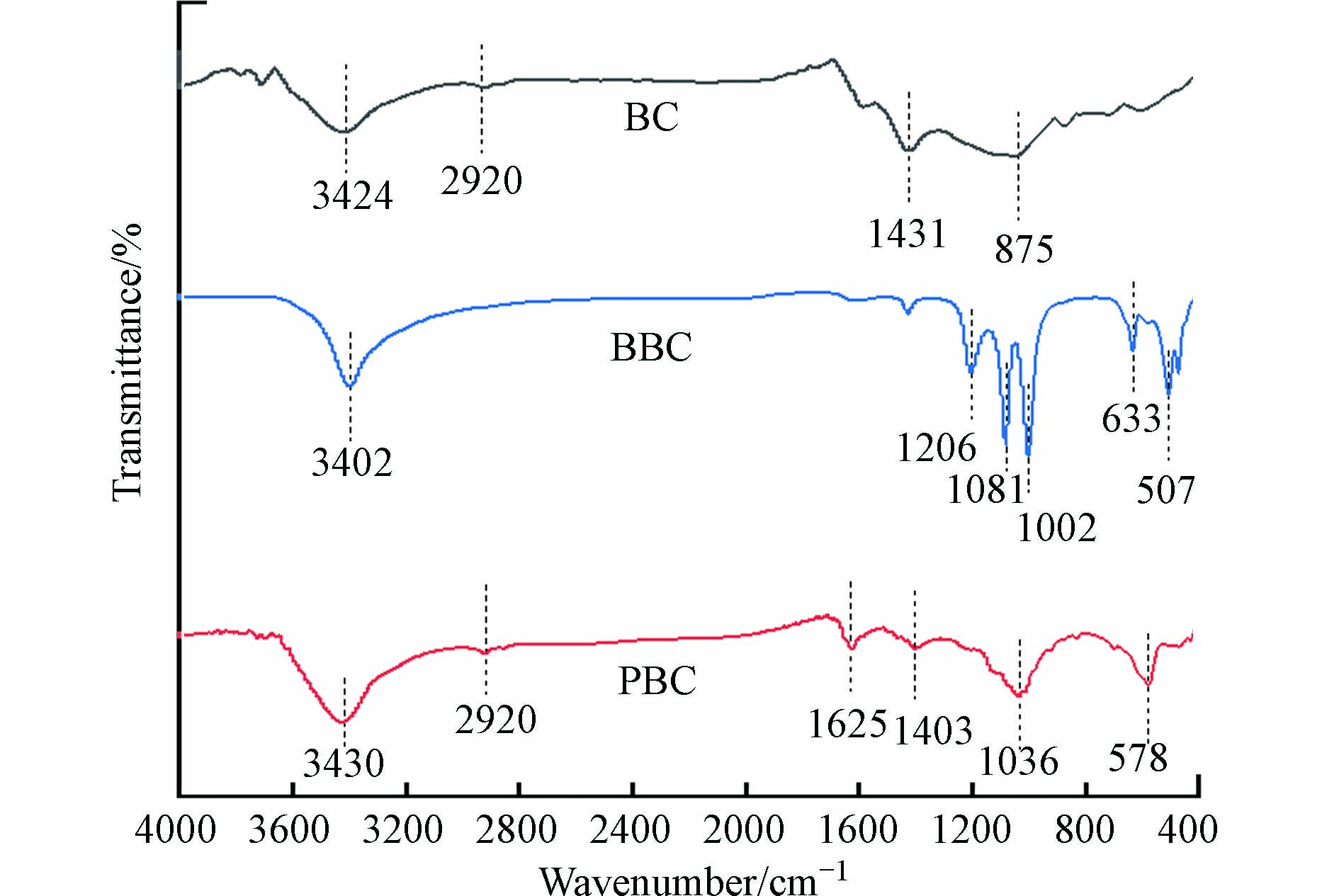
傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)分析结果表明: BC、BBC和PBC的主要官能团有O—H、C—H、C=O和C—O组成(图3). 其中在3424 cm−1处的特征峰归证实存在O—H的伸缩振动,2920 cm−1处的特征峰归属于C—H的弯曲振动峰[11],1625 cm−1处的特征峰是C=O的伸缩振动,1036 cm−1处是C—O的伸缩振动特征峰[12]. BBC在1000 cm−1到1500 cm−1产生了大量的C—O组,507 cm−1处和633 cm−1处特征峰应归属于Fe—O特征峰. PBC的FTIR谱图显示在578 cm−1出现了属于Fe—O的典型特征峰[13].
2.2 不同复合材料体系对活性红3BS的吸附和降解
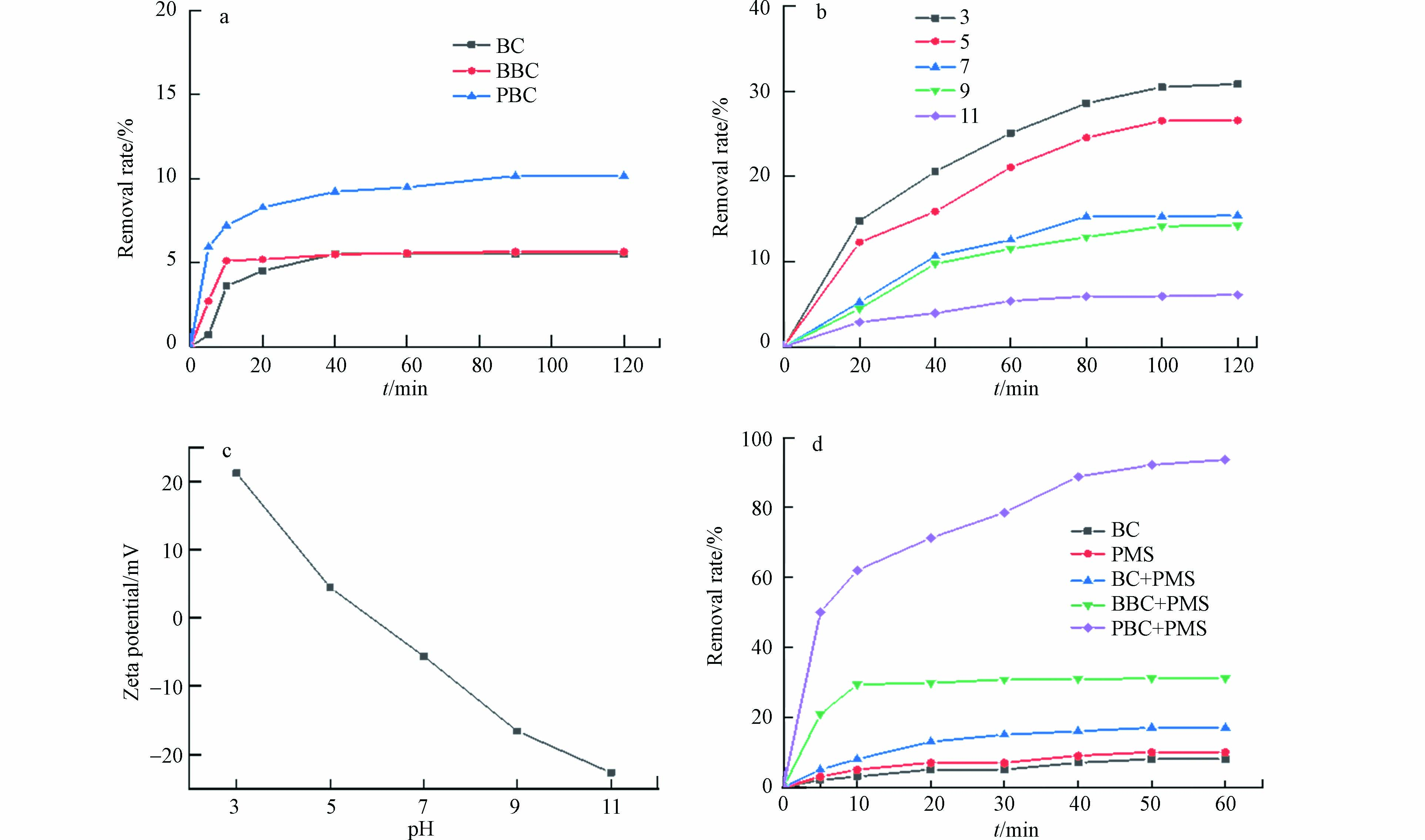
与BC和BBC相比,PBC显著提高了对活性红3BS(200 mg·L−1)的吸附效果,吸附能力分别提高了84.1%和79.5%(见图4a),Fe3O4的载入改善了生物炭的孔隙结构,提高材料的比表面积(表1),增强PBC对染料的吸附性能. 探讨了PBC在pH 3—11的范围内对染料的吸附作用,结果表明pH的增加会导致吸附效果逐渐下降(图4b). 结合Zeta电位结果(图4c),pH较低时碳材料表面带有强烈的正电荷,更容易吸附阴离子染料;随着pH的升高,碳材料表面去质子化带负电,与阴离子染料产生静电排斥从而降低了染料的去除效率[14].
表 1 BC、BBC、PBC的比表面积和孔隙结构Table 1. Specific surface area and pore structure of BC样品 Sample 比表面积/(m2·g−1) Surface area 孔容/(cm3·g−1) Pore volume 平均孔径/ nm Average pore diameter BC 41.090 0.022 3.439 BBC 52.743 0.057 4.834 PBC 147.621 4.725 2.586 PBC激活PMS对染料的催化降解能力明显优于BC、BBC以及单一的PMS,该反应体系在60 min内对200 mg·L−1染料去除率可达93.8 %(图4d),降解效率优于部分文献报道[15]. Fe3O4负载于生物炭表面不仅增强了对染料的吸附性能,而且能够通过Fe3O4中Fe2+和Fe3+电子穿梭进一步激活PMS产生更多活性物种,提高复合材料的协同降解能力. 在反应60 min后,活性红3BS的TOC去除率达到了67.1 %,这表明仍有部分物质没有被完全矿化[16].
2.3 Fe3O4@BC/PMS降解活性红3BS影响因素及机制分析
2.3.1 活性红3BS初始pH和PMS浓度影响
pH的变化会对Fe3O4@BC/PMS降解活性红3BS产生显著影响. 由图5(a)可知,在弱酸性条件下Fe3O4@BC对PMS的激活效果较好,pH为5时60 min内的降解率达到了84.69 %. 碱性条件下,随着pH的升高降解效率显著下降,推测是pH偏高时Fe3O4@BC表面的活性位点发生钝化,促进铁离子形成氢氧化铁沉淀,减弱了PBC对染料的吸附能力,同时降低了PMS产生自由基的能力.
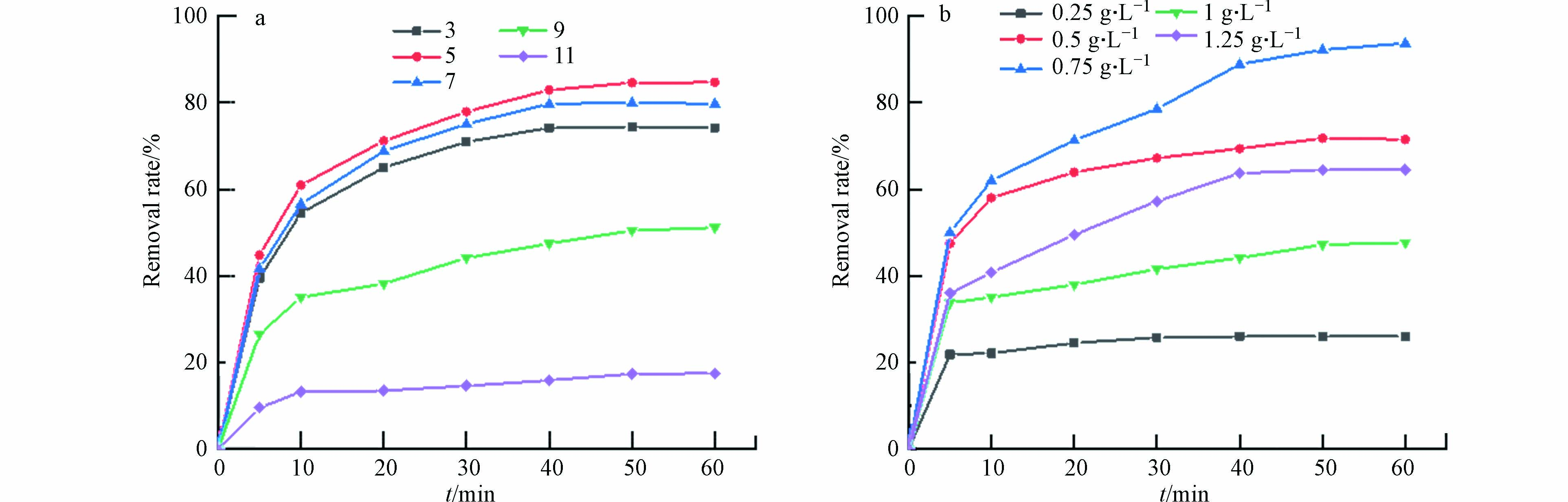
PMS投加量的增加可以提高活性红3BS的去除效率. 当PMS的投加量增加到0.75 g·L−1时,对染料的去除率达到93.8 %. 然而,当PMS的投加量继续提高,污染物的降解效率却不增反降. 分析原因,可能是过量的PMS会在短时间内产生大量的·OH和SO4·−与PMS自身产生淬灭反应,生成了氧化能力较弱的SO5·−,导致了SO4·−的利用率降低[17].
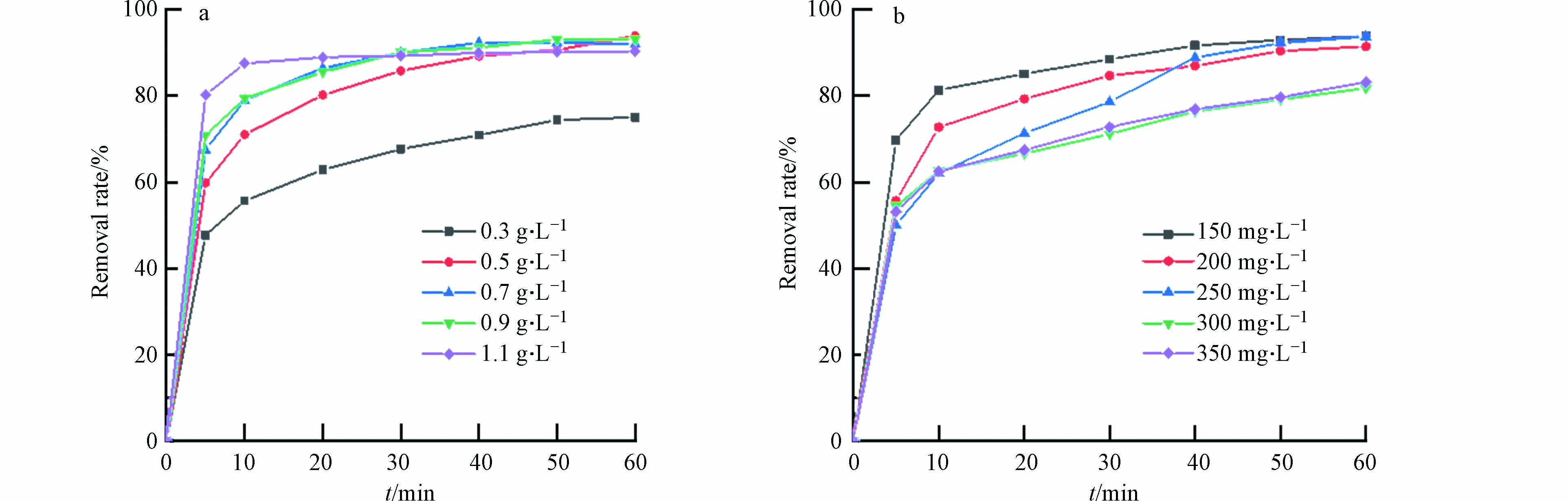
2.3.2 催化剂用量和活性红3BS浓度的影响
随着催化剂用量的增加,材料对活性红3BS的去除率也会逐步提升. 如图6(a)所示,当催化剂用量为0.5 g·L−1时,去除率达到了93.8 %. 继续增加催化剂的投加量,发现去除效果并不明显,这可能是该体系下PMS不足导致.
污染物的初始浓度升高对降解率影响并不显著. 如图6(b)所示,当污染物的初始浓度由150 mg·L−1增加到350 mg·L−1,60 min内污染物的降解率由95 %只下降到了81.8 %,可见Fe3O4@BC对高浓度染料废水也有较好的催化降解效果.
2.3.3 催化剂重复使用性能
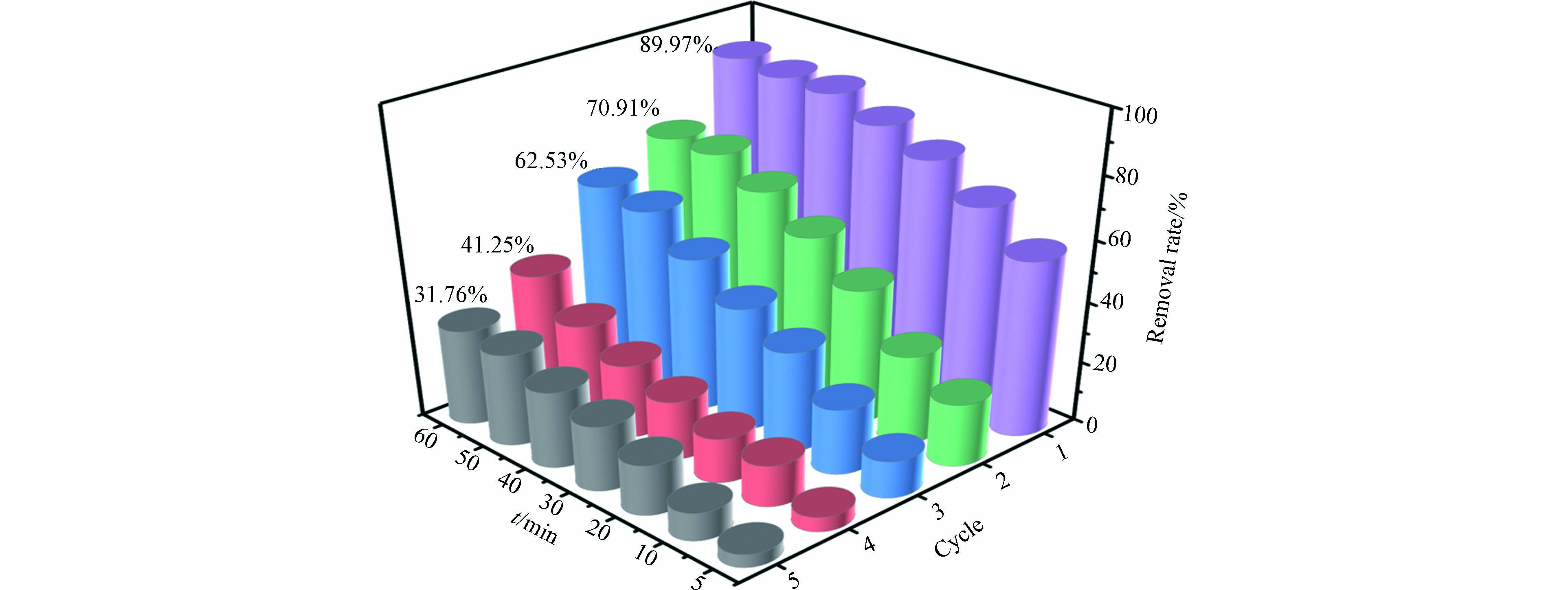
Fe3O4@BC在5次循环利用之后对活性红3BS仍然有一定的催化降解效果. 如图7所示,第一次实验活性红3BS降解率最高,污染物可以被大部分去除;第二次循环使用后,去除率达到70.91%;在随后的第3、4、5次循环中,去除率逐步下降,原因是反应过程中生物炭上的Fe3+和Fe2+循环参与对PMS的活化,造成铁离子溶出,导致了催化活性降低. 5次循环利用之后对污染物的降解率依然能够达到31.76 %,说明该材料是一种具有一定重复利用性的磁性催化剂.
2.3.4 Fe3O4@BC/PMS体系对活性红3BS的降解机制
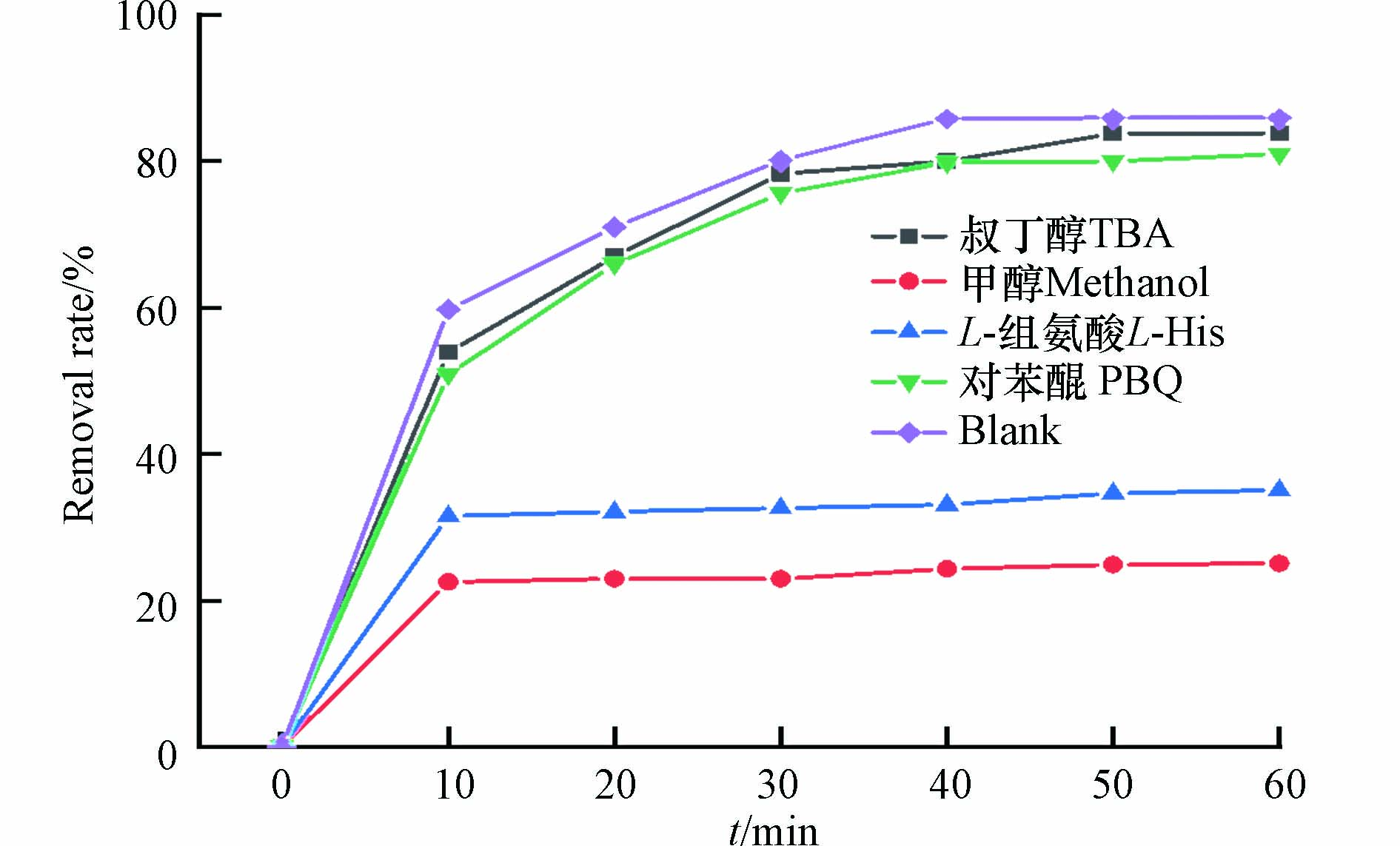
自由基淬灭实验确定磁性催化剂激活PMS起主要作用的自由基活性组分. 淬灭剂选用甲醇(MeOH)、叔丁醇(TBA)、对苯醌(PBQ)、L-组氨酸进行活性氧化物种猝灭实验. 甲醇是一种常见的·OH和SO4·−的自由基猝灭剂,二级反应速率常数k[MeOH,·OH]=9.7×108 mol·L−1·s−1,k[MeOH, SO4−·]=3.2×106 mol·L−1·s−1;叔丁醇是常用的·OH猝灭剂,反应常数k[·OH,TBA]=(3.8—7.6×108 mol·L−1·s−1);对苯醌可以抑制超氧自由基(·O2−), 反应速率常数为k[·O2−,PBA]=(1.0×109 mol·L−1·s−1);L-组氨酸捕获(1O2)的反应速率常数为1.6×106 mol·L−1·s−1[18].
图8展示了不同自由基淬灭剂对磁性生物炭活化PMS降解染料的影响. 投加叔丁醇和对苯醌对染料的去除并没有较大影响;投加甲醇会使染料的去除率下降60.79 %;L-组氨酸的加入会使染料的去除率下降50.82 %. 表明Fe3O4@BC/PMS体系中可能主要产生SO4−·和1O2而非·OH和·O2−[19]. 结合XPS分析反应前后 PBC 的化学价态变化(图9),PBC 拟合出的709.6 eV(Fe2+)和712.9 eV(Fe3+)两组峰,Fe2+和Fe3+的含量分别为66.1 %和33.9 %,反应后Fe2+的含量降低到了37.4 %,说明Fe3O4上颗粒的Fe3+和Fe2+存在电子转移机制,转化过程中的电子转移加速了污染物的降解[20]. 除此之外,生物炭表面的缺陷点位和部分官能团也可以作为活性点位活化PMS.
根据上述分析推测可能的降解机制. Fe3O4@BC活化PMS降解染料的机制主要包括自由基途径(SO4−·)和非自由基途径(1O2). 可能的反应过程见式(4—7):
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (7) 2.3.5 干扰离子与亚甲基蓝的降解
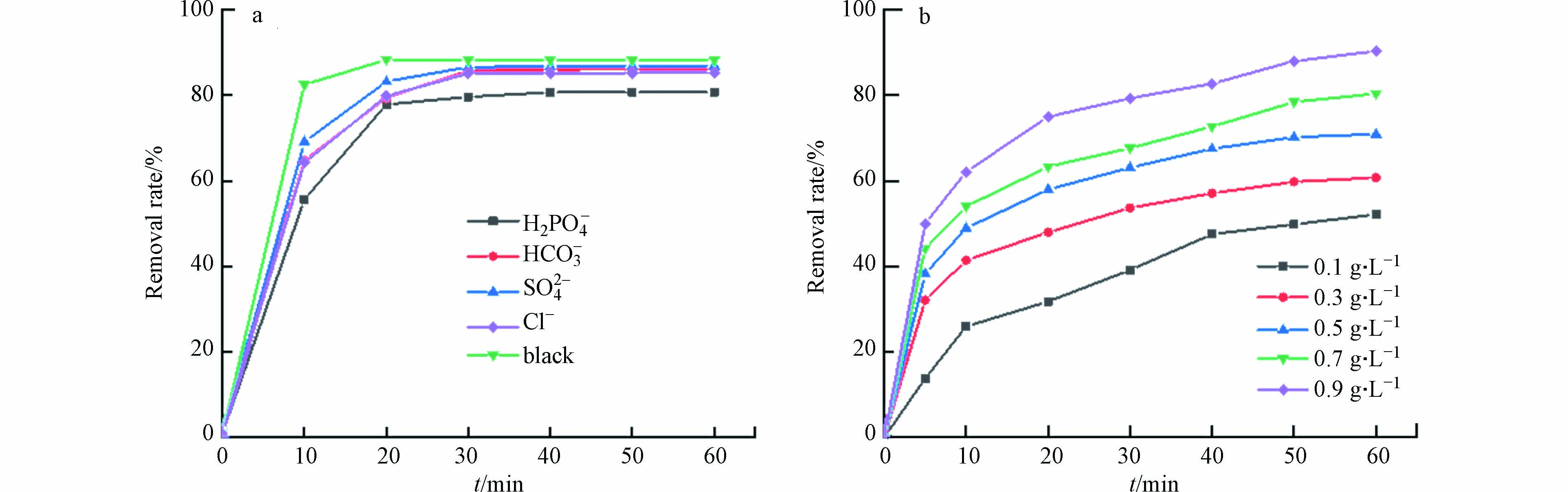
无机阴离子普遍存在于染料废水中,并且会对染料的降解效果产生影响[21]. 本实验选取了Cl−、HCO3−、SO42-和H2PO4−作为干扰离子,探究这些离子对活性红3BS催化降解的影响. 实验结果如图10(a)所示:干扰离子的添加对降解效率产生影响,尤其是H2PO4−的存在会使降解效率从88.2%下降到80.7%. 其原因可能是:(1)这些无机离子的引入会与染料竞争Fe3O4@BC上的活性位点;(2)无机离子可以清除体系中的自由基.
为考察Fe3O4@BC/PMS体系对其他类型染料降解能力,选取难降解蒽醌类染料亚甲基蓝作为目标污染物. 结果显示Fe3O4@BC/PMS体系对100 mg·L−1的亚甲基蓝具有良好的去除效果,催化剂投加量为0.9 g·L−1时,60 min内对亚甲基蓝的降解效率可以达到90.3%.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
本文利用生物沥滤将离子态铁负载到生物炭上,对铁负载生物炭二次热解改性,成功制备出具备磁性效应的铁基生物炭. Fe3O4@BC/PMS体系相较于原始生物炭的催化降解能力显著提升,对几种类型染料具有催化降解能力,多次循环利用后仍然保持较高的降解效率. 自由基猝灭实验探讨了复合材料对染料的降解机制,Fe3O4@BC/PMS体系中SO4−·和1O2主导了对染料的降解过程. 结果表明Fe3O4@BC材料在处理难降解的染料废水方面具有较高的应用前景,本研究为磁性生物炭改性材料处理染料废水方面提供了新方法.
-
表 1 Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)的XPS数据
Table 1. XPS data of Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)
催化剂Catalyst Olat/Osur Ru(4+)/Ru(0) Ru/β 0.44 1.71 Ru/MCM-41 0.58 0.18 Ru/Y 0.42 2.46 Ru/ZSM-5 0.41 0.94 表 2 Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)催化氧化性能数据和动力学参数
Table 2. Catalytic oxidation performance data and kinetic parameters of Ru/M(M=β/MCM-41/Y/ZSM-5)
催化剂Catalyst T50/℃ T90/℃ Ea/(kJ·mol−1) R2 TOF/(mmoltoluene·molRu−1·s−1) Ru/β 236 312 91.55 0.996 5.67 Ru/MCM-41 308 318 177.87 0.998 3.11 Ru/Y 227 290 82.61 0.991 5.71 Ru/ZSM-5 301 328 154.15 0.993 1.85 -
[1] 熊超, 李建军, 杨复沫, 等. 成都市冬季重污染过程中挥发性有机物污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(5): 590-596,603. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.05.014 XIONG C, LI J J, YANG F M, et al. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of VOCs during a heavy pollution process in winter in Chengdu [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(5): 590-596,603(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.05.014
[2] 王健. 负载型钌催化剂对VOCs的催化氧化研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院过程工程研究所, 2016. WANG J. Study on supported ruthenium catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of VOCs[D]. Beijing: Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016(in Chinese).
[3] 张金瑶, 王祖武, 余琬冰, 等. 负载型钌催化剂的制备对甲苯催化燃烧的影响 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(2): 65-68. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.02.010 ZHANG J Y, WANG Z W, YU W B, et al. Effect of preparation of supported ruthenium catalysts on toluene catalytic combustion [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(2): 65-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.02.010
[4] OEMAR U, ANG M L, HEE W F, et al. Perovskite LaxM1−xNi0.8Fe0.2O3 catalyst for steam reforming of toluene: Crucial role of alkaline earth metal at low steam condition [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 148/149: 231-242. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.001 [5] 段明华, 牟真, 李进军, 等. Co3O4/介孔分子筛催化剂对苯催化完全氧化的研究 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2008, 2(8): 1087-1091. DUAN M H, MU Z, LI J J, et al. Complete catalytic oxidation of benzene on Co3O4 catalysts supported on mesoporous molecular sieves [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2008, 2(8): 1087-1091(in Chinese).
[6] 袁金芳. 短孔道有序介孔材料的可控合成及吸附、催化性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2011. YUAN J F. Study on the controllable synthesis and adsorption, catalytic properties of well-ordered mesoporous materials with short channels[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2011(in Chinese).
[7] HE C, LI J J, CHENG J, et al. Comparative studies on porous material-supported Pd catalysts for catalytic oxidation of benzene, toluene, and ethyl acetate [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(15): 6930-6936. [8] 潘金鼎. 钌基纳米材料结构设计、制备及催化应用[D]. 北京: 中国科学院过程工程研究所, 2017. PAN J D. Structural design, preparation and catalytic application of ruthenium-based nanomaterials[D]. Beijing: Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017(in Chinese).
[9] DAI Q G, BAI S X, WANG J W, et al. The effect of TiO2 doping on catalytic performances of Ru/CeO2 catalysts during catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 142/143: 222-233. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.026 [10] MITSUI T, MATSUI T, KIKUCHI R, et al. Low-temperature complete oxidation of ethyl acetate over CeO2-supported precious metal catalysts [J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2009, 52(5): 464-469. doi: 10.1007/s11244-009-9186-4 [11] 赵瑰施, 张玲, 万玉秋, 等. 咪唑类离子液体在β沸石上的吸附 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(8): 1649-1656. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.08.2016010402 ZHAO G S, ZHANG L, WAN Y Q, et al. Adsorption of imidazolium ionic liquid onto β zeolites [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(8): 1649-1656(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.08.2016010402
[12] 袁恩辉. ZSM-5沸石分子筛的制备及应用研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2015. YUAN E H. Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite and their application[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2015(in Chinese).
[13] 吴迪, 刘洁, 印红玲, 等. 氮改性ZSM-5分子筛的苯吸附性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9): 2934-2942. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020051502 WU D, LIU J, YIN H L, et al. Study on benzene adsorption properties on nitrogen modified ZSM-5 zeolites [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9): 2934-2942(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020051502
[14] 李红伟, 李泽宇, 贠宏飞, 等. 高分散Ru-PEGx/NaY催化对硝基甲苯加氢制对甲基环己胺 [J]. 精细化工, 2018, 35(10): 1673-1677,1712. LI H W, LI Z Y, YUN H F, et al. Hydrogenation of p-nitrotoluene to p-methyl-cyclohexylamine over high dispersion Ru-PEGx/NaY catalyst [J]. Fine Chemicals, 2018, 35(10): 1673-1677,1712(in Chinese).
[15] 赵振国. 吸附作用应用原理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. ZHAO Z G. Application principle of adsorption action[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005(in Chinese).
[16] 张佳琦. Beta分子筛的合成及吸附性能研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2019. ZHANG J Q. Synthesis and adsorption properties of beta molecular sieves[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University, 2019(in Chinese).
[17] 邹思贝. Pt/泡沫沸石催化剂及其孔道调变对甲苯催化氧化性能影响研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020. ZOU S B. Pore-modified effect over toluene catalytic combustion performance of zeolite foam supported Pt catalysts[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[18] 张强. 单晶纳米/多级孔ZSM-5和Beta分子筛合成及催化性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019. ZHANG Q. Syntheses of single-crystalline nanosized/hierarchical ZSM-5 and Beta zeolites with excellent catalytic performance[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019(in Chinese).
[19] 张婷婷, 卜龙利, 宁轲, 等. 催化剂载体的优化及微波催化燃烧甲苯特性 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(12): 3468-3479. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202003046 ZAHNG T T, BU L L, NING K, et al. Catalyst carriers optimization and characteristics of microwave catalytic combustion of toluene [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(12): 3468-3479(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202003046
[20] 林立. Cu/Mn/La/MCM-41催化剂的合成及降解染料废水的研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2019. LIN L. Synthesis of Cu/Mn/La/MCM-41 catalyst and degradation of dye wastewater[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019(in Chinese).
[21] ZHANG J Y, RAO C, PENG H G, et al. Enhanced toluene combustion performance over Pt loaded hierarchical porous MOR zeolite [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.017 [22] 秦媛. 锰基催化剂催化氧化甲苯性能及其氧物种循环过程的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020. QIN Y. Study of the performance of toluene catalytic oxidation and the cycle of oxygen species over Mn-based catalysts[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[23] REN Z, WU Z L, SONG W Q, et al. Low temperature propane oxidation over Co3O4 based nano-array catalysts: Ni dopant effect, reaction mechanism and structural stability [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 180: 150-160. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.021 [24] 陈立. Ru基催化剂对氯代挥发性有机物(CVOCs)的催化氧化研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018. CHEN L. Catalytic oxidation of chlorinated volatile organic compounds over ruthenium-based catalysts[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018(in Chinese).
[25] 黄婷. 新型ZSM-5负载Ru双功能催化剂的费—托反应性能研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2017. HUANG T. Study on Fischer-Tropsch reaction performance of the new ZSM-5 load Ru dual-function catalyst[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2017(in Chinese).
[26] PENG R S, SUN X B, LI S J, et al. Shape effect of Pt/CeO2 catalysts on the catalytic oxidation of toluene [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 306: 1234-1246. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.056 [27] 郭瑶. SnO2催化材料用于甲苯深度氧化 : 指认其表面活性中心和影响活性的关键因素[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020. GUO Y. SnO2-based catalytic materials for toluene deep oxidation: identifying the surface active sites and the critical factors influencing the reaction performance[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2020(in Chinese).
[28] 李文秀, 许天行, 范俊刚, 等. 噻吩类硫化物在Ag(I)X分子筛上的选择性吸附 [J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2013, 29(5): 870-875. LI W X, XU T X, FAN J G, et al. Selective adsorption of thiophenic sulfur compounds on Ag(I)X adsorbent [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2013, 29(5): 870-875(in Chinese).
[29] GUO Y, ZENG L L, XU X L, et al. Regulating SnO2 surface by metal oxides possessing redox or acidic properties: The importance of active O2−/O22− and acid sites for toluene deep oxidation [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2020, 605: 117755. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117755 [30] 肖丽. 分子筛负载钙钛矿型催化剂催化燃烧VOCs的研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014. XIAO L. Study on catalytic combustion of VOCs by perovskite supported on zeolites[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2014(in Chinese).
[31] ANTUNES A P, RIBEIRO M F, SILVA J M, et al. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over CuNaHY zeolites: Coke formation and removal [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2001, 33(2): 149-164. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(01)00174-6 [32] 杨晓龙, 夏春谷, 唐立平, 等. 氧化镁载体和氧化钡助剂对钌基氨合成催化剂结构和性能的影响 [J]. 无机化学学报, 2011, 27(8): 1541-1549. YANG X L, XIA C G, TANG L P, et al. Effect of MgO support and BaO promoter on structure and catalytic activity of ruthenium catalysts for ammonia synthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2011, 27(8): 1541-1549(in Chinese).
[33] 杨晓龙, 夏春谷, 唐立平, 等. 氧化铝载体和氧化钡助剂对钌基氨合成催化剂结构和性能的影响 [J]. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26(12): 3263-3272. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20101223 YANG X L, XIA C G, TANG L P, et al. Effect of alumina support and Barium oxide on the structure and catalytic activity of ruthenium catalysts for ammonia synthesis [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2010, 26(12): 3263-3272(in Chinese). doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20101223
[34] 彭若斯. 二氧化铈负载铂催化剂催化氧化甲苯的性能与反应机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. PENG R S. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over platinum supported on ceria catalysts: Performance and reaction mechanism[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[35] 刘立忠. 高活性锰基双金属氧化物的制备及其低温催化氧化芳香类VOCs性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019. LIU L Z. Preparation of highly active manganese-based bimetallic oxides for low-temperature catalytic oxidation of aromatic VOCs[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2019(in Chinese).
[36] 罗萌萌. 铜掺杂不同结构锰氧化物催化剂的制备及其甲苯催化燃烧性能研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019. LUO M M. Preparation of copper modified manganese oxide catalysts with different structure and their performance for catalytic combustion of toluene[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019(in Chinese).
[37] 高君安, 李想, 史东军, 等. ZSM-5分子筛蜂窝状成型工艺及其吸附甲苯的性能研究 [J]. 现代化工, 2020, 40(6): 123-127. GAO J A, LI X, SHI D J, et al. Honeycomb molding process of ZSM-5 molecular sieves and adsorption to toluene [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2020, 40(6): 123-127(in Chinese).
[38] 方向晨, 杜艳泽, 张通. 沸石分子筛催化剂的“限域”效应 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2021, 51(2): 87-96. doi: 10.1360/SSC-2020-0186 FANG X C, DU Y Z, ZHANG T. Confinement effect in zeolite catalysts [J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica), 2021, 51(2): 87-96(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SSC-2020-0186
[39] 禇月英. 沸石分子筛孔道中催化反应机理的理论计算研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院武汉物理与数学研究所, 2013. ZHE Y Y. Theoretical calculation studies of catalytic reactions in zeolite channels[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, The Chinese Academy of Sciences University of Chinese Academy of Science, 2013(in Chinese).
[40] 蔡晓兰. 固体酸催化剂在烷基化反应中的应用[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2016. CAI X L. The application of solid acid catalyst in alkylation reaction[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese).
-





 下载:
下载: