-
土壤中的镉(Cd)具有强烈的移动速度和危害性[1-3]。Cd在生物体内极易蓄积,具有生殖发育毒性、神经毒性、致癌性等多种严重毒害性[4]。川芎植物的根茎可用于治疗经闭痛经、瘾瘕腹痛等,有很高的经济和药用价值。近年来,由于川芎主产区土壤Cd含量较高从而导致其用药部位(根部)Cd超标的问题,严重影响了川芎的用药安全,制约其对外出口。因此,解决川芎用药部位Cd含量超标的问题迫在眉睫。
向土壤中添加改良剂可以有效降低土壤重金属活性,抑制重金属的迁移[5-6]。团聚体是土壤的一种基本的物理和功能元素,重金属在土壤环境中的积累、迁移和有效性与土壤团聚体的性质密切相关[7]。研究团聚体内重金属的分布可以揭示改良剂降低重金属有效性的机制。Wolfgang等[8]在研究中发现了土壤重金属Cd主要富集在0.02—0.25 mm的团聚体粒级中。土壤团聚体作为土壤结构的基本组成单位,对探究土壤重金属的分布规律和其潜在影响机制有着非常重要的作用。
-
川芎种子(Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.)由四川省成都市彭州区某川芎种植基地提供。初始土壤的物理化学性质如下:pH为(5.63 ± 0.21);有机质为(28.93 ± 1.78) g·kg−1;总磷为(0.67 ± 0.05) g·kg−1;全氮为(1.22 ± 0.09) g·kg−1;孔隙度为(43.91%± 2.46%);总Cd为(1.52 ± 0.12) mg·kg−1。试验小区面积为46.62 m2。
-
经过改良剂初筛试验后本研究选取两种改良剂用于田间试验。改良剂1由轻质碳酸钙(CaCO3,97%)、钙基膨润土(蒙脱石,95%)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4, 95%)、生物炭、硅酸钠(Na2SiO3, 99%)、天然凹凸棒等质量混合而成;改良剂2由重质碳酸钙(CaCO3, 97%)、钙基膨润土、磷酸二氢钾、生物炭、硅酸钠、天然凹凸棒等质量混合而成。所有材料按照等质量比混合,过100目筛后混合制得土壤改良剂。田间试验共设7个处理,分别为不施加改良剂(对照)、改良剂1低浓度(0.5 t·hm−2)(T1-低)、改良剂1中浓度(1.5 t·hm−2)(T1-中)、改良剂1高浓度(5.0 t·hm−2)(T1-高)、改良剂2低浓度(0.5 t·hm−2)(T2-低)、改良剂2中浓度(1.5 t·hm−2)(T2-中)、改良剂2高浓度(5.0 t·hm−2)(T2-高)。对于川芎进行3次追肥,有机粪肥为集约化养殖场的鸡粪,含水量为76%。鸡粪的总Cd含量为(0.43 ± 0.04) mg·kg−1。
-
在川芎收获阶段,采用五点采样法,采集完整的植株样品和耕层(0—20 cm)土壤样品100 g。将川芎植物样品在105 ℃干燥30 min[9],切片、压碎、0.5 mm筛分、密封保存待测。土壤样品要筛分以保存。
-
植物样品:测定干燥后川芎的生物量。根据药典方法,将Cd的根、茎部分风干,经100目尼龙筛网制成药粉,在烧杯中称取1 g样品。然后加入10 mL硝酸-高氯酸(4:1)混合溶液,混合浸泡过夜。次日,将溶液在加热板上溶解,微沸至无色透明或微黄色。冷却后,将溶液转移到10 mL的量瓶中,用2%的硝酸溶液清洗容器,恒容振荡。然后用火焰原子吸收光谱仪测定镉的含量。
土壤样品:使用Tessier萃取法测定土壤中有效态Cd,采用火焰原子吸收光谱仪测定土壤中Cd含量。采用pHs-3C(水土比2.5∶1)测定土壤pH值;采用重铬酸钾法测定土壤有机质含量;土壤孔隙度根据土壤容重(环刀法)和比重(比重瓶法)计算得到;土壤团聚体根据萨维诺夫法分级[10]。
-
数据分析在经过SPSS25.0和Excel2019分析之后,使用Origin 2018进行做图,并且使用Duncan新复极差法进行处理间的差异显著性。
-
如表1所示(不同小写字母表示同列各处理间差异显著,P < 0.05),各处理的土壤pH、土壤有机质和速效磷均显著提升(P < 0.05),土壤有效态Cd得到显著降低。改良剂1处理下的土壤为弱酸性,与对照组相比,pH提高了0.32—0.59个单位。改良剂2处理下的土壤pH提升了0.38—0.80个单位。土壤有机质含量在施加改良剂之后增加了11.30%—26.29%。改良剂的添加可以提升土壤速效磷的含量,其中T2-高处理下速效磷浓度的提升最大(99.95%),较对照处理差异显著(P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,施加改良剂后土壤有效态Cd含量显著降低了9.52%—51.43%(P < 0.05)。不同施用量对土壤有效态Cd有显著影响。从低施用量到高施用量,改良剂2施用量的增加显著提升了Cd的固定化效率。T2-中和T2-高处理效果最好,均降低了51.43%。
土壤重金属的是否有效,在一定范围内与其pH值有一定关系。二者呈现负相关关系[11-12]。而在本次实验中,土壤pH的增加与两种改良剂中含有碱性物质的生物炭、方解石等有关系。并且生物炭对于提升土壤中钾离子和钠离子等等有很好的效果,与此同时可以减少土壤中的氢离子和金属铝离子,因此pH提升[13]。而在土壤的pH增加之后,土壤胶体的负电荷量提升,镉离子电吸附能力增加[14]。土壤中镉离子被两种改良剂中的生物炭和钙基膨润土而淹留。而土壤中的金属有效性得到减少的原因在于含有官能团羟基的醇类和酚类化合物的形成,金属离子有了更多的吸附点位[15]。
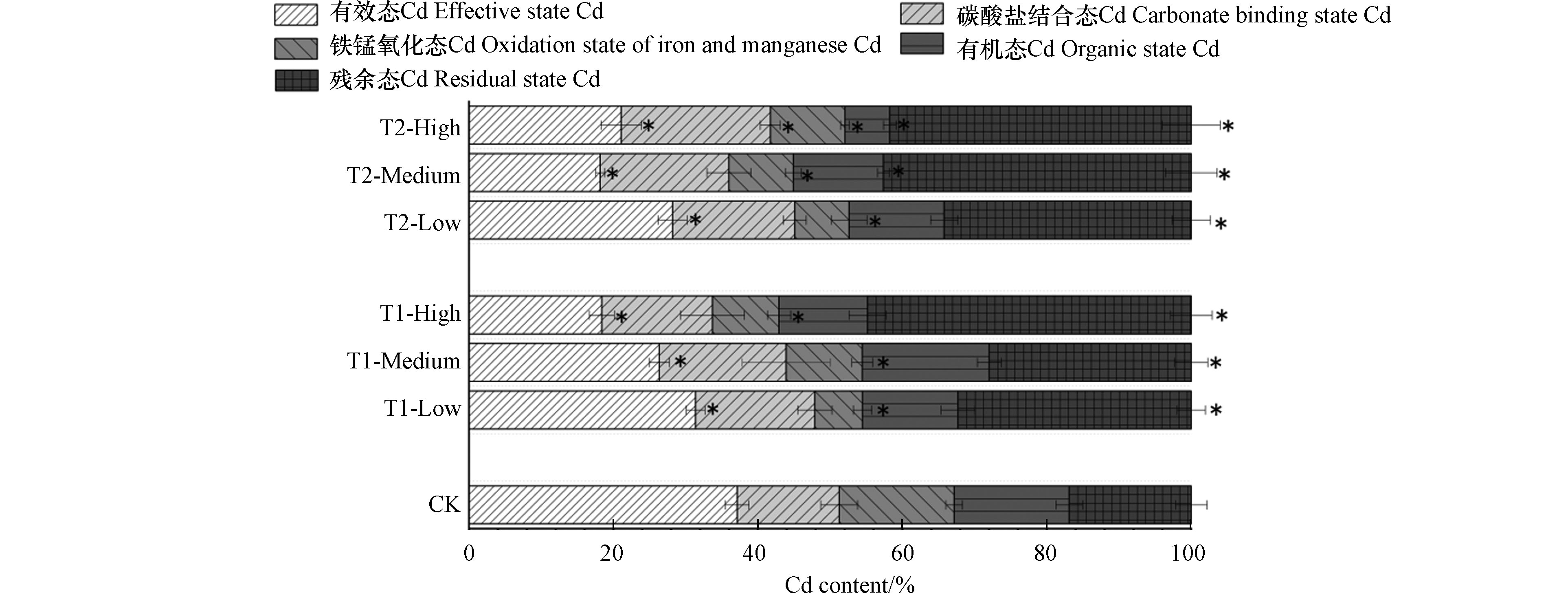
在川芎收获期,不同改良剂处理下的有效态Cd百分比含量均减少(图1),减少量在5.89%—18.76 %之间,其中T1-高处理效果最显著;不同处理对碳酸盐结合态Cd有着不同程度的提升,增加率为1.28%—6.56%,最为显著的为T2-高处理;铁锰氧化态Cd百分比含量均有所减少,其中减少最多的是T1-低处理,减少量为8.84%;改良剂对有机态Cd的影响是不同的,T1-中处理下的有机态Cd增加,增加量为0.53%,而其余处理均减少了其含量;残余态Cd的百分比含量变化较大,对比对照处理,增加量在9.4%—28.05 %之间,其中,T1-高处理增加最多。总的来说,改良剂使有效态Cd向残余态Cd转变,T1-低处理下的Cd总量未发生变化,依旧为1.414 mg·kg−1 ,而另两种梯度浓度总Cd含量均提升,T1-高处理下提升最高,为15.60%,而T2-中和T2-高处理的Cd总量均减少了14.18%,T2-中处理的总Cd含量提升了7.80%。
不同浓度改良剂的施加可以促进土壤Cd从有效态向其余形态的转变,这可以降低重金属生物有效性,从而使Cd的生物毒性降低。但无论是各种形态的Cd含量还是不同形态Cd的总和,一直在发生着改变,这是因为土壤重金属形态会随着土壤环境因子的改变而改变,它是处于一种动态的平衡[16]。
-
改良剂的施加降低了土壤容重。由表2可知,不同改良剂的施加降低了土壤容重和比重,增加了土壤孔隙度。对比对照处理,改良剂1处理组降低了土壤容重,土壤容重与改良剂浓度呈负相关关系,对容重的减少量为6.38%—10.64%,不同浓度处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);改良剂2处理组按照对土壤容重的减少效果为高>低>中浓度,减少量在10.64%—14.89%;对比对照处理,土壤比重的减少量为4.63%—10.42%,T2-高处理减少最多,除了T1-中和T2-高处理外,改良剂的处理效果差异不显著(P < 0.05);从测定结果可以看出,相较对照处理,不同处理中土壤孔隙度增加最多的是T2-高处理,增加了9.05%,所有处理差异均显著(P < 0.05)。
土壤容重代表了土壤的结构和有机质含量等状况,土壤容重越小,土壤越松软,透气性越好。土壤比重受到土壤固相组成物质的种类和相对含量的影响[17]。土壤比重的结果一定程度上可以反映土壤的矿物组成和有机质含量,有机质含量越高,土壤比重越低。土壤孔隙度是衡量土壤孔性的重要指标,与土壤容重和比重联系密切[18]。本试验中,改良剂的施加改善了土壤物理结构,这有利于川芎的生长。改良剂2对土壤结构的改善整体效果略微优于改良剂1。土壤结构是土壤中不同大小、形态和性质的土壤团聚体的总和。土壤结构通过影响土壤水分、通风、温度和机械阻力间接影响作物生长[19]。越坚硬的土壤,其孔隙度越低,水力传导系数越低,干燥时强度越高,这导致渗透减少,植物出苗和根系生长受到抑制[20]。
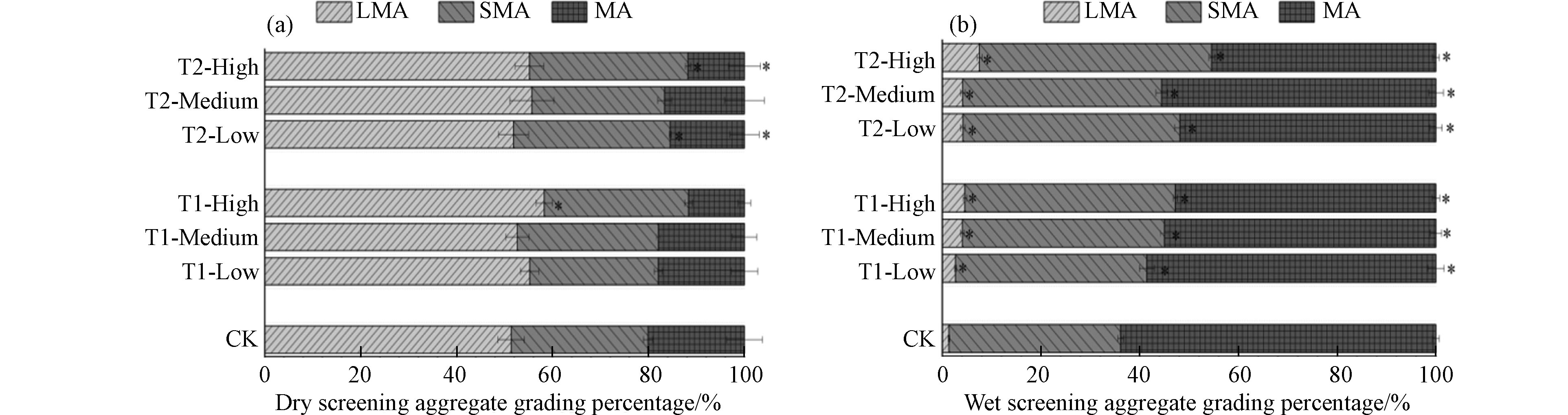
改良剂的施加可以促进微团聚体向粗大团聚体和细大团聚体的转变。本试验将土壤团聚体按粒径分为了3种,分别为粗大团聚体(>2000 μm)和细大团聚体(250—2000 μm)和微团聚体(<250 μm)[21]。如图2a所示,51.38%的土壤为粗大团聚体,在施入改良剂后,相较对照组而言,粗大团聚体增加,增幅为1.30%—6.89%;在细大团聚体中,除T1-低和T2-中处理外,其余处理均增加了细大团聚体的含量,增加了0.86%—4.52%;不同改良剂处理均减少了微团聚体的占比,减少量在2.13%—8.44%之间。如图2b所示,在未经处理的土壤中,1.37%的土壤主要为粗大团聚体,34.76%的土壤主要为细大团聚体,在施入改良剂后,粗大团聚体和细大团聚体含量增加显著,增幅分别为为1.31%—6.02%和4%—11.36%。对比对照处理,改良剂的施加减少了微团聚体的含量,减少量为5.31%—19.38%。不同改良剂的施加增加了粗大和细大团聚体的含量,并且查阅相关文文献,总结了土壤团聚体当中团聚性增强的原因跟以下因素有关:(1)添加改良剂的添加使得微团聚体结合成较大粒径团聚体的粘合剂,改良剂中带负电荷的微生物和官能团可以通过静电相互作用吸附土壤中的黏土和矿物质,形成稳定的团聚体[22-23]。(2)两种改良剂中的硅酸钠中的钠离子作为可变电荷的土壤胶体加速了土壤团聚体的胶结[24]。
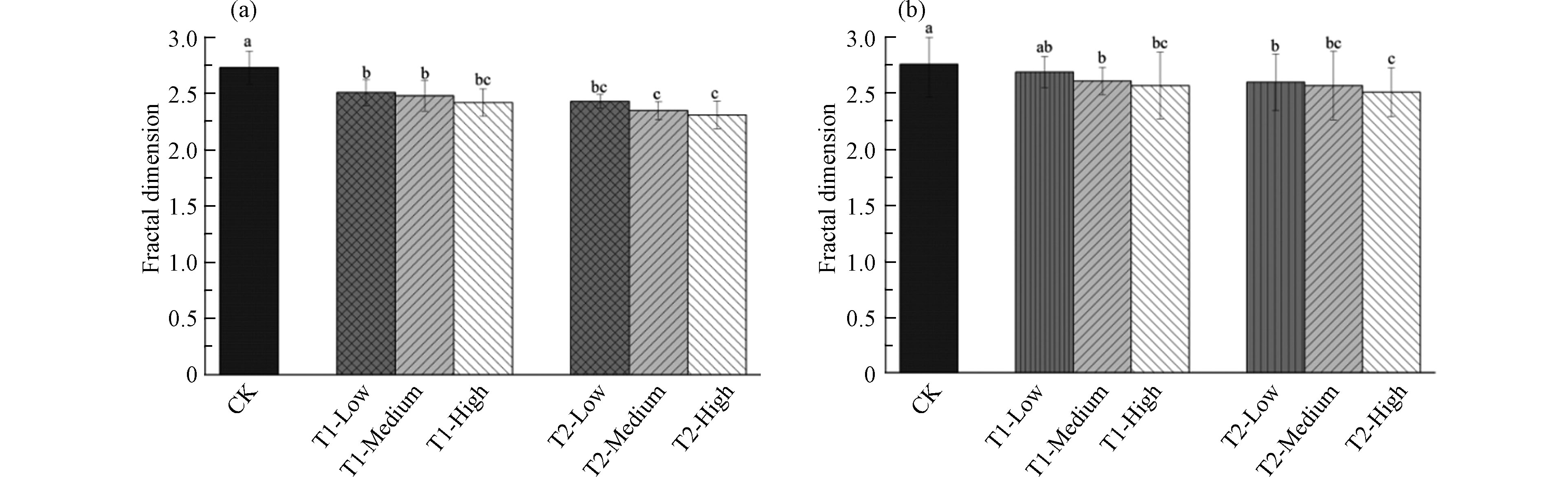
水稳性团聚体的分形维数(D)的值通常可以用来表征土壤的结构稳定性,且分形维数的越低,土壤团聚体的结构越稳定[25-26]。由图3b可知,通过实验研究发现湿筛法下,改良剂的施加降低了分形维数的值,相比对照组而言,改良剂1和改良剂2间无显著差异性,分形维数随着改良剂浓度梯度的增加而递减。对于非水稳性团聚体来说,实验结果与水稳性团聚体相似。Stegarescu等[27]发现,当施加了外源物质(黑麦、油菜和小麦秸秆)后,对土壤团聚体稳定性产生了影响。顾欣等[28]在盆栽条件下施加了生物炭,提高了玉米土壤的GMD(几何平均直径)和MWD(平均重量直径)的值,提升了种植土壤的机械稳定性。本研究中,两种改良剂均含钙基膨润土,它能够提升土壤大粒径土壤团聚体的含量,并且钙基膨润土的施加能够提升土壤有机碳的含量,土壤有机碳与微生物的存在可能会影响到土壤团聚体的稳定性[29]。
-
由表3可知,施加改良剂可以有效降低收获期川芎根部Cd含量。不同处理的川芎根部Cd含量均减少,除T2-低和T2-高处理外,不同处理差异显著(P < 0.05),降幅在41.51%—56.13%。同时,改良剂的添加显著增加了川芎的生物量(表3),T2-低、T2-高处理效果显著,增幅分别为53.50%和52.72%。在改良剂1的施加下,浓度不断提升,植物根部Cd含量降低,而生物量增加,二者呈现负相关关系,表明了植物在根部Cd含量减少的情况能够生长更好。而在改良剂施加后,土壤的pH值提高,且有效态Cd降低,植物周边的土壤理化性质得到一定程度的改善,因此土壤中对于影响植物生长的不利因素减少,植物能够更好的生长,由此提升了川芎生物量[30]。
-
为了探究混合改良剂添加对植物生物量和根部Cd含量影响的潜在机制,利用IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0分析了土壤化学指标、分型维数与川芎生物量和镉含量之间的相关关系(表4)。结果表明,川芎生物量与pH(R=0.980,P<0.001)、有机质(R=0.930,P=0.002)、速效磷(R=0.811,P=0.027)以及硝态氮(R=0.756,P=0.050)均成显著正相关;川芎根部Cd与pH(R=−0.855,P=0.014)、有机质(R=−0.902,P=0.005)、速效磷(R=−0.970,P<0.001)、硝态氮(R=−0.755,P=0.050)均成显著负相关,和分形维数(干筛R=0.863,P=0.012、湿筛R=0.802,P=0.030)呈显著正相关关系。
土壤pH的提高降低了土壤中有效态Cd对川芎根部的迁移效果,减少了川芎根部Cd含量。而速效磷含量的提高为川芎生长提供了充足的养分,有利于川芎生物量的积累。有机质对川芎根部Cd的积累的抑制作用体现在土壤颗粒之间通过有机质的胶结等作用形成微生物的细胞壁和产生代谢产物,可以提升土壤团聚体的稳定性,并且能够吸附和沉淀土壤中的重金属,对土壤有效态Cd的积累产生消极影响[31];而团聚体稳定性显著影响了川芎根部Cd的积累,根据数据分析以及查阅相关文献,分析原因可能如下:(1)分形维数越低,土壤团聚体稳定性越高,粗大和细大团聚体含量也越高。而较大团聚体可以保留住重金属离子,使得土壤中有效态Cd向川芎根部迁移减少,从而抑制川芎根部Cd含量[32]。(2)改良剂的施加增强了土壤团聚体稳定性,而团聚体中有效态Cd对“土壤—作物”中镉的转运和分布起到了关键作用[33],因此对川芎根部Cd起抑制作用。
-
(1)施加两种改良剂显著影响了土壤的化学和物理性质,其中土壤pH、有机质、速效磷和土壤孔隙度的含量得到提升,土壤有效态Cd、土壤比重和土壤容重得到有效降低。总体而言,改良剂2对土壤有效态Cd的降低效果优于改良剂1。
(2)土壤团聚体显著影响川芎根部Cd含量。土壤中大团聚体可以保留重金属离子,使得土壤中有效态Cd向川芎根部迁移减少,从而抑制川芎根部Cd含量。T2-低以及T2-中使用下,对川芎影响最为突出,并且考虑到实际应用和成本方面因素,最终选择T2-低浓度条件(即0.5 t·hm−2)。
改良剂对镉污染土壤团聚体稳定性和川芎镉积累的影响
Effects of soil aggregates stability on the cadmium accumulation and growth of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. in cadmium-contaminated soil
-
摘要: 为探究土壤改良剂的施用对团聚体稳定性及川芎镉积累的影响,本文基于川芎主产地种植园镉污染土壤设置田间试验,通过施加不同剂量改良剂1(轻质碳酸钙、石灰石、钙基膨润土、纳米磷酸二氢钾、生物炭、硅酸钠、凹凸棒)0.5 t·hm−2(T1-低)、1.5 t·hm−2(T1-中)、5.0 t·hm−2(T1-高)和改良剂2(重质碳酸钙、钙基膨润土、纳米磷酸二氢钾、生物炭、硅酸钠、凹凸棒)0.5 t·hm−2(T2-低)、1.5 t·hm−2(T2-中)、5.0 t·hm−2(T2-高),研究其对土壤团聚体的稳定性、有效态Cd含量以及川芎根部Cd含量与其生物量的影响。结果表明,在添加两种不同改良剂之后,土壤团聚体稳定性得到提升;土壤有效态Cd以及川芎根部Cd含量都有显著降低。对比空白处理,T2-高和T2-低处理效果最好,使得土壤有效态Cd和川芎根部Cd分别降低了51.43%和56.13%;并且生物量有所提升,T2-低处理效果最好,增幅为53.50%。根据相关性分析,发现土壤团聚体稳定性显著影响了川芎根部Cd积累。本实验结果,可为土壤改良剂施加过程中生物积累效应相关潜在机制的研究提供参考。Abstract: To search the correlation between soil aggregates stability and the cadmium(Cd) accumulation and growth of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort., this study took the soil of the main producing area of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.in Sichuan Province as the research object. The concentration of 0.5 t·hm−2, 1.5 t·hm−2 and 5.0 t·hm−2 of soil amendment 1 (precipitated calcium carbonate, limestone, calcium bentonite, nano potassium dihydrogen phosphate, biochar, sodium silicate, attapulgite) and soil amendment 2(heavy calcium carbonate, calcium bentonite, nano potassium dihydrogen phosphate, biochar, sodium silicate, attapulgite) were studied respectively to see what effects the modified soil have on the Cd accumulation and growth of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. The results showed that the stability of soil aggregates was improved after adding two different amendments. The content of available Cd in soil and root of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. decreased significantly. Compared with blank treatment, T2-high and T2-low treatments had the best effect, which reduced soil available Cd and root Cd by 51.43% and 56.13%, respectively. In addition, the biomass was improved, and the T2-low treatment had the best effect, increasing by 53.50%. According to correlation analysis, it was found that soil aggregate stability significantly affected Cd accumulation in root of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. The results of this experiment can provide a reference for the study of potential mechanisms related to bioaccumulation effect during the application of soil amendments.
-
Key words:
- soil aggregates /
- ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. /
- available cadmium /
- biomass
-
土壤中的镉(Cd)具有强烈的移动速度和危害性[1-3]。Cd在生物体内极易蓄积,具有生殖发育毒性、神经毒性、致癌性等多种严重毒害性[4]。川芎植物的根茎可用于治疗经闭痛经、瘾瘕腹痛等,有很高的经济和药用价值。近年来,由于川芎主产区土壤Cd含量较高从而导致其用药部位(根部)Cd超标的问题,严重影响了川芎的用药安全,制约其对外出口。因此,解决川芎用药部位Cd含量超标的问题迫在眉睫。
向土壤中添加改良剂可以有效降低土壤重金属活性,抑制重金属的迁移[5-6]。团聚体是土壤的一种基本的物理和功能元素,重金属在土壤环境中的积累、迁移和有效性与土壤团聚体的性质密切相关[7]。研究团聚体内重金属的分布可以揭示改良剂降低重金属有效性的机制。Wolfgang等[8]在研究中发现了土壤重金属Cd主要富集在0.02—0.25 mm的团聚体粒级中。土壤团聚体作为土壤结构的基本组成单位,对探究土壤重金属的分布规律和其潜在影响机制有着非常重要的作用。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 材料
川芎种子(Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.)由四川省成都市彭州区某川芎种植基地提供。初始土壤的物理化学性质如下:pH为(5.63 ± 0.21);有机质为(28.93 ± 1.78) g·kg−1;总磷为(0.67 ± 0.05) g·kg−1;全氮为(1.22 ± 0.09) g·kg−1;孔隙度为(43.91%± 2.46%);总Cd为(1.52 ± 0.12) mg·kg−1。试验小区面积为46.62 m2。
1.2 试验设计
经过改良剂初筛试验后本研究选取两种改良剂用于田间试验。改良剂1由轻质碳酸钙(CaCO3,97%)、钙基膨润土(蒙脱石,95%)、磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4, 95%)、生物炭、硅酸钠(Na2SiO3, 99%)、天然凹凸棒等质量混合而成;改良剂2由重质碳酸钙(CaCO3, 97%)、钙基膨润土、磷酸二氢钾、生物炭、硅酸钠、天然凹凸棒等质量混合而成。所有材料按照等质量比混合,过100目筛后混合制得土壤改良剂。田间试验共设7个处理,分别为不施加改良剂(对照)、改良剂1低浓度(0.5 t·hm−2)(T1-低)、改良剂1中浓度(1.5 t·hm−2)(T1-中)、改良剂1高浓度(5.0 t·hm−2)(T1-高)、改良剂2低浓度(0.5 t·hm−2)(T2-低)、改良剂2中浓度(1.5 t·hm−2)(T2-中)、改良剂2高浓度(5.0 t·hm−2)(T2-高)。对于川芎进行3次追肥,有机粪肥为集约化养殖场的鸡粪,含水量为76%。鸡粪的总Cd含量为(0.43 ± 0.04) mg·kg−1。
1.3 样品采集与分析
1.3.1 样品采集
在川芎收获阶段,采用五点采样法,采集完整的植株样品和耕层(0—20 cm)土壤样品100 g。将川芎植物样品在105 ℃干燥30 min[9],切片、压碎、0.5 mm筛分、密封保存待测。土壤样品要筛分以保存。
1.3.2 分析方法
植物样品:测定干燥后川芎的生物量。根据药典方法,将Cd的根、茎部分风干,经100目尼龙筛网制成药粉,在烧杯中称取1 g样品。然后加入10 mL硝酸-高氯酸(4:1)混合溶液,混合浸泡过夜。次日,将溶液在加热板上溶解,微沸至无色透明或微黄色。冷却后,将溶液转移到10 mL的量瓶中,用2%的硝酸溶液清洗容器,恒容振荡。然后用火焰原子吸收光谱仪测定镉的含量。
土壤样品:使用Tessier萃取法测定土壤中有效态Cd,采用火焰原子吸收光谱仪测定土壤中Cd含量。采用pHs-3C(水土比2.5∶1)测定土壤pH值;采用重铬酸钾法测定土壤有机质含量;土壤孔隙度根据土壤容重(环刀法)和比重(比重瓶法)计算得到;土壤团聚体根据萨维诺夫法分级[10]。
1.4 数据分析
数据分析在经过SPSS25.0和Excel2019分析之后,使用Origin 2018进行做图,并且使用Duncan新复极差法进行处理间的差异显著性。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 改良剂对土壤化学性质的影响
如表1所示(不同小写字母表示同列各处理间差异显著,P < 0.05),各处理的土壤pH、土壤有机质和速效磷均显著提升(P < 0.05),土壤有效态Cd得到显著降低。改良剂1处理下的土壤为弱酸性,与对照组相比,pH提高了0.32—0.59个单位。改良剂2处理下的土壤pH提升了0.38—0.80个单位。土壤有机质含量在施加改良剂之后增加了11.30%—26.29%。改良剂的添加可以提升土壤速效磷的含量,其中T2-高处理下速效磷浓度的提升最大(99.95%),较对照处理差异显著(P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,施加改良剂后土壤有效态Cd含量显著降低了9.52%—51.43%(P < 0.05)。不同施用量对土壤有效态Cd有显著影响。从低施用量到高施用量,改良剂2施用量的增加显著提升了Cd的固定化效率。T2-中和T2-高处理效果最好,均降低了51.43%。
表 1 改良剂对土壤化学性质的影响Table 1. Effects of amendments on soil chemical properties处理Treatment pH 有机质/(g·kg−1)Organic matter 速效磷/(mg·kg−1)Available phosphorus 有效态Cd/(mg·kg−1)Available cadmium 对 照 5.83±0.25 c 31.87±2.82 d 21.42±1.15 f 0.525±0.02 a T1-低 6.17±0.23 bc 35.47±2.39 c 34.34±0.95 e 0.475±0.02 b T1-中 6.15±0.23 bc 36.39±2.06 bc 36.68±0.98 c 0.375±0.02 c T1-高 6.42±0.35 ab 37.22±2.46 abc 38.24±0.74 c 0.300±0.03 e T2-低 6.61±0.09 a 36.43±1.07 bc 36.52±0.26 d 0.375±0.38 c T2-中 6.21±0.18 abc 39.45±1.20 ab 41.01±0.52 b 0.255±0.01 d T2-高 6.63±0.06 a 40.25±0.73 a 42.83±0.62 a 0.255±0.26 d 土壤重金属的是否有效,在一定范围内与其pH值有一定关系。二者呈现负相关关系[11-12]。而在本次实验中,土壤pH的增加与两种改良剂中含有碱性物质的生物炭、方解石等有关系。并且生物炭对于提升土壤中钾离子和钠离子等等有很好的效果,与此同时可以减少土壤中的氢离子和金属铝离子,因此pH提升[13]。而在土壤的pH增加之后,土壤胶体的负电荷量提升,镉离子电吸附能力增加[14]。土壤中镉离子被两种改良剂中的生物炭和钙基膨润土而淹留。而土壤中的金属有效性得到减少的原因在于含有官能团羟基的醇类和酚类化合物的形成,金属离子有了更多的吸附点位[15]。
在川芎收获期,不同改良剂处理下的有效态Cd百分比含量均减少(图1),减少量在5.89%—18.76 %之间,其中T1-高处理效果最显著;不同处理对碳酸盐结合态Cd有着不同程度的提升,增加率为1.28%—6.56%,最为显著的为T2-高处理;铁锰氧化态Cd百分比含量均有所减少,其中减少最多的是T1-低处理,减少量为8.84%;改良剂对有机态Cd的影响是不同的,T1-中处理下的有机态Cd增加,增加量为0.53%,而其余处理均减少了其含量;残余态Cd的百分比含量变化较大,对比对照处理,增加量在9.4%—28.05 %之间,其中,T1-高处理增加最多。总的来说,改良剂使有效态Cd向残余态Cd转变,T1-低处理下的Cd总量未发生变化,依旧为1.414 mg·kg−1 ,而另两种梯度浓度总Cd含量均提升,T1-高处理下提升最高,为15.60%,而T2-中和T2-高处理的Cd总量均减少了14.18%,T2-中处理的总Cd含量提升了7.80%。
不同浓度改良剂的施加可以促进土壤Cd从有效态向其余形态的转变,这可以降低重金属生物有效性,从而使Cd的生物毒性降低。但无论是各种形态的Cd含量还是不同形态Cd的总和,一直在发生着改变,这是因为土壤重金属形态会随着土壤环境因子的改变而改变,它是处于一种动态的平衡[16]。
2.2 改良剂对土壤物理性质的影响
改良剂的施加降低了土壤容重。由表2可知,不同改良剂的施加降低了土壤容重和比重,增加了土壤孔隙度。对比对照处理,改良剂1处理组降低了土壤容重,土壤容重与改良剂浓度呈负相关关系,对容重的减少量为6.38%—10.64%,不同浓度处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);改良剂2处理组按照对土壤容重的减少效果为高>低>中浓度,减少量在10.64%—14.89%;对比对照处理,土壤比重的减少量为4.63%—10.42%,T2-高处理减少最多,除了T1-中和T2-高处理外,改良剂的处理效果差异不显著(P < 0.05);从测定结果可以看出,相较对照处理,不同处理中土壤孔隙度增加最多的是T2-高处理,增加了9.05%,所有处理差异均显著(P < 0.05)。
表 2 改良剂对土壤结构的影响Table 2. Effects of amendments on soil structure处理Treatment 容重/(g·cm−3)Bulk Density 比重/(g·cm−3)Proportion 孔隙率/%Porosity 对 照 1.41±0.15 a 2.59±0.25 a 44.10±1.77 c T1-低 1.32±0.11 b 2.46±0.13 ab 46.47±1.60 b T1-中 1.27±0.10 bc 2.42±0.10 b 47.46±1.33 ab T1-高 1.26±0.08 bc 2.35±0.13 bc 46.19±1.26 b T2-低 1.23±0.11 c 2.36±0.16 bc 47.90±2.03 ab T2-中 1.26±0.12 bc 2.33±0.10 c 45.79±4.57 b T2-高 1.20±0.14 c 2.32±0.13 c 48.09±4.68 a 土壤容重代表了土壤的结构和有机质含量等状况,土壤容重越小,土壤越松软,透气性越好。土壤比重受到土壤固相组成物质的种类和相对含量的影响[17]。土壤比重的结果一定程度上可以反映土壤的矿物组成和有机质含量,有机质含量越高,土壤比重越低。土壤孔隙度是衡量土壤孔性的重要指标,与土壤容重和比重联系密切[18]。本试验中,改良剂的施加改善了土壤物理结构,这有利于川芎的生长。改良剂2对土壤结构的改善整体效果略微优于改良剂1。土壤结构是土壤中不同大小、形态和性质的土壤团聚体的总和。土壤结构通过影响土壤水分、通风、温度和机械阻力间接影响作物生长[19]。越坚硬的土壤,其孔隙度越低,水力传导系数越低,干燥时强度越高,这导致渗透减少,植物出苗和根系生长受到抑制[20]。
改良剂的施加可以促进微团聚体向粗大团聚体和细大团聚体的转变。本试验将土壤团聚体按粒径分为了3种,分别为粗大团聚体(>2000 μm)和细大团聚体(250—2000 μm)和微团聚体(<250 μm)[21]。如图2a所示,51.38%的土壤为粗大团聚体,在施入改良剂后,相较对照组而言,粗大团聚体增加,增幅为1.30%—6.89%;在细大团聚体中,除T1-低和T2-中处理外,其余处理均增加了细大团聚体的含量,增加了0.86%—4.52%;不同改良剂处理均减少了微团聚体的占比,减少量在2.13%—8.44%之间。如图2b所示,在未经处理的土壤中,1.37%的土壤主要为粗大团聚体,34.76%的土壤主要为细大团聚体,在施入改良剂后,粗大团聚体和细大团聚体含量增加显著,增幅分别为为1.31%—6.02%和4%—11.36%。对比对照处理,改良剂的施加减少了微团聚体的含量,减少量为5.31%—19.38%。不同改良剂的施加增加了粗大和细大团聚体的含量,并且查阅相关文文献,总结了土壤团聚体当中团聚性增强的原因跟以下因素有关:(1)添加改良剂的添加使得微团聚体结合成较大粒径团聚体的粘合剂,改良剂中带负电荷的微生物和官能团可以通过静电相互作用吸附土壤中的黏土和矿物质,形成稳定的团聚体[22-23]。(2)两种改良剂中的硅酸钠中的钠离子作为可变电荷的土壤胶体加速了土壤团聚体的胶结[24]。
水稳性团聚体的分形维数(D)的值通常可以用来表征土壤的结构稳定性,且分形维数的越低,土壤团聚体的结构越稳定[25-26]。由图3b可知,通过实验研究发现湿筛法下,改良剂的施加降低了分形维数的值,相比对照组而言,改良剂1和改良剂2间无显著差异性,分形维数随着改良剂浓度梯度的增加而递减。对于非水稳性团聚体来说,实验结果与水稳性团聚体相似。Stegarescu等[27]发现,当施加了外源物质(黑麦、油菜和小麦秸秆)后,对土壤团聚体稳定性产生了影响。顾欣等[28]在盆栽条件下施加了生物炭,提高了玉米土壤的GMD(几何平均直径)和MWD(平均重量直径)的值,提升了种植土壤的机械稳定性。本研究中,两种改良剂均含钙基膨润土,它能够提升土壤大粒径土壤团聚体的含量,并且钙基膨润土的施加能够提升土壤有机碳的含量,土壤有机碳与微生物的存在可能会影响到土壤团聚体的稳定性[29]。
2.3 土壤改良剂对川芎镉积累及生长的影响
由表3可知,施加改良剂可以有效降低收获期川芎根部Cd含量。不同处理的川芎根部Cd含量均减少,除T2-低和T2-高处理外,不同处理差异显著(P < 0.05),降幅在41.51%—56.13%。同时,改良剂的添加显著增加了川芎的生物量(表3),T2-低、T2-高处理效果显著,增幅分别为53.50%和52.72%。在改良剂1的施加下,浓度不断提升,植物根部Cd含量降低,而生物量增加,二者呈现负相关关系,表明了植物在根部Cd含量减少的情况能够生长更好。而在改良剂施加后,土壤的pH值提高,且有效态Cd降低,植物周边的土壤理化性质得到一定程度的改善,因此土壤中对于影响植物生长的不利因素减少,植物能够更好的生长,由此提升了川芎生物量[30]。
表 3 土壤改良剂对川芎根部Cd含量和川芎生物量的影响Table 3. Effects of soil conditioner on Cd content and biomass of Ligusticum chuanxiong hort处理Treatment 根部Cd/(mg·kg−1)Root Cd 生物量/(g·pot−1)Biomass 对 照 2.12±0.04 a 17.85±1.75 d T1-低 1.16±0.05 c 20.61±2.03 c T1-中 1.12±0.03 d 20.81±1.03 c T1-高 1.08±0.04 e 24.76±2.41 b T2-低 0.93±0.03 f 27.40±1.54 a T2-中 1.24±0.04 b 20.42±6.22 c T2-高 0.95±0.03 f 27.26±3.75 a 2.4 土壤团聚体稳定性与川芎生物量和镉积累的潜在关系
为了探究混合改良剂添加对植物生物量和根部Cd含量影响的潜在机制,利用IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0分析了土壤化学指标、分型维数与川芎生物量和镉含量之间的相关关系(表4)。结果表明,川芎生物量与pH(R=0.980,P<0.001)、有机质(R=0.930,P=0.002)、速效磷(R=0.811,P=0.027)以及硝态氮(R=0.756,P=0.050)均成显著正相关;川芎根部Cd与pH(R=−0.855,P=0.014)、有机质(R=−0.902,P=0.005)、速效磷(R=−0.970,P<0.001)、硝态氮(R=−0.755,P=0.050)均成显著负相关,和分形维数(干筛R=0.863,P=0.012、湿筛R=0.802,P=0.030)呈显著正相关关系。
表 4 川芎生物量和根部Cd与土壤指标之间的相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis of rhizoma chuanxiong biomass, root Cd and soil index川芎生物量Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort biomass 川芎根部CdLigusticum chuanxiong Hort root Cd R P R P pH 0.980** < 0.001 −0.855* 0.014 有效态Cd −0.578 0.174 0.658 0.108 有机质 0.930** 0.002 −0.902** 0.005 速效磷 0.811* 0.027 −0.970** < 0.001 硝态氮 0.756* 0.050 −0.755* 0.050 分形维数(干筛) −0.686 0.089 0.863* 0.012 分形维数(湿筛) −0.741 0.057 0.802* 0.030 土壤pH的提高降低了土壤中有效态Cd对川芎根部的迁移效果,减少了川芎根部Cd含量。而速效磷含量的提高为川芎生长提供了充足的养分,有利于川芎生物量的积累。有机质对川芎根部Cd的积累的抑制作用体现在土壤颗粒之间通过有机质的胶结等作用形成微生物的细胞壁和产生代谢产物,可以提升土壤团聚体的稳定性,并且能够吸附和沉淀土壤中的重金属,对土壤有效态Cd的积累产生消极影响[31];而团聚体稳定性显著影响了川芎根部Cd的积累,根据数据分析以及查阅相关文献,分析原因可能如下:(1)分形维数越低,土壤团聚体稳定性越高,粗大和细大团聚体含量也越高。而较大团聚体可以保留住重金属离子,使得土壤中有效态Cd向川芎根部迁移减少,从而抑制川芎根部Cd含量[32]。(2)改良剂的施加增强了土壤团聚体稳定性,而团聚体中有效态Cd对“土壤—作物”中镉的转运和分布起到了关键作用[33],因此对川芎根部Cd起抑制作用。
3. 结 论(Conclusion)
(1)施加两种改良剂显著影响了土壤的化学和物理性质,其中土壤pH、有机质、速效磷和土壤孔隙度的含量得到提升,土壤有效态Cd、土壤比重和土壤容重得到有效降低。总体而言,改良剂2对土壤有效态Cd的降低效果优于改良剂1。
(2)土壤团聚体显著影响川芎根部Cd含量。土壤中大团聚体可以保留重金属离子,使得土壤中有效态Cd向川芎根部迁移减少,从而抑制川芎根部Cd含量。T2-低以及T2-中使用下,对川芎影响最为突出,并且考虑到实际应用和成本方面因素,最终选择T2-低浓度条件(即0.5 t·hm−2)。
-
表 1 改良剂对土壤化学性质的影响
Table 1. Effects of amendments on soil chemical properties
处理Treatment pH 有机质/(g·kg−1)Organic matter 速效磷/(mg·kg−1)Available phosphorus 有效态Cd/(mg·kg−1)Available cadmium 对 照 5.83±0.25 c 31.87±2.82 d 21.42±1.15 f 0.525±0.02 a T1-低 6.17±0.23 bc 35.47±2.39 c 34.34±0.95 e 0.475±0.02 b T1-中 6.15±0.23 bc 36.39±2.06 bc 36.68±0.98 c 0.375±0.02 c T1-高 6.42±0.35 ab 37.22±2.46 abc 38.24±0.74 c 0.300±0.03 e T2-低 6.61±0.09 a 36.43±1.07 bc 36.52±0.26 d 0.375±0.38 c T2-中 6.21±0.18 abc 39.45±1.20 ab 41.01±0.52 b 0.255±0.01 d T2-高 6.63±0.06 a 40.25±0.73 a 42.83±0.62 a 0.255±0.26 d 表 2 改良剂对土壤结构的影响
Table 2. Effects of amendments on soil structure
处理Treatment 容重/(g·cm−3)Bulk Density 比重/(g·cm−3)Proportion 孔隙率/%Porosity 对 照 1.41±0.15 a 2.59±0.25 a 44.10±1.77 c T1-低 1.32±0.11 b 2.46±0.13 ab 46.47±1.60 b T1-中 1.27±0.10 bc 2.42±0.10 b 47.46±1.33 ab T1-高 1.26±0.08 bc 2.35±0.13 bc 46.19±1.26 b T2-低 1.23±0.11 c 2.36±0.16 bc 47.90±2.03 ab T2-中 1.26±0.12 bc 2.33±0.10 c 45.79±4.57 b T2-高 1.20±0.14 c 2.32±0.13 c 48.09±4.68 a 表 3 土壤改良剂对川芎根部Cd含量和川芎生物量的影响
Table 3. Effects of soil conditioner on Cd content and biomass of Ligusticum chuanxiong hort
处理Treatment 根部Cd/(mg·kg−1)Root Cd 生物量/(g·pot−1)Biomass 对 照 2.12±0.04 a 17.85±1.75 d T1-低 1.16±0.05 c 20.61±2.03 c T1-中 1.12±0.03 d 20.81±1.03 c T1-高 1.08±0.04 e 24.76±2.41 b T2-低 0.93±0.03 f 27.40±1.54 a T2-中 1.24±0.04 b 20.42±6.22 c T2-高 0.95±0.03 f 27.26±3.75 a 表 4 川芎生物量和根部Cd与土壤指标之间的相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of rhizoma chuanxiong biomass, root Cd and soil index
川芎生物量Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort biomass 川芎根部CdLigusticum chuanxiong Hort root Cd R P R P pH 0.980** < 0.001 −0.855* 0.014 有效态Cd −0.578 0.174 0.658 0.108 有机质 0.930** 0.002 −0.902** 0.005 速效磷 0.811* 0.027 −0.970** < 0.001 硝态氮 0.756* 0.050 −0.755* 0.050 分形维数(干筛) −0.686 0.089 0.863* 0.012 分形维数(湿筛) −0.741 0.057 0.802* 0.030 -
[1] 唐咏, 王萍萍, 张宁. 植物重金属毒害作用机理研究现状 [J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2006, 37(4): 551-555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2006.04.002 TANG Y, WANG P P, ZHANG N. Researches in heavy metal toxicity mechanism in plant [J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2006, 37(4): 551-555(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2006.04.002
[2] 程杰, 高压军. 镉毒害对小麦生理生态效应的研究进展 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2006, 13(6): 218-221, 227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.069 CHENG J, GAO Y J. Progress in studies on cadmium toxicity to psysiology and ecology effect of wheat [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 13(6): 218-221, 227(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2006.06.069
[3] MORENO J L, HERNÁNDEZ T, GARCIA C. Effects of a cadmium-contaminated sewage sludge compost on dynamics of organic matter and microbial activity in an arid soil [J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1999, 28(3): 230-237. doi: 10.1007/s003740050487 [4] 刘莉莉, 林岚, 殷霄, 等. 镉毒性研究进展 [J]. 中国职业医学, 2012, 39(5): 445-447. LIU L L, LIN L, YIN X, et al. Research progress on cadmium toxicity [J]. China Occupational Medicine, 2012, 39(5): 445-447(in Chinese).
[5] 黎大荣, 吴丽香, 宁晓君, 等. 不同钝化剂对土壤有效态铅和镉含量的影响 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2013, 39(3): 46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2013.03.012 LI D R, WU L X, NING X J, et al. Effects of different passivating agents on contents of available lead and cadmium in soil [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2013, 39(3): 46-49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2013.03.012
[6] 高瑞丽, 唐茂, 付庆灵, 等. 生物炭、蒙脱石及其混合添加对复合污染土壤中重金属形态的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(1): 361-367. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201606018 GAO R L, TANG M, FU Q L, et al. Fractions transformation of heavy metals in compound contaminated soil treated with biochar, montmorillonite and mixed addition [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(1): 361-367(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201606018
[7] PIRMORADIAN N, SEPASKHAH A R, HAJABBASI M A. Application of Fractal Theory to quantify Soil Aggregate Stability as influenced by Tillage Treatments [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2005, 90(2): 227-234. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2004.11.002 [8] WILCKE W, MOSBACH J, KOBŽA J, et al. Distribution of Al and heavy metals in bulk soil and aggregates at three sites contaminated by the emissions of a central Slovak Al smelter [J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 1998, 106(3/4): 389-402. doi: 10.1023/A:1005094624006 [9] 刘亚华, 徐文芬, 高杰, 等. 栽培川续断药材质量的综合考察 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(14): 7336-7338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.14.074 LIU Y H, XU W F, GAO J, et al. Comprehensive qualitative investigation on the cultivated dipsacu asperides materials [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(14): 7336-7338(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.14.074
[10] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. BAO S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2000(in Chinese).
[11] 蔡梅. 混合改良剂对土壤Cd污染的钝化修复研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. CAI M. Study on remediation of Cd contaminated soils by mixed amendments[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese).
[12] 胡文. 土壤—植物系统中重金属的生物有效性及其影响因素的研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2008. HU W. Heavy metal bio-availability and its affecting factors in soil-plant system[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2008(in Chinese).
[13] 杨惟薇, 张超兰, 曹美珠, 等. 4种生物炭对镉污染潮土钝化修复效果研究 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(1): 239-243. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2015.01.046 YANG W W, ZHANG C L, CAO M Z, et al. Immobilization and remediation of cadmium contaminated soil with four kinds of biochars [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(1): 239-243(in Chinese). doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2015.01.046
[14] 闫家普, 丁效东, 崔良, 等. 不同改良剂及其组合对土壤镉形态和理化性质的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(9): 1842-1849. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0187 YAN J P, DING X D, CUI L, et al. Effects of several modifiers and their combined application on cadmium forms and physicochemical properties of soil [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(9): 1842-1849(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0187
[15] 王英杰, 邹佳玲, 杨文弢, 等. 组配改良剂对稻田系统Pb、Cd和As生物有效性的协同调控 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(10): 4004-4010. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.10.044 WANG Y J, ZOU J L, YANG W T, et al. Synergetic control of bioavailability of Pb, Cd and as in the rice paddy system by combined amendments [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(10): 4004-4010(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.10.044
[16] 徐颖菲, 谢国雄, 章明奎. 改良剂配合水分管理减少水稻吸收土壤中镉的研究 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6): 356-360. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.06.050 XU Y F, XIE G X, ZHANG M K. Reduction of cadmium uptake of rice plant from soil by application of amendments combined with water management [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(6): 356-360(in Chinese). doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.06.050
[17] 关明, 于菲, 许连周, 等. 玉米秸秆生物炭添加对典型黑土保水性能的影响 [J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2019(10): 42-44. doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2019.10.0044 GUAN M, YU F, XU L Z, et al. Effects of biochar addition from maize straw on water-holding capacity of typical black soil [J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019(10): 42-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2019.10.0044
[18] 汪言在, 苏正安, 周明华. 北方农牧交错带表层土壤孔隙度特征及其影响因素 [J]. 草业科学, 2020, 37(7): 1249-1258. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0213 WANG Y Z, SU Z G, ZHOU M H. Characteristics and influence of topsoil porosity in the northern agro-pastoral ecotone [J]. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(7): 1249-1258(in Chinese). doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0213
[19] FIDALSKI J, BORDIN I, ALVESCS J, et al. Grazing heights, stocking rate, soil structure, and water infiltration in a crop-livestock integration [J]. Semina Ciências Agrárias, 2021, 42(1): 123-136. [20] AULER A C, ROMANIW J, SÁ J C M, et al. Improvement on soil structure and water retention after application of industrial organic waste as a crop fertilizer [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(7): 2771-2783. doi: 10.1007/s11368-020-02628-w [21] WU J T, LI H Q, LI F, et al. Distribution and fractionation of cadmium in soil aggregates affected by earthworms (Eisenia fetida) and manure compost [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2016, 16(9): 2286-2295. doi: 10.1007/s11368-016-1433-2 [22] LI S S, WANG M, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Alleviation of cadmium phytotoxicity to wheat is associated with Cd re-distribution in soil aggregates as affected by amendments [J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(31): 17426-17434. doi: 10.1039/C8RA03066A [23] RAO Z X, HUANG D Y, WU J S, et al. Distribution and availability of cadmium in profile and aggregates of a paddy soil with 30-year fertilization and its impact on Cd accumulation in rice plant [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 239: 198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.024 [24] LI Y L, DONG S F, QIAO J C, et al. Impact of nanominerals on the migration and distribution of cadmium on soil aggregates [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 262: 121355. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121355 [25] DARAPUNENI M K, IDOWU O J, SARIHAN B, et al. Growth characteristics of summer cover crop grasses and their relation to soil aggregate stability and wind erosion control in arid southwest [J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2021, 37(1): 11-23. doi: 10.13031/aea.13972 [26] NSABIMANA G, BAO Y H, HE X B, et al. Impacts of water level fluctuations on soil aggregate stability in the Three Gorges reservoir, China [J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(21): 9107. doi: 10.3390/su12219107 [27] STEGARESCU G, ESCUER-GATIUS J, SOOSAAR K, et al. Effect of crop residue decomposition on soil aggregate stability [J]. Agriculture, 2020, 10(11): 527. doi: 10.3390/agriculture10110527 [28] GUO L K, SHEN J, LI B, et al. Impacts of agricultural land use change on soil aggregate stability and physical protection of organic C [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 707: 136049. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136049 [29] 陈晓芬, 李忠佩, 刘明, 等. 不同施肥处理对红壤水稻土团聚体有机碳、氮分布和微生物生物量的影响 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(5): 950-960. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.05.010 CHEN X F, LI Z P, LIU M, et al. Effects of different fertilizations on organic carbon and nitrogen contents in water-stable aggregates and microbial biomass content in paddy soil of subtropical China [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(5): 950-960(in Chinese). doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.05.010
[30] 肖丹丹. 腐植酸对铅镉污染土壤中重金属形态及油菜抗氧化酶活性的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2017. XIAO D D. Effects of humic acid on havy metal forms and antioxidant enzymes activities in soil contaminated by lead and cadmium[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2017(in Chinese).
[31] HUANG B, YUAN Z J, LI D Q, et al. Loss characteristics of Cd in soil aggregates under simulated rainfall conditions [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 313-320. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.327 [32] LI S S, WANG M, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Use of soil amendments to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice by changing Cd distribution in soil aggregates [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(20): 20929-20938. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05431-4 [33] WANG Y L, XU Y M, LIANG X F, et al. Effects of mercapto-palygorskite on Cd distribution in soil aggregates and Cd accumulation by wheat in Cd contaminated alkaline soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 271: 129590. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129590 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: