-
重金属汞(Hg)和砷(As)是环境中典型污染物,具有持久性、累积性、生物毒性和沿食物链富集等多种特性;Hg和As可通过工业废水排放、地表径流和大气沉降等途径进入湖泊水体,造成湖泊水体污染,直接或间接危害人体健康[1-4]。南四湖属淮河流域,流域资源丰富[5],工业主要以高污染的能源企业、煤化工、造纸业、冶金业为主[6],从而导致南四湖水体受到一定程度的Hg和As的污染[7]。菹草作为南四湖重要的初级生产者之一[8],已由普通优势种演变为湖区绝对优势种[9]。由于受水体的理化性质、菹草密度等多种因素的影响,菹草对不同金属(Pb、Cd、Zn和Cu)的富集能力不同[10-11],且有研究表明菹草对Hg、As具有一定的富集作用[12]。目前对南四湖重金属的研究多集中在入湖河流和上级湖重金属元素的空间分布及赋存形态等方面,而对水生植物富集重金属的相关研究较少,因此研究南四湖菹草对重金属的富集特征对进一步揭示重金属在植物体内分布和南四湖重金属的污染防治具有重要意义。
本研究通过对南四湖菹草、上覆水和沉积物进行系统同步采样,分析菹草、上覆水和沉积物中Hg和As的含量及其空间分布特征,并计算菹草及各器官(茎、叶和果实)对Hg和As的富集系数,以探究南四湖Hg和As的分布特征以及菹草不同器官对Hg和As富集能力的差异,研究结果以期为南四湖水体重金属污染防治提供基础数据和科学依据。
-
南四湖位于山东省西南部(34°37′—35°32′N,116°34′—117°21′E),是山东省内最大的淡水湖泊[13],也是南水北调东线工程的主要调蓄水库[14]。湖区总流域面积约为1266 km2,总库容53.7×108 m3,平均水深1.46 m[15]。南四湖被湖腰处的二级坝一分为二,坝北为上级湖(南阳湖、独山湖和昭阳湖),坝南为下级湖(微山湖),上级湖入湖河流29条,出湖水经微山湖向南流经淮河,最后注入黄海[16]。南四湖湖底浅而平坦,水草茂盛,是典型的浅水草型湖泊[17]。菹草是生长于冬春季节、分布广泛的多年沉水植物,4—5月开花结果,夏季6月后逐渐衰退腐烂[9]。目前菹草已成为南四湖的优势沉水植物,占湖区面积比为24.55%,最大生物量可达792.52 g·m−2(干重)[18]。
-
于2019年4月菹草对数生长阶段的后期,在南四湖菹草生长区根据均匀性原则和可达性原则共设置49个采样点,运用GPS对采样点进行定位(图1),于每个采样点分别采集上覆水、菹草和表层沉积物样品各1个,共计147个样品。采用水草定量夹(CCYQ-2,中国科学院南京湖泊研究所专利)采集菹草样品并将其放入自封袋中;采用有机玻璃采水器在水面以下0.5 m处采集上覆水样品并置于聚乙烯瓶中;使用沉积物采样器采集表层沉积物样品置于自封袋里,现场混合均匀。密封冷藏保存并记录所有样品的编号和取样位置,然后立即运回实验室进行低温存储。
样品运回实验室后,对样品进行预处理,菹草样品先用自来水清洗3次,去除泥沙、污物,再用去离子水冲洗3次,用滤纸吸干水分,在冷冻机内冷冻干燥,将茎、叶和果实分别磨碎后存放在自封袋里;将表层沉积物样品干燥后,除去贝壳、石子、根系等杂质,磨碎后过100目筛备用。
-
上覆水样品采用氯化溴消解法,硫脲—抗坏血酸溶液还原;菹草、表层沉积物样品均采用王水(3
VHCl ∶1VHNO3 )水浴加热消解,硫脲—抗坏血酸溶液还原[12]。所有消解后的样品均采用双道原子荧光光度计(AFS-933,北京吉天)测定Hg和As含量。样品分析所用试剂均为优级纯,所用器皿均在20%的HNO3中浸泡24 h以上。另外,为保证分析的准确性,采用三平行样和加标回收法进行质控;其中,Hg和As含量的相对标准偏差均小于10%;同步分析了土壤成分分析标准物质(GSS-3)和国家标准物质灌木枝叶(GB W07603(GSV—2)),Hg和As的回收率在90%—110%之间。 -
采用生物富集系数法分析菹草(全植株)对水体中Hg和As的富集能力。生物富集系数(bioconcentration factor,BCF)是植物组织(干重)中物质的浓度(Cb)与溶解于水中的浓度(Cw)或沉积物中的浓度(Cs)之比[19-20],其公式为:BCF=Cb/Cw/s,其中,Cb为植物重金属的浓度,mg·kg−1;Cw为上覆水中重金属的浓度,mg·L−1;Cs为表层沉积物中重金属的浓度,mg·kg−1。生物富集系数越大,说明该植物对重金属的吸收富集能力越强[21]。
采用统计软件Excel 2019和SPSS 25.0处理数据,运用Origin 2021和ArcGIS 10.2完成绘图工作。
-
根据地表水功能区划,南四湖执行《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002)Ⅲ类水水质标准[22],如表1所示,上覆水Hg浓度的超标率为34.7%,其浓度均值是Ⅲ类水标准限值的11.76倍,最大值为4.91 μg·L−1,出现在20号采样点(图1),该点位于微山湖出湖口附近,靠近旅游区,垃圾排放等人类活动较为强烈可能是出现最大值的原因。所有点位As的浓度未超过标准限值。上覆水中Hg浓度是东平湖上覆水Hg浓度的1.53倍,但As的浓度仅为东平湖As浓度的0.51倍。
与南四湖底泥背景值[23]相比,表层沉积物Hg和As的平均含量均显著高于背景值(P < 0.05),分别是背景值的6.23倍和2.44倍。同时,表层沉积物中的Hg、As的平均含量低于洞庭湖[24],但高于内蒙古自治区的乌梁素海[25]。与以往南四湖的研究相比,表层沉积物中Hg含量显著高于2012年[26]的含量,As含量均显著高于 2002年[27]和 2012年[26]的含量(P<0.01)。菹草中Hg含量与东平湖[12]菹草Hg含量相比无显著差异(P>0.05),As含量显著高于东平湖[12]菹草As含量(P<0.05),是其1.43倍。且由表2可知,菹草叶中Hg的含量是茎和果实的1.22倍和1.56倍, 茎中As的含量分别是叶和果实的1.22倍和1.47倍。
-
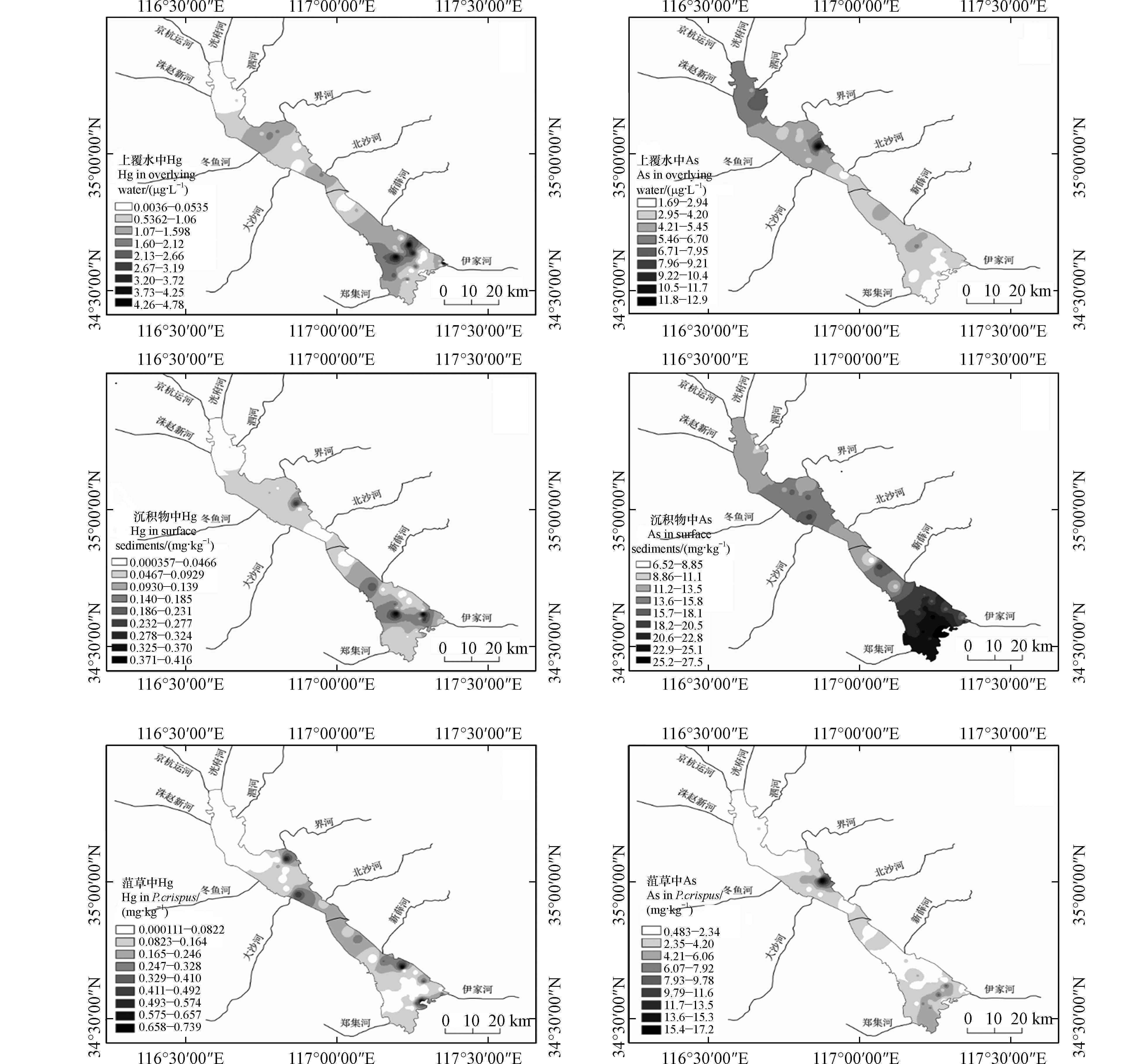
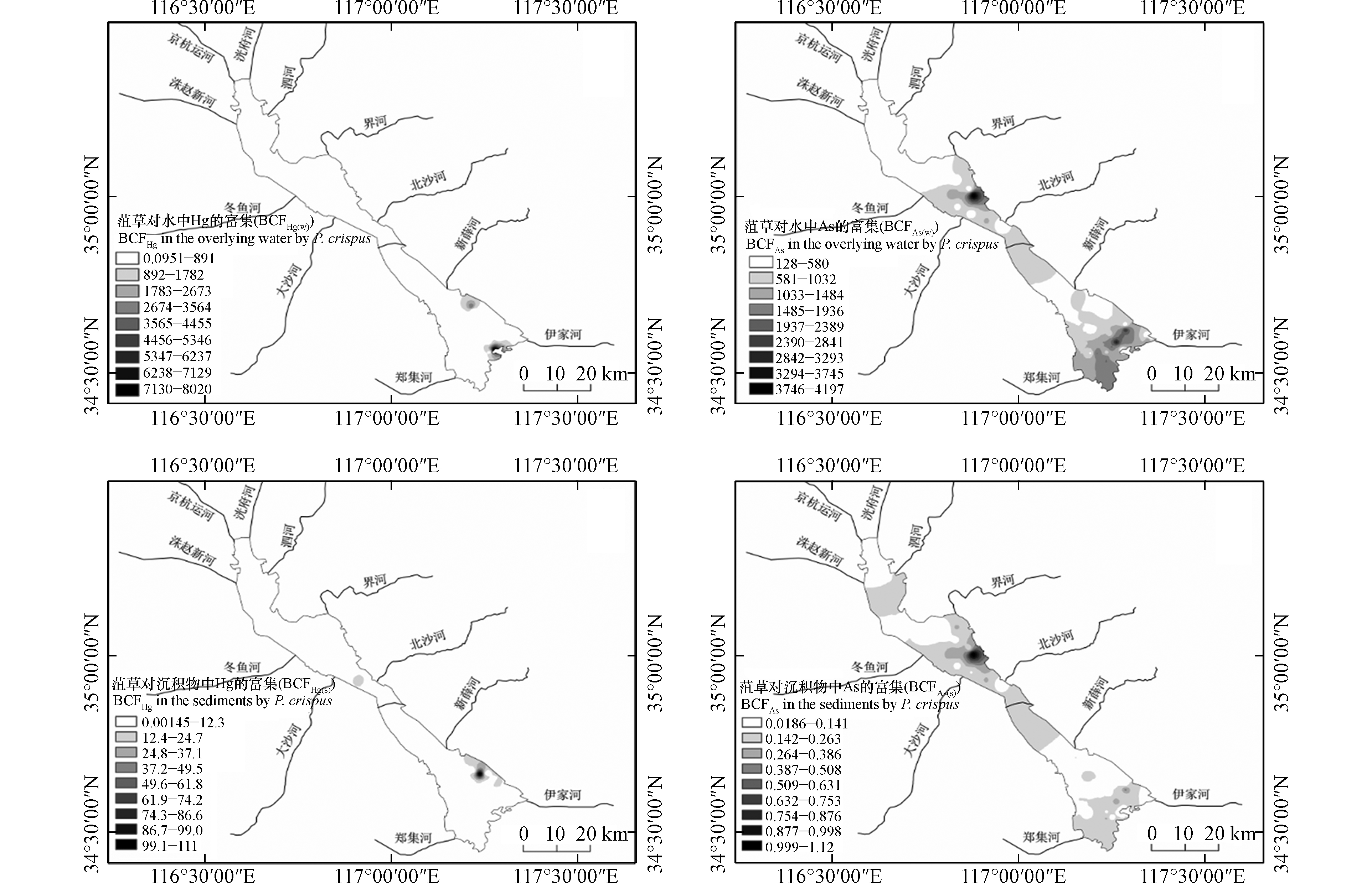
根据变异系数划分的相关标准[28],上覆水Hg和As的变异系数为106%和47%,均为高度变异(CV>36%),说明其空间分布差异很大,由图2可知,上覆水Hg浓度由上级湖向下级湖递增,在微山湖中部和东部出现3个高值区。通过分析可知,微山湖Hg浓度显著高于其他湖区的Hg浓度(P<0.05),其原因可能是微山湖地势低且处于下游,重金属随水流汇入微山湖。另外,近年来南四湖旅游业发展较快,部分旅游垃圾排放到湖中,造成了南四湖水体污染[26]。而上级湖上覆水中As浓度显著高于下级湖(P<0.01),并在独山湖东部出现高值区,其原因可能与上级湖入湖河流面源污染(生活污水、养殖废水等)的输入有关[29]。
表层沉积物Hg和As的变异系数分别为97%和29%,Hg含量为高度变异,空间分布差异大,As含量为中度变异(15%<CV<36%)。由图2可知,表层沉积物Hg含量在上级湖和下级湖均有高值区,在独山湖中部、微山湖中部和东部各形成一个高值区,独山湖出现高值区的原因可能是入湖河流经过兖州煤炭基地,煤炭中的Hg经废水、废气、粉尘等各种形式最终汇于南四湖[30]。微山湖出现高值区的原因可能与湖区旅游垃圾的排放有关,而且微山湖湖区面积大,流速小,易于颗粒的沉降和重金属的吸附[26]。微山湖表层沉积物中As含量显著高于其他湖区(P<0.01),并且在湖区西部形成高值区。如表3所示,沉积物中的As含量与上覆水中As浓度呈显著负相关关系,说明上覆水中的As沿水流方向自上级湖汇入下级湖的过程中,逐渐从上覆水中累积到沉积物。
菹草体内Hg和As的变异系数分别为131 %和97 %,均为高度变异,菹草Hg含量在独山湖、微山湖北部均出现高值区;南阳湖全湖和微山湖中部菹草Hg含量较低,且小于0.08 mg∙kg−1,由此导致菹草中Hg含量与表层沉积物中Hg含量虽然呈显著正相关关系(表3),但相关系数不高(r=0.204)。菹草中As含量在独山湖和微山湖的含量较高并在独山湖西部出现高值区,在南阳湖和微山湖北部As含量较低且小于2.35 mg·kg−1;这与表层沉积物As的空间分布具有一致性,且两者呈显著正相关。
-
如表4所示,菹草对上覆水Hg和As的平均富集系数均远大于1,且BCFAs(w)显著大于BCFHg(w)(P<0.05),说明菹草对上覆水中As的吸收和富集能力大于Hg。菹草对表层沉积物中Hg有一定的富集吸收能力;而对表层沉积物中的As的平均富集系数小于1,富集能力较弱,这与殷山红[12]研究结果一致。菹草对上覆水Hg和As的平均富集系数分别为菹草对沉积物的81倍和5329倍,表明菹草对上覆水中Hg、As的富集能力远高于对表层沉积物的富集能力。菹草的富集系数均是高度变异,说明其在南四湖的分布具有较大的空间差异性。
如图3所示,菹草各器官对水中Hg的平均富集能力顺序为叶>茎>果实,其中叶和茎的富集能力高于果实的富集能力,富集系数分别是果实的4.33倍和2.42倍,对水中As的富集能力顺序为茎>叶>果实,约是叶和果实富集系数的1.18倍和1.22倍;对沉积物中Hg富集能力的顺序为叶>茎>果实,其中叶的富集系数约是茎和果实的1.74倍和4.30倍;对表层沉积物中As富集能力的顺序为茎>叶>果实,茎的富集系数约分别是叶和果实的1.21倍和1.42倍。总体来说,菹草茎和叶的富集能力要高于果实,这可能是由于菹草茎和叶沉于水中,其表皮细胞无角质层和蜡质层的保护,使得茎和叶成为富集Hg和As的主要器官[31]。经分析可知,菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg、As的富集在各器官间并无显著差异性(P>0.05),但单个器官对上覆水和表层沉积物Hg和As的富集具有显著差异(图3),表现为茎和叶对上覆水中As的富集系数显著高于其对上覆水中Hg和表层沉积物中Hg和As的富集系数(P<0.05),果实对上覆水中As的富集系数显著高于其对表层沉积物中Hg和As的富集系数(P<0.05)。
-
由于菹草富集系数的空间变异大,因此进一步对其进行空间分布特征的分析,结果如图4所示。菹草对上覆水中Hg的富集系数在微山湖南部和北部各形成一个高值区,其他湖区富集系数没有明显的差异(P>0.05);菹草对表层沉积物中Hg富集系数在微山湖北部形成高值区,形成高值区的地方菹草Hg的含量都较高,这与上述菹草中Hg含量分布相一致。
由表5可知,菹草对上覆水中Hg富集系数与上覆水中Hg浓度呈极显著负相关关系,菹草对表层沉积物中Hg的富集系数与表层沉积物中Hg含量呈极显著负相关关系。这是由于菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg的富集系数高值区均在微山湖北部,而上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg的低值区在微山湖北部均有分布。同时说明菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg均具有较强的富集能力,从而导致上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg的含量较低。 菹草对水中As富集系数在独山湖东部和微山湖中部各形成一个高值区;菹草对表层沉积物中As的富集系数在独山湖北部形成一个高值区。菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中As的富集系数呈极显著正相关关系,且两者的高值区在空间分布上大致相同。菹草对上覆水中As的富集系数与上覆水中As浓度呈极显著负相关关系,说明菹草对上覆水中As富集能力较强,且与表层沉积物中As含量呈极显著正相关,与上述上覆水中As浓度与表层沉积物中As含量呈显著负相关关系相符合,进一步说明表层沉积物中As是由上覆水中As逐渐累积且As在菹草-上覆水-沉积物系统中具有一定的动态迁移能力[32]。总体来说,在菹草-上覆水-沉积物系统中,菹草通过生物富集作用将上覆水和表层沉积物中的Hg和As吸收转移至体内,具体表现为菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg的富集能力均较强,对上覆水中的As的富集能力大于对表层沉积物中As的富集能力,同时存在上覆水中的As随水流逐渐累积转移至表层沉积物的过程。而菹草对Hg和As富集系数的差异不仅与Hg和As在菹草-上覆水-沉积物系统迁移转化有关,上覆水的pH、水温、营养水平及其他因素也会影响菹草对重金属的富集[33]。因此,关于Hg和As在菹草-上覆水-沉积物系统的迁移转化机理需要进一步的研究和探索。
-
(1)南四湖上覆水中As浓度达到Ⅲ类水标准,Hg的超标率为34.7%;表层沉积物Hg和As含量分别是南四湖底泥背景值的6.23倍和2.44倍,菹草中Hg和As平均含量分别为0.14 mg∙kg−1和3.02 mg∙kg−1。
(2)菹草叶中Hg的平均含量分别为茎和果实的1.22倍和1.56倍,茎中As的平均含量分别为叶和果实的1.22倍和1.47倍。菹草不同器官对Hg的富集能力表现为叶>茎>果实,对As富集能力表现为茎>叶>果实。
(3)上覆水、菹草和表层沉积物中Hg和As含量的空间分布差异大,且出现局部的高值区。菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg和As富集系数均为高度变异,空间分布差异较大,且分别与上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg和As的含量呈极显著负相关关系(除菹草对沉积物As的富集系数外)。
南四湖菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中汞和砷的富集特征
Enrichment characteristics of mercury and arsenic by Potamogeton crispus in the overlying water and surface sediment of Nansi Lake
-
摘要: 为了解南四湖菹草对水体中汞(Hg)和砷(As)的富集能力,于2019年4月在南四湖采集了49个采样点的上覆水、菹草、表层沉积物样品,测定了样品中Hg和As的含量,并采用生物富集系数法(BCF)评价了菹草茎、叶和果实对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg和As的富集能力。结果表明,南四湖上覆水中Hg的超标率为34.7%,As浓度达到Ⅲ类水标准;表层沉积物Hg和As的平均含量分别为南四湖底泥背景值的6.23倍和2.44倍;菹草中Hg和As平均含量分别为0.14 mg∙kg−1和3.02 mg∙kg−1;Hg在叶中的含量分别是茎和果实的1.22倍和1.56倍;As在茎中的含量分别是叶和果实的1.22倍和1.47倍。上覆水、菹草和表层沉积物中的Hg、As含量的空间分布差异均较大,且出现局部的高值区。菹草各器官对Hg的富集能力表现为叶>茎>果实,对As富集能力为茎>叶>果实。菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg、As富集系数均为高度变异,空间分布差异较大,且与上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg、As含量具有相关关系,说明Hg和As在菹草-上覆水-沉积物系统中具有一定的动态迁移能力。Abstract: In order to understand the enrichment abilities of mercury (Hg) and arsenic (As) by Potamogeton crispus (P. crispus) in Nansi Lake, P. crispus, overlying water and surface sediment samples were synchronously collected in 49 sampling sites around the Nansi Lake in April, 2019. The total content of Hg and As in all the samples and in organs of P. crispus were analyzed, and the bioconcentration factors (BCFs) were calculated to assess the enrichment abilities of Hg and As by the whole plant and organs of P. crispus during its growing period. The results showed that Hg concentrations in 34.7% sampling sites exceeded the type Ⅲ standard value of the GB3838—2002 National Environment Quality Standards for Surface Water, while As concentrations were all lower than its corresponding type Ⅲ standard value. The average content of Hg and As in the surface sediment were 6.23 times and 2.44 times of the sediment background values of Nansi Lake, respectively. The average content of Hg and As in P. crispus were 0.14 mg∙kg−1 and 3.02 mg·kg−1, respectively. The average Hg content in leaves was severally 1.22 times and 1.56 times of those in stems and fruits, while the average As content in stems was 1.22 times and 1.47 times of those in leaves and fruits respectively. The spatial distribution of Hg and As content in overlying water, P. crispus and surface sediments differed greatly, and the high values of Hg and As occurred in different areas of the lake. The enrichment abilities of Hg in different organs of P. crispus were in the order of leaf > stem > fruit, while for As it was stem > leaf > fruit. The BCFs of Hg and As in overlying water and surface sediments by P. crispus were highly variable, and their spatial distribution was quite different. Moreover, the BCFs had some significant correlations with their corresponding content of Hg and As in overlying water and surface sediment, which suggested that Hg and As might have certain dynamic migration abilities in P. crispus, overlying water and sediment system.
-
Key words:
- mercury /
- arsenic /
- Potamogeton crispus /
- bioconcentration /
- water body /
- Nansi Lake
-
受控生态生保系统(controlled ecological life support system,CELSS)依据地球生态圈循环原理构建,在密闭空间实现食物、氧气和水等全部生保物资的持续再生供应,是目前公认的解决长期载人深空探测任务过程中人生命保障问题的有效途径[1-3]。CELSS系统中生活废水污染强度大,尿液和各类洗涤剂的浓度高,氨氮浓度高,碳氮比(C/N)低,如何高效低耗的完成生活废水的净化处理是系统水循环的重点和难点[4]。而通过微生物硝化反应将高含量的氮素转化成植物易于直接吸收利用的硝酸盐氮,是实现废水中氮素等矿物质营养元素的循环的有效途径[5-6]。微生物硝化反应是将氮素转化为硝酸盐氮的有效途径,pH会影响氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria,AOB)和亚硝酸盐氧化菌(nitrite-oxidizing bacteria,NOB)的生长和代谢,是生物硝化反应器效能的关键影响因素[7-9]。前期研究表明生物处理工艺能完成尿液废水、高强度生活废水的转化处理,并初步探究了pH对氮素转化性能的影响[10-11]。而针对CELSS系统中特征性生活废水的全程硝化工艺研究相对较少,尤其在pH对于硝化过程中碱度消耗的影响与减量化措施方面缺少系统性的研究。为了优化工艺运行条件和物质消耗,本研究在课题组前期构建BF-MBR(biofilm-membrane bioreactor)工艺的基础上,设计不同pH水平的长期硝化实验和短期硝化实验,考察好氧系统硝化性能与动力学,并评估硝化过程碱度的消耗情况,为CELSS系统中BF-MBR工艺运行参数选择提供依据,以求最大限度降低物质消耗的同时实现氮素的资源化处理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
本研究采用的前期构建的厌氧BF-MBR与好氧BF-MBR组合工艺(anBF-MBR+aBF-MBR)废水处理装置[12]。工艺流程如图1所示,主要由原水水箱、厌氧反应器、好氧反应器等组成。原水水箱、厌氧和好氧反应器(圆筒形)容积均为30 L,直径为300 mm,高450 mm,厌氧和好氧反应器中投放直径25 mm的轻质塑料环填料(有效比表面积>500 m2·m−3),采用外置式PVDF管式膜组件(尺寸6 mm×500 mm,内径30 nm)完成厌氧和好氧反应器的泥水分离,在好氧反应器内设传感器对溶解氧(dissolved oxygen,DO)和pH进行实时监测,并通过pH完成碱液投加和控制。此外,通过调节各水箱液位和出水流量调节水力停留时间(hydraulic retention time,HRT)。
实验采用1/5尿液强度的生活废水(废水中尿液的稀释倍数为5),根据前期CELSS集成实验中生活废水量和水质特征,采用新鲜尿液和各类洗涤剂配制而成[13],废水配方见表1。本研究新鲜尿液收集对象为某研究机构男性工作人员,收集时间为冬季(2021年12月—2022年1月),单次收集10 L于4 ℃低温存储后按需使用。
表 1 1/5尿液强度生活废水配方用量Table 1. The composition of domestic wastewater with 1/5 urine concentration项目 品牌 配水用量 牙膏 冷酸灵 2 cm 洗发水 飘柔长效清爽去屑 2 mL 沐浴露 舒肤佳 2 mL 洗衣液 蓝月亮深层洁净护理 2 mL 洗面奶 曼秀雷敦控油抗痘洁面乳(男士) 2 mL 洗手液 蓝月亮抑菌洗手液 3 mL 新鲜尿液 新鲜采集 4 L 自来水 约16 L 注:生活废水每次配水总量为20 L。 1.2 实验方法
1) pH对好氧硝化性能及碱液消耗量的影响。根据前期研究结果,AOB的适宜生存pH为7.0~8.5,NOB为6.0~7.5[14],本文目的是实现氮素的全程硝化,更加侧重将pH控制在NOB的适宜范围。因此,本实验设置6.0~6.1、6.4~6.5、7.1~7.2 3个pH水平,研究pH对好氧反应器的硝化性能,并考察碱度的消耗情况,为系统pH控制水平优化提供依据。
实验期间通过投加KHCO3溶液补充碱度并调节好氧反应器内pH。实验前8 d为启动期,当出水中氮素含量稳定后,开始控制单个反应器中HRT为(2.5±0.1) d,开始在3个pH水平下的阶段运行实验,实验过程维持好氧反应器中DO大于3.0 mg·L−1。为了降低pH突变对系统性能的影响,在第26~29天设置pH=6.4~6.5的过渡期,第29天开始进入pH=6.0~6.1阶段。在运行期间,根据好氧系统所消耗碱液的量和处理水量进行统计,计算出不同pH条件下单位质量氮素转换消耗碱液的质量,进而评估碱度消耗情况。具体各运行阶段及进水水质如表2所示。因新鲜尿液的收集过程未对具体人员及其饮食结构做出严格限定,因此,实际收集的尿液会存在变化,这也是各阶段水质指标有小幅波动的主要原因。
表 2 废水进水水质表Table 2. The water quality of influent wastewater阶段 时间段/d TOC/(mg·L−1) TN/(mg·L−1) NH4+-N/(mg·L−1) C/N 启动期 1~8 744±10 815±150 490±200 0.94 pH=6.4~6.5 9~16 831±15 865±50 519±300 0.96 pH=7.1~7.2 17~25 892±50 875±50 524±400 0.95 过渡期 26~28 831±15 865±50 519±300 0.96 pH=6.0~6.1 29~38 954±10 1089±50 714±200 0.88 2)不同pH水平硝化动力学研究。收集好氧反应器中活性污泥开展烧杯实验,考察pH短期效应对硝化过程的影响,并研究不同pH条件下的硝化反应动力学。具体方法为:取一定量的好氧反应器中层填料、混合液至4个烧杯中,静置沉淀排出上清液后得到泥膜混合物,加入模拟废水(以氯化铵为氮源、葡萄糖为碳源,氨氮和总有机碳(total organic carbon,TOC)质量浓度均为50 mg·L−1),调节各烧杯中的初始pH至设定范围,开始实验,实验过程中通过添加KHCO3溶液维持各烧杯的pH,同时记录碱液消耗量,各烧杯中溶解氧维持在2 mg·L−1以上,实时取样检测硝酸盐氮(NO3−-N)、亚硝酸盐氮(NO2−-N)、氨氮(NH4+-N)的质量浓度。
氨氧化过程和亚硝酸盐氧化过程的动力学参数可依据Monod方程建立的对质量浓度与时间之间的函数关系根据式(1)和式(2)进行拟合求得[15]。
−t=K1μmaxlnNt+1μmaxNt+mμmax (1) t=K2vmaxlnYt+1vmaxYt+nvmax (2) 式中:N、Y分别为底物氨氮和产物硝酸盐氮的质量浓度,mg·L−1;μmax、vmax分别为最大氨氧化速率和最大亚硝酸盐氧化速率,mg·(L·d)−1;K1、K2分别为氨氧化反应和亚硝酸盐氧化反应过程中半饱和常数,mg·L−1;m、n为常数。
单位污泥质量浓度单位时间内最大比氨氧化速率U1、单位氨氧化菌质量浓度单位时间内最大氨氧化速率U2、以及氨氧化菌最大比增长速率Umax动力学参数根据式(3)、式(4)和式(5)计算,同理可得出单位污泥质量浓度单位时间内最大比亚硝酸盐氧化速率V1、单位亚硝酸盐氧化菌质量浓度单位时间内亚硝酸盐氧化速率V2和亚硝酸盐氧化菌最大比增长速率Vmax。
U1=μmaxC1 (3) U2=μmaxC2 (4) Umax=μmaxC2Y (5) 式中:U1为单位污泥质量浓度单位时间内最大比氨氧化速率,g·(g·d)−1; U2为单位氨氧化菌质量浓度单位时间内最大氨氧化速率,g·(g·d)−1;Umax为氨氧化菌最大比增长速率,g·(g·d)−1;C1为体系中污泥质量浓度,2 000 mg·L−1,C2为AOB和NOB的质量浓度,分别为24 mg·L−1和14 mg·L−1;Y为产率系数,取0.1。
1.3 测试指标及方法
好氧反应器中pH和DO均采用工业级传感电极监测;TOC通过燃烧氧化非分散红外吸收法进行分析(SHIMADZU TOC-VCPH);氨氮(NH4+-N)含量通过阳离子色谱仪(Thermo Fishe Aquion,Dionox IonPac-CS12A阳离子色谱柱)分析;亚硝酸盐氮(NO2−-N)和硝酸盐氮(NO3−-N)含量通过阴离子色谱仪(DIONEX ICS-90,IonPac-AS14阴离子色谱柱)分析;氢氧根(OH−)、碳酸根(CO32-)和碳酸氢根(HCO3−)含量采用电位滴定法检测分析。总无机氮(total inorganic nitrogen,TIN)含量为氨氮、亚硝酸盐氮和硝酸盐氮含量之和;全程硝化率为好氧出水中硝态氮占总无机氮的百分比;硝化率为好氧出水中硝态氮和亚硝态氮之和占总无机氮的百分比;游离氨(free ammonia,FA)和游离亚硝酸(free nitrous acid,FNA)质量浓度参照DOWNING等研究给出的计算公式[16]。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 pH对高强度生活废水好氧硝化性能的影响
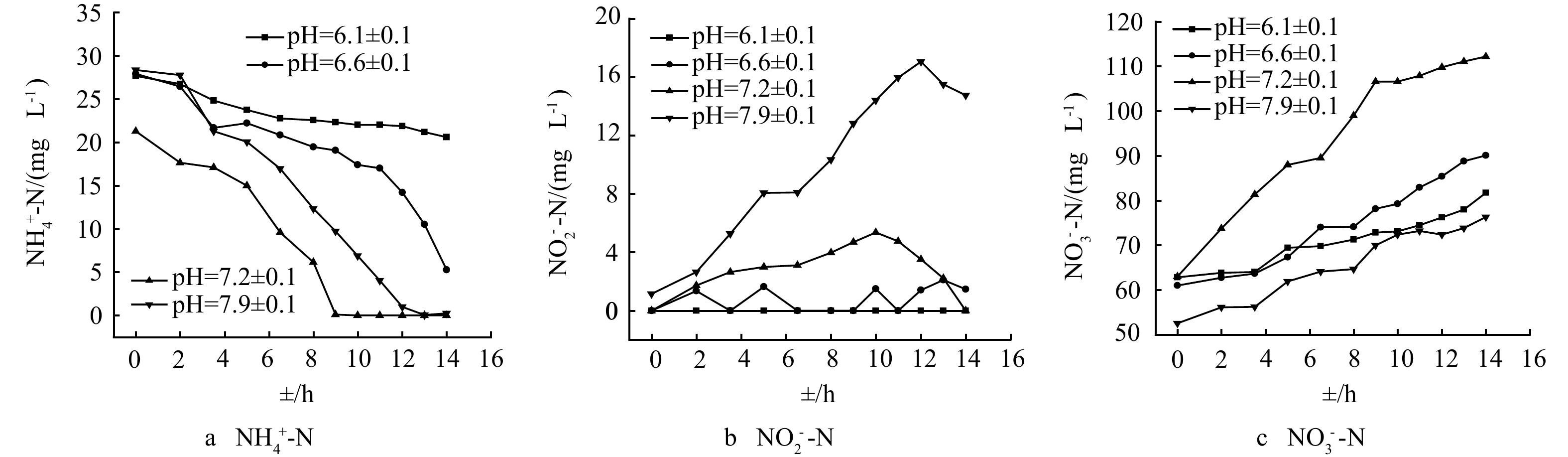
图2反应了不同pH下好氧反应器氮素和TOC的转化情况。如图2(a)和图2(b)所示,好氧系统pH发生变化时,其出水中NO2−-N、NH4+-N质量浓度以及硝化率会出现先升后降而后趋于稳定的变化趋势,且变化幅度随pH的增加而增大。在pH=6.4~6.5的阶段,稳定时平均全程硝化率和硝化率分别为97.8%和100%。当pH=7.1~7.2时,前期NO2−-N迅速上升,全程硝化率最低降至60.5%,说明此时好氧系统中NOB活性受到抑制,这与杨宏等[17]的研究结果相似。经过约5 d后,NO2−-N氧化性能得以恢复,平均全程硝化率上升至93.9%。pH调至6.0~6.1时,出水NH4+-N有轻微波动而后趋于稳定,稳定后出水NH4+-N低于5 mg·L−1,NO2−-N基本为0,该阶段的全程硝化率最高达到99.3%。程振敏等[10]通过废水处理再利用系统(wastewater treatment and reuse system, WTRS)处理1/10尿液质量浓度的模拟CELSS系统生活废水,结果表明,pH维持在6.5~7.0时,出水NH4+-N质量浓度低于20 mg·L−1,NO2−-N低于2 mg·L−1,能够实现有机化合物的矿化和氮素的转化,与本实验结果近似。
图2(c)为不同pH下好氧出水中TOC变化情况。各阶段出水平均TOC质量浓度均低于20 mg·L−1,TOC去除率均达到97%以上,说明pH对好氧系统TOC的去除率无明显影响。这点与NIU等[18]研究不同pH下好氧颗粒污泥处理高盐废水的性能时所得结果一致。
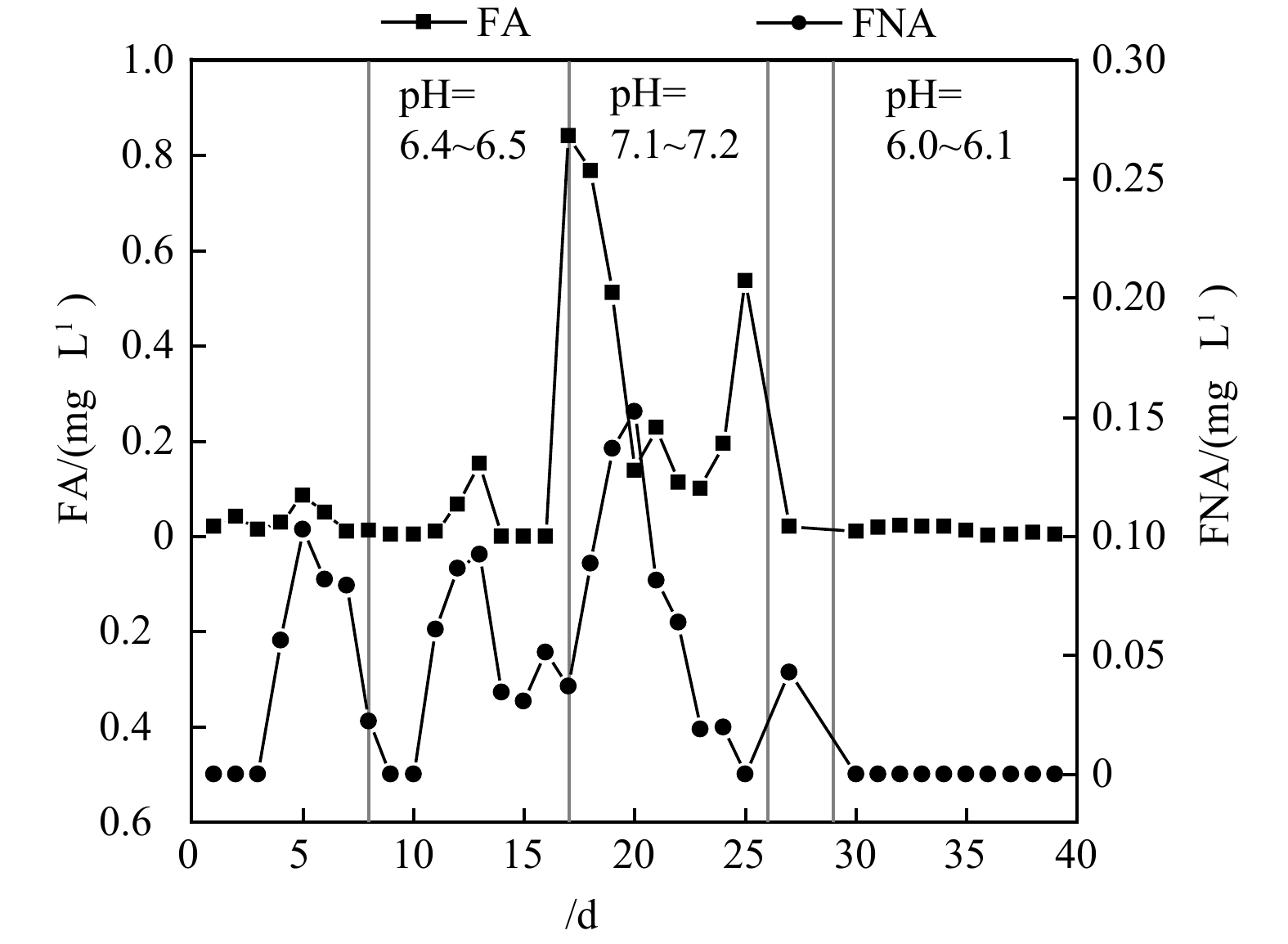
FA和FNA质量浓度与系统硝化性能密切相关,质量浓度到达一定水平时会抑制AOB和NOB的活性,且对这两类细菌的抑制程度不同[19]。ANTHONISEN等[20]研究表明发现,FA对NOB的抑制质量浓度为0.1~1.0 mg·L−1,对AOB的抑制质量浓度为10~150 mg·L−1。FNA对NOB的抑制质量浓度为0.011~0.07 mg·L−1,对AOB的抑制质量浓度为0.42~1.72 mg·L−1[21]。通过计算本文好氧反应器中的FA和FNA质量浓度,得出不同pH下好氧系统中FA、FNA质量浓度变化,如图3所示。
如图3所示,在pH=6.4~6.5阶段中期以及pH=7.1~7.2阶段前期,好氧系统中FA的质量浓度均短暂上升至0.110 mg·L−1,导致系统中NOB活性受到抑制,从而出现亚硝酸盐的短暂上升,但FNA的质量浓度并未达到形成抑制的水平。CIUDAD等[22]的研究也表明,pH的升高使FA质量浓度上升,进而抑制NOB活性,使亚硝酸盐积累。当pH下调至6.0~6.1时,好氧系统中FA和FNA质量浓度均很低,好氧系统硝化性能恢复良好,说明本实验水平的FA对NOB的抑制作用是可逆的。FAN等[8]开展的FA对NOB的抑制作用研究结果也表明,NOB能够适应FA的抑制,能在36.06~50.66 mg·L−1的高质量浓度条件下保持活性。
2.2 不同pH水平的硝化动力学
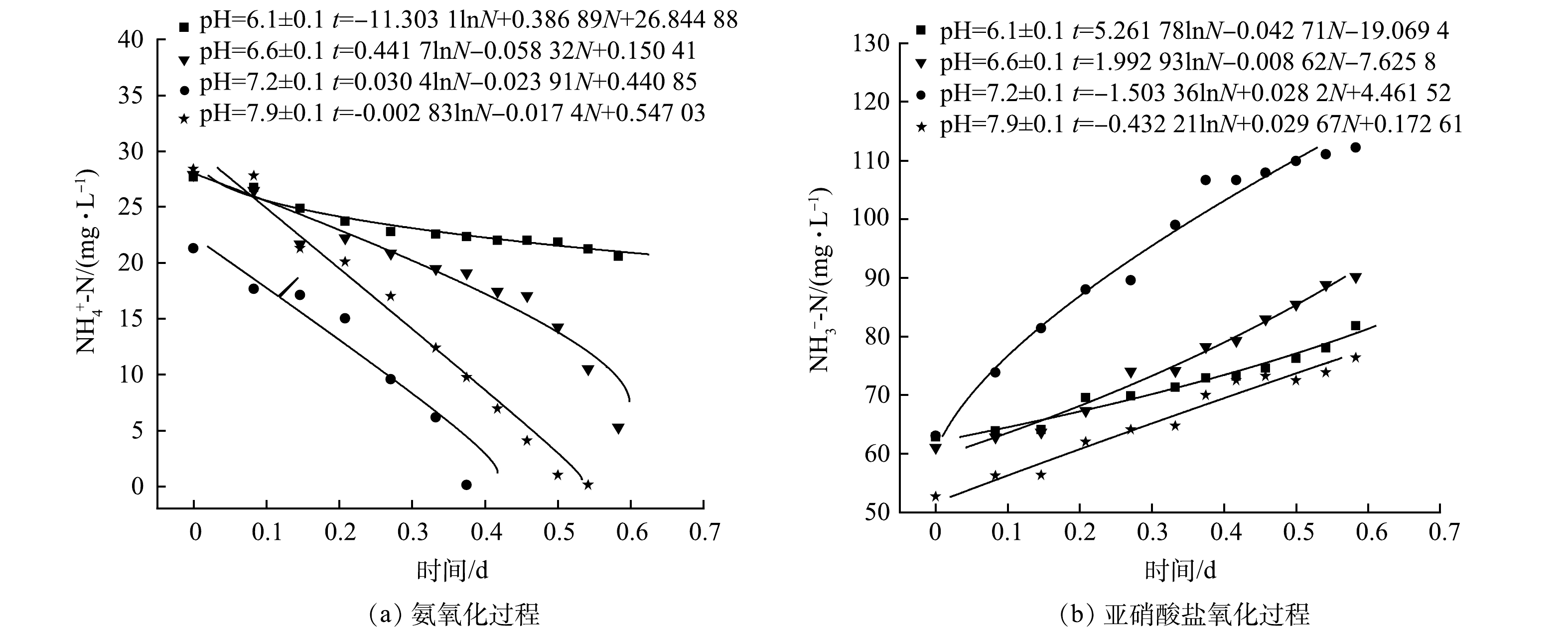
通过烧杯实验考察了不同pH条件下好氧反应器中活性污泥的硝化动力学,各pH体系中氮素质量浓度的变化如图4所示。由图4(a)可以看出,在不同pH的体系中初始氨氮质量浓度均低于废水起始质量浓度50 mg·L−1,说明活性污泥对氨氮起到一定的吸附作用,导致废水中氨氮质量浓度迅速降低[23]。随着反应时间的增加,在pH为7.2±0.1体系中最先将氨氮消耗完,其次为pH=7.9±0.1体系,而在2个酸性体系中氨转换速率最慢,初步说明碱性环境有利于氨氧化反应。这与WANG等[24]的研究结果相似,其氨化率在pH=7.5时达到最大。由图4(b)可知,碱性越强越易形成亚硝酸盐的积累,而所积累的亚硝酸盐在后期均会下降。ALBINA等[25]的研究中也得到了相似的变化趋势。其中pH=7.2±0.1的体系可在短时间内完成NO2−-N的氧化,这与图2(a)所示的母反应器中氮素变化趋势一致。由图4(c)可初步判断,pH=7.2±0.1体系的NO3−-N生成速率最快。由此说明NOB在弱碱性条件下活性较强。张昕等[26]的研究结果也表明,当pH=7.0时NOB的活性最高。
在生物硝化过程中,氨氧化速率与氨氮质量浓度的关系以及亚硝酸盐氧化速率与硝酸盐氮质量浓度的关系可用Monod方程来描述[27],利用式(1)、式(2)进行拟合,所得拟合结果如图5所示。根据式(3)、式(4)和式(5)计算不同pH下氨氧化和亚硝酸盐氧化过程的动力学参数,结果见表3和表4。由拟合结果可知,各pH体系中函数拟合度均可达0.96以上,说明Monod动力学方程能很好地描述本文好氧反应器中活性污泥的硝化过程。对氨氧化过程的计算结果表明,氨氧化速率随着pH的升高而增加,在碱性条件下各动力学参数值远大于酸性条件,表明碱性环境有利于提高AOB的活性并促进氨氧化过程。WANG等[28]的研究结果也得到了同样的趋势。由表4可知,NOB活性在pH为6.6±0.1时达到最高,此时NOB的最大比增长速率为0.829 d−1,最有利于实现全程硝化,该值与遇光禄等的研究结果相近[29]。
表 3 不同pH体系中氨氧化过程中动力学参数值Table 3. Kinetic parameter values of ammonia oxidation process in different pHspH 拟合度R12 μmax/(mg·(L·d)−1) K1/(mg·L−1) U1/(g·(g·d)−1) U2/(g·(g·d)−1) Umax/d−1 6.1±0.1 0.965 2.58 29.22 0.0013 0.108 0.011 6.6±0.1 0.982 17.15 7.57 0.0086 0.714 0.071 7.2±0.1 0.968 41.82 1.27 0.0209 1.743 0.174 7.9±0.1 0.966 57.47 0.16 0.0287 2.395 0.239 表 4 不同pH体系中亚硝酸盐氧化过程中动力学参数值Table 4. Kinetic parameter values of nitrite oxidation process in different pHspH 拟合度R22 vmax/(mg·(L·d)−1) K2/(mg·L−1) V1/(g·(g·d)−1) V2/(g·(g·d)−1) Vmax/d−1 6.1±0.1 0.966 23.41 123.20 0.0117 1.672 0.167 6.6±0.1 0.958 116.01 231.20 0.0580 8.286 0.829 7.2±0.1 0.962 35.46 53.31 0.0177 2.533 0.253 7.9±0.1 0.982 33.70 14.57 0.0169 2.407 0.241 由此可见,本文好氧反应器中获得的AOB适宜pH为7.8~8.0,NOB最适宜pH为6.4~6.7;当系统要实现氮素的全程硝化过程,避免亚硝的积累,较优的pH条件为6.6±0.1;当系统要通过短程硝化反硝化完成脱氮,则较优的pH条件为7.9±0.1。
2.3 碱度消耗与减量化分析
1)好氧反应器碱液消耗量。实验过程中首先采用KHCO3调节好氧反应器中的碱度,其理论耗碱量为14.29 g·g−1,碱度消耗为7.14 g·g−1。好氧反应器中KHCO3消耗量统计如表5所示。随着好氧反应器中pH的增大,单位质量氮素转换所消耗KHCO3的量也增加。pH为7.1~7.2时耗碱量最高,但仍远低于理论值,可能的原因为厌氧出水补充了好氧硝化所需部分碱度,同时也为好氧系统提供了良好的缓冲能力。经测试,厌氧出水pH均在9.05±0.96,出水中碳酸根为2.64 mol·L−1,碳酸氢根为43.92 mol·L−1。PAEPE等[30]通过微生物电解池-膜曝气生物膜反应器(microbial electrolysis cell-membrane-aerated biofilm reactor,MEC-MABR)处理源分离尿液的研究中也证实了这点。因在pH为6.0~6.1和6.4~6.5的条件下的碱液消耗量差别较小,又考虑到pH为6.4~6.5时更有利于硝化细菌生长和活性表达,因此,工艺运行较优pH应为6.4~6.5。此外,对好氧出水中的氢氧根、碳酸根和碳酸氢根进行检测,结果表明,好氧出水中含有6.24 mol·L−1碳酸氢根,说明好氧系统处理后的出水仍具备一定的缓冲能力。
表 5 好氧反应器中不同pH下的耗碱量Table 5. Alkali consumption in aBF-MBR at different pHspH KHCO3消耗量/(g·g−1) 当量碱度消耗(以CaCO3计)/(g·g−1) 6.4~6.5 5.65 2.82 7.1~7.2 7.44 3.72 6.0~6.1 5.59 2.80 2)短期效应实验碱液消耗量。在短期硝化实验中,同样对各pH体系中单位质量氮素转换所消耗的KHCO3的质量进行了统计。如表6所示,碱度的消耗随pH的增大而增大,且pH为7.9±0.1时的耗碱量超过了理论值。在pH为6.1±0.1、6.6±0.1的体系中耗碱量均较低且较为接近,这与好氧反应器实验结果一致。与好氧反应器长期运行KHCO3消耗情况比较可知,在不同pH体系中单位氮素转换所消耗KHCO3的量约为好氧反应器的2倍,进一步表明厌氧系统为后续的好氧系统提供了一定的碱度,节省了工艺运行物料的损耗。
表 6 短期效应实验中不同pH体系的耗碱量Table 6. Alkali consumption in short-term effect test at different pHspH KHCO3消耗量/(g·g−1) 当量碱度消耗(以CaCO3计)/(g·g−1) 6.1±0.1 10.58 5.29 6.6±0.1 11.46 5.73 7.2±0.1 14.23 7.12 7.9±0.1 22.78 11.39 3)不同类型碱液消耗情况。为进一步减少物料的损耗,在pH为6.4~6.5的条件下,分别采用KHCO3和KOH作为碱液,对比考察碱液投加量和好氧反应器的运行情况。根据统计结果可知,KHCO3作为碱液时的消耗量为7.02 g·g−1,当量碱度消耗(以CaCO3计)为3.51 g·g−1;KOH作为碱液时的消耗量为3.74 g·g−1,当量碱度消耗为3.34 g·g−1,KOH作为碱液时的消耗量远低于KHCO3。此外,在系统稳定运行期间,以KHCO3为碱液时好氧系统的硝化率为91.2%,以KOH为碱液时硝化率略有提升至94.6%,说明使用KOH作为碱液时不仅能够减少质量消耗,还能维持良好的硝化性能。
3. 结论
1)好氧生物反应系统能适应pH=6.0~7.2的变化,弱酸性条件下有利于实现氮素的全程硝化;系统中短时间内出现的FA抑制是可逆的,不会影响系统中NOB的活性。
2)从硝化动力学结果来看,pH=7.8~8.0时,系统中AOB活性最强,有利于实现短程硝化。pH=6.4~6.7时,NOB活性最强,有利于实现全程硝化。
3)氮素硝化过程所消耗碱液量随pH的上升而增加,综合考虑全程硝化性能和碱液减量化,好氧系统最佳pH为6.4~6.5,选用KOH补充硝化过程所需碱度。
-
表 1 南四湖上覆水、表层沉积物和菹草Hg、As含量水平
Table 1. Concentrations of Hg and As in overlying water、surface sediments and P. crispus of Nansi Lake
参数Parameters 上覆水Overlying water 表层沉积物Surface sediments 菹草(干重)P.crispus (dry weight) Hg/(μɡ∙L−1) As/(μɡ∙L−1) Hg/(mg∙L−1) As/(mg∙L−1) Hg/(mg∙L−1) As/(mg∙L−1) 平均值 Average 1.18 4.03 0.094 18.3 0.142 3.02 最小值 Minimum ND 1.69 ND 6.21 ND 0.31 最大值 Maximum 4.91 13.1 0.42 27.6 0.742 17.3 S.D. 1.25 1.9 0.091 5.42 0.187 2.94 CV/% 106 47 97 30 131 97 偏度系数 Coefficient of Skewness 1.66 2.59 2.15 −0.153 1.74 2.85 峰度系数 Coefficient of Kurtosis 2.57 9.87 5.06 −0.865 2.55 11.0 中国地表水Ⅲ类水质标准值[22]The type Ⅲ standard values of Surface Water[22] 0.1 50 — — — — 南四湖底泥背景值[23]The sediment background values of Nansi Lake[23] — — 0.015 7.5 — — 洞庭湖[24] Dongting Lake[24] — — 0.155 21.4 — — 乌梁素海[25] Wuliangsuhai Lake[25] — — 0.036 7.48 — — 南四湖[26]Nansi Lake[26] — — 0.048 14.1 — — 南四湖[27]Nansi Lake[27] — — 0.092 12.2 — — 东平湖[12] Dongping Lake[12] 0.769 7.86 0.072 17.1 0.169 2.11 注:“ND”代表低于检出限,下同; “—”表示无数据. Notes: “ND” means not detected, the same below; “—” means no data available. 表 2 Hg、As在茎、叶、果实中的含量水平
Table 2. Concentrations level of Hg and As in stem, leaf and fruit
参数 Parameters 茎 Stem 叶 Leaf 果实 Fruit Hg As Hg As Hg As 平均值 /(mg∙kg−1) 0.11 3.51 0.14 2.88 0.09 2.38 最小值 /(mg∙kg−1) ND 0.10 ND 0.03 ND 0.05 最大值/(mg∙kg−1) 0.70 30.91 0.74 13.65 0.46 12.26 S.D. 0.17 5.01 0.20 2.68 0.15 3.28 CV/% 144 142 144 92 169 137 偏度系数 Coefficient of Skewness 2.03 4.61 1.41 2.44 1.74 2.84 峰度系数 Coefficient of Kurtosis 4.17 24.2 0.842 6.33 2.13 8.67 表 3 上覆水、表层沉积物和菹草中 Hg 和 As含量的相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficients of concentrations of Hg and As in overlying water, surface sediments and P. crispus
参数 Parameters 上覆水 Overlying water 表层沉积物 Surface sediments 菹草 P. crispus Hg As Hg As Hg As/Overlying water −0.048 Hg/surface sediments 0.010 −0.083 As/surface sediments 0.023 −0.343 a 0.266 a Hg/P. crispus −0.163 0.108 0.204 b −0.108 As/P. crispus −0.135 −0.108 0.152 0.308 a −0.062 注:n=49;a P < 0.01;b P < 0.05. 表 4 南四湖菹草对上覆水和表层沉积物中Hg和As的富集水平
Table 4. Bioconcentration levels of Hg and As in overlying water and surface sediments by P. crispus
参数 Parameters BCFHg(w) BCFAs(w) BCFHg(s) BCFAs(s) 平均值 413 890 5.07 0.167 最小值 0 110 0 0.010 最大值 8271 4206 114 1.12 S.D. 1411 874 17.1 0.169 CV/% 342 98 337 101 表 5 菹草对上覆水、表层沉积物中 Hg 和 As 的富集系数的相关分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis of enrichment coefficients of Hg and As in overlying water and surface sediments by P. crispus
参数 Parameters Hg/(W) As/(W) Hg/(S) As/(S) BCFHg(w) BCFAs(w) BCFHg(s) BCFHg(w) −0.540 a 0.165 −0.122 −0.087 BCFAs(w) −0.062 −0.528 a 0.194 0.559 a 0.005 BCFHg(s) −0.126 0.138 −0.499 a −0.230 0.831 a −0.089 BCFAs(s) −0.281 0.024 0.047 0.063 0.264 0.708 a 0.059 注:n=49;a表示P < 0.01;W代表上覆水;S代表表层沉积物. Notes: n=49; a Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (two-tailed); W is for overlying water; S is for surface sediments. -
[1] 张家泉, 田倩, 许大毛, 等. 大冶湖表层水和沉积物中重金属污染特征与风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(6): 2355-2363. ZHANG J Q, TIAN Q, XU D M, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment from Daye Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(6): 2355-2363(in Chinese).
[2] 敖亮, 雷波, 王业春, 等. 三峡库区典型农村型消落带沉积物风险评价与重金属来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(1): 179-185. AO L, LEI B, WANG Y C, et al. Sediment risk assessment and heavy metal source analysis in typical country water level fluctuated zone (WLFZ) of the three gorges [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(1): 179-185(in Chinese).
[3] 张彦, 卢学强, 刘红磊, 等. 渤海湾天津段表层沉积物重金属分布特征及其来源解析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(6): 608-614. ZHANG Y, LU X Q, LIU H L, et al. Distribution characteristics and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Bohai Bay near Tianjin [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(6): 608-614(in Chinese).
[4] 方明, 吴友军, 刘红, 等. 长江口沉积物重金属的分布、来源及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(2): 563-569. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.02.024 FANG M, WU Y J, LIU H, et al. Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River estuary [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(2): 563-569(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.02.024
[5] 李爽. 基于SWAT模型的南四湖流域非点源氮磷污染模拟及湖泊沉积的响应研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2012. 153. LI S. Simulation of Non-Point Source pollution of Nitrogen, Phosphorus using SWAT model and response of lacustrine deposit in Nansihu Basin [D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2012. 153 (in Chinese).
[6] 刘恩峰, 沈吉, 杨丽原, 等. 南四湖及主要入湖河流表层沉积物重金属形态组成及污染研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(6): 1377-1383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.06.037 LIU E F, SHAN J, YANG L Y, et al. Chemical fractionation and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in the sediment of Nansihu Lake and its main inflow rivers, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(6): 1377-1383(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.06.037
[7] 王龙凤. 南四湖表层沉积物中典型重金属污染研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2014. 55. WANG LONG FENG. Study on typical heavy metals pollution in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake [D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2014. 55 (in Chinese).
[8] 张桂斋. 两类持久性有机污染物和重金属在南四湖食物链中的分布和生物积累[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2014. 119 ZHANG G Z. Distribution and bioaccumulation of two types of persistent organic pollutions and heavy metals in food web of Nansi Lake, China [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2014. 119(in Chinese).
[9] 焦银合, 于泉洲, 刘恩峰, 等. 基于遥感的南四湖菹草群落时空演变特征及其原因分析 [J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(1): 72-80, 93. JIAO Y H, YU Q Z, LIU E F, et al. The characteristics of and causes to spatiotemporal evolution Potamogeton crispus L. Community in Nansi Lake based on remote sensing data [J]. Forest Resources Management, 2020(1): 72-80, 93(in Chinese).
[10] 高海荣, 陈秀丽, 赵爱娟, 等. 5种沉水植物对重金属富集能力的对比研究 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2016, 42(4): 101-105. doi: 10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2016.04.021 GAO H R, CHEN X L, ZHAO A J, et al. Comparison of heavy metal accumulation by five submerged macrophytes [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2016, 42(4): 101-105(in Chinese). doi: 10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2016.04.021
[11] 张伟. 南四湖水体中汞的分布特征及风险评价研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2018. 53. ZHANG W. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of mercury in water of Nansi Lake [D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2018. 53(in Chinese).
[12] 殷山红, 张智博, 肖燕, 等. 东平湖菹草-上覆水-沉积物系统中汞、砷的赋存特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 635-643. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051203 YIN S H, ZHANG Z B, XIAO Y, et al. Distribution characteristic of mercury and arsenic in the Potamogeton crispus-overlying water- sediment system of Dongping Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 635-643(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051203
[13] 赵群群, 杨凯. 南四湖污染物排放对南水北调东线水质的影响及治理措施 [J]. 价值工程, 2010, 29(8): 105-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2010.08.064 ZHAO Q Q, YANG K. Influence and governance of Nansi Lake pollutants on water quality of south-north diversion project eastern route [J]. Value Engineering, 2010, 29(8): 105-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2010.08.064
[14] 郭森. 南四湖沉积物中重金属含量特征及历史反演[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2019. 58. GUO S. Characteristics and history of heavy metal content in sediments of the Nansi Lake [D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2019. 58(in Chinese).
[15] 张祖陆, 孙庆义, 彭利民, 等. 南四湖地区水环境问题探析 [J]. 湖泊科学, 1999, 11(1): 86-90. doi: 10.18307/1999.0114 ZHANG Z L, SUN Q Y, PENG L M, et al. Water environment problem in the Nansihu Lake [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 1999, 11(1): 86-90(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/1999.0114
[16] 于泉洲, 张祖陆, 高宾, 等. 基于RS和FRAGSTATS的南四湖湿地景观格局演变研究 [J]. 林业资源管理, 2013(1): 108-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2013.01.022 YU Q Z, ZHNAG Z L, GAO B, et al. Study on the changes of landscape pattern in Nansihu wetland based on RS and FRAGSTATS [J]. Forest Resources Management, 2013(1): 108-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6622.2013.01.022
[17] 李印霞, 刘碧波, 曹志林, 等. 菹草对巢湖底泥及上覆水环境影响的研究 [J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(3): 127-132. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.03.017 LI Y X, LIU B B, CAO Z L, et al. Study on environmental impact of Potamogeton crispus on sediment and overburden water of Chaohu Lake [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(3): 127-132(in Chinese). doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.03.017
[18] 马迎丽, 吴广州, 孟娟, 等. 菹草疯长对南四湖水质的影响 [J]. 河北渔业, 2016(11): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2016.11.005 MANG Y L, WU G Z, MEMG J, et al. Influence of Potamogeton crispus growth on water quality of Nansi Lake [J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2016(11): 14-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2016.11.005
[19] GRANEL T, ROBINSON B, MILLS T, et al. Cadmium accumulation by willow clones used for soil conservation, stock fodder, and phytoremediation [J]. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 2002, 40(8): 1331-1337. doi: 10.1071/SR02031 [20] LAFABRIE C, MAJOR K M, MAJOR C S, et al. Trace metal contamination of the aquatic plant Hydrilla verticillate and associated sediment in a coastal Alabama creek (Gulf of Mexico – USA) [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 68: 147-151. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.11.045 [21] 李庚飞. 某矿区附近不同作物对3种重金属富集能力的研究 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2012(26): 263-267. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.26.052 LI G F. Study on the concentration capacity to three kinds of heavy metals for different crops around the gold area [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012(26): 263-267(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.26.052
[22] 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB3838—2002, 地表水环境质量标准[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. State Environmental Protection Administration of China, State Administration for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine of China. Environmental quality standards for surface water: GB 3838—2002 [S], 2002(in Chinese).
[23] 杨丽原, 沈吉, 张祖陆, 等. 南四湖表层底泥重金属和营养元素的多元分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2003(2): 95-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2003.02.022 YANG L Y, SHEN J, ZHANG Z L, et al. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient in surface sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. China Environmental Science, 2003(2): 95-98(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2003.02.022
[24] 石雪芳, 张海涛, 张宇, 等. 洞庭湖表层沉积物中重金属污染评价与分析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(12): 267-277. SHI X F, ZHANG H T, ZHANG Y, et al. Analysis and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(12): 267-277(in Chinese).
[25] 马红. 乌梁素海沉积物中汞砷的分布特征及环境风险评价[D]. 内蒙古: 内蒙古农业大学, 2016. 61. MA H. Distribution characteristics and environmental risk assessment of Hg and As in sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake [D]. Inner Mongolia: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2016. 61(in Chinese).
[26] 刘良, 张祖陆. 南四湖表层沉积物重金属的空间分布、来源及污染评价 [J]. 水生态学杂志, 2013, 34(6): 7-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3075.2013.06.002 LIU L, ZHANG Z L. Spatial distribution, sources and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2013, 34(6): 7-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3075.2013.06.002
[27] 杨丽原, 沈吉, 张祖陆, 等. 南四湖表层底泥重金属污染及其风险性评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2003, 15(3): 252-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2003.03.009 YANG L Y, SHEN J, ZHANG Z L, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in superficial sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2003, 15(3): 252-256(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2003.03.009
[28] WILDING L P. Spatial variability: Its documentation, accommodation and implication to soil surveys [M]. Spatial Variations, 1985. [29] 曲晓华, 郭敬, 闫先名, 等. 南四湖沉积物重金属的季节性分布特征及评价 [J]. 山东农业科学, 2018, 50(9): 72-77. QU X H, GUO J, YAN X M, et al. Seasonal distribution characteristics and evaluation of heavy metals in sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 50(9): 72-77(in Chinese).
[30] 李爽, 张祖陆. 南四湖表层底泥重金属空间分布及污染程度评价 [J]. 水资源保护, 2012, 28(4): 6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2012.04.002 LI S, ZHNAG Z L. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2012, 28(4): 6-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2012.04.002
[31] LIANG P P, XING Y X, WEI C L, et al. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in the overlying water-sediment-plant-fish system in the Wuliangsuhai Lake by using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(2): 652-658. [32] 潘义宏, 王宏镔, 谷兆萍, 等. 大型水生植物对重金属的富集与转移 [J]. 生态学报, 2010,30(23): 6430-6441. PAN Y H, WANG H B, GU Z P, et al. Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals by macrophytes [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010,30(23): 6430-6441(in Chinese).
[33] DENG H G, ZHANG J, CHEN S Y, et al. Metal release/accumulation during the decomposition of Potamogeton crispus in a shallow macrophytic lake [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 42(4): 71-78. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-





 下载:
下载: