-
岩溶水是岩溶系统的重要组成部分,其化学组分受地质、水文地质和人类活动等多种因素的控制,并在径流过程中发生复杂的水化学作用,最终表现出独特的水化学组分特征[1-2]。岩溶水化学系统的变量与控制因素错综复杂,因此如何利用水化学组分特征识别水化学信息、分析各类水文地球化学作用及研究水化学组分的时空变化规律并最终实现对水化学演化过程的重新构建就成为了一个难题[3-4]。国内外对岩溶区水化学的研究主要集中在水化学组分和演化等方面[5-7],主要通过定性分析结合定量模拟的方法来完成水化学分析,例如采用水化学类型分析、离子组合比分析和多元统计分析等方法定性分析水化学各组分的来源和控制因素,采用水文地球化学模拟方法定量模拟分析水化学演化[8-11]。
我国是岩溶地貌最为典型的地区之一,总分布面积可达344×104 km2[12],以滇、黔、桂为主体的西南岩溶区分布最为广泛,东北、内蒙、华北和华东地区也有分布,受气候、地层岩性和地质构造等因素的影响,我国南北方岩溶及岩溶水存在较大的差异。以北方岩溶区为例,大量学者研究表明北方岩溶水水化学特征主要受碳酸盐岩和石膏的风化溶解[13-18]、去白云化的控制[13-15,17-18],同时也受到诸如上覆孔隙水混入[18]、煤系地层伴生硫化物矿物氧化[15-16]、人类工程活动[17]等其他因素的影响,且随着径流途径延伸和深度增加呈现一定的规律变化。而对于南方岩溶区,岩溶水水化学特征则是主要受到碳酸盐岩和石膏的风化溶解[19-25]、阳离子交替吸附作用的控制[19,21],同时也受到诸如硅酸盐矿物溶解[21,25]、孔隙水[24]、采煤活动和农业活动[21-25]等其他因素的制约,大部分地区具有明显的空间分异性[20,22-25]。
本文以滇东高原牛栏江流域寻甸县岩溶区地下水为研究对象,利用水化学数据,探讨地下水化学特征、演化进程及成因。研究区属牛栏江-滇池补水工程补给区,本研究对区域的水化学特征、水质保护和滇池生态恢复具有重要意义。
-
研究区位于云南省寻甸县境内,南距昆明市区90 km,地理坐标为东经102°41′—103°33′,北纬25°20′—26°01′。研究区属于高原季风气候,多年平均气温为14.5 ℃,多年平均降水量为1020.9 mm。降水多集中在5—10月,占全年降水量约80%。
研究区处于滇东高原盆谷亚区南部,属于云贵高原第二级阶梯[26],地势西北高,呈向东南倾斜阶梯状,中部地势略高,东西两侧低中山之间分布于大小不等的山间槽谷[27],东南侧受牛栏江水系的河流强烈切割,河谷深切。主体山势呈NE-SW向,连绵起伏,峰谷相间。研究区碳酸盐岩地层广泛分布,构造强烈,岩溶地貌发育,岩溶面积约占寻甸县辖区面积的45.6%。
研究区内地下水类型主要是以岩溶水和裂隙水为主,孔隙水零星分布。岩溶含水层可以分为纯质碳酸盐岩含水层和碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩含水层。纯质碳酸盐岩含水层包括有二叠系茅口组(P1m)和栖霞组(P1q),石炭系上统、中统(C3和C2)、下统摆佐组(C1b)和大塘组上司段(C1ds),以及寒武系龙王庙组(∈1l),岩石裂隙多被网脉状结晶方解石或白云石充填;碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩含水层包括有三叠系永宁镇组(T1y)、泥盆系宰格组(D3zg)、志留系关底组(S3g)和寒武系双龙潭组(∈2s),可见断续方解石和白云石细脉穿插。碎屑岩含水层包括有三叠系飞仙关组(T1f)、二叠系梁山组(P1l)、石炭系大塘组万寿山段(C1dw)和泥盆系海口组(D2h),多呈条带状分布,岩性以页岩、砂岩和泥岩为主,富水性中—弱,常构成区域内相对隔水层。区内地下水主要补给来源于大气降雨,岩溶地下水直接通过岩溶洼地、漏斗、漏水洞和部分溶蚀裂隙等渗入或注入补给。受地层岩性、地质构造和地形地貌等控制,地下水从中部分水岭部位向两侧径流,并以南侧牛栏江作为排泄基准面整体呈现从北向南的径流方向,与岩层走向和构造线延展方向大体相似,并多在岩层交界面附近以下降泉形式排泄。区内各含水层分布及特征分别见表1和图1。
-
采用现场测试和样品室内测试相结合的研究方法,选取具有代表性水样24组,其中包括岩溶泉16组、基岩裂隙水8组。采样时间为2017年8月,采样点位见图1。
pH值采用Multi340i 便携式水质多参数分析仪现场测定,室内分析主要阳离子(Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+)和阴离子(
HCO−3 、SO2−4 、Cl−)组分,使用聚乙烯瓶采集和保存水质样品,采样前进行标准清洗和润洗,每个水样其中一瓶加入浓度为65%的硝酸使其pH<2以测试阳离子浓度。Na++K+采用火焰光度法测定,Ca2+和Mg2+用乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法测定,HCO−3 采用极谱滴定法测定,SO2−4 采用硫酸钡比浊法测定,Cl−采用离子色谱仪测定。水样的室内分析测试由成都蜀通岩土工程检测监测中心承担。采用阳离子-阴离子浓度平衡法检测参数分析误差,测定误差均<5%。 -
对区内24组水样进行分析,水化学离子分析数据和离子概要统计见表2。由表2可知,pH值区间为7.56—9.18,平均为7.56,呈弱碱性,标准偏差较小;TDS与TH分别为22.70—458.40 mg·L−1和9.1—440.1 mg·L-1,平均含量分别为254.03 mg·L−1和220.88 mg·L−1,东西两区含量相差较大,标准偏差较大,主要源于东西两区地层岩性的不同。区内地下水水样的主要阳离子和阴离子的相对丰度分别为Ca2+>Mg2+>Na++K+和
HCO−3 >SO2−4 >Cl−。根据Piper图解[28](图2)分析,
HCO−3 和Ca2+分别是区内主导阴、阳离子,质量浓度所占比例分别为89.45%和46.42%;Mg2+次之,质量浓度所占比例为35.63%;阴离子方面SO2−4 、Cl−所占比例分别为7.57%和2.98%。区内水化学类型主要是以HCO3-Ca·Mg型(9组)和HCO3-Mg·Ca型(6组)为主,所占比例分别为37.5%和25.0%。从图2可以看出,东西两区阳离子分布差异较大,东区主要集中分布于阳离子三角图的Ca2+、Mg2+端附近,而西区分布较分散,其原因为东区水样点主要分布在D3zg、S3g、C1ds等碳酸盐岩含水层,碳酸盐岩的溶解促使Ca2+和Mg2+不断进入地下水;而西区水样点分布在P2β玄武岩含水层中,玄武岩中的硅酸盐岩类矿物风化溶解能力相对较弱,进入地下水中的Ca2+和Mg2+含量较少。东西两区阴离子中HCO−3 占比较大,且东区HCO−3 离子浓度远高于西区,这与阳离子中碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩的溶解差异基本相一致。研究区Na++K+、Ca2+和HCO−3 离子浓度标准偏差较大,分别为30.44、36.62和171.28,表明Na++K+、Ca2+和HCO−3 与其他离子相比,稳定性较弱,受制于研究区地质和水文地质等因素的影响较为强烈,使研究区部分水化学组分有明显空间分异性。 -
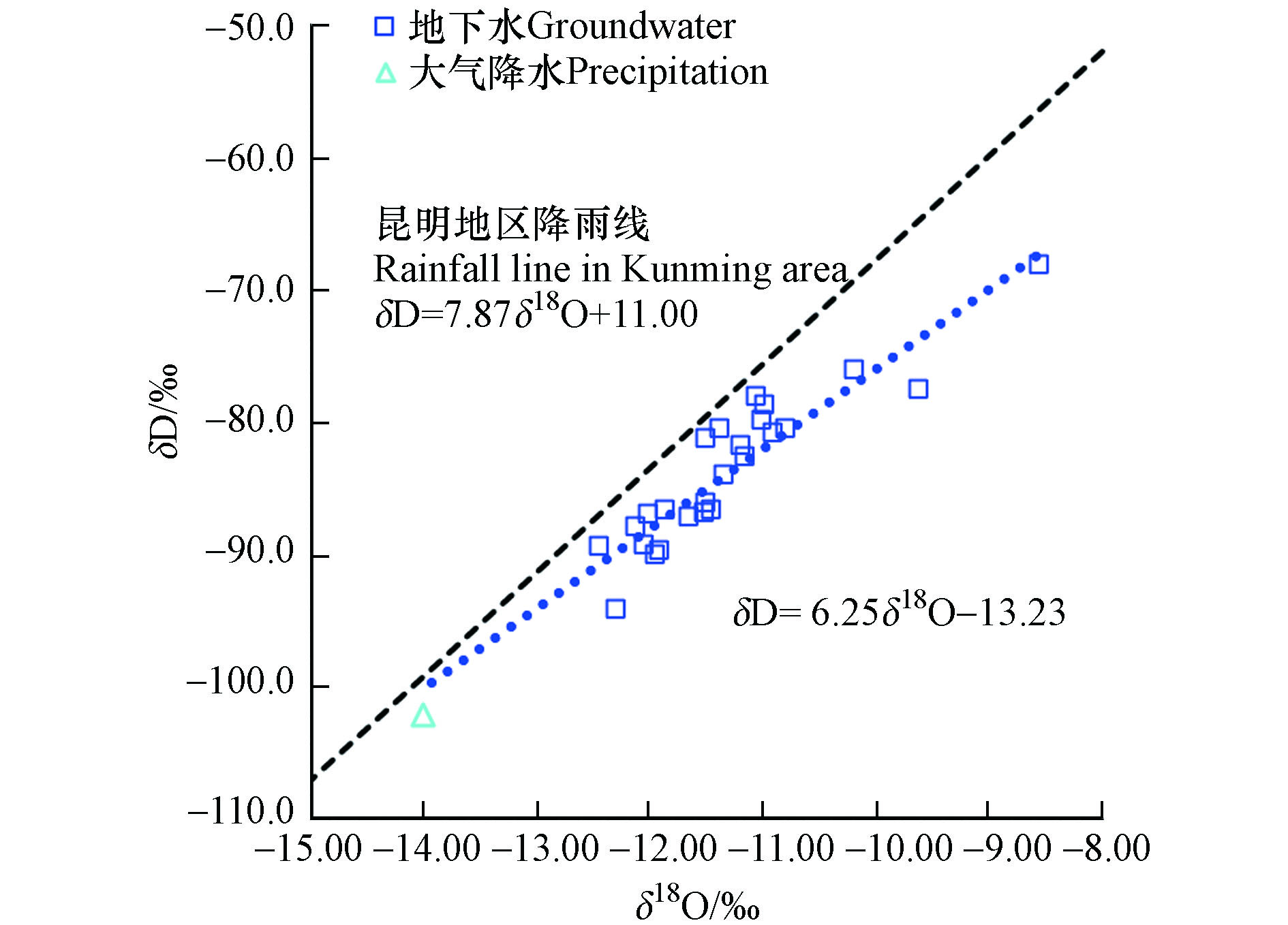
利用研究区地下水中δD和δ18O值绘制氢氧同位素特征关系图(图3),δ18O分布于−8.54‰—−14.00‰,均值为−11.39‰,δD分布于−68.20‰—−102.00‰,均值为−84.40‰,用最小二乘法得出拟合线方程为δD=6.25δ18O−13.23,r=0.8852,δD-δ18O关系方程斜率为6.25,小于昆明地区大气降雨线δD=7.87δ18O+11.00[29]的斜率7.87,有研究表明该地区受温度、雨量、高程、纬度等效应影响,使得降雨过程中δD与δ18O发生同位素分馏,使研究区δD与δ18O关系线斜率小于昆明地区大气降雨线[30]。区内各水样点位的δD与δ18O值间有较好的线性相关性,且略低于昆明地区大气降雨线,表明研究区内地下水的主要补给来源为大气降水,并受到一定程度的蒸发作用影响。
-
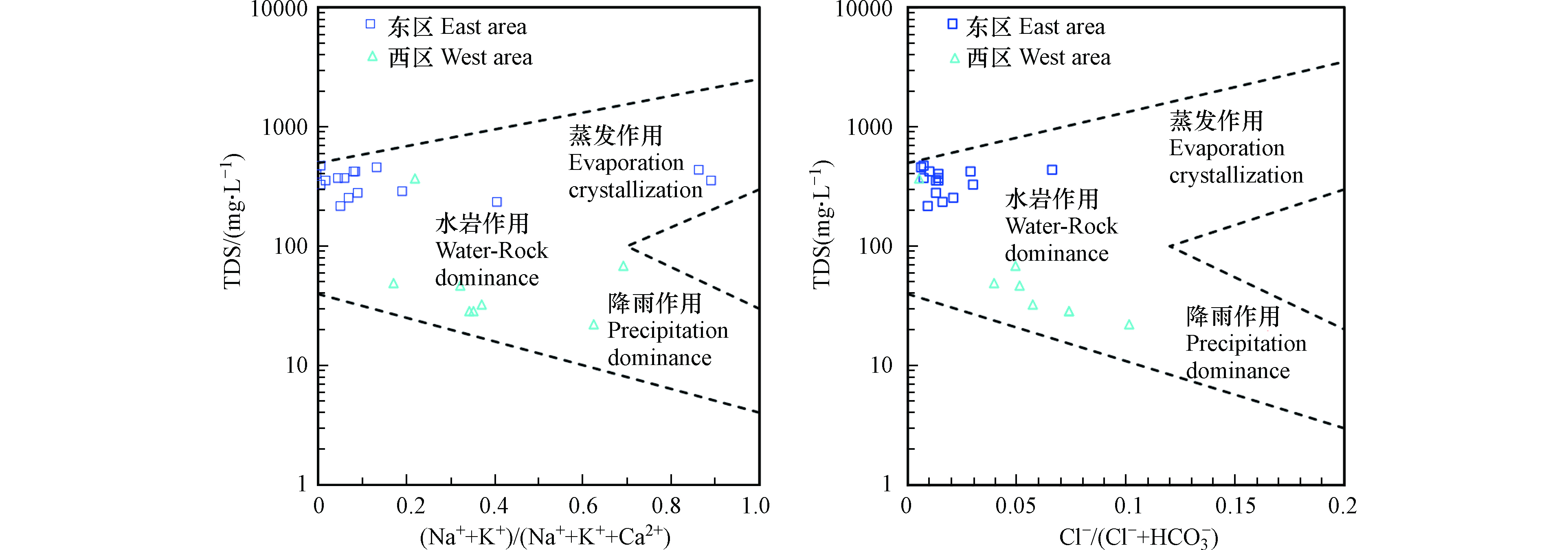
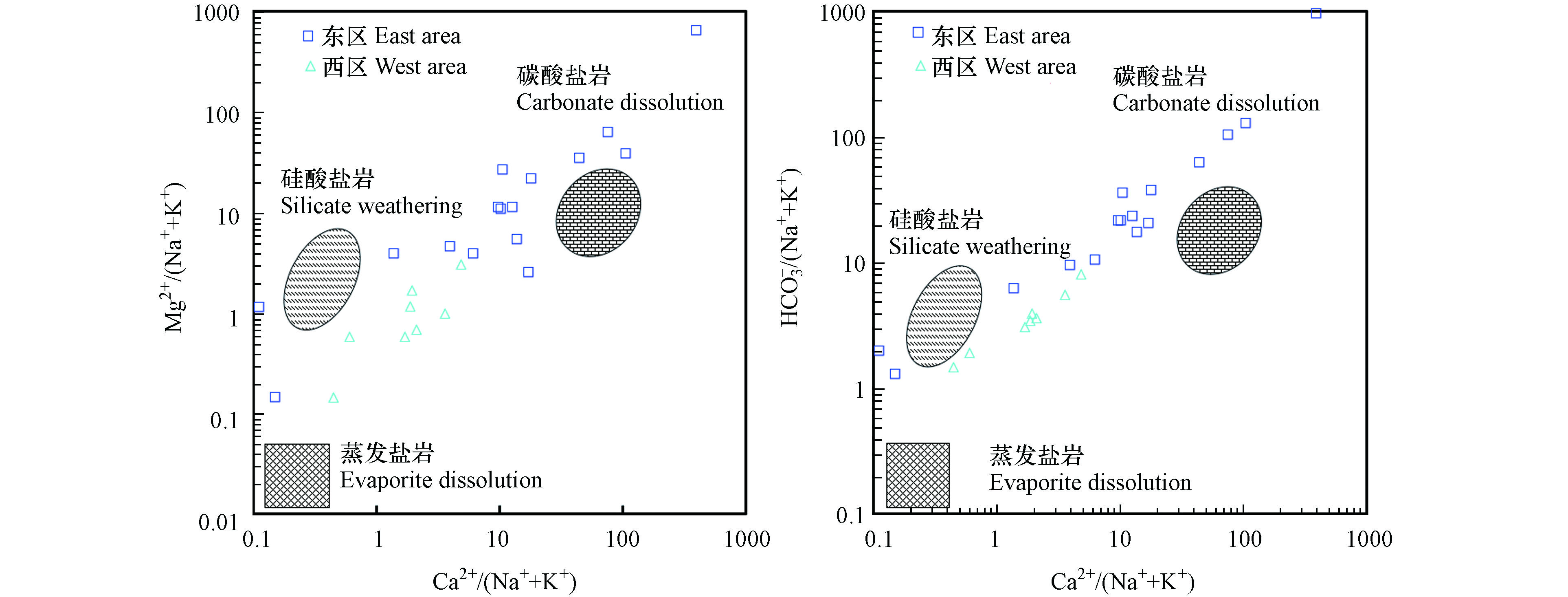
利用Gibbs图[32-33]指示水化学组分的形成作用,并结合Ca2+/(Na++K+)与Mg2+/(Na++K+)离子摩尔浓度比值关系图、Ca2+/(Na++K+)与
HCO−3 /(Na++K+)离子摩尔浓度比值关系图指示水化学组分的溶滤来源及碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩或蒸发盐岩等3种类型水的混合情况[34]。16组东区水样的Cl−/(Cl−+HCO−3 )摩尔浓度比值在0.0071—0.067之间,(Na++K+)/(Na++K++Ca2+)摩尔浓度比值在0.0025—0.90之间,基本位于水-岩作用区域(图4),表明研究区内水化学进程整体以溶滤作用为主,在Ca2+/(Na++K+)与Mg2+/(Na++K+)和Ca2+/(Na++K+)与HCO−3 /(Na++K+)离子摩尔浓度比值关系图(图5)中显示主要是受碳酸盐岩溶解控制,部分受到硅酸盐岩溶解影响,这是由于区内长兴组和茅口组(P1m和P1q)纯质碳酸盐岩大面积分布。SY07与SY12两个水样的Na++K+离子的毫克当量比例分别可达86.62%和89.56%,SY07位于纯质碳酸盐岩地层(C1ds),与处于同地层相近的SY08水样点水化学组分相差较大,说明二者在径流途径与循环时间上有差异;SY07在泉口部位沉积了大量的泉华,表明发生脱碳酸作用,HCO3-与Ca2+、Mg2+离子形成碳酸盐沉淀,造成Ca2+、Mg2+离子浓度降低[35],同时该水样点附近有居民区,可能受到人类活动影响;SY12位于碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩地层(S3g),Ca2+离子浓度较低,Na++K+离子浓度较高,说明岩溶水在径流途中可能发生阳离子交替吸附反应,Ca2+离子与围岩中的Na++K+发生了交换,同时该水样点附近有居民区,可能受到人类活动影响。
西区水样(8组)的Cl−/(Cl−+
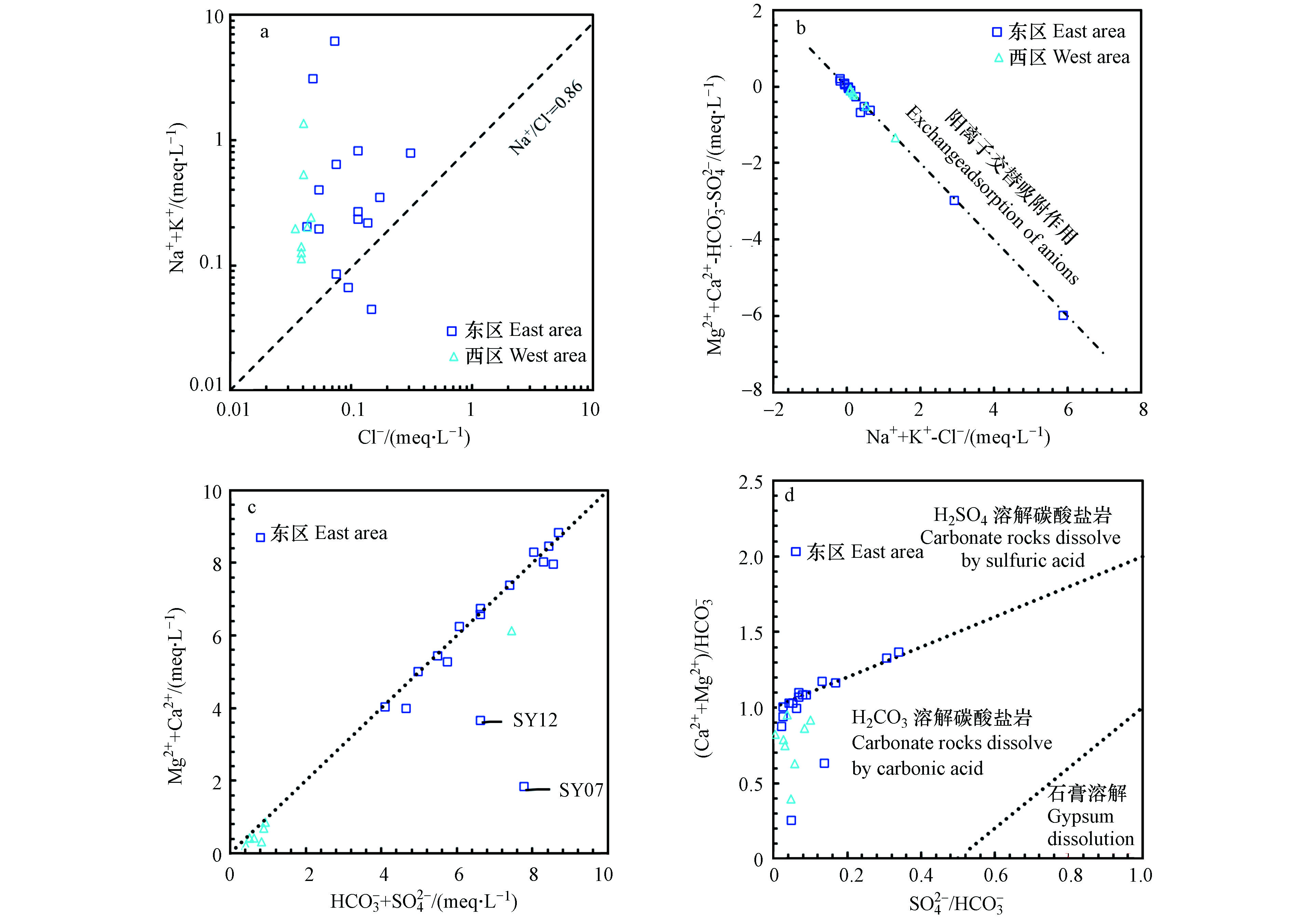
HCO−3 )值在0.0054—0.10之间,(Na++K+)/(Na++K++Ca2+)值在0.17—0.70之间,在Gibbs图显示水化学进程主要有水-岩作用和降雨作用主导,且Ca2+/(Na++K+)与Mg2+/(Na++K+)和Ca2+/(Na++K+)与HCO−3 /(Na++K+)离子关系图中显示主要受到硅酸盐岩溶解控制。西区主要以玄武岩地层为主,岩性溶解能力较差,导致水化学组分的含量均较小。SY22水样点位于分水岭附近,流量约0.1 L·s−1,可能受径流微弱的影响,水化学组分产生富集导致含量较高。区内地下水中K++Na+的空间变异性较大,东西两区的变异系数分别为188.88%和116.85%,浓度范围分别为0.19—140.74 mg·L−1和2.63— 31.92 mg·L−1。Cl−浓度范围为1.25—11.59 mg·L−1,较低的含量可以认为其主要来源为大气降水,多数水化学样的Na++K+的浓度高于Cl−,且有91.67%的地下水水样分布在雨水线(Na+/Cl−=0.86[36])的上方(图6a),表明其主要来源大气降雨外还有其他来源,盐岩与硅铝酸盐矿物的风化溶解和阳离子交替吸附作用也可能引起Na++K+浓度高于Cl−。通常可用[Ca2++Mg2+−
HCO−3 −SO2−4 ]与[Na++K+-Cl−]的当量变化来反映阳离子交替吸附作用中Ca2+、Mg2+与Na+、K+之间的交换[37],图6b中显示所有水样均很好的分布在[Ca2++Mg2+−HCO−3 −SO2−4 ]/[Na++K+−Cl−]=−1的比值线上,表明区内岩溶水和裂隙水均发生了阳离子交换,并且参与阳离子交替吸附作用的Ca2+、Mg2+与Na+、K+主要来源于围岩,人类活动影响较小。Pearson相关系数可以表示变量间的线性关系[38]。表3列出了区内水化学组分之间的Pearson相关系数,采用SPSS 19 for Windows系统软件计算。TDS是反映地下水中化学组分多寡的综合指标,与Ca2+、Mg2+、
HCO−3 和SO2−4 离子的相关系数分别为0.775、0.770、0.646和0.978,反映出上述离子是决定TDS值的主要因素,TH与上述离子的相关系数也与TDS较为接近,也进一步的证明了碳酸盐岩溶解控制区内地下水的水化学形成过程,反应方程式为:CaCO3+CO2+H2O=Ca2++2
HCO−3 CaMg(CO3)2+2CO2+2H2O=Ca2++Mg2++4
HCO−3 Ca2+与
SO2−4 的相关系数为0.583,HCO−3 与SO2−4 的相关系数为0.486,且Ca2++Mg2+与HCO−3 +SO2−4 的毫克当量值基本平衡(图6c),表明石膏(CaSO4)的溶解也是Ca2+和SO2−4 离子的主要来源;从图6d的[Ca2++Mg2+]/[HCO−3 ]与[SO2−4 ]/[HCO−3 ]的比例关系可看出主要区内地下水样集中于H2CO3溶解碳酸盐岩部分,并有部分略高于该线,说明地下水中Mg2+、Ca2+及HCO−3 主要源自碳酸对碳酸盐岩的溶解,其中部分地下水样品有H2SO4参与了碳酸盐岩的风化溶解。Na++K+与Ca2+和HCO−3 的相关系数分别为−0.208和0.298,表明硅铝酸盐矿物的风化溶解和阳离子交替吸附作用有一定影响,又与Cl−等离子无明显相关关系,一些专家学者对本研究区附近区域岩溶水水化学的研究表明,人类活动在区域内较为频繁,扰动了水化学组分的天然特征,使得一些离子浓度出现异常[39-40],推测人类活动,如农业施肥等是Na++K+的主要来源途径。 -
(1)研究区水化学类型主要是以HCO3-Ca·Mg型和HCO3-Mg·Ca为主,水岩作用控制区内的水化学类型。HCO3-和Ca2+是区内主要阴阳离子,分别占89.45%和46.42%,反映了碳酸盐岩溶解对区内水化学特征的控制作用,部分受硅酸盐岩溶解影响。
(2)δD与δ18O关系显示,研究区内地下水主要受大气降水补给。区内地下水化学形成过程受地层岩性影响较为显著,东、西两区地下水水化学特征差异较大。东区主要为碳酸盐岩地层,受水岩作用控制,岩溶发育;西区则是以玄武岩地层为主,溶解性能较差,受大气降水作用的影响更加显著。
(3)Mg2+、Ca2+、
HCO−3 、SO2−4 和Cl−主要受自然条件控制,Na++K+则是主要受农业活动等人类活动的影响,阳离子交替吸附作用亦对区内水化学组分有一定的影响。(4)上述结果为对牛栏江-滇池补水工程区的水化学特征、水质保护和滇池生态恢复提供了参考依据,但后续研究工作仍需结合其他方法进一步开展。
滇东高原牛栏江流域岩溶区地下水化学特征及成因分析
Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater in karst area of Niulanjiang River watershed of eastern Yunnan Plateau
-
摘要: 以滇东高原牛栏江流域岩溶区为例,利用水化学数据,探讨区内地下水化学特征及其成因。对研究区24组水样的水化学特征进行分析,结果表明,研究区水化学类型主要是以HCO3-Ca·Mg型和HCO3-Mg·Ca为主,
HCO−3 和Ca2+是区内主要阴阳离子,反映了水化学特征主要受碳酸盐岩溶解影响。δD与δ18O的关系显示,研究区内地下水主要受大气降水补给。地下水化学演化过程受地层岩性影响显著,岩石风化使东、西两区的地下水水化学特征有较大差异。Mg2+、Ca2+、HCO−3 、SO2−4 和Cl-主要受岩石风化、大气降雨等自然条件控制,受到人类活动影响较小,Na++K+则是主要受农业活动等人类活动的影响。本研究对牛栏江-滇池补水工程区的水化学特征、水质保护和滇池生态恢复具有重要意义。Abstract: Based on the data of hydrochemistry, this article mainly discussed the hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater in the karst area of Niulanjiang river watershed of eastern Yunnan Plateau. Hydrochemical characteristics of 24 samples were analyzed in the study area. The analysis shows that the hydrochemistry type in the study area belonged to HCO3-Ca·Mg type and HCO3-Mg·Ca type.HCO−3 and Ca2+ were the main anions and cations, reflecting that hydrochemical characteristics were mainly affected by the dissolution of carbonate rock. The relationship between δD and δ18O shows that atmospheric precipitation is the main recharge resources of groundwater in the study area. As a result of rock weathering, there are great differences in hydrochemical characteristics between the east and west area. Mg2+, Ca2+,HCO−3 ,SO2−4 , and Cl- were mainly affected by natural conditions, such as rock weathering and atmospheric rainfall; the impact of human activity was little. Meanwhile, Na++K+ was mainly affected by human activities as agricultural activity. This study had a significant value for hydrochemical characteristics and water quality protection of Niulanjiang river-Dianchi lake water supplement project, and for ecological restoration of Dianchi lake.-
Key words:
- eastern Yunnan Plateau /
- karst water /
- hydrochemical characteristics /
- evolution process /
- genesis
-
岩溶水是岩溶系统的重要组成部分,其化学组分受地质、水文地质和人类活动等多种因素的控制,并在径流过程中发生复杂的水化学作用,最终表现出独特的水化学组分特征[1-2]。岩溶水化学系统的变量与控制因素错综复杂,因此如何利用水化学组分特征识别水化学信息、分析各类水文地球化学作用及研究水化学组分的时空变化规律并最终实现对水化学演化过程的重新构建就成为了一个难题[3-4]。国内外对岩溶区水化学的研究主要集中在水化学组分和演化等方面[5-7],主要通过定性分析结合定量模拟的方法来完成水化学分析,例如采用水化学类型分析、离子组合比分析和多元统计分析等方法定性分析水化学各组分的来源和控制因素,采用水文地球化学模拟方法定量模拟分析水化学演化[8-11]。
我国是岩溶地貌最为典型的地区之一,总分布面积可达344×104 km2[12],以滇、黔、桂为主体的西南岩溶区分布最为广泛,东北、内蒙、华北和华东地区也有分布,受气候、地层岩性和地质构造等因素的影响,我国南北方岩溶及岩溶水存在较大的差异。以北方岩溶区为例,大量学者研究表明北方岩溶水水化学特征主要受碳酸盐岩和石膏的风化溶解[13-18]、去白云化的控制[13-15,17-18],同时也受到诸如上覆孔隙水混入[18]、煤系地层伴生硫化物矿物氧化[15-16]、人类工程活动[17]等其他因素的影响,且随着径流途径延伸和深度增加呈现一定的规律变化。而对于南方岩溶区,岩溶水水化学特征则是主要受到碳酸盐岩和石膏的风化溶解[19-25]、阳离子交替吸附作用的控制[19,21],同时也受到诸如硅酸盐矿物溶解[21,25]、孔隙水[24]、采煤活动和农业活动[21-25]等其他因素的制约,大部分地区具有明显的空间分异性[20,22-25]。
本文以滇东高原牛栏江流域寻甸县岩溶区地下水为研究对象,利用水化学数据,探讨地下水化学特征、演化进程及成因。研究区属牛栏江-滇池补水工程补给区,本研究对区域的水化学特征、水质保护和滇池生态恢复具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区概况
研究区位于云南省寻甸县境内,南距昆明市区90 km,地理坐标为东经102°41′—103°33′,北纬25°20′—26°01′。研究区属于高原季风气候,多年平均气温为14.5 ℃,多年平均降水量为1020.9 mm。降水多集中在5—10月,占全年降水量约80%。
研究区处于滇东高原盆谷亚区南部,属于云贵高原第二级阶梯[26],地势西北高,呈向东南倾斜阶梯状,中部地势略高,东西两侧低中山之间分布于大小不等的山间槽谷[27],东南侧受牛栏江水系的河流强烈切割,河谷深切。主体山势呈NE-SW向,连绵起伏,峰谷相间。研究区碳酸盐岩地层广泛分布,构造强烈,岩溶地貌发育,岩溶面积约占寻甸县辖区面积的45.6%。
研究区内地下水类型主要是以岩溶水和裂隙水为主,孔隙水零星分布。岩溶含水层可以分为纯质碳酸盐岩含水层和碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩含水层。纯质碳酸盐岩含水层包括有二叠系茅口组(P1m)和栖霞组(P1q),石炭系上统、中统(C3和C2)、下统摆佐组(C1b)和大塘组上司段(C1ds),以及寒武系龙王庙组(∈1l),岩石裂隙多被网脉状结晶方解石或白云石充填;碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩含水层包括有三叠系永宁镇组(T1y)、泥盆系宰格组(D3zg)、志留系关底组(S3g)和寒武系双龙潭组(∈2s),可见断续方解石和白云石细脉穿插。碎屑岩含水层包括有三叠系飞仙关组(T1f)、二叠系梁山组(P1l)、石炭系大塘组万寿山段(C1dw)和泥盆系海口组(D2h),多呈条带状分布,岩性以页岩、砂岩和泥岩为主,富水性中—弱,常构成区域内相对隔水层。区内地下水主要补给来源于大气降雨,岩溶地下水直接通过岩溶洼地、漏斗、漏水洞和部分溶蚀裂隙等渗入或注入补给。受地层岩性、地质构造和地形地貌等控制,地下水从中部分水岭部位向两侧径流,并以南侧牛栏江作为排泄基准面整体呈现从北向南的径流方向,与岩层走向和构造线延展方向大体相似,并多在岩层交界面附近以下降泉形式排泄。区内各含水层分布及特征分别见表1和图1。
表 1 区内含水层分布及特征Table 1. Characteristics and distribution of aquifer in study area含水层Aquifer 代号Code 主要岩性特征Main lithologic characteristics 水文地质特征Hydrogeological characteristics 富水性Water abundance 纯质碳酸盐岩含水层 P1m、P1q 灰岩、白云岩等 区内大面积分布,层厚约237—645m,为区内主要的岩溶含水层,岩溶管道极其发育,入渗条件好 强 C3、C2、C1b、C1ds、∈1l 呈NE向条带状分布于研究区中部,岩溶发育,为区内岩溶水的主要排泄层位,地下水动态随季节变化较大 碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩含水层 T1y、D3zg、S3g、∈2s 碳酸盐岩(灰岩、白云岩)夹碎屑岩(泥岩、页岩等) 呈NE向条带状分布于研究区中部,溶蚀较发育,介质以溶蚀裂隙为主,地下水动态随季节变化较大 中—强 碎屑岩含水层 T1f、D2h 砂岩、页岩、泥岩 呈条带状分布于研究区东侧,富水性、透水性都较弱,水位埋深约100m 中 P1l、C1dw 页岩、砂岩、煤线 呈条带状分布于研究区东侧,水量贫乏,透水性弱,常构成区域相对隔水层 弱 玄武岩含水层 P2β 玄武岩 大面积分布于研究区内,裂隙发育,地下水动态随季节变化大 中—强 1.2 研究方法
采用现场测试和样品室内测试相结合的研究方法,选取具有代表性水样24组,其中包括岩溶泉16组、基岩裂隙水8组。采样时间为2017年8月,采样点位见图1。
pH值采用Multi340i 便携式水质多参数分析仪现场测定,室内分析主要阳离子(Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+)和阴离子(
HCO−3 SO2−4 HCO−3 SO2−4 2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 水化学组分及特征
对区内24组水样进行分析,水化学离子分析数据和离子概要统计见表2。由表2可知,pH值区间为7.56—9.18,平均为7.56,呈弱碱性,标准偏差较小;TDS与TH分别为22.70—458.40 mg·L−1和9.1—440.1 mg·L-1,平均含量分别为254.03 mg·L−1和220.88 mg·L−1,东西两区含量相差较大,标准偏差较大,主要源于东西两区地层岩性的不同。区内地下水水样的主要阳离子和阴离子的相对丰度分别为Ca2+>Mg2+>Na++K+和
HCO−3 SO2−4 表 2 水文地球化学组分统计表(mg·L−1)Table 2. Statistical table of hydrogeochemical composition分区Region 编号No. pH Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO2−4 HCO−3 游离CO2 Free carbon dioxide 侵蚀性CO2 Corrosive carbon dioxide TH TDS 取样地层Sampling stratum 东区 SY01 7.79 14.44 50.60 33.00 2.83 8.61 342.20 2.07 2.13 262.20 280.60 D3zg SY02 7.27 6.09 51.57 34.18 4.16 12.30 321.90 15.51 1.06 269.50 269.30 C1ds SY03 7.36 4.86 53.35 27.75 5.01 16.40 285.10 8.27 2.13 247.40 249.90 C1ds SY04 7.78 5.38 50.03 71.70 4.26 32.30 478.00 5.17 0.00 420.00 402.70 S3g SY05 7.39 0.19 64.77 60.60 4.68 26.00 460.70 23.78 4.26 411.10 386.60 D3zg SY06 7.50 17.92 21.86 34.82 11.59 5.96 278.60 14.99 0.00 197.90 221.40 D3zg SY07 7.63 140.74 18.54 10.07 2.65 18.60 452.30 2.59 0.00 87.70 416.80 C1ds SY08 7.64 4.66 69.95 5.89 1.62 6.02 244.50 6.20 0.00 198.90 210.40 C1ds SY09 7.54 9.00 80.88 47.88 1.99 22.10 478.90 10.86 0.00 399.00 401.30 C1b SY10 7.34 18.49 100.55 35.20 4.16 27.10 490.30 18.10 0.00 396.00 430.60 C1ds SY11 7.34 1.95 77.32 34.08 2.75 76.70 309.40 13.44 0.00 333.30 347.50 ∈2s SY12 7.70 70.84 7.04 39.78 1.79 40.60 354.40 7.24 0.00 181.30 337.20 S3g SY13 7.89 1.51 101.28 45.49 3.45 107.80 397.80 6.51 0.00 440.10 458.40 S3g SY14 7.58 4.41 70.84 46.16 1.96 31.40 415.80 9.82 112.87 366.90 362.60 S3g SY15 7.16 7.83 96.43 20.87 6.39 48.00 347.20 26.37 10.65 326.70 353.10 P1m SY16 7.20 1.00 92.46 19.45 5.46 35.60 327.20 21.20 10.65 310.90 317.50 P1m 西区 SY17 7.21 2.93 4.78 2.50 1.37 2.35 29.50 3.62 10.65 22.20 28.70 P2β SY18 6.90 5.76 10.44 2.06 1.68 1.08 53.20 9.82 17.04 9.10 47.60 P2β SY19 6.88 4.52 6.56 1.33 1.25 0.82 35.40 7.76 15.97 21.90 32.20 P2β SY20 7.33 3.28 5.18 1.96 1.37 1.91 29.50 2.07 7.45 21.00 28.50 P2β SY21 8.85 12.44 4.70 0.93 1.43 1.79 47.30 0.00 2.13 15.60 68.20 P2β 西区 SY22 7.65 31.92 95.53 16.52 1.42 2.26 453.20 3.10 5.32 306.60 374.20 P2β SY23 7.32 2.63 10.93 4.03 1.35 1.61 56.10 7.76 14.91 43.90 48.60 P2β SY24 9.18 4.71 2.43 1.42 1.51 1.05 23.10 0.00 12.78 11.90 22.70 P2β 最大值 9.18 140.74 101.28 71.70 11.59 107.80 490.30 26.37 112.87 440.10 458.40 最小值 6.88 0.19 2.43 0.93 1.25 0.82 23.10 0.00 0.00 9.10 22.70 平均值 7.56 15.73 47.83 24.90 3.17 22.02 279.65 9.43 9.58 220.88 254.03 标准偏差 0.52 30.44 36.62 20.75 2.36 26.34 171.28 7.37 22.77 155.06 153.82 变异系数 0.07 1.94 0.77 0.83 0.74 1.20 0.61 0.78 2.38 0.70 0.61 根据Piper图解[28](图2)分析,
HCO−3 SO2−4 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 2.2 地下水补给来源
利用研究区地下水中δD和δ18O值绘制氢氧同位素特征关系图(图3),δ18O分布于−8.54‰—−14.00‰,均值为−11.39‰,δD分布于−68.20‰—−102.00‰,均值为−84.40‰,用最小二乘法得出拟合线方程为δD=6.25δ18O−13.23,r=0.8852,δD-δ18O关系方程斜率为6.25,小于昆明地区大气降雨线δD=7.87δ18O+11.00[29]的斜率7.87,有研究表明该地区受温度、雨量、高程、纬度等效应影响,使得降雨过程中δD与δ18O发生同位素分馏,使研究区δD与δ18O关系线斜率小于昆明地区大气降雨线[30]。区内各水样点位的δD与δ18O值间有较好的线性相关性,且略低于昆明地区大气降雨线,表明研究区内地下水的主要补给来源为大气降水,并受到一定程度的蒸发作用影响。
2.3 水化学形成作用与控制因素
利用Gibbs图[32-33]指示水化学组分的形成作用,并结合Ca2+/(Na++K+)与Mg2+/(Na++K+)离子摩尔浓度比值关系图、Ca2+/(Na++K+)与
HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 SY07与SY12两个水样的Na++K+离子的毫克当量比例分别可达86.62%和89.56%,SY07位于纯质碳酸盐岩地层(C1ds),与处于同地层相近的SY08水样点水化学组分相差较大,说明二者在径流途径与循环时间上有差异;SY07在泉口部位沉积了大量的泉华,表明发生脱碳酸作用,HCO3-与Ca2+、Mg2+离子形成碳酸盐沉淀,造成Ca2+、Mg2+离子浓度降低[35],同时该水样点附近有居民区,可能受到人类活动影响;SY12位于碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩地层(S3g),Ca2+离子浓度较低,Na++K+离子浓度较高,说明岩溶水在径流途中可能发生阳离子交替吸附反应,Ca2+离子与围岩中的Na++K+发生了交换,同时该水样点附近有居民区,可能受到人类活动影响。
西区水样(8组)的Cl−/(Cl−+
HCO−3 HCO−3 区内地下水中K++Na+的空间变异性较大,东西两区的变异系数分别为188.88%和116.85%,浓度范围分别为0.19—140.74 mg·L−1和2.63— 31.92 mg·L−1。Cl−浓度范围为1.25—11.59 mg·L−1,较低的含量可以认为其主要来源为大气降水,多数水化学样的Na++K+的浓度高于Cl−,且有91.67%的地下水水样分布在雨水线(Na+/Cl−=0.86[36])的上方(图6a),表明其主要来源大气降雨外还有其他来源,盐岩与硅铝酸盐矿物的风化溶解和阳离子交替吸附作用也可能引起Na++K+浓度高于Cl−。通常可用[Ca2++Mg2+−
HCO−3 SO2−4 HCO−3 SO2−4 Pearson相关系数可以表示变量间的线性关系[38]。表3列出了区内水化学组分之间的Pearson相关系数,采用SPSS 19 for Windows系统软件计算。TDS是反映地下水中化学组分多寡的综合指标,与Ca2+、Mg2+、
HCO−3 SO2−4 CaCO3+CO2+H2O=Ca2++2
HCO−3 CaMg(CO3)2+2CO2+2H2O=Ca2++Mg2++4
HCO−3 Ca2+与
SO2−4 HCO−3 SO2−4 HCO−3 SO2−4 SO2−4 HCO−3 SO2−4 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 表 3 水化学离子Pearson相关系数Table 3. Pearson correlation coefficient of physiochemical parametersNa++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO2−4 HCO−3 TH TDS pH Na++K+ 1 Ca2+ −0.208 1 Mg2+ −0.076 0.509* 1 Cl− −0.061 0.267 0.396 1 SO2−4 −0.029 0.583** 0.531** 0.184 1 HCO−3 0.298 0.739** 0.792** 0.341 0.486* 1 TH −0.162 0.877** 0.859** 0.380 0.642** 0.882** 1 TDS 0.297 0.775** 0.770** 0.327 0.646** 0.978** 0.891** 1 pH 0.084 −0.190 −0.051 −0.180 −0.040 −0.103 −0.131 −0.086 1 注:*P<0.05;**P<0.01. 3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)研究区水化学类型主要是以HCO3-Ca·Mg型和HCO3-Mg·Ca为主,水岩作用控制区内的水化学类型。HCO3-和Ca2+是区内主要阴阳离子,分别占89.45%和46.42%,反映了碳酸盐岩溶解对区内水化学特征的控制作用,部分受硅酸盐岩溶解影响。
(2)δD与δ18O关系显示,研究区内地下水主要受大气降水补给。区内地下水化学形成过程受地层岩性影响较为显著,东、西两区地下水水化学特征差异较大。东区主要为碳酸盐岩地层,受水岩作用控制,岩溶发育;西区则是以玄武岩地层为主,溶解性能较差,受大气降水作用的影响更加显著。
(3)Mg2+、Ca2+、
HCO−3 SO2−4 (4)上述结果为对牛栏江-滇池补水工程区的水化学特征、水质保护和滇池生态恢复提供了参考依据,但后续研究工作仍需结合其他方法进一步开展。
-
表 1 区内含水层分布及特征
Table 1. Characteristics and distribution of aquifer in study area
含水层Aquifer 代号Code 主要岩性特征Main lithologic characteristics 水文地质特征Hydrogeological characteristics 富水性Water abundance 纯质碳酸盐岩含水层 P1m、P1q 灰岩、白云岩等 区内大面积分布,层厚约237—645m,为区内主要的岩溶含水层,岩溶管道极其发育,入渗条件好 强 C3、C2、C1b、C1ds、∈1l 呈NE向条带状分布于研究区中部,岩溶发育,为区内岩溶水的主要排泄层位,地下水动态随季节变化较大 碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩含水层 T1y、D3zg、S3g、∈2s 碳酸盐岩(灰岩、白云岩)夹碎屑岩(泥岩、页岩等) 呈NE向条带状分布于研究区中部,溶蚀较发育,介质以溶蚀裂隙为主,地下水动态随季节变化较大 中—强 碎屑岩含水层 T1f、D2h 砂岩、页岩、泥岩 呈条带状分布于研究区东侧,富水性、透水性都较弱,水位埋深约100m 中 P1l、C1dw 页岩、砂岩、煤线 呈条带状分布于研究区东侧,水量贫乏,透水性弱,常构成区域相对隔水层 弱 玄武岩含水层 P2β 玄武岩 大面积分布于研究区内,裂隙发育,地下水动态随季节变化大 中—强 表 2 水文地球化学组分统计表(mg·L−1)
Table 2. Statistical table of hydrogeochemical composition
分区Region 编号No. pH Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO2−4 HCO−3 游离CO2 Free carbon dioxide 侵蚀性CO2 Corrosive carbon dioxide TH TDS 取样地层Sampling stratum 东区 SY01 7.79 14.44 50.60 33.00 2.83 8.61 342.20 2.07 2.13 262.20 280.60 D3zg SY02 7.27 6.09 51.57 34.18 4.16 12.30 321.90 15.51 1.06 269.50 269.30 C1ds SY03 7.36 4.86 53.35 27.75 5.01 16.40 285.10 8.27 2.13 247.40 249.90 C1ds SY04 7.78 5.38 50.03 71.70 4.26 32.30 478.00 5.17 0.00 420.00 402.70 S3g SY05 7.39 0.19 64.77 60.60 4.68 26.00 460.70 23.78 4.26 411.10 386.60 D3zg SY06 7.50 17.92 21.86 34.82 11.59 5.96 278.60 14.99 0.00 197.90 221.40 D3zg SY07 7.63 140.74 18.54 10.07 2.65 18.60 452.30 2.59 0.00 87.70 416.80 C1ds SY08 7.64 4.66 69.95 5.89 1.62 6.02 244.50 6.20 0.00 198.90 210.40 C1ds SY09 7.54 9.00 80.88 47.88 1.99 22.10 478.90 10.86 0.00 399.00 401.30 C1b SY10 7.34 18.49 100.55 35.20 4.16 27.10 490.30 18.10 0.00 396.00 430.60 C1ds SY11 7.34 1.95 77.32 34.08 2.75 76.70 309.40 13.44 0.00 333.30 347.50 ∈2s SY12 7.70 70.84 7.04 39.78 1.79 40.60 354.40 7.24 0.00 181.30 337.20 S3g SY13 7.89 1.51 101.28 45.49 3.45 107.80 397.80 6.51 0.00 440.10 458.40 S3g SY14 7.58 4.41 70.84 46.16 1.96 31.40 415.80 9.82 112.87 366.90 362.60 S3g SY15 7.16 7.83 96.43 20.87 6.39 48.00 347.20 26.37 10.65 326.70 353.10 P1m SY16 7.20 1.00 92.46 19.45 5.46 35.60 327.20 21.20 10.65 310.90 317.50 P1m 西区 SY17 7.21 2.93 4.78 2.50 1.37 2.35 29.50 3.62 10.65 22.20 28.70 P2β SY18 6.90 5.76 10.44 2.06 1.68 1.08 53.20 9.82 17.04 9.10 47.60 P2β SY19 6.88 4.52 6.56 1.33 1.25 0.82 35.40 7.76 15.97 21.90 32.20 P2β SY20 7.33 3.28 5.18 1.96 1.37 1.91 29.50 2.07 7.45 21.00 28.50 P2β SY21 8.85 12.44 4.70 0.93 1.43 1.79 47.30 0.00 2.13 15.60 68.20 P2β 西区 SY22 7.65 31.92 95.53 16.52 1.42 2.26 453.20 3.10 5.32 306.60 374.20 P2β SY23 7.32 2.63 10.93 4.03 1.35 1.61 56.10 7.76 14.91 43.90 48.60 P2β SY24 9.18 4.71 2.43 1.42 1.51 1.05 23.10 0.00 12.78 11.90 22.70 P2β 最大值 9.18 140.74 101.28 71.70 11.59 107.80 490.30 26.37 112.87 440.10 458.40 最小值 6.88 0.19 2.43 0.93 1.25 0.82 23.10 0.00 0.00 9.10 22.70 平均值 7.56 15.73 47.83 24.90 3.17 22.02 279.65 9.43 9.58 220.88 254.03 标准偏差 0.52 30.44 36.62 20.75 2.36 26.34 171.28 7.37 22.77 155.06 153.82 变异系数 0.07 1.94 0.77 0.83 0.74 1.20 0.61 0.78 2.38 0.70 0.61 表 3 水化学离子Pearson相关系数
Table 3. Pearson correlation coefficient of physiochemical parameters
Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO2−4 HCO−3 TH TDS pH Na++K+ 1 Ca2+ −0.208 1 Mg2+ −0.076 0.509* 1 Cl− −0.061 0.267 0.396 1 SO2−4 −0.029 0.583** 0.531** 0.184 1 HCO−3 0.298 0.739** 0.792** 0.341 0.486* 1 TH −0.162 0.877** 0.859** 0.380 0.642** 0.882** 1 TDS 0.297 0.775** 0.770** 0.327 0.646** 0.978** 0.891** 1 pH 0.084 −0.190 −0.051 −0.180 −0.040 −0.103 −0.131 −0.086 1 注:*P<0.05;**P<0.01. -
[1] 滕彦国, 左锐, 王金生, 等. 区域地下水演化的地球化学研究进展 [J]. 水科学进展, 2010, 21(1): 127-136. TENG Y G, ZUO R, WANG J S, et al. Progress in geochemistry of regional groundwater evolution [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2010, 21(1): 127-136(in Chinese).
[2] KEBEDE S, TRAVI Y, ALEMAYEHU T, et al. Groundwater recharge, circulation and geochemical evolution in the source region of the Blue Nile River, Ethiopia [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(9): 1658-1676. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.04.016 [3] SETIAWAN T, SYAH ALAM B Y C S S, HARYONO E, et al. Hydrochemical and environmental isotopes analysis for characterizing a complex Karst hydrogeological system of Watuputih area, Rembang, Central Java, Indonesia [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2020, 28(5): 1635-1659. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02128-8 [4] 管清花, 李福林, 王爱芹, 等. 济南市岩溶泉域地下水化学特征与水环境演化 [J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5): 653-662. GUAN Q H, LI F L, WANG A Q, et al. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution of Karst spring groundwater system in Jinan [J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5): 653-662(in Chinese).
[5] 于奭, 孙平安, 杜文越, 等. 人类活动影响下水化学特征的影响: 以西江中上游流域为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1): 72-79. YU S, SUN P A, DU W Y, et al. Effect of hydrochemistry characteristics under impact of human activity: A case study in the upper reaches of the xijiang river basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1): 72-79(in Chinese).
[6] LIU J, WANG H, JIN D W, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of Karst groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan formation in the Pingdingshan coalfield [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(6): 1-14. [7] HUANG H, CHEN Z H, WANG T, et al. Characteristics and processes of hydrogeochemical evolution induced by long-term mining activities in Karst aquifers, southwestern China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(29): 30055-30068. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05984-4 [8] 蒲俊兵, 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 等. 重庆岩溶地下河水文地球化学特征及环境意义 [J]. 水科学进展, 2010, 21(5): 628-636. PU J B, YUAN D X, JIANG Y J, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and environmental meaning of Chongqing subterranean Karst streams in China [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2010, 21(5): 628-636(in Chinese).
[9] SINGH A K, RAJ B, TIWARI A K, et al. Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality in the Jhansi district of Bundelkhand region, India [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 70(3): 1225-1247. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-2209-7 [10] 陈盟, 吴勇, 姚金钱. 地下水主要离子水文地球化学过程与矿井突水水源识别 [J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2016, 14(3): 123-131. CHEN M, WU Y, YAO J Q. Major ion hydrogeochemical processes and identification of mine's water-bursting source [J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2016, 14(3): 123-131(in Chinese).
[11] 刘伟江, 袁祥美, 张雅, 等. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学特征及演化过程分析 [J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6): 245-251. LIU W J, YUAN X M, ZHANG Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of Karst groundwater in Guiyang city [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 245-251(in Chinese).
[12] 蒋忠诚, 袁道先, 曹建华, 等. 中国岩溶碳汇潜力研究 [J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(2): 129-134. JIANG Z C, YUAN D X, CAO J H, et al. A study of carbon sink capacity of Karst processes in China [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 129-134(in Chinese).
[13] QIAN J Z, PENG Y X, ZHAO W D, et al. Hydrochemical processes and evolution of Karst groundwater in the northeastern Huaibei Plain, China [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(5): 1721-1729. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1805-3 [14] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 等. 柳林泉域岩溶地下水区域演化规律及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 2132-2142. HUANG Q B, QIN X Q, LIU P Y, et al. Regional evolution and control factors of Karst groundwater in Liulin spring catchment [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(5): 2132-2142(in Chinese).
[15] 唐春雷, 郑秀清, 梁永平. 龙子祠泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及成因 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(5): 2087-2095. TANG C L, ZHENG X Q, LIANG Y P. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground Karst water systems in the longzici spring catchment [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(5): 2087-2095(in Chinese).
[16] 唐春雷, 赵春红, 申豪勇, 等. 娘子关泉群水化学特征及成因 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1416-1423. TANG C L, ZHAO C H, SHEN H Y, et al. Chemical characteristics and causes of groups water in niangziguan spring [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1416-1423(in Chinese).
[17] WU X C, LI C S, SUN B, et al. Groundwater hydrogeochemical formation and evolution in a Karst aquifer system affected by anthropogenic impacts [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(9): 2609-2626. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00450-z [18] GAO Z J, LIU J T, XU X Y, et al. Temporal variations of spring water in Karst areas: A case study of Jinan spring area, Northern China [J]. Water, 2020, 12(4): 1009. doi: 10.3390/w12041009 [19] CHEN M, WU Y, GAO D D, et al. Identification of coal mine water-bursting source using multivariate statistical analysis and tracing test [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2017, 10(2): 1-14. [20] 汪炎林, 周忠发, 田衷珲, 等. 池武溪流域岩溶水SO42-的空间变化特征及其来源分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(12): 2690-2700. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017030105 WANG Y L, ZHOU Z F, TIAN Z H, et al. Analysis of the spatial variation and sources of SO42- in Karst water of Chiwu Revier [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 2690-2700(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017030105
[21] 李笑, 于奭, 李亮, 等. 石期河流域地下水化学特征及物质来源分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4021-4029. LI X, YU S, LI L, et al. Chemical characteristics of groundwater and material sources analysis in Shiqi river basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4021-4029(in Chinese).
[22] 林永生, 裴建国, 杜毓超, 等. 基于多元统计方法的岩溶地下水化学特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(11): 2394-2401. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016032801 LIN Y S, PEI J G, DU Y C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of Karst groundwater and their influencing factors based on multiple statistical analysis [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(11): 2394-2401(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016032801
[23] 王剑, 罗朝晖, 陈植华, 等. 滇东北毛坪铅锌矿区水化学特征及成因 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(6): 1421-1431. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017083102 WANG J, LUO Z H, CHEN Z H, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of water chemistry in maoping lead-zinc mine area, Northeastern Yunnan, China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(6): 1421-1431(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017083102
[24] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 等. 毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析 [J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456. YUAN J F, DENG G S, XU F, et al. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of Karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province [J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456(in Chinese).
[25] 叶慧君, 张瑞雪, 吴攀, 等. 六盘水矿区关键带岩溶水水化学演化特征及驱动因子 [J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(9): 2887-2898. YE H J, ZHANG R X, WU P, et al. Characteristics and driving factor of hydrochemical evolution in Karst water in the critical zone of Liupanshui mining area [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(9): 2887-2898(in Chinese).
[26] 王世杰, 张信宝, 白晓永. 中国南方喀斯特地貌分区纲要 [J]. 山地学报, 2015, 33(6): 641-648. WANG S J, ZHANG X B, BAI X Y. An outline of Karst geomorphology zoning in the Karst areas of Southern China [J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(6): 641-648(in Chinese).
[27] 王嘉学, 王教元, 肖梦景, 等. 滇东高原地理环境分异与城镇上山空间资源研究 [J]. 云南师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2014, 46(4): 48-53. WANG J X, WANG J Y, XIAO M J, et al. Geographic environment of the east plateau of Yunnan Province and spatial resources for constructing “Hill Towns” [J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences), 2014, 46(4): 48-53(in Chinese).
[28] PIPER A M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses [J]. Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 1944, 25(6): 914. doi: 10.1029/TR025i006p00914 [29] 王恒纯. 同位素水文地质概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 49. WANG H C. Hydrogeological conspectus on isotopes [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991: 49(in Chinese).
[30] 董小芳, 邓黄月, 郑祥民, 等. 长江流域降水中氢氧同位素特征及水汽来源 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(4): 78-84. DONG X F, DENG H Y, ZHENG X M, et al. Analysis of stable isotope characteristics and water vapor origins in atmospheric precipitation in the Yangtze River basin [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(4): 78-84(in Chinese).
[31] 张明亮. 滇东黔西地下水氢氧同位素特征 [J]. 四川地质学报, 2019, 39(3): 508-511. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2019.03.032 ZHANG M L. The δ18O and δD values of groundwater in east Yunnan and west Guizhou [J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2019, 39(3): 508-511(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2019.03.032
[32] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry [J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [33] MARANDI A, SHAND P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs diagram [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 97: 209-212. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.07.009 [34] GAILLARDET J, DUPRÉ B, LOUVAT P, et al. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 159(1/2/3/4): 3-30. [35] 苗迎, 孔祥胜, 宋朝静. 南宁市区地下水水化学特征及形成机制 [J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(3): 228-233. doi: 10.11932/karst20150304 MIAO Y, KONG X S, SONG Z J. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Nanning City [J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(3): 228-233(in Chinese). doi: 10.11932/karst20150304
[36] JIANG Y J, CAO M, YUAN D X, et al. Hydrogeological characterization and environmental effects of the deteriorating urban Karst groundwater in a Karst trough valley: Nanshan, SW China [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(5): 1487-1497. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1729-y [37] BARZEGAR R, MOGHADDAM A A, TZIRITIS E, et al. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and pollution sources of groundwater resources in the Marand plain, northwest of Iran [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(7): 1-16. [38] ACERO P, AUQUÉ L F, GALVE J P, et al. Evaluation of geochemical and hydrogeological processes by geochemical modeling in an area affected by evaporite karstification [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 529: 1874-1889. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.07.028 [39] 刘朋雨, 胡宝清, 覃小群, 等. 南盘江流域不同类型水水文地球化学特征 [J]. 广西师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2013, 30(1): 63-69. LIU P Y, HU B Q, QIN X Q, et al. Hydrological and geochemical characteristics of different types of water in nanpanjiang basin [J]. Journal of Guangxi Teachers Education University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 30(1): 63-69(in Chinese).
[40] 李水新, 闫志为, 劳文科, 等. 巧家县荞麦地河流域与金沙江右岸岩溶水水化学特征 [J]. 水利科技与经济, 2014, 20(2): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2014.02.002 LI S X, YAN Z W, LAO W K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of karst water in Qiaomaidi river basin and right bank of Jinsha river in Qiaojia county [J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy, 2014, 20(2): 5-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7175.2014.02.002
-










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: