-
汞是一种对人体和环境都具有严重毒性的重金属元素,对中枢神经系统有很强的毒性,被世界卫生组织列为第三类致癌物[1]。20世纪50年代日本发生的水俣病事件,使人们充分认识到汞(Hg),尤其是甲基汞(MeHg)对人类和动物的毒害[2]。
相关报道指出,每年全球人为排放至大气中的汞约2000吨[3-4],煤炭燃烧已被公认为世界上主要的人为汞排放源之一[5-7]。中国是世界上最大的煤炭生产国与消费国,2018年煤炭消耗量达到了27.38亿吨,约占全国能源消费比重的60%[8]。众多学者[9-17]对中国煤中汞含量进行了大量的研究,中国煤中汞含量为0.15—0.22 mg·kg−1,高于世界煤中汞含量(0.1 mg·kg−1)[18]。2015年中国燃煤汞排放量高达264.49 t[19],燃煤汞排放问题相当严峻[20-21]。排放进入大气中的汞可进行长距离的迁移并通过干湿沉降对土壤与水体造成汞污染,进一步威胁着人类健康与生态环境。
关于减少煤炭燃烧排放汞的措施主要分为燃烧前脱汞、燃烧中脱汞、燃烧后脱汞三类[22-23]。相对而言,燃烧前脱汞较为简单方便。煤炭洗选可作为燃烧前脱汞的一种有效手段[22]。 Zajusz-Zubek等[24]、Pan等[25]和冯立品等[26]认为,汞在煤中的赋存形态决定了汞的去除能力,煤中大部分与矿物结合的汞有被去除的可能。高硫煤中汞与硫分具有较强的亲和力,主要以黄铁矿或其他硫化物结合存在,与无机硫含量成正比[18, 27-29];低硫煤中汞多数以硫化物结合态和有机结合态为主,部分低硫煤可能因岩浆侵蚀作用使汞与硅酸盐等结合存在[30-31],故在理论上部分汞元素可通过煤炭洗选随灰分、硫分等被去除。Luttrel等[32]发现通过洗选,煤中汞最高脱除率约为80%,平均脱除率为46.71%,与煤中黄铁矿脱除率49.31%相似。另有研究表明,煤炭洗选后汞含量可降低10%—60%[33-36]。
目前研究多集中于高硫煤洗选过程中总汞的迁移与脱除,对于(特)低硫煤中汞元素的脱除行为及效果等方面相关研究报道较少,且未见煤中甲基汞相关方面研究。本文通过对煤中总汞与甲基汞含量的测定,针对其在低硫煤洗选过程中的迁移规律、脱除效果、质量平衡等进行综合研究,旨在为更好地理解煤炭洗选过程中汞元素的脱除行为提供科学依据。
-
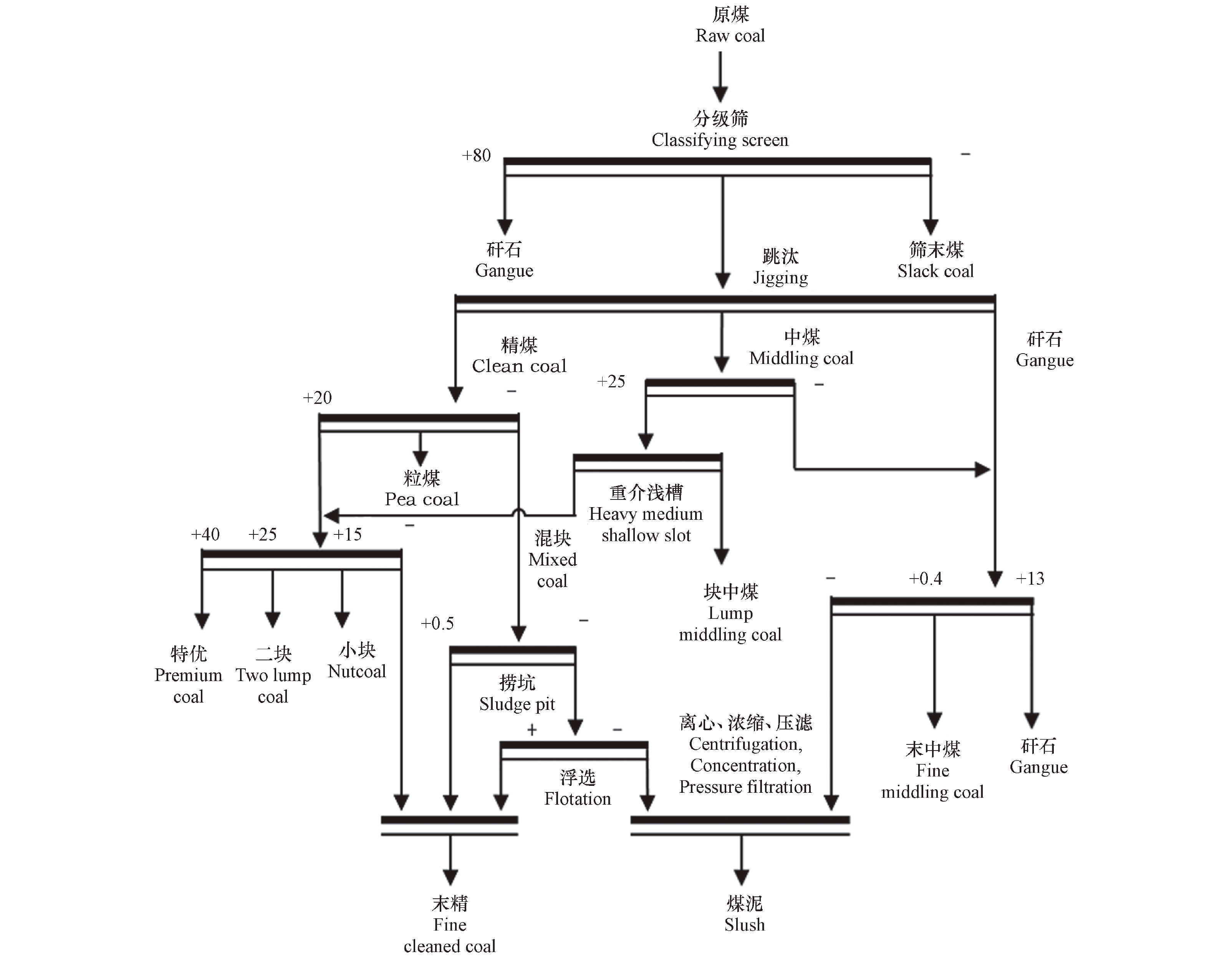
实验用煤采自焦作演马庄矿洗煤厂进料原煤与洗选产品。该厂采用“跳汰、浮选、压滤”联合洗选工艺,年入选能力60万吨。洗选产品根据加工方法与质量规格分为筛末煤、精煤(小块、粒煤、特优、二块、末精煤)、中煤(块中、末中煤)、副产品(矸石、煤泥),洗选工艺如图1所示。本文于2019.10—2019.11月期间,跟踪研究了该厂煤炭洗选过程,对原煤及洗选产品每周采集1次样品,连续采样4周。采集到的样品经过初步破碎后进行真空冷冻干燥和球磨机(PTFE研磨杯,玛瑙球研磨子)研磨,经200目尼龙筛筛分后分装于玻璃瓶中避光保存。
-
煤样中的灰分、硫分分别依据煤的工业分析方法《GB/T212—2008》和煤中全硫测定红外光谱法《GB/T25214—2010》,利用WS-G400自动工业分析仪、WS-S800全自动红外测硫仪进行测定;煤样中的总汞由DMA80测汞仪直接测定;煤样中甲基汞则通过KBr/H2SO4/CuSO4消解-CH2Cl2萃取/反萃取后,采用乙基化衍生-吹扫捕集-气相色谱-冷原子荧光(GC-CVAFS)方法进行测定[37-38]。
煤中汞元素富集程度由富集系数CC[39-40]表示,用相对脱除率R[32]表征各洗选产品总汞与甲基汞的脱除效果,对洗选前后汞元素的质量平衡进行计算,所采用的公式分别如(1)、(2)、(3)所示。
总汞富集系数:
式中,CC为总汞富集系数;Ci为本次采集煤样品汞元素含量;C0为世界煤样品中汞元素平均含量。
CC>100:异常富集;100>CC>10:高度富集;10>CC>5:中度富集;5>CC>2:轻度富集;2>CC>0.5:正常;CC<0.5:损失。
汞元素相对脱除率:
式中,R为汞元素的相对脱除率,100%;Cr 为本次采集原煤中汞元素含量;Ci 为本次采集洗选产品中汞元素含量。
若R值为正,汞元素在洗选产品中得到脱除,R值为负,汞元素则得到富集。
汞元素质量平衡:
式中,Cr为本次采集原煤中汞元素含量;m为原煤年入洗量,t;Ci 为本次采集洗选产品中汞元素含量;mi为洗选产品年产量,t。
-
原煤及洗选产品中总汞、甲基汞含量及其他参数如表1所示,根据我国相关标准GB/T15224.2—2010《煤炭质量分级第 2 部分:硫分》可知,本研究所采集的煤样品均属特低硫煤。原煤中总汞含量平均值约为(0.203±0.056) mg·kg−1,约为地壳中汞含量的2.5倍[29],与杨爱勇等[16]研究并整理的中国大部分煤中汞平均含量0.20 mg·kg−1相近,略低于Zheng[31]所研究的中国多数低硫煤中汞的平均含量0.24 mg·kg−1。原煤经破碎、跳态、重介、浮选等工艺洗选后,精煤、筛末煤、中煤、副产品(矸石、煤泥)总汞平均含量分别为(0.153±0.015) mg·kg−1、(0.251±0.049) mg·kg−1、(0.378±0.012) mg·kg−1和(0.343±0.07) mg·kg−1。与原煤相比,精煤总汞含量显著降低,其中特优煤总汞含量最低,仅0.128 mg·kg−1;中煤和副产品中总汞含量明显较高,其中矸石总汞含量高达0.392 mg·kg−1,约为特优煤总汞含量的3倍。
根据公式(1)计算得原煤及洗选产品中总汞富集系数CC为1.28—3.27,除精煤外其他产品汞富集系数均轻度富集,这表明了在该工艺下洗选出的精煤中汞富集程度达到合格(CC<2),筛末煤、中煤、矸石、煤泥中CC值较原煤升高,汞在其中发生了轻度富集(5>CC>2)。样品中总汞含量顺序为矸石>中煤>煤泥>筛末煤>精煤,这与冯立品等[41]对老石旦选煤厂研究结果一致。
值得注意的是,本研究在原煤及洗选产品中均检测到了甲基汞,其含量范围介于33.58—56.75 ng·kg−1之间,平均值为(45.48±9.06) ng·kg−1。与其他环境介质相比,原煤及洗选产品中的甲基汞含量处于较低水平,不仅低于贵州高汞矿区土壤甲基汞含量(0.13—15.00 ng·g−1)[42]和一般城市污水处理厂活性污泥中甲基汞含量(0.87—23.75 ng·g−1)[37],也低于小浪底水库沉积物中甲基汞含量(0.09—0.39 ng·g−1)[38]和三门峡水库沉积物中甲基汞含量(0.26—0.74 ng·g−1)[43],与三峡库区消落带沉积物中甲基汞含量相似(16—145 ng·kg−1)[44]。经过洗选后,大部分洗选产品中甲基汞含量较原煤均有不同程度的下降,特优、二块煤、末精煤、块中煤甲基汞含量下降较为明显,然而粒煤、末中煤的甲基汞含量分别达到了55.15 ng·kg−1、56.75 ng·kg−1,较原煤有所升高。
-
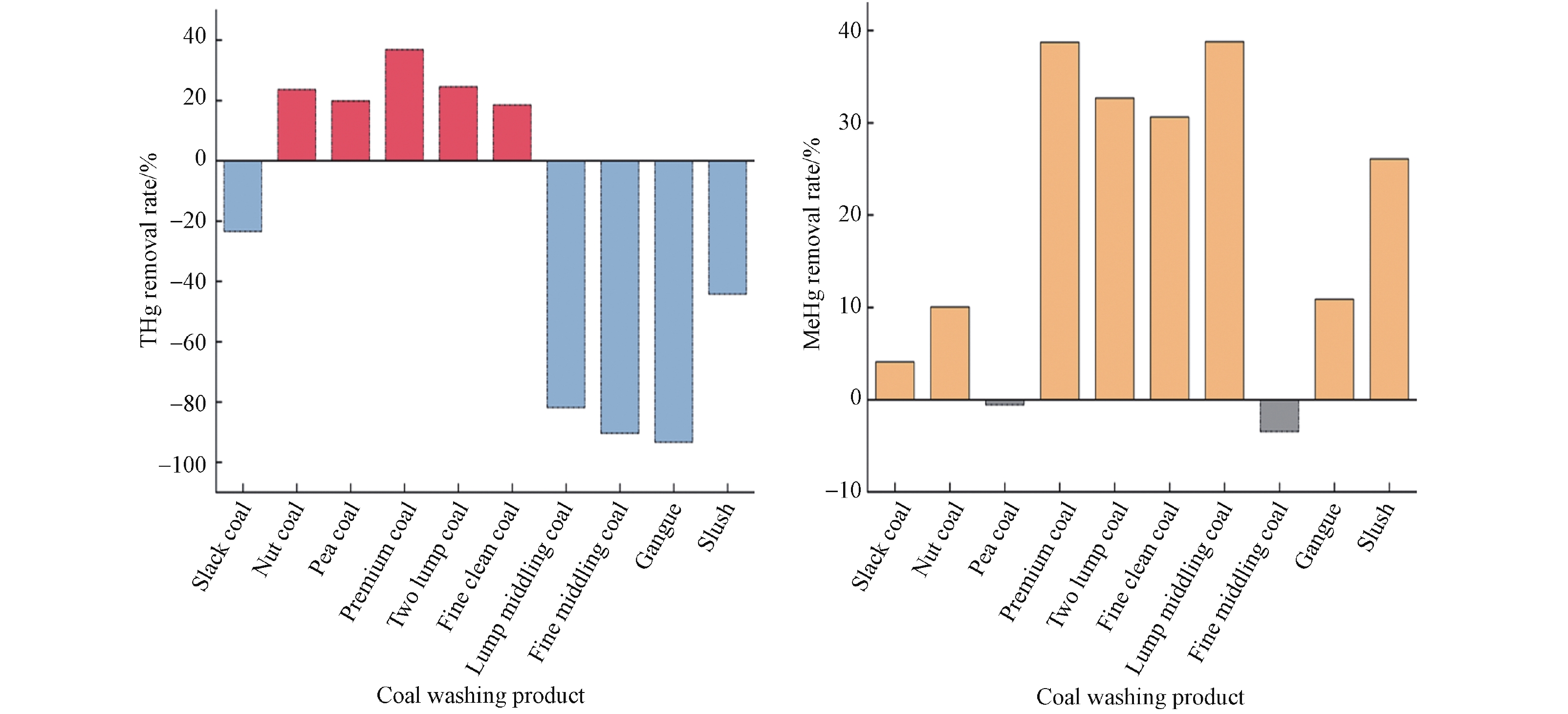
煤炭洗选过程中总汞脱除效果如图2所示。原煤经洗选后,精煤中的汞得到一定程度的脱除,平均脱除率为(24.68±7.24)%,其中小块煤、粒煤、特优、二块煤、末精煤的相对脱除率分别为23.62%、19.89%、36.83%、24.54%、18.51%。与此相对的是,汞在筛末煤、块中煤、末中煤、矸石、煤泥中得到明显的富集,脱除率分别为−23.44%、−81.83%、−90.36%、−93.30%、−44.25%。研究发现[25, 32, 36, 45-49],在大多数煤炭洗选过程中,汞在中煤与副产品矸石、煤泥中呈高度富集,在高质量产品精煤中得到一定量的脱除,这种迁移规律与本次观察相一致。也有报告指出,由于煤中汞赋存状态的不同,在洗选过程中可能会有差异性的表现,例如唐山矿选煤厂煤炭洗选后精煤中总汞含量较高,这是由于汞以细粒硫化物为载体分散于煤中所造成[45]。
甲基汞脱除率如图2所示。煤炭洗选过程中甲基汞大致呈脱除趋势,脱除率介于4.08%—38.78%之间,块中煤、特优、二块、末精煤中甲基汞脱除率均超过了30%,分别为38.78%、38.71%、32.68%、30.61%,具有相对较好的脱除效果。个别产品粒煤、末中煤甲基汞呈富集状态,相对脱除率分别为−0.55%、−3.46%。洗选过程中甲基汞无明显的迁移变化规律,在精煤、中煤、副产品中均出现不同程度的脱除或富集,这可能与其存在形式和煤炭洗选工艺有一定关系。
-
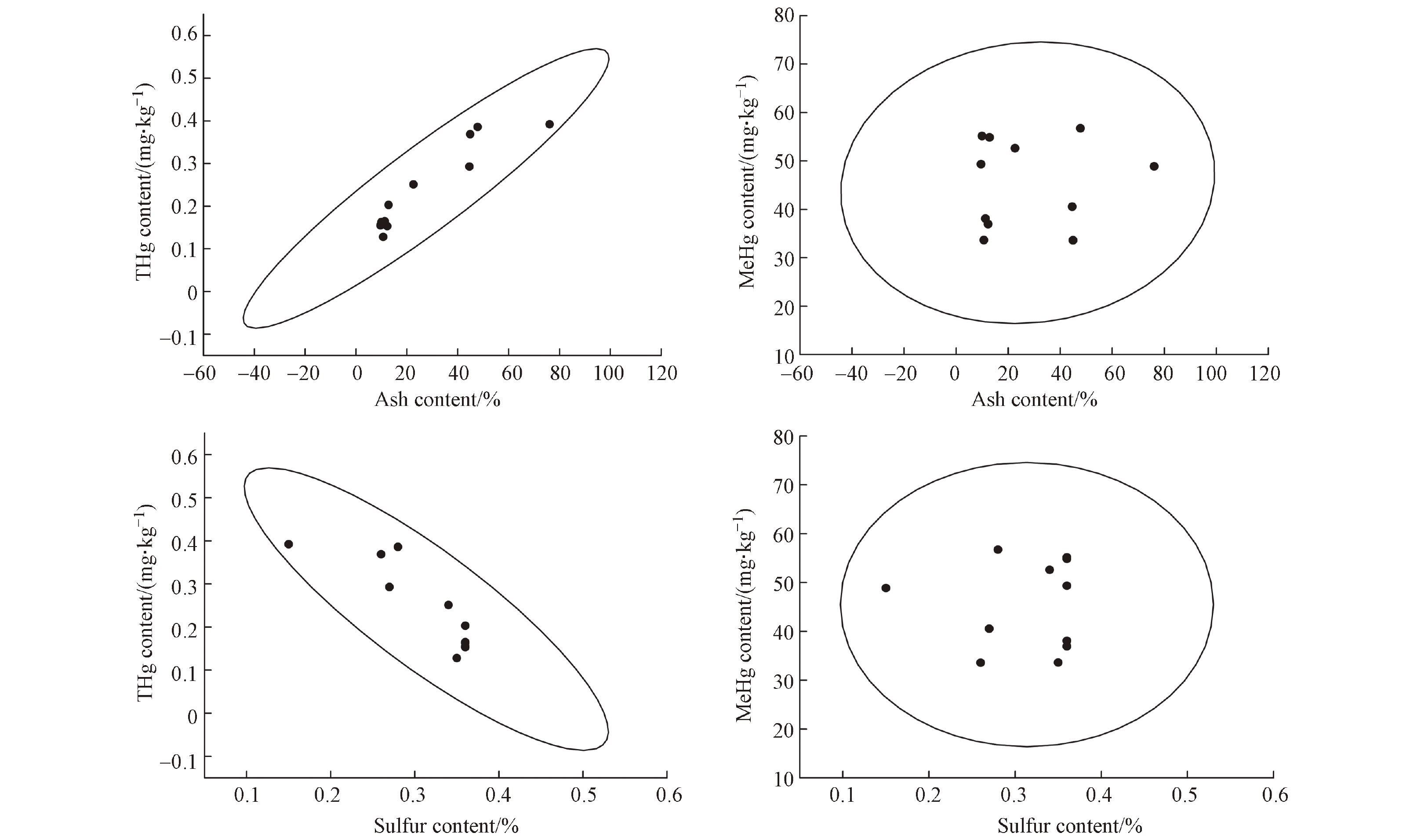
煤炭洗选后精煤中总汞与甲基汞得到一定程度的脱除,为更好的理解煤炭洗选过程中总汞与甲基汞随洗选产品的脱除行为,本文对总汞和甲基汞的脱除机理进行初步探讨,故对原煤及洗选产品中总汞/甲基汞与灰分/硫分进行皮尔森相关性分析。原煤及各洗选产品灰分、硫分平均含量见表1,煤样品中灰分范围为9.6%—76.1%,硫分范围为0.15%—0.36%,与总汞、甲基汞的关系如图3所示,对总汞/甲基汞与灰分/硫分相关性分析结果列于表2。
总汞/甲基汞与灰分/硫分的相关性分析表明灰分与总汞呈显著地正相关性(Sig. < 0.01、r = 0.931),硫分与总汞呈显著负相关(Sig. < 0.01、r = −0.865),甲基汞与灰分(Sig. = 0.839、r = 0.019)、硫分(Sig. = 0.998、r = 0.037)均极低度相关。由表1 可知,原煤通过跳汰、重介浅槽等洗选工艺后,中煤与副产品中灰分、总汞含量较原煤均明显升高,而硫分却得到脱除,灰分与总汞含量在矸石中达到峰值,硫分与原煤相比显著降低,仅为0.15%;然而精煤却有着相对较低的灰分与总汞含量,但仍保持着较高水平的硫分,这也体现出煤样中总汞与灰分、硫分三者之间的关系,总汞在洗选过程中的迁移受灰分的影响较大.
该相关性分析与白向飞对潞安矿区常村矿煤样中汞的赋存特征研究并得出该矿区煤中汞与粘土矿物、碳酸盐等非硫成灰矿物显著正相关,与硫分显著负相关这一结论相吻合[50],也和从龙斐关于煤炭洗选过程中汞与灰分、硫分的关系分析结果类似[51], Goodarzi研究也表明,某些煤中汞元素常以非硫化物相分布[52]。结合前人的研究与各洗选工艺的特点以及洗选产品中汞与灰分、硫分含量的关系,故推测该低硫煤中汞主要与粘土矿物及碳酸盐等非硫矿物结合存在,总汞在洗选过程中随灰分转移进入密度相对较高的中煤与副产品矸石、煤泥中。该结论与目前部分关于低硫煤中汞以硫化物结合态和有机结合态为主要存在形式的结论有所出入[15, 31],这可能是因为本研究所用煤样为特低硫煤,原煤硫分平均值为(0.36±0.037)% < 0.5%,煤中硫主要与有机物结合。通过灰分与硫分的相关性系数(r = −0.983)也可表明煤样中硫以有机硫为主。洗选产品中甲基汞与灰分、硫分未显示出相关性。由皮尔森相关性分析可知,灰分、硫分和总汞三者彼此均显著的相关,为衡量总汞与灰分/硫分之间关系的大小、强弱,分别控制灰分或硫分对总汞进行偏相关分析。总汞与灰分、硫分的显著性Sig.分别为0.001、0.014,偏相关系数r分别为0.874、0.744,均具有相对较好的偏相关性。结合皮尔森相关分析结果,可推断出部分总汞对有机硫分也具有一定的亲和性,与有机硫结合存在于煤中。
在相关性分析的基础上,对汞与灰分、硫分的关系进行了线性回归分析并对其系数进行标准化,其结果如表3所示。线性回归分析方程Sig. = 1.2×10−5,R2 = 0.9409,这表明煤中总汞含量与灰分或硫分之间具有良好的相关性。方程中常数的存在也意味着汞存在形态的复杂性,可能以其它形态如有机物结合态存在于煤中[25, 51],灰分的标准化系数(2.372) > 硫分的标准化系数(1.466),说明在本次研究中原煤及洗选产品中的汞对灰分的亲和力强于硫分,灰分为总汞的主要载体。
尽管没有直接证据,但是通过对煤中总汞/甲基汞和灰分/硫分的相关性分析表明,进料原煤中总汞主要以粘土矿物及碳酸盐等非硫成灰矿物为载体赋存于煤中,少部分汞与有机物结合,煤中硫分主要以有机硫为主,总汞对灰分的亲和力强于硫分,在洗选过程中的迁移受灰分的影响较大,随灰分的减少而得到一定的脱除;甲基汞与灰分、硫分无相关关系,各洗选产品中呈不同程度的脱除或富集,未显示出一定的迁移规律,这可能与其存在形式和不同洗选工艺的应用有一定关系,需对其进一步研究。
-
煤炭洗选过程中总汞与甲基汞年产量列于表4中。该厂原煤年处理量约为60万t,原煤中的总汞质量超过120 kg,洗选后精煤总汞质量为58.87 kg,约占原煤总汞质量的一半;洗选过程中约有29.16 kg的总汞进入筛末煤,占原煤总汞质量的23.54%;副产品矸石与煤泥中总汞质量为36.37 kg,略高于筛末煤,约为原煤的29.35%;中煤总汞质量最低仅为原煤的7.66%,为9.49 kg,各洗选产品中的总汞质量之和为133.89 kg。煤炭洗选前后总汞质量平衡为108.06%,误差可以接受[49]。尽管原煤经洗选过后精煤中总汞浓度较小,但由于其产量较高,残留在精煤中的总汞质量仍较高,而矸石等总汞含量较高的副产品却有着相对较小的产量,使得洗选后仍有一部分总汞留在精煤中而无法随矸石等产品被排出。
原煤中甲基汞年产量为33.48 g,洗选过程中甲基汞进入各洗选产品的比重分别为精煤44.71%,14.97 g;筛末煤18.28%,6.12 g;中煤2.84%,0.95 g;副产品14.25%,4.77 g。洗选后中煤与副产品煤泥、矸石中甲基汞总质量较小,大部分仍残留于精煤和筛末煤中。煤炭洗选后各产品中甲基汞质量总和为26.81 g。整个洗选过程煤中甲基汞的质量平衡为80.08%,平衡误差为19.92%。造成甲基汞质量平衡误差较大的原因一方面可能因为样品采集、分析时产生的偶然误差所造成;另一方面,该厂浮选工艺采用柴油作为主要浮选剂,甲基汞具有一定的脂溶性,浮选剂中可能富集了甲基汞,这或许是产生误差的主要原因。
通过洗选前后总汞与甲基汞的质量平衡可知,该低硫煤通过煤炭洗选,每万吨原煤中约有1.23 kg总汞、0.19 g甲基汞随筛末煤、中煤、副产品矸石与煤泥的排出而被去除,全厂总汞与甲基汞去除率分别为60.55%、35.37%,这说明煤炭洗选对煤中汞元素的脱除是有效地,一定程度上减少了因煤炭燃烧向大气排放汞的量。洗选产品中总汞与甲基汞所占质量比例如图4所示,筛末煤、中煤和副产品中总汞、甲基汞的质量比例分别占洗选产品总质量的56%、44%,尽管洗选后精煤中仍有总汞与甲基汞的残留,但整体含量较原煤有所降低。应加大原煤入洗率,进一步对煤中汞赋存形式进行研究,不断改善优化煤炭洗选工艺,增大对汞与甲基汞的去除。
依据王文峰等[53]对煤中有害元素潜在污染综合指数的评价等级划分,精煤平均总汞含量(0.153±0.015) mg·kg−1,属次洁净煤(Ⅱ),其他洗选产品总汞含量均 > 0.250 mg·kg−1,属较不洁净煤(Ⅲ)。结合图4,容易发现在筛末煤与末精煤中总汞、甲基汞均有着较高的质量比例,矸石、煤泥、小块煤、二块煤中总汞与甲基汞的比例均超过了5%,其中部分产品总汞或甲基汞单项质量比例超过了10%,总汞在块中煤的质量比例也大于5%。综合上述洗选产品总汞与甲基汞含量及质量比例,应注意筛末煤、末精煤、块中煤、末中煤、矸石与煤泥在存放和使用过程中可能对环境造成的汞污染问题。
-
(1)原煤及洗选产品总汞含量为0.128—0.392 mg·kg−1,富集系数CC为1.28—3.92,除精煤外均为轻度富集。在原煤及洗选产品中均检测到一定含量的甲基汞,含量介于33.58—56.75 ng·kg−1之间。通过煤炭洗选,精煤中总汞含量下降,甲基汞含量除粒煤、末中煤外均有所降低。
(2)经洗选后,精煤中总汞脱除率在18.51%—36.83%之间,其他洗选产品中总汞均有所富集,总汞与灰分正相关,与硫分负相关,煤中灰分为汞的主要载体。甲基汞脱除率为−3.46% — 38.78%,在各洗选产品中均有不同程度的脱除或富集,甲基汞与灰分、硫分均无相关性,无明显迁移规律,这可能与其存在形式和洗选工艺有关,需对煤炭洗选过程中汞元素的脱除进一步研究。
(3)煤炭洗选前后,总汞的质量平衡为108.06%,甲基汞质量平衡为80.08%,均在可接受范围内。该低硫煤通过煤炭洗选,约60.55%的总汞和35.37%的甲基汞随筛末煤、中煤与副产品的排出而被去除。结合汞含量与质量比例后,应注意筛末煤、末精煤、块中煤、末中煤、矸石与煤泥在存放和使用过程中可能对环境造成的汞污染问题。
甲基汞与总汞在低硫煤洗选过程中的脱除行为
Study on removal behavior of methylmercury and total mercury during the washing processes of low-sulfur coal
-
摘要: 以焦作市演马洗煤厂进料原煤及洗选产品为研究对象,对低硫煤中总汞与甲基汞含量进行测定,初步探讨了洗选过程中总汞与甲基汞的迁移规律、脱除效果及质量平衡。研究发现,原煤及洗选产品中总汞含量0.128—0.392 mg·kg−1;值得注意的是,原煤及洗选产品中均检出了甲基汞,含量为33.58—56.75 ng·kg−1。经过洗选,总汞在精煤中得到脱除,脱除率为24.68%,在筛末煤、中煤、副产品中被富集;甲基汞在大部分洗选产品中含量均有所降低,整体呈脱除趋势,脱除率为-3.46%—38.78%。该低硫煤中总汞与灰分显著正相关,与硫分呈负相关,在洗选过程中受灰分影响较大;甲基汞与灰分、硫分均极低相关,无明显的迁移规律。煤炭洗选前后的总汞质量平衡为108.06%,甲基汞质量平衡为80.08%。该低硫煤通过洗选,约60.55%的总汞和35.37%的甲基汞随筛末煤、中煤与副产品的排出而被去除,故需留意部分洗煤产品和副产品的存放与使用,避免可能对环境造成的汞污染问题。Abstract: Taking raw coal and washing products of Yanma coal preparation plant in Jiaozuo City as the research object, the content of total mercury (THg) and methyl mercury (MeHg) in low sulfur coal was determined, and the migration rule, removal efficiency and mass balance of THg and MeHg in the washing processes were also studied. The results showed that the THg in the raw coal and washing products ranged from 0.128 mg·kg−1 to 0.392 mg·kg−1. It should be noted that MeHg was detected in all the raw coal and washing products, with contents between 33.58—56.75 ng·kg−1. After washing, THg in clean coal products dropped by 24.68%. On the contrary, THg in slack coal, middling coal, and by-products increased; MeHg in most of the products decreased with relative removal rates of - 3.46%—38.78%. Mercury in coal was significantly positively correlated with ash content and negatively correlated with sulfur, indicating that the migration of THg in coal was mainly affected by ash content. MeHg was weakly correlated with ash and sulfur contents, showing no obvious migration trend. The mass balances closure was 108.06% and 80.08% for THg and MeHg, respectively. By washing, about 60.55% of the total mercury and 35.37% of the MeHg in the low sulfur coal are removed with the discharge of the slack coal, middling coal, and by-products. Therefore, attention should be paid to the storage and use of some coal washing products and by-products to avoid possible mercury pollution to the environment.
-
Key words:
- low-sulfur coal /
- total mercury /
- methylmercury /
- coal washing /
- removal efficiency
-
自1929年发现青霉素来,抗生素作为一种能够有效对抗细菌感染的药物已被广泛应用于人类和牲畜疾病的预防与治疗. Klein等[1]的研究表明,在2000年至2015年间,全球抗生素的消费量增加了65%,并且预测在没有政策干预的情况下,2030年全球抗生素消费量可能比2015年高出200%. 由抗生素大量使用诱导产生的抗生素耐药问题是人类面临的重要公共卫生挑战之一. 据估计,每年死于抗生素耐药性问题的人数高达70万,如果不采取适当的预防措施,到2050年,每年的死亡人数将接近1000万,超过癌症的死亡人数[2]. 存在于抗生素耐药菌(antibiotic resistant bacteria, ARB)中的抗生素抗性基因(antibiotic resistance genes, ARGs),作为一种新污染物,与传统污染物不同,可以通过细菌的繁殖,进行垂直基因转移(vertical gene transfer, VGT),在环境中大量扩增,也可以通过水平基因转移(horizontal gene transfer, HGT)在不同细菌间扩散,进一步诱导抗生素耐药性的产生,因而引起了广泛的关注[3-4].
覆盖地球71%表面积的海洋对人类的生存和发展具有重要意义,反过来也受到了人类活动的广泛影响,它不仅是各类陆源污染物的汇,同样也是ARGs的重要天然储库. 海洋环境中的ARGs可以存在于细菌等微生物体内,也可以在微生物死亡后释放到海水和沉积物中并长期存在[5-6]. 这些ARGs可以在海洋生物之间传播,也可以在海洋生物与人类之间传播,显然海洋介质在ARGs的传播中发挥着重要作用,但这种作用在很大程度上无法量化[6-7]. 全球约40%的人口居住在海岸线100 km2以内的沿海地区,海洋环境中ARGs的存在会对这一区域的人类健康带来前所未有的挑战[8]. 但目前人们对于海洋环境中ARGs的来源、组成和影响因素,仍缺乏系统的认识. 本研究在总结国内外最新研究的基础上,重点讨论了海洋环境中ARGs的主要来源,对比分析了不同海域ARGs的优势类型、浓度水平,以及多个影响因子对海水和沉积物中ARGs的潜在影响,探讨了海洋环境中ARGs的传播扩散路径以及潜在影响等,为深入研究和治理海洋环境ARGs污染,降低ARGs的生态和健康风险提供参考.
1. 海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因的来源(Sources of antibiotic resistance genes in marine environment)
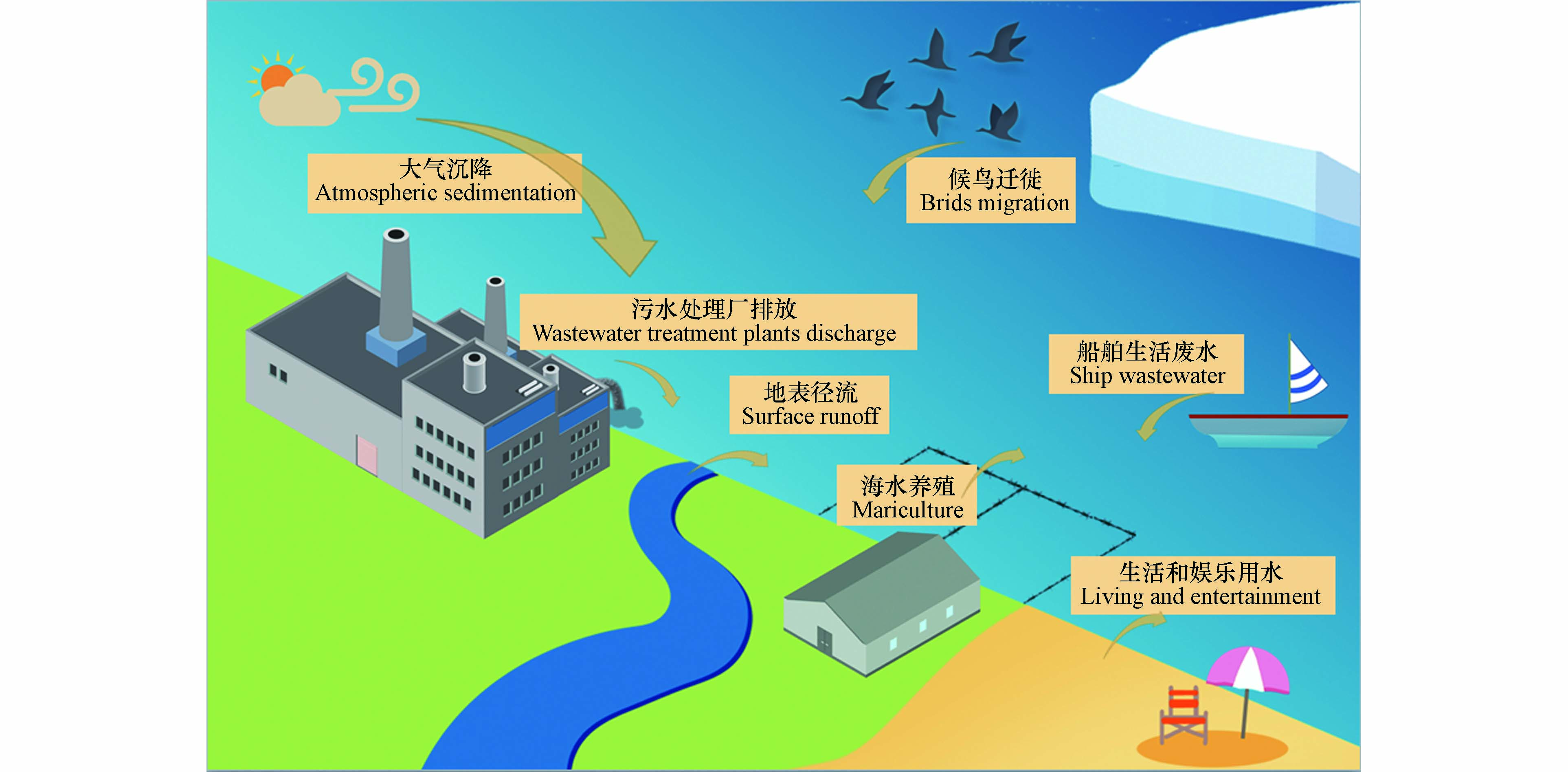
海洋环境中的污染物往往存在着复杂的来源,如污水处理厂排放、地表径流、船舶污染、人类近岸活动、大气远距离传输和候鸟迁徙等过程,这些过程给海洋环境带来了大量的污染物[9-12],其中就包括ARGs.
大多数污水处理厂的现有水处理方法不能有效地去除抗生素和ARGs,残留的抗生素和ARGs会通过污水处理厂的出水口排放到环境中,是河口和近海环境中ARGs的一大来源[13-15]. 在国内外许多海域,近海污水处理厂的废水排放是ARGs的重要来源之一. Huang等[16]的研究发现,市政污水处理厂的废水可能是福建九龙江口和闽江口的主要ARGs污染源. Makkaew等[17]的研究表明,污水直排输入会提高泰国邦盛和芭提雅海滩附近海水中ARGs的丰度. Fonti等[18]研究发现,在中亚得里亚海排放入海的废水中存在大量的ermB、qnrS、sul2和tetA等ARGs.
除此之外,地表径流也是海洋环境中ARGs的一个重要来源,人类和动物疾病治疗残留的大量抗生素和诱导产生的ARGs随着人为排放、雨水冲刷等途径直接入海或者进入河流,最终将排放到河口和近海环境中[13,19]. Dewi等[20]研究发现,澳大利亚悉尼海滩附近海水中的碳青霉素烯耐药菌很可能是通过雨水和其他淡水径流从陆源输入的. 河流排放是渤海[21]ARGs的重要来源之一,而胶州湾的ARGs则可能来自于河水和/或陆地废水排放[22].
包括近海海水养殖、居民生活、娱乐用水等的人类活动也会给海洋环境带来ARGs污染. 为了治疗和预防动物疾病,海水养殖过程中往往会投加大量的抗生素,这些抗生素将会导致海洋环境的ARGs污染[23-24]. 与自然海域相比,海水养殖场中ARGs丰度更高[25]. 在土耳其爱琴海居鲁克湾[26]进行的观测表明,水产养殖区具有更高的抗生素耐药风险. 韩国巨济附近海水中ARGs来源可能是沿海地区的港口和造船厂活动,而莞岛附近海水中ARGs的来源可能是水产养殖或农业活动[27].
候鸟尤其是海鸟在迁徙的过程中,也会携带ARGs并将其传播到更远的区域. 在美国东北部沿海水域,海鸟中分离出来的细菌的耐药性比在海洋哺乳动物中更普遍[28]. 斯瓦尔巴群岛朗伊尔城繁殖区的北极燕鸥泄殖腔内存在大量β-内酰胺类和喹诺酮类耐药菌[29]. 这些存在于海鸟体内的ARGs,将会随着海鸟的长距离迁移,传播到更远的区域.
除此之外,大气远距离传输和船舶生活污水排放等途径也将给海洋环境尤其是远洋环境带来ARGs污染,但目前仍缺乏相应的研究,人们对这些来源的贡献以及影响这些传播途径的因素知之甚少(图1).
2. 海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因的检测方法(Detection of antibiotic resistance genes in marine environment)
对于海洋环境中微生物抗生素耐药性的检测,主要包括传统的微生物培养-药敏试验的方法和采用分子生物学技术的聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction, PCR)、定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR, qPCR)、高通量qPCR(high-throughput qPCR, HT-qPCR)以及宏基因组检测等方法. 前者仅能检测海洋环境中可培养的ARB,而后者分析的对象则包括了可培养和不可培养的微生物,并可以进一步检测海洋环境中的ARGs,使得到的结果更为全面.
在一些早期的研究中,大多采用细菌培养-药敏试验的方法对海洋环境中细菌的耐药性进行检测[30-32]. 这种方法较为简单,且成本较低,可以检测细菌的耐药率,鉴别多重耐药菌. 其中,药敏试验部分主要包括纸片扩散法(K-B琼脂法)和稀释法,前者主要通过测量含抗生素在琼脂平板培养基上形成的抑菌环的直径,测定细菌的耐药强度;后者则是通过配置药物浓度梯度稀释的培养基,测定抗生素的最小抑菌浓度(minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC),进而得到细菌耐药强度[33].
一些研究会对得到的细菌进行进一步的DNA提取,并进行PCR检测,以进一步鉴定其中的ARGs种类[34-36]. 也有一些研究直接对海水或沉积物进行DNA提取,进一步PCR检测[37-38]. PCR检测主要是对特定DNA片段进行指数扩增,再采用琼脂糖凝胶电泳对扩增产物进行检测,以鉴别原始样品中是否存在目标DNA片段,这种检测方法耗时短、准确性强,能够定性分析海水和沉积物中的ARGs,但不能对其定量. 因此,近年来的许多研究采用了qPCR方法,对ARGs进行定量检测[39-41]. qPCR检测是在PCR检测的基础上,通过分析荧光信号在特定DNA片段指数扩增过程中的累积,对目标DNA片段进行定量的检测方法,这种方法可以更直观的表征海洋环境中ARGs组成和丰度的变化. 随着检测技术的发展,也有一些新的研究采用微滴式数字PCR(droplet digital PCR, ddPCR)[42]和HT-qPCR[43-44]对海洋环境中ARGs的组成进行分析,这些方法的灵敏度和检测效率更高.
随着测序技术的逐步发展,越来越多的研究采用了宏基因组检测的方法对海洋环境中ARGs的组成进行分析[45-47]. 宏基因组又名微生物环境基因组或环境基因组,主要是从环境中直接提取全部的DNA,并构建宏基因组文库,进行测序,更全面地识别出环境中ARGs的组成;也可通过基因克隆,构建文库进行筛选分析,发现新的ARGs[48].
3. 海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因污染现状(Current status of antibiotic resistance gene pollution in marine environment)
3.1 海水中抗生素抗性基因污染现状
海洋环境中的污染物既会受到附近人为污染源的强烈影响,也会随着海洋环流不断扩散,对遥远的大洋和极地产生影响,并长期存在于海水和沉积物中(图2). 因此,不同区域海水中ARGs的组成和丰度往往存在较大的差异,但总的来说,多药耐药基因,β-内酰胺类抗性基因和磺胺类抗性基因是常被检出的类型(表1).
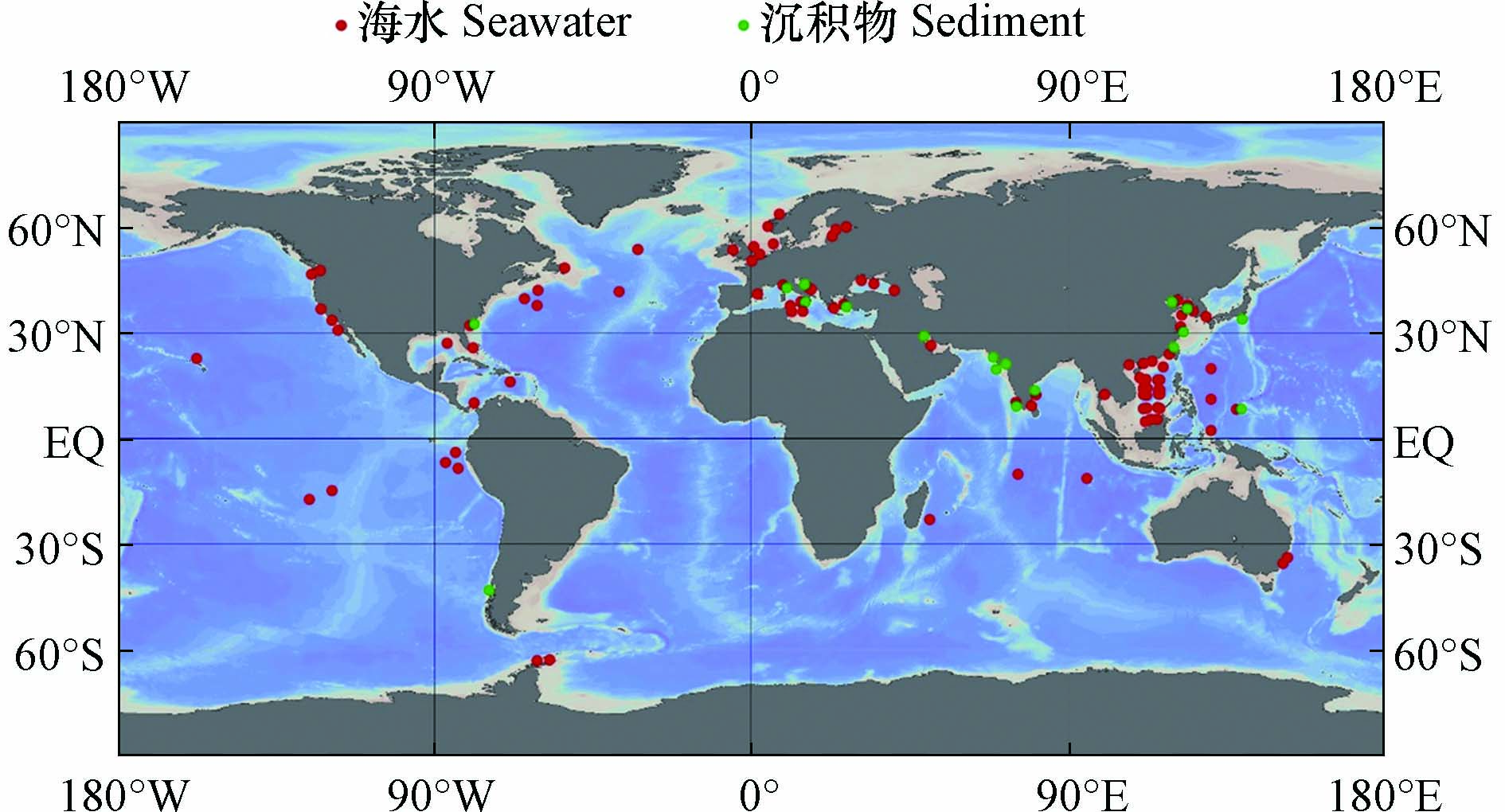 图 2 海水和沉积物中ARGs的相关研究(采用Ocean Data View[69]绘制)Figure 2. Researches of ARGs in seawater and sediments (Draw with Ocean Data View)
图 2 海水和沉积物中ARGs的相关研究(采用Ocean Data View[69]绘制)Figure 2. Researches of ARGs in seawater and sediments (Draw with Ocean Data View)河口和近海生态系统是陆源抗生素和ARGs入海的起点[39,49-50]. 对于印度洋附近海域,科钦河口肠外致病性大肠杆菌对β-内酰胺类抗生素氨苄西林耐药性最强(23.07%),其次是四环素(19.23%)[51]. 对于大西洋附近海域,西西里岛西北部近海地区的海水中β-内酰胺类抗性基因bla-TEM的检出率最高[38],亚得里亚海东部卡什泰拉湾的海水中β-内酰胺类抗生素耐药最强,其中检出率最高的抗性基因是bla-TEM[52],黑海近海地区海水中万古霉素类抗性基因vanB(2×10−1±1×10−1)和β-内酰胺类抗性基因bla-SHV(4×10−2±1×10−2)是相对丰度最高的ARGs[53],英吉利海峡和北海海域磺胺类抗性基因sul1占主导[54]. 在太平洋沿岸海域,泰国邦盛和芭堤雅海滩的海水中,bla-TEM在所有样品中均能检测到,磺胺类抗性基因sul1检出率为97.6%,四环素类抗性基因tetQ检出率为85.4%[17];我国通向南海的河口中,β-内酰胺类抗性基因和磺胺类抗性基因占主导[55-56];在渤海湾检出率最高的ARGs为磺胺类抗性基因sul1、sul2,β-内酰胺类抗性基因bla-TEM和四环素类抗性基因tetB,四者检出率均为100%[6]
而与近海环境相比,更开阔且受人类活动影响较小的大洋区域,ARGs的丰度相对较低. 在相对封闭的地中海,检测到的ARGs的平均相对丰度明显高于开阔的南大西洋[57]. 对于不同大洋区域,ARGs丰度也存在差异,西太平洋海水中ARGs的丰度((3.0×106±1.6×106) copies·mL−1)高于南大洋((1.7×106±1.0×106) copies·mL−1),ARGs丰度从最远的采样点到靠近陆地的采样点呈增加趋势,与人类活动或人为污染源有关[58]. 而对于同一区域,西太平洋中层和深层海水中观察到的ARGs丰度与在浅海中的差异并不显著,表明深海也是ARGs的汇[58]. 此外,在大西洋和北海的海水中,sul2基因在40年间无显著变化,但造成这一奇怪现象的原因仍不清楚[42].
极地通常被认为是脆弱且受人类影响最小的区域,但极地海洋环境中仍有ARGs的存在,不过南极海水中ARGs的丰度比地中海中低3—5个数量级,bla-TEM和tetW是地中海中最丰富的ARGs,而bla-TEM和bla-CTX-M-1是南极海域最丰富的ARGs,这种差异主要与人为污染有关. 地中海海水中ARGs的丰度更高,主要是由于受到沿岸人类活动带来的高抗生素选择压力和人类粪便污染的影响[63]. 在南极洲菲尔德斯地区,多肽、多药耐药和β-内酰胺抗性基因在海水中的含量也较为丰富.
表 1 不同海域海水中的ARGs的丰度Table 1. Abundance of ARGs in seawater of different areas海域Sea area 研究时间Time 研究方法Method ARGs 相对丰度(16S rRNA−1)Relative abundance 绝对丰度Absolute abundance 参考文献Reference 中国渤海湾 2015.07.12 qPCR tetM 5.15×10−5 [59] sul 10−5—10−3 泰国邦盛和芭堤雅海滩 2018.12, 2019.02—2019.08 qPCR bla-TEM 2.08—4.12 lg copies·100 mL−1 [17] 中国黄海和渤海 2018.08.18—2018.09.07 qPCR sul1, sul2, tetB, tetG, tetX, ermF, ermT, qnrA, qnrB, qnrS 21.1—8.00×103 copies·mL−1 [60] 西太平洋和南大洋 2019.10.31—2019.12.04 qPCR tetA, tetB, tetBP, tetD, tetZ, sul1, ermB, blaTEM, qnrD, oqxA (3.0×106±1.6×106) copies·mL−1 [58] 爱尔兰海 2018.09—2019.10 qPCR bla-TEM 2.6×103—6.3×103 GC·100 mL−1 [41] sul1 3.7×102—4.8×103 GC·100 mL−1 黑海 2019.07—08 qPCR vanB 2×10−1±1×10−1 [53] bla-SHV 4×10−2±1×10−2 bla-CMY 1×10−2±3×10−3 mcr-1 3×10−2±2×10−2 ermB 1×10−3±5×10−4 vanA 1×10−5±5×10−4 悉尼港河口玫瑰湾 2019.08—09 qPCR sul1 (7.96×101±2.16×102) copies·100 mL−1 [61] qnrS (1.38×103±3.23×103) copies·100 mL−1 tetA (9.98×103±3.03×103) copies·100 mL−1(2.87×105±2.50×105) copies·100 mL−1 波罗的海 2008.08,2009.09 qPCR tetB 1.8×102—7.3×102 copies·L−1 [62] bla-SHV 2.5×102—1.0×103 copies·L−1 ermB 5.0×101—3.0×102 copies·L−1 tetM 4.2×101—7.8×103 copies·L−1 sul1 2.5×101—1.7×104 copies·L−1 英吉利海峡和北海海域 2020.01 qPCR tetA 2.24 lg copies·mL−1 [54] sul1 1.52—3.55 lg copies·mL−1 3.2 沉积物中抗生素抗性基因污染现状
与流动的海水环境相比,沉积物更具有区域稳定性,因此ARGs更倾向于在沉积物中积累,沉积物中的ARGs丰富且持久[21,60](表2),所以沉积物的再悬浮也是海水中ARGs的一种重要来源[17,49,64]. 总的来说,多药耐药基因和磺胺类抗性基因是海洋沉积物中常被检出的类型(表2和图2).
表 2 不同海域沉积物中的ARGs丰度Table 2. Abundance of ARGs in sediment of different areas海域Sea area 研究时间Time 研究方法Method ARGs 相对丰度(16S rRNA−1)Relative abundance 绝对丰度(copies·g−1)Absolute abundance 参考文献Reference 中国渤海湾 2015.07.12 qPCR tetM 1.7×10−4 [59] sul 10−4—10−2 中国九龙江口和闽江口 2016.04 宏基因组 289种ARGs 1.05×10−1—2.93×10−1 [16] 中国黄海和渤海 2018.08.18—2018.09.07 qPCR sul1, sul2, tetB, tetG, tetX, ermF, ermT, qnrA, qnrB, qnrS 4.67×103—1.08×107 [60] 白令海北部 2007.05—06,2016.07,2015.11 qPCR sul1, sul2, sul3, tetA, tetB, tetM, tetC, tetD, aacC2, aacC3, aacC4, qepA, qnrB, qnrA, qnrS, qnrD, ermC, blaOXA-1, blaTEM-1, blaOXA-2, blaDHA-1, blaVIM-1, ampC, blaCMY-2, blaOXA-10, blaSHV-1, blaGES-1, blaNDM-1, blaKPC 10−9—10−5 [68] 中国渤海附近海河河口 2018.05 HT-qPCR 85种ARGs 9.06×106—2.93×108 [43] 对于印度洋周边海域,在科威特附近海域沉积物中β-内酰胺类、头孢菌素类和青霉素类抗性基因被频繁检出[65],而在库奇湾、康巴特湾和阿拉伯海的沉积物中,多药耐药抗性基因的占比几乎>40%[66]. 对于太平洋周边海域,多药耐药基因是东中国海九龙江口和闽江口主要的ARGs类型[16],氨基糖苷类、多药耐药和磺胺类耐药是渤海湾西部海河河口3种最主要的耐药类型,其主要的耐药机制为抗生素失活和外排泵(共占81.4%)[43].
在大洋区域的沉积物中,情况与近海不同,ARGs的检出率和种类数目明显低于海水中. Su等[67]在西太平洋雅浦海沟的一个沉积物样品中检出了杆菌肽抗性基因,在另外两个沉积物样品中则未检出任何ARGs,而在海水样品中则检出了包括万古霉素、大环内酯和多药耐药等多种ARGs,这可能与海沟的极端深度和远离人为污染有关.
在极地海洋沉积物中也检出了ARGs. 在北极和亚北极的白令海北部区域,sul1、sul2和sul3是最普遍存在的ARGs,但其丰度与渤海湾的海河河口和其他受人类严重影响的海域相比低约2—5个数量级[68].
4. 海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因的影响因素(Influencing factors of antibiotic resistance genes in marine environment)
除污水处理厂的排放、地表径流、船舶污染、人类近岸活动等常见ARGs污染源的影响外,海洋环境中ARGs的组成还受到多种生物和环境因素的影响.
微生物作为ARGs的直接宿主,其群落组成会对ARGs的组成产生重要影响,但在不同区域,ARGs往往有着不同的潜在宿主. 蛭弧菌门(Bdellovibrionota)、蓝细菌(Cyanobacteria)和Margulisbacteria是西太平洋和南大洋海水中ARGs的主要潜在宿主[58]. γ‐变形菌(Gammaproteobacteria)和α-变形菌(Alphaproteobacteria)是西太平洋和深海ARGs的主要潜在宿主[70]. 而拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)与黄海沉积物中大部分ARGs正相关,可能是其潜在宿主[71]. Yang等[57]通过对Tara Oceans项目收集的全球132个海水样品中ARGs组成分析发现,海杆菌(Marinobacter)、交替单胞菌(Alteromonas)、黄杆菌(Flavobacterium)和假交替单胞菌(Pseudoalteromonas)是这些样品中ARGs的主要潜在宿主. 这种差异可能是不同区域理化因子和优势菌群的差异导致的. 与大多数化学污染物不同,ARGs不仅能够长期存在于海洋环境中,而且还能够通过VGT随着宿主的增殖进一步扩增. Li等[72]对龟山岛附近浅海热液口海水的调查显示,细菌群落和物理化学因素对ARGs的组成存在较强的共同影响,细菌群落介导的VGT过程可能对浅海生态系统中ARGs的组成存在重要影响. 此外,它们还能通过HGT作用在不同细菌之间传递,在环境中逐渐增加[73-74]. 包括质粒、转座子、整合子等在内的可移动遗传元件(Mobile Genetic Elements, MGEs)通过接合、转化、转导等方式实现HGT[75]. 许多研究都发现intI1能够促进海水和沉积物中一些基因的传递[43,58-59,76]. 例如,Na等[77]研究显示,1类整合子intI1与sul1和sul2显著相关,表明1类整合子可以促进黄海海水和沉积物中这两种抗性基因的传播. 而亚得里亚海沉积物中,具有β-内酰胺抗性的大肠杆菌菌株则与IncF质粒之间表现出显著相关[78].
此外,抗生素作为诱导产生ARGs的直接驱动力,是许多区域ARGs组成和丰度的重要影响因素. 例如,在一些海水养殖区,抗生素的浓度与一些相应ARGs丰度呈显著正相关关系[64,79]. 在厦门西溪河口和台州椒江口也发现了相同的情况[44]. 在珠江口的沉积物、北黄海的海水和渤海湾水和沉积物中,sul1和sul2都与磺胺类抗生素均呈显著正相关[56,59,77],此外,在渤海湾的海水和沉积物中,tetW与土霉素也呈显著正相关[59]. 但这种情况并非是绝对的,同样是在黄、渤海沉积物中,Lu等[60]的研究则发现,ARGs与相应抗生素间无明显相关关系. 在辽河河口海水、泰国沿海海水、香港沿岸沉积物中,抗生素浓度也与ARGs无明显相关关系[39,80-81]. 这可能与抗生素浓度和水文动力学过程对污染物的影响有关,在抗生素浓度高的养殖等区域,对ARGs存在更强的选择压力,并且海水的运动也会稀释近海水体中的抗生素和ARGs,减弱二者的相关性[39].
非抗生素污染因素也可以通过共同选择过程等影响ARGs的组成和丰度[39,82]. 越来越多的证据表明,重金属[39]、微塑料[46]、有机污染物(包括苯扎氯铵消毒剂[83]、多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, PAHs)[84]、多氯联苯(polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs)[85]、杀虫剂[86]、等离子液体[87]、纳米粒子[88]等在内的多种因素都会影响环境中ARGs的组成和丰度. Yang等[46]研究发现,与海水相比,微塑料和大塑料中ARGs和MRGs的相对丰度均较高,塑料是ARGs的重要载体. Wang等[84]研究发现,PAHs促进了海水中intI1介导的ARGs的共轭转移. Li等[50]研究发现,有机污染物PAHs、PCBs和六溴环十二烷的浓度也与ARGs丰度呈正相关,这一结果可以通过上述污染物对intI1的上调来解释. 此外,也有许多研究表明,海水和沉积物中的重金属与ARGs间存在显著正相关,这与共选择机制作用有关[39,44,50].
与淡水环境相比,海洋具有独特的物理化学性质,包括pH、盐度、营养盐和微量元素水平等,这些因素也会影响ARGs的组成. Zhang等[6]研究表明,海水中溶解氧(dissolved oxygen, DO)和sul2、bla-TEM有强负相关,DO是表示海水自净能力的重要因素,ARGs与DO呈负相关,表明海水的自净能力越低,ARGs的丰度越高,即在低氧海水环境中,ARGs具有更高的浓度. 盐度是衡量海水性质的重要指标,不同研究区域地理位置和盐度变化范围存在差异,对ARGs的影响也就不同. 在大洋海域,盐度高且变化小,而河口和近海区域盐度低且变化幅度大[58]. 在西太平洋和南大洋海水中,盐度和ARGs丰度呈正相关关系[58]. 而在太平洋海域的南海珊瑚礁海域的海水中、渤海湾海河河口沉积物中、厦门西溪河口沉积物中,以及大西洋海域英吉利海峡和北海海水中,盐度和ARGs丰度则呈现负相关关系[43-44,90]. 这可能与污水排放和地表径流对海水的冲淡有关,携带有大量ARGs的污水和河水盐度较低,但会带来大量的ARGs输入,因而导致了这种负相关关系. 与盐度类似,不同海域海水和沉积物中ARGs与不同理化因子的关系也不同. 渤海和黄海海水中ARGs的组成主要受铵盐、硝酸盐和海水盐度的影响[60]. Lu等[44]研究表明,沉积物中ARGs的相对丰度与沉积物粒径和总有机碳(total organic carbon, TOC)含量呈正相关,与沉积物pH和氧化还原电位呈负相关,其中,沉积物粒径是影响ARGs丰度的主要因子. 英吉利海峡和北海海水中sul1与DO、pH和浊度显著正相关[54]. 福建闽江口沉积物中ARGs与TOC、总氮(Total Nitrogen, TN)和总磷(total phosphorus, TP)显著正相关,而九龙江口沉积物中ARGs则与TOC显著正相关,与TN和TP显著负相关[16]. 西太平洋和渤海海水中的糖肽、三氯生、磷霉素和大环内酯-林可酰胺-链阳菌素抗性基因与亚硝酸盐、硝酸盐、叶绿素a、DO呈正相关,而糖肽、三氯生、大环内酯-林可酰胺-链阳菌素和β-内酰胺抗性基因与盐度和DO呈负相关[70]. 总的来说,TOC与海水和沉积物中ARGs呈明显正相关,而不同区域营养盐和pH则对ARGs的组成呈现不同的影响. 有机碳作为微生物尤其是异养细菌的重要营养来源,可以影响微生物群落[90-91],因而与ARGs呈明显正相关;而不同区域营养盐浓度和微生物群落组成差异较大,因此对ARGs的影响也不同.
综上所述,ARGs与环境因子和生物因素的相关性存在区域差异,可能与不同环境中这些理化因子差异较大、以及微生物的适应过程不同有关. 在复杂的海洋生态系统中,存在多种影响ARGs组成和丰度的因素,但对此仍没有一致性认识,因此需要进一步的识别和量化,并揭示相关机制.
5. 海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因污染的生态与健康风险(Ecological and health risks of antibiotic resistance gene pollution in marine environment)
海洋微生物群落是地球上最丰富、最复杂的群落之一[92],因此海洋也成了ARGs巨大的汇. 虽然海洋环境中ARGs的污染目前可能是局部性的,但其后果具有全球相关性,这些首先存在于局域环境中的ARGs可以通过海洋环流运输、海鲜运输和消费、旅游等过程扩大污染范围,对公共卫生、生态系统功能和动物疾病防治等造成严重危害[93].
首先,沿海地区会受到ARGs污染,并给附近生活的人类造成健康威胁. 例如,公共海滩是潜在ARGs污染源,这些区域的休闲海水、沉积物和沙子中存在的ARGs会给海滩使用者带来潜在的健康风险[17,30,36,94-95]. 在大连的傅家庄海水浴场,海水中检出了多种抗生素耐药大肠杆菌,其中38%(26/69)的菌株对至少一种抗生素具有耐药性[96]. 在巴西的海滩,休闲水域的海水和沙子中,也检测出了多种ARGs[97].
其次,海洋环境中的ARGs可以通过洋流输送到遥远的地区,构成全球风险,最终对人类健康构成威胁. 例如,极地区域和深海中也检出了多种ARGs[47,63,70]. Tan等[68]研究发现,北极/亚北极区域存在多种ARGs,这些ARGs与人类特异性分子标记物显著相关,这意味着极地区域已受到人为源ARGs的污染,而这些人为源ARGs很可能是通过海洋环流等过程传输而来的. 除此之外,陆源ARGs可以通过大气传输影响海洋,而海洋环境中的ARGs也可以通过海-气交换进入大气环境,并通过大气长距离运输,进一步传播到更远的地区. 候鸟迁徙也是ARGs从海洋环境向外扩散的一个重要途径,多项研究表明,海鸟胃肠道和粪便中存在多种ARB和ARGs,它们即是环境中的被感染对象也是潜在的传播源[98-100].
此外,海水养殖设施对海水和沉积物中ARGs的积累和传播也具有重要作用. 随着海水养殖业的快速发展,使得大量投加抗生素治疗养殖生物的细菌感染等疾病成为了常态,这带来了大量的抗生素残留,而鱼、虾等海产品则会从海水养殖环境中摄取这些ARGs,并进一步通过食物链威胁人类健康[101-103]. 在不同国家的多种海产品中均检出了ARGs[104-106]. 例如,在印度孟买零售市场销售的海鲜中分离出了大肠杆菌,71.58%的菌株能够产生超广谱β-内酰胺酶[107]. 在中国12个沿海地区采集的虾的内脏中也检测到了114种ARGs,其中主要为多药耐药抗性基因(21.05%),其次是四环素类抗性基因(17.54%)[108]. 可见,这些存在于海水养殖环境及水产品中ARGs将会通过食用等途径,给人类健康带来风险.
6. 总结与展望(Summarization and prospect)
抗生素耐药性问题是一个全球性的公共卫生问题,也是整个世界,尤其是发展中国家面临的一个亟待解决的重要问题. 而海洋环境作为人类活动产生的污染物的重要归宿,也是ARGs的一个天然储库. 海洋环境中存在着多种ARGs,但目前关于海洋环境中ARGs种类组成和传播途径的相关研究较少,对ARGs的归趋及其影响因素还缺乏系统的认识,对海水和沉积物中ARGs的扩散机制仍有待进一步探索.
因此,建议在以下4个方面强化研究,以深入认识海洋环境中的ARGs污染过程及防控措施:(1)开展各个海域、各种模式下海洋环境中ARGs的来源、组成和丰度的相关研究,深入解析不同人为源和自然源对海洋环境ARGs的贡献. (2)丰富海洋环境中ARGs的相关数据,建立海洋ARGs污染数据库,调查抗生素污染以及由此引发的ARGs对海洋微生物的长期和短期影响,并建立和完善海洋环境中ARGs的生态风险和人类健康风险评价指标体系,研发近海海洋环境ARGs污染基准,为制定相应环境标准、规范海水养殖和近海污水处理排放提供理论依据. (3)深入探究海洋环境中各类理化因子和污染物对ARGs的选择压力及机制,研究海洋环境中ARGs的降解机制,明确ARGs与海洋微生物群落之间的关系,细化海洋生态系统中ARGs的环境行为,从而制定相应策略,以期遏制ARGs在海洋环境中的扩散. (4)明确海洋环境中ARGs扩散和传播的分子机制,基于基因组学、大数据分析和数值模型,预测海洋环境介质中ARGs的变化趋势.
-
表 1 原煤及洗选产品中总汞和甲基汞的含量及其相关参数
Table 1. Content and related parameters of THg and MeHg in raw coal and washing products
总汞含量/ (mg·kg−1)THg STD 甲基汞含量/ (ng·kg−1)MeHg STD 灰分/%Ash content 硫分/%Sulfur content 总汞富集系数THg CC 原煤Raw coal 0.203 0.056 54.85 11.1 12.8 0.36 2.03 筛末煤Slack coal 0.251 0.049 52.61 9.16 22.6 0.34 2.51 精煤Clean coal 小块煤 0.155 0.038 49.33 18.05 9.6 0.36 1.55 粒煤 0.163 0.028 55.15 10.58 10 0.36 1.63 特优 0.128 0.019 33.62 8.77 10.7 0.35 1.28 二块煤 0.153 0.043 36.93 11.18 12.3 0.36 1.53 末精煤 0.165 0.012 38.06 8.23 11.3 0.36 1.65 中煤Middlings 块中煤 0.369 0.051 33.58 8.21 44.9 0.26 3.69 末中煤 0.386 0.049 56.75 7.01 47.8 0.28 3.86 副产品By-product 矸石 0.392 0.077 48.88 16.46 76.1 0.15 3.92 煤泥 0.293 0.033 40.54 10.51 44.6 0.27 2.93 表 2 总汞/甲基汞和灰分/硫分的相关性系数
Table 2. Correlation factors of total mercury, methylmercury, ash and sulfur
灰分 Ash content 硫分 Sulfur content 总汞 THg 甲基汞 MeHg 灰分 Ash content 1.000 −0.983** 0.931** 0.019 显著性 Sig. 6.54 × 3.06 × 0.839 硫分 Sulfur content −0.983** 1.000 −0.865** 0.037 显著性 Sig. 6.54 × 5.77 × 0.998 注:**表示在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 ** indicates significant correlation at 0.01 level (double tails). 相关系数|r|>0.8,高度相关;0.8>|r|>0.5,中度相关;0.5>|r|>0.3,低度相关;|r|<0.3,极低度相关;r>0,正相关;r<0,为负相关。 Correlation coefficient |r|>0.8, high correlation; 0.8>|r|>0.5, moderate correlation; 0.5>|r|>0.3, low correlation; |r|<0.3, very low correlation; r>0, positive correlation; r<0, negative correlation. 表 3 煤中总汞线性回归分析
Table 3. Linear regression analysis of total mercury in coal
回归方程Regression equation 显著性Sig. R2 标准化系数 Standardization coefficient 灰分 Ash content 硫分 Sulfur content 总汞 THg CTHg=10.83×(CA/%)+2221.83×(CS/%)−753.12 1.2×10−5 0.9409 2.372 1.466 CTHg: THg content; CA: Ash content; CS: Sulfur content. 表 4 煤炭洗选过程中总汞与甲基汞产量
Table 4. Production of THg and MeHg in coal washing process
煤炭年产量/tAnnual output of coal 总汞年产量/kgAnnual output of THg 甲基汞年产量/gAnnual output of MeHg 原煤 Raw coal 61.03×104 123.9 33.48 筛末煤 Slack coal 11.64×104 29.16 6.12 精煤 Clean coal 小块煤 7.92×104 12.28 3.91 粒煤 1.08×104 1.76 0.6 特优 1.51×104 1.94 0.51 二块煤 4.74×104 7.26 1.75 末精煤 21.54×104 35.63 8.2 中煤 Middlings 块中煤 2.12×104 7.83 0.71 末中煤 4.30×103 1.66 0.24 副产品 By-product 矸石 4.93×104 19.33 2.41 煤泥 5.82×104 17.04 2.36 -
[1] KNEZOVIC Z, TRGO M, SUTLOVIC D. Monitoring mercury environment pollution through bioaccumulation in meconium [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2016, 101: 2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2016.01.013 [2] 冯新斌, 仇广乐, 付学吾, 等. 环境汞污染 [J]. 化学进展, 2009, 21(2): 436-457. FENG X B, QIU G L, FU X W, et al. Environmental mercury pollution [J]. Chemical Progress, 2009, 21(2): 436-457(in Chinese).
[3] WILSON S, KINDBOM K, YARAMENKA K, et al. Technical background report for the global mercury assessment 2013[M]. Norway, Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP), 2013. [4] KOCMAN D, HORVAT M, PIRRONE N, et al. Contribution of contaminated sites to the global mercury budget [J]. Environmental Research, 2013, 125: 160-170. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2012.12.011 [5] STREETS D, HAO J, WU Y, et al. Anthropogenic mercury emissions in China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(40): 7789-7806. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.08.029 [6] WU Y, WANG S X, STREETS D G, et al. Trends in Anthropogenic Mercury Emissions in China from 1995 to 2003 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(17): 5312-5318. [7] PACYNA J M, TRAVNIKOV O, DE SIMONE F, et al. Current and future levels of mercury atmospheric pollution on global scale [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 2016, 16(19): 12495-12511. doi: 10.5194/acp-16-12495-2016 [8] 中国国家统计局. 2019中国统计年鉴[R]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2019. National Bureau of statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2019 [R]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2019 (in Chinese) .
[9] 任德贻, 赵峰华, 张军营, 等. 煤中有害微量元素富集的成因类型初探 [J]. 地学前缘, 1999(S1): 17-22. REN D Y, ZHAO F H, ZHANG J Y, et al. Preliminary study on the genetic type of enrichment of harmful trace elements in coal [J]. Geoscience Frontier, 1999(S1): 17-22(in Chinese).
[10] 任德贻等著. 煤的微量元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. REN D Y, et al. Trace element geochemistry of coal [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006 (in Chinese)
[11] 张军营, 任德贻, 许德伟, 等. 煤中汞及其对环境的影响 [J]. 环境科学进展, 1999(3): 101-105. ZHANG J Y, REN D Y, XU D W, et al. Mercury in coal and its impact on environment [J]. Progress in Environmental Science, 1999(3): 101-105(in Chinese).
[12] 王起超, 沈文国, 麻壮伟. 中国燃煤汞排放量估算 [J]. 中国环境科学, 1999(4): 3-5. WANG Q C, SHEN W G, MA Z W. Estimation of mercury emission from coal combustion in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Sciences, 1999(4): 3-5(in Chinese).
[13] 黄文辉, 杨宜春. 中国煤中的汞 [J]. 中国煤田地质, 2002(S1): 38-41. HUANG W H, YANG Y C. Mercury in Chinese coal [J]. China Coalfield Geology, 2002(S1): 38-41(in Chinese).
[14] 唐修义, 黄文辉等著. 中国煤中微量元素[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2004. TANG X Y, HUANG W H, et al. Trace elements in Chinese coal [M]. Beijing: Commercial Press, 2004 (in Chinese).
[15] ZHENG L G, LIU G, CHOU C L. The distribution, occurrence and environmental effect of mercury in Chinese coals [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 384(1-3): 374-383. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.05.037 [16] 杨爱勇, 严智操, 惠润堂, 等. 中国煤中汞的含量、分布与赋存状态研究 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(32): 93-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.32.017 YANG A Y, YAN Z C, HUI R T, et al. Study on the content, distribution and occurrence of mercury in coal in China [J]. Science, Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(32): 93-100(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.32.017
[17] BAI X F, LI W H, WANG Y, et al. The distribution and occurrence of mercury in Chinese coals [J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 2017, 4(2): 172-182. [18] YUDOVICH Y E, KETRIS M P. Mercury in coal: A review [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2004, 62(3): 107-134. [19] GAO W D, JIANG W, ZHOU M M. The spatial and temporal characteristics of mercury emission from coal combustion in China during the year 2015 [J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2018, 10(3): 776-783. [20] 董灿. 我国人为源大气汞排放清单的分析研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2015. DONG C. Analysis of anthropogenic atmospheric mercury emission inventory in China [D]. Xi'an: University of Architecture and Technology, 2015 (in Chinese) .
[21] ZHANG L, WANG S X, WANG L, et al. Updated emission inventories for speciated atmospheric mercury from anthropogenic sources in China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(5): 3185-3194. [22] LIU C, ZHOU C C, CONG L F, et al. Removal of mercury from fine coal based on combined coal processing approaches [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(11): 12951-12958. [23] 侯淼, 刘然, 赵俊, 等. 烟气脱汞技术的研究与展望 [J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(5): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.05.004 HOU M, LIU R, ZHAO J, et al. Research and prospect of mercury removal from flue gas [J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(5): 17-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.05.004
[24] ZAJUSZ-ZUBEK E, KONIECZYŃSKJ J. Coal cleaning versus the reduction of mercury and other trace elements’ emissions from coal combustion processes [J]. Archives of Environmental Protection, 2014, 40(1): 115-127. doi: 10.2478/aep-2014-0012 [25] PAN J H, ZHOU C C, CONG L F, et al. Mercury in Chinese coals: Modes of occurrence and its removal statistical laws during coal separation [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 31(1): 986-995. [26] 冯立品, 刘红缨, 路迈西, 等. 汞在不同粒度、密度煤炭中分布规律 [J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 29(1): 166-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2010.01.043 FENG L P, LIU H Y, LU M X, et al. Distribution of mercury in coal with different particle size and density [J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology (Natural Science EditioN), 2010, 29(1): 166-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2010.01.043
[27] FENG X B, SOMMAR J, LINDQVIST O, et al. Occurrence, emissions and deposition of mercury during coal combustion in the Province Guizhou, China [J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 2002, 139(1-4): 311-324. [28] FENG X, HONG Y. Modes of occurrence of mercury in coals from Guizhou, People's Republic of China [J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(10): 1181-1188. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00077-0 [29] 雒昆利, 王五一, 姚改焕, 等. 渭北石炭二叠系煤中汞的含量及分布特征 [J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2000(3): 12-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2000.03.004 LUO K L, WANG W Y, YAO G H, et al. Content and distribution characteristics of mercury in permo carboniferous coal in Weibei [J]. Coalfield Geology and EXPloration, 2000(3): 12-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2000.03.004
[30] 郑刘根. 煤中汞的环境地球化学研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2008. ZHENG L G. Environmental geochemistry of mercury in coal [D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2008 (in Chinese) .
[31] ZHENG L G, LIU G J, CHOU C L. Abundance and modes of occurrence of mercury in some low-sulfur coals from China [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2008, 73(1): 19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2007.05.002 [32] LUTTRELL G H, KOHMUENCH J N, YOON R H. An evaluation of coal preparation technologies for controlling trace element emissions [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2000, 65: 407-422. [33] PAVLISH J H, SONDREAL E A, MANN M D, et al. Status review of mercury control options for coal-fired power plants [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2003, 82(2): 89-165. [34] MASON R, PIRRONE N. Mercury fate and transport in the global atmosphere[M]. Boston: Springer, 2009. [35] TOOLE-O'NEIL B, TEWALT S J, FINKELMAN R B, et al. Mercury concentration in coal—unraveling the puzzle [J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(1): 47-54. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00112-4 [36] LIU C, ZHOU C C, ZHANG N N, et al. Modes of occurrence and partitioning behavior of trace elements during coal preparation—A case study in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Fuel, 2019, 243: 79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.01.106 [37] 李花, 毛宇翔, 李永, 等. 汞在城市污水处理厂的赋存特征及质量平衡——甲基汞 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(8): 1287-1293. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.08.018 LI H, MAO Y X, LI Y, et al. Occurrence characteristics and mass balance of mercury in municipal wastewater treatment plants - methylmercury [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(8): 1287-1293(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.08.018
[38] 程柳, 毛宇翔, 麻冰涓, 等. 汞在小浪底水库的赋存形态及其时空变化 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1): 121-129. CHENG L, MAO Y X, MA B J, et al. Occurrence of mercury in Xiaolangdi Reservoir and its temporal and spatial variation [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1): 121-129(in Chinese).
[39] DAI S, SEREDIN V V, WARD C R, et al. Enrichment of U-Se-Mo-Re-V in coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: geochemical and mineralogical data from the Late Permian Guiding Coalfield, Guizhou, China [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50(2): 159-186. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0528-1 [40] ZHOU C C, ZHANG N N, PENG C B, et al. Arsenic in coal: Modes of occurrence, distribution in different fractions, and partitioning behavior during coal separation-A case study [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(4): 3233-3240. [41] 冯立品, 路迈西, 刘红缨, 等. 汞在选煤过程中的迁移规律研究 [J]. 洁净煤技术, 2008(4): 16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6772.2008.04.005 FENG L P, LU M X, LIU H Y, et al. Study on mercury migration in coal preparation process [J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2008(4): 16-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6772.2008.04.005
[42] QIU G L, FENG X B, WANG S F, et al. Mercury and methylmercury in riparian soil, sediments, mine-waste calcines, and moss from abandoned Hg mines in east Guizhou province, southwestern China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(3): 627-638. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.09.006 [43] 程柳, 麻冰涓, 周伟立, 等. 三门峡水库水体中不同形态汞的分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(12): 5032-5038. CHENG L, MA B J, ZHOU W L, et al. Distribution characteristics of different forms of mercury in Sanmenxia reservoir [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(12): 5032-5038(in Chinese).
[44] 王定勇, 朱金山. 三峡库区消落带沉积物中汞的赋存形态及生物可利用性研究 [J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(11): 14-20. WANG D Y, ZHU J S. Study on the speciation and bioavailability of mercury in the sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 35(11): 14-20(in Chinese).
[45] 吕芳丽, 路迈西, 冯立品, 等. 煤炭洗选中汞的迁移变化规律[C]//颗粒学前沿问题研讨会——暨第九届全国颗粒制备与处理研讨会, 中国山东威海, 2009. LU F L, LU M X, FENG L P, et al. The migration and variation of mercury in coal washing[C] // A symposium on the front edge of particle science and the Ninth National Symposium on particle preparation and treatment, Weihai, Shandong, China, 2009 (in Chinese) .
[46] 冯新斌, 洪业汤, 洪冰, 等. 煤中汞的赋存状态研究 [J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(2): 71-78. FENG X B, HONG Y T, HONG B, et al. Study on the occurrence of mercury in coal [J]. Mineral and Petrogeochemical Bulletin, 2001, 20(2): 71-78(in Chinese).
[47] 朱振武, 禚玉群. 煤炭洗选中有害痕量元素的迁移与脱除 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(10): 2434-2440. ZHU Z W, ZHEN Y Q. Migration and removal of harmful trace elements in coal washing [J]. Acta Coal Sinica, 2016, 41(10): 2434-2440(in Chinese).
[48] DZIOK T, STRUGALA A, WLODEK A. Studies on mercury occurrence in inorganic constituents of Polish coking coals [J]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2019, 26(9): 8371-8382. [49] 冯立品. 煤中汞的赋存状态和选煤过程中的迁移规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2009. FENG L P. Study on the occurrence of mercury in coal and its migration during coal preparation [D]. Beijing: China University of mining and Technology (Beijing), 2009 (in Chinese) .
[50] 白向飞. 中国煤中微量元素分布赋存特征及其迁移规律试验研究[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2003. BAI X F. Experimental study on the distribution and occurrence characteristics of trace elements in Chinese coal and their migration rules [D]. Beijing, General Institute of Coal Science, 2003 (in Chinese) .
[51] 丛龙斐. 煤中汞在分选过程中的迁移与脱除规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016. CONG L F. Study on migration and removal of mercury in coal during separation [D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016 (in Chinese) .
[52] GOODARZI F. Mineralogy, elemental composition and modes of occurrence of elements in Canadian feed-coals [J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(9): 1199-1213. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00023-6 [53] 王文峰, 秦勇, 傅雪海. 煤中有害元素潜在污染综合指数及洁净等级研究 [J]. 自然科学进展, 2005, 18(8): 973-980. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2005.08.011 WANG W F, QIN Y, FU X H. Study on the comprehensive index and cleanliness level of harmful elements in coal [J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2005, 18(8): 973-980(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2005.08.011
-






 下载:
下载: