-
沉积物作为湖泊生态系统的重要组成部分,累积了大量污染物质[1]。随着经济的快速发展,工农业废水与生活污水大量排放,重金属污染已成为湖泊的重要生态环境问题之一[2]。重金属在湖泊沉积物中的残留、释放、迁移和转化,极易造成水体的二次污染[2-3],且因其本身所具有的持久性、生物累积性及食物链放大性等特性[4-5],对水生动植物的生长发育及人类健康具有潜在威胁[5-6]。根据已有文献报道,水体沉积物中铜、铅的污染范围最广[7],在中国主要淡水湖泊沉积物中的被检出频次达60次以上[8],其平均浓度在所有重金属中排名前列[9]。因此,如何降低或防止沉积物中铜、铅等重金属离子的二次释放已成为环境污染治理的研究热点。
近年来,国内外研究学者对湖泊沉积物的重金属污染问题展开了许多有益的探索与研究。结果显示,以生物炭为覆盖材料的原位修复技术,因其成本低廉,性质稳定且不易对生态系统造成干扰的特点而比其他修复方法更受欢迎[10]。此外,经过化学修饰后的改性生物炭会比原始生物炭更具吸附活性[11],且氨基的负载将有助于生物炭表面对其他官能团的锚定[12]。马天行等[13]通过化学负载法制备纳米零价铁改性氨基生物炭提高了对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附性能,Yang等[12]报道了氨基改性生物炭对废水中Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附能力提高了5—8倍。但是,目前将氨基生物炭直接应用于沉积物中重金属污染控制的研究仍相对较少,且多围绕于单一离子的吸附,而复合重金属污染环境其实更能真实的反映自然条件下重金属的协同、竞争状态。
基于此,本研究以沉积物中污染问题突出且具有代表性的重金属铜、铅作为研究对象,通过酸碱改性法对原始生物炭进行氨基修饰,在高浓度重金属污染沉积物中开展氨基生物炭原位覆盖处理,结合传统化学提取法,研究不同水体酸碱度下Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放规律与氨基生物炭原位覆盖对高污染沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的修复效果,并采用零级动力学方程和Elovich方程对沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放动力学进行拟合,采用单因子水质标准比较法和USEPA的健康风险评价模型对模拟湖泊水体中重金属的污染情况与健康风险进行评价。以期为高污染湖泊沉积物的修复治理提供理论基础与数据支撑,对环境风险调控具有重要意义。
-
本研究氨基生物炭的制备方法基于王淑娟等[14]的试验方案,选取安徽省淮南市郊区农村的低成本稻壳为本研究的生物质原料,将收集好的稻壳用去离子水洗净后放置于60 ℃的干燥箱中烘干至恒重,随后把烘干好的稻壳装入平底瓷轴,放入管式炉中以2 mL·min−1的N2通入条件在5 ℃·min−1的升温环境中升温至500 ℃,保持2 h后将热解产物用超纯水洗涤以去除灰分,然后在60 ℃的真空干燥箱中干燥24 h,待自然降温后,研磨、过筛,保存于棕色试剂瓶中,标记为原始生物炭。将氨基官能团负载于原始生物炭上的具体方法为:冰水浴条件下,向圆底烧瓶中缓慢加入浓硫酸和浓硝酸,不断搅拌10 min后加入生物炭,并继续搅拌2 h。待冷却至室温后抽滤,用超纯水和乙醇反复洗涤至中性,再将得到的固体在75 ℃条件下烘干至恒重。称取一定量上述反应后的生物炭放入500 mL烧杯中,加入2.9 mol·L−1氨水和去离子水不断搅拌,接着加入硫代硫酸钠并继续搅拌1 h,再加入冰醋酸加热至80 ℃,升温回流数小时后再次抽滤。最后,用超纯水和乙醇反复洗涤直至中性,将得到的固体冷冻干燥2—3 d后所得样品即为氨基生物炭。
参考黄艳虹、王淑娟等[10, 14]方法,测定氨基修饰前后生物炭样品的理化性质,发现氨基生物炭的表面官能团含量、亲水性、芳香性、极性均较原始生物炭有所提高,比表面积及孔容度较原始生物炭增大了61%和6.5倍左右,氨基生物炭的表面性质得到了一定程度的改善,吸附性能显著增强。
-
模拟湖泊环境中的沉积物样品采集于北京农学院校内荷花池0—10 cm的表层沉积物。将取回的沉积物自然风干后研磨,过0.25 mm筛后保存于棕色试剂瓶中备用。根据研究数据统计,我国水系沉积物中的铜、铅含量平均值为21 mg·kg−1和25 mg·kg−1[15],国内外高污染湖泊沉积物中的重金属浓度范围在2000—8000 mg·kg−1[16-17]。为探究氨基生物炭应用于重金属高污染沉积物中的实际修复效果,将沉积物的污染浓度控制于5000 mg·kg−1,即在2.2 kg的沉积物样品中缓慢加入32.3 g的硝酸铜溶液与17.6 g的硝酸铅溶液,搅拌混合12 h,待其充分混匀后自然风干、陈化2 d。沉积物中铜、铅全量的测定方法参见GB17378.5—1998,取0.1 g沉积物样品用体积比为3∶1∶1的HNO3、HCl和HF溶液进行消解至清澈后转移至电热板上赶出剩余HF,随后用0.01 mol·L−1稀HNO3溶液将样品洗入容量瓶中,最终用火焰原子吸收分光光度法测定其加标前沉积物中铜、铅的含量分别为9.6 mg·kg−1和12.1 mg·kg−1,位于我国水系沉积物中铜、铅含量的平均值以下;加标后沉积物中铜、铅的含量分别为3940.8 mg·kg−1和5410.8 mg·kg−1,位于高污染湖泊沉积物中重金属实际浓度的范围区间,可以较好地模拟湖泊沉积物重金属污染的控制研究。依据中华人民共和国海洋沉积物质量标准(GB18668—2002),本研究所采集的沉积物质量标准属于第一类,污染后沉积物中的重金属离子浓度超出三类标准。
-
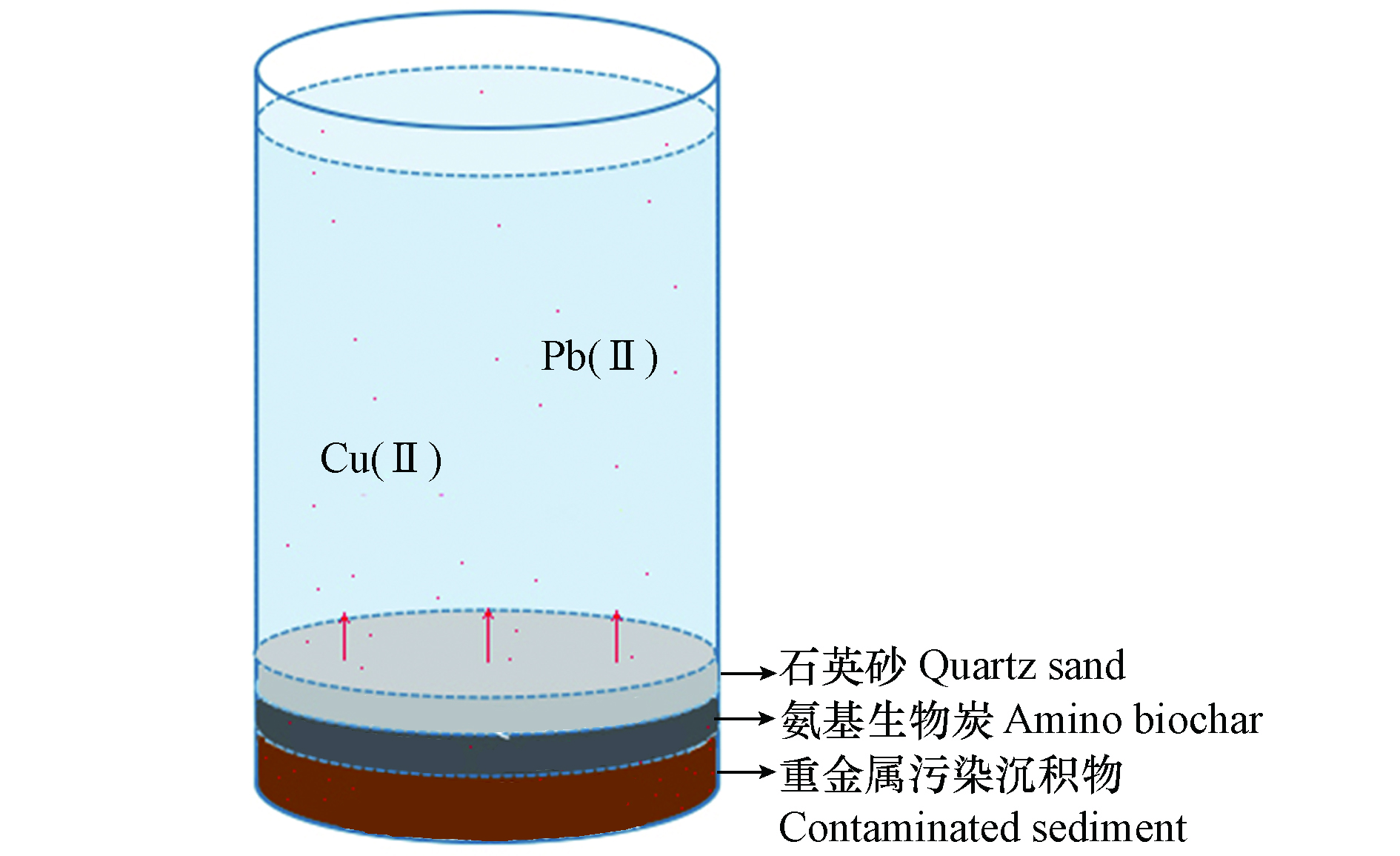
在实验开始前将所有的器皿和工具浸泡在次氯酸钠消毒剂中灭菌,玻璃仪器用去离子水洗涤后在90 ℃下烘干6 h冷却待用。随后称取37.5 g的污染沉积物平铺于250 mL烧杯底部,缓慢加入12 mL的去离子水浸润。为研究氨基生物炭覆盖与否对重金属铜、铅释放的影响,在污染沉积物的上方均匀平铺、覆盖0%和5%添加量的氨基生物炭,量取覆盖厚度并做好记录,然后缓慢加入8 mL的去离子水于生物炭表面以减少生物炭扬起,之后在生物炭表面覆盖25 g的石英砂以防止生物炭漂浮。最后缓慢的加入上覆去离子水至250 mL刻度线,具体实验示意图如图1所示。为研究上覆水pH对氨基生物炭修复效果的影响,研究使用0.01 mol·L−1的HNO3溶液和0.01 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液调节上覆水pH值分别在5、7、9的范围内,每24 h测定1次上覆水溶液的pH值使其达到目标pH。将所有填充好的烧杯用锡纸包裹覆盖,整齐摆放于100 r·min−1,25 ℃条件下的恒温震荡摇床内,以避免外部环境的影响,并保持水体湍流,促进传质。
自实验起始日起的第1 天、第3 天、第5 天,第10 天和第19 天的同一时间点采用主动采样法从每个烧杯中吸取5 mL上清液,加入0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3酸化,然后通过0.22 μm滤膜过滤,最终用原子吸收分光光度计(AAS,AA-6300,Shimadzu,日本)测定溶液中的Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)浓度。由于取样与蒸发导致的水量降低,每日需添加额外的去离子水以保持烧杯中的水位在指定高度。上述每个实验均设置3个平行,结果取平均值,数据采用Excel分析,Origin Pro 2015作图。
-
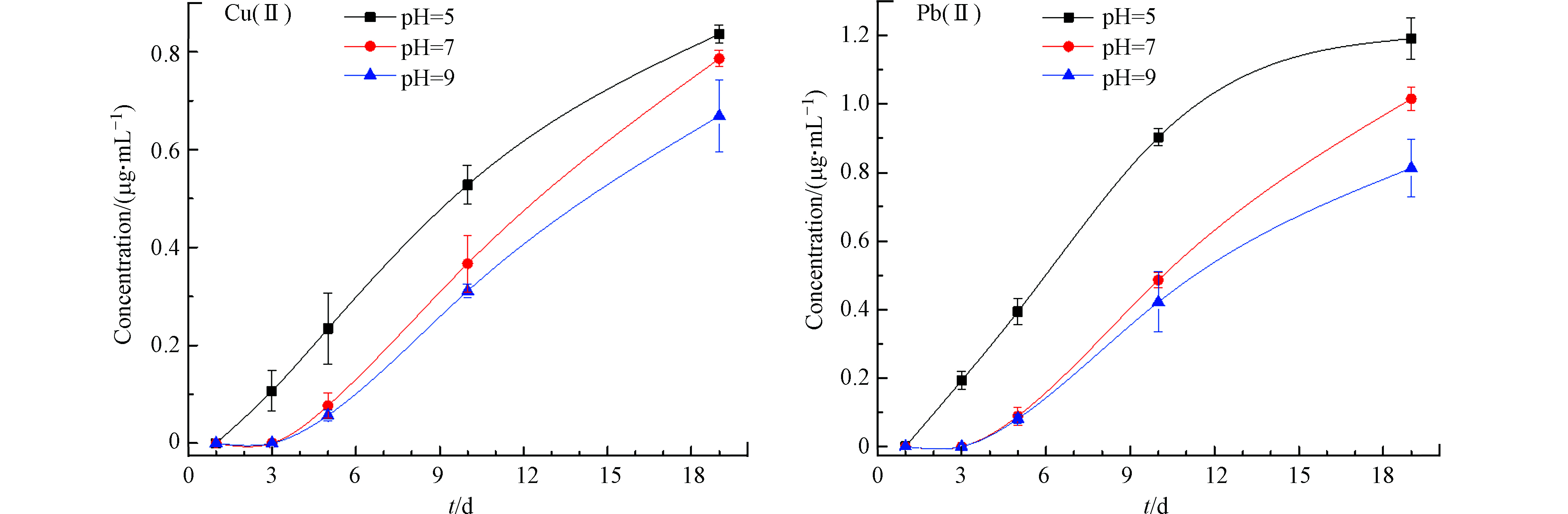
水体酸碱度是影响沉积物中重金属吸附、解吸、沉淀与溶解平衡的主要因素。图2为不同pH上覆水中重金属浓度的时间变化趋势,随着时间的推移,上覆水中的重金属含量均逐渐升高;水体中的重金属释放浓度随pH的降低而增多,pH=5的湖泊水环境中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)含量为pH=9环境下的1.25—2.14倍,酸性环境中的重金属释放浓度始终处于较高水平。此外,由于不同pH水体中的重金属离子赋存形态不同,对沉积物中重金属离子的迁移、转化及其生物有效性将具有重大影响[18]。已有研究表明,在pH<6的自然水体中铜、铅主要以Cu2+和Pb2+的形态存在;6<pH<12时主要以Cu(OH)+、Cu3(OH)42+、Cu(OH)2和Pb(OH)+、Pb3(OH)42+、Pb(OH)2的形态存在,且pH>7.7时,Cu(OH)2和Pb(OH)2开始形成;pH>12时主要以Cu(OH)3−和Pb(OH)3−的形态存在[19-20]。研究证明,水体pH会影响铜、铅的赋存形态,进而影响其在上覆水中的释放量。pH=5的酸性水环境中,重金属的溶解度较大,同时大量的H+会以竞争吸附的形式占据重金属离子在沉积物中的吸附位点,使吸附量减小,从而增大了重金属的释放能力,导致沉积物中的Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)有不断向上覆水中扩散的趋势[21]。而在pH=9的碱性水环境中,OH−易与重金属离子发生络合沉淀反应,水体中的颗粒态重金属含量增加,且在该条件下容易抑制生物炭的吸附效果,干扰对生物炭吸附效果的正确判断[22];在pH=7的中性水环境中,既含有大量的Cu(Ⅱ)与Pb(Ⅱ),同时也不会有过量的H+来竞争氨基生物炭的吸附点位,此时最有利于原位修复技术的实施,这与李仁英等[23]得出重金属释放量随上覆水pH值的减小而增大及Mohan等[19]关于生物炭的最佳吸附条件为pH=7的研究结果相一致。
-
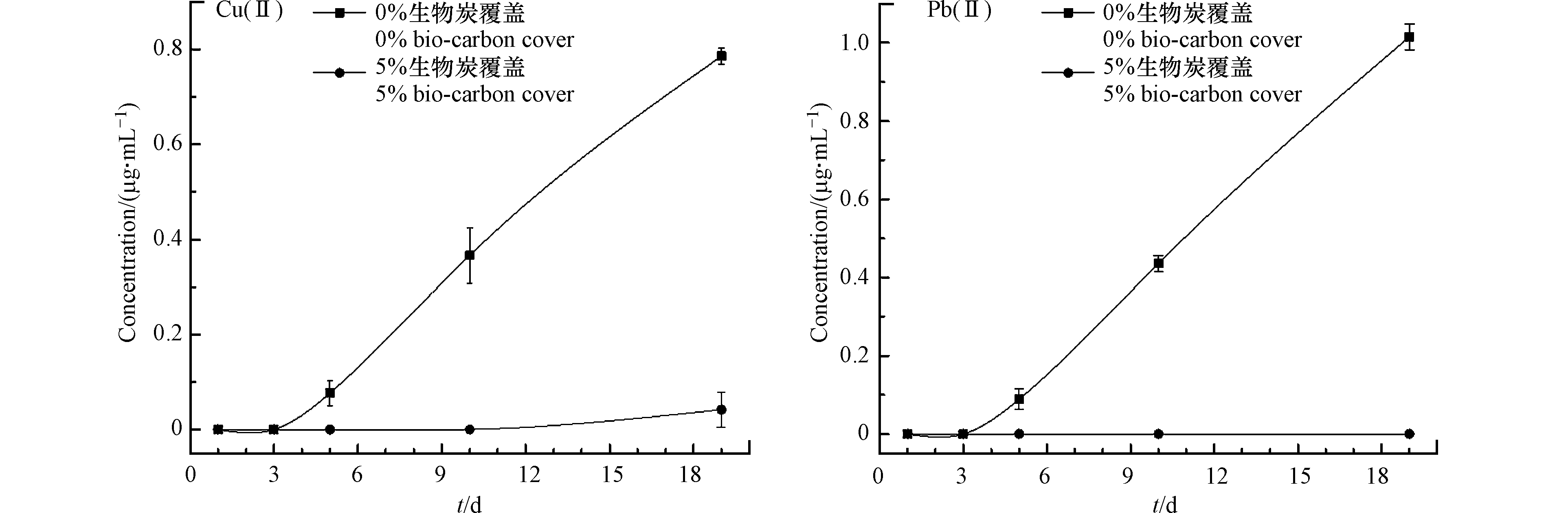
生物炭的覆盖厚度对污染物的阻隔、吸附具有关键作用。由于大多数湖泊水环境的pH接近为中性及弱碱性[24],且基于pH 7的上覆水模拟自然湖泊水环境,可以有效避免pH值对水环境中重金属离子赋存形态与氨基生物炭吸附能力的影响。故本研究针对高浓度重金属污染的沉积物及pH=7的上覆水环境,研究了氨基生物炭覆盖与否下重金属释放量的时间变化趋势,如图3所示。对比2种不同氨基生物炭覆盖量下沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放规律发现,0%氨基生物炭覆盖的情况下,上覆水中的重金属离子浓度随时间变化明显增多,可见沉积物中的重金属离子在不断地向上覆水中释放;5%氨基生物炭覆盖的环境下,上覆水中的Cu(Ⅱ)只有在第19天时有检出,且浓度仅为0.042 μg·mL−1,而Pb(Ⅱ)始终为0 μg·mL−1,有效降低了沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量达0.744—1.015 μg·mL−1。这表明氨基生物炭对沉积物中的重金属起到了明显的阻隔、吸附和抑制扩散的作用,从而使得Cu(Ⅱ)与Pb(Ⅱ)的释放量得到有效控制。此外,研究将第19天时有低浓度Cu(Ⅱ)检出的原因概括有二,一是由于实验过程中的水流扰动导致氨基生物炭发生浮动,以至于污染物贯通通道进入上覆水中;二是由于Cu(Ⅱ)与Pb(Ⅱ)在氨基生物炭界面中相互竞争结合位点,导致氨基生物炭对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附受到影响。基于上述结果,研究得出氨基生物炭可以阻隔沉积物中的细小通道,对沉积物中释放的重金属离子进行有效吸附,降低上覆水中的重金属离子浓度,且足够的厚度能防止覆盖材料的细小颗粒在水流扰动的作用下四处浮动,从而降低污染物贯穿通道的可能[25]。其吸附固化机理可解释为,氨基生物炭表面官能基团、矿物质成分、电荷及电离质子与环境介质中的重金属离子发生的静电作用、络合沉淀和离子交换反应的综合作用,以及其表面结构与重金属离子发生的物理吸附[10]。
-
通过模拟实验,本研究得出上覆水pH对重金属污染沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放具有明显影响,氨基生物炭在Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程中起到了关键控制作用。然而,污染物由沉积物释放到水体,再到最后的浓度检出具有一定的潜伏期,且释放过程复杂[26]。因此,开展氨基生物炭覆盖污染沉积物后的重金属释放动力学研究,对风险评估与治理决策具有重要意义。本研究主要采用零级动力学方程和Elovich方程对沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程进行了动力学拟合,结果如表1和表2所示,详细公式参数如下[27]:
零级动力学方程:
式中,Ct是某时间点上覆水中重金属离子的浓度值,μg·mL−1;t是指时间,d;k是基于污染物数量的速率常数。
Elovich方程:
式中,Ct是某时间点上覆水中重金属离子的浓度值,μg·mL−1;t是指时间,d;a和b分别是基于实验得出的常数。
当无氨基生物炭覆盖,且100 r·min−1水流扰动作用时,关于沉积物中重金属离子释放量与上覆水pH关系的动力学拟合结果如表1所示,对比拟合度大小可以得知,零级动力学方程与Elovich方程相比能更好的拟合Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放过程。从水体pH对拟合程度的影响来看,在pH=5的条件下,零级动力学方程与Elovich方程均能对Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程进行较好的动力学拟合,而pH=7和pH=9条件下的拟合效果相对较差。这种现象可能是由于重金属离子与沉积物表面产生的络合作用因碱性环境下H+的减少而得到促进,阻碍了正常的扩散行为,进而导致偏离扩散方程。氨基生物炭覆盖量对沉积物中重金属离子释放的动力学拟合结果如表2所示,比较方程间的拟合度关系可知,零级动力学方程比Elovich方程的拟合效果更佳,但在5%氨基生物炭覆盖环境下,Cu(Ⅱ)的零级动力学方程拟合度R2仅为0.6598,拟合效果远次于无氨基生物炭添加的样品结果。这说明在无氨基生物炭覆盖材料的阻隔、吸附作用下,污染物的释放速率相对更快,其释放速率只取决于沉积物与上覆水中的重金属离子浓度差。另需说明的是,由于氨基生物炭对重金属离子的阻隔、吸附作用使得Pb(Ⅱ)的释放量均为0 μg·mL−1,故无法得出相关拟合数据。最终研究结果显示,在无氨基生物炭覆盖下的水环境中可采用零级动力学方程对重金属的释放过程进行动力学拟合,预测从受污染沉积物扩散到上覆水中的Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量,从而为湖泊重金属污染防治提供一个可靠的行动指南。
-
重金属是一种难以降解,并具有一定持久性的环境污染物,其可以通过呼吸道、消化道和皮肤等各种途径进入人体体内,当累积到一定程度时会对人体健康产生危害,影响人体的神经系统和生长发育[5]。近年来,随着人类工农业活动的加剧,现代化和城市化水平的提高给湖泊水生态系统造成了严重污染,大量的重金属污染物伴随废水排放、大气沉降和地质构造活动等途径进入湖泊环境,并在湖泊沉积物中残留、累积、释放、迁移、转化,从而导致水质下降,对水生生态系统具有潜在威胁[6, 28]。
本研究选用单因子水质标准比较法[29],参照地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002),对模拟湖泊环境中铜、铅的污染现状进行了评价。通过采用USEPA推荐的健康风险评价模型,围绕重金属污染物在饮水消化吸收和皮肤接触吸收两种途径下对人体的健康风险进行了评价[30]。根据国际癌症研究机构(IARC)和世界卫生组织(WHO)编制的分类系统,铜、铅属于化学非致癌物质,模型中饮水消化和皮肤接触两种吸收途径的健康风险系数按照下列公式计算:
式中,HQin为非致癌物经饮水途径所致健康危害的个人平均年风险,a−1;HQd为非致癌物经皮肤接触途径所致健康危害的个人平均年风险,a−1;铜、铅通过饮水消化途径暴露的非致癌物质参考剂量RfDin分别为0.0050 mg·kg−1·d−1和0.0014 mg·kg−1·d−1;通过皮肤接触途径暴露的非致癌物质参考剂量RfDd mg·kg−1·d−1为RfDin·ABSg[29],ABSg是肠胃消化吸收因子,取1;Cw是水体中重金属的平均浓度,mg·L−1;IR是摄入频率,取2.2 l·d−1;BW是平均体重,取60 kg;L是人均寿命,取70 a;I为每次洗澡时皮肤对污染物的吸附量,mg·cm−2·次−1;Asb是皮肤接触面积,取16600 cm2;FE是洗澡频率,取0.3 次·d−1;EF是暴露频率,取365 d·a−1;ED是暴露延时,取35 a;AT是终身暴露时间,取12775 d;f是肠道吸附比率,取1;K是皮肤渗透系数,取0.001 cm·h−1;t是延滞时间,取1 h;TE是洗浴时间,取0.4 h·次−1。以上取值参考潘莎等[30]的相关研究。
根据单因子水质标准比较法,以及USEPA推荐的健康风险评价模型与相关评价参数,计算出不同氨基生物炭覆盖量下铜、铅的释放风险评价指标,如表3所示。将本研究中的水体重金属浓度值与地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002)相对比得出,0%氨基生物炭覆盖量下的沉积物释放至水体中的Cu(Ⅱ)浓度(0.786 μg·mL−1)接近可接受的国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值(≤1.0 μg·mL−1),Pb(Ⅱ)浓度(1.015 μg·mL−1)远高于国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值(≤0.05 μg·mL−1),这表明无氨基生物炭覆盖下的Cu(Ⅱ)释放量可能会威胁到一般水系,Pb(Ⅱ)释放量则已经严重影响到一般水系,并可能对人体健康造成一定危害。不同吸收途径下,铜、铅通过皮肤接触途径对人体健康所造成的危害远小于通过饮水途径所造成的危害(1.83×10−9 a−1<4.62×10−7 a−1),其中铅引起的个人健康风险大于铜。对于非致癌风险,一般认为风险指数超过1时会对人体健康产生危害[29],从表3可以看出,各项风险指数均远小于1,可认为模拟湖泊环境中的重金属污染物短期内不会对人体造成健康风险,但是随着环境中重金属污染物累积量的与日俱增,目前的非致癌风险值仍需引起人们的警惕。当生物炭覆盖量增加至5%时,Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量分别为0.042 μg·mL−1和0 μg·mL−1,水体中的重金属离子浓度显著低于国家标准值,非致癌风险指数下降2个数量级,这表明原位覆盖一定量的氨基生物炭可以切实保证湖泊水环境的安全。综上所述,以氨基生物炭为覆盖材料的原位修复技术可以通过吸附、沉淀、配合等方式抑制受污染沉积物中重金属离子的释放,从而降低上覆水中的重金属离子浓度,减小重金属污染对人体的危害风险,有效的实现了重金属污染防治。
改性生物炭为覆盖材料的原位修复技术,因其成本低廉、性质稳定且不易对生态系统造成干扰的特点而被视为具有广阔应用前景的环境修复技术之一[10]。现已有通过围挡方式,利用自制炭铺洒装置进行生物炭的水体原位修复技术中试试验的成功案例[31]。本研究中,采用自制氨基生物炭,于室内模拟环境下对沉积物中铜、铅的释放规律与氨基生物炭的修复效果展开了系统地探索,研究结论对高污染湖泊沉积物的修复治理具有重要参考价值。然而,目前氨基生物炭的原位修复技术仍是一个崭新的研究领域,尤其是生物炭的铺设、沉积与二次回收,以及野外环境下的中试试验与示范工程的实际应用效果等问题还有待进一步深入探讨与验证。
-
(1)沉积物中的重金属离子在模拟环境下的自然湖泊水中呈现不断向上覆水中扩散的趋势。是否覆盖氨基生物炭,沉积物中重金属的释放过程均符合零级动力学方程,其中无氨基生物炭覆盖下的零级动力学方程拟合度R2可达0.9以上。pH=5的湖泊水环境中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)含量为pH=9环境下的1.25—2.14倍,pH=7的中性水环境下最有利于原位修复技术的实施。
(2)5%的氨基生物炭覆盖量可通过吸附、沉淀、配合等方式安全地确保Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量低于国家标准值,并将湖泊环境中的重金属非致癌风险值降低2个数量级,明显抑制了Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放效果,大大降低了上覆水中的重金属离子浓度,对湖泊重金属的污染防治与健康风险防范具有重要作用。
氨基生物炭覆盖对沉积物中铜、铅释放的影响
Effect of amino biochar cover on copper and lead release in sediments
-
摘要: 沉积物是湖泊重金属污染物的源与汇,原位控制沉积物中重金属污染物的二次释放一直是研究关注的热点问题。本研究采用氨基生物炭对重金属污染沉积物进行原位覆盖,研究了不同水体酸碱度下Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放规律与氨基生物炭原位覆盖对重金属污染沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放控制效果,并采用零级动力学方程和Elovich方程对Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程进行了动力学拟合,采用单因子水质标准比较法和USEPA的健康风险评价模型对模拟湖泊水体中重金属的污染情况与健康风险进行了评价。研究结果表明,5%的氨基生物炭可降低沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量达0.744—1.015 μg·mL−1,有效减小了水体重金属的污染水平与健康风险;是否覆盖氨基生物炭,沉积物中重金属的释放过程均符合零级动力学方程;当水体pH=7时,更有利于氨基生物炭原位修复技术的实施。Abstract: Sediment is the source and sink of heavy metals contaminants in lakes. It is of growing concern for the in-situ control of the secondary release of heavy metals from contaminated sediments. In this study, the lake sediment-water environment was simulated, amino modified biochar was used as the covering material, the release law of Cu(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) from sediment to water was explored with different pH, the in-situ control effects of amino biochar coverage on Cu(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) in sediments were also evaluated. In addition, the kinetic fitting of the release process of Cu(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) were performed using zero order equation and Elovich equation, the pollution status and health risk of heavy metals in water were evaluated by single factor water quality comparison method and USEPA’s health risk assessment model. The results showed that 5% amino biochar could effectively inhibit the release of Cu(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) in sediments by 0.744—1.015 μg·mL−1 and reduce the pollution level and health risk of heavy metals in water. No matter whether the amino biochar was covered, the release process of heavy metals conformed to zero order equation. When the overlying water was in neutral condition, it was beneficial to the in-situ remediation of amino biochar coverage.
-
Key words:
- Cu(Ⅱ) /
- Pb(Ⅱ) /
- lake /
- amino modification of biochar /
- in-situ remediation
-
沉积物作为湖泊生态系统的重要组成部分,累积了大量污染物质[1]。随着经济的快速发展,工农业废水与生活污水大量排放,重金属污染已成为湖泊的重要生态环境问题之一[2]。重金属在湖泊沉积物中的残留、释放、迁移和转化,极易造成水体的二次污染[2-3],且因其本身所具有的持久性、生物累积性及食物链放大性等特性[4-5],对水生动植物的生长发育及人类健康具有潜在威胁[5-6]。根据已有文献报道,水体沉积物中铜、铅的污染范围最广[7],在中国主要淡水湖泊沉积物中的被检出频次达60次以上[8],其平均浓度在所有重金属中排名前列[9]。因此,如何降低或防止沉积物中铜、铅等重金属离子的二次释放已成为环境污染治理的研究热点。
近年来,国内外研究学者对湖泊沉积物的重金属污染问题展开了许多有益的探索与研究。结果显示,以生物炭为覆盖材料的原位修复技术,因其成本低廉,性质稳定且不易对生态系统造成干扰的特点而比其他修复方法更受欢迎[10]。此外,经过化学修饰后的改性生物炭会比原始生物炭更具吸附活性[11],且氨基的负载将有助于生物炭表面对其他官能团的锚定[12]。马天行等[13]通过化学负载法制备纳米零价铁改性氨基生物炭提高了对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附性能,Yang等[12]报道了氨基改性生物炭对废水中Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附能力提高了5—8倍。但是,目前将氨基生物炭直接应用于沉积物中重金属污染控制的研究仍相对较少,且多围绕于单一离子的吸附,而复合重金属污染环境其实更能真实的反映自然条件下重金属的协同、竞争状态。
基于此,本研究以沉积物中污染问题突出且具有代表性的重金属铜、铅作为研究对象,通过酸碱改性法对原始生物炭进行氨基修饰,在高浓度重金属污染沉积物中开展氨基生物炭原位覆盖处理,结合传统化学提取法,研究不同水体酸碱度下Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放规律与氨基生物炭原位覆盖对高污染沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的修复效果,并采用零级动力学方程和Elovich方程对沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放动力学进行拟合,采用单因子水质标准比较法和USEPA的健康风险评价模型对模拟湖泊水体中重金属的污染情况与健康风险进行评价。以期为高污染湖泊沉积物的修复治理提供理论基础与数据支撑,对环境风险调控具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 氨基生物炭的制备及其理化性质
本研究氨基生物炭的制备方法基于王淑娟等[14]的试验方案,选取安徽省淮南市郊区农村的低成本稻壳为本研究的生物质原料,将收集好的稻壳用去离子水洗净后放置于60 ℃的干燥箱中烘干至恒重,随后把烘干好的稻壳装入平底瓷轴,放入管式炉中以2 mL·min−1的N2通入条件在5 ℃·min−1的升温环境中升温至500 ℃,保持2 h后将热解产物用超纯水洗涤以去除灰分,然后在60 ℃的真空干燥箱中干燥24 h,待自然降温后,研磨、过筛,保存于棕色试剂瓶中,标记为原始生物炭。将氨基官能团负载于原始生物炭上的具体方法为:冰水浴条件下,向圆底烧瓶中缓慢加入浓硫酸和浓硝酸,不断搅拌10 min后加入生物炭,并继续搅拌2 h。待冷却至室温后抽滤,用超纯水和乙醇反复洗涤至中性,再将得到的固体在75 ℃条件下烘干至恒重。称取一定量上述反应后的生物炭放入500 mL烧杯中,加入2.9 mol·L−1氨水和去离子水不断搅拌,接着加入硫代硫酸钠并继续搅拌1 h,再加入冰醋酸加热至80 ℃,升温回流数小时后再次抽滤。最后,用超纯水和乙醇反复洗涤直至中性,将得到的固体冷冻干燥2—3 d后所得样品即为氨基生物炭。
参考黄艳虹、王淑娟等[10, 14]方法,测定氨基修饰前后生物炭样品的理化性质,发现氨基生物炭的表面官能团含量、亲水性、芳香性、极性均较原始生物炭有所提高,比表面积及孔容度较原始生物炭增大了61%和6.5倍左右,氨基生物炭的表面性质得到了一定程度的改善,吸附性能显著增强。
1.2 污染沉积物的制备及其理化特征
模拟湖泊环境中的沉积物样品采集于北京农学院校内荷花池0—10 cm的表层沉积物。将取回的沉积物自然风干后研磨,过0.25 mm筛后保存于棕色试剂瓶中备用。根据研究数据统计,我国水系沉积物中的铜、铅含量平均值为21 mg·kg−1和25 mg·kg−1[15],国内外高污染湖泊沉积物中的重金属浓度范围在2000—8000 mg·kg−1[16-17]。为探究氨基生物炭应用于重金属高污染沉积物中的实际修复效果,将沉积物的污染浓度控制于5000 mg·kg−1,即在2.2 kg的沉积物样品中缓慢加入32.3 g的硝酸铜溶液与17.6 g的硝酸铅溶液,搅拌混合12 h,待其充分混匀后自然风干、陈化2 d。沉积物中铜、铅全量的测定方法参见GB17378.5—1998,取0.1 g沉积物样品用体积比为3∶1∶1的HNO3、HCl和HF溶液进行消解至清澈后转移至电热板上赶出剩余HF,随后用0.01 mol·L−1稀HNO3溶液将样品洗入容量瓶中,最终用火焰原子吸收分光光度法测定其加标前沉积物中铜、铅的含量分别为9.6 mg·kg−1和12.1 mg·kg−1,位于我国水系沉积物中铜、铅含量的平均值以下;加标后沉积物中铜、铅的含量分别为3940.8 mg·kg−1和5410.8 mg·kg−1,位于高污染湖泊沉积物中重金属实际浓度的范围区间,可以较好地模拟湖泊沉积物重金属污染的控制研究。依据中华人民共和国海洋沉积物质量标准(GB18668—2002),本研究所采集的沉积物质量标准属于第一类,污染后沉积物中的重金属离子浓度超出三类标准。
1.3 原位覆盖实验
在实验开始前将所有的器皿和工具浸泡在次氯酸钠消毒剂中灭菌,玻璃仪器用去离子水洗涤后在90 ℃下烘干6 h冷却待用。随后称取37.5 g的污染沉积物平铺于250 mL烧杯底部,缓慢加入12 mL的去离子水浸润。为研究氨基生物炭覆盖与否对重金属铜、铅释放的影响,在污染沉积物的上方均匀平铺、覆盖0%和5%添加量的氨基生物炭,量取覆盖厚度并做好记录,然后缓慢加入8 mL的去离子水于生物炭表面以减少生物炭扬起,之后在生物炭表面覆盖25 g的石英砂以防止生物炭漂浮。最后缓慢的加入上覆去离子水至250 mL刻度线,具体实验示意图如图1所示。为研究上覆水pH对氨基生物炭修复效果的影响,研究使用0.01 mol·L−1的HNO3溶液和0.01 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液调节上覆水pH值分别在5、7、9的范围内,每24 h测定1次上覆水溶液的pH值使其达到目标pH。将所有填充好的烧杯用锡纸包裹覆盖,整齐摆放于100 r·min−1,25 ℃条件下的恒温震荡摇床内,以避免外部环境的影响,并保持水体湍流,促进传质。
自实验起始日起的第1 天、第3 天、第5 天,第10 天和第19 天的同一时间点采用主动采样法从每个烧杯中吸取5 mL上清液,加入0.01 mol·L−1 HNO3酸化,然后通过0.22 μm滤膜过滤,最终用原子吸收分光光度计(AAS,AA-6300,Shimadzu,日本)测定溶液中的Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)浓度。由于取样与蒸发导致的水量降低,每日需添加额外的去离子水以保持烧杯中的水位在指定高度。上述每个实验均设置3个平行,结果取平均值,数据采用Excel分析,Origin Pro 2015作图。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 上覆水pH对重金属的释放影响
水体酸碱度是影响沉积物中重金属吸附、解吸、沉淀与溶解平衡的主要因素。图2为不同pH上覆水中重金属浓度的时间变化趋势,随着时间的推移,上覆水中的重金属含量均逐渐升高;水体中的重金属释放浓度随pH的降低而增多,pH=5的湖泊水环境中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)含量为pH=9环境下的1.25—2.14倍,酸性环境中的重金属释放浓度始终处于较高水平。此外,由于不同pH水体中的重金属离子赋存形态不同,对沉积物中重金属离子的迁移、转化及其生物有效性将具有重大影响[18]。已有研究表明,在pH<6的自然水体中铜、铅主要以Cu2+和Pb2+的形态存在;6<pH<12时主要以Cu(OH)+、Cu3(OH)42+、Cu(OH)2和Pb(OH)+、Pb3(OH)42+、Pb(OH)2的形态存在,且pH>7.7时,Cu(OH)2和Pb(OH)2开始形成;pH>12时主要以Cu(OH)3−和Pb(OH)3−的形态存在[19-20]。研究证明,水体pH会影响铜、铅的赋存形态,进而影响其在上覆水中的释放量。pH=5的酸性水环境中,重金属的溶解度较大,同时大量的H+会以竞争吸附的形式占据重金属离子在沉积物中的吸附位点,使吸附量减小,从而增大了重金属的释放能力,导致沉积物中的Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)有不断向上覆水中扩散的趋势[21]。而在pH=9的碱性水环境中,OH−易与重金属离子发生络合沉淀反应,水体中的颗粒态重金属含量增加,且在该条件下容易抑制生物炭的吸附效果,干扰对生物炭吸附效果的正确判断[22];在pH=7的中性水环境中,既含有大量的Cu(Ⅱ)与Pb(Ⅱ),同时也不会有过量的H+来竞争氨基生物炭的吸附点位,此时最有利于原位修复技术的实施,这与李仁英等[23]得出重金属释放量随上覆水pH值的减小而增大及Mohan等[19]关于生物炭的最佳吸附条件为pH=7的研究结果相一致。
2.2 氨基生物炭对重金属的修复效果
生物炭的覆盖厚度对污染物的阻隔、吸附具有关键作用。由于大多数湖泊水环境的pH接近为中性及弱碱性[24],且基于pH 7的上覆水模拟自然湖泊水环境,可以有效避免pH值对水环境中重金属离子赋存形态与氨基生物炭吸附能力的影响。故本研究针对高浓度重金属污染的沉积物及pH=7的上覆水环境,研究了氨基生物炭覆盖与否下重金属释放量的时间变化趋势,如图3所示。对比2种不同氨基生物炭覆盖量下沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放规律发现,0%氨基生物炭覆盖的情况下,上覆水中的重金属离子浓度随时间变化明显增多,可见沉积物中的重金属离子在不断地向上覆水中释放;5%氨基生物炭覆盖的环境下,上覆水中的Cu(Ⅱ)只有在第19天时有检出,且浓度仅为0.042 μg·mL−1,而Pb(Ⅱ)始终为0 μg·mL−1,有效降低了沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量达0.744—1.015 μg·mL−1。这表明氨基生物炭对沉积物中的重金属起到了明显的阻隔、吸附和抑制扩散的作用,从而使得Cu(Ⅱ)与Pb(Ⅱ)的释放量得到有效控制。此外,研究将第19天时有低浓度Cu(Ⅱ)检出的原因概括有二,一是由于实验过程中的水流扰动导致氨基生物炭发生浮动,以至于污染物贯通通道进入上覆水中;二是由于Cu(Ⅱ)与Pb(Ⅱ)在氨基生物炭界面中相互竞争结合位点,导致氨基生物炭对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附受到影响。基于上述结果,研究得出氨基生物炭可以阻隔沉积物中的细小通道,对沉积物中释放的重金属离子进行有效吸附,降低上覆水中的重金属离子浓度,且足够的厚度能防止覆盖材料的细小颗粒在水流扰动的作用下四处浮动,从而降低污染物贯穿通道的可能[25]。其吸附固化机理可解释为,氨基生物炭表面官能基团、矿物质成分、电荷及电离质子与环境介质中的重金属离子发生的静电作用、络合沉淀和离子交换反应的综合作用,以及其表面结构与重金属离子发生的物理吸附[10]。
2.3 重金属的释放动力学研究
通过模拟实验,本研究得出上覆水pH对重金属污染沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放具有明显影响,氨基生物炭在Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程中起到了关键控制作用。然而,污染物由沉积物释放到水体,再到最后的浓度检出具有一定的潜伏期,且释放过程复杂[26]。因此,开展氨基生物炭覆盖污染沉积物后的重金属释放动力学研究,对风险评估与治理决策具有重要意义。本研究主要采用零级动力学方程和Elovich方程对沉积物中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程进行了动力学拟合,结果如表1和表2所示,详细公式参数如下[27]:
表 1 上覆水pH对重金属离子释放的动力学拟合Table 1. Kinetic fitting of the release of heavy metal ions by water-covered pH重金属离子Heavy metal ion 扰动强度Hydrodynamic 生物炭覆盖量Biochar coverage pH 零级动力学方程Zero-order kinetic equation Elovich方程Elovich equation R2 k R2 a b Cu(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 5 0.9803 0.0456 0.8978 −0.1141 0.2853 7 0.9263 0.0382 0.7489 −0.1687 0.2594 9 0.9227 0.0324 0.7441 −0.1448 0.2206 Pb(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 5 0.9310 0.0691 0.9312 −0.1364 0.4239 7 0.9262 0.0495 0.7515 −0.2186 0.3367 9 0.9314 0.0404 0.7679 −0.1739 0.2743 表 2 氨基生物炭覆盖量对重金属离子释放的动力学拟合Table 2. Kinetic fitting of heavy metal ion release by amino biochar coverage重金属离子Heavy metal ion 扰动强度Hydrodynamic 生物炭覆盖量Biochar coverage pH 零级动力学方程Zero-order kinetic equation Elovich方程Elovich equation R2 k R2 a b Cu(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 7 0.9263 0.0382 0.7489 −0.1687 0.2594 5% 0.6598 0.0016 0.4479 −0.0093 0.0111 Pb(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 7 0.9262 0.0495 0.7515 −0.2186 0.3367 5% ND ND ND ND ND 零级动力学方程:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 式中,Ct是某时间点上覆水中重金属离子的浓度值,μg·mL−1;t是指时间,d;k是基于污染物数量的速率常数。
Elovich方程:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 式中,Ct是某时间点上覆水中重金属离子的浓度值,μg·mL−1;t是指时间,d;a和b分别是基于实验得出的常数。
当无氨基生物炭覆盖,且100 r·min−1水流扰动作用时,关于沉积物中重金属离子释放量与上覆水pH关系的动力学拟合结果如表1所示,对比拟合度大小可以得知,零级动力学方程与Elovich方程相比能更好的拟合Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放过程。从水体pH对拟合程度的影响来看,在pH=5的条件下,零级动力学方程与Elovich方程均能对Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放过程进行较好的动力学拟合,而pH=7和pH=9条件下的拟合效果相对较差。这种现象可能是由于重金属离子与沉积物表面产生的络合作用因碱性环境下H+的减少而得到促进,阻碍了正常的扩散行为,进而导致偏离扩散方程。氨基生物炭覆盖量对沉积物中重金属离子释放的动力学拟合结果如表2所示,比较方程间的拟合度关系可知,零级动力学方程比Elovich方程的拟合效果更佳,但在5%氨基生物炭覆盖环境下,Cu(Ⅱ)的零级动力学方程拟合度R2仅为0.6598,拟合效果远次于无氨基生物炭添加的样品结果。这说明在无氨基生物炭覆盖材料的阻隔、吸附作用下,污染物的释放速率相对更快,其释放速率只取决于沉积物与上覆水中的重金属离子浓度差。另需说明的是,由于氨基生物炭对重金属离子的阻隔、吸附作用使得Pb(Ⅱ)的释放量均为0 μg·mL−1,故无法得出相关拟合数据。最终研究结果显示,在无氨基生物炭覆盖下的水环境中可采用零级动力学方程对重金属的释放过程进行动力学拟合,预测从受污染沉积物扩散到上覆水中的Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量,从而为湖泊重金属污染防治提供一个可靠的行动指南。
2.4 氨基生物炭覆盖下的重金属释放风险分析
重金属是一种难以降解,并具有一定持久性的环境污染物,其可以通过呼吸道、消化道和皮肤等各种途径进入人体体内,当累积到一定程度时会对人体健康产生危害,影响人体的神经系统和生长发育[5]。近年来,随着人类工农业活动的加剧,现代化和城市化水平的提高给湖泊水生态系统造成了严重污染,大量的重金属污染物伴随废水排放、大气沉降和地质构造活动等途径进入湖泊环境,并在湖泊沉积物中残留、累积、释放、迁移、转化,从而导致水质下降,对水生生态系统具有潜在威胁[6, 28]。
本研究选用单因子水质标准比较法[29],参照地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002),对模拟湖泊环境中铜、铅的污染现状进行了评价。通过采用USEPA推荐的健康风险评价模型,围绕重金属污染物在饮水消化吸收和皮肤接触吸收两种途径下对人体的健康风险进行了评价[30]。根据国际癌症研究机构(IARC)和世界卫生组织(WHO)编制的分类系统,铜、铅属于化学非致癌物质,模型中饮水消化和皮肤接触两种吸收途径的健康风险系数按照下列公式计算:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 式中,HQin为非致癌物经饮水途径所致健康危害的个人平均年风险,a−1;HQd为非致癌物经皮肤接触途径所致健康危害的个人平均年风险,a−1;铜、铅通过饮水消化途径暴露的非致癌物质参考剂量RfDin分别为0.0050 mg·kg−1·d−1和0.0014 mg·kg−1·d−1;通过皮肤接触途径暴露的非致癌物质参考剂量RfDd mg·kg−1·d−1为RfDin·ABSg[29],ABSg是肠胃消化吸收因子,取1;Cw是水体中重金属的平均浓度,mg·L−1;IR是摄入频率,取2.2 l·d−1;BW是平均体重,取60 kg;L是人均寿命,取70 a;I为每次洗澡时皮肤对污染物的吸附量,mg·cm−2·次−1;Asb是皮肤接触面积,取16600 cm2;FE是洗澡频率,取0.3 次·d−1;EF是暴露频率,取365 d·a−1;ED是暴露延时,取35 a;AT是终身暴露时间,取12775 d;f是肠道吸附比率,取1;K是皮肤渗透系数,取0.001 cm·h−1;t是延滞时间,取1 h;TE是洗浴时间,取0.4 h·次−1。以上取值参考潘莎等[30]的相关研究。
根据单因子水质标准比较法,以及USEPA推荐的健康风险评价模型与相关评价参数,计算出不同氨基生物炭覆盖量下铜、铅的释放风险评价指标,如表3所示。将本研究中的水体重金属浓度值与地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002)相对比得出,0%氨基生物炭覆盖量下的沉积物释放至水体中的Cu(Ⅱ)浓度(0.786 μg·mL−1)接近可接受的国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值(≤1.0 μg·mL−1),Pb(Ⅱ)浓度(1.015 μg·mL−1)远高于国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值(≤0.05 μg·mL−1),这表明无氨基生物炭覆盖下的Cu(Ⅱ)释放量可能会威胁到一般水系,Pb(Ⅱ)释放量则已经严重影响到一般水系,并可能对人体健康造成一定危害。不同吸收途径下,铜、铅通过皮肤接触途径对人体健康所造成的危害远小于通过饮水途径所造成的危害(1.83×10−9 a−1<4.62×10−7 a−1),其中铅引起的个人健康风险大于铜。对于非致癌风险,一般认为风险指数超过1时会对人体健康产生危害[29],从表3可以看出,各项风险指数均远小于1,可认为模拟湖泊环境中的重金属污染物短期内不会对人体造成健康风险,但是随着环境中重金属污染物累积量的与日俱增,目前的非致癌风险值仍需引起人们的警惕。当生物炭覆盖量增加至5%时,Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量分别为0.042 μg·mL−1和0 μg·mL−1,水体中的重金属离子浓度显著低于国家标准值,非致癌风险指数下降2个数量级,这表明原位覆盖一定量的氨基生物炭可以切实保证湖泊水环境的安全。综上所述,以氨基生物炭为覆盖材料的原位修复技术可以通过吸附、沉淀、配合等方式抑制受污染沉积物中重金属离子的释放,从而降低上覆水中的重金属离子浓度,减小重金属污染对人体的危害风险,有效的实现了重金属污染防治。
表 3 不同氨基生物炭覆盖量下的重金属释放风险评价指标Table 3. The release risk evaluation index of heavy metals under different amino biochar coverage重金属离子Heavy metal ion 评价指标Evaluation index 0%氨基生物炭覆盖量0% bio-carbon cover 5%氨基生物炭覆盖量5% bio-carbon cover Cu(Ⅱ) 释放量/(μg·mL−1) 0.786 0.042 HQin/a−1 8.23×10−8 4.40×10−9 HQd/a−1 3.26×10−10 1.74×10−11 国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值/(μg·mL−1) ≤1.0 Pb(Ⅱ) 释放量/(μg·mL−1) 1.015 0 HQin/a−1 3.80×10−7 0 HQd/a−1 1.50×10−9 0 国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值/(μg·mL−1) ≤0.05 合计 HQin/a−1 4.62×10−7 4.40×10−9 HQd/a−1 1.83×10−9 1.74×10−11 注:实验环境为100 r·min−1扰动强度,上覆水pH=7,(25±0.5) ℃条件下. Notes: The condition is 100 r·min−1 hydrodynamic, overlying water pH=7, (25±0.5) ℃. 改性生物炭为覆盖材料的原位修复技术,因其成本低廉、性质稳定且不易对生态系统造成干扰的特点而被视为具有广阔应用前景的环境修复技术之一[10]。现已有通过围挡方式,利用自制炭铺洒装置进行生物炭的水体原位修复技术中试试验的成功案例[31]。本研究中,采用自制氨基生物炭,于室内模拟环境下对沉积物中铜、铅的释放规律与氨基生物炭的修复效果展开了系统地探索,研究结论对高污染湖泊沉积物的修复治理具有重要参考价值。然而,目前氨基生物炭的原位修复技术仍是一个崭新的研究领域,尤其是生物炭的铺设、沉积与二次回收,以及野外环境下的中试试验与示范工程的实际应用效果等问题还有待进一步深入探讨与验证。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)沉积物中的重金属离子在模拟环境下的自然湖泊水中呈现不断向上覆水中扩散的趋势。是否覆盖氨基生物炭,沉积物中重金属的释放过程均符合零级动力学方程,其中无氨基生物炭覆盖下的零级动力学方程拟合度R2可达0.9以上。pH=5的湖泊水环境中Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)含量为pH=9环境下的1.25—2.14倍,pH=7的中性水环境下最有利于原位修复技术的实施。
(2)5%的氨基生物炭覆盖量可通过吸附、沉淀、配合等方式安全地确保Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)释放量低于国家标准值,并将湖泊环境中的重金属非致癌风险值降低2个数量级,明显抑制了Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的释放效果,大大降低了上覆水中的重金属离子浓度,对湖泊重金属的污染防治与健康风险防范具有重要作用。
-
表 1 上覆水pH对重金属离子释放的动力学拟合
Table 1. Kinetic fitting of the release of heavy metal ions by water-covered pH
重金属离子Heavy metal ion 扰动强度Hydrodynamic 生物炭覆盖量Biochar coverage pH 零级动力学方程Zero-order kinetic equation Elovich方程Elovich equation R2 k R2 a b Cu(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 5 0.9803 0.0456 0.8978 −0.1141 0.2853 7 0.9263 0.0382 0.7489 −0.1687 0.2594 9 0.9227 0.0324 0.7441 −0.1448 0.2206 Pb(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 5 0.9310 0.0691 0.9312 −0.1364 0.4239 7 0.9262 0.0495 0.7515 −0.2186 0.3367 9 0.9314 0.0404 0.7679 −0.1739 0.2743 表 2 氨基生物炭覆盖量对重金属离子释放的动力学拟合
Table 2. Kinetic fitting of heavy metal ion release by amino biochar coverage
重金属离子Heavy metal ion 扰动强度Hydrodynamic 生物炭覆盖量Biochar coverage pH 零级动力学方程Zero-order kinetic equation Elovich方程Elovich equation R2 k R2 a b Cu(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 7 0.9263 0.0382 0.7489 −0.1687 0.2594 5% 0.6598 0.0016 0.4479 −0.0093 0.0111 Pb(Ⅱ) 100 r·min−1 0% 7 0.9262 0.0495 0.7515 −0.2186 0.3367 5% ND ND ND ND ND 表 3 不同氨基生物炭覆盖量下的重金属释放风险评价指标
Table 3. The release risk evaluation index of heavy metals under different amino biochar coverage
重金属离子Heavy metal ion 评价指标Evaluation index 0%氨基生物炭覆盖量0% bio-carbon cover 5%氨基生物炭覆盖量5% bio-carbon cover Cu(Ⅱ) 释放量/(μg·mL−1) 0.786 0.042 HQin/a−1 8.23×10−8 4.40×10−9 HQd/a−1 3.26×10−10 1.74×10−11 国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值/(μg·mL−1) ≤1.0 Pb(Ⅱ) 释放量/(μg·mL−1) 1.015 0 HQin/a−1 3.80×10−7 0 HQd/a−1 1.50×10−9 0 国家地表水Ⅲ类标准限值/(μg·mL−1) ≤0.05 合计 HQin/a−1 4.62×10−7 4.40×10−9 HQd/a−1 1.83×10−9 1.74×10−11 注:实验环境为100 r·min−1扰动强度,上覆水pH=7,(25±0.5) ℃条件下. Notes: The condition is 100 r·min−1 hydrodynamic, overlying water pH=7, (25±0.5) ℃. -
[1] 季斌, 杭小帅, 梁斌, 等. 湖泊沉积物重金属污染研究进展 [J]. 污染防治技术, 2013, 26(5): 33-40. JI B, HANG X S, LIANG B, et al. Advances in heavy metals contamination of lake sediment [J]. Pollution Control Technology, 2013, 26(5): 33-40(in Chinese).
[2] 田林锋, 胡继伟, 秦樊鑫, 等. 红枫湖沉积物重金属元素地球化学特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(9): 1590-1598. TIAN L F, HU J W, QIN F X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Hongfeng lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(9): 1590-1598(in Chinese).
[3] KUNWAR P S, DINESH M, VINOD K S, et al. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti River sediments-a tributary of the Ganges, India [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 312(1-4): 14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.01.021 [4] YI Y J, WANG Z Y, ZHANG K, et al. Sediment pollution and its effect on fish through food chain in the Yangtze River [J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2008, 23(4): 338-347. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(09)60005-6 [5] 孟梅, 华玉妹, 朱端卫, 等. 生物炭对重金属污染沉积物的修复效果 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(12): 2543-2552. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.12.2016042803 MENG M, HUA Y M, ZHU D W, et al. Remediation effect of biochar on sediment contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(12): 2543-2552(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.12.2016042803
[6] ARNASON J G, FLETCHER B A. A 40+ year record of Cd, Hg, Pb, and U deposition in sediments of Patroon Reservoir, Albany County, NY, USA [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2003, 123(3): 383-391. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00015-0 [7] 陈明, 蔡青云, 徐慧, 等. 水体沉积物重金属污染风险评价研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(6): 1069-1074. CHENG M, CAI Q Y, XU H, et al. Research Progress of risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in water body sediments [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(6): 1069-1074(in Chinese).
[8] 滑丽萍, 华珞, 高娟, 等. 中国湖泊底泥的重金属污染评价研究 [J]. 土壤, 2006, 38(4): 366-373. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2006.04.003 HUA L P, HUA L, GAO J, et al. Heavy metal pollution of sediments of lakes in China [J]. Soils, 2006, 38(4): 366-373(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2006.04.003
[9] 刘昔, 王智, 王学雷, 等. 应用物种敏感性分布评价中国湖泊水体中重金属污染的生态风险 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(5): 1206-1217. doi: 10.18307/2018.0504 LIU X, WANG Z, WANG X L, et al. Ecological risks assessment of selected heavy metals in the waters of Chinese lakes based on species sensitivity distributions [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(5): 1206-1217(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2018.0504
[10] 黄艳虹, 高凡, 郭伟, 等. 基于梯度扩散薄膜技术(DGT)的氨基生物炭覆盖沉积物-水界面铜、铅释放研究 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(1): 58-69. doi: 10.18307/2020.0106 HUANG Y H, GAO F, GUO W, et al. Release of copper and lead from the sediment-water interface under in-situ coverage of amino biochar via Diffusive Gradients in Thin-films (DGT) [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(1): 58-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0106
[11] WANG S J, GUO W, GAO F, et al. Characterization and Pb(Ⅱ) removal potential of corn straw- and municipal sludge-derived biochars [J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2017, 4(9): 170402. doi: 10.1098/rsos.170402 [12] YANG G X, JIANG H. Amino modification of biochar for enhanced adsorption of copper ions from synthetic wastewater [J]. Water Research, 2014, 48(1): 396-405. [13] 马天行, 杨琛, 江鲜英, 等. 纳米零价铁改性氨基生物炭的制备及对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附和解吸特性 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(10): 5433-5439. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201603178 MA T X, YANG C, JIANG X Y, et al. Adsorption and desorption of Cd(Ⅱ) on amino biochar modified by nano zero valent iron [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(10): 5433-5439(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201603178
[14] 王淑娟, 郭伟, 史江红, 等. 氨基修饰稻壳生物炭对水溶液中铀的吸附动力学特性 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(2): 347-355. WANG S J, GUO W, SHI J H, et al. Adsorption kinetics of uranium(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution by amino modified rice husk biochar [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(2): 347-355(in Chinese).
[15] 朱青青, 王中良. 中国主要水系沉积物中重金属分布特征及来源分析 [J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(3): 305-313. ZHU Q Q, WANG Z L. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of the main river systems in China [J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(3): 305-313(in Chinese).
[16] 陈翠华, 倪师军, 何彬彬, 等. 江西德兴矿集区水系沉积物重金属污染分析 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2008, 17(5): 766-770. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2008.05.019 CHENG C H, NI S J, HE B B, et al. Heavy metal contamination in sediments of Dexing mines, Jiangxi, China [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2008, 17(5): 766-770(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2008.05.019
[17] GOSAR M, MILER M. Anthropogenic metal loads and their sources in stream sediments of the Meza River catchment area (NE Slovenia) [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(11): 1855-1866. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.009 [18] 李世玉, 刘彬, 杨常亮, 等. 上覆水pH值和总磷浓度对含铁盐的高砷沉积物中砷迁移转化的影响 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2015, 27(6): 1101-1106. doi: 10.18307/2015.0615 LI S Y, LIU B, YANG C L, et al. Effect of pH and total phosphorus concentration of overlying water on arsenic mobilization in the sediments containing high arsenic and iron salts [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2015, 27(6): 1101-1106(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2015.0615
[19] MOHAN D, SINGH P, SARSWAT A, et al. Lead sorptive removal using magnetic and nonmagnetic fast pyrolysis energy cane biochars [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2014, 448(12): 238-250. [20] 袁方. 不同pH值下重金属的形态及MEUF法对其去除机理的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2016. YUAN F. Investigation of the mechanisms of the heavy metal speciation and removal as a function of pH via micellar enhanced ultrafiltration [Dissertation]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[21] 王小庆, 郑乐平, 孙为民. 淀山湖沉积物孔隙水中重金属元素分布特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(4): 17-21. WANG X Q, ZHENG L P, SUN W M. The distribution characteristics of heavy metal elements in the pore water of sediment, Dianshan lake [J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(4): 17-21(in Chinese).
[22] 韩鲁佳, 李彦霏, 刘贤, 等. 生物炭吸附水体中重金属机理与工艺研究进展 [J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(11): 1-11. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.11.001 HAN L J, LI Y F, LIU X, et al. Remediation effect of biochar on sediment contaminated by heavy metals [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(11): 1-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.11.001
[23] 李仁英, 周志高, 杨浩. 上覆水pH对滇池沉积物重金属释放的影响[C]. 全国农业环境科学学术研讨会, 2011: 430-436. LI R Y, ZHOU Z G, YANG H. The effect of pH in overlying water on the release of heavy metals in sediment of Dianchi lake[J]. National Agricultural Environmental Science Symposium, 2011: 430-436 (in Chinese).
[24] 李敏, 成杭新, 李括. 中国淡水湖泊沉积物地球化学背景与环境质量基准建立的思考 [J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(4): 276-284. LI M, CHENG H X, LI K. Geochemical background of freshwater lake sediments: a constraint on the establishment of sediment quality guidelines in China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(4): 276-284(in Chinese).
[25] 李扬, 李锋民, 张修稳, 等. 生物炭覆盖对底泥污染物释放的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(8): 3071-3078. LI Y, LI F M, ZHANG X W, et al. Effects of biochar covering on the release of pollutants from sediment [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(8): 3071-3078(in Chinese).
[26] 王芹, 何岸飞. 植物吸收重金属动力学研究进展 [J]. 绿色科技, 2018, 10(5): 50-54. WANG Q, HE A F. Advances in dynamics of phytoremediation on heavy-metal contaminated soils [J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2018, 10(5): 50-54(in Chinese).
[27] ZHANG S, TIAN K, JIANG S F, et al. Preventing the release of Cu2+ and 4-CP from contaminated sediments by employing a biochar capping treatment [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(27): 7730-7738. [28] ABUDUWAILIL J, ZHANG Z Y, JIANG F Q. Evaluation of the pollution and human health risks posed by heavy metals in the atmospheric dust in Ebinur Basin in Northwest China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(18): 14018-14031. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4625-1 [29] 杨学福, 关建玲, 段晋明, 等. 渭河西安段水体重金属污染现状及其健康风险评价 [J]. 水土保持通报, 2014, 34(2): 152-156. YANG X F, GUAN J L, DUAN J M, et al. Heavy metal pollution and related health risk of Weihe river in Xi'an section [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 34(2): 152-156(in Chinese).
[30] 潘莎, 陈再琴, 汪钊宇, 等. 燃煤电厂周边河流中氟、砷和重金属污染健康风险评价 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2019, 31(4): 33-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2019.04.008 PAN S, CHEN Z Q, WANG Z Y, et al. Health risk assessment of fluorine, arsenic and heavy metals in river around coal-fired power plant [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2019, 31(4): 33-37(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2019.04.008
[31] 刘冬. 基于活性炭与生物炭的水体原位修复技术中试探讨 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(12): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.12.024 LIU D. Study on the technique of in-situ restoration of water based on activated carbon and biochar [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(12): 87-90(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.12.024
-




 下载:
下载: