-
我国水库众多,目前库容10万m3以上水库约10万座,其中小型水库(库容小于1 000万m3)占比超过96%[1]。国内小型水库分布不均,主要分布在湖南省、广东省、四川省、山东省、湖北省和云南省,合计占全国小型水库超过60%。江苏省共有注册登记水库921座,其中小型水库872座,占95%[2]。小型水库在防洪、灌溉、供水、养殖和生态环境方面发挥了重要的作用。但由于资金和管理方面原因,农村小型水库功能退化,如淤积渗漏严重、蓄水能力下降以及富营养化加剧等[3]。
南京市水库众多,有中小型水库250座,其中小型水库占95%。目前小型水库的水质状况尚不清楚,本研究针对南京市小型水库水质现状进行了两个时期(丰水期和枯水期)的调查和评价,为小型水库的水质管理提供基础资料。
-
本研究调查南京37座小型水库,具体分布在:六合区(三星、解放、平山、山曹、黄山水库),浦口区(大堰、百子岭、唐冲、大鱼塘、蒋山口、三五、前赵、戴塘水库),江宁区(谷里、高庄、高山、龙山、直山、牌坊、杨库、红星、明镜寺、小景庵、大岘、溧塘水库),溧水区(无想寺、老虎山、盛村、上塘湫、汤家、爱国、龙王庙、岔路口水库),高淳区(龙潡河、苗圃、尚仪三号、跃进水库)。这些水库按照流域地貌特征分为平原型水库和丘陵型水库,分别有21座和16座。。
于2018年7月(丰水期)和2019年4月(枯水期)对水库进行调查,枯水期大堰水库由于工程原因干涸,实际调查水库36个。每座水库在离大坝中间200 m处设置采样点位。现场指标在水深1 m处用YSI水质分析仪测定水温、溶解氧、电导率和pH,透明度(SD)用黑白盘测定。
化学指标包括总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、铵态氮(NH+4-N)、高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)和叶绿素a (Chl-a)。现场用5 L采水器采集上、中、下3层混合水样,即离水面0.5 m(上层)、离湖底0.5 m(下层)和中层底0.5 m(下层)和中层层[4],然后取10 L带回实验室处理分析。指标分析参考《湖泊富营养化调查规范》[5]。
水库水环境质量分别根据《地表水环境质量标准(GB3838—2002)》和综合营养状态指数评价[5-6],其中地表水环境质量标准用于水质类别评价,综合营养状态指数用于水库富营养程度评价见式(1)。
式(1)中,TLI为综合营养状态指数,Wi为第i种参数的营养状态指数的相关权重,TLI(i)为第i种参数的营养状态指数,见式(2~6)。
式(2,5)中,Chl-a、SD单位分别为μg/L和m,其它指标单位为mg/L。
TLI计算结果为0~100间的数值,该方法的评价标准为:TLI<30时为贫营养型;30≤TLI≤50时为中营养型;TLI>50为富营养型,其中≤60为轻度富营养型,60<TLI≤70为中度富营养型,TLI>70为中度富营养型。
丰水期和枯水期及平原型水库和丘陵型水库理化指标的比较采用独立样本t检验,利用SPSS18.0进行统计分析。
-
南京市小型水库丰水期和枯水期平均水温分别为32.3和17.4 ℃。丰水期和枯水期透明度平均值分别为0.98和0.82 m,两个时期无显著差异。丰水期pH、电导率和溶解氧平均值分别为8.42、0.24 ms/cm和6.29 mg/L,枯水期分别为8.75、0.23 ms/cm和10.62 mg/L。两个时期溶解氧差异显著(p<0.001),而pH和电导率差异不显著见表1。
丰水期总氮平均浓度1.01 mg/L,显著低于枯水期的1.49 mg/L。丰水期和枯水期总氮浓度最低的水库分别为红星和山曹水库,总氮浓度最高的水库分别为高庄和唐冲水库,两个时期低于III类水总氮标准(1 mg/L)的水库分别占59.5%和19.4%,高于V类水总氮标准的水库分别占比2.7%和13.9%。铵氮浓度总体较低,丰水期平均浓度0.09 mg/L,不显著低于枯水期的(0.11 mg/L)。丰水期和枯水期铵氮浓度最低的水库分别为明镜寺和大岘水库,铵氮浓度最高的水库分别为大鱼塘和岔路口水库。
丰水期总磷平均浓度0.06 mg/L,枯水期0.06 mg/L,两个时期无显著差异。丰水期和枯水期总磷浓度最低的水库均为小景庵水库,总磷浓度最高的水库均为戴塘水库,两个时期低于III类水总磷标准的水库分别占56.8%和58.3%,高于V类水总磷标准的只在丰水期的戴塘水库。
叶绿素a丰水期平均浓度31.80 μg/L,高于枯水期平均浓度21.18 μg/L(2.3~104.1 μg/L),但无显著差异。丰水期和枯水期叶绿素a浓度最低的水库分别为小景庵和明镜寺水库,叶绿素a浓度最高的水库分别为解放和高山水库。
高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)丰水期(平均4.92 mg/L)不显著高于枯水期的(平均4.58 mg/L)。丰水期和枯水期高锰酸盐指数最低的水库分别为小景庵和明镜寺水库,高锰酸盐指数最高的水库分别为高庄和高山水库。两个时期低于III类水高锰酸盐指数标准的水库分别占81.1%和80.6%,无高于IV类水高锰酸盐指数标准(10 mg/L)的水库。南京市平原型水库和丘陵型水库丰水期和枯水期理化指标和综合营养状态指数见表2。
-
丰水期和枯水期平原型水库总氮浓度均不显著高于丘陵型水库(p>0.1),总磷、叶绿素a、高锰酸盐指数均显著高于丘陵型水库(p<0.05),透明度显著低于丘陵型水库(p<0.05)。平原型水库和丘陵型水库丰水期总氮浓度均显著低于枯水期的(p<0.05),平原型水库丰水期叶绿素a浓度显著高于枯水期的(p=0.02),丘陵型水库丰水期透明度显著高于枯水期的(p=0.045),两个类型水库其他指标在丰水期和枯水期间无显著差异(p>0.05),见表2。
-
根据《地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838—2002)》[6],丰水期水库III、IV、V和劣V类水分别占比48.7%、24.3%、21.6%和5.4%,影响指标为总氮和总磷;枯水期分别占比13.9%、30.5%、41.7%和13.9%,影响指标主要为总氮。
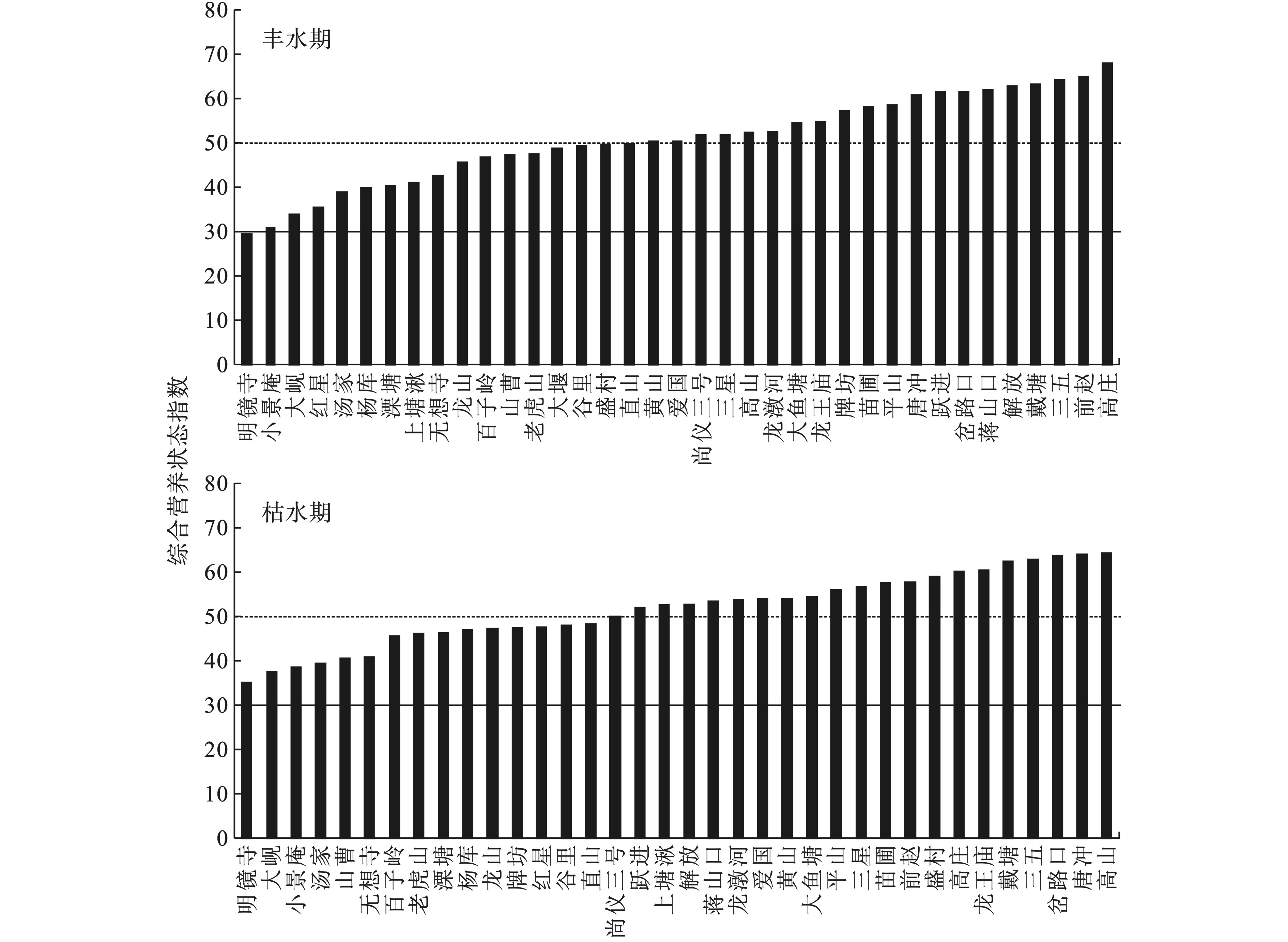
根据综合营养状态指数,丰水期水库贫营养、中营养和富营养分别占比2.7%、43.2%和54.1%,富营养水库中轻度富营养和中度富营养分别占比55.0%和45.0%。枯水期中营养和富营养分别占比44.4%和55.6%,富营养水库中轻度富营养和中度富营养分别占比70.0%和30.0%见图1(图中实线和虚线分别表示中营养和富营养标准)。丰水期和枯水期平原型水库TLI值均显著高于丘陵型水库( p <0.05)。平原型水库和丘陵型水库在丰水期和枯水期TLI值均无显著差异( p >0.05)。
-
富营养化是世界范围内湖泊和水库面临的主要问题之一[7]。对全国138个湖泊的调查表明,有85.4%的湖泊超过了富营养标准[8]。相比较而言,水库富营养程度低于湖泊。据《2018年中国水资源公报》显示,全国1097座水库中,中营养和富营养水库分别占比69.6%和30.4%。与2001年相比,几乎无贫营养水库,富营养水库比例提高近1倍,在最近几年稳定在30%左右,主要污染指标为总磷和高锰酸盐指数[9]。本次调查的小型水库与全国大中型水库评价相比,超过50%以上的水库处于富营养状态,主要污染指标为总氮和总磷,高锰酸盐指数多数不超过III类水标准,说明有机污染程度低,与南京市中型水库的污染状况类似[10-12]。
与大中型水库不同,小型水库蓄水量低,水体交换周期长,水环境容量小,使得水库水环境恶化后较难恢复。本次调查水库平均深度均低于6 m,属浅水湖泊范畴。这些水库较少或不受工业污染的影响,造成富营养化的原因主要是由于农田不合理的化肥施用造成的面源污染和水产养殖。此外,小型水库淤积速度快,沉积物磷释放造成的内源污染会促进水库富营养化[3, 13]。
面源污染是引起南京市小型水库富营养化的关键原因。对江苏沙河水库、新安江水库(千岛湖)和三峡库区面源污染的研究表明,面源污染是影响这三个水库富营养化的重要原因[14-16]。小型水库一般换水周期长,来自面源的污染物易在水库中滞留。姜峰等[17]估算了江苏省2009年农业面源排放总量,其中南京市总氮、总磷和CODMn年排放量分别为2.41、0.33和4.88万t,其中CODMn排放总量以畜禽养殖和水产养殖占比最高,分别为52.3%和21.7%,总氮和总磷排放总量分别以农用化肥和畜禽养殖占比最高,分别为61.8%和72.7%,而农村生活污水对总氮、总磷和CODMn的贡献均较小。本次调查水库CODMn对水质的影响较小,这与南京市畜禽养殖综合整治有关[18],尽管水产养殖也能促进水库富营养化[19-20],但本次调查只在富营养化程度比较高的水库(如解放水库)有不同程度的渔业活动,因此,总体来看畜禽养殖和水产养殖对南京市小型水库CODMn的影响较小。
南京市小型水库丰水期和枯水期总氮均是影响水质的主要指标,这主要归因于流域内农用化肥的影响[17]。总磷是丰水期影响水质的主要指标,尽管畜禽养殖可能对水库总磷增加有影响,但经过综合整治[17-18],其影响程度会削弱。研究表明,枯水期水体总磷较高主要受面源污染影响,而丰水期总磷较高主要受内源控制[21]。沉积物磷释放是浅水湖泊总磷升高的重要途径[22]。小型水库较浅,淤积速度快,来自面源的污染物沉降在水库底部,沉积物磷释放引起水中磷浓度的升高,促进藻类生长和叶绿素a浓度提高。本次调查虽然跨年度,但从春季和夏季总磷浓度来看,夏季水质类别低于IV类水库的总磷浓度均高于春季的,而优于IV类水库的夏季总磷浓度多数低于春季的,说明沉积物磷释放对南京市小型水库的富营养化起着重要的作用。
面源污染也与流域土地利用类型有关。尽管本研究没有详细分析水库流域的土地利用状况,但由于流域面积小,根据流域地貌将水库划分为平原型和丘陵型水库。丘陵型水库流域内多以林地为主,林地对水库氮磷的输入小于耕地和裸地[14],当林地面积较高(>71%),意味着作物耕地面积较少,水库富营养化程度较低[23]。本次调查丘陵型水库的营养水平显著小于平原型水库,说明流域土地利用差异会影响水库的富营养化程度。
-
对南京市37座小型水库水质调查表明,丰水期总氮平均浓度显著低于枯水期,丰水期总磷和高锰酸盐指数平均浓度和枯水期无显著差异。丰水期小型水库水质主要影响指标为总氮和总磷;枯水期水库水质主要影响指标为总氮。平原型水库水质劣于丘陵型水库。与全国以大中型水库为主的营养水平评价结果相比,南京市小型水库富营养程度高于大中型水库富营养比例,主要受面源污染、内源污染和流域土地类型影响,不合理的化肥施用和沉积物磷释放是水库富营养化的主要原因。因此,对于小型水库,除了要考虑水库本身的安全运行以外,其富营养化趋势值得关注。
南京市小型水库水质评价和富营养化分析
Water Quality Evaluation and Eutrophication Analysis of Small Reservoirs in Nanjing
-
摘要: 小型水库数量众多,在防洪、灌溉、供水、养殖和生态环境方面发挥了重要的作用。2018年7月(丰水期)和2019年4月(枯水期)对南京市37个小型水库水质进行了调查。丰水期总氮平均浓度1.01 mg/L,显著低于枯水期的1.49 mg/L。丰水期总磷平均浓度0.057 mg/L,枯水期0.055 mg/L,两个时期无显著差异。高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)丰水期平均浓度4.92 mg/L,不显著高于枯水期的4.58 mg/L。南京市小型水库丰水期以III类水为主(48.7%),V和劣V类占27.0%,影响指标为总氮和总磷;枯水期V类水比例较高(41.7%),其次是IV类水(30.5%),影响指标为总氮。两个时期富营养和中营养水库分别占比约55.0%和45.0%。平原型水库水质劣于丘陵型水库。结果表明,与大中型水库相比,小型水库水质更易受氮磷的影响,应重视小型水库的富营养化问题。Abstract: There is a great amount of the small reservoirs, and they play an important role in the flood control, irrigation, water supply, aquaculture and ecological environment. Thirty-seven small reservoirs in Nanjing were investigated for the water quality in July 2018 (wet season) and April 2019 (dry season). The average concentration of the total nitrogen (TN) in the wet season was 1.01 mg/L, which was significantly lower than that in the dry season (1.49 mg/L). There was no significant difference in the average concentration for the total phosphorus (TP) in the wet season (0.057 mg/L) or in the dry season (0.055 mg/L). The average concentration of CODMn in the wet season was 4.92 mg/L. It was a little higher than that in the dry season (4.58 mg/L). In the wet season, the water of Category III (48.7%) dominated the small reservoirs, and the water of both category V and inferior category V were 27.0% of the total. The influence indexes were TN and TP. In the dry season, there was a great percentage of the category V water (41.7%), followed by the category IV water (30.5%). The TN was the influence index. As for the two seasons, the ratios of the eutrophic and the mesotrophic reservoirs were 55.0% and 45.0%, respectively. The water quality of the plain-typed reservoirs was inferior to that of the hill-typed reservoirs. The results indicated that the water quality of the small reservoirs was easily impacted by the nitrogen and phosphorus compared with the large and middle reservoirs. The eutrophication of the small reservoir needed to be paid more attention.
-
Key words:
- Total Nitrogen /
- Total Phosphorus /
- Eutrophication /
- Non-point Source Pollution /
- Small Reservoir
-
工业园区大气污染排放总量核算为园区大气环境质量管控提供重要依据,同时有助于推进企业排污许可、项目审批、执法监管以及排污权交易等管理联动,与排污总量挂钩,有助于提升综合管理效能、制定相关的环境管理政策[1]和解决污染源管控不准、产业调整方向不明、环评审批总量落实难、第三方机构弄虚作假等问题具有重要意义[2-3]。目前,工业园区大气污染物排放总量的核算主要是统计园区内所有企业大气污染物排放量并进行加和代表该园区大气污染物的排放总量。现有对企业排放量核算方法主要有实测法、产排污系数法及物料衡算法。实测法是依据实际监测环统对象产生和外排废气流量及其污染物质量浓度,计算出废气的排放量及各种污染物的产生量和排放量 (在线监测和手工监测) [4]。产排污系数法是根据《产排污系数手册》[5]提供的工业行业产排污系数,只要根据企业的实际情况选择合适的产排污系数,即可核算出污染物的产生量和排放量[6]。物料衡算法是通过计算生产过程中物质的量的变化对生产过程中使用的物料变化情况进行定量分析的一种方法[7]。但上述通过对企业排放量核算园区总排放量的方法均存在一定的局限性,如实测法 (在线监测和手工监测) 存在设备安装联网成本较高,运维困难、无法测算无组织排放等问题且监控数据无法验证[8-9]。产排污系数法忽视了企业生产过程中采取不同污染处理技术的因素,在计算过程中仅以企业生产消耗的原材料或生产成品就确定了一个企业的排放系数,未考虑企业对于污染管理和处理技术方面的因素,具有一定的局限性[6]。产排污系数法对于关键系数的选取存在一定主观性且可能会忽略行业特征[5]。而物料衡算法计算过程复杂,生产过程中的物料损耗、污染物的无组织排放等因素无法准确估算,适用范围较小等[4,10]。与此同时,产排污系数法和物料衡算法通常需要对生产企业进行调研,对于企业数量和类型较多的工业园区,核算的人力成本和时间成本较高,难以实现动态核算更新。
本研究尝试探索基于环境监测站点的实时监测数据,结合大气污染物扩散模型和源参数反演算法,构建工业园区大气污染物实际排放总量反演算法,实现对园区无组织及低矮有组织大气污染物实际排放量的动态实时核算。该方法可极大地节省人力、物力,具有普遍适用性。该方法可作为实测法、物料衡算法及产排污系数法等传统排放总量核算方法的有益补充,同时有助于充分利用环境监测数据信息,明确环境质量与污染物排放的动态响应关系,为基于环境质量目标的动态污染排放管控提供参考。
1. 研究方法
1.1 示例园区基本情况及模拟网格构建
示例园区为东南沿海某重点石油化工产业基地,是国家石化产业布局方案中重点规划布局的新建石化产业基地。2021年,依据江苏省开展工业园区 (集中区) 污染物排放限值限量管理工作方案要求[2],建设了园区大气环境监测站点网络,并对园区企业大气污染排放情况进行了调查核算。该园区内共有涉及有机化学品的合成、储运、化学加工制造、危废治理、热电联产等污染排放企业20家。其生产及排放规模排名前10的企业VOCs排放总量占园区VOCs总排放量超过95%。因此,选取该10家企业作为主要研究对象,以VOCs的实际排放量实时反演为主要研究目标。由于本研究主要论证基于大气环境监测数据的污染排放总量实时反演的技术可行性,并讨论相关影响因素,故不考虑在工业园区尺度范围内VOCs的二次转化。
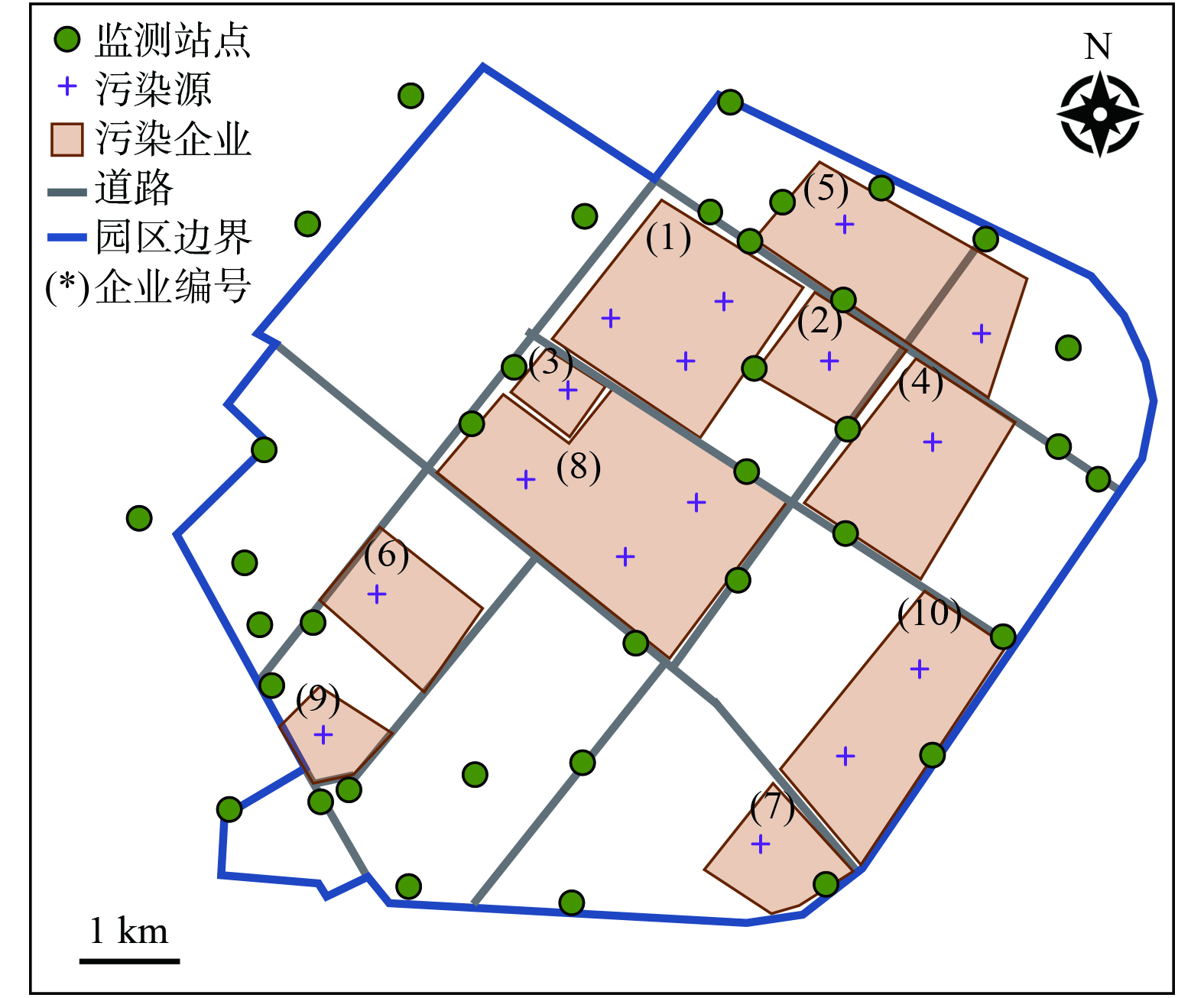
将园区在WGS-84地理坐标系下的企业排污单元及监测站点经纬度、园区边界及主要道路矢量图信息转化为UTM投影坐标系以方便进行数值模拟。图1为园区主要污染企业、监测站点、园区边界及主要道路的空间分布情况。
选取园区几何中心作为原点,计算各排污单元及监测站点的相对空间位置。表1为污染排放占比前10企业各污染排放点位的相对位置、排污许可中VOCs的年排放量 (许可排放量) ,以及通过在线监测、产能折算、产排污系数、物料衡算等方式核算的VOCs年排放量 (统计核算量) 。核算年度为2020年,部分企业如企业 (8) 、企业 (10) 在核算年度尚未正式投产,故其统计核算量处于缺失状态。在本研究过程中,相关企业已正式投产,故在模型模拟中将参考许可排放量作为污染源,考虑其排放过程对周边环境的影响。经统计,示例园区VOCs年排污许可量约为4 000 t。
表 1 示例园区污染源相对位置及VOCs年排放量Table 1. Relative location of pollution sources and annual emissions of VOCs in sample park企业编号 点位编号 相对位置 VOCs年排放量 X/m Y/m 许可排放量/(t·a−1) 统计核算量/(t·a−1) (1) 1-1 −105.69 1 939.64 558.06 305.68 1-2 694.15 1 513.34 1-3 1 080.49 2 126.93 (2) 2-1 2 191.57 1 535.64 231.22 52.70 (3) 3-1 −567.09 1 159.14 0.00 0.00 (4) 4-1 3 307.64 732.23 257.24 2.46 (5) 5-1 2 328.21 2 950.21 188.13 11.10 5-2 3 805.85 1 865.68 (6) 6-1 −2 494.02 −1 017.60 16.17 0.84 (7) 7-1 1 605.90 −3 561.35 1.01 0.46 (8) 8-1 −945.73 223.88 1 855.47 — 8-2 100.86 −572.14 8-3 842.90 27.32 (9) 9-1 −3 033.36 −2 506.92 23.64 0.14 (10) 10-1 2 488.31 −2 613.47 801.12 — 10-2 3 236.00 −1 661.56 1.2 环境监测数据处理
本研究基于工业园区地面监测站点实时监测数据开展大气扩散模拟。其中,模型采用的平均风场数据为园区内各监测站点小时平均风向的平均值,计算式见式 (1) 和式 (2) 。
u,v=−ws⋅sin(θπ180),−ws⋅cos(θπ180) (1) 式中:
u v ws θ um,vm=1N∑Ni=1ui,1N∑Ni=1vi (2) 式中:
um vm N ui vi 1.3 高斯烟羽大气污染扩散模型
高斯烟羽大气污染扩散模型是基于随机扩散形成高斯分布的污染物浓度场理想假设的第一代空气质量模型,适用于平坦地形下稳态风向中污染物的扩散模拟。随着研究的深入,进一步推出了第二代空气质量模式如AERMOD[11]、CALPUFF[12]和第三代空气质量模式如CMAQ[13],考虑了更为复杂的影响大气污染物扩散及二次转化的因素。然而,由于其快速简单的特点,高斯模型仍在应急处置、污染初步估算等领域被广泛应用[14]。本研究主要讨论基于环境监测站点监测数据开展工业园区大气污染排放总量实时反演的技术可行性,为简化起见,采用高斯烟羽大气污染扩散模型对该方案进行测试。在实际使用中,其他空气质量模型也可类似地应用于工业园区总量核算中。
高斯烟羽大气污染扩散模型的解析形式见式 (3) 。
C(x,y,z)=Q02πUσyσzexp(−(y−y0)22σ2y){exp(−(z−z0)22σ2z)+exp(−(z+z0)22σ2z)} (3) 式中:
Q0 U σy σz x C(x,y,z) y0 z0 x 定义
α Q0 Q0⋅α σy σz α(x,y,z)=C(x,y,z)Q0 (4) 本研究参考国标参数化方案《制定地方大气污染物排放标准的技术方法》 (GB/T 3840-91) [15]逐小时实时计算
σy σz σy,σz=γ1xα1,γ2xα2 (5) 式中:参数
γ1 γ2 α1 α2 1.4 优化函数构建及源参数反演算法
监测站点污染物的监测质量浓度为背景质量浓度、污染源贡献质量浓度和监测误差累加而成。假设园区存在监测站点N个,污染源M个,则对于任意监测站点i,有监测污染物质量浓度
di di=bg+∑Mj=1αij⋅Qj+εi (6) 式中:
bg εi εi=ε⋅χ (7) 式中:
ε χ 以此构造优化目标函数见式 (8) 。
minf=∑i(^bg+∑Mj=1αij⋅ˆQj−di)2+a∑Mj=1ˆQj2+b∑Mj=1|ˆQj| (8) 式中:
^bg ˆQj a b 1.5 误差分析
本研究主要采用平均绝对相对偏差 (Mean Absolute Relative Error, MARE) 作为排放总量反演误差的度量,其计算公式见式 (9) 。
MRAE=1T∑Tn=1|ˆxn−xnxn| (9) 式中:T为核算时段的小时数;
ˆxn xn |⋅| 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 数值模拟与排放总量反演
收集园区2023年1月1日0时至1月31日23时地面气象监测数据开展模拟研究。参考表1中收集的企业许可排放量数据设定模拟的污染源排放强度。其中,大型企业生产单元占地面积较大,存在多个排放点位 (如企业1) ,则将企业的年排放量均匀分配到每个排放点位。将各个点位的排放强度由t∙a−1转化为mg∙s−1带入公式 (3) 中,获取各污染源对监测点位贡献C,背景浓度设定为0~0.3 mg∙m−3的随机数。依照公式 (5) 可获得园区监测点位的监测浓度值
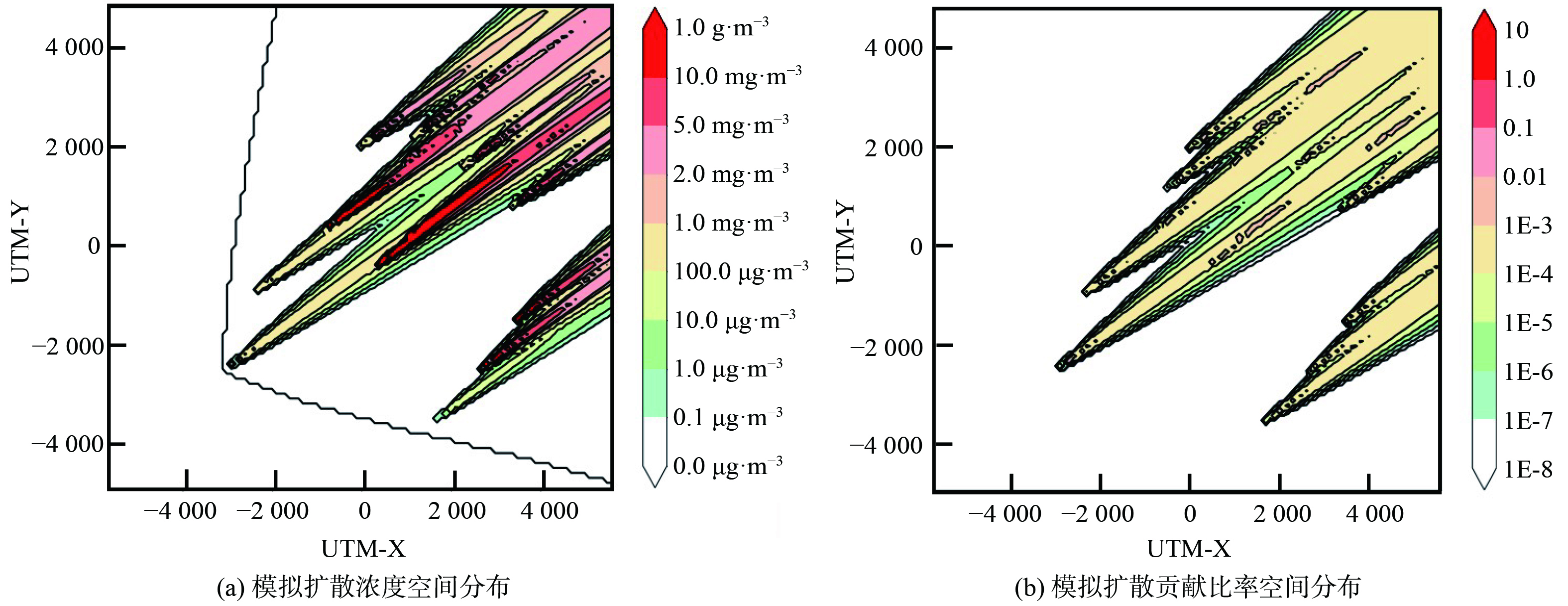
di 为验证基于环境监测数据对工业园区排放总量进行实时反演核算的有效性和适用性,研究设定了4个不同排放情景:高排放情景、中排放情景、低排放情景和周期排放情景。其中,高、中、低排放情景分别为实际排放量占许可排放量的100%、50%和10%,周期排放情景则设定园区排放以24 h为周期依照正弦函数在许可排放量的20%~120%内波动。图2展示了高排放情境下,园区2023年1月1日00时污染物质量浓度及污染源对监测点位贡献比率的空间分布情况。
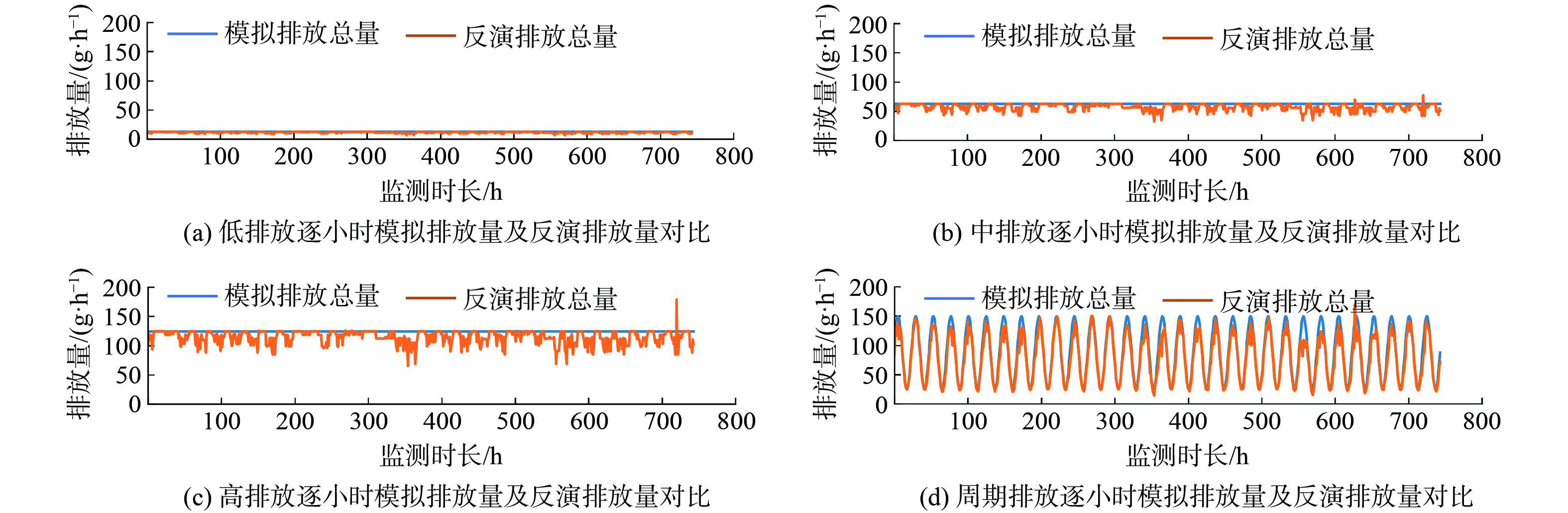
利用模拟的在线监测浓度值,以公式 (7) 为目标函数 (设定正则项为0) ,进行反演核算。图3展示了4种排放情景下逐小时的模拟排放量和反演排放量。结果表明,在该条件下模拟排放量逐小时变化曲线与模拟排放量的逐小时变化曲线基本一致,部分时刻存在明显偏差。
计算1月份逐小时反演排放总量与模拟排放总量的平均绝对相对偏差发现,在该条件下,模型反演背景浓度与模拟的实际背景浓度一致,其偏差极小,小时排放量反演偏差约为5.4%左右,且不同情境下偏差大小基本不变。这表明此时对园区的排放总量反演核算具有较好的效果。
同时,观察到图3中不同时刻的反演偏差有所差异,部分时段的反演偏差明显偏大。从反演机理考虑,该反演过程本质上是利用环境质量监测站点对污染源排放形成的扩散烟羽进行空间采样,再利用采样结果根据污染扩散公式对源排放参数进行约束优化,最终依靠目标函数优化寻找最符合采样结果的源排放参数。因此,采样过程的充分与否将直接影响反演效果。对于固定的污染源和监测点位分布,受气象条件影响的污染扩散烟羽的形态可能对采样造成影响。
为验证该猜想,对不同大气稳定度下的反演差异进行了统计分析(表2) 。结果表明,核算时段内大气稳定度等级主要集中于B、D、E、F这4种情况,总体呈现从A到F (强不稳定到稳定) ,反演偏差逐步增大的规律 (表3) 。参照标准GB/T 3840-91[15],反演效果较差的大气稳定度等级E、F主要出现于风速小于3.0 m∙s−1、太阳辐照等级较低的气象条件下。这一条件可能不利于污染物的扩散与传输,污染物空间分布较为集中,不利于监测点位对污染物扩散特征的监测采样,进而导致基于监测数据的反演效果较差。
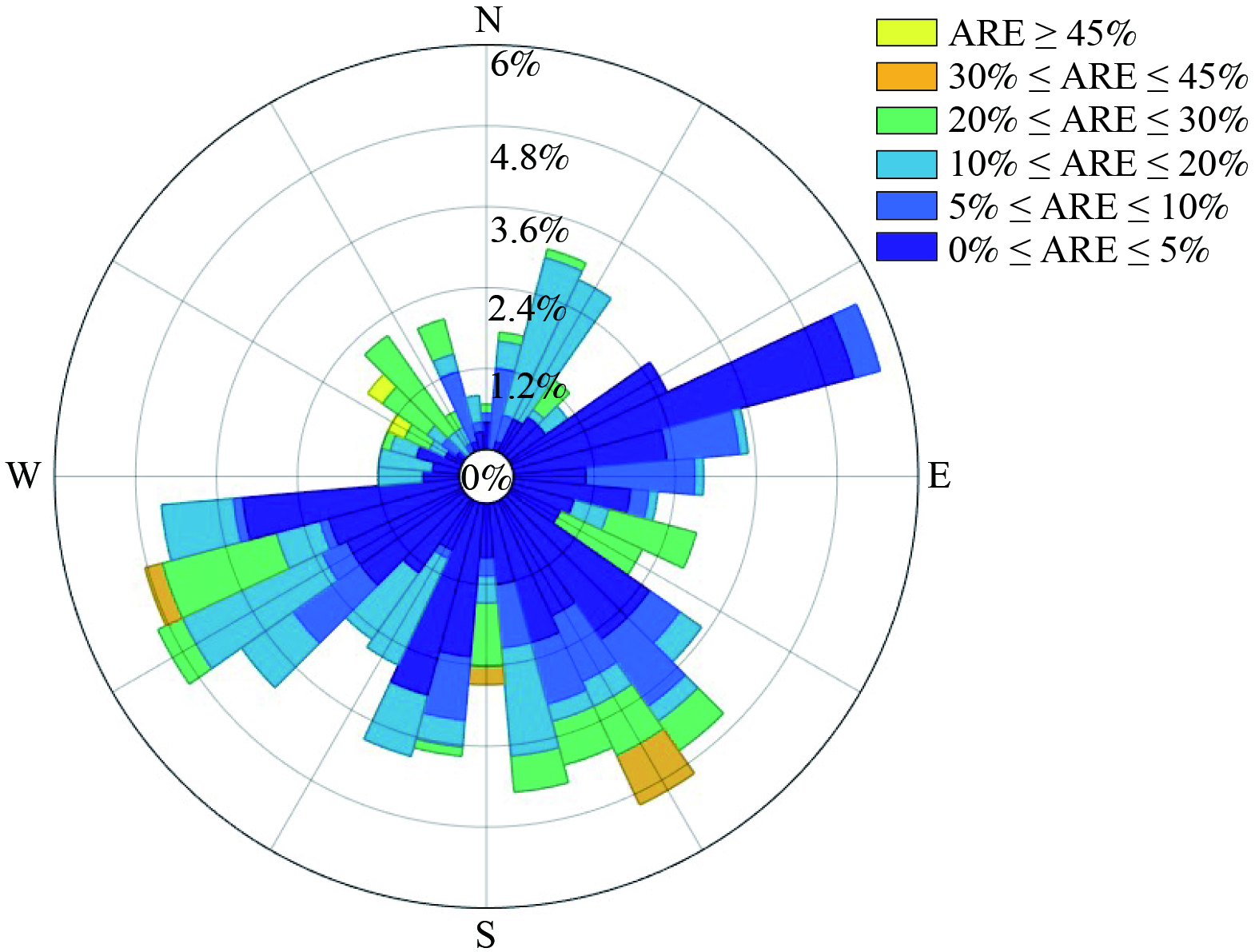
表 2 工业园区大气污染排放总量反演精度模拟评估Table 2. Simulation and Evaluation of the Precision of Inversion of Total Air Pollution Emissions in Industrial Parks情景模式 背景浓度反演偏差 (MARE) 小时排放量反演偏差 (MARE) 低排放情景 (0.00±0.00)% (5.39±7.43)% 中排放情景 (0.00±0.00)% (5.33±7.34)% 高排放情景 (0.00±0.00)% (5.54±7.50)% 周期排放情景 (0.00±0.00)% (5.33±7.34)% 表 3 排放总量反演精度与工业园区大气稳定度的关系Table 3. Relationship between the accuracy of total emission inversion and the atmospheric stability of industrial parks大气稳定度 小时数 平均绝对相对偏差 (MARE) A 16 (0.00±0.01)% B 156 (0.62±2.16)% C 3 (3.40±5.88)% D 140 (1.03±3.22)% E 151 (6.07±6.67)% F 278 (10.08±8.12)% 利用风玫瑰图分析反演效果与风向的关系,分析发现反演绝对相对误差 (ARE) 较高的时刻,风向主要分布在西北-东南方向 (图4) 。这一风向与园区主导风向正交。该方向上的反演效果较差可能与该方向监测站点布点相对稀疏有关。
2.2 监测站点布设对反演效果的影响
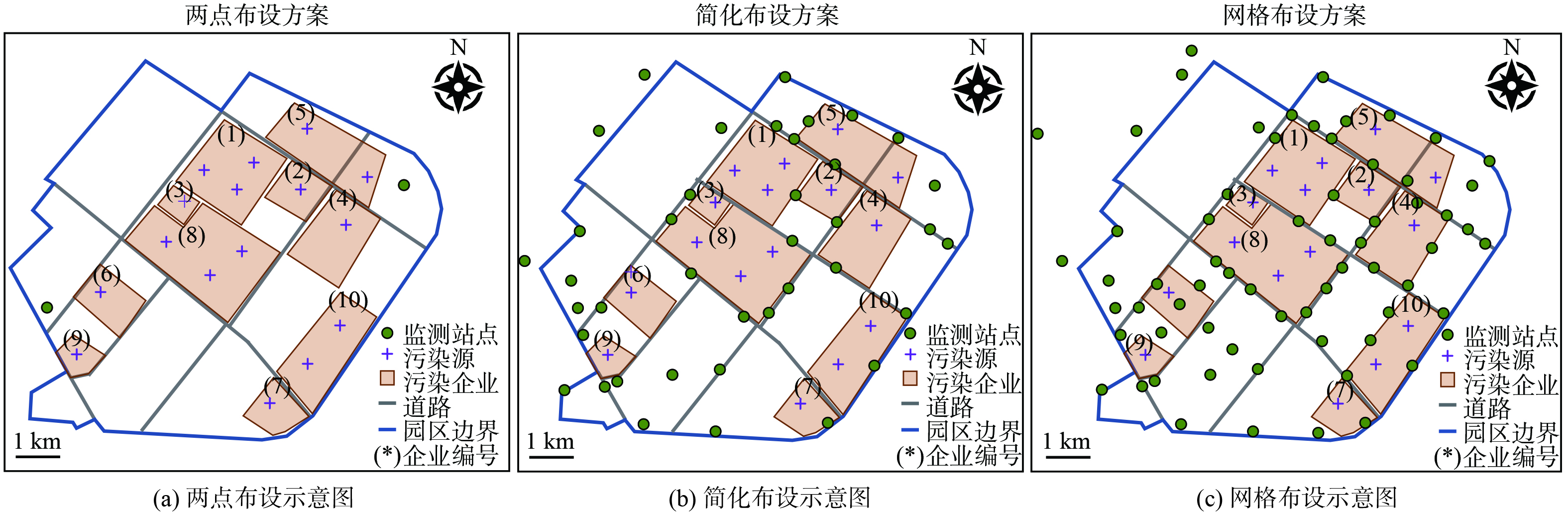
为进一步研究监测点位对反演效果的影响,对比了3种布点方案下的反演精度。两点布设指在园区主导风向的上下风向各布设一个监测点位;网格布设指在园区内及园区边界,依照1~2 km的距离网格式布设监测点位;简化布设则指介于两点布设与网格布设之间的一种情形,对应部分网格布设监测点位失效情形下的反演效果。前文的数据模拟实验是在简化布设条件下进行的。各布点方案的站点位置分布示意见图5。
不同布点方案对反演精度有显著影响(表4)。其中,两点布设方案在4种排放情境下偏差最大,基本无法对园区实际排放量进行有效评估。简化布设方案和网格化布设方案偏差均在可接受范围内。网格化布设方案偏差相比简化布设降低90%以上。因此,网格化布设方案能显著提高园区排放总量核算的精准度。这一结论进一步验证了前述采样充分程度显著影响反演精度的假设。从两点布设、简化布设到网格布设,监测站点的数量增多,对扩散烟羽的采样更加充分,对源排放参数的反演提供了更精确的约束,进而提升了反演的准确度。
表 4 不同布点方案下模型逐小时反演精度评估Table 4. Hourly Inversion accuracy evaluation of models under different layout schemes布点方案 监测站点数 平均绝对相对偏差 高排放情景 中排放情景 低排放情景 周期排放情景 两点布设 2 (75.55±34.42)% (75.68±34.20)% (76.06±33.83)% (75.56±34.39)% 简化布设* 40 (5.39±7.43)% (5.33±7.34)% (5.54±7.50)% (5.33±7.34)% 网格化布设 76 (0.36±1.55)% (0.39±1.69)% (0.48±2.28)% (0.40±1.83)% *注:本文2.1节采用简化布设条件,故本行结果采用表2中的数据。 2.3 监测站点数据质量对反演效果的影响
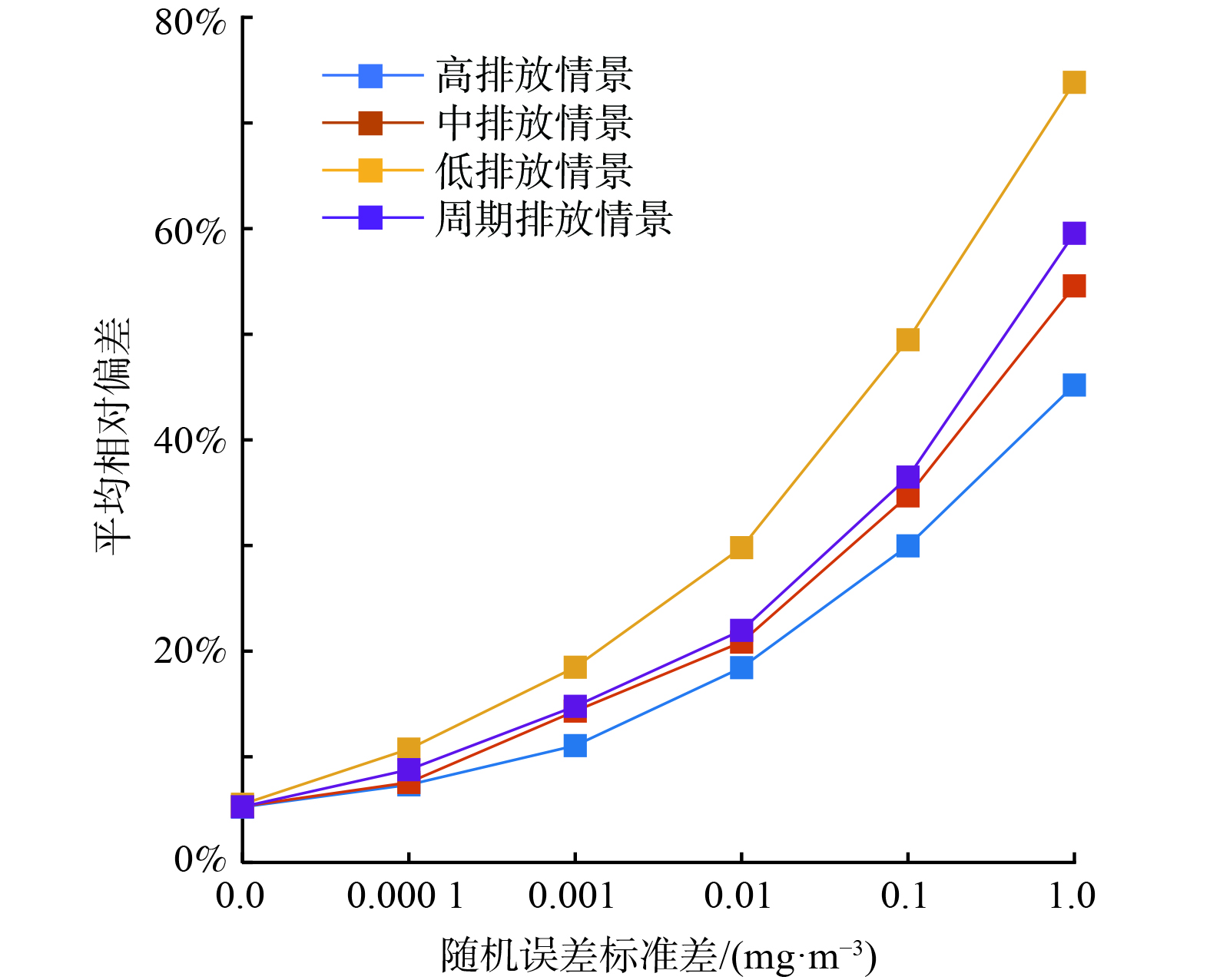
在实际应用中,由于系统误差、随机误差的存在,导致监测站点对污染扩散烟羽的采样可能存在不确定性。对于经过定期校验及规范运维的监测站点,可考虑随机误差为采样误差的主要来源,故本文讨论随机误差对反演精度的影响。依照公式 (5) 模拟不同排放情境下反演精度与随机误差强度的关系。结果表明,公式 (7) 中的正则项显著提高了反演模型在监测数据存在误差时的精度。当不考虑监测误差时,公式 (7) 中的正则项可设置为0 (即不考虑正则化损失函数) ,但当监测数据叠加随机误差时,不考虑正则项将导致反演结果显著偏离模拟实际排放量。以下分析的反演精确度均为通过贝叶斯优化迭代50次后取最佳一阶和二阶正则化系数获得的反演精度。对于本研究的示例园区,正则化因子取值为10−4到10−20之间。
实验表明,在考虑随机误差的情况下,4种排放情景的反演精度存在一定的差异 (这与不考虑随机误差的情况不同) 。反演精度随排放量的增加而提高,低排放情景下反演偏差最大。周期排放情境下的反演偏差则与中排放情景接近。对于低排放情景,随机误差的标准差达到0.01 mg∙m−3时,小时反演偏差达到了30%;对于中、高排放情景及周期排放情景,随机误差标准差达到0.1 mg∙m−3时,小时反演偏差约为30% (图6) 。即在简化布点方案下,可接受反演误差范围内可忍受的随机误差强度约为0.01~0.1 mg∙m−3。以该园区的主要VOCs污染物丙烷为例,在25 ℃常温下,该误差强度相当于5.6~55.6 ppb。该数值大于《环境空气挥发性有机物气象色谱连续监测系统技术要求及检测方法》 (HJ1010-2018) [20]规定的监测误差,但小于或相当于《挥发性有机化合物光离子化检测仪校准规范》 (JJF 1172-2007) [21]规定的空气微站测量TVOC的误差。这表明采用空气微站监测数据可能会增大对工业园区的VOCs排放总量反演核算偏差。
3. 结论
1) 以东南沿海某石化园区为例,讨论了基于环境监测数据开展工业园区大气污染物实际排放量实时反演核算的技术可行性。该技术可实时动态测算工业园区低矮有组织排放及无组织排放总量的能力,可作为在线监测法、产排污系数法等传统排放总量核算方法的有效补充,提升工业园区基于环境质量开展污染排放动态管控的能力。
2) 基于高斯大气扩散模型及Nelder-Mead优化反演算法,测试并讨论了反演核算方法的准确度及其影响因素。监测站点布设方案显著影响反演核算精度,网格化布点方案有效提高了反演核算精度。监测数据的随机误差显著影响反演核算精度,在简化布点方案下,园区监测站点对VOCs的浓度监测误差应控制在0.1 mg∙m−3以下。园区总排放强度对反演核算精度存在一定影响,总排放量大的园区反演核算精度较高。反演核算精度与实时气象条件有关,当气象条件不适宜模型模拟污染物扩散或不适宜监测站点对污染物分布进行有效采样时,可能造成反演精度的下降。
3) 在工业园区开展基于环境监测数据的大气污染物排放总量核算研究具有可行性。同时,监测站点对污染源排放扩散烟羽的采样充分程度是影响反演精度的重要因素。因此,需要在监测站点布设方案比选、监测站点数据质量控制等方面进行精细化管理,以达到最优反演核算效果。
-
表 1 南京市小型水库丰水期和枯水期理化指标平均值
理化指标 丰水期 枯水期 水温/℃ 32.3 17.4 透明度/m 0.98 0.82 pH 8.42 8.75 溶解氧/mg·L−1 6.29 10.62 电导率/ms·cm−1 0.24 0.23 总氮/mg·L−1 1.01 1.49 总磷/mg·L−1 0.06 0.06 叶绿素a/μg·L−1 31.80 21.18 高锰酸盐指数/mg·L−1 4.92 4.58 表 2 南京市平原型水库和丘陵型水库丰水期和枯水期理化指标和综合营养状态指数(TLI)
指标 平原型水库 丘陵型水库 丰水期 枯水期 丰水期 枯水期 总氮/mg·L−1 1.09±0.10 1.53±0.13 0.91±0.09 1.45±0.10 总磷/mg·L−1 0.08±0.01 0.07±0.01 0.03±0.00 0.04±0.01 叶绿素a /μg·L−1 47.27±5.52 28.71±5.24 11.50±2.73 11.77±2.83 透明度/m 0.55±0.05 0.64±0.07 1.54±0.18 1.03±0.14 高锰酸盐指数/mg·L−1 5.71±0.27 5.30±0.31 3.88±0.26 3.69±0.32 TLI 56.95±1.38 55.08±1.46 42.58±1.95 46.83±1.89 -
[1] 中华人民共和国水利部. 中国水利统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2009. [2] 周贵宝, 葛忆, 陆范彪. 江苏水库管理的经验与思考[J]. 中国水利, 2018(20): 63 − 65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2018.20.016 [3] 汤显强, 郭伟杰, 吴敏, 等. 农村小型水库功能退化分析及恢复对策[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2018, 35(2): 13 − 17. [4] 黄祥飞. 湖泊生态调查观测与分析[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1999. [5] 金相灿, 屠清英. 湖泊富营养化调查规范[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990. [6] 国家环境保护总局, 中国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838-2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [7] WAGNER T, ERICKSON L E. Sustainable management of eutrophic lakes and reservoirs[J]. Journal of Environmental Protection, 2017, 8(4): 436 − 463. doi: 10.4236/jep.2017.84032 [8] 杨桂山, 马荣华, 张路, 等. 中国湖泊现状及面临的重大问题与保护策略[J]. 湖泊科学, 2010, 22(6): 799 − 810. [9] 中华人民共和国水利部. 2018年中国水资源公报[EB/OL]. (2019-07-12)[2019-11-08]. http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/201907/t20190712_1349118.html. [10] 于忠华, 黄文钰, 舒金华. 南京市主要湖库水环境现状与演变趋势分析[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2005(4): 37 − 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7853.2005.04.018 [11] 陈文权, 沈来保, 芮同顺. 溧水县主要供水水库水质现状及富营养化分析[J]. 江苏水利, 2008(5): 40 − 41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7839.2008.05.019 [12] 王文侠, 陈非洲, 谷孝鸿. 南京市5座中型水库浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(1): 216 − 223. [13] 钱洪汶. 雅安市中小型水库水质现状及污染防治对策[J]. 黑龙江水利科技, 2012, 40(11): 141 − 142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7596.2012.11.069 [14] 李恒鹏, 陈伟民, 杨桂山, 等. 基于湖库水质目标的流域氮、磷减排与分区管理——以天目湖沙河水库为例[J]. 湖泊科学, 2013, 25(6): 785 − 798. doi: 10.18307/2013.0602 [15] 文军, 骆东奇, 罗献宝, 等. 千岛湖区域农业面源污染及其控制对策[J]. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(3): 126 − 129. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2004.03.032 [16] 张广纳, 邵景安, 王金亮, 等. 三峡库区重庆段农村面源污染时空格局演变特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(7): 1197 − 1209. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.07.012 [17] 姜峰. 江苏省农业面源污染时空特征及削减方案研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2012. [18] 王润之, 杜娟, 张振岚, 等. 南京地区猪场粪污处理方式调查分析[J]. 养猪, 2018(1): 81 − 83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1957.2018.01.028 [19] 陈花. 东莞中小型水库水污染现状与治理[J]. 广东水利水电, 2012(10): 15 − 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0112.2012.10.006 [20] 蒋艾青. 山区小型水库富营养化调查与评价[J]. 饲料研究, 2007(3): 55 − 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2813.2007.03.019 [21] CHEN F Z, SHU T T, JEPPESEN E, et al. Restoration of a subtropical eutrophic shallow lake in China: effects on nutrient concentrations and biological communities[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2013, 718(1): 59 − 71. doi: 10.1007/s10750-013-1603-9 [22] 范成新, 张路, 包先明, 等. 太湖沉积物-水界面生源要素迁移机制及定量化-2. 磷释放的热力学机制及源-汇转换[J]. 湖泊科学, 2006, 18(3): 207 − 217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2006.03.003 [23] KNOLL L B, HAGENBUCH E J, STEVENS M H, et al. Predicting eutrophication status in reservoirs at large spatial scales using landscape and morphometric variables[J]. Inland Waters, 2017, 5(3): 203 − 214. doi: 10.5268/IW-5.3.812 -




 下载:
下载: