-
近年来,土壤及地下水污染事件频发,其污染问题逐渐受到重视。土壤和地下水污染具有隐蔽性和滞后性,除了传统土壤和地下水采样分析,数值模拟方法是定量刻画土壤和地下水中污染物的运移的主要手段。通过数值模拟方法可以科学、可靠地预测土壤和地下水污染趋势,为污染防治工作提供技术支撑。
目前,土壤和地下水数值模拟研究分别形成成熟的研究方法和配套软件,取得了大量研究成果,在工程实践中广为运用。但已有研究大多数仅考虑单独介质开展数值模拟研究,少有研究将土壤和地下水作为一个整体看待。大量研究表明,土壤和地下水两者联系紧密,地表污染源通常在淋滤作用下通过土壤进而污染地下水含水层,土壤污染极易导致地下水污染,但土壤和地下水耦合数值模拟研究进展缓慢,对土壤和地下水交界面的污染物运移情况尚未摸清。本文对现有土壤和地下水水流及污染物运移的耦合模拟进展进行总结,旨在为进一步开展相关研究提供科学依据,为我国早日实现土壤与地下水污染协同防治奠定理论科学基础。
全文HTML
-
开展土壤和地下水数值模拟目的在于预测水流及污染物运移趋势,为提出相应的防控治理措施提供定量依据。数值模拟的基本步骤是构建水文地质概念模型、建立数学模型,通过解析解或数值方法求解描述水流及污染物状态的偏微分方程,常用的数值求解方法为限差分法、有限单元法、边界元法等,计算机模拟软件的发展也使大规模数值处理成为可能[1]。目前,土壤和地下水中水流与污染物迁移预测模拟方法不同,大部分研究是分别基于两套模拟预测系统开展的。而我国土壤和地下水模拟预测研究基础薄弱,受整体技术水平发展滞后和基础资料不完善的影响,针对土壤与地下水污染评估与风险预测相关研究,主要集中在基于采样结果的土壤或地下水现状评估,尚未建立基于模拟预测结果的动态风险预测系统。
-
非饱和水流和溶质运移研究是土壤水分和污染物运移的基础研究内容。在达西定律的基础上,1907年Buckingham考虑土壤基质势、含水量等因素,修正达西定律得到白金汉-达西定律;通过将白金汉-达西定律带入连续方程可以得到Richards方程[2]。目前,土壤非饱和带模拟预测主要是基于Richards方程构建水流模型和对流-弥散方程构建的溶质运移模型开展研究[2-3],而Hydrus系列软件是非饱和带水流和溶质运移的主要模拟工具,方程求解采用伽辽金线性有限元法,综合考虑了非饱和带中植物根茎吸收、溶质在液态下的对流-弥散现象和气态下的扩散现象、固液态和气液态转化、合成和降解等情况[4]。徐丽萍等[5]对室内有机玻璃箱滴灌条件下土壤水分运动进行了模拟,证明Hydrus能够以较高的精度模拟土壤水分运移。杨洋等[6]利用HYDRUS-1D模拟垃圾填埋场渗滤液中的氨氮在不同包气带结构和不同污染源特征下的迁移转化规律,预测场地污染物污染程度。
大量研究证明土壤固体颗粒的吸附解析作用对溶质运移产生影响。彭盼盼等[7]在对天津市某区域未来30年污染物六价铬在浅层土壤中运移规律进行数值模拟和分析预测,发现在降雨入渗淋洗和土壤颗粒吸附作用下,土壤中六价铬含量将处于较低状态,不造成污染。尹芝华等[8]则利用HYDRUS-2D软件构建土壤水分运动和溶质运移模型,模拟三氮在该场地非饱和带垂向以及向下游地表水体的迁移转化过程,发现非饱和带介质是氮污染负荷的有效缓冲区,但对硝态氮的吸附能力相对较弱,因此硝态氮为主要污染物。
除HYDRUS外,还有SWAP、COMSOL等成熟商业软件可用于模拟非饱和带水流和溶质运移。总体来看,单独针对土壤介质的水流和溶质运移研究已较为成熟,商用软件可以涵盖运移过程中可能发生的各种反应,取得了大量研究结果。
-
在现阶段地下水污染模拟预测模型的研究中,利用达西定律、质量守恒方程和水流连续性方程建立地下水水流模型、利用溶质运移理论构建地下水污染预测模型,是地下水模拟研究人员使用的主要方式。
美国材料与试验协会(ASTM)在地下水模拟预测的不同阶段制定了行业系列标准[9-11],如《场地问题地下水水流模拟应用标准指南》(ASTM D5447 - 04(2010))《地下水水流与溶质运移建模标准指南》(ASTM D5880 - 95(2006))《污染场地概念模型创建标准指南》(ASTM E1689 - 95(2008))等。英国环保署对地下水模拟预测工作制定了不同尺度的规范,分别颁布了针对大尺度地下水模拟的《地下水资源模拟导则》(2002)[12]、针对污染场地和污染物迁移模拟制定的《概念模型创建及数学模型选择与应用实用指南》(2001)[13]等。中国也于2014年发布《地下水污染模拟预测评估工作指南》,奠定了我国地下水污染模拟预测评估工作的基础。地下水模拟预测行业制度要求严,标准高,未来该学科的研究将逐渐细分,并呈现多学科融合的趋势。
目前最广为运用的三维地下水水流模拟软件是MODFLOW,采用网格中心点有限差分法求解,可以模拟各种条件下水流在地下含水层中的运动,同时允许用户开发外部程序强化主程序功能[14-15]。在MODFLOW模型基础上,综合三维地下水溶质运移数值模拟软件MT3DMS等开发的Visual MODFLOW可模拟地下水中水流和污染物的物理迁移和化学反应过程,展现三维可视化地下水水流模型[1,10]。魏亚强等[16]采用MODFLOW中的SEAWAT模块,对压裂液突破页岩储层以多点状同时进入地层的情形进行了变密度流的模拟,并分析了不同渗漏点与断层底部距离、不同断层倾角对压裂液运移的影响。陈喜等[17]用MODFLOW和水平衡模型对美国某地区地下水位进行了模拟,并分析了含水层补排水量,河流与地下水补排关系以及区域水平衡过程,揭示了独特沙丘地形和土壤特性对地下水补排量的影响。克热木·阿布都米吉提等[18]模拟某垃圾填埋场在无控制措施、防渗墙和抽水井单独及同时运用时的地下水渗滤液运移过程,给出抽水井和防渗墙最佳布设方位建议。饶磊等[19]利用Visual MODFLOW建立地下水流概念模型,以化学需氧量(COD)和氨氮质量浓度做为污染物运移模拟研究的主要指标,对污水处理站发生泄漏后进入地下水中的主要污染物进行溶质运移模拟,发现7 300 d后污染物将进入长江。但MODFLOW不考虑非饱和带模拟预测,无法准确表现饱和带与非饱和带的水流运动关系[20]。
除MODFLOW之外,常用的软件平台还有Feflow、GMS、Visual Groundwater等[1]。GMS综合Modflow、MT3DMS、Modpath等软件主要计算模块和PEST、UCODE、MAP等辅助模块,功能齐全,可以概念化建立水文地质概念模型,前、后处理功能更强大,能用来模拟绝大部分地下水水流和溶质运移[21]。
1.1. 土壤水分和污染物运移数值模拟
1.2. 地下水渗流和污染物运移数值模拟
-
随着将土壤和地下水作为一个整体看待的意识增强,关于土壤和地下水耦合模拟的研究成为近年来的热门话题,截止目前,针对土壤和地下水中水流运动耦合方法研究较多,而污染物运移研究还处于初步阶段。
-
针对土壤和地下水中水流运动的耦合方法研究大多关注地下水埋深和入渗补给关系。孟宪萌[22]分别对河流和地下水建模,通过动态水量交换机制实现耦合,对地块进行水均衡分析。韩双平等[23]通过人为控制潜水埋深开展农作物实验,发现包气带-潜水系统水分转化率均衡临界深度对土壤水-潜水转化系统起主导作用,进而决定了土壤水和潜水对农作物需水的调节作用。牛赟等[24]分析降水-土壤水和地下水相关性,构建回归模型,表明5 cm土壤体积含水量和地下水埋深高度相关。邓洁等[25]则总结了河渠与地下水相互转化耦合模型研究进展,分析了国外典型数值模拟软件在模拟河渠与地下水相互转化的特点。
综上,已有水流模拟数值耦合方法研究主要关注水分在包气带和潜水带中的水分运移转化关系以及地下水埋深在两个系统中的同步性,模拟耦合过程中需要考虑的参数包括土壤含水量、渗透系数、潜水埋深、水流通量等。
-
虽然关于水流在包气带和潜水带之间运动的模拟研究已较为成熟,但对于其中的污染物运移研究还处于初步阶段,相关研究主要集中于表明土壤和地下水对污染物的运移存在耦合作用,目前常见于国外文献,国内较少见。KEESSTRA et al[26]通过大量案例表明土壤优先流(指土壤在整个入流边界上接受补给,但水分和溶质绕过土壤基质,只通过少部分土壤体的快速运移)中溶解的污染物对地下水有显著影响,同时土壤也对可能迁移至地下水的污染物起到过滤和缓冲作用,但土壤污染物迁移模型有待进一步研究。曾献奎[27]构建凌海市地下水-地表水耦合数值模拟,基于HydroGeoSphere进行求解,分析总氮迁移规律。ARIAS-ESTEVEZ et al[28]指出污染物从土壤迁移至地下水主要是由于土壤优先流和胶态共输的作用,土壤和污染物的理化性质均对迁移速率起到重要作用,但目前地下水脆弱性仅考虑了土壤而未考虑污染物类型,对土壤和地下水的关联关系考虑不充分。WANG et al[29]发现天然有机物(NOM)对土壤中砷元素的移动性有重要影响,进而影响地下水砷污染的可能性。HOSSAIN et al[30] 通过大数据挖掘,运用二分树法构建土壤理化性质与地下水砷污染浓度关系模型,较准确的预测了孟加拉国地下水砷浓度分布。
土壤和地下水中污染物运移模拟大多数还停留在定性研究上,有待进一步开展针对包气带和潜水带渗透系数、理化性质等差异及其对土壤水中污染物在迁移进入地下水过程中的过滤、缓冲、稀释和转化作用的影响的定量研究。模拟耦合过程中需要考虑的参数包括土壤和污染物理化性质、污染物浓度等,特别应注意在介质交界面上参数的瞬时变化对污染物迁移路径和性质的影响。
-
目前已有部分软件可以针对土壤和地下水开展水流和溶质运移耦合数值模拟。Feflow采用有限元法进行非稳定水流和污染物运移三维模拟,对非承压含水层采用变动上边界的办法,根据水文地质条件生成有限单元网格,视具体情况定义所有边界条件及其限制条件、渗透系数、补排量等为常数或者变量,可用于模拟饱和带和非饱和带地下水流场变化和污染物在地下水中的迁移过程及其时间空间分布模式[31]。SUTRA是用于饱和带或非饱和带水流、溶质和能量运移的三维专业模型,广泛应用于模拟海水入侵过程[1]。下面主要以HYDRUS Package for MODFLOW(以下称HPM)为例介绍土壤和地下水耦合模拟过程。
HPM是较成熟的土壤和地下水中水流和溶质运移模拟耦合模块,由BEEGUM et al[32]自2007年起研发,于2008年正式向大众开放下载应用,并于2018年更新。张旭洋等[33]结合HPM软件和GIS技术,构建大沽河流域土壤水和地下水耦合模型,较好地预测了土壤水和地下水的时空变化状况和地下水补给量。
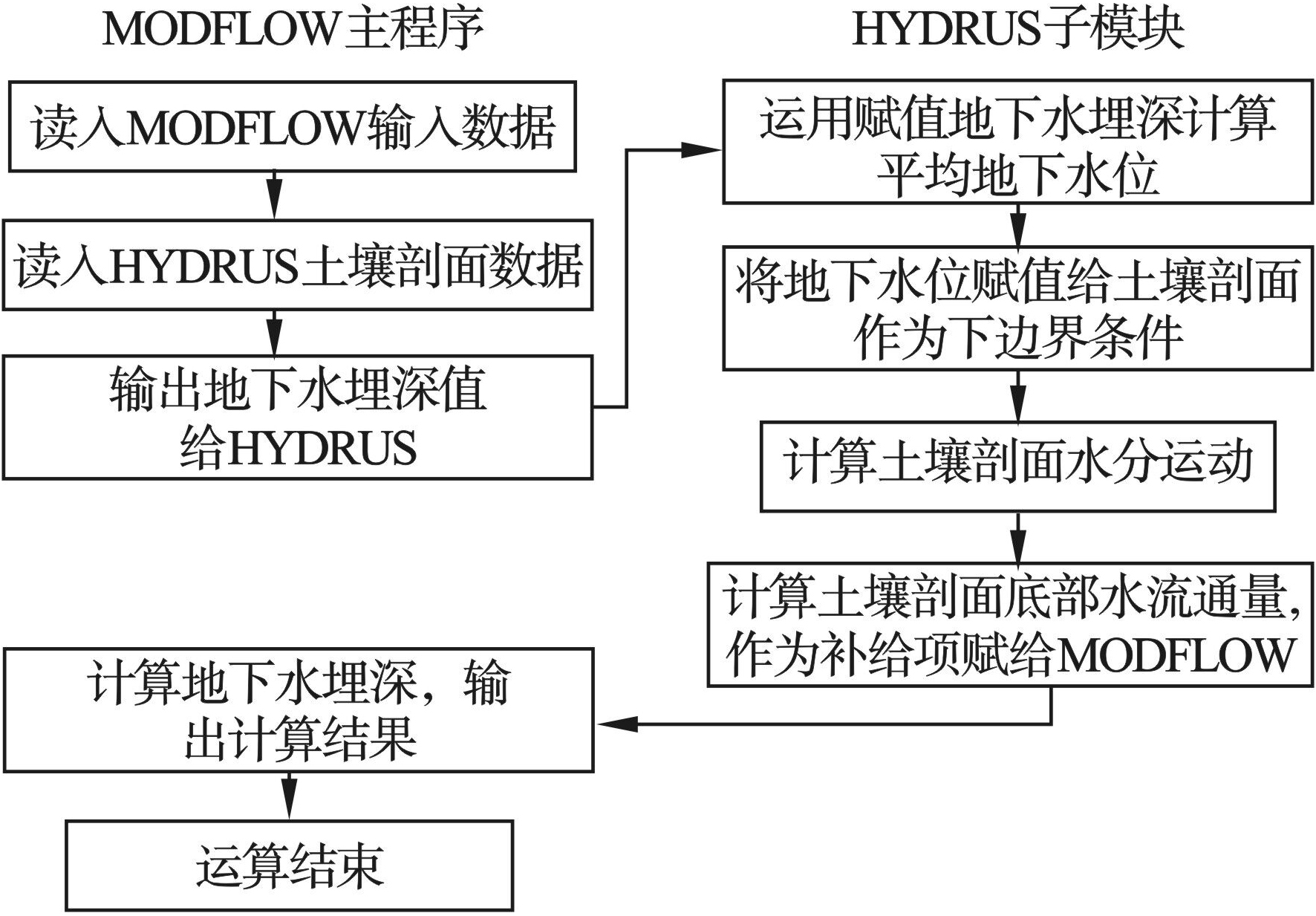
HPM将非饱和带Hydrus模块与饱和带MODFLOW模型关联,在MODFLOW中,整个区域被分为若干个单元格,整个模拟周期被分为若干个时段,在每个时段内,单元格遭受的外界影响被假设是恒定的[34]。HYDRUS则采用不同的分段方法,通常分段时长小于MODFLOW[32]。考虑耦合过程,HYDRUS将MODFLOW上一个时段计算得到的地下水埋深值H作为下个时段的底部边界条件,而Modflow则将Hydrus该时段计算得到的底部渗流量作为下个时段的补给量。模型流程见图1[33]。
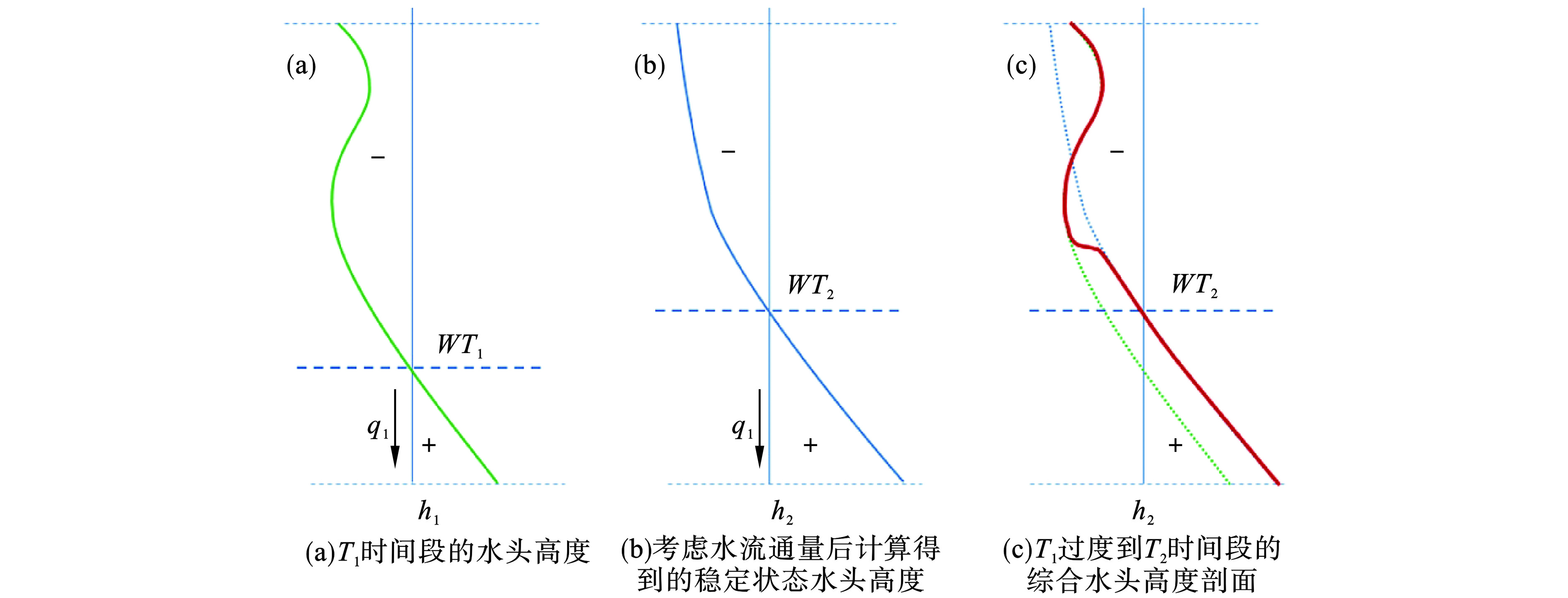
该耦合方法的缺陷在于它假设每个MODFLOW时段土壤剖面底部水头压力是恒定的,忽略了时段中水流通过包气带到达饱和带带来的水头变化,可能导致土壤剖面底部产生突然的水流通量,使总通量计算结果不准确[32]。这个缺陷可以通过调整水头高度算法改善,新算法下的水头高度剖面示意图见图2。
2018年,HPM升级到可模拟包气带和潜水带中污染物溶质运移。耦合过程中,HYDRUS模拟包气带中的水流和溶质运移情况,计算得到的土壤底部水流和溶质浓度通量被分别作为Modflow的地下水补给量和MT3DMS的入渗浓度[34]。但该模型对污染物在土壤和地下水界面的转换、过滤、稀释和缓冲关系未予考虑,有待进一步研究。
-
除了对水流和污染物溶质运移进行耦合模拟,已有研究和软件关注土壤和地下水耦合过程中热、压力等其他性质的变化和对水循环系统的影响以提高系统模拟精度。GSFLOW在MODFLOW的基础上,考虑天气、用地、补给等因素,可以综合模拟地下水和地表水径流。Parflow是伯克利劳伦斯实验室开发的地球水循环系统模拟预测软件,集成地下水和地表水、生态水,考虑水流与土壤、大气之间的联系,通过将陆面-底层包气带模型替换为地下水-顶层包气带模型耦合通用陆面模型(Common Land Model,土壤含水量单位时间变化率考虑光照、温度、水在液态和固态间的转化率、水的密度、蒸发量等)和地下水径流模型,更加真实地模拟了地球水活动[35]。MAXWELL et al [35]运用Parflow对比了耦合条件和非耦合条件下对某场地降雨量、径流量、热通量和蒸发量的模拟结果,发现耦合模型预测结果更加准确。这些拓展性质及参数对土壤和地下水系统的影响应在耦合过程给予适当的考虑,同时在数值模拟的过程当中应考虑流场、浓度场、温度场、应力场等多场耦合的复杂交互作用。
2.1. 水流耦合数值模拟
2.2. 污染物运移耦合数值模拟
2.3. HYDRUS for MODFLOW的发展
2.4. 拓展耦合数值模拟
-
目前对于土壤和地下水的数值预测模拟研究均过于独立,耦合系统研究大多关注水分运移,也考虑了土壤和地下水污染的同步性,关于污染物在土壤和地下水交界面的迁移转化研究较少,未建立成熟的土壤和地下水耦合数值模拟方法。当下我国土壤和地下水存在大量同步污染的情景,在土壤和地下水污染协同防治的新时代管理模式的背景下,对二者的耦合研究显得尤为重要,本文对土壤和地下水耦合数值模拟研究的发展方向进行了展望。
1)将数值模拟与大数据结合,利用统计学方法和人工智能技术确定不同类型场地土壤和地下水污染的关键参数,并分析关键参数对污染物空间分布规律的影响,剖析不同类型土壤和地下水污染中污染物的分布情况,探索污染物在土壤和地下水中分布的一致性和差异性,有助于进一步明确耦合作用关系。
2)在现有耦合方法的基础上,进一步分析土壤和地下水渗透系数、理化性质等差异对水流和溶质运移的影响,考虑耦合过程中污染物在包气带和潜水带交界面上复杂的输移转化关系,更精细地描绘污染物在运移过程中的浓度和路径变化,提高土壤和地下水耦合水流和溶质运移方法的准确性。
3)完善土壤和地下水耦合数值模拟系统。随着土壤和地下水耦合方法研究的进展,完善污染物在土壤和地下水耦合系统中的迁移模型,考虑整个土壤-地下水系统的输入-响应关系,整合现有模拟软件的部分功能,开发土壤-地下水耦合数值预测模拟系统,实现水流和溶质在土壤-地下水系统中的全路径动态模拟,同时配合污染评估和风险预测模块,形成基于模拟预测结果的动态污染评估和风险预测系统。



 下载:
下载: