-
重金属是我国土壤的主要污染物之一[1],因此,在我国土壤污染综合防治规划和土壤环境质量调查中被列为重点关注对象。根据《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》显示,我国土壤污染的前5大重金属污染因子为镉、镍、砷、铜与汞,土壤点位超标率均超过1.6%。其中,汞 (Hg) 与砷 (As) 在典型土壤中浓度较高,严重污染环境,危害人体健康[2]。基于此,这2种元素为场地调查中必检项目,同时也是第三次全国土壤普查中土壤环境质量的必检内容[3]。所以,构建简单、准确的方法用于测定土壤中的Hg与As,非常重要。
在分析方法中,前处理是方法成败的关键因素之一。目前,生态环境部,农业部,国家标准化委员会等发布关于土壤中Hg与As测定的标准方法有:水浴消解法[4-7],微波消解法[8]。但这些方法大多存在汞污染、时间长、能耗高、成本高、样品处理量小、设备昂贵、消解罐清洗流程复杂等问题。
为解决以上问题,本研究基于标准方法[4-7]的样品前处理方法,开发了一种利用一次性消解管的石墨消解-王水体系,用于土壤和沉积物中 Hg与As的简单、高效、快速前处理,并使用标准方法[8]的分析条件进行验证,方法优化了消解温度、消解时间、消解液用量、取样量等参数,确保前处理过程的简化与结果的准确性。研究结果可为土壤和沉积物中这2种重金属元素的测定提供一种成本低廉、样品通量大,简单准确的新方法,具有极好的应用推广前景。
-
1) 耗材。50mL聚丙烯 (PP) 塑料离心管。
2) 试剂。硝酸、盐酸均为优级纯;硫脲、抗坏血酸、硼氢化钾 (分析纯)
3) 标准品。1 000 mg∙L−1 Hg单元素标准溶液GSB G 62069-90;1 000 mg∙L−1 As GSB 04-1714-2004。4种土壤或沉积物分析标准物质:GBW07385 (GSS-29) (As:9.3±0.8mg∙kg−1,Hg:0.15±0.02mg∙kg−1) 上海市崇明县新海镇土壤,GBW07453 (GSS-24) 阳江市南海滩涂沉积物,GBW07981 (GSS-39) 海南万宁富硒土壤,GBW07982 (GSS-40) 陕西渭南关中平原区土壤。
-
原子荧光光度计 (AFS-8220,北京吉天仪器有限公司) ;石墨消解仪 (ED54,北京莱伯泰科仪器股份有限公司) ;离心机 (LC-LX-L40B,上海力辰仪器科技有限公司) ;电子天平 (SQP,赛多利斯(上海)贸易有限公司) 。
-
取风干土壤或沉积物样品 0.1~0.5 g (精确至 0.000 1 g) 于 50 mL 一次性塑料离心管中,加入5~15 mL (1+1) 王水,加盖拧紧后回旋半圈,摇匀于消解仪上100~130 ℃加热 0.5~2 h,中间摇动几次,取下冷却,用水稀释至刻度,摇匀后静止过夜,或在4 000~6 000 r·min−1下离心 (5~10) min,取上清液按照标准方法[8]测定汞或砷的条件,进行元素测定。
-
As:阴极灯电流 60 mA,负高压270 V,载气流量300 mL∙min−1,屏蔽气流量800 mL∙min−1,灵敏度线波长253.7。
Hg:阴极灯电流 12 mA,灵敏度线波长193.7,其他参数与 As一致。
-
分取10.0 mL置于50 mL容量瓶中,加入浓盐酸2.5 mL混匀,室温放置30 min,用实验用水定容至标线,混匀用于Hg的测定;另分取10.0 mL置于50 mL容量瓶中,加入浓盐酸5 mL,硫脲和抗坏血酸混合溶液10 mL混匀,室温放置30 min,用实验用水定容至标线,混匀用于As的测定。
-
现有标准方法前处理方法使用具塞玻璃比色管或聚四氟乙烯消解管或微波消解罐等,在重复使用过程中都需要使用较高浓度的硝酸溶液进行超过24 h浸泡,由于Hg元素容易产生记忆效应,因此极易被吸附残留。林海兰等[9]发现10 % (体积分数) HNO3 浸泡24 h仍不能有效去除比色管中残留的Hg。本研究在前期验证过程中发现,即使每次实验使用硝酸溶液浸泡24 h以上,随着使用次数的不断累加,Hg的残留不断增加,且无法根除。即便每次更换硝酸浸泡液,会延迟Hg污染的周期,但随着使用次数的增加,Hg污染的问题仍然存在。且频繁的更换硝酸浸泡液会导致大量硝酸浪费,且由此产生大量的危险废物,同时也增加了试剂的使用成本。
为彻底解决Hg污染问题,同时又不能增加成本,本研究采用一次性塑料 (PP) 离心管进行改进,且经过长时间大量的试剂空白和全程序空白验证发现,空白测定值均低于方法检出限,且塑料 (PP) 材质离心管无需浸泡,不但解决了Hg污染残留问题,还节约了硝酸和盐酸的用量,节约了成本。
-
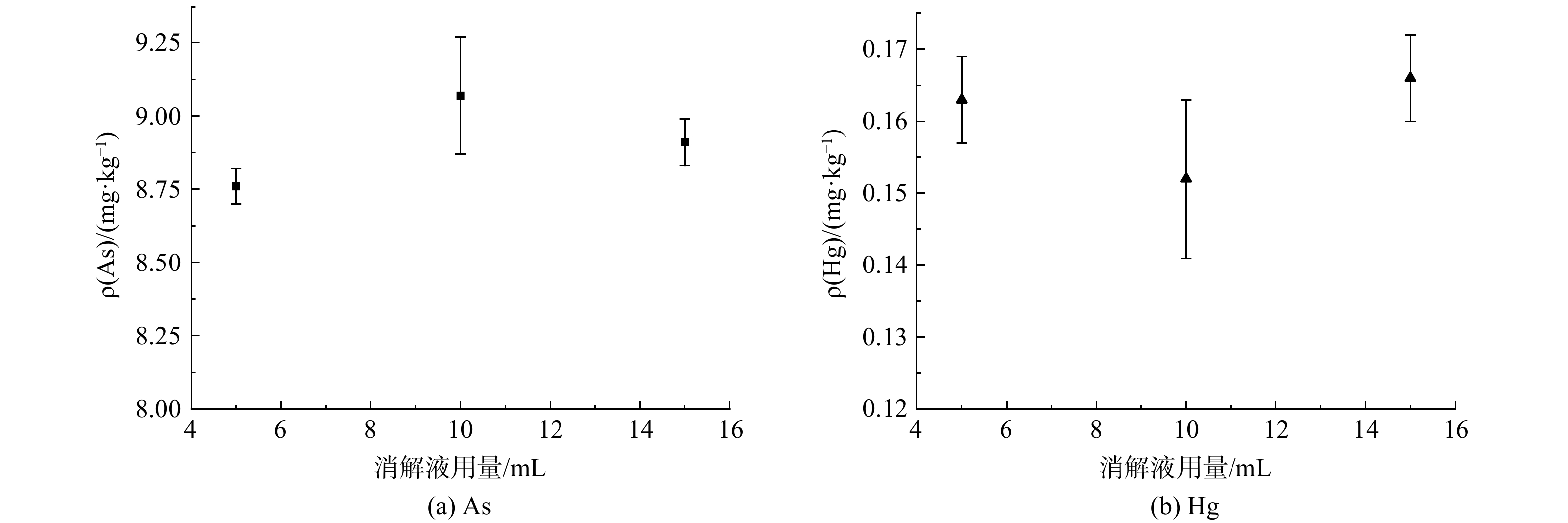
消解温度是影响消解效果的重要因素,文典等[10]和李蕾等[11]研究显示提高温度可极大缩短消化时间,但高温意味着高能耗,在达到良好的消解效果的条件下,温度越低能耗越低。本研究对100、110、120、125 ℃,4组消化温度 (消解液 10 mL,消解时间2 h,取样量0.5 g) 的影响。图1是不同消解温度下GSS-29的 Hg、As,测定结果。可以看出,4种消解温度下的Hg、As测定值均落在了标准值范围内,准确度较高,且标准偏差均小于2.5%,结合能耗,选择100 ℃作为消解温度。
-
本研究对消解液的用量进行了优化:考察了5、10、15 mL (1∶1) 王水加入量 (消解温度100 ℃,消解时间2 h,取样量0.5 g) 的影响。结果显示 (见图2) ,Hg、As所有的测定结果均在标准值允许的范围内,且RSD均小于5%。由于采用的是密闭体系,不会产生消解液的损失,因此5 mL (1∶1) 王水足以充分提取样品中的Hg、As,而消解液的用量越大,消耗的盐酸和硝酸的量也就越大,成本增加,同时产生的危险废物的量也增加。因此,从环保及节约成本的角度,本方法最终选择加入5 mL (1∶1) 王水。
-
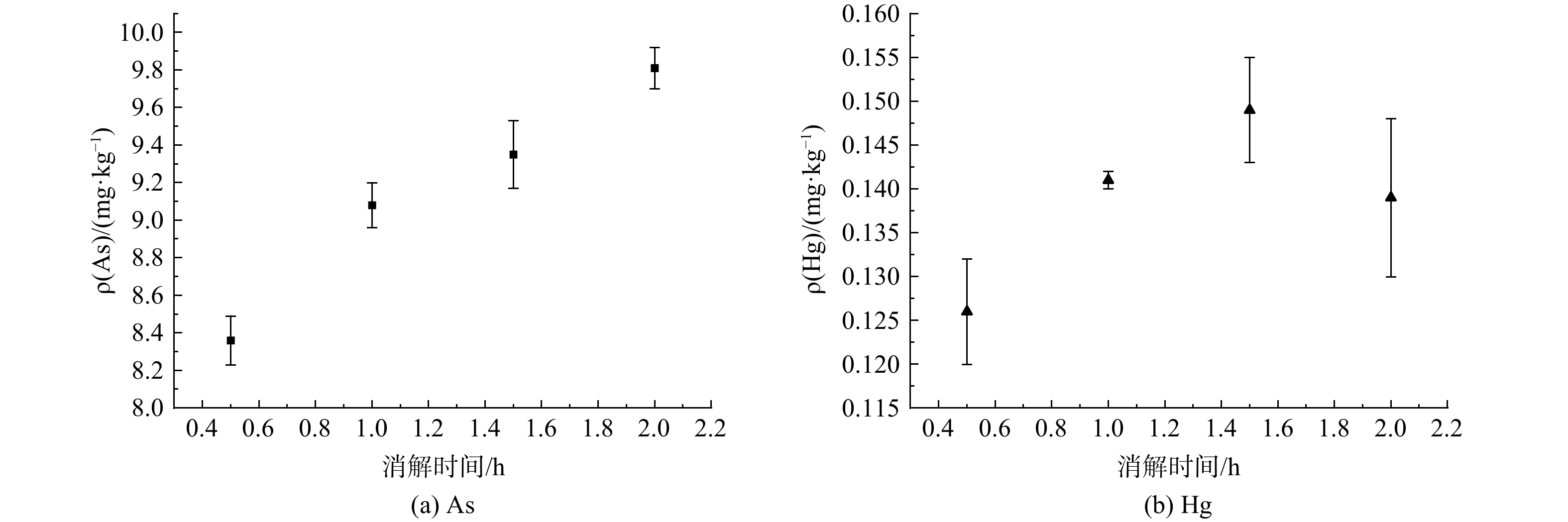
本研究对消解时间进行了优化,考察了0.5、1、1.5、2 h (消解温度100 ℃,消解液5 mL,取样量0.5 g) 的影响。结果显示 (见图3) ,Hg、As在消解0.5 h时,测定结果均出现低于标准值允许的最小值的情况;消解1、1.5、2 h的情况下,Hg、As所有的测定结果均在标准值允许的范围内,且RSD均小于5%。实验结果表明,在消解时间低于1 h时,样品中的Hg、As不能充分的被提取至消解液中,在消解时间超过1 h时,样品中的Hg、As已经可以充分的被提取至消解液中,达到准确测定的要求。考虑到消解时间越长,对结果的准确测定已无明显的提升意义,且时间越长能耗越高,因此,本实验最终确定的消解时间为1 h。
-
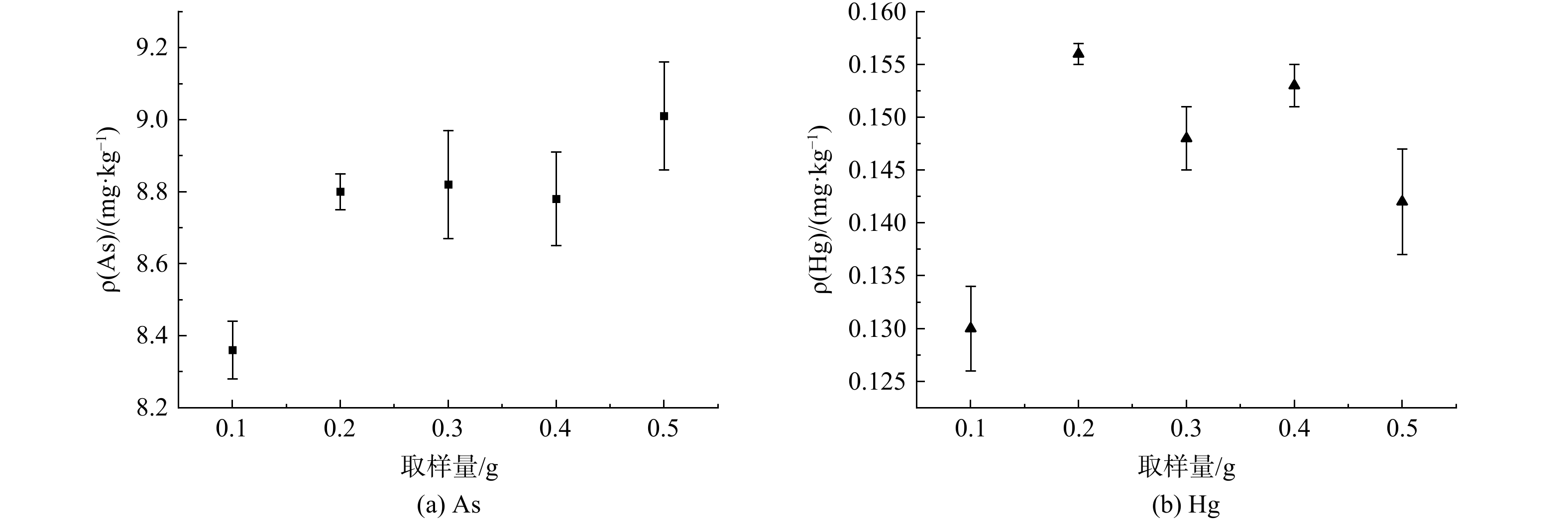
本研究对合适的取样量进行了优化,考察了0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 g取样量在以上最优条件 (消解温度100 ℃,消解液5 mL,消解时间1 h) 下的测定结果。结果表明 (见图4) ,取样量为0.1 g时,Hg、As的测定结果均出现低于标准值允许的最小值的结果;取样量在0.2~0.5 g时,Hg、As的测定结果均在标准值允许的范围内。在对仪器的分析条件进行分析时发现,在相同的稀释条件下,当取样量不超过0.1 g时,样品进入仪器分析时的浓度接近或低于校准曲线的最低点,进而增加了仪器分析的误差,增加了结果准确测定的风险。因此,本实验选取0.2~0.5 g为最佳的取样量。
-
为进一步评估本研究方法的性能,在上述得出的最佳条件下,选取GSS-24沉积物标准样品,GSS-39和GSS-40土壤标准样品,分别于2022年6月~12月期间,取一种标准样品每天测定,不同人进行测定,每种样品测定30 d,共计90个样品。由表1 可以看出,3种标准样品Hg、As测定的结果均在标准值允许范围内,Hg的相对标准偏差为3.4%~6.5%,相对误差为−9.3%~9.3%,再现性限为0.003~0.005 mg∙kg−1;As的标准偏差为2.9%~3.6%,相对误差为−7.0%~5.1%,再现性限为0.4~0.5 mg∙kg−1,说明该方法具有再现性好、精密度好、稳定性好等优点。
-
本研究选取2种上海市松江区某地块土壤和1种上海市某河道河底沉积物样品,使用本方法测定Hg、As浓度。在样品中分别加入Hg、As标准溶液进行加标回收试验 (Hg、As加标量与样品含量分别约为2∶1,1∶1) ,结果显示 (见表2) ,3种样品中Hg的平均加标回收率为93.2%~104.5%,RSD为3.1%~5.9%, As的平均加标回收率为 95.9%~103.5%, RSD为1.7%~2.9% (n=6) 。结果表明,本方法的准确度较高,满足准确度要求。
-
将本方法测定Hg、As所用的消解液用量、消解过程、是否需要清洗消解管,相对误差,相对标准偏差等与其他方法的进行了比较,结果见表3,可以看出本方法的相对误差和相对标准偏差与其他方法处于同一水平,但因本方法使用一次性消解管无需清洗;消解过程只需添加好消解液放置石墨消解仪上消解1 h,过程中无需其他操作,操作更加简单;采用一次性塑料管消除了因重复使用消解管产生汞的残留,解决了汞污染问题;一次性塑料管相比于聚四氟乙烯管/罐、玻璃比色管成本更加低廉,且消解液用量更少,更加节约成本。
-
1) 建立了一种基于王水石墨密封消解体系的前处理新方法,结合原子荧光可用于土壤和沉积物中Hg与As的测定,其相对标准偏差、相对误差、再现性限均优于标准方法。
2) 最佳实验条件为一次性塑料离心管,消解温度100 ℃,消解液 (1∶1王水) 用量5 mL,消解时间1 h,样品取样量0.2~0.5 g。
3) 本方法因采用成本低廉的一次性塑料管,无需消解管清洗,并解决了汞污染问题,消解过程无需其它操作,消解液用量少,具有操作简单、成本低、无汞污染等优点,可用于大通量土壤和沉积物中Hg、As含量的测定。
基于王水石墨密封消解体系-原子荧光法测定土壤和沉积物中汞、砷
Determination of mercury and arsenic in soils and sediments using aqua regia graphite sealed digestion system based atomic fluorescence spectrometry
-
摘要: 为解决土壤和沉积物样品中的汞、砷前处理中的一些问题,如耗时长、清洗流程复杂及汞污染等,建立了一种基于王水石墨密封消解体系的前处理新方法,结合原子荧光可用于土壤和沉积物中Hg和As的测定。在最优条件下,2种重金属元素测定结果表明,本方法具有较低的相对误差 (Hg, -9.3%~9.3%; As,-7.0%~5.1%) ,较高的加标回收率 (Hg, 93.2%~104.5%; As, 95.9%~103.5%) 。此外,本方法相关性能指标均优于现行标准方法,具有稳定性好、精密度好、准确度高等优点。更重要的是,本方法因采用成本低廉的一次性塑料管,无需消解管清洗,避免了汞的污染。而且,消解过程无需其它操作,消解液用量少,具有操作简单、成本低、无汞污染等优点,可用于大通量土壤和沉积物Hg、As含量的测定。Abstract: Some problems in pre-treatment of soil and sediment sample would influence the analysis performance, such as time consuming, complex cleaning process and mercury pollution. Herein, a novel regia graphite sealed digestion system integrated with atomic fluorescence method was established for the determination of Hg and As from soils and sediments. Under the optimized conditions, the low relative errors and satisfactory recoveries were obtained after samples measurement as (Hg, -9.3%~9.3%; As, -7.0%~5.1%), and (Hg, 93.2%~104.5%; As, 95.9%~103.9%), respectively. Importantly, our method indicated better than the current standard one because of its excellent stability, good precision/accuracy, and no mercury was released owing to avoiding the procedure of cleaning digestion pipe, which was necessary using traditional approaches. In summary, the fabricated method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and no mercury pollution, indicating great potentials in Hg and As analysis from large-flux soils and sediments.
-
Key words:
- Pre-treatment /
- Soil and sediment /
- Mercury, arsenic /
- Determine
-
重金属是我国土壤的主要污染物之一[1],因此,在我国土壤污染综合防治规划和土壤环境质量调查中被列为重点关注对象。根据《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》显示,我国土壤污染的前5大重金属污染因子为镉、镍、砷、铜与汞,土壤点位超标率均超过1.6%。其中,汞 (Hg) 与砷 (As) 在典型土壤中浓度较高,严重污染环境,危害人体健康[2]。基于此,这2种元素为场地调查中必检项目,同时也是第三次全国土壤普查中土壤环境质量的必检内容[3]。所以,构建简单、准确的方法用于测定土壤中的Hg与As,非常重要。
在分析方法中,前处理是方法成败的关键因素之一。目前,生态环境部,农业部,国家标准化委员会等发布关于土壤中Hg与As测定的标准方法有:水浴消解法[4-7],微波消解法[8]。但这些方法大多存在汞污染、时间长、能耗高、成本高、样品处理量小、设备昂贵、消解罐清洗流程复杂等问题。
为解决以上问题,本研究基于标准方法[4-7]的样品前处理方法,开发了一种利用一次性消解管的石墨消解-王水体系,用于土壤和沉积物中 Hg与As的简单、高效、快速前处理,并使用标准方法[8]的分析条件进行验证,方法优化了消解温度、消解时间、消解液用量、取样量等参数,确保前处理过程的简化与结果的准确性。研究结果可为土壤和沉积物中这2种重金属元素的测定提供一种成本低廉、样品通量大,简单准确的新方法,具有极好的应用推广前景。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
1) 耗材。50mL聚丙烯 (PP) 塑料离心管。
2) 试剂。硝酸、盐酸均为优级纯;硫脲、抗坏血酸、硼氢化钾 (分析纯)
3) 标准品。1 000 mg∙L−1 Hg单元素标准溶液GSB G 62069-90;1 000 mg∙L−1 As GSB 04-1714-2004。4种土壤或沉积物分析标准物质:GBW07385 (GSS-29) (As:9.3±0.8mg∙kg−1,Hg:0.15±0.02mg∙kg−1) 上海市崇明县新海镇土壤,GBW07453 (GSS-24) 阳江市南海滩涂沉积物,GBW07981 (GSS-39) 海南万宁富硒土壤,GBW07982 (GSS-40) 陕西渭南关中平原区土壤。
1.2 实验设备
原子荧光光度计 (AFS-8220,北京吉天仪器有限公司) ;石墨消解仪 (ED54,北京莱伯泰科仪器股份有限公司) ;离心机 (LC-LX-L40B,上海力辰仪器科技有限公司) ;电子天平 (SQP,赛多利斯(上海)贸易有限公司) 。
1.3 实验方法
取风干土壤或沉积物样品 0.1~0.5 g (精确至 0.000 1 g) 于 50 mL 一次性塑料离心管中,加入5~15 mL (1+1) 王水,加盖拧紧后回旋半圈,摇匀于消解仪上100~130 ℃加热 0.5~2 h,中间摇动几次,取下冷却,用水稀释至刻度,摇匀后静止过夜,或在4 000~6 000 r·min−1下离心 (5~10) min,取上清液按照标准方法[8]测定汞或砷的条件,进行元素测定。
1.4 仪器工作参数
As:阴极灯电流 60 mA,负高压270 V,载气流量300 mL∙min−1,屏蔽气流量800 mL∙min−1,灵敏度线波长253.7。
Hg:阴极灯电流 12 mA,灵敏度线波长193.7,其他参数与 As一致。
1.5 分析方法
分取10.0 mL置于50 mL容量瓶中,加入浓盐酸2.5 mL混匀,室温放置30 min,用实验用水定容至标线,混匀用于Hg的测定;另分取10.0 mL置于50 mL容量瓶中,加入浓盐酸5 mL,硫脲和抗坏血酸混合溶液10 mL混匀,室温放置30 min,用实验用水定容至标线,混匀用于As的测定。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 消解管的选取
现有标准方法前处理方法使用具塞玻璃比色管或聚四氟乙烯消解管或微波消解罐等,在重复使用过程中都需要使用较高浓度的硝酸溶液进行超过24 h浸泡,由于Hg元素容易产生记忆效应,因此极易被吸附残留。林海兰等[9]发现10 % (体积分数) HNO3 浸泡24 h仍不能有效去除比色管中残留的Hg。本研究在前期验证过程中发现,即使每次实验使用硝酸溶液浸泡24 h以上,随着使用次数的不断累加,Hg的残留不断增加,且无法根除。即便每次更换硝酸浸泡液,会延迟Hg污染的周期,但随着使用次数的增加,Hg污染的问题仍然存在。且频繁的更换硝酸浸泡液会导致大量硝酸浪费,且由此产生大量的危险废物,同时也增加了试剂的使用成本。
为彻底解决Hg污染问题,同时又不能增加成本,本研究采用一次性塑料 (PP) 离心管进行改进,且经过长时间大量的试剂空白和全程序空白验证发现,空白测定值均低于方法检出限,且塑料 (PP) 材质离心管无需浸泡,不但解决了Hg污染残留问题,还节约了硝酸和盐酸的用量,节约了成本。
2.2 消解温度的优化
消解温度是影响消解效果的重要因素,文典等[10]和李蕾等[11]研究显示提高温度可极大缩短消化时间,但高温意味着高能耗,在达到良好的消解效果的条件下,温度越低能耗越低。本研究对100、110、120、125 ℃,4组消化温度 (消解液 10 mL,消解时间2 h,取样量0.5 g) 的影响。图1是不同消解温度下GSS-29的 Hg、As,测定结果。可以看出,4种消解温度下的Hg、As测定值均落在了标准值范围内,准确度较高,且标准偏差均小于2.5%,结合能耗,选择100 ℃作为消解温度。
2.3 消解液用量的优化
本研究对消解液的用量进行了优化:考察了5、10、15 mL (1∶1) 王水加入量 (消解温度100 ℃,消解时间2 h,取样量0.5 g) 的影响。结果显示 (见图2) ,Hg、As所有的测定结果均在标准值允许的范围内,且RSD均小于5%。由于采用的是密闭体系,不会产生消解液的损失,因此5 mL (1∶1) 王水足以充分提取样品中的Hg、As,而消解液的用量越大,消耗的盐酸和硝酸的量也就越大,成本增加,同时产生的危险废物的量也增加。因此,从环保及节约成本的角度,本方法最终选择加入5 mL (1∶1) 王水。
2.4 消解时间的优化
本研究对消解时间进行了优化,考察了0.5、1、1.5、2 h (消解温度100 ℃,消解液5 mL,取样量0.5 g) 的影响。结果显示 (见图3) ,Hg、As在消解0.5 h时,测定结果均出现低于标准值允许的最小值的情况;消解1、1.5、2 h的情况下,Hg、As所有的测定结果均在标准值允许的范围内,且RSD均小于5%。实验结果表明,在消解时间低于1 h时,样品中的Hg、As不能充分的被提取至消解液中,在消解时间超过1 h时,样品中的Hg、As已经可以充分的被提取至消解液中,达到准确测定的要求。考虑到消解时间越长,对结果的准确测定已无明显的提升意义,且时间越长能耗越高,因此,本实验最终确定的消解时间为1 h。
2.5 取样量的确定
本研究对合适的取样量进行了优化,考察了0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 g取样量在以上最优条件 (消解温度100 ℃,消解液5 mL,消解时间1 h) 下的测定结果。结果表明 (见图4) ,取样量为0.1 g时,Hg、As的测定结果均出现低于标准值允许的最小值的结果;取样量在0.2~0.5 g时,Hg、As的测定结果均在标准值允许的范围内。在对仪器的分析条件进行分析时发现,在相同的稀释条件下,当取样量不超过0.1 g时,样品进入仪器分析时的浓度接近或低于校准曲线的最低点,进而增加了仪器分析的误差,增加了结果准确测定的风险。因此,本实验选取0.2~0.5 g为最佳的取样量。
2.6 标准样品分析
为进一步评估本研究方法的性能,在上述得出的最佳条件下,选取GSS-24沉积物标准样品,GSS-39和GSS-40土壤标准样品,分别于2022年6月~12月期间,取一种标准样品每天测定,不同人进行测定,每种样品测定30 d,共计90个样品。由表1 可以看出,3种标准样品Hg、As测定的结果均在标准值允许范围内,Hg的相对标准偏差为3.4%~6.5%,相对误差为−9.3%~9.3%,再现性限为0.003~0.005 mg∙kg−1;As的标准偏差为2.9%~3.6%,相对误差为−7.0%~5.1%,再现性限为0.4~0.5 mg∙kg−1,说明该方法具有再现性好、精密度好、稳定性好等优点。
表 1 标准土壤/沉积物样品中Hg、As测定的相对误差,再现性 (n = 30)Table 1. Relative error and reproducibility of Hg and As determination in standard soil/sediment samples元素 标准样品编号 标准值/ (mg∙kg−1) 测定值/ (mg∙kg−1) RSD/% 相对误差/% 再现性限/ (mg∙kg−1) 汞 GSS-24 0.075±0.007 0.075±0.005 6.5 −9.3~9.3 0.005 GSS-39 0.075±0.004 0.075±0.003 3.4 −5.3~5.3 0.003 GSS-40 0.081±0.007 0.081±0.004 5.0 −8.6~7.4 0.004 砷 GSS-24 15.8±0.9 15.7±0.5 2.9 −5.7~5.1 0.5 GSS-39 12.9±0.9 12.5±0.4 3.6 −7.0~3.9 0.4 GSS-40 13.1±1 12.9±0.4 3.3 −6.9~3.8 0.4 2.7 实际样品分析及加标回收
本研究选取2种上海市松江区某地块土壤和1种上海市某河道河底沉积物样品,使用本方法测定Hg、As浓度。在样品中分别加入Hg、As标准溶液进行加标回收试验 (Hg、As加标量与样品含量分别约为2∶1,1∶1) ,结果显示 (见表2) ,3种样品中Hg的平均加标回收率为93.2%~104.5%,RSD为3.1%~5.9%, As的平均加标回收率为 95.9%~103.5%, RSD为1.7%~2.9% (n=6) 。结果表明,本方法的准确度较高,满足准确度要求。
表 2 实际样品中Hg、As含量测定及加标回收实验结果 (n=6)Table 2. Results of As and Hg determination in samples and the spiked assays (n=6)元素 样品类型 加标前测定结果/(mg∙kg−1) 加标量/(mg∙kg−1) 加标后测定结果/(mg∙kg−1) 平均加标回收率/% RSD/% Hg 土壤 0.044±0.003 0.1 0.137±0.007 93.2 5.0 土壤 0.026±0.003 0.05 0.074±0.004 95.3 5.9 沉积物 0.066±0.007 0.15 0.223±0.007 104.5 3.1 As 土壤 10.5±0.5 7.5 17.8±0.3 96.8 1.7 土壤 14.6±0.3 12.5 27.5±0.8 103.5 2.9 沉积物 10.8±0.5 10 20.4±0.6 95.9 2.8 2.8 本方法与其他方法对比
将本方法测定Hg、As所用的消解液用量、消解过程、是否需要清洗消解管,相对误差,相对标准偏差等与其他方法的进行了比较,结果见表3,可以看出本方法的相对误差和相对标准偏差与其他方法处于同一水平,但因本方法使用一次性消解管无需清洗;消解过程只需添加好消解液放置石墨消解仪上消解1 h,过程中无需其他操作,操作更加简单;采用一次性塑料管消除了因重复使用消解管产生汞的残留,解决了汞污染问题;一次性塑料管相比于聚四氟乙烯管/罐、玻璃比色管成本更加低廉,且消解液用量更少,更加节约成本。
表 3 本方法与其他测定Hg、As的方法参数比较Table 3. Comparison of the parameters of this method with others for the determination of Hg and As元素 方法 消解液用量/ (王水) 消解容器 消解过程 是否需要清洗 相对误差/% RSD/% 参考文献 Hg 王水石墨密封消解体系 5 mL (1∶1) 塑料管 100 ℃,1.0 h 否 −9.3~9.3 3.4~6.5 本方法 水浴消解 10 mL (1∶1) 玻璃比色管 100 ℃,2.0 h 是 — — [5-6] 微波消解 8 mL 聚四氟乙烯消解罐 100 ℃ 2 min,150 ℃ 3 min,180 ℃ 25 min 是 −12.5~12.5 1.4~11.7 [8] 石墨消解微敞开体系 6 mL (1∶1) 聚四氟乙烯消化管 150 ℃ 20 min 是 −5.0~8.3 3.2~7.5 [11] As 王水石墨密封消解体系 5 mL (1∶1) 塑料管 100 ℃,1.0 h 否 −7.0~5.1 2.9~3.6 本方法 水浴消解 10 mL (1∶1) 玻璃比色管 100 ℃,2.0 h 是 — — [4,7] 微波消解 8 mL 聚四氟乙烯消解罐 100 ℃ 2 min,150 ℃ 3 min,180 ℃ 25 min 是 -7.5~4.7 0.7~8.9 [8] 石墨消解微敞开体系 6 mL (1∶1) 聚四氟乙烯消化管 150 ℃ 20 min 是 −4.7~2.3 2.9~4.0 [11] 3. 结论
1) 建立了一种基于王水石墨密封消解体系的前处理新方法,结合原子荧光可用于土壤和沉积物中Hg与As的测定,其相对标准偏差、相对误差、再现性限均优于标准方法。
2) 最佳实验条件为一次性塑料离心管,消解温度100 ℃,消解液 (1∶1王水) 用量5 mL,消解时间1 h,样品取样量0.2~0.5 g。
3) 本方法因采用成本低廉的一次性塑料管,无需消解管清洗,并解决了汞污染问题,消解过程无需其它操作,消解液用量少,具有操作简单、成本低、无汞污染等优点,可用于大通量土壤和沉积物中Hg、As含量的测定。
-
表 1 标准土壤/沉积物样品中Hg、As测定的相对误差,再现性 (n = 30)
Table 1. Relative error and reproducibility of Hg and As determination in standard soil/sediment samples
元素 标准样品编号 标准值/ (mg∙kg−1) 测定值/ (mg∙kg−1) RSD/% 相对误差/% 再现性限/ (mg∙kg−1) 汞 GSS-24 0.075±0.007 0.075±0.005 6.5 −9.3~9.3 0.005 GSS-39 0.075±0.004 0.075±0.003 3.4 −5.3~5.3 0.003 GSS-40 0.081±0.007 0.081±0.004 5.0 −8.6~7.4 0.004 砷 GSS-24 15.8±0.9 15.7±0.5 2.9 −5.7~5.1 0.5 GSS-39 12.9±0.9 12.5±0.4 3.6 −7.0~3.9 0.4 GSS-40 13.1±1 12.9±0.4 3.3 −6.9~3.8 0.4 表 2 实际样品中Hg、As含量测定及加标回收实验结果 (n=6)
Table 2. Results of As and Hg determination in samples and the spiked assays (n=6)
元素 样品类型 加标前测定结果/(mg∙kg−1) 加标量/(mg∙kg−1) 加标后测定结果/(mg∙kg−1) 平均加标回收率/% RSD/% Hg 土壤 0.044±0.003 0.1 0.137±0.007 93.2 5.0 土壤 0.026±0.003 0.05 0.074±0.004 95.3 5.9 沉积物 0.066±0.007 0.15 0.223±0.007 104.5 3.1 As 土壤 10.5±0.5 7.5 17.8±0.3 96.8 1.7 土壤 14.6±0.3 12.5 27.5±0.8 103.5 2.9 沉积物 10.8±0.5 10 20.4±0.6 95.9 2.8 表 3 本方法与其他测定Hg、As的方法参数比较
Table 3. Comparison of the parameters of this method with others for the determination of Hg and As
元素 方法 消解液用量/ (王水) 消解容器 消解过程 是否需要清洗 相对误差/% RSD/% 参考文献 Hg 王水石墨密封消解体系 5 mL (1∶1) 塑料管 100 ℃,1.0 h 否 −9.3~9.3 3.4~6.5 本方法 水浴消解 10 mL (1∶1) 玻璃比色管 100 ℃,2.0 h 是 — — [5-6] 微波消解 8 mL 聚四氟乙烯消解罐 100 ℃ 2 min,150 ℃ 3 min,180 ℃ 25 min 是 −12.5~12.5 1.4~11.7 [8] 石墨消解微敞开体系 6 mL (1∶1) 聚四氟乙烯消化管 150 ℃ 20 min 是 −5.0~8.3 3.2~7.5 [11] As 王水石墨密封消解体系 5 mL (1∶1) 塑料管 100 ℃,1.0 h 否 −7.0~5.1 2.9~3.6 本方法 水浴消解 10 mL (1∶1) 玻璃比色管 100 ℃,2.0 h 是 — — [4,7] 微波消解 8 mL 聚四氟乙烯消解罐 100 ℃ 2 min,150 ℃ 3 min,180 ℃ 25 min 是 -7.5~4.7 0.7~8.9 [8] 石墨消解微敞开体系 6 mL (1∶1) 聚四氟乙烯消化管 150 ℃ 20 min 是 −4.7~2.3 2.9~4.0 [11] -
[1] 章海波, 骆永明, 李远, 等. 中国土壤环境质量标准中重金属指标的筛选研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2014, 51(3): 429-438. [2] 环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染调查公报[Z]. 中华人民共和国中央人民政府门户网站, 2014-04-17. [3] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行): GB 36600-2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2018. [4] 中华人民共和国农业部. 土壤检测 第11部分: 土壤总砷的测定: NY/T 1121.11-2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [5] 中华人民共和国农业部. 土壤检测 第10部分: 土壤总汞的测定: NY/T 1121.10-2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [6] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 土壤质量 总汞、总砷、总铅的测定 原子荧光法 第1部分: 土壤中总汞的测定: GB/T 22105.1-2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 土壤质量 总汞、总砷、总铅的测定 原子荧光法 第2部分: 土壤中总砷的测定: GB/T 22105.2-2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [8] 环境保护部. 土壤和沉积物汞、砷、硒、铋、锑的测定 微波消解/原子荧光法: HJ 680-2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2014. [9] 林海兰, 朱日龙, 于磊, 等. 水浴消解-原子荧光光谱法测定土壤和沉积物中砷、汞、硒、锑和铋[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(5): 1528. [10] 文典, 严冬, 赵沛华, 等. 快速高通量全消解ICP-MS法测定《全国土壤污染状况详查》项目中14种元素[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(6): 1432. [11] 李蕾, 卢燕湘, 鄢韬. 基于石墨消解微敞开体系的快速王水提取-原子荧光法测定土壤中砷和汞[J]. 分析试验室, 2023, 7(42): 872-877. -




 下载:
下载: