-
NOx是主要的大气污染物,其大量排放会破坏臭氧层形成酸雨[1-2],危害人群和动植物的健康[3-4]。我国已相继出台一系列严格的NOx排放行业限值标准,有效降低NOx排放已成为行业关注重点。选择性催化还原 (selective catalytic reduction,SCR) 技术为最有效且应用最广泛的NOx脱除技术之一[5-6]。蜂窝状催化剂具有机械强度好、床层阻力小等优点[7],而涂覆法具有操作方法简单、前驱体材料用量少、活性组分利用率高等优点[8]。通过涂覆方法制备的蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2整体式催化剂占据了大部分市场。KONG等[9]和DE-LA-TORRE等[10]等均证明了在没有添加剂的情况下,催化剂的负载量和牢固性极差,这表明添加剂在涂覆整体催化剂过程中的重要性。孟鹏通等[11]使用聚乙烯醇 (polyvinyl alcohol,PVA) 和拟薄水铝石 (SB粉) 两种粘结剂制备Cu-SSZ-13/堇青石整体式催化剂,发现PVA制备的催化剂具有更好的涂层稳定性和脱硝活性。虽然涂覆式蜂窝状催化剂应用广泛,但其工艺仍存在涂覆不均匀[12]、涂层不稳定等缺点,故导致其涂覆效果差,从而降低脱硝性能。除此之外,烟气成分较复杂,存在HC、SOx、H2O等物质,其均会造成SCR催化剂中毒失活,从而影响催化剂的脱硝效果[13]。目前,针对整体式催化剂的中毒影响原因的分析较少,尤其是针对HCs对SCR催化剂中毒的研究。
为提高催化剂的脱硝效率,本课题组拟探究涂覆式蜂窝状钒钨钛催化剂的涂优化配方,重点分析C3H8、SO2和H2O对催化剂的影响原因。本研究以蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂为基础,首先采用正交实验的方法,以PVA的质量分数 (0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%) 、吐温-20的质量分数 (0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%) 、pH (1.5、4.5、7.5、10) 为3因素,以负载率、附着率以及200~550 ℃的NO转化率作为响应值,进行3因素4水平的正交实验。通过正交实验得到最优配方后,进行整体式蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂的制备,并对其进行活性、抗C3H8、SO2和H2O中毒性能瞬态和稳定性测试,最后通过粒径检测、SEM、XPS、H2-TPR和NH3-TPD的表征手段,对SCR性能的影响因素进行分析,探究其对蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂涂覆效果及SCR性能影响,以期为涂覆式蜂窝状催化剂的优化合成及其实际应用提供参考。
-
将一定量的偏钒酸铵 (NH4VO3,AR) 、偏钨酸铵 (H28N6O41W12,AR) 、二氧化钛 (TiO2,AR) 、30%酸性硅溶胶 (SiO2, (30±1) %SiO2水溶液) 、吐温-20 (C26H50O10,AR) 和聚乙烯醇溶液 (C2H4O,5%C2H4O水溶液) 依次溶解在去离子水中以获得浸渍液,用硝酸 (HNO3,GR) 和氨水 (H5NO,AR) 调节pH。将46 cpsi的商业蜂窝状堇青石 (250 mm×250 mm×300 mm) 作为载体,整体浸入溶液中以负载活性成分。使用洗耳球对通道进行吹扫疏通,然后将得到的样品置于110 °C的烘箱中烘干3 h,以蒸发催化剂表面的水和挥发性有机溶剂。之后,将所得的整体催化剂块转移到马弗炉中在120 ℃煅烧3 h,然后升温至550 °C煅烧5 h。获得V2O5质量分数为1%、WO3质量分数为9%的催化剂,记为V-W-Ti/CC。
-
催化剂的附着率测试是采用数控超声清洗仪 (昆山市超声仪器有限公司,KQ-400 DE) 进行,其工作功率为40 kW,振动频率为40 kHz。以超纯水为介质,将催化剂样品浸没在水中超声20 min后,于110 ℃下干燥5 h,称重测量催化剂涂层的质量损失。为减小实验的随机性,分别进行了6组平行实验。由式 (1) 和式 (2) 计算催化剂涂层的负载率和附着率。
式中:m0为空白堇青石的质量,g;m1为浸渍负载后催化剂的质量,g;m2为超声脱落后催化剂的质量,g。
-
浆料的粒径通过Bettersize 300plus激光/图像粒度粒形分析仪 (丹东百特仪器有限公司) 进行测试。扫描电镜 (scanning electron microscope,SEM) 采用JSM-6700F (日本电子公司 (JEOL) ) 测定。X射线光电子能谱 (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS) 采用ESCALAB 250Xi K-alpha (美国赛默飞公司) 测定,方法为单色化Al靶测试。H2-程序升温还原 (H2-temperature programmed reduction,H2-TPR) 采用化学吸附分析仪Chembet (美国康塔公司) 测定:每个样品在300 ℃下用N2预处理1 h;总流速为50 mL·min−1;之后以10 ℃·min−1的加热速率和10% H2/Ar 气体从50 ℃升温至700 ℃,依时间记录TCD信号。NH3-程序升温脱附 (NH3-temperature programmed desorption,NH3-TPD) 采用化学吸附分析仪Chembet (美国康塔公司) 测定:通入流量为50 mL·min−1 N2,以10 ℃·min−1升温至 300 ℃,预处理1 h;降温至100 ℃,保持气体总流量不变,吸附10% NH3/N2时间为1 h; 然后N2吹扫1 h,待基线稳定后,以 10 ℃·min−1升温至 750 ℃,依时间记录TCD信号。
-
活性测试在固定床反应装置 (北京金麟搏泰科贸有限公司) 中进行。用石英棉包裹整体式催化剂4周,然后置于石英反应管内部,在具有程序温控的反应炉中进行反应。将热电偶放置在石英反应管催化剂孔隙中以记录催化剂反应温度。使用烟气分析仪 (北京雪迪龙科技股份有限公司,SCS-900UV) 连续分析NO的变化情况。SCR反应条件:NO (体积分数0.1%) 、NH3 (体积分数0.1%)、 O2 (体积分数10%)、C3H8 (体积分数0.1%) 、SO2 (体积分数0.03%)、 H2O (体积分数7%),N2作为平衡气,体积空速为5 556 h−1。在温度为200~550 ℃内间隔50 ℃采集数据,每个温度下至少反应30 min,进行SCR反应性能测试。NO转化率计算公式如式 (3) 所示。
式中:[NO]in为NO的进口体积分数;[NO]out为NO的出口体积分数。
-
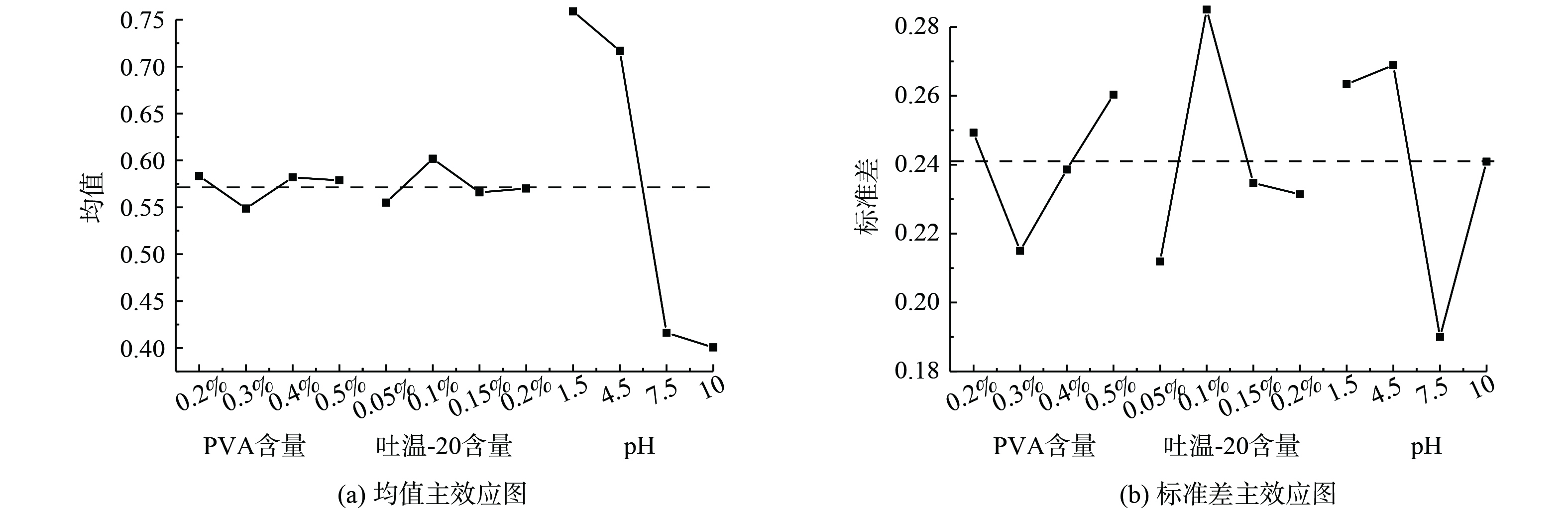
浆料的质量是影响催化剂的重要因素[14],也直接影响着催化剂涂层的质量。良好的涂层通常以均匀、高负载和强附着力为特征。通常认为负载率大于20%表示负载能力优秀;附着率大于90%附着性能良好[15]。基于大量数据,正交实验可科学地挑选出具有代表性的数据点,进行高效、简便的实验。前期含有PVA、吐温-20、聚乙二醇、可溶性淀粉、羧甲基纤维素钠的有机添加剂筛选实验结果表明,PVA和吐温−20共同存在的浆料稳定性最好,且该浆料制备的催化剂有着良好的负载和附着效果。之后进行了PVA和吐温−20的适宜质量分数筛选,发现当PVA质量分数超过0.5%、吐温−20质量分数超过0.2%时,浆料的流动性明显变差,催化剂表面发生浆料堆积和洞口堵塞现象。而当PVA质量分数小于0.2%、吐温−20质量分数小于0.05%时,催化剂表面出现大面积载体裸露,涂覆效果变差。因此,选取常用且适宜的PVA质量分数 (0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%) 和吐温-20质量分数 (0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%) 进行正交实验。此外,pH对催化剂也有着重要影响。DONG等[16]发现在钒酸溶液中,溶液酸度增加,催化剂表面酸性和活性中心的数量随之增加,从而提高了催化剂的脱硝活性。LI等[17]发现在pH为4时,钒钨钛浆料较稳定性。梁银等[18]在碱性条件下制备钒基催化剂发现,比酸性条件会使催化剂脱硝性能更好,故本实验选取pH (1.5、4.5、7.5、10) 进行正交实验。因此,最终选用PVA质量分数为0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%,吐温-20质量分数为0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%,pH为1.5、4.5、7.5、10,作为3因素4水平,以负载率、附着率以及200~550 ℃的NO转化率作为响应值,进行正交实验。考虑到当pH为7.5和10时,其在表面形成明显且多的裂痕,并且附着性很差,故不考虑其活性问题,结果如表1和表2所示。根据正交实验结果,分别列出了均值响应表 (表3) 、标准差响应表 (表4) ,并据此制出了均值主效应图 (图1 (a) ) 、标准差主效应图 (图1 (b) ) 。
图1 (a) 表明,对于负载率、附着率以及200~550 ℃的NO转化率这3组响应值,pH的影响>吐温-20质量分数>PVA质量分数,并且当PVA质量分数为0.2%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%且pH为1.5时理论上拥有最高的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。图1 (b) 表明,pH的离散性>吐温-20质量分数>PVA质量分数,这说明pH对其结果的影响波动最大,PVA质量分数对结果的影响波动较小。该正交实验的平均值为0.573 2,除了负载率和200 ℃的NO转化率越接近均值越好,附着率和250~550 ℃的NO转化率均越高于均值越好,因此反应在标准差响应表上则越高于平均标准差越好。在PVA质量分数为0.2%和0.5%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%且pH为1.5和4.5时的标准差均在平均标准差以上,具有良好的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。综合来看,当PVA质量分数为0.2%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%、pH为1.5条件下的浆料会有更合适的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。为验证该条件下的负载效果,对其制备的催化剂进行了验证,结果见表3。使用该优化配方制备的催化剂进行了6组平行实验,制备出催化剂的平均负载率为26.69%、平均附着率为93.79%,相比于其他对照实验组拥有最好的负载率和附着率。因此,采用PVA质量分数为0.2%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%、pH为1.5的浆料进行后续SCR性能测试。
-
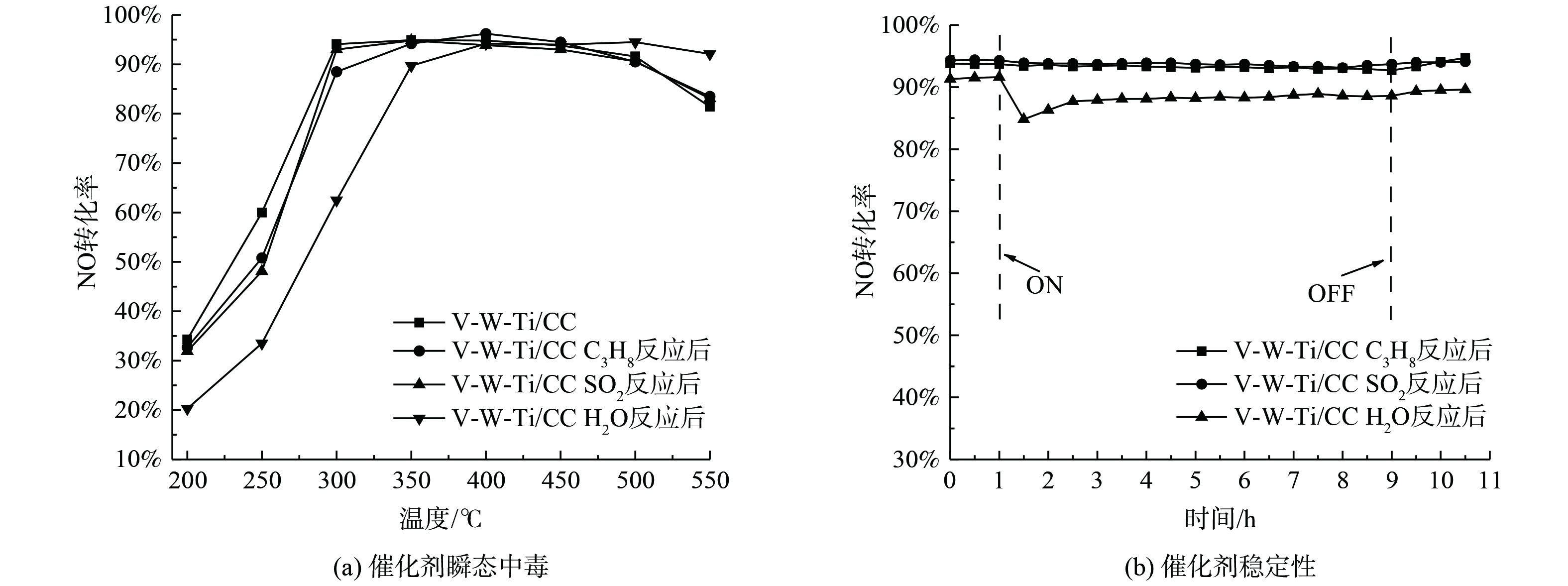
通过2.1正交实验筛选出的最优配方制备V-W-Ti/CC催化剂,并对其进行活性及稳定性测试 (图2) 。如图2 (a) 所示,使用该配方制备的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂有着良好的催化活性和抗中毒性能。在未中毒的情况下,300~550 ℃的NO转化率均大于80%,其中300~500 ℃的NO转化率大于90%;而C3H8和SO2中毒主要影响在低温250 ℃的情况下,其活性分别为50.8%和48.1%,相比于未中毒催化剂 (其活性为60%) 分别下降了9.2%和11.9%,但其在中高温区 (300~550 ℃) 仍有着良好的催化性能表现。但H2O中毒对其全部低温区间影响均较大,在200~300 ℃的NO转化率分别为20.3%、33.5%、62.5%,比未中毒催化剂 (其活性在200 ℃、250 ℃、300 ℃的活性分别为34.3%、60%、94.1%) 分别降低了14%、26.5%和31.6%,其在中高温区 (350~550 ℃) 有着良好的催化性能表现。之后,在350 ℃进行催化剂的稳定性测试。如图2 (b) 所示,在350 ℃时C3H8和SO2对该催化剂几乎没有影响,且NO转化率一直稳定在90%以上,H2O中毒的催化剂先出现明显下降再逐步提升,最终稳定在约88%,停止通入H2O后,催化剂的NO转化率缓慢提升。此前,李富宽等[19]制备整体式钒钨钛催化剂在300~500 ℃的SCR活性达到80%以上;SHEN等[20]制备的整体式钒钨钛催化剂在350~550 ℃的SCR活性达到80%以上。与以上催化剂相比,本研究制备的V-W-Ti/CC在300~550 ℃区间达到80%以上,拓宽了50 ℃的温度区间。此外,ZHAO等[21]制备的整体式钒钨钛催化剂在400 ℃时加入0.02% SO2或2% H2O情况下,活性仅稳定在约83%。而本研究制备的V-W-Ti/CC在375 ℃时加入0.03% SO2或7% H2O情况下,活性分别稳定在约93%或86%,催化活性有明显提升。以上均说明通过该浆料配方制备的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂面对C3H8、SO2和H2O中毒时均有良好的抗中毒性能和稳定性。
-
为探究使用PVA和吐温-20拥有更好负载率和附着率的原因,进行了粒径分析和SEM表征,并针对催化剂拥有良好催化活性及在C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后催化剂在低温区明显下降而中高温区仍保持催化活性的原因进行了XPS、NH3-TPD和H2-TPR表征,分析结果如下。
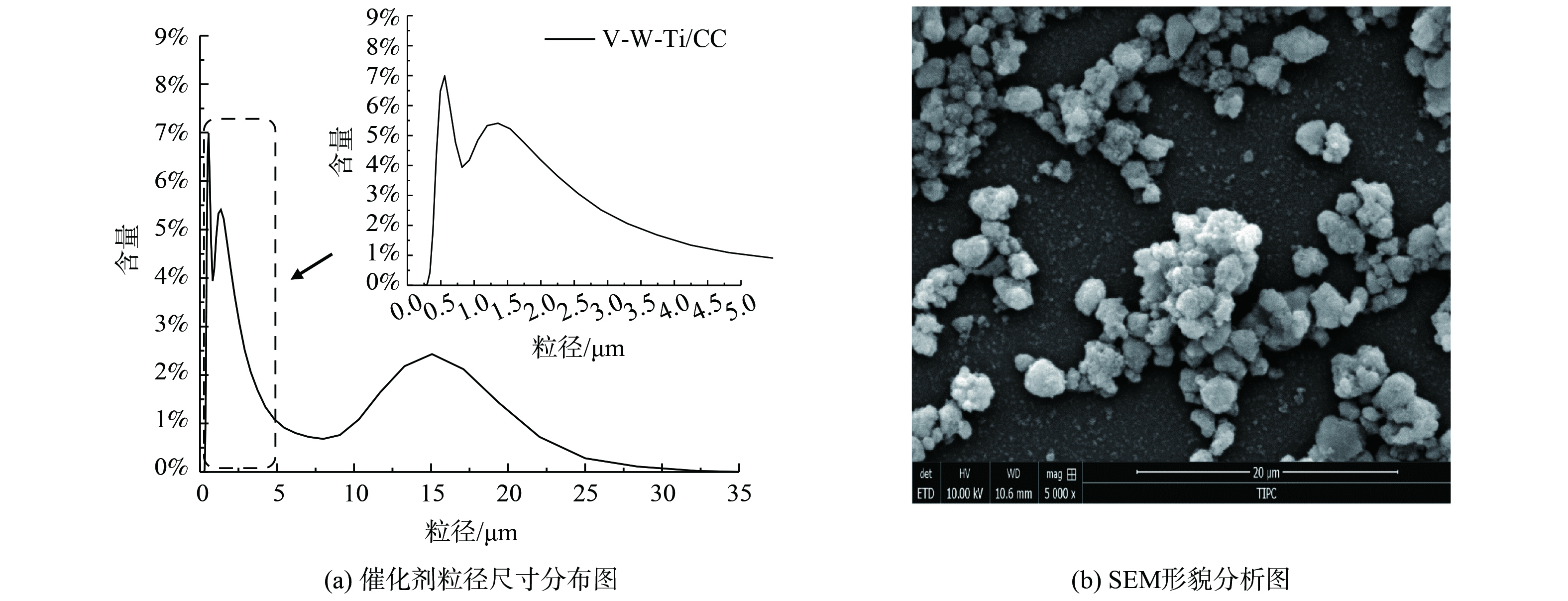
1) 催化剂粒径及表面形貌分析。涂层附着力与浆料的粒径有关。载体涂层的粘附有2种机械机制,分别为载体涂层颗粒之间的“锚定”和互锁,以及载体表面的不规则性和粉末颗粒之间发生的固体界面力[22]。因此,为获得成功的整体涂层,催化剂颗粒应小于表面粗糙度[23]。由于堇青石载体的大孔隙率约为5 μm,故负载粒径最佳范围应小于5 μm[24]。大粒径的存在会导致浆料沉淀速度快、在堇青石表面堆积,导致浆料不能进入堇青石内部发生锚定作用,故导致脱落效果明显[9]图3 (a) 表明,该配方制备的催化剂浆料粒径为0~35 μm,其集中分布区域为0.2~0.7 μm、0.7~5 μm、5~30 μm,其中粒径在0.2~0.7 μm浆料最多。小于5 μm粒径浆料质量分数为83%,且其平均粒径为3.5 μm,小于堇青石载体的孔径,这可能是该配方所制备的浆料的负载率和附着率较好的原因。
通过扫描电镜观察不同添加剂对催化剂的微观组织形貌的影响,结果见图3 (b) 。在放大5 000倍的情况下,该配方制备的催化剂颗粒较均匀,无明显团聚作用,这与粒径测试结果相一致。
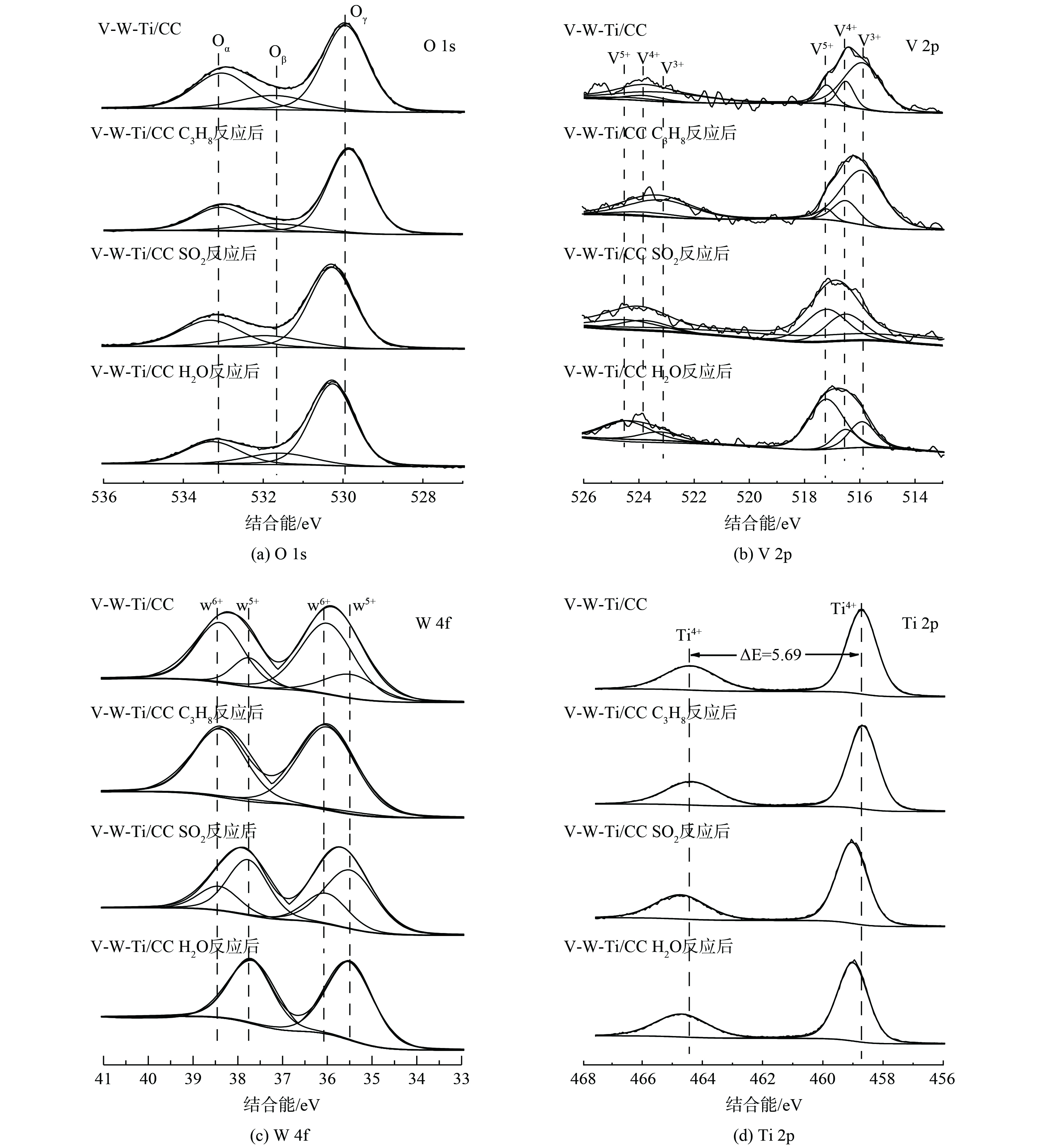
2) 催化剂表面物种及价态分析。催化剂的表面物种类型及其价态分布情况可通过XPS检测结果进行分析 (图4) 。NH3-SCR是一种有氧参与反应,表面活性氧对催化活性至关重要。O 1s测试结果如图4 (a) 所示。一般来说,位于529.72~529.96 eV 的峰 (Oγ) 对应于晶格氧O2-[25]。而在531.42~532.12 eV的峰 (Oβ) 对应于表面化学吸附的氧物质或氧物质的电离[26-27]。介于533.01~533.16 eV的峰(Oα) 被认为是羟基物质或吸附水[28]。其中,Oα和Oβ均属于表面活性氧物种,具有较高迁移率,有利于NO氧化成NO2进行快速SCR反应和不同价态活性物种之间进行氧化还原循环[29]。根据O 1s光谱定量得出(Oα+Oβ)/(Oα+Oβ+Oγ)的相对比值,如表4所示。与V-W-Ti/CC催化剂相比,经过C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂表面上的不稳定氧物种质量分数均有下降,从而导致了催化剂催化活性下降,这与2.2性能测试结果相一致。
如图4 (b) 为催化剂的V 2p XPS光谱。V 2p1/2峰的位置在524.13~524.18 eV,V 2p3/2峰的位置在516.18~516.58 eV[30]。V 2p3/2 XPS 峰分为V5+、V4+和V3+ 3个峰,分别对应于517.04~517.43 eV、516.45~516.48 eV、515.60~515.76 eV[31]。SCR活性与催化剂的表面(V3++V4+)/Vn+相关[32]。通过峰值反卷积计算表面上V5+、V4+和V3+物种的分布情况,如表6所示。除了经过C3H8反应后的催化剂低价态V3+和V4+这两者比例有所升高,而经SO2和H2O中毒的催化剂均明显下降。V3+和V4+被认为是催化剂中的缺陷V位点,催化剂表面缺陷越多,催化剂表面与NH3的反应越活跃,使得催化剂表面酸性位点强度增加[30]。经SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂V3+和V4+的含量明显下降,故降低了其SCR催化活性,这与活性测试结果相一致。
图4 (c) 为催化剂的W 4f XPS图谱。W5+和W6+的W 4f7/2的结合能分别为35.45~35.51 eV和35.94~36.19 eV。W5+和W6+的W 4f5/2分别为37.62~37.93 eV和38.22~38.64 eV[33]。与V-W-Ti/CC催化剂相比,经C3H8反应后的催化剂W5+/(W5++W6+)的比例明显减少,这可能是导致在C3H8存在时活性下降的主要原因。此外,虽然SO2和H2O制备的催化剂的W5+/(W5++W6+)的比例增加,但其W 4f的结合能明显变小,这可能是因为SO2和H2O的添加影响了WOx物种的周围环境,促进了四面体WOx向八面体WOx的转化,而这种转化会削弱WOx物种的还原性,并不利于活性提高[34],因此同样导致催化剂活性下降。
图4 (d) 为Ti 2p 的XPS图谱。4种催化剂的Ti 2p1/2位于464.39~464.75 eV,Ti 2p3/2 的峰位于458.70~459.06 eV,这是锐钛矿中Ti4+物种的特征二氧化钛[35-36]。V-W-Ti/CC催化剂和经C3H8反应后的催化剂结合能较低,这说明Ti为富电子状态。而经SO2和H2O催化剂结合能变大。这可能表明SO2和H2O会抑制Ti物种的结合能,使其向高结合能转变[37]。
综上所述,C3H8反应后的催化剂表面活性氧和活性W5+物种质量分数降低,而活性V3+和V4+物种质量分数升高的现象。这可能是由于C3H8与NH3同时竞争V位点,C3H8氧化过程中生成的CO等中间体会抑制V4+的进一步氧化[38],从而维系了部分V4+物种的数量。V物种的抑制间接促进了W=O直接与NO的氧化活化反应[39],从而使W5+物种质量分数降低。SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂表面活性氧和活性V3+和V4+质量分数降低,且活性W5+质量分数升高的现象。这可能是由于在SO2存在时,V3+被氧化形成VOSO4[40],同时SO2与W-O-W发生反应,W6+被还原为W5+[41]。而H2O存在的条件下,H2O与NH3竞争活性位点,并且使Lewis酸性位点羟基化,抑制Brønsted酸上的NH4+和NO的相互反应[42],从而导致表面活性氧和活性V3+和V4+由于质量分数降低,且活性W5+含量升高的现象。虽然SO2和H2O反应后活性W5+质量分数升高,但由于其添加影响了WOx物种的周围环境,削弱WOx物种的还原性,并不利于活性提高[43],同样会导致催化剂活性下降。
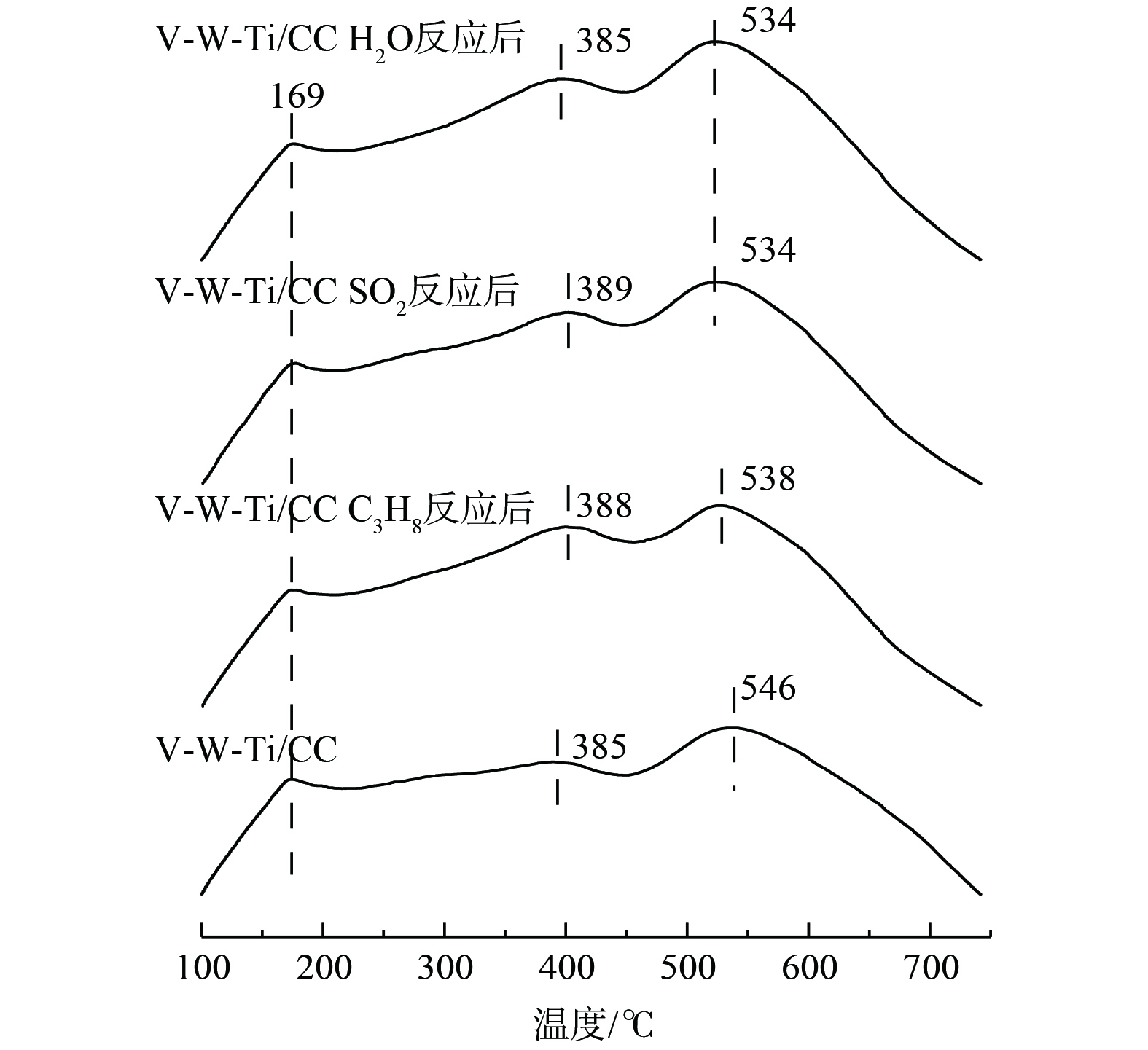
3)催化剂表面酸性分析。催化剂的酸量及强度可用NH3-TPD进行分析 (图5) 。新鲜和反应后的催化剂均出现3个脱附峰。其中,169 ℃对应的峰为弱Brønsted酸位上氨物种的脱附峰,387 ℃左右对应的脱附峰为强Brønsted酸上氨物种的脱附峰[44],540 ℃左右为 Lewis强酸位的脱附峰[45]。表5表明,与新鲜催化剂相比,加入C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂在低温区的物理吸附的酸强度和物种变化甚微,而在中温区不仅Brønsted酸强略有增加且物种增多。这可能是由于C3H8反应时生成的中间体、SO2反应时生成的硫酸盐及H2O存在时将部分Lewis酸性位转化为Brønsted酸位,从而出现中温区酸量增多的现象。同时,高温区Lewis酸强度略有降低。在低温时,V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂的脱硝效果主要依赖中性酸位数量和氧化还原性能[46]。虽然加入C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂有着数量更高的中性酸数量但是其氧化还原性能明显下降 (见2.3.4) 。此外,C3H8、SO2和H2O存在时与NH3竞争反应位点,使NH4+和配位NH3无法参与反应,从而降低了吸附NH3反应速率,进而减弱了催化剂在低温条件下的催化效果。而中高温时,主要依靠V位点提供的强Lewis酸位维持其热稳定性,C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂仍保持着较多数量的酸性数量。根据前人研究得知,在中高温时,C3H8[38]、SO2[47]和H2O[48]对催化剂的抑制作用减弱,因此这可能是催化剂在低温下活性下降但仍能保持中高温活性不变的原因。
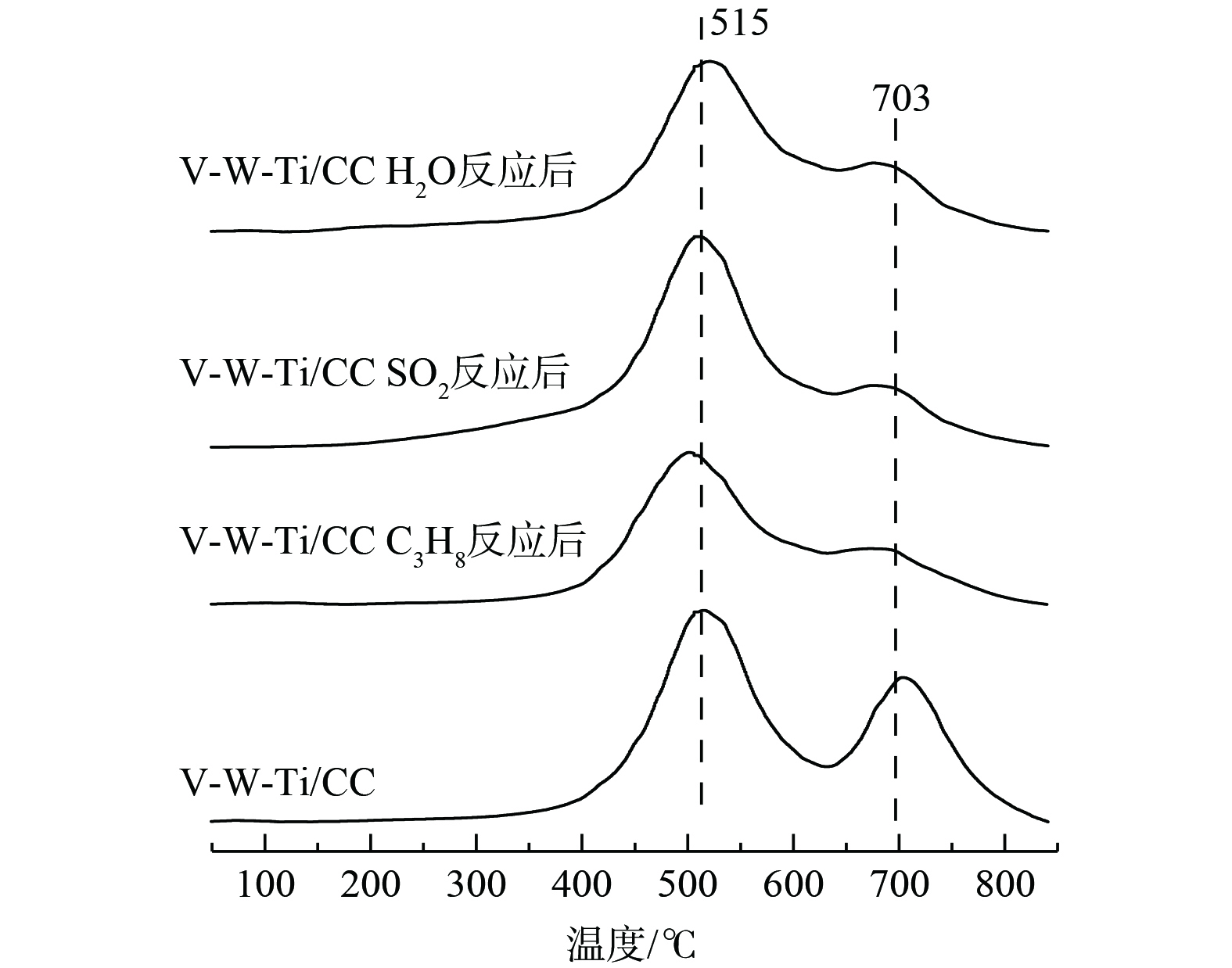
4)催化剂氧化还原性能分析。催化剂的氧化还原能力可通过H2-TPR检测结果 (图6) 进行分析。新鲜的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂在515 °C和704 °C处出现2个还原峰。其中,以515 ℃为中心的为V5+还原为V3+的还原峰[49]和W6+还原为W4+的还原峰的重叠[50],以703 ℃为中心的为W4+还原为W的还原峰[51]。与新鲜催化剂相比,C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂还原峰位置并无明显变化,但还原峰面积明显减少。这表明H2消耗量有显著降低,亦说明在经过C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后,催化剂表面高价态V5+或W6+以及W4+含量均有下降,这与XPS结果一致。因此,降低催化剂的氧化还原性能,会导致低温下的催化剂的活性有明显下降。
-
1) 当PVA和吐温-20质量分数分别为0.2%和0.1%,pH为1.5时制备的浆料有较好的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。在添加C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后,该催化剂在低温下有明显抑制作用。2) 该配方制备的浆料其粒径<5 μm的比例高达83%,这可使粒径和载体更好的发生“锚定”和互锁,使其具有更好的负载率和稳定性。C3H8、SO2和H2O对催化剂的抑制作用主要归结为降低催化剂的氧化还原性能。虽然低温下抑制作用明显,但是使用该配方制备的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂在中高温区 (300~550 ℃) 仍有着良好的催化活性和抗中毒性能。3) 低温时,C3H8、SO2和H2O存在时竞争反应位点,使NH4+和配位NH3无法参与反应,从而降低了催化剂在低温条件下的催化效果。而中高温时,由于C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂仍保持着较多数量的强酸数量,并且C3H8、SO2和H2O对催化剂的抑制作用减弱,故保持了较好的中高温活性。在350~500 ℃区间活性、C3H8、SO2和H2O反应催化活性均大于80%以上,且350 ℃的稳定性均高于88%。4) 该催化剂面对C3H8、SO2和H2O中毒时均有良好的抗中毒性能和稳定性。该配方制备的催化剂具有优异的SCR性能,是制备涂覆型整体式催化剂的优良浆料配方。
涂覆式蜂窝状钒钨钛催化剂的SCR及抗中毒性能
SCR and anti-poisoning properties of coated honeycomb vanadium-tungsten-titanium oxides catalyst
-
摘要: 为制备性能优异的涂覆式蜂窝状SCR催化剂用于高效去除NOx,采用正交实验探究添加剂对催化剂的涂覆效果及SCR性能影响。结果表明,当PVA和吐温-20含量分别为0.2%和0.1%,pH为1.5时制备的浆料有较好的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。而后对整体式蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂进行SCR性能测试,其在350~500 ℃区间活性、耐C3H8、SO2和H2O反应催化活性均在80%以上,在350 ℃时稳定性均高于88%。通过粒径分析、SEM的表征结果表明,该配方制备的浆料能有效减少组分团聚作用,使其小于堇青石孔径,从而拥有较高的负载率和附着率。通过XPS、H2-TPR和NH3-TPD的表征结果表明,C3H8、SO2和H2O物质的加入会使促进反应的活性物质含量降低,与反应物竞争活性位点,从而降低催化剂氧化还原性能,进而影响催化剂催化活性。但在中高温区间,通过该配方制备的催化剂仍保持良好的酸性位和酸性数量,且与反应物竞争作用降低,从而在中高温度区间仍能保持良好的性能。本研究可为涂覆式蜂窝状催化剂的优化合成、提升其去除氮氧化物及抗中毒性能提供参考。Abstract: In order to prepare a coated honeycomb SCR catalyst with excellent performance for efficient NOx removal, orthogonal test was used to investigate its influence on the coating effect and SCR performance of the catalyst. The results showed that when the content of PVA and Tween-20 were 0.2% and 0.1%, respectively, and the pH was 1.5, the slurry had better load rate, adhesion rate and NO conversion rate. After obtaining the optimal formula, the SCR performance of the monolithic honeycomb V2O5-WO3-TiO2/cordierite catalyst was tested. The catalytic activity of C3H8、SO2 and H2O were all greater than 80% in the range of 350 ℃ to 500 ℃, and the stability was higher than 88% at 350 ℃. Finally, the characterization results by particle size analysis and SEM showed that the slurry prepared by this formulation effectively reduced the agglomeration effect of components to be smaller than the cordierite pore size, thus possessing a high loading and adhesion rate. The characterization results by XPS, H2-TPR and NH3-TPD showed that the addition of C3H8、SO2 and H2O substances decreased the content of active substances that promoted the reaction and competed with the reactants for the active sites, thus reducing the catalyst redox performance and consequently affecting the catalytic activity. However, in the middle and high temperature intervals, the catalysts prepared by this formulation still maintained good acidic sites and acidic amounts with the reduced competition with reactants, thus maintaining good performance in the middle and high temperature intervals. This study can provid a reference for the optimal synthesis of coated honeycomb catalysts and improving the nitrogen oxide removal and anti-poisoning properties.
-
Key words:
- honeycomb catalyst /
- coating /
- selective catalytic reduction /
- cordierite carrier /
- orthogonal test /
- toxic resistance
-
NOx是主要的大气污染物,其大量排放会破坏臭氧层形成酸雨[1-2],危害人群和动植物的健康[3-4]。我国已相继出台一系列严格的NOx排放行业限值标准,有效降低NOx排放已成为行业关注重点。选择性催化还原 (selective catalytic reduction,SCR) 技术为最有效且应用最广泛的NOx脱除技术之一[5-6]。蜂窝状催化剂具有机械强度好、床层阻力小等优点[7],而涂覆法具有操作方法简单、前驱体材料用量少、活性组分利用率高等优点[8]。通过涂覆方法制备的蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2整体式催化剂占据了大部分市场。KONG等[9]和DE-LA-TORRE等[10]等均证明了在没有添加剂的情况下,催化剂的负载量和牢固性极差,这表明添加剂在涂覆整体催化剂过程中的重要性。孟鹏通等[11]使用聚乙烯醇 (polyvinyl alcohol,PVA) 和拟薄水铝石 (SB粉) 两种粘结剂制备Cu-SSZ-13/堇青石整体式催化剂,发现PVA制备的催化剂具有更好的涂层稳定性和脱硝活性。虽然涂覆式蜂窝状催化剂应用广泛,但其工艺仍存在涂覆不均匀[12]、涂层不稳定等缺点,故导致其涂覆效果差,从而降低脱硝性能。除此之外,烟气成分较复杂,存在HC、SOx、H2O等物质,其均会造成SCR催化剂中毒失活,从而影响催化剂的脱硝效果[13]。目前,针对整体式催化剂的中毒影响原因的分析较少,尤其是针对HCs对SCR催化剂中毒的研究。
为提高催化剂的脱硝效率,本课题组拟探究涂覆式蜂窝状钒钨钛催化剂的涂优化配方,重点分析C3H8、SO2和H2O对催化剂的影响原因。本研究以蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂为基础,首先采用正交实验的方法,以PVA的质量分数 (0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%) 、吐温-20的质量分数 (0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%) 、pH (1.5、4.5、7.5、10) 为3因素,以负载率、附着率以及200~550 ℃的NO转化率作为响应值,进行3因素4水平的正交实验。通过正交实验得到最优配方后,进行整体式蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂的制备,并对其进行活性、抗C3H8、SO2和H2O中毒性能瞬态和稳定性测试,最后通过粒径检测、SEM、XPS、H2-TPR和NH3-TPD的表征手段,对SCR性能的影响因素进行分析,探究其对蜂窝状V2O5-WO3-TiO2/堇青石催化剂涂覆效果及SCR性能影响,以期为涂覆式蜂窝状催化剂的优化合成及其实际应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 催化剂的制备
将一定量的偏钒酸铵 (NH4VO3,AR) 、偏钨酸铵 (H28N6O41W12,AR) 、二氧化钛 (TiO2,AR) 、30%酸性硅溶胶 (SiO2, (30±1) %SiO2水溶液) 、吐温-20 (C26H50O10,AR) 和聚乙烯醇溶液 (C2H4O,5%C2H4O水溶液) 依次溶解在去离子水中以获得浸渍液,用硝酸 (HNO3,GR) 和氨水 (H5NO,AR) 调节pH。将46 cpsi的商业蜂窝状堇青石 (250 mm×250 mm×300 mm) 作为载体,整体浸入溶液中以负载活性成分。使用洗耳球对通道进行吹扫疏通,然后将得到的样品置于110 °C的烘箱中烘干3 h,以蒸发催化剂表面的水和挥发性有机溶剂。之后,将所得的整体催化剂块转移到马弗炉中在120 ℃煅烧3 h,然后升温至550 °C煅烧5 h。获得V2O5质量分数为1%、WO3质量分数为9%的催化剂,记为V-W-Ti/CC。
1.2 样品测试及表征
1.2.1 负载与脱落效果
催化剂的附着率测试是采用数控超声清洗仪 (昆山市超声仪器有限公司,KQ-400 DE) 进行,其工作功率为40 kW,振动频率为40 kHz。以超纯水为介质,将催化剂样品浸没在水中超声20 min后,于110 ℃下干燥5 h,称重测量催化剂涂层的质量损失。为减小实验的随机性,分别进行了6组平行实验。由式 (1) 和式 (2) 计算催化剂涂层的负载率和附着率。
负载率=m1−m0m0 (1) 附着率=1−m1−m2m1−m0 (2) 式中:m0为空白堇青石的质量,g;m1为浸渍负载后催化剂的质量,g;m2为超声脱落后催化剂的质量,g。
1.2.2 表征
浆料的粒径通过Bettersize 300plus激光/图像粒度粒形分析仪 (丹东百特仪器有限公司) 进行测试。扫描电镜 (scanning electron microscope,SEM) 采用JSM-6700F (日本电子公司 (JEOL) ) 测定。X射线光电子能谱 (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy,XPS) 采用ESCALAB 250Xi K-alpha (美国赛默飞公司) 测定,方法为单色化Al靶测试。H2-程序升温还原 (H2-temperature programmed reduction,H2-TPR) 采用化学吸附分析仪Chembet (美国康塔公司) 测定:每个样品在300 ℃下用N2预处理1 h;总流速为50 mL·min−1;之后以10 ℃·min−1的加热速率和10% H2/Ar 气体从50 ℃升温至700 ℃,依时间记录TCD信号。NH3-程序升温脱附 (NH3-temperature programmed desorption,NH3-TPD) 采用化学吸附分析仪Chembet (美国康塔公司) 测定:通入流量为50 mL·min−1 N2,以10 ℃·min−1升温至 300 ℃,预处理1 h;降温至100 ℃,保持气体总流量不变,吸附10% NH3/N2时间为1 h; 然后N2吹扫1 h,待基线稳定后,以 10 ℃·min−1升温至 750 ℃,依时间记录TCD信号。
1.3 催化剂的活性评价
活性测试在固定床反应装置 (北京金麟搏泰科贸有限公司) 中进行。用石英棉包裹整体式催化剂4周,然后置于石英反应管内部,在具有程序温控的反应炉中进行反应。将热电偶放置在石英反应管催化剂孔隙中以记录催化剂反应温度。使用烟气分析仪 (北京雪迪龙科技股份有限公司,SCS-900UV) 连续分析NO的变化情况。SCR反应条件:NO (体积分数0.1%) 、NH3 (体积分数0.1%)、 O2 (体积分数10%)、C3H8 (体积分数0.1%) 、SO2 (体积分数0.03%)、 H2O (体积分数7%),N2作为平衡气,体积空速为5 556 h−1。在温度为200~550 ℃内间隔50 ℃采集数据,每个温度下至少反应30 min,进行SCR反应性能测试。NO转化率计算公式如式 (3) 所示。
NO转化率=[NO]in−[NO]out[NO]in×100\% (3) 式中:[NO]in为NO的进口体积分数;[NO]out为NO的出口体积分数。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 正交实验
浆料的质量是影响催化剂的重要因素[14],也直接影响着催化剂涂层的质量。良好的涂层通常以均匀、高负载和强附着力为特征。通常认为负载率大于20%表示负载能力优秀;附着率大于90%附着性能良好[15]。基于大量数据,正交实验可科学地挑选出具有代表性的数据点,进行高效、简便的实验。前期含有PVA、吐温-20、聚乙二醇、可溶性淀粉、羧甲基纤维素钠的有机添加剂筛选实验结果表明,PVA和吐温−20共同存在的浆料稳定性最好,且该浆料制备的催化剂有着良好的负载和附着效果。之后进行了PVA和吐温−20的适宜质量分数筛选,发现当PVA质量分数超过0.5%、吐温−20质量分数超过0.2%时,浆料的流动性明显变差,催化剂表面发生浆料堆积和洞口堵塞现象。而当PVA质量分数小于0.2%、吐温−20质量分数小于0.05%时,催化剂表面出现大面积载体裸露,涂覆效果变差。因此,选取常用且适宜的PVA质量分数 (0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%) 和吐温-20质量分数 (0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%) 进行正交实验。此外,pH对催化剂也有着重要影响。DONG等[16]发现在钒酸溶液中,溶液酸度增加,催化剂表面酸性和活性中心的数量随之增加,从而提高了催化剂的脱硝活性。LI等[17]发现在pH为4时,钒钨钛浆料较稳定性。梁银等[18]在碱性条件下制备钒基催化剂发现,比酸性条件会使催化剂脱硝性能更好,故本实验选取pH (1.5、4.5、7.5、10) 进行正交实验。因此,最终选用PVA质量分数为0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%,吐温-20质量分数为0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%,pH为1.5、4.5、7.5、10,作为3因素4水平,以负载率、附着率以及200~550 ℃的NO转化率作为响应值,进行正交实验。考虑到当pH为7.5和10时,其在表面形成明显且多的裂痕,并且附着性很差,故不考虑其活性问题,结果如表1和表2所示。根据正交实验结果,分别列出了均值响应表 (表3) 、标准差响应表 (表4) ,并据此制出了均值主效应图 (图1 (a) ) 、标准差主效应图 (图1 (b) ) 。
表 1 3因素4水平正交实验表 (负载率、附着率)Table 1. Table of three-factor, four-level orthogonal experiments (loading rate, adhesion rate)编号 PVA质量分数 吐温质量分数 pH 负载率 附着率 1 0.2% 0.05% 1.5 24.59% 91.86% 2 0.2% 0.1% 4.5 29.66% 61.53% 3 0.2% 0.15% 7.5 29.02% 55.70% 4 0.2% 0.2% 10 22.86% 61.94% 5 0.3% 0.05% 4.5 26.67% 54.99% 6 0.3% 0.1% 1.5 27.26% 84.93% 7 0.3% 0.15% 10 21.41% 49.33% 8 0.3% 0.2% 7.5 28.85% 47.79% 9 0.4% 0.05% 7.5 29.51% 47.19% 10 0.4% 0.1% 10 23.96% 66.97% 11 0.4% 0.15% 1.5 25.06% 96.12% 12 0.4% 0.2% 4.5 26.76% 67.60% 13 0.5% 0.05% 10 23.87% 50.14% 14 0.5% 0.1% 7.5 25.42% 69.58% 15 0.5% 0.15% 4.5 24.93% 82.15% 16 0.5% 0.2% 1.5 25.23% 84.87% 表 2 3因素4水平正交实验表 (200~550 ℃的NO转化率)Table 2. Table of three-factor four-level orthogonal experiments (NO conversion at 200~550 °C)编号 PVA 质量分数 吐温 质量分数 pH 反应温度 200 ℃ 250 ℃ 300 ℃ 350 ℃ 400 ℃ 450 ℃ 500 ℃ 550 ℃ 1 0.2% 0.05% 1.5 35.05% 60.59% 93.41% 94.73% 95.25% 92.64% 90.67% 81.78% 2 0.2% 0.1% 4.5 28.32% 57.62% 92.99% 93.92% 95.64% 92.84% 90.87% 81.98% 5 0.3% 0.05% 4.5 29.31% 53.07% 93.00% 87.58% 94.46% 92.84% 91.07% 82.97% 6 0.3% 0.1% 1.5 33.86% 59.83% 94.10% 92.34% 94.85% 93.04% 90.48% 81.39% 11 0.4% 0.15% 1.5 35.64% 60.00% 95.56% 95.11% 95.84% 92.45% 90.87% 82.97% 12 0.4% 0.2% 4.5 31.68% 57.03% 86.48% 90.16% 95.25% 93.04% 90.28% 81.39% 15 0.5% 0.15% 4.5 22.38% 51.09% 87.66% 94.12% 94.26% 92.64% 89.29% 78.02% 16 0.5% 0.2% 1.5 34.85% 61.58% 93.99% 94.91% 94.23% 93.44% 90.48% 79.80% 表 3 催化剂负载效果验证表Table 3. Verification table of catalyst coating effect效果参数 样品1 样品2 样品3 样品4 样品5 样品6 均值 负载率 26.29% 26.12% 28.02% 26.03% 26.31% 27.35% 26.69% 附着率 93.23% 93.72% 94.49% 92.69% 97.05% 91.53% 93.79% 表 4 不同反应条件下V-W-Ti/CC催化剂的表面物种类型及价态分布情况Table 4. Surface species types and valence distribution of V-W-Ti/CC catalysts for different reaction cases样品名称 Oα+β V3++V4+ W5+ V-W-Ti/CC 41.3% 87.2% 25.1% V-W-Ti/CC C3H8反应后 35.2% 94.9% 3.3% V-W-Ti/CC SO2反应后 40.7% 72.8% 69.9% V-W-Ti/CC H2O反应后 36.2% 38.5% 99.7% 图1 (a) 表明,对于负载率、附着率以及200~550 ℃的NO转化率这3组响应值,pH的影响>吐温-20质量分数>PVA质量分数,并且当PVA质量分数为0.2%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%且pH为1.5时理论上拥有最高的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。图1 (b) 表明,pH的离散性>吐温-20质量分数>PVA质量分数,这说明pH对其结果的影响波动最大,PVA质量分数对结果的影响波动较小。该正交实验的平均值为0.573 2,除了负载率和200 ℃的NO转化率越接近均值越好,附着率和250~550 ℃的NO转化率均越高于均值越好,因此反应在标准差响应表上则越高于平均标准差越好。在PVA质量分数为0.2%和0.5%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%且pH为1.5和4.5时的标准差均在平均标准差以上,具有良好的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。综合来看,当PVA质量分数为0.2%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%、pH为1.5条件下的浆料会有更合适的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。为验证该条件下的负载效果,对其制备的催化剂进行了验证,结果见表3。使用该优化配方制备的催化剂进行了6组平行实验,制备出催化剂的平均负载率为26.69%、平均附着率为93.79%,相比于其他对照实验组拥有最好的负载率和附着率。因此,采用PVA质量分数为0.2%、吐温-20质量分数为0.1%、pH为1.5的浆料进行后续SCR性能测试。
2.2 催化剂活性及稳定性评价
通过2.1正交实验筛选出的最优配方制备V-W-Ti/CC催化剂,并对其进行活性及稳定性测试 (图2) 。如图2 (a) 所示,使用该配方制备的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂有着良好的催化活性和抗中毒性能。在未中毒的情况下,300~550 ℃的NO转化率均大于80%,其中300~500 ℃的NO转化率大于90%;而C3H8和SO2中毒主要影响在低温250 ℃的情况下,其活性分别为50.8%和48.1%,相比于未中毒催化剂 (其活性为60%) 分别下降了9.2%和11.9%,但其在中高温区 (300~550 ℃) 仍有着良好的催化性能表现。但H2O中毒对其全部低温区间影响均较大,在200~300 ℃的NO转化率分别为20.3%、33.5%、62.5%,比未中毒催化剂 (其活性在200 ℃、250 ℃、300 ℃的活性分别为34.3%、60%、94.1%) 分别降低了14%、26.5%和31.6%,其在中高温区 (350~550 ℃) 有着良好的催化性能表现。之后,在350 ℃进行催化剂的稳定性测试。如图2 (b) 所示,在350 ℃时C3H8和SO2对该催化剂几乎没有影响,且NO转化率一直稳定在90%以上,H2O中毒的催化剂先出现明显下降再逐步提升,最终稳定在约88%,停止通入H2O后,催化剂的NO转化率缓慢提升。此前,李富宽等[19]制备整体式钒钨钛催化剂在300~500 ℃的SCR活性达到80%以上;SHEN等[20]制备的整体式钒钨钛催化剂在350~550 ℃的SCR活性达到80%以上。与以上催化剂相比,本研究制备的V-W-Ti/CC在300~550 ℃区间达到80%以上,拓宽了50 ℃的温度区间。此外,ZHAO等[21]制备的整体式钒钨钛催化剂在400 ℃时加入0.02% SO2或2% H2O情况下,活性仅稳定在约83%。而本研究制备的V-W-Ti/CC在375 ℃时加入0.03% SO2或7% H2O情况下,活性分别稳定在约93%或86%,催化活性有明显提升。以上均说明通过该浆料配方制备的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂面对C3H8、SO2和H2O中毒时均有良好的抗中毒性能和稳定性。
2.3 催化剂物理化学性质分析
为探究使用PVA和吐温-20拥有更好负载率和附着率的原因,进行了粒径分析和SEM表征,并针对催化剂拥有良好催化活性及在C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后催化剂在低温区明显下降而中高温区仍保持催化活性的原因进行了XPS、NH3-TPD和H2-TPR表征,分析结果如下。
1) 催化剂粒径及表面形貌分析。涂层附着力与浆料的粒径有关。载体涂层的粘附有2种机械机制,分别为载体涂层颗粒之间的“锚定”和互锁,以及载体表面的不规则性和粉末颗粒之间发生的固体界面力[22]。因此,为获得成功的整体涂层,催化剂颗粒应小于表面粗糙度[23]。由于堇青石载体的大孔隙率约为5 μm,故负载粒径最佳范围应小于5 μm[24]。大粒径的存在会导致浆料沉淀速度快、在堇青石表面堆积,导致浆料不能进入堇青石内部发生锚定作用,故导致脱落效果明显[9]图3 (a) 表明,该配方制备的催化剂浆料粒径为0~35 μm,其集中分布区域为0.2~0.7 μm、0.7~5 μm、5~30 μm,其中粒径在0.2~0.7 μm浆料最多。小于5 μm粒径浆料质量分数为83%,且其平均粒径为3.5 μm,小于堇青石载体的孔径,这可能是该配方所制备的浆料的负载率和附着率较好的原因。
通过扫描电镜观察不同添加剂对催化剂的微观组织形貌的影响,结果见图3 (b) 。在放大5 000倍的情况下,该配方制备的催化剂颗粒较均匀,无明显团聚作用,这与粒径测试结果相一致。
2) 催化剂表面物种及价态分析。催化剂的表面物种类型及其价态分布情况可通过XPS检测结果进行分析 (图4) 。NH3-SCR是一种有氧参与反应,表面活性氧对催化活性至关重要。O 1s测试结果如图4 (a) 所示。一般来说,位于529.72~529.96 eV 的峰 (Oγ) 对应于晶格氧O2-[25]。而在531.42~532.12 eV的峰 (Oβ) 对应于表面化学吸附的氧物质或氧物质的电离[26-27]。介于533.01~533.16 eV的峰(Oα) 被认为是羟基物质或吸附水[28]。其中,Oα和Oβ均属于表面活性氧物种,具有较高迁移率,有利于NO氧化成NO2进行快速SCR反应和不同价态活性物种之间进行氧化还原循环[29]。根据O 1s光谱定量得出(Oα+Oβ)/(Oα+Oβ+Oγ)的相对比值,如表4所示。与V-W-Ti/CC催化剂相比,经过C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂表面上的不稳定氧物种质量分数均有下降,从而导致了催化剂催化活性下降,这与2.2性能测试结果相一致。
如图4 (b) 为催化剂的V 2p XPS光谱。V 2p1/2峰的位置在524.13~524.18 eV,V 2p3/2峰的位置在516.18~516.58 eV[30]。V 2p3/2 XPS 峰分为V5+、V4+和V3+ 3个峰,分别对应于517.04~517.43 eV、516.45~516.48 eV、515.60~515.76 eV[31]。SCR活性与催化剂的表面(V3++V4+)/Vn+相关[32]。通过峰值反卷积计算表面上V5+、V4+和V3+物种的分布情况,如表6所示。除了经过C3H8反应后的催化剂低价态V3+和V4+这两者比例有所升高,而经SO2和H2O中毒的催化剂均明显下降。V3+和V4+被认为是催化剂中的缺陷V位点,催化剂表面缺陷越多,催化剂表面与NH3的反应越活跃,使得催化剂表面酸性位点强度增加[30]。经SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂V3+和V4+的含量明显下降,故降低了其SCR催化活性,这与活性测试结果相一致。
图4 (c) 为催化剂的W 4f XPS图谱。W5+和W6+的W 4f7/2的结合能分别为35.45~35.51 eV和35.94~36.19 eV。W5+和W6+的W 4f5/2分别为37.62~37.93 eV和38.22~38.64 eV[33]。与V-W-Ti/CC催化剂相比,经C3H8反应后的催化剂W5+/(W5++W6+)的比例明显减少,这可能是导致在C3H8存在时活性下降的主要原因。此外,虽然SO2和H2O制备的催化剂的W5+/(W5++W6+)的比例增加,但其W 4f的结合能明显变小,这可能是因为SO2和H2O的添加影响了WOx物种的周围环境,促进了四面体WOx向八面体WOx的转化,而这种转化会削弱WOx物种的还原性,并不利于活性提高[34],因此同样导致催化剂活性下降。
图4 (d) 为Ti 2p 的XPS图谱。4种催化剂的Ti 2p1/2位于464.39~464.75 eV,Ti 2p3/2 的峰位于458.70~459.06 eV,这是锐钛矿中Ti4+物种的特征二氧化钛[35-36]。V-W-Ti/CC催化剂和经C3H8反应后的催化剂结合能较低,这说明Ti为富电子状态。而经SO2和H2O催化剂结合能变大。这可能表明SO2和H2O会抑制Ti物种的结合能,使其向高结合能转变[37]。
综上所述,C3H8反应后的催化剂表面活性氧和活性W5+物种质量分数降低,而活性V3+和V4+物种质量分数升高的现象。这可能是由于C3H8与NH3同时竞争V位点,C3H8氧化过程中生成的CO等中间体会抑制V4+的进一步氧化[38],从而维系了部分V4+物种的数量。V物种的抑制间接促进了W=O直接与NO的氧化活化反应[39],从而使W5+物种质量分数降低。SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂表面活性氧和活性V3+和V4+质量分数降低,且活性W5+质量分数升高的现象。这可能是由于在SO2存在时,V3+被氧化形成VOSO4[40],同时SO2与W-O-W发生反应,W6+被还原为W5+[41]。而H2O存在的条件下,H2O与NH3竞争活性位点,并且使Lewis酸性位点羟基化,抑制Brønsted酸上的NH4+和NO的相互反应[42],从而导致表面活性氧和活性V3+和V4+由于质量分数降低,且活性W5+含量升高的现象。虽然SO2和H2O反应后活性W5+质量分数升高,但由于其添加影响了WOx物种的周围环境,削弱WOx物种的还原性,并不利于活性提高[43],同样会导致催化剂活性下降。
3)催化剂表面酸性分析。催化剂的酸量及强度可用NH3-TPD进行分析 (图5) 。新鲜和反应后的催化剂均出现3个脱附峰。其中,169 ℃对应的峰为弱Brønsted酸位上氨物种的脱附峰,387 ℃左右对应的脱附峰为强Brønsted酸上氨物种的脱附峰[44],540 ℃左右为 Lewis强酸位的脱附峰[45]。表5表明,与新鲜催化剂相比,加入C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂在低温区的物理吸附的酸强度和物种变化甚微,而在中温区不仅Brønsted酸强略有增加且物种增多。这可能是由于C3H8反应时生成的中间体、SO2反应时生成的硫酸盐及H2O存在时将部分Lewis酸性位转化为Brønsted酸位,从而出现中温区酸量增多的现象。同时,高温区Lewis酸强度略有降低。在低温时,V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂的脱硝效果主要依赖中性酸位数量和氧化还原性能[46]。虽然加入C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂有着数量更高的中性酸数量但是其氧化还原性能明显下降 (见2.3.4) 。此外,C3H8、SO2和H2O存在时与NH3竞争反应位点,使NH4+和配位NH3无法参与反应,从而降低了吸附NH3反应速率,进而减弱了催化剂在低温条件下的催化效果。而中高温时,主要依靠V位点提供的强Lewis酸位维持其热稳定性,C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂仍保持着较多数量的酸性数量。根据前人研究得知,在中高温时,C3H8[38]、SO2[47]和H2O[48]对催化剂的抑制作用减弱,因此这可能是催化剂在低温下活性下降但仍能保持中高温活性不变的原因。
表 5 V-W-Ti/CC催化剂反应前后表面酸性对比Table 5. Comparison of surface acidity of V-W-Ti/CC catalysts before and after the reaction样品名称 峰位置及酸量 低温区/ ℃ 酸量/ (μmol·g−1) 中温区/ ℃ 酸量/ (μmol·g−1) 高温区/ ℃ 酸量/ (μmol·g−1) 总酸量/ (μmol·g−1) V-W-Ti/CC 169 71 385 293 546 445 808 V-W-Ti/CC C3H8反应后 169 69 388 381 538 486 936 V-W-Ti/CC SO2反应后 169 67 389 358 534 498 923 V-W-Ti/CC H2O反应后 169 70 385 348 534 551 969 4)催化剂氧化还原性能分析。催化剂的氧化还原能力可通过H2-TPR检测结果 (图6) 进行分析。新鲜的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂在515 °C和704 °C处出现2个还原峰。其中,以515 ℃为中心的为V5+还原为V3+的还原峰[49]和W6+还原为W4+的还原峰的重叠[50],以703 ℃为中心的为W4+还原为W的还原峰[51]。与新鲜催化剂相比,C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂还原峰位置并无明显变化,但还原峰面积明显减少。这表明H2消耗量有显著降低,亦说明在经过C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后,催化剂表面高价态V5+或W6+以及W4+含量均有下降,这与XPS结果一致。因此,降低催化剂的氧化还原性能,会导致低温下的催化剂的活性有明显下降。
3. 结论
1) 当PVA和吐温-20质量分数分别为0.2%和0.1%,pH为1.5时制备的浆料有较好的负载率、附着率和NO转化率。在添加C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后,该催化剂在低温下有明显抑制作用。2) 该配方制备的浆料其粒径<5 μm的比例高达83%,这可使粒径和载体更好的发生“锚定”和互锁,使其具有更好的负载率和稳定性。C3H8、SO2和H2O对催化剂的抑制作用主要归结为降低催化剂的氧化还原性能。虽然低温下抑制作用明显,但是使用该配方制备的V-W-Ti/CC催化剂在中高温区 (300~550 ℃) 仍有着良好的催化活性和抗中毒性能。3) 低温时,C3H8、SO2和H2O存在时竞争反应位点,使NH4+和配位NH3无法参与反应,从而降低了催化剂在低温条件下的催化效果。而中高温时,由于C3H8、SO2和H2O反应后的催化剂仍保持着较多数量的强酸数量,并且C3H8、SO2和H2O对催化剂的抑制作用减弱,故保持了较好的中高温活性。在350~500 ℃区间活性、C3H8、SO2和H2O反应催化活性均大于80%以上,且350 ℃的稳定性均高于88%。4) 该催化剂面对C3H8、SO2和H2O中毒时均有良好的抗中毒性能和稳定性。该配方制备的催化剂具有优异的SCR性能,是制备涂覆型整体式催化剂的优良浆料配方。
-
表 1 3因素4水平正交实验表 (负载率、附着率)
Table 1. Table of three-factor, four-level orthogonal experiments (loading rate, adhesion rate)
编号 PVA质量分数 吐温质量分数 pH 负载率 附着率 1 0.2% 0.05% 1.5 24.59% 91.86% 2 0.2% 0.1% 4.5 29.66% 61.53% 3 0.2% 0.15% 7.5 29.02% 55.70% 4 0.2% 0.2% 10 22.86% 61.94% 5 0.3% 0.05% 4.5 26.67% 54.99% 6 0.3% 0.1% 1.5 27.26% 84.93% 7 0.3% 0.15% 10 21.41% 49.33% 8 0.3% 0.2% 7.5 28.85% 47.79% 9 0.4% 0.05% 7.5 29.51% 47.19% 10 0.4% 0.1% 10 23.96% 66.97% 11 0.4% 0.15% 1.5 25.06% 96.12% 12 0.4% 0.2% 4.5 26.76% 67.60% 13 0.5% 0.05% 10 23.87% 50.14% 14 0.5% 0.1% 7.5 25.42% 69.58% 15 0.5% 0.15% 4.5 24.93% 82.15% 16 0.5% 0.2% 1.5 25.23% 84.87% 表 2 3因素4水平正交实验表 (200~550 ℃的NO转化率)
Table 2. Table of three-factor four-level orthogonal experiments (NO conversion at 200~550 °C)
编号 PVA 质量分数 吐温 质量分数 pH 反应温度 200 ℃ 250 ℃ 300 ℃ 350 ℃ 400 ℃ 450 ℃ 500 ℃ 550 ℃ 1 0.2% 0.05% 1.5 35.05% 60.59% 93.41% 94.73% 95.25% 92.64% 90.67% 81.78% 2 0.2% 0.1% 4.5 28.32% 57.62% 92.99% 93.92% 95.64% 92.84% 90.87% 81.98% 5 0.3% 0.05% 4.5 29.31% 53.07% 93.00% 87.58% 94.46% 92.84% 91.07% 82.97% 6 0.3% 0.1% 1.5 33.86% 59.83% 94.10% 92.34% 94.85% 93.04% 90.48% 81.39% 11 0.4% 0.15% 1.5 35.64% 60.00% 95.56% 95.11% 95.84% 92.45% 90.87% 82.97% 12 0.4% 0.2% 4.5 31.68% 57.03% 86.48% 90.16% 95.25% 93.04% 90.28% 81.39% 15 0.5% 0.15% 4.5 22.38% 51.09% 87.66% 94.12% 94.26% 92.64% 89.29% 78.02% 16 0.5% 0.2% 1.5 34.85% 61.58% 93.99% 94.91% 94.23% 93.44% 90.48% 79.80% 表 3 催化剂负载效果验证表
Table 3. Verification table of catalyst coating effect
效果参数 样品1 样品2 样品3 样品4 样品5 样品6 均值 负载率 26.29% 26.12% 28.02% 26.03% 26.31% 27.35% 26.69% 附着率 93.23% 93.72% 94.49% 92.69% 97.05% 91.53% 93.79% 表 4 不同反应条件下V-W-Ti/CC催化剂的表面物种类型及价态分布情况
Table 4. Surface species types and valence distribution of V-W-Ti/CC catalysts for different reaction cases
样品名称 Oα+β V3++V4+ W5+ V-W-Ti/CC 41.3% 87.2% 25.1% V-W-Ti/CC C3H8反应后 35.2% 94.9% 3.3% V-W-Ti/CC SO2反应后 40.7% 72.8% 69.9% V-W-Ti/CC H2O反应后 36.2% 38.5% 99.7% 表 5 V-W-Ti/CC催化剂反应前后表面酸性对比
Table 5. Comparison of surface acidity of V-W-Ti/CC catalysts before and after the reaction
样品名称 峰位置及酸量 低温区/ ℃ 酸量/ (μmol·g−1) 中温区/ ℃ 酸量/ (μmol·g−1) 高温区/ ℃ 酸量/ (μmol·g−1) 总酸量/ (μmol·g−1) V-W-Ti/CC 169 71 385 293 546 445 808 V-W-Ti/CC C3H8反应后 169 69 388 381 538 486 936 V-W-Ti/CC SO2反应后 169 67 389 358 534 498 923 V-W-Ti/CC H2O反应后 169 70 385 348 534 551 969 -
[1] RESITOGLU I A. The effect of biodiesel on activity of diesel oxidation catalyst and selective catalytic reduction catalysts in diesel engine [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 148. [2] QIE F X, ZHU J Y, RONG J F, et al. Biological removal of nitrogen oxides by microalgae, a promising strategy from nitrogen oxides to protein production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 292: 122037. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122037 [3] GUILLAUME P C, ROBERT M, AKSHAY A, et al. Public health impacts of excess NOx emissions from Volkswagen diesel passenger vehicles in Germany[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2017, 12(3): 034014. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa5987 [4] MACIEJ S, NICOLE J, ROB B, et al. Long-term exposure to particulate matter, NO2 and the oxidative potential of particulates and diabetes prevalence in a large national health survey[J]. Environment International, 2017, 108: 228-236. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.08.017 [5] GHOLAMI Z, LUO G H, GHOLAMI F, et al. Recent advances in selective catalytic reduction of NOx by carbon monoxide for flue gas cleaning process: a review[J]. Catalysis Reviews - Science and Engineering, 2021, 63(1): 68-119. doi: 10.1080/01614940.2020.1753972 [6] FORZATTI P, NOVA I, TRONCONI E. Enhanced NH3 selective catalytic reduction for NOx abatement[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(44): 8366-8368. doi: 10.1002/anie.200903857 [7] 刘应书, 张璇, 卞文博, 等. 涂覆型蜂窝体催化剂的制备与烟气一氧化碳催化净化性能 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2022: 1-14. [8] 赵春林, 马子然, 王宝冬, 等. 固定源废气处理的催化剂涂覆工艺研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(10): 4015-4023. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2019-2122 [9] KONG X L, QIU M H, WANG A R, et al. Influence of alumina binders on adhesion and cohesion during preparation of Cu‐SAPO‐34/monolith catalysts[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2018, 15(6): 1490-1501. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13008 [10] DE-LA-TORRE U, PEREDA-AYO B, MOLINER M, et al. Cu-zeolite catalysts for NOx removal by selective catalytic reduction with NH3 and coupled to NO storage/reduction monolith in diesel engine exhaust aftertreatment systems[J]. Applied Catalysis, B Environmental:An International Journal Devoted to Catalytic Science and Its Applications, 2016, 187(6): 419-427. [11] 孟鹏通, 范超, 吕文婷, 等. 整体式堇青石负载的Cu-SSZ-13分子筛催化剂的制备及其氨选择性催化还原脱硝性能[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2020, 48(10): 1216-1223. [12] KLIMCZAK M, KERN P, HEINZELMANN T. High-throughput study of the effects of inorganic additives and poisons on NH3-SCR catalysts-Part I: V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis, B Environmental: An International Journal Devoted to Catalytic Science and Its Applications, 2010, 95(1/2): 39-47. [13] 胡宜康, 徐斌, 曹智焜, 等. Cu基分子筛催化剂抗中毒性能的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(1): 171-176. doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20191104.005 [14] ROUSTAPISHEH M, KARAMI D, MAHINPEY N. The fabrication of Ce promoted Ni/Mg/Al mixed oxides hydrotalcite washcoated alloy, monolith catalyst for catalytic steam cracking of vacuum gas oil [J]. Catalysis Today, 2021. [15] 朱恒, 董长青, 王晓东, 等. V-Mo/TiO2堇青石负载型脱硝催化剂的制备和性能[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(9): 168-174. [16] DONG G J, ZHANG Y F, ZHAO Y, et al. Effect of the pH value of precursor solution on the catalytic performance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 in the low temperature NH3-SCR of NOx[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2014, 42(12): 1455-1463. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(15)60003-2 [17] LI F K, SHEN B X, TIAN L H, et al. Enhancement of SCR activity and mechanical stability on cordierite supported V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst by substrate acid pretreatment and addition of silica[J]. Powder Technology:An International Journal on the Science and Technology of Wet and Dry Particulate Systems, 2016, 297: 384-391. [18] 梁银, 洪武, 于飞, 等. 碱性环境制备V-SCR催化剂提升De-NOx性能[J]. 工业催化, 2021, 29(5): 54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1143.2021.05.009 [19] 李富宽, 沈伯雄, 田灵辉, 等. 堇青石负载V2O5-WO3-TiO2方法比较[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 5016-5022. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201601047 [20] SHEN M Q, XU L L, WANG J Q, et al. Effect of synthesis methods on activity of V2O5/CeO2/WO3-TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(3): 259-267. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60023-6 [21] ZHAO K, HAN W L, TANG Z C, et al. Investigation of coating technology and catalytic performance over monolithic V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Colloids and Surfaces, A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 503(8): 53-60. [22] AGRAFIOTIS C, TSETSEKOU A. The effect of powder characteristics on washcoat quality. Part I: Alumina washcoats[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(7): 815-824. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(99)00218-6 [23] MITRA B, KUNZRU D. Washcoating of different zeolites on cordierite monoliths[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(1): 64-70. [24] HUANG G F, GUO X L, HAN Y F, et al. Effect of extrusion dies angle on the microstructure and properties of (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V in situ titanium matrix composite[J]. Materials Science & Engineering, A Structural Materials:Properties, Misrostructure and Processing, 2016, 667: 317-325. [25] LIU Z M, ZHANG S X, LI J H, et al. Novel V2O5-CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with low vanadium loading for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 158-159: 11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.03.049 [26] LIU S, YAO P, PEI M M, et al. Significant differences of NH3-SCR performances between monoclinic and hexagonal WO3 on Ce-based catalysts[J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2021, 8(10): 2988-3000. doi: 10.1039/D1EN00519G [27] RUSSO N, FINO D, SARACCO G, et al. Studies on the redox properties of chromite perovskite catalysts for soot combustion[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 229(2): 459-469. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2004.11.025 [28] WANG X X, CONG Q L, CHEN L, et al. The alkali resistance of CuNbTi catalyst for selective reduction of NO by NH3: A comparative investigation with VWTi catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 246: 166-179. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.049 [29] HU W S, ZHANG Y H, LIU S J, et al. Improvement in activity and alkali resistance of a novel V-Ce(SO4)2/Ti catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 206: 449-460. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.036 [30] ZHAO X, HUANG L, LI H R, et al. Promotional effects of zirconium doped CeVO4 for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 183: 269-281. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.10.052 [31] KWON D W, LEE S, KIM J, et al. Influence of support composition on enhancing the performance of Ce-V on TiO2 comprised tungsten-silica for NH3-SCR[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 359: 112-123. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.07.002 [32] BONINGARI T, KOIRALA R, SMIRNIOTIS P G. Low-temperature catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over vanadia-based nanoparticles prepared by flame-assisted spray pyrolysis: Influence of various supports[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 140-141: 289-298. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.033 [33] XIONG Z B, LI Z Z, LI C X, et al. Starch bio-template synthesis of W-doped CeO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Influence of ammonia titration [J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2021, 148. [34] 赵梦梦, 陈梦寅, 张鹏举, 等. 共沉淀法掺杂SiO2对V2O5-WO3/TiO2 催化剂SCR性能的影响[J]. 分子催化, 2017, 31(3): 223-235. [35] WANG Y G, LI B, ZHANG C L, et al. Ordered mesoporous CeO2-TiO2 composites: Highly efficient photocatalysts for the reduction of CO2 with H2O under simulated solar irradiation[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 130-131: 277-284. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.019 [36] YAO X J, ZHANG L, LI L L, et al. Investigation of the structure, acidity, and catalytic performance of CuO/Ti0.95Ce0.05O2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 at low temperature[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 150-151: 315-329. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.007 [37] NI K W, PENG Y W, DAI G Y, et al. Ceria accelerates ammonium bisulfate decomposition for improved SO2 resistance on a V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst in low-temperature NH3-SCR [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2022, 140. [38] ZHENG L, ZIMINA A, CASAPU M, et al. Hydrocarbon and soot oxidation over cerium and iron doped vanadium SCR catalysts[J]. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(24): 6272-6284. doi: 10.1002/cctc.202001314 [39] 胡文硕, 邹任智, 董毅, 等. 钒钨铈催化剂的低温SCR反应机理研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2021, 42(1): 239-245. [40] WANG X M, DU X S, ZHANG L, et al. Promotion of NH4HSO4 decomposition in NO/NO2 contained atmosphere at low temperature over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst for NO reduction[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2018, 559: 112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.04.025 [41] 钟毓秀, 尹子骏, 苏胜, 等. WO3/TiO2 催化剂活性组分W对SO2的氧化特性[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2022, 28(10): 136-144. [42] 余岳溪, 廖永进, 束航, 等. SO2与H2O对商用钒钨钛脱硝催化剂毒化作用综述[J]. 中国电力, 2016, 49(12): 168-173. [43] CHEN M Y, ZHAO M M, TANG F S, et al. Effect of Ce doping into V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts on the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2017, 35(12): 1206-1215. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2017.06.004 [44] 刘雪松, 汪澜, 房晶瑞, 等. 水热处理和钨添加对低钒催化剂高温脱硝性能的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 29(4): 1363-1370. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2019-1121 [45] GUO M Y, LIU Q L, LIU C X, et al. Rational design of novel CrZrO catalysts for efficient low temperature SCR of NO [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 413. [46] 张道军, 马子然, 孙琦, 等. 选择催化还原(SCR)反应机理研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(4): 1611-1623. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2018-1195 [47] ZHANG L, WANG D, LIU Y, et al. SO2 poisoning impact on the NH3-SCR reaction over a commercial Cu-SAPO-34 SCR catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 156-157: 371-377. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.03.030 [48] PAN S W, LUO H C, LI L, et al. H2O and SO2 deactivation mechanism of MnOx/MWCNTs for low-temperature SCR of NOx with NH3[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2013, 377: 154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.05.009 [49] LEE K J, KUMAR P A, MAQBOOL M S, et al. Ceria added Sb-V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for low temperature NH3-SCR: Physico-chemical properties and catalytic activity[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 142-143: 705-717. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.071 [50] WANG Y Z, YI W, YU J, et al. Novel methods for assessing the SO2 poisoning effect and thermal regeneration possibility of MOx-WO3/TiO2 (M = Fe, Mn, Cu, and V) catalysts for NH3-SCR[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 54(19): 12612-12620. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c02840 [51] LI X, LI X S, LI J H, et al. High calcium resistance of CeO2 –WO3 SCR catalysts: Structure investigation and deactivation analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 317: 70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.027 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: