-
化学合成工业的蓬勃发展,在给人类生活带来便捷、高效、舒适生活的同时,亦给生态环境保护和人类健康带来巨大安全隐患。其中,废水中的酚类污染物主要来源于焦化厂、煤气发生站、合成酚厂、制药厂、合成纤维厂等化工生产过程产生的含酚废水[1],酚类化合物在生物体内能够使细胞组织失去活性[2],由于其高毒性、难降解、易生物积累等特性而受到广泛关注[3],苯酚、间甲酚、2,4-二氯酚、对硝基苯酚等6种酚类被列为我国水体优先控制污染物黑名单。如何去除与回收工业废水中的酚类化合物是目前国内外化工与环境领域关注的焦点问题之一。
目前,水体中酚类化合物的常用去除方法主要有萃取法[4]、吸附法[5-6]、生物降解法[7-8]及高级氧化法[9-10]等。溶剂萃取法工艺简单、易操作,但仅用于对高浓度含酚废水进行预处理;吸附法脱酚效率不高,需与其他脱酚方法联用;生物降解法经济可靠,但一般用来处理较低浓度的含酚废水;高级氧化法处理效果好,但成本高,目前工业上应用较少。乳化液膜法在20世纪70年代初期提出,能实现对液相中酚的分离与富集[11],具有低能耗、低成本、界面面积大、传质速率高、操作简单等特点,受到国内外研究者的广泛关注[12-13]。
传统乳化液膜多采用石油基溶剂,如煤油[14-15]、环乙烷[16]、正庚烷[17]等,具有毒性且不可被生物降解、不能再生,如果排放到环境中将对环境产生巨大危害[18]。采用绿色可持续的植物油来代替传统石油基溶剂是目前的一大研究趋势。棕榈油已被报道作为乳化液膜的绿色稀释剂用于分离苯酚(83%)[19]、银(97%)[20]、活性染料(90%)[18]、铬(97%)[21]等,其中分离苯酚的效果并不理想。本研究采用棕榈油作为绿色稀释剂来制备乳化液膜用于去除和回收焦化废水中的苯酚,以聚异丁烯多丁二酰亚胺(T-155)作为表面活性剂同时配以载体正辛醇,以期提高GELM体系分离酚的能力。本研究以模拟含酚废水为研究对象,通过单因素实验研究油内比、表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、内水相浓度、制乳时间及制乳转速对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,考察表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、内水相浓度、油内比、乳外比、搅拌转速和萃取时间苯酚去除率的影响,并研究该乳化液膜对不同酚类的去除效果和对苯酚的富集能力,以期为实验室研究与工业化应用提供参考。
-
试剂:工业煤油、氢氧化钠、正辛醇、铁氰化钾、氯化铵、氨水、4-氨基安替比林、苯酚均为分析纯;T-155、棕榈油为工业级;仪器:722光栅分光光度计、JJ-1A160W数显电动搅拌器(金坛新瑞)、JRJ300-SH型剪切乳化搅拌机(上海沪析)。
-
取一定量的乳化液置于玻璃毛细管内,放置24 h,观察破乳情况,记录破乳量,破乳率按式(1)计算。用乳化液膜分离提取模拟废水中的苯酚,苯酚去除率按式(2)计算,提取前后苯酚富集倍数按式(3)计算。
式中:Vt为放置24 h后乳化液的破乳量,mL;V0为放入毛细管中的乳化液的体积,mL;Ƞ为破乳率,%;
ρ0 为模拟废水苯酚初始浓度,mg·L−1;ρA 为萃取水相的苯酚浓度,mg·L−1;ρE 为破乳后水相中的苯酚浓度,mg·L−1;n为脱酚率,%;m为苯酚富集倍数。采用4-氨基安替比林分光光度法(HJ 503-2009)测定废水中苯酚的含量、重铬酸钾法(HJ 828-2017)测定废水的COD。
-
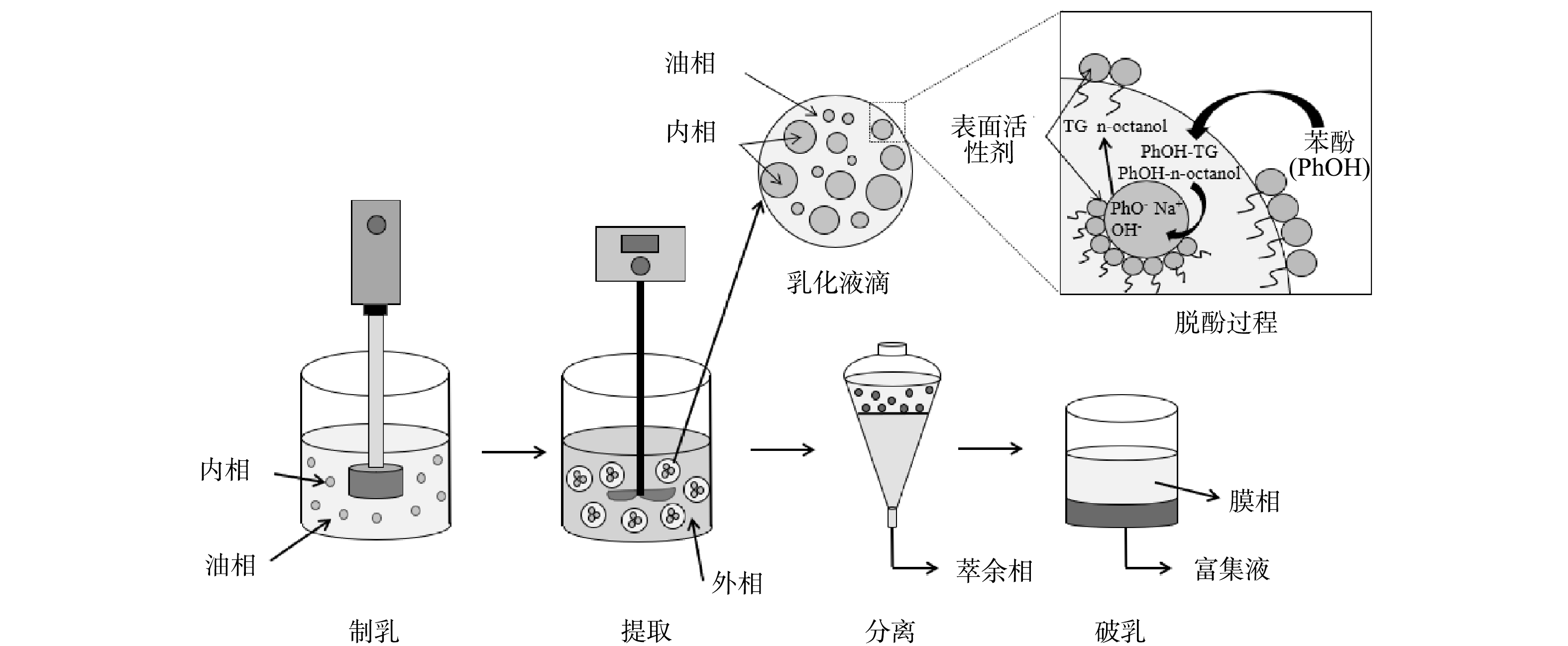
将苯酚与去离子水混合配制成一定浓度的模拟废水,以模拟废水为研究对象,研究制备的乳化液膜对酚的去除能力。有研究指出[22],棕榈油和煤油按7∶3的比例混合得到的乳液最稳定,因此本研究中棕榈油与煤油的比例确定为7∶3。先将棕榈油和煤油按比例混合,然后将表面活性剂溶解于棕榈油和煤油的混合物中,用电动搅拌器对混合物进行搅拌,并加入载体。待搅拌均匀后,加入一定浓度的NaOH溶液作为内相,如图1所示,将搅拌好的液体立即用剪切乳化搅拌机制乳[23],即可制得油包水型(W/O)乳白色油状液膜。按照一定的乳外比(乳液与外相溶液的体积比),将一定量的乳化液加入到含酚废水中,并用电动搅拌器使混合液搅拌均匀。W/O型乳化液分散至外相中形成水包油再包水型(W/O/W)乳化液膜体系。待传质过程结束后,停止搅拌,让混合液静置分层,然后取出50 mL下层清液,用于测定酚含量。同时收集分层后的乳液,通过加热破乳使乳化液与内水相分离,浓缩回收内水相中的苯酚。
-
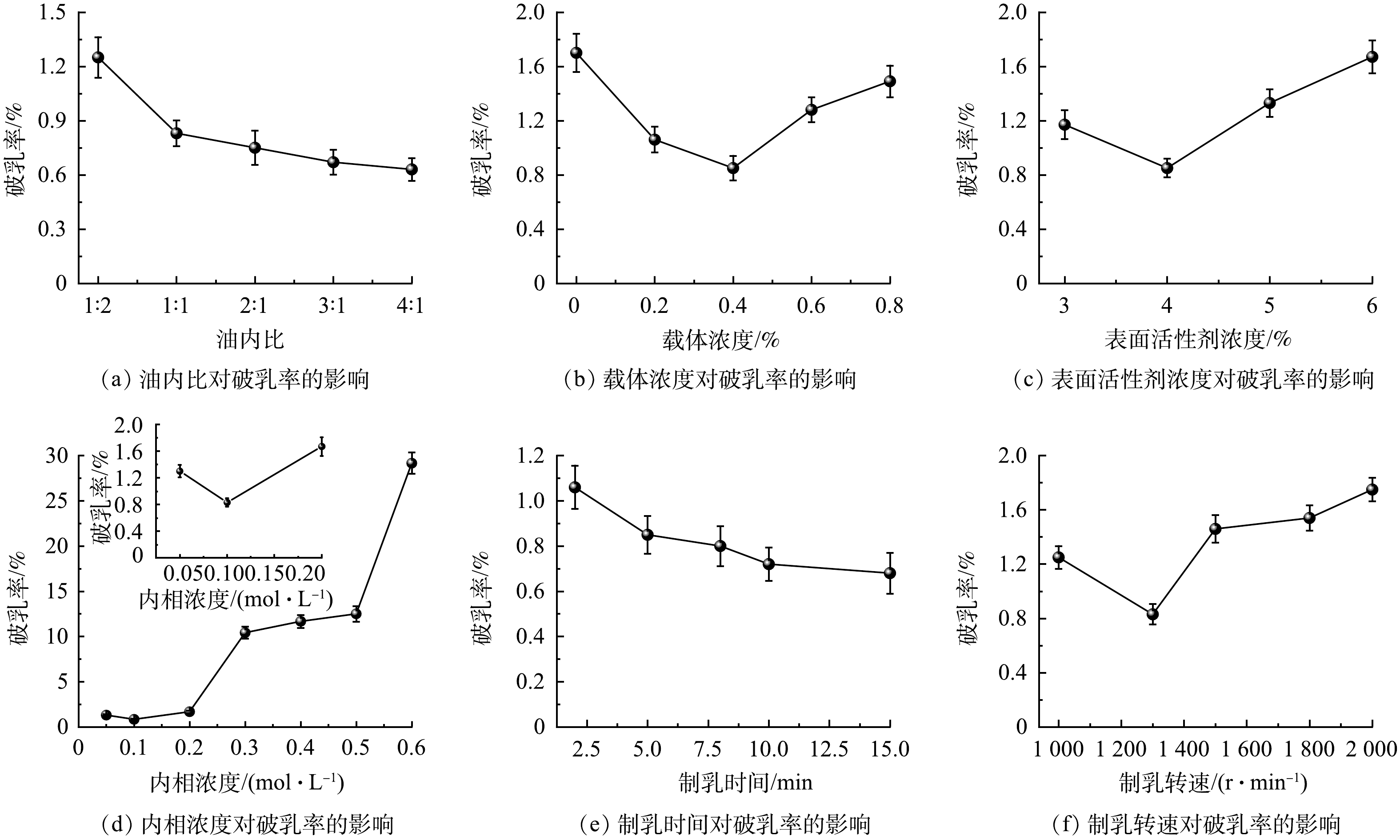
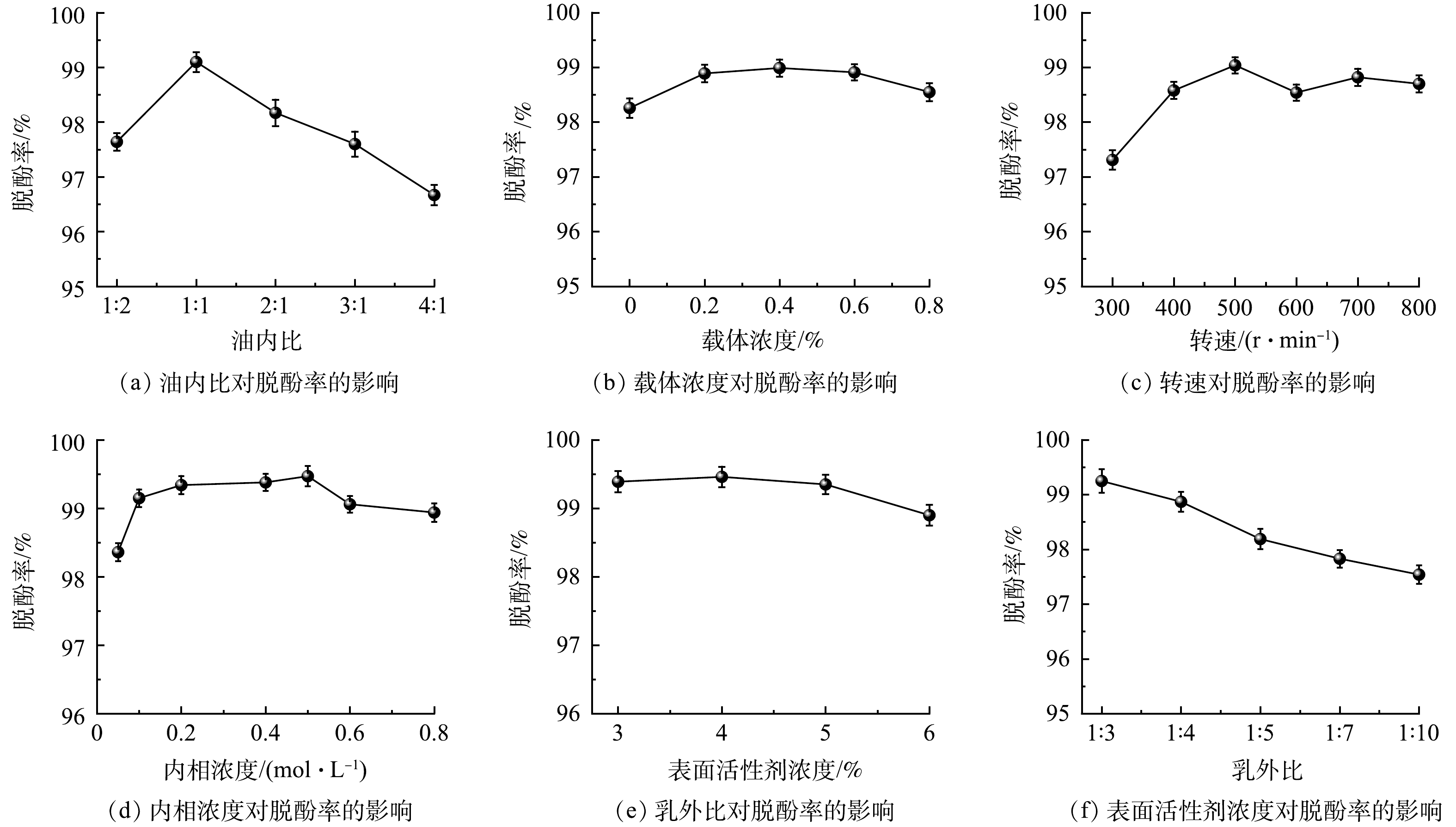
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,体积分数为4%的T-155为表面活性剂,体积分数为0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1,制乳转速为1 300 r·min−1,制乳时间5 min,研究不同油内比对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,结果如图2(a)所示。油内比增大时乳化液的破乳率会下降。油内比较低时有机溶剂不足以实现对内相溶液的适当包封,从而使得液膜较薄,乳液不稳定[24]。油内比增大会使得液膜变厚,稳定性提高。但油内比过大会导致液膜的黏度、厚度增大,使待分离物质在膜内的传质速率下降,所以应该在保证稳定性较好的前提下选择较小的油内比。本实验确定油内比为1∶1。在研究表面活性剂浓度、内相浓度、油内比、制乳转速以及制乳时间相同的实验条件下,研究不同载体浓度对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,结果如图2(b)所示。破乳率随着载体浓度的增加会先增大后减小,在载体浓度为0.4%时破乳率最低。AHMAD等[25]指出,过多的载体会使更多的溶质从外相快速转移到内相,导致外相和内相之间渗透梯度的显著变化,从而使得乳化液滴膨胀、液膜破裂。本实验选用载体正辛醇的浓度为0.4%。
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,油内比为1∶1,内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1,制乳转速为1 300 r·min−1,制乳时间5 min,研究不同表面活性剂浓度对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,结果如图2(c)所示。可见,破乳率随着表面活性剂的增加会先升高后降低,在表面活性剂浓度为4%时破乳率最低。增加表面活性剂的浓度可以降低表面张力,从而形成更多的细小液滴,产生更稳定的乳液[26]。但随着表面活性剂用量增加到一定量时,会降低了乳化液滴的运动速率,导致液滴发生溶胀[27]。本实验选用表面活性剂T-155的浓度为4%。在研究表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、油内比、制乳转速以及制乳时间相同的实验条件下,研究不同内相浓度对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,结果如图2(d)所示。当内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1时,破乳率最低,在内相浓度大于0.1 mol·L−1后,随着浓度的增大,液膜的稳定性变差。KUMAR等[28]指出,在较高内相氢氧化钠浓度下,氢氧化钠会与表面活性剂发生反应,使表面活性剂水解,从而导致乳化液膜的稳定性降低。本实验选用内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1。
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,4%的T-155为表面活性剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,油内比为1∶1,内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1,制乳转速为1 300 r·min−1,研究不同制乳时间对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,结果如图2(e)所示。可见,制乳时间越长,乳化液的破乳率越低,制乳时间大于5 min后,破乳率变化不大。制乳时间越长,液膜粒径就越小,粒径分布范围也就越小,分散效果越好,反之分散效果会降低,导致乳化液膜的稳定性受到影响[29]。并且过长的乳化时间会使得内相液滴一直在高速剪切下,导致进入内相的水的转移速率增加,从而造成膜破损[30]。本实验选用制乳时间为5 min。在研究表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、油内比、内相浓度以及制乳时间相同的实验条件下,研究不同制乳转速对乳化液膜稳定性的影响,结果如图2(f)所示。制乳转速为1 300 r·min−1时,破乳率最低。油相在剪切力的作用下分散为均匀的乳化液颗粒,当剪切力过大时会破坏乳化液颗粒,使得乳滴半径太小而会快速结合,当膜无法克服碰撞力时便导致乳液液滴破裂[19]。本实验选用制乳转速为1 300 r·min−1。
-
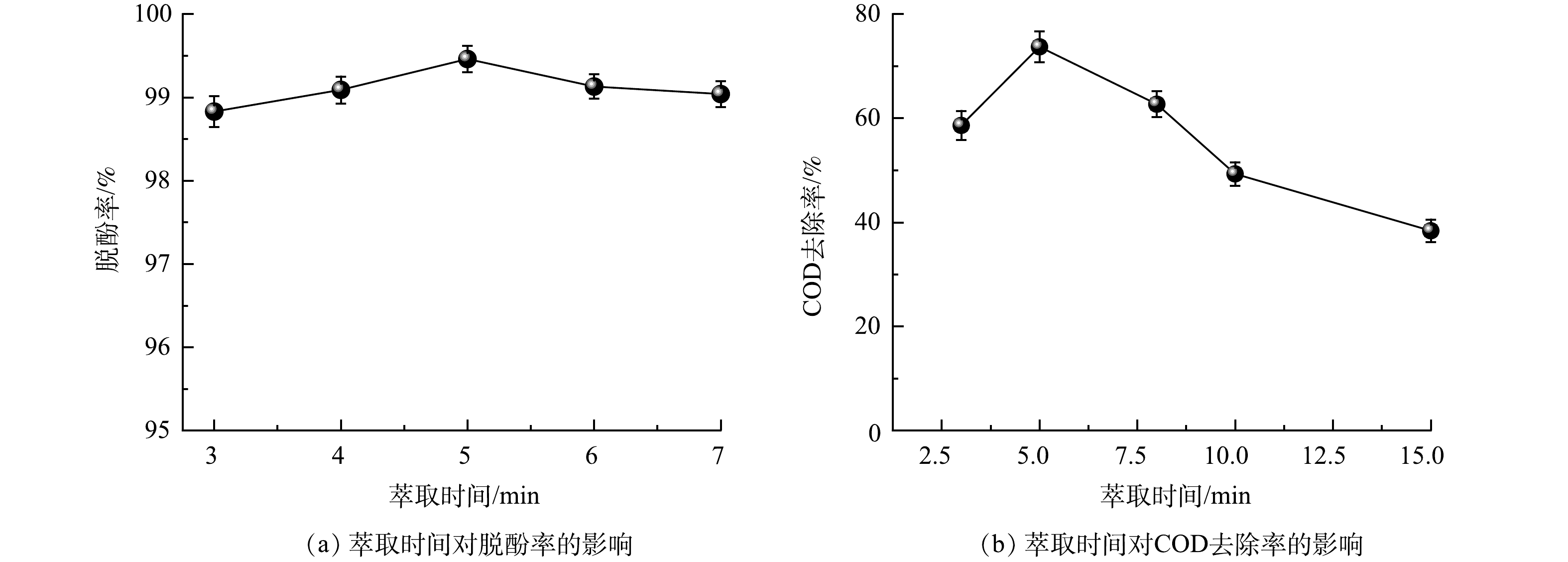
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,4%的T-155为表面活性剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1,乳外比为1:3,搅拌转速500 r·min−1,萃取时间5 min,研究不同油内比对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图3(a)所示。油内比是制备乳化液膜时添加的油相与内相的体积比。随着油内比的增加,脱酚率会先升高后降低,当油内比为1:1时脱酚率最高。从经济角度来看,降低油内比可以减少制备乳化液膜原料的使用量,从而提高经济效益;从处理效果方面来看,提高油内比可以形成更稳定的乳液,但油内比过大会使得液膜厚度增加,导致待分离物质在膜内的传质速率下降[31],脱酚率下降。本实验选择油内比为1∶1。在研究表面活性剂浓度、内相浓度、油内比、乳外比、搅拌转速以及萃取时间相同的实验条件下,研究不同载体浓度对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图3(b)所示。随着载体浓度的增加,脱酚率先增加而后基本保持不变。载体正辛醇是直链氢键缔合溶剂,能与酚形成弱氢键缔合物[32],可实现对苯酚的选择性迁移,使得传质效率增大。由于棕榈油中的主要成分甘油三酯可以与苯酚形成苯酚-甘油三酯络合物,故棕榈油的存在有利于Ⅱ型传质,可促进苯酚迁移至膜内,而外加载体有利于脱酚率的进一步提高。当外加载体正辛醇的浓度增加到0.4%时,脱酚率达到最大值,说明此时载体浓度最佳。当载体浓度继续增加时,载体会有富余,经济效益下降,同时载体过多会使得乳液粘度变大而增加传质阻力[33],导致脱酚率降低。因此,本实验选择载体浓度为0.4%。
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,4%的T-155为表面活性剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度为0.1 mol·L−1,油内比为1∶1,乳外比为1∶3,萃取时间5 min,研究不同的搅拌转速对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图3(c)所示。当转速为500 r·min−1时脱酚率最高。搅拌速度越高,强化了乳化液膜的传质过程,同时会产生较大表面积的细小液滴,可促进苯酚转移至膜内[34]。反之,当转速过低时,乳液不易分散完全,导致传质效果不好,脱酚率低。但在过高的搅拌速度下,形成的乳液液滴尺寸小,液膜变薄,乳液液滴会迅速聚结,最终导致膜破裂,脱酚率下降。因此,本实验选择的转速为500 r·min−1。在研究表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、油内比、乳外比、搅拌转速以及萃取时间相同的实验条件下,研究不同内相浓度对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图3(d)所示。随着内相浓度的增加,当内相浓度小于0.5 mol·L−1时,脱酚率会有所增加,而当内相浓度超过0.5 mol·L−1时,脱酚率不随内相浓度的增大而增加。内相浓度越高,传质推动力增大,脱酚率变大。但NaOH浓度过高会使得乳化液膜的稳定性下降,同时高浓度的内相试剂会在外相和内相之间产生显着的渗透压差,导致乳液液滴尺寸增加,液滴更易破裂[35],ROUHANI等[36]研究也表明,内相试剂浓度过大时会降低液膜厚度,从而导致脱酚率下降。从乳化液稳定性和脱酚率的角度来看,当NaOH浓度为0.2 mol·L−1时液膜破乳率较低,脱酚率也较高,因此,本实验选择内相浓度为0.2 mol·L−1。
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度0.2 mol·L−1,油内比为1∶1,乳外比为1∶3,搅拌转速500 r·min−1,萃取时间5 min,研究不同载体浓度对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图3(e)所示。当表面活性剂浓度为4%时,脱酚率最大。表面活性剂的加入可以降低界面张力,有助于小粒径的乳液液滴的形成,从而增大外相与乳化液膜之间的接触表面积[37],有利于酚的迁移,但当表面活性剂增大到一定量之后会导致液膜厚度增加、界面粘度变大从而使得传质阻力增大[38],脱酚率降低。因此,本实验选择表面活性剂浓度为4%。在研究表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、内相浓度、油内比、搅拌转速以及萃取时间相同的实验条件下,研究不同乳外比对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图3(f)所示。随着乳外比的增大,脱酚率也相应增大。HUSSEIN等[39]发现较低的乳外比会使得外相和乳液之间的渗透压差增加,从而导致液膜更易破裂,脱酚率下降。而对于一定体积的外水相而言,乳外比越大,用来萃取的乳液量就越大,乳液与外水相的接触面积越大,使得脱酚率提高,但消耗的乳液多,经济效益下降。实际应用中需用较小的乳外比达到所要求的条件。本实验选择乳外比为1∶3。
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,4%的T-155为表面活性剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度0.2 mol·L−1,油内比为1∶1,乳外比为1∶3,搅拌转速500 r·min−1,研究不同的萃取时间对100 mg·L−1的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图4(a)所示。随着萃取时间的增大,脱酚率先升高后降低,当萃取时间为5 min时,脱酚率最大。萃取时间的增加有助于将大的乳液液滴破碎成大量较小的乳液液滴,从而增大传质表面积[40],使得酚与液膜接触越充分,提高脱酚率。但随着萃取时间的延长,由于更多的外相分子转移到内相中,会使乳液溶胀,最终导致膜破裂增加[28],脱酚率下降。因此,本实验选择萃取时间为5 min。在研究表面活性剂浓度、载体浓度、内相浓度、油内比、乳外比以及搅拌转速相同的实验条件下,研究萃取时间对100 mg·L−1的不同酚类模拟废水COD去除率的影响,结果如图4(b)所示。随着萃取时间的增大COD去除率先增大后减小,这与萃取时间对脱酚率的影响规律一致,当萃取时间为5 min时,COD去除率最大,达到73.71%。
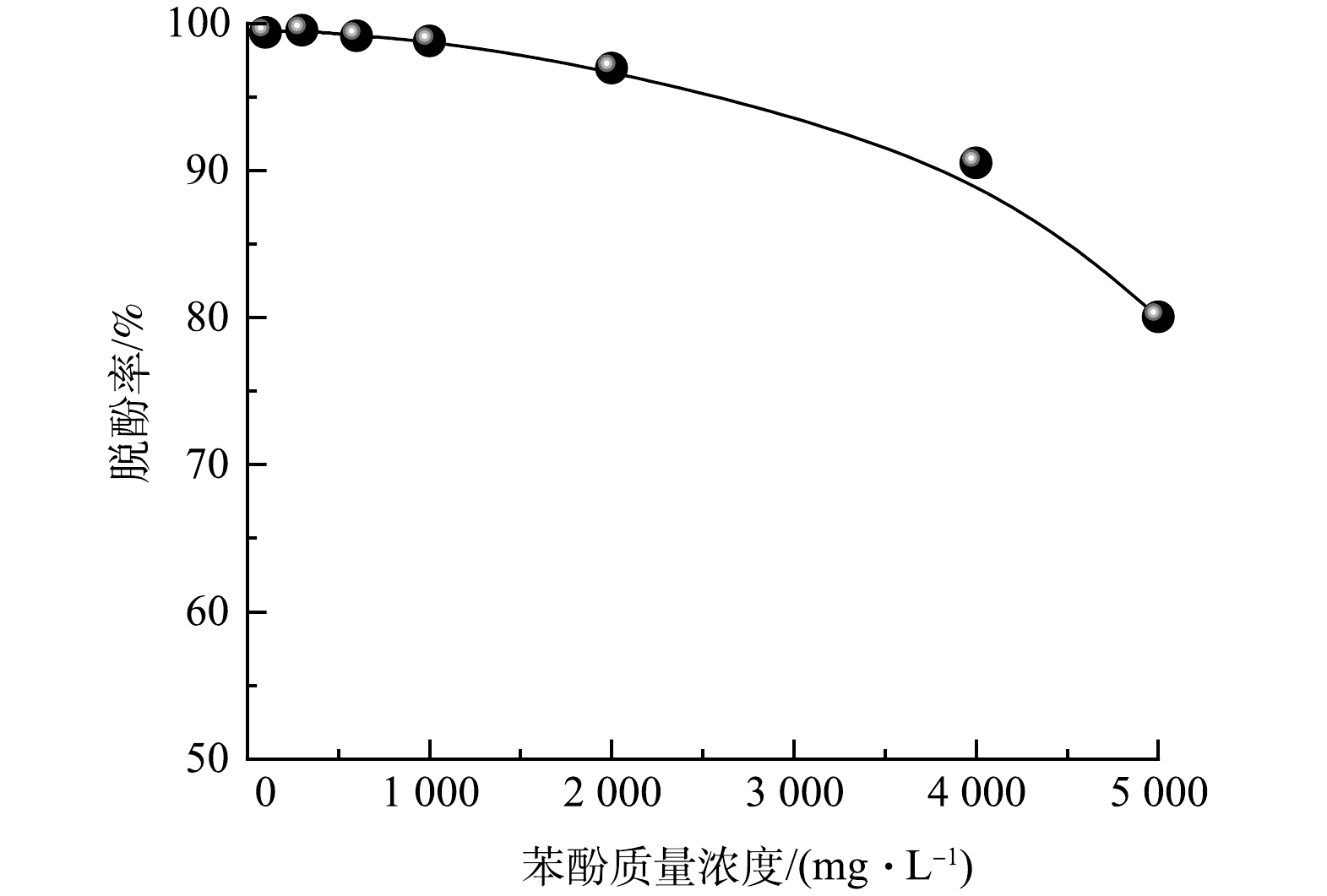
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,4%的T-155为表面活性剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度0.2 mol·L−1,油内比为1∶1,乳外比1∶3,搅拌转速500 r·min−1,萃取时间5 min,研究该乳化液膜体系对不同浓度的模拟苯酚废水去除率的影响,结果如图5所示。在初始苯酚质量浓度小于1 000 mg·L−1的情况下,苯酚浓度的变化对脱酚率的影响不大,在初始苯酚质量浓度达到300 mg·L−1时脱酚率最高,达到99.53%。当初始苯酚质量浓度大于1 000 mg·L−1时,随着苯酚浓度的增大,脱酚率有所下降,但在初始苯酚浓度为4 000 mg·L−1时,脱酚率仍达90.51%,说明该乳化液膜体系在处理高浓度含酚废水方面具有一定优势。苯酚浓度的提高可以增加传质推动力,从而使得脱酚率增大,但当苯酚浓度提高到一定值后,由于液膜中NaOH的量一定,液膜能脱除的酚有限,从而使得脱酚率下降。
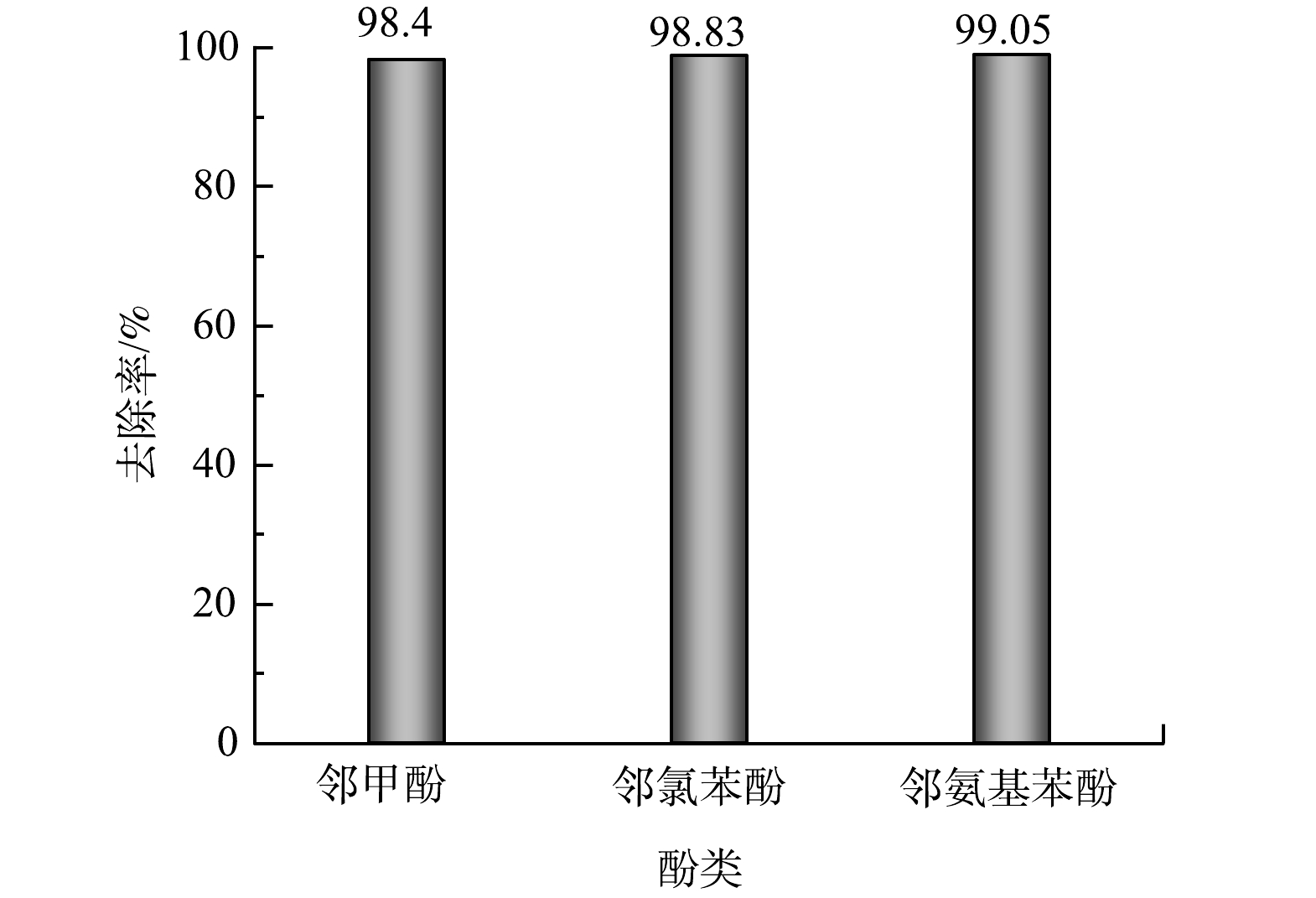
以棕榈油和煤油的混合物为膜溶剂,4%的T-155为表面活性剂,0.4%的正辛醇为载体,内相浓度0.2 mol·L−1,油内比为1∶1,乳外比1∶3,搅拌转速500 r·min−1,萃取时间5 min,研究该乳化液膜体系对不同酚类模拟废水去除率的影响,结果如图6所示。该乳化液膜体系对于邻甲酚、邻氯苯酚和邻氨基苯酚这3种酚类去除率均较高,去除率均接近99%,说明该乳化液膜体系对于与苯酚化学性质相似的酚类的脱除效果较好。
-
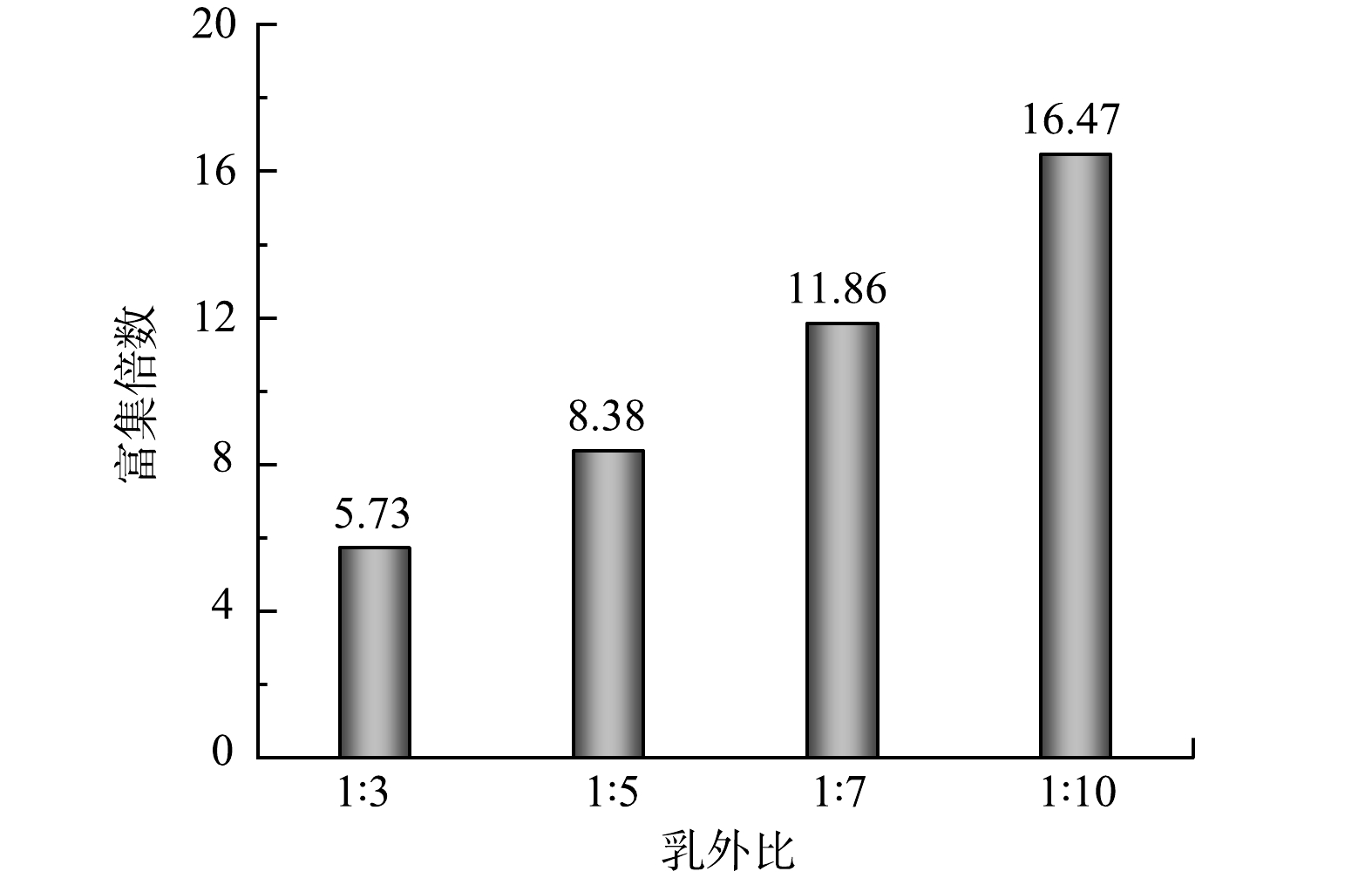
本实验进行了通过加热破乳来回收乳化液膜中的酚研究。在70 ℃的恒温水浴锅中,将液膜提取分离后的乳状液(乳液相)加热120 min,即可实现破乳。将破乳后的水相分离出来,测定水相中的酚浓度,计算苯酚富集倍数。对于相同的乳化液膜,改变乳外比,分析其对苯酚富集倍数的影响,结果如图7中所示。由图7以看出,随着乳外比的增加,苯酚富集倍数增大,从1∶3处理比的5.73倍到1∶10处理比的16.47倍富集。
-
1)当表面活性剂T-155浓度为4%、载体正辛醇浓度为0.4%、内相试剂NaOH溶液浓度为0.1 mol·L−1、油内比1∶1、在1 300 r·min−1的转速下进行5 min高速剪切制乳是制备乳化液膜的最佳条件。
2)当表面活性剂T-155浓度为4%、载体正辛醇浓度为0.4%、内相试剂NaOH溶液浓度为0.2 mol·L−1、油内比1∶1、乳外比为1∶3,在500 r·min−1的转速下萃取5 min除酚率可达99.45%,COD去除率可达73.71%,并且该乳化液膜体系对于邻甲酚、邻氯苯酚和邻氨基苯酚这3种酚类去除率均接近99%,当初始酚质量浓度达到4 000 mg·L−1时,脱酚率仍然接近90%。
3)该乳化液膜对苯酚的富集倍数随乳外比的增大而增大,在乳外比为1∶10时富集倍数可达16.47。
乳化液膜法对废水中酚的高效去除与富集
Efficient removal and enrichment of phenol from wastewater via emulsion liquid membrane method
-
摘要: 采用绿色高效的乳化液膜法(GELM)去除与富集废水中的酚类污染物,建立了以棕榈油和煤油混合物(7:3)为膜溶剂、聚异丁烯多丁二酰亚胺(T-155)为表面活性剂、正辛醇为载体的乳化液膜体系,提高了GELM法分离酚的能力,并研究了各因素对液膜稳定性及对废水中苯酚的分离富集效果的影响。乳化液稳定性和分离酚的实验结果表明,在最优条件下,乳液稳定性好,且该乳化液膜对废水中苯酚和COD去除率分别为99.5%和74%,对邻甲酚、邻氯苯酚、邻氨基苯酚等酚类污染物的除酚率均达~99%,在初始酚浓度4000 mg·L−1时,除酚率仍然达~90%,说明该体系可实现对酚的高效去除。此外乳化液膜对苯酚的富集倍数随乳外比的增大而增大,在乳外比为1∶10时苯酚富集约16倍,说明该体系实现了对苯酚的有效富集。研究结果可为废水中酚类污染物的去除与资源化回收提供绿色、高效、低成本解决方法。Abstract: A green and high-efficient emulsion liquid membrane (GELM) method was developed to remove and enrich phenol pollutants from phenol contaminated wastewater. The emulsion liquid membrane was established with a mixture of palm oil and kerosene (7∶3) as membrane solvent, polyisobutylene polysuccinimide (T-155) as surfactant, and n-octanol as carrier, which improved phenol removal ability by GELM. The effects of various factors on the stability of emulsion liquid membrane and the separation and enrichment effect of phenol in wastewater were studied. The results of emulsion liquid stability and phenol separation experiments showed that under the optimal conditions, the emulsion was stable, and the removal rates of phenol and COD were 99.5% and 74%, respectively. The removal rates of o-cresol, o-chlorophenol and o-aminophenol reached 99%. When the initial phenol concentration was 4000 mg·L−1, the removal rate of phenol was still close to 90%, indicating the system can remove phenol efficiently. In addition, the enrichment ratio of phenol increased with the emulsion ratio. When the emulsion ratio was 1∶10, the enrichment of phenol was about 16 times, indicating the proposed scheme could effectively enrich phenol. This research provided a green, efficient, and low-cost solution for the removal and recycling of phenol pollutants in wastewater.
-
Key words:
- green emulsion liquid membrane /
- stability /
- removal rate of phenol /
- enrichment
-
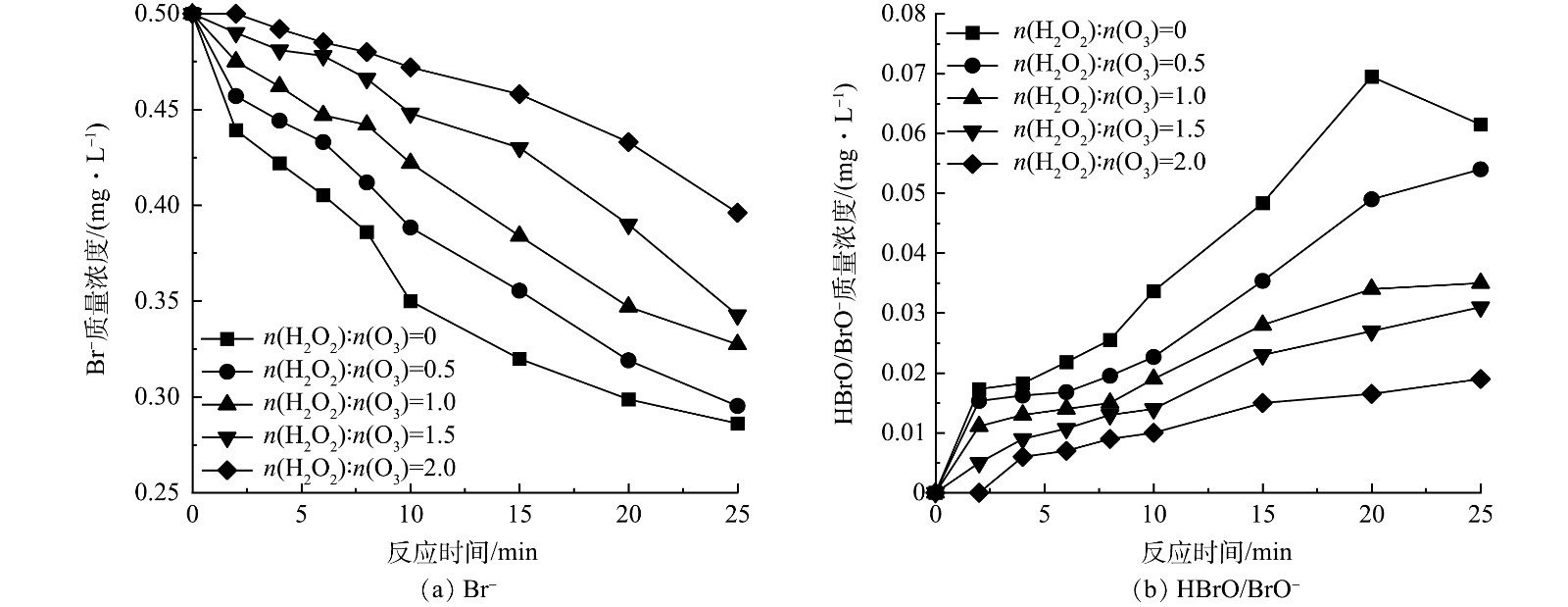
臭氧混凝耦合工艺(hybrid ozonation-coagulation,HOC)是基于传统污水深度处理工艺“混凝-沉淀-过滤”处理流程长、溶解性有机物去除效果差的问题提出并构建的,具有臭氧氧化与混凝同时进行、溶解性有机物去除率高的特点[1-3]。然而在进行高Br−浓度废水处理时,例如工业盐水、肥料废水等[4-5],HOC工艺中的臭氧和由于臭氧与混凝剂的互促增效反应产生的·OH[6]会将Br−氧化为潜在致癌物质溴酸盐(BrO3−)[7-9],而我国《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB 5749-2022)规定,饮用水中BrO3−含量不能高于0.01 mg·L−1。
近年来,臭氧氧化过程的BrO3−消毒副产物的控制方法受到国内外相关研究领域学者的广泛重视[10-13]。在臭氧氧化体系中,BrO3−的生成途径主要分为2种[14-15]:臭氧直接氧化和·OH间接氧化,2种氧化途径均伴随着中间产物HBrO/BrO−的生成,因此,HBrO/BrO−的继续氧化是控制Br−转化为BrO3−的重要限制反应[16]。而有研究表明,H2O2能通过与HBrO/BrO−反应阻碍其继续氧化为BrO3−,从而有效地延缓溴酸盐消毒副产物的生成[13]。此外,H2O2能加速臭氧分解生成·OH,控制BrO3−生成的同时可提高有机物的去除效果,但·OH的间接氧化也会促进BrO3−的生成[11, 17]。目前HOC工艺中H2O2控制下的溴酸盐消毒副产物的抑制效能尚未探讨,抑制原理也有待进一步探究。
基于以上研究结果,本研究探究在不同臭氧投加量下HOC工艺的有机物处理效果和BrO3−生成情况,考察H2O2投加量对HOC工艺中BrO3−生成的抑制效能,通过对BrO3−生成贡献率和Br−消耗动力学的分析,明确HOC体系中BrO3−的主要生成途径和H2O2抑制原理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验用水
实验用水为外加KBr(Br−质量浓度为500 μg·L−1)的二级出水,二级出水来自西安某城市污水处理厂的二沉池,主要水质指标参数如下:pH为7.56±0.23,TOC为(5.43±1.66) mg·L−1,Br−为 (117±8) μg·L−1。
1.2 实验方法与装置
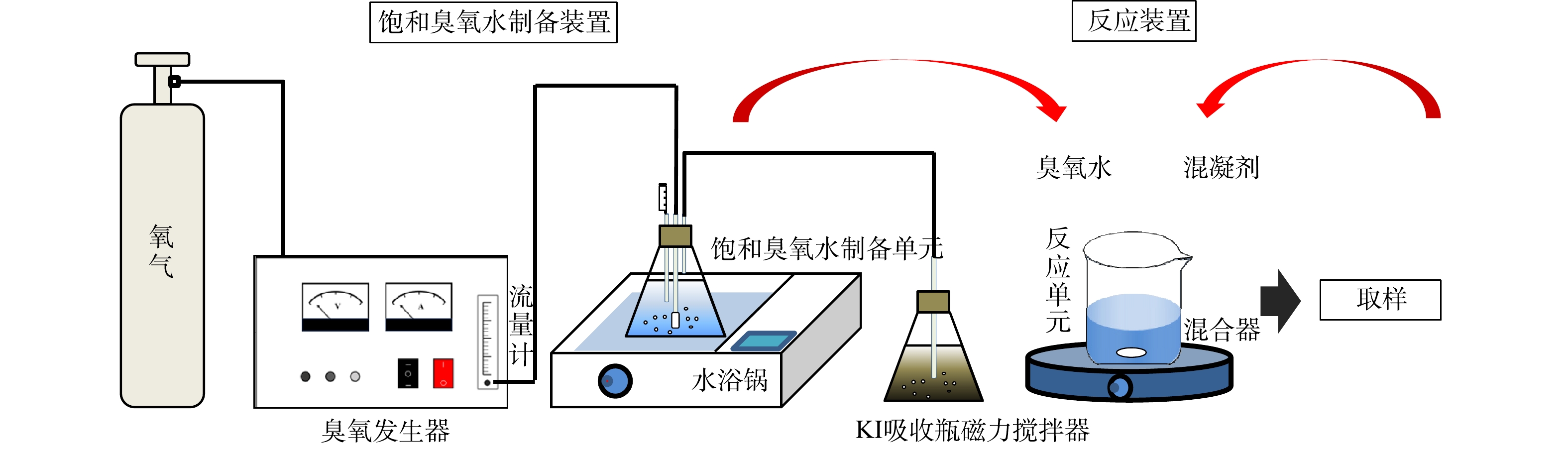
饱和臭氧水制备装置和HOC反应装置如图1所示,由气体流量计控制氧气源臭氧发生器(济南三康,SK-CFQ-3P)的出口流量为16 L·h−1,整个装置在0~4 ℃的水浴温度下持续曝气2 h后臭氧达饱和状态,本研究所投加的臭氧质量浓度为4.5、8.0、11.3 mg·L−1。HOC实验在外加Br−的100 mL二级出水中进行,混凝剂AlCl3·6H2O的投加量为15 mg·L−1。实验前使用0.2 mmol·L−1的磷酸缓冲溶液和1 mol·L−1的H2SO4溶液调节pH在7±0.2左右,然后加入混凝剂快搅1 min (转速300 r·min−1),饱和臭氧水和过氧化氢(n(H2O2):n(O3) = 0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0)在快搅结束后迅速加入体系,继而慢搅25 min (转速100 r·min−1),取不同反应时间的水样进行总有机碳(TOC)、溴离子(Br−)、溴酸根(BrO3−)、次溴酸(HBrO/BrO−)等指标的测定。
在探究HOC体系中BrO3−的生成贡献率时,取不同反应时间的水样经0.45 μm滤头过滤后快速测定臭氧质量浓度。由于对氯苯甲酸(pCBA)与·OH的反应速率k·OH,pCBA=5.0×109 L·(mol·s)−1远高于与O3的反应速率kO3,pCBA<0.15 L·(mol·s)−1[18],因此采用pCBA作为·OH的探针间接测定·OH的浓度。实验前向反应体系中加入0.5 μmol·L−1的pCBA,水样中pCBA的浓度测定前使用Na2S2O3淬灭·OH。
1.3 分析测试方法
样品经0.45 μm滤头过滤、H2SO4酸化、N2吹脱3 min处理后,使用岛津TOC-VCPH分析仪测定TOC。饱和臭氧水质量浓度采用靛蓝比色法测定[19],气态臭氧采用碘量法测定[20]。Br−和BrO3−的质量浓度由热电阴离子色谱(ICS-1100 Dionex)测定,色谱柱为Dionex IonPacTM AS23(4×250 mm)。样品经固相萃取装置进行预处理:首先使用Bond Elut-C18小柱去除有机物;再使用Dionex OnGuardTM Ⅱ Ag/H小柱去除过渡金属离子和氯离子。HBrO/BrO−的质量浓度由苯酚衍生法测定[21],样品在pH为3、70 ℃的水浴条件下与苯酚反应1 h,反应后使用高效液相色谱法测定4-溴苯酚的质量浓度[22]。·OH浓度由pCBA探针法间接测定,pCBA浓度采用高效液相色谱法测定[23]。
1.4 数据分析方法
Rct为某段时间内·OH暴露量与O3暴露量的比值(式(1))[24],Rct值通过式(2)计算。HOC体系中臭氧直接氧化和·OH间接氧化对BrO3−生成的贡献f(O3)和f(·OH)由式(3)~(5)[25-26]计算。
Rct=∫C(⋅OH)dt∫C(O3)dt (1) ln(C(pCBA)C(pCBA)0)=−Rctk⋅OH,pCBA∫C(O3)dt (2) 式中:C(·OH)为·OH的浓度,mol·L−1;C(O3)为O3的浓度,mol·L−1;C(pCBA)0和C(pCBA)分别为pCBA的初始浓度和反应后浓度,mol·L−1;k·OH,pCBA为pCBA与·OH的反应速率常数,5.0×109 L·(mol·s)−1。
fBr−,⋅OH=kBr−,⋅OHC(Br−)C(⋅OH)kBr - ,⋅OHC(Br−)C(⋅OH)+kBr−,O3C(Br−)C(O3) (3) fBr−,⋅OH=1.1×109Rct160+1.1×109Rct (4) fBr−,O3=1−fBr−,⋅OH (5) 式中:fBr−,·OH为·OH间接氧化的贡献率f(·OH);fBr−,O3为臭氧直接氧化的贡献率f(O3);C(Br−)为Br−的浓度,mol·L−1;C(·OH)为·OH的浓度,mol·L−1;kBr−,·OH为Br−与·OH的反应速率常数,1.1×109 L·(mol·s)−1[13];kBr−,O3为Br−与O3的反应速率常数,160 L·(mol·s)−1;C(O3)为O3的浓度,mol·L−1[13]。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 有机物的去除及溴酸盐的产生和抑制
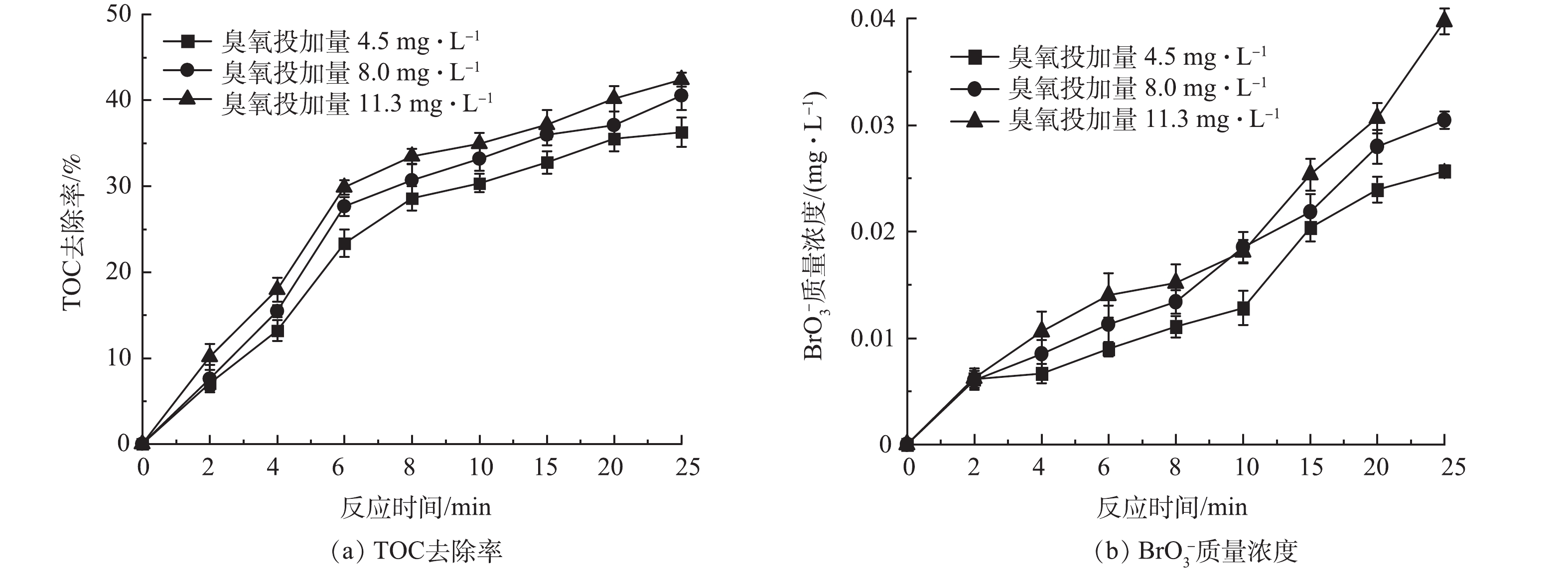
图2为不同臭氧投加量下HOC体系对二级出水中有机物的处理效果和生成的BrO3−质量浓度的变化。当臭氧投加量为4.5、8.0、11.3 mg·L−1时,反应25 min后HOC体系对TOC的去除率分别达到36.29%、40.56%和42.41%,BrO3−的生成量分别为0.026、0.030和0.040 mg·L−1,有机物的去除率和BrO3−质量浓度均随着臭氧投加量的增大而增加。这是因为在HOC体系中混凝剂既可以作为混凝剂发挥混凝作用,又可以作为催化剂催化臭氧产生·OH[1-3, 6],随着臭氧投加量的增加,O3和·OH的含量增大,体系的氧化能力增强,强化了有机物去除的同时使更多的Br−被O3直接或·OH间接氧化为BrO3−[14-15]。同时,由图2(b)可以看到,在3种臭氧投加量下,反应8 min后HOC体系中的BrO3−质量浓度均已经超过0.01 mg·L−1,即国家饮用水标准规范(GB 5749-2022)的BrO3−质量浓度限值,因此需对HOC体系中溴酸盐的生成进行控制。
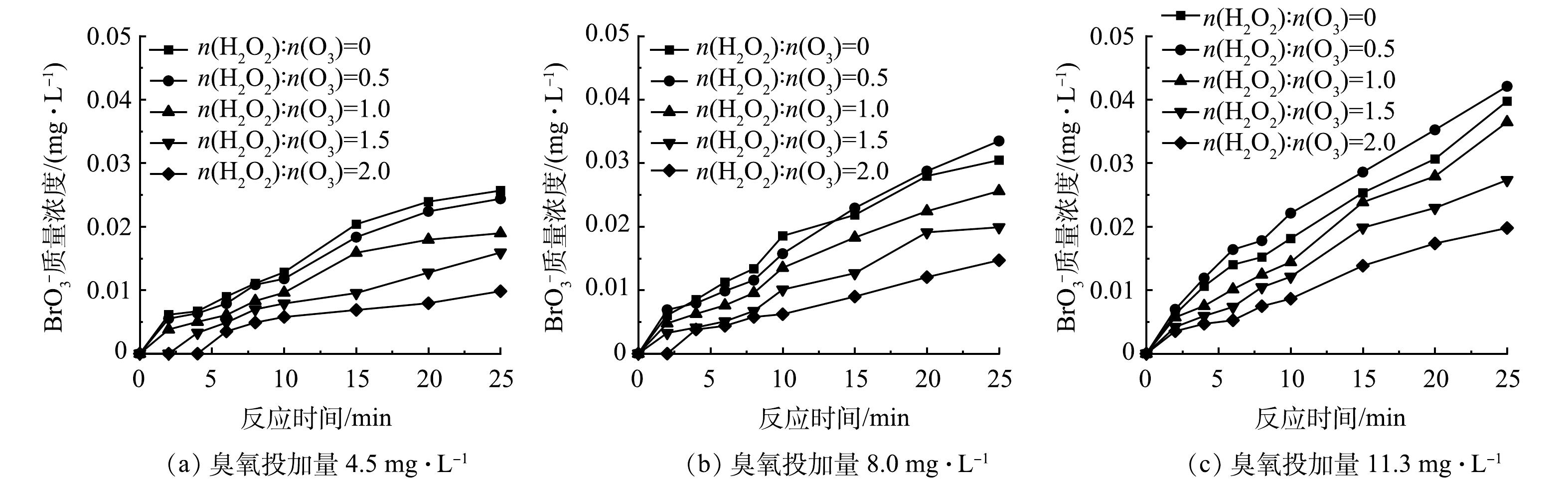
图3为不同H2O2投加量(n(H2O2):n(O3)=0.5、1、1.5和2)下HOC体系BrO3−质量浓度的变化。对于不同臭氧投加量的HOC体系,当n(H2O2):n(O3)>0.5时,H2O2对体系中BrO3−的生成具有明显的抑制作用,并且抑制作用随着H2O2投加量的增大而增强,其中当臭氧投加量为4.5 mg·L−1、n(H2O2):n(O3)=2时(图3(a)),H2O2对BrO3−的抑制率可达60%,BrO3−的生成量略低于0.01 mg·L−1。这与MIZUNO等[27]的研究结果一致,即n(H2O2):n(O3)超过1.25时能将BrO3−质量浓度控制在0.01 mg·L−1以下。这是因为过量的H2O2与生成BrO3−的重要中间产物HBrO/BrO−反应,将其还原回Br−,阻断了BrO3−的生成路径[28],同时H2O2的投加还会促进O3分解,降低了O3的暴露量,减少了HBrO/BrO−的生成,进而抑制了BrO3−的产生[11]。
由图3还可以看出,随着臭氧投加量的增加,H2O2对HOC体系中BrO3−生成的抑制效果变差,在臭氧投加量分别为4.5、8.0和11.3 mg·L−1时,当n(H2O2):n(O3)=2时对BrO3−的最大抑制率分别为60%、52%和42%,说明随着臭氧投加量的增大,O3暴露量升高,BrO3−生成量也随之增加[29]。因此,在较高臭氧投加量下投加相同摩尔比的H2O2难以达到低臭氧投加量时较好的抑制效果[30],但H2O2的投加延缓了HOC体系中BrO3−的生成。
2.2 H2O2抑制下的溴酸盐贡献率分析
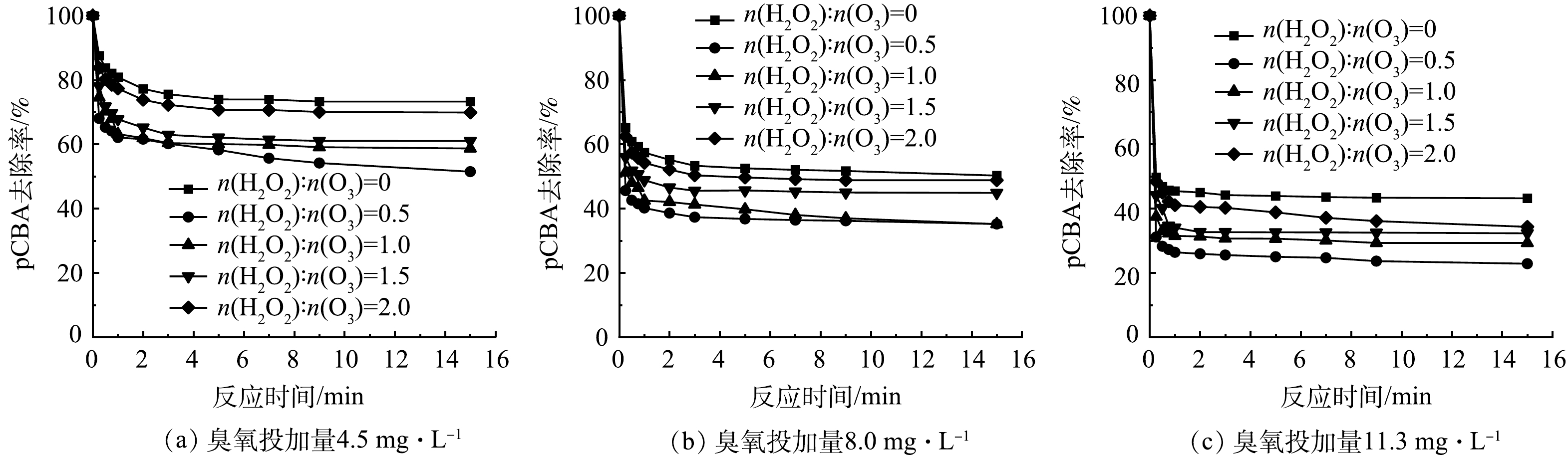
在HOC工艺中,BrO3−由Br−经臭氧直接氧化和·OH间接氧化2种途径生成[14-15],实验探究了不同臭氧投加量下投加H2O2时2种途径对BrO3−生成的贡献率。H2O2抑制条件下不同臭氧投加量的HOC体系中pCBA去除曲线(·OH的含量变化)如图4所示。随着臭氧投加量的增大,pCBA去除量增加,说明HOC体系中生成了更多的·OH。在同一臭氧投加量下,随着H2O2投加量的增大,pCBA去除量减少,说明HOC体系中的·OH浓度降低,这归因于低浓度的H2O2能促进O3分解产生·OH,而高浓度的H2O2不仅促进·OH的产生还会与·OH反应,消耗体系中的·OH[31-32]。
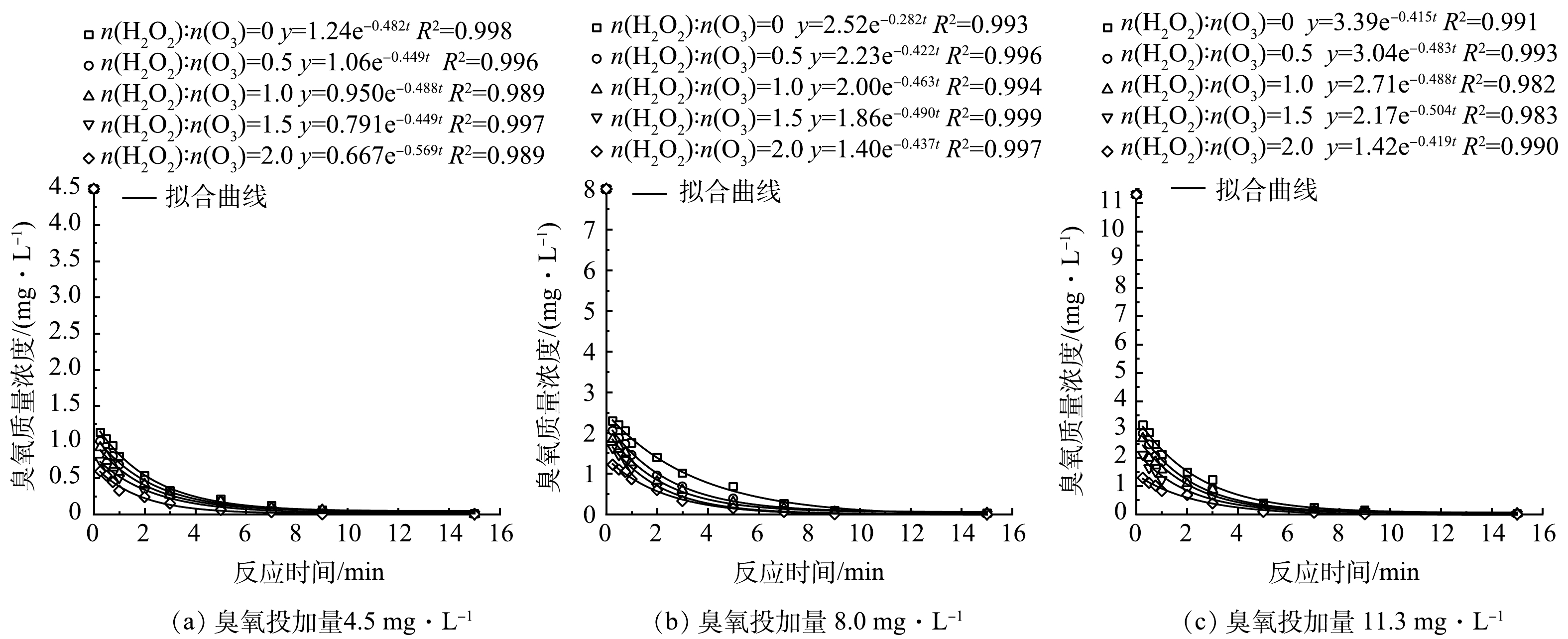
臭氧自分解反应一级动力学方程拟合曲线如图5所示,随着H2O2投加量的增大,HOC体系中臭氧分解前15 s的瞬时臭氧需求量(instantaneous O3 demand,IOD)增大,说明H2O2促进了臭氧的分解,降低了臭氧的质量浓度,进而抑制了BrO3−的臭氧直接氧化产生过程[33]。
H2O2抑制条件下的不同臭氧投加量的Rct值如图6所示,在HOC的反应初始阶段Rct值快速下降,中后期保持恒定。当臭氧投加量相同时,随着H2O2投加量的增大,Rct值增大,说明H2O2促进了O3的分解,使单位臭氧产生的·OH量增加;而随着臭氧投加量的增大,H2O2投加量相同时,Rct降低,说明O3的暴露量随着臭氧投加量的增加而增大。
HOC体系中·OH间接氧化和臭氧直接氧化对BrO3−生成的贡献f(·OH)和f(O3)如表1所示,结果表明,未投加H2O2时HOC体系中臭氧直接氧化对BrO3−的生成起主要作用,在不同臭氧投加量下,臭氧直接氧化的贡献率f(O3)均维持在80%以上。随着臭氧投加量的增加,HOC体系中O3的暴露量增大,臭氧直接氧化的贡献率增大,当臭氧投加量为11.3 mg·L−1时f(O3)可达到98%。
表 1 H2O2抑制条件下不同臭氧投加量的溴酸盐生成贡献率Table 1. Contribution rate of Bromate formation at different ozone dosages with the addition of H2O2臭氧/(mg·L−1) n(H2O2):n(O3) 不同反应时间下的f(·OH)/f(O3) 0.5 min 0.75 min 1 min 2 min 3 min 5 min 7 min 9 min 15 min 4.5 0 0.16/0.84 0.13/0.87 0.11/0.89 0.10/0.90 0.09/0.91 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.5 0.17/0.83 0.13/0.87 0.14/0.86 0.09/0.91 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.10/0.90 0.11/0.89 0.13/0.87 1 0.25/0.75 0.21/0.79 0.26/0.74 0.17/0.83 0.15/0.85 0.13/0.87 0.13/0.87 0.13/0.87 0.13/0.87 1.5 0.36/0.64 0.28/0.72 0.26/0.74 0.19/0.81 0.18/0.82 0.15/0.85 0.15/0.85 0.15/0.85 0.15/0.85 2 0.34/0.66 0.27/0.73 0.23/0.77 0.20/0.80 0.18/0.82 0.17/0.83 0.16/0.84 0.17/0.83 0.17/0.83 8.0 0 0.12/0.88 0.09/0.91 0.08/0.92 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.04/0.96 0.03/0.97 0.03/0.97 0.03/0.97 0.5 0.13/0.87 0.10/0.90 0.09/0.91 0.07/0.93 0.06/0.94 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.06/0.94 1 0.15/0.85 0.12/0.88 0.16/0.84 0.09/0.91 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.09/0.91 0.10/0.90 1.5 0.19/0.81 0.14/0.86 0.13/0.87 0.10/0.90 0.09/0.91 0.07/0.93 0.07/0.93 0.07/0.93 0.07/0.93 2 0.24/0.76 0.18/0.82 0.16/0.84 0.11/0.89 0.11/0.89 0.09/0.91 0.09/0.91 0.09/0.91 0.09/0.91 11.3 0 0.08/0.92 0.06/0.94 0.05/0.95 0.03/0.97 0.03/0.97 0.02/0.98 0.02/0.98 0.02/0.98 0.02/0.98 0.5 0.14/0.86 0.11/0.89 0.10/0.90 0.06/0.94 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.06/0.94 1 0.20/0.80 0.13/0.87 0.11/0.89 0.07/0.93 0.06/0.94 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 0.05/0.95 1.5 0.18/0.82 0.24/0.76 0.19/0.81 0.13/0.87 0.10/0.90 0.09/0.91 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 0.08/0.92 2 0.21/0.79 0.21/0.79 0.18/0.82 0.11/0.89 0.09/0.91 0.08/0.92 0.09/0.91 0.10/0.90 0.11/0.89 随着H2O2投加量的增大,·OH对BrO3−生成的贡献率f(·OH)增大,f(O3)相应降低,臭氧投加量为4.5 mg·L−1时,投加n(H2O2):n(O3)=2的H2O2相较于未投加H2O2使反应初始阶段f(·OH)由15.83%增加至34.44%,反应后期f(·OH)由7.90%增加至16.88%。在H2O2的抑制条件下,反应时间在0~5 min内f(·OH)逐渐减少,f(O3)逐渐增加且均在60%以上;在5~15 min的反应时间内臭氧与·OH的贡献率基本保持稳定,且f(O3)保持在80%以上。因此,在H2O2抑制条件下臭氧直接氧化仍是HOC体系中BrO3−生成的主要途径。
2.3 HOC体系中H2O2抑制原理
为探究HOC体系中H2O2对BrO3−生成的抑制原理,测定了臭氧投加量为4.5 mg·L−1时H2O2抑制条件下的Br−和HBrO/BrO−质量浓度变化如图7所示,BrO3−质量浓度变化如图3(a)所示。反应前期,由于H2O2的抑制,体系中HBrO/BrO−质量浓度保持在较低水平,Br−的消耗和BrO3−的生成都较为缓慢;在反应中后期,随着H2O2的消耗,其抑制作用减弱,难以继续抑制Br−的氧化,HBrO/BrO−开始积累,BrO3−生成速度加快。H2O2投加量越大,HBrO/BrO−维持低质量浓度的时间越长,BrO3−的最终生成量越低,当n(H2O2):n(O3)=2时,HBrO/BrO−在反应前10 min的质量浓度均在0.01 mg·L−1以下,BrO3−最终生成量也在0.01 mg·L−1以下。
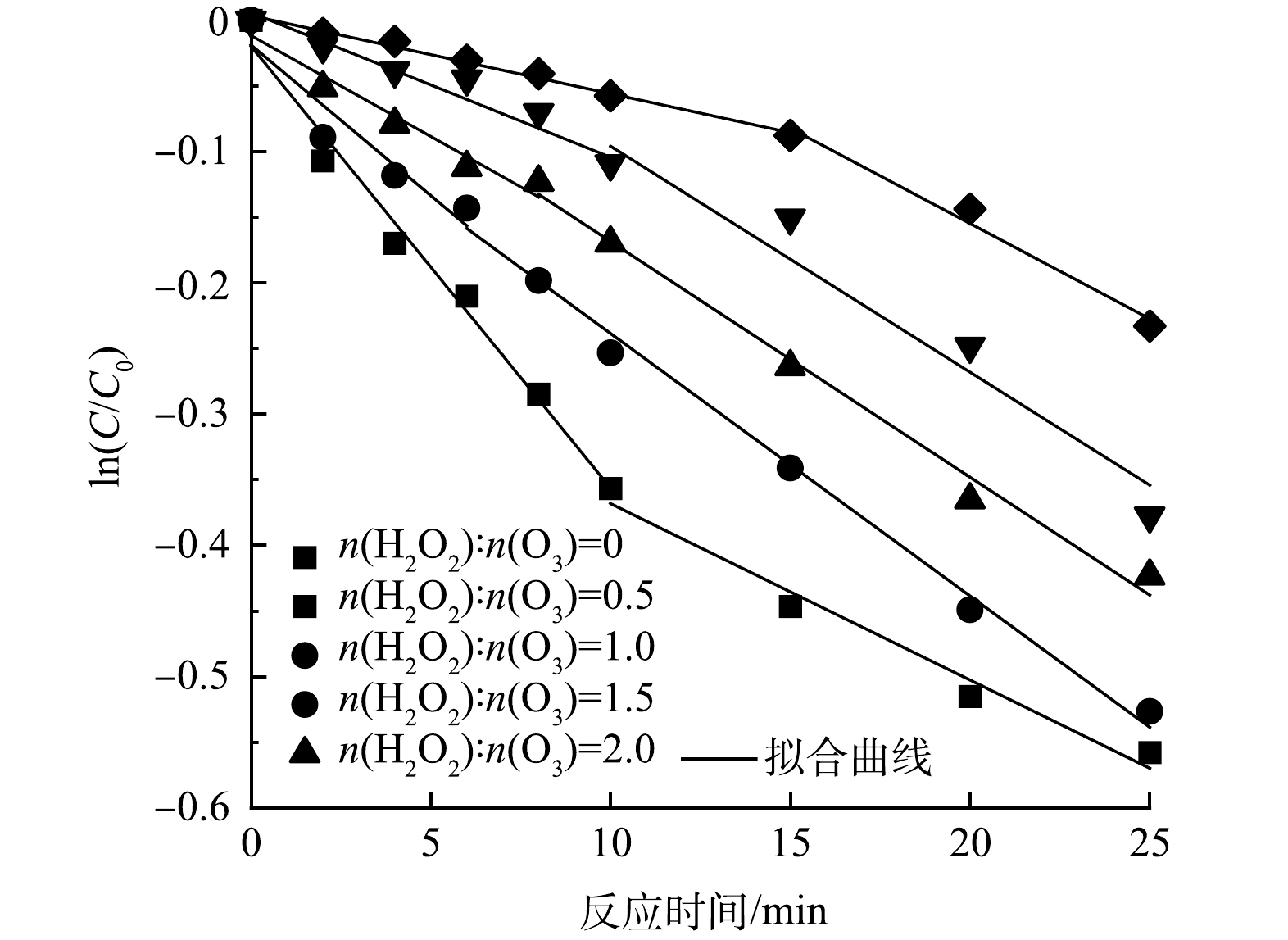
Br−的ln(C/C0)-t散点图如图8所示,可将Br−质量浓度的消耗过程分为快速阶段和慢速阶段,对两消耗阶段进行拟合,得到了不同H2O2投加量下的Br−拟一级反应速率常数kobs,具体拟合结果见表2。
表 2 H2O2抑制条件下的Br-消耗的一级速率常数(kobs)Table 2. kobs of Br- consumption with the addition of H2O2n(H2O2):n(O3) 反应时间/min 拟合方程式 k/min-1 R2 0 0~10 y = −0.033 7x−0.019 70 0.033 7 0.985 10~25 y = −0.013 4x−0.234 00 0.013 4 0.976 0.5 0~6 y = −0.022 9x−0.018 86 0.022 9 0.950 6~25 y = −0.020 0x−0.038 59 0.020 0 0.990 1 0~8 y = −0.015 4x−0.011 67 0.015 4 0.955 8~25 y = −0.018 0x+0.011 12 0.018 0 0.990 1.5 0~10 y = −0.011 0x+0.005 83 0.011 0 0.971 10~25 y = −0.017 2x+0.076 27 0.017 2 0.983 2 0~15 y = −0.005 9x+0.003 51 0.005 9 0.991 15~25 y = -0.014 5x+0.135 60 0.014 5 0.983 根据表2,在H2O2抑制条件下的HOC体系中,当n(H2O2):n(O3)>0.5时,Br−的消耗由原本的先快速消耗后慢速消耗[34]变成了先慢速消耗后快速消耗。在反应前期,由于H2O2的抑制作用,Br−的消耗速率常数降低,且H2O2投加量越大,消耗速率常数越低,当n(H2O2):n(O3)=2时,Br−的消耗速率常数低至0.005 9 min−1。同时,H2O2投加量越大,Br−的慢速消耗时间越长,相同反应时间下BrO3−的生成量越低,说明H2O2的投加有效延缓了HOC体系中Br−的消耗和BrO3−的生成[11, 17]。在反应后期,H2O2被消耗,抑制能力减弱,Br−的消耗速率常数开始增大,BrO3−质量浓度逐渐增大。随着H2O2投加量的增大,反应后期剩余H2O2增多,促进了臭氧自分解以及·OH和H2O2的反应,快速消耗阶段的kobs减小,有效的降低了反应后期BrO3−的生成量。
因此,在HOC体系中,H2O2对BrO3−消毒副产物的抑制主要通过两个阶段进行:在反应前期,H2O2阻断了HBrO/BrO−被氧化为BrO3−的反应,有效抑制了Br−的消耗和BrO3−的生成;在反应后期,残留的H2O2加速了体系中臭氧的分解,当H2O2足够时还会与·OH反应,使反应后期体系中活性氧物质含量降低,有效减少了BrO3−的生成。在HOC体系中使用H2O2控制BrO3−的生成时,可以在保证有机物去除效果的同时通过控制反应时间处于慢速反应阶段控制BrO3−的生成。
2.4 HOC工艺运行条件的优化
在HOC体系中,H2O2对BrO3−消毒副产物的抑制主要通过慢速反应前期和快速反应后期进行,而慢速反应前期充分的H2O2能迅速地与HBrO/BrO−反应,减少BrO3−的生成,是抑制BrO3−的生成的主要阶段。
TOC去除结果表明,8.0 mg·L−1和11.3 mg·L−1的臭氧投加量对TOC的去除效果并未显著优于4.5 mg·L−1臭氧投加量,因此,控制臭氧投加量在4.5 mg·L−1,可在源头上降低BrO3−的生成量。同时,控制HOC工艺反应时间不超过15 min可以保证HOC工艺具有30%以上的有机物去除率;当n(H2O2):n(O3)=2时,可以将HOC工艺中的慢速反应前期的反应时间延长至15 min,进而控制BrO3−的生成量在0.01 mg·L−1以下。
3. 结论
1) HOC体系中随着臭氧投加量增大,TOC去除率升高, BrO3−质量浓度增大。当臭氧投加量为11.3 mg·L−1时,TOC去除率可达42.41%,但生成的BrO3−质量浓度达0.04 mg·L−1,远超国家饮用水标准规范(GB 5749-2022)。当n(H2O2):n(O3)>0.5时,H2O2能有效的抑制HOC体系中BrO3−的生成。
2) HOC体系中臭氧直接氧化是BrO3−生成的主要途径,f(O3)维持在80%以上,随着臭氧投加量增大,O3暴露量增大,f(O3)增大。在H2O2抑制条件下,反应前期f(·OH)增大,最大可达35.77%,而f(O3)均在60%以上,臭氧氧化仍是HOC体系中BrO3−生成的主要途径。
3)在H2O2抑制条件下的HOC体系中,Br−的消耗反应为先慢速反应后快速反应。反应前期H2O2抑制了Br−的氧化,且随着H2O2投加量增大,慢速反应时间增长,有效延缓了BrO3−的生成;反应后期H2O2被消耗,Br−消耗速率增大,BrO3−浓度增大,而随着H2O2投加量的增大,体系中活性氧物质减少,抑制了BrO3−的生成。
4)通过控制臭氧投加量为4.5 mg·L−1、反应时间不超过15 min以及n(H2O2):n(O3)=2可以保证HOC体系的有机物去除率在30%以上,同时控制BrO3−的生成量在0.01 mg·L−1以下。
-
[1] 李亚峰, 张策, 单连斌, 等. 三维电极电Fenton法对苯酚废水处理效果实验研究[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(9): 1-5. [2] MALAKOOTIAN M, HEIDARI M R. Removal of phenol from steel wastewater by combined electrocoagulation with photo-Fenton[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2018, 78(6): 1260-1267. doi: 10.2166/wst.2018.376 [3] 史胜利, 冯佳, 谢树莲, 等. 生物质材料去除酚类污染物的研究进展[J]. 辽宁化工, 2022, 51(12): 1744-1747. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2022.12.022 [4] CHEN G F, GAO M L. Experimental study on extraction and dephenolization of MK comeplex extractant[J]. Coal Chemical Industry, 2018, 46(2): 49-57. [5] GALDINO A L, OLIVEIRA J, MAGALHAES M L, et al. Prediction of the phenol removal capacity from water by adsorption on activated carbon[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2021, 84(1): 135-143. doi: 10.2166/wst.2021.196 [6] LIU H, KIM G E, HONG C O, et al. Treatment of phenol wastewater using nitrogen-doped magnetic mesoporous hollow carbon[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 271: 129595. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129595 [7] NIU Z Y, JIA Y T, CHEN Y C, et al. Positive effects of bio-nano Pd(0) toward direct electron transfer in Pseudomona putida and phenol biodegradation - ScienceDirect[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 161: 356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.011 [8] SELLAMI K, COUVERT A, NASSRALLAH N, et al. Bio-based and cost-effective method for phenolic compounds removal using cross-linked enzyme aggregates[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 403: 124021. [9] YOU Y Y, HE Z. Phenol degradation in iron-based advanced oxidation processes through ferric reduction assisted by molybdenum disulfide[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 312: 137278. [10] DWINANDHA D, ZHANG B, FUJII M. Prediction of reaction mechanism for OH radical-mediated phenol oxidation using quantum chemical calculation[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 291: 132763. [11] 齐亚兵, 杨清翠. 煤化工废水脱酚技术研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(5): 1414-1419. [12] ZHU G P, WANG Y T, HUANG Q L, et al. Emulsion liquid membrane for simultaneous extraction and separation of copper from nickel in ammoniacal solutions[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2022, 188: 107849. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107849 [13] BANERJEE S, SIVAMANI S. Estimation of model parameters in the extraction of Cr(VI) from wastewater by an emulsion liquid membrane[J]. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 2022, 45(6): 1141-1147. doi: 10.1002/ceat.202200043 [14] RAVAL A R, KOHLI H P, MAHADWAD O K. Application of emulsion liquid membrane for removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution: Extraction and stability studies[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 2022, 12: 100398. doi: 10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100398 [15] INYANG V, LOKHAT D. Propionic acid recovery from dilute aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) technique: optimization using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) experimental design[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2022, 57(2): 284-300. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2021.1890774 [16] GASSER M S, KADRY H F, HELAL A S, et al. Optimization and modeling of Uranium recovery from acidic aqueous solutions using liquid membrane with Lix-622 as Phenolic-oxime carrier[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022, 180: 25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2022.02.002 [17] SHOKRI A, DARAEI P, ZERESHKI S. Water decolorization using waste cooking oil: An optimized green emulsion liquid membrane by RSM[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 33: 101021. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101021 [18] OTHMAN N, SULAIMAN R N R, RAHMAN H A, et al. Simultaneous extraction and enrichment of reactive dye using green emulsion liquid membrane system[J]. Environmental Technology, 2019, 40(11): 1476-1484. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2018.1424258 [19] ROSLY M B, JUSOH N, OTHMAN N, et al. Stability of emulsion liquid membrane using bifunctional diluent and blended nonionic surfactant for phenol removal[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing- Process Intensification, 2020, 148: 107790. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2019.107790 [20] JUSOH N, OTHMAN N, SULAIMAN R N R, et al. Optimization of synergistic green emulsion liquid membrane stability for enhancement of silver recovery from aqueous solution[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 39(2): 423-430. doi: 10.1007/s11814-021-0921-2 [21] FATIHA M, NORELA J, NORASIKIN O, et al. Development of stable green emulsion liquid membrane process via liquid–liquid extraction to treat real chromium from rinse electroplating wastewater[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 66: 231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2018.05.034 [22] OTHMAN N, NOAH N, SHU L Y, et al. Easy removing of phenol from wastewater using vegetable oil-based organic solvent in emulsion liquid membrane process[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 25(1): 45-52. [23] 庞敏. 乳化液膜法脱酚的研究[D]. 大庆: 大庆石油学院, 2010. [24] AHMAD A L, SHAFIE Z M H M, ZAULKIFLEE N D, et al. Preliminary study of emulsion liquid membrane formulation on acetaminophen removal from the aqueous phase[J]. Membranes, 2019, 9(10): 133. doi: 10.3390/membranes9100133 [25] AHMAD A L, ZAULKIFLEE N D, KUSUMASTUTI A, et al. Removal of acetaminophen from aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membrane: Emulsion Stability Study[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 58(2): 713-719. [26] ZERESHKI S, DARAEI P, SHOKRI A. Application of edible paraffin oil for cationic dye removal from water using emulsion liquid membrane[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 356: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.05.037 [27] ZERESHKI S, SHOKRI A, KARIMI A. Application of a green emulsion liquid membrane for removing copper from contaminated aqueous solution: Extraction, stability, and breakage study using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 325: 115251. [28] KUMAR A, THAKUR A, PANESAR P S. Extraction of hexavalent chromium by environmentally benign green emulsion liquid membrane using tridodecyamine as an extractant[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 70: 394-401. [29] 焦潇帅, 王力, 颜冰川, 等. 乳化液膜去除焦化废水中苯酚的初步研究[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2020, 40(4): 119-125. [30] KUMAR A, THAKUR A, PANESAR P S. Stability analysis of environmentally benign green emulsion liquid membrane[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 2018, 39(10): 1510-1517. doi: 10.1080/01932691.2017.1421079 [31] AKKAR S, MOHAMMED S. The feasibility of emulsion liquid membrane for the extraction of organic acids from wastewater[J]. IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 1076(1): 012021. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/1076/1/012021 [32] 张海燕, 庞敏, 吴韦等. 正辛醇为载体的乳化液膜法脱酚[J]. 化工进展, 2010, 29(12): 2400-2404. [33] NASAB D P, KELISHAMI R A, et al. Selective separation and enrichment of neodymium and gadolinium by emulsion liquid membrane using a novel extractant CYANEX (R) 572[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 117: 63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2017.11.008 [34] ZAULKIFLEE N, AHMAD A, SUGUMARAN J, et al. Stability study of emulsion liquid membrane via emulsion size and membrane breakage on acetaminophen removal from aqueous solution using TOA[J]. ACS omega, 2020, 5(37): 23892-23897. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03142 [35] HAO M, KÖKKıLıÇ O, MARION C M, et al. The extraction of nickel by emulsion liquid membranes using Cyanex 301 as extractant[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 96(7): 1585-1596. doi: 10.1002/cjce.23100 [36] ROUHANI S H R, DAVARKHAH R, ZAHERI P, et al. Separation of molybdenum from spent HDS catalysts using emulsion liquid membrane system[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2020, 153: 107958. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2020.107958 [37] SUJATHA S, RAJASIMMAN M. Development of a green emulsion liquid membrane using waste cooking oil as diluent for the extraction of arsenic from aqueous solution - Screening, optimization, kinetics and thermodynamics studies[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 41: 102055. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102055 [38] KUMAR A, THAKUR A, PANESAR P S. A review on emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) for the treatment of various industrial effluent streams[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2019, 18(1): 153-182. doi: 10.1007/s11157-019-09492-2 [39] HUSSEIN M A, MOHAMMED A A, Atiya M A. Application of emulsion and Pickering emulsion liquid membrane technique for wastewater treatment: An overview[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(36): 36184-36204. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06652-3 [40] JUSOH N, OTHMAN N, ROSLY M B. Extraction and recovery of organic compounds from aqueous solution using emulsion liquid membrane process[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2021, 47(P6): 1301-1306. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王鑫,李恩泽,肖夏慧,程芳琴. 乳液在分离技术中的研究进展及应用. 应用化工. 2025(02): 478-483 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: